Page 1

User Manual
Product Model:
Layer 2 Managed Gigabit Ethernet Switch
Release 1.00
DGS-3700 Series
©Copyright 2009. All rights reserved
Page 2

DGS-3700-12/DGS-3700-12G Series Layer 2 Gigabit Ethernet Switch User Manual
_________________________________________________________________________________
Information in this document is subject to change without notice.
© 2009 D-Link Corporation. All rights reserved.
Reproduction in any manner whatsoever without the written permission of D-Link Corporation is strictly forbidden.
Trademarks used in this text: D-Link and the D-LINK logo are trademarks of D-Link Corporation; Mic rosoft and Windows are regist ered tradem arks
of Microsoft Corporation.
Other trademarks and trade names may be used in this document to refer to either the entities claiming the marks and nam es or their products.
D-Link Corporation disclaims any proprietary interest in trademarks and trade names other than its own.
July 2009 P/N
651370012005G
ii
Page 3

DGS-3700-12/DGS-3700-12G Series Layer 2 Gigabit Ethernet Switch User Manual
Table of Contents
Preface ......................................................................................................................................................................... xi
Intended Readers ......................................................................................................................................................... 1
Typographical Conventions........................................................................................................................................................ 1
Notes, Notices, and Cautions ....................................................................................................................................... 1
Web-based Switch Configuration ................................................................................................. 2
Introduction ................................................................................................................................................................... 2
Login to Web Manager ............................................................................................................................................................... 2
Web-based User Interface ......................................................................................................................................................... 3
Web Pages ................................................................................................................................................................................ 4
Configuration ................................................................................................................................. 6
Device Information ........................................................................................................................................................ 7
System Information ....................................................................................................................................................... 7
Serial Port Settings ....................................................................................................................................................... 8
IP Address .................................................................................................................................................................... 9
Setting the Swith’s IP Address using the Console Interface .................................................................................................... 11
Interface Settings ........................................................................................................................................................ 11
IPv6 Route Settings .................................................................................................................................................... 13
IPv6 Neighbor Settings ............................................................................................................................................... 13
Port Configuration ....................................................................................................................................................... 14
Port Settings ............................................................................................................................................................................ 14
Port Description ....................................................................................................................................................................... 15
Port Error Disabled .................................................................................................................................................................. 16
Static ARP Settings .................................................................................................................................................... 16
User Accounts ............................................................................................................................................................ 17
System Log Configuration .......................................................................................................................................... 20
System Log Settings ................................................................................................................................................................ 20
System Log Server .................................................................................................................................................................. 20
System Severity Settings ............................................................................................................................................ 22
DHCP Relay................................................................................................................................................................ 23
DHCP Relay Global Settings ................................................................................................................................................... 23
DHCP Relay Interface Settings ................................................................................................................................................ 26
DHCP Relay Option 60 Default Settings .................................................................................................................................. 26
DHCP Relay Option 60 Settings .............................................................................................................................................. 27
DHCP Relay Option 61 Default Settings .................................................................................................................................. 27
DHCP Relay Option 61 Settings .............................................................................................................................................. 28
Out of Band Management Settings ............................................................................................................................ 28
External Alarm Settings .............................................................................................................................................. 29
DHCP Auto Configuration Sett ings ............................................................................................................................. 29
MAC Address Aging Time .......................................................................................................................................... 30
Web Settings .............................................................................................................................................................. 30
iii
Page 4

DGS-3700-12/DGS-3700-12G Series Layer 2 Gigabit Ethernet Switch User Manual
Telnet Settings ............................................................................................................................................................ 30
Password Encryption .................................................................................................................................................. 31
Clipaging Settings ....................................................................................................................................................... 31
Firmware Information .................................................................................................................................................. 31
Dual Configuration Settings ........................................................................................................................................ 32
Ping Test ..................................................................................................................................................................... 33
Local Loopback Ports Settings ................................................................................................................................... 34
VLAN Counter Settings ............................................................................................................................................... 35
SNTP Settings ............................................................................................................................................................ 36
Time Settings ........................................................................................................................................................................... 36
TimeZone Settings ................................................................................................................................................................... 37
MAC Notification Settings ........................................................................................................................................... 38
MAC Notification Global Settings ............................................................................................................................................. 38
MAC Notification Port Settings ................................................................................................................................................. 39
SNMP Settings ........................................................................................................................................................... 40
SNMP Global State Settings .................................................................................................................................................... 41
SNMP View Table .................................................................................................................................................................... 41
SNMP Group Table .................................................................................................................................................................. 42
SNMP User Table .................................................................................................................................................................... 43
SNMP Community Table.......................................................................................................................................................... 44
SNMP Host Table .................................................................................................................................................................... 45
SNMP v6Host Table ................................................................................................................................................................ 45
SNMP Engine ID ...................................................................................................................................................................... 46
SNMP Trap Configuration ........................................................................................................................................................ 47
Time Range Settings .................................................................................................................................................. 47
sFlow ........................................................................................................................................................................... 48
sFlow Global State Settings ..................................................................................................................................................... 48
sFlow Analyzer Server Settings ............................................................................................................................................... 48
sFlow Flow Sampler Settings ................................................................................................................................................... 49
sFlow Counter Poller Settings .................................................................................................................................................. 50
Single IP Management ............................................................................................................................................... 51
Single IP Settings ..................................................................................................................................................................... 52
Topology .................................................................................................................................................................................. 53
Tool Tips .................................................................................................................................................................................. 56
Right-Click................................................................................................................................................................................ 57
Menu Bar ................................................................................................................................................................................. 59
Firmware Upgrade ................................................................................................................................................................... 60
Configuration File Backup/Restore .......................................................................................................................................... 60
Upload Log File ........................................................................................................................................................................ 61
DDM ............................................................................................................................................................................ 61
Browse DDM Status List .......................................................................................................................................................... 61
DDM Settings ........................................................................................................................................................................... 61
DDM Temperature Threshold S etting s .................................................................................................................................... 62
DDM Voltage Threshold Settings ............................................................................................................................................. 63
iv
Page 5

DGS-3700-12/DGS-3700-12G Series Layer 2 Gigabit Ethernet Switch User Manual
DDM Bias Current Threshold Settings ..................................................................................................................................... 63
DDM Tx Power Threshold Settings .......................................................................................................................................... 64
DDM Rx Power Threshold Settings ......................................................................................................................................... 64
L2 Features ................................................................................................................................... 66
Jumbo Frame .............................................................................................................................................................. 66
VLANs ......................................................................................................................................................................... 67
Understanding IEEE 802.1p Priority ........................................................................................................................................ 67
VLAN Description ..................................................................................................................................................................... 67
IEEE 802.1Q VLANs ................................................................................................................................................................ 68
Double VLANs ......................................................................................................................................................................... 72
802.1Q VLAN .............................................................................................................................................................. 74
Subnet VLAN .............................................................................................................................................................. 78
Subnet VLAN Settings ............................................................................................................................................................. 78
VLAN Precedence Settings...................................................................................................................................................... 78
Q-in-Q ......................................................................................................................................................................... 79
Q-in-Q Settings ........................................................................................................................................................................ 79
VLAN Translation Settings ....................................................................................................................................................... 80
Q-in-Q and VLAN Translation Rules ........................................................................................................................................ 81
802.1v Protocol VLAN ................................................................................................................................................ 82
802.1v Protocol Group Settings ............................................................................................................................................... 82
802.1v Protocol VLAN Settings ................................................................................................................................................ 83
RSPAN Settings ......................................................................................................................................................... 84
GVRP Settings ............................................................................................................................................................ 84
GVRP Global Settings ................................................................................................................................................ 85
MAC-based VLAN Settings ........................................................................................................................................ 86
PVID Auto Assign Settings ......................................................................................................................................... 86
Port Trunking .............................................................................................................................................................. 87
LACP Port Settings ..................................................................................................................................................... 89
Traffic Segmentation ................................................................................................................................................... 90
BPDU Tunneling Settings ........................................................................................................................................... 91
IGMP Snooping .......................................................................................................................................................... 92
IGMP Snooping Settings .......................................................................................................................................................... 92
IGMP Snooping Rate Limit Settings ......................................................................................................................................... 94
IGMP Snooping Static Group Settings ..................................................................................................................................... 94
IGMP Multicast Group Profile Settings ..................................................................................................................................... 95
IGMP Snooping Multicast VLAN Settings ................................................................................................................................ 95
IPv4 Multicast Profile Settings .................................................................................................................................................. 96
IPv4 Limited Multicast Range Settings ..................................................................................................................................... 97
IPv4 Max Multicast Group Settings .......................................................................................................................................... 97
MLD Snooping ............................................................................................................................................................ 98
MLD Snooping Settings ........................................................................................................................................................... 98
MLD Snooping Rate Limit Settings ........................................................................................................................................ 100
MLD Snooping Static Group Settings .................................................................................................................................... 101
MLD Mul ticast Group Profile Settings .................................................................................................................................... 101
v
Page 6

DGS-3700-12/DGS-3700-12G Series Layer 2 Gigabit Ethernet Switch User Manual
MLD Snooping Multicast VLAN Settings ................................................................................................................................ 102
IPv6 Multicast Profile Settings ................................................................................................................................................ 103
IPv6 Limited Multicast Range Settings ................................................................................................................................... 104
IPv6 Max Multicast Group Settings ........................................................................................................................................ 104
Port Mirror ................................................................................................................................................................. 105
Loopback Detection Settings .................................................................................................................................... 106
Spanning Tree .......................................................................................................................................................... 107
STP Bridge Global Settings ................................................................................................................................................... 109
STP Port Settings .................................................................................................................................................................. 111
MST Configuration Identification ............................................................................................................................................ 112
STP Instance Settings ........................................................................................................................................................... 113
MSTP Port Information .......................................................................................................................................................... 114
Forwarding & Filtering ............................................................................................................................................... 115
Unicast Forwarding ................................................................................................................................................................ 115
Multicast Forwarding .............................................................................................................................................................. 115
Multicast Filtering Mode ......................................................................................................................................................... 116
LLDP ......................................................................................................................................................................... 116
LLDP Global Settings ............................................................................................................................................................. 117
LLDP Port Settings ................................................................................................................................................................ 118
LLDP Management Address List ........................................................................................................................................... 119
LLDP Basic TLVs Settings ..................................................................................................................................................... 119
LLDP Dot1 TLVs Settings ...................................................................................................................................................... 120
LLDP Dot3 TLVs Settings ...................................................................................................................................................... 121
LLDP Statistics System .......................................................................................................................................................... 121
LLDP Local Port Information .................................................................................................................................................. 122
LLDP Remote Port Information .............................................................................................................................................. 123
CFM .......................................................................................................................................................................... 123
CFM Port Settings .................................................................................................................................................................. 123
CFM CCM PDUs Forwarding Mode ....................................................................................................................................... 124
CFM MPs Reply LTRs ........................................................................................................................................................... 124
CFM MIPCCM Lis t ................................................................................................................................................................. 124
Connectivity Fault Management Settings ............................................................................................................................... 125
CFM Loopback Settings ......................................................................................................................................................... 126
CFM Linktrace Settings .......................................................................................................................................................... 127
Ethernet OAM ........................................................................................................................................................... 128
Ethernet OAM Settings .......................................................................................................................................................... 128
Ethernet OAM Configuration Settings .................................................................................................................................... 129
QoS ............................................................................................................................................. 130
Advantages of QoS ................................................................................................................................................... 130
Understanding QoS .................................................................................................................................................. 131
HOL Blocking Pevention ........................................................................................................................................... 133
Bandwidth Control .................................................................................................................................................... 133
Traffic Control ........................................................................................................................................................... 134
802.1p Default Priority .............................................................................................................................................. 136
vi
Page 7

DGS-3700-12/DGS-3700-12G Series Layer 2 Gigabit Ethernet Switch User Manual
802.1p User Priority .................................................................................................................................................. 137
QoS Scheduling Mechanism .................................................................................................................................... 137
QoS Scheduling ........................................................................................................................................................ 138
In Band Manage Settings ......................................................................................................................................... 139
SRED ........................................................................................................................................................................ 140
SRED Settings ....................................................................................................................................................................... 140
SRED Drop Counter .............................................................................................................................................................. 142
DSCP Trust Settings .............................................................................................................................................................. 142
DSCP Map Settings ............................................................................................................................................................... 142
802.1p Map Settings .............................................................................................................................................................. 144
Security ....................................................................................................................................... 145
Safeguard Engine ..................................................................................................................................................... 145
Trusted Host ............................................................................................................................................................. 147
IP-MAC-Port Binding ................................................................................................................................................ 147
IMP Binding Global Settings .................................................................................................................................................. 147
IMP Binding Port Settings ...................................................................................................................................................... 148
IMP Binding Entry Settings .................................................................................................................................................... 150
DHCP Snooping Entries ........................................................................................................................................................ 151
MAC Block List ....................................................................................................................................................................... 151
Port Security ............................................................................................................................................................. 151
Port Security Port Settings ..................................................................................................................................................... 151
Port Security VLAN Settings .................................................................................................................................................. 152
Port Security Entries .............................................................................................................................................................. 153
DHCP Server Screening Settings ............................................................................................................................. 153
DHCP Screening Port Settings .............................................................................................................................................. 154
DHCP Offer Filtering .............................................................................................................................................................. 154
802.1X ....................................................................................................................................................................... 155
802.1X Port-Based and Host-Based Access Control ............................................................................................................. 155
Understanding 802.1X Port-ba sed and Host-based Network Access Control........................................................................ 158
Port-Based Network Access Control ...................................................................................................................................... 158
Host-Based Network Access Control ..................................................................................................................................... 159
802.1X Global Settings .......................................................................................................................................................... 160
802.1X Port Settings .............................................................................................................................................................. 160
802.1X User ........................................................................................................................................................................... 162
Authentication RADIUS Server .............................................................................................................................................. 162
Initialize Port(s) ...................................................................................................................................................................... 163
Reauthenticate Port(s) ........................................................................................................................................................... 163
Guest VLAN Configuration ..................................................................................................................................................... 164
Guest VLAN ........................................................................................................................................................................... 165
SSL Settings ............................................................................................................................................................. 165
Download Certificate .............................................................................................................................................................. 166
Ciphersuite ............................................................................................................................................................................. 166
SSH ........................................................................................................................................................................... 168
SSH Settings .......................................................................................................................................................................... 168
vii
Page 8

DGS-3700-12/DGS-3700-12G Series Layer 2 Gigabit Ethernet Switch User Manual
SSH Authmode and Algorithm Settings ................................................................................................................................. 169
SSH User Authentication Lists ............................................................................................................................................... 170
Access Authentication Control .................................................................................................................................. 171
Authentication Policy Settings ................................................................................................................................................ 173
Application Authentication Settings ........................................................................................................................................ 173
Authentication Server Group .................................................................................................................................................. 174
Authentication Server ............................................................................................................................................................. 175
Login Method Lists ................................................................................................................................................................. 176
Enable Method Lists .............................................................................................................................................................. 177
Local Enable Password Settings ............................................................................................................................................ 178
RADIUS Accounting Settings ................................................................................................................................................. 179
MAC-based Access Control...................................................................................................................................... 180
Notes About MAC-based Access Control .............................................................................................................................. 180
MAC-based Access Control Settings ..................................................................................................................................... 180
MAC-based Access Control Local Settings............................................................................................................................ 182
Web Authentication ................................................................................................................................................... 183
Conditions and Limitations ..................................................................................................................................................... 184
Web-based Access Control Settings ...................................................................................................................................... 184
Web-based Access Control User Settings ............................................................................................................................. 185
NetBIOS Filtering ...................................................................................................................................................... 186
NetBIOS Filtering Settings ..................................................................................................................................................... 186
ACL ............................................................................................................................................. 187
ACL Configuration Wizard ........................................................................................................................................ 187
Access Profile List .................................................................................................................................................... 188
CPU Interface Filtering ............................................................................................................................................. 205
CPU Access Prof ile List ............................................................................................................................................ 206
ACL Finder ................................................................................................................................................................ 217
ACL Flow Meter ........................................................................................................................................................ 217
Monitoring .................................................................................................................................. 220
Device Status ............................................................................................................................................................ 220
Cable Diagnostic ....................................................................................................................................................... 220
CPU Utilization .......................................................................................................................................................... 221
Port Utilization ........................................................................................................................................................... 222
Packet Size ............................................................................................................................................................... 222
Memory Utilization .................................................................................................................................................... 224
Packets ..................................................................................................................................................................... 224
Received (RX) ........................................................................................................................................................................ 224
UMB_cast (RX) ...................................................................................................................................................................... 226
Transmitted (TX) .................................................................................................................................................................... 227
Errors ........................................................................................................................................................................ 230
Received (RX) ........................................................................................................................................................................ 230
Transmitted (TX) .................................................................................................................................................................... 231
Port Access Control .................................................................................................................................................. 233
viii
Page 9

DGS-3700-12/DGS-3700-12G Series Layer 2 Gigabit Ethernet Switch User Manual
RADIUS Authentication .......................................................................................................................................................... 233
RADIUS Account Client ......................................................................................................................................................... 234
Authenticator State ................................................................................................................................................................ 236
Authenticator Statistics .......................................................................................................................................................... 237
Authenticator Session Statistics ............................................................................................................................................. 238
Authenticator Diagnostics ...................................................................................................................................................... 239
Browse ARP Table ................................................................................................................................................... 241
VLAN ......................................................................................................................................................................... 242
Browse VLAN ......................................................................................................................................................................... 242
Show VLAN Ports ..................................................................................................................................................... 243
IGMP Snooping ........................................................................................................................................................ 243
Browse IGMP Router Port...................................................................................................................................................... 243
IGMP Snooping Group ........................................................................................................................................................... 243
IGMP Snooping Forwarding Table ......................................................................................................................................... 244
Browse IGMP Snooping Counter ........................................................................................................................................... 244
MLD Snooping .......................................................................................................................................................... 245
Browse MLD Router Port ....................................................................................................................................................... 245
MLD Snooping Group ............................................................................................................................................................ 245
MLD Snooping Forwarding Table .......................................................................................................................................... 246
Browse MLD Snooping Counter ............................................................................................................................................. 247
Browse Session Table .............................................................................................................................................. 247
CFM .......................................................................................................................................................................... 247
CFM Packet Counter List ....................................................................................................................................................... 247
CFM Packet Counter CCM List .............................................................................................................................................. 248
Browse CFM Fault MEP......................................................................................................................................................... 248
Browse CFM Port MP List ...................................................................................................................................................... 248
MAC Address Table .................................................................................................................................................. 249
Browse VLAN Counter Statistics .............................................................................................................................. 249
Ethernet OAM ........................................................................................................................................................... 250
Browse Ethernet OAM Event Log .......................................................................................................................................... 250
Browse Ethernet OAM Stati stics ............................................................................................................................................ 250
Historical Counter & Utilization ................................................................................................................................. 252
Browse Historical Counter...................................................................................................................................................... 252
Browse Historical Utilization ................................................................................................................................................... 253
System Log ............................................................................................................................................................... 253
Save Services and Tools ........................................................................................................... 255
Save Configuration ID 1 ............................................................................................................................................ 255
Save Configuration ID 2 ............................................................................................................................................ 256
Save Log ................................................................................................................................................................... 256
Save All ..................................................................................................................................................................... 256
Configuration File Backup & Restore ....................................................................................................................... 257
Upload Log File ......................................................................................................................................................... 257
Reset ......................................................................................................................................................................... 257
ix
Page 10

DGS-3700-12/DGS-3700-12G Series Layer 2 Gigabit Ethernet Switch User Manual
Download Firmware .................................................................................................................................................. 258
Reboot System ......................................................................................................................................................... 258
Mitigating ARP Spoofing Attacks Using Packet Content ACL ............................................... 259
System Log Entries ................................................................................................................... 267
Glossary...................................................................................................................................... 278
Password Recovery Procedure ................................................................................................ 280
x
Page 11

DGS-3700-12/DGS-3700-12G Series Layer 2 Gigabit Ethernet Switch User Manual
Preface
The DGS-3700 Series User Manual is divided into sections that describe the system installation and operating
instructions with examples.
Section 1, Introduction to Web-based Switch Management – Describes how to connect to and use the W ebbased switch management feature on the Switch.
Section 2, Configuration – A detailed discussion about configuring some of the basic functions of the Switch,
including accessing the System information, Serial Port Settings, IP Address, Interface Settings, IPv6 Route
Settings, IPv6 Neighbor Settings, Port Configuration, Static ARP Settings, User Accounts, System Log
Configuration, S ystem Sev erity Set tings , DH CP Re la y, Out of B and Managem ent Setti ngs, Extern al Alar m Setti ngs,
DHCP Auto Configurati on Sett ings , MAC Addr es s Aging Time, Web Settings, Tel net S etti ngs , P as sw ord E nc ryption,
Clipaging Settings, Firmware Information, Dual Configuration Settings, Ping Test, Local Loopback Port Settings,
VLAN Counter Settings , SNTP Settings, MAC Notificat ion Settings, SNMP Settings, T ime Range Settings, sFlow,
Single IP Management and DDM.
Section 3, L2 Features – A discussion of the Layer 2 features on the Switch, including Jumbo Frame, 802.1Q
VLAN, Subnet VLAN, QinQ, 802.1v Protoc ol VLAN , R SP AN Sett in gs , GVRP Settings, GVRP G lo bal Set tings, MACbased VLAN Settings, PVID Auto Ass ign Settings , Port Trunk ing, LACP Port Set tings, Traff ic Segmentation, BPDU
Tunneling Settings, IGMP Snooping, MLD Snooping, Port Mirror, Loopback Detection Settings, Spanning Tree,
Forwarding & Filtering, LLDP, CFM and Ethernet OAM.
Section 4, QoS – F eatures information on Switch QoS f unctions, including HOL Blocking Pre vention, Bandwidth
Control, Traffic Control, 802.1P Default Priority, 802.1P User Priority, QoS Scheduling Mechanism, QoS Scheduling,
In Band Manage Settings and SRED.
Section 5, Security – Fe atures information on S witch security functions, inc lud ing Saf eguard Engine, Trus ted Hos t,
IP-MAC-Port Bindin g, Port Security, DHCP S erver Screening, 802. 1X, SSL Settings, SSH, Access Authentication
Control, MAC-based Access Control, Web Authentication, and NetBIOS Filtering Settings.
Section 6, ACL – Discussion on the ACL functions of the Switch, including ACL Configuration Wizard, Access
Profile List, CPU Access Prof ile List, ACL Find er , and ACL Flo w Met er.
Section 7, Monitoring – Features information about the monitoring functions on the Switch including, Cable
Diagnostic, CPU Utilization, Port Utilizat ion, Packet Size, Memory Utilization, Packets , Errors, Port Access Control,
Browse ARP Table, Bro wse VLAN, IGMP Snooping, MLD Snoo ping, Browse Session Table, CFM, MAC Addr ess
Table, Browse VLAN Counter Statistics, Ethernet OAM and Historical Counter & Utilization.
Section 8, Save Services and Tools – Save Configuration ID 1, Save Configuration ID 2, Save Log, Save All,
Configuration File Backup and Restore, Upload Log File, Reset, Download Firmware, and Reboot System.
Appendix A, Mitigating ARP Spoofing Attacks Using Packet Content ACL – This section introduces ARP
protocol, ARP spoof ing attacks, and the counter measure br ought by D-Link's switches to counter ARP spoofing
attacks.
Appendix B, System Log Entries – This table lists all the possible entr ies and the ir correspondin g meanings tha t
will appear in the System Log of this Switch.
Appendix C, Glossary – Lists definitions for terms and acronyms used in this document.
Appendix D, Passw ord R ecover y Proced ure - This section describes the procedure for resetting passwords on D-
Link Switches.
xi
Page 12
DGS-3700-12/DGS-3700-12G Series Layer 2 Gigabit Ethernet Switch User Manual
Boldface Typewriter
Menu Name > Menu
Intended Readers
The DGS-3700 Series Man ual contains information for setup and management of the Switch. This manual is intended
for network managers familiar with network management concepts and terminology.
Typographical Con venti ons
Convention Description
[ ] In a command line, square brackets indicate an optional entry. For example: [copy
filename] means that optionally you can type copy followed by the name of the file. Do not
type the brackets.
Bold font Indicates a button, a toolbar icon, menu, or menu i tem. For example: Ope n t he File menu
and choose Cancel. Used for em phasis. Ma y also in dicate s ystem messages or prom pts
appearing on your screen. For example: You have mail. Bold font is also used to
represent filenames, program names and commands. For example: use the copy
command.
Indicates comm ands and responses to prompts that must be typed exactl y as printed in
Font
the manual.
Initial capital letter Indicates a window name. Names of keys on the keyboard have initial capitals. For
example: Click Enter.
Italics Indicates a window n ame or a field. Also can indicate a variables or parameter that is
replaced with an appropr iate word or string. For exam ple: type filename means that you
should type the actual filenam e instead of the word sh o wn in italic.
Menu Name > Menu Option Indicates the menu structure. Device > Port > Port
Option
Properties means the Port Properties menu option u nder the Port menu option that is
located under the Device menu.
Notes, Notices, and Cautions
A NOTE indicates important information that helps you make better use of your device.
A NOTICE i ndicates either potential dam age to hardware or loss of data and te lls you
how to avoid the problem.
A CAUTION indicates a potential for property damage, personal injury, or death.
1
Page 13

DGS-3700-12/DGS-3700-12G Series Layer 2 Gigabit Ethernet Switch User Manual
Section 1
Web-based Switch Configuration
Introduction
Login to Web Manager
Web-based User Interface
Web Pages
Introduction
All software functions of the Switch can be m anag ed, configured and m onitore d via the embedde d we b-bas e d (H T ML)
interface. The Switch c an be managed from remote s tations anywhere on the network thr ough a standard browser
such as Opera, Netscape Navigator/Communicator, or Micros oft Internet Explorer. The browser acts as a uni versal
access tool and can communicate directly with the Switch using the HTTP protocol.
The Web-based m anagement module and the Cons ole program (and Telnet) are dif ferent ways to access the sam e
internal switching s oftware and conf igure it. Thus, al l settings encount ered in web-based management ar e the same
as those found in the console program.
Login to Web Manager
To begin managing the Switch, simply run the browser you have installed on your com puter and point it to the IP
address you have defined for the device. The URL in the address bar should read something like:
http://123.123.123.123, where the numbers 123 represent the IP address of the Switch.
NOTE: The Factory default IP address for the Switch is 10.90.90.90.
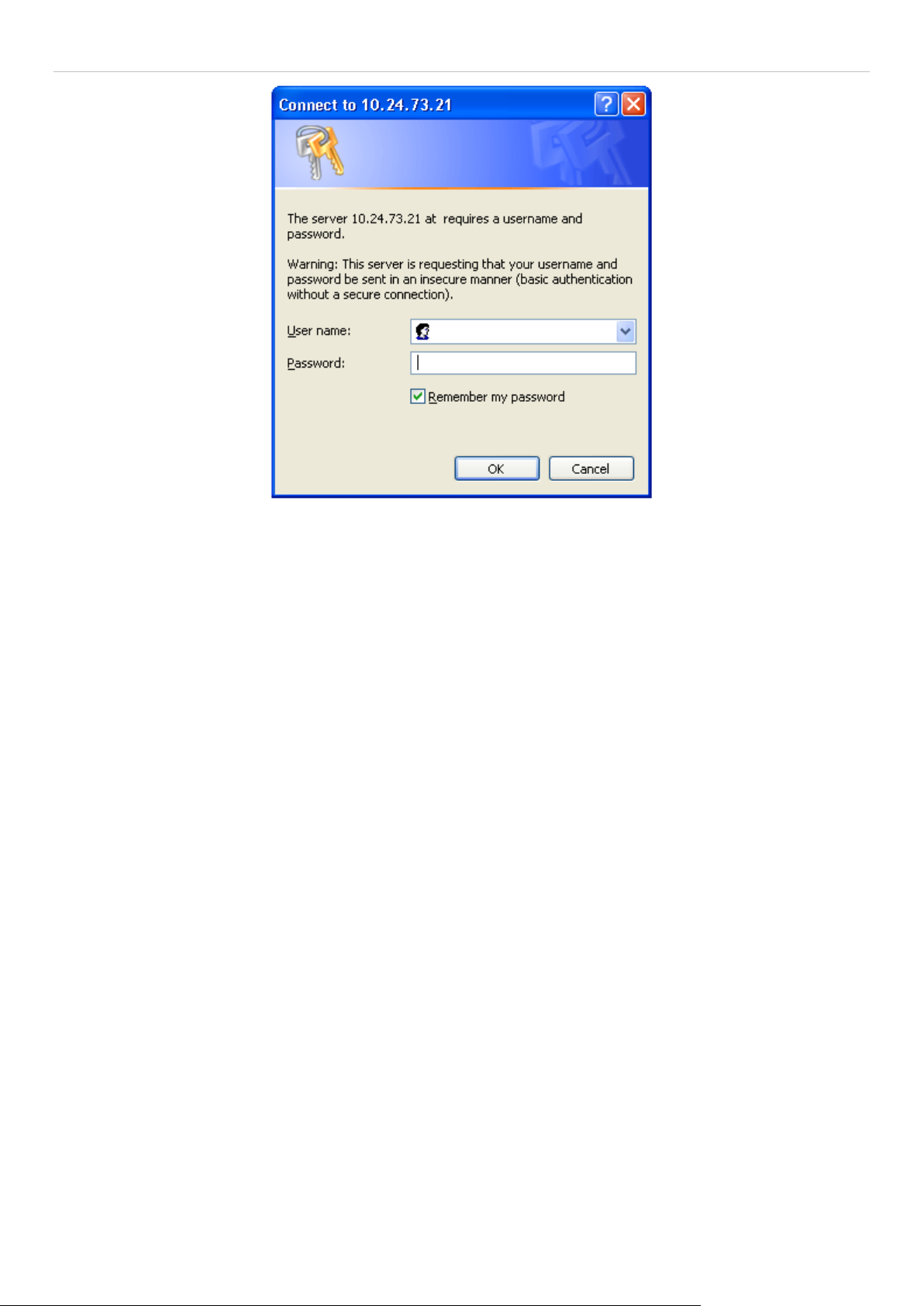
This opens the management module's user authentication window, as seen below.
2
Page 14
DGS-3700-12/DGS-3700-12G Series Layer 2 Gigabit Ethernet Switch User Manual
Figure 1 - 1 Enter Network Password dialog
Enter “admin” in bo th the Us er Nam e and Pass word fields and clic k OK. T his will open t he W eb-based user interface.
The Switch management features available in the web-based manager are explained below.
Web-based User Interface
The user interface provides access to various Switch configuration and m anagement windows, allows you to view
performance statistics, and permits you to graphically monitor the system status.
Areas of the User Interface
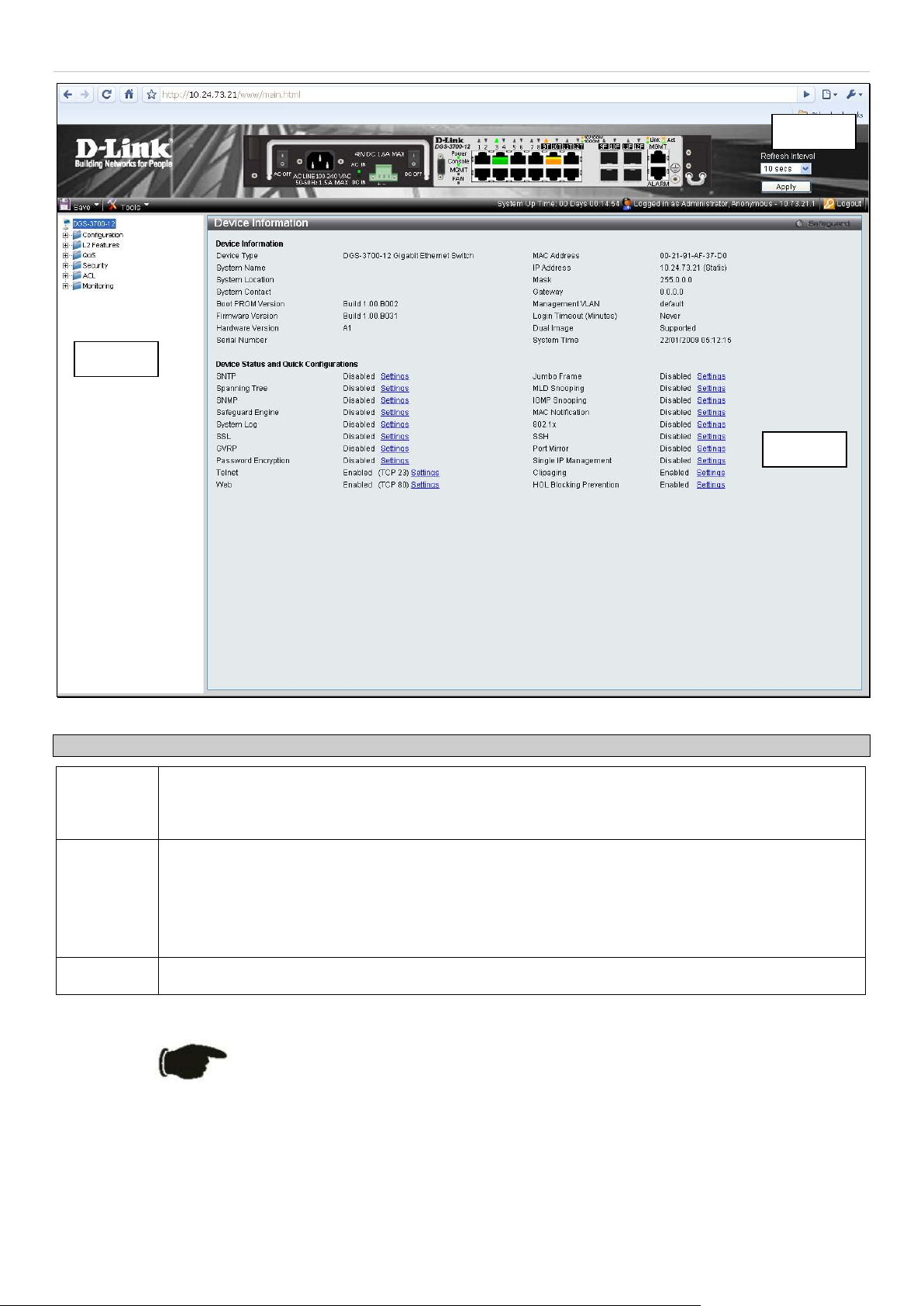
The figure below shows the us er interface. The user interface is di vided into three distinct areas as desc ribed in the
table.
3
Page 15
Area 1
DGS-3700-12/DGS-3700-12G Series Layer 2 Gigabit Ethernet Switch User Manual
Area 2
Area 3
Area Function
Area 1
Area 2
Area 3
Select the folder or window to be displayed. T he folder icons can be ope ned to display the h yperlinked window buttons and subfolders conta ined within them. Click the D-Link logo to go to the DLink website.
Presents a graphical near real-time im age of the front panel of the Switch. T his area displays the
Switch's ports and expansion modules, showing port activity, duplex mode, or flow control,
depending on the specified mode.
Various areas of the graphic can be selected for performing managem ent functions, including port
configuration.
Presents switch information based on your selection and the entry of configuration data.
Figure 1 - 2 Main Web-Manager page
NOTICE: Any changes made to the Switch configuration during the
current session mus t be s a ved in th e S ave Changes web m enu (ex pl ain ed
below) or use the command line interface (CLI) command save.
Web Pages
When you connect to the management m ode of the Switch with a web br owser, a login windo w is displayed. E nter a
user name and password to access the Switch's management mode.
4
Page 16

DGS-3700-12/DGS-3700-12G Series Layer 2 Gigabit Ethernet Switch User Manual
Below is a list and description of the main folders available in the web interface:
Configuration – A detaile d discussion about configur ing some of the basic functions of the Switch, accessing the
System information, Serial Port Settings, IP Address, Interface Settings, IPv6 Route Settings, IPv6 Neighbor
Settings, Port Configuration, Static ARP Settings, User Accounts, System Log Configuration, System Severity
Settings, DHCP Relay, Out of Band Management Settings, External Alarm Settings, DHCP Auto Configuration
Settings, MAC Address Aging Time, Web Settings, Telnet Settings, Password Encryption, Clipaging Settings,
Firmware Information, Dual Configuration Settings, Ping Test, Local Loopback Port Settings, VLAN Counter
Settings, SNTP Settings, MAC Notification Settings, SNMP Settings, Time Range Settings, sFlow, Single IP
Management and DDM.
L2 Features – A discussion of the Layer 2 features on the Switch, includ ing Jum bo Frame, 802.1Q VLAN, Sub net
VLAN, QinQ, 802.1v Protoc ol VLAN, RSPAN Settings, GVR P Settings, GVRP Global Settings, MAC-based VLAN
Settings, PVID Auto Assign Settings, Port Trunking, LACP Port Settings, Traffic Segmentation, BPDU Tunneling
Settings, IGMP Snooping, MLD Snooping, Port Mirror, Loopb ack Detection Settings, Spa nning Tree, For warding &
Filtering, LLDP, CFM and Ethernet OAM.
QoS – Features information on Switch QoS functions, including HOL Blocking Prevention, Bandwidth Control,
Traffic Control, 802.1P Default Priority, 802.1P User Priority, QoS Sc he dul in g Me chani s m, QoS Scheduling, In Band
Manage Settings and SRED.
Security – Features inf ormation on Switch securit y functions, including S afeguard Engine, Trusted H ost, IP-MACPort Binding, Port Security, DHCP Server Scr eening, 802.1X, SSL Settings, SSH, Access Authentication Cont rol,
MAC-based Access Control, Web Authentication, and NetBIOS Filtering Settings.
ACL – Discussion on the ACL functions of the Switch, including ACL Configuration Wizard, Access Profile List, CPU
Access Profile List, ACL Finder, and ACL Flow Meter.
Monitoring – Features inform ation about the monitoring func tions on the Switch inclu ding, Cable Diagnosti c, CPU
Utilization, Port Utilization, Packet Size, Memory Utilization, Packets, Errors, Port Access Control, Browse ARP
Table, Browse VLAN, IGMP Sno oping, MLD Snooping, Br owse Session Table, CFM, MAC Address Table, Browse
VLAN Counter Statistics, Ethernet OAM and Historical Counter & Utilization and System Log.
NOTE: Be sure to configure the user name and password in the User
Accounts window before connecting the Switch to the greater network.
5
Page 17

DGS-3700-12/DGS-3700-12G Series Layer 2 Gigabit Ethernet Switch User Manual
Configuration
Device Information
System Information
Serial Port Settings
IP Address
Interface Settings
IPv6 Route Settings
IPv6 Neighbor Settings
Port Configuration
Static ARP Settings
User Accounts
System Log Configuration
Section 2
System Severity Settings
DHCP Relay
Out of Band Management Settings
External Alarm Settings
DHCP Auto Configuration Settings
MAC Address Aging Time
Web Settings
Telnet Settings
Password Encryption
Clipaging Settings
Firmware Information
Dual Configuration Settings
Ping Test
Local Loopback Ports Settings
VLAN Counter Settings
SNTP Settings
MAC Notification Settings
SNMP Settings
Time Range Settings
sFlow
Single IP Management
DDM
6
Page 18
DGS-3700-12/DGS-3700-12G Series Layer 2 Gigabit Ethernet Switch User Manual
Device Information
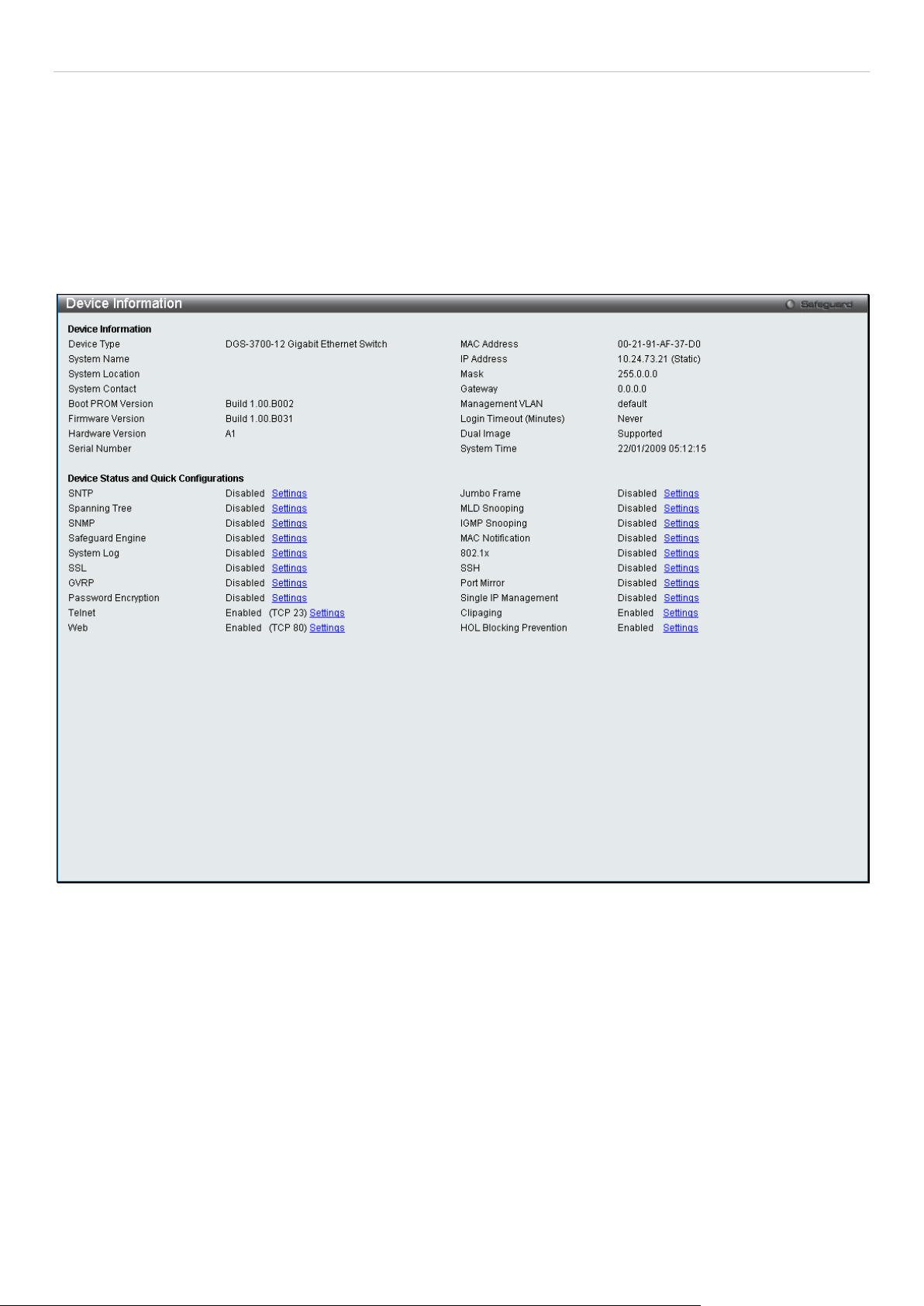
This window con tains the m ain settings for all m ajor functions on the S witch and appear s automaticall y when you log
on. To return to the Device Information window, click the DGS-3700-12/DGS-3700-12G Web Management Tool
folder. The Device Information window shows the Switch’s MAC Address (assigned by the factory and
unchangeable), the Boot PROM Version, Firmware Version, Hardware Version and Serial Number as well as
other information about different settings on the Switch. This information is helpful to keep track of PROM and
firmware updates and t o obtain the Switch's MAC address f or entry into another network device's addr ess table, if
necessary. In addit io n, this window displays the status of f unc tions on th e S witc h t o q uic k l y as ses s the i r current global
status. Some func tions are hyper-link ed to their configurati on window for eas y access from the Device Information
window.
Figure 2 - 1 Device Information window
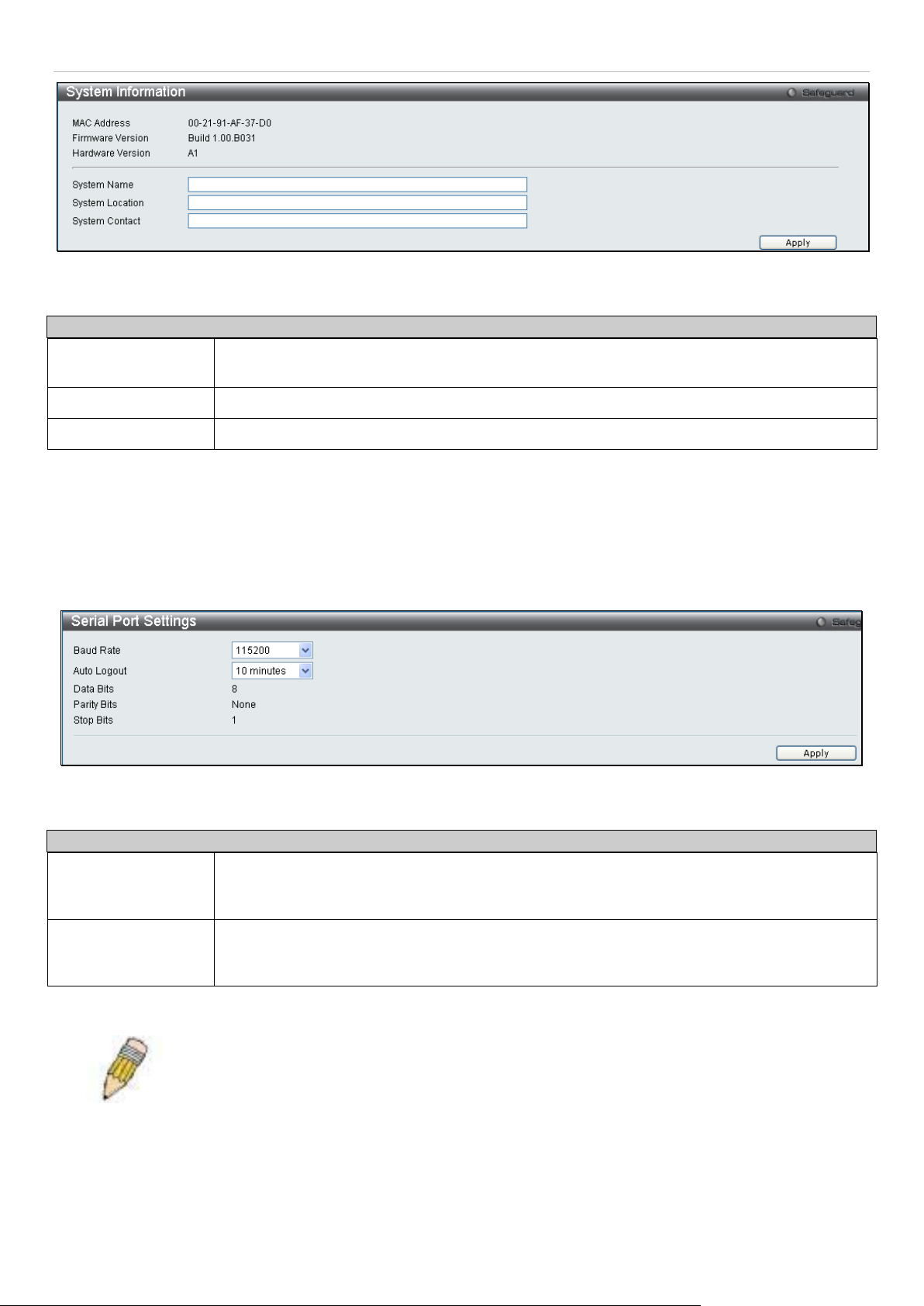
System Information
This window contains the System Information details. The user may enter a System N ame, System Location and
System Contact to aid in defining the Switch, to the user's preference. This window displays the MAC Address,
Firmware Version and Hardware Version.
To view this window, click Configuration > System Information as shown below:
7
Page 19
DGS-3700-12/DGS-3700-12G Series Layer 2 Gigabit Ethernet Switch User Manual
the default setting.
Figure 2 - 2 System Information window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter Description
System Name
System Location
System Contact
Click Apply to implement changes made.
Enter a system name for the Switch, if so desired. This name will identify it in the Switch
network.
Enter the location of the Switch, if so desired.
Enter a contact name for the Switch, if so desired.
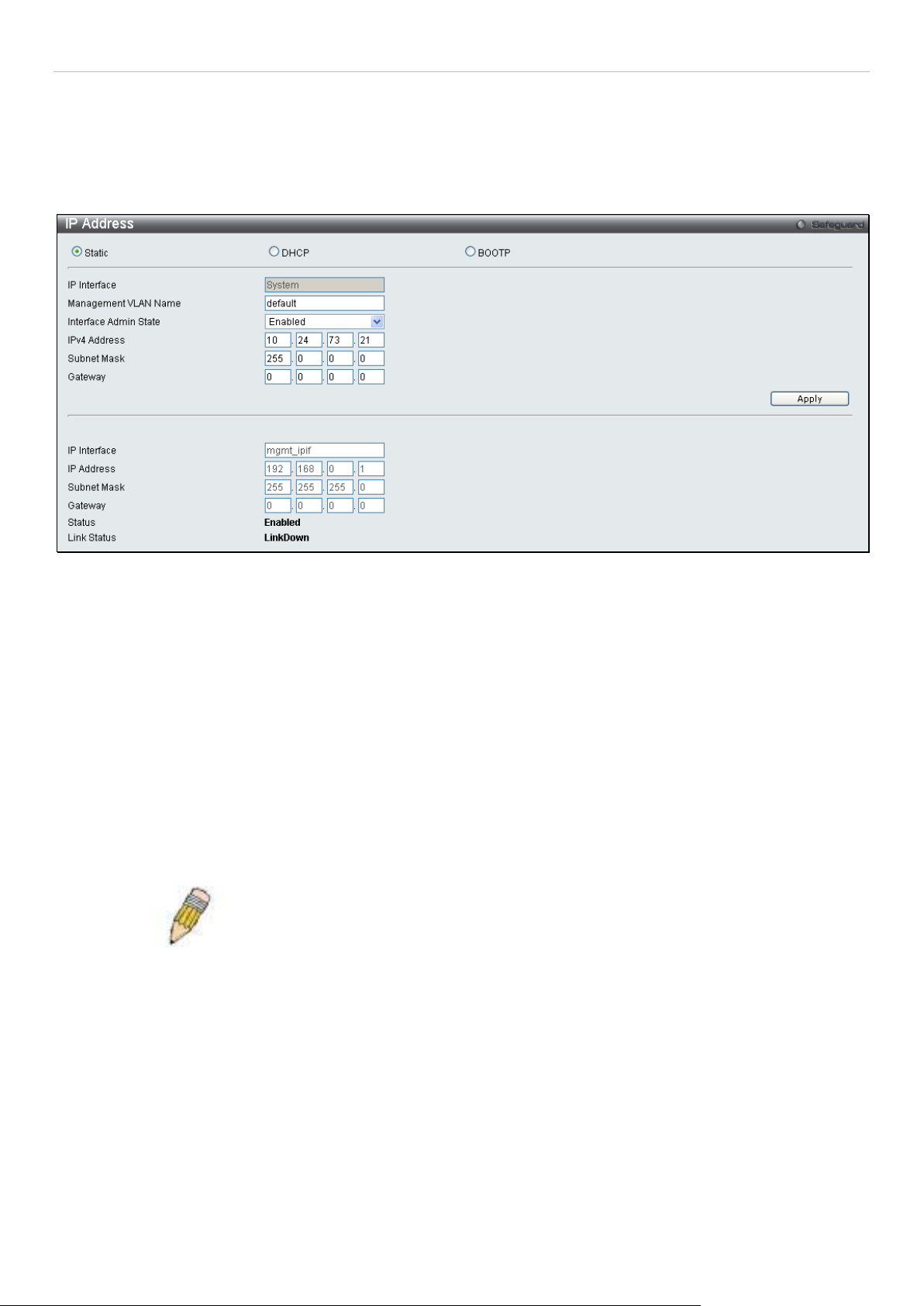
Serial Port Settings
The following window co nta ins infor mation about the Serial Port Sett in gs inclu di ng the B aud Rate and the Auto Log out
settings.
To view this window, click Configuration > Serial Port Settings as shown below:
Figure 2 - 3 Serial Port Settings window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter Description
Baud Rate
Auto Logout
Click Apply to implement changes made.
This field specifies the baud rate for the serial port on the Switch. There are four possible
baud rates to choose f rom, 9600, 19200, 38400 and 115200. For a conn ection to the Switch
using the CLI interface, the baud rate must be set to 115200, which is the default setting.
Select the logout tim e us ed f or the cons ol e in terface. This automatic all y logs t h e u ser out af ter
an idle period of tim e, as defined. Choose from the following options : 2 Minutes, 5 Minutes, 1 0
Minutes, 15 Minutes or Never. The default setting is 10 minutes.
NOTE: If a user configures the serial port’s baud rate, the baud rate will take ef fect and save
immediate ly. B aud rat e set tings wi ll no t chan ge e ven if the us er r esets or r eboo ts th e Swi tch. T he
Baud rate will only change when the user configures it again. The serial port’s baud rate setting is
not stored in th e Switch’s conf iguration fil e. Resetting t he Switch will no t restore the bau d rate to
8
Page 20
DGS-3700-12/DGS-3700-12G Series Layer 2 Gigabit Ethernet Switch User Manual
IP Address
The IP address ma y initially be set using the console interface prior to connecting to it throug h the Ethernet. If the
Switch IP address has not yet been change d, read the introduction of the DGS-3700 Series CLI Manual for more
information.
To view this window, click Configuration > IP Address as shown below:
Figure 2 - 4 IP Address Settings window
The upper part of the pag e allows you to manual ly assign the S witch's IP a ddress , subnet m ask, and defaul t gatewa y
address:
1. Select Static at the top of the screen.
2. Enter the appropriate IP Address and Subnet Mas k .
3. If you want to access the Switch from a dif fer ent subn et fr om the on e it is insta lled on, enter the I P addr ess of
the Gateway. If you will m anage t he Switc h fr om the subne t on which it is insta lled, you can leave th e defaul t
address (0.0.0.0) in this field.
4. If no VLANs have been pre vious ly configured on the Sw itch, you can use the default VLAN Name. The default
VLAN c ontains all of the Switch p orts as m embers. If VLANs have been pr eviously conf igured on the S witch,
you will need to enter the Management VLAN Name of the VLAN that contains the port connected to the
management station th at will acc ess the Switc h. The S witch will a llow managem ent acc ess fr om stations wi th
the same VID listed here.
NOTE: The Switch's factory default IP address is 10.90.90.90 with a
subnet mask of 255.0.0.0 and a default gateway of 0.0.0.0.
To use the BOOTP or DHCP protocols to assign the Switch an IP address, subnet mask, and default gateway
address:
Select BOOTP or DHCP, this will determine how the Switch will be assigned an IP address.
The lower part of the page is to display the Out-of-band management information that has been configured in
Configuration > Out of Band Management Settings window.
The IP Address Settings options are:
9
Page 21
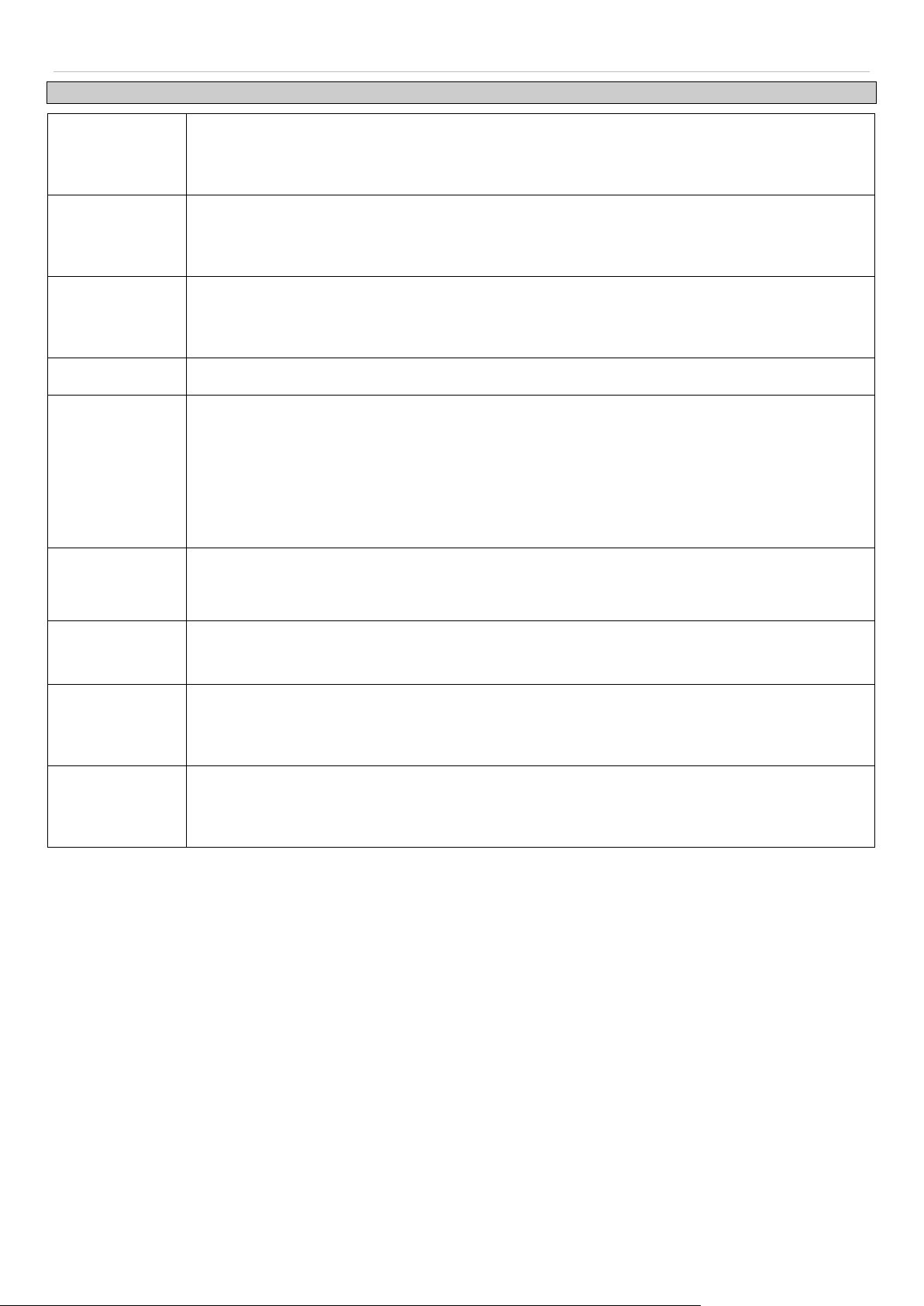
DGS-3700-12/DGS-3700-12G Series Layer 2 Gigabit Ethernet Switch User Manual
Interface Admin
Parameter Description
Static
DHCP
BOOTP
IP Interface
Management
VLAN Name
State
Allows the entry of an IP address, Subnet Mask, and a Def ault Gateway for the Switch. Thes e
fields should be of the form xxx. xxx.xxx.xxx , where each x xx is a num ber (represente d in decim al
form) between 0 and 2 55. This address should be a unique addr ess on the n etwork assigned for
use by the network administrator.
The Switch will sen d out a DHCP broadcas t request when it is powered up. T he DHCP pro tocol
allows IP address es, network masks, and defaul t gateways to be assigned b y a DHCP server . If
this option is set, the Sw itch will first look for a DHCP server to provide it with this information
before using the default or previously entered settings.
The Switch will send out a BOOTP broadcast request when it is powered up. The BOOTP
protocol allows IP addr esses, network masks , and default gateways to be assigned b y a central
BOOTP server. If t his optio n is set, the S witch will first lo ok f or a BOOT P server t o provide it with
this information before using the default or previously entered settings.
This field displays the IP Interface that is currently being used on the Switch.
This allows the entry of a VLAN Name from which a management station will be allowed to
manage the Switch usin g TCP/IP (in-band via web manager or Telne t). M anagement stations th at
are on VLANs other than the one entered here will not be able to m anage the Switch in-band
unless their IP address es are entered in the Securit y IP Management window. If VLANs have
not yet been configur ed for the Switch, t he default VL AN contains all of the Switc h's ports. Ther e
are no entries in th e Security IP Mana gement table, by d efault, so any m anagement station that
can connect to the Switch can access the Switch until a management VLAN is specified or
Management Station IP Addresses are assigned.
This field enables or disables the Interface Admin State. When the state is enabled, the IPv4
processing will be start ed when the IPv4 addr ess is configured on t he IPIF. The IPv6 proc essing
will be started when the IPv6 address is explicitly configured on the IPIF.
IPv4 Address
The address should specify a host address and length of the network prefix. There can be
multiple IPv4 addresses defined on an interface. Thus, as a new address is defined, it is added on
this IP Interface.
Subnet Mask
A Bitmask that determ ines the extent of the subnet that the S witch is on. Shoul d be of the form
xxx.xxx.xxx.xx x, where each xxx is a number (repr esented in decimal) bet ween 0 and 255. The
value should be 255.0.0.0 for a Class A network, 255.255.0.0 for a Class B network, and
255.255.255.0 for a Class C network, but custom subnet masks are allowed.
Gateway
IP address that determ ines where pack ets with a destination a ddress outside th e current subnet
should be sent. This is usually the address of a rout er or a host ac ting as an IP gate way. If your
network is not part of an Intranet, or you do not want the S witch to be accessible outside your
local network, you can leave this field unchanged.
Click Apply to implement changes made.
10
Page 22
DGS-3700-12/DGS-3700-12G Series Layer 2 Gigabit Ethernet Switch User Manual
Setting the Swith’s IP Address using the Console Interface
Each Switch must be ass igned its own I P Address, which is used for c omm unication with an SN MP network m anager
or other TCP/IP application (for example BOOTP, TFTP). The Switch’s default IP address is 10.90.90.90. You can
change the default Switch IP address to meet the specification of your networking address scheme.
The IP address for the Switch must be set before it can be managed with the W eb-based manager. The Swit ch IP
address can be aut omaticall y set usin g BOOT P or DHCP protocols , in wh ich cas e the actu al addres s assigned to the
Switch must be known. T he IP address may be set using the C ommand Line Interfac e (CLI) over the console serial
port as follows:
Starting at the command line prompt, enter the commands config ipif System ipaddress
xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx/yyy.yyy.yyy.yyy, where the x’s represent the IP address to be assigned to the IP interface named
System and the y’s represent the corresponding subnet mask.
Alternatively, you can enter config ipif System ipaddress xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx/z, where the x’s represents the corresponding
number of subnets in CIDR notation.
The IP interface named System on the Switch can be assigned an IP address and subnet mask which can then be
used to connect a management station to the Switch’s Telnet or Web-based management agent.
The system message Success indicated that the command was executed successfully. The Switch can now be
configured and managed via Telnet and the CLI or via the Web-based management ag ent us ing th e abo ve ip addr ess
to connect to the Switch.
Interface Setti ngs
This window allows the user to create and configure interfaces on the Switch.
To view this window, click Configuration > Interface Settings as shown below:
Figure 2 - 5 Interface Settings window
The following parameters can be configured:
Parameter Description
Interface Name
VLAN Name
Interface Admin.
State
Click Create to create the entry or D elete All to delete all the current IP Interface entries.
Enter the name you wish to give the IP Interface.
Enter the name of the VLAN corresponding to the System interface.
Allows the user to enable or disable the interface administration state.
To edit the VLAN Name or Admin. State click the IPv4 Edit or IPv6 Edit button as shown below.
Figure 2 - 6 Interface Settings Edit window
11
Page 23
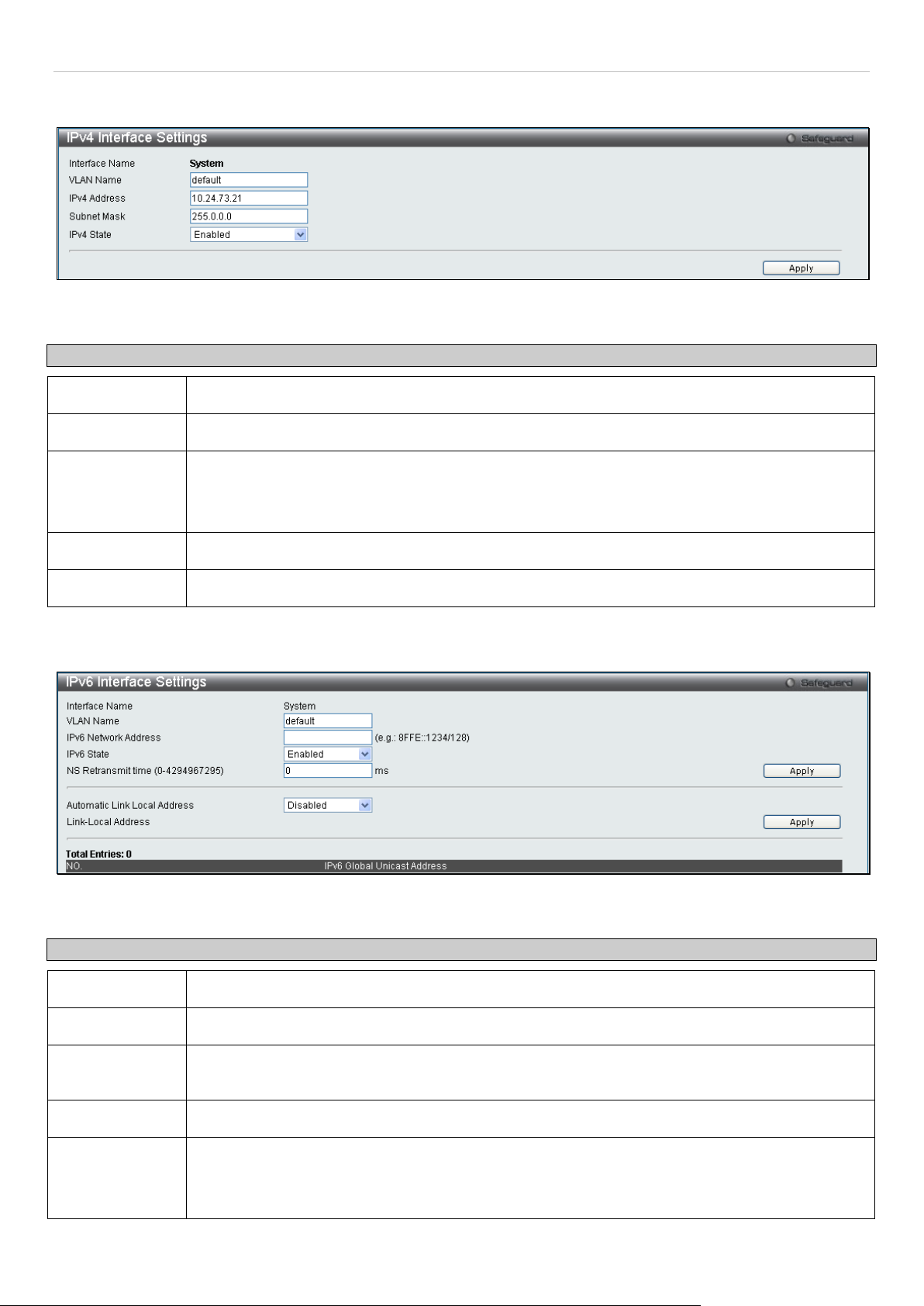
DGS-3700-12/DGS-3700-12G Series Layer 2 Gigabit Ethernet Switch User Manual
IPv6 Network
NS Retransmit
Enter the new VLAN Name and Admin. State and click Apply. To edit an entry for IPv4 features click the
corresponding IPv4 Edit button.
Figure 2 - 7 IPv4 Interface Settings Edit window
The following parameters can be configured:
Parameter Description
Interface Name
VLAN Name
IPv4 Address
Displays the interface being edited.
Enter the name of the VLAN corresponding to the interface.
Enter an alternative IPv4 address. Currently an interface can only have one IPv4 address defined.
Therefore multinetting configuration of IPv4 must be done through creation of a secondary
interface on the sam e VLAN, instead of dir ectly config uring multiple I Pv4 addresses on the same
interface.
Subnet Mask
IPv4 State
Enter the corresponding subnet mask.
This function allows user to enable the IPv4 address on the IP interface.
Click Apply to implement changes made.
To edit an entry for IPv6 features click the corresponding IPv6 Edit button.
The following parameters can be configured:
Parameter Description
Interface Name
VLAN Name
Address
IPv6 State
time (0-
4294967295)
Figure 2 - 8 IPv6 Interface Settings Edit window
Displays the interface being edited.
Enter the name of the VLAN corresponding to the interface.
Enter the IPv6 Network Address to be configured. The interface can have multiple IPv6 addresses
defined. Configuration of IPv6 addresses must be done through the command config ipif.
Allows the user to enable or disable the IPv6 state on the interface.
This field is used to set the interval, in milliseconds that the Switch will produce neighbor
solicitation pack ets to be s ent out over the local net work . This is use d to disc over IP v6 neigh bors
on the local network. The user may select a time between 0 and 4294967295 milliseconds. The
default is 0.
12
Page 24
DGS-3700-12/DGS-3700-12G Series Layer 2 Gigabit Ethernet Switch User Manual
Automatic Link
Enables or disables the automatic configurat ion of link local addresses when there are no IPv6
Local Address
Click Apply to implement changes made.
addresses explicitly configured. When an IPv6 address is explicitly configured, the link local
address will be aut omatically configur ed, and the IPv6 processing will be started. When there is
no IPv6 address explicitl y configure d, by default, li nk local ad dress is not c onfigured and th e IPv6
processing will b e disab le d. By enabling this aut omatic configuration, the link local ad dr ess will b e
automatically configured and IPv6 processing will be started.
IPv6 Route Settings
This window allows the user to create and configure IPv6 Route interfaces to the Switch’s IP routing table.
To view this window, click Configuration > IPv6 Route Settings as shown below:
Figure 2 - 9 IPv6 Route Settings window
The following parameters can be configured:
Parameter Description
Interface Name
Nexthop
Address
Metric (1-65535)
Backup State
Click Apply to implement changes made. To remove any entry, click the Delete All button.
Enter the name you wish to give the IPv6 Route Interface.
Enter the IPv6 address for the next hop router.
Allows the entr y of a ro uti n g pr ot oc ol metric entry repres enti ng the n umber of routers betw ee n t he
Switch and the IP address above. The default setting is 1.
The user may choose b etween Prim ary and Back up. If the Prim ary Static/Def ault Route f ails, the
Backup Route will support the entry.
IPv6 Neighbor Settings
This window allows the user to creat e and config ure IPv6 Neig hbor settings on the Switch . The Switch ’s current IPv6
neighbor settings will be displayed in the table at the bottom of this window.
To view this window, click Configuration > IPv6 Neighbor Settings as shown below:
The following parameters can be configured:
Figure 2 - 10 IPv6 Neighbor Settings window
13
Page 25
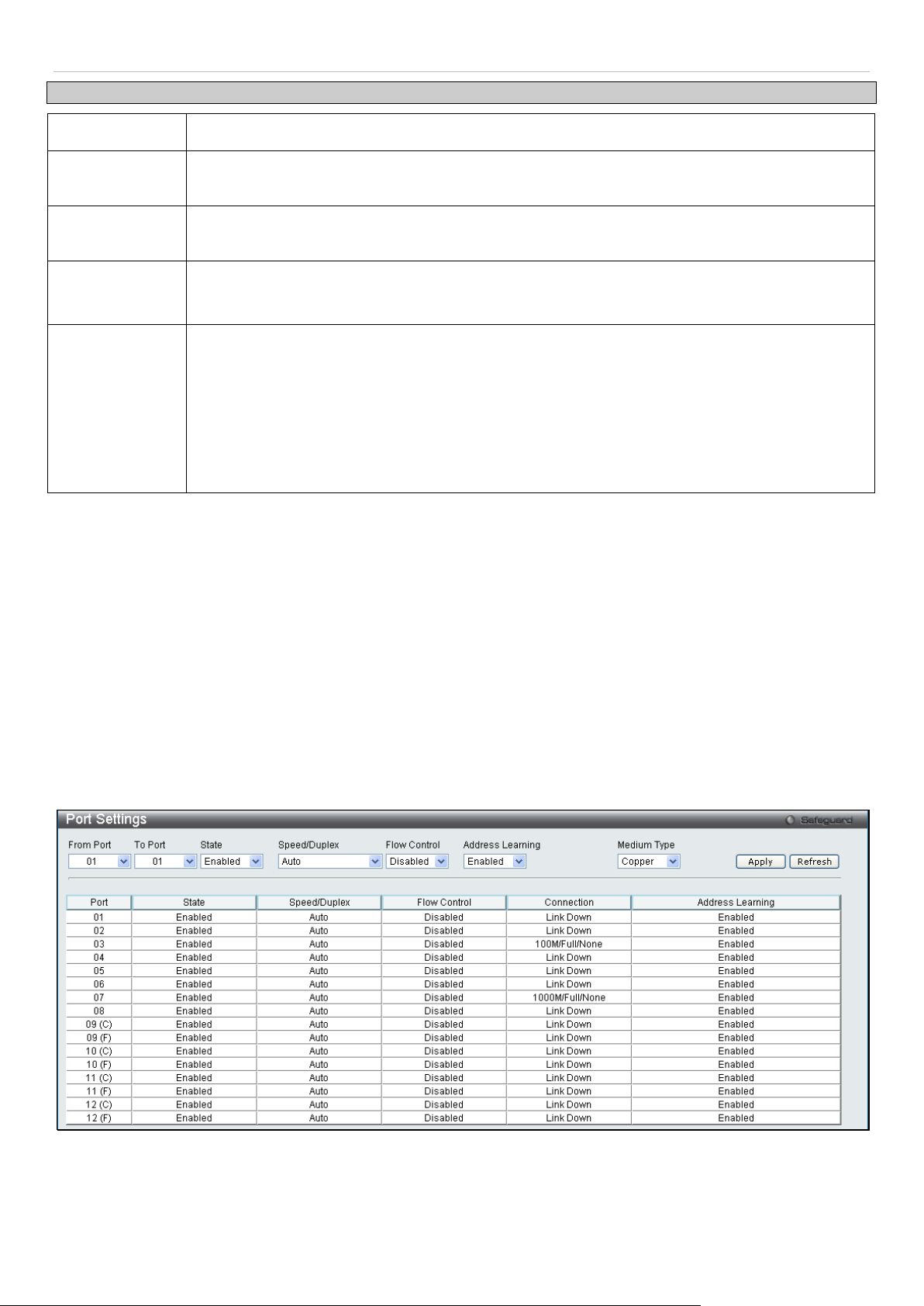
DGS-3700-12/DGS-3700-12G Series Layer 2 Gigabit Ethernet Switch User Manual
Neighbor IPv6
neighbors of the IP interface previously created.
Parameter Description
Interface Name
Address
Link Layer MAC
Address
Interface Name
State
Click Add to add a new entry, click Find to search for a specific entry or click Clear to remove an entry.
Enter the interface name of the IPv6 neighbor you wish to configure.
Enter the neighbor IPv6 address of the entry you wish to configure.
Enter the MAC address of the neighbor device to be added as an IPv6 neighbor on the IP
interface.
In order to search f or a previously configured Interfac e name enter the appropriate inform ation
and click Find. To remove a prev iously configured Interface enter the I nterface name and click
Clear.
To find or delete specific entries use the pull down menu to select All, Address, Static, or
Dynamic.
All – Select All to view all configured neighbor devices which are IPv6 neighbors of the IP
interface previously created.
Address – Select Address and enter the IPv6 address of the entry you wish to find.
Static – Select Static to view all statically entered IPv6 neighbors on the Switch.
Dynamic – Select Dynamic to view all dynamically configured neighbor devices which are IPv6
Port Configuration
This section contains information for configuring various attributes and properties for individual physical ports,
including port speed and flow control.
Port Settings
To view this window, click Configuration > Port Configuration > Port Settings as shown below:
To configure switch ports:
Choose the port or sequential range of ports using the From Port / To Port port pull-down menus.
Use the remaining pull-down menus to configure the parameters described below:
The following parameters can be configured:
Figure 2 - 11 Port Settings window
14
Page 26

DGS-3700-12/DGS-3700-12G Series Layer 2 Gigabit Ethernet Switch User Manual
will allow the port to
Parameter Description
From Port / To Port
State
Speed/Duplex
Flow Control
Use the pull-down menus to select the port or range of ports to be configured.
Toggle this field to either enable or disable a given port or group of ports.
Toggle the Speed/Duplex field to either se lect the s peed an d duplex/ half-dup lex s tate of th e
port. Auto denot es aut o-negotiation between 1 0 an d 1 00 Mb ps de vices , i n f ull- or half-duplex.
The Auto sett in g al lo ws t he port to automatically determine the f as test setti ngs th e d ev ic e t he
port is connected to can ha ndle, and then to use thos e settings. The other options are Auto,
10M/Half, 10M/Full, 100M/Half and 100M/Full, 1000M/Full_M, 1000M/Full_S and 1000M/Full.
There is no automatic adjustment of port settings with any option other than Auto.
The Switch allows the us er to config ure two types of gigabit connec tions; 1000M/Full_M and
1000M/Full_S. G igabit connections on ly support full duplex connect ions and take on certain
characteristics that are different from the other choices listed.
The 1000M/Full_M (master) and 1000M/Full_S (slave) parameters refer to connections
running a 1000BASE-T cable for connection between the Switch port and other device
capable of a gigabit connection. The master setting (1000M/Full_M)
advertise capabilities r elat e d to du pl ex, s peed and physical layer type. T he master setting will
also determine the m aster and sla ve relat ionship b etween th e t wo connected ph ysical la yers.
This relationship is necessary for establishing the timing control between the two physical
layers. The timing control is set on a master physical layer by a local source. The slave
setting (1000M/Full_S) uses loop timing, where the timing comes form a data stream
received from the m aster. If one connection is set f or 1000M/Full_M, the other side of the
connection mus t be set for 1000M/Full_S. An y other configuration will result in a link down
status for both ports.
Displays the flo w control scheme used for the various port configurations . Ports configured
for full-duplex use 802 .3x flow control, half-dup lex ports use backpressur e flow control, and
Auto ports use an automatic selection of the two. The default is Disabled.
Address Learning When Enabled, destination and source MAC addresses are automatically listed in the
forwarding table. The default setting is Enabled.
Medium Type
Click Apply to implement the new settings on the Switch. Click Refresh to reload the page.
This applies onl y to the Co mbo ports. If configuring the Combo p orts this def ines the t ype of
transport medium used. SFP ports shou ld be set at Fiber and t he Combo 10 00BASE-T ports
should be set at Copper.
Port Description
The Switch supports a port description feature where the user may assign names to various ports on the Switch.
Use the From Port / To Port pull-down menu to choose a port or range of ports to describe, and then enter a
description of the port(s). Click Apply to set the descriptions in the Port Description Table.
The Medium Type applies only to the Combo ports. If configuring the Combo ports this defines the type of tranport
medium used. SFP ports should be nominated Fiber and the Combo 1000BASE-T ports should be nominated Copper.
The result will be displayed in the appropriate switch port number slot (C for copper ports and F for fiber ports).
To view this window, click Configuration > Port Configuration > Port Description as shown below:
15
Page 27

DGS-3700-12/DGS-3700-12G Series Layer 2 Gigabit Ethernet Switch User Manual
Figure 2 - 12 Port Description window
Port Error Disabled
The following window will display the information about ports that have had their connection status disabled, for
reasons such as Loopback Detection or link down status.
To view this window, click Configuration > Port Configuration > Port Error Disabled as shown below.
Figure 2 - 13 Port Error Disabled window
The following parameters are displayed:
Parameter Description
Port
Port State Describes the current running state of the port, whether Enabled or Disabled.
Connection Status
Reason
Displays the port that has been error disabled.
This field will read the uplink status of the individual ports, whether enabled or Disabled.
Describes the reason why the port has been error-disabled, such as a STP loopback
occurrence.
Static ARP Settings
The Address Resolutio n Protoc ol (ARP) is a TC P/IP pr otocol t hat con verts I P addres ses into ph ysica l addres ses. T his
table allows network managers to view, define, m odify and delete ARP inf ormation for spec ific devices. Sta tic entries
can be defined in the ARP Table. When static entries are defined, a permanent entry is entered and is used to
translate IP address to MAC addresses.
To view this window, click Configuration > Static ARP Settings as shown below:
16
Page 28
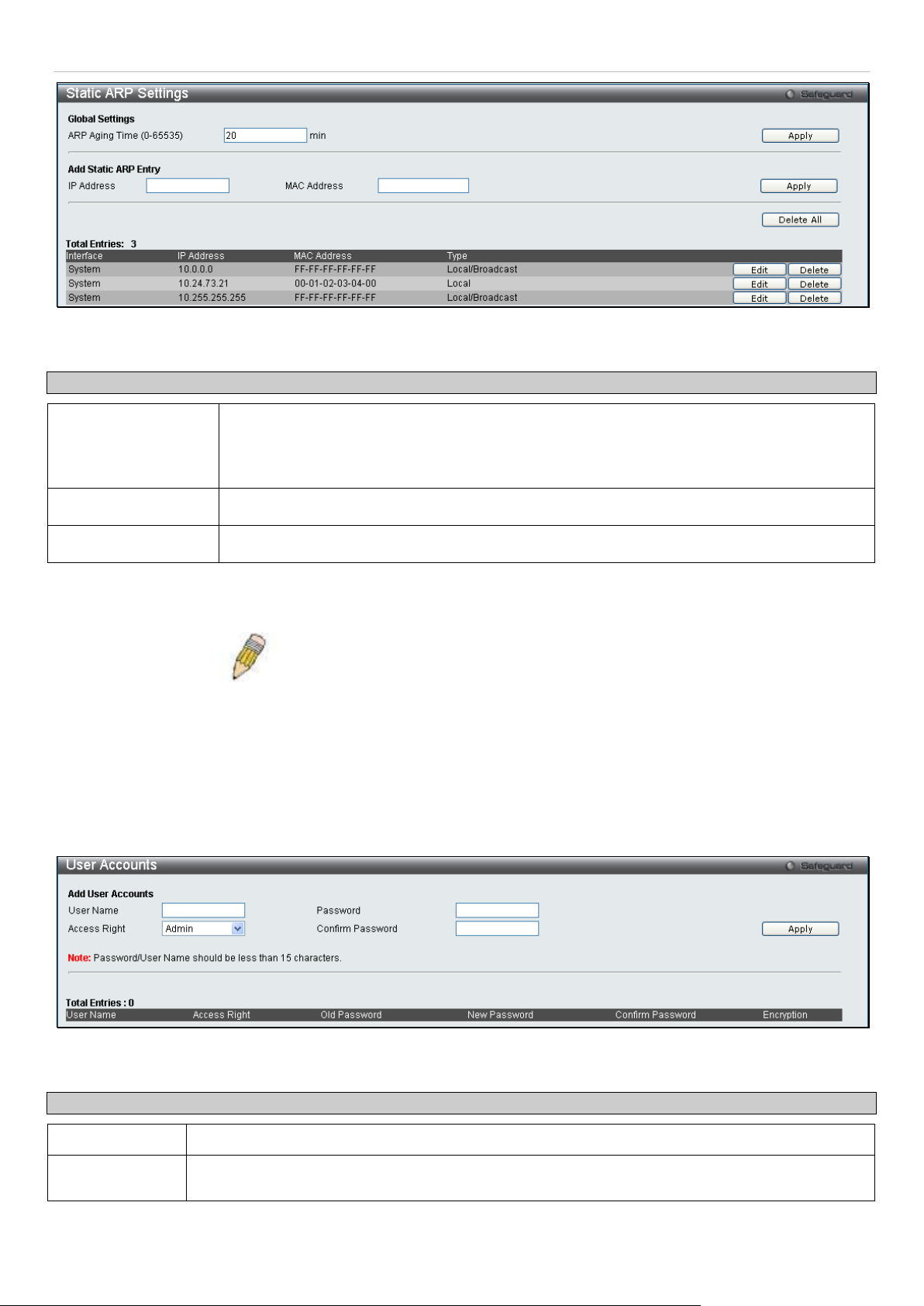
DGS-3700-12/DGS-3700-12G Series Layer 2 Gigabit Ethernet Switch User Manual
available to users with Admin privileges m ay not be available to those with User or Operator
The following fields can be set:
Parameter Description
Figure 2 - 14 Static ARP Settings window
ARP Aging Time
(0-65535)
IP Address
MAC Address
After entering the IP Addr ess and MAC Addres s of the Static ARP e ntry, click Apply to im plement the new entr y. To
completely clear the Static ARP Settings, click the Delete All button.
The user may globally set the maximum amount of time, in minutes, that an Address
Resolution Protocol (ARP) entry can remain in the Switch’s ARP table, without being
accessed, before it is dro pped from the tabl e. The value m ay be set in the range of 0-65535
minutes with a default setting of 20 minutes.
The IP address of the ARP entry.
The MAC address of the ARP entry.
NOTE: The Switch supports up to 255 static ARP entries.
User Accounts
Use the User Account Management window to control user privileges, create new users and view existing User
Accounts.
To view this window, click Configuration > User Accounts as shown below:
Figure 2 - 15 User Accounts window
The following fields can be set:
Parameter Description
User Name
Access Right There are three levels of user privileges, Admin, Operator and User. Some menu selections
The name of the user, an alphanumeric string of up to 15 characters.
17
Page 29
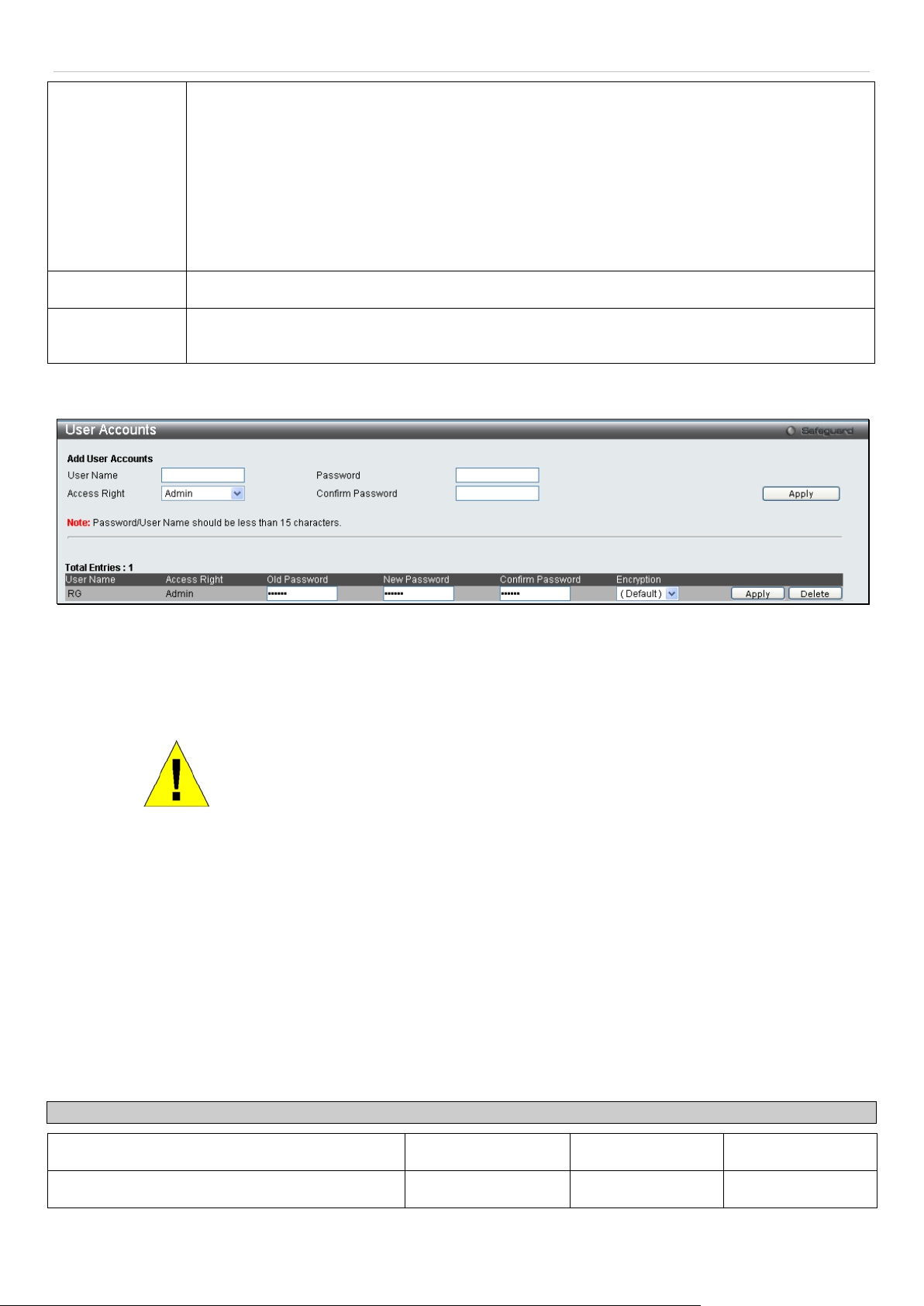
DGS-3700-12/DGS-3700-12G Series Layer 2 Gigabit Ethernet Switch User Manual
level privileges.
There are 3 leve ls of securit y offered on the Switch, the Operator level privilege will allow us ers
to configure and view conf igurations on the Switch, except f or those involving security features,
which are still left to the Admin level privilege. Operator le vel user s c an be a uth e ntic at ed thr o ugh
either the local authe nticati on m ethod of the Switc h, or through t he Acc ess Auth entic ation Contr ol
feature, discussed later in this document. Once the user has logged in to the Switch in the
Operator level, c ertain security screens and windows wi ll not be made available to view, or to
configure. Only Admin level users have access to these features.
(Table 2 - 1 below summarizes Admin, Operator and User level privileges)
New Password
Confirm New
Password
To add a new user, enter the appropriat e information and click Apply. To del ete an account cl ick the correspond ing
Delete button. To modify an existing user account, click Edit as shown below.
Enter the Old Pass word for the account, the Ne w Password you wish to use, and retype the new passw ord in the
Confirm Password field. Us e the drop-down m enu to select the type of enc ryption (Default, Plain T ext or Sha 1), and
click Apply.
Enter a password for the new user.
Retype the new password.
Figure 2 - 16 User Accounts window
Admin, Operator and User Pri vileges
Recently added to the levels of security offered on the Switch, the Operator level priv ilege will allow users to configure
and view conf igurations on the S witch, except for those in volving security features , which are still left t o the Admin
privilege. Operator us ers c an be auth ent ic ate d thr o ug h eit her th e loc a l au the ntication method of the Sw itch, or thr oug h
the Access Authentication Control feature, discussed later in this document. Once the user has logged in to the Switch
in the Operator level, cer tain security screens and windows will not be made availab le to view, or to configure. Onl y
Admin level users have access to these features.
There are three lev els of user privileges, Admin, Operator and User. Som e menu selections available to users with
Admin privileges may not be available to those with User or Operator privileges.
The following table summarizes the Admin, Operator and User privileges:
Management Admin Operator User
Configuration Yes Yes Read-only
Network Monitoring Yes Yes Read-only
NOTICE: In case of lost passwords or password c orruption, please refer to the
D-Link website an d the White Paper entitled “Pass word Recovery Procedure”,
which will guide you through the steps necessary to resolve this issue.
18
Page 30
DGS-3700-12/DGS-3700-12G Series Layer 2 Gigabit Ethernet Switch User Manual
Community Strings and Trap Stations Yes Yes Read-only
Update Firmware and Configuration Files Yes No No
System Utilities Yes Yes No
Factory Reset Yes No No
User Account Management
Add/Update/Delete User Accounts Yes No No
View User Accounts Yes No No
Table 2 - 1 Admin, Operator and User Privileges
19
Page 31

DGS-3700-12/DGS-3700-12G Series Layer 2 Gigabit Ethernet Switch User Manual
System Log Configuration
This section contains information for configuring various attributes and properties for System Log Configurations,
including System Log Settings and System Log Host.
System Log Settings
This window allows the user to enable or disable the System Log and specify the System Log Save Mode Settings.
To view this window, click Configuration > System Log Configuration > System Log Settings as shown below:
Figure 2 - 17 System Log Settings window
The following parameters can be set:
Parameter Description
System Log To activate the System Log select Enabled or Disabled.
Save Mode
Minutes (1-65535)
To add a new entry, enter the appropriate information and click Apply.
Use this drop-dow n menu to spec ify the method that will trigger a log entry. You can choose
between On Demand, Time Interval and Log Trigger.
On Demand – This method will o nly save log files whe n they manually tel l t he S wi tc h to do s o,
using the Save Log link in the Save folder.
Time Interval – This m ethod configures a time interval b y which the Switch will save the log
files. The user may set a time between 1 and 65535 minutes.
Log Trigger – This method will save log files to the Switch every time a log event occurs on the
Switch.
Enter a time interval, in minutes, for which you would like a log entry to be made.
System Log Server
The Switch can send Syslog messages to up to four designated servers using the System Log Server.
To view this window, click Configuration > System Log Configuration > System Log Server as shown below:
The following parameters can be set:
Figure 2 - 18 System Log Server window
20
Page 32

DGS-3700-12/DGS-3700-12G Series Layer 2 Gigabit Ethernet Switch User Manual
Numerical Facility Code Numerical Facility Code
Parameter Description
Server ID
Server IP Address
UDP Port
(514 or 6000-65535)
Severity
Facility
Syslog server settings index (1-4).
The IP address of the Syslog server.
Type the UDP port number used for sending Syslog messages. The default is 514.
This drop-down menu all ows you to selec t the level o f m essages that w ill be sen t. The options
are Warning, Informational, and All.
Some of the operating s ystem daemons and processes have been assigned Facilit y values.
Processes and daem ons that have not been exp licitly assigne d a Facility m ay use any of th e
"local use" facilities or they may use the "user-level" Facility. Those F acilities that have been
designated are shown in th e following: Bold font ind icates the fac ility values th at the Switc h is
currently employing.
0
1
2
3
4
5
7
8
9
10
11
kernel messages
user-level messages
mail system
system daemons
security/authorization messages
messages generated intern ally by
syslog line printer subsyste m
network news subsystem
UUCP subsystem
clock daemon
security/authorization messages
FTP daemon
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
NTP subsystem
log audit
log alert
clock daemon
local use 0 (local0)
local use 1 (local1)
local use 2 (local2)
local use 3 (local3)
local use 4 (local4)
local use 5 (local5)
local use 6 (local6)
local use 7 (local7)
Status Choose Enabled or Disabled to activate or deactivate.
To add a new entry, enter the appropriate information and click Apply.
21
Page 33

DGS-3700-12/DGS-3700-12G Series Layer 2 Gigabit Ethernet Switch User Manual
System Severity Settings
The Switch can be configured to allow alerts be logg ed or s ent as a t rap to an SN MP a gent or both. The level at whic h
the alert triggers either a log entry or a trap m essage can be set as well. Us e the System Severi ty Settings menu to
set the criteria for alerts. The current settings are displayed below the Settings menu.
To view this window, click Configuration > System Severity Settings as shown below:
Figure 2 - 19 System Severity Settings
Use the drop-down menus to configure the parameters described below.
Parameter Description
System Severity Choose how the a lerts ar e used f rom the dro p-do wn menu. Select log to send the alert of the
Severity Type configur ed to the Switc h’s log for ana lysis. Choos e trap to send it to an SNMP
agent for analysis. Select all to send the chosen alert type to an SNMP agent and the
Switch’s log for analysis.
Severity Level
Click Apply to implement the new System Severity Settings.
Choose what level of alert wil l trigger sen ding the log entry or trap m essage as defined by the
Severity Name. Selec t critical t o send onl y critical eve nts to the Switch’s log or SNMP ag ent.
Choose warning to send critical and warning events to the Switch’s log or SNMP agent.
Select information to send informational, warning and critical events to the Switch’s log or
SNMP agent.
22
Page 34

DGS-3700-12/DGS-3700-12G Series Layer 2 Gigabit Ethernet Switch User Manual
Disabled – If the field is toggled to Disabled the relay agent will not insert and remove
DHCP Relay
The DHCP Rela y folder co ntains s ix windo ws regar ding t he DHCP r ela y funct ions on the Switc h. T he DH CP windo ws
include DHCP Relay Global Settings, DHCP Relay Interface Settings, DHCP Relay Option 60 Default Settings,
DHCP Relay Option 60 Settings, DHCP Realy Option 61 Default Settings and DHCP Relay Option 61 Settings.
DHCP Relay Global Settings
This window is used to e nable and c onfigure D HCP Relay Global Settings on the Switch. The relay hops count limit
allows the maximum number of hops (routers) that the DHCP messages can be relayed through to be set. If a
packet’s hop count is m ore tha n the hop c ount l imit, th e pack et is dropp ed. T he range is between 1 and 16 hops, with
a default value of 4. The relay time threshold sets the m inimum time (in seconds) that the Switch will wait before
forwarding a DHCP REQUEST packet. If the value in the seconds field of the packet is less than the relay time
threshold, the packet will be dropped. The range is between 0 and 65,536 seconds, with a default value of 0 seconds.
To view this window, click Configuration > DHCP Relay > DHCP Relay Global Settings as shown below:
Figure 2 - 20 DHCP Relay Global Settings window
The following fields can be set:
Parameter Description
DHCP Relay State This field can be toggled between Enabled and Disabled using the pull-down menu. It is
used to enable or disable the DHCP Relay service on the Switch. The default is Disabled.
DHCP Relay Hops
Count Limit (1-16)
DHCP Relay Time
Threshold (0-65535)
DHCP Relay Option
82 State
This field allows an entry bet ween 1 and 16 to define the m aximum num ber of router hops
DHCP messages can be forwarded across. The default hop count is 4.
Allows an entry between 0 and 65535 seconds, and defines the maximum time limit for
routing a DHCP p acket. If a value of 0 is entered, the S witch will not process the value in
the seconds field of the DHCP packet. If a non-zero value is entered, the Switch will use
that value, along with the hop count to determine whether to forward a given DHCP packet.
This field can be toggled between Enabled and Disabled using the pull-down menu. It is
used to enable or disabl e t he D HC P A ge nt Inf or mation Option 82 on the Switch. T he default
is Disabled.
Enabled – When this field is toggled to Enabled the relay agent will insert and remove
DHCP relay inform ation (option 82 field) in messages bet ween DHCP servers and clients.
When the relay agent rec ei ves th e D HC P r eq ues t, i t a dds the opt ion 82 inf or mation, and the
IP address of the relay agent (if the relay agent is configured), to the packet. Once the
option 82 inform ation has b een ad ded to the pack et it is s ent on to the DH CP s erver. W hen
the DHCP server rece ives t he pac k et, if the s erver is capab le of option 82, it can im plem ent
policies like restric ting the num ber of IP address es that can be ass igned to a sin gle remote
ID or circuit ID. T hen the DHCP server ec hoes the option 82 f ield in the DHCP reply. The
DHCP server unicasts the reply to the bac k to the rel ay agent if the req uest was rela yed to
the server by the relay agent. The switch verifies that it originally inserted the option 82
data. Finally, the relay agent removes the option 82 field and forwards the packet to the
switch port that connects to the DHCP client that sent the DHCP request.
23
Page 35

DGS-3700-12/DGS-3700-12G Series Layer 2 Gigabit Ethernet Switch User Manual
DHCP relay inform ation (option 82 field) in messages bet ween DHCP servers and clients,
and the check and policy settings will have no effect.
DHCP Relay Agent
Information Option 82
Check
DHCP Relay Agent
Information Option 82
Policy
DHCP Relay Option
60 State
This field can be toggled between Enabled and Disabled using the pull-down menu. It is
used to enable or disable the S witches ability to check the v alidity of the pac ket’s option 8 2
field.
Enabled – W hen the field is toggled to Enable, t he relay agent will c heck the validit y of the
packet’s option 82 f ield. I f t he switch receives a packet that contains t he op tio n-82 field from
a DHCP client, the switch drops the packet because it is invalid. In pac kets received from
DHCP servers, the relay agent will drop invalid messages.
Disabled – When the field i s toggled to Disabled, the relay agent wil l not check the validit y
of the packet’s option 82 field.
This field can be to ggl ed b et wee n R epl ac e, Drop, and Keep by using the pull-do wn menu. It
is used to set the Switches polic y for handling p ack ets when the DHCP Agent Information
Option 82 Check is set to Disabled. The default is Replace.
Replace – The option 82 field will be replaced if the option 82 field already ex ists in the
packet received from the DHCP client.
Drop – The pack et w ill be d r oppe d if the op ti on 82 f ie ld alr ea d y exis ts in the pac ket received
from the DHCP client.
Keep – The optio n 82 field will be retaine d if the optio n 82 field alread y exists in the pac ket
received from the DHCP client.
This function enables or disables the DHCP option 60 state. W hen option 60 is enabl ed, if
the packet does not have opt ion 60, then the rela y servers cannot be determined based on
option 60. The relay servers will be determined based on either option 60 or per IPIF
configured servers. If the relay servers are determined bas ed on option 60, then the IPIF
configured servers will be ignore d. If t he r ela y server s are not d eterm ined b y option 60 then
the IPIF configured servers will be used to determine the relay servers.
DHCP Relay Option
61 State
This function enables or disables the DHCP option 61 state. W hen option 61 is enabled, if
the packet does not have opt ion 61, then the rela y servers cannot be determined based on
option 61. The r ela y servers wil l be determined bas ed on o ption 61 and the IPIF configured
servers will be ignored. If the relay ser vers are not deter mined e ither b y option 6 0 or optio n
61, then IPIF configured servers will be used to determine the relay servers.
Click Apply to implement any changes that have been made.
NOTE: If the Switch receives a packet that contains the option-82 field from a DHCP client and the
information-check ing feature is enabled, the switch drops the pack et because it is invalid. H owever, in
some instances, you might configure a client with the option-82 field. In this situation, you should
disable the inform ation-check feature so that the s witch does not remove the o ption-82 field from the
packet. You can configure the action that the switch takes when it receives a packet with existing
option-82 information by configuring the DHCP Agent Information Option 82 Policy.
24
Page 36

DGS-3700-12/DGS-3700-12G Series Layer 2 Gigabit Ethernet Switch User Manual
The Implementation of DHCP Inf orm a t ion Option 82 on the Switch
The config dhcp_relay option_82 command conf igures the DHCP rela y agent information optio n 82 setting of the
switch. The formats for the circuit ID sub-option and the remote ID sub-option are as follows:
NOTE: For the circuit ID sub-opt ion of a standalone switch, th e module field is always
zero.
Circuit ID sub-option format:
1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7.
1 6 0 4 VLAN
1 byte 1 byte 1 byte 1 byte 2 bytes 1 byte 1 byte
a. Sub-option type
b. Length
c. Circuit ID type
d. Length
e. VLAN: the incoming VLAN ID of DHCP client packet.
f. Module: For a standal one switch, the Module is always 0; For a st ackable switch, the M odule is the
Unit ID.
g. Port: The incoming port number of DHCP client packet, port number starts from 1.
Remote ID sub-option format:
1. 2. 3. 4. 5.
2 8 0 6 MAC address
1 byte 1 byte 1 byte 1 byte 6 bytes
Module Port
1. Sub-option type
2. Length
3. Remote ID type
4. Length
5. MAC address: The Switch’s system MAC address.
Figure 2 - 21 Circuit ID and Remote ID Sub-option Format
25
Page 37

DGS-3700-12/DGS-3700-12G Series Layer 2 Gigabit Ethernet Switch User Manual
DHCP Relay Interface Settings
This window allo ws the user to s et up a server, by IP address , for rel aying D HCP inf ormat ion to the Switch. T he user
may enter a previously configured IP interface on the Switch that will be connected directly to the DHCP/BOOTP
server using the following window. Proper ly configured s ettings will be disp layed in the DHCP Relay Interface Tab le
at the bottom of the following window. The user may add up to four server IP’s per IP interface on the Switch.
To view this window, click Configuration > DHCP Relay > DHCP Relay Interface Settings as s hown below:
Figure 2 - 22 DHCP Relay Interface Settings an d DH CP Rela y Interf a ce Tab le w i ndow
The following parameters may be configured or viewed:
Parameter Description
Interface
Server IP
Click Apply to implement changes made.
The IP interface on the Switch that will be connected directly to the Server.
Enter the IP address of the D HCP server. Up to four server IPs can be configur ed per IP
Interface.
DHCP Relay Option 60 Default Settings
This window allows t he user to configure th e DHCP Relay Option 60 Default s ervers. When there are no matching
servers found for the packet based on option 60, the relay servers will be determined by the default relay server
setting. Similiarly when there is no m atch found for the packet, the relay servers will be determ ined based on the
default relay servers.
To view this window, click Configuration > DHCP Relay > DHCP Relay Option 60 Default Settings as shown
below:
Figure 2 - 23 DHCP Relay Option 60 Default Settings windo w
The following parameters may be configured:
Parameter Description
Relay IP Address
Mode Use the pull down menu to choose either Relay or Drop. W hen drop is spec ified, the packet
Click Add to add a new Relay IP Address entry. Click Apply to implement changes made. To remove any entries click
the corresponding Delete button.
Enter the specified IP address for the DHCP relay forward.
with no matching ru les f ound will be dr oppe d with out f urther pr ocess . W hen r ela y is selected
the packet will be relayed based on the relay rules.
26
Page 38

DGS-3700-12/DGS-3700-12G Series Layer 2 Gigabit Ethernet Switch User Manual
DHCP Relay Option
DHCP Relay Option 60 Settings
This window is used to configure option 60 relay rules on the Switch. Different strings can be specified for the same
relay server, and the same string can be specified with multiple relay servers. The system will relay the packet to all
the matching servers.
To view this window, click Configuration > DHCP Relay > DHCP Relay Option 60 Settings as shown below:
Figure 2 - 24 DHCP Relay Option 60 Settings window
The following parameters may be configured:
Parameter Description
String
Server IP
Match Type Use the drop down menu to select either Exact Match or Partial Match.
Click Add to add a new entry. To search for a particular entry enter the correct IP Address or String and click Find. To
delete an entry select it and click Delete.
Enter the specified string, up to a maximum of 255 alphanumeric characters.
Enter the relay server IP address.
Exact Match – The option 60 string in the packet must fully match the specified string.
Partial Match – T he opti on 60 string in the pack et onl y needs to partially match the spec ified
string.
DHCP Relay Option 61 Default Settings
This window is used to configure the DHCP Relay Option 61 Default Settings. These settings are used to determine
the rule to process those packets that have no option 61 matching rules.
To view this window, click Configuration > DHCP Relay > DHCP Relay Option 61 Default Settings as shown
below:
The following parameters may be configured:
Parameter Description
61 Default
Click Apply to implement changes made.
Figure 2 - 25 DHCP Relay Option 61 Default Settings windo w
Use the pull down menu to choose either Relay or Drop. W hen drop is spec ified, the packet
with no matching ru les f ound will be dr oppe d with out f urther pr ocess . W hen r elay i s selec ted
the packet will be relayed based on the relay rules.
Enter the IP Address of the entry you wish to configure.
27
Page 39

DGS-3700-12/DGS-3700-12G Series Layer 2 Gigabit Ethernet Switch User Manual
DHCP Relay Option 61 Settings
This command is used to a dd a rule to the r elay server based on opt ion 61. The matching rule can be based on either
the M AC address or b y using a user-specified s tring. Only one rela y server can be specif ied for a MAC-ad dress or a
string. If the exist ing relay servers are det ermined based on option 6 0, and one rela y server is determined bas ed on
option 61, the final relay servers will be the union of these two sets of servers.
To view this window, click Configuration > DHCP Relay > DHCP Relay Option 61 Settings as shown below:
Figure 2 - 26 DHCP Relay Option 61 Settings window
The following parameters may be configured:
Parameter Description
Client ID Use the drop down menu to select th e method of ide ntification for the C lient ID either MAC
Address or String. The MAC Address will specify the hardware address of the cli ent and the
String will specif y the client ID. Choose a m ethod and enter the a ppropriate infor mation into
the box provided.
Relay Rule Use the pull down menu to choose either Relay or Drop. W hen drop is specif ied, the packet
with no matching ru les f ound will be dr oppe d with out f urther pr ocess . W hen r elay i s selec ted
the packet will be relayed based on the relay rules. Choose a method and enter the
appropriate information into the box provided.
Click Add to create a new entry. To remove an entry, enter the appropriate Client ID information and click Delete. To
delete all entries click Delete All.
Out of Band Management Settings
This window is used to configure the RJ-45 Out-of-band (OOB) management port on the Switch. The OOB port is
physically isolated from the data channels of the Switch. This port allows administrators manage the device remotely
without the impact data channel congestion. The OOB management is a method to manage devices while sharing the
network bandwidth with other management traffic. The OOB port allows Management packets and ARP requests to
pass while other packets will be dropped.
To view this window, click Configuration > Out of Band Management Settings as shown below:
Figure 2 - 27 Out of Band Management Settings window
The following parameters may be configured:
28
Page 40

DGS-3700-12/DGS-3700-12G Series Layer 2 Gigabit Ethernet Switch User Manual
Parameter Description
IP Address
Subnet Mask
Gateway
Status Allows the user to Enable or Disable the IP interface.
Link Status
Click Apply to implement changes.
Enter the IP address of the interface.
Enter the Subnet mask of the interface.
Enter the default gateway of the out of band management networks.
Displays the current configurations of the out of band management interface.
External Alarm Settings
This window is used to dis play and config ure the mess ages receiving f rom the RJ-45 alar m port when ex ternal alarm
occurs. The alarm port is designed to collect the alarm message generated by the 3-par ty alarm generator . While
receiving the alarm messages, the Switch will send out alarm traps to the NMS according to the message you
configured.
To view this window, click Configuration > External Alarm Settings as shown below:
Figure 2 - 28 External Alarm Settings window
To modify an existi ng message click the correspondi ng Edit button and retype the new Alarm Message as shown
below.
Figure 2 - 29 External Alarm Settings window – Edit
Enter the new information and click Apply to implement changes made.
DHCP Auto Configuration Settings
The DHCP auto conf iguration function on the Switch wil l load a previously saved configur ation file for current use.
When DHCP auto conf iguration is Enabled on the Switch, the DHC P reply will contain a configurat ion file and path
name. It will then request the file from the TFTP server specified in the reply.
To view this window, click Configuration > DHCP Auto Configuration Settings as shown below:
Figure 2 - 30 DHCP Auto Configuration Settings window
29
Page 41

DGS-3700-12/DGS-3700-12G Series Layer 2 Gigabit Ethernet Switch User Manual
When DHCP autoconfiguration is Enabled, the Switch becomes a DHCP client automatically after rebooting. The
DHCP server mus t have the TFTP server IP ad dress and configuration fil e name, and be configured t o deliver this
information in the data f ield of the DHCP reply packet. The TFTP s erver must be running and have the requested
configuration file in its base directory when the request is received fr om the Switch. Consult the DHCP server and
TFTP server software instructions for information on loading a configuration file.
If the Switch is unable to com plete the autoconfigurati on process the previous ly saved local configurat ion file present
in Switch memory will be loaded.
MAC Ad dr e s s Aging Time
This table specifies the length of time a learned MAC Address will remain in the forwarding table without being
accessed (that is, how long a learned MAC Address is allowed to remain idle). To change this, enter a value
representing the MAC address age-out time in seconds. The MAC Address Aging Time can be set to any value
between 10 and 1,000,000 seconds. The default setting is 300 seconds.
To view this window, click Configuration > MAC Address Aging Time as shown below:
Figure 2 - 31 MAC Address Aging Time window
Web Settings
Web-bas ed management is Enabled by default. If you choose to disable this by selecting Disabled, you will lose the
ability to configure the system through the web interface as soon as these settings are applied.
To view this window, click Configuration > Web Settings as shown below:
Figure 2 - 32 Web Settings window
Telnet Settings
Telnet configuration is Enabled by default. If you do not want to allow configuration of the system through Telnet
choose Disabled. The TCP ports are numbered between 1 and 65535. The "well-known" TCP port for the Telnet
protocol is 23.
To view this window, click Configuration > Telnet Settings as shown below:
Figure 2 - 33 Telnet Settings window
30
Page 42

DGS-3700-12/DGS-3700-12G Series Layer 2 Gigabit Ethernet Switch User Manual
firmware images for use. Image ID 1 will be the default boot up firm ware for the Switch unless
Password Encrypt ion
Password Encryption Status can be Enabled or Disabled in this w ind ow, it is Disabled by default. Password encr yption
allows the user to encr ypt a password in the configuration file for additio nal security. Select Enabled t o change the
password into encrypted form. When password encryption is disabled, the password will be in plain text form. However,
if the user specifies the password in encrypted f orm, or if the password has bee n converted to e ncrypted f orm b y the
last Enable password enc ryption comm and, the password will st ill be in encr ypted form and cannot be rever ted back
to plaintext form.
To view this window, click Configuration > Password Encryption as shown below:
Figure 2 - 34 Password Encryption window
Clipaging Settings
Clipaging Status can be Enabled or Disabled in this wi ndow, it is Enabled by default. Clipa ging settings are used whe n
issuing a com mand whic h causes the co nsole sc reen t o rapidl y scroll through several pages. T his comm and will c ause
the console to pause at the end of each page.
To view this window, click Configuration > Clipaging Settings as shown below:
Figure 2 - 35 Clipaging Settings window
Firmware Information
The following screen allows the user to view information about current firmware images stored on the Switch.
To view this window, click Configuration > Firmware Information as shown below:
Figure 2 - 36 Firmware Information window
This window holds the following information:
Parameter Description
ID
States the image ID number of the firmware in the Switch’s mem ory. The Switch can store two
31
Page 43

DGS-3700-12/DGS-3700-12G Series Layer 2 Gigabit Ethernet Switch User Manual
otherwise configured by the user.
Version
Size (Bytes)
Update Time
From
User
States the firmware version.
States the size of the corresponding firmware, in bytes.
States the specific time the firmware version was downloaded to the Switch.
States the IP address of the origin of the firmware. There are five ways firmware may be
downloaded to the Switch.
R – If the IP address has this letter attached, it denot es a firmware upgrade through t he serial
port RS232.
T – If the IP address has this letter attached to it, it denotes a firmware upgrade through Telnet.
S – If the IP addr ess has this letter attached to i t, it denotes a firmware upgrade t hrough the
Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP).
W – If the IP ad dress has this letter attache d to it, it denotes a firmware up grade through the
web-based management interface.
SSH – If the IP addr ess has these three letters att ached, it denotes a firm ware update through
SSH.
SIM – If the IP addres s has these letters attached, it denotes a firmware upgrade through the
Single IP Management feature.
States the user who do wnloaded the firmware. T his field may read “Anon ymous” or “Unknown”
for users that are unidentified.
Dual Configuration Settings
The following window is used to configure firmware information set in the Switch. The DGS-3700 Series has the
capability to store two firmware images in its memory.
To view this window, click Configuration > Dual Configuration Settings as shown below:
Figure 2 - 37 Dual Configuration Settings
This window displays the following information:
Parameter Description
ID
Version
States the ID num ber of the configuration file locate d in the Switch’s mem ory. The Switch can
store two configuration files for use. ID 1 will be the default boot up configuration file for the
Switch unless otherwise configured by the user.
Displays the firmware version set in the Switch.
32
Page 44

DGS-3700-12/DGS-3700-12G Series Layer 2 Gigabit Ethernet Switch User Manual
Echo packets to the specified IP address until th e program is stopped. Or the user ma y opt to
Size(bytes)
Update time
From
User
Boot Click the Boot button under this headi ng to us e this c onfigurat ion f ile as th e boot up firm ware for
Active Click the Active button to enable the configuration file settings.
Delete Click the Delete button under this heading to delete this configuration file from the Switch’s
Displays the size of the configuration file, in bytes.
Displays the time that the configuration file was updated to the Switch.
Displays the location from which the configuration file was uploaded.
Displays the name of the user (device) that updated this configuration file. Unknown users will be
displayed as Anonymous.
the Switch. This will apply upon the next reboot of the Switch .
memory.
Ping Test
Ping is a small program that s ends ICM P Ech o pack ets to the I Pv6 or IP v4 addre ss you specif y. The des tinat ion node
then responds to or "echoes" the p ackets sent f rom the Switch. This is ver y useful to verif y connectivity b etween the
Switch and other nodes on the network.
To view this window, click Configuration > Ping Test as shown below:
Figure 2 - 38 Ping Test window
The following parameters may be configured:
Parameter Description
IPv4 Ping Test
Target IP Address
Repeat Pinging for
Enter the Target IPv4 Address of the host.
Check the Infinite t imes radio button, which will tell the ping program to keep sending ICMP
33
Page 45

DGS-3700-12/DGS-3700-12G Series Layer 2 Gigabit Ethernet Switch User Manual
choose a specific number of times to ping the Target IP Address by entering a number
between 1 and 255.
Timeout Select a timeout period between 1 and 10 seconds for this Ping message to reach its
destination. If the p acket fails to find the IP v4 ad dr ess i n th is spec if ied time, the Ping pack et will
be dropped.
IPv6 Ping Test
Target IP Address
Interface Name
Repeat Pinging for
Size
Timeout Select a timeout period between 1 and 10 seconds for this Ping message to reach its
Click Start to initiate the Pi ng pro gram
Enter the Target IPv6 Address of the host.
Enter the Target Interface Name of the host.
Check the Infinite t imes radio button, which will tell the ping program to keep sending ICMP
Echo packets to the specified IP address until th e program is stopped. Or the user ma y opt to
choose a specific number of times to ping the Target IP Address by entering a number
between 1 and 255.
Use this parameter t o set the dat agram size of the pa cket, or the num ber of bytes in each pin g
packet. Users may set a size between 1 and 6000 bytes with a default setting of 100 bytes.
destination. If the p acket fails to find the IP v6 ad dr ess i n th is spec if ied time, the Ping pack et will
be dropped.
Local Loopback Ports Settings
The Local Loopback Ports Settings are used to start or stop the internal loopback test on selected ports, or set
to/recover externa l loopback mode. W hen internal loopback is enabled, the device starts to send test packets to the
port, and keeps m onitoring the packets received. When internal loopback is disabl ed, the loopback test is terminated
and the result is displayed. A port can only operate in one loopback mode at a time. When external loopback is
enabled, the MAC/PH Y is set to external loopback mode. When exter na l loop back is disabled, t he MAC /PH Y res umes
normal operation.
To view this window, click Configuration > Local Loopback Ports Settings as shown below:
Figure 2 - 39 Local Loopback Ports Settings window
The following parameters may be configured:
Parameter Description
From Port / To Port Select a port or group of ports to Enable or Disable the Loca l Loopback Ports Settings us ing
34
Page 46

DGS-3700-12/DGS-3700-12G Series Layer 2 Gigabit Ethernet Switch User Manual
the pull-down menus.
Loopback Mode
State Select Enable to start internal loopback test; for external loopback, set port(s) to external
Click Appy to implement changes.
This function allows the user to select MAC Internal/MAC External or PHY Internal/PHY
External. MAC and PHY represent the layer on which the loopback is performed while the
Internal or External represents the local loopback mode.
loopback mode. Se lect Disable to st op internal loopback test; for external loopb ack, recover
port(s) from external loopback mode.
VLAN Counter Settings
The VLAN Counter Settings table is used to create the control entry for VLAN traffic flow statistsics . The user can
create control entries to c ount statistics for specific VLANs, or to count statis tics for specific port s on specific VLANs.
The statistics can be either byte count or packet count and can be counted for different frame types.
To view this window, click Configuration > VLAN Counter Settings as sh own below:
Figure 2 - 40 VLAN Counter Settings window
The following parameters may be configured:
Parameter Description
VID List
VLAN Name
Ports (e.g.:1-5)
Packet Type
Counter Type
VID (1-4094)
Click Add to create a new entry. To remove an entry click Delete to delete all entries click Delete All.
Check the radius button to identify the VLAN by its VLAN ID. Enter the VID or VID list you wish
to configure.
Check the radius button to identify the VLANs by their VLAN name.
Enter a list of ports, or check the All Port s check box to specify all the ports.
Use the drop down menu to select the packet type.
broadcast – Specifies to count broadcast packets.
unicast – Specifies to count unicast packets.
multicast – Specifies to count multicast packets.
all – Specifies to count all packets.
Use the drop down menu to select the counter type. To count at the packet level select Packet,
to count at the byte level specify Byte.
To search for a particular VLAN, enter the VID and click Find.
35
Page 47

DGS-3700-12/DGS-3700-12G Series Layer 2 Gigabit Ethernet Switch User Manual
SNTP Settings
The Simple Network Time Protocol Settings can be configured in the next two windows.
Time Settings
This window is used to configure the time settings for the Switch.
To view this window, click Configuration > SNTP Settings > Time Settings as shown below:
Figure 2 - 41 Time Settings window
The following parameters can be set or are displayed:
Parameter Description
Status
SNTP State Use the radius button to select an Enabled or Disabled SNTP state.
Current Time
Time Source
SNTP First Server
SNTP Second Server
SNTP Poll Interval in
Seconds (30-99999)
Date (DD/MM/YYYY)
Time in (HH:MM:SS)
Click Apply to implement changes made.
Displays the Current Time set on the Switch.
Displays the time source for the system.
SNTP Settings
This is the IP address of the primary server the SNTP information will be taken from.
This is the IP address of the secondary server the SNTP information will be taken from.
This is the interval, in seconds, between requests for updated SNTP information.
Set Current Time
Enter the current date in day, month and year to update the system clock.
Enter the current time in hours, minutes, and seconds.
36
Page 48

DGS-3700-12/DGS-3700-12G Series Layer 2 Gigabit Ethernet Switch User Manual
TimeZone Settings
The following window is used to configure time zones and Daylight Savings time settings for SNTP.
To view this window, click Configuration > SNTP Settings > TimeZone Settings as shown below:
Figure 2 - 42 Time Zone and DST Settings window
The following parameters can be set:
Parameter Description
Time Zone and DST
Daylight Saving
Time State
Daylight Saving
Time Offset in
Minutes
Time Zone Offset
from GMT in +/HH:MM
Using repeating m ode will enable DST seasonal time adjustm ent. Repeating mode requires that the DST beginning
and ending date be specified using a form ula. For example, specify to begin DST on Saturday during the second
week of April and end DST on Sunday during the last week of October.
Use this pull-down menu to enable or disable the DST Settings.
Use this pull-down menu to specify the amount of time that will constitute your local DST offset
30, 60, 90, or 120 minutes.
Use these pull-down menus to specify your local time zone's offset from Greenwich Mean
Time (GMT.)
DST Repeating Settings
37
Page 49

DGS-3700-12/DGS-3700-12G Series Layer 2 Gigabit Ethernet Switch User Manual
From :Which Week
of the Month
From: Day of the
Week
From: Month
From: Time in
HH:MM
To: Which Week of
the Month
To: Day of the
Week
To: Month
To:Time in HH:MM
Using annual m ode will enable DST seasonal time adjustment. Annual m ode requires that the DST beg inning and
ending date be specified concisely. For example, specify to begin DST on April 3 and end DST on October 14.
Enter the week of the month that DST will start.
Enter the day of the week that DST will start on.
Enter the month DST will start on.
Enter the time of day that DST will start on.
Enter the week of the month the DST will end.
Enter the day of the week that DST will end.
Enter the month that DST will end.
Enter the time DST will end.
DST Annual Settings
From: Month
From: Day
From: Time in
HH:MM
To: Month
To: Day
To: Time in HH:MM
Click Apply to implement changes made to the Time Zone and DST window.
Enter the month DST will start on, each year.
Enter the day of the week DST will start on, each year.
Enter the time of day DST will start on, each year.
Enter the month DST will end on, each year.
Enter the date DST will end on, each year.
Enter the time of day that DST will end on, each year.
MAC Notification Settings
MAC Notification is used to monitor MAC ad dr ess es le arned and entered into the f or warding data bas e. To globally set
MAC notification on the Switch, open the following window by opening the MAC Notification Settings in the
Configuration folder.
MAC Notification Global Settings
This window is used to configure the MAC Notification Global Settings for the Switch.
To view this window, click Configuration > MAC Notification Settings > MAC Notification Global Settings as
shown below:
38
Page 50

DGS-3700-12/DGS-3700-12G Series Layer 2 Gigabit Ethernet Switch User Manual
Figure 2 - 43 MAC Notification Global Settings window
The following parameters may be viewed and modified:
Parameter Description
State
Interval
(1-2147483647 sec)
History Size
(1-500)
Click Apply to implement changes.
Enable or disable MAC notification globally on the Switch.
The time in seconds between notifications.
The maximum number of entries listed in the history log used for notification. Up to 500
entries can be specified.
MAC Notification Port Settings
This window is used to configure the MAC Notification Port Settings for the Switch.
To view this w in dow, click Configuration > MAC Notification Settings > MAC Notification Port Settings as shown
below:
The following parameters may be modified:
Parameter Description
From Port / To Port
State
Click Apply to implement changes.
Select a port or group of ports to enable for MAC notification using the pull-do wn menus.
Enable MAC Notification for the ports selected using the pull-down menu.
Figure 2 - 44 MAC Notification Port Settings window
39
Page 51

DGS-3700-12/DGS-3700-12G Series Layer 2 Gigabit Ethernet Switch User Manual
SNMP Settings
Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) is an OSI Layer 7 (Application Layer) designed specifically for
managing and monitoring network devices. SNMP enables network management stations to read and modify the
settings of gateways, routers, switches, and other network devices. Use SNMP to configure system features for proper
operation, monitor performance and detect potential problems in the Switch, switch group or network.
Managed devices t hat support SNMP include software ( referred to as an agent), which runs locally on the dev ice. A
defined set of variables (managed objec ts) is maintai ned by the SNMP age nt and used to m anage the devi ce. These
objects are defined in a Management Information Base (MIB), which provides a standard presentation of the
information controll ed by the on-board SNMP agent . SNMP defin es both the format of the MIB specific ations and th e
protocol used to access this information over the network.
The DGS-3700 Series s upports the SNMP versions 1, 2c, and 3. T he default SNMP setting is disabled. You m ust
enable SNMP. Once SNMP is enabled you can choose which version you want to use to m onitor and control the
Switch. The three versions of SNMP vary in the level of s ecurity provided between the managem ent station and the
network device.
In SNMP v.1 and v.2, user authe ntication is accomplis hed using 'community strings', which f unction like passwords.
The remote user SNMP ap plication and th e Switch SNMP m ust use the sam e community string. SNMP packets from
any station that has not been authenticated are ignored (dropped).
The default community strings for the Switch used for SNMP v.1 and v.2 management access are:
• public - Allows authorized management stations to retrieve MIB objects.
• private - Allows authorized management stations to retrieve and modify MIB objects.
SNMPv3 uses a more sophisticated authentication process that is separated into two parts. The first part is to
maintain a list of users and their attributes that are allowed to act as SN MP managers. The second part describes
what each user on that list can do as an SNMP manager.
The Switch allows grou ps of us ers to be listed and c onf igured with a shar ed s et of pr ivileg es. T he SNM P v ers ion m ay
also be set for a liste d gr oup of SNM P m anagers. T hu s, you ma y create a gr oup of SNM P m anager s that are a llo wed
to view read-only information or receive traps using SNMPv1 while assigning a higher level of security to another
group, granting read/write privileges using SNMPv3.
Using SNMPv3 individual users or groups of SNMP managers can be allowed to perform or be restricted from
performing specific SNM P management functions. The functions a llowed or restricted are defined usi ng the Object
Identifier (OID) assoc iated with a specific MIB. An additional layer of s ecurity is available for SN MPv3 in that SNMP
messages ma y b e encrypted. To read more about how to configure SNMPv3 s ettings for the Switch read the next
section.
Traps
Traps are messages that al ert net work per sonnel of events that oc cur on th e Swit ch. T he events can be as serious as
a reboot (someone accidentally turned OFF the Switch), or less serious like a port status change. The Switch
generates traps and sends them to the trap recipient (or network manager). T ypical traps include trap mes sages for
Authentication Failure, Topology Change and Broadcast\Mult icas t Stor m.
MIBs
The Switch in the M an age ment Information Base ( MI B) s tor es management and c ount er inf ormation. The Switch us es
the standard MIB-II Man agement Information Base module. Cons equently, values for MIB objects can be retrieved
from any SNMP-based network m anagem ent sof tware. In additi on to the sta ndard MIB-II, the Switch also s upports its
own proprietary enterpris e MIB as an extended Management Inf ormation Base. Specifying the MIB Objec t Identifier
may also retrieve the proprietary MIB. MIB values can be either read-only or read-write.
The DGS-3700 Ser ies inc orpor ates a flexi ble SNMP m anagem ent f or the s witch ing en vironm ent. SNM P m anagem ent
can be customized to suit t he needs of the net work s and the pr efer ences of the network adm inistrator. U se t he SNMP
V3 menus to select the SNMP version used for specific tasks.
The DGS-3700 Series supports the Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) versions 1, 2c, and 3. The
administrator can specif y th e SNMP versio n used to m onitor and co ntrol the Switc h. The thr ee vers ions of SN MP var y
in the level of security provided between the management station and the network device.
SNMP settings are conf igured usin g the m enus locate d on the SNMP V3 folder o f the web m anager. W orkstations on
the network that are allowed SNMP privileged access to the Switch can be restricted with the Management Station IP
Address window.
40
Page 52

DGS-3700-12/DGS-3700-12G Series Layer 2 Gigabit Ethernet Switch User Manual
SNMP Global State Settings
The SNMP Global State Settings is used to globally enable or disable the SNMP Settings on the switch.
To view this window, click Configuration > SNMP Settings > SNMP Global State Settings as shown below:
Figure 2 - 45 SNMP Global State Settings window
SNMP View Table
This window is used t o as s i gn views to c om munity strings that d efine which MIB obj ects c an b e accessed by a rem ote
SNMP manager.
To view this window, click Configuration > SNMP Settings > SNMP View Table as shown below:
Figure 2 - 46 SNMP View Table window
The following parameters can be set:
Parameter Description
View Name
Subtree OID
View Type Select Included to include this object in the list of objects that an SNMP manager can
To implement the new settings, click Apply. To delete an entry click the corresponding Delete button.
Type an alphanum eric string of up to 32 charac ters. This is used t o identify the ne w SNMP
view being created.
Type the Object Ide ntifier (OID ) Subtree for the view. The OID ident ifies an objec t tree (MI B
tree) that will be included or excluded from access by an SNMP manager.
access. Select Excluded to exclude this object from the list of objects that an SNMP
manager can access.
41
Page 53

DGS-3700-12/DGS-3700-12G Series Layer 2 Gigabit Ethernet Switch User Manual
SNMP Group Table
An SNMP Group created with this table maps SNMP users (identified in the SNMP User Table) to the views created in
the previous menu.
To view this window, click Configuration > SNMP Settings > SNMP Group Table as shown below:
Figure 2 - 47 SNMP Group Table window
To delete an existing SNMP Group Table entry, click the corresponding Delete button.
The following parameters can be set:
Parameter Description
Group Name
Read View Name
Write View Name
Notify View Name
User-based
Security Model
Type an alphanum eric string of up to 32 characters. This is used to identify the new SNM P
group of SNMP users.
This name is used to specify the SNMP group created can request SNMP messages.
Specify a SNMP group n am e for users that are allo wed SNM P write priv ileges to the Switch's
SNMP agent.
Specify a SNMP group n ame for users that can rec eive SNMP trap mess ages generated by
the Switch's SNMP agent.
SNMPv1 – Specif ies that S NMP vers i on 1 will be used .
SNMPv2 – Specifies that SNMP version 2c will be used. The SNMPv2 supports both
centralized and distribu ted network management strategies. It includes improvements in the
Structure of Management Information (SMI) and adds some security features.
SNMPv3 – Specifies that the SNMP version 3 will be used. SNMP v3 provides s ecure acces s
to devices through a combination of authentication and encrypting packets over the network.
Security Level
To implement the new settings, click Apply.
The Security Level settings only apply to SNMPv3.
NoAuthNoPriv – Specifies that there will be no authorization and no encryption of packets
sent between the Switch and a remote SNMP manager.
AuthNoPriv – S pecifies that authorization will be requ ired, but there will be no encryption of
packets sent between the Switch and a remote SNMP manager.
AuthPriv – Specifies that authorization will be required, and that packets sent between the
Switch and a remote SNMP manger will be encrypted.
42
Page 54

DGS-3700-12/DGS-3700-12G Series Layer 2 Gigabit Ethernet Switch User Manual
SNMP User Table
This window displays all of the SNMP User's currently configured on the Switch and also allows you to add new users.
To view this window, click Configuration > SNMP Settings > SNMP User Table as shown below:
Figure 2 - 48 SNMP User Table window
The following parameters may be set:
Parameter Description
User Name
Group Name
SNMP Version V1 – Indicates that SNMP version 1 is in use.
SNMP V3 Encryption None – Indicates that there is no SNMP V3 Encryption
Auth-Protocol by
Password
Priv-Protocol by
Password
An alphanumeric string of up to 32 characters. This is used to identify the SNMP users.
This name is used to specify the SNMP group created can request SNMP messages.
V2 – Indicates that SNMP version 2 is in use.
V3 – Indicates that SNMP vers ion 3 is in use.
Password – Indicates that t her e is SNMP V3 Encryption through a password
Key – Indicates that there is SNMP V3 Encryption through a key.
MD5 – Indicates that the HMAC-MD5-96 authentication level will be used.
SHA – Indicates that the HMAC-SHA authentic at ion prot ocol wi ll be used.
None – Indicates that no authorization protocol is in use.
DES – Indicates that DES 56-bit encryption is in use based on the CBC-DES (DES-56)
standard.
Auth-Protocol by Key MD5 – Indicates that the HMAC-MD5-96 authentication level will be used.
SHA – Indicates that the HMAC-SHA authentic at ion prot ocol wi ll be used.
Priv-Protocol by
password
None – Indicates that no authorization protocol is in use.
DES – Indicates that DES 56-bit encryption is in use based on the CBC-DES (DES-56)
standard.
43
Page 55

DGS-3700-12/DGS-3700-12G Series Layer 2 Gigabit Ethernet Switch User Manual
Password
Key
To implement cha nges made, click Apply. To delete an ex isting SNMP User Table entr y, cl ick the corresponding
Delete button.
Enter a Password when SNMP V3 Encrypti on is enabl ed for Pass word m ode.
Enter a Key when SNMP V3 Encryption is enabled for Key mode.
SNMP Community Table
Use this table to view existing SNMP Community Table configurations and to c reate a SNMP community string to
define the relationship between the SNMP manager and an agent. The community string acts like a password to
permit access to the ag ent on the Switch. One or more of the f ollowing characteristics can be associat ed with the
community string:
• An Access List of IP addres ses of SNMP managers that are permitted to use the community string to gain
access to the Switch's SNMP agent.
• Any MIB view that defines the subset of all MIB objects will be accessible to the SNMP community.
• Read/write or read-only level permission for the MIB objects accessible to the SNMP community.
To view this window, click Configuration > SNMP Settings > SNMP Community Table as shown below:
Figure 2 - 49 SNMP Community Table window
The following parameters can set:
Parameter Description
Community Name
View Name
Access Right Read Only – Sp ecifies that SNMP comm unity members using the comm unity string create d
To implement the new settings, click Apply. To delete an entry from the SNMP Community Table, click the
corresponding Delete button.
Type an alphanumeric string of up to 32 characters that is used to ide ntify members of an
SNMP community. This string is used like a password to give remote SNMP managers
access to MIB objects in the Switch's SNMP agent.
Type an alphanumeric string of up to 32 character s that is used to iden tify the group of MIB
objects that a remote SN MP manager is allowed to acc ess on the Switch. The view nam e
must exist in the SNMP View Table.
can only read the contents of the MIBs on the Switch.
Read Write – Specifies that SNMP c omm unit y member s using t he com m unit y string cr eated
can read from, and write to the contents of the MIBs on the Switch.
44
Page 56

DGS-3700-12/DGS-3700-12G Series Layer 2 Gigabit Ethernet Switch User Manual
based Security
Protocol (SNMP) version 1, is a network management protocol that provides a means to
SNMP Host Table
The SNMP Host Table window is used to set up SNMP trap recipients.
To view this window, click Configuration > SNMP Settings > SNMP Host Table as shown below:
Figure 2 - 50 SNMP Host Table window
The following parameters can set:
Parameter Description
Host IP Address
User-based Security
Model
Security Level NoAuthNoPriv – To specify a NoAuthNoPriv security level.
Community String/
SNMP V3 User Name
To implement your new settings, click Apply.
Type the IP address of the remote management stati on that will serve as the SNMP hos t
for the Switch.
SNMPv1 – Specif ies that S NMP vers i on 1 will be used .
SNMPV2c – Specifies that SNMP version 2 will be used.
SNMPV3 – To specif y that the SNMP vers io n 3 will be used.
AuthNoPriv – To specify an AuthNoPriv security level.
AuthPriv – To specify an AuthPriv security level.
Type in the community string or SNMP V3 user name as appropriate.
SNMP v6Host Table
This window is used to specify the IPv6 host IP address to which the trap packets will be sent.
To view this window, click Configuration > SNMP Settings > SNMP v6Host Table as shown below:
Figure 2 - 51 SNMP V6Host Table window
The following parameters can be configured:
Parameter Description
Host Ipv6 Address
UserModel
Enter the IPv6 host IP address to which the trap packet will be sent.
Used the drop down menu to select the user-based security model.
SNMPv1 – Specif ies that S NMP vers i on 1 will be used . T he Simpl e Network Management
45
Page 57

DGS-3700-12/DGS-3700-12G Series Layer 2 Gigabit Ethernet Switch User Manual
monitor and control network devices.
String/SNMPv3 User
SNMPv2 – Specifies that SNMP version 2 will be used. The SNMP v2 supports both
centralized and distributed net wor k management strategies. It includes improvements in
the Structure of Management Information (SMI) and adds some security features.
SNMPv3 – Specif ies that S NMP vers i on 3 will be used . SNMP v3 pro vid es secur e acces s
to devices through a combination of authentication and encrypting packets over the
network. SNMP v3 adds:
• Message integrity − ensures that packets have not been tampered with during
transit.
• Authentication − determines if an SNMP message is from a valid source.
• Encryption − scrambles the contents of messages to prevent it being viewed by
an unauthorized source.
Security Level
Community
Name
Click Apply to implement changes made.
When SNMPv3 is in use, it is necessary to choose the security level. Use the drop down
menu to select from the following:
−
noauth_nopriv
sent between the Switch and a remote SNMP manager.
auth_nopriv − Specifies that authorization will be required, but there will be no encryption
of packets sent between the Switch and a remote SNMP manager.
auth_priv − Spec if ies tha t authorization will be re quired, and that pack ets s ent bet ween the
Switch and a remote SNMP manger will be encrypted.
Enter an alphanum eric string that will be used to aut horize a remote SNMP manager to
access the Switch’s SNMP agent. Alternatively enter the SNMPv3 user name.
Specifies that there will be no authorization and no encryption of packets
SNMP Engine ID
The Engine ID is a unique identifier used for SNMP V3 implementations. This is an alphanumeric string used to
identify the SNMP engine on the Switch.
To view this window, click Configuration > SNMP Settings > SNMP Engine ID as shown below:
To change the Engine ID, enter the new Engine ID in the space provided and click the Apply button.
Figure 2 - 52 SNMP Engine ID window
46
Page 58

DGS-3700-12/DGS-3700-12G Series Layer 2 Gigabit Ethernet Switch User Manual
SNMP Trap Configuration
The following window is used to enable and disable trap settings for the SNMP function on the Switch.
To view this window, click Configuration > SNMP Settings > SNMP Trap Configuration as shown below:
Figure 2 - 53 SNMP Trap Configuration window
To enable or disable th e Traps State and/or the Authenticate Tr aps State, use the correspon ding pull-dow n menu to
change and click Apply.
Time Range Settings
The Time Range window is used in co njunction with the Access Profile feature to determine a st arting point and a n
ending point, based on days of the week, when an Access Prof ile configuration will b e enabled on the Swit ch. Once
configured here, the t im e range setti ngs are t o be applie d to an acc ess pr ofile ru le us ing the Access Prof ile tabl e. The
user may enter up to 64 time range entries on the Switch.
To view this window, click Configuration > Time Range Settings as shown below:
Figure 2 - 54 Time Range Settings window
Parameter Description
Range Name
Hours
Enter a name of no m ore than 32 alphanumeric c haracters that will be used to identify this time
range on the Switch. This range name will be used in the Access Profile table to identify the
access profile and associated rule to be enabled during this time range.
This parameter is us ed to set the time in th e day that this time rang e is to be enabled using t he
following parameters:
• Start Time - Use this parameter to identify the starting time of the time range, in hours,
minutes and seconds, based on the 24-hour time system.
• End Time - Use this parameter to identify the ending time of the time range, in hours,
minutes and seconds, based on the 24-hour time system.
Weekdays
Click Apply to implement changes made. Currently configured e ntries wil l be displayed in the Tim e R ange Inf ormation
table in the bottom half of the window shown above.
Use the check box es to select the corresponding days of the week that this time range is to be
enabled. Tick the Select All Days check box to configure this time range for every day of the week.
47
Page 59

DGS-3700-12/DGS-3700-12G Series Layer 2 Gigabit Ethernet Switch User Manual
sFlow
The sFlow folder contains four windows to enable and configure the sFlow settings on the Switch.
sFlow Global State Settings
This table is used to e nab le or disable the sFlo w G l oba l Stat e Sett in gs on the Switch. The sFlow version, a ddress and
state configurations can also be viewed in this table.
To view this window, click Configuration > sFlow > sFlow Global State Settings as shown below:
Figure 2 - 55 Time Range Settings window
Select Disabled or Enabled and click Apply.
sFlow Analyzer Server Settings
This window is used to con figure the sFlo w analyzer server sett ings. You can sp ecify more than one ana lyzer server
with the same IP address but with differ ent UDP port numbers. You can have up to four unique c ombinations of IP
address and UDP port numbers.
To view this window, click Configuration > sFlow > sFlow Analyzer Server Settings as shown below:
Figure 2 - 56 sFlow Analyzer Server Settings window
The following parameters can be configured:
Parameter Description
Analyzer Server ID (1-4)
Owner Name
Up to four
The entity making use of this s flow analyzer server. When owner is set or modif ied, the
sFlow Analyzer Servers can be configured.
48
Page 60

DGS-3700-12/DGS-3700-12G Series Layer 2 Gigabit Ethernet Switch User Manual
timeout value will become 400 automatically.
Timeout (1-2000000)
Collector Address
Collector Port (1-65535)
Max Datagram size
(300-1400)
Click Apply to implement the changes made.
The length of time bef ore the server is timed out. W hen the anal yzer server tim es out, all
of the flow samplers and counter pollers associated with this analyzer server will be
deleted. “Infinite” in dicat es t hat t he analyzer server will never time out. If not specif ied, th e
default value is 400.
The IP address of the analyzer ser ver. If not specif ied, the address will be 0.0.0.0 which
means that the entry will be inactive.
The destination UDP port for sending the sFlow d atagrams. If not specified, the def ault
value is 6364.
The maximum number of data bytes that can be packed in a single sample datagram. If not
specified, the default value is 1400.
sFlow Flow Sampler Settings
This table is used to crea te sFlow flow sam pler settin gs on the S witch. B y config ur ing the s am pling functi on for a por t,
a sample packet received by this port will be encapsulated and forwarded to the analyzer server at the specified
interval.
To view this window, click Configuration > sFlow > sFlow Flow Sampler Settings as shown below:
Figure 2 - 57 sFlow Flow Sampler Settings window
The following parameters can be configured:
Parameter Description
From Port / To Port
Analyzer Server ID (1-
4)
Rate (0-65535)
MAX Header Size (18-
256)
Click Apply to implement the changes made.
Specifies the port or list of ports to be configured.
The analyzer server id specifies the ID of a server analyzer where the packet will be
forwarded.
The sampling rate for packet sampling. The actual rate is the configured rate value
multiplied by 256. For exa mple, if the rate i s 20, the actual rate 5120. One packet will be
sampled from about 5120 pac kets. If set to 0, the sampler is disabled. If the ra te is not
specified, its default value is 0.
The maximum num ber of leading bytes in the pack et which wil l be sam pled, encaps ulated
and forwarded to the server. If not specified, the default value is 128.
49
Page 61

DGS-3700-12/DGS-3700-12G Series Layer 2 Gigabit Ethernet Switch User Manual
sFlow Counter Poller Settings
This window is used t o create the sf low count er poller s ettings on t he Switch. W ithin the sflow c ounter pol ler f unction,
the port statistics coun ter information will be forwarded to the s erver at the configured interval. Thes e counters are
RFC 2233 counters.
To view this window, click Configuration > sFlow > sFlow Counter Poller Settings as s hown below:
Figure 2 - 58 sFlow Counter Poller Settings window
The following parameters can be configured:
Parameter Description
From Port / To Port
Analyzer Server ID
(1-4)
Interval (20-120)
Click Apply to implement the changes made.
Specifies the port or list of ports to be configured.
The analyzer server id specifies the ID of a server analyzer where the packet will be
forwarded.
Specifies the maxim um number of seconds betw een successive statist ic counter inform ation.
To disable the interval check the Disabled box.
50
Page 62

DGS-3700-12/DGS-3700-12G Series Layer 2 Gigabit Ethernet Switch User Manual
Single IP Management
Simply put, D-Link Sing le IP Ma nagem ent is a c oncep t that wil l stack switches togeth er over Ethernet inste ad of using
stacking ports or modules. There are some advantages in implementing the "Single IP Management" feature:
1. SIM can simplify management of small workgroups or wiring closets while scaling the network to handle
increased bandwidth demand.
2. SIM can reduce the number of IP address needed in your network.
3. SIM can eliminate any specialized cables for stacking connectivity and remove the distance barriers that
typically limit your topolog y options when us in g other st ac king technology.
Switches using D-Link Single IP Management (labeled here as SIM) must conform to the following rules:
SIM is an optional feature on the Switch and can e asily be enabled or disabled through the C ommand Line Inter face
or Web Interface. SIM grouping has no effect on the normal operation of the Switch in the user's network.
There are three classifications for SIM. The Commander Switch (CS), which is the master switch of the group,
Member Switch (MS), which is a switch that is recognized by the CS a m ember of a SIM group, and a Candidate
Switch (CaS), which is a Switch that has a physical link to the SI M gr o up b ut h as not b een r ec ogn ized b y the CS as a
member of the SIM group.
A SIM group can only have one Commander Switch (CS).
All switches in a part icular SIM group m ust be in the same IP sub net (broadcast domain). M embers of a SI M group
cannot cross a router.
A SIM group accepts up to 33 switches (numbered 0-32), including the Commander Switch (numbered 0).
There is no limit to th e num ber of SIM grou ps in t he sam e I P subnet (bro adcas t dom ain), ho wever a single s witch c an
only belong to one group.
If multiple VLANs are configured, the SIM group will only utilize the system VLAN on any switch.
SIM allows interm ediate devices that do not support SIM. T his enables the user to m anage switches that are more
than one hop away from the CS.
The SIM group is a group of s witches that are managed as a single entit y. SIM switches may take on three differ ent
roles:
1. Commander Switch (CS) – This is a switch th at h as been manually configured as the c ontro ll ing d ev ice f or a
group, and takes on the following characteristics:
It has an IP Address.
It is not a commander switch or member switch of another Single IP group.
It is connected to the member switches through its management VLAN.
2. Member Swi tch (M S) – This is a switch that has joined a single IP group and is accessible from the CS, and it
takes on the following characteristics:
It is not a CS or MS of another Single IP group.
It is connected to the CS through the CS management VLAN.
3. Candidate Switch (CaS) – This is a switch that is read y to join a SIM group bu t is not yet a mem ber of the
SIM group. The Candidat e S witch m ay join the SIM gr oup of a sw itch b y manual ly conf iguring it to be a MS of
a SIM group. A switc h configured as a CaS is not a member of a SIM group and will tak e on the following
characteristics:
It is not a CS or MS of another Single IP group.
It is connected to the CS through the CS management VLAN
After configuring one s witch to operate as the CS of a SIM group, add itional switches may join the group thr ough a
direct connection to the Commander switch. Only the Commander switch will allow entry to the candidate switch
enabled for SIM. The C S will then serve as the in band entr y point for access to the MS. T he CS's IP address will
become the path to all MS 's of the group and the CS's Administrator' s password, and/or authentication will c ontrol
access to all MS's of the SIM group.
With SIM enabled, the applications in the CS will redirect the packet instead of executing the packets. The
applications will dec ode th e packet f rom the a dminist rator, m odify som e data, the n send i t to the MS. After exec ution,
the CS may receive a response packet from the MS, which it will encode and send it back to the administrator.
When a CS becom es a MS, it autom aticall y becom es a mem ber of the f irst SNMP comm unity (includ e read/ write and
read only) to which t he CS bel ongs. Ho wever, if a MS has its own IP address , it can b elong to SN MP comm unities t o
which other switches in the group, including the CS, do not belong.
51
Page 63

DGS-3700-12/DGS-3700-12G Series Layer 2 Gigabit Ethernet Switch User Manual
The Upgrade to v1.6
To better improve SI M management, the DGS-37 00 Series has been upgrad ed to version 1.6 in this re lease. Many
improvements have been made, including:
1. The Commander S witc h ( CS) no w has t he c a pab il ity to automaticall y redisc o ver member switches that h av e lef t th e
SIM group, either through a reboot or web malfunction. This feature is accomplished through the use of Discover
packets and Maintain pack ets that previousl y set SIM members will em it after a reboot. Once a MS has had its MAC
address and password s aved to the C S’s database, if a r eboot oc curs in the MS, the C S wil l keep this MS inform ation
in its database and when a MS has been rediscovered, it will add th e MS back into the SIM tree autom atically. No
configuration will be necessary to rediscover these switches.
There are some instances where pre-saved MS sw itches cannot be rediscov ered. For example, if the Switch is still
powered down, if it has become the member of another group, or if it has been configured to be a Commander Switch,
the rediscovery process cannot occur.
2. The topology m ap now i nclud es new features for connect ions that are a
member of a port trunk ing group. It will display the speed and num ber of
Ethernet connections creating this port trunk group, as shown in the
adjacent picture.
3. This version will support multiple switch upload and downloads for firmware, configuration files and log files, as
follows:
• Firmware – The switch now supports multiple MS firmware downloads from a TFTP server.
• Configuration Files – This switch now supports multiple downloading and uploading of configuration files
both to (for configuration restoration) and from (for configuration backup) MS’s, using a TFTP server.
• Log – The switch now supports uploading multiple MS log files to a TFTP server.
4. The user may zoom in and zoom out when utilizing the top ology window to get a better, m ore defined view of the
configurations.
Single IP Settings
All switches are s et as Can didate (CaS) s witches as t heir f actor y default conf igurat ion and Sin gle I P Man ag em ent will
be disabled. This window is used to enable the SIM for the Switch using the Web interface.
To view this window, click Configuration > Single IP Management > Single IP Settings as shown below:
Figure 2 - 59 Single IP Settings window (disabled)
Change the SIM State to Enabled, and the Role State to Commander using the pull-down menu and click Apply.
52
Page 64

DGS-3700-12/DGS-3700-12G Series Layer 2 Gigabit Ethernet Switch User Manual
Figure 2 - 60 Single IP Settings window (enabled)
The following parameters can be set:
Parameters Description
SIM State Use the p ull-down menu to either en able or disable the SIM s tate on the Switch. Disabled will
render all SIM functions on the Switch inoperable.
Role State
Group Name
Discovery
Interval (30-90)
Hold Time Count
(100-255)
Click Apply to implement the settings.
After enabling the S witch to be a Commander Switch (CS), the Single I P Management folder will then contain four
added links to aid the user in configuring SIM through the web, including Topology, Firmware Upgrade and
Configuration Backup/Restore and Upload Log File.
Use the pull-down menu to change the SIM role of the Switch. The two choices are:
Candidate – A Can didate Switch (C aS) is not the m ember of a SIM group but is connected to a
Commander Switch. This is the default setting for the SIM role.
Commander – Choos ing this parameter will make the Switch a Comm ander Switch (CS). The
user may join other switche s to this Swit ch, over Ether net, to be par t of its SIM gr oup. Choosi ng
this option will also enable the Switch to be configured for SIM.
The user may enter a name for the group.
The user may set the discovery protocol interval, in seconds that the Switch will send out
discovery packets . Returning inf ormation t o a Comm ander Switch will include inform ation about
other switches connected to it. (Ex. MS, CaS). The user may set the D iscover y Interv al from 30
to 90 seconds.
This parameter m ay be se t for the time, in seconds the Switch will ho ld information sent to it
from other switches, uti lizing the Discover y Interval. The user may set the hold time from 100
to 255 seconds.
Topology
The Topology window will be us ed to c o nf igure a nd manage the Switch with in the SIM gr oup an d requ ir es J a va s cr ipt
to function properly on your computer.
The Java Runtime Environment on your server should initiate and lead you to the topology window, as seen below.
53
Page 65

DGS-3700-12/DGS-3700-12G Series Layer 2 Gigabit Ethernet Switch User Manual
Figure 2 - 61 Single IP Management window – Tree View
The Tree View window holds the following information under the Data tab:
Parameter Description
Device Name
This field will d isp la y the Device N am e of the s witche s in the SIM gr oup conf igur ed b y the user . If
no Device Nam e is configu red by the name, it will be gi ven the nam e defau lt and tag ged with t he
last six digits of the MAC Address to identify it.
Remote Port
Displays the number of the physical port on the CS t hat the MS or CaS is con nected to. The CS
will have no entry in this field.
Speed
Local Port
Displays the connection speed between the CS and the MS or CaS.
Displays the number of the physical port on the M S or CaS that the CS is connected to. The CS
will have no entry in this field.
MAC Address
Model Name
Displays the MAC address of the corresponding Switch.
Displays the full model name of the corresponding Switch.
To view the Topology Map, click the View menu in t he toolbar and then Topo logy, which will produce th e following
window. The Topology View will refresh itself periodically (20 seconds by default).
54
Page 66

DGS-3700-12/DGS-3700-12G Series Layer 2 Gigabit Ethernet Switch User Manual
Figure 2 - 62 Topology view
This window will displa y how the devices within the Singl e IP Managem ent Group are conn ected to other gr oups and
devices. Possible icons in this screen are as follows:
Icon Description
Group
Layer 2 commander switch
Layer 3 commander switch
Commander switch of other group
Layer 2 member switch.
Layer 3 member switch
Member switch of other group
Layer 2 candidate switch
Layer 3 candidate switch
Unknown device
Non-SIM devices
55
Page 67

DGS-3700-12/DGS-3700-12G Series Layer 2 Gigabit Ethernet Switch User Manual
Tool Tips
In the Topology view w indow, the mouse plays an im portant role in configuration and in vie wing device information.
Setting the mouse c ursor over a specific device in t he topology window (tool tip) will display the same information
about a specific device as the Tree view does. See the window below for an example.
Figure 2 - 63 Device Information Utilizing the Tool Tip
Setting the mouse c ursor over a li ne bet ween t wo de vices w ill displa y the c onnect ion sp eed bet ween t he t wo devices ,
as shown below.
Figure 2 - 64 Port Speed Utilizing the Tool Tip
56
Page 68

DGS-3700-12/DGS-3700-12G Series Layer 2 Gigabit Ethernet Switch User Manual
Right-Click
Right-clicking on a device will allow the user to perfor m various funct ions, depending on the role of the S witch in the
SIM group and the icon associated with it.
Group Icon
Figure 2 - 65 Right-Clicking a Group Icon
The following options may appear for the user to configure:
Collapse – To collapse the group that will b e repres en ted b y a
single icon.
Expand – To expand the SIM group, in detail.
Property – To pop up a window to display the group
information.
This window holds the following information:
Parameter Description
Device Name
Module Name
MAC Address
This field will displa y the Device Nam e of the switches in the SIM group config ured by the user.
If no Device Name is configured by the nam e, it will be g iven the nam e default a nd tagged w ith
the last six digits of the MAC Address to identify it.
Displays the full module name of the switch that was right-clicked.
Displays the MAC Address of the corresponding Switch.
Figure 2 - 66 Property window
Local Port No.
Remote Port No.
Port Speed
Click Close to close the Property window.
Displays the num ber of t he ph ysical por t on the MS or C aS tha t the C S is co nnec ted to. T he C S
will have no entry in this field.
Displays the num ber of t he ph ysical por t on the CS that th e M S or Ca S is co nnec ted to. T he CS
will have no entry in this field.
Displays the connection speed between the CS and the MS or CaS
57
Page 69

DGS-3700-12/DGS-3700-12G Series Layer 2 Gigabit Ethernet Switch User Manual
Commander Switch Icon
Figure 2 - 67 Right-Clicking a Commander Icon
The following options may appear for the user to configure:
Collapse – To collapse the group that will be represented by a single icon.
Expand – To expand the SIM group, in detail.
Property – To pop up a window to display the group information.
Member Switch Icon
Figure 2 - 68 Right-Clicking a Member icon
The following options may appear for the user to configure:
Remove from group – Remove a member from a group.
Configure – Launch the web management to configure the Switch.
Property – To pop up a window to display the device information.
Candidate Switch Icon
Figure 2 - 69 Right-Clicking a Candidate icon
The following options may appear for the user to configure:
Add to group – Add a can didate to a grou p. Cl ick ing this o ption will revea l the fol low ing dia log f or the user to e nter a
password for authent ication from the Candidate S witch before being added to the SI M group. Click OK to enter the
password or Cancel to exit the window.
58
Page 70

DGS-3700-12/DGS-3700-12G Series Layer 2 Gigabit Ethernet Switch User Manual
Figure 2 - 70 Input password window
Property – To pop up a window to display the device information, as shown below.
Menu Bar
The Single IP Management window contains a menu bar for device configurations, as seen below.
Figure 2 - 71 Menu Bar of the Topology View
The five menus on the menu bar are as follows.
File
Print Setup – Will view the image to be printed.
Print Topology – Will print the topology map.
Preference – Will set display properties, such as polling interval, and the views to open at SIM startup.
Group
Add to group – Add a can didate to a grou p. Cl ick ing this o ption will revea l the fol lowing dialog for the us er t o ent er a
password for authent ication from the Candidate S witch before being added to the SI M group. Click OK to enter the
password or Cancel to ex it the wind o w.
Figure 2 - 72 Input password window
Remove from Group – Remove an MS from the group.
Device
Configure – Will open the web manager for the specific device.
View
Refresh – Update the views with the latest status.
Topology – Display the Topology view.
Help
About – Will display the SIM information, including the current SIM version.
59
Page 71

DGS-3700-12/DGS-3700-12G Series Layer 2 Gigabit Ethernet Switch User Manual
Figure 2 - 73 About window
Firmware Upgrade
This screen is used to upgrade firmware from the Commander Switch to the Member Switch. Member Switches will be
listed in the table and w ill be specif ied by Port (port on the CS where t he MS resides) , MAC Address, Mod el Name
and Version. To specif y a certain Switch for firmware download, cl ick its corresponding check box under the Port
heading. To update the firmware, enter the Server IP Address where the firmware resides and enter the
Path/Filename of the firmware. Click Download to initiate the file transfer.
To view this window, click Configuration > Single IP Management > Firmware Upgrade as shown below:
Figure 2 - 74 Firmware Upgrade window
Configuration File Backup/Restore
This screen is used to upgr ade configuration files from the Commander Switch to the Mem ber Switch using a T FTP
server. Member Switches will be listed in the table and will be specified by ID, Port (port o n the CS where the MS
resides), M AC Addre ss, Model Name and Firmware Version. To update the configurat ion file, enter t he Server IP
Address where the file resides a nd enter the Path/Filename of the configurat ion file. Click Restore to initiate the file
transfer from a TFTP server to the Switch. Click Backup to backup the configuration file to a TFTP server.
To view this window, click Configuration > Single IP Management > Configuration File Backup/Restore as shown
below:
Figure 2 - 75 Configuration File Backup/Resto re window
60
Page 72

DGS-3700-12/DGS-3700-12G Series Layer 2 Gigabit Ethernet Switch User Manual
Upload Log File
The following windo w is used to upload log files from SIM m ember switches to a s pecified PC. To up load a log file,
enter the Server IP addr ess of the SIM m ember switch and then enter a Path\Filename on your PC where you wish to
save this file. Click Upload to initiate the file transfer.
To view this window, click Configuration > Single IP Management > Upload Log File as shown below:
Figure 2 - 76 Upload Log File window
DDM
This folder contains windo ws that perform Digital Diagnostic Monitoring functions on the Sw itch. There are windows
that allow the user to view the digital diagnostic monitoring status of SFP modules inserting to the Switch and to
configure alarm settings, warning settings, temperature threshold settings, voltage threshold settings, bias current
threshold settings, Tx power threshold settings, and Rx power threshold settings.
Browse DDM Status List
This window displays the current operating digital diagnostic monitoring parameters and their values on the SFP
module for specified ports.
To view this window, click Configuration > DDM > Browse DDM Status List as shown below:
Figure 2 - 77 Browse DDM Status List window
To view the status f or a s p ec if ic por t or lis t of por ts, enter the port list a nd c l ick Find. T o displ a y the s tatus f or al l p ort s,
check the All Ports box and click Find.
DDM Settings
The DDM settings windo w allows the us er to configur e the action tha t will occur f or specific por ts when an exceeding
alarm threshold or warning threshold event is encountered.
To view this window, click Configuration > DDM > DDM Settings as shown below:
61
Page 73

DGS-3700-12/DGS-3700-12G Series Layer 2 Gigabit Ethernet Switch User Manual
The following fields can be configured:
Parameter Description
Figure 2 - 78 DDM Settings window
Trap Log
From Port / To Port
State
Shutdown
Click Apply to implement changes made.
Specifies whether or not to send the tr ap and lo g, when the o perating p arameter ex ceeds the
alarm or warning threshold.
Specifies a port or range of ports to be configured.
Specifies to Enable or Disable the DDM settings state.
Specifies whether or not to shutdown the port, when the operating parameter exceeds the
Alarm or Warning threshold.
DDM Temperature Threshold Settings
This table is used to configure the DDM Temperature Threshold Settings for specific ports on the Switch.
To view this window, click Configuration > DDM > DDM Temperature Threshold Settings as shown below:
Figure 2 - 79 DDM Temperature Threshold Settings window
The following fields can be configured:
Parameter Description
From Port / To Port
High Alarm
Low Alarm
High Warning
Low Warning
Click Apply to implement changes made.
Specifies a port or range of ports to be configured.
This is the highest threshold for the alarm. When the operating parameter rises above this
value, action associated with the alarm will be taken.
This is the lowest threshold for the alarm. When the operating parameter falls below this value,
action associated with the alarm is taken.
This is the highest thresh old for the warning. W hen the operating parameter r ises above this
value, action associated with the warning is taken.
This is the lowest threshold for the warning. W hen the operating parameter falls below this
value, action associated with the warning is taken.
62
Page 74

DGS-3700-12/DGS-3700-12G Series Layer 2 Gigabit Ethernet Switch User Manual
DDM Voltage Threshold Settings
This table is used to configure the DDM Voltage Threshold Settings for specific ports on the Switch.
To view this window, click Configuration > DDM > DDM Voltage Threshold Settings as shown below:
Figure 2 - 80 DDM Voltage Threshold Settings window
The following fields can be configured:
Parameter Description
From Port / To Port
High Alarm
Low Alarm
High Warning
Low Warning
Click Apply to implement changes made.
Specifies a port or range of ports to be configured.
This is the highest threshold for the alarm. When the operating parameter rises above this
value, action associated with the alarm will be taken.
This is the lowest threshold for the alarm. When the operating parameter falls below this value,
action associated with the alarm is taken.
This is the highes t threshold for the warning. W hen the operating param eter rises above this
value, action associated with the warning is taken.
This is the lowest threshold for the warning. W hen the operating parameter falls below this
value, action associated with the warning is taken.
DDM Bias Current Threshold Settings
This table is used to configure the threshold of the bias current for specific ports on the Switch.
To view this window, click Configuration > DDM > DDM Bias Current Threshold Settings as shown below:
The following fields can be configured:
Parameter Description
From Port / To Port
High Alarm
Low Alarm
Specifies a port or range of ports to be configured.
This is the highest threshold for the alarm. When the operating parameter rises above this
value, action associated with the alarm will be taken.
This is the lowest threshold for the alarm. When the operating parameter falls below this value,
action associated with the alarm is taken.
Figure 2 - 81 DDM Bias Current Threshold Settings window
63
Page 75

DGS-3700-12/DGS-3700-12G Series Layer 2 Gigabit Ethernet Switch User Manual
High Warning
Low Warning
Click Apply to implement changes made.
This is the highest thresh old for the warning. W hen the operating parameter r ises above this
value, action associated with the warning is taken.
This is the lowest threshold for the warning. W hen the operating parameter falls below this
value, action associated with the warning is taken.
DDM Tx Power Threshold Settings
This table is used to configure the threshold of Tx power for specific ports on the Switch.
To view this window, click Configuration > DDM > DDM Tx Power Threshold Settings as shown below:
Figure 2 - 82 DDM Tx Power Threshold Settings window
The following fields can be configured:
Parameter Description
From Port / To Port
High Alarm
Low Alarm
High Warning
Low Warning
Click Apply to implement changes made.
Specifies a port or range of ports to be configured.
This is the highest threshold for the alarm. When the operating parameter rises above this
value, action associated with the alarm will be taken.
This is the lowest threshold for the alarm. When the operating parameter falls below this value,
action associated with the alarm is taken.
This is the highest thresh old for the warning. W hen the operating parameter r ises above this
value, action associated with the warning is taken.
This is the lowest threshold for the warning. W hen the operating parameter falls below this
value, action associated with the warning is taken.
DDM Rx Power Threshold Settings
This table is used to configure the threshold of Rx power for specific ports on the Switch.
To view this window, click Configuration > DDM > DDM Rx Power Threshold Settings as shown below:
Figure 2 - 83 DDM Rx Power Threshold Settings window
64
Page 76

DGS-3700-12/DGS-3700-12G Series Layer 2 Gigabit Ethernet Switch User Manual
The following fields can be configured:
Parameter Description
From Port / To Port
High Alarm
Specifies a port or range of ports to be configured.
This is the highest threshold for the alarm. When the operating parameter rises above this
value, action associated with the alarm will be taken.
Low Alarm
This is the lowest threshold for the alarm. When the operating parameter falls below this value,
action associated with the alarm is taken.
High Warning
This is the highest thresh old for the warning. W hen the operating parameter r ises above this
value, action associated with the warning is taken.
Low Warning
This is the lowest threshold for the warning. W hen the operating parameter falls below this
value, action associated with the warning is taken.
Click Apply to implement changes made.
65
Page 77

DGS-3700-12/DGS-3700-12G Series Layer 2 Gigabit Ethernet Switch User Manual
L2 Features
Jumbo Frame
802.1Q VLAN
Subnet VLAN
QinQ
802.1v Protocol VLAN
RSPAN Settings
GVRP Settings
GVRP Global Settings
MAC-based VLAN Settings
PVID Auto Assign Settings
Port Trunking
LACP Port Settings
Section 3
Traffic Segmentation
BPDU Tunneling Settings
IGMP Snooping
MLD Snooping
Port Mirror
Loopback Detection Settings
Spanning Tree
Forwarding & Filtering
LLDP
CFM
Ethernet OAM
The following sectio n will aid the user in configuring Layer 2 functions for the Switch . The Switch includes various
functions all discussed in detail in the following section.
Jumbo Frame
This window will enab le or disable t he Jumbo Fram e function on the S witch. The default is Disabled. W hen enab led,
jumbo frame (frames larger than the standard Ethernet frame size of 1536 bytes) of up to 13K (and 13312 bytes
tagged) can be transmitted by the Switch.
To view this window, click L2 Features > Jumbo Frame as shown below:
Figure 3 - 1 Jumbo Frame window
Click Apply to implement changes made.
66
Page 78

DGS-3700-12/DGS-3700-12G Series Layer 2 Gigabit Ethernet Switch User Manual
VLANs
Understanding IEEE 802.1p Priority
Priority tagging is a func tio n define d b y the IEE E 802. 1p standar d des igned t o prov ide a m eans of m anaging traf fic on
a network where m any different types of data may be trans mitted simultane ously. It is intend ed to alleviate problems
associated with the delivery of time critical data over congested networks. The quality of applications that are
dependent on such tim e critical data, such as video conferencin g, can be severely and adversely affec ted by even
very small delays in transmission.
Network devices that are in compliance with the IEEE 802.1p standard have the ability to recognize the priority level of
data packets. These dev ices can also assign a prior it y label or ta g to p ac kets. Compliant devices c an a lso s t r ip prior ity
tags from packets. This priority tag determines the pa cket's degree of expeditiou sness and determines the queu e to
which it will be assigned.
Priority tags are given values from 0 to 7 with 0 being assigned to the lowest priority data and 7 assigned to the
highest. The highest prior ity tag 7 is generally only used for data associated with video or audio appl ications, which
are sensitive to e ven slight delays, or for data fr om specified end users whose data transmissions warrant spec ial
consideration.
The Switch allo ws you to further ta ilor h o w pr ior ity tagged data packets are handled o n your network. Us ing q ueues to
manage priority tagged data allows you to specify its r elative priorit y to suit the needs of your networ k. There m ay be
circumstances where it would be ad vantageous to group t wo or more dif ferently tagge d pack ets into the sam e queue.
Generally, however, it is recommended tha t the highest priorit y queue, Queue 7, be r eserved for data pac kets with a
priority value of 7. Pack ets that have not been given any priority value are placed in Queue 0 and thus given the
lowest priority for delivery.
Strict mode and weighted round robin s ystem are em ployed on the Switch to det ermine the rate at whic h the queu es
are emptied of packets. The ratio used for clearing the queues is 4:1. This means that the highest priority queue,
Queue 7, will clear 4 packets for every 1 packet cleared from Queue 0.
Remember, the priori ty queue set tings on t he Switch a re for all ports, and a ll devices c onnected to the Switch will be
affected. This priorit y queuing s ystem will be espec ially benef icial if your network employs switches with the c apability
of assigning priority tags.
VLAN Description
A Virtual Local Are a Network (VLAN) is a networ k topology configur ed according to a logica l scheme rather than the
physical layout. VL ANs can be use d to combine a ny collection of LAN segm ents into an autonom ous user g roup that
appears as a single LAN. VLANs also logic ally segment th e network into dif ferent broadc ast domains so th at packet s
are forwarded onl y betw ee n ports with in t he VL AN. Typically, a VLAN c orr es p ond s to a p artic u lar s ub net, alt houg h n ot
necessarily.
VLANs can enhance performance by conserving bandwidth, and improve security by limiting traffic to specific
domains.
A VLAN is a collection of end nodes grouped by logic instead of physical location. End nodes that frequently
communicate with each other are assigned to the same VLAN, regardless of where they are physically on the
network. Logicall y, a VLAN c an be equa ted to a br oadcas t domain, b ecause broadcast packets are forwar ded to on ly
members of the VLAN on which the broadcast was initiated.
Notes About VLANs
No matter what basis is used to uniquel y identify end nodes and assign these nodes VLAN membership, packets
cannot cross VLANs without a network device performing a routing function between the VLANs.
The Switch supports IEEE 802.1Q VLANs and Port-Based VLANs. The port untagging function can be used to
remove the 802.1Q tag from packet headers to maintain compatibility with devices that are tag-unaware.
The Switch's defaul t is to as sign all ports to a single 802.1Q VLAN named "def ault." The "def ault" VLAN has a VID =
1. The member ports of Port-based VLANs may overlap, if desired.
67
Page 79

DGS-3700-12/DGS-3700-12G Series Layer 2 Gigabit Ethernet Switch User Manual
IEEE 802.1Q VLANs
Some relevant terms:
Tagging – The act of putting 802.1Q VLAN information into the header of a packet.
Untagging – The act of stripping 802.1Q VLAN information out of the packet header.
Ingress port – A port on a switch where packets are f lowing into the Switch and VL AN decisions must be
made.
Egress port – A port on a switch where packets are flowing out of the Switch, either to another switch or to an
end station, and tagging decisions must be made.
IEEE 802.1Q (tagge d) VLA Ns ar e im plem ented on th e Switch. 802.1Q VL ANs require taggin g, whic h en ables them to
span the entire network (assuming all switches on the network are IEEE 802.1Q-compliant). VLANs allow a network to
be segmented in or der to r educ e the s i ze of broa dc as t domains. All pack ets ente r ing a VL AN wi ll only be forwarded t o
the stations (over IEEE 802.1Q enabled switches) that are members of that VLAN, and this includes broadcast,
multicast and unicast packets from unknown sources.
VLANs can also pro vide a level of security to your network. IEEE 802.1Q VLANs will only deliver packets between
stations that are members of the VLAN.
Any port can be configured as either tagging or untagging. The untagging feature of IEEE 802.1Q VLANs allows
VLANs to work with legacy switches that don' t recognize VLAN tags in p acket headers. The tagging feature allows
VLANs to span multiple 802.1Q -com pliant s witches through a s ing le ph ysical con nection an d allo ws Spa nnin g Tr ee to
be enabled on all ports and work normally.
The IEEE 802.1Q standard restricts the forwarding of unta gged packets to the V LAN of which the receiv ing port is a
member.
The main characteristics of IEEE 802.1Q are as follows:
Assigns packets to VLANs by filtering.
Assumes the presence of a single global spanning
tree.
Uses an explicit tagging scheme with one-level
tagging.
802.1Q VLAN Packet Forwarding
Packet forwarding dec isions are made based upon the
following three types of rules:
Ingress rules – rules relevant to the classification of
received frames belonging to a VLAN.
Forwarding rules between ports - decides whether to
filter or forward the packet.
Egress rules – determines if the packet must be sent
tagged or untagged.
Figure 3 - 2 IEEE 802.1Q Packet Forwarding
68
Page 80

DGS-3700-12/DGS-3700-12G Series Layer 2 Gigabit Ethernet Switch User Manual
802.1Q VLAN Tags
The figure below shows the 802.1Q VLAN tag. There are four additional octets inserted after the source MAC
address. Their prese nce is indicated b y a value of 0x8100 in the EtherT ype field. When a pack et's EtherType field is
equal to 0x8100, the pack et carries the IEEE 802.1Q /802.1p tag. T he tag is contained in t he following two o ctets and
consists of 3 bits of us er pr i orit y, 1 b it of Can on ic al F or mat Identifier (CFI - used for encapsulati ng T oken Ring packets
so they can be carried acr oss Ether net back bones), an d 12 bits of VLAN ID ( VID). The 3 bits of user priorit y are used
by 802.1p. The VID is th e VLAN i dentifier an d is used by the 802. 1Q stand ard. Becaus e the VID is 1 2 bits l ong, 4094
unique VLANs can be identified.
The tag is inserted in to the pac ket header m ak ing the entire pac ket longer by 4 oc tets. All of t he inform ation origi nally
contained in the packet is retained.
Figure 3 - 3 IEEE 802.1Q Tag
The EtherType and VLAN ID are inserted af ter the MAC source addres s, but befo re the origi nal EtherT ype/Length or
Logical Link Control. Because the packet is now a bit longer than it was originally, the Cyclic Redundancy Check
(CRC) must be recalculated.
Figure 3 - 4 Adding an IEEE 802.1Q Tag
69
Page 81

DGS-3700-12/DGS-3700-12G Series Layer 2 Gigabit Ethernet Switch User Manual
Port VLAN ID
Packets that are tagged (are carrying the 802.1Q VID information) can be transmitted from one 802.1Q compliant
network device to another w ith the VLAN inform ation i ntact. This a llows 8 02.1Q VLANs to s pan net work de vices (and
indeed, the entire network, if all network devices are 802.1Q compliant).
Unfortunately, not all network devices are 802. 1Q compliant. Thes e devices are referr ed to as tag-unaware. 802.1Q
devices are referred to as tag-aware.
Prior to the adoption of 802.1Q VLANs, port-based and MAC-based VLANs were in common use. These VLANs relied
upon a Port VLAN ID (PVID) to forward packets. A packet received on a given port would be assigned that port's PVID
and then be forwarded to the port that corresponded to the packet's destination address (found in the Switch's
forwarding table). If the PVID of the port that received the packet is different from the PVID of the port that is to
transmit the packet, the Switch will drop the packet.
Within the Switch, diff erent PVIDs m ean different VLANs (remember that two VL ANs cannot comm unicate with out an
external router). So, VLAN identification based upon the PVIDs cannot create VLANs that extend outside a given
switch (or switch stack).
Every physical port on a s witch has a PVID. 802.1Q ports are also assig ned a PVID, for use with in the Switch. If no
VLANs are defined on the Switch, all ports are then assigned to a default VLAN with a PVID equal to 1. Untagged
packets are assigned th e PVID of the port on which they were receive d. Forwarding decisions are based upon this
PVID, in so far as VLANs are concerned. Tagged pack ets are forwarded according to t he VID contained within the
tag. Tagged pack ets are also assigned a PVID, but the P VID is not used to make pack et-forwarding decisions, the
VID is.
Tag-aware switches must keep a table to relate PVIDs within the Switch to VIDs on the network. The Switch will
compare the VID of a pac ket to be tr ansm itted to the VID of the port that is to tr ansm it the pack et. If the t wo VIDs are
different, the Switch will drop the p acket. Because of the existenc e of the PV ID for untagg ed packets and the VID for
tagged packets, tag-aware and tag-unaware network devices can coexist on the same network.
A switch port can have only one PVID , but can have as many VIDs as the Switch has mem ory in its VLAN table t o
store them.
Because some devices on a network may be tag-unaware, a decision m ust be made at each port on a tag-aware
device before pack ets are transm itted - should the pack et to be transm itted have a tag or not? If the transm itting port
is connected to a tag-unaware dev ice, the packet should be untagge d. If the transm itting port is connected to a tagaware device, the packet should be tagged.
Tagging and Untagging
Every port on an 802.1Q compliant switch can be configured as tagging or untagging.
Ports with tagging e nabled will put t he VID num ber, pri ority and ot her VLA N infor mation into t he hea der of all packets
that flow into and out of it. If a packet has previousl y been tagged, the port will not alter the packet, thus keeping th e
VLAN information intac t. O ther 802.1Q compliant devices on the network to make packet-forwarding decisions can
then use the VLAN information in the tag.
Ports with untagging enabled will strip the 802.1Q ta g from all packets that flow into and out of those ports. If the
packet doesn't have an 802.1Q VLAN tag, the port will not alter the packet. Thus, all packets received by and
forwarded by an untagging port will have no 802.1Q VLAN information. (Remember that the PVID is only used
internally within the Switch). Untagging is used to send packets from an 802.1Q-compliant net work device to a noncompliant network device.
Ingress Filtering
A port on a switch where p ackets are flowing in to the Switch and VL AN decisions must be made is refer red to as an
ingress port. If ingress filtering is enabled for a port, the Switch will examine the VLAN information in the packet
header (if present) and decide whether or not to forward the packet.
If the packet is t agged with VLAN inf orm ation, th e ingr ess port w ill f irst det erm ine if the ingres s port its elf is a m em ber
of the tagged VLAN. If it is not, the packet will be dr opped. If the ingress port is a member of the 802.1Q V LAN, the
Switch then determ ines if the destination port is a mem ber of the 802.1Q VLAN. If it is not, the pack et is dropped. If
the destination port is a mem ber of the 802.1Q V LAN, the pack et is forward ed and the dest ination port tr ansm its it to
its attached network segment.
If the packet is not tagged with VLAN information, the ingress port will tag the packet with its own PVID as a VID (if the
port is a tagging port). T he switch then determines if the des tination port is a member of the sam e VLAN (has the
70
Page 82

DGS-3700-12/DGS-3700-12G Series Layer 2 Gigabit Ethernet Switch User Manual
same VID) as the ingress port. If it does not, the packet is dropped. If it has the same VID, the packet is forwarded and
the destination port transmits it on its attached network segment.
This process is referred to as ingress filtering and is used to conserve bandwidth within the Switch by dropping
packets that are not on the sam e VLAN as the ingress port at the point of reception. T his eliminates the subseque nt
processing of packets that will just be dropped by the destination port.
Default VLANs
The Switch initiall y configur es one VLAN, VID = 1, c alled "default." T he factor y def ault setting as signs a ll ports on the
Switch to the "default." As ne w VLANs ar e conf ig ured in Port -based mode, their respective member ports are removed
from the "default."
Packets cannot cross VLANs. If a mem ber of one VLAN wants to connect to another VLAN, th e link mus t be through
an external router.
NOTE: If no VLANs are c onfigured on the S witch, then all pack ets will be forwarded to an y
destination port. Packets with unknown source addresses will be flooded to all ports.
Broadcast and multicast packets will also be flooded to all ports.
An example is presented below:
VLAN Name VID Switch Ports
System (default) 1 5, 6, 7, 8, 21, 22, 23, 24
Engineering 2 9, 10, 11, 12
Marketing 3 13, 14, 15, 16
Finance 4 17, 18, 19, 20
Sales 5 1, 2, 3, 4
Table 3 - 1 VLAN Example - Assigned Ports
Port-based VLANs
Port-based VLANs limit traffic that flows into and out of switch ports. Thus, all devices connected to a port are
members of the VLAN( s) the por t belongs to, wh ether ther e is a s ingle com puter direc tly connec ted to a switc h, or an
entire department.
On port-based VLANs, NIC s do not n eed to be ab le to identif y 802.1Q tags i n pac k et headers. NIC s send a nd r eceive
normal Ethernet packets. If the packet's destination lies on the same segment, communications take place using
normal Ethernet prot ocols. Even though this is al wa ys the case, when the destinati on for a packet lies on another
switch port, VLAN considerations come into play to decide if the packet gets dropped by the Switch or delivered.
VLAN Segmentation
Take for example a pack et that is transm itted by a machine on Port 1 that is a member of VLAN 2. If the destinati on
lies on another port (f ound through a normal forwarding ta ble lookup), the Switch then lo oks to see if the other port
(Port 10) is a m ember of V LAN 2 (a nd can t herefore r eceive VLAN 2 p ackets ). If Port 10 is not a mem ber of VLAN 2,
then the packet will be dr o pped b y the Switch and will not r each its des tinat ion. If Port 10 is a m ember of VLAN 2, t he
packet will go throu gh. This selective forwardi ng feature based on VLAN c riteria is how VLANs segm ent networks.
The key point being that Port 1 will only transmit on VLAN 2.
Network resources can be shared acr os s VL ANs . This is achieved by setting up overl app in g VL ANs . T hat is ports can
belong to more than one VLAN gro up. For example, by setti ng VLAN 1 members to ports 1, 2, 3 and 4 and VLAN 2
members to ports 1, 5, 6 and 7, Port 1 will belong to tw o VLAN groups. Ports 8, 9 and 10 are not configured to a ny
VLAN group. This means ports 8, 9 and 10 are in the same VLAN group.
71
Page 83

DGS-3700-12/DGS-3700-12G Series Layer 2 Gigabit Ethernet Switch User Manual
802.1Q CEVLAN Tag
VLAN and Trunk Groups
The members of a tr unk group have the s ame VLAN setting. An y VLAN setti ng on the members of a trunk group will
apply to the other member ports.
NOTE: In order to us e VLAN segmentation in conjun ction with port trunk groups , you can first
set the port trunk group(s), and then you may configure VLAN s ettings. If you wish to change
the port trunk grouping wit h VLANs alread y in place, you will not need t o reconfigure the VLAN
settings after chan ging the port tru nk group sett ings. VLAN s ettings wil l autom atic all y change in
conjunction with the change of the port trunk group settings.
Double VLANs
Double or Q-in-Q VLANs allow network providers to expand their VLAN configurations to place customer VLANs
within a larger inclusive VLAN, which adds a new layer to the VLAN configuration. This basically lets large ISP's
create L2 Virtual Private Networks and als o create transparent LANs for their customers , which will connect two or
more customer LAN points without over-complicating configurations on the client's side. Not only will overcomplication be avoided, but also now the adm inistrator has over 4000 VLANs in which over 4000 VLANs can be
placed, therefore greatly expanding the VLAN ne twork and enabling greater su pport of customers utilizing m ultiple
VLANs on the network.
Double VLANs are basically VLAN tags placed within existing IEEE 802.1Q VLANs which we will call SPVIDs (Service
Provider VLAN IDs). These VLANs are marked by a TPID (Tagged Protocol ID), configured in hex form to be
encapsulated within the V LAN tag of the packet. This identif ies the packet as double-tagged and s egregates it from
other VLANs on the network, therefore creating a hierarchy of VLANs within a single packet.
Here is an example Double VLAN tagged packet.
Destination
Address
Consider the example below:
Source
Address
SPVLAN (TPID +
Service Provider
VLAN Tag)
(TPID + Customer VLAN
Tag)
Ether
Type
Payload
72
Page 84

DGS-3700-12/DGS-3700-12G Series Layer 2 Gigabit Ethernet Switch User Manual
Figure 3 - 5 Double VLAN Example
In this example, the Service Provider Access Network switch (Provider edge switch) is the device creating and
configuring Double VLANs with different SPVIDs for specific customers (say Customer A and Customer B). Both
CEVLANs (Customer VLANs), CEVLAN 10 are tagged with the SPVID 100 (for Customer A) and SPVID 200 (for
Customer B) on th e Service Pr ovider Acc ess Network , thus being a member of two VLANs o n the Service Provider’s
network. In this wa y, the Custom er can retain the ir norm al VLAN ID’s and t he Service Pr ovider can se perate multiple
Customer VLANs using SPVLANs, thus greatly regulating traffic and routing on the Service Provider switch. This
information is then route d to the Service Provider’s m ain network and regarded there as on e VLAN, with one set of
protocols and one routing behavior.
Regulations for Double VL ANs
Some rules and regulations apply with the implementation of the Double VLAN procedure.
1. All ports must be configured for the SPVID and its corresponding TPID on the Service Provider’s edge switch.
2. All ports must be configured as Access Ports or Uplink ports. Access ports can onl y be Ethernet ports whil e
Uplink ports must be Gigabit ports.
3. Provider Edge switches must allow frames of at least 1522 bytes or more, due to the addition of the SPVID
tag.
4. Access Ports must be an un-tagged port of the service provider VLANs. Uplink Ports must be a tagged port of
the service provider VLANs.
5. The switch cannot have both double and normal VLANs co-existing. Once the change of VLAN is made, all
Access Control lists are cleared and must be reconfigured.
6. Once Double VLANs are enabled, GVRP must be disabled.
7. All packets sent from the CPU to the Access ports must be untagged.
8. The following functions will not operate when the switch is in Double VLAN mode:
• Guest VLANs
73
Page 85

DGS-3700-12/DGS-3700-12G Series Layer 2 Gigabit Ethernet Switch User Manual
• Web-based Access Control
• IP Multicast Routing
• GVRP
• All Regular 802.1Q VLAN functions
802.1Q VLAN
The 802.1Q VLAN window lists all previously configured VLANs by VLAN ID and VLAN Name.
To view this window, click L2 Features > 8 02.1Q VLAN as shown below:
Figure 3 - 6 Current 802.1Q Static VLANs Entries window
To create a new 802.1Q V LAN entry or edit an existing on e, click the Add/Edit VLAN tab at the top of the 802.1Q
VLAN window. A new window will appear, as shown below, to configure the port settings and to assign a unique name
and number to the new VLAN. See the table below for a description of the parameters in the new window.
NOTE: After al l I P inter f ac es are s et f or your c o nf igurations, VLANs on th e
switch can be routed without any additional steps.
74
Page 86

DGS-3700-12/DGS-3700-12G Series Layer 2 Gigabit Ethernet Switch User Manual
Figure 3 - 7 802.1Q VLAN window – Add/Edit VLAN Tab
To return to the 802.1Q VLAN window, click the VLAN List Tab at the top of the window. To change an exis ting
802.1Q VLAN entry, click the correspondin g Edit button. A ne w window will ap pear to config ure the port settings and
to assign a unique nam e and num ber to the ne w VLA N. See the table b elo w for a desc ript ion of t he param eters in th e
new menu.
NOTE: The Switch supports up to 4k static VLAN entries.
Figure 3 - 8 802.1Q VLAN window – Edit window
The following fields can then be set in either the Add/Edit VLAN or Edit 802.1Q VLAN windows:
Parameter Description
VID Allows the entry of a VLAN ID, or displays the VLAN ID of an existing VLAN in the Edit
window. VLANs can be identified by either the VID or the VLAN name.
VLAN Name Allows the entry of a name f or a new VLAN , or modif ying the V LAN nam e in the Edit window.
VLAN Name should be no more than 32 characters in length.
75
Page 87

DGS-3700-12/DGS-3700-12G Series Layer 2 Gigabit Ethernet Switch User Manual
Advertisement
Enabling this function will allow the Switch to send out GVRP packets to outside sources,
notifying that they may join the existing VLAN.
Port Settings
Tagged
Untagged
Forbidden
Allows an individual port to be specified as member of a VLAN.
Specifies the port as 802.1Q tagged. Checking the box will designate the port as Tagged.
Specifies the port as 802.1Q untagged. Checking the box will designate the port as untagged.
Select this to specify the port as not being a member of the VLAN and that the port is
forbidden from becoming a member of the VLAN dynamically.
Not Member
Allows an individual port to be specified as a non-VLAN member.
Click Apply to implement changes made.
To search for a VLAN clic k the Find VL AN tab at the top of the s c reen w hich w ill displ a y the f ol lo wing window, enter a
VLAN ID and click Find to display the settings for a previously configured VLAN.
Figure 3 - 9 802.1Q VLAN window – Find VLAN window
To create a VLAN Batch entry click the VLAN Batch Settings tab at the top of the screen which will display the
following win do w .
76
Page 88

DGS-3700-12/DGS-3700-12G Series Layer 2 Gigabit Ethernet Switch User Manual
Figure 3 - 10 802.1Q VLAN window – VLAN Batch Settings window
The following fields can be set in the VL AN Batch Settings windows:
Parameter Description
VID List (e.g 2-5)
Advertisement
Enter a VLAN ID List that can be added, deleted or configured.
Enabling this function will allow the Switch to send out GVRP packets to outside sources,
notifying that they may join the existing VLAN.
Port List (e.g. 1-5)
Tagged
Untagged
Forbidden
Allows an individual port list to be added or deleted as a member of the VLAN.
Specifies the port as 802.1Q tagged. Checking the box will designate the port as Tagged.
Specifies the port as 802.1Q untagged. Checking the box will designate the port as untagged.
Select this to specify the port as not being a member of the VLAN and that the port is
forbidden from becoming a member of the VLAN dynamically.
Click Apply to implement changes made.
77
Page 89

DGS-3700-12/DGS-3700-12G Series Layer 2 Gigabit Ethernet Switch User Manual
Subnet VLAN
Subnet VLAN Settings
The subnet VLAN settings are used to create, find or delete a subnet VLAN entry. A subnet VLAN entr y is an IP
subnet-based VLAN classification r ule. If an untagged or pr iority-tagge d IP pack et is recei ved on a port, its source I P
address will be used to m atc h the sub net VL AN entries . If the sour ce IP is in the s ubnet of an e ntry, the packet will be
classified to the VLAN defined for this subnet.
To view this window, click L2 Features > Subnet VLAN > Subnet VLAN Settings as shown below:
Figure 3 - 11 Subnet VLAN Settings window
The following parameters can be configured:
Parameter Description
VLAN Name
VLAN ID
IPv4 Network
Address
IPv6 Network
Address
Priority
Enter the appropriate information and click Add to create a new entry. To search for a particular entry enter the
appropriate inform ation and clic k Find. To rem ove an entry clic k Delete. To view all entries on the Switch c lick Show
All to remove all entries click Delete All.
The VLAN Name to be associated with the subnet.
The VLAN ID to be associated with the subnet.
Is used to specif y an IPv4 network address. The form at is ipaddress/pref ix length. The pref ix
length of the IPv4 network address cannot be greater than 64.
Is used to specif y an IPv6 network address. The form at is ipaddress/ prefix length. The pref ix
length of the IPv6 network address cannot be greater than 64.
The priority to be associated with the subnet. Its range is 0-7.
VLAN Precedence Settings
The VLAN precedence sett ings are used to config ure VLAN class ification preced ence on each p ort. You can spec ify
the order of MAC-based V LAN classifications and subnet VLAN c lassifications. If a port’s VLAN class ificataion is a
MAC-based precedence, MAC-based VL AN clas s if icati on wil l proc ess first. If MAC-based VLAN classification fails, the
subnet VLAN classif ication will be executed. If a port’ s VLAN classification is subnet VL AN precedence, the subnet
VLAN classification will process first. If subnet VLAN clas sification fails, the MAC-based VLAN clas sification will be
executed.
To view this window, click L2 Features > Subnet VLAN > VLAN Precedence Settings as shown below:
78
Page 90

DGS-3700-12/DGS-3700-12G Series Layer 2 Gigabit Ethernet Switch User Manual
Figure 3 - 12 VLAN Precedence Settings window
The following parameters can be configured:
Parameter Description
From Port / To Port
VLAN Precedence
Click Apply to implement changes made.
Specify the port or range of ports you wish to configure.
Use the drop down m enu to s elect the VLAN pr ecede nce, c hoose either MAC Ba sed VL AN or
Subnet VLAN.
MAC Based VLAN – Specif ies that the MAC-based VLAN classificat ion is given precedence
over the subnet VLAN classification.
Subnet VLAN – Specifies that the subnet VLAN classification is given precedence over the
MAC-based VLAN classification.
Q-in-Q
Q-in-Q Settings
This function allows the user to enable or disable the Q-in-Q function. Q-in-Q is designed for service providers to carry
traffic from multiple users across a network. Q-in-Q is used to maintain customer specific VLAN and Layer 2 protocol
configurations even when the same VLAN ID is being used by different customers. This is achieved by inserting
SPVLAN tags into the customer’s frames when they enter the service provider’s network, and then removing the tags
when the frames leave the network.
Customers of a s ervic e pro vi der may have diff erent or s pecif ic requ ir ements regarding their internal VLAN I D s and the
number of VLANs tha t can be supporte d. Theref ore cu stom ers in the sam e servic e provider network ma y have VLAN
ranges that overlap, w hich m ight c ause traf fic to becom e m ixed up. So assig ning a unique r ange of VLAN IDs to each
customer might cause restrictions on some of their configurations requiring intense processing of VLAN mapping
tables which may exceed the VLAN mapping limit. Q-in-Q uses a single service provider VLAN (SPVLAN) for
customers who have multiple VLANs. Customer’s VLAN IDs are segregated within the service provider’s network
even when they use the same customer specific VLAN ID. Q-in-Q expands the VLAN space available while pres er ving
the customer’s original tagged packets and adding SPVLAN tags to each new frame.
To view this window, click L2 Features > QinQ > QinQ Settings as shown below :
79
Page 91

DGS-3700-12/DGS-3700-12G Series Layer 2 Gigabit Ethernet Switch User Manual
The following fields can be set:
Parameter Description
Figure 3 - 13 QinQ Settings window
From Port / To Port
Role
Missdrop
Outer TPID
Use Inner Priority
Add Inner Tag(hex:
0x1-0xffff)
Click Apply to implement changes.
A consecutive group of ports that ar e part of the VLAN configurat ion startin g with the s elected
port.
The user can choose between UNI or NNI role.
UNI – To select a user-network interface which specifies that communication between the
specified user and a specified network will occur.
NNI – To select a network-to-network interface specifies that communication between two
specified networks will occur.
Use the drop down menu to enable or disable m issdrop. If missdrop is enable d, the packet
that does not matc h an y as s ignment rule in the Q-in-Q prof ile wil l be dr o ppe d. If disabled, then
the packet will be assigned to the PVID of the receiving port.
The Outer TPID is used for learning and switching packets.
The priority given to the inner tag will be copied to the outer tag if this setting is enabled.
Specify whether to add inner tag for ingress untagged packets. If set, the inner tag will be
added for the ingr ess untagged packets and thus the packets egress to the NNI port will be
double tagged.
VLAN Translation Settings
VLAN translation tra nslates the VLAN ID carried in t he data p ackets it receives from private ne tworks into thos e used
in the Service Providers network.
To view this window, click L2 Features > QinQ > VLAN Translation Settings as shown below:
80
Page 92

DGS-3700-12/DGS-3700-12G Series Layer 2 Gigabit Ethernet Switch User Manual
Figure 3 - 14 VLAN Translation Settings window
The following fields can be set:
Parameter Description
From Port / To Port
CVID (1-4094)
Action
SPVID (1-4094)
Priority (0-7)
Click Apply to make a new entry and Delete All to remove a VLAN Translation entry.
A consecutive group of ports that ar e part of the VLAN configurat ion startin g with the s elected
port.
The customer VLAN ID List to which the tagged packets will be added.
Specify if you want SPVID packets to be added or replaced.
This configures the VLAN to join the Service Providers VLAN as a tagged member.
Select a priority for the VLAN ranging from 0-7. With 7 having the highest priority.
Q-in-Q and VLAN Translation Rules
For ingress untagged packets at UNI por ts:
1. The switch does not reference the VLAN translation table.
2. Check switch VLAN tabl es. T he sequence: mac-based VLAN -> subnet-bas ed VL AN -> protocl-base d VLAN > port-based VLAN. If matched, the m atc hed VLAN will become this packet's 'SPVLAN'.
For ingress tagged packets at UNI ports
1. The switch will look up the VLAN translation table. If matched, the VLAN tag will be translated (replace
CEVLAN with SVLAN, or add SPVLAN).
2. Otherwise, check switch VLAN tab les. The sequenc e is the sam e as above. T he mat ched VLAN will bec ome
this packet's 'SPVLAN'.
81
Page 93

DGS-3700-12/DGS-3700-12G Series Layer 2 Gigabit Ethernet Switch User Manual
802.1v Protocol VLAN
802.1v Protocol Group Settings
The table a llo ws the user t o create Pr otoc ol VLAN gr oups and add prot ocols t o th at group. T he 802.1 v Proto col VL AN
Group Settings supports multiple VLANs for each protocol and allows the user to configure the untagged ports of
different protocols on the same physical port. For example it allows the user to configure an 802.1Q and 802.1v
untagged port on the same physical port. The lower half of the table displays any previously created groups.
To view this window, click L2 Features > 802.1v Protocol VLAN > 802.1v Protocol Group Settings as shown
below:
Figure 3 - 15 802.1v Protocol Group Settings window
The following fields can be set:
Parameter Description
Group ID Select an ID number for the group, between 1 and 16.
Group Name
Protocol
Protocol Value
(0-FFFF)
Click Add to make a new entry and Delete All to remove an entry.
This is used to id ent ify the new Protocol V LA N group. Type an alphan umeric string of up to 32
characters.
This function maps packets to protocol-defined VLANs b y examining the type octet within th e
packet header to discover the t ype of protoc ol associa ted with it. Use the dro p-down m enu to
toggle between Ethernet_II, IEEE802.3_LLC and IEEE802.3_SNAP.
Enter a value for the Group.
82
Page 94

DGS-3700-12/DGS-3700-12G Series Layer 2 Gigabit Ethernet Switch User Manual
802.1v Protocol VLAN Settings
The table allows the user to configure Protocol VLAN settings. The lower half of the table displays any previously
created settings.
To view this window, click L2 Features > 802.1v Protocol VLAN > 802.1v Protocol VLAN Settings as shown below:
Figure 3 - 16 Protocol VLAN Settings w indow
The following fields can be set:
Parameter Description
Group ID
Group Name
VID (1-4094)
VLAN Name
802.1p Priority
Click the correspondi ng ra dio b utton t o selec t a pr evious ly conf igure d Grou p ID fr om the dropdown menu.
Click the correspond ing radio button to sel ect a previously config ured Group Name from the
drop-down menu.
Click the radio button t o enter the VID. T his is the VLAN ID that , along with the VLAN Name,
identifies the VLAN the user wishes to create.
Click the radio button to enter a VLAN Name. This is the VLAN Name that, along with the
VLAN ID, identifies the VLAN the user wishes to create.
This parameter is s pecified if you want to re-write the 802.1p default priorit y previously set in
the Switch, which is used to determine the CoS queue to which packets are forwarded to.
Once this field is specified, packets accepted by the Switch that match this priority are
forwarded to the CoS queue specified previously by the user.
Click the corresponding box if you want to set the 802.1p default priori ty of a packet to the
value entered in the Priority (0-7) field, which meets the criteria specified previously in this
command, before for warding it on to the specified C oS queue. Otherwise, a pack et will have
its incoming 802.1p user priority re-written to its or iginal value before being for warded by the
Switch.
For more information on pr iority queues, CoS queues and m apping for 802.1p, see the QoS
section of this manual.
Port List (e.g.: 1-6)
Search Port List
Select the specif ied ports you wish to configure b y entering the port number in this field, or
check the Select All Ports box.
This function allows the user to search all previously configured port list settings and display
them on the lower half of the table. To search for a port list enter the port number you wish to
view and click Find. To display all previously configured port lists on the bottom half of the
screen click the Show All button, to clear all previously configured lists click the Delete All
button.
83
Page 95

DGS-3700-12/DGS-3700-12G Series Layer 2 Gigabit Ethernet Switch User Manual
RSPAN Settings
This table controls the RSPAN function. The purpose of the RSPAN function is to mirror the packets to a remote
switch. The pack et travels from the s witch where the m onitored packet is rece ived, through the int ermediate switch,
then to the switch where the sniffer is attached. The first switch is also named the source switch. RSPAN VLAN
mirroring will only wor k wh en RSPAN Global Sett ings are enabled. RSPAN r edirec t funct ion will work whe n RSP AN is
enabled and at least one RSPAN VLAN has been configured with redirect ports.
To view this window, click L2 Features > RSPAN Settings as shown below:
Figure 3 - 17 RSPAN Settings window
Enter the VLAN Name or VID and click Create. To remove an entry click Delete, to modify an entry click the
corresponding Modify button.
Figure 3 - 18 RSPAN Settings window – Edit
Enter the Source Ports or Redirect Ports you wish to Add or Delete a nd cl ic k Apply. To r eturn t o the RSPAN Settings
window click <<Back.
GVRP Settings
The table allows the user to deter mine whether the Switch will share its VLA N configuration information with other
GARP VLAN Registr at io n Protoc o l (G V RP) enabled switches. I n ad dit ion, I ngress Checking ca n b e us ed to limit traffic
by filtering incom ing packets whose PVID do not match the PVID of the port. R esults can be see n in the table under
the configuration settings, as seen below.
To view this window, click L2 Features > GVRP Settings as shown below:
Figure 3 - 19 GVRP Settings window
84
Page 96

DGS-3700-12/DGS-3700-12G Series Layer 2 Gigabit Ethernet Switch User Manual
accepted, and
The following fields can be set:
Parameter Description
From Port / To Port
GVRP
PVID
Ingress Check This field can be toggled using the space bar between Enabled and Disabled. Enabled
Acceptable Frame
Type
These two fields allow you to spec ify the ra nge of port s that w ill be incl uded in t he Port -based
VLAN that you are creating using the 802.1Q Port Settings window.
The Group VLAN Registration Protocol (GVRP) enables the port to dynamically become a
member of a VLAN. GVRP is Disabled by default.
The read-only field in the 802.1Q Port Table shows the current PVID assignment for each
port, which may be manuall y assigned to a VLAN when created in the 802.1Q Port Settings
table. The Switch's def au lt i s t o ass ign a l l ports to the d ef ault V LA N with a VID of 1. The PVID
is used by the port to tag outg oing, untagged packets , and to make filtering decisions about
incoming packets. If the port is specified to accept only tagged frames - as tagging, and an
untagged packet is forwarded to the port for transm ission, the port will add an 802.1Q tag
using the PVID to write the VID in the tag. When the packet arrives at its destination, the
receiving device wi ll use the P VID to m ake VLAN for warding decis ions. If the port rec eives a
packet, and Ingres s filtering is enabled, th e port wil l compare the VID of th e incom ing packet
to its PVID. If the two ar e unequ al, the port will drop the pack et. If the two ar e eq ual, the port
will receive the packet.
enables the port to compare the VID tag of an incoming packet with the PVID number
assigned to the port. If the two are different, the port filters (drops) the packet. Disabled
disables ingress filtering. Ingress Checking is Disabled b y default .
This field denotes the t ype of frame that will be acce pted by the port. The user m ay choose
between Tagged Only, which means only VLAN tagged frames will be
Admit_All, which mean both tagged and untagged frames will be accepted. Admit_All is
enabled by default.
Click Apply to implement changes made.
GVRP Global Settings
The GVRP allows in terop erabi lit y with o ther s witches, so the v alues of th e GVRP tim ers c an be co nfigured . T his tabl e
is used to set the GVRP Global Settings.
To view this window, click L2 Features > GVRP Global Settings as shown below:
Figure 3 - 20 GVRP Timer Settings window
The following fields can be set:
Parameter Description
Join Time
(100-100000)
Leave Time
(100-100000)
The time in milliseco nds that specifies the amount o f time between the Switch receiving t he
information about bec omin g a mem ber of t he group and ac tuall y joining t he group. T he def ault
is 200.
The time in milliseconds that specifies the maximum amount of time between the Switch
receiving a leave group message from a host, and the Switch issuing a group membership
query. The default is 600. The Leave Time must be greater than 2 join times.
85
Page 97

DGS-3700-12/DGS-3700-12G Series Layer 2 Gigabit Ethernet Switch User Manual
Leave All Time
(100-100000)
NNI BPDU
Address
Click Apply to implement changes made.
The time in milliseconds that specifies the amount of time the Switch will take to Leave All
groups. The default is 10000. The Leave All Time must be greater than the Leave Time.
This specifies the GVRP’s pdu MAC address of the NNI port.
Dot1d – Specifies GVRP’s pdu MAC address of NNI port using 802.1d.
Dot1ad – Specifies GVRP’s pdu MAC address of NNI port using 802.1ad.
MAC-based VLAN Settings
This table is us ed to create MAC-base d VLAN entries on the s witch. A MAC Address can be mapped to any ex isting
static VLAN and m ultiple MAC addr esses can be mapped to the sam e VLAN. W hen a s tatic MAC-based VLAN entry
is created for a user, the traffic from this user is able to be serviced under the specified VLAN regardless of the
authentiucation function operated o n the port. T herefore each entr y specifies a re lationship of a s ource MAC addres s
with a VLAN.
To view this window, click L2 Features > MAC-based VLAN Settings as shown below:
Figure 3 - 21 MAC-based VLAN Settings window
The following fields can be set
Parameter Description
MAC Address Specify the MAC address to be reauthenticated by entering it into the M AC Address field.
VLAN Name
Click Find, Add or Delete All for changes to take affect.
Enter the VLAN name of a previously configured VLAN.
PVID Auto As sign Settings
This commands Enables or Disables PVID Auto Assign on the Switch. PV ID is the VLAN that the s witch will use for
forwarding and fi ltering purposes. If PVID Auto-Assign is Enabled, PVID will b e possibly changed b y previously set
PVID or VLAN co nfigurat ions. When a user c onfig ures a port to VLAN X ’s untagged m ember ship, t his por t’s PVID will
be updated with VLAN X . In the form of a VLAN list command, PVID is u pdated with the last it em on the VLAN lis t.
When a user removes a port from the untagged membership of the PVID’s VLAN, the port’s PVID will be assigned to a
default VLAN. When PVID Auto Assign is Disabled, PVID can only be changed b y PVID configuration (use r changes
explicitly). The VLAN configuration will not automatically change the PVID. The default setting is Enabled.
To view this window, click L2 Features > PVID Auto Assign Settings as shown below:
Figure 3 - 22 PVID Auto Assign Settings window
86
Page 98

DGS-3700-12/DGS-3700-12G Series Layer 2 Gigabit Ethernet Switch User Manual
Port Trunking
Understanding Port Trunk Gr oups
Port trunk groups ar e used to combine a number of por ts together to make a single hig h-bandwidth data pipeline.
DGS-3700 Series supp orts up t o 6 por t trunk gr oups w ith 2 t o 8 ports in each group. A pot ential b it rat e of 8000 Mb ps
can be achieved.
Figure 3 - 23 Example of Port Trunk Group
The Switch treats all ports in a trunk group as a single port. Data trans mitted to a specific host (des tination address)
will always be trans mitted over the same por t in a trunk group. This al lows packets in a data str eam to arrive in the
same order they were sent.
NOTE: If any ports within the trunk group become disconnected, packets intended for the
disconnected ports will be load shared am ong the other unl inked ports of the link aggregation
group.
Link aggregation a llo ws s e vera l p or ts to be gro uped together and to ac t as a s ingle link. This gi ves a bandwidth that is
a multiple of a single link's bandwidth.
Link aggregation is m ost c ommonly used t o link a bandwidt h intens ive net work device or d evices, such as a server, to
the backbone of a network.
The Switch allows th e creation of up to 6 link aggregation groups , each group consis ting of 2 to 8 link s (ports). The
aggregated links must be contiguous (they must have sequential port numbers) except the four (optional) Gigabit
ports, which can on ly belong to a single l ink aggrega tion group. All of the ports in the gro up must be m embers of the
87
Page 99

DGS-3700-12/DGS-3700-12G Series Layer 2 Gigabit Ethernet Switch User Manual
same VLAN, and their STP status, static multicast, traffic control; traffic segmentation and 802.1p default priority
configurations must be identical. Port locking, port mirroring and 802.1X must not be enabled on the trunk group.
Further, the aggregated links must all be of the same speed and should be configured as full duplex.
The Master Port of the group is to be configured by the user, and all configuration options, including the VLAN
configuration that can be applied to the Master Port, are applied to the entire link aggregation group.
Load balancing is automatically applied to the port s in the ag gr ega ted group, and a link failure withi n the gr ou p caus es
the network traffic to be directed to the remaining links in the group.
The Spanning Tree Protoc ol will treat a link aggregat ion group as a single link , on the switch level. On t he port level,
the STP will use the port par ameters of the Mas ter Port in the calculat ion of port cost and in de termining the s tate of
the link aggregati on group. If two red undant l ink aggre gation gr oups are configur ed on the Switch, STP wil l block one
entire group; in the same way STP will block a single port that has a redundant link.
To view this window, click L2 Features > Port Trunking as shown below:
Figure 3 - 24Port Trunking window
The following fields can be set
Parameter Description
Algorithm
The algorithm that the Swit ch uses to balance the loa d across the ports that m ake up the port
trunk group is def ined by this def inition. Choose MAC Sourc e, MAC Destinatio n, MAC Source
Dest, IP Source, IP Destinatio n or IP Source Dest (See the Li nk Aggregation section of this
manual).
Group ID Select an ID number for the group, between 1 and 6.
Type
This pull-down m enu allows you to select bet ween Static a nd LACP ( Link Aggregati on Control
Protocol). LACP allows for the automatic detection of links in a Port Trunking Group.
Master Port
State
Choose the Master Port for the trunk group using the pull-down menu.
Trunk groups can be toggled between Enabled and Disabled. This is used to turn a port
trunking group on or of f. This is useful for di agnostics, to quick ly isolate a bandwidth intensive
network device or to ha ve an absolute backup aggregat ion group that is not under aut omatic
control.
Active Port
Member Ports
Shows the port that is currently forwarding packets.
Choose the members of a trunked group. Up to eight ports per group c an be assigned to a
group.
Flooding Port
A trunking group m ust designate one port to allow transm ission of broadcasts and unknown
unicasts.
Click Apply to implement changes made.
88
Page 100

DGS-3700-12/DGS-3700-12G Series Layer 2 Gigabit Ethernet Switch User Manual
LACP Port Settings
The LACP Port Settings window is used to create port trunking groups on the Switch. Using the follo wing window,
the user may set which ports will be active and passive in processing and sending LACP control frames.
To view this window, click L2 Features > LACP Port Settings as shown below:
Figure 3 - 25 LACP Port Settings window
The following fields can be set
Parameter Description
From Port / To Port
Activity
Click Apply to implement changes made.
A consecutive group of ports may be configured starting with the selected port.
Active – Active LACP ports are c apa bl e of pr oces s ing and s e nding LACP control frames. This
allows LACP compliant devices to negotiate the aggregated link so the group may be
changed dynamicall y as needs require. In ord er to utilize the abil ity to change an aggre gated
port group, that is, to add or s ubtract ports from the group, at least one of the participating
devices must designate LACP ports as active. Both devices must support LACP.
Passive – LACP ports that are designated as passive cannot initially send LACP control
frames. In order to allo w the linked port group to negoti ate adjustments and mak e changes
dynamically, one end of the connection must have "active" LACP ports (see above).
89
 Loading...
Loading...