D-link DFE-528TX INSTALLATION
DFE-528TX
Fast Ethernet Adapter
for PCI Bus
User’s Guide
Rev_083001F
Printed in Taiwan

ii
Table of Contents
Introduction................................................................................................... 1
Contents of Package.................................................................................. 2
Technology Basics..................................................................................... 3
About Fast Ethernet ......................................................................................3
About Auto-Negotiation.................................................................................4
About PCI Bus...............................................................................................5
Feature ..........................................................................................................5
Flow Control ..............................................................................................5
Networking Basics...................................................................................... 6
Computer Identification .................................................................................6
Sharing Files .................................................................................................8
Sharing Printers...........................................................................................14
Networking with Windows 2000............................................................19
Configuring Your Network Settings.............................................................19
Configuring your Network Identification......................................................20
Configuring the IP Address for TCP/IP.......................................................23
Sharing Drives.............................................................................................27
Sharing Folders...........................................................................................30
Sharing a Printer .........................................................................................33
Troubleshooting........................................................................................39

iii
Verify Each Computers Identification......................................................39
Verify Network Adapter Installation.........................................................39
Verify Cable Connections .......................................................................41
Understanding Indicators........................................................................41
Diagnostics and Checking Communications..........................................41
Running Diagnostics on the Network Adapter........................................43
Pinging your DFE-528TX Card ...............................................................46
Contacting Technical Support...............................................................48
Specifications.............................................................................................49
D-Link Offices.............................................................................................50
Limited Warranty .......................................................................................51
Registration.................................................................................................55

1
Introduction
The D-Link DFE-528TX is ideal for the small office or home office environment.
After completing the steps in this manual, you will have the ability to share
information and resources - such as files and printers - and take full advantage of a
"connected" environment for work and play!
The DFE-528TX comes with drivers for the most popular operating systems and
can be integrated into a larger network. However, this Guide is designed to help
you network two computers running Windows 95/98, Windows Me and Windows
2000 in a peer-to-peer configuration. Yet, the standards compliant DFE-528TX
gives you the flexibility to expand and customize your Ethernet / Fast Ethernet
network at will.
The Ethernet standard allows you to connect computers and devices at speeds up to
10 Mbps. Fast Ethernet allows speeds up to 100 Mbps. A Dual-Speed 10/100 Mbps
Ethernet / Fast Ethernet network combines both standards allowing computers and
devices of different speeds to communicate with each other. The DFE-528TX is a
Dual-Speed 10/100 Mbps Ethernet / Fast Ethernet network card.
2
Contents of Package
DFE-528TX Fast Ethernet Adapter
DFE-528TX Fast Ethernet Adapter
1
Driver CD
2
User’s Manual
3
Quick Install Guide
4
Package Contents

3
Technology Basics
About Fast Ethernet
Fast Ethernet is a network technology specified by IEEE Standard 802.3u. It
extends the traditional 10Mbps Ethernet technology to achieve 100Mbps
transmission and reception, while retaining the same CSMA/CD Ethernet protocol.
Thus, while Fast Ethernet provides a tenfold increase in network capacity, it is
wholly compatible with traditional 10Mbps Ethernet network facilities. This
compatibility is the key to easy and efficient upgrades to 100Mbps in your network
areas needing greater bandwidth. Upgrading selected areas to Fast Ethernet does
not require hardware or software changes in network areas where traditional
10Mbps Ethernet is providing good service. For upgrading, Fast Ethernet is the
clear choice in terms of cost-effectiveness, as well as convenience and smoothness
in transition.
Category 5 cabling is required for 100Base-TX Fast Ethernet in order to provide full
duplex operation. Full duplex 100Base-TX operation allows simultaneous
transmission and reception, both at 100Mbps, thus providing service potentially
equal to 200Mbps connection.
To provide compatibility in traditional 10Mbps Ethernet environments (where, for
example, DFE-528TX adapters are installed anticipating upgrade of supporting hub
equipment to Fast Ethernet,) the DFE-528TX also supports traditional 10Mbps
Ethernet operation, in full-duplex as well as half-duplex modes. Selection of the
best operation mode in any given installation is automatically governed by autonegotiation.

4
About Auto-Negotiation
You have probably had the experience of making a dialup connection through a
modem, and have heard the exchanges between your modem and the modem at the
other end of the telephone line. As irritating as those few seconds of noise may be,
they do let you know that your modem and the remote modem are on the job,
preparing for your intended communication with the remote computer.
When the two modems have tested the phone-line quality and settled on the
combination of shared options and parameters which will provide the best data
communication over the connecting phone line, then you are given the “connect”
message which signals the end of the intermodem negotiation and the beginning of
your intended communication with the remote computer.
Auto-negotiation between devices within an Ethernet LAN is similar in concept, but
much briefer. The two devices involved in the auto-negotiation will be the DFE528TX Adapter serving your station (installed in your computer), and the hub
through which it is connected to the LAN. The options to be negotiated between
the DFE-528TX and its supporting hub includes Ethernet type (100BASE-TX Fast
Ethernet of 10BASE-T Ethernet) and duplex mode (half-duplex, being one-way-ata-time, or full duplex, being simultaneous transmit-and receive.)
Startup communication between the two devices occurs when both devices are
powered up. Once the cable connection and the Network Operating System
software is satisfied, the preparatory process of auto-negotiation between the DFE528TX and its supporting hub proceeds automatically. If the hub has autonegotiation functionality, it and the DFE-528TX exchange a series of messages,
each device signals its capabilities and listens for corresponding information about
the other. The auto-negotiation process requires only a few milliseconds, and the
two devices select the best communication parameters supported by both.
If the hub does not support auto-negotiation, the (single capability) message will be

5
recognized by the DFE-528TX auto-negotiation facility, which will switch to those
settings of its own capabilities, which match that of the hub.
Auto-negotiation reoccurs any time the linkage is restored, making the line ready
again for optimal data communications.
About PCI Bus
Your DFE-528TX Adapter delivers outstanding performance by fully exploiting the
advance features of your computer’s PCI bus. DFE-528TX Adapters utilize the Bus
Master Mode of the PCI bus, allowing direct transfers of Ethernet packet content
between computer memory and the adapter’s controller, thus minimizing network
demands on the CPU. The adapter’s controller function provides the additional
benefit of reduced command processing overhead.
The working relationship between a DFE-528TX adapter and main memory,
working in Bus Master mode, is powered by the Bridge/Memory Controller of the
PCI bus. This reduces the CPU role in network operations, thus freeing the CPU to
service other tasks, with resulting improvement in overall computing (multitasking)
performance. At the same time, it produces superior network throughput by
reducing latency (waiting for CPU service) during transmissions and receptions.
Feature
Flow Control
The DFE-528TX implements IEEE 802.3x compliant flow control for full duplex,
which provides traffic management functions for full-duplex operation. Flow
control allows for enhanced full duplex operation with switches. When operating at
full duplex (requiring a direct connection to a switch) and the switch’s data buffer is
about to overflow, a Pause frame will be transmitted to the DFE-528TX. The
ensuing idle time keeps the buffer from overflowing and prevents data from being
lost. This enhancement can improve network throughput, avoid collisions and
prevent lost data, helping the network achieve optimal performance.

6
Networking Basics
You may have had some ideas about how to use your new network prior to
installing the DFE-528TX – sharing files, printing from any computer on the
network, or accessing the Internet on multiple computers with one connection. This
section will help you get started on those ideas or even give you some new ones.
However, this section is not intended to be a comprehensive guide to networking, it
is just an outline of a few networking basics.
If you installed your DFE-528TX on computers running Windows 95, you got an
opportunity to give each computer a name during the installation of the network
system software. If you had previously given your Windows 95 computers names or
if you are using Windows 98, you may need to verify that each computer has a
unique name and common workgroup name.
Computer Identification
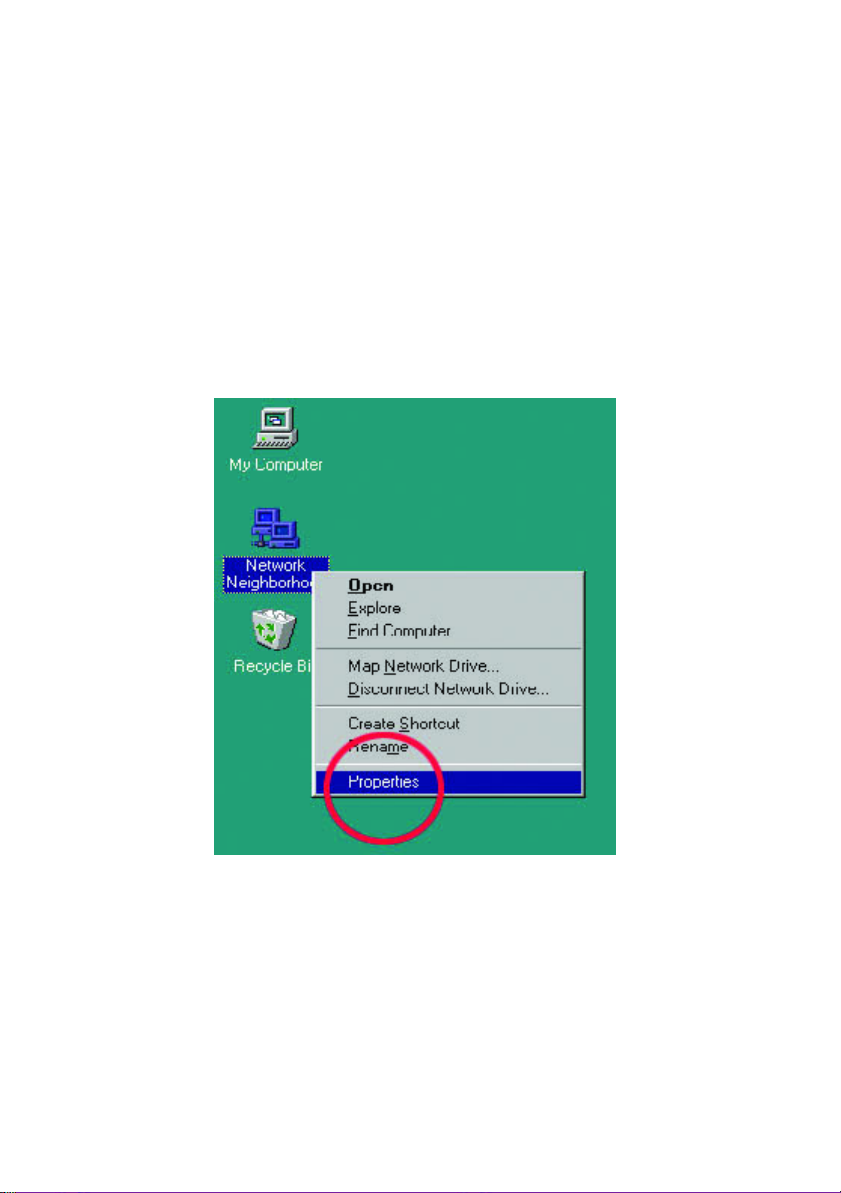
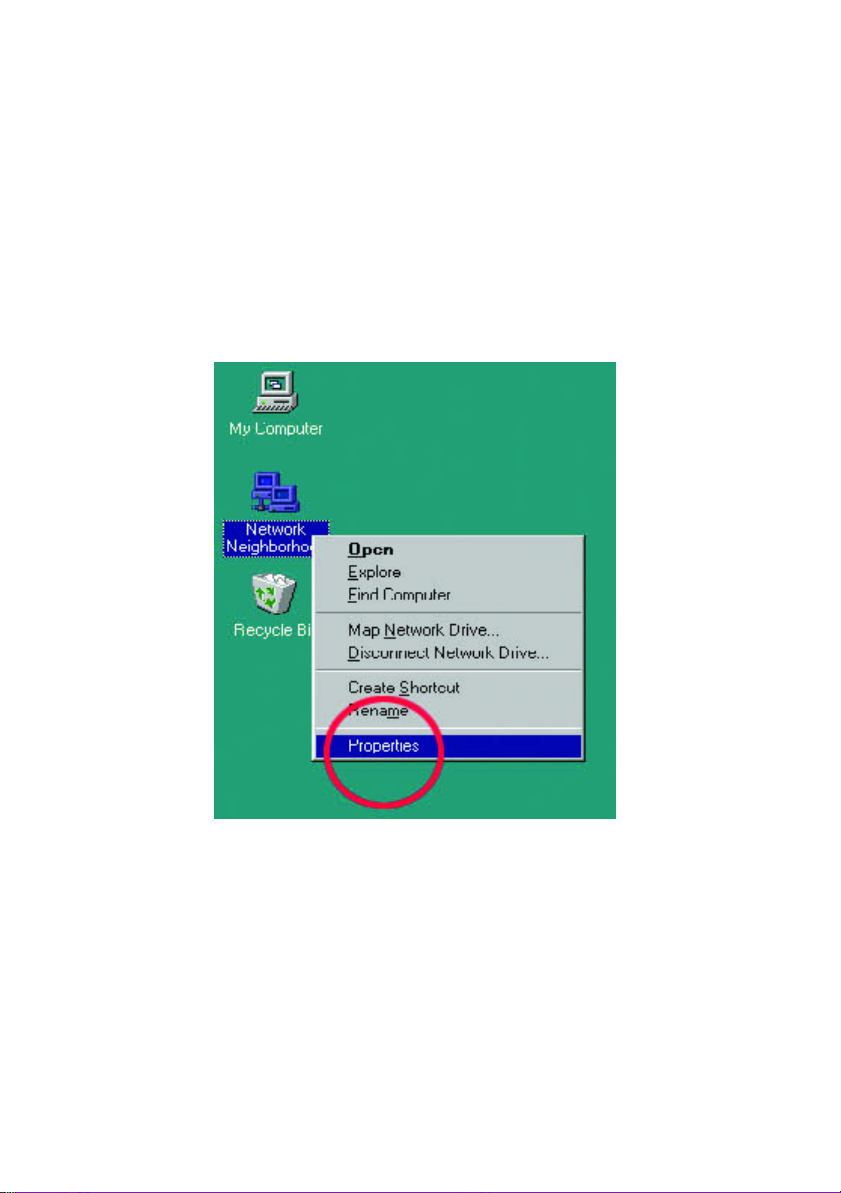
1. On your Desktop, right-click the icon "Network Neighborhood" and select
"Properties" from the context menu.
7
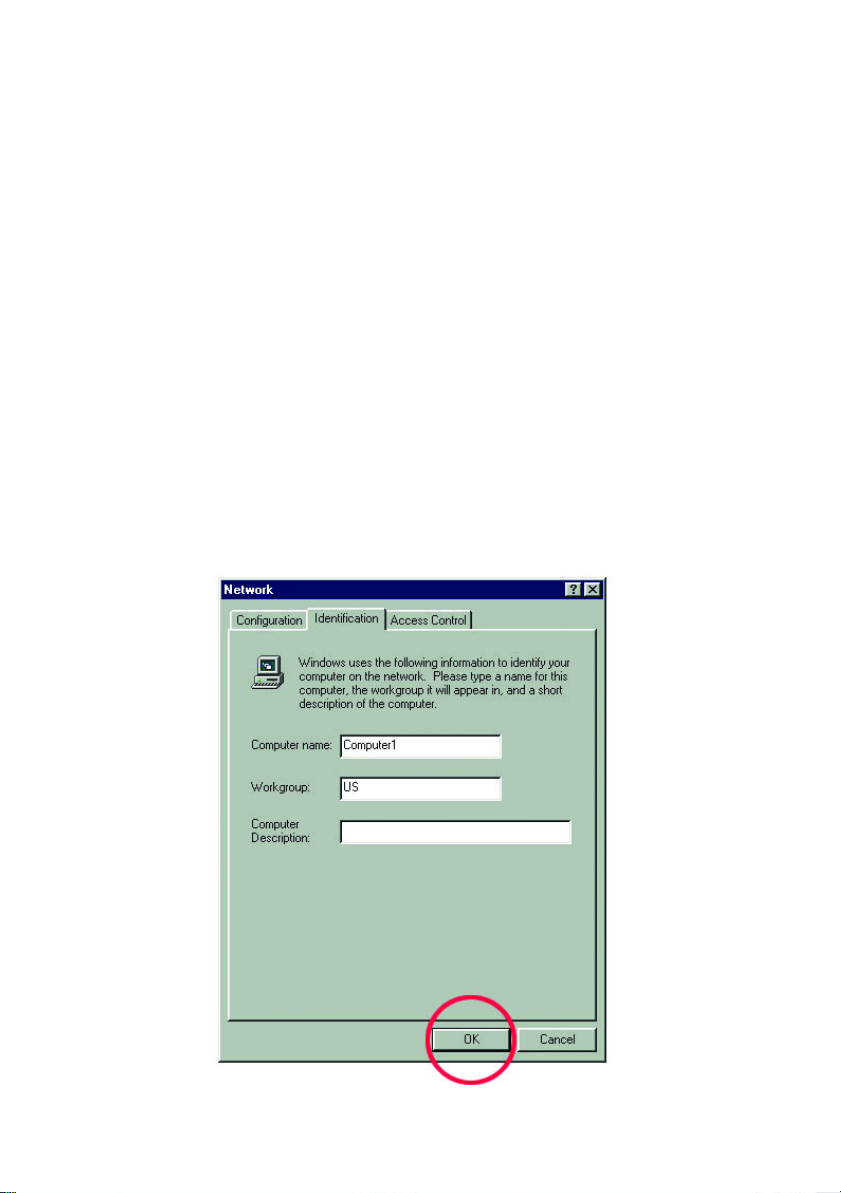
Click the "Identification" tab on the top of the dialog box.
2. Type a unique, identifying name for this particular computer in the "Computer
name:" box. This will be the name that other computers on your network will
use to communicate with this computer. Each computer’s name must be unique
on a particular network or confusion will result. (The computer’s name should
be 15 or fewer characters with no spaces.)
3. Type the workgroup name this computer will be a part of in the "Workgroup:"
box. All of the computers on your network should have an identical Workgroup
name.
4. The "Computer Description:" box is optional. You may enter a description that
will help you identify this computer on your network. Then click OK.
5. Repeat this process for each computer on your network to ensure that they all
have a unique "Computer Name" and identical "Workgroup."
8
Sharing Files
With your computers connected together on a network, you may now open and save
files on another computer. You will be able to specify particular folders or disk
drives to "share" and even password protect them. The steps below will enable you
to share specific files and folders with other computers on your network.
1. On your Desktop, right-click the icon "Network Neighborhood" and select
"Properties" from the context menu.
9
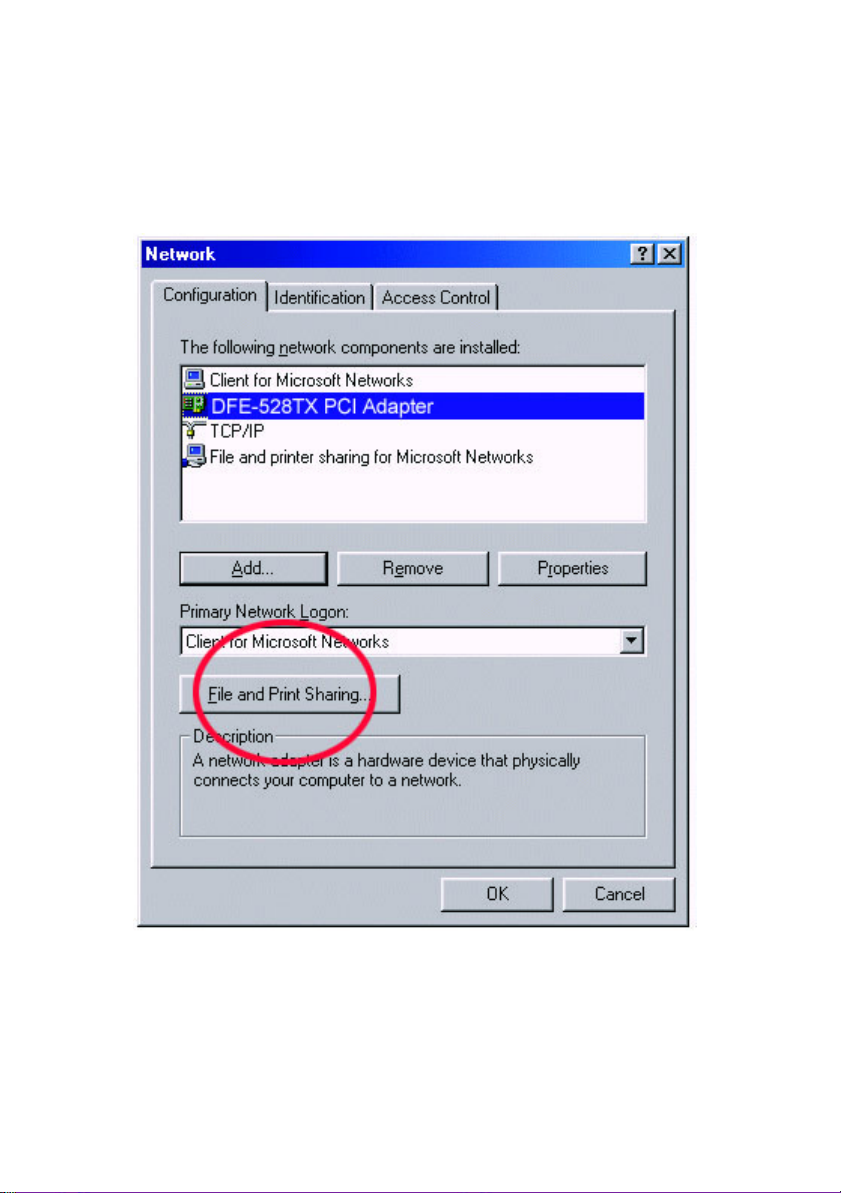
This dialog box is where you will configure most of your computers’ network
settings. It is also available through the "Network" icon in the Control Panel.
2. Click the "File and Print Sharing…" button.
10
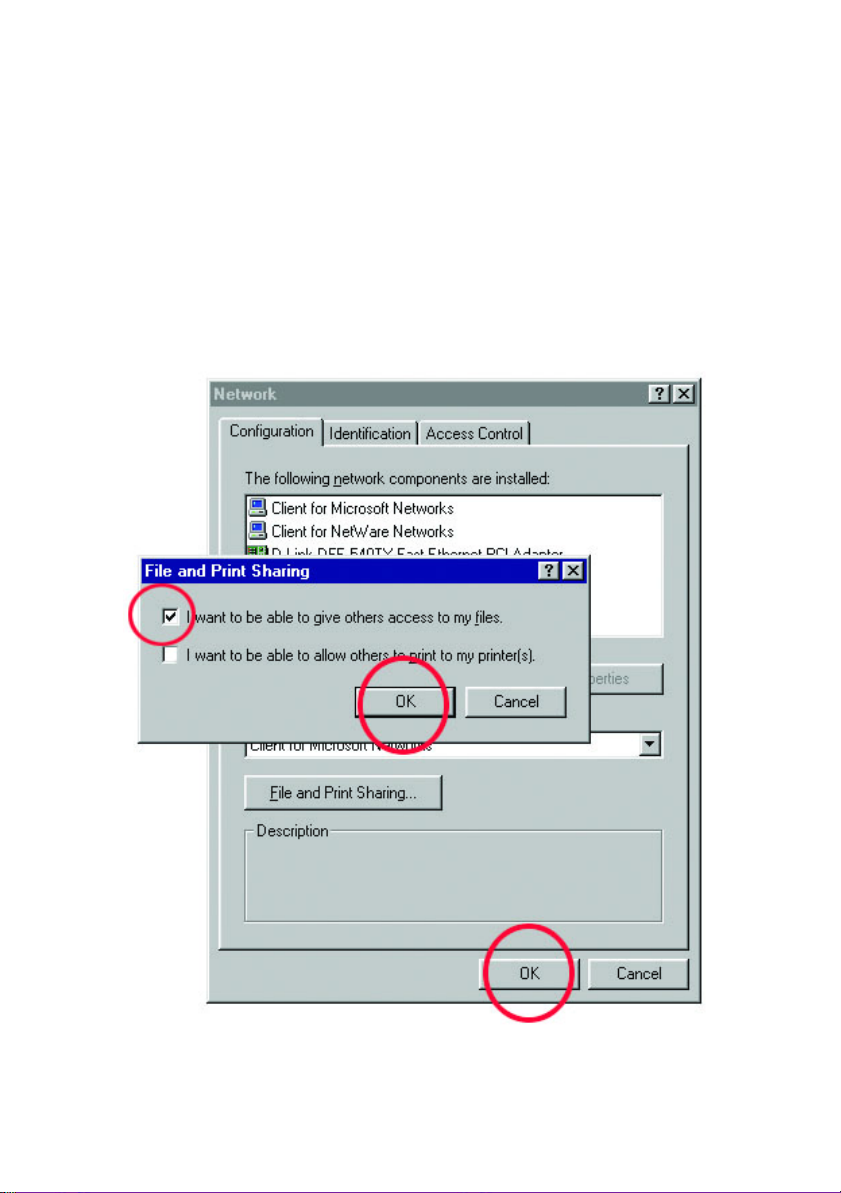
3. Select "I want to be able to give others access to my files."
4. Click OK on the "File and Print Sharing" dialog box.
5. Click OK on the "Network" dialog box.
6. Provide the Windows 95/98 installation CD or diskette(s) if prompted or
direct Windows to the proper location of the installation files. Reboot if
prompted.
11
7. You will now be able to identify a particular folder or disk drive to share. You
may want to share a folder that both you and a colleague/family member need
to access occasionally. Or, maybe you want to share a CD-ROM drive so your
other computer that does not have one can read CD’s. Both of these processes
are the same. Only the disk drives and folders that you specifically identify as
shared will be accessible to other computers on your network.
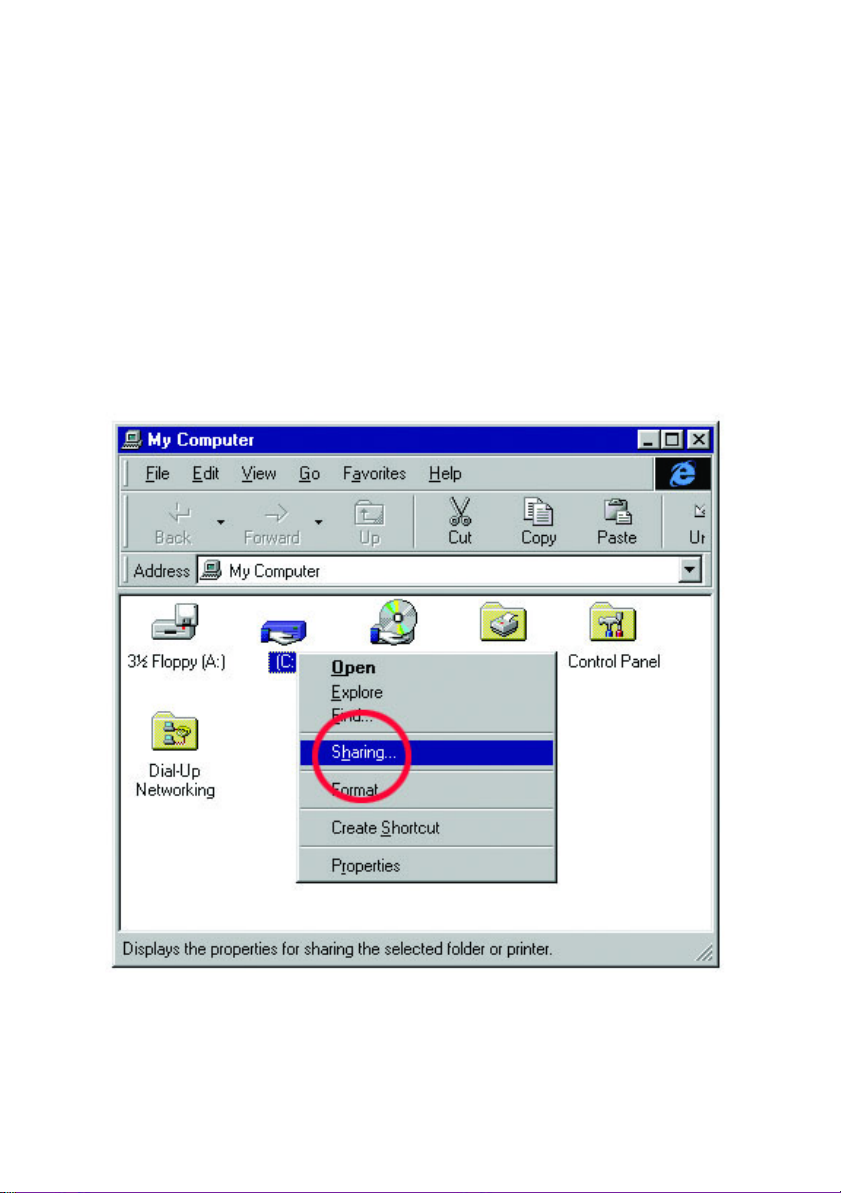
8. Find the disk drive or folder you want to share with Windows Explorer or the
"My Computer" icon on your desktop.
9. Right-click on the disk drive or folder icon and select "Sharing…"

12
10. Select "Share As:" to set the parameters for sharing this particular disk drive
or folder.
The "Share Name:" box is used to identify the disk drive or folder you are sharing to
other computers on the network. You can give it any name you wish. However, a
specific identification may help as more resources on your network are shared. The
"Comment:" box is optional. You can use this box to further describe the disk drive
or folder for others on the network.
"Access Type:" allows you to designate how much someone else on the network
can do with this disk drive or folder. "Read-Only" allows others to only look at or
open the files on the disk drive or in the folder. "Full" allows others to read, write,
open, save, copy, move, and delete files on the disk or in the folder. "Depends on
Password" gives other computers access conditional upon the password they
provide.
"Passwords:" allow you to apply a level of security to your shared disk drives and
folders. Another computer (user) will be required to enter the password you
designate here before accessing the disk drive or folder. Two passwords are used to
give two levels of security (or access) to others on the network using the "Depends
on Password" setting. Leaving the "Password" boxes empty gives everyone on the
network access to the disk drive or folder.
11. Navigate to the computer with the shared disk drive or folder (recognized by
the "Computer Name" you provided), and double-click. You should now see
the disk drive or folder. Double-click. If you specified a password when
sharing this disk drive or folder, you will be prompted for the password.

13
12. You can access a disk drive or folder shared over the network from most
Windows 95/98 applications. To make this process easier, Windows allows
you to map these disk drives and folders to a drive letter on another computer.
For example, on a computer where you are accessing a shared folder from
another computer, inside Windows Explorer right-click and select "Map
Network Drive…" You will then be able to assign an available drive letter.
Checking "Reconnect at logon" allows Windows to map this network drive
each time you start your computer.
14
Sharing Printers
"Sharing" a printer connected to one computer with other computers on your
network can be very convenient - allowing you to print from any computer on the
network. The steps below will enable you to print with other computers on your
network.
1. On your Desktop, right-click the icon "Network Neighborhood" and select
"Properties" from the context menu.
15
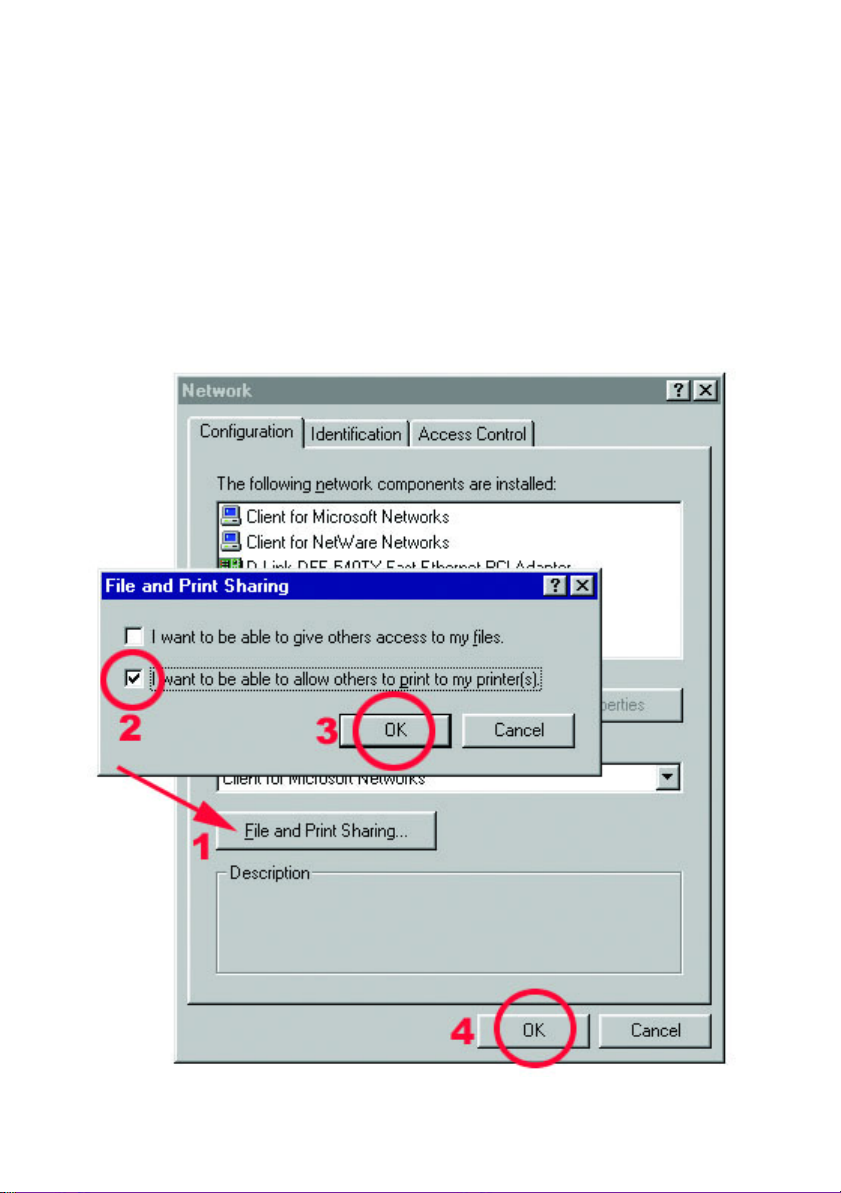
1. Click "File and Print Sharing…"
2. Select "I want to be able to allow others to print to my printer(s)."
3. Click OK on the "File and Print Sharing" dialog box.
4. Click OK on the "Network" dialog box.
5. Provide the Windows 95/98 installation CD or diskette(s) if prompted or
direct Windows to the proper location of the installation files. Reboot if
prompted.
 Loading...
Loading...