Page 1
http://www.delta.com.tw/products/plc.asp
A
V
V
V
V
V
V
V
V
V
V
V
V
V
V
V
V
DVP02DA-S
DVP02DA-S Analog Output Module
Instruction Sheet
1
Please carefully read this instruction thoroughly prior to use the DVP02DA-S.
The DC input power must be OFF before any maintenance.
This is an OPEN-TYPE built-in DVP02DA-S, and the DVP02DA-S is certified to meet the safety
requirements of IEC 61131-2 (UL 508) when installed in the enclosure to prevent high
temperature, high humidity, exceessive vibration, corrosive gases, liquids, airbome dust or
metallic particles. Also, it is equipped with protective methods such as some special tool or key
to open the enclosure, so as to avoid the hazard to users or any damage to the DVP02DA-S.
Do not connect the AC power to any of the input/output terminals, or it may the DVP02DA-S.
Make sure that all the wiring is well conducted prior to power On.
Do not touch the internal circuit for at least 1 minute after the power is Off.
Make sure that DVP02DA-S is properly grounded , to avoid any electromagnetic noise.
2
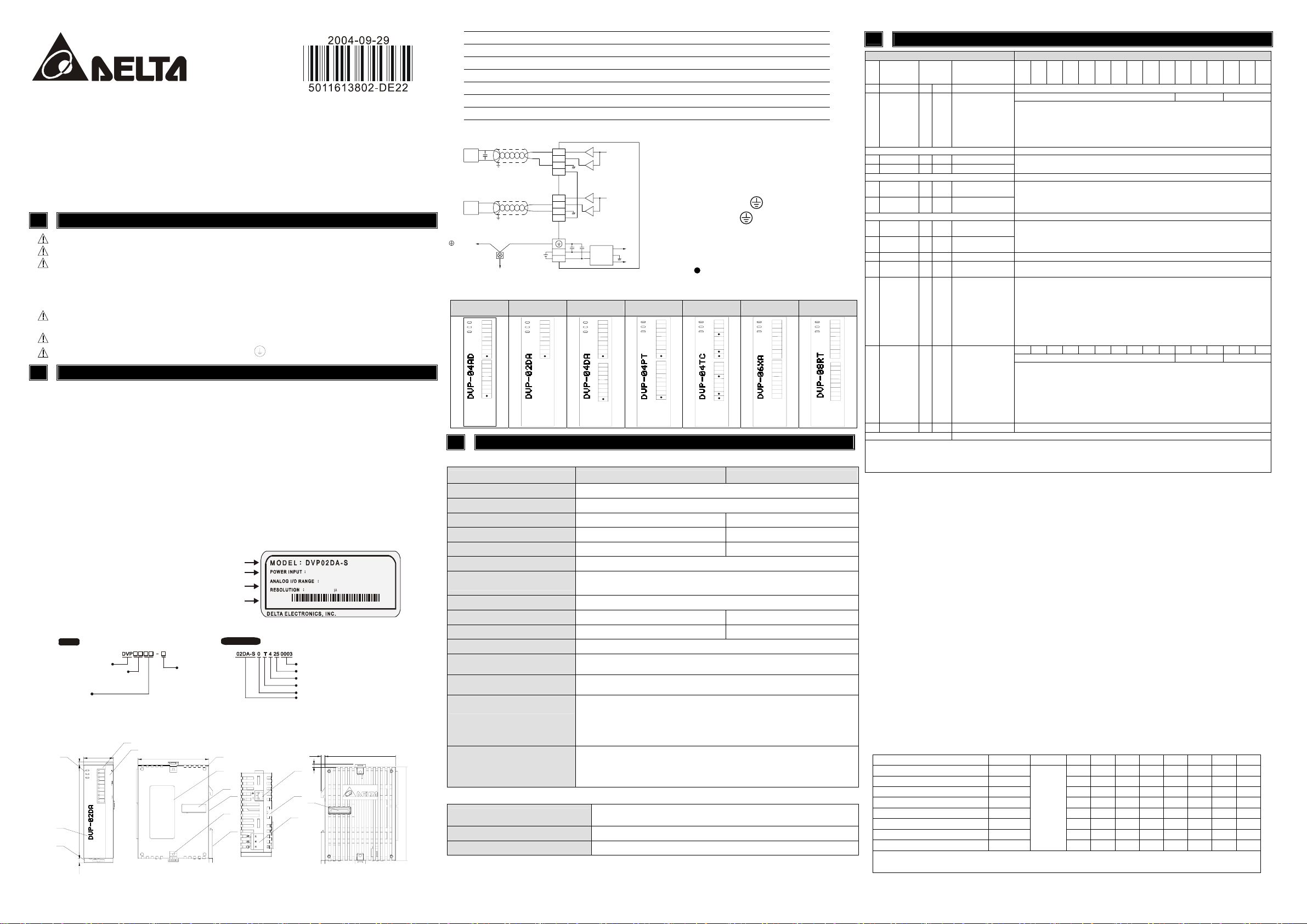
2.1 Model Explanation and Peripherals
Thank you for choosing DELTA DVP PLC Series. The analog output module of DVP02DA-S series
can read/write the data of analog output module by using commands FROM / TO via DVP-PLC
SS/SA/SX Series MPU program. The analog output module receives 2 group 12-bit digital data
from PLC MPU and converts it into 2 points analog output signal (voltage or current). There are 49
CR (Control Register) in each module and there are 16 bits in each register.
The software version of DVP02DA-S analog output module can be updated via RS-485
communication. Power unit and module are separate. Size is small and easy to install.
Users can select output either voltage or current via wiring. Voltage output range is 0V ~ +10V DC
(resolution is 2.5 mV). Current output range is 0mA ~ 20mA (resolution is 5 µA).
Nameplate Explanation
Input power Supply Spec.
Analog Input /Output Module Spec.
Barcode, series and version
Model Explanation
Model
Product Series
Input + Output points
Model type
AD: Analog input module
DA: Analog output module
PT: Platinum temperature sensors (PT-100)
TC: Thermocouple sensors (Type J/K)
2.2 Product Profile and Outline
1
25.20
3.00
90.00
2
3
4.00
4
5
V+
C
I+
H
COM
1
FG
V+
C
I+
H
COM
2
FG
●
S: for SS series MPU
P: for EP series MPU
H: fo r EH serie s MPU
XA: Analog input/output mixed module
RT: Resistor Thermocouple
HC: Input module of high-speed counter
PU: single axis positioning unit
60.00
WARNING
INTRODUCTION
PLC model
Serial Number
6
7
8
10
9
3
Unit:mm
20.4VDC ~ 28.8 VDC
0V ~ + 10V or 0mA ~ +20mA
2.5 mV or 5 A
02DA-S0T3250003VX.XX
Production series
Production week
Production year (2004)
Production place (Taoyuan)
Serial number of version
Production Model
3.4
3.00
11
12
14
13
MADE IN XXXXXX
60.00
90.00
1. Status indicator (Power, RUN and ERROR) 8. Expansion port
2. Model name 9. Expansion unit clip
3. DIN rail clip 10. DIN rail (35mm)
4. I/O terminals 11. RS-485 Communication port
5. I/O point indicator 12. Mounting rail of the expansion unit
4
DVP-02DA Analog Output Module Explanation
CR
Parameters
No
#0 H 4032
6. Mounting hole of the expansion unit 13. DC Power input
7. Nameplate 14. Expansion port
2.3 External wiring
AC drive, recorder,
scale valve...
AC drive, recorder,
scale valve...
terminal of
power module
Voltage output
0V ~ 10V
*
2
Isolation wire 1
Current output
0mA~20m
Isolation wire 1
*
System
Grounding
Class 3 Grounding
Ω
(100 or less)
CH1
V+
I+
COM
*
FG
CH2
V+
I+
COM
FG
*
DC24V
24+
24-
3
DC/DC
converter
CH1
CH2
Note 1: Please isolate analog output and other
power wiring.
Note 2: If noise interferes from loaded input wiring
terminal is significant, please connect a
capacitor with 0.1~0.47µF 25V for noise
filtering.
Note 3: Please connect
terminal and
power module
analog output module
terminal to system earth point and make
+15V
AG
-15V
system earth point be grounded or
connects to machine cover.
Warning: DO NOT wire to the No function terminal
#2 ~ #9 Reserved
#10 H 403C
#11 H 403D
#12~#21 Reserved
#22 H 4048
#23 H 4049
#24 ~ #27 Reserved
#28 H 404E
#29 H 404F
#30 H 4050
#31 H 4051
#32 H 4052
2.4 Terminal of analog module layout
DVP04AD-S DVP02DA-S DVP04DA-S DVP04PT-S DVP04TC-S DVP06XA-S DVP08RT-S
+
I+
COM
FG
+
I+
COM
FG
+
I+
COM
FG
+
I+
COM
FG
3
COM
COM
+
I+
FG
+
I+
FG
COM
COM
COM
COM
+
I+
FG
+
I+
FG
+
I+
FG
+
I+
FG
STANDARD SPECIFICATIONS
L+
L-
IFG
L+
L-
IFG
L+
L-
IFG
L+
L-
IFG
L+
L-
SLD
L+
L-
SLD
L+
L-
SLD
L+
L-
SLD
COM
COM
COM
COM
COM
COM
+
I+
+
I+
+
I+
+
I+
+
I+
+
I+
L1+
L1L2+
L2L3+
L3L4+
L4FG
L51
L5L6+
L6-
L7+
L7-
L8+
L8FG
#33 H 4053
#34 H 4054
#35~#48 System used
3.1 Specifications
Digital/Analog (2D/A) Module Voltage Output Current Output
Power Supply Voltage 24 VDC (20.4VDC~28.8VDC) (–15%~+20%)
Analog Input Channel 2 channels / each module
Analog Output Range 0~10V 0~20mA
Digital Data Range 0~4000 0~4000
Resolution 12 bits (1
=2.5 mV) 12 bits (1
LSB
LSB
=5 µA)
Output Impedance 0.5Ω or lower
Overall Accuracy
Response Time
Max. Output Current
Tolerance Carried Impedance
±0.5% of full scale of 25℃(77℉)
±1% of full scale during 0~55℃ (32~131℉)
3 ms × channels
20mA (1KΩ~2MΩ) -
- 0〜500Ω
Digital Data Format 2’s complementary of 16-bit, 13 Significant Bits
Isolation Method Isolation between digital area and analog area. But no isolation
among channels.
Protection
Voltage output has short circuit protection but a long period of short
circuit may cause internal wire damage and current output break.
MODBUS ASCII/RTU Mode. Communication baud rate of 4800 /
9600 / 19200 / 38400 / 57600 / 115200. For ASCII mode, format is
Communication Mode (RS-485)
7Bits, even, 1 stop bit (7 E 1), while RTU mode format is 8Bits, even,
1 stop bit (8 E 1). The RS-485 is disabled when the DVP02AD-S is
connected in series with an MPU.
If DVP02DA-S modules are connected to MPU, the modules are
Connect to DVP-PLC MPU in
Series
numbered from 0 – 7. 0 is the closest and 7 is the furthest to the
MPU. 8 modules is the max and they do not occupy any digital I/O
points of the MPU.
3.2 Other Specification
Max. Rated Consuming Power
Environment Condition and Wiring Follow the DVP-PLC MPU
Spec of Prevent Static Electricity All places between terminals and ground comply with the spec
24 VDC (20.4VDC~28.8VDC) (–15%〜+20%), 3W, supply from
external power
Explanation:
1. The content of CR#0 is model type, user can read the data from program to check if there is
expansion module.
2. CR#1 is used to set two internal channels working mode of analog output module. Every channel
has four modes to set that can set individually. For example: if set CH1 to mode 2 (b2~b0=010),
CH2 to mode 1(b5~b3=001). It needs to set CR#1 to H000A. The factory setting of CR#1 is H0000.
3. CR#2 ~ CR#9, CR#12 ~ CR#21, CR#24 ~ CR#27 Reserved.
4. CR #10 ~ CR#11 display CH1 and CH2 output signal. The setting range is K0~K4000. Factory
setting is K0 and unit is LSB.
5. R#22 ~ CR#23 means the value to adjust OFFSET value of CH1 and CH2. The factory setting is K0
and unit is LSB. If output value equal to 0 after calculating, the adjustable range of analog output
voltage or current is -2000~+2000.
Voltage adjustable range: -5V~+5V(-2000
Current adjustable range: -10mA~+10mA (-2000
6. R#28 ~ CR#29 means the value of adjust GAIN value of CH1 and CH2. The factory setting is K2000
and unit is LSB. If output value equal to 2000 after calculating, the adjustable range of analog output
voltage or current is -1600~+8000.
Voltage adjustable range: -4V~+20V(-1600
Current adjustable range: -8mA ~+40mA (-1600
current). When
value variation will be larger. When this value exceeds this range, the resolution of output signal
will be thick and the variation of value will be smaller.
7. CR#30 is the fault code. Please refer to the following chart.
Fault Description
Power Source Abnormal
Analog Input Value Error
Setting Mode Error
Offset/Gain Error
Hardware Malfunction
Digital Range Error
Average Times Setting Error
Command Error
Note: Each fault code will have corresponding bit (b0~b7). Two or more faults may happen at the same time. 0
CR (Control Register)
RS-485
Address
Latched Register Name b15 b14 b13 b12 b11 b10 b9 b8 b7 b6 b5 b4 b3 b2 b1 b0
R Model type
○
R/W Output mode setting
○
R/W CH1 output value
○
R/W CH2 output value
○
R/W To adjust OFFSET
○
value of CH1
R/W To adjust OFFSET
○
value of CH2
R/W To adjust GAIN
○
value of CH1
R/W To adjust GAIN
○
value of CH2
R Error status It is the data register to save all error status. Please refer to fault code chart for detail.
╳
R/W Communication
○
address setting
R/W Communication
○
Baud Rate setting
R/W Reset to factory
○
setting and set
characteristics
adjustable priority
R Software version. In hexadecimal to display software version. For example: H 010A means 1.0A.
○
○ means latched. , ╳ means not latched.
R means can read data by using FROM command via RS-485.
W means can write data by using TO command via RS-485.
LSB (Least Significant Bit): 1. Voltage output: 1
System used, data length is 8 bits (b7~b0). DVP-04AD model code=H 49
Output mode setting: factory setting is H0000.
Mode 0: output voltage mode (0V~10V).
Mode 1: output voltage mode (2V~10V).
Mode 2: output current mode (4mA~20mA).
Mode 3: output current mode (0mA~20mA).
Mode 4: none use.
The output setting range of channel CH1~CH2 is K0~K4000. Factory setting is K0
and unit is LSB.
It is used to set the OFFSET value of CH1~CH2. The setting range is
K-2000~K2000. The factory setting is K0 and unit is LSB.
It is used to set the GAIN value of CH~CH2. The setting range is K-1600~K8000.
The factory setting is K2000 and unit is LSB.
It is used to set RS-485 communication address. The setting range is from 01 to 255
and the factory setting is K1.
It is used to set communication baud rate (4800, 9600, 19200, 38400, 57600,
115200bps). Communication format: ASCII mode is 7Bit, even bit, 1 stop bit (7 E 1),
while RTU mode is 8Bit, even bit, 1 stop bit (8 E 1).
b0: 4800 bps (bit/sec). b1: 9600 bps (bit/sec). (factory setting)
b2: 19200 bps (bit/sec). b3: 38400 bps (bit/sec).
b4: 57600 bps (bit/sec). b5: 115200 bps (bit/sec).
b6-b13: reserved.
b14: exchange low and high byte of CRC check code (only for RTU mode)
b15: ASCII / RTU mode selection
b15 b14 b13 b12 b11 b10 b9 b8 b7 b6 b5 b4 b3 b2 b1 b0
Output latched setting, factory setting H0000.
Give CH1 setting for example:
1. When b0=0, user can set OFFSET and GAIN value of CH1 (CR#22, CR#28).
When b1=1, inhibit user to adjust OFFSET and GAIN value of CH1 (CR#22,
CR#28).
2. b1 means if characteristic register is latched. b1=0 (factory setting, latched), b1=1
(not latched).
3. When b2 is set to 1, all settings will be reset to factory setting.
LSB
~+2000
LSB
LSB
Reserved CH2 CH1 #1 H 4033
Reserved CH2 CH1
=10V/8000=2.5mV. 2. Current output: 1
).
LSB
LSB
~+8000
~+8000
LSB
~+2000
LSB
).
LSB
).
).
LSB
Please be noticed that GAIN VALUE – OFFSET VALUE = +400
this value within this range, the resolution of the output signal will be thin and the
Content b15~b8 b7 b6 b5 b4 b3 b2 b1 b0
K1(H1) 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1
K2(H2) 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0
K4(H4) 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0
K8(H8) 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0
K16(H10) 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0
K32(H20) 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0
K64(H40) 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0
K128(H80)
means normal and 1 means fault happened.
Reserved
1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
~+6000
LSB
=20mA/4000=5µA.
LSB
(voltage or
LSB
Page 2
8. CR#31 is used to set RS-485 communication address. The setting range is from 01 to 254. The
factory setting is K1.
9. CR#32 is used to set RS-485 communication baud rate: 4800, 9600, 19200, 38400, 57600, 115200
bps, b0: 4800bps, b1: 9600bps, (factory setting) b2: 19200bps, b3: 38400 bps, b4: 57600 bps, b5:
115200 bps, b6-b13: reserved, b14: exchange low and high byte of CRC check code. (only for RTU
mode) b15=0: ASCII mode, =1: RTU mode.
10. CR#33 is used to set the internal function priority. For example: characteristic register. Output latched
function will save output setting to the internal memory before power loss.
11. CR#34 is software version of model type.
12. CR#35~ CR#48 are used for system.
13. The corresponding parameters address H4032~H4062 of CR#0~CR#48 are provided for user to
read/write data via RS-485.
A. Communication baud rate: 4800, 9600, 19200, 38400, 57600, 115200 bps.
B. Communication format: ASCII mode is 7Bit, even bit, 1 stop bit (7 E 1). Communication
format of RTU mode is 8Bit, even bit, 1 stop bit (8 E 1).
C. Function code: 03H—read data from register. 06H—write one WORD into register.
10H—write multiple WORD into register.
5
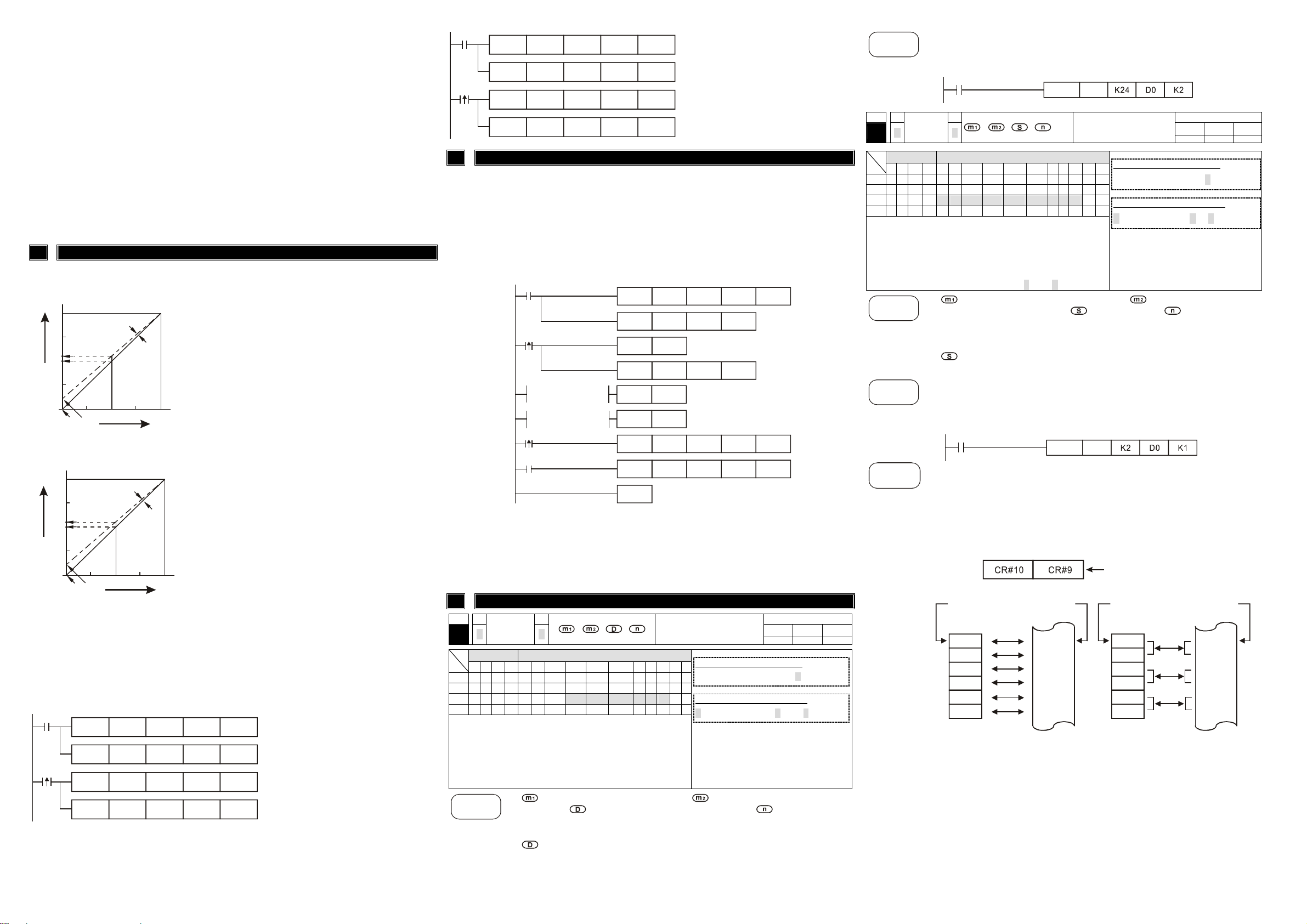
Adjust D/A Conversion Characteristic Curve
5.1 Adjust D/A Conversion Characteristic Curve
Voltage output mode
voltage
output
10V
6V
5V
2V
0
GAIN
OFFSET
mode 1
mode 0
+2000 +4000
Digital input
Mode 0 of CR#1: GAIN = 5V(2000
OFFSET=0V (0
Mode 1 of CR#1: GAIN = 6V(2400
OFFSET=2V (800
GAIN: The setting range of voltage output value when
digital input value is K2000 should be
-4V~+20V(-1600
OFFSET: The setting range of voltage output value when
digital input value is K0 should be
-5V~+5V(-2000
GAIN-OFFSET:
Setting range: +1V~+15V (+400
).
LSB
),
LSB
)
LSB
),
LSB
LSB
~+8000
LSB
~ +2000
LSB
).
).
LSB
).
LSB
~ +6000
LSB
Current output mode
LSB
LSB
LSB
LSB
LSB
LSB
).
).
).
),
).
),
LSB
current
output
20mA
12mA
10mA
4mA
0
GAIN
OFFSET
mode 2
mode 3
+2000 +4000
digital input
Mode 2 of CR#1: GAIN = 12mA(2400
OFFSET=4mA (800
Mode 3 of CR#1: GAIN = 10mA(2000
OFFSET=0mA (0
GAIN: The setting range of current output when digital
input value is K2000 should be -8mA~+40mA
(-1600
~+8000
LSB
OFFSET: The setting range of current output when digital
input value is K0 should be -10mA ~+10mA
GAIN-OFFSET:
(-2000
Setting range: +2mA~+30mA (+400
~+6000
~+2000
LSB
LSB
).
The charts above are D/A conversion characteristic curve of voltage input mode and current input
mode. Users can adjust conversion characteristic curve by changing OFFSET values (CR#22~CR#23)
and GAIN values (CR#28~CR#29) depend on application.
LSB (Least Significant Bit): 1.voltage input: 1
=20mA/4000=5µA.
1
LSB
=10V/8000=2.5mV. 2.current input:
LSB
5.2 Program Example for Adjusting D/A Conversion Characteristics Curve
Example 1: Setting OFFSET value of CH1 to 0V(=K0
M1002
X0
TO
TO
TO
TO
K1
K1
K1
K1
K1
K33
K22
K28
H18 K1
H0 K1
K0
K1000
Example 2: Setting OFFSET value of CH2 to 2mA (=K400
) and GAIN value is 2.5V(=K1000
LSB
Writing H18 into CR#1 of analog output
module#0. Setting CH2 to mode 3
(current output -20mA~ +20mA).
Writing H0 into CR#33 and allow CH2 to
adjust characteristics.
When X0 switches from OFF to ON,
K1
K1
of OFFSET value will be written to
K0
LSB
CR#22 and K1000
of GAIN value will
LSB
be written to CR#28.
) and GAIN value to 18mA (=K3600
LSB
LSB
).
).
LSB
M1002
TO
K1
K1
H10 K1
Writing H10 into CR#1 of analog output
module#0. Setting CH2 to mode 2
(current output +4mA~ +20mA).
Writing H0 into CR#33 and allow the
adjust characteristic of CH1 and CH2.
When X0 switches from OFF to ON,
K1
of OFFSET value will be written
K400
LSB
to CR#23 and K3600
K1
will be written to CR#29.
of GAIN value
LSB
X0
TO
TO
TO
K1
K1
K1
K33
K23
K29
H0 K1
K400
K3600
6
Initial PLC Start-up
Lamp display
1. When power is on, POWER LED will be lit and ERROR LED will be lit for 0.5 second.
2. Normal run: POWER LED should be lit and ERROR LED should turn off. When power supply is
lower than 19.5V, ERROR LED will blink continuously till the power supply is higher than 19.5V.
3. When it connects to PLC MPU in series, RUN LED on MPU will be lit and A/D LED or D/A LED
should blink.
4. After receiving the first RS-485 command during controlling by RS-485, A/D LED or D/A LED
should blink.
5. After converting, ERROR LED should blink if input or output exceeds upper bound or below the
lower bound.
Program example:
M1000
M1013
=K4000 RST
=
M1
M1
D100 D100
K4000
FROM
INC D100
ADD D101 K5
TO
TO
D101D101
K1 K1 K1
K1
RST
END
K0K1
D0CMP H49
D0
M0
D101
H10
D100
K1
K2K10
Explanation:
Reading the data of model type from expansion module K1 and check to see if the data is H49
(DVP-02DA-S model type).
D100 will increase K1 and D101 will increase K5 every second.
When value of D100 and D101 attain to K4000, they will be reset to 0.
For DVP-02DA-S model, M1 will be on and set the output mode: CH1 mode to 0, CH2 mode to 2.
Writing output setting CR#10 and CR#11 to D100 and D101. Analog output will vary with D100 and
D101 value.
7
API
FROM
D
78
Bit device Word device
P
X Y M S K H KnX KnY KnM KnS T C D E F
m1
m2
D
n
¼ ¼
¼ ¼
¼ ¼
¼ ¼ ¼ ¼ ¼ ¼ ¼ ¼
Note: The usage range of operand m
The usage range of operand m2: ES/EP: 0-48,
EH: 0-254.
The usage range of operand n: ES/EP: n=
1~(49-m2), EH: 1~(255-m2).
Command Explanation
Read special module CR
data
is 0~7.
1
Adaptive model
ES EP EH
16-bit command (9 STEPS)
FROM
Continuous
execution
FROMP
Pulse
execution
32-bit command (17 STEPS)
DFROM
Continuous
execution
DFROMP
Pulse
execution
Flag: When M1083=On, it allows
to enable interrupt during
FROM/TO. Refer to
following for detail.
ES series model doesn’t support pulse
Command
Explanation
execution command (FROMP, DFROMP).
: the module number you are probing. : the number of Controlled Registers
to be read.
to read at one time.
DVP-series PLC uses this command to read CR data of each special module.
: the data register location for storing data. : the number of CRs
: When assigning bit operand, K1~K4 are used for 16-bit and K5~K8 are used
for 32-bit.
Please refer the footnote below for calculation of the special module number.
Program
Example
Read the content of CR#24 and CR#25 of module#0 and save it into D0 and D1,
2pcs data are read in one time when n=2.
The command will be executed when X0=ON. When X0=OFF, nothing will occur and
the stored data has no change.
X0
FROM K0
API
79
TO
D
P
Bit device Word device
X Y M S K H KnX KnY KnM KnS T C D E F
m
1
m
2
S
n
Note: The usage range of operand m
Command
Explanation
Program
Example
Footnote
¼ ¼
¼ ¼
¼ ¼ ¼ ¼ ¼ ¼ ¼ ¼ ¼ ¼ ¼
¼ ¼
is 0~7.
1
The usage range of operand m2: ES/EP: 0-48,
EH: 0-254.
The usage range of operand n: ES/EP: n=
1~(49-m2), EH: 1~(255-m2).
For ES series, it doesn’t support pulse
execution command (TOP, DTOP)
: the module number you are probing. : the number of Controlled
Registers that will be written to.
to write to one time.
DVP-series PLC uses this command to write data into Controlled Registers of
special modules.
: When assigning bit operand, K1~K4 are used for 16-bit and K5~K8 are
used for 32-bit.
Using the 32-bit command DTO. The program will write D11 and D10 into CR#3
and CR#2 of special module#0. DTO only allows one group of data to be written at
a time (n=1).
Command is executed when X0=ON, command won’t be executed when X0=OFF,
and the stored data will have no change.
X0
The rules for adding multiple special modules to a Main Processing Unit:
m1: The maximum number of special modules attached to an MPU is 8. The
order of module closest to the MPU is 0, and the module furthest from the
MPU is 7.
m2: The number of Controlled Registers (CR) built in is 49. (#0~#48).
FROM/TO command read/write 16-bit CR data in one command, while
DFROM/DTO command to read/write 32-bit CR data in one command.
Example below:
Upper 16-bit Lower 16-bit
(n=2 for 16-bit command and n=1 for 32-bit are equal controlled registers used).
Assigned
Equipment
D0
D1
D2
D3
D4
D5
Assigned
CR
CR#5
CR#6
CR#7
CR#8
CR#9
CR#10
16-bit command when n=6 32-bit command when n=3
In ES series models, flag M1083 is not provided. When FROM/TO command is
executed, all interrupts (including external or internal interrupt subroutines) will be
disabled. All interrupts will be executed after FROM/TO command is completed.
Besides, FROM/TO command also can be executed in the interrupt subroutine.
The function of the flag M1083 (FROM/TO mode exchange) provided in EP/EH
series models:
1. When M1083=Off, all interrupts (including external or internal interrupt
subroutines) will be disabled when FROM/TO command is executed. The
Interrupts will resumed after FROM/TO command complete. Please be
advised FROM/TO command can be executed in the interrupt subroutine.
2. When M1083=On, if an interrupt enable occurs while FROM/TO command are
executing, the interrupt FROM/TO command will be blocked till the requested
interrupt finish. Unlike M1080 off situation, FROM/TO command cannot be
executed in the interrupt subroutine.
Special module CR
data write
16-bit command (9 STEPS)
Continuous
TO
execution
32-bit command (17 STEPS)
Continuous
DTO
execution
Flag: When M1083 On, it allows
to enable interrupt during
FROM/TO. Refer to following for
detail.
: the data to write. : the number of CRs
DTO K0
Assigned CR numer
Adaptive model
ES EP EH
DTOP
Assigned
Equipment
D0
D1
D2
D3
D4
D5
Pulse
TOP
execution
Pulse
execution
Assigned
CR
CR#5
CR#6
CR#7
CR#8
CR#9
CR#10
 Loading...
Loading...