Page 1

Dell XC730xd Web-scale Converged
Appliance
Owner's Manual
Page 2

Notes, Cautions, and Warnings
NOTE: A NOTE indicates important information that helps you make better use of your computer.
CAUTION: A CAUTION indicates either potential damage to hardware or loss of data and tells you
how to avoid the problem.
WARNING: A WARNING indicates a potential for property damage, personal injury, or death.
Copyright © 2015 Dell Inc. All rights reserved. This product is protected by U.S. and international copyright and
intellectual property laws. Dell™ and the Dell logo are trademarks of Dell Inc. in the United States and/or other
jurisdictions. All other marks and names mentioned herein may be trademarks of their respective companies.
Rev. A00
Page 3

Contents
1 About your system................................................................................................ 8
Supported configuration.......................................................................................................................8
Front panel features and indicators......................................................................................................8
Diagnostic indicators...........................................................................................................................10
Hard drive indicator codes..................................................................................................................12
iDRAC Direct LED indicator codes......................................................................................................13
Back-panel features and indicators....................................................................................................14
NIC indicator codes.............................................................................................................................16
Power indicator codes........................................................................................................................ 16
Documentation matrix........................................................................................................................ 19
Dell documentation...................................................................................................................... 20
Nutanix documentation................................................................................................................20
Quick Resource Locator ...............................................................................................................21
2 Performing initial system configuration ....................................................... 23
Setting up your system....................................................................................................................... 23
Methods of setting up and configuring the iDRAC IP address .........................................................23
Logging in to iDRAC............................................................................................................................23
Installing the operating system...........................................................................................................24
Remote management ........................................................................................................................24
Downloading and installing drivers and firmware............................................................................. 24
3 Pre-operating system management applications........................................ 25
Navigation keys................................................................................................................................... 25
About System Setup............................................................................................................................26
Entering System Setup.................................................................................................................. 26
System Setup Main Menu..............................................................................................................27
Editing system BIOS screen settings.............................................................................................27
Editing system information...........................................................................................................28
Editing memory settings............................................................................................................... 28
Editing processor settings.............................................................................................................29
Editing SATA Settings.....................................................................................................................31
Editing boot settings screen......................................................................................................... 34
Editing network settings................................................................................................................34
Editing integrated devices details................................................................................................. 35
Editing serial communication settings......................................................................................... 36
Editing system profile ................................................................................................................... 37
Editing system security................................................................................................................. 39
3
Page 4

Editing miscellaneous settings......................................................................................................41
About Boot Manager...........................................................................................................................42
Entering Boot Manager ................................................................................................................ 42
Boot Manager main menu............................................................................................................ 42
Changing the boot order....................................................................................................................43
Choosing the system boot mode.......................................................................................................43
Assigning a system and setup password............................................................................................43
Deleting or changing an existing system password and setup password........................................44
4 Installing and removing system components...............................................45
Safety instructions...............................................................................................................................45
Before working inside your system.................................................................................................... 45
After working inside your system....................................................................................................... 45
Recommended tools.......................................................................................................................... 46
Front bezel.......................................................................................................................................... 46
Removing the front bezel............................................................................................................. 46
Installing the front bezel............................................................................................................... 47
Removing the system cover............................................................................................................... 47
Installing the system cover.................................................................................................................48
Inside the system................................................................................................................................ 49
Cooling shroud................................................................................................................................... 50
Removing the cooling shroud.......................................................................................................51
Installing the cooling shroud.........................................................................................................51
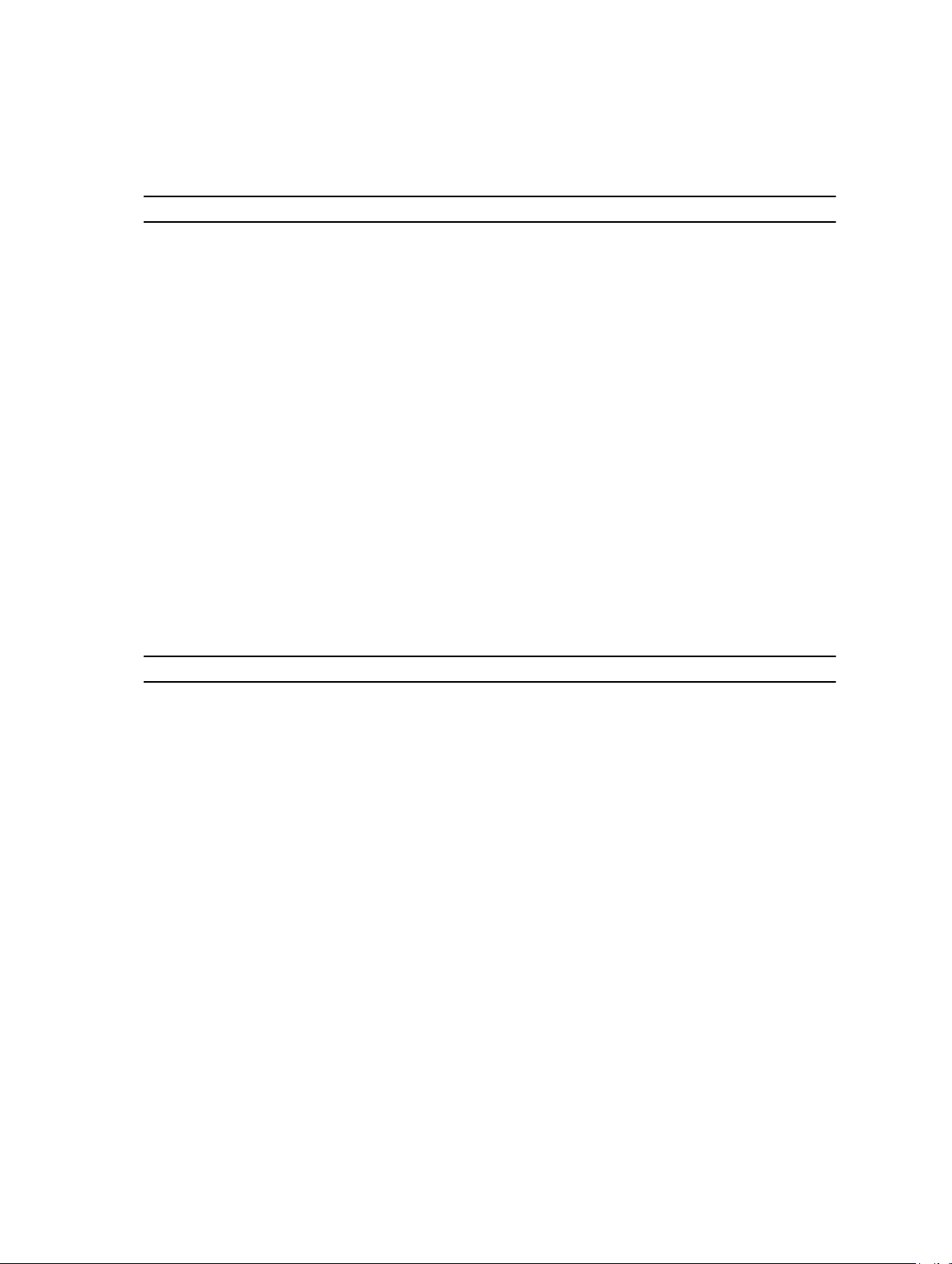
Cooling fans........................................................................................................................................ 52
Removing a cooling fan................................................................................................................ 52
Installing a cooling fan.................................................................................................................. 53
Cooling-fan assembly.........................................................................................................................54
Removing the cooling-fan assembly........................................................................................... 54
Installing the cooling-fan assembly..............................................................................................55
System memory.................................................................................................................................. 56
General memory module installation guidelines.........................................................................59
Sample memory configurations................................................................................................... 59
Removing memory modules........................................................................................................60
Installing memory modules.......................................................................................................... 62
SATADOM............................................................................................................................................63
Removing the SATADOM..............................................................................................................64
Installing the SATADOM................................................................................................................65
Heat sinks and processors..................................................................................................................66
Removing a processor.................................................................................................................. 66
Installing a processor.....................................................................................................................71
PCIe card holder..................................................................................................................................73
Removing the PCIe card holder....................................................................................................73
4
Page 5

Installing the PCIe card holder......................................................................................................74
Opening and closing the PCIe card holder latch.........................................................................75
Cable retention bracket...................................................................................................................... 76
Removing the cable retention bracket.........................................................................................76
Installing the cable retention bracket........................................................................................... 77
Integrated storage controller card......................................................................................................77
Removing the integrated storage controller card........................................................................77
Installing the integrated storage controller card......................................................................... 79
Expansion cards and expansion-card risers...................................................................................... 80
Expansion card installation guidelines......................................................................................... 80
Removing an expansion card from expansion-card riser 2 or 3................................................. 81
Installing an expansion card into the expansion-card riser 2 or 3..............................................82
Removing an expansion card from the expansion-card riser 1.................................................. 83
Installing an expansion card into the expansion-card riser 1......................................................84
Removing expansion-card risers..................................................................................................85
Installing expansion-card risers....................................................................................................92
Internal dual SD module..................................................................................................................... 92
Removing an internal SD card...................................................................................................... 92
Installing an internal SD card........................................................................................................ 93
Removing the internal dual SD module ...................................................................................... 93
Installing the internal dual SD module ........................................................................................ 95
Network daughter card.......................................................................................................................95
Removing the network daughter card ........................................................................................ 95
Installing the network daughter card........................................................................................... 97
System battery.....................................................................................................................................97
Replacing the system battery........................................................................................................97
Power supply units..............................................................................................................................99
Hot Spare feature........................................................................................................................100
Removing the power supply unit blank..................................................................................... 100
Installing the power supply unit blank........................................................................................101
Removing an AC power supply unit........................................................................................... 101
Installing an AC power supply unit.............................................................................................102
Wiring instructions for a DC power supply unit.........................................................................103
Removing a DC power supply unit.............................................................................................104
Installing a DC power supply unit...............................................................................................105
System board.....................................................................................................................................105
Removing the system board.......................................................................................................105
Installing the system board......................................................................................................... 107
Trusted Platform Module.................................................................................................................. 110
Installing the Trusted Platform Module ..................................................................................... 110
Re-enabling the TPM for BitLocker users................................................................................... 111
Re-enabling the TPM for TXT users.............................................................................................111
5
Page 6

Hard drives......................................................................................................................................... 112
Removing a 2.5 inch hard-drive blank........................................................................................112
Installing a 2.5 inch hard-drive blank..........................................................................................113
Removing a 2.5 inch hard-drive blank (back)............................................................................. 113
Installing a 2.5 inch hard-drive blank (back)...............................................................................114
Removing a 3.5 inch hard-drive blank........................................................................................114
Installing a 3.5 inch hard-drive blank..........................................................................................115
Removing a hot-swap hard drive................................................................................................115
Installing a hot-swap hard drive..................................................................................................117
Removing a hard drive from a hard-drive carrier....................................................................... 117
Installing a hard drive into a hard-drive carrier.......................................................................... 118
Hard-drive backplane........................................................................................................................118
Removing the hard-drive backplane.......................................................................................... 118
Installing the hard-drive backplane............................................................................................ 122
Removing the optional hard-drive backplane (back).................................................................123
Removing the control panel....................................................................................................... 125
Installing the control panel......................................................................................................... 126
Removing the I/O panel.............................................................................................................. 127
Installing the I/O panel................................................................................................................128
Removing the hard-drive backplane from the hard-drive tray................................................. 129
Installing the hard-drive backplane in the hard-drive tray........................................................130
5 Troubleshooting your system........................................................................ 132
Safety first—for you and your system...............................................................................................132
Troubleshooting system startup failure............................................................................................132
Troubleshooting external connections............................................................................................132
Troubleshooting the video subsystem.............................................................................................132
Troubleshooting a USB device......................................................................................................... 132
Troubleshooting iDRAC Direct (USB XML configuration)................................................................133
Troubleshooting iDRAC Direct (laptop connection)....................................................................... 134
Troubleshooting a serial I/O device................................................................................................. 134
Troubleshooting a NIC......................................................................................................................134
Troubleshooting a wet system......................................................................................................... 135
Troubleshooting a damaged system................................................................................................136
Troubleshooting the system battery................................................................................................ 136
Troubleshooting power supply units................................................................................................137
Power source problems.............................................................................................................. 137
Power supply unit problems....................................................................................................... 137
Troubleshooting cooling problems..................................................................................................138
Troubleshooting cooling fans.......................................................................................................... 138
Troubleshooting system memory.................................................................................................... 139
Troubleshooting an SD card.............................................................................................................140
6
Page 7

Troubleshooting a hard drive........................................................................................................... 140
Troubleshooting a storage controller...............................................................................................141
Troubleshooting expansion cards....................................................................................................142
Troubleshooting processors.............................................................................................................142
System messages.............................................................................................................................. 143
Warning messages...................................................................................................................... 143
Diagnostic messages...................................................................................................................143
Alert messages.............................................................................................................................143
6 Using system diagnostics................................................................................144
Dell Embedded System Diagnostics.................................................................................................144
When to use the Embedded System Diagnostics......................................................................144
Running the Embedded System Diagnostics from Boot Manager........................................... 144
Running the Embedded System Diagnostics from the Dell Lifecycle Controller.................... 144
System diagnostic controls.........................................................................................................145
7 Jumpers and connectors................................................................................ 146
System board jumper settings..........................................................................................................146
System board connectors.................................................................................................................147
Disabling a forgotten password........................................................................................................149
8 Technical specifications..................................................................................150
9 Getting help.......................................................................................................156
Contacting Dell................................................................................................................................. 156
Locating your system Service Tag....................................................................................................156
Documentation feedback.................................................................................................................156
Quick Resource Locator .................................................................................................................. 156
7
Page 8
About your system
The Dell XC730xd system is web-scale converged appliance based on the Dell PowerEdge R730xd that
supports two Intel Xeon E5-2600 v3 processors, up to 24 DIMMs, and 24 hard drives/SSDs.
NOTE: The systems support only internal, hot-swappable hard drives.
Supported configuration
Systems Configurations
1
Twelve hard-drive
systems
Twenty four hard-drive
systems
Up to twelve 3.5 inch hard drives.
Up to twenty-four 2.5 inch hard drives.
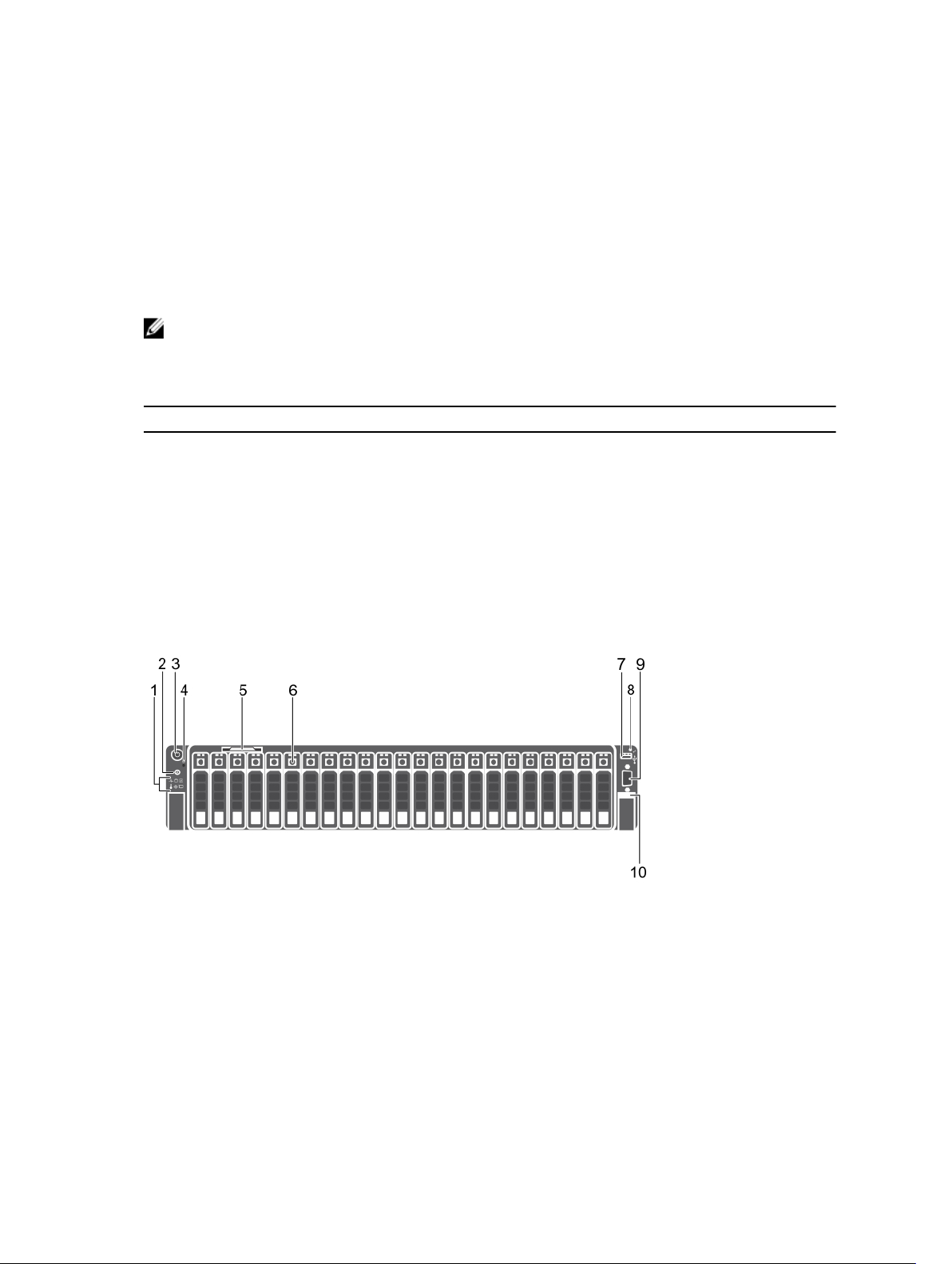
Front panel features and indicators
Figure 1. Front panel features and indicators (2.5 inch hard drive/SSD chassis)
8
Page 9
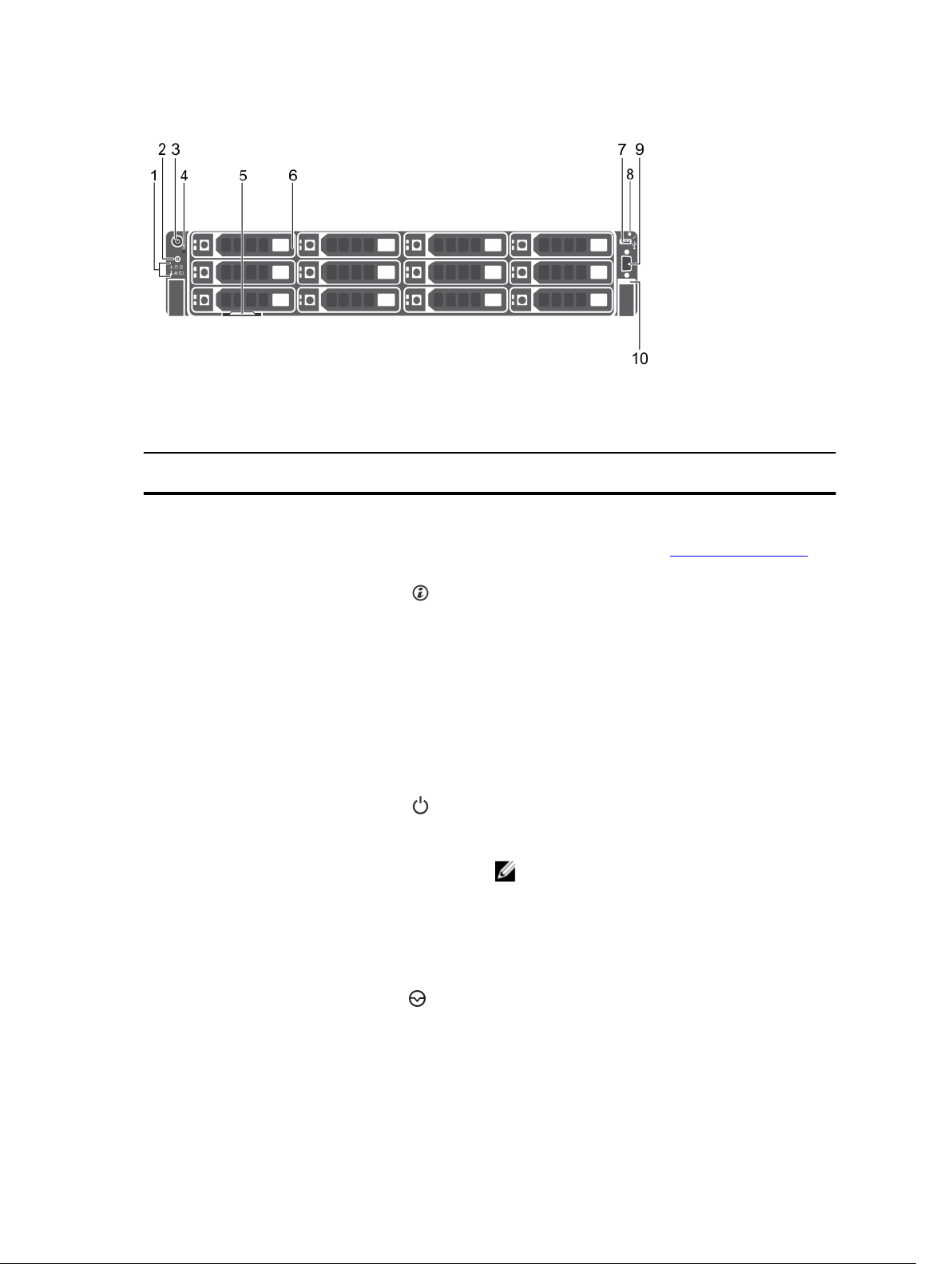
Figure 2. Front panel features and indicators (3.5 inch hard drive chassis)
Item Indicator, Button, or
Icon Description
Connector
1 Diagnostic indicators The diagnostic indicators light up to display error
status.
For more information, see Diagnostic indicators.
2 System identification
button
You can use the identification buttons on the front
— and back panels to locate a particular system
within a rack. When one of these buttons is
pressed, the system status indicator on the back
flashes until one of the buttons is pressed again.
Press to toggle the system ID on and off. If the
system stops functioning during POST, press and
hold the system ID button for more than five
seconds to enter the BIOS progress mode. To
reset iDRAC (if not disabled by entering iDRAC
Setup mode by pressing ) press and hold the
button for more than 15 seconds.
3 Power-on indicator,
Power button
The power-on indicator lights when the system
power is on. The Power button controls the power
supply output to the system.
NOTE: On the Advanced Configuration and
Power Interface (ACPI)-compliant operating
systems (OSs), turning off the system by using
the power button causes the system to
perform a graceful shutdown before power to
the system is disconnected.
4 NMI button
Use the Non-Maskable Interrupt (NMI) button to
troubleshoot software and device driver errors
while running certain OSs. Press the NMI button
using the end of a paper clip
9
Page 10
Item Indicator, Button, or
Connector
5 Information tag A slide-out label panel, which allows you to record
Icon Description
Use the NMI button only if directed by qualified
support personnel or by the OS's documentation
.
system information such as Service Tag, NIC, MAC
address.
6 Hard drives
7 USB management port/
iDRAC Direct
8 iDRAC Direct LED
indicator
9 Video connector Enables you to connect a display to the system.
2.5 inch hard
drive/SSD
systems
3.5 inch hard
drive systems
Allows you to connect USBdevices to the system
or provides access to the iDRAC Direct features.For
more information, see the Integrated Dell Remote
Access ControllerUser’s Guide at dell.com/
esmmanuals. The USB management portis USB
2.0-compliant.
The indicator lights up to display error status.
Up to twenty four 2.5 inch
hot-swappable hard drives.
Up to twelve 3.5 inch hotswappable hard drives.
Diagnostic indicators
The diagnostic indicators on the system front panel display error status during system startup.
NOTE: The diagnostic indicators are not present if the system is equipped with an LCD display.
NOTE: The diagnostic indicators are present only on the 24–hard drive systems.
NOTE: No diagnostic indicators are lit when the system is switched off. To start the system, plug it
into a working power source and press the Power button.
Table 1. Diagnostic indicators
Icon Description Condition Corrective action
None required.
See the System Event Log or system
messages for the specific issue. For more
information on error messages, see the Dell
Event and Error Messages Reference Guide
at dell.com/esmmanuals.
10
Health
indicator
If the system is on, and in
good health, the indicator
lights solid blue.
The indicator blinks amber if
the system is on or in
standby, and if any error
exists (for example, a failed
fan or hard drive).
Page 11

Icon Description Condition Corrective action
Invalid memory configurations can cause
the system to halt at startup without any
video output. See Getting help.
Hard drive
indicator
Electrical
indicator
Temperatur
e indicator
Memory
indicator
The indicator blinks amber if
a Hard drive experiences an
error.
The indicator blinks amber if
the system experiences an
electrical error (for example,
voltage out of range, or a
failed power supply or
voltage regulator).
The indicator blinks amber if
the system experiences a
thermal error (for example, a
temperature out of range or
fan failure).
The indicator blinks amber if
a memory error occurs.
See the System Event Log to determine the
Hard drive that has an error. Run the
appropriate Online Diagnostics test. Restart
system and run embedded diagnostics
(ePSA).
See the System Event Log or system
messages for the specific issue. If it is due
to a problem with the power supply, check
the LED on the power supply. Re-seat the
power supply by removing and reinstalling
it. If the problem persists, see Getting help.
Ensure that none of the following
conditions exist:
• A cooling fan is removed or has failed.
• System cover, cooling shroud, EMI filler
panel, memory-module blank, or backfiller bracket is removed.
• Ambient temperature is too high.
• External airflow is obstructed.
See Getting help.
See the system event log or system
messages for the location of the failed
memory. Reinstall the memory device. If
the problem persists, see Getting help.
PCIe
indicator
The indicator blinks amber if
a PCIe card experiences an
error.
Restart the system. Update any required
drivers for the PCIe card. Re-install the
card. If the problem persists, see Getting
help.
NOTE: For more information on
supported PCIe cards, see Expansion
card installation guidelines.
11
Page 12
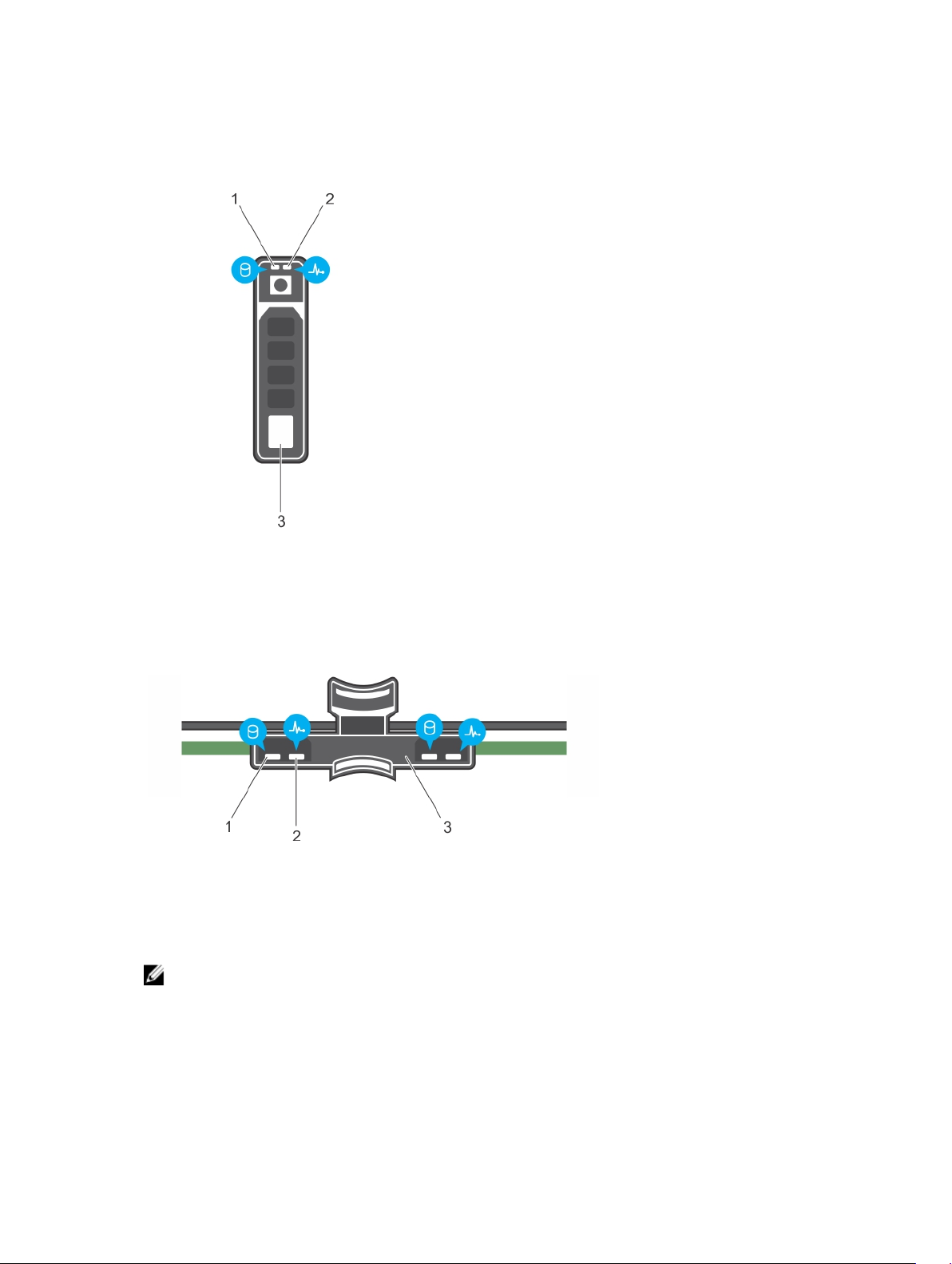
Hard drive indicator codes
Figure 3. Hard drive indicators
1. Hard drive activity indicator 2. Hard drive status indicator
3. Hard drive
Figure 4. HDD indicators on the hard-drive tray backplane
1. Hard drive activity indicator 2. Hard drive status indicator
3. Hard drive backplane on hard-drive tray
NOTE: If the Hard drive is in Advanced Host Controller Interface (AHCI) mode, the status indicator
(on the right side) does not function and remains off.
12
Page 13
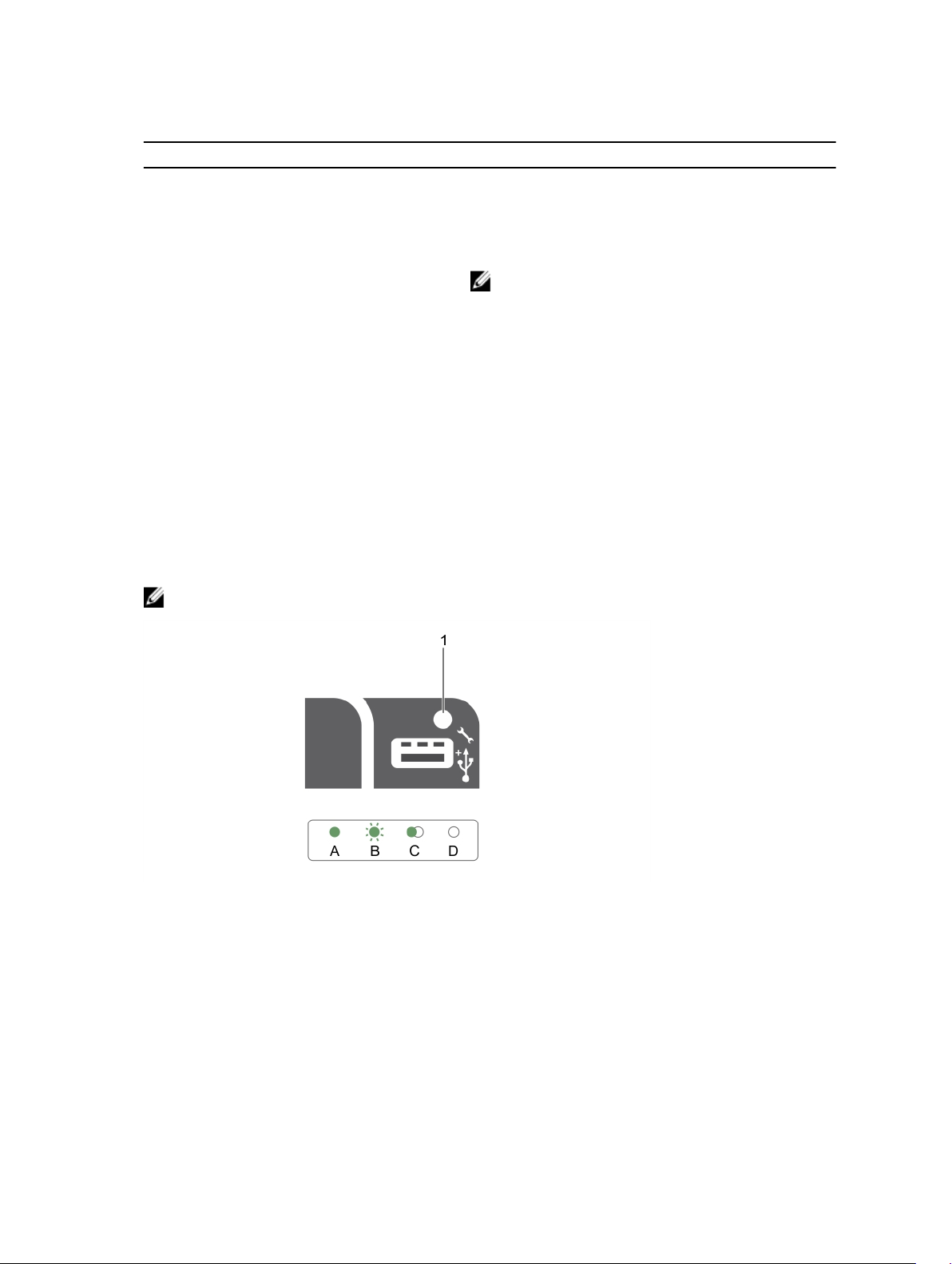
Table 2.
Drive-status indicator pattern Condition
Blinks green two times per second Identifying drive or preparing for removal. HDD or SSD
location is enabled or one of more HDDs or SSDs is in
the failed state on the Nutanix Web GUI.
Off Drive ready for insertion or removal.
NOTE: The drive status indicator remains off until
all hard drives are initialized after the system is
turned on. Drives are not ready for insertion or
removal during this time.
Blinks green, amber, and turns off Predicted drive failure
Blinks amber four times per second Drive failed
Blinks green slowly Drive rebuilding
Steady green Drive online
Blinks green three seconds, amber three
seconds, and turns off six seconds
Rebuild aborted
iDRAC Direct LED indicator codes
NOTE: The iDRAC Direct LED indicator does not light up for the USB mode.
Figure 5. iDRAC Direct LED indicator
1. iDRAC Direct status indicator
The table below displays iDRAC Direct activity when configuring iDRAC Direct by using the management
port (USB XML Import).
13
Page 14
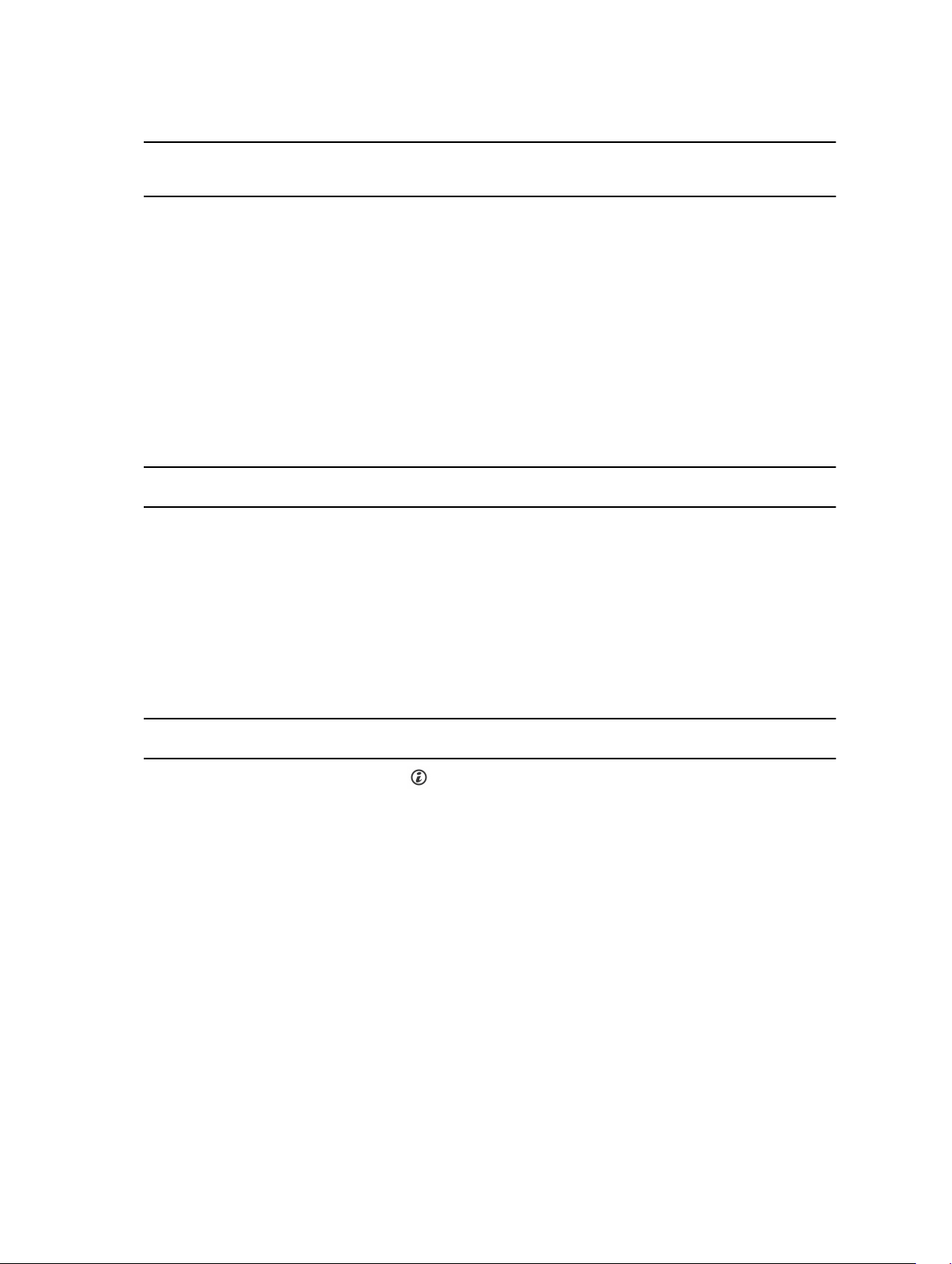
Table 3. iDRAC Direct by using the management port (USB XML Import).
Convention iDRAC Direct
A Green Lights green for a minimum of 2 seconds at the beginning and end
B Flashing green Indicates file transfer or any operation tasks.
C Green and turns
D Not lit Indicates that the USB is ready to be removed or that a task is
The table below displays iDRAC Direct activity when configuring iDRAC Direct using your laptop and
cable (Laptop Connect).
Table 4. iDRAC Direct using your laptop and cable (Laptop Connect).
iDRAC Direct LED
indicator pattern
Solid green for two
seconds
Flashing green (on
for two seconds and
off for two seconds)
LED indicator
pattern
off
Condition
Indicates that the laptop is connected.
Indicates that the laptop connected is recognized.
Condition
of a file transfer.
Indicates that the file transfer is complete.
complete.
Turns off Indicates that the laptop is unplugged.
Back-panel features and indicators
Item Indicator, button, or
connector
1 System identification
button
Icon Description
You can use the identification buttons
on the front to locate a particular system
within a rack. When one of these
buttons is pressed, the system status
indicator on the back flashes until one of
the buttons is pressed again.
Press to toggle the system ID on and off.
If the system stops responding during
POST, press and hold the system ID
button for more than five seconds to
enter the BIOS progress mode.
14
Page 15

Item Indicator, button, or
connector
Icon Description
To reset iDRAC (if not disabled in F2
iDRAC setup) press and hold the button
for more than 15 seconds.
2 System identification
connector
3 iDRAC8 Enterprise port Dedicated management port for
4 Half-height PCIe
expansion-card slot (3)
5 Serial connector Allows you to connect a serial device to
6 Video connector Allows you to connect a VGA display to
7 USB connector (2) Allows you to connect USB devices to
8 Full-height PCIe
expansion-card slot (3)
9 Ethernet connector (4) Four integrated 10/100/1000 Mbps NIC
Connects the optional system status
indicator assembly through the optional
cable management arm.
iDRAC8.
Allows you to connect up to three halfheight PCI Express expansion cards.
the system.
the system.
the system. The ports are USB 3.0compliant.
Allows you to connect up to three fullheight PCI Express expansion cards.
These are reserved for Dell PERC H310
and LSI 9207-8i.
connectors
or
Four integrated connectors that include:
• Two 10/100/1000 Mbps NIC
connectors
• Two 100 Mbps/1 Gbps/10 Gbps SFP
+/10 GbE T connectors
10 Power supply unit (PSU1)
11 Power supply unit
(PSU2)
12 vFlash media card slot Allows you to insert a vFlash media card.
13 Two HDD blanks
AC 495 W, 750 W, or
1100 W
DC 495 W, 750 W, or
1100 W
15
Page 16
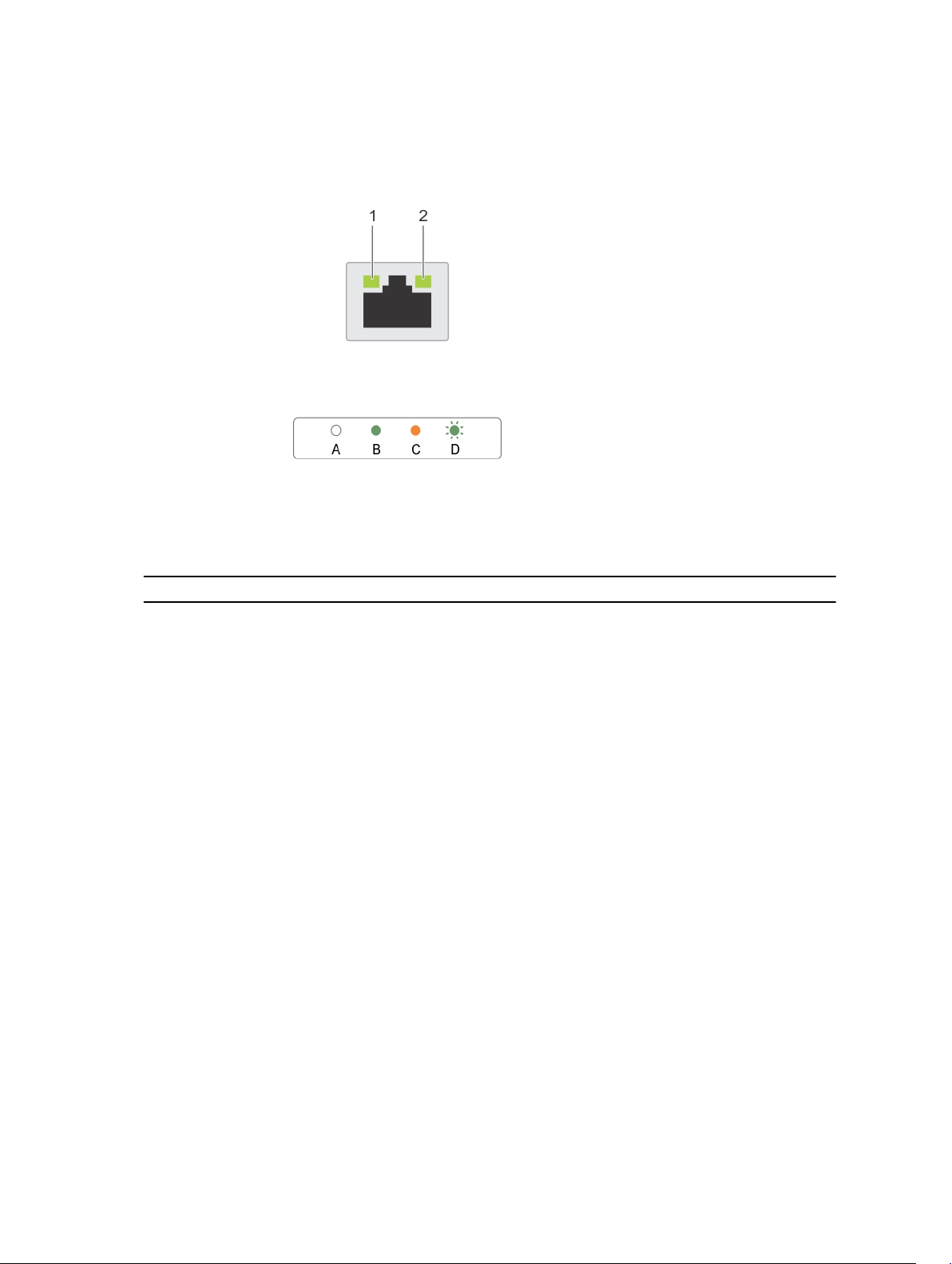
NIC indicator codes
Figure 6. NIC indicators
1. link indicator 2. activity indicator
Indicator Indicator code
A Link and activity indicators are off The NIC is not connected to the
network.
B Link indicator is green The NIC is connected to a valid
network at its maximum port
speed (1 Gbps or 10 Gbps).
C Link indicator is amber The NIC is connected to a valid
network at less than its maximum
port speed.
D Activity indicator is blinking green Network data is being sent or
received.
Power indicator codes
Each AC power supply unit (PSU) has an illuminated translucent handle and each DC power supply unit
(when available) has an LED that serves as an indicator to show whether power is present or a power fault
has occurred.
16
Page 17

Figure 7. AC power supply unit status indicator
1. AC power supply unit status indicator/handle
Table 5. AC Power indicator
Convention Power indicator
Condition
pattern
A Green The handle indicator lights green indicating that a valid power
source is connected to the power supply unit and that the power
supply unit is operational.
B Flashing green When updating the firmware of the power supply unit, the power
supply unit handle flashes green.
C Flashing green
and turns off
When hot-adding a power supply unit (PSU), the power supply unit
handle flashes green five times at 4 Hz rate and turns off. This
indicates that the power supply unit is mismatched with the other
power supply unit (in terms of efficiency, feature set, health status,
and supported voltage). Replace the power supply unit that has the
flashing indicator with a power supply unit that matches the capacity
of the other installed power supply unit.
NOTE: For AC power supplies, use only PSUs with the Extended
Power Performance (EPP) label on the back. Mixing PSUs from
previous generations of servers can result in a PSU mismatch
condition or failure to power on.
D Flashing amber Indicates a problem with the power supply unit.
17
Page 18
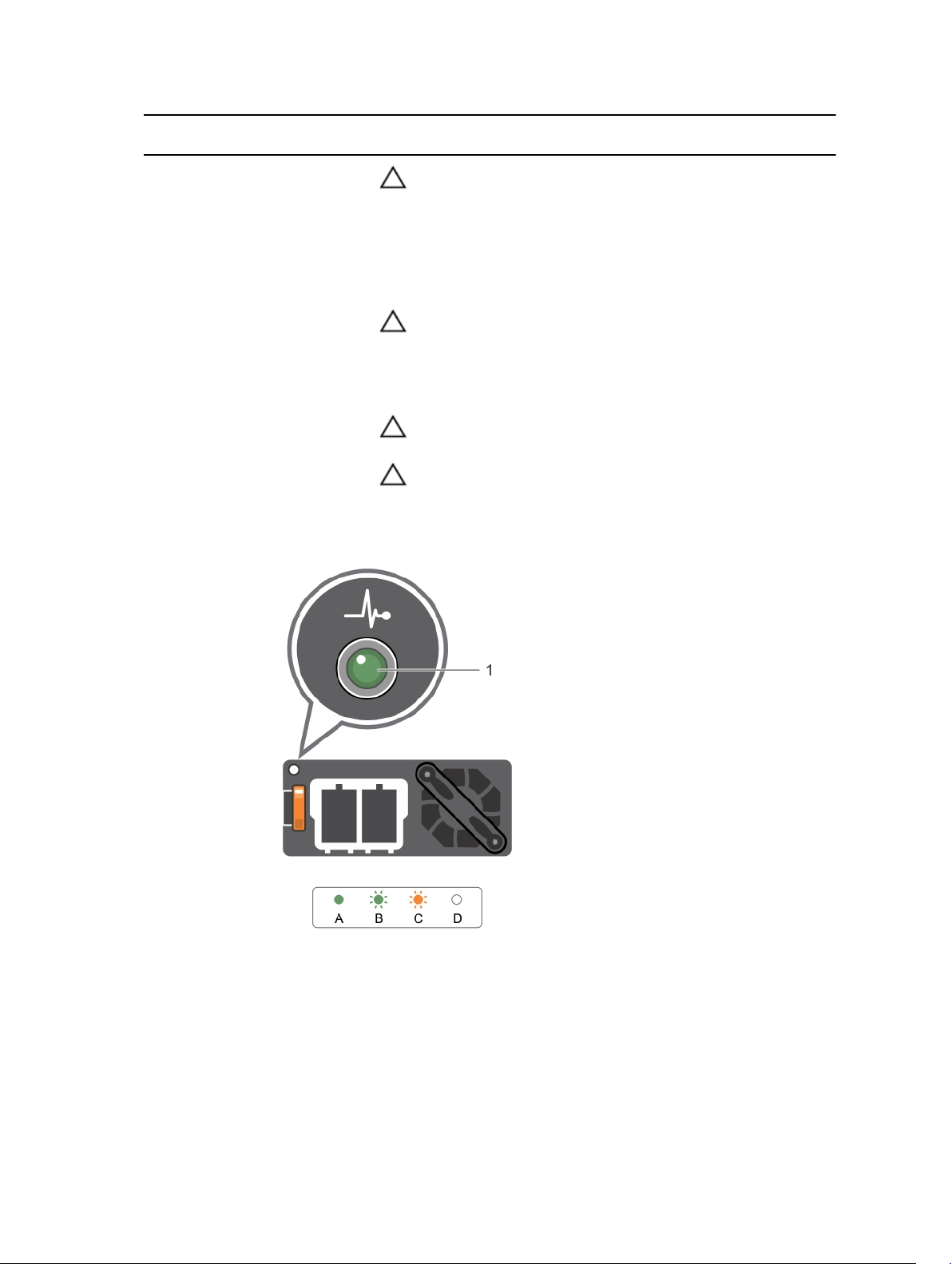
Convention Power indicator
Condition
pattern
CAUTION: When correcting a power supply unit mismatch,
replace only the power supply unit with the flashing indicator.
Swapping the opposite power supply unit to make a matched
pair can result in an error condition and unexpected system
shutdown. To change from a High Output configuration to a
Low Output configuration or vice versa, you must power
down the system.
CAUTION: AC power supplies support both 220 V and 110 V
input voltages with the exception of Titanium power supplies,
which support only 220 V. When two identical power supplies
receive different input voltages, they can output different
wattages, and trigger a mismatch.
CAUTION: If two power supplies are used, they must be of the
same type and have the same maximum output power.
CAUTION: Combining AC and DC power supplies is not
supported and triggers a mismatch.
E Not lit Power is not connected.
Figure 8. DC power supply unit status indicator
1. DC power supply unit status indicator
18
Page 19

Table 6. DC Power indicator
Convention Power indicator
pattern
A Green The handle/LED indicator lights green indicating that a valid power
B Flashing green When hot-adding a power supply unit, power supply unit LED
C Flashing amber Indicates a problem with the power supply unit.
Condition
source is connected to the power supply unit and that the power
supply unit is operational.
flashes green. This indicates that the power supply unit is
mismatched with the other power supply unit (in terms of
efficiency, feature set, health status, and supported voltage).
Replace the power supply unit that has the flashing indicator with a
power supply unit that matches the capacity of the other installed
power supply unit.
CAUTION: When correcting a power supply unit mismatch,
replace only the power supply unit with the flashing
indicator. Swapping the opposite power supply unit to make
a matched pair can result in an error condition and
unexpected system shutdown. To change from a High
Output configuration to a Low Output configuration or vice
versa, you must power down the system.
CAUTION: AC power supplies support both 220 V and 110 V
input voltages with the exception of Titanium power
supplies, which support only 220 V. When two identical
power supplies receive different input voltages, they can
output different wattages, and trigger a mismatch.
CAUTION: If two power supplies are used, they must be of
the same type and have the same maximum output power.
CAUTION: Combining AC and DC power supplies is not
supported and triggers a mismatch.
D Not lit Power is not connected.
Documentation matrix
The documentation matrix provides information about the documents you use to configure and deploy
the Dell web-scale converged appliance solution.
WARNING: See the safety and regulatory information that shipped with your system. Warranty
information may be included with this document or as a separate document.
Make sure that you read through any media that ships with your system that provides documentation and
tools for configuring and managing your system, including those pertaining to the OS, system
management software, system updates, and system components that you purchased with your system.
NOTE: URLs such as dell.com/support or dell.com/support/home are not active, because you
must type the URL from your location to access your specific language.
19
Page 20
For the full name of an abbreviation or acronym used in this document, see the Glossary at dell.com/
support/home.
NOTE: Always check for updates on dell.com/support/home and read through the updates first,
because they often supersede information in other documents.
NOTE: While upgrading your system, it is recommended that you download and install the latest
BIOS, driver, and systems management firmware on your system from dell.com/support.
The following tables list the documents provided by Dell and Nutanix.
Dell documentation
Dell documentation is either included with your shipment or available at the Dell website at dell.com/
xcseriesmanuals.
Dell documentation for:
• Dell iDRAC is available at dell.com/esmmanuals.
• Dell OpenManage Essentials is available at dell.com/openmanagemanuals.
To access Dell documentation:
1. On the Dell Support page, scroll down to General Support, and then click Servers, Storage &
Networking.
2. Click Engineered Solutions and select the documentation you require.
Table 7. Dell reference documentation for the Dell XC730xd Web-scale Converged Appliance
To learn about… Refer to…
Setup instructions of your Dell XC730xd, including
the technical specifications
Getting Started Guide
Hardware details of your Dell XC730xd Owner’s Manual
How to install your Dell XC730xd in a rack
How to deploy and set up this solution Solutions Guide
Setting up and using Dell iDRAC 8
Using OpenManage Essentials to monitor, perform
updates, view hardware, and view inventory on
your system
Dell Rack Install Guide
Dell iDRAC 8 Quick Start Guide
Dell OpenManage Essentials User’s Guide
Nutanix documentation
Most Nutanix documentation is available at https://portal.nutanix.com/#/page/docs on the Nutanix
Documents page. However, two documents are available behind the Nutanix document portal. Nutanix
documentation is listed by version, category, and type. Make sure that you select the appropriate version
of documentation for this release, which is 4.0 or later. Or refer to the Nutanix OS to find corresponding
documentation support.
To access most Nutanix documentation:
20
Page 21
1. Go to https://portal.nutanix.com/#/page/docs.
2. Select the documentation you require from the list specified in Table 10.
NOTE: To access the Hardware Replacement Documentation using the open document portal, use
the Filter By controls in the upper right corner of the page. Select NOS, 4.x, and XC730xd to display
this document.
To access the NOS Advanced Administration Guide and Advanced Setup Guide:
1. Go to https://portal.nutanix.com/#login.
2. Log in to your portal and select Documentation.
3. On the Nutanix Documents page, select the documentation you require.
Table 8. Nutanix reference documentation
To learn about… Refer to…
Setup instructions for your solution. Setup Guide
Setup instructions for environments with special
requirements and restrictions
Instructions and reference for administering the
Nutanix Operation System (NOS) outside the
Nutanix Prism UI (such as cluster start/stop,
manual upgrade, changing passwords,
reconfiguring IP addresses, and troubleshooting
tools).
Comprehensive instructions and references for the
Nutanix UI, including overview information.
Managing VMware ESXi hosts that run NOS,
including VMware vCenter requirements.
Managing Hyper-V hosts that run NOS. Hyper-V Administration Guide
Comprehensive references for the Nutanix REST
API.
Comprehensive references for Controller Virtual
Machine (CVM) utilities, nCLI commands, and
Nutanix PowerShell cmdlets.
Software instructions for hardware components
that are not functioning.
Advanced Setup Guide
NOS Advanced Administration Guide
Web Console Guide
vSphere Administration Guide
API Reference
Command Reference
Hardware Replacement Documentation
Quick Resource Locator
Use the Quick Resource Locator (QRL) to get immediate access to system information and how-to
videos. This can be done by visiting dell.com/QRL or by using your smartphone or tablet and a model
specific Quick Resource (QR) code located on your Dell system. To try out the QR code, scan the
following image.
21
Page 22
Figure 9. Quick Resource Locator
22
Page 23

Performing initial system configuration
After you receive your system, you must set up your system, install the operating system if it is not preinstalled, and set up and configure the system iDRAC IP address.
Setting up your system
1. Unpack the server.
2. Install the server into the rack. For more information on installing the server into the rack, see your
system Rack Installation Placemat at dell.com/xcseriesmanuals.
3. Connect the peripherals to the system.
4. Connect the system to its electrical outlet.
5. Turn the system on by pressing the Power button or using iDRAC.
6. Turn on the attached peripherals.
Methods of setting up and configuring the iDRAC IP address
You can set up the Integrated Dell Remote Access Controller (iDRAC) IP address by using one of the
following interfaces:
2
• iDRAC Settings utility.
• Lifecycle Controller.
• Dell Deployment Toolkit.
• Server LCD panel.
You can configure iDRAC IP using:
1. iDRAC Web Interface.
For more information on setting up and configuring iDRAC, see the Integrated Dell Remote Access
Controller User's Guide at dell.com/esmmanuals.
2. Remote Access Controller ADMin (RACADM).
For more information, see the RACADM Command Line Interface Reference Guide and the
Integrated Dell Remote Access Controller User's Guide.
3. Remote Services that includes Web Services Management (WS-Man). For more information, see the
Lifecycle Controller Remote Services Quick Start Guide.
Logging in to iDRAC
You can log in to iDRAC as an iDRAC local user, a Microsoft Active Directory user, or a Lightweight
Directory Access Protocol (LDAP) user. You can also log in by using Single Sign-On or a Smart Card. The
23
Page 24

default user name is root and password is calvin. For more information on logging in to iDRAC and iDRAC
licenses, see the Integrated Dell Remote Access Controller User's Guide at dell.com/esmmanuals.
You can also access iDRAC using RACADM. For more information, see the RACADM Command Line
Interface Reference Guide and the Integrated Dell Remote Access Controller User's Guide available at
dell.com/esmmanuals.
Installing the operating system
If the server is shipped without an operating system, install the supported operating system on the server
by using one of the following methods:
• Dell Systems Management Tools and Documentation media. See the operating system
documentation at dell.com/operatingsystemmanuals.
• Dell Lifecycle Controller. See the Lifecycle Controller documentation at dell.com/esmmanuals.
• Dell OpenManage Deployment Toolkit. See the OpenManage documentation at dell.com/
openmanagemanuals.
For information on the list of operating systems supported on your system, see the operating systems
support matrix at dell.com/ossupport.
Remote management
To perform out-of-band systems management using iDRAC, you must configure iDRAC for remote
accessibility, set up the management station and managed system, and configure the supported Web
browsers. For more information, see the Integrated Dell Remote Access Controller User’s Guide at
dell.com/esmmanuals.
You can also remotely monitor and manage the server by using the Dell OpenManage Server
Administrator software and OpenManage Essentials systems management console. For more
information, see dell.com/openmanagemanuals.
Downloading and installing drivers and firmware
Dell recommends that you download and install the latest BIOS, drivers, and systems management
firmware on your system.
Prerequisites
Ensure that you clear the web browser cache.
Steps
1. Go to Support.Dell.com.
2. Under Support in the Customized support section type your Service Tag into the Enter your Service
Tag or Express Service code box.
NOTE: If you do not have the Service Tag, select Detect My Product to allow the system to
automatically detect your Service Tag, or under General support select your product page.
3. Click Drivers & downloads.
The drivers that are applicable to your selection are displayed.
4. Download the drivers you require to a diskette drive, USB drive, CD, or DVD.
24
Page 25
3
Pre-operating system management applications
The pre-operating system management applications for your system helps you manage different settings
and features of your system without booting to the operating system.
Your system has the following pre-operating system management applications:
• System Setup
• Boot Manager
• Dell Lifecycle Controller
Dell Lifecycle Controller allows you to perform useful tasks such as configuring BIOS and hardware
settings, deploying operating system, updating drivers, and saving hardware profiles. For more
information about Dell Lifecycle Controller, see the documentation at dell.com/esmmanuals.
Navigation keys
The navigation keys can help you access the pre-operating system management applications.
Table 9. Navigation keys
Key Description
Page Up Moves to the previous screen.
Page Down Moves to the next screen.
Up arrow Moves to the previous field.
Down
arrow
Enter Enables you to type a value in the selected field (if applicable) or follow the link in the field.
Spacebar Expands or collapses a drop-down list, if applicable.
Tab Moves to the next focus area.
Esc Moves to the previous page until you view the main screen. Pressing Esc in the main
F1 Displays the System Setup help.
F2 Enables you to enter System Setup
Moves to the next field.
NOTE: This feature is applicable for the standard graphical browser only.
screen exits System BIOS/iDRAC Settings/Device Settings/Service Tag Settings and
proceeds with system boot.
25
Page 26

Key Description
F10 Enables you to enter Lifecycle Controller
F11 Enables you to enter Boot Manager
F12 Enables you to enter PXE boot
About System Setup
Using System Setup, you can configure the BIOS settings, iDRAC settings, and device settings of your
system.
NOTE: There are a several generic server settings that appear during system setup that do not apply
to this system, such as RAID or UEFI.
You can access System Setup in two ways:
• Standard Graphical Browser — This is enabled by default.
• Text Browser — This is enabled using Console Redirection.
To enable Console Redirection:
• On the System Setup page, click System BIOS.
• On the Serial Communications page, click Serial Communication, and then select On with Console
Redirection.
NOTE: By default, help text for the selected field is displayed in the graphical browser. To view the
help text in the text browser, press F1.
From System Setup, you can:
• Change the NVRAM settings after you add or remove hardware
• View the system hardware configuration
• Enable or disable integrated devices
• Set performance and power management thresholds
• Manage system security
Entering System Setup
1. Turn on or restart your system.
2. Press F2 immediately after you see the following message:
<F2> = System Setup
If your operating system begins to load before you press F2, allow the system to finish booting, and
then restart your system and try again.
NOTE: If an error message is displayed while the system is starting, make a note of the
message. For more information, see System messages.
NOTE: After installing a memory upgrade, it is normal for your system to display a message the
first time you start your system.
26
Page 27
System Setup Main Menu
Table 10. System setup main menu
Option Description
System BIOS Enables you to configure BIOS settings.
iDRAC Settings Enables you to configure iDRAC settings.
The iDRAC Settings utility is an interface to set up and configure the
iDRAC parameters by using UEFI. You can enable or disable various
iDRAC parameters by using the iDRAC Settings utility. For more
information about this utility, see the Integrated Dell Remote Access
Controller User’s Guide at dell.com/esmmanuals.
Device Settings Enables you to configure device settings.
Editing system BIOS screen settings
You can use the System BIOS screen to view the BIOS settings. You can also edit some of the settings
such as Boot Order, System Password, Setup Password, and enable or disable USB ports.
Go to System Setup Main Menu, and then click System BIOS.
The System BIOS screen is displayed.
System BIOS screen settings
The System BIOS screen details are explained below.
Table 11. System BIOS
Menu Item Description
System Information Displays information about the system such as the system model name,
BIOS version and Service Tag.
Memory Settings Displays information and options related to the installed memory.
Processor Settings Displays information and options related to the processor such as speed,
cache size, and so on.
SATA Settings Displays options to enable or disable the integrated SATA controller and
ports.
Boot Settings Displays options to specify the boot mode (BIOS or UEFI). Enables you to
modify UEFI and BIOS boot settings.
Network Settings Displays options to change the network settings.
Integrated Devices Displays options to enable or disable integrated device controllers and
ports, and to specify related features and options.
Serial Communication Displays options to enable or disable the serial ports and specify related
features and options.
System Profile Settings Displays options to change the processor power management settings,
memory frequency, and so on.
System Security Displays options to configure the system security settings like, system
password, setup password, Trusted Platform Module (TPM) security, and
27
Page 28

Menu Item Description
so on. It also enables or disables support for the power and NMI buttons
on the system.
Miscellaneous Settings Displays options to change the system date, time, and so on.
Editing system information
You can use the System Information screen to view system properties such as Service Tag, system
model, and the BIOS version.
1. Go to System Setup Main Menu, and then click System BIOS.
2. On System BIOS, click System Information.
The System Information screen is displayed.
System information screen settings
The System Information screen details are explained as follows:
Table 12. System information
Menu Item Description
System Model Name Displays the system model name.
System BIOS Version Displays the BIOS version installed on the system.
System Management
Engine Version
System Service Tag Displays the system Service Tag.
System Manufacturer Displays the name of the system manufacturer.
System Manufacturer
Contact Information
System CPLD Version Displays the current revision of the system CPLD firmware.
UEFI Compliance Version Displays the system firmware UEFI compliance level.
Displays the current revision of the Management Engine firmware.
Displays the contact information of the system manufacturer.
Editing memory settings
You can use the Memory Settings screen to view all the memory settings. You can also enable or disable
some memory configurations such as system memory testing and node interleaving.
1. Go to System Setup Main Menu, and then click System BIOS.
2. On System BIOS, click Memory Settings.
The Memory Settings screen displays..
Memory screen settings
The Memory Settings screen details are explained as follows:
28
Page 29

Table 13. Memory settings
Menu Item Description
System Memory Size Displays the amount of memory installed in the system.
System Memory Type Displays the type of memory installed in the system.
System Memory Speed Displays the system memory speed.
System Memory Voltage Displays the system memory voltage.
Video Memory Displays the amount of video memory.
System Memory Testing Specifies whether system memory tests are run during system boot.
Options are Enabled and Disabled. By default, the System Memory
Testing option is set to Disabled.
Memory Operating Mode Specifies the memory operating mode. The options available are
Optimizer Mode, Advanced ECC Mode, Mirror Mode, Spare Mode,
Spare with Advanced ECC Mode, and Dell Fault Resilient Mode. By
default, the Memory Operating Mode option is set to Optimizer Mode.
NOTE: The Memory Operating Mode can have different defaults
and available options based on the memory configuration of your
system.
NOTE: The Dell Fault Resilient Mode establishes an area of memory
that is fault resilient. This mode can be used by an operating system
that supports the feature to load critical applications or enables the
operating system kernel to maximize system availability.
Node Interleaving Specifies if Non-Uniform Memory architecture (NUMA) is supported. If
this field is Enabled, memory interleaving is supported if a symmetric
memory configuration is installed. If Disabled, the system supports
NUMA (asymmetric) memory configurations. By default, Node
Interleaving
Snoop Mode Specifies the Snoop Mode options. Snoop Mode options available are
Home Snoop, Early Snoop, Cluster on Die. By default, the Snoop Mode
option is set to Early Snoop. The field is only available when Node
Interleaving is Disabled.
option is set to Disabled.
Editing processor settings
You can use the Processor Settings screen to view the processor settings. You can also enable
virtualization technology, hardware prefetcher, and logical processor idling.
1. Go to System Setup Main Menu, and then click System BIOS.
2. On System BIOS, click Processor Settings.
The Processor Settings screen displays.
Processor settings screen
The Processor Settings screen details are explained as follows:
29
Page 30

Table 14. Processor settings
Menu Item Description
Logical Processor Enables or disables the logical processors and displays the number of
logical processors. If the Logical Processor option is set to Enabled, the
BIOS displays all the logical processors. If this option is set to Disabled,
the BIOS only displays one logical processor per core. By default, the
Logical Processor option is set to Enabled.
Alternate RTID (Requestor
Transaction ID) Setting
Enables you to allocate more RTIDs to the remote socket, thereby
increasing cache performance between the sockets or easing work in
normal mode for NUMA. By default, the Alternate RTID (Requestor
Transaction ID) Setting is set to Disabled.
Virtualization Technology Enables or disables the additional hardware capabilities provided for
virtualization. By default, the Virtualization Technology option is set to
Enabled.
Address Translation Service
(ATS)
Defines the Address Translation Cache (ATC) for devices to cache the
DMA transactions. This field provides an interface to a chipset's Address
Translation and Protection Table to translate DMA addresses to host
addresses. By default, the option is set to Enabled.
Adjacent Cache Line
Prefetch
Optimizes the system for applications that require high usage of
sequential memory access. By default, the Adjacent Cache Line Prefetch
option is set to Enabled. You can disable this option for applications that
require high usage of random memory access.
Hardware Prefetcher Enables or disables the hardware prefetcher. By default, the Hardware
Prefetcher option is set to Enabled.
DCU Streamer Prefetcher Allows you to enable or disable the Data Cache Unit (DCU) streamer
prefetcher. By default, the DCU Streamer Prefetcher option is set to
Enabled.
DCU IP Prefetcher Enables or disables the Data Cache Unit (DCU) IP prefetcher. By default,
the DCU IP Prefetcher option is set to Enabled.
Execute Disable Enables or disables the execute disable memory protection technology.
By default, the Execute Disable option is set to Enabled.
Logical Processor Idling Enables or disables the operating system capability to put logical
processors in the idling state in order to reduce power consumption. By
default, the option is set to Disabled.
Configurable TDP Allows reconfiguration of Thermal Design Power (TDP) to lower levels.
TDP refers to the maximum amount of power the cooling system is
required to dissipate.
X2Apic Mode Enables or disables the X2Apic mode.
Dell Controlled Turbo
NOTE: Depending on the number of installed CPUs, there may be
up to four processor listings.
Controls the turbo engagement. Enable this option only when System
Profile is set to Performance.
Number of Cores per
Processor
Controls the number of enabled cores in each processor. By default, the
Number of Cores per Processor option is set to All.
Processor 64-bit Support Specifies if the processor(s) support 64-bit extensions.
30
Page 31

Menu Item Description
Processor Core Speed Displays the maximum core frequency of the processor.
Processor 1
NOTE: Depending on the number of installed CPUs, there may be
up to four processors listings. The following settings are displayed
for each processor installed in the system.
• Family-Model-Stepping: Displays the family, model and stepping of
the processor as defined by Intel.
• Brand: Displays the brand name reported by the processor.
• Level 2 Cache: Displays the total L2 cache.
• Level 3 Cache: Displays the total L3 cache.
• Number of Cores: Displays the number of cores per processor.
Editing SATA Settings
You can use the SATA Settings screen to view the SATA settings of SATA devices and enable RAID on
your system.
1. Go to System Setup Main Menu, and then click System BIOS .
2. On System BIOS , click SATA Settings.
The SATA Settings screen displays.
SATA settings screen
The SATA Settings screen details are explained below.
Table 15. SATA settings
Menu Item Description
Embedded SATA Enables the embedded SATA to be set to Off, ATA, AHCI, or RAID modes.
By default, the Embedded SATA option is set to AHCI.
Security Freeze Lock Sends Security Freeze Lock command to the Embedded SATA drives
during POST. This option is applicable only to ATA and AHCI mode.
Write Cache Enables or disables the command for Embedded SATA drives during
POST.
Port A Sets the drive type of the selected device. For Embedded SATA settings
in ATA mode, set this field to Auto to enable BIOS support. Set it to OFF
to turn off BIOS support.
For AHCI mode or RAID mode, BIOS always enables support.
Model: Displays the drive model of the selected device.
Drive Type: Displays the type of drive attached to the SATA port.
Capacity: Displays the total capacity of the hard drive. The field is
undefined for removable media devices such as optical drives.
Port B Sets the drive type of the selected device. For Embedded SATA settings
in ATA mode, set this field to Auto to enable BIOS support. Set it to OFF
to turn off BIOS support.
31
Page 32

Menu Item Description
For AHCI mode or RAID mode, BIOS always enables support.
Model: Displays the drive model of the selected device.
Drive Type: Displays the type of drive attached to the SATA port.
Capacity: Displays the total capacity of the hard drive. The field is
undefined for removable media devices such as optical drives.
Port C Sets the drive type of the selected device. For Embedded SATA settings
in ATA mode, set this field to Auto to enable BIOS support. Set it to OFF
to turn off BIOS support.
For AHCI mode or RAID mode, BIOS always enables support.
Model: Displays the drive model of the selected device.
Drive Type: Displays the type of drive attached to the SATA port.
Capacity: Displays the total capacity of the hard drive. The field is
undefined for removable media devices such as optical drives.
Port D Sets the drive type of the selected device. For Embedded SATA settings
in ATA mode, set this field to Auto to enable BIOS support. Set it to OFF
to turn off BIOS support.
For AHCI mode or RAID mode, BIOS always enables support.
Model: Displays the drive model of the selected device.
Drive Type: Displays the type of drive attached to the SATA port.
Capacity: Displays the total capacity of the hard drive. The field is
undefined for removable media devices such as optical drives.
Port E Sets the drive type of the selected device. For Embedded SATA settings
in ATA mode, set this field to Auto to enable BIOS support. Set it to OFF
to turn off BIOS support.
For AHCI mode or RAID mode, BIOS always enables support.
Model: Displays the drive model of the selected device.
Drive Type: Displays the type of drive attached to the SATA port.
Capacity: Displays the total capacity of the hard drive. The field is
undefined for removable media devices such as optical drives.
Port F Sets the drive type of the selected device. For Embedded SATA settings
in ATA mode, set this field to Auto to enable BIOS support. Set it to OFF
to turn off BIOS support.
For AHCI mode or RAID mode, BIOS always enables support.
Model: Displays the drive model of the selected device.
Drive Type: Displays the type of drive attached to the SATA port.
32
Page 33

Menu Item Description
Capacity: Displays the total capacity of the hard drive. The field is
undefined for removable media devices such as optical drives.
Port G Sets the drive type of the selected device. For Embedded SATA settings
in ATA mode, set this field to Auto to enable BIOS support. Set it to OFF
to turn off BIOS support.
For AHCI mode or RAID mode, BIOS always enables support.
Model: Displays the drive model of the selected device.
Drive Type: Displays the type of drive attached to the SATA port.
Capacity: Displays the total capacity of the hard drive. The field is
undefined for removable media devices such as optical drives.
Port H Sets the drive type of the selected device. For Embedded SATA settings
in ATA mode, set this field to Auto to enable BIOS support. Set it to OFF
to turn off BIOS support.
For AHCI mode or RAID mode, BIOS always enables support.
Model: Displays the drive model of the selected device.
Drive Type: Displays the type of drive attached to the SATA port.
Capacity: Displays the total capacity of the hard drive. The field is
undefined for removable media devices such as optical drives.
Port I Sets the drive type of the selected device. For Embedded SATA settings
in ATA mode, set this field to Auto to enable BIOS support. Set it to OFF
to turn off BIOS support.
For AHCI mode or RAID mode, BIOS always enables support.
Model: Displays the drive model of the selected device.
Drive Type: Displays the type of drive attached to the SATA port.
Capacity: Displays the total capacity of the hard drive. The field is
undefined for removable media devices such as optical drives.
Port J Sets the drive type of the selected device. For Embedded SATA settings
in ATA mode, set this field to Auto to enable BIOS support. Set it to OFF
to turn off BIOS support.
For AHCI mode or RAID mode, BIOS always enables support.
Model: Displays the drive model of the selected device.
Drive Type: Displays the type of drive attached to the SATA port.
Capacity: Displays the total capacity of the hard drive. The field is
undefined for removable media devices such as optical drives.
33
Page 34

Editing boot settings screen
You can use the Boot Settings screen to set the Boot mode to either BIOS or UEFI. It also allows you to
specify the boot order.
1. Go to System Setup Main Menu, and then click System BIOS.
2. On System BIOS, click Boot Settings.
The Boot Settings screen displays.
Boot Settings
The Boot Settings screen details are explained as follows:
Table 16. Boot settings
Menu Item Description
Boot Mode Enables you to set the boot mode of the system.
NOTE: This system supports only BIOS boot mode.
CAUTION: Switching the boot mode may prevent the system from
booting if the operating system is not installed in the same boot
mode.
NOTE: Setting this field to UEFI disables the BIOS Boot Settings
menu. Setting this field to BIOS disables the UEFI Boot Settings
menu.
If the operating system supports UEFI, you can set this option to UEFI.
Setting this field to BIOS allows compatibility with non-UEFI operating
systems. By default, the Boot Mode option is set to BIOS.
NOTE: This system supports only BIOS boot mode.
Boot Sequence Retry
Hard-Disk Failover Specifies which devices in the Hard-Disk Drive Sequence are attempted
Boot Option Settings Configures the boot sequence and the boot devices.
Enables or disables the Boot Sequence Retry feature. If this field is
enabled and the system fails to boot, the system reattempts the boot
sequence after 30 seconds. By default, the Boot Sequence Retry option
is set to Enabled.
in the boot sequence. When the option is Disabled, only the first hard
disk device in the list is attempted to boot. When set to Enabled, all hard
disk devices are attempted in order, as listed in the Hard-Disk Drive
Sequence
. This option is not enabled for UEFI Boot Mode.
Editing network settings
You can use the Network Settings screen to modify Preboot eXecution Environment (PXE) device
settings. Network Settings are only available in UEFI boot mode. BIOS does not control network settings
in the BIOS boot mode. For BIOS boot mode, the network settings are handled by the network
controllers option ROM.
1. Go to System Setup Main Menu, and then click System BIOS.
2. On System BIOS, click Network Settings.
34
Page 35

The Network Settings screen displays.
Network settings screen
The Network Settings screen details are explained as follows:
Table 17. Network settings
Menu Item Description
PXE Device n (n = 1 to 4) Enables or disables the device. When enabled, a UEFI boot option is
created for the device.
PXE Device n Settings (n = 1
to 4)
Allows you to control the configuration of the PXE device.
Editing integrated devices details
You can use the Integrated Devices screen to view and configure the settings of all integrated devices
including the video controller, integrated RAID controller, and the USB ports.
1. Go to System Setup Main Menu, and then click System BIOS.
2. On System BIOS, click Integrated Devices.
The Integrated Devices screen displays.
Integrated devices screen details
The Integrated Devices screen details are explained below.
Table 18. Integrated devices
Menu Item Description
USB 3.0 Setting Enables or disables the USB 3.0 support. Enable this option only if your
operating system supports USB 3.0. If you disable this option, devices operate
at USB 2.0 speed. USB 3.0 is disabled by default.
User Accessible USB
Ports
Internal USB Port Enables or disables the internal USB port. By default, the option is set to
Integrated RAID
Controller
Integrated Network
Card 1
Embedded NIC1 and
NIC2
Enables or disables the USB ports. Selecting Only Back Ports On disables the
front USB ports, selecting All Ports Off disables all USB ports. The USB
keyboard and mouse operates during boot process in certain operating
systems. After the boot process is complete, the USB keyboard and mouse do
not work if the ports are disabled.
NOTE: Selecting Only Back Ports On and All Ports Off disables the USB
management port and also restrict access to iDRAC features.
Enabled.
Enables or disables the integrated RAID controller. By default, the option is
set to Enabled.
Enables or disables the integrated network card.
NOTE: The Embedded NIC1 and NIC2 option is only available on
systems that do not have Integrated Network Card 1.
Enables or disables the Embedded NIC1 and NIC2 . If set to Disabled, the NIC
may still be available for shared network access by the embedded
35
Page 36

Menu Item Description
management controller. The embedded NIC1 and NIC2 option is only
available on systems that do not have NDCs. This option is mutually exclusive
with the Integrated Network Card 1 option. Configure this function using the
NIC management utilities of the system.
I/OAT DMA Engine Enables or disables the I/OAT option. Enable only if the hardware and
software support the feature.
Embedded Video
Controller
Current State of
Embedded Video
Controller
SR-IOV Global Enable Enables or disables the BIOS configuration of Single Root I/O Virtualization
OS Watchdog Timer If your system stops responding, this OS Watchdog Timer aids in the recovery
Memory Mapped I/O
above 4GB
Slot Disablement Enables or disables the available PCIe slots on your system. The Slot
Enables or disables the Embedded Video Controller. By default, the
embedded video controller is Enabled. Current state of Embedded Video
Controller is Enabled. Current State of Embedded Video Controller is a read
only field, indicating the current state for the Embedded Video Controller. If
the Embedded Video Controller is the only display capability in the system
(that is, no add-in graphics card is installed), then the Embedded Video
Controller is automatically used as the primary display even if the Embedded
Video Controller setting is
Displays the current state of the Embedded Video Controller. Current State
of Embedded Video Controller is a read only field, indicating the current
state for the Embedded Video Controller.
(SR-IOV) devices. By default, the SR-IOV Global Enable option is set to
Disabled.
of your operating system. When this field is set to Enabled, the operating
system is allowed to initialize the timer. When the option is set to Disabled
(the default), the timer has no effect on the system.
Enables or disables the support for PCIe devices that require large amounts of
memory. By default, the option is set to Enabled.
Disablement feature controls the configuration of PCIe cards installed in the
specified slot. Slot disablement must be used only when the installed
peripheral card is preventing booting into the operating system or causing
delays in system startup. If the slot is disabled, both the Option ROM and UEFI
driver are disabled.
Disabled.
Editing serial communication settings
You can use the Serial Communication screen to view the properties of the serial communication port.
1. Go to System Setup Main Menu, and then click System BIOS.
2. On System BIOS, click Serial Communication.
The Serial Communication screen is displayed
Serial Communication screen settings
The Serial Communication screen details are explained below.
36
Page 37

Table 19. Serial communication
Menu Item Description
Serial Communication Selects serial communication devices (Serial Device 1 and Serial Device 2)
in the BIOS. This is where you can select BIOS console redirection and
specify the port address. By default, Serial Communication option is set
to Auto.
Serial Port Address With Serial Communication, you can set the port address for serial
devices. By default, the Serial Port Address option is set to Serial Device
1=COM2, Serial Device 2=COM1
NOTE: You can only use Serial Device 2 for Serial Over LAN (SOL).
To use console redirection by SOL, configure the same port address
for console redirection and the serial device.
NOTE: Every time the system boots, the BIOS syncs the serial MUX
setting saved in iDRAC. The serial MUX setting can independently be
changed in iDRAC. Therefore, loading the BIOS default settings from
within the BIOS setup utility may not always revert this setting to the
default setting of Serial Device 1.
External Serial Connector With the External Serial Connector, you can associate the External Serial
Connector to Serial Device 1, Serial Device 2, or the Remote Access
Device using this field.
NOTE: You can only use Serial Device 2 for Serial Over LAN (SOL).
To use console redirection by SOL, configure the same port address
for console redirection and the serial device.
NOTE: Every time the system boots, the BIOS syncs the serial MUX
setting saved in iDRAC. The serial MUX setting can independently be
changed in iDRAC. Therefore, loading the BIOS default settings from
within the BIOS setup utility may not always revert this setting to the
default setting of Serial Device 1.
Failsafe Baud Rate Displays the Failsafe baud rate for console redirection. The BIOS attempts
to determine the baud rate automatically. This Failsafe baud rate is used
only if the attempt fails, and the value must not be changed. By default,
the Failsafe Baud Rate option is set to 115200.
Remote Terminal Type Sets the remote console terminal type. By default, the Remote Terminal
Type option is set to VT 100/VT 220.
Redirection After Boot Enables or disables the BIOS console redirection when the operating
system is loaded. By default, the Redirection After Boot option is set to
Enabled.
Editing system profile
You can use the System Profile Settings screen to enable system performance settings such as power
management.
1. Go to System Setup Main Menu, and then click System BIOS.
2. On System BIOS, click System Profile Settings.
The System Profile Settings screen is displayed.
37
Page 38

System profile screen settings
The System Profile Settings screen details are explained as follows:
Table 20. System profile settings
Menu Item Description
System Profile Sets the system profile. If you set the System Profile option to a mode other than
Custom, the BIOS automatically sets the rest of the options. You can only change
the rest of the options if the mode is set to Custom. By default, the System Profile
option is set to Performance Per Watt Optimized (DAPC). DAPC is Dell Active
Power Controller.
NOTE: The following parameters are available only when the System Profile is
set to Custom.
• CPU Power Management: Sets the CPU power management. By default, the
CPU Power Management option is set to System DBPM (DAPC). DBPM is
Demand-Based Power Management.
• Memory Frequency: Sets the speed of the system memory. You can select
Maximum Performance, Maximum Reliability, or a specific speed.
• Turbo Boost: Enables or disables the processor to operate in turbo boost
mode. By default, the Turbo Boost option is set to Enabled.
• Energy Efficient Turbo: Enables or disables the Energy Efficient Turbo.
Energy Efficient Turbo (EET) is a mode of operation where a processor’s core
frequency is adjusted within the turbo range based on workload.
• C1E: Enables or disables the processor to switch to a minimum performance
state when it is idle. By default, the C1E option is set to Enabled.
• C States: Enables or disables the processor to operate in all available power
states. By default, the C States option is set to Enabled.
• Collaborative CPU Performance Control: Enables or disables the CPU power
management. When set to Enabled, the CPU power management is controlled
by the OS DBPM and the System DBPM (DAPC). By default, the option is set to
Disabled.
• Memory Patrol Scrub: Sets the memory patrol scrub frequency. By default, the
Memory Patrol Scrub option is set to Standard.
• Memory Refresh Rate: Sets the memory refresh rate to either 1x or 2x. By
default, the Memory Refresh Rate option is set to 1x.
• Uncore Frequency: Selects the Processor Uncore Frequency.
Dynamic mode allows the processor to optimize power resources across the
cores and uncore during runtime. The optimization of the uncore frequency to
either save power or optimize performance is influenced by the setting of the
Energy Efficiency Policy.
• Energy Efficient Policy: Enables you to selects the Energy Efficient Policy.
The CPU uses the setting to manipulate the internal behavior of the processor
and determines whether to target higher performance or better power savings.
• Number of Turbo Boot Enabled Cores for Processor 1:
NOTE: If there are two processors installed in the system, you see an entry
for Number of Turbo Boost Enabled Cores for Processor 2.
Controls the number of turbo boost enabled cores for processor 1. By default,
the maximum number of cores is enabled.
• Monitor/Mwait: Enables the Monitor/Mwait instructions in the processor. By
default, the Monitor/Mwait option is set to Enabled for all system profiles,
except Custom.
38
Page 39

Menu Item Description
NOTE: You can only disable this option if C States option in Custom mode
is disabled.
NOTE: When C States is enabled in Custom mode, changing the Monitor/
Mwait setting does not impact system power/performance.
Editing system security
You can use the System Security screen to edit some settings such as setting the system password, setup
password and disabling the power button.
1. Go to System Setup Main Menu, and then click System BIOS.
2. On System BIOS, click System Security.
The System Security screen is displayed.
System security screen settings
The System Security Settings screen details are explained as follows:
Table 21. System security settings
Menu Item Description
Intel AES-NI Improves the speed of applications by performing encryption and
decryption using the Advanced Encryption Standard Instruction Set and is
set to Enabled by default.
System Password Sets the system password. This option is set to Enabled by default and is
read-only if the password jumper is not installed in the system.
Setup Password Sets the setup password. This option is read-only if the password jumper
is not installed in the system.
Password Status Locks the system password. By default, the Password Status option is set
to Unlocked.
TPM Security
TPM Information Changes the operational state of the TPM. By default, the TPM Activation
TPM Status Displays the TPM status.
TPM Command
NOTE: The TPM menu is available only when the TPM module is
installed.
Allows you to control the reporting mode of the Trusted Platform
Module (TPM). By default, the TPM Security option is set to Off. You can
only modify the TPM Status, TPM Activation , and Intel TXT fields if the
TPM Status field is set to either On with Pre-boot Measurements or On
without Pre-boot Measurements.
option is set to No Change.
CAUTION: Clearing the TPM results in the loss of all keys in the
TPM. The loss of TPM keys may affect booting to the operating
system.
Clears all the contents of the TPM. By default, the TPM Clear option is set
to
No.
39
Page 40

Menu Item Description
Intel TXT Enables or disables the Intel Trusted Execution Technology (TXT). To
enable Intel TXT, Virtualization Technology must be enabled and TPM
Security must be Enabled with Pre-boot measurements. By default, the
Intel TXT option is set to Off
Power Button Enables or disables the Power button on the front of the system. By
default, the Power Button option is set to Enabled.
NMI Button Enables or disables the NMI button on the front of the system. By default,
the NMI Button option is set to Disabled.
AC Power Recovery Sets how the system reacts after AC power is restored to the system. By
default, the AC Power Recovery option is set to Last.
AC Power Recovery Delay Sets how the system supports staggering of power up after AC power is
restored to the system. By default, the AC Power Recovery Delay option
is set to Immediate.
User Defined Delay (60s to
240s)
UEFI Variable Access Provides varying degrees of securing UEFI variables. When set to
Secure Boot Enables Secure Boot, where the BIOS authenticates each pre-boot image
Secure Boot Policy When Secure Boot policy is Standard, the BIOS uses the system
Secure Boot Policy
Summary
Sets the User Defined Delay when the User Defined option for AC Power
Recovery Delay is selected.
Standard (the default) UEFI variables are accessible in the Operating
System per the UEFI specification. When set to Controlled, selected UEFI
variables are protected in the environment and new UEFI boot entries are
forced to be at the end of the current boot order.
using the certificates in the Secure Boot Policy. Secure Boot is disabled
by default.
manufacturer’s key and certificates to authenticate pre-boot images.
When Secure Boot policy is Custom, the BIOS uses the user-defined key
and certificates. Secure Boot policy is Standard by default.
Displays the list of certificates and hashes that secure boot uses to
authenticate images.
Secure Boot Custom Policy Settings screen
Secure Boot Custom Policy Settings is displayed only when Secure Boot Policy is set to Custom.
In the System Setup Main Menu, click System BIOS → System Security → Secure Boot Custom Policy
Settings
The Secure Boot Custom Policy Settings screen details are explained as follows:
Table 22. Secure boot custom policy settings
Menu Item Description
Platform Key Imports, exports, deletes, or restores the platform
Key Exchange Key Database Allows you to import, export, delete, or restore
Authorized Signature Database Imports, exports, deletes, or restores entries in the
40
.
key (PK).
entries in the Key Exchange Key (KEK) Database.
Authorized Signature Database (db).
Page 41

Menu Item Description
Forbidden Signature Database Imports, exports, deletes, or restores entries in the
Forbidden Signature Database (dbx).
Editing miscellaneous settings
You can use the Miscellaneous Settings screen to perform some configurations such as updating the
asset tag, and changing the system date and time.
1. Go to System Setup Main Menu, and then click System BIOS.
2. On System BIOS, click Miscellaneous Settings.
The Miscellaneous Settings screen displays.
Miscellaneous settings screen
The Miscellaneous Settings screen details are explained as follows:
Table 23. Miscellaneous settings
Menu Item Description
System Time System Time lets you set the time on the system.
System Date System Date lets you set the date on the system.
Asset Tag Displays the asset tag and lets you to modify it for
security and tracking purposes.
Keyboard NumLock Keyboard NumLock lets you set whether the
system boots with the NumLock enabled or
disabled. By default the Keyboard NumLock is set
to On.
NOTE: This option does not apply to 84-key
keyboards.
F1/F2 Prompt on Error Enables or disables the F1/F2 prompt on error. By
default, F1/F2 Prompt on Error is set to Enabled.
The F1/F2 prompt also includes keyboard errors.
Load Legacy Video Option ROM You can determine whether the system BIOS loads
the legacy video (INT 10H) option ROM from the
video controller. Selecting Enabled in the
operating system does not support UEFI video
output standards. This field is only for UEFI boot
mode. You cannot set this to
Secure Boot mode is enabled.
In-System Characterization This option enables or disables In-System
Characterization. By default, In-System
Characterization is set to Disabled. The two other
options are Enabled and Enabled - No Reboot.
NOTE: The default setting for In-System
Characterization is subject to change in
future BIOS releases.
Enabled if UEFI
41
Page 42

Menu Item Description
When enabled, In-System Characterization (ISC)
runs during POST upon detecting relevant
change(s) in system configuration to optimize
system power and performance. ISC takes about
20 seconds to run, and system reset is required for
ISC results to be applied. The Enabled - No Reboot
option runs ISC and continues without applying
ISC results until the next time system reset occurs.
The Enabled option runs ISC and forces an
immediate system reset so that ISC results can be
applied. It takes the system longer to be ready due
to the forced system reset. When disabled, ISC
does not run.
About Boot Manager
With Boot Manager you can add, delete, and arrange boot options. You can also access System Setup
and boot options without restarting the system.
Entering Boot Manager
The Boot Manager screen allows you to select boot options and diagnostic utilities.
1. Turn on or restart your system.
2. Press F11 when you see the message <F11> = Boot Manager.
If your operating system begins to load before you press F11, allow the system to finish booting, and
then restart your system and try again.
Boot Manager main menu
Table 24. Boot manager main menu
Menu Item Description
Continue Normal Boot The system attempts to boot to devices starting
with the first item in the boot order. If the boot
attempt fails, the system continues with the next
item in the boot order until the boot is successful
or no more boot options are found.
One Shot Boot Menu Takes you to the boot menu where you can select
a one time boot device to boot from.
Launch System Setup Allows you to access the System Setup.
Launch Lifecycle Controller Exits the Boot Manager and invokes the Lifecycle
Controller program.
System Utilities Launches system utilities menu such as system
diagnostics and UEFI shell.
42
Page 43

Changing the boot order
You may have to change the boot order if you want to boot from a USB key or an optical drive. The
instructions given below may vary if you have selected BIOS for Boot Mode.
1. In the System Setup Main Menu, click System BIOS → Boot Settings.
2. Click Boot Option Settings → Boot Sequence.
3. Use the arrow keys to select a boot device, and use the + and - keys to move the device down or up
in the order.
4. Click Exit, click Yes to save the settings on exit.
Choosing the system boot mode
With System Setup, you can to specify the boot mode for installing your operating system:
• BIOS boot mode (the default) is the standard BIOS-level boot interface.
• UEFI boot mode is an enhanced 64-bit boot interface based on Unified Extensible Firmware Interface
(UEFI) specifications that overlays the system BIOS.
You must select the boot mode in the Boot Mode field of the Boot Settings screen of System Setup.
Once you specify the boot mode, the system boots in the specified boot mode and you then proceed to
install your operating system from that mode. Thereafter, you must boot the system in the same boot
mode (BIOS or UEFI) to access the installed operating system. Trying to boot the operating system from
the other boot mode causes the system to halt at startup.
NOTE: Operating systems must be UEFI-compatible to be installed from the UEFI boot mode. DOS
and 32-bit operating systems do not support UEFI and can only be installed from the BIOS boot
mode.
NOTE: For the latest information on supported operating systems, go to dell.com/ossupport.
Assigning a system and setup password
Prerequisites
NOTE: The password jumper enables or disables the System Password and Setup Password
features. For more information about the password jumper settings, see System board connectors.
You can assign a new System Password and Setup Password or change an existing System Password
and Setup Password only when the password jumper setting is enabled and Password Status is
Unlocked.
If the password jumper setting is disabled, the existing System Password and Setup Password are deleted
and you need not provide the system password to boot the system.
About this task
To assign a System Password and Setup Password, follow the steps below:
Steps
1. To enter System Setup, press F2 immediately after a power-on or reboot.
2. From the System Setup Main Menu, select System BIOS and press Enter.
43
Page 44

3. On the System BIOS screen, select System Security and press Enter.
4. On the System Security screen, verify that Password Status is Unlocked.
5. Select System Password, enter your system password, and press Enter or Tab.
Use the following guidelines to assign the system password:
• A password can have up to 32 characters.
• The password can contain the numbers 0 through 9.
• Only the following special characters are allowed: space, (”), (+), (,), (-), (.), (/), (;), ([), (\), (]), (`).
A message prompts you to re-enter the system password.
6. Re-enter the system password, and click OK.
7. Select Setup Password, enter your system password and press Enter or Tab.
A message prompts you to re-enter the setup password.
8. Re-enter the setup password, and click OK.
9. Press Esc to return to the System BIOS screen. Press Esc again.
A message prompts you to save the changes.
NOTE: Password protection does not take effect until the system reboots.
Deleting or changing an existing system password and setup password
Prerequisites
Ensure that the Password jumper is set to enabled and the Password Status is Unlocked before
attempting to delete or change the existing System and/or Setup password. You cannot delete or change
an existing System or Setup password if the Password Status is Locked.
Steps
1. To enter System Setup, press F2 immediately after a power on or restart.
2. From the System Setup Main Menu, select System BIOS and press Enter.
The System BIOS screen is displayed.
3. On the System BIOS Screen, select System Security and press Enter.
The System Security screen is displayed.
4. On the System Security screen, verify that Password Status is Unlocked.
5. Select System Password, alter or delete the existing system password and press Enter or Tab.
6. Select Setup Password, alter or delete the existing setup password and press Enter or Tab.
If you change the System and Setup password a message prompts you to re-enter the new
password. If you delete the System and Setup password, a message prompts you to confirm the
deletion.
7. Press Esc to return to the System BIOS screen. Press Esc again, and a message prompts you to save
the changes.
44
Page 45

Installing and removing system components
Safety instructions
WARNING: Whenever you need to lift the system, get others to assist you. To avoid injury, do not
attempt to lift the system by yourself.
WARNING: Opening or removing the system cover when the system is on may expose you to a
risk of electric shock.
CAUTION: Do not operate the system without the cover for a duration exceeding five minutes.
NOTE: Operating the system without the system cover can result in component damage.
CAUTION: Many repairs may only be done by a certified service technician. You should only
perform troubleshooting and simple repairs as authorized in your product documentation, or as
directed by the online or telephone service and support team. Damage due to servicing that is
not authorized by Dell is not covered by your warranty. Read and follow the safety instructions
that came with the product.
4
NOTE: Dell recommends that you always use a static mat and static strap while working on
components inside the system.
NOTE: To ensure proper operation and cooling, you must populate all bays in the system at all
times with either a module or with a blank.
Before working inside your system
1. Turn off the system, including any attached peripherals.
2. Disconnect the system from the electrical outlet and disconnect the peripherals.
3. If installed, remove the front bezel.
For more information, see Removing the front bezel.
4. Remove the system cover.
For more information, see Removing the system cover.
After working inside your system
1. Install the system cover.
For more information, see Installing the system cover.
2. Install the optional bezel.
45
Page 46

For more information, see Installing the front bezel.
3. Reconnect the system to its electrical outlet and peripherals.
4. Turn the system on, including any attached peripherals.
Recommended tools
You need the following tools to perform the removal and installation procedures:
• Key to the bezel lock. This is only required when you have a bezel.
• #2 Phillips screwdriver
• #1 Phillips screwdriver
• T6, T8, T10, and T15 Torx screwdrivers
The following tools are required for assembling cables for a DC power supply unit (PSU):
• AMP 90871-1 hand-crimping tool or equivalent
• Tyco Electronics 58433-3 or equivalent
• Wire-stripper pliers capable of removing insulation from size 10 AWG solid or stranded, insulated
copper wire
NOTE: Use alpha wire part number 3080 or equivalent (65/30 stranding).
Front bezel
Removing the front bezel
1. Unlock the bezel lock at the left end of the bezel.
2. Lift the release latch next to the bezel lock.
3. Pull the left end of the bezel, unhook the right end and remove the bezel.
46
Page 47

Figure 10. Removing and installing the front bezel
Installing the front bezel
1. Hook the right end of the bezel onto the chassis.
2. Fit the free end of the bezel onto the system.
3. Secure the bezel with the keylock.
Related video
http://www.Dell.com/XCSeries/XC730xd/Bezel
Removing the system cover
Prerequisites
1. Ensure that you read the Safety instructions.
2. Turn off the system, including any attached peripherals.
3. Disconnect the system from the electrical outlet and peripherals.
4. Remove the optional bezel. For more information see Removing the front bezel.
Steps
1. Rotate the latch release lock counter clockwise to the unlocked position.
2. Lift the latch and rotate the latch toward the back of the system.
47
Page 48

The system cover slides back and the tabs on the system cover disengages from the slots on the
chassis.
NOTE: The position of the latch may vary depending on the configuration of your system.
3. Hold the cover on both sides, and lift the cover away from the system.
Figure 11. Removing and installing the system cover
1. system cover 2. latch
3. latch release lock
Related videos
http://www.Dell.com/XCSeries/XC730xd/Cover
Installing the system cover
Prerequisites
Ensure that you read the Safety instructions.
48
Page 49

Steps
1. Align the slots of the system cover with the tabs on the chassis.
2. Press the cover release latch, and push the cover toward the front of the chassis until the latch locks
into place.
3. Turn the latch release lock clockwise to the locked position.
4. Install the optional bezel.
5. Reconnect the system to its electrical outlet and turn the system on, including any attached
peripherals.
Inside the system
CAUTION: Many repairs may only be done by a certified service technician. You should only
perform troubleshooting and simple repairs as authorized in your product documentation, or as
directed by the online or telephone service and support team. Damage due to servicing that is
not authorized by Dell is not covered by your warranty. Read and follow the safety instructions
that came with the product.
49
Page 50

Figure 12. Inside the system—Dell XC730xd
1. cooling-fan in the cooling-fan assembly (6) 2. processor (2)
3. DIMMs (24) 4. internal USB port
5. hard-drive backplane (back) 6. vFlash media slot
7. hard drive (2) (back) 8. power supply unit (2)
9. expansion-card riser 3 10. network daughter card
11. expansion-card riser 2 12. expansion-card riser 1
13. hard-drive backplane
Cooling shroud
50
Page 51

Removing the cooling shroud
Prerequisites
CAUTION: Many repairs may only be done by a certified service technician. You should only
perform troubleshooting and simple repairs as authorized in your product documentation, or as
directed by the online or telephone service and support team. Damage due to servicing that is
not authorized by Dell is not covered by your warranty. Read and follow the safety instructions
that came with the product.
1. Ensure that you read the Safety instructions.
2. Follow the procedure listed in Before working inside your system.
CAUTION: Never operate your system with the cooling shroud removed. The system may get
overheated quickly, resulting in shutdown of the system and loss of data.
Steps
Hold the shroud and lift it away from the system.
Figure 13. Removing and installing the cooling shroud
1. cooling shroud 2. touch point (2)
Next steps
1. Replace the cooling shroud. See Installing the cooling shroud.
2. Follow the procedure listed in After working inside your system.
Installing the cooling shroud
Prerequisites
CAUTION: Many repairs may only be done by a certified service technician. You should only
perform troubleshooting and simple repairs as authorized in your product documentation, or as
directed by the online or telephone service and support team. Damage due to servicing that is
not authorized by Dell is not covered by your warranty. Read and follow the safety instructions
that came with the product.
51
Page 52

1. Ensure that you read the Safety instructions.
2. Route the cables inside the system along the chassis wall and secure the cables using the cable-
securing bracket.
Steps
1. Align the tabs on the cooling shroud with the securing slots on the chassis.
2. Lower the cooling shroud into the chassis until it is firmly seated.
Next steps
1. Follow the procedure listed in After working inside your system.
Cooling fans
Your system supports six hot-swappable cooling fans.
NOTE: In the event of a problem with a particular fan, the fan number is referenced by the system
management software, allowing you to easily identify and replace the proper fan by noting the fan
numbers on the cooling-fan assembly.
Removing a cooling fan
Prerequisites
1. Ensure that you read the Safety instructions.
2. Follow the procedure listed in Before working inside your system.
CAUTION: Many repairs may only be done by a certified service technician. You should only
perform troubleshooting and simple repairs as authorized in your product documentation, or as
directed by the online or telephone service and support team. Damage due to servicing that is
not authorized by Dell is not covered by your warranty. Read and follow the safety instructions
that came with the product.
CAUTION: The cooling fans are hot-swappable. To maintain proper cooling while the system is
on, replace only one fan at a time.
NOTE: The procedure for removing each fan is identical.
Steps
Press the fan release tab and lift the cooling fan out of the cooling-fan assembly.
52
Page 53

Figure 14. Removing and installing a cooling fan
1. cooling-fan assembly 2. cooling-fan connector (6)
3. fan release tab (6) 4. cooling fan (6)
5. cooling-fan connector on system board
(6)
Next steps
1. Replace the cooling fan. See Installing a cooling fan
2. Follow the procedure listed in After working inside your system.
Related videos
http://www.Dell.com/XCSeries/XC730xd/Fans
Installing a cooling fan
Prerequisites
1. Ensure that you read the Safety instructions.
2. Follow the procedure listed in Before working inside your system.
53
Page 54

CAUTION: Many repairs may only be done by a certified service technician. You should only
perform troubleshooting and simple repairs as authorized in your product documentation, or as
directed by the online or telephone service and support team. Damage due to servicing that is
not authorized by Dell is not covered by your warranty. Read and follow the safety instructions
that came with the product.
Steps
1. Align the plug at the base of the cooling fan with the connector on the system board.
2. Slide the cooling fan into the securing slots until the tabs lock into place.
Next steps
Follow the procedure listed in After working inside your system.
Cooling-fan assembly
Removing the cooling-fan assembly
Prerequisites
1. Ensure that you read the Safety instructions.
2. Follow the procedure listed in Before working inside your system.
CAUTION: Many repairs may only be done by a certified service technician. You should only
perform troubleshooting and simple repairs as authorized in your product documentation, or as
directed by the online or telephone service and support team. Damage due to servicing that is
not authorized by Dell is not covered by your warranty. Read and follow the safety instructions
that came with the product.
Steps
1. Unlock the cooling-fan assembly from the chassis by lifting the release levers upward.
2. Lift the cooling-fan assembly out of the chassis.
54
Page 55
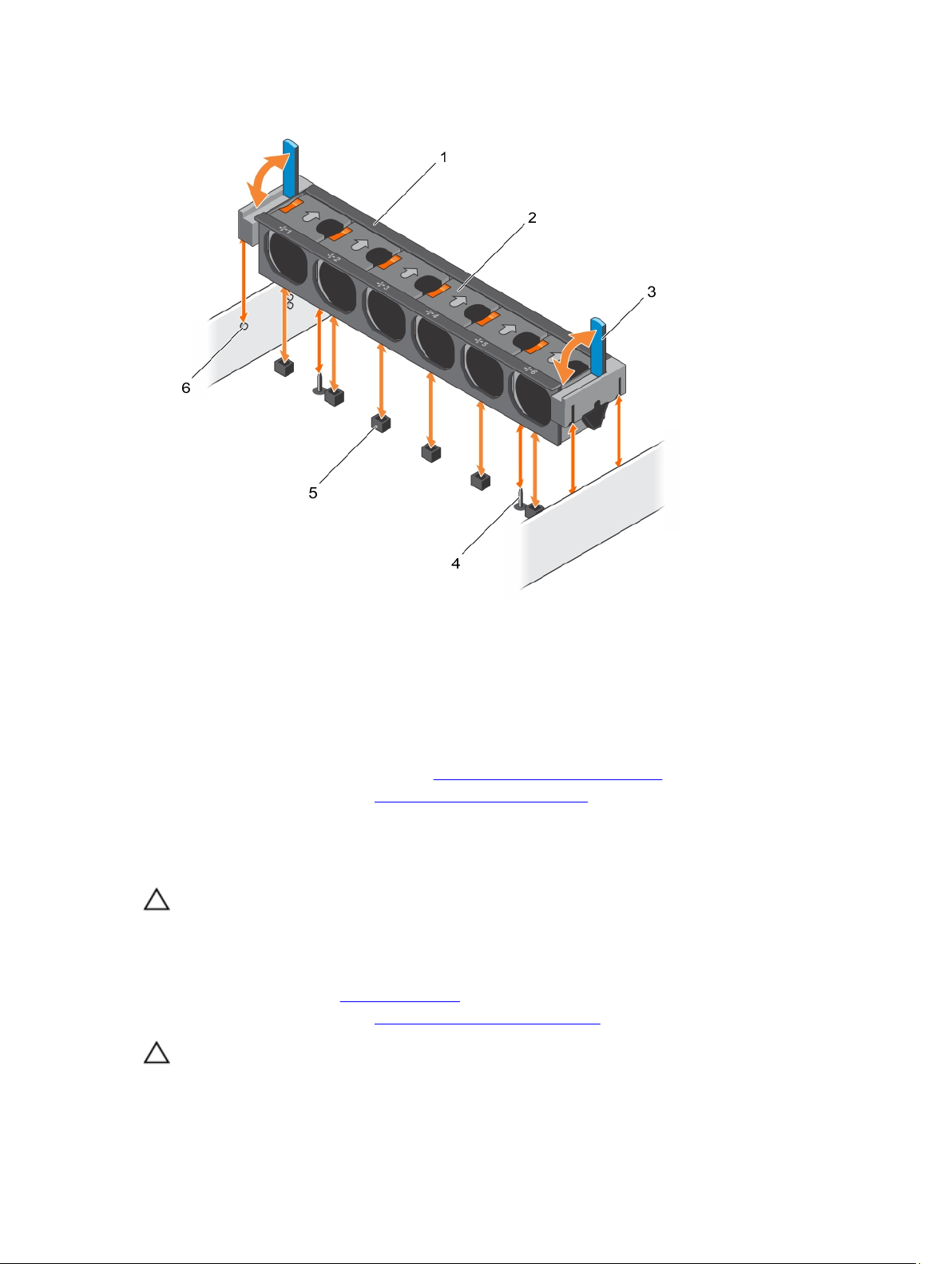
Figure 15. Removing and installing the cooling-fan assembly
1. cooling-fan assembly 2. cooling fan (6)
3. release lever (2) 4. guide pin on the system board (2)
5. cooling-fan connector (6) 6. guide pin on the chassis (6)
Next steps
1. Replace the cooling-fan assembly. See Installing the cooling-fan assembly
2. Follow the procedure listed in After working inside your system.
Installing the cooling-fan assembly
Prerequisites
CAUTION: Many repairs may only be done by a certified service technician. You should only
perform troubleshooting and simple repairs as authorized in your product documentation, or as
directed by the online or telephone service and support team. Damage due to servicing that is
not authorized by Dell is not covered by your warranty. Read and follow the safety instructions
that came with the product.
1. Ensure that you read the Safety instructions.
2. Follow the procedure listed in Before working inside your system.
CAUTION: Ensure that the cables are correctly installed and retained by the cable retention
bracket before installing the cooling-fan assembly. Incorrectly installed cables may get damaged.
55
Page 56

Steps
1. Align the cooling-fan assembly slots with the guide pins on the chassis.
2. Slide the cooling-fan assembly into the chassis.
3. Lock the cooling-fan assembly into the chassis by lowering the release levers until firmly seated.
Next steps
Follow the procedure listed in After working inside your system.
System memory
Your system supports DDR4 registered DIMMs (RDIMMs), and load reduced DIMMs (LRDIMMs).
NOTE: MT/s indicates DIMM speed in MegaTransfers per second.
Memory bus operating frequency can be 1333 MT/s, 1600 MT/s, 1866 MT/s, or 2133 MT/s depending on
the following factors:
• DIMM type (RDIMM or LRDIMM)
• Number of DIMMs populated per channel
• System profile selected (for example, Performance Optimized, Custom, or Dense Configuration
Optimized)
• Maximum supported DIMM frequency of the processors
The system contains 24 memory sockets split into two sets of 12 sockets, one set per processor. Each 12socket set is organized into four channels. In each channel, the release levers of the first socket are
marked white, the second socket black, and the third socket green.
NOTE: DIMMs in sockets A1 to A12 are assigned to processor 1 and DIMMs in sockets B1 to B12 are
assigned to processor 2.
56
Page 57

Figure 16. Memory socket locations
57
Page 58

Figure 17. Memory socket locations
Memory channels are organized as follows:
Processor 1 channel 0: slots A1, A5, and A9
channel 1: slots A2, A6, and A10
channel 2: slots A3, A7, and A11
channel 3: slots A4, A8, and A12
Processor 2 channel 0: slots B1, B5, and B9
channel 1: slots B2, B6, and B10
channel 2: slots B3, B7, and B11
58
Page 59

channel 3: slots B4, B8, and B12
The following table shows the memory populations and operating frequencies for the supported
configurations.
Table 25. The memory populations and operating frequencies for the supported configurations.
DIMM Type DIMMs Populated/
Channel
RDIMM 1 2133, 1866, 1600, 1333 Dual rank or single rank
2 2133, 1866, 1600, 1333 Dual rank or single rank
3 1866, 1600, 1333 Dual rank or single rank
LRDIMM 1 2133, 1866, 1600, 1333 Quad rank
2 2133, 1866, 1600, 1333 Quad rank
3 1866, 1600, 1333 Quad rank
Operating Frequency (in
MT/s)
1.2 V
Maximum DIMM Rank/Channel
General memory module installation guidelines
This system supports Flexible Memory Configuration, you can configure and run the system in any valid
chipset architectural configuration. The following are the recommended guidelines for installing memory
modules:
• RDIMMs and LRDIMMs must not be mixed.
• x4 and x8 DRAM based DIMMs can be mixed..
• Up to three dual- or single-rank RDIMMs can be populated per channel.
• Up to three LRDIMMs can be populated per channel regardless of rank count.
• Populate DIMM sockets only if a processor is installed. For single-processor systems, sockets A1 to
A12 are available. For dual-processor systems, sockets A1 to A12 and sockets B1 to B12 are available.
• Populate all sockets with white release tabs first, then black, and then green.
• Populate the sockets by highest rank count in the following order — first in sockets with white release
levers, then black, and then green. For example, if you want to mix single-rank and dual-rank DIMMs,
populate dual-rank DIMMs in the sockets with white release tabs and single-rank DIMMs in the
sockets with black release tabs.
• When mixing memory modules with different capacities, populate the sockets with memory modules
with highest capacity first. For example, if you want to mix 4 GB and 8 GB DIMMs, populate 8 GB
DIMMs in the sockets with white release tabs and 4 GB DIMMs in the sockets with black release tabs.
• In a dual-processor configuration, the memory configuration for each processor should be identical.
For example, if you populate socket A1 for processor 1, then populate socket B1 for processor 2, and
so on.
• Memory modules of different capacities can be mixed provided other memory population rules are
followed (for example, 4 GB and 8 GB memory modules can be mixed).
• Mixing of more than two DIMM capacities in a system is not supported.
• Populate four DIMMs per processor (one DIMM per channel) at a time to maximize performance.
Sample memory configurations
The following tables show sample memory configurations for one and two processor configurations that
follow the appropriate memory guidelines.
59
Page 60

NOTE: 1R, 2R, and 4R in the following tables indicate single-, dual-, and quad-rank DIMMs
respectively.
Table 26. Memory configurations—two processors
System
capacity (in
GB)
64 16 4
128 16 8
256 16 16
384 16 24
512 32 16
768 32 24
DIMM size (in
GB)
Number of
DIMMs
DIMM rank,
organization, and
frequency
2R, x4, 2133 MT/s,
2R, x4, 1866 MT/s,
2R, x4, 2133 MT/s,
2R, x4, 1866 MT/s,
2R, x4, 2133 MT/s,
2R, x4, 1866 MT/s,
2R, x4, 2133 MT/s,
2R, x4, 1866 MT/s,
LRDIMM, 4R, x4, 2133
MT/s
LRDIMM, 4R, x4, 1866
MT/s
LRDIMM, 4R, x4, 1600
MT/s
DIMM slot population
A1, A2, B1, B2
A1, A2, A3, A4, B1, B2, B3, B4
A1, A2, A3, A4, A5, A6, A7, A8,
B1, B2, B3, B4, B5, B6, B7, B8
A1, A2, A3, A4, A5, A6, A7, A8,
A9, A10, A11, A12, B1, B2, B3, B4,
B5, B6, B7, B8, B9, B10, B11, B12
A1, A2, A3, A4, A5, A6, A7, A8,
B1, B2, B3, B4, B5, B6, B7, B8
A1, A2, A3, A4, A5, A6, A7, A8,
A9, A10, A11, A12, B1, B2, B3, B4,
B5, B6, B7, B8, B9, B10, B11, B12
Removing memory modules
Prerequisites
CAUTION: Many repairs may only be done by a certified service technician. You should only
perform troubleshooting and simple repairs as authorized in your product documentation, or as
directed by the online or telephone service and support team. Damage due to servicing that is
not authorized by Dell is not covered by your warranty. Read and follow the safety instructions
that came with the product.
1. Ensure that you read the Safety instructions.
2. Follow the procedure listed in Before working inside your system.
3. Remove the cooling shroud.
4. If installed, remove the cooling-fan assembly. For more information, see Removing the cooling-fan
assembly
WARNING: The memory modules are hot to touch for some time after the system has been
powered down. Allow the memory modules to cool before handling them. Handle the memory
modules by the card edges and avoid touching the components or metallic contacts on the
memory module.
60
Page 61

CAUTION: To ensure proper system cooling, you must install memory-module blanks in any
memory socket that is not occupied. Remove memory-module blanks only if you intend to install
memory modules in those sockets.
Steps
1. Locate the appropriate memory module socket.
CAUTION: Handle each memory module only by the card edges, making sure not to touch
the middle of the memory module or metallic contacts.
2. To release the memory module from the socket, simultaneously press the ejectors on both ends of
the memory-module socket.
Figure 18. Removing and installing a memory module
1. memory-module 2. memory-module socket
3. memory module socket ejector (2)
Related videos
http://www.Dell.com/XCSeries/XC730xd/DIMMS
61
Page 62

Installing memory modules
Prerequisites
CAUTION: Many repairs may only be done by a certified service technician. You should only
perform troubleshooting and simple repairs as authorized in your product documentation, or as
directed by the online or telephone service and support team. Damage due to servicing that is
not authorized by Dell is not covered by your warranty. Read and follow the safety instructions
that came with the product.
1. Ensure that you read the Safety instructions.
2. Follow the procedure listed in Before working inside your system.
3. Remove the cooling shroud.
4. Removing the cooling-fan assembly.
WARNING: The memory modules are hot to touch for some time after the system has been
powered down. Allow the memory modules to cool before handling them. Handle the memory
modules by the card edges and avoid touching the components or metallic contacts on the
memory module.
CAUTION: To ensure proper system cooling, memory-module blanks must be installed in any
memory socket that is not occupied. Remove memory-module blanks only if you intend to install
memory modules in those sockets.
Steps
1. Locate the appropriate memory-module socket.
CAUTION: Handle each memory module only by the card edges, making sure not to touch
the middle of the memory module or metallic contacts.
2. If a memory module or a memory-module blank is installed in the socket, remove it.
NOTE: Retain the removed memory-module blanks for future use.
CAUTION: To prevent damage to the memory module or the memory-module socket during
installation, do not bend or flex the memory module; insert both ends of the memory module
simultaneously.
3. Align the edge connector of the memory module with the alignment key of the memory module
socket, and insert the memory module in the socket.
NOTE: The memory-module socket has an alignment key that allows you to install the memory
module in the socket in only one orientation.
CAUTION: Do not apply pressure at the center of the memory module; apply pressure at both
ends of the memory module evenly.
4. Press the memory module with your thumbs until the socket levers firmly click into place.
62
Page 63

Figure 19. Installing the memory module
1. memory module 2. alignment key
3. memory-module socket ejector (2)
When the memory module is properly seated in the socket, the levers on the memory module socket
align with the levers on the other sockets that have memory modules installed.
5. Repeat steps 1 to 4 of this procedure to install the remaining memory modules.
Next steps
1. Install the cooling shroud.
2. Follow the procedure listed in After working inside your system.
3. Press F2 to enter System Setup, and check the System Memory setting.
The system should have already changed the value to reflect the installed memory.
4. If the value is incorrect, one or more of the memory modules may not be installed properly. Repeat
step 4 through step 5 of this procedure, checking to ensure that the memory modules are firmly
seated in their sockets.
5. Run the system memory test in the system diagnostics.
SATADOM
A SATADOM is a disk-on-module (DOM) form factor with an incorporated standard SATA data
connection. By default, the SATADOM comes with a power cable installed and is set in a Read/Write
position.
The SATADOM uses an onboard SATA controller and does not require an additional controller.
With Nutanix, you can locate the boot device on a separate controller from the data drives, which
improves system disk performance.
63
Page 64

Removing the SATADOM
Prerequisites
1. Ensure that you read the Safety instructions.
2. Follow the procedure listed in Before working inside your system.
3. Remove the cooling shroud prior to removing SATADOM. For information about removing the
cooling shroud, see Removing the cooling shroud
.
CAUTION: Many repairs may only be done by a certified service technician. You should only
perform troubleshooting and simple repairs as authorized in your product documentation, or as
directed by the online or telephone service and support team. Damage due to servicing that is
not authorized by Dell is not covered by your warranty. Read and follow the safety instructions
that came with the product.
Steps
1. Unplug the power cable from the SATADOM Tape Backup Unit (TBU) power connector.
2. Press the lock release on the SATADOM and pull it up and away from the system.
NOTE: After removing the SATADOM, place it in an anti-static container for reuse, return, or
temporary storage.
NOTE: Dell recommends that you do not modify the SATADOM Read/Write default setting.
64
Page 65

Figure 20. Removing and installing SATADOM
1. SATADOM
3. power cable 4. SATADOM TBU power connector
Next steps
Follow the procedure listed in After working inside your system.
2. SATA connector
Installing the SATADOM
Prerequisites
1. Ensure that you read the Safety instructions.
2. Follow the procedure listed in Before working inside your system.
3. Remove the cooling shroud prior to installing SATADOM. For information about removing the
cooling shroud, see Removing the cooling shroud
.
CAUTION: Many repairs may only be done by a certified service technician. You should only
perform troubleshooting and simple repairs as authorized in your product documentation, or as
directed by the online or telephone service and support team. Damage due to servicing that is
not authorized by Dell is not covered by your warranty. Read and follow the safety instructions
that came with the product.
NOTE: Dell recommends that you do not modify the SATADOM Read/Write default setting.
65
Page 66

Steps
1. Press the lock release on the SATADOM and plug the SATADOM into the preferred SATADOM
connector on the system board.
NOTE: The preferred SATADOM connector is SATA0 and is indicated in blue. You can also use
SATA1 connector that is indicated in black.
2. Plug the power cable into the SATADOM TBU power connector on the system board.
Next steps
Follow the procedure listed in After working inside your system.
Heat sinks and processors
Use the following procedure when:
• Installing an additional processor
• Replacing a processor
NOTE: To ensure proper system cooling, you must install a processor blank in any empty processor
socket.
Removing a processor
Prerequisites
CAUTION: Many repairs may only be done by a certified service technician. You should only
perform troubleshooting and simple repairs as authorized in your product documentation, or as
directed by the online or telephone service and support team. Damage due to servicing that is
not authorized by Dell is not covered by your warranty. Read and follow the safety instructions
that came with the product.
NOTE: To ensure proper system cooling, you must install a processor blank in any empty processor
socket.
1. Ensure that you read the Safety instructions.
2. Keep the #2 Phillips screwdriver handy.
3. If you are upgrading your system, download the latest system BIOS version from dell.com/support
and follow the instructions included in the compressed download file to install the update on your
system.
NOTE: You can update the system BIOS using the Lifecycle Controller.
4. Follow the procedure listed in Before working inside your system.
5. If installed, remove the cooling fan assembly.
6. If installed, remove the full-length PCIe cards.
7. Remove the cooling shroud.
WARNING: The heat sink and processor are hot to the touch for some time after the system has
been powered down. Allow the heat sink and processor to cool before handling them.
CAUTION: Never remove the heat sink from a processor unless you intend to remove the
processor. The heat sink is necessary to maintain proper thermal conditions.
Steps
1. To remove the heat sink:
66
Page 67

a. Loosen one of the screws that secure the heat sink to the system board.
Wait 30 seconds for the heat sink to loosen from the processor.
b. Remove the screw diagonally opposite the screw you first removed.
c. Repeat the procedure for the remaining two screws.
d. Remove the heat sink.
Figure 21. Removing and installing a processor
1. heat sink 2. captive screws (4)
3. processor socket 4. slots (4)
67
Page 68

Figure 22. Removing and installing a processor heat sink
1. captive screw (4) 2. heat sink
3. processor socket 4. slot (4)
68
Figure 23. Removing and installing a processor heat sink
1. captive screw (4) 2. heat sink
3. processor socket 4. slot (4)
Page 69
CAUTION: The processor is held in its socket under strong pressure. Be aware that the
release lever can spring up suddenly if not firmly grasped.
Figure 24. Processor shield
1. close first socket release lever 2. lock icon
3. processor 4. open first socket release lever
5. unlock icon
2. To remove the processor:
a. Release the open first socket-lever near the unlock icon by pushing the lever down and out
from under the tab.
b. Similarly, release the close first socket-release lever near the lock icon by pushing the lever
down and out from under the tab. Lift the lever 90 degrees upward.
c. Lower the open first socket-release lever to lift the processor shield.
69
Page 70

Figure 25. Removing and installing a processor
1. close first socket-release lever 2. pin-1 indicator of processor
3. processor 4. slot (4)
5. processor shield 6. open first socket-release lever
7. socket 8. socket keys (4)
d. Hold the tab on the processor shield and lift the processor shield until the open first socket-
release lever lifts up.
CAUTION: The socket pins are fragile and can be permanently damaged. Be careful not to
bend the pins in the socket when removing the processor out of the socket.
e. Lift the processor out of the socket and leave the open first socket-release lever up.
NOTE: If you are permanently removing the processor, you must install a socket protective
cap in the vacant socket to protect the socket pins and keep the socket free of dust.
NOTE: After removing the processor, place it in an anti-static container for reuse, return, or
temporary storage. Do not touch the bottom of the processor. Touch only the side edges of
the processor.
Next steps
1. Replace the heat sinks and processors. See Installing a processor.
2. Follow the procedure listed in After working inside your system.
70
Page 71

Installing a processor
Prerequisites
CAUTION: Many repairs may only be done by a certified service technician. You should only
perform troubleshooting and simple repairs as authorized in your product documentation, or as
directed by the online or telephone service and support team. Damage due to servicing that is
not authorized by Dell is not covered by your warranty. Read and follow the safety instructions
that came with the product.
1. Ensure that you read the Safety instructions.
2. Keep the #2 Phillips screwdriver handy.
3. If you are upgrading your system, download the latest system BIOS version from dell.com/support
and follow the instructions included in the compressed download file to install the update on your
system.
NOTE: You can update the system BIOS using the Lifecycle Controller.
4. Follow the procedure listed in Before working inside your system.
5. If installed, remove the cooling fan assembly.
6. If installed, remove the full-length PCIe card.
7. Remove the cooling shroud.
WARNING: The heat sink and processor are hot to the touch for some time after the system
has been powered down. Allow the heat sink and processor to cool before handling them.
CAUTION: Never remove the heat sink from a processor unless you intend to remove the
processor. The heat sink is necessary to maintain proper thermal conditions.
NOTE: If you are installing a single processor, it must be installed in socket CPU1.
Steps
1. Remove the heat sink.
2. Remove the heat sink.
3. Unpack the new processor.
If the processor has previously been used in a system, remove any remaining thermal grease from
the processor using a lint-free cloth.
4. Locate the processor socket.
5. If applicable, remove the socket protective cap.
6. Release the open first socket-release lever near the unlock icon by pushing the lever down and
out from under the tab.
7. Similarly, release the close first socket-release lever near the lock icon by pushing the lever down
and out from under the tab. Lift the lever 90 degrees upward.
8. Hold the tab near the lock symbol on the processor shield and lift it up and out of the way.
9. To install the processor in the socket:
CAUTION: Positioning the processor incorrectly can permanently damage the system board
or the processor. Be careful not to bend the pins in the socket.
CAUTION: While removing or reinstalling the processor, wipe your hands of any
contaminants. Contaminants on the processor pins such as thermal grease or oil can damage
the processor.
71
Page 72

a. Align the processor with the socket keys.
CAUTION: Do not use force to seat the processor. When the processor is positioned
correctly, it engages easily into the socket.
b. Align the pin-1 indicator of the processor with the triangle on the socket.
c. Place the processor on the socket such that the slots on the processor align with the socket keys.
CAUTION: Do not use force to seat the processor. When the processor is positioned
correctly, it engages easily into the socket.
d. Close the processor shield.
e. Lower the close first socket-release lever near the lock icon and push it under the tab to lock
it..
f.
Similarly, lower the open first socket-release lever near the unlock icon and push it under the
tab to lock it.
10. To install the heat sink:
a. If applicable, remove the existing thermal grease from the heat sink using a clean lint-free cloth.
b. Apply thermal grease on the top of the processor. Use the thermal-grease syringe included with
your processor kit to apply the grease in a thin spiral on the top of the processor as shown in the
figure.
CAUTION: Applying too much thermal grease can result in excess grease coming in
contact with and contaminating the processor socket.
72
Figure 26. Applying thermal grease on the top of the processor
1. processor 2. thermal grease
Page 73

3. thermal-grease syringe
NOTE: The thermal-grease is intended for one-time use only. Dispose of the syringe after
you use it.
c. Place the heat sink onto the processor.
d. Tighten the four screws to secure the heat sink to the system board.
NOTE: Tighten the screws diagonally opposite to each other. Do not over-tighten the heat
sink retention screws when installing the heat sink. To prevent over-tightening, tighten the
retention screw until resistance is felt, and stop once the screw is seated. The screw tension
should be no more than 6 in-lb (6.9 kg-cm).
Next steps
1. Install the cooling shroud.
2. If applicable, install the PCIe card.
3. If applicable, install the cooling fan assembly.
4. Follow the procedure listed in After working inside your system.
5. While booting, press F2 to enter the System Setup and check that the processor information
matches the new system configuration.
6. Run the system diagnostics to verify that the new processor operates correctly.
PCIe card holder
Removing the PCIe card holder
Prerequisites
1. Ensure that you read the Safety instructions.
2. Follow the procedure listed in Before working inside your system.
3. If installed, remove the full-length PCIe card.
CAUTION: Many repairs may only be done by a certified service technician. You should only
perform troubleshooting and simple repairs as authorized in your product documentation, or as
directed by the online or telephone service and support team. Damage due to servicing that is
not authorized by Dell is not covered by your warranty. Read and follow the safety instructions
that came with the product.
CAUTION: Do not use your system without the PCIe card holder installed. The PCIe card holder is
necessary to ensure proper system cooling.
Steps
1. Press the release tab and slide the card holder toward the back of the chassis to release the PCIe
card holder from the chassis.
2. Lift the PCIe card holder out of the chassis.
NOTE: To ensure proper system cooling, you must replace the PCIe card holder.
73
Page 74

Figure 27. Removing and installing the PCIe card holder
1. PCIe card holder 2. release tab
Next steps
1. Replace the PCIe card holder. See Installing the PCIe card holder.
2. Follow the procedure listed in After working inside your system.
Installing the PCIe card holder
Prerequisites
1. Ensure that you read the Safety instructions.
2. Follow the procedure listed in Before working inside your system.
CAUTION: Many repairs may only be done by a certified service technician. You should only
perform troubleshooting and simple repairs as authorized in your product documentation, or as
directed by the online or telephone service and support team. Damage due to servicing that is
not authorized by Dell is not covered by your warranty. Read and follow the safety instructions
that came with the product.
CAUTION: Do not use your system without the PCIe card holder installed. The PCIe card holder is
necessary to ensure proper system cooling.
Steps
1. Align the PCIe card holder with the notches and tabs on the power supply unit cage.
2. Press the release tab and slide PCIe card holder toward the front of the chassis until firmly seated.
Next steps
1. If applicable, replace the full-length PCIe card.
2. Follow the procedure listed in After working inside your system.
74
Page 75

Opening and closing the PCIe card holder latch
Prerequisites
1. Ensure that you read the Safety instructions.
2. Follow the procedure listed in Before working inside your system.
CAUTION: Many repairs may only be done by a certified service technician. You should only
perform troubleshooting and simple repairs as authorized in your product documentation, or as
directed by the online or telephone service and support team. Damage due to servicing that is
not authorized by Dell is not covered by your warranty. Read and follow the safety instructions
that came with the product.
Steps
1. To open the PCIe card holder latch, press the release tab.
2. To close the PCIe card holder latch, rotate the latch clockwise until it locks.
NOTE: Before installing a full-length PCIe card, the PCIe card holder latch must be closed.
When the full-length PCIe card is installed, open the PCIe card holder latch. Before removing
the full-length PCIe card, you must close the PCIe card holder latch.
Figure 28. Opening and closing the PCIe card holder latch
1. PCIe card holder 2. release tab
3. PCIe card holder
Next steps
Follow the procedure listed in After working inside your system.
75
Page 76

Cable retention bracket
Removing the cable retention bracket
Prerequisites
1. Ensure that you read the Safety instructions.
2. Follow the procedure listed in Before working inside your system.
3. Remove the cooling shroud.
4. Remove the PCIe card holder.
5. Remove all cables routed through the cable retention bracket.
CAUTION: Many repairs may only be done by a certified service technician. You should only
perform troubleshooting and simple repairs as authorized in your product documentation, or as
directed by the online or telephone service and support team. Damage due to servicing that is
not authorized by Dell is not covered by your warranty. Read and follow the safety instructions
that came with the product.
Steps
1. Pull the tab to release it from the notch and slide the cable retention bracket toward the front of the
chassis to release it from the chassis.
2. Lift the cable retention bracket out of the chassis.
Figure 29. Removing and installing the cable retention bracket
1. alignment pin (2) 2. tab
3. cable retention bracket
76
Page 77

Next steps
1. Replace the cable retention bracket. See Installing the cable retention bracket
2. Follow the procedure listed in After working inside your system.
Related video
http://www.Dell.com/XCSeries/XC730xd/cabling
Installing the cable retention bracket
Prerequisites
1. Ensure that you read the Safety instructions.
2. Follow the procedure listed in Before working inside your system.
3. Remove the cooling shroud.
4. Remove the PCIe card holder.
CAUTION: Many repairs may only be done by a certified service technician. You should only
perform troubleshooting and simple repairs as authorized in your product documentation, or as
directed by the online or telephone service and support team. Damage due to servicing that is
not authorized by Dell is not covered by your warranty. Read and follow the safety instructions
that came with the product.
Steps
1. Align the cable retention bracket with the alignment pins on the chassis.
2. Slide the cable retention bracket along the chassis wall until the tab clicks and locks the slots.
3. Place all cables to be routed in the cable retention bracket.
Next steps
1. Install the PCIe card holder.
2. Install the cooling shroud.
3. Follow the procedure listed in After working inside your system.
Integrated storage controller card
Your system includes a dedicated expansion-card slot on the system board for an integrated controller
card. The integrated storage controller card provides the integrated storage subsystem for your system’s
internal hard drives. The controller supports SAS and SATA hard drives as supported by the version of the
storage controller included with your system.
Removing the integrated storage controller card
Prerequisites
1. Ensure that you read the Safety instructions.
2. Follow the procedure listed in Before working inside your system.
77
Page 78

3. Remove the cooling shroud.
4. Remove the expansion-card riser 1.
5. Keep the #2 Phillips screwdriver handy.
CAUTION: Many repairs may only be done by a certified service technician. You should only
perform troubleshooting and simple repairs as authorized in your product documentation, or as
directed by the online or telephone service and support team. Damage due to servicing that is
not authorized by Dell is not covered by your warranty. Read and follow the safety instructions
that came with the product.
Steps
1. Loosen the screws that secure the integrated storage controller cable to the integrated storage-
controller card connector on the system board.
2. Lift the integrated storage controller cable out.
3. Lift one end of the card and angle it to disengage the card from the integrated storage-controller
card holder on system board.
4. Lift the card out of the chassis.
Figure 30. Removing and installing the integrated storage controller card
1. integrated storage controller cable 2. integrated storage controller card
78
Page 79

3. integrated storage-controller card
connector on the system board
Next steps
1. Replace the expansion-card riser 1.
2. Replace the cooling shroud.
3. Follow the procedure listed in After working inside your system.
4. integrated storage controller card
holder
Installing the integrated storage controller card
Prerequisites
1. Ensure that you read the Safety instructions.
2. Follow the procedure listed in Before working inside your system.
3. Remove the cooling shroud.
4. Remove the expansion-card riser 1.
5. Keep the #2 Phillips screwdriver handy.
CAUTION: Many repairs may only be done by a certified service technician. You should only
perform troubleshooting and simple repairs as authorized in your product documentation, or as
directed by the online or telephone service and support team. Damage due to servicing that is
not authorized by Dell is not covered by your warranty. Read and follow the safety instructions
that came with the product.
Steps
1. Align the end of the integrated storage-controller card opposite the connector with the integrated
storage-controller card holder.
2. Lower the connector side of the integrated storage-controller card into the integrated storage-
controller card connector on the system board.
Ensure that the tabs on the system board align with the screw holes on the integrated storage-
controller card.
3. Align the screws on the integrated storage-controller card cable with the screw holes on the
connector.
4. Tighten the screws to secure the integrated storage-controller card cable with the integrated
storage-controller card connector on the system board.
Next steps
1. Replace the expansion-card riser 1.
2. Replace the cooling shroud.
3. Follow the procedure listed in After working inside your system.
Related video
Figure 31.
http://www.Dell.com/XCSeries/XC730xd/SC
79
Page 80

Expansion cards and expansion-card risers
NOTE: A missing or an unsupported expansion-card riser logs an SEL event. It does not prevent
your system from powering on and no BIOS POST message or F1/F2 pause is displayed.
Expansion card installation guidelines
Depending on your system configuration:
The following PCI Express generation 3 expansion cards are supported:
Table 27. Supported expansion cards
Riser PCIe slot Processor
connection
1 1 Processor 2 Low Profile Half Length x8 x16
1 2 Processor 2 Low Profile Half Length x8 x16
1 3 Processor 2 Low Profile Half Length x8 x16
2 4 Processor 2 Full Height Full Length x16 x16
2 5 Processor 1 Full Height Full Length x8 x16
3 (default) 6 Processor 1 Full Height Full Length x8 x16
3 (alternate) 6 Processor 1 Full Height Full Length x16 x16
3 (default) 7 Processor 1 Full Height Full Length x8 x16
NOTE: To use PCIe slots 1 through 4 on the riser, both the processors must be installed.
NOTE: The expansion-card slots are not hot-swappable.
The following table provides guidelines for installing expansion cards to ensure proper cooling and
mechanical fit. The expansion cards with the highest priority should be installed first using the slot priority
indicated. Install all other expansion cards in card priority and slot priority order.
Table 28. Expansion card installation order
Card priority Card type Slot priority Max allowed
Height Length Link width Slot width
1 PCIe Bridge 4 1
2 10 Gb NICs (full height) 4,6,5 3
10 Gb NICs (low profile) 2,3,1 3
3 1 Gb NICs (full height) 4,6,5 3
1 Gb NICs (low profile) 2,3,1 1
4 Integrated RAID integrated slot 1
5 NDC integrated slot 3
80
Page 81

Removing an expansion card from expansion-card riser 2 or 3
Prerequisites
CAUTION: Many repairs may only be done by a certified service technician. You should only
perform troubleshooting and simple repairs as authorized in your product documentation, or as
directed by the online or telephone service and support team. Damage due to servicing that is
not authorized by Dell is not covered by your warranty. Read and follow the safety instructions
that came with the product.
1. Ensure that you read the Safety instructions.
2. Follow the procedure listed in Before working inside your system.
3. When removing a card from Riser 3, ensure that the PCIe holder latch is closed.
Steps
1. Disconnect any cables connected to the expansion card.
2. Lift the expansion-card latch out of the slot.
3. Hold the expansion card by its edges, and remove it from the expansion-card connector.
4. If you are removing the card permanently, install a metal filler bracket over the empty expansion slot
opening and close the expansion-card latch.
5. Replace the expansion-card latch into the slot.
6. Close the expansion-card locking tabs.
NOTE: You must install a filler bracket over an empty expansion slot to maintain Federal
Communications Commission (FCC) certification of the system. The brackets also keep dust
and dirt out of the system and aid in proper cooling and airflow inside the system.
81
Page 82

Figure 32. Removing and installing an expansion card from expansion-card riser 2 or 3
1. expansion card 2. expansion-card latch
3. expansion-card riser 4. power connector
5. expansion-card connector
Next steps
Follow the procedure listed in After working inside your system.
Related video
http://www.Dell.com/XCSeries/XC730xd/PCI
Installing an expansion card into the expansion-card riser 2 or 3
Prerequisites
1. Ensure that you read the Safety instructions.
82
Page 83
2. Follow the procedure listed in Before working inside your system.
CAUTION: Many repairs may only be done by a certified service technician. You should only
perform troubleshooting and simple repairs as authorized in your product documentation, or as
directed by the online or telephone service and support team. Damage due to servicing that is
not authorized by Dell is not covered by your warranty. Read and follow the safety instructions
that came with the product.
Steps
1. Unpack the expansion card and prepare it for installation.
For instructions, see the documentation accompanying the card.
2. Lift the expansion-card latch and remove the filler bracket.
3. Holding the card by its edges, position the card so that the connector on the expansion card aligns
with the expansion-card connector on the riser.
4. Insert the card-edge connector firmly into the expansion-card connector until the card is fully
seated.
5. Press the touch points to open the expansion-card locking tabs.
6. Replace the expansion-card latch.
7. If applicable, connect the cables to the expansion card.
Next steps
1. Follow the procedure listed in After working inside your system.
2. Install any device drivers required for the card as described in the documentation for the card.
Removing an expansion card from the expansion-card riser 1
Prerequisites
CAUTION: Many repairs may only be done by a certified service technician. You should only
perform troubleshooting and simple repairs as authorized in your product documentation, or as
directed by the online or telephone service and support team. Damage due to servicing that is
not authorized by Dell is not covered by your warranty. Read and follow the safety instructions
that came with the product.
1. Ensure that you read the Safety instructions.
2. Follow the procedure listed in Before working inside your system.
3. Disconnect any cables connected to the expansion card.
4. Remove the expansion-card riser.
NOTE: Only use the expansion card riser 1 when both the processors are installed.
Steps
1. Press tab A and rotate the latch clockwise.
2. Press tab B and rotate the latch downward.
3. Remove the expansion card from the expansion-card riser.
4. If you are removing the card permanently, install a metal filler bracket over the empty expansion slot
opening and close the expansion-card latch.
5. Close the latches of tab A and tab B.
83
Page 84

NOTE: You must install a filler bracket over an empty expansion slot to maintain Federal
Communications Commission (FCC) certification of the system. The brackets also keep dust
and dirt out of the system and aid in proper cooling and airflow inside the system.
Figure 33. Removing and installing an expansion-card from expansion-card riser 1
1. tab A 2. expansion-card riser 1 cage
3. expansion-card connector 4. tab B
5. latch 6. expansion card
Next steps
1. Install the expansion-card riser. For more information, see Installing expansion-card risers.
2. Follow the procedure listed in After working inside your system.
Installing an expansion card into the expansion-card riser 1
Prerequisites
1. Ensure that you read the Safety instructions.
2. Follow the procedure listed in Before working inside your system.
3. Remove the expansion-card riser.
84
Page 85

CAUTION: Many repairs may only be done by a certified service technician. You should only
perform troubleshooting and simple repairs as authorized in your product documentation, or as
directed by the online or telephone service and support team. Damage due to servicing that is
not authorized by Dell is not covered by your warranty. Read and follow the safety instructions
that came with the product.
NOTE: Only use the expansion card riser 1 when both the processors are installed.
Steps
1. Unpack the expansion card and prepare it for installation.
For instructions, see the documentation accompanying the card.
2. Press tab A and rotate the latch clockwise.
3. Press tab B and rotate the latch down.
4. Holding the card by its edges, position the card so that the card-edge connector aligns with the
expansion-card connector.
5. Insert the card-edge connector firmly into the expansion-card connector until the card is fully
seated.
6. Close the latches of tab A and tab B.
Next steps
1. Install the expansion-card riser. For more information, see Installing expansion-card risers.
2. If applicable, connect any cables to the expansion card.
3. Follow the procedure listed in After working inside your system.
4. Install any device drivers required for the card as described in the documentation for the card.
Removing expansion-card risers
Prerequisites
CAUTION: Many repairs may only be done by a certified service technician. You should only
perform troubleshooting and simple repairs as authorized in your product documentation, or as
directed by the online or telephone service and support team. Damage due to servicing that is
not authorized by Dell is not covered by your warranty. Read and follow the safety instructions
that came with the product.
1. Ensure that you read the Safety instructions.
2. Follow the procedure listed in Before working inside your system.
3. If installed, remove any expansion card installed on riser 2 and 3.
NOTE: Only use the expansion card riser 1 when both the processors are installed.
Steps
Holding the slots on the expansion-card riser, lift the riser from the riser connector on the system
board.
NOTE: To remove expansion-card risers 2 and 3, hold the edges of the expansion-card riser.
NOTE: To ensure proper system cooling, the riser 1 blank must be installed in the riser 1 slot.
Remove the riser 1 blank only if you are installing riser 1.
85
Page 86

Figure 34. Removing and installing the expansion card riser 1
1. expansion-card riser 1 cage 2. expansion-card riser 1
3. riser guide-back (right) 4. riser guide-back (left)
5. expansion-card riser 1 connector 6. riser guide-front
86
Page 87

Figure 35. Identifying connectors on the expansion card riser 1
1. expansion-card slot 1 2. expansion-card slot 2
3. expansion-card slot 3
87
Page 88

Figure 36. Removing and installing the expansion card riser 2
1. power connector 2. expansion-card riser 2
3. riser guide-back 4. expansion-card riser 2 connector
5. riser guide-front
88
Page 89

Figure 37. Identifying connectors on the expansion card riser 2
1. expansion-card slot 4 2. expansion-card slot 5
3. power connector
89
Page 90

Figure 38. Removing and installing the expansion card riser 3
1. riser guide-front 2. power connector
3. expansion-card riser 3 4. riser guide-back
5. expansion-card riser 3 connector
90
Page 91

Figure 39. Identifying connectors on the expansion card riser 3 (default)
1. expansion-card slot 6 2. expansion-card slot 7
3. power connector
Figure 40. Identifying connectors on the expansion card riser 3 (alternate)
1. expansion-card slot 6 2. power connector
Next steps
1. If applicable, remove or install an expansion card on the riser.
2. If applicable, replace the expansion-card riser.
3. Follow the procedure listed in After working inside your system.
91
Page 92

Installing expansion-card risers
Prerequisites
1. Ensure that you read the Safety instructions.
2. Follow the procedure listed in Before working inside your system.
3. If applicable, reinstall the expansion cards into the expansion-card riser 1.
CAUTION: Many repairs may only be done by a certified service technician. You should only
perform troubleshooting and simple repairs as authorized in your product documentation, or as
directed by the online or telephone service and support team. Damage due to servicing that is
not authorized by Dell is not covered by your warranty. Read and follow the safety instructions
that came with the product.
Steps
1. Align the expansion-card riser with the connectors and the riser guides on the system board.
2. Lower the expansion-card riser into place until the expansion-card riser is fully seated in the
connector.
Next steps
1. Install the expansion cards into the expansion-card risers 2 or 3.
2. Follow the procedure listed in After working inside your system.
3. Install any device drivers required for the card as described in the documentation for the card.
Internal dual SD module
Removing an internal SD card
Prerequisites
1. Ensure that you read the Safety instructions.
2. Follow the procedure listed in Before working inside your system.
CAUTION: Many repairs may only be done by a certified service technician. You should only
perform troubleshooting and simple repairs as authorized in your product documentation, or as
directed by the online or telephone service and support team. Damage due to servicing that is
not authorized by Dell is not covered by your warranty. Read and follow the safety instructions
that came with the product.
Locate the SD card slot on the internal dual SD module and press the card to release it from the slot.
Steps
1. Remove the PCIe Card.
2. Remove riser 3.
3. Locate the SD card slot on the internal dual SD module and press the card to release it from the slot.
Next steps
Follow the procedure listed in After working inside your system.
Related videos
92
Page 93

http://www.Dell.com/XCSeries/XC730xd/IDSDM
Installing an internal SD card
Prerequisites
1. Ensure that you read the Safety instructions.
2. Follow the procedure listed in Before working inside your system.
3. If installed, remove the cooling shroud.
CAUTION: Many repairs may only be done by a certified service technician. You should only
perform troubleshooting and simple repairs as authorized in your product documentation, or as
directed by the online or telephone service and support team. Damage due to servicing that is
not authorized by Dell is not covered by your warranty. Read and follow the safety instructions
that came with the product.
NOTE: To use an SD card with your system, ensure that the Internal SD Card Port is enabled in the
System Setup.
Steps
1. Locate the SD card connector on the internal dual SD module. Orient the SD card appropriately and
insert the contact-pin end of the card into the slot.
NOTE: The slot is keyed to ensure of correct card insertion correct insertion of the card.
2. Press the card into the card slot to lock it into place.
Next steps
Follow the procedure listed in After working inside your system.
1. If removed, replace the cooling shroud.
2. Follow the procedure listed in After working inside your system.
Removing the internal dual SD module
Prerequisites
CAUTION: Many repairs may only be done by a certified service technician. You should only
perform troubleshooting and simple repairs as authorized in your product documentation, or as
directed by the online or telephone service and support team. Damage due to servicing that is
not authorized by Dell is not covered by your warranty. Read and follow the safety instructions
that came with the product.
1. Ensure that you read the Safety instructions.
2. Follow the procedure listed in Before working inside your system.
Steps
1. Locate the internal dual SD module on the system board.
2. If installed, remove the SD cards.
3. Hold the plastic pull tab and pull the dual SD module out of the system board.
93
Page 94

Figure 41. Removing and installing the Internal Dual SD Module (IDSDM)
1. Internal Dual SD module 2. LED status indicator (2)
3. SD card 4. SD card slot 2
5. SD card slot 1 6. IDSDM connector
Table 29. The following table describes the IDSDM indicator codes.
Convention IDSDM indicator code Description
A Green Indicates that the card is online
B Flashing green Indicates rebuild or activity
C Flashing amber Indicates card mismatch or that the card has
failed
D Amber Indicates that the card is offline, has failed, or is
write protected
94
Page 95

Convention IDSDM indicator code Description
E Not lit Indicates that the card is missing or is
Next steps
Follow the procedure listed in After working inside your system
Installing the internal dual SD module
Prerequisites
CAUTION: Many repairs may only be done by a certified service technician. You should only
perform troubleshooting and simple repairs as authorized in your product documentation, or as
directed by the online or telephone service and support team. Damage due to servicing that is
not authorized by Dell is not covered by your warranty. Read and follow the safety instructions
that came with the product.
1. Ensure that you read the Safety instructions.
2. Follow the procedure listed in Before working inside your system
Steps
1. Locate the IDSDM connector on the system board. To locate the IDSDM connector, see System
board connectors
2. Align the connectors on the system board and the dual SD module.
3. Push the dual SD module until it is firmly seated on the system board.
Next steps
1. Install the SD vFlash media card(s).
NOTE: Temporarily label each SD card with its corresponding slot before removal. Replace the
SD card(s) into the same slots.
2. Follow the procedure listed in After working inside your system
Network daughter card
Removing the network daughter card
Prerequisites
1. Ensure that you read the Safety instructions.
2. Follow the procedure listed in Before working inside your system.
3. If installed, remove expansion card(s) from the expansion-card riser 2.
4. Keep the #1 Phillips screwdriver handy.
CAUTION: Many repairs may only be done by a certified service technician. You should only
perform troubleshooting and simple repairs as authorized in your product documentation, or as
directed by the online or telephone service and support team. Damage due to servicing that is
not authorized by Dell is not covered by your warranty. Read and follow the safety instructions
that came with the product.
95
Page 96

Steps
1. Using a #1 Phillips screwdriver, loosen the captive screws that secure the network daughter card to
the system board.
2. Hold the network daughter card by the edges on either side of the touch point and lift the card to
remove it from the connector on the system board.
3. Slide the network daughter card away from the back of the system until the Ethernet connectors are
clear of the slot in the back panel.
4. Lift the network daughter card out of the chassis.
Figure 42. Removing and installing the Network Daughter Card (NDC)
1. captive screw socket (2) 2. connector on the system board
3. captive screw (2) 4. touch point (2)
5. network daughter card 6. back panel slot for Ethernet connectors
Next steps
1. Replace the network daughter card. See Installing the network daughter card.
2. Follow the procedure listed in After working inside your system.
Related videos
96
Page 97

http://www.Dell.com/XCSeries/XC730xd/NDC
Installing the network daughter card
Prerequisites
1. Ensure that you read the Safety instructions.
2. Follow the procedure listed in Before working inside your system.
3. If applicable, remove the expansion card(s) in the expansion-card riser 2.
4. Keep the #1 Phillips screwdriver handy.
CAUTION: Many repairs may only be done by a certified service technician. You should only
perform troubleshooting and simple repairs as authorized in your product documentation, or as
directed by the online or telephone service and support team. Damage due to servicing that is
not authorized by Dell is not covered by your warranty. Read and follow the safety instructions
that came with the product.
Steps
1. Angle the card so that the Ethernet connectors fit through the slot in the back panel.
2. Align the captive screws on the card with the captive screw sockets on the system board.
3. Press the touch points on the card until the card connector is firmly seated on the system board
connector.
4. Using a #1 Phillips screwdriver, tighten the captive screws to secure the network daughter card to
the system board.
Next steps
1. If applicable, install the expansion card(s) in the expansion-card riser 2.
2. Follow the procedure listed in After working inside your system.
System battery
Replacing the system battery
Prerequisites
1. Ensure that you read the Safety instructions.
2. Follow the procedure listed in Before working inside your system.
3. Remove the cooling shroud.
WARNING: There is a danger of a new battery exploding if it is incorrectly installed. Replace the
battery only with the same or equivalent type recommended by the manufacturer. For more
information, see the safety information that shipped with your system.
CAUTION: Many repairs may only be done by a certified service technician. You should only
perform troubleshooting and simple repairs as authorized in your product documentation, or as
directed by the online or telephone service and support team. Damage due to servicing that is
not authorized by Dell is not covered by your warranty. Read and follow the safety instructions
that came with the product.
97
Page 98

Steps
1. Locate the battery socket. For more information, see System board connectors.
CAUTION: To avoid damage to the battery connector, you must firmly support the connector
while installing or removing a battery.
2. Place your finger between the securing tabs at the negative side of the battery connector and lift the
battery out of the socket.
Figure 43. Removing the system battery
1. positive side of the battery connector
2. system battery
3. negative side of the battery connector
3. To install a new system battery, hold the battery with the "+" facing up and slide it under the securing
tabs.
4. Press the battery into the connector until it snaps into place.
98
Page 99

Figure 44. Installing the system battery
1. system battery 2. positive side of the battery
Next steps
1. Install the cooling shroud.
2. Follow the procedure listed in After working inside your system.
3. While booting, press <F2> to enter System Setup and ensure the battery is operating properly.
4. Enter the correct time and date in System Setup Time and Date fields.
5. Exit System Setup.
Related videos
http://www.Dell.com/XCSeries/XC730xd/Battery
Power supply units
Your system supports one of the following:
• Two 495 W, 750 W, or 1100 W AC power supply modules or
• Two 1100 W DC power supply modules or
• Two 750 W mixed mode power supply modules
NOTE: Titanium power supply unit is nominally rated for 200 VAC to 240 VAC input only.
99
Page 100

NOTE: When two identical PSUs are installed, power supply redundancy (1+1 – withredundancy or
2+0 – without redundancy) is configured in system BIOS. In redundant mode, power is supplied to
the system equally from both PSUs when Hot Spare is disabled. When Hot Spare is enabled, one of
the PSUs are put into standby when system usage is low to maximize efficiency.
NOTE: If two power supply units are used, they must be of the same maximum output power.
NOTE: For AC power supply units, use only power supply units with the Extended Power
Performance (EPP) label on the back. Mixing power supply units from previous generations of
servers can result in a power supply unit mismatch condition or failure to power on.
Hot Spare feature
Your system supports the Hot Spare feature that significantly reduces the power overhead associated
with power supply redundancy.
When the Hot Spare feature is enabled, one of the redundant power supplies is switched to a sleep state.
The active power supply supports 100 percent of the load, thus operating at higher efficiency. The power
supply in the sleep state monitors output voltage of the active power supply. If the output voltage of the
active power supply drops, the power supply in the sleep state returns to an active output state.
If having both power supplies active is more efficient than having one power supply in a sleep state, the
active power supply can also activate a sleeping power supply.
The default power supply settings are as follows:
• If the load on the active power supply is more than 50 percent, then the redundant power supply is
switched to the active state.
• If the load on the active power supply falls below 20 percent, then the redundant power supply is
switched to the sleep state
You can configure the Hot Spare feature using the iDRAC settings. For more information on iDRAC
settings, see the Integrated Dell Remote Access Controller User’s Guide at dell.com/support/home.
Removing the power supply unit blank
If you are installing a second power supply unit, remove the power supply unit blank in the bay by
pulling the blank outward.
CAUTION: To ensure proper system cooling, the power supply blank must be installed in the
second power supply bay in a non-redundant configuration. Remove the power supply blank
only if you are installing a second power supply.
100
 Loading...
Loading...