Page 1
10-INCH CONTRACTOR TABLE SAW
Scie de table de 10 pouces
(254 mm) pour entrepreneurs
Sierra de mesa de 10 pulgadas
(254 mm) para contratista
Français (34)
Español (67)
www.DeltaMachinery.com
Instruction Manual
Manuel d’utilisation
Manual de instrucciones
INSTRUCTIVO DE OPERACIÓN, CENTROS
DE SERVICIO Y PÓLIZA DE GARANTÍA.
LÉASE ESTE INSTRUCTIVO
ANTES DE USAR EL PRODUCTO.
To reduce risk of serious injury, thoroughly read and comply with all warnings and instructions in
this manual and on product.
KEEP THIS MANUAL NEAR YOUR SAW FOR EASY REFERENCE AND TO INSTRUCT OTHERS
36-5000
36-5100
36-5052
36-5152
Page 2
TABLE OF CONTENTS
IMPORTANT SAFETY INSTRUCTIONS ...................................3
Safety Logos ...................................................................... 3
GENERAL POWER TOOL SAFETY RULES ........................... 3
TABLE SAW SAFETY RULES .................................................. 5
POWER CONNECTIONS .......................................................... 7
Power Source ...................................................................... 7
Grounding Instructions ....................................................... 7
Extension Cords .................................................................. 8
UNPACKING ............................................................................. 9
Components and Parts List ................................................9
Hardware Package ............................................................ 10
ASSEMBLY ..............................................................................11
Stand ................................................................................. 11
Fixed Wheels and Stationary Feet .................................... 12
Extension Wings ...............................................................12
Front and Rear Rails ......................................................... 13
Wood Extension Table ...................................................... 14
Fence Guide and Power Control Box ............................... 14
Throat Plate .......................................................................15
Blade and Riving Knife ..................................................... 15
Anti-kickback Pawls .......................................................... 15
Blade Guard ..................................................................... 16
Rip Fence .......................................................................... 16
Miter Gauge ......................................................................16
On-Board Storage ............................................................. 16
Adjusting the 90° and 45° Positive Bevel Stops ..............17
Securing Saw to Floor ......................................................17
PREPARING TO CUT .............................................................17
Raising and Lowering the Blade ....................................... 18
Tilting the Blade ................................................................ 18
Selecting and Storing Saw Blades ................................... 19
Changing the Saw Blade .................................................. 19
Riving Knife Position ......................................................... 19
Height Settings .......................................................... 20
Checking Riving Knife Alignment .............................. 20
Using the Miter Gauge ......................................................21
Using Blade Guard Assembly ........................................... 21
Checking Fence Alignment .............................................. 21
OPERATION .............................................................................22
Starting and Stopping the Saw.........................................22
Overload Protection .......................................................... 24
Making Cuts ...................................................................... 23
Rip Cuts .............................................................. 24
Bevel Rip Cuts ..................................................... 24
Cross-Cuts ......................................................... 25
Bevel Cross-Cuts ................................................ 25
Miter Cuts ............................................................ 25
Compound Miter Cuts ......................................... 26
Large Panel Cuts .................................................26
Non-Through Cuts ............................................................ 26
Non-through Cuts................................................26
Dado Cuts ...........................................................27
Using Cutting Aids ............................................................ 27
Push Sticks .......................................................... 27
Auxiliary Rip Fence Facing .................................. 28
Auxiliary Miter Gage Facing .............................. 28
Push Blocks ......................................................... 28
Featherboards ..................................................... 29
Cutoff Gauge ....................................................... 29
Jigs ......................................................................29
ALIGNMENT ............................................................................ 30
Riving Knife Alignment With The Blade ............................30
Adjusting The Miter Stops ................................................ 30
Aligning Fence Parallel To Miter Slot ................................ 31
Aligning Fence Perpendicular to the Table .......................31
240 VOLT SINGLE PHASE OPERATION ................................32
MAINTENANCE ....................................................................... 33
TROUBLESHOOTING ............................................................. 33
ACCESSORIES ........................................................................ 33
WARRANTY ............................................................................. 34
PARTS, SERVICES AND WARRANTY ASSISTANCE ...........34
REPLACEMENT PARTS ..........................................................34
FRENCH ................................................................................... 34
SPANISH ...................................................................................67
FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION
The DELTA® #36-5000 series 10-inch Contractor
Table Saw is designed for portability and high quality
performance. It includes: basic machine, sturdy tubular
steel stand, integral dust chute, a T-Square® fence
system, t-slot miter gage, 15-amp induction motor,
on/off switch, cast iron table, extension wings, seethrough blade guard with anti-kickback fingers, and
10-inch carbide blade.
NOTICE: The manual cover illustrates the current production model. All other illustrations contained in the manual
are representative only and may not be exact depictions of the actual labeling or accessories included. They are
intended for illustrative purposes only.
SPECIFICATIONS
Max depth of cut at 90 degrees: 3-½"
Max depth of cut at 45 degrees: 2-½”
Max rip to right of blade: 30" or 52"
Max rip to left of blade: 15"
Max width of dado: 13/16"
MOTOR SPECIFICATIONS:
Amps 15/7.5
Voltage 120/240
2
Page 3

IMPORTANT SAFETY INSTRUCTIONS
CAREFULLY READ AND FOLLOW ALL WARNINGS AND INSTRUCTIONS ON YOUR PRODUCT
AND IN THIS MANUAL. SAVE THIS MANUAL. MAKE SURE ALL USERS ARE FAMILIAR WITH ITS
WARNING AND INSTRUCTIONS WHEN USING THE TOOL. Improper operation, maintenance or modification of
tools or equipment could result in serious injury and/or property damage.
If you have any questions or concerns relative to the use of your tool or the contents of this manual, stop using the
tool and contact DELTA® Power Equipment Corporation Customer Care at 1-800-223-7278.
SAFETY LOGOS
The definitions below describe the level of severity for each signal word. Please read the manual and pay attention
to these symbols.
Indicates an imminently hazardous situation which, if not avoided, will result in death or serious
injury.
Indicates a potentially hazardous situation which, if not avoided, could result in death or serious
injury.
Indicates a potentially hazardous situation which, if not avoided, may result in minor or moderate
injury.
GENERAL POWER TOOL SAFETY RULES
Failure to follow these rules may
result in serious personal injury.
1. READ INSTRUCTION MANUAL AND KNOW YOUR
TOOL. Read and familiarize yourself with entire
instruction manual. Learning the tool’s proper
applications, limitations, and specific potential
hazards will greatly minimize the possibility of
accidents and injury. Make sure all users are familiar
with its warnings and instructions before using tool.
2. KEEP GUARDS AND SAFETY DEVICES IN PLACE
and working properly.
3. REMOVE ADJUSTING KEYS AND WRENCHES.
Form habit of checking to see that all adjusting keys
and wrenches are removed before starting tool.
4. KEEP WORK AREA CLEAN AND WELL LIT.
Cluttered or poorly-lit work areas, surfaces and
benches can lead to accidents.
5. DO NOT USE OR STORE TOOL IN DANGEROUS
ENVIRONMENTS. Exposure to rain and damp or
wet locations can result in shock or electrocution,
or damage the tool. Do not operate electric tools
near flammable liquids or in gaseous or explosive
atmospheres. Motors and switches in these tools
may spark and ignite fumes.
6. KEEP CHILDREN AND BYSTANDERS AWAY from
work area.
7. LOCK TOOLS AND WORK AREA. Use padlocks,
and master switches, or remove and store starter
keys to prevent operation by children and other
unauthorized users.
8. DO NOT FORCE TOOL OR WORKPIECE. Operate
tool at intended speed and feed rate for better and
safer operation.
9. USE PROPER TOOL. Do not force tool to do a task
for which it was not designed.
10. DO NOT ABUSE POWER CORDS. NEVER yank
cord to disconnect from receptacle, crush cord, or
expose it to heat, oil or sharp objects.
11. USE PROPER EXTENSION CORD. If you use an
extension cord, make sure it is in good condition
and heavy enough to carry the current your product
will draw. An undersized cord will cause a drop
in line voltage, resulting in loss of power and
overheating. See Extension Cord Chart for correct
size depending on cord length and data plate
ampere rating. If in doubt, use the next smaller
gauge number. The smaller the gauge number, the
heavier the cord. When working outside, make sure
extension cord is rated for outdoor use. Consult
power connection section of this manual for
Extension Cord Chart and power connection safety.
12. SECURE WORKPIECE. Use clamps or a vise to
hold the workpiece when practical. It is safer than
using your hands and frees both hands to operate
tool.
13. DO NOT OVERREACH. Keep proper footing and
balance to maintain control.
14. MAINTAIN TOOLS WITH CARE. Keep tools
sharp and clean for best and safest performance.
Follow instructions for lubricating and changing
accessories.
15. DISCONNECT TOOL from power source before
servicing, adjusting or changing set-ups or blades,
bits, cutters and other accessories.
16. TO REDUCE RISK OF ACCIDENTAL STARTING,
make sure power switches are in “OFF” position
before plugging tool in.
17. Do not touch the plug’s metal prongs when
unplugging or plugging in the cord.
continued on page 4
3
Page 4

GENERAL POWER TOOL SAFETY RULES
18. USE RECOMMENDED ACCESSORIES. Consult
manual for recommended accessories. Use of
inappropriate accessories may cause personal
injury or property damage.
19. NEVER STAND ON TOOL. Serious injury could
occur if the tool tips or if you unintentionally contact
the cutting surface.
20. CHECK TOOLS FOR DAMAGE. Before using,
and after tool or accessory has been dropped or
damaged, check guards and affected parts for
alignment of moving parts, binding of moving
parts, breakage of parts, and any other condition
that may affect its operation to make sure tool will
operate properly and all parts will perform their
intended function. Do not use a damaged product.
A guard or any other part that is damaged should
be properly repaired or replaced using factoryapproved service parts.
21. USE PROPER FEED DIRECTION. Feed workpiece
against the direction of rotation of the tool’s blade,
cutter, or abrasive surface. Feeding in the other
direction may cause the workpiece to be thrown at
high speed.
22. NEVER LEAVE TOOL RUNNING UNATTENDED.
TURN POWER OFF. Do not leave tool until it comes
to a complete stop. In the event of a power failure,
move switch to “OFF” position.
23. STAY ALERT, WATCH WHAT YOU ARE DOING,
AND USE COMMON SENSE. Do not use power
tools when tired or under the influence of drugs,
alcohol, or medication. A moment of inattention
while operating power tools may result in injury.
24. SERVICE PARTS. Use only identical replacement
parts when servicing your tool.
25. WEAR PROPER APPAREL. Do not wear loose
clothing, gloves, neckties, rings, bracelets, or other
jewelry which may get caught in moving parts.
Nonslip protective footwear is recommended. Wear
protective hair covering to contain long hair.
26. WEAR PROPER EYE PROTECTION. All persons
in work area should wear safety glasses with side
shields. Everyday eyeglasses with impact resistant
lenses are not safety glasses. Eye equipment
should comply with ANSI Z87.1 standards.
27. HEARING PROTECTION. All people in work area
should wear proper hearing protection consistent
with noise levels and exposure. Hearing equipment
should comply with ANSI S3.19 standards.
28. DUST PROTECTION. Use of power tools can
generate and/or disburse dust, which may cause
serious and permanent respiratory or other injury,
including silicosis (a serious lung disease), cancer,
and death. Direct particles away from face and
body. Always operate tool in well-ventilated area
and provide for proper dust removal. Use dust
collection system whenever possible. Avoid
breathing dust and avoid prolonged contact with
dust. Allowing dust to get into your mouth or eyes,
or lay on your skin may promote absorption of
harmful material. Use properly fitting NIOSH/OSHA
approved respiratory protection appropriate for the
dust exposure and wash exposed areas with soap
and water.
PROPOSITION 65 WARNING:
power sanding, sawing, grinding, drilling, and other
construction activities may contain chemicals known to
the state of California to cause cancer, birth defects or
other reproductive harm. Some examples are:
• Lead from lead-based paints
• Crystalline silica from bricks and cement and other
masonry products
• Asbestos dust
• Arsenic and chromium from chemically-treated
lumber
Dust created by
SAVE THESE INSTRUCTIONS.
Refer to them often and use them to instruct others.
If tool is loaned to someone, also loan them these instructions.
Your risk from these exposures varies depending on
how often you do this type of work. To reduce your
exposure to these chemicals: work in a well-ventilated
area and work with approved safety equipment, such
as dust masks that are specially designed to filter out
microscopic particles.
4
Page 5

TABLE SAW SAFETY RULES
Failure to follow these rules may result in serious personal injury.
• SEE GENERAL POWER TOOL SAFETY SECTION OF THIS MANUAL. Read entire instruction manual before
operating saw. Learning the saw's proper applications, limitations, and specific potential hazards will greatly
minimize the possibility of accidents and injury. Make sure all users are familiar with its warnings and instructions
before using saw.
• SEE POWER CONNECTION SECTION OF THIS MANUAL for instructions and warnings regarding power cords and
connections.
TERMINOLOGY
The following terms will be used throughout the manual and you should become familiar with them.
– Through-cut refers to any cut that completely cuts
through the workpiece.
– Non-through cut refers to any cut that does not
completely cut through the workpiece.
_ Push stick refers to a wooden or plastic stick, usually
homemade, that is used to push a small workpiece
through the saw and keeps the operator’s hands clear
of the blade.
– Kickback occurs when the saw blade binds in the cut
or between the blade and the fence and thrusts the
workpiece back toward the operator.
Failure to follow these rules may result
in serious personal injury.
1. NEVER Perform freehand cutting, plunge cutting,
resawing, or cove cutting.
2. WEAR EYE PROTECTION, appropriate apparel,
hearing protection and dust protection as specified
in the General Power Tool Safety Section of this
manual.
3. USE SAW BLADE GUARD, RIVING KNIFE AND
ANTI-KICKBACK PAWLS. Your saw is equipped
with a modular blade guard, riving knife and
anti-kickback pawl assembly, each component
of which should be used for every possible
operation, including all through cuts. This
assembly is discussed in more detail below. Make
sure components are securely installed prior to
operation.
4. KEEP HANDS AND OTHER BODY PARTS OUT OF
THE BLADE PATH. NEVER have any part of your
body in line with the path of the saw blade.
5. USE A PUSH STICK that is appropriate to the
application to push and hold down a workpiece
through the completion of the cut. A push stick is
a wooden or plastic stick, usually homemade, that
should be used whenever the size or shape of the
workpiece would cause you to place your hands
within 6 in. (152 mm) of the blade. Instructions for
making a push stick are included in this manual.
6. AVOID KICKBACK. Pay particular attention to
instructions (below) for reducing risk of kickback.
7. NO FREEHAND CUTS. Always use a rip fence,
miter gauge, or other appropriate devices to guide
or hold down the workpiece. Use hold-downs, jigs,
fixtures or feather boards to help guide and control
– Freehand refers to cutting without the use of a miter
gauge or rip fence or any other means of guiding or
holding the workpiece other than the operator’s hand.
– Plunge cutting refers to blind cuts in the workpiece
made by either raising the blade through the workpiece
or lowering the workpiece down to the blade.
– Re-sawing – Flipping material to make a cut the saw is
not capable of making in one pass.
– Cove cutting – Also known as coving, cove cutting is an
operation where the work is fed at an angle across the
blade.
the workpiece. Accessories for use with your saw
are available at extra cost from your local dealer or
authorized service center.
8. DO NOT USE RIP FENCE AND MITER GAUGE AT
THE SAME TIME.
9. DO NOT REACH OVER/REACH AROUND. Never
reach over, in back of, or around the cutting tool
with either hand while the blade is in motion.
10. STABILITY. Make sure table saw is properly
assembled and located on a stable surface before
use to keep saw from moving during cut.
11. PROPER ASSEMBLY. Do not operate this saw until
it is completely assembled and installed according
to the instructions.
12. CHECK WORKPIECE AND SET-UP before
each operation. Knots, irregularities, or nails
in workpiece and positioning mistakes or
incomplete set-up may interfere with or affect saw
performance and personal safety.
13. USE PROPER THROAT PLATE. The proper throat
plate must be in place and properly secured at all
times to reduce the risk of a thrown workpiece and
possible injury.
14. USE CORRECT BLADE AND RIVING KNIFE for the
intended operation. The blade must be installed
so the points of the teeth are pointing toward the
front of the saw. Do not use oversized blade or
blade with incorrect arbor opening. Always tighten
the blade arbor nut securely. Before use, inspect
the blade for cracks or missing teeth. Do not use
a damaged or dull blade. Always use blade within
the thickness range for which the riving knife is
designed.
5
continued on page 6
Page 6
TABLE SAW SAFETY RULES (continued)
15. AVOID AWKWARD OPERATIONS AND HAND
POSITIONS where a sudden slip could cause a
hand to move into a saw blade. Operate with table
at or near waist level for maximum balance and
control. Anticipate effect of workpiece size on
your ability to adjust position and maintain control
through completion of cut.
16. KEEP ARMS, HANDS AND FINGERS AT LEAST SIX
INCHES AWAY FROM THE BLADE.
17. NEVER CUT METALS, CEMENT BOARD OR
MASONRY. Certain man-made materials have
special instructions for cutting on table saws.
Follow the manufacturer’s recommendations at all
times.
18. NEVER ATTEMPT TO FREE A STALLED BLADE
OR TRAPPED WORKPIECE without first turning
the machine off and disconnecting the saw from the
power source.
19. NEVER START THE MACHINE WITH THE
WORKPIECE AGAINST THE BLADE to reduce the
risk of a thrown workpiece.
20. NEVER PERFORM LAYOUT, ASSEMBLY OR SETUP WORK ON THE TABLE/WORK AREA when the
saw is running.
21. BEFORE LEAVING THE SAW , wait for the blade to
come to a complete stop, then disconnect from the
power source, clean the table and work area, and
lock out switch to prevent unauthorized use.
22. SUPPORT YOUR WORKPIECE based on its size
and the type of operation to be performed. Hold
the work firmly against the fence and down against
the table surface. Do not leave a wide panel or long
board (or other large workpiece) unsupported – the
weight of the board may causes it to shift on the
table resulting in loss of control.
23. AN UNFAMILIAR NOISE OR EXCESSIVE
VIBRATION may indicate a problem with your
saw. If this happens, turn it off and disconnect it
from the power source until the problem has been
located and corrected. Contact customer service
for assistance if the problem cannot be solved.
24. OBTAIN ADVICE from your supervisor, instructor, or
another qualified person if you are not thoroughly
familiar with the operation of this machine.
Knowledge is safety.
SAW BLADE GUARD, ANTI-KICKBACK PAWLS
AND RIVING KNIFE ASSEMBLY
Your table saw is equipped with a blade guard, antikickback pawls and riving knife assembly that covers
the blade and reduces the possibility of accidental
blade contact. The riving knife is a flat plate that fits
into the cut made by the saw blade and effectively
fights kickback by lessening the tendency of the blade
to bind in the cut. Two anti-kickback pawls are located
on the sides of the riving knife that allow the wood
to pass through the blade in the cutting direction but
reduce the possibility of the material being thrown
backwards toward the operator. The blade guard and
anti-kickback pawls can only be used when making
through cuts that sever the wood. When making
rabbets and other non-through cuts, the blade guard
and anti-kickback pawls must be removed and riving
knife lowered to the non-through cut position marked
on the riving knife.
Use all components of the guarding system (blade
guard assembly, riving knife and anti-kickback pawls)
for every operation for which they can be used
including all through-cutting. If you elect not to use
any of these components for a particular application,
exercise additional caution regarding control of the
workpiece, the use of push sticks, the position of
your hands relative to the blade, the use of safety
glasses, the means to avoid kickback and all other
warnings contained in this manual and on the saw
itself. Replace the guarding systems as soon as you
return to through-cutting operations. Keep the guard
assembly in working order.
MAKING A PUSH STICK
In order to operate your table saw safely, you must
use a push stick whenever the size or shape of the
workpiece would otherwise cause your hands to be
within 6 inches (152 mm) of the saw blade or other
cutter. A push stick is included with this saw.
No special wood is needed to make additional push
sticks as long as they are sturdy and long enough
and the wood is free of knots, checks and cracks. A
length of 16 inches (400 mm) is recommended with a
notch that fits against the edge of the workpiece to
prevent slipping. It’s a good idea to have several push
sticks of the same minimum length, 16 inches (400
mm), with different size notches for different workpiece
thicknesses.
The shape can vary to suit your own needs as long as
it performs its intended function of keeping your hands
away from the blade. Angling the notch so the push
stick can be held at a 20- to 30-degree angle from the
saw’s table will help you to hold down the workpiece
while also moving it through the saw. Refer to diagram
in cutting aids section on page 25 of this manual.
6
Page 7

TABLE SAW SAFETY RULES (continued)
KICKBACKS
Kickbacks can cause serious injury. A kickback occurs
when a part of the workpiece binds between the saw
blade and the rip fence, or other fixed object, and
rises from the table and is thrown toward the operator.
Kickbacks can be avoided by attention to the following
conditions.
HOW TO REDUCE THE RISK OF
KICKBACKS AND PROTECT YOURSELF
FROM POSSIBLE INJURY:
• Be certain that the rip fence is parallel to the saw
blade.
• DO NOT rip by applying the feed force to the section
of the workpiece that will become the cut-off (free)
piece. Feed force when ripping should always be
applied between the saw blade and the fence; use a
push stick for narrow work, 6 inches (152 mm) wide or
less.
• Keep saw blade guard, riving knife and antikickback assembly in place and operating properly.
The riving knife must be in alignment with the saw
blade and the anti-kickback assembly must stop
a kickback once it has started. Check their action
before ripping by pushing the wood under the antikickback assembly. The teeth must prevent the
wood from being pulled toward the front of the saw.
If any part of assembly is not operational, return to
the nearest authorized service center for repair.
• Plastic and composite materials (like hardboard) may
be cut on your saw. However, since these are usually
quite hard and slippery, the anti-kickback pawls may
not stop a kickback. Therefore, be especially attentive
to following proper set up and cutting procedures for
ripping.
• Use saw blade guard, anti-kickback pawls, and riving
knife assembly for every possible operation, including
all through-cut sawing.
• Push the workpiece past the saw blade prior to
releasing control.
• NEVER rip a workpiece that is twisted or warped,
or does not have a straight edge to guide along the
fence.
• NEVER saw a large workpiece that cannot be
controlled.
• NEVER use the fence as a guide or length stop when
crosscutting.
• NEVER saw a workpiece with loose knots, flaws, nails
or other foreign objects.
• NEVER rip a workpiece shorter than 10 inches (254
mm).
• NEVER use a dull blade. A dull blade should be
replaced or re-sharpened.
POWER CONNECTIONS
POWER SOURCE
This saw is equipped with a 15-amp motor for use with
a 120-volt, 60-HZ alternating current. It can be re-wired
for use with a 240-volt power source by a qualified
electrician. See instructions below regarding proper
connections for your saw as wired.
For voltage, the wiring in a shop is as important as
the motor’s rating. A line intended only for lights may
not be able to properly carry the current needed for a
power tool motor; wire that is heavy enough for a short
distance may be too light for a greater distance; and a
line that can support one power tool may not be able to
support two or three.
DO NOT EXPOSE THE MACHINE TO RAIN OR OPERATE THE MACHINE IN DAMP LOCATIONS.
GROUNDING INSTRUCTIONS
THIS MACHINE MUST BE GROUNDED WHILE IN USE TO PROTECT THE OPERATOR FROM
ELECTRIC SHOCK.
In the event of a malfunction or breakdown, grounding
provides a path of least resistance for electric current
to reduce the risk of electric shock. This machine is
equipped with an electric cord having a grounding
conductor and a grounding plug. The plug must be
plugged into a matching receptacle that is properly
installed and grounded in accordance with all local
codes and ordinances.
Do not modify the plug as provided on your saw
or as rewired by your electrician. If it will not fit the
7
A separate electrical circuit should be used for your
machines. This circuit should not be less than #12
wire and should be protected with a 20-amp time lag
fuse. If an extension cord is used, use only 3-wire
extension cords which have 3-prong grounding-type
plugs and matching receptacle which will accept the
machine’s plug. Before connecting the machine to the
power line, make sure the switch (s) is in the “OFF”
position and be sure that the electric current is of the
same characteristics as indicated on the machine. A
substantial voltage drop will cause a loss of power and
overheat the motor. It may also damage the machine.
receptacle, have the proper receptacle installed by a
qualified electrician.
Improper connection of the equipment-grounding
conductor can result in risk of electric shock. The
conductor with insulation having an outer surface that
is green with or without yellow stripes is the grounding
conductor. If repair or replacement of the electric cord
or plug is necessary, do not connect the equipmentgrounding conductor to a live terminal.
Page 8
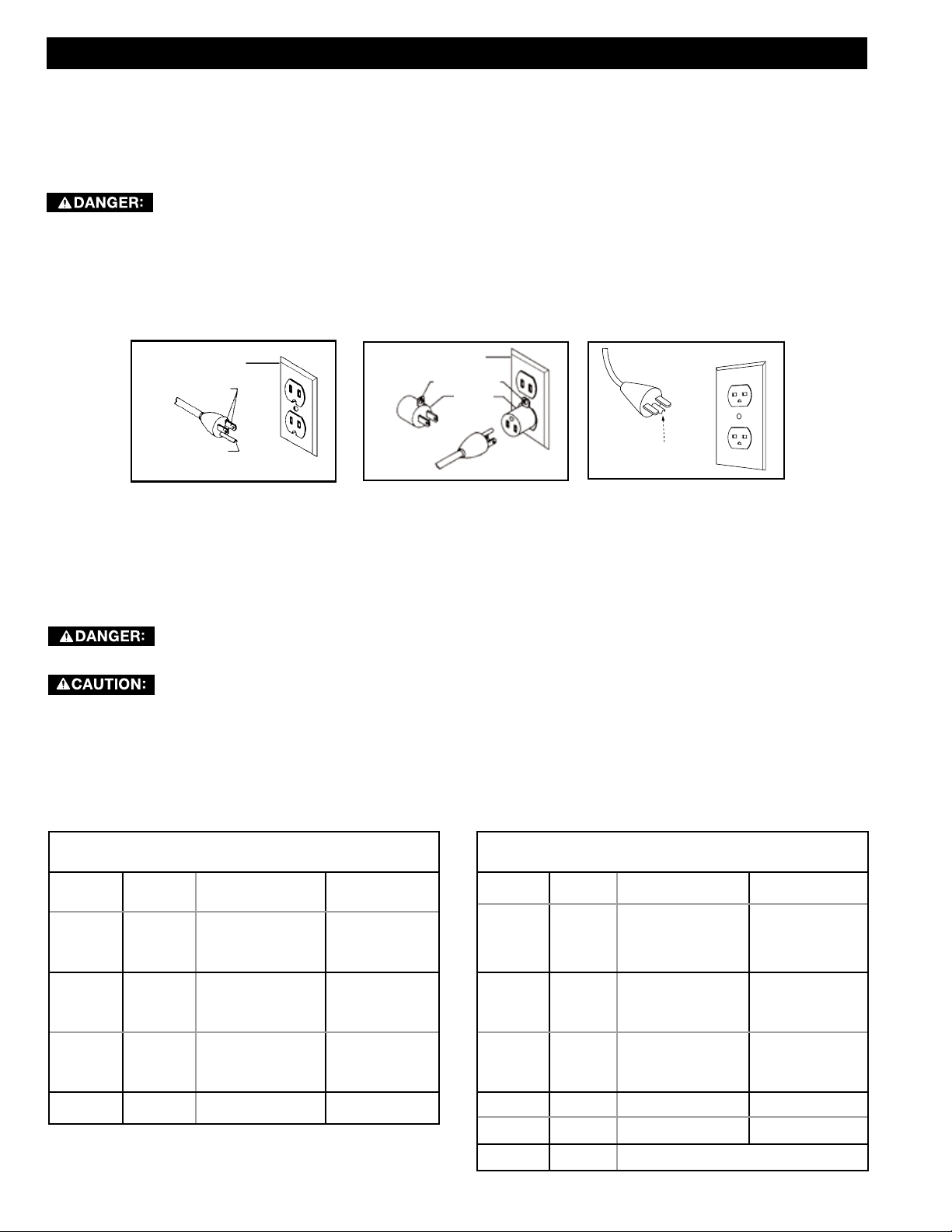
POWER CONNECTIONS
(continued)
Check with a qualified electrician or service personnel
if the grounding instructions are not completely
understood, or if in doubt as to whether the machine is
properly grounded.
Use only 3-wire extension cords that have 3-prong
3-conductor receptacles that accept the machine’s
plug, as shown in Figure A, or a properly grounded
receptacle with a grounding means adaptor, as shown
in Figure B.
Repair or replace damaged or worn cord immediately.
grounding type plugs and matching, properly grounded
IN ALL CASES, MAKE CERTAIN THE RECEPTACLE IN QUESTION IS PROPERLY GROUNDED. IF
YOU ARE NOT SURE, HAVE A qualified ELECTRICIAN CHECK THE RECEPTACLE.
This is a grounded, cord-connected tool intended for use on a supply circuit having a nominal voltage of 120 volts.
It is intended to for use on a circuit that has an outlet as shown in FIG. A. It has a plug as shown in FIG A. If you
have a 2 pole receptacle as shown in FIG. B you may use a temporary adapter, as shown in FIG. B. if a properly
grounded outlet is not available. The green ear lug extending from the adapter must be connected to a permanent
grounded outlet box. The temporary adapter should be used only until a properly grounded outlet can be installed
by a qualified electrician.
GROUNDED
OUTLET BOX
CURRENT
CARRYING
PRONGS
GROUNDING BLADE
IS LONGEST OF THE 3 BLADES
FIG. A
GROUNDED OUTLET BOX
GROUNDING
MEANS
ADAPTER
FIG. B
Grounding Pin
FIG. C
This tool may be converted to 240 volt power supply circuit by a qualified electrician. If it is converted to 240 volts
it must be equipped with a grounding plug shown in FIG. C and must be connected to an outlet as shown in FIG. C,
which is connected to a permanent ground. No adapter is available or should be used with this tool when converted
to 240 volts.
EXTENSION CORDS
Never use a damaged extension cord. Check extension cords before each use. If damaged,
replace immediately. Touching the damaged area could case electrical shock resulting in serious injury.
Keep the extension cord clear of the work area. Position the cord so it will not get caught on lumber,
tools or other obstructions
• Use proper extension cords. Make sure your extension cord is a 3-wire extension cord which has a 3-prong
grounding type plug and matching receptacle which will accept the machine’s plug, as described in this manual’s
Grounding Instructions. When using an extension cord, be sure to use one heavy enough to carry the current of the
machine. An undersized cord will cause a drop in line voltage, resulting in loss of power and overheating. The table
below shows the maximum gauge to use depending on the cord length. If in doubt, use the next heavier gauge. The
smaller the gauge number, the heavier the cord. Only round, jacketed cords listed by Underwriter’s Laboratories (UL)
should be used.
MINIMUM GAUGE EXTENSION CORD
RECOMMENDED SIZES FOR USE WITH STATIONARY ELECTRIC MACHINES
Ampere
Rating
0-6
0-6
0-6
0-6
6-10
6-10
6-10
6-10
10-12
10-12
10-12
10-12
12-16
12-16
Volts Total Length of
Cord in Feet
240
240
240
240
240
240
240
240
240
240
240
240
240
240
up to 50
50-100
100-200
200-300
up to 50
50-100
100-200
200-300
up to 50
50-100
100-200
200-300
up to 50
50-100
Gauge of
Extension Cord
18 AWG
16 AWG
16 AWG
14 AWG
18 AWG
16 AWG
14 AWG
12 AWG
16 AWG
16 AWG
14 AWG
12 AWG
14 AWG
12 AWG
Ampere
Rating
6-10
6-10
6-10
6-10
10-12
10-12
10-12
10-12
12-16 120 up to 25 14 AWG
12-16 120 25-50 12 AWG
12-16 120
MINIMUM GAUGE EXTENSION CORD
RECOMMENDED SIZES FOR USE WITH STATIONARY ELECTRIC MACHINES
0-6
0-6
0-6
0-6
Volts Total Length of
Cord in Feet
120
120
120
120
120
120
120
120
120
120
120
120
up to 25
25-50
50-100
100-150
up to 25
25-50
50-100
100-150
up to 25
25-50
50-100
100-150
GREATER THAN 50 FEET NOT RECOMMENDED
Gauge of
Extension Cord
18 AWG
16 AWG
16 AWG
14 AWG
18 AWG
16 AWG
14 AWG
12 AWG
16 AWG
16 AWG
14 AWG
12 AWG
8
Page 9
UNPACKING
• The machine is heavy, two people are required to
unpack and lift.
• Use a safety strap to avoid tip over when lifting
machine.
• Prior to tool assembly and use, read this manual
thoroughly to familiarize yourself with proper
assembly, maintenance and safety procedures.
Check shipping carton and machine for damage
before unpacking. Carefully remove components in
top foam layer. Remove the top layer of foam then
remove all components in the bottom layer of foam.
Lay out all parts on a piece of cardboard or other
clean, flat surface. Two or more people are needed to
lift the saw out of the carton. Always check for and
remove protective shipping materials around motors
and moving parts. Do not discard shipping carton and
packing materials until you have carefully inspected the
contents, assembled the machine and are satisfied that
it operates correctly.
Compare package contents to Component Parts List
and Hardware Package List prior to assembly to make
sure all items are present. Carefully inspect parts to
make sure no damage occurred during shipping. If
any parts are missing, damaged or preassembled, do
not assemble. Instead, call DELTA
1-800-223-7278 for assistance.
After assembly remove any protective materials and
coatings from all of the parts and the table saw. The
protective coatings can be removed by spraying
WD-40
This may need to be redone several times before all of
the protective coatings are removed completely.
After cleaning, apply a good quality paste wax to any
unpainted cast iron surfaces. Make sure to buff out the
wax before assembly.
®
on them and wiping them off with a soft cloth.
®
Customer Care at
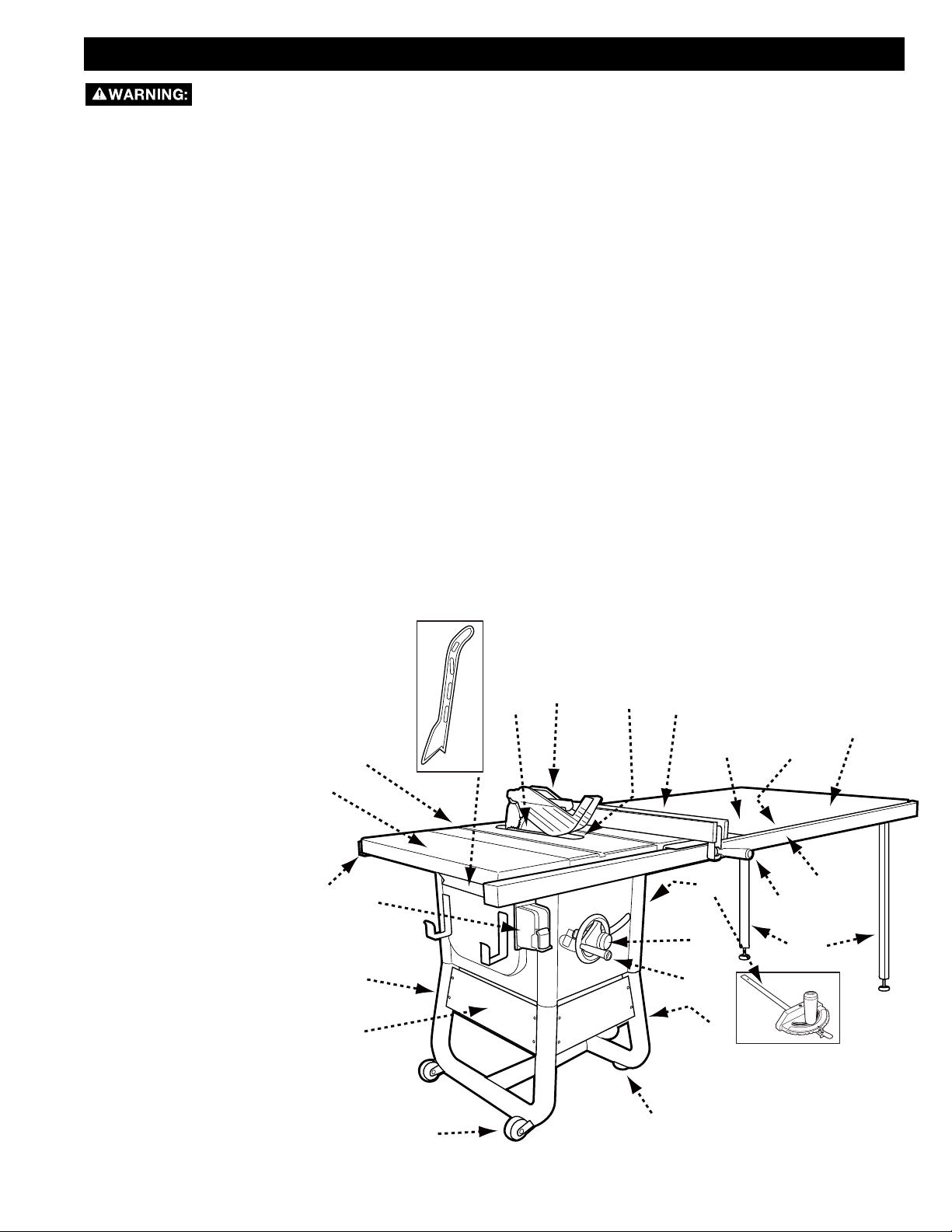
COMPONENT
PARTS LIST
DESCRIPTION (QTY)
1. Table Saw with attached
Carbide Blade, and ClosedEnd Wrench (1)
2. Extension Wing
3. Switch Box (attached to
saw) (1)
4. Tubular Stand (2)
5. Support Panels (4)
6. Fixed Wheels (2)
7. Adjustable Feet (2)
8. Pivoting Pedal and Caster
(not shown) (attached to
saw) (1)
9. Handwheel Handles (2)
(attached to saw)
10. Lock Knobs (2)
11. Miter Gauge (1)
12. Rip Fence Handle (1)
13. Extension Wing (2) with
36-5000 and 5100
(1) with 36-5052 and
36-5152
14. Rip Fence (1)
15. Throat Plate (1)
16. Blade Guard and
Anti-Kickback Pawls
17. Blade (1)
18. Push Stick (1)
19
2
1
4
5
These contents in
separate carton
19. Rear Rail
20. Fence Guide
21. Front Fence Rail
18
3
6
17
16
These contents in separate carton
for 36-5052 and 36-5152 only
22. Wood Table Extension
23. Legs
15
14
22
13
11
21
20
12
10
23
9
8
7
9
Page 10

UNPACKING
HARDWARE PACKAGES
(continued)
30" Fence versions (36-5000 and 36-5100)
Description Qty. Where used
M8 x 70mm Carriage bolt 1 Connect stand halves
M8 nyloc nut 1 Connect stand halves
M8 spring washer 1 Connect stand halves
M6 x 72 mm Carriage bolt 4 Connect stand leg to stand
M6 lock nut 4 Connect stand leg to stand
M8 x 53mm axle pin 2 Wheels
M8 locking nut 2 Wheels
M6 x 10mm Phillips head self tapping screw 16 Stand Panels
5/16-18 x 7/8" Hex Head screw w/spring washer 17 Wings to table 6, wing to wing 3,
1/4-20 x 1/2" Hex Soc button head screw 6 Guid tube to rail
5/16-18 x 1" Flat head screw 8 Front rail to table and wings 8
5/16-18 hex flange nut 19 Wings to table 6, wing to wing 3
Rail alignment gauge 1
Conical Toothed washer 5/16” 1 On 1 screw for the front rail going into table
Flat Toothed washer 5/16” 1 On 1 screw for the rear rail going into table
*
rear rail
rear rail 8, Front rail 8
for electrical ground.
for electrical ground.
8
(36-5000),
* Hardware supplied will accommodate the 36-5000 model saw that uses the most hardware.
Item #
Parts List
153
155
154
144
145
151
155
146
58
35
19
16
190
191
192
52" Fence versions (36-5052 and 36-5152)
Description Qty. Where used
M8 x 70mm Carriage bolt 1 Connect stand halves
M8 nyloc nut 1 Connect stand halves
M8 spring washer 1 Connect stand halves
M6 x 72mm Carriage bolt 4 Connect stand leg to stand
M6 lock nut 4 Connect stand leg to stand
M8 x 53mm axle pin 2 Wheels
M8 locking nut 2 Wheels
M6 x 10mm Phillips head self tapping screw 16 Stand Panels
5/16-18 x 7/8" Hex Head screw w/spring washer 15 Wings to table 6, rear rail 6,
5/16-18 Flat washer 6 wing to wood table, both sides on 36-5052
1/4-20 x 1/2" Hex Soc button head screw 8 Guide tube to rail
5/16-18 x 1" Flat head screw 6 Front rail to table and wings 6
5/16-18 Hex flange nut 15
1/4-20 X 1 1/2" Hex Head Screw 6 Rails to wood table
1/4" Flat washer 12 Rails to wood table
1/4-20 hex nuts 12 Rails to wood table
#8 x 3/4" Phillips head self tapping screw 8 legs to table
#10-32 x 1 3/4" screws 4 legs to table
#10 flat washer 4 legs to table
#10-32 hex nuts 4 legs to table
Rail alignment gauge 1
Conical Toothed washer 5/16” 1 On 1 screw for the front rail going into table
Flat Toothed washer 5/16” 1 On 1 screw for the rear rail going into table
**
Wing to wood ta
Rear rail 6, Front rail 6, wing to wood
table 3,
for electrical ground.
for electrical ground.
(36-5052)
ble 3
Item #
Parts List
153
155
154
144
145
151
155
146
58
193
35
19
16
183
184
185
182
180
179
181
190
191
192
** Hardware supplied will accommodate the 36-5052 model saw that uses the most hardware.
10
Page 11
ASSEMBLY
B
• Do not lift saw without help. Hold it close to your
body while lifting. Keep knees bent and lift with your
legs, not your back.
• Fully assemble saw with leg assembly prior to use.
Leg assembly is an integral and necessary part of the
support structure for this saw.
• Do not modify saw, or create accessories not
recommended for use with this saw.
• Make sure power switch is in “OFF” position before
connecting to power supply.
• Do not connect to power supply until assembly is
complete
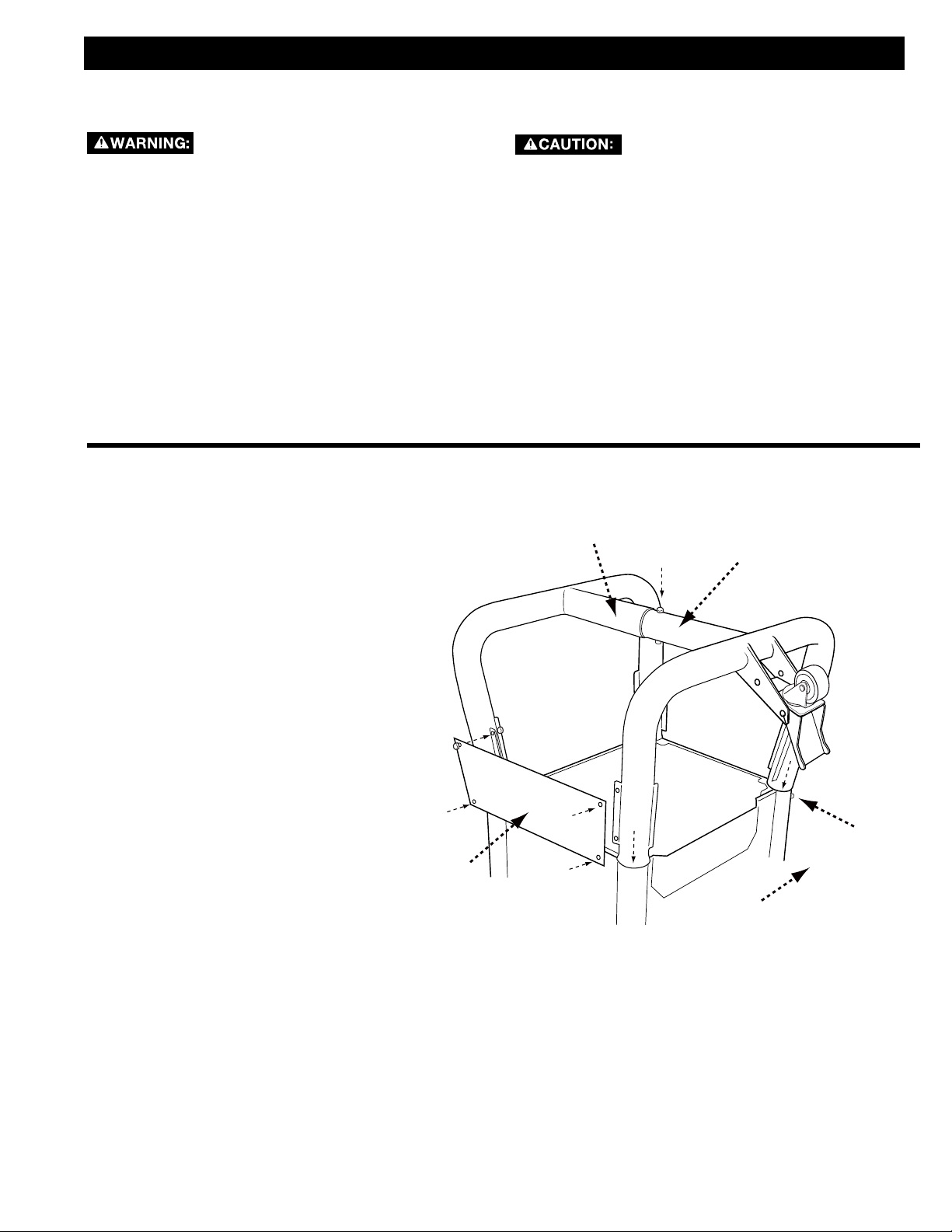
STAND
Avoid contact with blade teeth. Keep
blade stored or lowered when possible.
TOOLS REQUIRED FOR ASSEMBLY
(not included)
• Slotted screwdriver
• Phillips head screwdriver
• 8mm wrench
• 10mm wrench
• 12mm wrench
• 13mm wrench
• 3/8-inch wrench
• 7/16-inch wrench
• 1/2-inch wrench
• 9/16-inch wrench
• 6mm Allen hex wrench
• 5/32-
• 3/16-inch Allen wrench
inch Allen wrench
1. Connect the two tube legs by inserting
the end of the left leg (A) into the end
of the right leg (B) as shown in Figure 1.
Secure with a M8 x 70mm carriage bolt,
lock washer and nyloc nut and tighten.
2. Insert the four open ends of the tube
legs into the leg collars (C) as shown.
Secure each leg with a 6mm x 70mm
bolt and nut.
3. Attach the back and front leg support
panels (D) to the legs using four M6 x
12mm self-tapping bolts.
A
C
D
Saw Front
11
FIGURE 1
Page 12
ASSEMBLY
(continued)
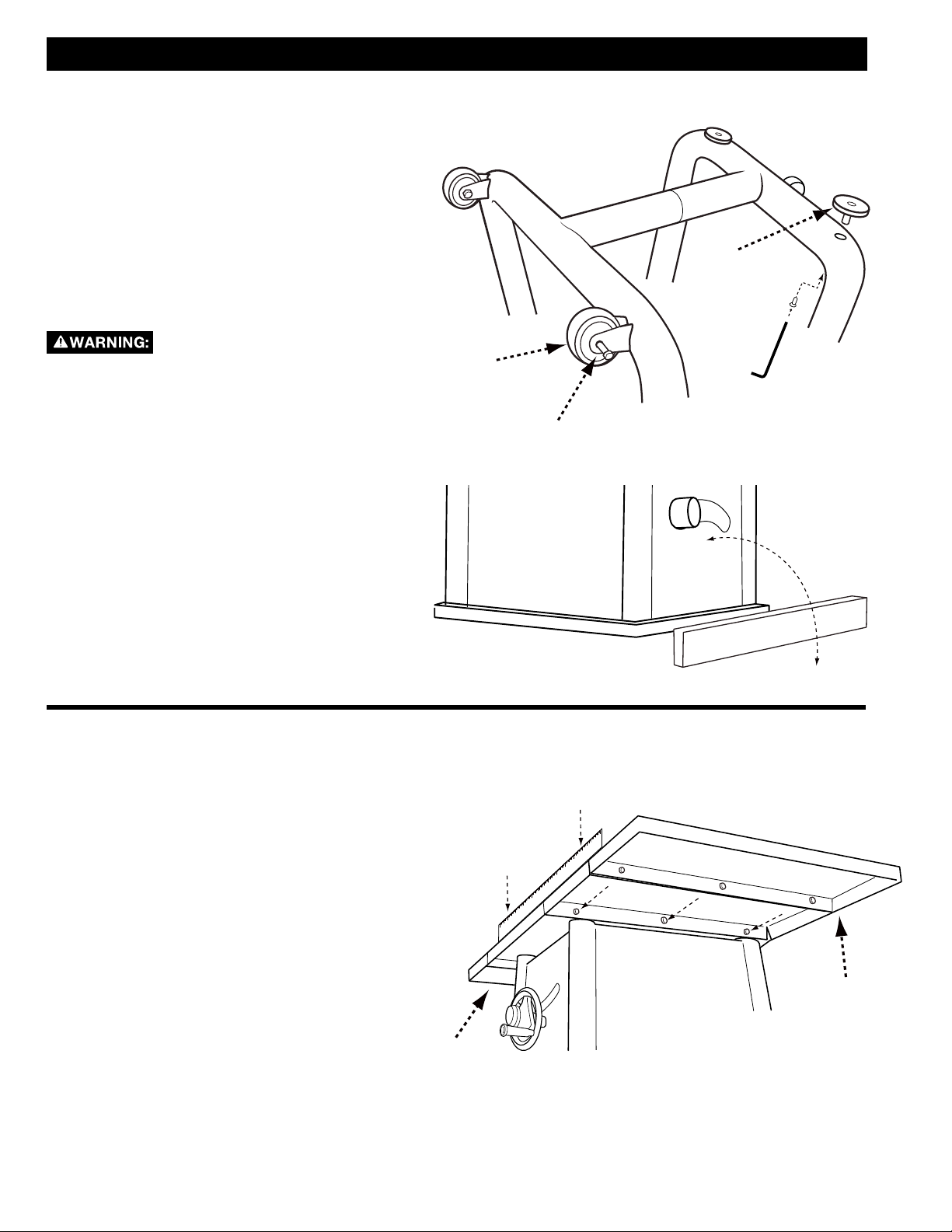
FIXED WHEELS AND STATIONARY FEET
1. Attach the two fixed wheels (A) to the two
left leg, opposite the pivot caster, using the
carriage shoulder bolt as in Figure 2.
2. Screw the adjustable feet (C) into the threaded
inserts in the right leg, next to the pivot caster.
3. Lay a scrap piece of 2x4 in back of the saw, as
shown in Figure 3, to prevent damage to the
dust chute when righting the saw.
4. Stand the saw right side up.
The machine is heavy, two
people are required to stand the
machine up.
5. The two adjustable feet (C) can be raised and
lowered by rotating them. The feet may be
adjusted to level the saw and locked in place
with the locking set screws already assembled
in the frame, using a 6mm allen hex wrench.
See Figure 2.
A
C
FIGURE 2
B
EXTENSION WINGS
For Models with Three Extension Wings
1. Attach the left side extension wing (A) to the
table using three 5/16-18 x 7/8” hex head
screws.
2. Lay the two remaining wings upside down on
the saw table. Place the side of the wing that
will mount to the saw table near the edge of
the saw table, so that the hole pattern in the
wing matches the hole pattern of the saw. If
you have cast iron wing, it will mount to the
saw table. Place the other wing adjacent to
the wing so the holes patterns match. Fasten
the two wings together using three 5/16-18
x 7/8 inch hex head screws and mating hex
flange nuts.
3. Turn the two wings fastened together (B) over
and fasten them to the saw table using three
5/16-18 x 7/8 inch hex head screws.
4. Make sure the top edges of the wings are flush
with the top of the table and tighten all six
screws.
A
FIGURE 3
12
11
10
9
8
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
INCH
0
B
FIGURE 4
12
Page 13
ASSEMBLY
Table
Gauge
Rail
Table
Gauge
Rail
(continued)
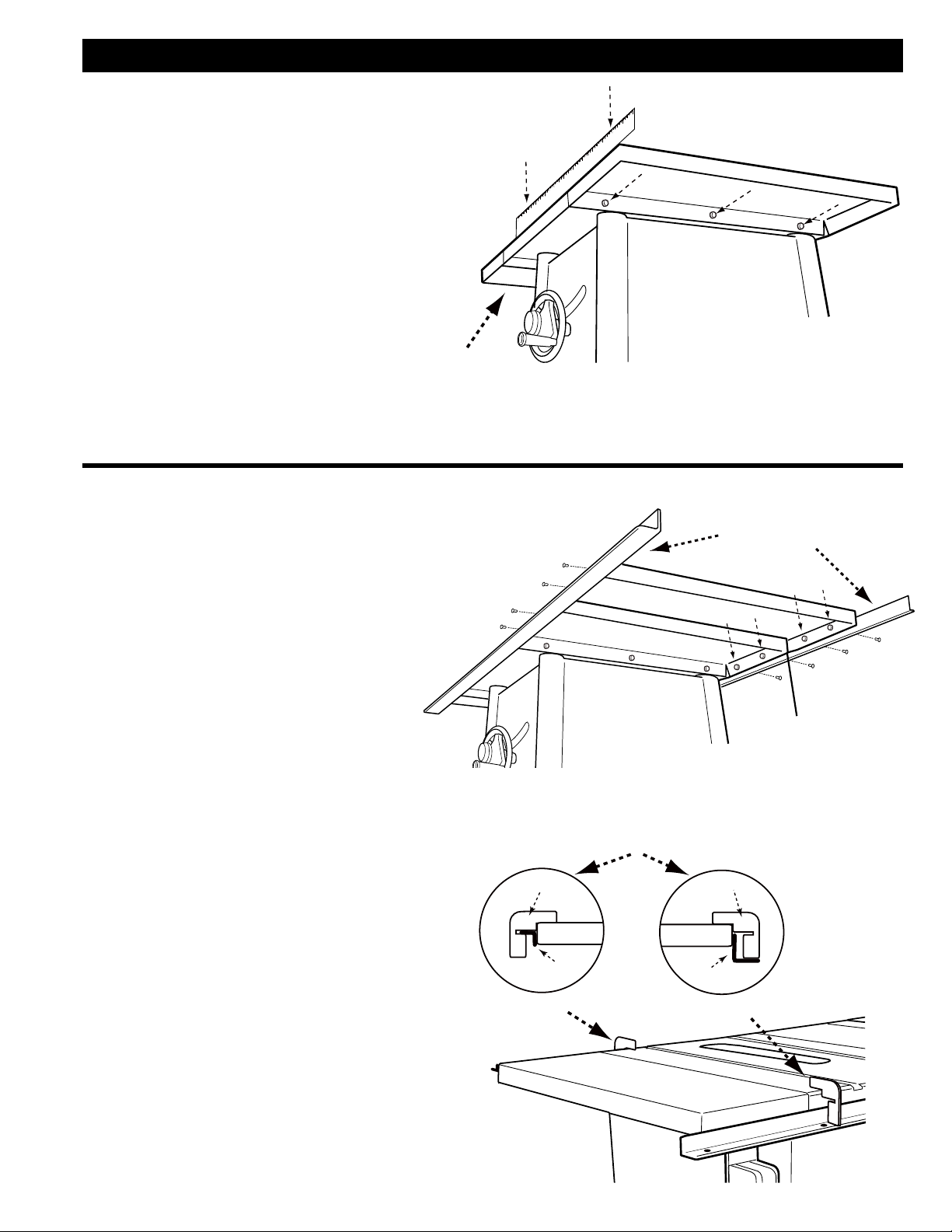
EXTENSION WINGS
For Models with Two Extension
Wings and a Wood Extension Table
1. Attach the left and right side extension
wings (A) to the table using three 5/1618 x 7/8” hex head screws for each
wing.
2. Make sure the top edges of the wings
are flush with the top of the table and
tighten all six screws.
3. Proceed to rail assembly.
FRONT AND REAR RAILS
1. Attach the front rail (A) (2” X 2” X 57” for
the 30” rip capacity models), (2” X 2” X
79” for the 52” rip capacity models), to
the saw table and extension wings using
5/16-18 x 1 1/8inch flat head screws.
Align the holes in the rail with the holes
in the table and extension wings.
2. Use supplied rail alignment gage (B) to
ensure the rail is the proper distance
from the top of the table at each side of
the cast iron table. (fig 6) Then use the
alignment gage to set the same proper
distance for the extension wings.
3. Align the rear rail to the holes in the
rear of the saw table and extension
wings. Attach the rear rail to the saw
table using two 5/16-18 x 7/8 Hex head
screws.
4. Attach the rear rail to the extension
wings using 5/16-18 X 7/8 inch hex head
screws and Hex flange nuts.
5. Use supplied rail alignment gage (B) to
ensure the rail is the proper distance
from the top of the table at each side of
the cast iron table. (fig 6) Then use the
alignment gage to set the same proper
distance for the extension wings.
A
2
1
INCH
0
Back
12
11
10
9
8
7
6
5
4
3
FIGURE 5
A
C
B
Front
FIGURE 6
13
Page 14
ASSEMBLY
D
G
(continued)
WOOD EXTENSION TABLE
52” rip capacity models only
1. Lay the wood table (A) upside down on floor or
bench.
2. Position legs (B) in corner as shown (fig 7) the
vertical wall of the angle plate on the leg should
be against the end wood wall (C) of the table.
3. Fasten the legs to the table board with (8) #8 x
5/8” self-tapping screws (D).
4. Carefully drill through the holes in the vertical
angle plate holes and the wood wall of the table
with a ¼ inch drill. Feed the #10 by 1 ¾” screws
(E) through the drilled holes from the outside,
then assemble the #10 washers and nuts onto
the screws and tighten.
5. Loosely assemble (3) 5/16-18 x 7/8 inch screws,
washers and nuts (F) into the three holes in the
side of the extension wing as shown. (fig 8)
6. Carefully lower the slotted steel angle table
bracket (G) down onto the screws on the
extension wing. Tighten the screws after the
wood table is leveled with the extension wing.
7. Using the rail alignment gauge (H) adjust the
feet in the legs (I) so the top of the table is at the
proper distance from the rail.
8. Drill ¼ inch holes through the rail holes (J) into
the wood table on the front and back rails. (fig 9)
9. Fasten wood table to rails with ¼-20 X 1 ½ inch
screws, flat washers, lock washers, and nuts.
A
F
B
E
C
FIGURE 7
FIGURE 8
J
H
I
FENCE GUIDE AND POWER CONTROL BOX
1. Connect the fence guide tube (A) by inserting the smaller
end into the larger end. See Figure 10
2. Attach the fence guide to the front rail using four (for
30" versions) six (for 52" versions) 1/4-20 x 1/2-inch hex
button head screws and ¼-inch spring washers
through the holes (B) on the bottom side of
the front rail.
3. Align the two holes in the power
control box bracket with the holes
underneath the front rail (C), located
on the left side of the saw. Secure
the power control box to the front rail
using two1/4-20 x 1/2-inch button
head screws.
4. Fix the hanging power cord at rear side of
front rail by wire clip and M5 x 6mm round
head cross screw.
C
FIGURE 9
A
B
FIGURE 10
14
Page 15
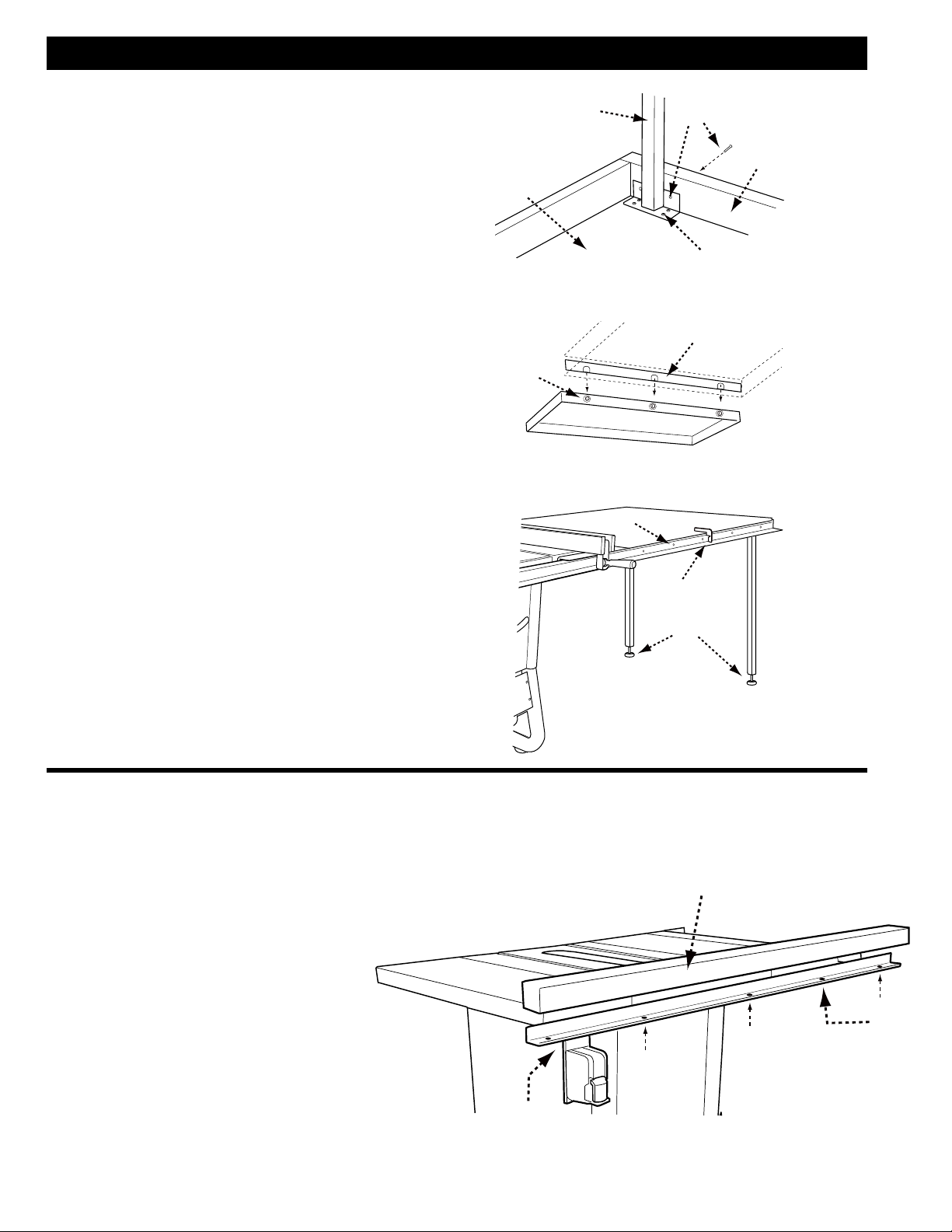
THROAT PLATE
ASSEMBLY
(continued)
1. To install throat plate, lower blade below tabletop,
then carefully feed the throat plate, with plate end
first, from the front of the table to the rear, keeping
the blade centered within the slot on the throat
plate. See Figure 11. The plate should rest within
the cavity in the tabletop on top of 5 flat head
screws.
2. Ensure that the throat plate is flush with the top of
the table.
3. If the throat is not flush with the tabletop, adjust
the height of the throat plate using the five set
screws (A) below the throat plate.
NOTE: When installing riving knife, anti-kickback
pawls and blade guard, blade must be at 90° setting
and raised to the maximum height. See Raising and
Lowering Blade, page 18.
BLADE AND RIVING KNIFE
To reduce the risk of serious
personal injury, the riving knife must
be installed and properly positioned for every
possible through and non-through cut.
1. Your saw is shipped with the blade and riving knife
installed and properly aligned. The riving knife
comes installed in the low, non-through cutting
position. Prior to operating your saw, check
to make sure the alignment of the blade to the
A
FIGURE 11
miter slot and the riving knife to the blade was not
affected by shipping. To check alignment of the
blade and riving knife, see page 28 in the Alignment
section of this manual.
2. The riving knife comes installed in the low, nonthrough cutting position. To attach the antikickback pawls and blade guard assemblies, the
riving knife must be in the raised position as shown
in Figure 12. To raise and lower the riving knife, see
Riving Knife Height Settings on page 20.
ANTI-KICKBACK PAWLS AND BLADE GUARD
ANTI-KICKBACK PAWLS
To reduce the risk of serious
personal injury, anti-kickback pawls
must be in place when making a through cut.
1. Refer to Figure 12 and locate the anti-kickback
pawls mounting slot (A) in the middle of the top
edge of the riving knife.
2. Slide slot in the middle of the anti-kickback pawls
assembly along the top of the riving knife until the
stem (B) locates the center slot on the riving knife.
3. Depress the stem on the anti-kickback pawls
assembly (B) to allow the assembly to drop
into the slot. Push down on the anti-kickback
pawls assembly until it snaps into place and
locks. Release stem. NOTE: Pull up on the anti-
kickback pawls to make sure it is locked in
place.
15
To remove the anti-kickback pawls, depress the stem
(B) and pull the anti-kickback assembly off the riving
knife.
B
A
FIGURE 12
Page 16
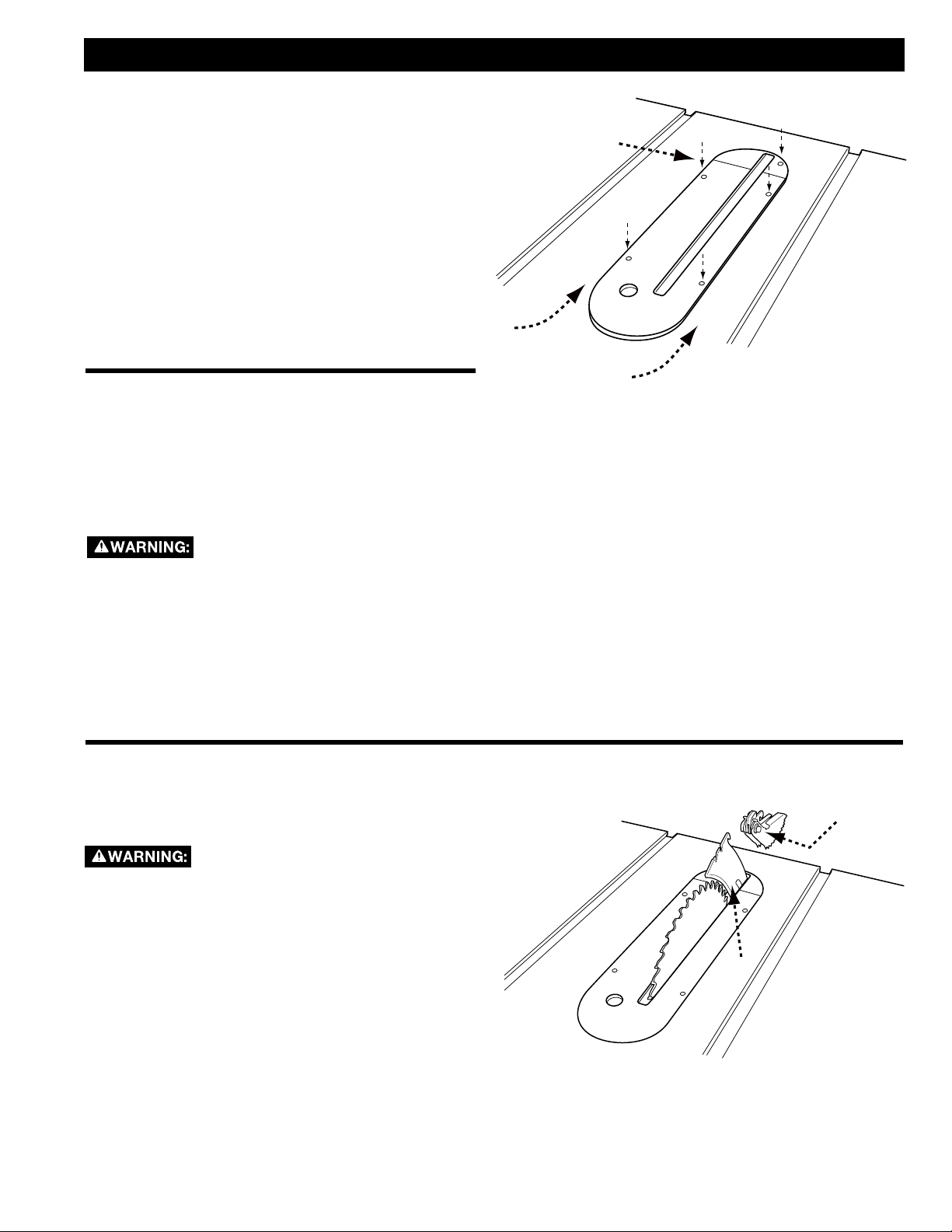
ASSEMBLY
BLADE GUARD
To reduce the risk of serious personal
injury, the blade guard must be in
place when making a through cut.
1. While holding the blade guard assembly (A) in a
vertical position, hook the locating pin (B) at the
back end of the blade guard assembly into the slot
at the back edge of the riving knife.
2. Rotate the blade guard assembly toward the front
of the saw until the metal portion (C) of the blade
guard assembly is parallel to the table as shown in
Figure 13.
3. While holding down on the front of the metal
portion of the guard (C) press the blade guard
lock lever (D) down until it snaps into the locked
position. Check to make sure the guard is locked
onto the riving knife by pulling on the guard. If the
guard is not locked, the blade guard lock lever will
flip up to the unlocked position.
If the metal portion of the blade guard
assembly (C) is not parallel to the
table, the riving knife is not in the raised position.
Remove blade guard assembly and anti-kickback
pawls and raise riving knife, then reinstall the antikickback pawls and the blade guard assembly.
(continued)
D
C
A
B
FIGURE 13
To remove the blade guard assembly:
1. Lift the blade guard assembly lock lever (D) to the
unlocked position.
2. Rotate the guard back and slide the pin (B) from the
riving knife slot.
RIP FENCE
Attach the handle to the fence cam
The rip fence slides onto the rear fence rail so that the
hook is under the rear rail and rides on the front guide
tube. The fence locks in place by applying pressure in
a downward motion on the rip fence handle. Rip fence
alignment should be checked prior to using your saw.
To check alignment of the rip fence, see alignment
instructions on page 29.
MITER GAUGE
Insert miter gauge into each miter slot to make sure it
slides freely. See Adjusting the Miter Stops section on
page 28 for adjustment of miter gauge accuracy.
ON-BOARD STORAGE
The Delta #36-5000 series contractor table saw
comes with on-board storage for the provided miter
gauge, arbor wrench, push stick and fence. There
is also on-board storage for spare saw blades (sold
separately). The miter gauge, spare blade and arbor
wrench storage areas are located on the right side
panel of the machine and come pre-installed.
On-board storage for the fence and the push stick is
located on the left side of the saw.
16
Page 17
(continued)
ASSEMBLY
ADJUSTING 90° AND 45° POSITIVE BEVEL STOPS
There are positive stops at each end of the bevel
range. To ensure accurate cuts, the positive stops
must be positioned at exactly at 90° and 45°. The bevel
stops are properly adjusted as shipped. However, for
maximum accuracy, you should check the position
of the stops upon assembly and from time to time to
assure that the settings remain satisfactory. To check
the position of the stops and adjust if necessary, refer
to Figure 14 and do the following.
1. Release the blade tilt lock knob.
2. Rotate the blade tilt handwheel clockwise and tilt the
blade away from, then back toward perpendicular
until the stop is reached the "stop position".
3. Using a carpenter’s square, check the angle of the
blade face to the table, as shown in Figure 20b,
page 20. If the blade is at 90° to the table, proceed
to Step 6.
4. If the blade is not perpendicular to the table, turn
handwheel to slightly tilt the blade away from the
stop position then adjust the 90° stop by rotating
the socket set screw located in the table top
immediately in front of the left side of throat plate
(A). Re-check angle using the carpenter’s square
and continue to adjust until the blade is at 90
degrees when returned to the stop position.
5. Rotate the blade tilt wheel counterclockwise until
it rests on the 45° stop. Then repeat Steps 4 and
5, adjusting the 45° stop by rotating the socket set
screw located in front of the right side of the throat
plate. (B)
B
A
FIGURE 14
SECURING SAW TO FLOOR
This saw is designed for portability. Do
not attempt to use the saw to cut a
large or cumbersome workpiece without first taking
appropriate steps to protect against tipping the saw.
Examples of appropriate steps include the use of
support tables and/or securing the saw legs to the floor
by replacing the saw feet with connecting bolts or by
attaching the legs to a floor mounted bracket with
u-straps.
PREPARING TO CUT
Failure to comply with the following
warnings may result in serious
personal injury.
ALWAYS
•
with the blade before operating the switch to start
the saw. Blade contact could result in kickback or
thrown workpiece.
• To reduce the risk of accidental starting, ALWAYS
make sure the switch is in the off position before
plugging saw into power source.
make sure your workpiece is not in contact
DO NOT
•
this tool. Failure to heed this warning could result in
serious personal injury.
• Turn unit off and disconnect it from power source
before installing and removing accessories, before
adjusting and when making repairs. An accidental
start-up can cause injury.
• Prior to operating the saw, make sure you are familiar
with its features and controls, and have made all
necessary adjustments as described below.
use blades rated less than the speed of
17
Page 18

PREPARING TO CUT
ASSEMBLY
RAISING AND LOWERING THE
BLADE
For most applications, it is recommended that you
raise the blade 1/8-inch (3.2mm) to 1/4-inch (6.4mm)
above the top surface of the workpiece.
Raise or lower the blade with the hand wheel (A)
located on the front of the saw (fig 15).
1. Before raising or lowering the blade, be
sure to loosen the lock knob (B) by turning it
counterclockwise.
2. To raise the saw blade, turn the hand wheel
clockwise. To lower the saw blade, turn the hand
wheel counter-clockwise.
3. Tighten lock knob to keep blade at the desired
height. Only a small amount of force is required to
lock the blade raising mechanism securely. Any
added force merely puts unnecessary strain on the
locking device.
4. When done operating the saw, and when
performing maintenance, adjustments or repairs,
lower blade below surface of table.
(continued)
B
A
FIGURE 15
TILTING THE BLADE
The blade can be tilted up to 45° to the left using the
blade tilt wheel (A) located on the right side panel of
the saw. The angle of tilt is measured by the bevel
gauge on the front of the saw. To tilt the saw blade:
1. Loosen the lock knob (B) counterclockwise and
turn the hand wheel clockwise. A pointer on
the front of the saw indicates the angle of tilt in
½-degree increments.
2. To lock the saw blade at your desired angle, tighten
the lock knob by rotating it clockwise.
A
B
FIGURE 16
18
Page 19
PREPARING TO CUT
ASSEMBLY
SELECTING AND STORING SAW BLADES
(continued)
Riving knives must be matched to saw blade
dimensions in order to function effectively.
The saw blade furnished with your new saw is a
10-inch (254 mm) combination blade, used for cross
cutting (across the grain) and ripping (with the grain)
through the workpiece. The arbor hole of the blade is
5/8-inch (16 mm) diameter. This blade will produce a
good quality cut for most applications.
There are many types of blades available to do specific
and special jobs such as cross cut only, rip only, dado
cuts thin plywood, paneling, etc.
CHANGING THE SAW BLADE
• Use only 10-inch (254 mm) diameter blades with
5/8-inch (16mm) arbor holes, rated at 3,600 rpm or
higher, 0.102-inch (2.6mm) minimum kerf width and
0.073-inch (1.8mm) maximum body thickness.
• To reduce the risk of injury, turn unit off and
disconnect it from power source before installing
and removing blades and accessories, before
adjusting and when making repairs. An accidental
start-up can cause injury.
1. Remove the throat plate and raise the saw blade
to its maximum height.
2. Push and hold arbor lock button (A) shown in
Figure 17.
3. Use included arbor wrench to remove the blade
retaining nut and flange (B). Remove old blade.
Use only saw blades designed for maximum safe
operating speeds of 3,600 RPM or greater.
Saw blades should always be kept sharp. It is
recommended that you locate a reputable sharpening
service to sharpen your blades when needed.
Never stack blades on top of one another to store.
Place material such as cardboard between them to
keep the blades from coming in contact with one
another, or place them in storage drawer.
Abrasive wheels or blades (including diamond) should
not be used on this saw.
4. Place the new blade on the arbor
with the teeth pointing down as
the blade rotates toward the
front of the saw table.
5. Replace and tighten the blade
retaining nut and flange.
6. Replace throat plate.
A
B
FIGURE 17
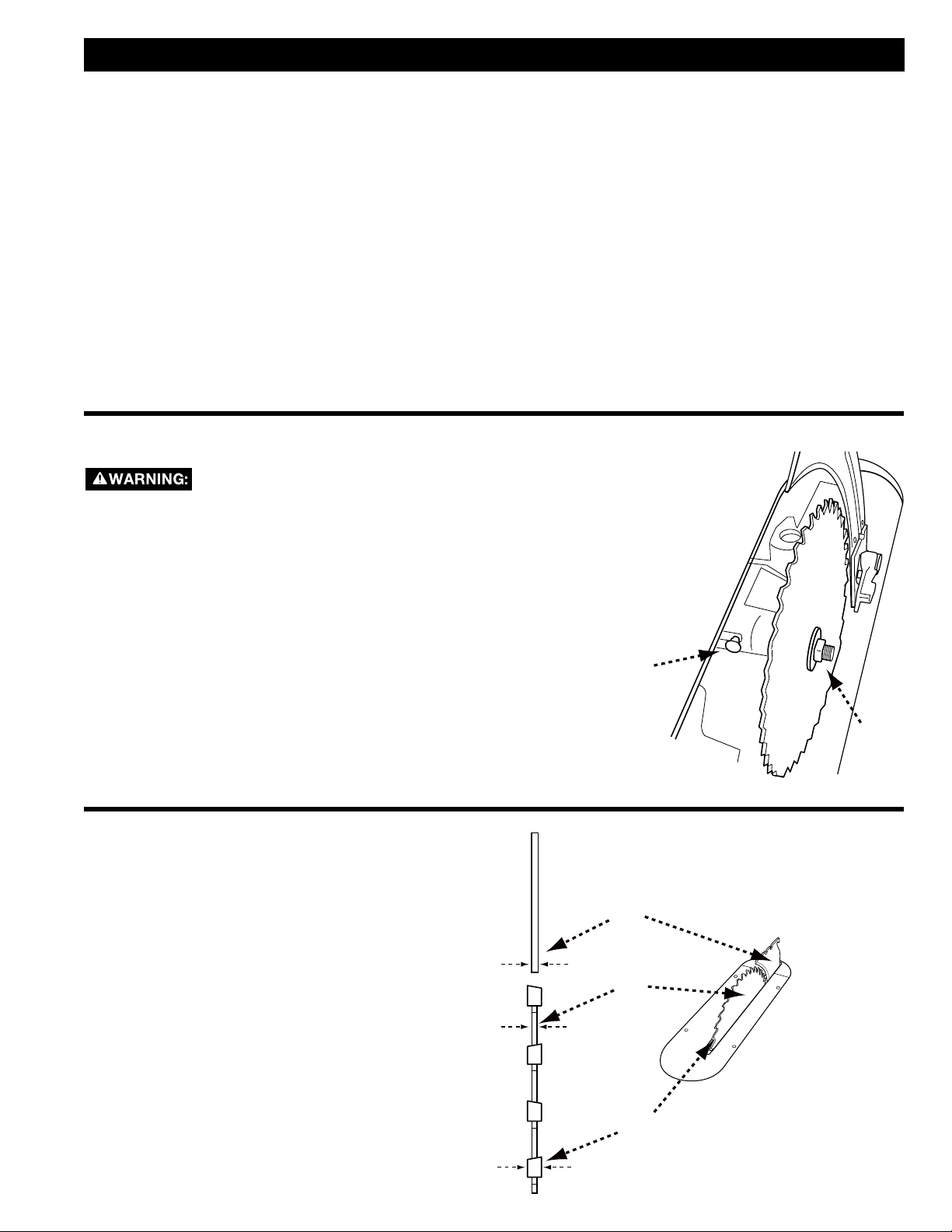
RIVING KNIFE POSITION
NOTE: Safety devices, blade guard assembly and anti-
kickback assembly have been removed in Figure 18 in
order to show the location of specific features. When
operating the saw, these safety devices should be in
place and working properly.
The riving knife is a flat plate that fits into the cut made
by the saw blade and effectively fights kickback by
lessening the tendency of the blade to bind in the cut.
It must be installed and properly positioned for every
through cut and for every non-through cut unless the
riving knife would interfere with the workpiece.
The riving knife thickness (A) must be greater than the
blade body or plate thickness (B) and less than the
kerf or cutting width (C) as shown in Figure 15. The
riving knife provided with this saw is 2.2mm thick and
may be used only with a 10-inch (254mm) blade with
0.102-inch (2.6mm) minimum kerf width and 0.073-inch
(1.8mm) maximum body thickness. Do not attempt to
use this riving knife with blades that are not
within these dimensions.
A
B
C
FIGURE 18
19
Page 20
PREPARING TO CUT
A
B
(continued)
RIVING KNIFE HEIGHT
SETTINGS
The height of the riving knife should be adjusted based
on the type of cut being made. For all through cuts
(when the wood is completely severed), it should be
in the raised position, with anti-kickback fingers and
guard installed. For non-through cuts (when the blade
does not penetrate the top of the workpiece), the
riving knife should be in the lowered position and antikickback fingers and guard removed.
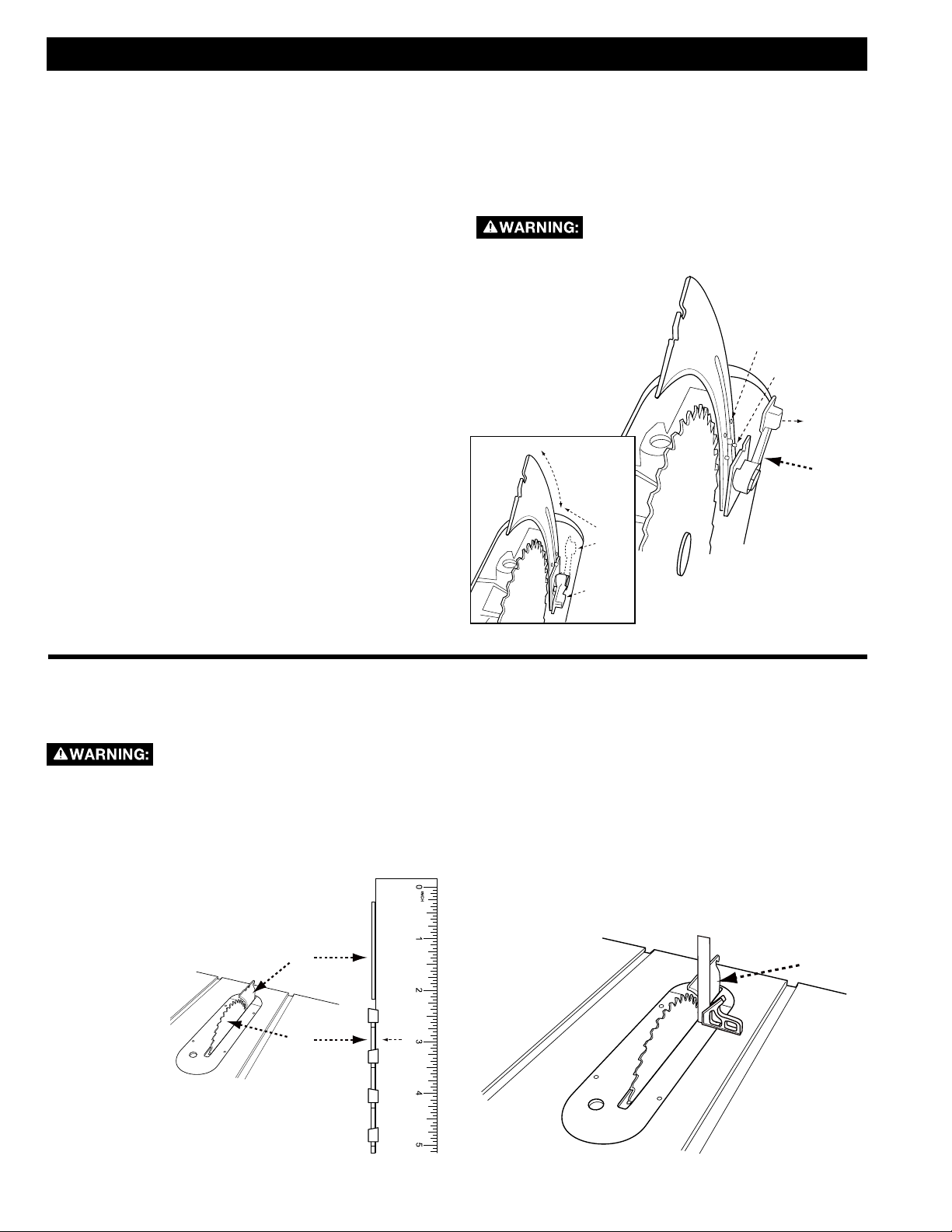
TO RAISE OR LOWER THE RIVING KNIFE:
1. Remove throat plate.
2. Raise blade to full height above table.
3. Pull riving knife release lever (A) up to release riving
knife from clamping mechanism. See Figure 19.
4. Push riving knife and release lever to the arbor side
of the blade to disengage riving knife from pins.
a. To adjust the riving knife into the through-cut
position, pull riving knife up to lower detent
pins.
b. To move the riving knife into the non-through
cut position, push it down to upper detent
pins.
NOTE: When adjusting the riving knife up or down, be
sure to pull in a radial motion, as shown.
1. Release lever and pull on riving knife to make sure it
is properly seated in the raised or lowered position.
2. Securely clamp riving knife by pushing riving
knife clamping lever back down to the horizontal
position.
3. Replace throat plate.
DO NOT operate saw unless riving
knife is securely clamped in the raised
position for through-cutting or the lowered position
for non through-cutting.
Lower
Position
Detents
Upper Position
Detents on Pins
Pull Away
to Release
Riving Knife
A
Adjust
Locked
FIGURE 19
CHECKING RIVING KNIFE
ALIGNMENT
Before connecting the table saw to
the power source and operating the
saw, always inspect the blade guard assembly and
riving knife for proper alignment and clearance with
saw blade. Check the riving knife alignment after
each blade change.
TO CHECK ALIGNMENT:
1. Horizontal Alignment: Lay a
straight edge on the table against
blade face (A) and make sure
it extends out along the
riving knife (B),
as shown
in Figure
20a. The
riving knife
should just
touch the
straight
edge.
Be sure the straight edge
goes between the teeth and
rests on the blade face and
the riving knife for proper
alignment.
FIGURE 20a
1. Vertical Alignment: Place a carpenter’s square on
the table and against the blade face and make sure
it extends up along the riving knife (B) as shown in
figure 20b. The riving knife and blade should touch
the carpenter’s square with no gaps. Be sure the
straight edge goes between the teeth and rests
on the blade face and the riving knife for proper
alignment.
If the riving knife and blade are out of horizontal or
vertical alignment, refer to riving knife alignment
instructions on page 30 of this manual.
B
FIGURE 20b
20
Page 21
PREPARING TO CUT
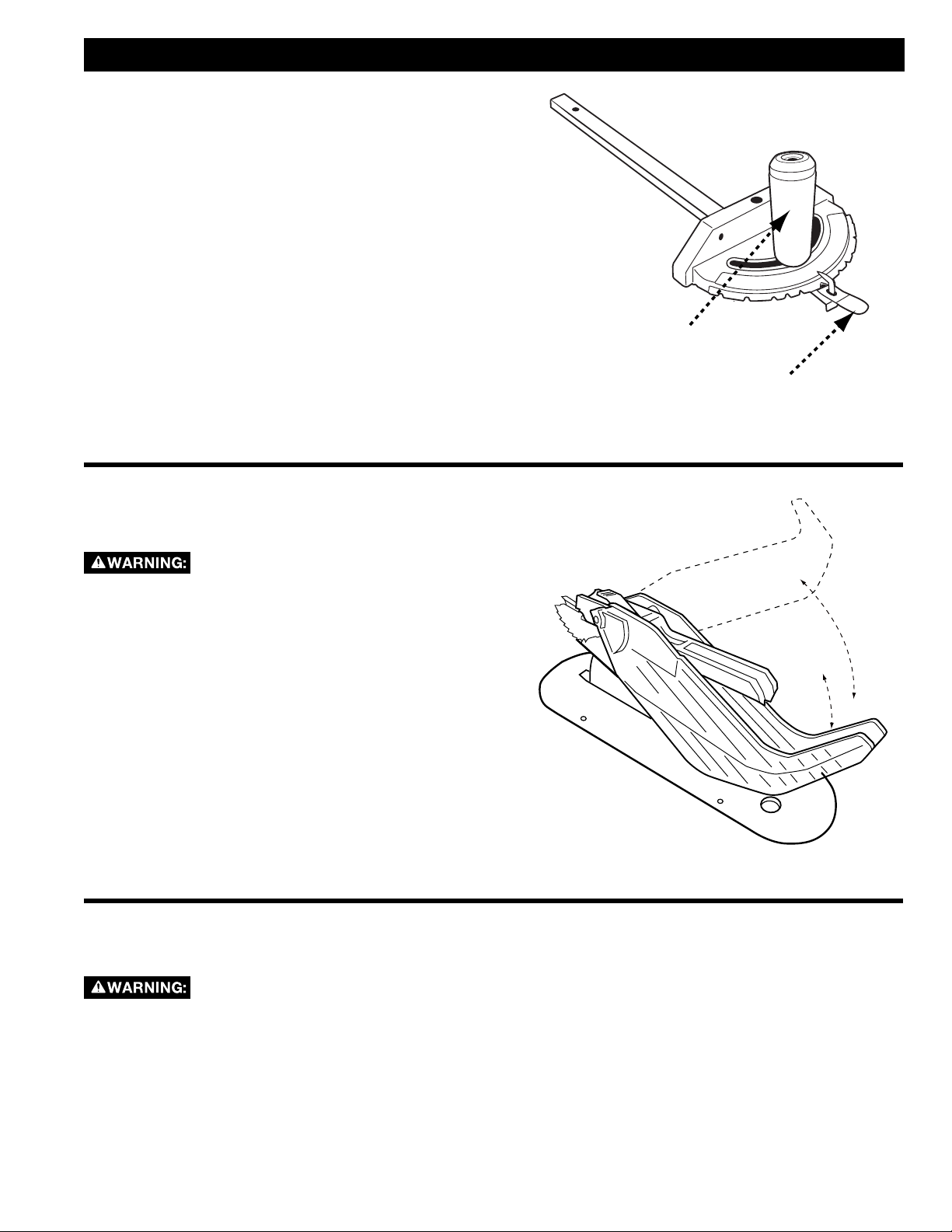
USING THE MITER GAUGE
The miter gauge is equipped with adjustable index
stops at 90°, 75°, 60°, 45° and 30°. To set the miter for
an angled cut, see Figure 21 and:
1. Loosen the handle (A).
2. Depress the thumb lever (B).
3. Move the body of the miter gauge to the desired
angle.
4. Release the thumb lever and retighten the handle.
The miter gauge is equipped with a washer on the end
of the bar which fits into the t-slot in the table. This
allows the miter gauge to be pulled off the front edge
of the table without falling. This allows for an increased
workpiece capacity in front of the blade.
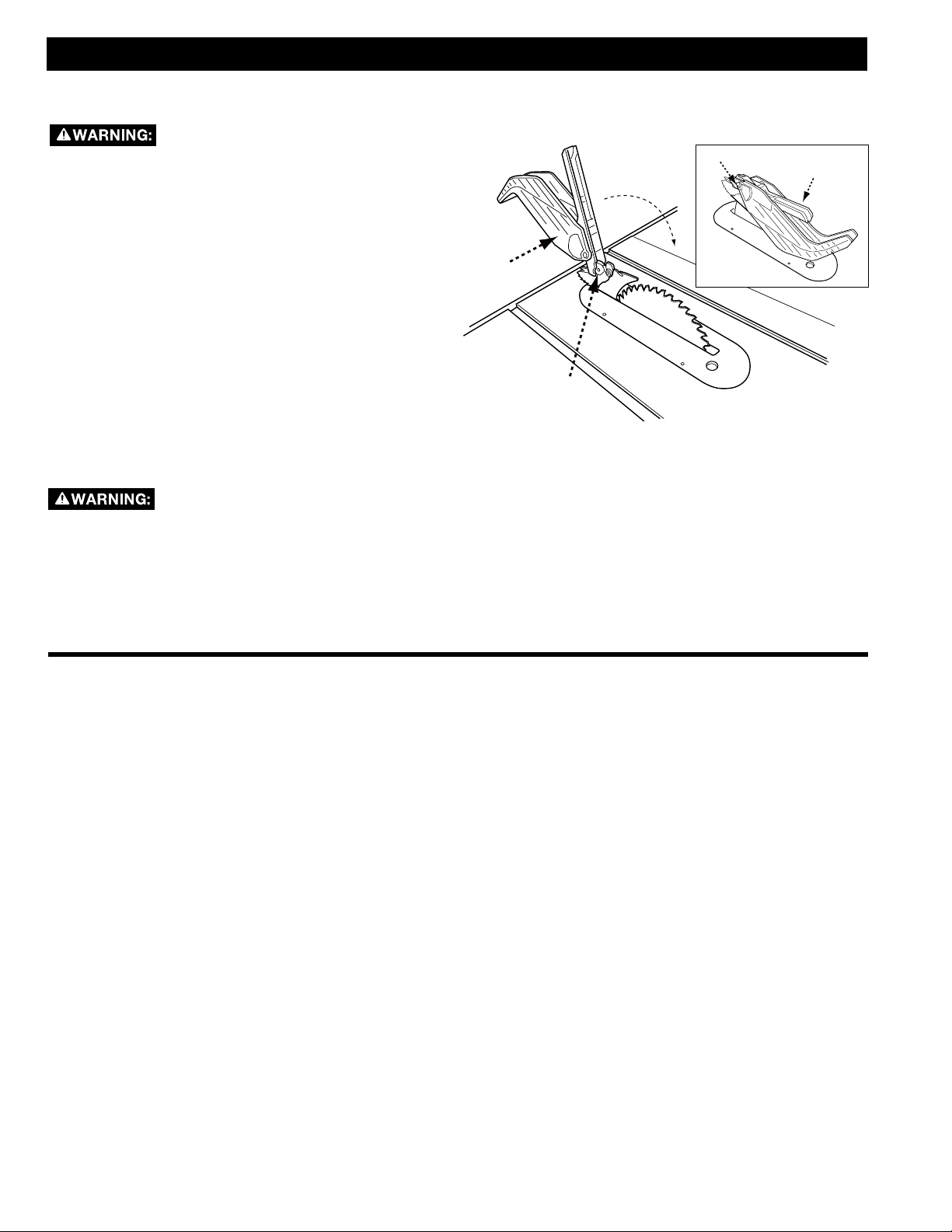
USING BLADE GUARD
ASSEMBLY
(continued)
A
FIGURE 21
B
The anti-kickback pawls and blade
guard must be used for all throughcuts. Keep both guard shields down and arms, hands
and fingers away from the blade, blade guard and
anti-kickback pawls when power is on to prevent
serious injury. See assembly instructions on page 13
for proper installation and removal of anti-kickback
pawls and blade guard.
If there is a need to briefly raise the blade guard (for
example, to make a measurement) the guard can be
parked in a raised position.
1. Refer to Figure 22 and, lifting the guard from the
front, raise the guard shield until it snaps into a
locked position above the table. One or both guard
shields can be raised.
2. When done making the measurement, return guard
to operating position.
CHECKING FENCE ALIGNMENT
Do not attempt to use a rip fence that
is not properly aligned.
Every time you use the rip fence, check its alignment
to make sure the fence is parallel to the miter slot. To
check the alignment of your rip fence, place the fence
adjacent to miter slot and lock the fence in place. If the
fence is not aligned to the miter slot from the front to
the back, see instructions for aligning rip fence on page
29 of this manual. If you are not able to successfully
align the rip fence, replace the rip fence or contact
1-800-223-7278 for further instructions.
FIGURE 22
21
Page 22
OPERATION
Failure to comply with the following the warnings may result in serious personal injury.
READ ENTIRE MANUAL. In addition to reading these operating instructions, it is important to read and understand
the entire manual before operating this saw. Follow all applicable instructions regarding assembly, preparation, and
adjustment prior to making any cuts and comply with all safety rules and warnings in this section and elsewhere
throughout this manual.
1. Each time you use the saw, run through the
following checklist:
• Are the power source and power connections
adequate for the saw?
• Are the saw and work area free of clutter and
by-standers?
• Is the blade tight and properly aligned?
• Does the riving knife thickness match the blade?
• Are the blade and riving knife properly aligned?
• Is the operator qualified to make the cut and familiar
with all of the relevant safety rules, warnings and
instructions included in this manual?
• Is the operator and everyone in proximity to the saw
wearing appropriate eye, hearing and respiratory
equipment?
• Are the bevel angle and height adjustment knobs
locked in the proper position?
• Is the blade set at the proper height?
• If ripping, is the rip fence parallel to the blade and
securely locked in position?
• If crosscutting, is the miter gauge knob tight?
• If making through cuts with a standard blade, are
the blade guard riving knife and anti-kickback pawls
properly attached and properly functioning with both
guards contacting the table surface?
• Is there proper clearance and support for the
workpiece as it leaves the blade?
• Are any cutting aids needed? If so, are they in place,
or within reach for proper use?
2. The use of attachments and accessories not
recommended by DELTA® Power Equipment
Corporation may result in injury.
3. Replace or sharpen the anti-kickback fingers
when the points become dull.
4. Make sure saw is stable and cutting can be
accomplished without tipping the saw. Do not
attempt to cut large workpieces without securing
saw to a stable surface. To properly secure the
saw, see instructions in section entitled Securing
Saw to the Floor on page 15 of this manual.
5. Never use the fence and miter gauge together
without using a cutoff block as previously
described.
6. The proper throat plate must be in place at all
times.
7. If your saw makes an unfamiliar noise or if it
vibrates excessively, cease operating immediately
until the source has been located and the problem
corrected.
8. Never perform freehand cutting, plunge cutting,
re-sawing or cove cutting.
AVOID KICKBACK
A kickback can occur when the workpiece pinches
the blade, or binds between the saw blade and the
rip fence or other fixed object. This can cause the
workpiece to rise from the table and/or be thrown back
toward the operator. See instructions for reducing the
risk of kickback on page 7 of this manual.
IF KICKBACK OCCURS, turn the saw "OFF" and verify
proper alignment of the blade, riving knife and miter
gauge or rip fence, and the proper functioning of the
riving knife, anti-kickback assembly and blade guard
assembly before resuming work.
STARTING AND STOPPING THE SAW
The POWER switch (Figure 23) is located
underneath the front left extension wing.
1. To turn the saw "ON", pull the red paddle switch
(A) up and toward you.
2. To turn the saw "OFF", push the red paddle
switch in.
When not in use, the saw should be turned off and
the power switch locked out to prevent unauthorized
use. To lock out power switch, use a standard long
shackle lock, with a shackle that is at least 2 ¾ inches (70mm) long and with shackle posts no larger
than 9/32-inch (7mm) thick.
22
B
A
FIGURE 23
Page 23
OPERATION
OVERLOAD PROTECTION
(continued)
Your saw is supplied with overload protection. If the
motor shuts off or fails to start due to overloading
(cutting stock too fast, using a dull blade, using the
saw beyond its capacity, etc.) or low voltage, let the
motor cool three to five minutes. Then depress the red
MAKING CUTS
Failure to comply with the following
the warnings may result in serious
personal injury.
• Never touch the free end of the workpiece or a free
piece that is cut off, while the power is on and/or the
saw blade is rotating. Blade contact or binding may
occur, resulting in a thrown workpiece
• When sawing a long workpiece or a panel, use a
work support, such as a sawhorse, rollers or outfeed
table at the same height as the table surface of the
saw.
• Never try to pull the workpiece back with the blade
turning. If you need to pull the workpiece back or lift
it off the table, turn the switch off, allow the blade to
stop, raise the anti-kickback teeth on each side of
the riving knife if necessary, and slide the workpiece
out.
reset button (B), on the motor under the saw, shown in
Figure 20, and restart the saw.
NOTICE: If the motor continually shuts off due to
overloading, contact a qualified electrician.
• Before connecting the table saw to the power source
or operating the saw, always inspect the blade guard
assembly and riving knife for proper alignment and
clearance with saw blade. Check alignment after
each change of beveling angle.
• A rip fence should ALWAYS be used for ripping
operations to prevent loss of control and personal
injury. Always lock the fence to the rail. NEVER
perform a ripping operation freehand.
• When making bevel cuts, place the fence on the right
side of the blade so that the blade is tilted away from
the fence and hands. Keep hands clear of the blade
and use a push stick to feed the workpiece unless
the workpiece is large enough to allow you to hold it
more than 6inches (152 mm) from the blade.
• Before leaving the saw unattended, lock out power
switch, or take other appropriate measures to
prevent unauthorized use of the saw.
Cross Cut Mitered Crosscut
Beveled Cross Cut
Rip Cut
Beveled Rip Cut Compound Miter Cut
23
Page 24
OPERATION
A
(continued)
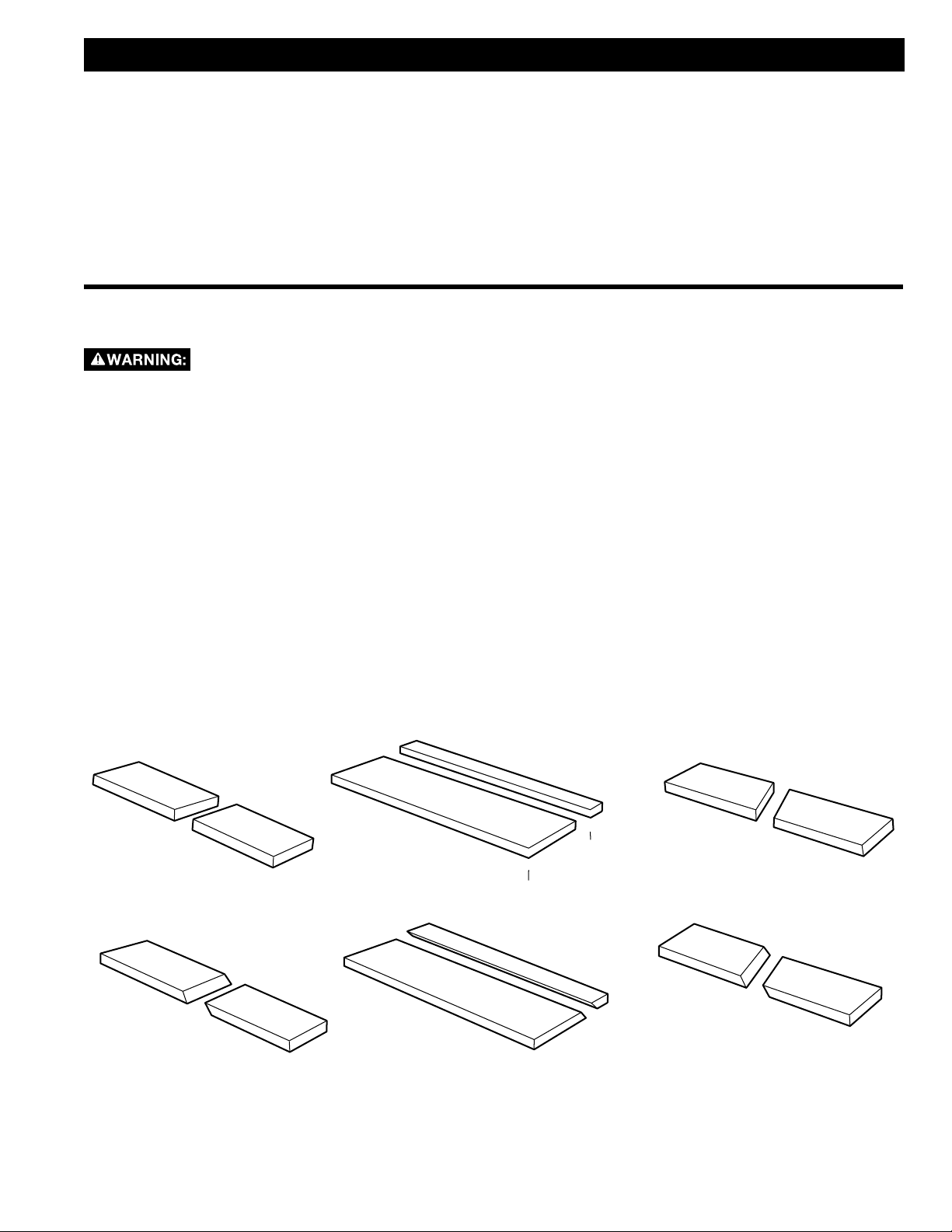
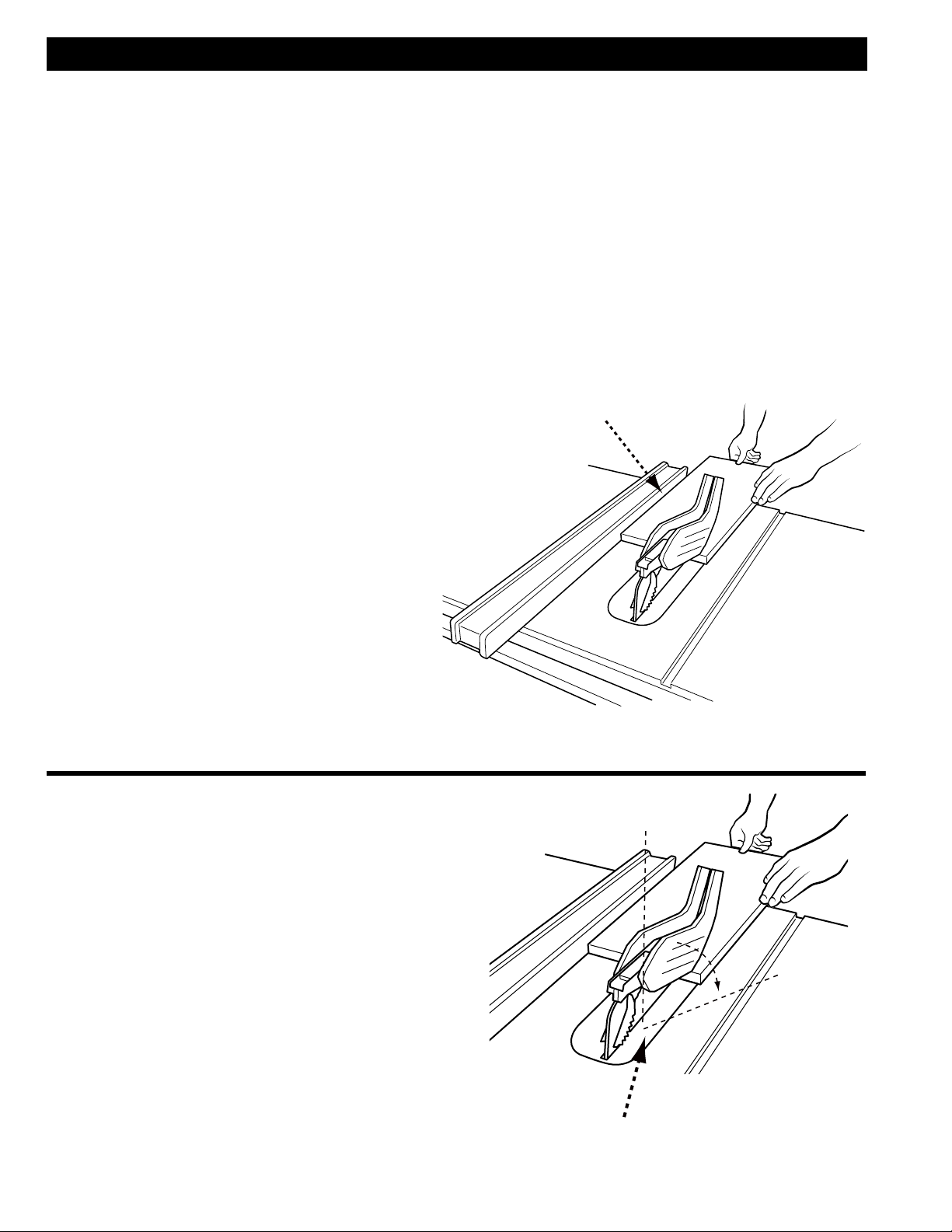
RIP CUTS
1. Remove miter gauge
2. Make sure bevel angle is set to 0°.
3. Set blade to correct height for workpiece.
4. Install rip fence and lock it down parallel with and
at desired distance from blade.
5. Keep fingers at least 6 inches from the blade at
all times. When the hand cannot be safely put
between the blade and the rip fence, select a
larger workpiece, or use a push stick and other
cutting aids, as needed, to control the workpiece.
6. Make sure the workpiece is clear of the blade (at
least 1 inch or 25mm away) before starting the
saw
7. Turn saw on.
8. Hold the workpiece flat on the table and against
the fence (A). The workpiece must have a straight
edge against the fence and must not be warped,
twisted or bowed. See proper hand position in
Figure 24.
9. Let blade build up to full speed before moving
workpiece into the blade.
10. Both hands can be used while starting the cut as
long as hands remain 6 inches from the blade.
11. Keep the workpiece against the table and fence
and slowly feed the workpiece rearward all the
way through the saw blade. Do not overload the
motor by forcing the workpiece into the blade.
12. Use the push stick and any other cutting aids,
as needed, to hold the workpiece against the
table and fence, and push the workpiece past the
blade. A push stick is included with this saw, and
instructions are included to make additional push
sticks and other cutting aids.
13. Do not push or hold onto the free or cut-off side of
the workpiece.
14. Continue pushing the workpiece until it is clear of
the blade. Do not overload the motor by forcing the
workpiece into the blade.
15. When cut is complete, turn saw off. Wait for blade
to come to a complete stop before removing
workpiece from table.
A
BEVEL RIPPING
Bevel ripping is the same as ripping except the
bevel angle (A) is set to an angle other than 0°.
When making a bevel rip cut, place the fence on
the right side of the blade so that the blade is tilted
away from the fence and hands.
FIGURE 24
0º
45º
FIGURE 25
24
Page 25
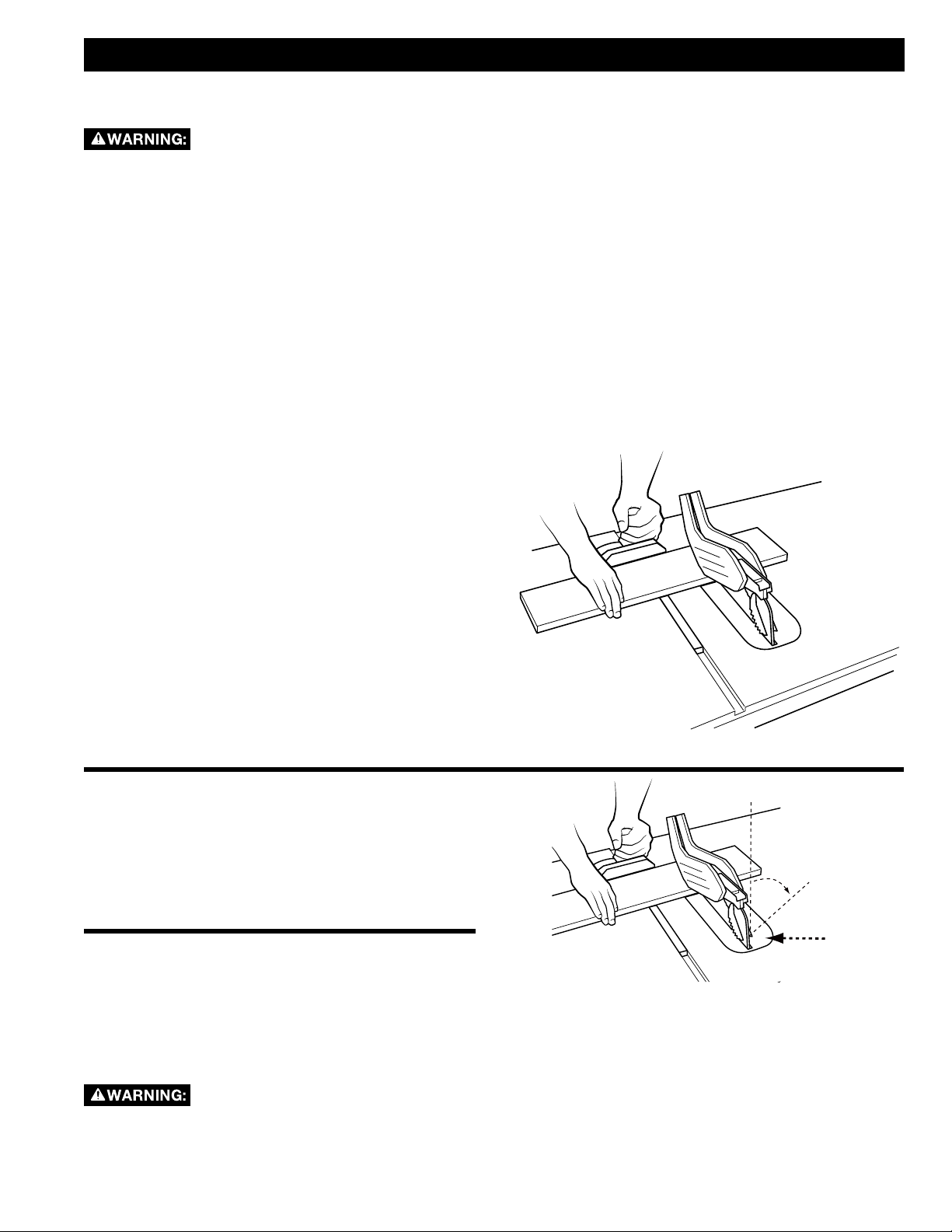
OPERATION
(continued)
CROSSCUTTING
• NEVER use the fence as a guide or length stop when
crosscutting.
• The cut-off piece must never be confined in any
through-sawing (cutting completely through the
workpiece) operation—to prevent pinching blade
which may result in a thrown workpiece and possibly
injury.
• When using a block as a cut-off gauge, the block
must be at least 3/4-inch (19mm) thick. It is very
important that the rear end of the block be secured in
a position where the workpiece is clear of the block
before it enters the blade to prevent binding of the
workpiece.
You can use the miter gauge in either table slot on nonbevel cuts. To increase surface area of miter gauge
face, add an auxiliary face (See Cutting Aids section on
page 27 of this manual.)
To make a crosscut, refer to Figure 26 and follow this
process:
1. Remove rip fence.
2. Make sure bevel angle is set to 0°.
3. Set blade to correct height for workpiece.
4. Place miter gauge in either miter slot.
5. Set miter gauge to 0° and tighten miter gauge lock
knob
6. Hands must remain at least 6 inches from blade
throughout entire cut. If workpiece is too small to
keep hands at least 6 inches away from the blade,
select a larger workpiece, or attach an auxiliary face
to the miter gauge and attach workpiece to auxiliary
face, For instructions about making auxiliary faces,
see Cutting Aids section on page 28 of this manual.
7. Make sure the workpiece is clear of the blade - at
least 1 inch or 25mm away - before starting the saw.
8. Turn saw on.
9. Let blade build up to full speed before moving
workpiece into the blade.
10. Hand closest to blade should be placed on miter
gauge lock knob and hand farthest from blade
should hold workpiece firmly against the miter gage
face. Do not push or hold onto the free or cut-off
side of the workpiece.
11. Slowly feed the workpiece rearward all the way
through the saw blade. Do not overload the motor
by forcing the workpiece into the blade.
12. When cut is complete, turn saw off. Wait for blade
to come to a complete stop before removing cut off
piece from table.
FIGURE 26
BEVEL CROSSCUTTING
Bevel crosscutting is the same as crosscutting except
the bevel angle (A) is set to an angle other than 90°.
When making a bevel crosscut, place the miter gauge
in the right miter slot so that the blade is tilted away
from the gauge and hands. See Figure 27.
MITER CUTS
Miter cuts are cross cuts with the miter gauge set at
an angle other than 90°. For instructions about setting
miter gauge angles, see Preparing to Cut. To adjust the
preset index miter stops, see Adjusting the Miter Stops
on page 28 of this manual.
• Miter angles less than 45˚ may force the blade guard
assembly into the saw blade causing damage to the
blade guard assembly and personal injury. Before
starting the motor, test the operation by feeding
the workpiece into the blade guard assembly. If the
25
0º
45º
A
FIGURE 27
blade guard assembly contacts the blade, place the
workpiece under the blade guard assembly but not
touching the blade - before starting the motor.
• Certain workpiece shapes, such as molding may not
lift the blade guard assembly properly. With the power
off, feed the workpiece slowly into the blade guard
area and until the workpiece touches the blade. If the
blade guard assembly contacts the blade, place the
workpiece under the blade guard assembly - but not
touching the blade - before starting the motor.
Page 26
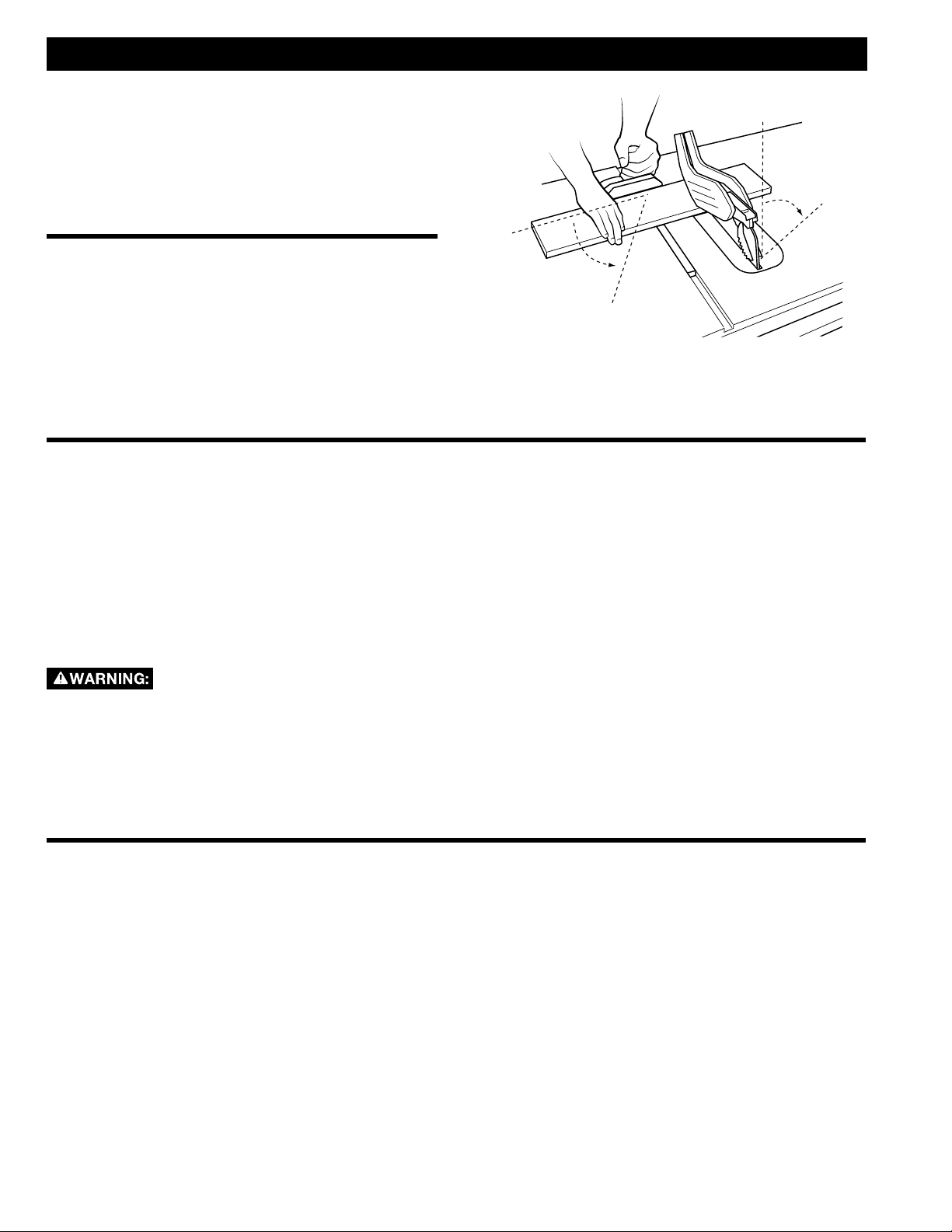
OPERATION
(continued)
COMPOUND MITER CUTS
This is a combination of bevel crosscutting and
mitering. Refer to Figure 28 and follow the instructions
for both bevel crosscutting and mitering. Remember to
use the right miter slot for all bevel cuts.
90º
LARGE PANEL CUTS
Place workpiece supports at the same height as the
saw table behind saw to support the cut workpiece,
and alongside (s) of saw, as needed. Depending on
shape of panel, use rip fence or miter gauge to control
workpiece. If a workpiece is too large to use either a rip
fence or a miter gauge, it is too large for this saw.
DADOS AND OTHER NON-THROUGH CUTS
The use of a non-through cut is essential to cutting
grooves, rabbets and dados. Non-through cuts can be
made using a standard blade having a diameter of 10
inches or less, or a dado blade up to 13/16 inch wide
with a diameter of 8 inches or less. Non-through cuts
are the only type of cuts that should be made without
the blade guard assembly installed. Make sure the blade
guard assembly is reinstalled upon completion of this
type of cut.
• When making non-through cuts, follow all applicable
warnings and instructions listed below in addition to
those listed above for the relevant through cut.
• When making a non-through cut, blade is covered by
workpiece during most of cut. Be alert to exposed
blade at start and finish of every cut.
• Never feed wood with hands when making any
non-through cuts such as rabbets or dados. Always
use miter gauge, push blocks or push sticks, and
featherboards where appropriate.
• Read the appropriate section which describes the
type of cut in addition to this section on non-through
or dado cuts. For example, if your non-through cut is a
straight cross cut, read and understand the section on
straight cross cuts before proceeding.
• Once all dado and non-through cuts are completed,
unplug saw and reinstall riving knife or return it to
raised position. Install anti-kickback pawls and blade
guard.
• Carefully follow the instructions accompanying any
specialized blades such as dado blades and molding
cutters for proper installation, set up and operation.
0º
45º
30º
FIGURE 28
MAKING A NON-THROUGH CUT
1. Unplug saw.
2. Unlock release lever.
3. Adjust bevel angle to 0°.
4. Lock release lever.
5. Remove blade guard and anti-kickback pawls.
6. Place riving knife in “lowered” position. (see RIVING
KNIFE HEIGHT SETTINGS Section on page 20)
7. Set blade to correct depth for workpiece. See
instructions below for use of Dadoes and other
specialized blades.
8. Depending on shape and size of wood, use either
rip fence or miter gauge.
9. Plug saw into power source and turn saw on.
10. Let blade build up to full speed before moving
workpiece into blade.
11. Always use push blocks, push sticks, and/or
featherboards when making non-through cuts to
reduce the risk of serious injury.
12. When cut is made, turn saw off. Wait for blade
to come to a complete stop before removing
workpiece.
If a deep dado cut is required, use several successive
passes rather than attempting to make it with one pass.
26
Page 27
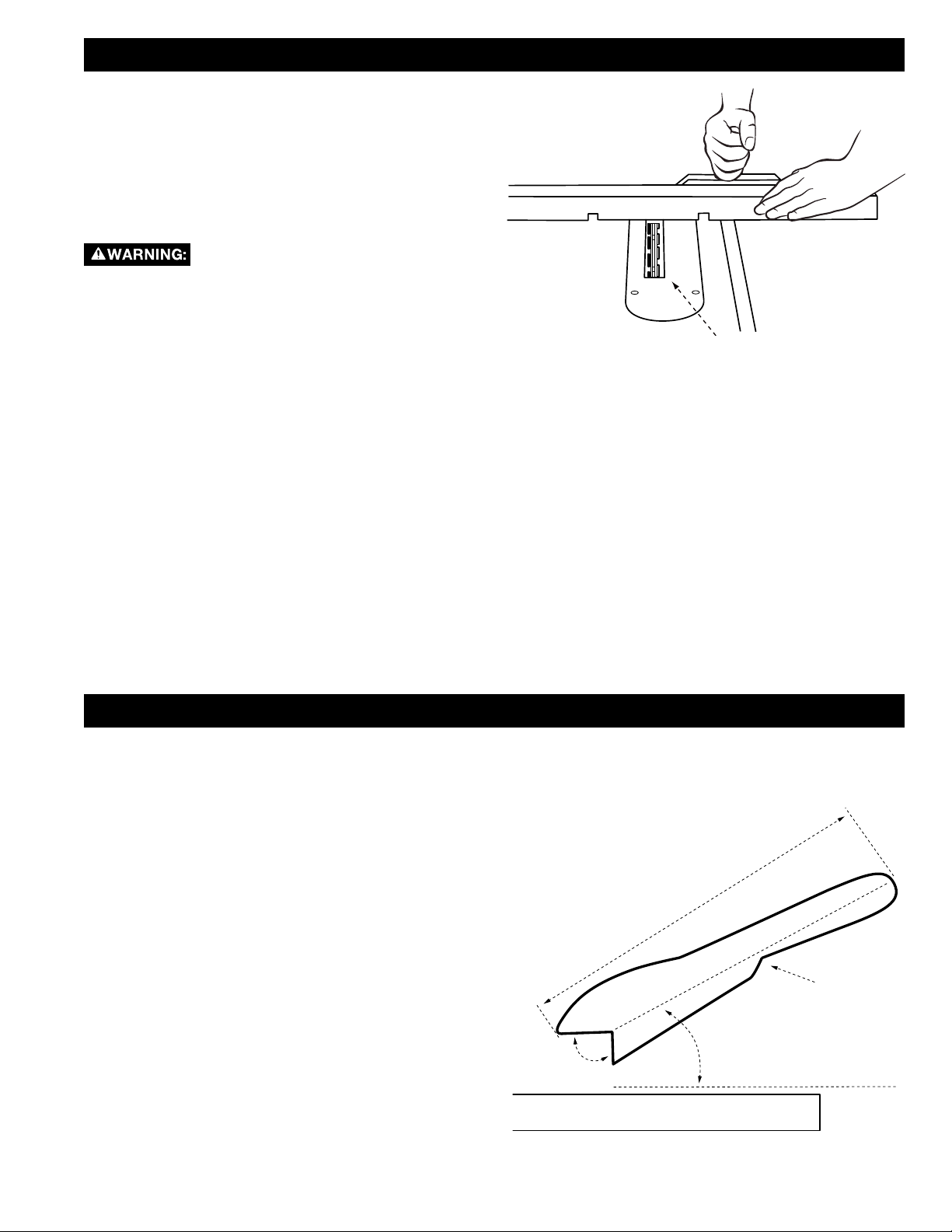
OPERATION
MAKING A DADO CUT
Dado blades are stacked blades that can be used when
making non-through cuts including through cut slots.
Dado blades require a special throat plate. Dado blades
and throat plates are all sold separately.
• Carefully follow the instructions accompanying
the dado blade for proper installation, set up
and operation. Additional guides can be found
in woodworking and carpentry websites and
publications.
13
• Do not attempt to stack dado blades thicker than
inch (20.64mm) Do not use dado blades larger than
8-inches (200 mm) in diameter.
• The riving knife and blade guard assemblies cannot
be used when dadoing. They must be removed
as described in Riving Knife and Blade Guard
Operations section. Use EXTREME care when using
the dado without the blade guard assembly and riving
knife.
• Use push sticks, hold-downs, jigs, fixtures or feather
boards to help guide and control the workpiece when
the guard cannot be used.
• Be sure to reinstall riving knife, anti-kickback pawls
blade guard and standard throat plate, and check
adjustments when the dado cuts are complete.
/16
(continued)
FIGURE 30
• The accessory dado head set throat plate, shown
in Figure 30, must be used in place of the standard
throat plate. Be sure the throat plate is level to the
table before you proceed.
• Always check dado blade clearance with other
components before plugging in the saw.
• Never attempt to use the dado head in a bevel
position.
NOTE: The standard outer arbor flange cannot be
used with certain dado blade combinations. In those
cases, tighten the arbor nut directly against the dado
blade set. Save the outer arbor flange for use with
other blades and dado combinations.
CUTTING AIDS AND ACCESSORIES
PUSH STICK
In order to operate your table saw safely, you must
use a push stick whenever the size or shape of the
workpiece would otherwise cause your hands to be
within 6-inches (152mm) of the saw blade or other
cutter. A push stick is included with this saw.
No special wood is needed to make additional pushsticks as long as it is sturdy and long enough with no
knots, checks or cracks. A length of approximately 16
inches (400mm) is recommended with a notch that fits
against the edge of the workpiece to prevent slipping.
It’s a good idea to have several push sticks of the same
minimum length, 16 inches (400mm), with different size
notches for different workpiece thicknesses.
The shape can vary to suit your own needs as long as
it performs its intended function of keeping your hands
away from the blade. Angling the notch so the push
stick can be held at a 20- to 30-degree angle from the
saw's table will help you to hold down the workplace
while also moving the saw.
To construct a push stick, refer to the layout shown in
Figure 31.
90º
15.7”
Saw Table
FIGURE 31
20º
notch
prevents
hand slips
27
Page 28
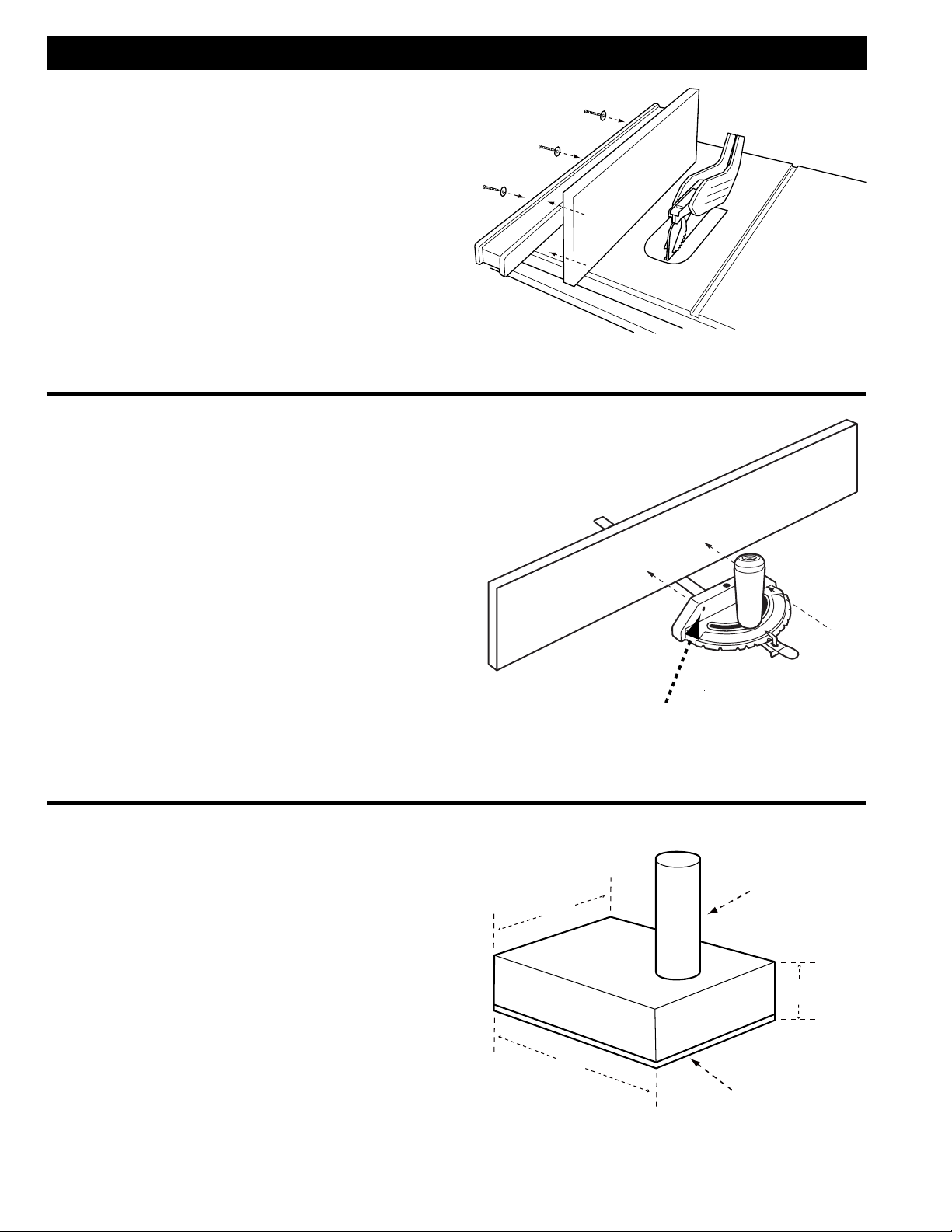
CUTTING AIDS AND ACCESSORIES
AUXILIARY RIP FENCE FACING
Use an auxiliary rip fence facing when needed for
special cuts, such as ripping material that is thin
enough to slide under the rip fence provided with
your saw, or when a taller rip fence is necessary to
complete your cut. To add an auxiliary wood facing
to one or both sides of the rip fence, select a piece
of wood with smooth surfaces, Attach the wood to
the rip fence with two clamps. (see Figure 32) For
most work, 3/4-inch (19mm) or 1-inch (25mm) stock
is suitable.
AUXILIARY MITER GAUGE FACING
An auxiliary miter gauge facing is used to increase
the surface area of the miter gauge face.
If desired, you can fit the miter gauge with an
auxiliary wood facing that should be at least 1-inch
(25mm) higher than the maximum depth of cut, and
at least as wide as the miter gauge.
This auxiliary wood facing can be fastened to the
front of the miter gauge by using two wood screws
through the holes (A) provided in the miter gauge
body and into the wood facing. See Figure 33.
Make sure the screws are long enough to secure
the facing, but do not extend all the way through
the wood.
(continued)
FIGURE 32
PUSH BLOCK
1. Select a piece of wood about 4-inches wide,
6-inches long and 1- to 2-inches thick (a cutoff
from a 2 by 4 makes a good blank for a push
block).
2. Drill a hole in the block and glue in a dowel
to use as a handle (you can angle the hole to
provide a more comfortable grip on the handle).
3. Glue a piece of rough or soft material such as
sandpaper or rubber to the bottom of the block
to grip the workpiece (old mouse pads work
well). See Figure 34.
A
FIGURE 33
Wooden
dowel
4”
2”
6”
Sandpaper
or old
mouse pad
material
28
FIGURE 34
Page 29
CUTTING AIDS AND ACCESSORIES
FEATHERBOARD
(continued)
Featherboards are used to keep the work in contact
with the fence and table (Figure 35), and help prevent
kickback. Featherboards are especially useful when
ripping small workpieces and for completing nonthrough cuts. The end is angled with a series of narrow
slots to give a friction hold on the workpiece, It is
locked in place on the table or fence with a c-clamp.
To avoid binding between the
workpiece and the blade, make sure a
horizontal feather board presses only on the uncut
portion of the workpiece in front of the blade.
Dimensions for making a typical featherboard are
shown in Figure 35. Make your featherboard from a
straight piece of wood that is free of knots and cracks.
Clamp featherboards to the fence and/or table so that
the featherboard will hold the workpiece against the
fence or table.
1. Select a solid piece of lumber approximately
¾-inch thick, 2 ½-inches wide and 12-inches long.
2. Mark the center width on one end of stock. Miter
width to 70° (see miter cut section for information
on miter cuts).
3. Set rip fence to allow approximately a 1/4-inch
“finger” to be cut in the stock.
4. Feed stock only to mark previously made at 6
inches.
5. Turn saw off and allow blade to completely stop
rotating before removing stock.
6. Reset rip fence and cut spaced rips into
workpiece to allow approximately 1/4-inch fingers
and 1/8-inch spaces between fingers.
1/8”
1/4”
70º
3/4”
4.5”
FIGURE 35
CUT OFF GAUGE
When crosscutting a number of pieces to the same
length, you can clamp a block of wood (A) (See Figure
36) to the fence and use it as a cut-off gauge. The block
(A) must be at least 3/4-inch (19 mm) thick to prevent
the cut off piece from binding between the blade
and the fence. Once the cut-off length is determined,
lock the fence and use the miter gauge to feed the
workpiece into the blade.
Always position the cut-off gauge in
front of the saw blade.
JIGS
Jigs may be created with a variety of special set-ups
to control particular workpiece shapes for particular
cuts. Guidance on how to make specialized jigs can
be found in woodworking and carpentry websites and
publications.
12”
A
3/4”
FIGURE 36
Do not attempt to create or use a jig
unless you are thoroughly familiar with
table saw safety. Do not use any jig that could result
in pinching a kerf or jamming the workpiece between
the jig and the blade. Incorrect setups may cause
kickback which could result in serious injury.
29
Page 30
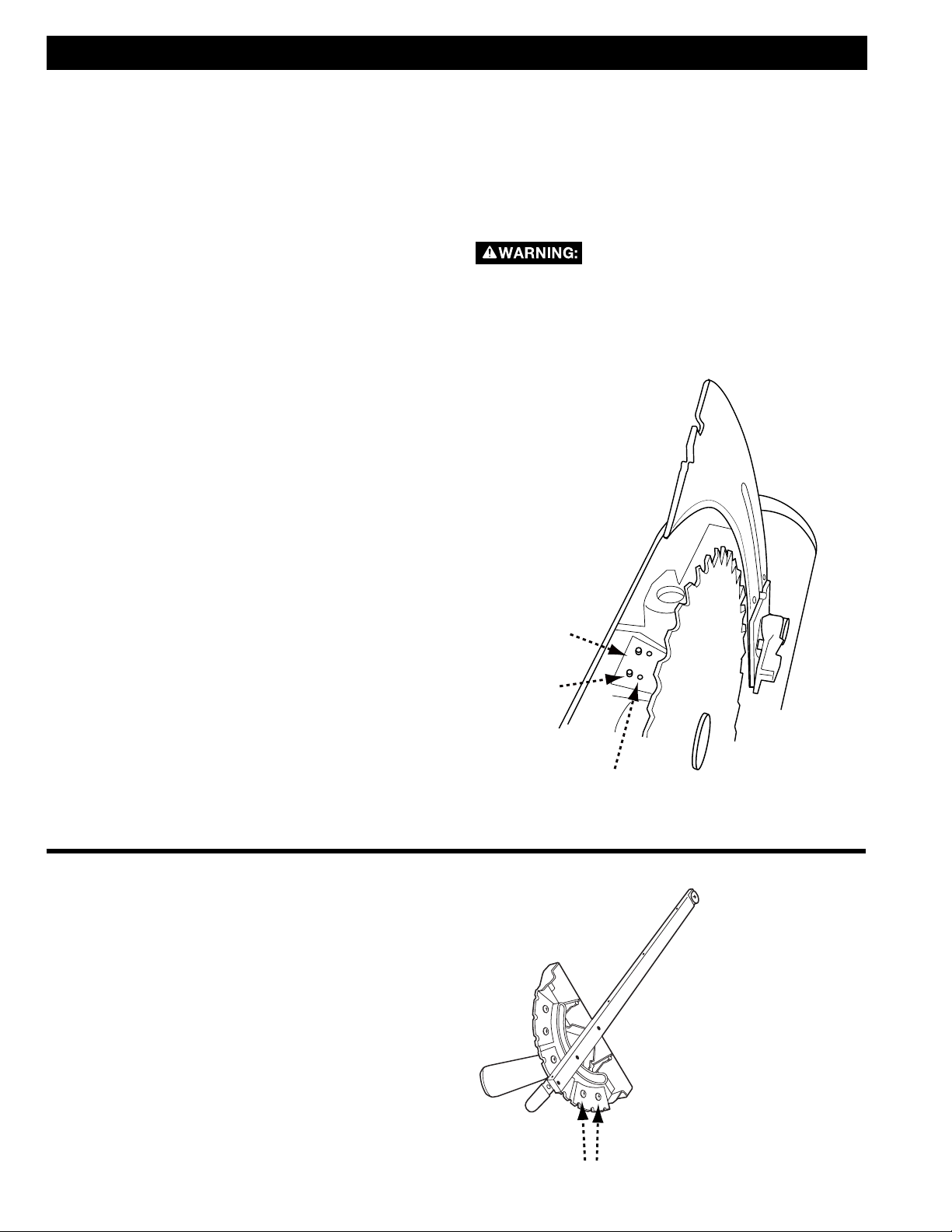
ALIGNMENT
RIVING KNIFE ALIGNMENT
WITH THE BLADE
Alignment between the riving knife and blade is set
at the factory and, in most cases, will not need to
be adjusted. However, the alignment should always
be checked after installing blade or riving knife, and
can be adjusted if necessary. If riving knife is out of
alignment with blade, adjustment is needed. Riving
knife must be in alignment front to back (horizontally)
and top to bottom (vertically).
To adjust the riving alignment, see Figure 37 and
proceed as follows:
1. Remove the throat plate, blade guard and antikickback assemblies.
2. Raise the blade to full depth of cut and set the tilt
angle to 0°.
3. Raise the riving knife to the through-cutting or
highest position.
4. Slightly loosen the two socket head cap screws (C).
5. Lay straight edge against the blade face and
riving knife as instructed for checking horizontal
alignment (see Figure 20a, page 20).
6. Adjust the set screws (A) to move the riving knife in
line with the blade according to its position when
you checked the alignment above.
7. Lay the straight edge on the opposite side of the
blade. Both sides of the riving knife should be
within the thickness of the blade body.
8. If it is not possible to align both sides of riving knife
within the thickness of the blade body, you need to
use a different size blade. See Blade Selection on
page 17.
9. Tighten the two socket head cap screws.
10. Place a carpenter’s square on the table, and against
the blade face and riving knife as instructed for
checking vertical alignment (See Figure 20b, page
20). Then verify that the riving knife is perpendicular
to table and in-line with the blade face.
11. If needed, use the set screws (D) to align the riving
knife with blade face and the square.
12. Fully tighten the two socket head cap screws.
13. Replace throat plate, blade guard and anti-kickback
assemblies before use.
If any dragging or binding of the
workpiece is encountered as it
reaches the riving knife, turn unit off and disconnect
machine from power source and readjust the riving
knife/blade alignment or replace the blade. Never
attempt to back partially-cut workpiece out of blade
while blade is moving.
B
C
A
FIGURE 37
ADJUSTING THE MITER STOPS
To adjust the index stops for angles other than 90°,
75°, 60°, 45° and 30°:
1. Loosen the miter gauge handle.
2. Loosen the 2 screws for the miter stop segment
for the desired new angle. (A) is shown in Figure
35.
3. Move the stop to proper position.
4. Re-tighten the 2 segment screws and handle.
FIGURE 38
A
30
Page 31

ALIGNMENT
(continued)
ALIGNING FENCE PARALLEL TO
MITER SLOT
1. Move fence adjacent to right miter gauge and
secure to the guide tube by lowering the fence
clamping lever.
2. If the fence face (A) figure 39, is not parallel to the
miter slot (B), raise the clamping lever and lift the
fence and place it on the saw table.
3. Adjust the one or both of the set screws (C) 1/4
turn or less.
4. Replace fence on guide tube and repeat steps 1
through 3. If fence is closer to parallel, turn the set
screw in the same direction but a little less. If the
fence is further out of parallel, turn the set screw in
the opposite direction.
5. Repeat steps 1 through 3.
A
C
ALIGNING FENCE
PERPENDICULAR TO THE
TABLE
1. Move fence over the cast iron table and secure
to the guide tube by lowering the fence clamping
lever.
2. Use a square to check that the fence face is
perpendicular to the table.
3. If the fence face is not perpendicular to the table,
release the clamping lever and slightly adjust one
of the slotted set screws (A) figure 40 until the
fence face is perpendicular to the table.
4. Secure the fence to the guide tube to insure the
fence remains perpendicular. If not, repeat steps 1
through 4.
A
B
FIGURE 39 FIGURE 40
240 VOLT SINGLE PHASE OPERATION
The 120/240 volt, dual-voltage motor supplied with your machine was shipped prepared for 120 volt operation.
It can be converted for 240 volt operation. For conversion from 120 volt to 240 volt, please call ahead to DELTA
Customer Care at 1-800-223-7278.
31
Page 32

MAINTENANCE
To reduce the risk of injury, turn unit off and disconnect it from power source before cleaning or servicing, before
installing and removing accessories, before adjusting and when making repairs. An accidental start-up can cause
injury.
KEEP MACHINE CLEAN
Periodically blow out all air passages with dry
compressed air. All plastic parts should be cleaned
with a soft damp cloth. NEVER use solvents to clean
plastic parts. They could possibly dissolve or otherwise
LUBRICATION & RUST PROTECTION
Apply hardwood flooring paste wax to the machine
table occasionally or use a commercially available
protective product designed for this purpose. Follow
the manufacturer’s instructions for use and safety.
MAINTENANCE REMINDERS
Wear certified safety equipment for eye, hearing and
respiratory protection while using compressed air.
Specific areas which require regular maintenance
include:
RIVING KNIFE CLAMP PLATE: Keep this area free of
dust and debris buildup. Blow out area regularly with
compressed air.
NOTE: If the riving knife clamp can't move freely,
have the saw serviced by authorized DELTA® Power
Equipment Corporation service center personnel.
damage the material.
Wear certified safety equipment for eye, hearing and
respiratory protection while using compressed air.
To clean cast iron tables of rust, you will need the
following materials: a medium sized scouring pad, a
can of spray lubricant and a can of degreaser. Apply
the spray lubricant and polish the table surface with
the scouring pad. Degrease the table, then apply the
protective product as described above.
WORM GEARS: Keep the worm gears free of dust
and debris buildup. Blow out area regularly with
compressed air. Use a lithium-based multipurpose
grease as needed on these gears.
CLEAN SAWDUST BUILDUP OUT OF CABINET
PERIODICALLY: NOTE: Debris can also be removed
from the saw from below the throat plate, inside the
dust port.
TROUBLESHOOTING
For assistance with your machine, visit our website at www.DeltaMachinery.com for a list of service centers
or call DELTA® Power Equipment Customer Care at 1-800-223-7278.
FAILURE TO START
If your machine fails to start, check to make sure the prongs on the cord plug are making good contact in the
receptacle, and check reset button on power switch housing. Also, check for blown fuses or open circuit breakers in
your power line.
ACCESSORIES
A complete line of accessories is available from your DELTA® Supplier, DELTA® Factory Service Centers,
and DELTA® Factory Service Centers, and DELTA® Authorized Service Centers. Please visit our Web Site
www.DeltaMachinery.com for an online catalog or for the name or your nearest supplier.
Since accessories other than those offered by DELTA® have not been tested with this product,
use of such accessories could be hazardous. For safest operation, only DELTA® recommended
accessories should be used with this product.
32
Page 33

WARRANTY
To register your tool for warranty service visit our website at www.DeltaMachinery.com.
Five Year Limited New Product Warranty
DELTA will repair or replace, at its expense and at its option, any new DELTA machine, machine part, or machine accessory
which in normal use has proven to be defective in workmanship or material, provided that the customer returns the product
prepaid to a DELTA factory service center or authorized service station with proof of purchase of the product within five years
and provides DELTA with reasonable opportunity to verify the alleged defect by inspection.
For all refurbished DELTA product, the warranty period is 180 days.
DELTA will not be responsible for any asserted defect which has resulted from normal wear, misuse, abuse or repair or alteration
made or specifically authorized by anyone other than an authorized DELTA service facility or representative.
Under no circumstances will DELTA be liable for incidental or consequential damages resulting from defective products. Some
states do not allow the exclusion or limitation of incidental or consequential damages, so
the above limitation or exclusion may not apply to you.
This warranty is DELTA’s sole warranty and sets forth the customer’s exclusive remedy, with respect to defective products; all
other warranties, express or implied, whether of merchantability, fitness for purpose, or otherwise, are expressly disclaimed by
DELTA.
For further detail of warranty coverage and warranty repair information call 1-800-223-7278. This warranty gives you specific
legal rights and you may have other rights which vary in certain states or provinces.
LATIN AMERICA: This warranty does not apply to products sold in Latin America. For products sold in Latin America,
see country specific warranty information contained in the packaging, call the local company or see website for warranty
information.
PARTS, SERVICE AND WARRANTY ASSISTANCE
All DELTA® machines and accessories are manufactured to high quality standards and are serviced by a network of
DELTA® Authorized Service Centers. To obtain additional information regarding your DELTA® quality product or to
obtain parts, service, warranty assistance, or the location of the nearest service center, please call 1-800-223-7278.
REPLACEMENT PARTS
Use only identical replacement parts. For a parts list or to order parts, visit our website at
www.DeltaMachinery.com/service. You can also order parts from your Authorized Warranty Service
Center or by calling Technical Service Manager at 1-800-223-7278 to receive personalized support from one
of our highly-trained representatives.
FREE WARNING LABEL REPLACEMENT
If your warning labels become illegible or are missing, call
1-800-223-7278
for a free replacement.
33
Page 34

DESCRIPTION FONCTIONNELLE
La Scie de table de 10 pouces (254 mm) pour
entrepreneurs de Delta (N° 36-5000 série) se
distingue par sa portabilité et sa haute performance.
Elle comprend : machine de base, support en acier
tubulaire robuste, goulotte à poussière intégré, système
de guidage T-Square®, guide à onglets pour fente
en T, moteur à induction de 15 ampères, interrupteur
marche/arrêt, table en fonte, ailes d'extension, protègelame transparent avec doigts anti-retour et lame
carbure de 10 pouces (254 mm).
AVIS : la couverture du manuel illustre le modèle de production actuel. Toutes les autres illustrations du manuel
sont uniquement à titre de représentation et peuvent ne pas illustrer fidèlement l'étiquetage ou les accessoires
réellement inclus. Elles sont uniquement destinées à des fins d'illustration.
CARACTÉRISTIQUES
Profondeur de coupe maximale à 90 degrés : 3-½"
Profondeur de coupe maximale à 45 degrés : 2-½”
Coupe maximale à droite de la lame : 30"
Coupe maximale à gauche de la lame : 15"
Largeur de fente maximale : 13/16"
SPÉCIFICATIONS DU MOTEUR :
Ampérage 15
Voltage 120/240
CONSIGNES DE SÉCURITÉ IMPORTANTES
LISEZ ATTENTIVEMENT ET SUIVEZ TOUS LES AVERTISSEMENTS ET LES
INSTRUCTIONS SUR VOTRE PRODUIT ET DANS LE PRÉSENT MANUEL. CONSERVEZ
CE MANUEL. ASSUREZ-VOUS QUE TOUS LES OPÉRATEURS SONT FAMILIARISÉS AVEC LES
AVERTISSEMENTS ET LES INSTRUCTIONS LORS DE L'UTILISATION DE L'OUTIL. Tout fonctionnement, tout
entretien ou toute modification inappropriés des outils ou de l’équipement pourraient entraîner des blessures
graves et/ou des dommages matériels.
Si vous avez des questions ou des préoccupations relatives à l'utilisation de votre outil ou au contenu du présent
manuel, arrêtez d'utiliser l'outil et contactez le Service à la clientèle de DELTA
1-800-223-7278.
®
Power Equipment Corporation au
LOGOS DE SÉCURITÉ
Les définitions ci-dessous décrivent le niveau de sévérité associé à chaque terme d'avertissement. Veuillez lire le
manuel et faire attention à ces symboles.
Indique une situation imminente extrêmement dangereuse qui, si elle n’est pas évitée, entraînera la
mort ou une blessure grave.
Indique une situation potentiellement dangereuse qui, si elle n’est pas évitée, pourrait
entraîner la mort ou une blessure grave.
Indique une situation potentiellement dangereuse qui, si elle n’est pas évitée, peut entraîner
une blessure mineure ou modérée.
RÈGLES DE SÉCURITÉ GÉNÉRALES
DES OUTILS ÉLECTRIQUES
Le non-respect de ces règles
peut provoquer des blessures
graves.
1. LIRE LE MANUEL D'INSTRUCTIONS ET FAIRE
CONNAISSANCE AVEC L'OUTIL. Lisez et
familiarisez-vous avec le manuel d'instructions
dans son intégralité. Apprenez la bonne utilisation
et les limites de l'outil, ainsi que les dangers
connexes, pour minimiser le risque d’accidents et
de blessures. Assurez-vous que tous les opérateurs
sont familiarisés avec les avertissements et les
instructions avant d'utiliser l'outil.
2. GARDER LES DISPOSITIFS DE PROTECTION
ET DE SÉCURITÉ EN PLACE et en bon état de
fonctionnement.
3. RETIRER LES CLÉS D’AJUSTEMENT ET LES
CLÉS À MOLETTE. Habituez-vous à vérifier que
les clés d’ajustement et les clés à molette ont été
retirées de l’outil avant de le mettre en marche.
4. MAINTENIR L’ESPACE DE TRAVAIL PROPRE ET
BIEN ÉCLAIRÉ. Les espaces, surfaces et bancs
de travail en désordre ou mal éclairés peuvent
conduire à des accidents.
34
suite à la page 34
Page 35

RÈGLES DE SÉCURITÉ GÉNÉRALES
DES OUTILS ÉLECTRIQUES
5. NE PAS UTILISER OU ENTREPOSER L'OUTIL
DANS DES ENVIRONNEMENTS DANGEREUX.
L'exposition à la pluie et aux endroits humides ou
mouillés peuvent entraîner un choc électrique ou
une électrocution ou endommager l'outil. Ne pas
faire fonctionner les outils électriques à proximité
de liquides inflammables ou dans des atmosphères
explosives ou gazeuses. Les moteurs et les
interrupteurs de ces outils peuvent provoquer des
étincelles et enflammer les vapeurs.
6. GARDER LES ENFANTS ET LES SPECTATEURS À
DISTANCE de la zone de travail.
7. BLOQUER LES OUTILS ET L'ESPACE DE
TRAVAIL. Utilisez des cadenas, des interrupteurs
principaux, ou enlevez et rangez les clés de
démarrage pour empêcher l'utilisation par des
enfants et des opérateurs non autorisés.
8. NE PAS FORCER L'OUTIL OU LA PIÈCE. Faites
fonctionner l'outil à la vitesse et l'alimentation
prévue pour un fonctionnement à la fois meilleur et
plus sûr.
9. UTILISER L'OUTIL APPROPRIÉ. Ne forcez pas
l'outil à effectuer une tâche pour laquelle il n'a pas
été conçu.
10. NE PAS MALMENER LES CORDONS
D'ALIMENTATION. NE tirez jamais sur le cordon
pour le débrancher, ne l'écrasez pas, ne l'exposez
pas à la chaleur, à l'huile ou aux objets pointus.
11. UTILISER LA RALLONGE APPROPRIÉE. Lorsque
vous utilisez une rallonge, assurez-vous d'utiliser
une rallonge en bon état et suffisamment épaisse
pour transporter le courant requis par votre outil.
Une rallonge d’un calibre trop petit provoquera
une chute de tension, entraînant une perte de
puissance et une surchauffe. Voir le Tableau des
rallonges pour le calibre approprié en fonction
de la longueur du cordon et de l’ampérage de la
plaque signalétique. En cas de doute, utiliser le
calibre immédiatement inférieur. Plus le numéro de
calibre est petit, plus le cordon est épais. Lorsque
vous travaillez à l'extérieur, utilisez uniquement des
rallonges conçues pour une utilisation à l'extérieur.
Consultez la section Raccordements électriques
du présent manuel pour le Tableau des rallonges et
la sécurité des raccordements électriques.
12. FIXER LA PIÈCE. Utilisez des serre-joints ou un
étau pour tenir la pièce en place, le cas échéant.
Cela sera plus sûr que d'utiliser vos mains qui
seront ainsi libérées pour le travail.
13. NE PAS TENDRE LE BRAS. Gardez un bon
positionnement de vos pieds et un bon équilibre à
tout moment pour maintenir un contrôle adéquat.
14. ENTRETENIR LES OUTILS AVEC SOIN. Gardez les
outils affûtés et propres pour une utilisation efficace
et sécuritaire. Suivez les indications relatives à la
lubrification et au changement d’accessoires.
15. DÉBRANCHER L'OUTIL de la source
d'alimentation avant l'entretien, le réglage ou
la modification de l'installation ou des lames,
mèches, couteaux et autres accessoires.
35
16. POUR RÉDUIRE LE RISQUE DE MISE EN
MARCHE ACCIDENTELLE, assurez-vous que les
interrupteurs sont en position « OFF » (arrêt) avant
de brancher l'outil.
17. Ne touchez pas aux broches métalliques de la
fiche au moment de brancher ou de débrancher le
cordon.
18. UTILISER LES ACCESSOIRES RECOMMANDÉS.
Consultez le manuel pour les accessoires
recommandés. L'utilisation d'accessoires
inappropriés peut entraîner des blessures ou des
dommages matériels.
19. NE JAMAIS SE TENIR DEBOUT SUR L’OUTIL.
Des blessures graves peuvent se produire en cas
de basculement de l’outil ou en cas de contact
accidentel avec la surface de coupe.
20. CONTRÔLER L'OUTIL POUR D'ÉVENTUELS
DOMMAGES. Avant toute utilisation, et après
que l'outil ou l'accessoire soit tombé ou ait été
endommagé, inspectez attentivement les
protections ou autres pièces concernées pour
vérifier l’alignement, le blocage ou la cassure des
pièces mobiles et toute autre condition qui pourrait
en modifier le fonctionnement pour s'assurer
que l'outil et ses pièces pourront fonctionner
correctement et effectuer le travail pour lequel ils
sont conçus. N'utilisez pas un produit endommagé.
Une protection ou une autre pièce endommagée
doit être correctement réparée ou remplacée par des
pièces de rechange autorisées par le fabricant.
21. UTILISER LA BONNE DIRECTION
D'ENGAGEMENT. Engagez la pièce dans le sens
contraire de la rotation de la lame, du couteau ou
de la surface abrasive. L’engager dans l’autre sens
risque de projeter la pièce en l’air à grande vitesse.
22. NE JAMAIS LAISSER L’OUTIL EN MARCHE
SANS SURVEILLANCE. COUPER LE COURANT.
Ne laissez pas l’outil tant qu’il ne s'est pas
entièrement arrêté. En cas de panne de courant,
placez l’interrupteur en position « OFF ».
23. RESTER VIGILANT, SURVEILLER SES GESTES
ET FAIRE PREUVE DE BON SENS LORS DE
L’UTILISATION D’UN APPAREIL ÉLECTRIQUE.
N'utilisez pas d'outils électriques quand vous êtes
fatigué ou sous l’influence de drogues, d’alcool
ou de médicaments. Un moment d’inattention
pendant l’utilisation d’un outil électrique peut
entraîner des blessures graves.
24. PIÈCES DE RECHANGE. Utilisez uniquement des
pièces de rechange identiques lors de l'entretien
de votre outil.
25. PORTER DES VÊTEMENTS APPROPRIÉS.
Évitez de porter des vêtements amples, des
gants, des cravates, des bagues, des bracelets
ou tout autre bijou, car ils peuvent se coincer
dans les pièces mobiles. Le port de chaussures
de protection à semelles antidérapantes est
recommandé. Portez un chapeau de protection
pour contenir les cheveux longs.
suite à la page 35
Page 36

RÈGLES DE SÉCURITÉ GÉNÉRALES
DES OUTILS ÉLECTRIQUES
26. PORTER DES LUNETTES DE PROTECTION.
Toutes les personnes dans la zone de travail
doivent porter des lunettes de sécurité avec écrans
latéraux. Les lunettes de vue ordinaires avec
des verres résistants aux chocs ne sont pas des
lunettes de sécurité. L’équipement de protection
oculaire doit être conforme aux normes ANSI Z87.1.
27. PROTECTION DE L'OUÏE. Toutes les personnes
dans la zone de travail doivent porter une protection
auditive appropriée compatible avec les niveaux de
bruit et d'exposition. L’équipement de protection
auditive doit être conforme aux normes ANSI S3.19.
28. PROTECTION CONTRE LA POUSSIÈRE.
L'utilisation d'outils électriques peut générer et/
ou disperser la poussière, ce qui peut provoquer
AVERTISSEMENT RELATIF À LA PROPOSITION 65 :
Les poussières créées par le ponçage électrique, la
coupe, le broyage, le perçage et d’autres activités
de construction contiennent des produits chimiques
identifiés par l’État de Californie comme facteurs de
cancer, d’anomalies congénitales ou d’autres préjudices
relatifs à la reproduction. Voici quelques exemples :
• Le plomb des peintures à base de plomb
• La silice cristalline des briques et du ciment et
autres matériaux de maçonnerie
• La poussière d'amiante
• L’arsenic et le chrome du bois d’œuvre traité
chimiquement
des lésions graves et permanentes des voies
respiratoires ou d'autres blessures, y compris
la silicose (une pathologie pulmonaire grave), le
cancer et la mort. Diriger les particules à distance
du visage et du corps. Toujours utiliser l’outil
dans un endroit bien aéré et prévoir un moyen
d’évacuation approprié de la poussière. Utilisez
un dispositif de dépoussiérage, le cas échéant.
Évitez de respirer la poussière et évitez le contact
prolongé avec la poussière. Laisser la poussière
pénétrer dans la bouche ou les yeux ou se
déposer sur la peau peut favoriser l’absorption
d’une matière nocive. Utilisez un dispositif de
protection respiratoire approprié homologué par le
NIOSH/l’OSHA pour l’exposition à la poussière et
laver les régions exposées à l’eau et au savon.
Votre risque en cas d'exposition à ces substances
varie selon la fréquence à laquelle vous effectuez
ce genre d’activité. Pour réduire votre exposition à
ces produits chimiques, travaillez dans un endroit
bien ventilé et avec de l’équipement de protection
approuvé, comme des masques antipoussières
spécialement conçus pour filtrer les particules
microscopiques.
CONSERVEZ CES INSTRUCTIONS.
Consultez-les souvent et utilisez-les pour instruire les autres.
Si vous prêtez cet outil à quelqu'un, prêtez-lui aussi ces instructions.
36
Page 37

RÈGLES DE SÉCURITÉ DE LA SCIE DE TABLE
Le non-respect de ces règles peut provoquer des blessures graves.
• VOIR LA SECTION RÈGLES DE SÉCURITÉ GÉNÉRALES DES OUTILS ÉLECTRIQUES DU PRÉSENT MANUEL.
Lisez le manuel d'instructions en intégralité avant d'utiliser la scie. Apprendre la bonne utilisation et les limites de la
scie, ainsi que les dangers potentiels connexes, pour minimiser le risque d’accidents et de blessures. Assurez-vous
que tous les opérateurs soient familiarisés avec les avertissements et les instructions avant d'utiliser la scie.
• VOIR LA SECTION BRANCHEMENTS ÉLECTRIQUES DU PRÉSENT MANUEL pour les instructions et les
avertissements relatifs aux cordons d'alimentation et aux branchements électriques.
TERMINOLOGIE
Les termes suivants seront utilisés dans le manuel et vous devez les connaître.
– « Coupe transversale » désigne toute coupe qui
traverse complètement la pièce.
– « Coupe non-transversale » désigne toute coupe qui
ne traverse pas complètement la pièce.
_ « Poussoir » désigne un bâton en bois ou en plastique,
généralement fait maison, qui est utilisé pour pousser
une petite pièce à travers la scie et ainsi maintenir les
mains de l'opérateur à distance de la lame.
– Le « rebond » se produit lorsque la lame de scie se
coince dans la coupe ou entre la lame et le guide et
projette la pièce en arrière vers l'opérateur.
– « Main levée » désigne la coupe effectuée sans
guide à onglets ou guide longitudinal ou sans
aucun moyen de guidage ou de maintien de la
pièce autre que la main de l'opérateur.
– « Coupe en plongée » désigne des coupes aveugles
dans la pièce effectuées soit en élevant la lame à
travers la pièce, soit en abaissant la pièce vers la lame.
– « Recoupe » désigne le fait de retourner la pièce
pour faire une coupe que la scie n'est pas capable
d'effectuer en un seul passage.
– « Coupe courbée », également appelée coupe
corniche, est une opération où la pièce est passée
en position inclinée à travers la lame.
Le non-respect de ces règles
peut provoquer des blessures
graves.
1. N'effectuez JAMAIS de coupe à main levée, de
coupe en plongée, de recoupe ou de coupe courbée.
2. PORTEZ DES LUNETTES DE PROTECTION, des
vêtements appropriés, une protection auditive et
une protection contre la poussière comme spécifié
dans la section Règles de sécurité générales des
outils électriques du présent manuel.
3. UTILISER LE PROTÈGE-LAME DE LA SCIE, LE
COUTEAU DIVISEUR ET LES DOIGTS ANTIRETOUR. Votre scie est équipée d'un protège-lame
modulaire, d'un couteau diviseur et d'un ensemble
de doigts anti-retour, dont chaque composant doit
être utilisé dans toutes les opérations possibles, y
compris les coupes transversales. Cet ensemble
est examiné plus en détail ci-dessous. Assurezvous que les composants sont correctement
installés avant l'utilisation.
4. GARDER LES MAINS ET LES AUTRES PARTIES
DU CORPS HORS DE LA TRAJECTOIRE DE LA
LAME. NE mettez jamais une partie de votre corps
dans la trajectoire de la lame de scie.
5. UTILISER UN POUSSOIR approprié à l'opération
en cours pour pousser et maintenir une pièce
jusqu'à ce que la coupe soit terminée. Un poussoir
est un bâton en bois ou en plastique, généralement
fait maison, qui doit être utilisé chaque fois que
la taille ou la forme de la pièce vous amènerait à
placer vos mains à moins de 6 po (152 mm) de la
lame. Les instructions pour fabriquer un poussoir
sont incluses dans ce manuel.
6. ÉVITER LE REBOND. Portez une attention
particulière aux instructions (ci-dessous) pour
réduire le risque de rebond.
7. PAS DE COUPES À MAIN LEVÉE. Utilisez un
guide longitudinal, un guide à onglets ou d'autres
dispositifs appropriés pour guider ou maintenir la
pièce. Utilisez des serre-tôles, des gabarits, des
accessoires ou des planches à languettes pour
aider à guider et contrôler la pièce. Les accessoires
à utiliser avec votre scie sont disponibles auprès
de votre revendeur local ou un centre de service
agréé, moyennant un coût supplémentaire.
8. NE PAS UTILISER LE GUIDE LONGITUDINAL ET
LE GUIDE À ONGLETS EN MÊME TEMPS.
9. NE PAS TENDRE LE BRAS PAR-DESSUS /
AUTOUR DE LA SCIE. Ne tendez pas le bras par
dessus, derrière ou autour de l'outil de coupe
pendant que la lame est en mouvement.
10. STABILITÉ. Assurez-vous que la scie de table est
correctement assemblée et placée sur une surface
stable avant de l'utiliser afin qu'elle ne se déplace
pas pendant la coupe.
11. ASSEMBLAGE CORRECT. N'utilisez pas cette
scie avant qu’elle soit entièrement assemblée et
installée conformément aux instructions.
12. VÉRIFIER LA PIÈCE ET L'INSTALLATION avant
chaque opération. La présence de nœuds,
irrégularités ou clous dans la pièce, les erreurs
de positionnement ou une installation incomplète
peuvent gêner ou affecter les performances de la
scie, ainsi que la sécurité des personnes.
13. UTILISER UNE PLAQUE À GORGE APPROPRIÉE.
La plaque à gorge appropriée doit être en place et
bien fixée en permanence afin de réduire le risque
de projection d'une pièce et les blessures.
14. UTILISER LA LAME ET LE COUTEAU DIVISEUR
APPROPRIÉS pour l'opération prévue. La lame
doit être installée de sorte que les pointes des
dents soient dirigées vers l'avant de la scie.
N'utilisez pas de lame surdimensionnée ou de
lame avec une ouverture d'arbre incorrecte. Serrez
toujours fermement l'écrou de l'arbre de la lame.
Avant utilisation, vérifiez la lame pour fissures
37
suite à la page 37
Page 38

RÈGLES DE SÉCURITÉ DE LA SCIE DE TABLE (suite)
ou dents manquantes. N'utilisez pas de lames
émoussées ou endommagées. Utilisez toujours
des lames dans la gamme d'épaisseurs pour
laquelle le couteau diviseur est conçu.
15. ÉVITER LES OPÉRATIONS ET LES POSITIONS
INCONFORTABLES DE LA MAIN où un glissement
soudain peut entraîner la main sur une lame de
scie. Utilisez la scie avec une table à ou proche du
niveau de la taille pour un équilibre et un contrôle
maximum. Anticipez les effets liés à la taille de la
pièce sur votre capacité à ajuster la position et
garder le contrôle jusqu'à la fin de la coupe.
16. GARDER LES BRAS, LES MAINS ET LES DOIGTS
À AU MOINS SIX POUCES DE LA LAME.
17. NE JAMAIS COUPER DES MÉTAUX, DES
PANNEAUX DE CIMENT OU DE LA MAÇONNERIE.
Certains matériaux synthétiques ont des instructions
spéciales pour la coupe sur scie à table. Suivez les
recommandations du fabricant en permanence.
18. NE JAMAIS TENTER DE DÉBLOQUER UNE
PIÈCE COINCÉE OU BLOQUÉE sans d'abord
éteindre la machine et débrancher la scie de la
source d'alimentation.
19. NE JAMAIS DÉMARRER LA MACHINE AVEC LA
PIÈCE CONTRE LA LAME afin de réduire le risque
de projection de la pièce.
20. NE JAMAIS EFFECTUER DES TRAVAUX
D'ARRANGEMENT, D'ASSEMBLAGE OU DE
PRÉPARATION SUR LA TABLE OU L’ESPACE DE
TRAVAIL pendant que la scie est en marche.
21. AVANT DE LAISSER LA SCIE, attendre que la
lame s'arrête complètement, puis la débrancher
de la source d'alimentation, nettoyer la table et
l'espace de travail et verrouiller l'interrupteur pour
empêcher toute utilisation non autorisée.
22. SOUTENIR LA PIÈCE en fonction de sa taille et du
type d'opération à effectuer. Maintenez fermement
la pièce contre le guide et contre la surface de
la table. Ne laissez pas un panneau large ou une
planche longue (ou une autre pièce volumineuse)
sans soutien - en raison de son poids, la planche
risquerait de se déplacer sur la table, entraînant
ainsi une perte de contrôle.
23. DES BRUITS INCONNUS OU DES VIBRATIONS
EXCESSIVES peuvent indiquer un problème avec
votre scie. Dans ce cas, mettez-la hors tension et
débranchez-la de la source d'alimentation jusqu'à
ce que le problème ait été trouvé et corrigé. Si le
problème persiste, contactez le service à la clientèle.
24. DEMANDEZ CONSEIL à votre superviseur,
formateur ou autre personne qualifiée si vous ne
savez pas parfaitement comment fonctionne cet
appareil.
ENSEMBLE PROTÈGE-LAME, DOIGTS ANTI-RETOUR
ET COUTEAU DIVISEUR DE LA SCIE
Votre scie de table est équipée d'un ensemble
protège-lame, doigts anti-retour et couteau diviseur
qui couvre la lame et réduit la possibilité de contact
accidentel avec la lame. Le couteau diviseur est une
plaque plane qui s'insère dans la coupe faite par la
lame de la scie et permet de minimiser les rebonds
en réduisant la tendance de la lame à se coincer dans
la coupe. Deux doigts anti-retour sont situés sur les
côtés du couteau diviseur qui permettent au bois de
passer à travers la lame dans la direction de coupe,
mais qui réduisent le risque de projection du matériau
vers l'arrière sur l'opérateur. Le protège-lame et les
doigts anti-retour ne peuvent être utilisés que pour
des coupes qui traversent le bois. Lors de feuillures
et autres coupes non-traversantes, le protège-lame
et les doigts anti-retour doivent être enlevés et le
couteau diviseur abaissé à la position de coupe non-
traversante indiquée sur le couteau diviseur.
Utilisez tous les éléments du système de protection
(ensemble protège-lame, couteau diviseur et doigts
anti-retour) pour chaque opération dans laquelle
ils peuvent être utilisés, y compris dans la coupe
traversante. Si vous choisissez de ne pas utiliser l'un
de ces éléments pour une application particulière,
redoublez de prudence vis-à-vis du contrôle de la
pièce, de l'utilisation des poussoirs, la position de vos
mains par rapport à la lame, l'utilisation de lunettes
de sécurité, les moyens d'éviter le rebond et toutes
les autres mises en garde contenues dans ce manuel
et sur la scie elle-même. Réinstallez les éléments de
protection dès que vous revenez à des opérations de
coupe traversante. Gardez l'ensemble de protection
en bon état de fonctionnement.
CONSTRUIRE UN POUSSOIR
Pour utiliser votre scie de table en toute sécurité,
vous devez utiliser un poussoir lorsque, en raison
de la taille ou de la forme de la pièce, vos mains se
trouveraient à une distance inférieure à 6 pouces (152
mm) de la lame de la scie ou d'un autre couteau. Un
poussoir est inclus avec cette scie.
Il n'est pas nécessaire d'utiliser un bois particulier
pour fabriquer des poussoirs à condition qu'ils soient
solides et suffisamment longs et que le bois soit
exempt de nœuds, gerces et fissures. On recommande
une longueur de 16 pouces (400 mm) avec une
encoche qui s'adapte contre le bord de la pièce pour
éviter tout glissement. Il est pratique d'avoir sous la
main plusieurs poussoirs de 16 pouces (400 mm) de
long avec des encoches de différentes tailles pour
s'adapter à différentes épaisseurs de pièce.
La forme peut varier en fonction de vos propres
besoins tant qu’elle exerce sa fonction prévue de
garder vos mains à distance de la lame. Orienter
l'encoche de sorte que le poussoir puisse être
maintenu à un angle de 20 à 30 degrés de la table à
scie vous aidera à maintenir la pièce contre la table
tout en la déplaçant à travers la scie. Reportez-vous au
schéma de la section Accessoires de coupe à la page
57 du présent manuel.
38
Page 39

RÈGLES DE SÉCURITÉ DE LA SCIE DE TABLE (suite)
REBONDS
Les rebonds peuvent causer des blessures graves. Un
rebond se produit lorsque la pièce pince la lame ou se
coince entre la lame de la scie et le guide longitudinal
ou tout autre élément fixe et se soulève de la table pour
être projetée vers l'opérateur. Les rebonds peuvent être
évités en faisant attention aux conditions suivantes.
COMMENT RÉDUIRE LE RISQUE DE
REBOND ET VOUS PROTÉGER CONTRE
D'ÉVENTUELLES BLESSURES :
• S’assurer que le guide longitudinal est parallèle à la
lame de la scie.
• NE PAS exécuter une coupe en exerçant une pression
sur la portion fixe de la pièce qui deviendra la pièce
coupée (libre). Au cours d'une coupe longitudinale, il
est nécessaire d'exercer une pression entre la lame de
la scie et le guide. Utiliser un poussoir pour les pièces
courtes de 6 pouces (152 mm) de largeur ou moins.
• Maintenir le protège-lame, le couteau diviseur et
l'ensemble anti-retour en position et en bon état de
fonctionnement. Le couteau diviseur doit être aligné
avec la lame de la scie et l'ensemble anti-retour
doit arrêter un effet de rebond une fois la machine
amorcée. Vérifier le bon fonctionnement de l'ensemble
anti-retour avant la coupe longitudinale en poussant
une pièce de bois sous l'ensemble anti-retour. Les
dents doivent empêcher la projection de la pièce
de bois vers l’avant de la scie. Si un élément de
l'ensemble n'est pas opérationnel, retournez-le au
centre de service agréé le plus proche pour réparation.
• Il est possible de couper des matières plastiques
et composites (comme des panneaux durs)
avec la scie. Toutefois, puisque ces matières
sont généralement très dures et glissantes, il est
possible que les doigts anti-retour ne puissent
pas contenir un effet de rebond. Il faut donc suivre
attentivement les procédures d'installation et de
coupe lors de coupes longitudinales.
• Utiliser un ensemble de protège-lame, de doigts
anti-retour et couteau diviseur pour toutes les
opérations où cela est possible, y compris en cas
de coupe traversante.
• Lors de coupes longitudinales, pousser la pièce de
l'autre côté de la lame de scie avant de relâcher la
pièce.
• Ne JAMAIS effectuer une coupe longitudinale sur
une pièce qui est tordue ou déformée ou qui n’a
pas de bord droit à faire glisser le long du guide.
• Ne JAMAIS scier une grande pièce qui ne peut pas
être contrôlée.
• NE JAMAIS utiliser le guide comme une butée
longitudinale lors des coupes transversales.
• Ne JAMAIS scier une pièce qui présente des
nœuds instables, des défauts, des clous ou tout
autre corps étranger.
• Ne JAMAIS couper une pièce de moins de 10
pouces (254 mm).
• Ne JAMAIS utiliser une lame émoussée. Une lame
émoussée doit être remplacée ou affûtée.
BRANCHEMENTS ÉLECTRIQUES
SOURCE D'ALIMENTATION
Cette scie est équipée d'un moteur de 13 ampères pour
une utilisation sur courant alternatif de 120 volts et 60
Hz. Elle peut être re-câblée par un électricien qualifié
pour une utilisation avec une source d'alimentation de
240 volts. Voir les instructions ci-dessous concernant les
branchements appropriés pour le câblage de votre scie.
Pour la tension, le câblage de l'atelier est aussi
important que la puissance du moteur. Une ligne
conçue uniquement pour l'éclairage peut ne pas être
en mesure de transférer correctement le courant
nécessaire au moteur d'un outil électrique; un fil
suffisamment épais pour une distance courte peut être
trop fin pour une distance plus longue, et une ligne
pouvant supporter un outil électrique peut ne pas être
en mesure de supporter deux ou trois outils.
NE PAS UTILISER L’APPAREIL DANS UN ENDROIT HUMIDE OU MOUILLÉ ET NE PAS L’EXPOSER
À LA PLUIE.
DIRECTIVES DE MISE À LA TERRE
CET APPAREIL DOIT ÊTRE MIS À LA TERRE LORSQU’IL EST UTILISÉ POUR PROTÉGER
L’OPÉRATEUR CONTRE L’ÉLECTROCUTION.
En cas de mauvais fonctionnement ou de panne,
la mise à la terre fournit un chemin de moindre
résistance au courant électrique visant à réduire
le risque d’électrocution. Cet appareil est muni
d’un cordon électrique doté d'un conducteur
39
Un circuit électrique séparé devrait être utilisé pour
vos appareils. Les fils du circuit doivent être au moins
de calibre 12 et être protégés par un fusible à action
différée de 20 ampères. Si vous utilisez une rallonge,
utilisez uniquement des rallonges à trois fils avec des
fiches de mise à la terre à trois broches et la prise
correspondante qui acceptera la fiche de la machine.
Avant de raccorder la machine à l’alimentation,
s’assurer que le ou les interrupteurs sont sur la position
« OFF » (arrêt) et que le courant électrique possède
les mêmes caractéristiques que celles indiquées sur la
machine. Une chute de tension importante entraînera
une perte de puissance et une surchauffe du moteur.
Cela peut également endommager la machine.
de terre et d'une fiche de mise à la terre. La fiche
doit être branchée sur une prise correspondante
qui soit correctement installée et mise à la terre,
conformément aux codes et règlements locaux.
Ne pas modifier la fiche fournie sur votre scie ou
Page 40

BRANCHEMENTS ÉLECTRIQUES
(suite)
re-câblée par votre électricien. Si elle ne rentre pas
dans la prise, faites installer une prise adéquate par un
électricien qualifié.
Le raccordement inapproprié du conducteur de terre
de l’équipement peut provoquer l’électrocution. Le
fil conducteur avec isolation et doté d'une surface
extérieure verte, avec ou sans rayures jaunes, est
le conducteur de terre. Si la réparation ou le
remplacement du cordon électrique ou de la fiche
s’avère nécessaire, ne pas raccorder le conducteur
de terre de l’équipement à une borne sous tension.
Si les consignes de mise à la terre ne sont pas
complètement comprises ou en cas de doute
concernant la mise à la terre de l’appareil, se
renseigner auprès d’un électricien ou du personnel de
service agréés.
Utiliser uniquement des cordons à 3 fils avec des fiches
de mise à la terre à 3 broches et des prises adaptées
à la fiche de la machine, comme illustré à la Figure
A, ou une prise correctement reliée à la terre avec un
adaptateur mis à la terre, comme illustré à la Figure B.
Réparez ou remplacez immédiatement tout cordon
endommagé ou usé.
DANS TOUS LES CAS, ASSUREZ-VOUS QUE LE RÉCEPTACLE EN QUESTION EST BIEN RELIÉ
À LA TERRE. EN CAS DE DOUTE, FAITES VÉRIFIER LA PRISE PAR UN ÉLECTRICIEN QUALIFIÉ.
Il s'agit d'un outil raccordé à un cordon et mis à la terre, destiné à une utilisation sur un circuit d’alimentation ayant
une puissance nominale de 120 volts. Il est conçu pour une utilisation sur un circuit qui comporte une prise, comme
le montre la FIG. A. Il est doté d'une fiche comme illustré dans la Figure A. Si vous avez une prise à 2 pôles, comme
le montre la FIG. B. vous pouvez utiliser un adaptateur temporaire, comme le montre la FIG. B. Si vous ne disposez
pas d'une prise correctement mise à la terre. La cosse à oreille verte dépassant de l'adaptateur doit être connectée
à une boîte de courant reliée à la terre en permanence. L'adaptateur temporaire doit uniquement être utilisé jusqu'à
ce qu'une sortie correctement mise à la terre puisse être installée par un électricien qualifié.
BOÎTE DE COURANT
RELIÉE À LA TERRE
BROCHES PORTEUSES
DE COURANT
BOÎTE DE COURANT
RELIÉE À LA TERRE
MOYENS DE MISE
À LA TERRE
ADAPTATEUR
LA LAME DE
MISE À LA TERRE EST LA PLUS
LONGUE DES 3
FIG. A
FIG. B
Broche de mise à la terre
FIG. C
Cet outil peut être converti pour un circuit d'alimentation de 240 volts par un électricien qualifié. S'il est converti à
240 volts, il doit être équipé d'une fiche de mise à la terre comme le montre la FIG.C et doit être branché sur une
prise, comme le montre la FIG. C, reliée à une mise à la terre permanente. Aucun adaptateur n'est disponible ou doit
être utilisé avec cet outil en cas de conversion à 240 volts.
RALLONGES
N'utilisez jamais une rallonge endommagée. Vérifiez les rallonges avant chaque utilisation. Si la
rallonge est endommagée, remplacez-la immédiatement. Toucher la zone endommagée pourrait provoquer un
choc électrique entraînant des blessures graves.
Maintenez la rallonge hors de l'espace de travail. Positionnez le cordon afin qu'il n'accroche
pas aux pièces de bois, outils et autres obstacles.
• Utilisez des rallonges appropriées. Veillez à utiliser une rallonge en bon état et vérifiez qu’il s’agit d’une rallonge
à 3 fils avec une fiche de mise à la terre à 3 broches et que vous disposez d’une prise adaptée à la fiche de la
machine, tel que décrit dans les Instructions de mise à la terre figurant dans le présent manuel. Lorsque vous
utilisez une rallonge, assurez-vous qu’elle soit d'un calibre suffisamment élevé pour alimenter la machine en
électricité. Une rallonge d’un calibre trop petit provoquera une chute de tension, entraînant une perte de puissance
et une surchauffe. Le tableau ci-dessous indique le calibre maximal à utiliser en fonction de la longueur du cordon.
En cas de doute, utilisez le calibre immédiatement supérieur. Plus le numéro de calibre est petit, plus le cordon est
épais. Utilisez exclusivement des cordons ronds, chemisés, répertoriés par Underwriters Laboratories (UL).
40
Page 41

CALIBRE MINIMUM POUR RALLONGE
CALIBRES RECOMMANDÉS POUR UTILISATION SUR
DES APPAREILS ÉLECTRIQUES STATIONNAIRES
Intensité Volts Longueur totale du
0-6
0-6
0-6
0-6
6-10
6-10
6-10
6-10
10-12
10-12
10-12
10-12
12-16
12-16
240
240
240
240
240
240
240
240
240
240
240
240
240
240
cordon en pieds
jusqu'à 50
50-100
100-200
200-300
jusqu'à 50
50-100
100-200
200-300
jusqu'à 50
50-100
100-200
200-300
jusqu'à 50
50-100
Calibre de la
rallonge
18 AWG
16 AWG
16 AWG
14 AWG
18 AWG
16 AWG
14 AWG
12 AWG
16 AWG
16 AWG
14 AWG
12 AWG
14 AWG
12 AWG
DÉBALLAGE
CALIBRE MINIMUM POUR RALLONGE
CALIBRES RECOMMANDÉS POUR UTILISATION SUR
DES APPAREILS ÉLECTRIQUES STATIONNAIRES
Intensité Volts Longueur totale du
0-6
0-6
0-6
0-6
6-10
6-10
6-10
6-10
10-12
10-12
10-12
10-12
12-16 120 jusqu'à 25 14 AWG
12-16 120 25-50 12 AWG
12-16 120
120
120
120
120
120
120
120
120
120
120
120
120
cordon en pieds
jusqu'à 25
25-50
50-100
100-150
jusqu'à 25
25-50
50-100
100-150
jusqu'à 25
25-50
50-100
100-150
IL EST DÉCONSEILLÉ D'UTILISER UNE LONGUEUR DE
PLUS DE 50 PIEDS (15,24 M).
Calibre de la
rallonge
18 AWG
16 AWG
16 AWG
14 AWG
18 AWG
16 AWG
14 AWG
12 AWG
16 AWG
16 AWG
14 AWG
12 AWG
• La machine est lourde, deux personnes sont
nécessaires pour la déballer et la soulever.
• Placez une courroie de sécurité autour de la
machine pour éviter qu’elle bascule lors du levage.
• Avant d'assembler et d'utiliser la machine, lisez
attentivement ce manuel pour vous familiariser
avec les procédures d’assemblage, d’entretien et
de sécurité appropriées.
Vérifiez que l’emballage d’expédition et la machine ne
sont pas endommagés avant de le déballer. Retirez
délicatement les composants de la couche de mousse
supérieure. Enlevez la couche de mousse supérieure,
puis retirez tous les composants de la couche de
mousse inférieure. Posez toutes les pièces sur un
morceau de carton ou autre surface plane et propre.
Au moins deux personnes ou plus sont nécessaires
pour sortir la scie du carton. Toujours vérifier et retirer
les matériaux d’emballage de protection autour des
moteurs et des pièces mobiles. Ne jetez pas le carton
d'expédition et les matériaux d'emballage avant d'en
avoir soigneusement vérifié le contenu, assemblé la
machine et être certain qu'elle fonctionne correctement.
Comparez le contenu du colis avec la liste des
composants et des pièces et la liste des sachets de
quincaillerie avant l'assemblage pour vous assurer que
rien ne manque. Inspectez soigneusement les pièces
pour vous assurer qu'il n'y a eu aucun dommage
pendant le transport. Si des pièces sont manquantes,
endommagées ou prémontées, ne pas assembler. Au
lieu de cela, appelez le Service à la clientèle DELTA
®
au
1-800-223-7278 pour obtenir de l'aide.
Après le montage, retirez les matériaux et enduits de
protection de toutes les pièces et de la scie de table.
Les enduits de protection peuvent être retirés en les
pulvérisant de WD-40
®
et en les essuyant avec un
chiffon doux. Il peut être nécessaire de renouveler
cette étape plusieurs fois avant que tous les enduits
de protection soient complètement enlevés.
Après nettoyage, appliquez une cire en pâte de bonne
qualité à toutes les surfaces en fonte non peintes.
Assurez-vous de bien lustrer la cire avant le montage.
41
Page 42

DÉBALLAGE
(suite)
LISTE DES
COMPOSANTS
DESCRIPTION (QTÉ)
1. Établi de scie avec lame au
carbure et clé plate (1)
2. Rallonge extensible
3. Boîtier de commutation
(attaché à la scie) (1)
4. Support tubulaire (2)
5. Panneaux de support (4)
6. Roulettes intégrées (2)
7. Pieds réglables (2)
8. Pédale et roulette pivotante
(cachées) (fixées à la scie)
(1)
9. Manivelles à poignée (2)
(fixées à la scie)
10. Boutons de blocage (2)
11. Guide à onglets (1)
12. Poignée du guide de
refente (1)
13. Rallonge extensible (2) avec
36-5000 et 5100 (1) avec
36-5052 et 36-5152
14. Guide de refente (1)
15. Plaque à gorge (1)
16. Carter de lame et griffes
anti retour
17. Lame (1)
18. Poussoir (1)
19
2
Contenu de l'autre
boîte
19. Rail arrière
20. Rail de guidage du
guide
21. Rail avant du guide
1
18
3
4
5
6
17
Contenu de la boîte pour 36-5052
et 36-5152 seulement
22. Table de rallonge en bois
23. Pieds
16
15
14
13
11
12
10
23
9
8
7
22
21
20
42
Page 43

DÉBALLAGE
ENSEMBLES DE QUINCAILLERIE
Versions avec guide de 30" (36-5000 et 36-5100)*
(suite)
Description Qté Emplacement d'utilisation
Boulon de carrosserie 8mm x 70mm 1 Relie les moitiés du support
Écrou frein M8 1 Relie les moitiés du support
Rondelle à ressort M8 1 Relie les moitiés du support
Boulon de carrosserie M6 x 70mm 4 Relie le pied du support au support
Écrou de blocage M6 4 Relie le pied du support au support
Goupille axiale M8 x 53mm 2 Roulettes
Écrou de blocage M8 2 Roulettes
Vis auto taraudeuse M6 x 10mm à tête Phillips 16 Panneaux du support
Vis tête hex. 5/16-18 x 7/8" avec rondelle
à ressort
Vis à tête bombée 1/4 -20 x ½'' hex. creuse 6 Tube de guide au rail
Vis à tête plate 5/16-18 x 1'' 8 Rail avant à établi et rallonges 8
Écrou à bride hex. 5/16-18 19 Rallonges à établi 6, rallonge à
Jauge d'alignement du rail 1
Rondelle crantée conique 5/16'' 1 Sur 1 vis pour le rail avant allant dans
Rondelle crantée plate 5/16'' 1 On 1 screw for the rear rail going into table 192
17 Rallonges à établi 6, rallonge à
rallonge 3, rail arrière 8
rallonge 3 (36-5000), rail arrière 8, rail avant 8
l'établi pour la mise à terre.
Élt. n°/ liste
des pièces
153
155
154
144
145
151
155
146
58
35
19
16
190
191
* La quincaillerie fournie servira à la scie modèle 36-5000 qui utilise le plus de quincaillerie.
Versions guide 52" (36-5052 et 36-5152) **
Description Qté Emplacement d'utilisation
Boulon de carrosserie 8mm x 70mm 1 Relie les moitiés du support
Écrou frein M8 1 Relie les moitiés du support
Rondelle à ressort M8 1 Relie les moitiés du support
Boulon de carrosserie M6 x 70mm 4 Relie le pied du support au support
Écrou de blocage M6 4 Relie le pied du support au support
Goupille axiale M8 x 53mm 2 Roulettes
Écrou de blocage M8 2 Roulettes
Vis auto taraudeuse M6 x 10mm à tête Phillips 16 Panneaux du support
Vis tête hex. 5/16-18 x 7/8" avec rondelle
à ressort
Rondelle plate 5/16-18 6 Rallonge à établi en bois, deux côtés
Vis à tête bombée hex. creuse 1/4 -20 x 1/2'' 8
Vis à tête plate 5/16-18 x 1'' 6
Écrou à bride hex. 5/16-18 15
Vis à tête hex. 1/4-20 x 1 1/2'' 6
Rondelle plate 1/4'' 1
Écrous hex. 1/4-20 1
Vis auto-taraudeuse tête Phillips #8 x 3/4'' 8
Vis #10-32 x 3/4'' 4
Rondelle plate #10 4
Écrous hex. #10-32 4
Jauge d'alignement du rail 1
Rondelle crantée conique 5/16'' 1
Rondelle crantée plate 5/16'' 1
15 Rallonges à établi 6, rail arrière 6,
rallonge à établi en bois 3
sur 36-5052
Tube de guide au rail
Rail avant à établi et rallonges 6
Rail arrière 6, rail avant 6, rallonge à
établi en bois 3, (36-5052)
Rails à établi en bois
2
2
Rails à établi en bois
Rails à établi en bois
Pieds à table
Pieds à table
Pieds à table
Pieds à table
Sur 1 vis pour le rail avant allant dans
l'établi pour la mise à terre.
Sur 1 vis pour le rail arrière allant dans
l'établi pour la mise à terre.
Élt. n°/ liste
des pièces
153
155
154
144
145
151
155
146
58
193
35
19
16
183
184
185
182
180
179
181
190
191
192
** La quincaillerie fournie servira à la scie modèle 36-5000 qui utilise le plus de quincaillerie.
43
Page 44

MONTAGE
• Ne soulevez pas la scie sans aide. Tenez-la près de
votre corps en soulevant. Gardez les genoux pliés
et soulevez en utilisant les jambes, pas le dos.
• Assemblez complètement la scie avec le
piètement avant de l'utiliser. Le piètement est une
partie intégrante et nécessaire de la structure de
support de cette scie.
• Ne modifiez pas la scie, ne créez pas
d'accessoires non recommandés pour utilisation
avec cette scie.
• Assurez-vous que l'interrupteur d'alimentation
est en position « OFF » (arrêt) avant de brancher
l'alimentation électrique.
• Ne branchez pas sur le secteur avant que le
montage soit terminé
Évitez tout contact avec les dents
de la lame. Laissez la lame rangée
ou abaissée si possible.
OUTILS REQUIS POUR LE MONTAGE
(NON INCLUS) :
• Tournevis plat
• Tournevis à tête Phillips
• Clé de 8mm
• Clé de 10mm
• Clé de 12mm
• Clé de 13mm
• Clé de 3/8''
• Clé de 7/16''
• Clé de 1/2''
• Clé de 9/16''
• Clé hex. Allen de 6mm
• Clé hex. Allen de 5/32''
• Clé hex. Allen de 3/16''
SOCLE
1. Connectez les deux pattes tubes en insérant
l'extrémité de la patte gauche (A) dans l'extrémité
de la patte droite (B) comme le montre la Figure 1.
Fixez avec boulon de carrosserie M8 X 70 mm et
un écrou autobloquant, puis serrez à la main.
2. Insérez les quatre extrémités ouvertes des pattes
tubes dans les colliers des pattes (C), comme
illustré. Fixez chaque patte avec un boulon et un
écrou de 6 mm x 70 mm.
3. Fixez les panneaux de support de patte arrière et
avant (D) sur les pattes à l'aide de quatre boulons
autotaraudeur M6 x 12 mm.
B
A
C
D
Avant de la scie
FIGURE 1
44
Page 45

MONTAGE
ROUES ET PIEDS FIXES
1. Fixez les deux roues fixes (A) sur les deux
pattes gauches, en face de la roulette
pivotante, à l'aide des boulons à épaulement de
carrosserie comme dans la Figure 2.
2. Vissez les pieds réglables (C) dans les inserts
filetés de la patte droite, à côté de la roulette
pivotante.
3. Placez un morceau de 2x4 au dos de la scie,
comme le montre la Figure 3, pour éviter
d'endommager le capteur de poussière lors
du relevage de la scie.
4. Relevez la scie côté droit vers le haut.
La machine est lourde,
deux personnes sont
nécessaires pour la lever.
5. Les deux pieds réglables (C) peuvent être
soulevés et abaissés en les faisant tourner.
Les pieds peuvent être réglés pour niveler
la scie et verrouillés en place avec les vis de
calage verrouillables à l'aide d'une clé Allen
de 6 mm. Voir Figure 2.
(suite)
C
A
B
FIGURE 2
RALLONGES EXTENSIBLES
Pour les modèles avec trois rallonges
extensibles
1. Attacher la rallonge extensible du côté gauche
(A) à l'établi à l'aide de trois vis à tête plate
5/16-18 x 7/8”.
2. Placer les deux rallonges extensibles restantes
sens dessus dessous sur l'établi. Placer le
côté de la rallonge à monter sur l'établi de scie
près du rebord de l'établi de scie, de sorte
que la disposition des trous de la rallonge
corresponde à celle des trous de la scie. Si
vous avez une rallonge en fonte, elle sera
montée sur l'établi de scie. Placer l'autre
rallonge de manière adjacente à la rallonge de
sorte que les dispositions des trous coïncident.
Attacher les deux rallonges ensemble à l'aide
de trois vis à tête hex. 5/16-18 x 7/8'' et des
écrous à bride hex. correspondants.
3. Retourner les deux rallonges attachées
ensemble (B) et les attacher à l'établi de scie à
l'aide de trois vis à tête hex. 5/16-18 x 7/8''.
FIGURE 3
4. S'assurer que les rebords supérieurs des
rallonges sont au même niveau que le sommet
de l'établi et resserrer les six vis.
12
11
10
9
8
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
INCH
0
A
FIGURE 4
B
45
Page 46

Table
Jauge
Rail
Table
Jauge
Rail
RALLONGES
EXTENSIBLES
Pour les modèles avec deux
rallonges extensibles et une table
de rallonge en bois.
1. Attacher les rallonges extensibles des
côtés gauche et droit (A) à l'établi à
l'aide de trois vis à tête plate 5/16- 18 x
7/8” pour chacune.
2. S'assurer que les rebords supérieurs
des rallonges sont au même niveau que
le sommet de l'établi et resserrer les six
vis.
3. Passer au montage des rails.
MONTAGE
A
(suite)
3
2
1
INCH
0
12
11
10
9
8
7
6
5
4
FIGURE 5
RAIL AVANT ET ARRIERE
1. Attacher le rail (A) avant (2”x2”x57” pour
les modèles de capacité de refente de
30”), (2”x2”x79” pour les modèles de
capacité de refente de 52”), à l'établi et
aux rallonges extensibles à l'aide des vis
à tête plate 5/16-18 x 1 1/8''. Aligner les
trous du rail avec ceux de l'établi et des
rallonges extensibles.
2. Utiliser la jauge d'alignement du rail
fournie (B) pour s'assurer que le rail est
à une distance appropriée du sommet
de l'établi de chaque côté de l'établi en
fonte (fig 6). Puis utiliser la jauge pour
établir la même distance appropriée
pour les rallonges extensibles.
3. Aligner le rail arrière sur les trous situés
à l'arrière de l'établi de scie et sur les
rallonges extensibles. Attacher le rail
arrière à l'établi de scie à l'aide de deux
vis à tête hex. 5/16-18 x 7/8.
4. Attacher le rail arrière aux rallonges
extensibles à l'aide de trois vis à tête
hex. 5/16-18 x 7/8'' et des écrous à
bride hex. correspondants.
5. Utiliser la jauge d'alignement du rail
(B) pour s'assurer que le rail est à une
distance appropriée du sommet de
l'établi de chaque côté de l'établi en
fonte (fig 6). Puis utiliser la jauge pour
établir la même distance appropriée
pour les rallonges extensibles.
Arrière
A
Avant
C
FIGURE 6
46
Page 47

MONTAGE
A
B
C
G
J
(suite)
TABLE DE RALLONGE EN BOIS
Seulement pour les modèles de capacité de
refente de 52”
1. Placer la table en bois (A) sens dessus dessous sur le
sol ou un banc.
2. Placer les pieds (B) dans les coins tel illustré (fig 7), la
paroi verticale de la plaque d'angle devant être contre la
jupe en bois d'extrémité (C) de la table.
3. Fixer les pieds au panneau de table à l'aide de (8) #8 x
5/8” vis auto taraudeuses (D).
4. Utiliser une mèche de ¼'' pour percer avec soin au
travers des trous de la plaque d'angle verticale des trous
dans la jupe de la table en bois. Placer de l'extérieur
les vis #10 x 1 3⁄4” (E) dans les orifices percés, puis
assembler les rondelles et écrous #10 sur les vis et
serrer.
5. Placer sans les serrer les vis (3) 5/16-18 x 7/8'', rondelles
et écrous (F) dans les trois trous sur le côté de la
rallonge extensible tel illustré (fig 8).
6. Faire descendre avec soin le support angulaire de la
table (G) de sorte que les rainures coïncident avec les
vis de la rallonge extensible. Serrer les vis une fois la
table en bois à niveau avec la rallonge extensible.
A
F
B
FIGURE 7
FIGURE 8
E
C
D
H
7. Utiliser la jauge d'alignement du rail (H) pour régler les
pieds (I) de sorte que le sommet de la table est à une
distance appropriée du rail.
8. Percer des trous de ¼'' au travers des trous des rails
avant et arrière (J) dans la table en bois (fig 9).
9. Attacher la table en bois aux rails à l'aide de vis 1⁄4-20 x
1 1⁄2'',rondelles plates, rondelles de blocage et écrous.
FIGURE 9
I
GUIDE DE BUTÉE ET BOÎTE DE COMMANDE DE PUISSANCE
1. Reliez les deux moitiés du guide de butée (A et B) en
insérant l’extrémité la plus petite dans l’extrémité la plus
grande. Voir Figure 10.
2. Fixez le guide de butée au rail avant à l’aide de cinq
vis hexagonales à tête ronde de 1/4-20 x 1/2 pouces
(514,35 mm x 12,70 mm) et de cinq ressort freins
de ¼ pouces (6,35 mm) à travers les trous
(C) sur le côté inférieur du rail avant.
3. Alignez les deux trous du support de la
boîte de commande de puissance avec
les trous sous le rail avant (D), situé sur le
côté gauche de la scie. Fixez la boîte de
commande de puissance au rail avant à
l’aide de deux vis à tête ronde de 1/4-20 x 1/2
pouces (514,35 mm x 12,70 mm).
4. Fixez le cordon d'alimentation suspendu sur le
côté arrière du rail avant au moyen d'une broche
d'agrafe et d'une vis à tête ronde M5 x 6 mm.
FIGURE 10
47
Page 48

PLAQUE À GORGE
MONTAGE
(suite)
1. Pour installer la plaque à gorge, abaissez la lame en
dessous du plateau de la table, puis faites passer
soigneusement la plaque à gorge, extrémité fendue
d’abord, de l’avant de la table à l’arrière, en gardant
la lame centrée dans la fente de la plaque à gorge.
Voir Figure 11. La plaque doit reposer à l’intérieur
de la cavité dans le plateau de la table.
2. Assurez-vous que la plaque à gorge est alignée
avec la partie supérieure de la table.
3. Si la plaque n’est pas alignée avec le plateau de
la table, ajustez la hauteur de la plaque à gorge au
moyen des quatre vis de pression (A).
REMARQUE : Lors de l’installation du couteau diviseur,
des doigts anti-retour et du protège-lame, la lame doit
être au réglage de 90 degrés et élevée à la hauteur
maximale. Voir Lever et abaisser la lame, à la page 48.
LAME ET COUTEAU DIVISEUR
Pour réduire le risque de
blessures graves, le couteau
diviseur doit être installé et positionné
correctement pour chaque coupe traversante et
non traversante possible.
1. La scie est livrée avec la lame et le couteau
diviseur installés et alignés correctement. Le
couteau diviseur est installé dans la position de
coupe basse, non traversante. Avant d’utiliser
votre scie, assurez-vous que l’alignement de
la lame dans la fente à onglets et du couteau
A
FIGURE 11
diviseur par rapport à la lame n’a pas été affecté
par le transport. Pour vérifier l’alignement de la
lame et du couteau diviseur, voir page 60 dans la
section Alignement de ce manuel.
2. Le couteau diviseur est installé dans la position
de coupe basse, non traversante. Pour fixer les
doigts anti-retour et les ensembles protège-lame,
le couteau diviseur doit être en position relevée,
comme indiqué sur la Figure 9. Pour lever et
abaisser le couteau diviseur, voir Réglages de la
hauteur du couteau diviseur à la page 50.
DOIGTS ANTI-RETOUR ET PROTÈGE-LAME
DOIGTS ANTI-RETOUR
Pour réduire le risque de
blessures graves, les doigts
anti-retour doivent être en place lorsque vous
effectuez une coupe traversante.
1. Reportez-vous à la Figure 12 et localisez la fente
de montage des doigts anti-retour (A) au milieu du
bord supérieur du couteau diviseur.
2. Faites coulisser la fente au milieu de l’ensemble de
doigts anti-retour le long de la partie supérieure du
couteau diviseur jusqu’à ce que la tige (B) localise
la fente centrale sur le couteau diviseur.
3. Enfoncez la tige sur l’ensemble de doigts antiretour (B) pour permettre à l’ensemble de tomber
dans la fente. Appuyez sur l’ensemble de doigts
anti-retour jusqu’à ce qu’il s’enclenche et se
verrouille. Relâchez la tige. REMARQUE : Tirez
sur les doigts anti-retour pour vous assurer qu’ils
sont bien verrouillés en place.
Pour retirer les doigts anti-retour, appuyez sur la tige
(B) et tirez l’ensemble de doigts anti-retour hors du
couteau diviseur.
48
B
A
FIGURE 12
Page 49

MONTAGE
PROTÈGE-LAME
Pour réduire le risque de
blessures graves, le protègelame doit être en place lorsque vous effectuez
une coupe traversante.
1. Tout en maintenant l’ensemble protège-lame (A) en
position verticale, accrochez le goujon de guidage
(B) à l’extrémité arrière de l’ensemble protège-lame
dans la fente sur le bord arrière du couteau diviseur.
2. Faites tourner l’ensemble protège-lame vers l’avant
de la scie jusqu’à ce que la partie métallique (C) de
l’ensemble protège-lame soit parallèle à la table
comme le montre la Figure 13.
3. Tout en maintenant enfoncé l’avant de la partie
métallique du protège-lame (C), appuyez sur le levier
de verrouillage du protège-lame (D) jusqu’à ce qu’il
s’enclenche en position verrouillée. Assurez-vous
que le protège-lame est verrouillé sur le couteau
diviseur en tirant sur le protège-lame. Si le protègelame n’est pas verrouillé, le levier de verrouillage du
protège-lame retournera à la position déverrouillée.
(suite)
A
B
FIGURE 13
D
C
Si la partie métallique de
l’ensemble protège-lame (C)
n’est pas parallèle à la table, le couteau diviseur
n’est pas dans la position relevée. Retirez
l’ensemble protège-lame et les doigts anti-retour et
relevez le couteau diviseur, puis réinstallez les
doigts anti-retour et l’ensemble protège-lame.
GUIDE LONGITUDINAL
Reliez la poignée à la came du guide
Le guide longitudinal coulisse sur le rail de la butée
arrière de sorte que le crochet soit sous le rail arrière
et se déplace sur le tube de guidage avant. La butée
se verrouille en place en appliquant une pression dans
un mouvement vers le bas sur la poignée du guide
longitudinal. L’alignement du guide longitudinal doit
être vérifié avant d’utiliser votre scie. Pour vérifier
l’alignement du guide longitudinal, voir les instructions
d’alignement à la page 61.
GUIDE À ONGLETS
Pour retirer l’ensemble protège-lame :
1. Soulevez le levier de verrouillage du protège-lame
(D) à la position déverrouillée.
2. Tournez le protège-lame vers l’arrière et faites glisser
le goujon (B) hors de la fente du couteau diviseur.
RANGEMENT INTÉGRÉ
La scie sur table DELTA no 36-5000 série pour les
entrepreneurs est livrée avec un rangement intégré
pour le guide à onglets, la clé à arbre, le poussoir et la
butée fournis. Il y a aussi un rangement intégré pour les
lames de scie de rechange (vendues séparément). Les
espaces de rangement pour le guide à onglets, la lame
de rechange et la clé à arbre sont situés sur le panneau
latéral droit de la machine et sont préinstallés.
Les espaces de rangement intégrés pour la butée et le
poussoir se trouvent sur le côté gauche de la scie.
Insérez le guide à onglets dans chaque fente pour
vous assurer qu’il coulisse librement. Voir la section
Réglage des butées d’onglet à la page 60 pour le
réglage de précision du guide à onglets.
49
Page 50

MONTAGE
(suite)
AJUSTEMENT DES BUTÉES FIXES POUR L’ANGLE
DE BISEAU DE 90° ET 45°
Il y a des butées fixes à chaque extrémité de la plage
de biseau. Pour assurer des coupes précises, les
butées fixes doivent être positionnées exactement à
90° et 45°. Les butées coniques sont correctement
réglées en usine. Cependant, pour une précision
maximale, vous devez vérifier la position des butées
lors de l’assemblage et de temps en temps pour vous
assurer que les réglages restent satisfaisants. Pour
vérifier la position des butées et l'ajuster si nécessaire,
reportez-vous à la Figure 14 et procédez comme suit.
1. Relâchez le bouton de verrouillage de l’inclinaison
de la lame.
2. Faites tourner le volant de commande
d’inclinaison de la lame dans le sens horaire et
inclinez la lame à l'opposé du, puis de nouveau
vers le sens perpendiculaire jusqu’à ce que la
butée ait atteint la position « arrêt ».
3. En utilisant une équerre de menuisier, vérifiez
l’angle de la lame par rapport à la table, comme le
montre la Figure 17b, page 50. Si la lame est à 90°
par rapport à la table, passez à l’étape 6.
4. Si la lame n’est pas perpendiculaire à la table,
tournez le volant de commande pour incliner
légèrement la lame à l'opposé de la position
d’arrêt, puis ajustez la butée de 90° en tournant
la vis de pression à tête creuse située dans le
plateau de la table immédiatement en avant de la
partie gauche de la plaque à gorge (A). Revérifiez
l’angle avec l’équerre de menuisier et continuez à
ajuster jusqu’à ce que la lame soit à 90 degrés lors
du retour à la position d’arrêt.
5. Tournez le volant de commande d’inclinaison de
la lame en sens antihoraire jusqu’à ce qu’il repose
sur la butée de 45°. Ensuite, répétez les étapes 4
et 5, en réglant la butée de 45° en tournant la vis
de pression à tête creuse située en avant de la
partie droite de la plaque à gorge. (B)
A
FIGURE 14
B
FIXATION DE LA SCIE AU SOL
Cette scie se distingue par sa
portabilité. N’essayez pas
d’utiliser la scie pour couper une pièce grande ou
encombrante sans prendre les mesures appropriées
pour vous protéger contre le risque de basculement
de la scie. Les exemples de mesures appropriées
comprennent l’utilisation de tables de support et/ou la
fixation des pattes de la scie au sol en remplaçant les
pieds de la scie avec des boulons de raccordement
ou en reliant les pattes à un support monté au sol
avec des sangles en U.
PRÉPARATION POUR COUPER
Le non-respect des
avertissements suivants peut
entraîner des blessures
graves.
• TOUJOURS s’assurer que la pièce d’usinage n’est
pas en contact avec la lame avant d'actionner le
commutateur pour démarrer la scie. Le contact
avec la lame pourrait entraîner le rebond ou la
projection d'une pièce.
• Pour réduire le risque de démarrage accidentel,
TOUJOURS s’assurer que le commutateur est
en position arrêt avant de brancher la scie à la
source d’alimentation.
• NE PAS utiliser de lames de qualité inférieure
à la vitesse de cet outil. Le non-respect de cet
avertissement peut entraîner des blessures graves.
• Éteindre la machine et la débrancher de la source
d’alimentation avant d’installer et de retirer tout
accessoire, avant d'effectuer des réglages et
des réparations. Un démarrage inopportun peut
provoquer des blessures.
• Avant de faire fonctionner la scie, veillez à
vous familiariser avec ses caractéristiques et
commandes et vérifiez que vous avez fait tous les
ajustements nécessaires comme décrit ci-dessous.
50
Page 51

PRÉPARATION POUR COUPER
MONTAGE
SOULEVER ET ABAISSER
LA LAME
Pour la plupart des applications, il est recommandé de
soulever la lame de 1/8 pouces (3,2 mm) à ¼ pouces
(6,4 mm) au-dessus de la surface supérieure de la pièce.
Relevez ou abaissez la lame avec le volant de
commande (A) situé à l’avant de la scie (voir Figure 15).
1. Avant de soulever ou d’abaisser la lame, veillez
à desserrer le bouton de verrouillage (B) en le
tournant dans le sens antihoraire.
2. Pour soulever la lame de la scie, tournez le volant
de commande dans le sens horaire. Pour abaisser
la lame de la scie, tournez le volant de commande
dans le sens antihoraire.
3. Serrez le bouton de verrouillage pour maintenir
la lame à la hauteur désirée. Seule une légère
pression suffit à verrouiller fermement le
mécanisme de soulèvement de la lame. Toute
pression supplémentaire applique simplement une
tension inutile sur le dispositif de verrouillage.
4. Lorsque vous avez terminé d’utiliser la scie
et lors de l’entretien, des ajustements ou des
réparations, abaissez la lame en dessous de la
surface de la table.
(suite)
B
A
FIGURE 15
INCLINAISON DE LA LAME
La lame peut être inclinée jusqu’à 45° vers la gauche
à l’aide du volant d’inclinaison de la lame (A) situé
sur le panneau latéral droit de la scie. L’angle
d’inclinaison est mesuré par la jauge de biseau sur la
face avant de la scie. Pour incliner la lame de la scie :
1. Desserrez le bouton de verrouillage (B) dans le
sens antihoraire et tournez le volant de commande
dans le sens horaire. Un indicateur sur l’avant
de la scie indique l’angle d’inclinaison par des
incréments d'½ degré.
2. Pour verrouiller la lame de la scie à l’angle désiré,
serrez le bouton de verrouillage en le tournant
dans le sens horaire.
A
B
FIGURE 16
51
Page 52

PRÉPARATION POUR COUPER
MONTAGE
(suite)
SÉLECTION ET RANGEMENT DES LAMES DE SCIE
Les couteaux diviseurs doivent être adaptés aux
dimensions de la lame de scie afin de fonctionner
efficacement.
La lame de scie fournie avec votre nouvelle scie est
une lame combinée de 10 pouces (254 mm), utilisée
pour la coupe transversale (à travers le grain) et
longitudinale (dans le sens du grain) à travers la
pièce. L’alésage central de la lame est de 5/8 pouces
(16 mm) de diamètre. Cette lame produira une coupe
de bonne qualité pour la plupart des applications.
Il existe de nombreux types de lames disponibles
pour réaliser des travaux spécifiques et particuliers
comme coupe transversale seulement, coupe
longitudinale seulement, rainurage de contreplaqué
fin, lambrissage, etc.
Utilisez uniquement des lames de scie conçues pour
des vitesses d’exploitation maximales sécuritaires de
3 600 tr/m ou plus.
Les lames de scie doivent toujours être bien affûtées. Il
est recommandé de trouver un service d’affûtage réputé
pour affûter vos lames lorsque cela est nécessaire.
Ne jamais empiler les lames l’une sur l’autre pour les
ranger. Placer du matériau tel que du carton entre
chaque lame pour les empêcher de se toucher, ou les
placer dans le tiroir de rangement.
Des meules ou des lames (y compris les diamants)
abrasives ne doivent pas être utilisées sur cette scie.
CHANGEMENT DE LA LAME
• Utilisez seulement des lames de 10 pouces (254 mm)
de diamètre avec des alésages centraux de
5/8 pouces (16 mm), évaluées à 3 600 tours par
minute ou plus, avec une largeur de trait de scie
minimale de 0,102 pouces (2,6 mm) et une épaisseur
de corps maximale de 0,073 pouces (1,8 mm).
• Pour réduire le risque de blessures, éteignez
la machine et débranchez-la de la source
d’alimentation avant d’installer et d’enlever les
lames et accessoires, avant d'effectuer des
ajustements et des réparations. Un démarrage
inopportun peut provoquer des blessures.
1. Retirez la plaque à gorge et soulevez la lame de la
scie à sa hauteur maximale.
2. Appuyez et maintenez enfoncé le bouton de
verrouillage de l’arbre (A) montré à la Figure 17.
3. Utilisez la clé d’arbre incluse pour enlever l’écrou
POSITION DU COUTEAU
DIVISEUR
REMARQUE : Les dispositifs de sécurité, l’ensemble
protège-lame et l’ensemble anti-retour ont été enlevés
dans la Figure 18, afin de montrer l’emplacement des
caractéristiques spécifiques. Lorsque vous utilisez la
scie, ces dispositifs de sécurité doivent être en place
et fonctionner correctement.
Le couteau diviseur est une plaque plane qui s'insère
dans la coupe faite par la lame de la scie et permet de
minimiser les rebonds en réduisant la tendance de la
lame à se coincer dans la coupe. Il doit être installé
et positionné correctement pour chaque coupe
traversante et pour chaque coupe non traversante à
moins que le couteau diviseur ne gène la pièce.
L’épaisseur du couteau diviseur (A) doit être supérieure
à celle du corps de la lame ou de la plaque (B) et
inférieure à la largeur de trait de scie ou de découpe
(C) comme le montre la Figure 15. Le couteau diviseur
fourni avec cette scie fait 2,2 mm d’épaisseur et peut
être utilisé uniquement avec une lame de 10 pouces
(254 mm) pour une largeur minimale du trait de scie
de fixation et la bride de la lame (B). Enlevez
l'ancienne lame.
4. Placez la nouvelle lame sur l’arbre
avec les dents vers le bas lorsque
la lame tourne vers l’avant de la
table de sciage.
5. Replacez et serrez l’écrou de
fixation de la lame et la bride.
6. Replacez la plaque à gorge.
A
B
FIGURE 17
de 0,102 pouces (2,6 mm) et une épaisseur
maximale du corps de 0,073 pouces (1,8 mm).
Ne pas essayer d’utiliser ce couteau diviseur
avec des lames qui ne respectent pas ces
dimensions.
A
B
C
FIGURE 18
52
Page 53

PRÉPARATION POUR COUPER
couteau diviseur
Détentes de la position
supérieure sur goupilles
A
B
(suite)
RÉGLAGES DE HAUTEUR DU
COUTEAU DIVISEUR
La hauteur du couteau diviseur doit être ajustée
en fonction du type de coupe effectuée. Pour
toutes les coupes traversantes (lorsque le bois est
complètement sectionné), il doit être en position
relevée, avec les doigts anti-retour et le protège-lame
installés. Pour les coupes non traversantes (lorsque
la lame ne pénètre pas dans le haut de la pièce), le
couteau diviseur doit être en position basse, avec les
doigts anti-retour et le protège-lame enlevés.
POUR SOULEVER OU ABAISSER LE
COUTEAU DIVISEUR :
1. Retirez la plaque à gorge.
2. Relevez la lame à sa hauteur maximale au-dessus
de la table.
3. Tirez le levier de dégagement du couteau diviseur
(A) vers le haut pour libérer le couteau diviseur du
mécanisme de serrage. Voir Figure 19.
4. Poussez le couteau diviseur et le levier de
dégagement sur le côté de l’arbre de la lame pour
dégager le couteau diviseur des goupilles.
a. Pour régler le couteau diviseur en position
coupe traversante, tirez le couteau diviseur
vers le haut jusqu’aux goupilles de détente
inférieures.
b. Pour déplacer le couteau diviseur en
position coupe non traversante, poussez-le
vers le bas jusqu’aux goupilles de détente
supérieures.
REMARQUE : Lors du réglage du couteau diviseur
vers le haut ou vers le bas, n’oubliez pas de tirer
dans un mouvement radial, comme indiqué.
1. Dégagez le levier et tirez sur le couteau diviseur
pour vous assurer qu’il est correctement installé
en position relevée ou abaissée.
2. Fixez fermement le couteau diviseur en poussant
le levier de serrage du couteau diviseur vers le bas
à la position horizontale.
3. Replacez la plaque à gorge.
NE PAS faire fonctionner la
scie à moins que le couteau
diviseur ne soit bien serré
dans la position relevée
pour la coupe traversante
ou dans la position
abaissée pour la coupe
non traversante.
Détentes
de la position
inférieure
Tirez pour
libérer le
A
Ajuster
Verrouillé
FIGURE 19
VÉRIFICATION DE L’ALIGNEMENT
DU COUTEAU DIVISEUR
Avant de connecter la scie
de table à la source
d’alimentation et d'utiliser la scie, contrôlez toujours
l’alignement et le dégagement de l’ensemble
protège-lame et du couteau diviseur par rapport à la
lame de la scie. Vérifiez l’alignement du couteau
diviseur après chaque changement de lame.
POUR VÉRIFIER L’ALIGNEMENT :
1. Alignement horizontal : Placez un
bord droit sur la table contre la face
de la lame (A) et assurez-vous
qu’il s’étend le long
du couteau
diviseur (B),
comme le
montre la
Figure 17a.
Le couteau
diviseur
doit à peine
toucher le bord droit.
Assurez-vous que le bord
droit passe entre les dents et
repose sur la face de la lame
et le couteau diviseur pour
un alignement correct.
FIGURE 20a
1. Alignement vertical : Placez une équerre de
menuisier sur la table contre la face de la lame et
assurez-vous qu’elle s’étend le long du couteau
diviseur (B), comme le montre la Figure 17b.
Le couteau diviseur et la lame doivent toucher
l’équerre de menuisier en continu. Assurez-vous
que le bord droit passe entre les dents et repose
sur la face de la lame et le couteau diviseur pour
un alignement correct.
Si le couteau diviseur et la lame sont hors de
l’alignement horizontal ou vertical, reportez-vous aux
instructions d’alignement du couteau diviseur à la
page 60 de ce manuel.
B
FIGURE 20b
53
Page 54

PRÉPARATION POUR COUPER
UTILISATION DU GUIDE
À ONGLETS
Le guide à onglets est équipé de butées d’indexage
réglables à 90°, 75°, 60°, 45° et 30°. Pour régler l’onglet
en vue d'une coupe en biseau, voir Figure 18 et :
1. Desserrez la poignée (A).
2. Appuyez sur la gâchette de pouce (B).
3. Déplacez le corps du guide à onglets à l’angle
désiré.
4. Relâchez la gâchette de pouce et resserrez la
poignée.
Le guide à onglets est équipé d’une rondelle sur
l’extrémité de la barre qui s'insère dans la fente en T
de la table. Ceci permet de tirer le guide à onglets hors
du bord avant de la table sans tomber. Cela permet
d'accueillir une pièce plus grande devant la lame.
UTILISATION DE L’ENSEMBLE
PROTÈGE-LAME
(suite)
A
B
FIGURE 21
Les doigts anti-retour et le
protège-lame doivent être
utilisés pour toutes les coupes traversantes. Gardez
les deux écrans de protection abaissés et les bras,
les mains et les doigts loin de la lame, du protègelame et des doigts anti-retour lorsque l’alimentation
est allumée afin d’éviter des blessures graves. Voir
les instructions de montage à la page 45 pour
l’installation et l’enlèvement corrects des doigts antiretour et du protège-lame.
Si vous devez brièvement soulever le protège-lame (par
exemple, pour effectuer une mesure) le protège-lame
peut être bloqué en position surélevée.
1. Reportez-vous à la Figure 22 et, en soulevant
le protège-lame par l’avant, soulevez l'écran de
protection jusqu’à ce qu’il s’enclenche en position
verrouillée au-dessus de la table. Vous pouvez
soulever l’un ou les deux écrans de protection.
2. Lorsque vous avez terminé la mesure, remettez le
protège-lame dans sa position de fonctionnement.
VERIFICATION DE
L’ALIGNEMENT DU GUIDE
N’essayez pas d’utiliser un
guide longitudinal qui n’est pas
aligné correctement.
Chaque fois que vous utilisez le guide longitudinal,
vérifiez son alignement pour vous assurer que le guide
est parallèle à la fente. Pour vérifier l’alignement de
votre guide longitudinal, placez le guide adjacent à la
fente et verrouillez le guide en place. Si le guide n’est
pas aligné sur la fente de l’avant à l’arrière, consultez les
instructions pour aligner le guide longitudinal à la page
61 de ce manuel. Si vous n'arrivez pas à aligner le guide
longitudinal, remplacez le guide longitudinal ou appelez
le 1-800-223-7278 pour de plus amples instructions.
FIGURE 22
54
Page 55

FONCTIONNEMENT
Le non-respect des avertissements suivants peut entraîner des blessures graves.
LIRE LE MANUEL EN ENTIER. En plus de lire ces instructions de fonctionnement, il est important de lire et
comprendre le manuel en entier avant d’utiliser cette scie. Suivez toutes les instructions en vigueur concernant
l’assemblage, la préparation et l’ajustement avant d’effectuer des coupes et conformez-vous à toutes les règles
de sécurité et tous les avertissements dans cette section et dans le reste de ce manuel.
1. Chaque fois que vous utilisez la scie, parcourez
la liste de vérification suivante :
• La source d’alimentation et les raccordements
électriques sont-ils adaptés à la scie?
• La scie et la zone de travail sont-elles libres de
tout encombrement et de spectateurs?
• La lame est-elle bien serrée et bien alignée?
• L’épaisseur du couteau diviseur correspond-elle à
la lame?
• La lame et le couteau diviseur sont-ils
correctement alignés?
• L’opérateur est-il qualifié pour effectuer des
coupes et s’est-il familiarisé avec l'ensemble des
règles, avertissements et instructions de sécurité
figurant dans ce manuel?
• L’opérateur et les autres personnes se trouvant à
proximité de la scie portent-ils des équipements de
protection oculaire, auditive et respiratoire adéquats?
• Les boutons de réglage de l’angle de biseau et de la
hauteur sont-ils verrouillés dans la bonne position?
• La lame est-elle réglée à la bonne hauteur?
• En cas de coupes longitudinales, le guide
longitudinal est-il parallèle à la lame et est-il bien
verrouillé en position?
• En cas de coupes transversales, le bouton du
guide à onglets est-il bien serré?
• En cas de coupes traversantes avec une lame
standard, le protège-lame, le couteau diviseur et
les doigts anti-retour sont-ils correctement reliés
et fonctionnent-ils correctement avec les deux
protèges-lame en contact avec la surface de la table?
• Y a t-il un dégagement et un soutien adéquats
pour la pièce lorsqu'elle quitte la lame?
• Des accessoires de coupe sont-ils nécessaires? Si
oui, sont-ils en place ou à portée de main pour une
utilisation correcte?
2. L’utilisation de pièces et accessoires non
recommandés par DELTA® Power Equipment
Corporation peut entraîner des blessures.
3. Remplacez ou affûtez les doigts anti-retour
lorsque les pointes deviennent ternes.
4. Assurez-vous que la scie est stable et que la
coupe peut être réalisée sans renverser la scie.
N’essayez pas de couper de grandes pièces
sans fixer la scie à une surface stable. Pour fixer
correctement la scie, voir les instructions dans la
section intitulée Fixer la scie au sol à la page 47
de ce manuel.
5. Ne jamais utiliser la butée et le guide à onglets
en même temps sans l’aide d’un bloc coupée,
comme décrit précédemment.
6. La plaque à gorge appropriée doit être en place
en permanence.
7. Si votre scie produit un bruit étrange ou si elle
vibre excessivement, arrêtez-la immédiatement
jusqu'à ce que la cause soit localisée et le
problème corrigé.
8. Ne jamais effectuer de coupe à main levée,
coupe en plongée, recoupe ou coupe courbée.
ÉVITER LE REBOND
Un rebond peut se produire lorsque la pièce pince
la lame ou se coince entre la lame et le guide
longitudinal ou tout autre élément fixe. Cela peut
entraîner le soulèvement et/ou la projection de la
pièce vers l’opérateur. Voir les instructions pour
réduire le risque de rebond à la page 38 de ce manuel.
EN CAS DE REBOND, éteignez la scie (« OFF ») et
vérifiez le bon alignement de la lame, du couteau
diviseur et du guide à onglets ou du guide longitudinal
et le bon fonctionnement du couteau diviseur, de
l’ensemble anti-retour et de l’ensemble protège-lame
avant de reprendre le travail.
DÉMARRAGE ET ARRÊT DE LA SCIE
Le commutateur POWER (MARCHE / ARRÊT) (Figure
23) est situé sous la rallonge avant gauche de la table.
1. Pour allumer la scie (« ON »), tirez l'interrupteur à
palette rouge (A) vers le haut et vers vous.
2. Pour éteindre la scie (« OFF »), enfoncez
l'interrupteur à palette rouge.
Lorsqu’elle n’est pas utilisée, la scie doit être éteinte et
le commutateur d’alimentation verrouillé pour empêcher
toute utilisation non autorisée. Pour verrouiller le
commutateur d’alimentation, utilisez un cadenas à
arceau long standard, avec un arceau d'au moins 2 ¾
pouces (70 mm) de longueur et avec des tiges d’arceau
ne dépassant pas 9/32 pouces (7 mm) d'épaisseur.
55
B
A
FIGURE 23
Page 56

FONCTIONNEMENT
PROTECTION DE SURCHARGE
(suite)
Votre scie est livrée avec une protection contre les
surcharges. Si le moteur s’arrête ou ne parvient pas
à démarrer en raison d’une surcharge (découpe trop
rapide, utilisation d’une lame émoussée, utilisation
de la scie au-delà de sa capacité, etc.) ou une
basse tension, laissez le moteur refroidir trois à cinq
EFFECTUER DES COUPES
Le non-respect des
avertissements suivants peut
entraîner des blessures graves.
• Ne jamais toucher l’extrémité libre de la pièce ou
une pièce libre qui est coupée, pendant que la
machine est sous tension et/ou la lame tourne. Le
contact avec la lame ou un coincement peuvent
se produire, entraînant la projection de la pièce.
• Lorsque vous sciez une pièce longue ou un panneau,
utilisez un support de travail, comme un chevalet
de sciage, des rouleaux ou une table de sortie à la
même hauteur que la surface de la table de sciage.
• Ne jamais essayer de retirer la pièce pendant que
la lame tourne. Si vous avez besoin de retirer la
pièce ou de la soulever hors de la table, coupez
le contact, laissez la lame s’arrêter, soulevez les
dents anti-retour de chaque côté du couteau
diviseur, si nécessaire, puis faites glisser la pièce
pour la sortir.
minutes. Puis appuyez sur le bouton de réinitialisation
rouge (B) sur le moteur sous la scie, montré à la
Figure 23, et redémarrez la scie.
AVIS : Si le moteur s’arrête régulièrement en raison
d’une surcharge, contactez un électricien qualifié.
• Avant de connecter la scie sur table à la source
d’alimentation ou de faire fonctionner la scie,
contrôlez toujours l’alignement et le dégagement
de l’ensemble protège-lame et du couteau diviseur
par rapport à la lame de la scie. Vérifiez l’alignement
après chaque changement de l’angle de biseautage.
• Un guide longitudinal doit TOUJOURS être utilisé
pour les opérations longitudinales afin d'éviter
la perte de contrôle et les blessures. Toujours
verrouiller la butée au rail. Ne JAMAIS effectuer
une opération longitudinale à main levée.
• Lorsque vous effectuez des coupes en biseau,
placez la butée sur le côté droit de la lame de
sorte que la lame soit inclinée à l'opposé de la
butée et des mains. Gardez les mains éloignées
de la lame et utilisez un poussoir pour faire
avancer la pièce à moins que la pièce soit assez
grande pour vous permettre de la tenir à plus de 6
pouces (152 mm) de la lame.
• Avant de laisser la scie sans surveillance,
verrouillez le commutateur d’alimentation ou prenez
d’autres mesures appropriées pour empêcher toute
utilisation non autorisée de la scie.
Coupe transversale Coupe transversale d'onglets
Coupe transversale en biseau
Coupe longitudinale
Coupe longitudinale
Coupe d’onglets composée
en biseau
56
Page 57

FONCTIONNEMENT
A
(suite)
COUPES LONGITUDINALES
1. Retirez le guide à onglets
2. Assurez-vous que l’angle de biseau est réglé sur 0°.
3. Réglez la lame à la hauteur correcte pour la pièce.
4. Installez le guide longitudinal et verrouillez-le
parallèlement à la lame et à la distance désirée de
la lame.
5. Gardez les doigts à au moins 6 pouces (152,39
mm) de la lame en permanence. Lorsqu'il est
impossible de passer la main en toute sécurité
entre la lame et le guide longitudinal, choisissez
une pièce plus grande ou utilisez un poussoir et
d’autres accessoires de coupe, au besoin, pour
contrôler la pièce.
6. Assurez-vous que la pièce est éloignée de la lame
(au moins 1 pouce ou 25 mm de distance) avant de
démarrer la scie
7. Allumez la scie.
8. Maintenez la pièce à plat sur la table et contre le
guide (A). La pièce doit avoir un bord droit contre
le guide et ne doit pas être déformée, tordue ou
courbée. Voir la position correcte des mains dans
la Figure 24.
9. Laissez la lame atteindre sa pleine vitesse avant
de déplacer la pièce vers la lame.
10. Il est possible d'utiliser les deux mains pour
débuter la coupe, aussi longtemps que les mains
restent à 6 pouces (152,39 mm) de la lame.
11. Maintenez la pièce contre la table et le guide et
déplacez lentement la pièce vers l’arrière à travers
la lame de la scie. Ne surchargez pas le moteur en
forçant la pièce vers la lame.
12. Utilisez le poussoir et d’autres accessoires de
coupe, au besoin, pour maintenir la pièce contre
la table et le guide, et poussez la pièce de l'autre
côté de la lame. Un poussoir est fourni avec
cette scie et des instructions sont incluses pour
construire des poussoirs supplémentaires et
d’autres accessoires de coupe.
13. Ne poussez pas et ne tenez pas l'extrémité libre
ou coupée de la pièce.
14. Continuez à pousser la pièce jusqu’à ce qu’elle
soit éloignée de la lame. Ne surchargez pas le
moteur en forçant la pièce vers la lame.
15. Quand la coupe est terminée, éteignez la scie.
Attendez que la lame s’arrête complètement avant
de retirer la pièce de la table.
A
FIGURE 24
COUPE EN BISEAU
La coupe en biseau est identique à la coupe
simple, sauf que l’angle de biseau (A) est réglé sur
un angle autre que 0°. Lorsque vous effectuez une
coupe longitudinale en biseau, placez la butée sur
le côté droit de la lame de sorte que la lame soit
inclinée à l'opposé de la butée et des mains.
0º
45º
FIGURE 25
57
Page 58

FONCTIONNEMENT
0º
(suite)
COUPE TRANSVERSALE
• NE JAMAIS utiliser le guide comme une butée
longitudinale lors des coupes transversales.
• La pièce coupée ne doit jamais être coincée
pendant une opération de coupe traversante (couper
complètement à travers la pièce) - pour empêcher
le pincement de la lame, ce qui pourrait entraîner la
projection de la pièce et des blessures potentielles.
• Lorsque vous utilisez un bloc comme une jauge de
coupure, le bloc doit faire au moins ¾ pouces
(19 mm) d’épaisseur. Il est très important que
l’extrémité arrière du bloc soit fixée dans une position
où la pièce est éloignée du bloc avant son entrée
dans la lame pour éviter le coincement de la pièce.
Vous pouvez utiliser le guide à onglets dans l’une
des fentes de la table pour les coupes pas en biseau.
Pour augmenter la surface du revêtement du guide à
onglets, ajoutez un revêtement auxiliaire (voir la section
Accessoires de coupe à la page 58 de ce manuel).
Pour effectuer une coupe transversale, reportez-vous
à la Figure 26 et suivez ce processus :
1. Retirez le guide longitudinal.
2. Assurez-vous que l’angle de biseau est réglé sur 0°.
3. Réglez la lame à la hauteur correcte pour la pièce.
4. Placez le guide à onglets dans l’une des fentes
d’onglet.
5. Réglez le guide à onglets sur 0° et serrez le bouton
de verrouillage du guide à onglets
6. Les mains doivent rester à au moins 6 pouces
(152,39 mm) de la lame tout au long de la coupe.
Si la pièce est trop petite pour garder les mains
à au moins 6 pouces de la lame, choisissez une
pièce plus grande ou fixez un revêtement auxiliaire
au guide à onglets et fixez la pièce au revêtement
auxiliaire. Pour des instructions sur la fabrication de
revêtements auxiliaires, voir la section Accessoires
de coupe à la page 58 de ce manuel.
7. Assurez-vous que la pièce est éloignée de la lame au moins 1 pouce ou 25 mm de distance - avant de
démarrer la scie.
8. Allumez la scie.
9. Laissez la lame atteindre sa pleine vitesse avant de
déplacer la pièce vers la lame.
10. La main la plus proche de la lame doit être placée
sur le bouton de verrouillage du guide à onglets
et la main la plus éloignée de la lame doit tenir
fermement la pièce contre le revêtement du guide à
onglets. Ne poussez pas et ne tenez pas l'extrémité
libre ou coupée de la pièce.
11. Poussez lentement la pièce en arrière à travers la
lame de la scie. Ne surchargez pas le moteur en
forçant la pièce vers la lame.
12. Quand la coupe est terminée, éteignez la scie.
Attendez que la lame s’arrête complètement avant
d’enlever la pièce coupée de la table.
FIGURE 26
COUPE TRANSVERSALE
EN BISEAU
La coupe transversale en biseau est identique à la
coupe transversale simple, sauf que l’angle de biseau
(A) est réglé sur un angle autre que 90°. Lors d’une
coupe transversale en biseau, placez le guide à onglets
dans la fente droite de sorte que la lame soit inclinée à
l'opposé du guide et des mains. Voir Figure 27.
COUPES D’ONGLETS
Les coupes d’onglet sont des coupes transversales
avec le guide à onglets réglé sur un angle autre que
90°. Pour des instructions sur la configuration des
angles du guide à onglets, voir Préparation pour
couper. Pour ajuster les butées d’onglet d’indexage
préréglées, voir Réglage des butées d’onglets à la
page 60 de ce manuel.
• Les angles d’onglet inférieurs à 45˚ peuvent forcer
l’ensemble protège-lame dans la lame de la scie,
pouvant endommager l’ensemble protège-lame et
causer des blessures. Avant de démarrer le moteur,
vérifiez le fonctionnement en faisant avancer la
45º
A
FIGURE 27
pièce dans l’ensemble protège-lame. Si l’ensemble
protège-lame entre en contact avec la lame, placez
la pièce sous l’ensemble protège-lame, mais pas au
contact de la lame - avant de démarrer le moteur.
• Certaines formes de pièces, telles que le moulage,
peuvent ne pas soulever l’ensemble protègelame correctement. Avec l’alimentation coupée,
faites avancer lentement la pièce dans la zone du
protège-lame jusqu’à ce que la pièce touche la
lame. Si l’ensemble protège-lame entre en contact
avec la lame, placez la pièce sous l’ensemble
protège-lame, mais pas au contact de la lame avant de démarrer le moteur.
58
Page 59

FONCTIONNEMENT
(suite)
COUPES D’ONGLETS
COMPOSÉES
Il s’agit d’une combinaison entre coupe transversale en
biseau et coupe d'onglets. Voir Figure 28 et suivre les
instructions à la fois pour les coupes transversales en
biseau et les coupes d'onglets. N’oubliez pas d’utiliser
la fente à droite pour toutes les coupes en biseau.
90º
COUPES DE GRANDS PANNEAUX
Placez les supports de pièce à la même hauteur que
la table de sciage derrière la scie pour soutenir la
pièce coupée et sur le(s) côté(s) de la scie, selon les
besoins. Selon la forme du panneau, utilisez le guide
longitudinal ou le guide à onglets pour contrôler la
pièce. Si une pièce est trop grande pour utiliser un
guide longitudinal ou un guide à onglets, elle est trop
grande pour cette scie.
30º
FIGURE 28
RAINURAGES ET AUTRES COUPES NON TRAVERSANTES
L’utilisation d’une coupe non traversante est essentielle
pour couper des rainures, feuillures et entailles. Les
coupes non traversantes peuvent être réalisées avec une
lame standard ayant un diamètre de 10 pouces (254 mm)
ou moins, ou avec une lame à fentes jusqu’à 13/16 pouces
(20,63 mm) de largeur avec un diamètre de 8 pouces
(203,2 mm) ou moins. Les coupes non traversantes sont le
seul type de coupes à effectuer sans l’ensemble protègelame installé. Assurez-vous que l’ensemble protège-lame
est réinstallé à la fin de ce type de coupe.
• Pour effectuer des coupes non traversantes, suivez
tous les avertissements et les instructions indiqués
ci-dessous en plus de ceux énumérés ci-dessus
pour la coupe traversante concernée.
• Lorsque vous effectuez une coupe non traversante,
la lame est couverte par la pièce pendant la majeure
partie de la coupe. Faites attention à la lame
exposée au début et à la fin de chaque coupe.
• Ne faites jamais avancer le bois avec les mains lorsque
vous effectuez des coupes non traversantes, comme
des feuillures ou des rainurages. Utilisez toujours le
guide à onglets, des blocs poussoirs ou des poussoirs
et des planches à languettes le cas échéant.
• Lisez la section appropriée qui décrit le type de
coupe, en plus de cette section sur les coupes non
traversantes ou de rainurage. Par exemple, si votre
coupe non traversante est une coupe transversale
droite, vous devez lire et comprendre la section relative
aux coupes transversales droites avant de poursuivre.
• Une fois que toutes les coupes de rainurage et non
traversantes sont terminées, débranchez la scie
et réinstallez le couteau diviseur ou remettez-le en
position surélevée. Installez les doigts anti-retour et
le protège-lame.
• Suivez attentivement les instructions accompagnant
les lames spécialisées telles que des lames de
rainurage et des coupeurs de moulage pour
l'installation, la mise en place et le fonctionnement
adéquats.
0º
45º
EFFECTUER UNE COUPE NON TRAVERSANTE
1. Débranchez la scie.
2. Déverrouillez le levier de desserrage.
3. Ajustez l’angle de biseau à 0°.
4. Verrouillez le levier de desserrage.
5. Retirez le protège-lame et les doigts anti-retour.
6. Placez le couteau diviseur en position « abaissée ».
(Voir la section POSITION DU COUTEAU DIVISEUR
à la page 50)
7. Réglez la lame sur la profondeur correcte pour la
pièce. Voir les instructions ci-dessous pour l’utilisation
de lames de rainurage et d’autres lames spécialisées.
8. Selon la forme et la taille du bois, utilisez le guide
longitudinal ou le guide à onglets.
9. Branchez la scie dans la source d’alimentation et
allumez la scie.
10. Laissez la lame atteindre sa pleine vitesse avant de
déplacer la pièce vers la lame.
11. Utilisez toujours des blocs poussoirs, des
poussoirs et/ou des planches à languettes lors de
coupes non traversantes pour réduire le risque de
blessures graves.
12. Quand la coupe est terminée, éteignez la scie.
Attendez que la lame s’arrête complètement avant
de retirer la pièce.
Si une coupure de rainurage profonde est nécessaire,
utilisez plusieurs passages successifs plutôt
qu’essayer d'effectuer la coupe en un seul passage.
59
Page 60

FONCTIONNEMENT
EFFECTUER UNE COUPE DE
RAINURAGE
Les lames de rainurage sont des lames empilées
qui peuvent être utilisées dans les coupes non
traversantes, y compris des fentes de coupe
traversante. Les lames de rainurage nécessitent une
plaque à gorge spéciale. Les lames de rainurage et les
plaques à gorge sont toutes vendues séparément.
• Suivez attentivement les instructions accompagnant
la lame de rainurage pour une installation, une
mise en place et un fonctionnement adéquats. Des
guides supplémentaires sont disponibles sur des
sites Web et publications dédiés au travail du bois
et à la menuiserie.
• N’essayez pas d’empiler des lames de rainurage
dont l'épaisseur est supérieure à 13/16 pouces
(20,64 mm) N’utilisez pas de lames de rainurage de
plus de 8 pouces (200 mm) de diamètre.
• Le couteau diviseur et les ensembles protège-lame
ne peuvent pas être utilisés lors du rainurage. Ils
doivent être enlevés comme décrit dans la section
Utilisation du couteau diviseur et du protègelame. Soyez EXTRÊMEMENT prudent lorsque
vous utilisez la lame de rainurage sans l’ensemble
protège-lame et le couteau diviseur.
• Utilisez des poussoirs, des serre-tôles, des
gabarits, des montages ou des planches à
languettes pour aider à guider et contrôler la pièce
lorsque le protège-lame ne peut pas être utilisé.
• Veillez à réinstaller le couteau diviseur, les doigts
anti-retour, le protège-lame et la plaque à gorge
(suite)
FIGURE 30
standard et vérifiez les réglages lorsque les
coupes de rainurage sont terminées.
• La plaque à gorge accessoire à tête de rainurage,
illustrée à la Figure 307, doit être utilisée à la place
de la plaque à gorge standard. Assurez-vous que
la plaque à gorge est au niveau de la table avant
de poursuivre.
• Vérifiez toujours le dégagement des lames de
rainurage par rapport aux autres composants
avant de brancher la scie.
• Ne jamais tenter d’utiliser la tête de rainurage dans
une position de biseau.
REMARQUE : La bride d’arbre externe standard ne
peut pas être utilisée avec certaines combinaisons de
lames de rainurage. Dans ce cas, serrez l’écrou à arbre
directement sur l’ensemble de lames de rainurage.
Gardez la bride à arbre externe pour une utilisation
avec d’autres lames et combinaisons de rainurage.
ACCESSOIRES DE COUPE ET ACCESSOIRES
POUSSOIR
Pour faire fonctionner votre scie de table en toute
sécurité, vous devez utiliser un poussoir si, en raison
de la taille ou la forme de la pièce, vos mains se
trouveraient à moins de 6 pouces (152 mm) de la lame
de la scie ou de tout autre outil de coupe. Un poussoir
est inclus avec cette scie.
Il n'est pas nécessaire d'utiliser un bois spécial pour
fabriquer des poussoirs supplémentaires tant qu'il est
suffisamment robuste et long, ne comporte pas de
nœuds, gerces ou fissures. Une longueur d’environ
16 pouces (400 mm) est recommandée avec une
encoche qui s’adapte contre le bord de la pièce pour
éviter les glissements. Il est pratique d'avoir sous la
main plusieurs poussoirs de 16 pouces (400mm) de
long avec des encoches de différentes tailles pour
s'adapter à différentes épaisseurs de pièce.
La forme peut varier en fonction de vos propres besoins
tant qu’elle exerce sa fonction prévue de garder vos
mains à distance de la lame. Incliner l’encoche de sorte
que le poussoir puisse être maintenu à un angle de 20 à
30 degrés de la table de sciage vous aidera à maintenir
la pièce tout en déplaçant la scie.
Pour fabriquer un poussoir, reportez-vous au schéma
indiqué dans la Figure 31.
60
15.7”
90º
Table de la scie
20º
FIGURE 31
Encoche
pour empêcher
le glissement
des mains
Page 61

ACCESSOIRES DE COUPE ET ACCESSOIRES
2”
6”
Papier de verre
ou vieux tapis
de souris
Cheville
en bois
4”
REVÊTEMENT AUXILIAIRE DU
GUIDE LONGITUDINAL
Utilisez un revêtement auxiliaire du guide longitudinal
en cas de besoin pour des coupes spéciales, telles
que les coupes longitudinales d’un matériau qui est
assez mince pour glisser sous le guide longitudinal
fourni avec votre scie ou quand un guide longitudinal
plus haut est nécessaire pour finaliser votre coupe.
Pour ajouter un revêtement auxiliaire en bois sur l’un
ou les deux côtés du guide longitudinal, choisissez
un morceau de bois avec des surfaces lisses. Fixez
le bois au guide longitudinal avec deux pinces. (Voir
Figure 32) Pour la plupart des travaux, une dimension
de ¾ pouces (19 mm) ou d’1 pouce (25 mm) est
appropriée.
REVÊTEMENT AUXILIAIRE DU GUIDE À ONGLETS
Un revêtement auxiliaire du guide à onglets est utilisé
pour augmenter la surface du revêtement du guide à
onglets.
Si vous le souhaitez, vous pouvez doter le guide à
onglets d'un revêtement auxiliaire en bois qui devrait
être d’au moins 1 pouce (25 mm) plus élevé que la
profondeur de coupe maximale et au moins aussi
large que le guide à onglets.
Ce revêtement auxiliaire en bois peut être fixé à
l’avant du guide à onglets par deux vis à bois à travers
les trous (A) fournis dans le corps du guide à onglets
et dans le revêtement en bois. Voir Figure 33. Assurezvous que les vis sont suffisamment longues pour fixer
le revêtement, mais sans traverser le bois.
A
(suite)
FIGURE 32
BLOC POUSSOIR
1. Choisissez un morceau de bois d’environ 4 pouces
(101,6 mm) de largeur, 6 pouces (152,39 mm)
de longueur et 1 à 2 pouces (25,4 à 50,8 mm)
d’épaisseur (une chute d’une planche de 2 par 4
est idéale pour se fabriquer un bloc poussoir).
2. Percez un trou dans le bloc et collez-y une cheville
qui servira de poignée (vous pouvez incliner le trou
afin d'obtenir une prise en main plus confortable
de la poignée).
3. Collez un morceau de matériau mou ou rugueux
tel que du papier de verre ou du caoutchouc à la
partie inférieure du bloc pour prendre en main la
pièce (les vieux tapis de souris fonctionnent bien).
Voir Figure 34.
FIGURE 33
FIGURE 34
61
Page 62

ACCESSOIRES DE COUPE ET ACCESSOIRES
PLANCHE À LANGUETTES
(suite)
Les planches à languettes sont utilisées pour
maintenir la pièce en contact avec le guide et la table
(Figure 35) et aider à éviter les rebonds. Les planches
à languettes sont particulièrement utiles lors de la
coupe longitudinale de petites pièces et pour finaliser
des coupes non traversantes. L’extrémité est inclinée
avec une série de fentes étroites pour donner une
prise de frottement sur la pièce. Elle est verrouillée en
place sur la table ou le guide avec un serre-joint.
Pour éviter un coincement
entre la pièce et la lame,
assurez-vous qu’une planche à languettes horizontale
appuie uniquement sur la partie non coupée de la
pièce en face de la lame.
Les dimensions pour construire une planche à
languettes typique sont présentées dans la Figure 32.
Construisez votre planche à languettes à partir d’un
morceau de bois droit qui est exempt de nœuds et
de fissures. Serrez les planches à languettes au guide
et/ou à la table de sorte que la planche à languettes
tienne la pièce contre le guide ou la table.
1. Choisissez un morceau de bois d'environ ¾
pouce d'épaisseur, 2 ½ pouces de large et 12
pouces de long.
2. Marquez la largeur du centre sur une extrémité
du morceau. Largeur d’onglet à 70° (voir la
section Coupe d’onglet pour des informations
sur les coupes d’onglet).
3. Réglez le guide longitudinal pour permettre la
découpe d'un « doigt » d’environ ¼ pouces (6,35
mm) dans le morceau.
4. Faites avancer le morceau seulement jusqu’au
marquage indiqué précédemment à 6 pouces
(152,39 mm).
5. Éteignez la scie et laissez la lame s’arrêter
complètement avant de retirer le morceau.
6. Ajustez le guide et effectuez des coupes
longitudinales dans la pièce pour obtenir des
entailles d'environ ¼ pouces (6,35 mm), séparées
de 1/8 pouces (3,17 mm).
1/8”
1/4”
70º
3/4”
4.5”
FIGURE 35
JAUGE DE COUPURE
Lorsque vous coupez transversalement un certain
nombre de pièces à la même longueur, vous pouvez
serrer un bloc de bois (A) (voir Figure 36) au guide et
l’utiliser comme une jauge de coupure. Le bloc (A) doit
faire au moins ¾ pouces (19 mm) d’épaisseur pour
empêcher le coincement de la pièce coupée entre la
lame et le guide. Une fois que la longueur de coupe
est déterminée, verrouillez le guide et utilisez le guide
à onglets pour faire avancer la pièce dans la lame.
Positionnez toujours la jauge
de coupure en face de la
lame de scie.
GABARITS
Il est possible de créer des gabarits avec diverses
configurations spéciales pour contrôler des formes
particulières de pièces pour des coupes particulières.
Des conseils sur la façon de fabriquer des gabarits
spécialisés sont disponibles dans les sites Web et les
publications dédiés au travail du bois et à la menuiserie.
12”
A
3/4”
FIGURE 36
N’essayez pas de créer ou
d’utiliser un gabarit si vous
n’êtes pas parfaitement familier avec la sécurité de
la scie de table. N’utilisez pas de gabarits qui
pourraient causer un pincement du trait de scie ou
un coincement de la pièce entre le gabarit et la lame.
Les installations incorrectes peuvent causer un
rebond qui pourrait entraîner des blessures graves.
62
Page 63

ALIGNEMENT
A
ALIGNEMENT DU COUTEAU
DIVISEUR AVEC LA LAME
L’alignement entre le couteau diviseur et la lame est
réglé à l’usine et, dans la plupart des cas, n’aura
pas besoin d’être ajusté. Toutefois, l’alignement doit
toujours être vérifié après l’installation de la lame ou
du couteau diviseur et peut être ajusté si nécessaire.
Si le couteau diviseur n’est pas aligné avec la lame,
un ajustement est nécessaire. Le couteau diviseur doit
être aligné d’avant en arrière (horizontalement) et de
haut en bas (verticalement).
Pour ajuster l’alignement du couteau diviseur, voir
Figure 37 et procéder comme suit :
1. Retirez la plaque à gorge, l’ensemble protège-lame
et l’ensemble anti-retour.
2. Relevez la lame à sa pleine profondeur de coupe
et réglez l’angle d’inclinaison sur 0°.
3. Soulevez le couteau diviseur à sa position de
coupe traversante, c'est-à-dire la plus haute.
4. Desserrez légèrement les deux vis d’assemblage à
six pans creux (C).
5. Placez le bord droit contre la face de la lame et
le couteau diviseur comme indiqué pour vérifier
l’alignement horizontal (voir Figure 20a, page 50).
6. Ajustez les vis de pression (A) pour déplacer le
couteau diviseur en ligne avec la lame selon sa
position lorsque vous avez vérifié l’alignement
ci-dessus.
7. Placez le bord droit de l’autre côté de la lame. Les
deux côtés du couteau diviseur doivent être dans
l’épaisseur du corps de la lame.
8. S’il n’est pas possible d’aligner les deux côtés
du couteau diviseur dans l’épaisseur du corps
de la lame, vous devez utiliser une lame de taille
différente. Voir Sélection de la lame à la page 49.
9. Serrez les deux vis d’assemblage à six pans creux.
10. Placez une équerre de menuisier sur la table
contre la face de la lame et le couteau diviseur
comme indiqué pour vérifier l’alignement vertical
(voir Figure 20b, page 50). Ensuite, vérifiez si le
couteau diviseur est perpendiculaire à la table et
en ligne avec la face de la lame.
11. Si nécessaire, utilisez les vis de pression (D) pour
aligner le couteau diviseur avec la face de la lame
et l’équerre.
12. Serrez à fond les deux vis d’assemblage à six
pans creux.
13. Replacez la plaque à gorge, l’ensemble protègelame et l’ensemble anti-retour avant l’utilisation.
En cas de traînement ou de
coincement de la pièce
lorsqu’elle atteint le couteau diviseur, éteignez la
machine, débranchez-la de la source d’alimentation
et réajustez l’alignement du couteau diviseur / de la
lame ou remplacez la lame. Ne tentez jamais
d’enlever la pièce partiellement coupée de la lame
tandis que la lame est en mouvement.
B
C
FIGURE 37
AJUSTEMENT DES BUTÉES
D’ONGLETS
Pour ajuster les butées d’indexage pour des angles
autres que 90°, 75°, 60°, 45° et 30° :
1. Desserrez la poignée du guide à onglets.
2. Desserrez les deux vis pour le segment de butée
d’onglet pour le nouvel angle désiré. (A) est
représenté dans la Figure 38.
3. Déplacez la butée sur la bonne position.
4. Resserrez les deux vis du segment et la poignée.
FIGURE 38
A
63
Page 64

ALIGNEMENT
(suite)
ALIGNEMENT PARALLÈLE DU
GUIDE À LA FENTE À ONGLETS
1. Déplacez le guide à côté du guide à onglets
du côté droit et fixez-le au tube de guidage en
abaissant le levier de serrage du guide.
2. Si la paroi du guide (A) Figure 39 n’est pas
parallèle à la fente (B), soulevez le levier de
serrage et levez le guide et placez-le sur la table
de sciage.
3. Ajustez l’une ou les deux vis de pression (C) d'1/4
de tour ou moins.
4. Replacez le guide sur le tube de guidage et
répétez les étapes 1 à 3. Si le guide est plus
proche de la parallèle, tournez la vis de pression
dans la même direction, mais un peu moins. Si le
guide est plus loin de la parallèle, tournez la vis de
pression dans la direction opposée.
5. Répétez les étapes 1 à 3.
A
C
ALIGNEMENT PERPENDICULAIRE
DU GUIDE À LA TABLE
1. Déplacez le guide sur la table en fonte et fixez-le au
tube de guidage en abaissant le levier de serrage
du guide.
2. Utilisez une équerre pour vérifier si la paroi du
guide est perpendiculaire à la table.
3. Si la paroi du guide n’est pas perpendiculaire
à la table, libérez le levier de serrage et ajustez
légèrement l’une des vis de pression à encoches
(A) Figure 37 jusqu’à ce que la paroi du guide soit
perpendiculaire à la table.
4. Fixez le guide au tube de guidage pour que le
guide reste perpendiculaire. Sinon, répétez les
étapes 1 à 4.
A
B
FIGURE 39 FIGURE 40
FONCTIONNEMENT SUR 240 VOLTS MONOPHASÉ
Le moteur bitension 120/240 volts fourni avec votre machine a été livré prêt pour un fonctionnement sur 120
volts. Il peut être converti pour fonctionner sur 240 volts. Pour effectuer la conversion de 120 volts à 240 volts,
communiquez d’abord avec le Service à la clientèle DELTA au 1-800-223-7278.
64
Page 65

ENTRETIEN
Pour réduire le risque de blessures, éteignez la machine et débranchez-la de la source d’alimentation avant de la
nettoyer ou la réparer, installer et retirer des accessoires, ou effectuer des réglages et réparations. Un démarrage
inopportun peut provoquer des blessures.
GARDER LA MACHINE PROPRE
Souffler périodiquement de l’air comprimé sec à
l'intérieur de tous les conduits d’air. Toutes les pièces
en plastique doivent être nettoyées avec un chiffon
doux humide. N'utilisez JAMAIS de solvant pour
nettoyer les pièces en plastique. Il pourrait dissoudre
ou endommager le matériel.
Portez des équipements de sécurité certifiés pour
la protection oculaire, auditive et respiratoire lors de
l’utilisation d’air comprimé.
GRAISSAGE ET PROTECTION CONTRE LA CORROSION
Appliquez de la cire en pâte pour planchers de bois
brut sur la table de la machine de temps en temps ou
utilisez un produit de protection disponible dans le
commerce et prévu à cet effet. Suivez les instructions
du fabricant pour l'utilisation et la sécurité.
RAPPELS D'ENTRETIEN
Portez des équipements de sécurité certifiés pour
la protection oculaire, auditive et respiratoire lors de
l’utilisation d’air comprimé.
Les points spécifiques qui nécessitent un entretien
régulier sont :
PLAQUE DE FIXATION DU COUTEAU DIVISEUR :
Gardez cette zone exempte d'accumulations de
poussière et de débris. Soufflez régulièrement la zone à
l'air comprimé.
REMARQUE : Si la pince du couteau diviseur ne peut
pas se déplacer librement, faites entretenir la scie
par le personnel d'un centre de service autorisé par
DELTA
®
Power Equipment Corporation.
Pour nettoyer la rouille des tables en fonte, vous aurez
besoin du matériel suivant : un tampon à récurer de
taille moyenne, un bidon de lubrifiant de pulvérisation
et un bidon de dégraissant. Appliquez le lubrifiant de
pulvérisation et polissez la surface de la table avec le
tampon à récurer. Dégraissez la table puis appliquez le
produit de protection comme décrit ci-dessus.
ENGRENAGES À VIS SANS FIN : Gardez les
engrenages à vis sans fin exempts d'accumulations de
poussière et de débris. Soufflez régulièrement la zone
à l'air comprimé. Utilisez une graisse multi-usages à
base de lithium sur ces engrenages si nécessaire.
ÉLIMINEZ PÉRIODIQUEMENT L'ACCUMULATION
DE SCIURE DANS LE CAISSON : REMARQUE : Il est
également possible d'éliminer les débris de la scie
par le dessous de la plaque à gorge, à l'intérieur du
capteur de poussière.
DÉPANNAGE
Pour de l’aide avec votre machine, visitez notre site Web à www.DeltaMachinery.com pour une liste des
centres de service ou appelez le Service à la clientèle DELTA® Power Equipment au 1-800-223-7278.
ÉCHEC DU DÉMARRAGE
Si votre machine ne démarre pas, assurez-vous que les broches de la fiche du cordon sont bien en contact dans
la prise et vérifiez le bouton de réinitialisation sur le boîtier du commutateur d’alimentation. Vérifiez également s’il
y a des fusibles grillés ou des disjoncteurs ouverts dans votre ligne électrique.
ACCESSOIRES
Une gamme complète des accessoires est disponible auprès de votre fournisseur DELTA®, des centres
de service du fabricant DELTA® et des centres de service autorisés DELTA®." Rendez-vous sur notre site Web
www.DeltaMachinery.com pour obtenir un catalogue en ligne ou pour connaître le nom du fournisseur le plus
près de chez vous.
Étant donné que les accessoires autres que ceux proposés par DELTA® n’ont pas été testés
avec ce produit, leur utilisation pourrait s’avérer dangereuse. Pour une utilisation plus sûre,
seuls les accessoires recommandés par DELTA® devraient être utilisés avec ce produit.
65
Page 66

GARANTIE
Pour enregistrer votre outil pour le service sous garantie, veuillez visiter notre site Web www.DeltaMachinery.com.
Garantie limitée de cinq ans pour les produits neufs
DELTA réparera ou remplacera, à ses frais et à sa discrétion, toute nouvelle machine DELTA, pièce de machine
ou accessoire de machine qui, en usage normal, présente un vice de fabrication ou de matériel, à condition
que le client retourne le produit par port prépayé à un centre de service du fabricant DELTA ou un centre de
service autorisé avec la preuve d’achat du produit dans les cinq ans et donne DELTA la possibilité raisonnable
de vérifier le défaut allégué en réalisant une inspection.
Pour tous les produits DELTA remis à neuf, la période de garantie est de 180 jours.
DELTA ne sera pas tenue responsable de tout défaut confirmé qui découlerait de l’usure normale, d’une
mauvaise utilisation, d’abus ou de réparations ou d’altérations faites ou expressément autorisées par une
personne autre qu’un centre de service ou représentant DELTA autorisé.
En aucun cas, DELTA ne sera tenue responsable des dommages accessoires ou indirects résultant de produits
défectueux. Certains états n’autorisent pas l’exclusion ou la limitation des dommages accessoires ou indirects,
donc la limitation ou l’exclusion susmentionnées peuvent ne pas s’appliquer à vous.
Cette garantie est l’unique garantie de DELTA et définit par la présente le recours exclusif du client en ce qui
concerne les produits défectueux toutes les autres garanties, expresses ou implicites, de qualité marchande,
de conformité aux besoins ou autre, sont formellement rejetées par DELTA.
Pour plus de détails sur la couverture de la garantie et les réparations visées par la garantie, composez le
1-800-223-7278. La présente garantie vous donne des droits légaux précis et vous pouvez avoir d’autres droits
qui varient selon les États et les provinces.
AMÉRIQUE LATINE : La présente garantie ne s’applique pas aux produits vendus en Amérique latine. Pour
les produits vendus en Amérique latine, consultez les informations de garantie relatives au pays en question
contenues dans l’emballage, appelez la société locale ou consultez la section garantie sur le site Web.
ASSISTANCE PIÈCES, ENTRETIEN ET GARANTIE
Toutes les machines et tous les accessoires DELTA® sont fabriqués selon des normes de qualité élevée et sont
entretenus par un réseau de centres de service autorisés DELTA®. Pour en savoir davantage sur votre produit de
qualité DELTA® ou pour obtenir des pièces, de l'entretien, de l’aide avec la garantie ou connaître l’emplacement du
centre de service le plus proche de chez vous, veuillez composer le 1-800-223-7278.
PIÈCES DE RECHANGE
Utilisez uniquement des pièces de rechange identiques. Pour obtenir une liste de pièces ou commander des pièces,
rendez-vous sur notre site à l’adresse www.DeltaMachinery.com/service. Vous pouvez également commander des
pièces auprès de votre centre de service de garantie autorisé ou en appelant le directeur du service technique au
1-800-223-7278 pour recevoir un soutien personnalisé de l’un de nos représentants hautement qualifiés.
REMPLACEMENT GRATUIT DES ÉTIQUETTES DE MISE EN GARDE
Si vos étiquettes de mise en garde sont devenues illisibles ou sont manquantes, composez le
un remplacement gratuit.
1-800-223-7278
pour
66
Page 67

DESCRIPCIÓN FUNCIONAL
La sierra de mesa de 10 pulgadas (254 mm) para
contratista DELTA® #36-5000 series está diseñada
para que sea fácil de transportar y tener una alta
calidad de desempeño. Incluye: máquina básica,
soporte de acero tubular macizo, conducto para polvo
integral, un sistema de tope guía T-Square®, galga
de inglete de ranura en T, motor de inducción de 15
amperes, interruptor de encendido/apagado, mesa
de hierro fundido, alas de extensión, guarda para hoja
transparente con dedos anti contragolpes y una hoja de
carburo de 10 pulgadas (254 mm).
producción actual. Otras ilustraciones que contiene el manual son únicamente representativas y pueden no ser
imágenes exactas de las etiquetas o accesorios reales incluidos. Son únicamente para fines de ilustración.
ESPECIFICACIONES
Máx. profundidad de corte a 90 grados: 3-½"
Máx. profundidad de corte a 45 grados: 2-½”
Máx. inclinación a la derecha de la hoja: 30"
Máx. inclinación a la izquierda de la hoja: 15"
Máx. ancho de la ranura: 13/16"
ESPECIFICACIONES DEL MOTOR:
Amperes 15
Voltaje 120/240
AVISO: La portada del manual muestra el modelo de
INSTRUCCIONES DE SEGURIDAD IMPORTANTES
LEA CON ATENCIÓN Y SIGA TODAS LAS ADVERTENCIAS E INSTRUCCIONES DE SU
PRODUCTO Y DE ESTE MANUAL. GUARDE ESTE MANUAL. ASEGÚRESE DE QUE TODOS
LOS USUARIOS ESTÉN FAMILIARIZADOS CON LAS ADVERTENCIAS E INSTRUCCIONES AL USAR LA
HERRAMIENTA. La operación, mantenimiento o modificación inadecuada de las herramientas o equipo podría
resultar en una lesión grave y/o daños a la propiedad.
Si tiene cualquier duda o inquietud en relación al uso de su herramienta o al contenido de este manual, detenga el uso
de la herramienta y comuníquese con atención al cliente de DELTA® Power Equipment Corporation al 1-800-223-7278.
LOGOTIPOS DE SEGURIDAD
Las siguientes definiciones describen el nivel de gravedad de cada palabra de alarma. Por favor, lea el manual y
preste atención a estos símbolos.
Indica una situación de peligro inminente que, de no evitarse, ocasionará la muerte o una lesión grave.
Indica una situación de peligro potencial que, de no evitarse, podría ocasionar la muerte o
una lesión grave.
Indica una situación de peligro potencial que, de no evitarse, pudiera ocasionar una lesión
menor o moderada.
REGLAS GENERALES DE SEGURIDAD
PARA HERRAMIENTAS ELÉCTRICAS
No seguir estas reglas puede
provocar graves lesiones personales.
1. LEA EL MANUAL DE INSTRUCCIONES Y
CONOZCA SU HERRAMIENTA. Lea y familiarícese
con todo el manual de instrucciones. Conocer
las aplicaciones adecuadas, limitaciones y
riesgos potenciales específicos de la herramienta
minimizará en gran medida la posibilidad de sufrir
accidentes o una lesión. Asegúrese de que todos los
usuarios estén familiarizados con las advertencias e
instrucciones antes de usar la herramienta.
2. MANTENGA LAS GUARDAS Y DISPOSITIVOS
DE SEGURIDAD EN SU LUGAR y funcionando
adecuadamente.
3. QUITE LAS LLAVES DE AJUSTE Y DE TUERCAS.
Cree el hábito de verificar que todas las llaves
de ajuste y tuercas se hayan quitado antes de
arrancar la herramienta.
4. MANTENGA EL ÁREA DE TRABAJO LIMPIA
Y CON BUENA ILUMINACIÓN. Las áreas,
superficies y bancos de trabajo desordenados
o con poca iluminación pueden provocar
accidentes.
5. NO USE NI ALMACENE LA HERRAMIENTA EN
AMBIENTES PELIGROSOS. La exposición a la
lluvia o lugares húmedos o mojados puede resultar
en una descarga eléctrica o electrocución, o en
daños a la herramienta. No opere herramientas
eléctricas cerca de líquidos inflamables ni en
67
continúa en la página 66
Page 68

REGLAS GENERALES DE SEGURIDAD
PARA HERRAMIENTAS ELÉCTRICAS
atmósferas gaseosas o explosivas. Los motores e
interruptores de estas herramientas pueden crear
chispas y encender los gases.
6. MANTENGA ALEJADOS A NIÑOS Y
ESPECTADORES del área de trabajo.
7. BLOQUEE LAS HERRAMIENTAS Y ÁREAS
DE TRABAJO. Use candados e interruptores
maestros, o bien retire y almacene las llaves de
arranque para evitar que niños y usuarios no
autorizados operen la herramienta.
8. NO APLIQUE FUERZA A UNA HERRAMIENTA
O PIEZA DE TRABAJO. Opere la herramienta a
la velocidad y tasa de avance prevista para una
operación óptima y más segura.
9. USE LA HERRAMIENTA ADECUADA. No fuerce la
herramienta a realizar una tarea para la cual no fue
diseñada.
10. NO MALTRATE LOS CABLES DE CORRIENTE.
NUNCA jale del cable para desconectarlo del
tomacorriente, no aplaste el cable ni lo exponga al
calor, aceite ni objetos afilados.
11. USE EL CABLE DE EXTENSIÓN ADECUADO. Si
utiliza un cable de extensión, asegúrese de que esté
en buenas condiciones y tenga el calibre suficiente
para llevar la corriente que necesitará su producto.
Un cable de menor calibre provocará una caída en
el voltaje de línea, lo que provocará una pérdida de
energía y sobrecalentamiento. Consulte la Tabla de
cables de extensión para obtener el calibre correcto
dependiendo de la longitud del cable y el amperaje
indicados en la placa nominal. En caso de dudas,
use el siguiente calibre más pequeño. Entre más
pequeño sea el número de calibre, más pesado será
el cable. Cuando trabaje a la intemperie, asegúrese
de que la extensión esté clasificada para uso en
exteriores. Consulte la sección de conexión a la
fuente de poder en este manual para consultar la
Tabla de cables de extensión y la seguridad de la
conexión a la fuente de poder.
12. ASEGURAR LA PIEZA DE TRABAJO. Use
abrazaderas o una pinza para retener la pieza de
trabajo cuando sea práctico. Es más seguro que
usar sus manos y libera ambas manos para operar
la herramienta.
13. NO SE ESTIRE DEMASIADO. Mantenga un apoyo y
equilibrio adecuados para conservar el control.
14. DEBE DAR MANTENIMIENTO A LAS
HERRAMIENTAS. Mantenga las herramientas
afiladas y limpias para un desempeño óptimo y
más seguro. Siga las instrucciones para lubricar y
cambiar los accesorios.
15. DESCONECTE LA HERRAMIENTA de la fuente
de poder antes de dar servicio, ajustar o cambiar
montajes u hojas, brocas, cortadores y otros
accesorios.
16. PARA REDUCIR EL RIESGO DE UN ARRANQUE
ACCIDENTAL, asegúrese de que los interruptores
de energía estén en la posición "OFF" (Apagado)
antes de conectar el cable de la herramienta.
17. No toque las puntas de metal del enchufe
cuando desconecte o conecte el cable.
18. USE LOS ACCESORIOS RECOMENDADOS.
Consulte el manual para saber cuáles son los
accesorios recomendados. El uso de accesorios
inadecuados podría causar lesiones personales o
daños a la propiedad.
19. NUNCA SE PARE SOBRE LA HERRAMIENTA.
Una lesión grave podría ocurrir si las puntas de la
herramienta o usted tienen contacto por accidente
con la superficie de corte.
20. COMPRUEBE QUE LAS HERRAMIENTAS
NO ESTÉN DAÑADAS. Antes de usar una
herramienta, y después de que una herramienta
o accesorio se haya caído o dañado, compruebe
la alineación de las piezas móviles, la unión de
las piezas móviles, que no haya piezas quebradas
en las guardas y piezas afectadas ni cualquier
otra condición que pudiera afectar la operación
y asegúrese de que la herramienta funcionará
correctamente y todas las partes funcionarán de
acuerdo a su función prevista. No use un producto
dañado. Una guarda o cualquier otra pieza que
esté dañada debe repararse adecuadamente
o reemplazarse usando piezas de servicio
aprobadas de fábrica.
21. USE LA DIRECCIÓN DE AVANCE ADECUADA.
Avance la pieza de trabajo en contra la dirección
de rotación de la hoja, cortador o superficie
abrasiva de la herramienta. Alimentar en la
dirección opuesta puede provocar que la pieza de
trabajo sea expulsada a altas velocidades.
22. NUNCA DEJE LA HERRAMIENTA FUNCIONANDO
SIN SUPERVISIÓN. APAGUE LA HERRAMIENTA.
No deje la herramienta hasta que esta se detenga
por completo. En caso de un apagón, cambie el
interruptor a la posición "OFF" (Apagado).
23. ESTÉ ALERTA, PONGA ATENCIÓN A LO QUE
ESTÁ HACIENDO Y USE EL SENTIDO COMÚN. No
use herramientas eléctricas cuando esté cansado o
bajo el efecto de drogas, alcohol o medicamentos.
Un momento de distracción al operar herramientas
eléctricas podría resultar en una lesión.
24. PIEZAS DE SERVICIO. Use únicamente refacciones
idénticas al dar servicio a su herramienta.
25. USE ROPA ADECUADA. No use ropa holgada,
guantes, corbatas, anillos, pulseras u otra joyería
que pudiera quedar atrapada en las piezas
móviles. Se recomienda utilizar calzado protector
anti deslizante. Use gorras protectoras de cabello
para sujetar el cabello largo.
26. USE PROTECCIÓN DE OJOS ADECUADA.
Todas las personas que estén en el área de
trabajo deben usar lentes de seguridad con
escudos laterales. Los anteojos cotidianos con
lentes resistentes a impactos no son lentes de
seguridad. El equipo ocular debe cumplir con los
estándares de ANSI Z87.1.
continúa en la página 67
68
Page 69

REGLAS GENERALES DE SEGURIDAD
PARA HERRAMIENTAS ELÉCTRICAS
27. PROTECCIÓN DE OÍDOS. Todas las personas en
el área de trabajo deben usar protección de oídos
adecuada consistente con los niveles y exposición
al ruido. El equipo auditivo debe cumplir con los
estándares de ANSI S3.19.
28. PROTECCIÓN CONTRA EL POLVO. El uso de
herramientas eléctricas puede generar o expulsar
polvo que podría causar lesiones respiratorias
graves y permanentes, así como otras lesiones
incluyendo silicosis (una enfermedad pulmonar
grave), cáncer y la muerte. Dirija las partículas
lejos del rostro y el cuerpo. Siempre opere la
herramienta en un área con buena ventilación y
proporcione una eliminación de polvo adecuada.
Use el sistema de recolección de polvo cuando sea
posible. Evite respirar el polvo y evite el contacto
prolongado con este. Permitir que el polvo entre a
la boca u ojos, o bien que permanezca en la piel,
puede promover la absorción de material dañino.
Use protección respiratoria aprobada por NIOSH/
OSHA de ajuste adecuado para la exposición al
polvo y lave las áreas expuestas con jabón y agua.
ADVERTENCIA DE LA PROPUESTA 65:
creado por lijar, aserrar, rectificar, barrenar con
herramienta eléctrica, así como otras actividades de
construcción, puede contener químicos reconocidos
por el estado de California como causantes
de cáncer, defectos congénitos u otros daños
reproductivos. Algunos ejemplos son:
• Plomo de pinturas con base de plomo
• Sílice cristalina de ladrillos y cemento y otros
productos de mampostería
El polvo
GUARDE ESTAS INSTRUCCIONES.
Consúltelas a menudo y úselas para adiestrar a otros.
En caso de prestar la herramienta, también preste estas instrucciones.
69
• Polvo de asbesto
• Arsénico y cromo de madera tratada con químicos
El riesgo debido a estas exposiciones varía
dependiendo de la frecuencia con la que se realice
este tipo de trabajo. Para reducir la exposición a estos
químicos: trabaje en un área con buena ventilación
y trabaje con el equipo de seguridad aprobado tal
como mascarillas anti polvo que están diseñadas
específicamente para filtrar partículas microscópicas.
Page 70

REGLAS DE SEGURIDAD DE LA SIERRA DE MESA
No seguir estas reglas puede provocar graves lesiones personales.
• CONSULTE LA SECCIÓN DE SEGURIDAD GENERAL PARA HERRAMIENTAS ELÉCTRICAS EN ESTE
MANUAL. Lea todo el manual de instrucciones antes de operar la sierra. Conocer las aplicaciones adecuadas,
limitaciones y riesgos potenciales específicos de la sierra minimizará en gran medida la posibilidad de sufrir
accidentes y lesiones. Asegúrese de que todos los usuarios estén familiarizados con las advertencias e
instrucciones antes de usar la sierra.
• CONSULTE LA SECCIÓN DE CONEXIÓN A LA FUENTE DE PODER EN ESTE MANUAL para obtener las
instrucciones y advertencias en cuanto a cables de corriente y conexiones.
TERMINOLOGÍA
Los siguientes términos se usarán en todo el manual y debe familiarizase con ellos.
– Corte completo se refiere a cualquier corte que
corta por completo la pieza de trabajo.
– Corte sin traspaso se refiere a cualquier corte que
no corta por completo la pieza de trabajo.
_ Empujador se refiere a un palo de madera o plástico,
usualmente de fabricación casera, que se usa para
empujar una pieza de trabajo pequeña por la sierra y
mantiene las manos del operador lejos de la hoja.
– Un contragolpe ocurre cuando la hoja de sierra se
amarra en el corte o entre la hoja y el tope guía y
avienta la pieza de trabajo hacia el operador.
– A mano libre se refiere a cortar sin usar una galga
de inglete o un tope guía para corte al hilo o
cualquier otro medio para guiar o retener la pieza
de trabajo, excepto las manos del operador.
– Corte por penetración se refiere a cortes ciegos en
la pieza de trabajo realizados ya sea elevando la
hoja por la pieza de trabajo o bajando esta a la hoja.
– Reaserramiento - voltear el material para hacer un
corte que la sierra no es capaz de realizar en una
sola pasada.
– Corte cóncavo - también conocido como corte
en bóveda, es una operación donde la pieza de
trabajo pasa a un ángulo por la hoja.
No seguir estas reglas puede
provocar graves lesiones
personales.
1. NUNCA realice cortes de manos libres, cortes por
penetración, reaserramientos ni cortes cóncavos.
2. USE PROTECCIÓN DE OJOS, ropa adecuada,
protección de oídos y protección contra polvo según
se especifique en la sección de seguridad general
para herramientas eléctricas de este manual.
3. USE LA GUARDA PARA HOJA DE SIERRA,
SEPARADOR Y TRINQUETES ANTI
CONTRAGOLPE. La sierra está equipada con un
ensamble de guarda para hoja modular, separador
y un trinquete anti contragolpe, cada uno de estos
componentes debe usarse en cada operación
posible, incluyendo en todos los cortes completos.
Este ensamble se explica a continuación con mayor
detalle. Asegúrese de que los componentes se
instalen firmemente antes de utilizar la sierra.
4. MANTENGA LAS MANOS Y OTRAS PARTES DEL
CUERPO LEJOS DEL TRAYECTO DE LA HOJA.
NUNCA coloque ninguna parte de su cuerpo en el
trayecto de la hoja de sierra.
5. USE UN EMPUJADOR que sea adecuado para
la aplicación para empujar y sujetar una pieza de
trabajo hasta terminar el corte. Un empujador es un
palo de madera o plástico, usualmente casero, que
debe usarse cuando el tamaño o forma de la pieza de
trabajo haría que colocara sus manos a 6 pulgadas
(152 mm) de la hoja. Las instrucciones para fabricar
un empujador se incluyen en este manual.
6. EVITAR LOS CONTRAGOLPES. Preste atención
especial a las instrucciones (a continuación) para
reducir el riesgo de contragolpes.
7. NO REALIZAR CORTES A MANO LIBRE. Siempre
use un tope guía, galga de inglete u otros
dispositivos adecuados para guiar o sujetar la
pieza de trabajo. Use retenedores, plantillas de
guía, accesorios o tableros con canto biselado
para ayudar a guiar y controlar la pieza de
trabajo. Los accesorios para usar con la sierra
están disponibles a un costo adicional con su
distribuidor local o centro de servicio autorizado.
8. NO USE UN TOPE GUÍA PARA CORTE AL HILO Y
GALGA DE INGLETE AL MISMO TIEMPO.
9. NO SE ESTIRE DEMASIADO. Nunca se estire
sobre, encima o alrededor de la herramienta de
corte con ninguna de las manos mientras la hoja
está en movimiento.
10. ESTABILIDAD. Asegúrese de que la sierra de
mesa esté ensamblada correctamente y colocada
sobre una superficie estable antes de usarla para
evitar que esta se mueva durante un corte.
11. ENSAMBLE ADECUADO. No opere esta sierra
hasta que esté completamente ensamblada e
instalada de conformidad con las instrucciones.
12. VERIFIQUE LA PIEZA DE TRABAJO Y LA
PREPARACIÓN antes de cada operación. Los
nudos, irregularidades o clavos en una pieza de
trabajo y los errores de posicionamiento o una
preparación incompleta pueden interferir o afectar
el desempeño de la sierra y la seguridad personal.
13. USE LA PLACA DE GARGANTA ADECUADA. La
placa de garganta adecuada debe estar colocada
y asegurada firmemente en todo momento para
reducir el riesgo de expulsar una pieza de trabajo
y provocar una posible lesión.
14. USE LA HOJA Y SEPARADOR CORRECTOS
para la operación prevista. La hoja debe instalarse
de modo que las puntas de los dientes estén
apuntando hacia el frente de la sierra. No use
una hoja o separador demasiado grande con
una abertura incorrecta de eje. Siempre apriete
firmemente la tuerca del eje de la hoja. Antes de
70
continúa en la página 69
Page 71

REGLAS DE SEGURIDAD DE LA SIERRA DE MESA (continuación)
usar, inspeccione la hoja para comprobar que no
tenga grietas ni dientes rotos. No use una hoja
dañada o sin filo. Siempre use la hoja dentro del
rango de grosor para la cual está diseñado el
separador.
15. EVITE REALIZAR OPERACIONES O POSICIONES
MANUALES INCÓMODAS donde un resbalón
repentino podría provocar que una mano se mueva
hacia la hoja de sierra. Opere con la mesa al nivel o
cerca del nivel de la cintura para mejor equilibrio y
control. Anticipe el efecto que el tamaño de la pieza
de trabajo tendrá en su habilidad para ajustar la
posición y mantener el control hasta terminar el corte.
16. MANTENGA LOS BRAZOS, MANOS Y DEDOS
AL MENOS A SEIS PULGADAS DE DISTANCIA DE
LA HOJA.
17. NUNCA CORTE METALES, PLACAS DE
CEMENTO O MAMPOSTERÍA. Ciertos materiales
hechos por el hombre tienen instrucciones
especiales para cortar en sierras de mesa. Siga las
recomendaciones del fabricante en todo momento.
18. NUNCA INTENTE LIBERAR UNA HOJA ATASCADA
O UNA PIEZA DE TRABAJO ATRAPADA sin antes
apagar la máquina y desconectar la sierra de la
fuente de poder.
19. NUNCA INTENTE ARRANCAR LA MÁQUINA CON
LA PIEZA DE TRABAJO CONTRA LA HOJA para
reducir el riesgo de que la pieza de trabajo sea
expulsada.
20. NUNCA REALICE TRABAJOS DE DISEÑO,
ENSAMBLE O PREPARACIÓN SOBRE LA MESA
O ÁREA DE TRABAJO cuando la sierra esté en
funcionamiento.
21. ANTES DE DEJAR LA SIERRA , espere a que la
hoja se detenga por completo, luego desconecte
la máquina de la fuente de poder, limpie la mesa
y el área de trabajo, y bloquee el interruptor para
evitar el uso no autorizado.
22. SUJETE LA PIEZA DE TRABAJO en base al
tamaño y el tipo de operación a realizar. Sujete
firmemente la pieza de trabajo contra la guía y
hacia abajo contra la superficie de la mesa. No
deje un panel ancho o tabla larga (u otra pieza de
trabajo grande) sin soporte, pues el peso de esta
pudiera causar que se moviera en la mesa, lo que
resultaría en una pérdida de control.
23. UN RUIDO DESCONOCIDO O VIBRACIÓN EN
EXCESO pudiera indicar un problema con la sierra.
Si esto ocurre, apáguela y desconéctela de la
fuente de poder hasta que encontrar y corregir el
problema. Comuníquese con servicio al cliente para
solicitar ayuda si es imposible resolver el problema.
24. BUSQUE CONSEJO de su supervisor, instructor u
otra persona calificada si no está completamente
familiarizado con la operación de esta máquina. El
conocimiento es seguridad.
ENSAMBLE DE LA GUARDA PARA HOJA DE SIERRA,
TRINQUETES ANTI CONTRAGOLPES Y SEPARADOR
La sierra de mesa está equipada con un ensamble
de guarda para hoja, trinquetes anti contragolpes y
separador que cubre la hoja y reduce la posibilidad de
un contacto accidental con esta. El separador es una
placa plana que se acomoda en el corte realizado por
la hoja de sierra y combate eficazmente el contragolpe
reduciendo la tendencia de la hoja a atascarse en el
corte. Dos trinquetes anti contragolpe se encuentran
a los lados del separador que permiten el paso de
la madera por la hoja en la dirección del corte pero
reduce la posibilidad de que el material sea expulsado
hacia el operador. La guarda para hoja y los trinquetes
anti contragolpe solo pueden usarse cuando se
realizan cortes completos que separan la madera.
Al realizar rebajos y otros cortes sin traspaso, deben
quitarse la guarda para hoja y los trinquetes anti
contragolpes; además, el separador debe bajarse a la
posición de corte sin traspaso marcada en el mismo.
Use todos los componentes del sistema de guardas
(ensamble de guarda para hoja, separador, y
trinquetes anti contragolpe) para cada operación
en la cual pueden usarse incluyendo todos los
cortes completos. Si elige no usar ninguno de estos
componentes para una aplicación en particular, tenga
especial cuidado en cuanto al control de la pieza
de trabajo, el uso de empujadores, la posición de
sus manos con respecto a la hoja, el uso de lentes
de seguridad, los medios para evitar contragolpes
y el resto de las advertencias mencionadas en este
manual y en la misma sierra. Reemplace los sistemas
de guardas en cuanto regrese a operaciones de corte
completo. Mantenga el ensamble de guardas en
buenas condiciones de funcionamiento.
CÓMO FABRICAR UN EMPUJADOR
Para poder utilizar de manera segura la sierra de
mesa, debe usar un empujador cuando el tamaño o
forma de la pieza de trabajo ocasionaría que de alguna
manera sus manos estén a 6 pulgadas (152 mm) de
la hoja de la sierra u otro cortador. Un empujador se
incluye con esta sierra.
No es necesario ningún tipo especial de madera para
fabricar empujadores adicionales siempre y cuando
sean macizos y suficientemente largos y la madera esté
libre de nudos, imperfecciones y grietas. Se recomienda
una longitud de 16 pulgadas (400 mm) con una muesca
que se ajuste contra el borde de la pieza de trabajo para
evitar que se resbale. Es una buena idea tener varios
empujadores de la misma longitud mínima, 16 pulgadas
(400 mm), con muescas de diferentes tamaños para
diferentes grosores de piezas de trabajo.
La forma puede variar para adaptarse a sus propias
necesidades siempre que realice la función prevista
de mantener sus manos alejadas de la hoja. Inclinar
la muesca a un ángulo para que el empujador pueda
sostenerse a un ángulo de 20 a 30 grados de la mesa
de la sierra le ayudará a sostener la pieza de trabajo
al tiempo que pasa por la sierra. Consulte el diagrama
en la sección de auxiliares de corte en la página 88 de
este manual.
71
Page 72

REGLAS DE SEGURIDAD DE LA SIERRA DE MESA (continuación)
CONTRAGOLPES
Los contragolpes pueden ocasionar lesiones graves.
Un contragolpe ocurre cuando una parte de la pieza
de trabajo se atasca entre la hoja de sierra y el tope
guía para corte al hilo u otro objeto fijo, se eleva
de la mesa y es expulsada hacia el operador. Los
contragolpes pueden evitarse prestando atención a las
siguientes condiciones.
CÓMO REDUCIR EL RIESGO DE
CONTRAGOLPES Y PROTEGERSE
DE UNA POSIBLE LESIÓN:
• Asegúrese de que el tope guía para corte al hilo
esté paralelo con la hoja de sierra.
• No corte al hilo aplicando la fuerza de avance a la
sección de la pieza de trabajo que se convertirá en la
pieza cortada (libre). Cuando realice un corte al hilo, la
fuerza de avance siempre debe aplicarse entre la hoja
de la sierra y la guía; use un empujador para trabajos
angostos, 6 pulgadas (152 mm) de ancho o menos.
• Mantenga el ensamble de guarda para hoja de
sierra, separador y anti contragolpe en su lugar y
funcionando correctamente. El separador debe estar
alineado con la hoja de sierra y el ensamble anti
contragolpe debe detener un contragolpe una vez
que ha iniciado. Verifique su acción antes de cortar
al hilo empujando la madera por abajo del ensamble
anti contragolpe. Los dientes deben evitar que la
madera se jale hacia el frente de la sierra. Si cualquier
parte del ensamble no está funcionando, regrese
la máquina al centro de servicio autorizado más
cercano para su reparación.
• Los materiales de plástico y compuestos (como
madera prensada) pueden cortarse en la sierra. Sin
embargo, puesto que usualmente estos son bastante
duros y resbalosos, los trinquetes anti contragolpe
pueden no detener un contragolpe. Por lo tanto,
ponga atención especial a la siguiente preparación y
procedimientos adecuados para cortar al hilo.
• Use el ensamble de guarda para hoja de sierra,
trinquetes anti contragolpe y separador en cada
operación posible, incluyendo todos los cortes
completos.
• Empuje la pieza de trabajo más allá de la hoja de
sierra antes de soltarla.
• NUNCA corte al hilo una pieza de trabajo que esté
torcida o deformada, o bien que no tenga un borde
recto para guiarla por el tope guía.
• NUNCA corte una pieza de trabajo larga que no
pueda controlar.
• NUNCA use el tope guía como una guía o tope de
largo al realizar un corte transversal.
• NUNCA corte una pieza de trabajo con nudos
sueltos, defectos, clavos u otros objetos extraños.
• NUNCA corte al hilo una pieza de trabajo con una
longitud menor a 10 pulgadas (254 mm).
• NUNCA use una hoja sin filo. Una hoja sin filo debe
reemplazarse o afilarse.
CONEXIONES A LA FUENTE DE PODER
FUENTE DE PODER
Esta sierra está equipada con un motor de 13 amperes
para usarse con 120 voltios, 60 HZ de corriente alterna.
Un electricista calificado puede recablearla para usarla
con una fuente de poder de 240 voltios. Consulte las
siguientes instrucciones acerca de las conexiones
adecuadas para la sierra según el sistema eléctrico.
Para el voltaje, el cableado en un taller es tan
importante como la clasificación del motor. Una línea
prevista únicamente para iluminación puede no ser
capaz de llevar correctamente la corriente necesaria
para el motor de una herramienta eléctrica; un cable
que es suficientemente pesado para una distancia corta
puede ser demasiado ligero para una distancia larga; y
una línea que puede soportar una herramienta eléctrica
puede no ser capaz de soportar dos o tres.
NO EXPONGA LA MÁQUINA A LA LLUVIA NI LA UTILICE EN LUGARES HÚMEDOS.
INSTRUCCIONES PARA LA CONEXIÓN A TIERRA
ESTA MÁQUINA DEBE CONECTARSE A TIERRA DURANTE SU USO PARA PROTEGER AL
OPERADOR DE UNA DESCARGA ELÉCTRICA.
En caso de un mal funcionamiento o avería, la conexión
a tierra proporciona a la corriente eléctrica una ruta
de menor resistencia para reducir el riesgo de una
descarga eléctrica. Esta máquina está equipada con
un cable eléctrico que tiene un conductor a tierra para
equipos y un enchufe con conexión a tierra. El enchufe
debe conectarse a un tomacorriente adecuado que
esté debidamente instalado y conectado a tierra de
conformidad con todos los códigos y ordenanzas locales.
No modifique el enchufe que se proporciona con la
Debe usarse un circuito eléctrico aparte para las
máquinas. Este circuito no debe ser menor a un
alambre #12 y debe protegerse con un fusible de acción
retardada de 20 amperes. Si usa un cable de extensión,
use solo cables de 3 alambres que tengan enchufes de
tipo conexión a tierra de 3 puntas y un tomacorriente
correspondiente que conecte el enchufe de la máquina.
Antes de conectar la máquina a la corriente, asegúrese
de que el interruptor esté en la posición "OFF"
(apagado) y asegúrese de que la corriente eléctrica
tenga las mismas características que las indicadas en
la máquina. Una caída significativa de voltaje provocará
una pérdida de potencia y sobrecalentará el motor.
También puede dañar la máquina.
sierra o que un electricista haya recableado. Si no es
posible conectarlo al tomacorriente, pida a un electricista
calificado que instale un tomacorriente adecuado.
La conexión inadecuada del conductor a tierra para
equipos puede resultar en un riesgo de descarga
eléctrica. El conductor con aislamiento que tiene una
superficie exterior verde con o sin rayas amarillas es el
conductor a tierra. Si es necesario reparar o reemplazar
el cable eléctrico o enchufe, no conecte el conductor a
tierra para equipo a una terminal energizada.
72
Page 73

CONEXIONES A LA FUENTE DE PODER
Verifique con un electricista calificado o personal de
servicio si las instrucciones de conexión a tierra no se
entienden por completo o si tiene dudas acerca de si
la máquina está correctamente conectada a tierra.
Use únicamente cables de extensión de 3 alambres
que tengan enchufes de tipo conexión a tierra de
3 puntas, tomacorrientes de 3 conductores
debidamente conectados a tierra que puedan
conectar el enchufe de la máquina, como se muestra
en la Figura A, o un tomacorriente debidamente
conectado a tierra con un adaptador de conexión a
tierra, como se muestra en la Figura B.
Repare o reemplace inmediatamente cables dañados o
desgastados.
(continuación)
EN TODOS LOS CASOS, ASEGÚRESE DE QUE EL TOMACORRIENTE EN CUESTIÓN ESTÉ
DEBIDAMENTE CONECTADO A TIERRA. SI NO ESTÁ SEGURO, PIDA A UN ELECTRICISTA
CALIFICADO QUE REVISE EL TOMACORRIENTE.
Esta es una herramienta conectada por cable y a tierra diseñada para usarse en un circuito eléctrico con un
voltaje nominal de 120 voltios. Está diseñada para usarse en un circuito que tenga un tomacorriente como se
muestra en la FIG. A. Tiene un enchufe como se muestra en la FIG A. Si tiene un tomacorriente bipolar como se
muestra en la FIG. B, puede utilizar un adaptador temporal como se muestra en la FIG. B si no está disponible un
tomacorriente con conexión a tierra. La orejeta verde que sobresale del adaptador debe conectarse a una caja
de tomacorriente conectada a tierra permanente. El adaptador temporal debe usarse únicamente hasta que un
electricista calificado pueda instalar un tomacorriente con conexión a tierra.
TOMACORRIENTE
CONECTADO A TIERRA
PUNTAS
TRANSPORTADORAS
DE CORRIENTE
TOMACORRIENTE CON
CONEXIÓN A TIERRA
MEDIO DE
CONEXIÓN A
TIERRA
ADAPTADOR
LA PUNTA DE CONEXIÓN A TIERRA
ES LA MÁS LARGA DE LAS 3 PUNTAS
FIG. A
FIG. B
Punta de conexión
a tierra
FIG. C
Un electricista calificado puede convertir esta herramienta a un circuito de suministro de energía de 240 voltios. Si
se convierte a 240 voltios, debe ser equipada con un enchufe con conexión a tierra que se muestra en la FIG. C y
debe conectarse a un tomacorriente como se muestra en la FIG. C, que esté conectado a una conexión a tierra
permanente. No hay un adaptador disponible ni debe usarse con esta herramienta cuando se convierte a 240 voltios.
CABLES DE EXTENSIÓN
Nunca use un cable de extensión dañado. Revise los cables de extensión antes de cada uso. Si
están dañados, reemplácelos de inmediato. Tocar el área dañada podría provocar una descarga
eléctrica que resultaría en una lesión grave.
Mantenga los cables de extensión lejos del área de trabajo. Coloque el cable de manera que no
quede atrapado en la madera, herramientas ni otras obstrucciones.
• Use cables de extensión adecuados. Asegúrese de que el cable de extensión sea un cable de 3 alambres que
tenga un enchufe de tipo conexión a tierra de 3 puntas y un tomacorriente correspondiente adecuado para el
enchufe de la máquina, según se describe en las instrucciones de conexión a tierra de este manual. Cuando use
un cable de extensión, asegúrese de usar uno suficientemente pesado para soportar la corriente de la máquina.
Un cable de menor calibre provocará una caída en el voltaje de línea, lo que provocará una pérdida de energía y
sobrecalentamiento. La siguiente tabla muestra el calibre máximo a usar dependiendo de la longitud del cable. En
caso de dudas, use el siguiente calibre más pesado. Entre más pequeño sea el número de calibre, más pesado será
el cable. Deben usarse únicamente cables revestidos y redondos indicados por Underwriter's Laboratories (UL).
DE CABLES DE EXTENSIÓN RECOMENDADOS PARA USARSE CON MÁQUINAS
Amperaje Voltios Longitud total del
0-6
0-6
0-6
0-6
6-10
6-10
6-10
6-10
10-12
10-12
10-12
10-12
12-16
12-16
TAMAÑO DE CALIBRE MÍNIMO
ELÉCTRICAS ESTACIONARIAS
Calibre del cable
cable en pies
240
240
240
240
240
240
240
240
240
240
240
240
240
240
Hasta 50
50-100
100-200
200-300
Hasta 50
50-100
100-200
200-300
Hasta 50
50-100
100-200
200-300
Hasta 50
50-100
de extensión
18 AWG
16 AWG
16 AWG
14 AWG
18 AWG
16 AWG
14 AWG
12 AWG
16 AWG
16 AWG
14 AWG
12 AWG
14 AWG
12 AWG
DE CABLES DE EXTENSIÓN RECOMENDADOS PARA USARSE CON MÁQUINAS
Amperaje Voltios Longitud total del
0-6
0-6
0-6
0-6
6-10
6-10
6-10
6-10
10-12
10-12
10-12
10-12
12-16 120 Hasta 25 14 AWG
12-16 120 25-50 12 AWG
12-16 120
73
TAMAÑO DE CALIBRE MÍNIMO
ELÉCTRICAS ESTACIONARIAS
Calibre del cable
cable en pies
120
120
120
120
120
120
120
120
120
120
120
120
Hasta 25
25-50
50-100
100-150
Hasta 25
25-50
50-100
100-150
Hasta 25
25-50
50-100
100-150
NO SE RECOMIENDAN LONGITUDES MAYORES
A 50 PIES
de extensión
18 AWG
16 AWG
16 AWG
14 AWG
18 AWG
16 AWG
14 AWG
12 AWG
16 AWG
16 AWG
14 AWG
12 AWG
Page 74

DESEMPAQUE
• La máquina es pesada, se necesitan dos personas
para desempacarla y levantarla.
• Use una correa de seguridad para evitar una
volcadura al levantar la máquina.
• Antes de ensamblar y usar la herramienta, lea
con atención este manual para familiarizarse con
los procedimientos adecuados de ensamblado,
mantenimiento y seguridad.
Verifique que la caja de envío y la máquina no estén
dañadas antes de desempacarla. Con cuidado retire
los componentes de la capa de espuma superior.
Retire la capa superior de espuma, luego retire todos
los componentes de la capa inferior de espuma.
Coloque todas las partes en un pedazo de cartón u
otra superficie plana y limpia. Se necesitan dos o más
personas para levantar y sacar la sierra de la caja.
Siempre busque y retire los materiales protectores
de empaque alrededor de los motores y piezas
móviles. No deseche la caja de envío y materiales
de empacado hasta que haya inspeccionado con
atención el contenido, ensamblado la máquina y esté
seguro de que funciona correctamente.
Compare el contenido del paquete con la lista de
componentes y la lista de paquete de tornillería antes
del ensamble para asegurarse de que todos los
artículos estén presentes. Inspeccione con cuidado
las piezas para asegurarse de que no se hayan
dañado durante el envío. Si falta alguna pieza, o está
dañada o preensamblada, no ensamble la sierra. En
lugar de ello, llame al servicio al cliente de DELTA
1-800-223-7278 para solicitar ayuda.
Después de ensamblar, retire todo el material y los
recubrimientos protectores de todas las piezas y de
la sierra de mesa. Los recubrimientos protectores
pueden retirarse rociando WD-40
y quitándolos usando un paño suave. Es posible
que deba hacer esto varias veces para quitar por
completo todos los recubrimientos protectores.
Después de limpiarla, aplique cera en pasta de buena
calidad a cualquier superficie de hierro fundido
sin pintar. Asegúrese de quitar la cera puliendo la
superficie antes de ensamblar.
®
sobre ellos
®
al
LISTA DE
ELEMENTOS
DESCRIPCIÓN (CANT.)
1. Sierra de mesa con disco de
corte de carburo, y llave de
estrella (1)
2. Ala de extensión
3. Caja de interruptor (unida a la
sierra) (1)
4. Estructura tubular del soporte (2)
5. Paneles de soporte (4)
6. Ruedas fijas (2)
7. Patas ajustables (2)
8. Pivote de las patas y ruedas (no
se muestra) (unido a la sierra) (1)
9. Asas de volante (2) (unidas a la
sierra)
10. Pomos de bloqueo (2)
11. Regla de ingletes (1)
12. Manija de la guía de corte (1)
13. Ala de extensión (2) con las
36-5000 y 5100 (1), la 36-5052 y
con la 36-5152
14. Guía de corte (1)
15. Placa de embocadura (1)
16. Protección del disco y trinquete
antirrebote
17. Disco de corte (1)
18. Empujador (1)
Contenidos en caja
aparte
19. Perfil trasero
20. Tubo de la guía
21. Perfil frontal de la guía
1
2
19
3
4
5
6
18
17
Contenidos en caja aparte, sólo
para 36-5052 y 36-5152
22. Ala de madera para la mesa
23. Patas
16
15
14
13
21
11
12
10
23
9
8
7
22
20
74
Page 75

DESEMBALADO
PAQUETES DE FERRETERÍA
Modelos con guía de 30 pulg. (36-5000 y 36-5100)*
(continuación)
Descripción Cant. Dónde se utiliza
Perno de cabeza redonda y cuello cuadrado M8 x 70mm 1 Conectar ambas mitades de la estructura del soporte
Tuerca Nyloc M8 1 Conectar ambas mitades de la estructura del soporte
Arandela de presión M8 1 Conectar ambas mitades de la estructura del soporte
Perno de cabeza redonda y cuello cuadrado M6 x 70mm 4 Conectar pata al soporte
Contratuerca M6 4 Conectar pata al soporte
Pasador de eje M8 x 53mm 2 Ruedas
Tuerca de seguridad M8 2 Ruedas
Tornillo Phillips autorroscante M6 x 10mm 16 Paneles del soporte
Tornillo hexagonal con arandela de
presión 5/16-18 x 7/8"
Tornillo de cabeza hexagonal redondeada1/4-20 x 1/2" 6 Tubo de guía al perfil
Tornillo de cabeza plana 5/16-18 x 1" 8 Perfil frontal a mesa y alas 8
Tuerca con brida hexagonal 5/16-18 19 Alas a mesa 6, ala a ala 3 (36-5000),
Plantilla de alineación de guía 1
Arandela cónica dentada 5/16” 1 En 1 tornillo del perfil frontal a la mesa
Arandela plana dentada 5/16” 1 En 1 tornillo del perfil trasero a la mesa
Los accesorios de ferretería proporcionados sirven para la sierra modelo 36-5000, que es la que más requiere.
*
17 Alas a mesa 6, ala a ala 3, perfil trasero 8
perfil trasero 8, perfil frontal 8
para conexión eléctrica a tierra.
para conexión eléctrica a tierra.
Modelos con guía de 52 pulg. (36-5052 y 36-5152) **
Nº de
parte
153
155
154
144
145
151
155
146
58
35
19
16
190
191
192
Descripción Cant. Dónde se utiliza
Perno de cabeza redonda y cuello cuadrado M8 x 70mm 1 Conectar ambas mitades de la estructura del soporte
Tuerca Nyloc M8 1 Conectar ambas mitades de la estructura del soporte
Arandela de presión M8 1 Conectar ambas mitades de la estructura del soporte
Perno de cabeza redonda y cuello cuadrado M6 x 70mm 4 Conectar pata al soporte
Contratuerca M6 4 Conectar pata al soporte
Pasador de eje M8 x 53mm 2 Ruedas
Tuerca de seguridad M8 2 Ruedas
Tornillo Phillips autorroscante M6 x 10mm 16 Paneles del soporte
Tornillo hexagonal con arandela de presión
5/16-18 x 7/8"
Arandela plana 5/16-18 6 Ala a mesa de madera, ambos
Tornillo de cabeza hexagonal redondeada1/4-20 x 1/2" 8
Tornillo de cabeza plana 5/16-18 x 1" 6
Tuerca con brida hexagonal 5/16-18 15
Tornillo hexagonal 1/4-20 X 1 1/2" 6
Arandela plana 1/4" 1
Tuercas hexagonales 1/4-20 12
Tornillo Phillips autorroscante #8 x 3/4" 8
Tornillos #10-32 x 1 3/4" 4
Arandelas planas #10 4
Tuercas hexagonales #10-32 4
Plantilla de alineación de guía 1
Arandela cónica dentada 5/16” 1
Arandela plana dentada 5/16” 1
15 Alas a mesa 6, perfil trasero 6, ala
a mesa de madera 3 (36-5052)
lados en 36-5052
Tubo de guía al perfil
Perfil frontal a mesa y alas 6
Perfil trasero 6, perfil frontal 6, ala
a mesa de madera 3, (36-5052)
Perfiles a la mesa de madera
2
Perfiles a la mesa de madera
Perfiles a la mesa de madera
Patas a la mesa
Patas a la mesa
Patas a la mesa
Patas a la mesa
En 1 tornillo del perfil frontal a la mesa
para conexión eléctrica a tierra.
En 1 tornillo del perfil trasero a la mesa
para conexión eléctrica a tierra.
Nº de
parte
153
155
154
144
145
151
155
146
58
193
35
19
16
183
184
185
182
180
179
181
190
191
192
** Los accesorios de ferretería proporcionados sirven para la sierra modelo 36-5052, que es la que más requiere.
75
Page 76

ENSAMBLE
de la sierra
• No levante la sierra sin ayuda. Sosténgala cerca
de su cuerpo al tiempo que la levanta. Mantenga
las rodillas dobladas y levante con sus piernas y
no su espalda.
• Ensamble por completo la sierra con el ensamble
de patas antes de usarla. El ensamble de patas es
una parte integral y necesaria de la estructura de
soporte de esta sierra.
• No modifique la sierra ni fabrique accesorios no
recomendados para el uso con la sierra.
• Asegúrese de que el interruptor de energía esté en
la posición "OFF" (Apagado) antes de conectar a
la fuente de poder.
• No la conecte a una fuente de poder hasta
completar el ensamble.
Evite el contacto con los dientes de la
hoja. Mantenga la hoja almacenada y
abajo cuando sea posible.
SOPORTE
1. Conecte las dos patas tubulares insertando el
extremo de la pata izquierda (A) en el extremo de
la pata derecha (B) como se muestra en la Figura
1. Sujétela con un perno hexagonal de perno
de cabeza redonda M8 x 70 mm y una tuerca
autoblocante y apriete manualmente.
2. Inserte los cuatro extremos abiertos de las patas
tubulares en los collares de la pata (C) como se
muestra. Sujete cada pata con un perno de 6 mm x
70 mm y una tuerca.
3. Sujete los paneles de soporte de la pata trasera
y frontal (D) a las patas usando cuatro pernos
autorroscantes M6 x 12mm.
HERRAMIENTAS NECESARIAS PARA EL
MONTAJE (NO INCLUÍDAS):
• Destornillador de punta plana
• Destornillador Phillips
• Llave 8mm
• Llave 10mm
• Llave 12mm
• Llave 13mm
• Llave 3/8-pulg.
• Llave 7/16-pulg.
• Llave 1/2-pulg.
• Llave 9/16-pulg.
• Llave Allen hexagonal 6mm
• Llave Allen 5/32-pulg.
• Llave Allen 3/16-pulg.
B
A
C
D
Parte frontal
FIGURA 1
76
Page 77

ENSAMBLE
(continuación)
RUEDAS FIJAS Y PATAS ESTACIONARIAS
1. Sujete las dos ruedas fijas (A) a las dos
patas izquierdas, al lado opuesto de la rueda
pivotante, usando el perno de cabeza redonda
de tope como en la Figura 2.
2. Atornille las patas ajustables (C) en los
insertos roscados de la pata derecha, junto a
la rueda pivotante.
3. Coloque un trozo de desecho de 2 x 4 en la
parte posterior de la sierra, como se muestra
en la Figura 3, para evitar dañar el conducto
para polvo cuando se enderece la sierra.
4. Coloque el lado derecho de la sierra hacia arriba.
La máquina es pesada, se
necesitan dos personas para
poner la máquina de pie.
5. Las dos patas ajustables (C) se pueden girar
para subirlas y bajarlas. Las patas pueden
ajustarse al nivel de la sierra y bloquearse en
su lugar con los tornillos de fijación usando una
llave hexagonal Allen de 6 mm. Vea la Figura 2.
A
B
C
FIGURA 2
ALAS DE EXTENSIÓN
Para modelos con tres alas de
extensión
1. Acople el ala de extensión izquierda (A) a
la mesa utilizando tres tornillos de cabeza
hexagonal 5/16-18 x 7/8 pulg.
2. Coloque las dos alas restantes boca abajo
en la mesa de la sierra. Coloque el lado
del ala que irá unida a la mesa de la sierra
cerca del borde de la mesa, de forma que el
patrón de agujeros del ala coincida con el
patrón de agujeros de la sierra. Si tiene un
ala de hierro colado, irá montada en la mesa
de la sierra. Coloque la otra ala adyacente a
ésta de forma que los patrones de agujeros
coincidan. Una las dos alas con tres tornillos
de cabeza hexagonal 5/16-18 x 7/8 pulg. y
las correspondientes tuercas de brida
hexagonales.
3. Dé la vuelta a las dos alas acopladas entre sí
A
FIGURA 3
(B) y atorníllelas a la mesa de la sierra usando tres
tornillos de cabeza hexagonal 5/16-18 x 7/8 pulg.
4. Asegúrese que los bordes superiores de las alas
están enrasados con la superficie de la mesa y
apriete los seis tornillos.
12
11
10
9
8
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
INCH
0
FIGURA 4
77
B
Page 78

ENSAMBLE
Mesa
Calibrador
Riel
Mesa
Calibrador
Riel
(continuación)
ALAS DE EXTENSIÓN
Para modelos con dos alas de
extensión y una mesa de madera
de extensión
1. Acople las alas derecha e izquierda (A)
a la mesa usando tornillos de cabeza
hexagonal 5/16- 18 x 7/8 pulg. para
cada ala.
2. Asegúrese que los bordes superiores
de las alas están enrasados con la
superficie de la mesa y apriete los seis
tornillos.
3. Proceda a montar los perfiles.
PERFILES DELANTERO Y
TRASERO
1. Monte el perfil delantero (A) (2x2x57
pulg. para los modelos con capacidad
de corte de 30 pulg.), (2x2x79 pulg. Para
los modelos con capacidad de corte de
52pulg.), a la mesa de la sierra y alas de
extensión usando tornillos de cabeza
plana 5/16-18 x 1 1/8 pulg. Alinee los
orificios en el perfil con los de la mesa y
alas.
2. Use la plantilla de alineación de la guía
(B) para asegurarse que el perfil está a
la distancia adecuada del borde de la
mesa a cada lado de la mesa de hierro
colado. (fig 6) Use también la plantilla
para mantener la misma distancia del
perfil a las alas de extensión.
3. Alinee el perfil trasero a los orificios en
la parte trasera de la mesa de la sierra
y alas de extensión. Acople el perfil
trasero a la mesa de la sierra usando
dos tornillos de cabeza hexagonal 5/1618 x 7/8.
4. Acople el perfil trasero a las alas
usando tornillos de cabeza hexagonal
5/16-18 X 7/8 pulg. y tuercas de brida
hexagonales.
5. Use la plantilla de alineación de guía
suministrada (B) para asegurarse que
el perfil está a la distancia correcta de
la superficie de la mesa a cada lado
de la mesa de hierro colado. (fig 6) Use
también la plantilla para mantener la
misma distancia del perfil a las alas de
extensión.
A
9
8
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
INCH
0
Parte posterior
11
10
12
FIGURA 6
FIGURA 5
Parte frontal
A
C
78
Page 79

ENSAMBLE
G
J
(continuación)
MESA DE EXTENSIÓN DE
MADERA
Sólo modelos con capacidad de corte de 52 pulg.
1. Coloque el sobre de madera (A) boca abajo en el suelo
o bancada.
2. Coloque las patas (B) en las esquinas, tal y como se
muestra (fig 7) la parte vertical de la pletina de la pata
debe estar contra el faldón del sobre de la mesa (C).
3. Atornille las patas al sobre con tornillos
autorroscantes (8) #8 x 5/8 pulg. (D).
4. Utilice un taladro con broca de 1⁄4 pulg. para perforar
cuidadosamente el faldón de la mesa, usando los
orificios de la pletina de la pata como plantilla.
Coloque los tornillos #10 x 1 3⁄4 pulg. (E) en los
orificios taladrados desde el exterior, luego coloque
las arandelas y tuercas #10 en los tornillos y apriete.
5. Monte sin apretar los tornillos (3) 5/16-18 x 7/8 pulg.,
arandelas y tuercas (F) en los tres orificios laterales del
ala, tal y como se muestra (fig 8).
6. Haga descender cuidadosamente el soporte angular
de la mesa para que las ranuras coincidan con los
tornillos del ala (G). Apriete los tornillos una vez la
mesa de madera esté a nivel con el ala de extensión.
7. Usando la plantilla de alineación de perfiles (H), ajuste
las patas de la mesa (I) para que la superficie de la
mesa esté a la distancia adecuada del perfil.
8. Taladre agujeros de 1⁄4 pulg. a través de los orificios
de los perfiles delantero y trasero (J) en la mesa de
madera (fig 9).
9. Acople la mesa de madera a los perfiles con tornillos
1⁄4-20 x 1 1⁄2 pulg., arandelas planas, arandelas de
seguridad, y tuercas.
A
F
B
FIGURA 7
FIGURA 8
FIGURA 9
E
C
D
H
I
TOPE GUÍA Y CAJA DE CONTROL DE ENERGÍA
1. Conecte las dos mitades del tope guía (A y B) insertando el extremo más
pequeño en el extremo más grande. Vea la Figura 7.
2. Sujete el tope guía al riel frontal usando cinco tornillos
de cabeza hexagonal de 1/4-20 x 1/2 pulgada y resorte
de seguridad de ¼ de pulgada por los orificios (C) en el
lado inferior del riel frontal.
3. Alinee los dos orificios en la
abrazadera de la caja de control
de energía con los orificios
inferiores del riel frontal (D)
ubicados en el lado izquierdo
de la sierra. Asegure la caja de
control de energía al riel frontal
usando dos tornillos de cabeza
redonda de 1/4-20 x 1/2 pulgada.
4. Sujete el cable de corriente sobrante al
lado posterior del riel frontal con una
abrazadera de alambre y un tornillo de
cabeza redonda en cruz M5 x 6 mm.
C
79
A
B
FIGURA 10
Page 80

ENSAMBLE
PLACA DE GARGANTA
(continuación)
1. Para instalar la placa de garganta, baje la hoja
hasta abajo de la parte superior de la mesa, luego
con cuidado deslice la placa de garganta, primero
el extremo ranurado, desde la parte frontal de
la mesa hasta la parte posterior, manteniendo la
hoja centrada dentro de la ranura en la placa de
garganta. Vea la Figura 11. La placa debe descansar
dentro de la cavidad en la parte superior de la mesa.
2. Asegúrese de que placa de garganta esté al ras
con la parte superior de la mesa.
3. Si la garganta no está al ras con la parte superior
de la mesa, ajuste la altura de la placa de garganta
usando los cuatro tornillos de fijación (A).
NOTA: Al instalar el separador, los trinquetes anti
contragolpe y la guarda para hoja, la hoja debe estar
en la posición de 90° y elevada a la máxima altura.
Consulte la sección de elevación y descenso la hoja
en la página 79.
HOJA Y SEPARADOR
Para reducir el riesgo de una
lesión grave personal, el
separador debe estar instalado y debidamente
posicionado en cada corte completo y sin
traspaso posible.
1. La sierra se envía con la hoja y el separador
instalados y alineados correctamente. El separador
viene instalado en la posición inferior para corte sin
traspaso. Antes de operar la sierra, verifique que la
alineación de la hoja con la ranura del inglete y del
separador con la hoja no se haya afectado durante
A
FIGURA 11
el envío. Para verificar la alineación de la hoja y el
separador, consulte la página 91 en la sección de
alineación en este manual.
2. El separador viene instalado en la posición inferior
para corte sin traspaso. Para sujetar los ensambles
de trinquetes anti contragolpe y guarda para hoja,
el separador debe estar en la posición elevada
como se muestra en la Figura 9. Para elevar y bajar
el separador, consulte la sección de ajustes de
altura del separador en la página 81.
TRINQUETES ANTI CONTRAGOLPE Y GUARDA PARA HOJA
TRINQUETES ANTI CONTRAGOLPE
Para reducir el riesgo de lesiones
graves personales, los trinquetes
anti contragolpe deben colocarse cuando se realiza
un corte completo.
1. Consulte la Figura 12 y ubique la ranura de montaje
de los trinquetes anti contragolpe (A) en medio del
borde superior del separador.
2. Deslice la ranura situada en medio del ensamble de
los trinquetes anti contragolpe por la parte superior
del separador hasta que el vástago (B) encuentre la
ranura central en el separador.
3. Empuje el vástago en el ensamble de trinquetes
anti contragolpe (B) para dejar que el ensamble
caiga dentro de la ranura. Empuje el ensamble
de trinquetes anti contragolpe hacia abajo hasta
escuchar un chasquido y que quede firme.
Suelte el vástago. NOTA: Jale los trinquetes anti
contragolpe hacia arriba para comprobar que
estén correctamente sujetados.
FIGURA 12
Para quitar los trinquetes anti contragolpe, empuje el
vástago (B) y jale del ensamble de anti contragolpes
para retirarlo del separador.
80
A
B
Page 81

ENSAMBLE
GUARDA PARA HOJA
Para reducir el riesgo de lesiones
graves personales, la guarda
para hoja debe colocarse cuando se realiza un
corte completo.
1. Al tiempo que sostiene el ensamble de guarda para
hoja (A) en posición vertical, enganche el pasador
de posicionamiento (B) situado en la parte posterior
del ensamble de guarda para hoja dentro de la
ranura situada en el borde posterior del separador.
2. Gire el ensamble de guarda para hoja hacia la parte
frontal de la sierra hasta que la parte metálica (C)
del ensamble de guarda para hoja esté paralelo con
la mesa como se muestra en la Figura 13.
3. Al tiempo que sujeta la parte frontal de la parte
metálica de la guarda (C) presione la palanca de
bloqueo de la guarda para hoja (D) hacia abajo
hasta escuchar un chasquido para trabarla en su
lugar. Verifique que la guarda esté enganchada al
separador jalando de la misma. Si la guarda no está
sujetada, la palanca de bloqueo de la guarda para
hoja se levantará a la posición de desbloqueo.
(continuación)
A
B
FIGURA 13
D
C
Si la parte metálica del ensamble
de guarda para hoja (C) no está
paralela a la mesa, el separador no está en la
posición elevada. Retire el ensamble de guarda para
hoja y los trinquetes anti contragolpe y suba el
separador, luego vuelva a instalar los trinquetes anti
contragolpe y el ensamble de guarda para hoja.
TOPE GUÍA PARA CORTE
AL HILO
Sujete la agarradera a la leva de la guía
El tope guía para corte al hilo se desliza hacia dentro
del riel guía posterior de modo que el gancho esté
abajo del riel posterior y quede montado sobre el
tubo de la guía frontal. La guía se bloquea en su lugar
aplicando presión en un movimiento descendente
sobre la agarradera del tope guía para corte al hilo.
La alineación del tope guía para corte al hilo debe
verificarse antes de usar la sierra. Para verificar la
alineación del tope guía para corte al hilo, consulte la
instrucciones de alineación en la página 92.
Para retirar el ensamble de la guarda para
hoja:
1. Levante la palanca de bloqueo del ensamble de la
guarda para hoja (D) a la posición de desbloqueo.
2. Gire la guarda hacia atrás y deslice el pasador (B)
de la ranura del separador.
ALMACENAMIENTO INCLUIDO
La sierra de mesa para contratista Delta #36-5000
series incluye un almacenamiento para la galga
de inglete, llave de eje, empujador y tope guía
proporcionados. Además hay un almacenamiento
incluido para hojas de sierra de repuesto (de venta
por separado). Las áreas de almacenamiento para la
galga de inglete, la hoja de repuesto y llave del eje se
encuentran en el panel lateral derecho de la máquina y
están preinstaladas.
El almacenamiento incluido para la guía y el empujador
se encuentra al lado izquierdo de la sierra.
GALGA DE INGLETE
Inserte la galga de inglete en cada ranura de inglete
para asegurar que se deslice sin problemas. Consulte
la sección de ajuste de topes de inglete en la página 91
para ajustar la precisión de la galga de inglete.
81
Page 82

(continuación)
ENSAMBLE
AJUSTE DE LOS TOPES BISELADOS POSITIVOS DE 90° Y 45°
Hay topes positivos en cada extremo del rango de
biselado. Para garantizar cortes exactos, los topes
positivos deben colocarse exactamente a 90° y 45°.
Los topes biselados están correctamente ajustados
al momento del envío. Sin embargo, para mayor
precisión, debe revisar la posición de los topes
después del ensamblado y de vez en cuando
para garantizar que los ajustes continúan siendo
satisfactorios. Para comprobar la posición de los
topes y, de ser necesario, realizar un ajuste, consulte
la Figura 14 y realice los siguientes pasos.
1. Suelte la perilla de bloqueo para inclinar la hoja.
2. Gire la rueda manual de inclinación de la rueda
hacia la derecha para inclinar la hoja alejándola de la
posición perpendicular para luego regresarla hasta
que el tope alcance la "posición de tope".
3. Usando una escuadra, compruebe el ángulo de
la parte frontal de la hoja con la mesa como se
muestra en la Figura 20b, en la página 81. Si la hoja
está a 90° con la mesa, continúe con el paso 6.
4. Si la hoja no está perpendicular con la mesa,
gire la rueda manual para inclinar ligeramente
la hoja y alejarla de la posición de tope, luego
ajuste el tope de 90° girando el tornillo con hueco
hexagonal ubicado en la parte superior de la mesa
inmediatamente al frente del lado izquierdo de la
placa de garganta (A). Vuelva a revisar el ángulo
usando una escuadra y continúe ajustando hasta
que la hoja esté a 90 grados cuando se regresa a
la posición de tope.
5. Gire la rueda de inclinación de la hoja hacia la
izquierda hasta llegar al tope de 45°. Luego repita
los pasos 4 y 5, ajustando el tope de 45° al girar el
tornillo de cabeza hexagonal ubicado en la parte
frontal del lado derecho de la placa de garganta. (B)
B
A
FIGURA 14
SUJECIÓN DE LA SIERRA
AL PISO
Esta sierra está diseñada para ser
fácil de transportar. No intente
usar la sierra para cortar una pieza de trabajo grande o
difícil sin antes seguir los pasos adecuados para evitar
volcar la sierra. Ejemplos de los pasos adecuados
incluyen el uso de mesas de soporte y/o asegurar las
patas de la sierra al piso reemplazando las patas de la
PREPARACIÓN PARA CORTES
Ignorar las siguientes
advertencias pudiera resultar
en graves lesiones personales.
SIEMPRE
•
esté en contacto con la hoja antes de presionar el
interruptor para arrancar la sierra. El contacto con la
hoja podría resultar en un contragolpe o la expulsión
de la pieza de trabajo.
• Para reducir el riesgo de un arranque accidental,
SIEMPRE asegúrese de que el interruptor esté en la
posición de apagado antes de conectar la sierra a
una fuente de poder.
NO
•
la de esta herramienta. No seguir esta advertencia
podría resultar en graves lesiones personales.
asegúrese de que la pieza de trabajo no
use hojas con una tasa de velocidad menor a
sierra con pernos de acoplamiento o sujetando las
patas a un soporte montado en el piso con
abrazaderas en U.
• Apague la unidad y desconéctela de la fuente de
poder antes de instalar y quitar accesorios, antes
de ajustar y al realizar reparaciones. Un arranque
accidental puede provocar una lesión.
• Antes de utilizar la sierra, asegúrese de estar
familiarizado con sus funciones y controles y haber
realizado todos los ajustes necesarios que se
describen a continuación.
82
Page 83

PREPARACIÓN PARA CORTES
ENSAMBLE
ELEVACIÓN Y DESCENSO
DE LA HOJA
En la mayoría de las aplicaciones, se recomienda que
eleve la hoja 1/8 pulg. (3.2 mm) a 1/4 pulg. (6.4 mm) por
encima de la superficie superior de la pieza de trabajo.
Suba o baje la hoja con la rueda manual (A) situada
en la parte frontal de la sierra (consulte la Figura 15).
1. Antes de subir o bajar la hoja asegúrese de aflojar
la perilla de bloqueo (B) girándola hacia la izquierda.
2. Para subir la hoja de sierra, gire la rueda manual
hacia la derecha. Para bajar la hoja de sierra, gire la
rueda manual hacia la izquierda.
3. Apriete la perilla de bloqueo para mantener la hoja
a la altura deseada. Solo se necesita un poco de
fuerza para trabar firmemente el mecanismo de
elevación de la hoja. Cualquier fuerza adicional
solo aplica tensión innecesaria en el dispositivo
de bloqueo.
4. Después de usar la sierra y al realizar el
mantenimiento, ajustes o reparaciones, baje la hoja
por debajo de la superficie de la mesa.
(continuación)
B
A
FIGURA 15
INCLINACIÓN DE LA HOJA
La hoja se puede inclinar hasta 45° a la izquierda
usando la rueda de inclinación de hoja (A) ubicada
en el panel lateral derecho de la sierra. El ángulo de
inclinación se mide con el calibre de bisel en la parte
frontal de la sierra. Para inclinar la hoja de sierra:
1. Afloje la perilla de bloqueo (B) hacia la izquierda y
gire la rueda manual hacia la derecha. Un indicador
en la parte frontal de la sierra indica el ángulo de
inclinación en incrementos de ½ grado.
2. Para bloquear la hoja de sierra al ángulo deseado,
apriete la perilla de bloqueo girándola hacia la
derecha.
A
B
FIGURA 16
83
Page 84

PREPARACIÓN PARA CORTES
ENSAMBLE
(continuación)
SELECCIÓN Y ALMACENAMIENTO DE LAS HOJAS DE SIERRA
Los separadores deben coincidir con las dimensiones
de la hoja de sierra para poder funcionar eficazmente.
La hoja de sierra proporcionada con la sierra nueva
es una hoja de combinación de 10 pulgadas (254 mm)
usada para cortes transversales (en contra de la veta)
y cortes al hilo (con la veta) en la pieza de trabajo. El
orificio del eje de la hoja mide 5/8 de pulgada (16 mm)
de diámetro. Esta hoja producirá un corte de buena
calidad en la mayoría de las aplicaciones.
Existen muchos tipos de hojas disponibles para
realizar trabajos específicos y especiales tales
como corte transversal únicamente, cortes al
hilo únicamente, cortes ranurados en madera
contrachapada, revestimiento de madera, etc.
CAMBIO DE LA HOJA DE LA SIERRA
• Use solo hojas de 10 pulgadas (254 mm) de
diámetro con orificios de eje de 5/8 pulg. (16 mm),
tasa de 3,600 rpm o más, un ancho de corte mínimo
de 0.102 pulgadas (2.6 mm) y un grosor máximo de
0.073 pulgadas (1.8 mm).
• Para reducir el riesgo de lesiones, apague la unidad
y desconéctela de la fuente de poder antes de
instalar y quitar hojas y accesorios, antes de ajustar
y al realizar reparaciones. Un arranque accidental
puede provocar una lesión.
1. Retire la placa de garganta y eleve la hoja de sierra
a la altura máxima.
2. Presione y sostenga el botón de bloqueo del eje (A)
que se muestra en la Figura 17.
3. Use la llave de eje incluida para quitar la tuerca y
brida retenedora de hoja (B). Retire la hoja usada.
Use solo hojas de sierra diseñadas para las máximas
velocidades de operación segura de 3,600 RPM o más.
Las hojas de sierra siempre deben mantenerse
afiladas. Se recomienda que ubique un servicio de
afilado de buena reputación para afilar las hojas
cuando sea necesario.
Nunca apile las hojas una sobre la otra durante el
almacenamiento. Coloque un material tal como
cartón entre ellas para evitar que las hojas tengan
contacto una con otra o colóquelas en una gaveta de
almacenamiento.
No deben usarse muelas u hojas abrasivas
(incluyendo las de diamante) con esta sierra.
4. Coloque la nueva hoja en el eje
con los dientes hacia abajo en
la dirección que gira la hoja
hacia la parte frontal de la
mesa de la sierra.
5. Coloque y apriete la tuerca
y brida retenedora de hoja.
6. Vuelva a colocar la placa
de garganta.
A
B
FIGURA 17
POSICIÓN DEL SEPARADOR
NOTA: Los dispositivos de seguridad, el ensamble
de guarda para hoja y ensamble de anti contragolpe
se han quitado en la Figura 18 para poder mostrar
el lugar de características específicas. Al operar la
sierra, estos dispositivos de seguridad deben estar
instalados y funcionando correctamente.
El separador es una placa plana que se acomoda
en el corte realizado por la hoja de sierra y combate
eficazmente el contragolpe reduciendo la tendencia
de la hoja a atascarse en el corte. Debe estar
instalado y posicionado correctamente en cada corte
completo y en cada corte sin traspaso a menos que el
separador interfiera con la pieza de trabajo.
El grosor del separador (A) debe ser mayor que el
cuerpo de la hoja o grosor de la placa (B) y menor
que el ancho de corte (C) como se muestra en la
Figura 15. El separador incluido con esta sierra mide
2.2 mm de grosor y puede usarse únicamente con
una hoja de 10 pulgadas (254 mm) con un ancho de
corte mínimo de 0.102 pulgadas (2.6 mm) y un
grosor máximo de 0.073 pulgadas (1.8 mm). No
intente usar este separador con hojas que no
tengan estas dimensiones.
A
B
C
FIGURA 18
84
Page 85

PREPARACIÓN PARA CORTES
Jale para liberar
Frenos posicionadores
superiores en los pernos
A
B
(continuación)
AJUSTES DE ALTURA
DEL SEPARADOR
La altura del separador debe ajustarse en base al tipo
del corte a realizar. Para todos los cortes completos
(cuando la madera se separa por completo), debe
estar en la posición elevada con los dedos anti
contragolpe y guarda instalados. Para cortes sin
traspaso (cuando la hoja no penetra la parte superior
de la pieza de trabajo), el separador debe estar en la
posición descendente y los dedos anti contragolpe y
la guarda no deben estar instalados.
PARA SUBIR O BAJAR EL SEPARADOR:
1. Retire la placa de garganta.
2. Eleve la hoja a la máxima altura sobre la mesa.
3. Jale la palanca de desbloqueo del separador
(A) para liberar el separador del mecanismo de
sujeción. Vea la Figura 19.
4. Empuje el separador y palanca de desbloqueo al
lado del eje de la hoja para soltar el separador de
los pasadores.
a. Para ajustar el separador en la posición de
corte completo, jálelo hacia arriba hacia los
pernos posicionadores inferiores.
b. Para mover el separador a la posición de
corte sin traspaso, empújelo hacia abajo
hacia los pernos posicionadores superiores.
NOTA: Al ajustar el separador hacia abajo o arriba,
asegúrese de jalar en un movimiento circular como
se muestra.
1. Suelte la palanca y jale del separador para
asegurarse de que está correctamente colocado
en la posición elevada o descendente.
2. Sujete firmemente el separador empujando la
palanca de sujeción del separador hacia abajo a la
posición horizontal.
3. Vuelva a colocar la placa de garganta.
NO utilice la sierra a menos que
el separador esté sujetado
firmemente en la posición elevada para cortes
completos o en la posición descendente para cortes
sin traspaso.
Frenos
posicionadores
inferiores
el separador
A
Ajustar
Bloqueado
FIGURA 19
REVISIÓN DE LA ALINEACIÓN
DEL SEPARADOR
Antes de conectar la sierra de
mesa a la fuente de poder y
utilizarla, siempre inspeccione el ensamble de guarda
para hoja y el separador para verificar la alineación y
la distancia con la hoja de sierra. Revise la alineación
del separador después de cada cambio de hoja.
PARA COMPROBAR LA ALINEACIÓN:
1. Alineación horizontal: Coloque una
regla en la mesa contra la parte
frontal de la hoja (A) y asegúrese
de que se extienda a lo largo
del separador (B) como se
muestra en la
Figura 20a.
El separador
debe tocar
ligeramente
la regla.
Asegúrese
de que
la regla
se acomode entre los
dientes y descanse sobre
la parte frontal de la hoja
y el separador para una
alineación correcta.
FIGURA 20a
1. Alineación vertical: Coloque una escuadra sobre la
mesa y contra la parte frontal de la hoja, y asegúrese
de que se extienda a lo largo del separador (B)
como se muestra en la Figura 20b. El separador y
la hoja deben tocar la escuadra sin ningún espacio.
Asegúrese de que la regla se acomode entre los
dientes y descanse sobre la parte frontal de la hoja y
el separador para una alineación correcta.
Si el separador y la hoja no están alineados horizontal o
verticalmente, consulte las instrucciones de alineación
del separador en la página 91 de este manual.
B
FIGURA 20b
85
Page 86

PREPARACIÓN PARA CORTES
USO DE LA GALGA DE INGLETE
La galga de inglete está equipada con topes divisores
ajustables a 90°, 75°, 60°, 45° y 30°. Para preparar el
inglete para un corte en ángulo, consulte la Figura 21 y:
1. Afloje la manilla (A).
2. Presione la palanca de desmontaje.
3. Mueva el cuerpo de la galga de inglete al ángulo
deseado.
4. Suelte la palanca de desmontaje y vuelva a apretar
la manija.
La galga de inglete está equipada con una arandela
en el extremo de la barra que se acomoda en la
ranura en T de la mesa. Esto permite que la galga
de inglete se quite del borde frontal de la mesa sin
caerse. Con esto hay mayor espacio para la pieza de
trabajo enfrente de la hoja.
USO DEL ENSAMBLE DE
GUARDA PARA HOJA
Los trinquetes anti contragolpe
y la guarda para hoja deben
usarse con todos los cortes completos. Mantenga
los escudos protectores abajo y los brazos, manos y
dedos lejos de la hoja, la guarda para hoja y
trinquetes anti contragolpe cuando está encendida
la sierra para evitar lesiones graves. Consulte las
instrucciones de ensamble en la página 76 para
información sobre la instalación y remoción de los
trinquetes anti contragolpe y guarda para hoja.
Si hay necesidad de elevar ligeramente la guarda para
hoja (por ejemplo, para tomar medidas), la guarda
puede dejarse en una posición elevada.
1. Consulte la Figura 22 y, levantando la guarda
desde el frente, eleve el escudo protector hasta
llegar a la posición de bloqueado que se indica
con un chasquido. Pueden elevarse uno o ambos
escudos protectores.
2. Al terminar de tomar las medidas, regrese la guarda
a la posición de funcionamiento.
(continuación)
A
B
FIGURA 21
FIGURA 22
REVISIÓN DE LA ALINEACIÓN
DE LA GUÍA
No intente utilizar un tope guía
para corte al hilo que no esté
correctamente alineado.
Cada vez que utilice el tope guía para corte al hilo,
compruebe su alineación para asegurarse de que la
guía esté paralela a la ranura de inglete. Para verificar
la alineación del tope guía para corte al hilo, coloque
la guía adyacente a la ranura de inglete y sujete la
guía en su lugar. Si la guía no está alineada con la
ranura de inglete desde la parte frontal a la posterior,
consulte las instrucciones para la alineación del tope
guía para corte al hilo en la página 92 de este manual.
Si no puede alinear con éxito el tope guía para corte
al hilo, reemplace el tope guía o comuníquese al
1-800-223-7278 para solicitar más instrucciones.
86
Page 87

FUNCIONAMIENTO
No respetar las siguientes advertencias puede resultar en graves lesiones personales.
LEA TODO EL MANUAL. Además de leer estas instrucciones de uso, es importante leer y comprender todo el
manual antes de utilizar esta sierra. Siga todas las instrucciones que apliquen sobre el ensamble, preparación y
ajuste antes de realizar cualquier corte y siga todas las reglas de seguridad y advertencias en esta sección y en
otras secciones de este manual.
1. Cada vez que use la sierra, repase la siguiente
lista de verificación:
• ¿Son adecuadas la fuente de poder y las
conexiones a la fuente de poder para la sierra?
• ¿La sierra y el área de trabajo están libres de
obstrucciones y espectadores?
• ¿Está la hoja apretada y correctamente alineada?
• ¿El grosor del separador coincide con la hoja?
• ¿La hoja y el separador están correctamente
alineados?
• ¿El operador está calificado para realizar el corte
y familiarizado con todas las reglas, advertencias
e instrucciones de seguridad relevantes que se
incluyen en este manual?
• ¿El operador y todas las personas que están cerca
de la sierra están usando protección de ojos,
oídos y equipo respiratorio adecuados?
• ¿El ángulo de bisel y las perillas de ajuste de
altura están bloqueados en la posición correcta?
• ¿La hoja está situada a la altura adecuada?
• Si realiza un corte al hilo, ¿el tope guía para corte
al hilo está paralelo con la hoja y enganchado
firmemente en la posición?
• Si realiza un corte transversal, ¿está apretada la
perilla de la galga de inglete?
• Si realiza cortes completos con una hoja estándar,
¿están la guarda para hoja, separador y trinquetes
anti contragolpe correctamente instalados y
funcionando adecuadamente con ambas guardas
tocando la superficie de la mesa?
• ¿Hay espacio libre y soporte adecuados para la
pieza de trabajo a medida que sale de la hoja?
• ¿Es necesario tener auxiliares de corte? Si es así,
¿están instalados o al alcance para su uso correcto?
2. El uso de aditamentos y accesorios no
recomendados por DELTA® Power Equipment
Corporation pudiera resultar en lesiones.
3. Reemplace o afile los dedos anti contragolpe
cuando las puntas pierdan filo.
4. Asegúrese de que la sierra esté estable y
puedan realizarse cortes sin volcar la sierra.
No intente cortar piezas de trabajo largas sin
asegurar la sierra a una superficie estable. Para
asegurar correctamente la sierra, consulte las
instrucciones en la sección titulada sujeción de
la sierra al piso en la página 78 de este manual.
5. Nunca use el tope guía y galga de inglete juntos
sin usar un bloque de corte como se describió
anteriormente.
6. La placa de garganta adecuada debe estar
instalada en todo momento.
7. Si la sierra produce un ruido desconocido o si
vibra en exceso, deje de usarla inmediatamente
hasta ubicar y corregir la fuente del problema.
8. Nunca realice cortes a mano libre, cortes por
penetración, reaserramientos ni cortes cóncavos.
EVITAR LOS CONTRAGOLPES
Un contragolpe puede ocurrir cuando la pieza de
trabajo presiona la hoja o se atasca entre la hoja de
sierra y el tope guía para corte al hilo u otro objeto fijo.
Esto puede causar que la pieza de trabajo se eleve de
la mesa o sea expulsada hacia el operador. Consulte
las instrucciones para reducir el riesgo de contragolpes
en la página 70 de este manual.
SI OCURRE UN CONTRAGOLPE, apague la sierra
y verifique la alineación de la hoja, el separador y la
galga de inglete o el tope guía para corte al hilo, y el
funcionamiento adecuado del separador, ensamble de
anti contragolpe y el ensamble de guarda para hoja
antes de reanudar el trabajo.
ARRANQUE Y PARO DE LA SIERRA
El interruptor POWER (encendido) (Figura 23) se
encuentra abajo del ala de extensión izquierda frontal.
1. Para encender la sierra, levante el encendedor de
paleta rojo (A) y jálelo hacia usted.
2. Para apagar la sierra, baje el encendedor de
paleta rojo.
Cuando no está en uso, la sierra debe apagarse y
el interruptor de alimentación debe bloquearse para
evitar el uso no autorizado. Para bloquear el interruptor
de alimentación, use un candado de grillete largo
estándar, con un grillete que mida al menos 2 ¾
pulgadas (70 mm) de largo y los postes de este no
sean mayores a 9/32 de pulgada (7 mm) de grosor.
87
B
A
FIGURA 23
Page 88

FUNCIONAMIENTO
(continuación)
PROTECCIÓN CONTRA
SOBRECARGAS
La sierra se proporciona con protección contra
sobrecargas. Si el motor se apaga o no arranca
debido a una sobrecarga (está cortando el material
muy rápido, usa una hoja sin filo, usa la sierra más
allá de su capacidad, etc.) o bajo voltaje, deje enfriar
el motor durante tres a cinco minutos. Luego presione
REALIZACIÓN DE CORTES
No respetar las siguientes
advertencias puede resultar en
graves lesiones personales.
• Nunca toque el extremo suelto de la pieza de trabajo
o una pieza suelta cortada, mientras la sierra esté
encendida o la hoja de la sierra esté girando. Puede
ocurrir un contacto o atasco con la hoja lo que
resultaría en la expulsión de la pieza de trabajo.
• Al aserrar una pieza de trabajo o panel largo, use
un soporte para la pieza, tal como un caballete,
rodillos o mesa de salida que estén a la misma
altura que la superficie de la mesa de la sierra.
• Nunca intente hacer retroceder la pieza de trabajo
con la hoja girando. Si necesita retroceder la pieza
de trabajo o levantarla de la mesa, apague la sierra,
espere a que la hoja se detenga, eleve los dientes
anti contragolpe en cada lado del separador si es
necesario, y retire la pieza de trabajo.
• Antes de conectar la sierra de mesa a la fuente
de poder o utilizarla, siempre inspeccione el
ensamble de guarda para hoja y el separador para
el botón rojo de restablecimiento (B) en el motor
debajo de la sierra, que se muestra en la Figura 20 y
vuelva a encender la sierra.
AVISO: Si el motor se apaga continuamente debido
a una sobrecarga, comuníquese con un electricista
calificado.
verificar la alineación y el espacio libre con la hoja
de sierra. Verifique la alineación después de cada
cambio de ángulo de biselado.
• SIEMPRE debe usar un tope guía para corte al
hilo para las operaciones de cortes al hilo a fin
de evitar perder el control y lesiones personales.
Siempre enganche la guía al riel. NUNCA realice
una operación de corte al hilo a mano libre.
• Cuando realice cortes biselados, coloque la guía
en el lado derecho de la hoja de modo que esta se
incline en dirección contraria a la guía y las manos.
Mantenga las manos retiradas de la hoja y use
un empujador para empujar la pieza de trabajo a
menos que esta sea suficientemente grande para
permitir sujetarla a más de 6 pulgadas (152 mm)
de distancia de la hoja.
• Antes de dejar la sierra desatendida, bloquee el
interruptor de alimentación o tome otras medidas
adecuadas para evitar el uso no autorizado de la
sierra.
Corte transversal Corte transversal
Corte al hilo
en inglete
Corte transversal biselado
Corte al hilo biselado Corte de inglete compuesto
88
Page 89

FUNCIONAMIENTO
A
(continuación)
CORTES AL HILO
1. Retire la galga de inglete
2. Asegúrese de que el ángulo de biselado esté
posicionado en 0°.
3. Ajuste la hoja a la altura correcta para la pieza de
trabajo.
4. Instale el tope guía para corte al hilo y
engánchelo paralelo con la hoja y a la distancia
deseada de la misma.
5. Mantenga los dedos al menos a 6 pulgadas de
distancia de la hoja en todo momento. Cuando
la mano no pueda colocarse de manera segura
entre la hoja y el tope guía para corte al hilo,
seleccione una pieza de trabajo más grande o use
un empujador y otros auxiliares de corte, según
sea necesario, para controlar la pieza de trabajo.
6. Asegúrese de que la pieza de trabajo esté
retirada de la hoja (al menos 1 pulgada o 25 mm
de distancia) antes de encender la sierra.
7. Encienda la sierra.
8. Sujete la pieza de trabajo horizontalmente sobre
la mesa y contra la guía (A). La pieza de trabajo
debe tener un borde recto contra la guía y no
debe estar deforme, torcida ni doblada. Vea la
posición correcta de las manos en la Figura 24.
9. Espere a que la hoja alcance la velocidad
completa antes de mover la pieza de trabajo
hacia la hoja.
10. Ambas manos pueden usarse al iniciar el corte
siempre que estas permanezcan a 6 pulgadas de
distancia de la hoja.
11. Mantenga la pieza de trabajo contra la mesa
y guía y empújela lentamente hacia atrás
pasando por la hoja de la sierra hasta el final.
No sobrecargue el motor forzando la pieza de
trabajo contra la hoja.
12. Use el empujador y cualquier otro auxiliar de
corte, según sea necesario, para sujetar la pieza
de trabajo contra la mesa y la guía, y empuje la
pieza de trabajo hasta que pase por la hoja. Un
empujador se incluye con esta sierra. Además, se
incluyen instrucciones para fabricar empujadores
adicionales y otros auxiliares de corte.
13. No empuje ni sujete el lado suelto o cortado de la
pieza de trabajo.
14. Continúe empujando la pieza de trabajo hasta que
esté retirada de la hoja. No sobrecargue el motor
forzando la pieza de trabajo contra la hoja.
15. Cuando termine el corte, apague la sierra. Espere
a que la hoja se detenga por completo antes de
retirar la pieza de trabajo de la mesa.
A
FIGURA 24
CORTE AL HILO BISELADO
Cortar al hilo biselado es igual al corte al hilo
excepto que el ángulo de biselado (A) se ajusta a
un ángulo excepto 0°. Cuando realice un corte al
hilo biselado, coloque la guía en el lado derecho
de la hoja de modo que esta se incline lejos de la
guía y las manos.
0º
45º
FIGURA 25
89
Page 90

FUNCIONAMIENTO
(continuación)
CORTE TRANSVERSAL
• NUNCA use el tope guía como una guía o tope de
largo al realizar un corte transversal.
• La pieza cortada nunca debe confinarse en
ninguna operación de corte completo (cortar por
completo la pieza de trabajo), para evitar pinchar
la hoja, lo que puede resultar en la expulsión de la
pieza de trabajo y lesiones posibles.
• Al usar un bloque como un calibre de corte, el
bloque debe medir al menos 3/4 pulgada (19 mm) de
grosor. Es muy importante que el extremo posterior
del bloque se fije en una posición donde la pieza de
trabajo esté alejada del bloque antes de entrar a la
hoja para evitar atascar la pieza de trabajo.
Puede usar la galga de inglete en la ranura de la mesa
en cortes sin biselado. Para aumentar el área de
superficie de la cara de la galga de inglete, agregue
una cara auxiliar (consulte la sección de auxiliares de
corte en la página 89 de este manual).
Para realizar un corte transversal, consulte la Figura
26 y siga este proceso:
1. Retire el tope guía para corte al hilo.
2. Asegúrese de que el ángulo de biselado esté
posicionado en 0°.
3. Ajuste la hoja a la altura correcta para la pieza de
trabajo.
4. Coloque la galga de inglete en cualquiera de las
ranuras de inglete.
5. Ajuste la galga de inglete a 0° y apriete la perilla de
bloqueo de la galga de inglete.
6. Las manos deben permanecer al menos 6 pulgadas
de distancia de la hoja durante todo el corte.
Si una pieza de trabajo es demasiado pequeña
para mantener las manos al menos a 6 pulgadas
de distancia de la hoja, seleccione una pieza de
trabajo más grande o coloque una cara auxiliar
a la galga de inglete y sujete la pieza de trabajo
a la parte frontal del auxiliar, para instrucciones
sobre cómo hacer auxiliares, consulte la sección
auxiliares de corte en la página 89 de este manual.
7. Asegúrese de que la pieza de trabajo esté lejos de
la hoja, al menos 1 pulgada o 25 mm de distancia,
antes de encender la sierra.
8. Encienda la sierra.
9. Espere a que la hoja alcance la velocidad completa
antes de mover la pieza de trabajo hacia la hoja.
10. La mano más cercana a la hoja debe colocarse
en la perilla de bloqueo de la galga de inglete y la
mano más alejada de la hoja debe sujetar la pieza
de trabajo firmemente contra la parte frontal de la
galga de inglete. No empuje ni sujete el lado suelto
o cortado de la pieza de trabajo.
11. Lentamente empuje la pieza de trabajo pasándola
por la hoja de sierra. No sobrecargue el motor
forzando la pieza de trabajo contra la hoja.
12. Cuando termine el corte, apague la sierra. Espere
a que la hoja se detenga por completo antes de
retirar la pieza cortada de la mesa.
FIGURA 26
CORTE TRANSVERSAL BISELADO
El corte transversal biselado es igual al corte
transversal excepto que el ángulo de biselado (A) se
ajusta a un ángulo distinto a 90°. Cuando realice un
corte transversal biselado, coloque la galga de inglete
en la ranura de inglete derecha de modo que la hoja se
incline lejos de la galga y las manos. Vea la Figura 27.
CORTES DE INGLETE
Los cortes de inglete son cortes transversales con la
galga de inglete ajustada en un ángulo excepto 90°.
Para instrucciones sobre cómo ajustar los ángulos de
la galga de inglete, consulte la sección preparación
para cortes. Para ajustar los topes de inglete divisores
preestablecidos consulte la sección ajuste de los topes
de inglete en la página 91 de este manual.
• Los ángulos de inglete menores a 45° pueden forzar
el ensamble de guarda para hoja contra la hoja
de la sierra, lo que provocaría daños al ensamble
de guarda para hoja y lesiones personales. Antes
de arrancar el motor, pruebe el funcionamiento
empujando la pieza de trabajo por el ensamble de
guarda para hoja. Si el ensamble de guarda para
0º
45º
A
FIGURA 27
hoja hace contacto con la hoja, antes de arrancar
el motor coloque la pieza de trabajo abajo del
ensamble de guarda para hoja pero sin tocar la hoja.
• Ciertas formas de piezas de trabajo, tales como
molduras, pueden no levantar correctamente el
ensamble de guarda para hoja. Con la sierra apagada,
empuje lentamente la pieza de trabajo hacia el área
de la guarda para hoja hasta que la pieza de trabajo
toque la hoja. Si el ensamble de guarda para hoja
hace contacto con la hoja, coloque la pieza de trabajo
abajo del ensamble de guarda para hoja pero sin
tocar la hoja antes de arrancar el motor.
90
Page 91

FUNCIONAMIENTO
(continuación)
CORTES DE INGLETE
COMPUESTOS
Este es una combinación de corte transversal
biselado e ingletes. Consulte la Figura 28 y siga
las instrucciones para corte transversal biselado e
ingletes. Recuerde usar la ranura de inglete derecho
para todos los cortes biselados.
90º
CORTES DE PANEL LARGOS
Coloque los soportes de la pieza de trabajo a la misma
altura que la mesa de sierra atrás de la sierra para
apoyar la pieza de trabajo cortada y a lo largo de la
sierra, si es necesario. Dependiendo de la forma del
panel, use el tope guía para corte al hilo o galga de
inglete para controlar la pieza de trabajo. Si una pieza
de trabajo es demasiado grande para usar ya sea un
tope guía para corte al hilo o una galga de inglete,
entonces es demasiado larga para esta sierra.
RANURAS Y OTROS CORTES SIN TRASPASO
El uso de un corte sin traspaso es esencial para cortar
muescas, rebajos y ranuras. Los cortes sin traspaso
pueden realizarse usando una hoja estándar con un
diámetro de 10 pulgadas o menos, o una hoja para
ranurar de hasta 13/16 de pulgada de ancho con
un diámetro de 8 pulgadas o menos. Los cortes
sin traspaso son el único tipo de cortes que deben
realizarse sin el ensamble de guarda para hoja instalado.
Asegúrese de que el ensamble de guarda para hoja se
vuelva a instalar después de terminar este tipo de corte.
• Al realizar cortes sin traspaso, siga todas las
advertencias e instrucciones aplicables enumeradas
a continuación además de las mencionadas
anteriormente para el corte completo relevantes.
• Cuando realice un corte sin traspaso, la pieza de
trabajo cubre la hoja durante la mayoría del corte. Esté
alerta a la hoja expuesta al inicio y fin de cada corte.
• Nunca empuje madera con las manos cuando
realice cualquier corte sin traspaso tales como
rebajes o ranuras. Siempre use una galga de inglete,
bloques de empuje o empujadores y tablas de
cuñas donde sea adecuado.
• Lea la sección correspondiente que describe el tipo
de corte además de esta sección sobre los cortes
sin traspaso o de ranuras. Por ejemplo, si el corte
sin traspaso es un corte transversal recto, lea y
comprenda esta sección sobre cortes transversales
rectos antes de continuar.
• Una vez realizados todos los cortes de ranura y sin
traspaso, desconecte la sierra y vuelva a instalar el
separador o regréselo a la posición elevada. Instale
los trinquetes anti contragolpe y la guarda para hoja.
• Siga con atención todas las instrucciones que
acompañan a cualquier hoja especializada tal como
hojas para ranurar y cortadores de moldura para la
instalación, preparación y funcionamiento adecuados.
0º
45º
30º
FIGURA 28
REALIZAR UN CORTE SIN
TRASPASO
1. Desconecte la sierra.
2. Desenganche la palanca de desbloqueo.
3. Ajuste el ángulo de biselado a 0°.
4. Enganche la palanca de desbloqueo.
5. Retire la guarda para hoja y trinquetes anti
contragolpe.
6. Coloque el separador en la posición
"descendente". (consulte la sección POSICIÓN DE
SEPARADOR en la página 81).
7. Ajuste la hoja a la profundidad correcta para
la pieza de trabajo. Consulte las siguientes
instrucciones para el uso de ranuras y otras hojas
especializadas.
91
8. Dependiendo de la forma y tamaño de la madera,
use el tope guía para corte al hilo o galga de inglete.
9. Conecte la sierra a una fuente de poder y
enciéndala.
10. Espere a que la hoja alcance la velocidad completa
antes de mover la pieza de trabajo hacia la hoja.
11. Siempre use bloques de empuje, empujadores y/o
tablas de cuña al realizar cortes sin traspaso para
reducir el riesgo de lesiones graves.
12. Cuando termine el corte, apague la sierra. Espere
a que la hoja se detenga por completo antes de
retirar la pieza de trabajo.
Si se requiere de un corte de ranura, realice varias
pasadas sucesivas en vez de intentar hacerlo en una
sola pasada.
Page 92

FUNCIONAMIENTO
REALIZAR UN CORTE
DE RANURA
Las hojas para ranurar son hojas apiladas que pueden
usarse para realizar cortes sin traspaso incluyendo
ranuras de corte completo. Las hojas para ranurar
requieren de una placa de garganta especial. Las
hojas para ranurar y las placas de garganta se venden
por separado.
• Siga con atención las instrucciones que acompañan
a la hoja para ranurar para una instalación,
preparación y funcionamiento adecuados. Pueden
encontrarse guías adicionales en sitios web y
publicaciones de ebanistería y carpintería.
• No intente apilar hojas para ranurar con un grosor
mayor a
para ranurar con un diámetro mayor a 8 pulgadas
(200 mm).
• Los ensambles del separador y la guarda para
hoja no pueden usarse en la ranuración. Deben
quitarse como se describe en la sección de
operaciones de la guarda para hoja y separador.
Tenga MUCHO cuidado al usar la hoja para ranurar
sin el ensamble de guarda para hoja y separador.
• Use empujadores, retenedores, plantillas de guía,
accesorios o tableros con canto biselado para
ayudar a guiar y controlar la pieza de trabajo
cuando no pueda usarse la guarda.
• Asegúrese de volver a instalar el separador, los
trinquetes anti contragolpe, la guarda para hoja y
la placa de garganta estándar, asimismo revise los
13
/16 de pulgada (20.64 mm). No use hojas
(continuación)
FIGURA 30
ajustes cuando se terminen los cortes de ranuras.
• Debe usar la placa de garganta para ajuste del
cabezal para ranurar de accesorio, mostrado
en la Figura 30, en vez de la placa de garganta
estándar. Asegúrese de que la placa de garganta
esté al nivel de la mesa antes de continuar.
• Siempre verifique que no haya obstrucciones
entre la hoja para ranurar y otros componentes
antes de conectar la sierra.
• Nunca intente usar el cabezal para ranurar en una
posición de biselado.
NOTA: La brida del eje exterior estándar no puede
usarse con ciertas combinaciones de hojas para
ranurar. En esos casos, apriete la tuerca del eje
directamente contra el juego de hojas para ranurar.
Guarde la brida del eje exterior para usarla con
otras hojas y combinaciones de ranurado.
AUXILIARES Y ACCESORIOS DE CORTE
EMPUJADOR
Para poder utilizar de manera segura la sierra de mesa,
debe usar un empujador cuando el tamaño o forma de la
pieza de trabajo ocasionaría que de alguna manera sus
manos estén a 6 pulgadas (152 mm) de la hoja de sierra
u otro cortador. Un empujador se incluye con esta sierra.
No es necesario ningún tipo especial de madera para
fabricar empujadores adicionales siempre que estos
sean macizos y suficientemente largos, sin nudos,
imperfecciones o grietas. Se recomienda una longitud
de 16 pulgadas (400 mm) aproximadamente con una
muesca que se ajuste contra el borde de la pieza de
trabajo para evitar que se resbale. Es una buena idea
tener varios empujadores de la misma longitud mínima,
16 pulgadas (400 mm), con muescas de diferentes
tamaños para diferentes grosores de piezas de trabajo.
La forma puede variar para adaptarse a sus propias
necesidades siempre que realice la función prevista
de mantener sus manos alejadas de la hoja. Inclinar
la muesca a un ángulo para que el empujador pueda
sostenerse a un ángulo de 20 a 30 grados de la mesa
de la sierra le ayudará a sostener la pieza de trabajo al
tiempo que pasa por la sierra.
Para hacer un empujador, consulte el diseño que se
muestra en la Figura 31.
92
15.7”
90º
Mesa de la sierra
20º
FIGURA 31
La muesca
evita que se
resbale la mano
Page 93

AUXILIARES Y ACCESORIOS DE CORTE
ratón de computadora
REFRENTADO DEL TOPE GUÍA
PARA CORTE AL HILO AUXILIAR
Use un refrentado del tope guía para corte al hilo
auxiliar cuando sea necesario para cortes especiales,
tales como material de corte al hilo que es
suficientemente delgado para deslizarse por debajo
del tope guía proporcionado con la sierra o cuando
se necesita un tope guía más alto para terminar el
corte. Para añadir un refrentado de madera auxiliar
a uno o ambos lados del tope guía para corte al hilo,
seleccione un trozo de madera con superficies lisas,
sujete la madera al tope guía con dos abrazaderas.
(consulte la Figura 32). Para la mayoría de los trabajos,
es ideal un material de 3/4 de pulgada (19 mm) o 1
pulgada (25 mm).
REFRENTADO DE LA GALGA DE INGLETE AUXILIAR
Un refrentado de la galga de inglete auxiliar se utiliza
para aumentar el área de superficie de la parte frontal
de la galga de inglete.
Si lo desea, puede ajustar la galga de inglete con
un refrentado de madera auxiliar que debe medir al
menos 1 pulgada (25mm) más de altura que la máxima
profundidad del corte y al menos del mismo ancho que
la galga de inglete.
Este refrentado de madera auxiliar puede sujetarse
a la parte frontal de la galga de inglete usando dos
tornillos para madera a través de los orificios (A)
proporcionados en el cuerpo de la galga de inglete
y hacia el refrentado de madera. Vea la Figura 33.
Asegúrese de que los tornillos sean suficientemente
largos para asegurar el refrentado, pero que no
sobresalgan de la madera.
FIGURA 32
A
(continuación)
BLOQUE DE EMPUJE
1. Seleccione un trozo de madera de
aproximadamente 4 pulgadas de ancho, 6
pulgadas de largo y 1 a 2 pulgadas de grosor
(un recorte de una tabla de 2 por 4 sirve como
una buena base para un bloque de empuje).
2. Barrene un orificio en el bloque y pegue una
espiga para usarla como agarradera (puede
hacer el orificio en ángulo para que la sujeción
de la agarradera sea más cómoda).
3. Pegue una trozo de material áspero o liso tal
como una lija o caucho a la parte inferior del
bloque para sujetar la pieza de trabajo (las
almohadillas para ratón de computadora son
adecuadas para esto). Vea la Figura 34.
FIGURA 33
Clavija
de madera
4”
2”
6”
Lija o material de
almohadilla para
FIGURA 34
93
Page 94

AUXILIARES Y ACCESORIOS DE CORTE
TABLAS DE CUÑA
(continuación)
Las tablas de cuña se usan para mantener el trabajo
en contacto con la guía y la mesa (Figura 32) y ayudan
a prevenir los contragolpes. Las tablas de cuña son
especialmente útiles al cortar al hilo piezas de trabajo
pequeñas y para completar los cortes sin traspaso.
El extremo está angulado con una serie de ranuras
angostas que para ofrecer una sujeción de fricción
en la pieza de trabajo, se engancha en la mesa o guía
con una abrazadera en C.
Para evitar atascos entre la pieza
de trabajo y la hoja, asegúrese
de que la tabla de cuña horizontal presione
únicamente la parte sin cortar de la pieza de trabajo
en la parte frontal de la hoja.
Las dimensiones para fabricar una tabla de cuña
típica se muestran en la Figura 35. Fabrique una tabla
de cuña con un trozo de madera recto que no tenga
nudos ni grietas. Sujete las tablas de cuña a la guía
o a la mesa de modo que la tabla de cuña sujete la
pieza de trabajo contra la guía o mesa.
1. Seleccione un trozo sólido de madera de
aproximadamente ¾ de pulgada de grosor, 2 ½
pulgada de ancho y 12 pulgadas de largo.
2. Marque el ancho central en un extremo del
material. Incline el ancho a 70° (consulte la
sección de corte de inglete para información
sobre los cortes de inglete).
3. Coloque el tope guía para corte al hilo de
modo que permita el corte de un "dedo" de
aproximadamente 1/4 de pulgada en el material.
4. Empuje el material únicamente a la marca
realizada anteriormente a 6 pulgadas.
5. Apague la sierra y espere a que la hoja se
detenga por completo antes de retirar el material.
6. Vuelva a colocar el tope guía y realice los cortes
espaciados en la pieza de trabajo para formar
dedos de aproximadamente 1/4 de pulgada y
espacios de 1/8 de pulgada entre ellos.
1/8”
1/4”
70º
3/4”
4.5”
FIGURA 35
CALIBRE DE CORTE
Al realizar cortes transversales en varias piezas a la
misma longitud, puede sujetar un bloque de madera
(A) (consulte la Figura 36) a la guía y usarlo como un
calibre de corte. El bloque (A) debe medir al menos 3/4
de pulgada (19 mm) de grosor para evitar que la pieza
que está cortando se atasque entre la hoja y la guía.
Después de determinar la longitud del corte, enganche
la guía y use la galga de inglete para empujar la pieza
de trabajo hacia la hoja.
Siempre posicione el calibre de
corte en la parte frontal de la
hoja de sierra.
PLANTILLAS
Pueden crearse plantillas con una variedad de ajustes
especiales para controlar formas particulares de piezas
de trabajo para cortes especiales. Las instrucciones
sobre cómo hacer plantillas especializadas pueden
encontrarse en sitios web y publicaciones de
ebanistería y carpintería.
12”
A
3/4”
FIGURA 36
No intente crear ni usar una
plantilla a menos que esté
completamente familiarizado con la seguridad de la
sierra de mesa. No use ninguna plantilla que podría
presionar un corte o atascar la pieza de trabajo
entre la plantilla y la hoja. Los ajustes incorrectos
pueden provocar contragolpes que podrían resultar
en lesiones graves.
94
Page 95

ALINEACIÓN
ALINEACIÓN DEL SEPARADOR
CON LA HOJA
La alineación entre el separador y la hoja se fija
en la fábrica y, en la mayoría de los casos, no será
necesario ajustarla. Sin embargo, la alineación
siempre debe verificarse después de instalar la hoja
y separador, y de ser necesario puede ajustarse. Si el
separador está desalineado con la hoja, en necesario
realizar un ajuste. El separador debe estar alineado
desde la parte frontal a posterior (horizontalmente) y
de la parte superior a inferior (verticalmente).
Para ajustar la alineación del separador, consulte la
Figura 37 y continúe de la siguiente manera:
1. Retire los ensambles de la placa de garganta, la
guarda para hoja y anti contragolpe.
2. Eleve la hoja a la profundidad completa de corte y
ajuste el ángulo de inclinación en 0°.
3. Eleve el separador a la posición más alta o de
corte completo.
4. Afloje ligeramente los dos tornillos de cabeza de
sombrerete (C).
5. Coloque la regla contra la parte frontal de la hoja y
el separador como se indica para la revisión de la
alineación horizontal (consulte la Figura 20a en la
página 81).
6. Ajuste los tornillos de fijación (A) para para
mover el separador en línea con la hoja según
su posición cuando verificó la alineación
anteriormente.
7. Coloque la regla en el lado opuesto de la hoja.
Ambos lados del separador deben estar dentro del
grosor del cuerpo de la hoja.
8. Si no es posible alinear ambos lados del separador
dentro del grosor del cuerpo de la hoja, debe usar
una hoja de tamaño diferente. Consulte la sección
sobre selección de hojas en la página 80.
9. Apriete los dos tornillos de cabeza de sombrerete.
10. Coloque una escuadra sobre la mesa y contra la
parte frontal de la hoja y separador como se indica
para la revisión de la alineación vertical (consulte
la Figura 20b en la página 81). Luego verifique que
el separador esté perpendicular a la mesa y en
línea con la parte frontal de la hoja.
11. De ser necesario, use los tornillos de fijación (D)
para alinear el separador con la parte frontal de la
hoja y la escuadra.
12. Apriete por completo los dos tornillos de cabeza
de sombrerete.
13. Vuelva a colocar los ensambles de placa de
garganta, guarda para hoja y anti contragolpe
antes de usar la sierra.
Si detecta un arrastre o atasco
de la pieza de trabajo a medida
que alcanza el separador, apague la unidad y
desconecte la máquina de la fuente de poder, vuelva
a ajustar la alineación del separador u hoja o
reemplace la hoja. Nunca intente retroceder una
pieza de trabajo parcialmente cortada de la hoja
mientras la hoja está en movimiento.
B
C
A
FIGURA 37
AJUSTE DE LOS TOPES
DE INGLETE
Para ajustar los topes divisores para ángulos distintos
a 90°, 75°, 60°, 45° y 30°:
1. Afloje la manija de la galga de inglete.
2. Afloje los 2 tornillos del segmento del tope del
inglete hasta el nuevo ángulo deseado. (A) se
muestra en la Figura 38.
3. Mueva el tope a la posición correcta.
4. Vuelva a apretar los dos tornillos del segmento y
manija.
95
FIGURA 38
A
Page 96

ALINEACIÓN
(continuación)
ALINEACIÓN PARALELA DE
LA GUÍA CON LA RANURA
DEL INGLETE
1. Mueva la guía adyacente a la galga de inglete
derecha y asegúrela al tubo de guía bajando la
palanca de sujeción de la guía.
2. Si la parte frontal de la guía (A), Figura 39, no está
paralela a la ranura del inglete (B), eleve la palanca
de sujeción y levante la guía, luego colóquela sobre
la mesa de la sierra.
3. Ajuste uno o ambos tornillos de fijación (C) 1/4 de
vuelta o menos.
4. Vuelva a colocar la guía sobre el tubo de guía y
repita los pasos 1 a 3. Si la guía está casi paralela,
gire el tornillo de fijación en la misma dirección pero
un poco menos. Si la guía aún no está paralela, gire
el tornillo de fijación en la dirección opuesta.
5. Repita los pasos 1 a 3.
A
ALINEACIÓN PERPENDICULAR
DE LA GUÍA CON LA MESA
1. Mueva la guía sobre la mesa de hierro fundido y
asegúrela al tubo de guía bajando la palanca de
sujeción de la guía.
2. Use una escuadra para comprobar que la parte
frontal de la guía esté perpendicular a la mesa.
3. Si la parte frontal de la guía no está perpendicular
a la mesa, suelte la palanca de sujeción y ajuste
ligeramente uno de los tornillos de fijación
ranurados (A), Figura 40, hasta que la parte frontal
de la guía esté perpendicular con la mesa.
4. Sujete la guía al tubo de guía para asegurar que la
guía continúe estando perpendicular. Si no es así,
repita los pasos 1 a 4.
A
C
B
FIGURA 39 FIGURA 40
OPERACIÓN MONOFÁSICA A 240 VOLTIOS
El motor de voltaje dual de 120/240 voltios proporcionado con su máquina fue enviado con preparación para operar
a 120 voltios. Puede convertirse para operar a 240 voltios. Para la conversión de 120 a 240 voltios, por favor llame
con anticipación a Servicio al Cliente de DELTA al 1-800-223-7278.
96
Page 97

MANTENIMIENTO
Para reducir el riesgo de lesiones, apague la unidad y desconéctela de la fuente de poder antes de limpiar, dar
servicio, instalar y quitar accesorios, antes de ajustar y al realizar reparaciones. Un arranque accidental puede
provocar una lesión.
MANTENGA LIMPIA LA MÁQUINA
Sopletee periódicamente todos los conductos de aire
con aire comprimido seco. Todas las partes de plástico
deben limpiarse con un paño húmedo y suave. NUNCA
use solventes para limpiar las partes de plástico.
Pueden disolver o dañar de alguna manera el material.
Use equipo de seguridad certificado para protección
ocular, auditiva y respiratoria al usar aire comprimido.
LUBRICACIÓN Y PROTECCIÓN CONTRA OXIDACIÓN
Ocasionalmente aplique cera en pasta para pisos de
madera a la mesa de la máquina o use un producto
protector disponible comercialmente diseñado para
este propósito. Siga las instrucciones del fabricante
para su uso y seguridad.
Para limpiar la oxidación de las mesas de hierro
fundido, necesitará los siguientes materiales:
RECORDATORIOS DE
MANTENIMIENTO
Use equipo de seguridad certificado para protección
ocular, auditiva y respiratoria al usar aire comprimido.
Áreas específicas que requieren de un
mantenimiento frecuente incluyen:
PLACA DE SUJECIÓN DEL SEPARADOR: Mantenga
esta área libre de polvo y acumulación de basura.
Limpie el área frecuentemente con aire comprimido.
NOTA: Si la abrazadera del separador no se mueve
libremente, pida que la sierra sea reparada por el
personal de un centro de servicio de DELTA
Equipment.
®
Power
una almohadilla para tallar de tamaño mediano,
una lata de lubricante en rociador y una lata de
desengrasante. Aplique el lubricante en rociador y
pula la superficie de la mesa con la almohadilla para
tallar. Desengrase la mesa, luego aplique el producto
protector como se describió anteriormente.
ENGRANAJES SINFÍN: Mantenga los engranajes
sinfín libres de polvo y acumulación de basura. Limpie
el área frecuentemente con aire comprimido. Use
una grasa multipropósito a base de litio según sea
necesario en estos engranajes.
LIMPIE PERIÓDICAMENTE LA ACUMULACIÓN DE
ASERRÍN EN EL GABINETE: NOTA: La basura también
puede limpiarse de la sierra desde abajo de la placa de
garganta, dentro del puerto de polvo.
RESOLUCIÓN DE PROBLEMAS
Para solicitar ayuda con su máquina, visite nuestro sitio web en www.DeltaMachinery.com para obtener
una lista de los centros de servicio o llame a atención al cliente de DELTA® Power Equipment al
1-800-223-7278.
LA SIERRA NO ARRANCA
Si su máquina no arranca, verifique que las puntas del enchufe tengan un buen contacto con el tomacorriente y
verifique el botón de restablecimiento en el alojamiento del interruptor de alimentación. Asimismo, verifique que no
haya fusibles fundidos o un disyuntor abierto en su línea de alimentación.
ACCESORIOS
Una línea completa de accesorios está disponible con su proveedor DELTA®, centros de servicio
de fábrica DELTA® y centros de servicio de fábrica DELTA® y centros de servicio autorizado DELTA®.
Visite nuestro sitio web www.DeltaMachinery.com para obtener un catálogo en línea o el nombre de su
proveedor más cercano.
Puesto que los accesorios distintos a los ofrecidos por DELTA® aún no han sido probados
con este producto, el uso de dichos accesorios podría ser peligroso. Para una operación
más segura, solo deben usarse accesorios recomendados por DELTA® con este producto.
97
Page 98

GARANTÍA
Para registrar su herramienta a fin de recibir el servicio de garantía, visite nuestro sitio web en
www.DeltaMachinery.com.
Garantía de producto nuevo limitada por cinco años
DELTA reparará o reemplazará, a su cargo y opción, cualquier máquina, repuesto o accesorio de la máquina DELTA que se
haya comprobado en condiciones de uso normales como defectuoso en mano de obra o material, siempre que el cliente
devuelva el producto con porte prepagado a un centro de servicio de fábrica DELTA o a una estación de servicio autorizada
con el comprobante de compra del producto en un plazo de cinco años y le proporcione a DELTA la oportunidad razonable
para verificar el presunto defecto mediante una inspección.
El periodo de garantía para todo producto DELTA reacondicionado es de 180 días.
DELTA no será responsable de ningún defecto encontrado que sea resultado del desgaste normal, uso indebido, maltrato
o reparación o alteración realizada o específicamente autorizada por ninguna parte que no sea una instalación o
representante de servicio autorizado de DELTA.
Bajo ninguna circunstancia se considerará a DELTA como responsable por daños accidentales o indirectos derivados de
productos defectuosos. Algunos estados no permiten la exclusión o limitación de daños accidentales o indirectos, por lo
que la limitación o exclusión anteriormente mencionada puede no aplicar en su caso.
Esta es la única garantía de DELTA y establece el recurso exclusivo con respecto a productos defectuosos; todas las demás
garantías, expresas o implícitas, ya sea de comerciabilidad, idoneidad para un propósito o de otro tipo, están expresamente
excluidas por DELTA.
Para obtener más detalles sobre la cobertura de la garantía e información de la garantía de reparación, llame al 1-800223-7278. Esta garantía le otorga derechos legales específicos y es posible que usted tenga otros derechos que varían en
ciertos estados o provincias.
AMÉRICA LATINA: Esta garantía no aplica a los productos vendidos en América Latina. Para los productos vendidos en
América Latina, consulte la información de garantía específica del país que se incluye en el empaque, llame a la empresa local
o consulte el sitio web para obtener información de la garantía.
ASISTENCIA SOBRE GARANTÍA, SERVICIO O PIEZAS
Todas las máquinas y accesorios DELTA® están fabricados en cumplimiento de altos estándares de calidad
y reciben el servicio técnico de una red de centros de servicio autorizado DELTA®. Para obtener información
adicional acerca de su producto de calidad DELTA® o para obtener asistencia sobre la garantía, el servicio o
piezas, o para localizar el centro de servicio más cercano llame al 1-800-223-7278.
REFACCIONES
Use únicamente piezas de repuesto idénticas. Para una lista de piezas o para hacer un pedido de piezas, visite
nuestro sitio web en www.DeltaMachinery.com/service. Además puede hacer un pedido de las piezas en el
centro autorizado de servicio de garantía o puede llamar al gerente de servicio técnico al 1-800-223-7278 para
recibir asistencia personalizada de uno de nuestros expertos representantes.
REEMPLAZO GRATUITO DE ETIQUETAS DE ADVERTENCIA
Si le faltan etiquetas de advertencia o se han vuelto ilegibles, llame al
1-800-223-7278
para un reemplazo gratuito.
98
Page 99

99
Page 100

99 Roush St.
Anderson, SC 29625
1-800-223-7278
www.DeltaMachinery.com
Copyright © 2014 DELTA® Power Equipment Corporation DPEC003239
Revised: 10-08-2014
 Loading...
Loading...