Page 1

Dell™ Serial-Attached SCSI 6/iR
Integrated and Adapter
User’s Guide
Model UCS-61
Page 2

Page 3

Dell™ Serial-Attached SCSI 6/iR
Integrated and Adapter
User’s Guide
Model UCS-61
www.dell.com | support.dell.com
Page 4

Notes, Notices, and Cautions
NOTE: A NOTE indicates important information that helps you make better use of
your computer.
NOTICE: A NOTICE indicates either potential damage to hardware or loss of data
and tells you how to avoid the problem.
CAUTION: A CAUTION indicates a potential for property damage, personal injury,
or death.
________________________________________
Information in this document is subject to change without notice.
© 2007-2008 Dell Inc. All rights reserved.
Reproduction of these materials in any manner whatsoever without the written permission of Dell Inc.
is strictly forbidden.
Trademarks used in this text: Dell, the DELL logo, Dell Precision, PowerEdge, and OpenManage are
trademarks of Dell Inc.; Intel is a registered trademark of Intel Corporation; Microsoft, Windows,
Windows Server, and Windows Vista are either trademarks or registered trademarks of Microsoft
Corporation in the United States and/or other countries; Novell, NetWare, and SUSE are registered
trademarks of Novell, Inc. in the United States and other countries; Red Hat Linux and Red Hat
Enterprise Linux are registered trademarks of Red Hat, Inc.; LSI Logic, Fusion-MPT, Integrated
Mirroring, and Integrated Striping are trademarks or registered trademarks of LSI Logic Corporation;
DR-DOS is a registered trademark of DRDOS, Inc.
Other trademarks and trade names may be used in this document to refer to either the entities claiming
the marks and names or their products. Dell Inc. disclaims any proprietary interest in trademarks and
trade names other than its own.
Model UCS-61
July 2008 P/N JM360 Rev. A01
Page 5

Contents
1 CAUTION: Safety Instructions. . . . . . . . . . 9
SAFETY: General . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
SAFETY: When Working Inside Your System
SAFETY: Protecting Against
Electrostatic Discharge
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
. . . . . . . 9
2Overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
About RAID. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
RAID Levels
RAID Terminology
Integrated Striping
Integrated Mirroring
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
3 SAS 6/iR Features . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
4 Hardware Installation
Installing the SAS 6/iR Adapter . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
Contents 3
Page 6

5 Driver Installation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
Installing the Windows Driver. . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
Creating the Driver Media
Pre-Installation Requirements
Installing the Driver During a Windows
Server 2003 or Windows XP
Operating System Installation
Installing the Driver During a Windows
Server 2008 or Windows Vista Installation
Installing a Windows Server 2003,
Windows Server 2008, Windows Vista,
or Windows XP Driver for
a New RAID Controller
Updating an Existing Windows
Server 2003, Windows Server 2008,
Windows XP, or Windows Vista Driver
. . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
. . . . . . . . . . . 24
. . . . . . . . . . . . 25
. . . . . 26
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27
. . . . . . . 28
4 Contents
Installing Linux Driver
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
Installing Red Hat Enterprise Linux
Operating Systems using the
Driver Update Diskette
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30
Red Hat Enterprise Linux 5 Installation
and Disk Enumeration
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
Installing SUSE Linux Enterprise Server
Using the Driver Update Diskette
SUSE Linux Enterprise Server 10
Installation and Disk Enumeration
Installing the RPM Package
With DKMS Support
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 33
. . . . . . . . . . 31
. . . . . . . . . 32
Page 7

6 SAS 6/iR BIOS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 35
POST Messages . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 35
BIOS Fault Code Messages
. . . . . . . . . . . . 35
Configuration Utility
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 36
Starting the Configuration Utility
Functions Performed
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 36
Navigating the Configuration Utility
Integrated RAID Configuration and
Management Screens
Select New Array Type
Create New Array
View Array
Manage Array
Exit Screen
Performing Configuration Tasks
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 37
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 38
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 38
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 41
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 41
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 42
. . . . . . . . . . . . . 42
Creating an Integrated
Striping Virtual Disk
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 42
Creating a Integrated
Mirroring Virtual Disk
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 43
Viewing Virtual Disk Properties
Synchronizing a Virtual Disk
Activating a Virtual Disk
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . 45
Migrating and Activating a Virtual Disk
Deleting a Virtual Disk
Hot Spare Failover
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 46
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 46
Replacing and Rebuilding
a Degraded Virtual Disk
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . 46
. . . . . . . . . . 36
. . . . . . . . 37
. . . . . . . . . . 44
. . . . . . . . . . . . 45
. . . . . . 45
Contents 5
Page 8

7 Troubleshooting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 49
BIOS Boot Order . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 49
General Problems
Physical Disk Related Issues
Configuration Utility Error Messages
BIOS Error Messages
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 49
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . 50
. . . . . . . . . . 51
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 52
A Updating the Firmware . . . . . . . . . . . . . 55
Firmware Update Utility . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 55
B Getting Help . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 57
Obtaining Assistance . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 57
Technical Support and Customer Service
Online Services
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 58
Automated Order-Status Service
Dell Enterprise Training
Problems With Your Order
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 59
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 59
. . . . . 58
. . . . . . . . . . 59
6 Contents
Product Information
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 59
Returning Items for Warranty Repair or Credit
Before You Call
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 60
. . . . . 60
Page 9

C Regulatory Notices . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 61
D Corporate Contact Details
(Taiwan Only)
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 63
Glossary
Index
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 73
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 65
Contents 7
Page 10

8 Contents
Page 11

CAUTION: Safety Instructions
Use the following safety guidelines to help ensure your own personal safety and to help protect
your system and working environment from potential damage.
NOTE: See the caution and safety statements in your Dell™ PowerEdge™ system
or Dell Precision™ workstation.
SAFETY: General
• Observe and follow service markings. Do not service any product except as explained in
your user documentation. Opening or removing covers that are marked with the triangular
symbol with a lightning bolt may expose you to electrical shock. Components inside these
compartments should be serviced only by a trained service technician.
• If any of the following conditions occur, unplug the product from the electrical outlet and
replace the part or contact your trained service provider:
– The power cable, extension cable, or plug is damaged.
– An object has fallen into the product.
– The product has been exposed to water.
– The product has been dropped or damaged.
– The product does not operate correctly when you follow the operating instructions.
• Use the product only with approved equipment.
• Operate the product only from the type of external power source indicated on the
electrical ratings label. If you are not sure of the type of power source required, consult
your service provider or local power company.
• Handle batteries carefully. Do not disassemble, crush, puncture, short external contacts,
dispose of in fire or water, or expose batteries to temperatures higher than
60 degrees Celsius (140 degrees Fahrenheit). Do not attempt to open or service batteries;
replace batteries only with batteries designated for the product.
SAFETY: When Working Inside Your System
Before you remove the system covers, perform the following steps in the sequence indicated.
CAUTION: Except if expressly otherwise instructed in Dell documentation, only trained
service technicians are authorized to remove the system cover and access any of the
components inside the system.
NOTICE: To help avoid possible damage to the system board, wait for 5 seconds after
turning off the system before removing a component from the system board or disconnecting
a peripheral device.
Safety Instructions 9
Page 12

1
Turn off the system and any devices.
2
Ground yourself by touching an unpainted metal surface on the chassis before touching
anything inside the system.
3
While you work, periodically touch an unpainted metal surface on the chassis to dissipate any
static electricity that might harm the internal components.
4
Disconnect your system and devices from their power sources. To reduce the potential of
personal injury or shock, disconnect any telecommunication lines from the system.
In addition, take note of these safety guidelines when appropriate:
• When you disconnect a cable, pull on its connector or on its strain-relief loop, not on the
cable itself. Some cables have a connector with locking tabs; if you are disconnecting this
type of cable, press in on the locking tabs before disconnecting the cable. As you pull the
connectors apart, keep them evenly aligned to avoid bending any connector pins. Also, before
you connect a cable, make sure that both connectors are correctly oriented and aligned.
• Handle components and cards with care. Do not touch the components or contacts on a
card. Hold a card by its edges or by its metal mounting bracket. Hold a component such as
a microprocessor chip by its edges, not by its pins.
SAFETY: Protecting Against Electrostatic Discharge
Electrostatic discharge (ESD) events can harm electronic components inside your computer.
Under certain conditions, ESD may build up on your body or an object, such as a peripheral, and
then discharge into another object, such as your computer. To prevent ESD damage, you should
discharge static electricity from your body before you interact with any of your computer’s internal
electronic components, such as a memory module. You can protect against ESD by touching a
metal grounded object (such as an unpainted metal surface on your computer’s I/O panel) before
you interact with anything electronic. When connecting a peripheral (including handheld digital
assistants) to your computer, you should always ground both yourself and the peripheral before
connecting it to the computer. In addition, as you work inside the computer, periodically touch an
I/O connector to remove any static charge your body may have accumulated.
You can also take the following steps to prevent damage from electrostatic discharge:
• When unpacking a static-sensitive component from its shipping carton, do not remove the
component from the antistatic packing material until you are ready to install the
component. Just before unwrapping the antistatic package, be sure to discharge static
electricity from your body.
• When transporting a sensitive component, first place it in an antistatic container or
packaging.
• Handle all electrostatic sensitive components in a static-safe area. If possible, use antistatic
floor pads and work bench pads.
10 Safety Instructions
Page 13
Overview
The Dell™ Serial-Attached SCSI (SAS) 6/iR controller is Dell’s next generation
controller with integrated redundant array of independent disks (RAID)
capabilities. SAS technology is not backward compatible with the previous
generation of SCSI devices. All SAS 6/iR controllers are half-length, standardheight PCI-E cards, except for the SAS 6/iR Integrated controller on the blade
servers and on the Precision workstations. The SAS 6/iR controllers are
supported on platforms with PCI-E x4, x8 and x16 connectors.
Figure 2-1. SAS 6/iR Adapter Hardware Architecture
1
2
1 SAS x4 internal connector 2 PCI-E connector
Overview 11
Page 14

About RAID
RAID is a group of multiple independent physical disks that provide high
performance or better data availability by increasing the number of drives
used for saving and accessing data. A RAID disk subsystem improves
I/O performance and data availability. The physical disk group appears to the
host system as a single storage unit. Data throughput improves because
multiple disks can be accessed simultaneously. RAID systems also improve
data storage availability and fault tolerance.
RAID Levels
RAID 0 uses disk striping to provide high data throughput, especially for large
files in an environment that requires no data redundancy.
Integrated Mirroring or RAID 1 uses disk mirroring so that data written to
one physical disk is simultaneously written to another physical disk. This is
good for small databases or other applications that require small capacity, but
complete data redundancy.
NOTICE: Lost data on an Integrated Striping virtual disk cannot be recovered in the
event of a physical disk failure.
RAID Terminology
Integrated Striping
Integrated Striping (RAID 0) allows you to write data across multiple physical
disks instead of just one physical disk. Integrated Striping involves partitioning
each physical disk storage space into 64 KB stripes. These stripes are
interleaved in a repeated sequential manner. The part of the stripe on a single
physical disk is called a stripe element.
For example, in a four-disk system using only Integrated Striping, segment 1 is
written to disk 1, segment 2 is written to disk 2, and so on. Integrated Striping
enhances performance because multiple physical disks are accessed
simultaneously, but Integrated Striping does not provide data redundancy.
Figure 2-2 shows an example of Integrated Striping.
12 Overview
Page 15
Figure 2-2. Example of Integrated Striping (RAID 0)
stripe element 1
stripe element 5
stripe element 9
stripe element 2
stripe element 6
stripe element 10
stripe element 3
stripe element 7
stripe element 11
stripe element 4
stripe element 8
stripe element 12
Integrated Mirroring
With Integrated Mirroring (RAID 1), data written to one disk is
simultaneously written to another disk. If one disk fails, the contents of the
other disk can be used to run the system and rebuild the failed physical disk.
The primary advantage of Integrated Mirroring is that it provides 100 percent
data redundancy. Because the contents of the disk are completely written to a
second disk, the system can sustain the failure of one disk. Both disks contain
the same data at all times. Either physical disk can act as the operational
physical disk.
NOTE: Mirrored physical disks improve read performance by read load balance.
Figure 2-3. Example of Integrated Mirroring (RAID 1)
stripe element 1
stripe element 2
stripe element 3
stripe element 4 stripe element 4 duplicated
stripe element 1 duplicated
stripe element 2 duplicated
stripe element 3 duplicated
Overview 13
Page 16

14 Overview
Page 17

SAS 6/iR Features
This section provides the specifications of Dell™ Serial-Attached SCSI (SAS)
6/iR controller. The following table compares the specifications of the
SAS 6/iR Adapter and SAS 6/iR Integrated.
Table 3-1. Specifications of SAS 6/iR
Specification SAS 6/iR Adapter SAS 6/iR Integrated
SAS technology Yes Yes
Support for x4, x8, or x16
PCI Express Host Interface
Form Fa c t o r
I/O controller (IOC)
Operating voltage
requirements
Communication to the
system
Communication to end
devices
Ye s Ye s
Standard-Height,
Half-Length PCI Adapter
LSI SAS 1068e LSI SAS 1068e
Core Speed: 255 MHz Core Speed: 255 MHz
+12V, +3.3V, +3.3Vaux +12V, +3.3V, +3.3Vaux
PCI-E lanes System dependent
SAS Links SAS Links
Standard-Height, HalfLength PCI on all systems
except on blade servers
(where the dimension do
not follow industry
standards) and some
Precision workstations
(where the controller has
been integrated on the
mother board)
SAS 6/iR Features 15
Page 18

Table 3-1. Specifications of SAS 6/iR (continued)
Specification SAS 6/iR Adapter SAS 6/iR Integrated
SAS Connectors 2 x4 Internal 2 x4 Internal connectors on
all systems, with two
exceptions: 4 x1 on
Precision workstations with
controller integrated on the
motherboard, no SAS
connector on the controller
for the blades (I/O is routed
though the PCI connector)
Lead Free Yes Yes
®
Windows Server® 2003 Family, Windows® XP,
®
Enterprise Linux® Versions 4 and 5, SUSE®
Supported operating
systems
Microsoft
Microsoft Windows Server 2008 Family, Windows Vista™,
Red Hat
Linux Enterprise Server Version 10.
Dell-compliant SAS and
SATA compatibility
Dell supported direct
connected end devices
Ye s Ye s
Dell-compliant physical
disks
Dell-compliant physical
disks
SMART error support
through management
Ye s Ye s
applications
Backplane supported
systems
Ye s Ye s
Hardware-based RAID RAID 0, RAID 1 RAID 0, RAID 1
Maximum number of
22
virtual disks
16 SAS 6/iR Features
Page 19

Table 3-1. Specifications of SAS 6/iR (continued)
Specification SAS 6/iR Adapter SAS 6/iR Integrated
Storage management
software
OpenManage™ Storage
Services, SAS RAID
Storage Manager
OpenManage Storage
Services, SAS RAID
Storage Manager
NOTE: The management software that is supported depends on the specific platform.
Support for internal tape
drive
Support for Global
Hotspare
Maximum number of
Hotspares
No No
Ye s Ye s
22
SAS 6/iR Features 17
Page 20

18 SAS 6/iR Features
Page 21

Hardware Installation
This chapter describes how to install the Dell™ Serial-Attached SCSI (SAS)
6/iR Adapter.
NOTE: If the SAS 6/iR Integrated is embedded on the system motherboard, it does not
require any installation. See your system’s Hardware Owner’s Manual or the User’s
Guide for instructions.
Installing the SAS 6/iR Adapter
CAUTION: For some systems, only trained service technicians are authorized to
remove the system cover and access any of the components inside the system.
Before performing any procedure, see the safety information that shipped with
your system.
1
Unpack the SAS 6/iR Adapter and check for damage.
NOTE: Contact Dell if the controller is damaged.
2
Turn off the system and attached peripherals, and disconnect the system
from the electrical outlet. See your system’s
or the
User’s Guide
3
Disconnect the system from the network and remove the cover of the
system. See your system’s
for more information on opening the system.
4
Select an appropriate
back of the system aligned with the PCI-E slot you have selected.
for more information on power supplies.
Hardware Owner’s Manual
PCI-E slot. Remove the blank filler bracket on the
Hardware Owner’s Manual
or the
User’s Guide
NOTE: For more information about your system’s PCI-E slots, see your
system’s Hardware Owner’s Manual.
5
Align the SAS 6/iR Adapter to the P
6
Insert the controller gently, but firmly, until the controller is firmly seated
in the PCI-E slot. See Figure 4-1.
CI-E
slot you have selected.
Hardware Installation 19
Page 22
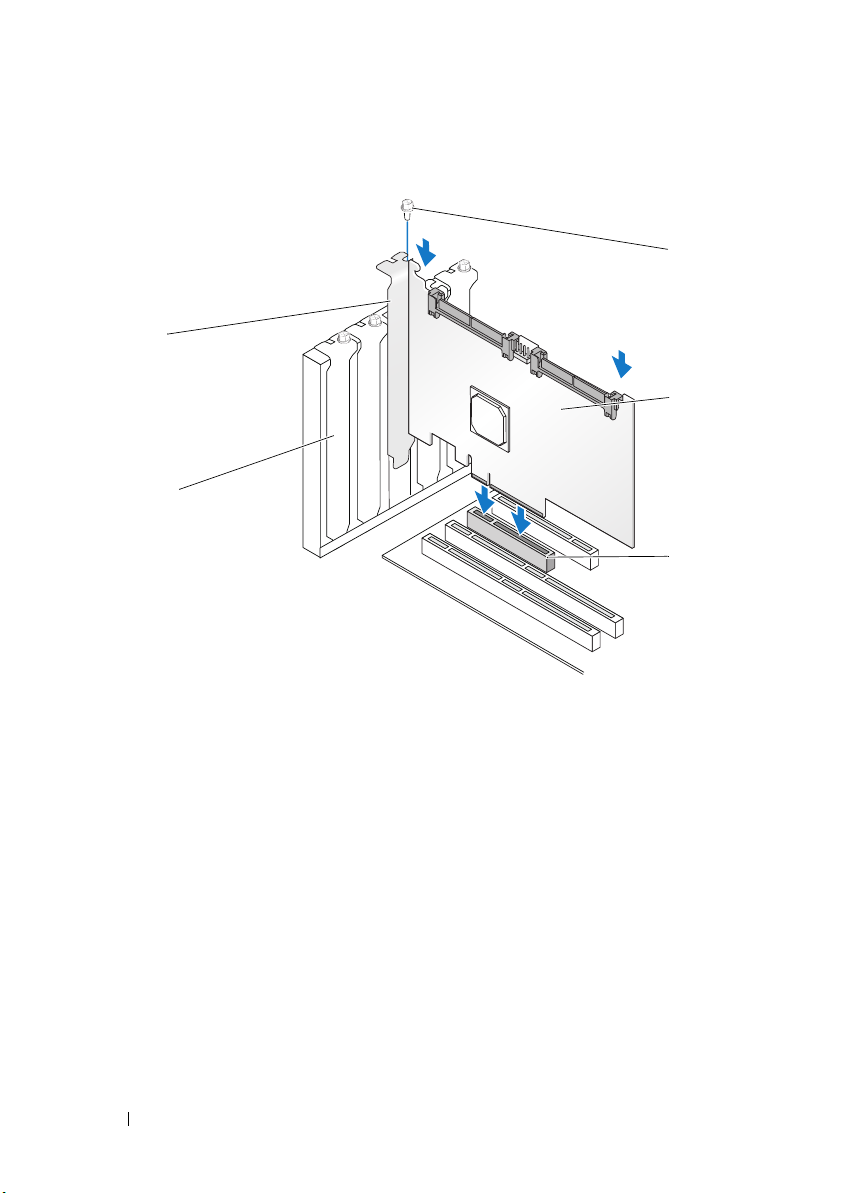
Figure 4-1. Installing a SAS 6/iR Adapter
4
5
1
2
3
1 bracket screw 2 SAS 6/iR Adapter 3 PCI-E slot
4 PCI bracket 5 filler bracket
7
Tighten the bracket screw, if any, or use the system’s retention clips to
secure the controller to the system’s chassis.
8
Connect the cables from the end devices or the backplane of the system to
the controller. See Figure 4-2.
20 Hardware Installation
Page 23
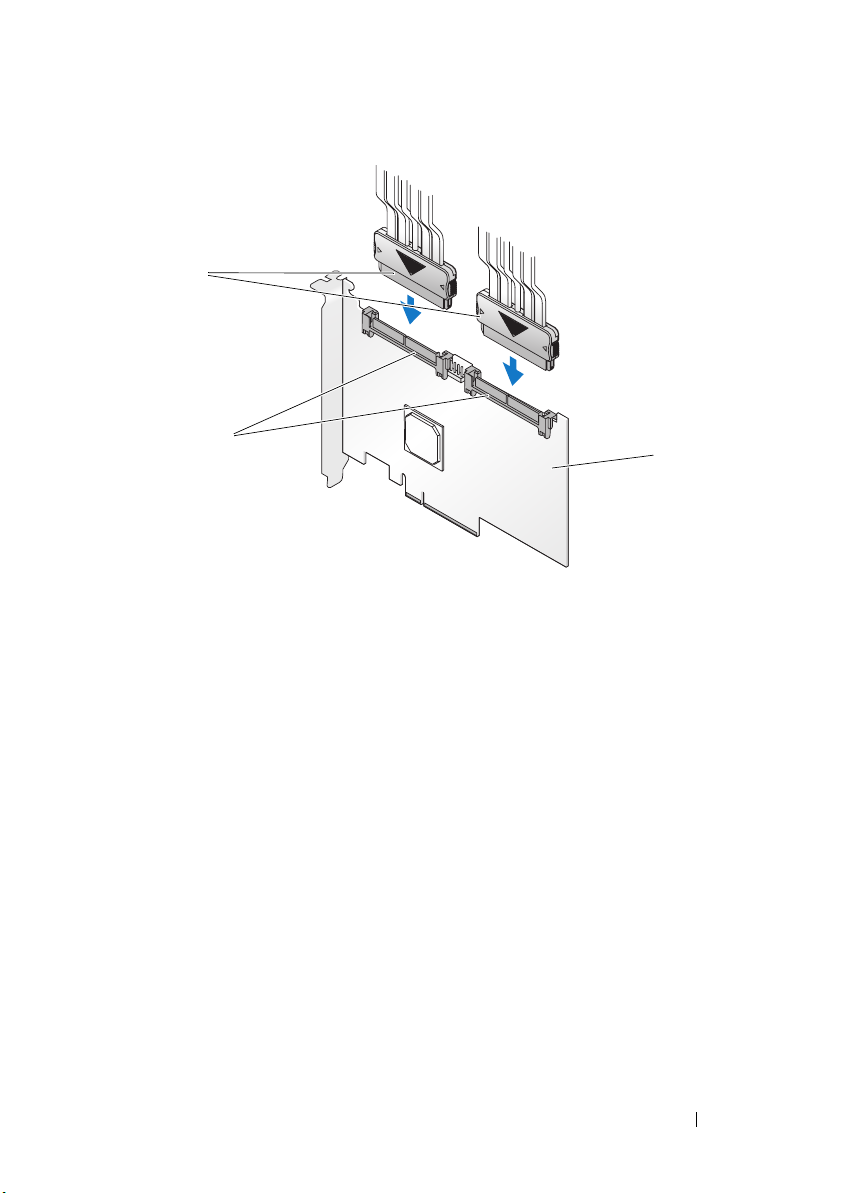
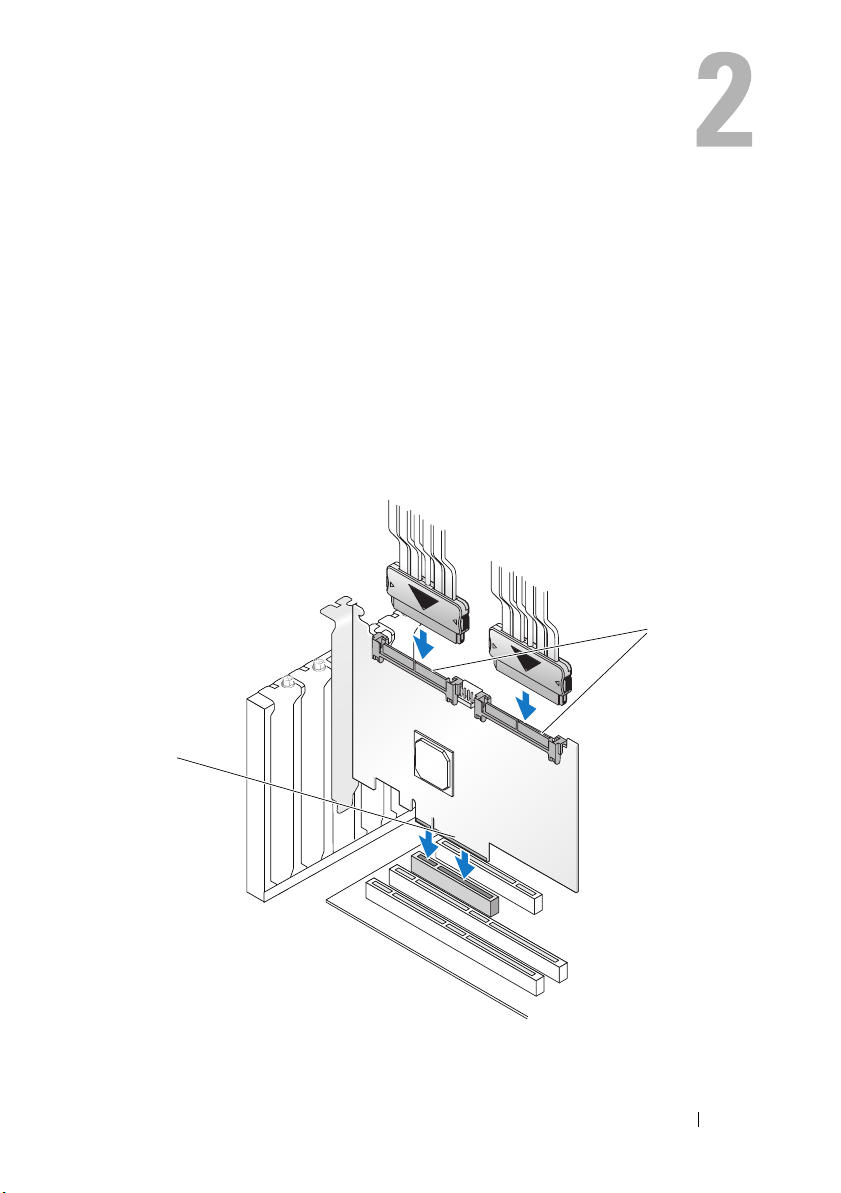
Figure 4-2. Connecting the Cable
3
2
1 SAS 6/iR Adapter 2 SAS x4 internal connector 3 cable
9
Replace the cover of the system. See your system’s
Manual
10
Reconnect the power cable(s) and network cables, and then turn on the
or the
User’s Guide
for more information on closing the system.
Hardware Owner’s
system.
1
Hardware Installation 21
Page 24

22 Hardware Installation
Page 25

Driver Installation
The
Dell™ Serial-Attached SCSI (SAS) 6/iR controller
drivers to operate with Microsoft
Linux operating systems.
This chapter contains the procedures for installing the drivers for the following
operating systems:
• Microsoft Windows Server
• Microsoft Windows Server 2008 Server family
• Microsoft Windows XP
• Red Hat Linux Versions 4 and 5
• SUSE Linux Enterprise Server Version 10
• Windows Vista™
The four methods for installing a driver that are discussed in this chapter are:
• During operating system installation.
• After adding a new SAS 6/iR controller on an existing operating system.
• Updating existing drivers.
• Installing from a
This media includes the drivers.
NOTE: Operating system installation on a RAID 1 or a RAID 0 virtual disk is
supported only when the virtual disk is in an optimal state.
Dell Precision™ Workstation Operating System
®
Windows®, Red Hat® Linux®, and SUSE®
®
2003 Server family
requires software
media.
NOTE: To ensure you have the latest version of any driver mentioned in this
section, check the Dell Support website at support.dell.com. If a newer version
exists, you can download the driver to your system.
Driver Installation 23
Page 26

Installing the Windows Driver
This section documents the procedures used to install the Windows driver.
Creating the Driver Media
Perform the following steps to create the driver media:
Browse to the download section for the system from the Dell Support
1
website at
2
Locate and download the latest SAS 6/iR controller driver to the system.
3
Follow the instructions on the Dell Support website for extracting the
driver to the media.
Pre-Installation Requirements
Before you install the operating system:
• Read the Microsoft
operating system.
• Ensure that your system has the latest BIOS, firmware, and driver updates.
If required, download the latest BIOS, firmware, and driver updates from
the Dell Support website at
• Create a device driver media (diskette, USB drive, CD, or DVD).
Creating the Device Driver Media
Use one of the methods described in the following sections to create the
device driver media.
support.dell.com
Getting Started
.
document that ships with your
support.dell.com
.
Downloading Drivers From the Dell Systems Service and Diagnostic Tools Media
1
Insert the
The
2
Select your server model and operating system (Microsoft Windows
Server 2003).
3
Click
24 Driver Installation
Dell Systems Service and Diagnostics Tools
Welcome to Dell Service and Diagnostic Utilities
Continue
.
media into a system.
screen is displayed.
Page 27

4
From the list of drivers displayed, select the driver that you require. Select the
self-extracting zip file and click
DVD, or USB drive. Repeat this step for all the drivers that you require.
5
During the operating system installation described in "Installing the Driver
During a Windows Server 2003 or Windows XP Operating System
Installation" on page 25 and "Installing the Driver During a Windows
Server 2008 or Windows Vista Installation" on page 26, use the media that
you created with the
Downloading Drivers From the Dell Support Site
1
Go to
support.dell.com
2
Click
Drivers and Downloads
3
Enter the service tag of your system in the
select your system’s model.
4
Select the
Category
5
The drivers that are applicable to your selection are displayed. From the
available list, download the drivers that you require to a diskette drive,
USB drive, CD, or DVD.
6
During the operating system installation described in "Installing the Driver
During a Windows Server 2003 or Windows XP Operating System Installation"
on page 25 and "Installing the Driver During a Windows Server 2003 or
Windows XP Operating System Installation" on page 25, use the media that
you created with the
System Type, Operating System, Driver Language, and
from the drop-down list.
Load Driver
Load Driver
Run
. Copy the driver to a diskette drive, CD,
option to load mass storage drivers.
.
.
Choose by Service Tag
option to load mass storage drivers.
field or
Installing the Driver During a Windows Server 2003 or Windows XP Operating System Installation
Perform the following steps to install the driver during operating system
installation.
1
Boot the system using the Microsoft Windows XP/Microsoft Windows
Server 2003 media.
2
When the message
RAID driver
Within a few minutes, a screen appears that asks for additional controllers
in the system.
Press F6 if you need to install a third party SCSI or
appears, press the <F6> key immediately.
Driver Installation 25
Page 28

3
Press the <S> key.
The system prompts for the driver media to be inserted.
NOTE: The driver can be provided using a properly formatted USB key.
support.dell.com for additional details.
Check
4
Insert the driver media in the media drive and press <Enter>.
A list of SAS controllers appears.
5
Select the right driver for the installed controller and press <Enter> to
load the driver.
NOTE: For Windows Server 2003, a message can appear that states that the
driver that you provided is older or newer than the existing Windows driver.
Press <S> to use the driver that is on the media.
6
Press <Enter> again to continue the installation process as usual.
Installing the Driver During a Windows Server 2008 or Windows Vista Installation
Perform the following steps to install the driver during operating system
installation.
1
Boot the system using the Microsoft Windows Vista/Microsoft Windows
Server 2008 media.
2
Follow on-screen instructions until you reach the “Where do you want to
install Vista/2008”; then select “Load driver...”
3
The system prompts for the media to be inserted. Insert the installation
media and browse to the proper location when prompted.
4
Select the appropriate SAS 6/iR controller from the list, click “Next” and
continue installation as usual.
NOTE: Windows Server 2008 and Windows Vista operating systems include
native support for the SAS 6/iR RAID controller and the driver is automatically
installed. Check
26 Driver Installation
support.dell.com
for driver updates.
Page 29

Installing a Windows Server 2003, Windows Server 2008, Windows Vista, or Windows XP Driver for a New RAID Controller
Perform the following steps to configure the driver for the RAID controller on
a system that already has Windows installed.
1
Turn off the system.
2
Install the new RAID controller in the system.
3
Turn on the system.
The Windows operating system detects the new controller and displays a
message to inform the user.
4
The
Found New Hardware Wizard
detected hardware device.
NOTE: Windows 2008 and Vista include a device driver to support the SAS
controllers. The system automatically detects the new controller and installs
the driver. Check the version of the driver installed by Windows and update if
necessary.
5
Click
Next
.
6
On the
my device
7
Make the Driver Files available and browse to the proper location from the
Locate device driver
and click
Next
.
Locate Driver Files screen.
8
Click
Next
.
9
The wizard detects and installs the appropriate device drivers for the new
RAID controller.
10
Click
Finish
to complete the installation.
11
Reboot the server if Windows request to do so.
screen pops up and displays the
screen, select
Search for a suitable driver for
Driver Installation 27
Page 30

Updating an Existing Windows Server 2003, Windows Server 2008, Windows XP, or Windows Vista Driver
Perform the following steps to update the Microsoft Windows driver for the
SAS 6/iR controller already installed on your system
NOTE: It is important that you close all applications on your system before you
update the driver.
1
Select
Start→
The
System Properties
NOTE: For systems running a Microsoft Windows Server 2003 operating
system, click Start
2
Click on the
3
Click
Device Manager
The
Device Manager
NOTE: An alternative method is to open Device Manager. In Windows
Explorer, right click on “My Computer” and select “Manage”. The Computer
Management windows will open; select "Device Manager" in the left panel.
4
Double-click on
NOTE: In Windows 2008 and Windows Vista, SAS is listed under Storage
Controllers.
5
Double-click the RAID controller for which you want to update the driver.
6
Click the
Upgrade Device Driver Wizard
The
Settings→
Control Panel→ System
screen appears.
→
Control Panel→ System.
Hardware
tab.
.
screen appears.
SCSI and RAID Controllers
Driver
tab and click
Update Driver
screen appears.
.
.
.
.
7
Make the driver files available with the USB key, or other media.
8
Select
Install from a list or specific location
9
Click
Next.
10
Follow the steps in the wizard and browse to the location of the driver files.
11
Select the INF file from the USB key or other media.
12
Click
Next
and continue the installation steps in the Wizard.
13
Click
Finish
to exit the wizard and reboot the system for the changes to
.
take place.
28 Driver Installation
Page 31

Installing Linux Driver
Use the procedures in this section to install the driver for Linux. The driver is
updated frequently. To ensure that you have the current version of the driver,
download the updated Linux driver from the Dell Support website at
support.dell.com
Creating a Driver Diskette
.
Before beginning the installation, copy the drivers from the Service and
Diagnostic Utilities media or download the driver appropriate for Linux from
the Dell Support website at
support.dell.com.
This file includes two Red Hat
Package Managers (RPMs) and driver update disk files. The package also
contains the Dynamic Kernel Module Support (DKMS) Red Hat Package
Manager (RPM) file, source code, and release notes.
Refer to the documentation website at support.dell.com for more
information on DKMS.
The package is a zipped tar file. After downloading the package to a Linux
system, perform the following steps.
1
Unzip the package using gunzip.
2
Untar the file using
3
Use the dd command to create a driver update disk. Use the appropriate
tar -xvf
.
image for the purpose.
dd if=<name of the dd image file> of=/dev/fd0
NOTE: You can create a driver update disk on a Windows system using the
program dcopynt.
NOTE: The output file “of” might be different, depending on how your
operating system maps the floppy driver. The floppy drive does not need to be
mounted in order to execute the “dd” command.
4
Use the diskette for operating system installation as described later in
this section.
Driver Installation 29
Page 32

Creating a Driver Update Diskette Using DKMS
Perform the following steps to create the DUD using the DKMS tool:
NOTE: To work, the driver needs to be installed on the system where this procedure
is carried out.
1
Install the DKMS-enabled megaraid_sas driver rpm package.
2
Type the following command in any directory:
dkms mkdriverdisk –m megaraid_sas –v <driver
version> -k <kernel version> -d <distro>
NOTE: The values for the –d option are suse for SLES diskettes and
redhat for RHEL diskettes.
NOTE: For further information on usage of DKMS, refer to the dkms main page.
This starts the process to create the megaraid_sas DUD image. After the
DUD image has been built, you can find it in the DKMS tree for the
megaraid_sas driver. See the output of the
dkms mkdriverdisk
command for the exact path.
Installing Red Hat Enterprise Linux Operating Systems using the Driver Update Diskette
Perform the following steps to install Red Hat Enterprise Linux (versions 4
and 5) and the appropriate driver.
1
Boot normally from the Red Hat Enterprise Linux installation media.
2
At the command prompt, type:
linux expert dd
3
When the install prompts for a driver diskette, insert the diskette and press
<Enter>.
Refer to "Creating a Driver Diskette" on page 29 for information about
creating a driver diskette.
4
Complete the installation as directed by the installation program.
The driver will be installed.
30 Driver Installation
Page 33

Red Hat Enterprise Linux 5 Installation and Disk Enumeration
The operating system may not boot when Red Hat Enterprise Linux 5 is
installed on a system that has a serial-attached SAS 6i/R controller connected
to more than two hard drives. The issue occurs when the hard drives are
configured with more than one RAID configuration or when one RAID
volume along with one or two individual disks are connected to the controller.
In this scenario, the Red Hat Enterprise Linux 5 installer installs the Grand
Unified Bootloader (GRUB) to the incorrect hard drive. To avoid this issue,
complete the following steps during the operating system installation:
1
Insert the Red Hat Enterprise Linux 5 media and proceed through the
installation screens to the
2
Select
Review
and
3
Click
Next
. Proceed through the installation screens to the GRUB location
screen and select the
4
Click
Next
.
5
Select
Change Driver Order
6
In the Disk Order window, change the disks to the following order:
/dev/sdb
/dev/sdc
(if present)
/dev/sda
7
Click OK and then continue with the Red Hat Enterprise Linux 5
installation.
Drive Selection
Modify Partition Layout
screen.
.
Configure Advanced Bootloader Options
.
tab.
Installing SUSE Linux Enterprise Server Using the Driver Update Diskette
NOTE: Refer to "Creating a Driver Diskette" on page 29 for information about
creating a driver diskette.
To install SUSE Linux Enterprise Server (version 9 or 10) using the DUD:
1
Insert the appropriate SUSE Linux Enterprise Server (version 9 or 10)
Service Pack media in the system.
2
Select <F5> for the driver update disk.
NOTE: Press <F5> for SLES 10 installation and <F6> for SLES 9 installation as
shown on screen.
3
Select
Installation
from the menu.
Driver Installation 31
Page 34

4
Press <Enter> to load the Linux kernel.
5
At the prompt
click
OK
Please insert the driver update floppy
.
The system selects the driver from the diskette and installs it. The system
then displays the message
,
DRIVER UPDATE ADDED
6
Click OK.
with the description of the driver module.
If you want to install from another driver update medium, continue with
the following steps.
7
The system displays the message
MEDIUM
8
Select the appropriate driver update medium.
.
PLEASE CHOOSE DRIVER UPDATE
The system selects the driver from the disk and installs it.
NOTE: SLES 9 Gold media is required when you install any SLES 9 service
pack.
SUSE Linux Enterprise Server 10 Installation and Disk Enumeration
The operating system may not boot when SUSE Linux Enterprise Server 10 is
installed on a system that has the SAS 6/iR controller with more than two
hard drives connected. The issue occurs when the hard drives are configured
with more than one RAID configuration, or when one RAID volume along
with one or two individual disks are connected to the controller. In these
scenarios, the SUSE Linux Enterprise Server 10 installer will install the grand
unified bootloader (GRUB) to the incorrect hard drive. To avoid this issue,
complete the following steps during the operating system installation:
1
Insert the SUSE Linux installation media and proceed with the
installation screens to the
Expert
tab, and then select
2
The Boot Loader Settings window appears.
3
Select the
Boot Loader Installation
Installation Details
Installation Settings
Booting
.
window. Select the
.
tab and then select
Boot Loader
32 Driver Installation
Page 35

4
In the Disk Order window, change the disks to the following order:
/dev/sdb
/dev/sdc
(if present)
/dev/sda
5
Click OK and then click
Finish
to return to the
Installation Settings
screen.
6
Continue with the SUSE Linux Enterprise Server 10 installation.
Installing the RPM Package With DKMS Support
Perform the following steps to install the RPM package with DKMS support:
1
Uncompress the gzipped tarball driver release package
2
Install the DKMS package using the command:
<version>.noarch.rpm
3
Install the driver package using the command:
megaraid_sas-<version>.noarch.rpm
NOTE: Use rpm -Uvh <package name> when updating an existing
package.
4
If the previous device driver is in use, a reboot is required for the updated
driver to take effect
5
Verify that the driver has been loaded.
rpm –ihv dkms-
rpm –ihv
Upgrading the Kernel
When upgrading to a new kernel, you must reinstall the DKMS-enabled
driver packages. Perform the following steps to update or install the driver for
the new kernel:
1
In a terminal window, type the following:
dkms build -m <module_name> -v <module version>
-k <kernel version>
dkms install -m <module_name> -v <module version>
-k <kernel version>
2
To check whether the driver is successfully installed in the new kernel,
type:
dkms status
Driver Installation 33
Page 36

You must see a message similar to the following one on the screen to
confirm installation:
<driver name>, <driver version>, <new kernel
version>: installed
3
If the previous device driver is in use, a reboot is required for the updated
driver to take effect.
34 Driver Installation
Page 37

SAS 6/iR BIOS
The BIOS of the Dell™ Serial-Attached SCSI (SAS) 6/iR controller offers the
following features:
• Support for multiple SAS adapters
• POST Memory Management (PMM) support
• Redundant Array of Independent Disks (RAID) configuration tool
• Read-only memory (ROM) BIOS recovery image
• POST status error messaging
• Compatibility with Console Redirection
• POST accessible, text-based configuration utility (CTRL-C)
POST Messages
During POST, the BIOS displays messages that provide the status and
identification information of the SAS 6/iR controller, and also displays errors
detected during the POST process.
The BIOS POST identification banner prints the BIOS identification,
copyright information, and the controller version. It displays the list of
controllers and devices detected at initialization in a hierarchical order. The
BIOS also prompts you to start the Configuration Utility during the
POST process.
BIOS Fault Code Messages
If an error is encountered in the BIOS during POST, the BIOS Configuration
Utility forces you to acknowledge BIOS errors by halting the POST process
after the error display. You must press any key to continue. The BIOS
Configuration Utility allows you to choose to continue booting or stop
booting if errors are encountered.
SAS 6/iR BIOS 35
Page 38

Configuration Utility
Starting the Configuration Utility
1
Boot the system.
2
Press <Ctrl><C> during POST when prompted.
If you wait too long and the operating system logo appears, continue to
wait until the operating system completes bootup. Then restart your
system and try again.
The Configuration Utility menu screen displays.
Functions Performed
NOTE: The screens are organized in a hierarchical fashion and navigation hints are
displayed at the bottom of each screen. See the online help for additional
information about the utility.
Table 6-1. Functions Performed by the Configuration Utility
Function Description
Adapter List Lists all the SAS 6/iR controllers in the system.SAS 5 controllers
will also be listed.
Global
Properties
Adapter
Properties
Select New
Array Type
Create New
Array
View Array Displays the properties for the existing array and the option to
Manage Array Provides options for managing the current array.
Manage Hot
Spares
SAS Topology Lists the physical topology for the selected controller.
Lists static and modifiable properties applicable to all SAS 6/iR
controllers in the system.
Main screen for the selected controller. Lists the static and
modifiable properties for the selected SAS 6/iR controller. Provides
a menu for additional screens.
Provides the option to view existing arrays or create new arrays.
Provides the ability to add devices to the specified new array.
enter the Mange Array screen.
Provides the ability to add or remove global hot spares.
36 SAS 6/iR BIOS
Page 39

Table 6-1. Functions Performed by the Configuration Utility (continued)
Function Description
Device
Properties
Advanced
Adapter
Properties
Advanced
Device
Properties
PHY Properties Lists the properties for the PHYs for the selected controller.
Lists the properties of physical devices attached to the selected
controller.
Lists the advanced properties for the selected controller.
Lists static and modifiable advanced properties for all devices
attached to the selected controller.
Navigating the Configuration Utility
The navigation hints are displayed at the bottom of each screen. Online help
is also available in the utility.
NOTE: After you press <CTRL><C>, press <Enter> on the adapter to manage it.
Integrated RAID Configuration and Management Screens
Integrated RAID (IR) configuration and management involves many screens,
all of which are accessed by selecting RAID Properties on the Adapter
Properties screen.
• If no RAID arrays are currently configured, you are prompted to create
aRAID array.
• If at least one RAID array is currently configured, select
Array
to manage the array(s), or select the appropriate option to configure
a new array.
The screens in the RAID configuration and management properties area are:
• Select New Array Type
• Create New Array
• View Array
• Manage Array
View Existing
SAS 6/iR BIOS 37
Page 40

Select New Array Type
The two options for creating a new array are Create R1 Volume and Create
R0 Volume. Additional information about the disk type options appear on
the screen.
Create New Array
The Create New Array screen allows you to select disks for a new array.
1
Press <C> to create the array once the array is configured.
2
Save the changes when prompted to do so.
3
Press <F3> to confirm the changes.
After the array is created, the utility returns to the Adapter Properties screen.
See the table below for the array properties description.
NOTE: It is recommended that you back up your data prior to adding or updating
configurations.
Table 6-2. Array Field Descriptions
Field Description
Array
Number
Array
Identifier
Array Type Type of array (R1 or R0)
Array Scan
Order
Array Size
(MB)
Number of current array out of total arrays configured
Identifier text for the current array
Scan order for the current array
Size of the array
NOTE: In order to facilitate coercion on new larger disk drives, the disk size
must be coerced down with a factor of 128 MB. Additionally, to comply with
the latest Disk Data Format standard, 512 MB of space must be reserved for
RAID metadata on the drive. This results in several hundred MB of space
being removed from the usable size of an array when it is created.
38 SAS 6/iR BIOS
Page 41

Table 6-2. Array Field Descriptions (continued)
Field Description
Array
Status
Device
Slot
Number
Device
Identifier
RAID Disk Specifies whether or not the disk is part of a RAID array (Yes or No). This
Hotspare Specifies whether or not the disk is a hotspare
Status of the current array
The status definitions are given as:
Optimal—All members of the array are online and ready.
Degraded—One or more members of a RAID 1 array have failed or are
offline. The array can be returned to the Optimal state by replacing the
failed or offline member.
Disabled—The array has been disabled
Quiesced—The array has been quiesced
Resync—The array is resynchronizing
Failed—The array has failed
PermDegraded—The array is permanently degraded. This state indicates
that the failure threshold on the primary member was reached while no
secondary was available for correction. The data on the array may be
accessible, but the array cannot be returned to the optimal state.
Inactive—The imported array is inactive. The array must be activated
before it can be accessed.
Slot number in which the specified device sits
Identifier text for the specified device
field is grayed out under the following conditions:
• The disk does not meet the minimum requirements for use in a RAID
array.
• The disk is not large enough to mirror existing data on the primary
physical disk.
• The disk is a part of another array.
SAS 6/iR BIOS 39
Page 42

Table 6-2. Array Field Descriptions (continued)
Field Description
Drive
Status
Predicted
Failure
Size (MB) Actual physical size of the selected disk in the array.
Ok - Disk is online and fully functional.
Missing - Diskette is not detected.
Failed - Disk is not accessible or has reported a failure.
Initing - Disk is initializing.
CfgOffln - Disk is offline at host's request.
UserFail - Disk is marked failed at host's request.
Offline - Disk is offline for some other reason.
Inactive - Disk has been set to inactive.
Not Syncd - Data on disk is not synchronized with the rest of the array.
Primary - Disk is the primary disk for a 2 disk mirror and is OK.
Secondary - Disk is the secondary disk for a 2 disk mirror and is OK.
Wrg Typ e - Device is not compatible for use as part of a RAID array.
Too Small - Disk is too small to mirror existing data.
Max Dsks - Maximum # of disks allowed for this type of array reached
Maximum # of total IR disks on a controller reached.
No SMART - Disk doesn't support SMART and can't be used in a RAID
array.
Wrg Intfc - Device interface (SAS/SATA) differs from existing IR disks.
Indicates whether device SMART is predicting device failure.
NOTE: The SAS 6ir controllers do support Drive Status LED operation on Dell
PowerEdge systems which include drive status LEDs. Status LED support is only
supported for drives which are configured as members of a Virtual Disk or Hot Spare.
SAS 6iR supported Drive Status LED states may vary from those supported by other
hardware based RAID solutions such as PERC 6.
NOTE: Replacing a member of an array in the Permanently Degraded state will result in
the new physical disk being displayed as failed since resynchronization is possible. This
does not indicate an actual failure on the new physical disk.
40 SAS 6/iR BIOS
Page 43

View Array
The View Array screen allows you to view the current array configuration.
Press <Alt+N> to view the next array. See the table above to view
descriptions of each virtual disk property.
Manage Array
The Manage Array screen is used to manage the current array. The options
are Manage Hotspares, Synchronize Mirror, Activate Array, and Delete Array.
A confirmation is requested for each action.
Table 6-3. Manage Array Field Descriptions
Field Description
Identifier The identifier of the array
Type The RAID type of the array
Scan Order The scan order of the array
Size (MB) The coerced size of the array
NOTE: In order to facilitate coercion on new larger disk drives, the disk
size must be coerced down with a factor of 128 MB. Additionally, to
comply with the latest Disk Data Format standard, 512 MB of space must
be reserved for RAID metadata on the drive. This results in several
hundred MB of space being removed from the usable size of an array
when it is created.
Status The status of the array
Manage
Hotspares
Synchronize
RAID 1
This option is used to create or delete global hot spares. Using this
option you can also:
• Assign a hot spare, (Integrated Raid 1 configurations only).
• Display each drive’s type, size and hot spare status.
This option is used to synchronize the R1 array.
This option is not accessible under the following conditions:
• The array is inactive.
• The array does not need to be resynchronized.
• R0 array is used.
SAS 6/iR BIOS 41
Page 44

Table 6-3. Manage Array Field Descriptions (continued)
Field Description
Activate
Array
Delete Array This option is used to delete the currently displayed array.
This option is used to activate an inactive (foreign) array. The option is
grayed out if there are no inactive arrays.
Exit Screen
It is important to exit the SAS BIOS Configuration Utility properly, because
some changes take effect only when you exit. From the Adapter List, press
<Esc> to exit. In addition, a similar exit screen appears when you exit most
other screens, and it can be used to save settings.
Performing Configuration Tasks
Creating an Integrated Striping Virtual Disk
An Integrated Striping (IS) virtual disk, also referred to as RAID 0, offers the
ability to stripe data across multiple physical disks. RAID 0 volumes offer
increased capacity by combining multiple physical disks into a single virtual
disk. RAID 0 volumes also offer increased performance by striping disk access
across multiple physical disks. Follow these steps to create a RAID 0 virtual
disk on a SAS 6/iR controller.
1
Select a controller from the
2
Select the
3
Select
RAID 0 virtual disk or a RAID 1 virtual disk.
The next screen shows a list of disks that can be added to a virtual disk.
RAID Properties
Create
RAID 0
Adapter List
option.
Volume
in the Configuration Utility.
when you are prompted to create either a
4
Move the cursor to the
disk, change “No” to “Yes” by pressing the <+>, <->, or space bar.
As disks are added, the
of the new virtual disk.
NOTICE: All data will be lost upon creation of the virtual disk.
42 SAS 6/iR BIOS
RAID Disk
Virtual Disk Size
column. To add a disk to the virtual
field changes to reflect the size
Page 45

There are several limitations when creating a
RAID 0
virtual disk:
• All disks must be either Dell-compliant SAS or SATA physical disks.
• SAS and SATA physical disks cannot be used in the same virtual disk.
• There must be at least 2 physical disks in a virtual disk.
• No more than 8 physical disks are allowed in a virtual disk.
5
Press <C> and then select
Save changes
when the virtual disk has been
fully configured.
6
Press <F3> to confirm that existing data will be lost with the creation of
the virtual disk. The Configuration Utility will pause while the virtual disk
is being created.
NOTICE: RAID 0 does not provide any data protection in the event of disk failure.
It is primarily used to increase performance.
NOTE: Once the number of disks in a RAID virtual disk is set, it cannot be changed.
NOTE: The maximum size of the virtual disk that contains the bootable operating
system is 2 Terabytes. This is due to operating system restrictions.The maximum
array size (non-bootable) is 16 Terabytes.
Creating a Integrated Mirroring Virtual Disk
An Integrated Mirroring (IM) virtual disk, also referred to as RAID 1, offers
the ability to mirror data from one physical disk onto another one. RAID 1
volumes offer increased reliability by combining two physical disks into a
single virtual disk such that each disk contains a mirrored copy of the other’s
data. Follow these steps to create a RAID 1 virtual disk on a SAS 6/iR
controller that does not currently have a virtual disk configured.
1
Select a controller from the
2
Select the
3
Select
RAID Properties
Create RAID 1 Volume
a RAID 0 virtual disk or a RAID 1 virtual disk.
The next screen shows a list of disks that can be added to a virtual disk.
4
Move the cursor to the
disk, change “No” to “Yes” by pressing the <+>, <->, or space bar.
Adapter List
in the Configuration Utility.
option.
when you are prompted to create either
RAID Disk
column. To add a disk to the virtual
NOTICE: Data on both disks will be lost. It is recommended that you back up all
data before performing these steps.
SAS 6/iR BIOS 43
Page 46

5
There are several limitations when creating a RAID 1 virtual disk:
• All disks must be either Dell-compliant SAS or SATA physical disks.
• SAS and SATA physical disks cannot be used in the same virtual disk.
• There must be 2 physical disks in a RAID 1 virtual disk.
6
Press <C> and then select
Save changes
when the virtual disk has been
fully configured.
NOTE: There is an option to create a hot spare for a RAID 1 virtual disk.
The Create RAID 1 screen allows the option to assign a hot spare. Only drives
that are compatible with the new virtual disk configuration can be selected.
The maximum number of hot spares allowed is two.
7
Press <F3> to confirm that existing data will be lost with the creation of
the virtual disk. The Configuration Utility will pause while the virtual disk
is being created.
NOTE: RAID 1 provides protection against the failure of a single physical disk.
When a disk fails, the physical disk can be replaced and the data re-mirrored to the
physical disk, maintaining data integrity.
Viewing Virtual Disk Properties
Follow these steps to view the properties of RAID 0 and RAID 1 virtual disks:
1
Select a controller from the
2
Select the
RAID Properties
• If there are no existing virtual disks, you will be prompted to create a
RAID 0 or a RAID 1 virtual disk.
• If there is one existing virtual disk, select
• If there are two existing virtual disks, press <Alt+N> to view the next
virtual disk.
• If a compatible global hot spare exists it displays with the members of
the virtual disk.
3
Press <Enter> when the
current virtual disk.
Adapter List
option.
Manage Array
in the Configuration Utility.
View Existing Array
.
item is selected to manage the
44 SAS 6/iR BIOS
Page 47

Synchronizing a Virtual Disk
Synchronizing a virtual disk means that the firmware synchronizes the data on
the secondary disk(s) with the data on the primary disk of the mirror.
Follow these steps to start synchronization for a RAID 1 virtual disk:
1
Select
Synchronize Mirror
2
Press Y to start the synchronization or N to cancel it.
.
Activating a Virtual Disk
A virtual disk can become inactive if, for example, it is removed from one SAS
6/iR controller and moved to another one. The Activate option allows you
to reactivate an inactive virtual disk that has been added to a system.
This option is only available when the selected virtual disk is currently inactive.
NOTE: Do not migrate a volume or hotspares to a different system unless that
system does not currently have the maximum number of virtual disks and hotspares.
The maximum number of virtual disks is two and the maximum number of hotspares
is two. Exceeding this number may result in undesirable behavior.
1
Select
Activate Mirror
2
Press Y to proceed with the activation or press N to abandon it.
After a pause, the virtual disk will become active.
NOTE: Activation of migrated virtual disks is only supported when the migrated
virtual disk(s) is in an optimal state and contains all the physical disks.
.
NOTE: If a virtual disk with defined hot spare drives is migrated to a SAS6/iR
controller that has a native virtual disk with defined hot spares already configured,
and the total number of hot spares is greater than the maximum supported number
of hot spares (2) then the migrated hot spare drive(s) will be deleted. After a reboot,
those drives are displayed as basic drives on the system. You can then create the
desired virtual disk and hot spare drive configuration using CTRL-C or the RAID
management application.
Migrating and Activating a Virtual Disk
Virtual disks and hot spares can be migrated from other SAS 6/IR controllers
only. Virtual disks cannot be migrated from any other controllers, including
the SAS 5 series of controllers or PERC series of controllers. During the
migration process, all systems must be powered down prior to removing and
SAS 6/iR BIOS 45
Page 48

replacing drives. Volumes that are migrated to another controller will be
inactive and must therefore be activated.To activate a virtual disk see
"Activating a Virtual Disk" on page 45.
Deleting a Virtual Disk
NOTICE: Before deleting a virtual disk, be sure to back up all data on the virtual
disk that you want to keep.
Follow these steps to delete a selected virtual disk:
1
Select
Delete Virtual Disk
2
Press Y to delete the virtual disk or press N to abandon the deletion.
3
Press <F3> to confirm deletion of the virtual disk. After a pause, the
.
firmware deletes the virtual disk.
NOTICE: If the physical disks of a virtual disk are removed and the virtual disk’s
configuration is subsequently deleted from the SAS 6/iR controller, the physical
disks show up only as simple disks with no RAID association if they are placed back
onto the same SAS 6/iR controller. Once the virtual disk is removed from a SAS 6/iR
controller using the BIOS Configuration Utility (regardless whether the physical
disks members are present), the virtual disk cannot be restored.
Hot Spare Failover
If a RAID 1 virtual disk enters a degraded state, a compatible hot spare
automatically begins rebuilding the degraded virtual disk. The "missing" or
"failed" member of the degraded virtual disk displays as a ‘missing’ global hot
spare. The "missing" or "failed" drive must be replaced with a drive compatible
with an existing virtual disk(s).
Replacing and Rebuilding a Degraded Virtual Disk
In the event of a physical disk failure in a RAID 1 virtual disk, you will need to
replace the disk and resynchronize the virtual disk. Synchronization occurs
automatically on replacing the physical disk using the following steps.
Replace the failed physical disk with a blank disk of the same type and of
1
equal or greater capacity.
2
Check your management application or the BIOS Configuration Utility
(Ctrl-C) to ensure synchronization started automatically.
46 SAS 6/iR BIOS
Page 49

NOTE: During the rebuilding of a volume the synchronization will be restarted from
the beginning if a hard drive is added or removed from the system. Wait until any
synchronization processes have been completed before adding or removing hard
drives.
NOTE: Always remove any configuration information from hard drives if they are to
be removed from a system. This can be completed by deleting the RAID
configuration through the BIOS configuration utility or an operating system unless
you are migrating these hard drives to a different system level application. SAS 6/iR
hotspare functionality requires that the slots in which hard drives are inserted be
associated with the virtual disks they are a part of. Do not insert hard drives with
foreign or old (out of date) configuration information stored on those hard drives
into slots that are associated with existing virtual disks.
NOTE: If the system is rebooted while the rebuild is in progress, the rebuild will be
restarted from the beginning. The rebuild time for a volume varies depending on the
size of the member disks and any additional system activity. A system with no
additional activity executes a rebuild at approximately 30 MB per second.
SAS 6/iR BIOS 47
Page 50

48 SAS 6/iR BIOS
Page 51

Troubleshooting
To get help with problems with your Dell™ Serial-Attached SCSI (SAS) 6/iR
controller, you can Contact Dell or access the Dell Support website at
support.dell.com.
BIOS Boot Order
If you intend to boot to the controller, ensure it is set appropriately in the
system's BIOS boot order. See your system documentation for more
information.
General Problems
NOTE: For additional troubleshooting information, see the SAS RAID Storage
Manager User’s Guide and the OpenManage Storage Services User’s Guide.
Table 7-1. General Problems
Problem Suggested Solution
No Physical Disks
Found message appears
during a CD installation of a
Windows operating system.
The message appears due to one of the following
reasons:
• The driver is not supported on the operating system.
(applicable to Windows 2003 and Windows XP
operating systems only)
• The controller BIOS is disabled.
• Physical disks are not connected or seated properly.
The corresponding solutions to the three causes of the
message are:
• Press <F6> to install the Device Driver
during installation.
• Enter the BIOS Configuration Utility to enable
the BIOS. See "SAS 6/iR BIOS" on page 35.
• Verify if the physical disks are connected or
seated properly.
Troubleshooting 49
Page 52

Physical Disk Related Issues
Table 7-2. Physical Disk Issues
Problem Suggested Solution
The system does
not boot from
the SAS 6/iR
controller.
Physical disk is
not enumerated
during POST.
One of the
physical disks in
the array shows
the status as
"Failed".
Integrated
Mirroring (IM)
virtual disk does
not rebuild.
Ensure that the boot disk is attached to the controller at the lowest
ID and check the controller and the physical disk boot order in the
system BIOS.
NOTE: See your system documentation for information about boot
device selection.
• Go to the Configuration Utility and ensure that the physical disk
is not enumerated in the SAS topology.
• Verify the cable connection.
• Reseat the physical disk.
• Check and reseat the cable.
• Check the SAS cables.
• Reseat the physical disk.
• Check the enclosure or the backplane for damage.
• Contact Dell if the problem persists.
• Enter the Configuration Utility and ensure the physical disk is
enumerated in the SAS topology.
• Ensure the new disk is of the same drive type as the other disk in
the virtual disk (SAS/SATA).
• Ensure the new disk is of equal or greater capacity as the other
disk in the virtual disk.
• Ensure the new disk is not detected as an inactive virtual disk
under the RAID Properties menu. Delete the newly inserted
inactive disk.
• Ensure the inserted disk has the same ID as the disk it is
replacing. Assign the correct ID to the disk or use the
Secondary Disk
• Ensure the new disk is a Dell supported SAS or SATA disk.
feature in the M
anage Array
Manage
menu.
50 Troubleshooting
Page 53

Configuration Utility Error Messages
NOTE: These error messages are displayed inside the Configuration Utility.
Restart your system and retry if you encounter any of these.
NOTE: If the error message continues to be displayed even after following the
steps mentioned in Table 7-3 for the resolution of the error, contact Dell Support for
advanced troubleshooting. For information on how to contact Dell Technical
Support, see "Getting Help" on page 57.
Table 7-3. Configuration Utility Error Messages
Message Meaning and Suggested Solution
An error occurred while
reading non-volatile
settings.
An error occurred while
reading current
controller settings.
Advanced Device
Properties settings not
found.
Error obtaining PHY
properties configuration
information.
Configuration Utility
Options Image
checksum error.
Can't load default
Configuration Utility
options.
An error occurred while
writing non-volatile
settings.
An error reading any one of a number of settings
from the firmware. Reseat the controller and
reboot.
Controller setup and initialization has failed.
Reboot the system.
Failed to read vital configuration page from
firmware. Reflash the firmware and reboot.
Failed to read vital configuration page from
firmware.Reflash the firmware and reboot.
Failed to properly read Configuration Utility
options from flash. Restart and retry. If the issue
persists, reflash the firmware on the controller.
Failed to allocate memory for Configuration
Utility options structure.
An error occurred while writing one or more
settings to the firmware.
Troubleshooting 51
Page 54

BIOS Error Messages
Table 7-4. BIOS Error Messages
Message Meaning
Press <Ctrl+C> to
Enable BIOS
Adapter at Baseport
xxxx is not
responding where xxxx
is the baseport of
the controller
Following SAS targets
are not responding...
Adapter configuration
may have changed,
reconfiguration is
recommended!
Press CTRL-C to run
Dell SAS 6
Configuration
Utility…
Initializing... Displays while the BIOS is waiting to initialize.
SAS discovery error Indicates that there was a discovery error reported by
When the BIOS is disabled, you are given the option
to enable it by entering the configuration utility. You
can change the setting to Enabled in the
configuration utility.
If the controller does not respond for any reason but
is detected by the BIOS, it displays this warning and
continues. Shut down the system and try to reseat
the controller. If this message appears again, Contact
Dell.
When the BIOS determines that previously
configured physical disks are not connected to the
controller, the BIOS displays this warning and
continues to boot. The system continues to boot. See
"Physical Disk Related Issues" on page 50 for
troubleshooting tips.
Start the Configuration Utility and confirm the
configuration of the SAS 6/iR controller.
the firmware and may be accompanied by more such
messages. Enter the Configuration Utility to
investigate.
52 Troubleshooting
Page 55

Table 7-4. BIOS Error Messages (continued)
Message Meaning
Integrated RAID
exception detected:
Volume (xx:yy:zzz) is
currently in state
“STATE”
Device not available Device may not be ready at this time. The device will
Spinning up the
device!
ERROR! Device is not
responding to Read
Capacity
Failed to add device,
too many devices!
ERROR! Adapter
Malfunctioning!
MPT firmware fault The LSI Logic MPT firmware faulted. Contact Dell.
The BIOS detected an exception with one or more
RAID virtual disk. For additional troubleshooting
information, see the error message "Volume
(xx:yy:zzz) is currently in state
“STATE”.
Lists the current state of the specified virtual disk
when it is not optimal. The state may include:
• INACTIVE: The virtual disk is inactive, possibly
foreign, or could be in any one of the states
mentioned below.
• DEGRADED: The virtual disk is in a degraded state
and has lost redundancy.
• RESYNCING: The virtual disk is degraded and
currently rebuilding.
• FAILED: The virtual disk has an error and is in a
failed state.
• MISSING: The virtual disk is no longer present
though a record of it remains.
be retried. If the problem persists, restart your
system.
The device currently being scanned is being spun up.
The device did not respond to a read capacity
command. Contact Dell.
Could not allocate resources for additional devices.
The adapter did not initialize properly. There may be
a problem with the adapter configuration. Reload the
BIOS configuration. Invoke the configuration utility
again and see if the issue persists.
Troubleshooting 53
Page 56

Table 7-4. BIOS Error Messages (continued)
Message Meaning
Adapter removed from
boot order!
Updating Adapter
List!
Adapter(s) disabled
by user
Adapter configuration
may have changed,
reconfiguration is
suggested!
Memory allocation
failed
Invalid or corrupt
image
Image upload failed Could not upload the image for the Configuration
Image not found Could not locate the image for the Configuration
Unable to load LSI
Configuration Utility
Unable to load LSI
Logic Corp MPT BIOS
MRT BIOS Fault 02h
encountered at
adapter PCI (XXh,
XXh,XXh)
Fusion-MPT Firmware
fault code 0706h
An controller that was previously in the boot order
was not found. It has either been removed from the
system or moved to a different slot.
A new adapter was found for which there is no record.
A record will be created for it.
An adapter was found, but it has been disabled in the
Configuration Utility and will not be used by the
BIOS.
A controller has been moved or reinstalled in the
system. Add it to the boot order using the available
resources.
The controller could not allocate enough memory to
load the Configuration Utility, its strings file, or its
options file. Reboot the system.
One of the images for the Configuration Utility, its
strings file, or its options file is corrupt. Reload the
BIOS. Reflash the firmware.
Utility, its strings file, or its options file. Reload the
BIOS.Reflash the firmware.
Utility, its strings file, or its options file.
Could not load the Configuration Utility. This error
usually follows one of the four previous messages.
The controller was downgraded from the current
firmware revision to an earlier revision which cannot
support the current configuration information and
cannot be initialized. Contact Dell support for
assistance.
54 Troubleshooting
Page 57

Updating the Firmware
Updating the Dell™ Serial-Attached SCSI (SAS) 6/iR controller firmware is
achieved by flashing the firmware. The firmware can be flashed while the
controller is in use. The system must be restarted for the changes to the
firmware to take effect. If there is a failure while flashing the firmware (such
as a power outage) the controller reverts back to the earlier version of the
firmware.
NOTE: If you flash the firmware while using the controller, you may notice
temporary degradation in the controller's performance.
Firmware Update Utility
Firmware update utility can be run from a variety of operating systems.
Firmware flash is automated and no user intervention is required. You can
obtain firmware flash utility from the Dell™ PowerEdge™ Service and
Diagnostic Utilities media that shipped with your system.
Running the firmware update utility from the operating system is not
supported on Dell workstations. You have to perform a manual update. In the
event of new firmware release, check the Dell Support website at
support.dell.com for the latest firmware updates and the firmware
update procedure.
Updating the Firmware 55
Page 58

56 Updating the Firmware
Page 59

Getting Help
Obtaining Assistance
CAUTION: If you need to remove the computer cover, first disconnect the
computer power and modem cables from all electrical outlets.
If you need assistance with a technical problem, perform the following steps:
1
Complete the procedures in the section "Troubleshooting Your System" of
your system’s
2
Run the system diagnostics and record any information provided.
3
Use Dell's extensive suite of online services available at Dell Support at
support.dell.com
procedures.
For more information, see "Online Services" on page 58.
4
If the preceding steps have not resolved the problem, call Dell for technical
assistance.
NOTE: Call the support service from a phone near or at the system so that the
support staff can assist you with any necessary procedures.
NOTE: Dell’s Express Service Code system may not be available in all countries.
When prompted by Dell's automated telephone system, enter your Express
Service Code to route the call directly to the proper support personnel. If you do
not have an Express Service Code, open the
double-click the
For instructions on using the technical support service, see "Dell Enterprise
Training" on page 59 and "Before You Call" on page 60.
Hardware Owner’s Manual
for help with installation and troubleshooting
Express Service Code
.
Dell Accessories
icon, and follow the directions.
folder,
NOTE: Some of the following services are not always available in all locations
outside the continental U.S. Call your local Dell representative for information
on availability.
Getting Help 57
Page 60

Technical Support and Customer Service
Dell's support service is available to answer your questions about Dell™
hardware. Our support staff use computer-based diagnostics to provide fast,
accurate answers.
To contact Dell's support service, see "Before You Call" on page 60, and then see
the contact information for your region or go to
support.dell.com
.
Online Services
You can access Dell Support at support.dell.com. Select your region on the
WELCOME TO DELL SUPPORT page, and fill in the requested details to
access help tools and information.
You can learn about Dell products and services on the following websites:
www.dell.com
www.dell.com/ap
www.dell.com/jp
www.euro.dell.com
www.dell.com/la
www.dell.ca
You can access Dell Support through the following websites and e-mail
addresses:
• Dell Support websites
support.dell.com
support.jp.dell.com
support.euro.dell.com
• Dell Support e-mail addresses
mobile_support@us.dell.com
support@us.dell.com
la-techsupport@dell.com (Latin America and Caribbean countries only)
apsupport@dell.com
(Asian/Pacific countries only)
(Japan only)
(Europe only)
(Latin American and Caribbean countries)
(Canada only)
(Japan only)
(Europe only)
(Asian/Pacific countries only)
58 Getting Help
Page 61

• Dell Marketing and Sales e-mail addresses
apmarketing@dell.com
sales_canada@dell.com (Canada only)
• Anonymous file transfer protocol (FTP)
ftp.dell.com/
(Asian/Pacific countries only)
Log in as user:
anonymous
, and use your e-mail address as your password.
Automated Order-Status Service
To check on the status of any Dell products that you have ordered, you can
go to
support.dell.com
A recording prompts you for the information needed to locate and report on
your order. See the contact information for your region.
, or you can call the automated order-status service.
Dell Enterprise Training
Dell Enterprise training is available; see
information. This service may not be offered in all locations.
www.dell.com/training
for more
Problems With Your Order
If you have a problem with your order, such as missing parts, wrong parts, or
incorrect billing, contact Dell for customer assistance. Have your invoice or
packing slip available when you call. See the contact information for your
region.
Product Information
If you need information about additional products available from Dell, or if you
would like to place an order, visit the Dell website at
telephone number to call to speak to a sales specialist, see the contact
information for your region.
www.dell.com
. For the
Getting Help 59
Page 62

Returning Items for Warranty Repair or Credit
Prepare all items being returned, whether for repair or credit, as follows:
1
Call Dell to obtain a Return Material Authorization Number, and write it
clearly and prominently on the outside of the box.
For the telephone number to call, see the contact information for your
region.
2
Include a copy of the invoice and a letter describing the reason for the
return.
3
Include a copy of any diagnostic information indicating the tests you have
run and any error messages reported by the system diagnostics.
4
Include any accessories that belong with the item(s) being returned (such
as power cables, media such as CDs and diskettes, and guides) if the return
is for credit.
5
Pack the equipment to be returned in the original (or equivalent) packing
materials.
You are responsible for paying shipping expenses. You are also responsible
for insuring any product returned, and you assume the risk of loss during
shipment to Dell. Collect-on-delivery (C.O.D.) packages are not accepted.
Returns that are missing any of the preceding requirements will be refused at
our receiving dock and returned to you.
Before You Call
NOTE: Have your Express Service Code ready when you call. The code helps Dell's
automated-support telephone system direct your call more efficiently.
NOTE: See your system’s Hardware Owner’s Manual for the telephone numbers
and codes provided to contact Dell Support.
If possible, turn on your system before you call Dell for technical assistance and
call from a telephone at or near the system. You may be asked to type some
commands at the keyboard, relay detailed information during operations, or try
other troubleshooting steps possible only at the system itself. Ensure that the
system documentation is available.
CAUTION: Before servicing any components inside your system, see your Product
Information Guide for important safety information.
60 Getting Help
Page 63

Regulatory Notices
For additional regulatory information, please go to the Regulatory
Compliance Homepage on www.dell.com at the following location:
www.dell.com/regulatory_compliance.
Appendix C 61
Page 64

62 Appendix C
Page 65

Corporate Contact Details (Taiwan Only)
Pursuant to Article 11 of the Commodity Inspection Act, Dell provides the following corporate
contact details for the certified entity in Taiwan for the products addressed by this document:
Dell B.V. Taiwan Branch
20/F, No. 218, Sec. 2, Tung Hwa S. Road,
Tai p ei , Tai wa n
Appendix D 63
Page 66

64 Appendix D
Page 67

Glossary
This section defines or identifies technical terms, abbreviations, and acronyms
used in this document.
A
Adapter
An adapter enables the computer system to access peripheral devices by
converting the protocol of one bus or interface to another. An adapter may also
provide specialized function. Adapters may reside on the system board or be an
add-in card. Other examples of adapters include network and SCSI adapters.
B
BIOS
(Basic Input/Output System) The part of the operating system in a system that
provides the lowest level interface to peripheral devices. BIOS also refers to the Basic
Input/Input Output System of other “intelligent” devices, such as RAID controllers.
BIOS Configuration Utility
The BIOS Configuration Utility reports and enables the configuration of
controller properties. The utility resides in the controller BIOS and its operation
is independent of the operating systems on your system. The BIOS
Configuration Utility, also known as Ctrl-C, is built on elements called controls.
Each control performs a function.
C
Coercion
Coercion is the process of rounding down the number of Logical blocks used
for the physical members of a virtual disk to a common number. This allows
drives with different absolute capacities, which can vary between drive
manufacturers and drive families, to share a common stripe size and count as
members of the virtual disk. Coercion necessarily results in a smaller capacity
than was available on the un-coerced basic physical drive.
Glossary 65
Page 68

Controller
A chip that controls the transfer of data between the microprocessor and
memory or between the microprocessor and a peripheral device such as a
physical disk or the keyboard. In Storage Management, the hardware or logic
that interacts with storage devices to write and retrieve data and perform storage
management. RAID controllers perform RAID functions such as striping and
mirroring to provide data protection.
D
Disk
A non-volatile, randomly addressable, rewriteable mass storage device, including
rotating magnetic, optical and solid-state storage devices, or non-volatile
electronic storage elements.
DKMS
DKMS stands for Dynamic Kernel Module Support. It is designed to create a
framework where kernel dependent module source can reside so that it is very
easy to rebuild modules as you upgrade kernels. This will allow Linux vendors to
provide driver drops without having to wait for new kernel releases while also
taking out the guesswork for customers attempting to recompile modules for
new kernels.
Driver
A device driver, often called a driver for short, is a program that allows the
operating system or some other program to interface correctly with a peripheral
device such as a printer, a network PC card or the SAS 6/iR controller.
DUD (Driver Update Diskette)
Acronym for driver update diskette. A DUD is an image of a diskette stored as a
regular file. To use it, you have to create a real diskette from this file. The steps used
to create the diskette depend on how the image is supplied.
66 Glossary
Page 69

F
Firmware
Software stored in read-only memory (ROM) or Programmable ROM (PROM).
Firmware is often responsible for the behavior of a system when it is first turned
on. A typical example would be a monitor program in a system that loads the
full operating system from disk or from a network and then passes control to the
operating system.
Flash Memory
Sometimes referred as simply "flash", is a compact, solid-state, rewriteable,
non-volatile memory device that retains its data when the power is turned off.
It offers fast access time, low power consumption, and relative immunity to
severe shock or vibration. It is a special type of EEPROM that can be erased and
reprogrammed in blocks instead of one byte at a time. Many modern PCs have
their BIOS stored on a flash memory chip so that it can easily be updated if
necessary. Such a BIOS is sometimes called a flash BIOS.
H
Hardware
The mechanical, magnetic, electronic, and electrical components making up a
computer system constitutes its hardware.
Hot Add/Remove
It is the addition/removal of a component while the system is running and
operating normally.
L
Link
A connection between any two PCI Express devices is known as a link.
Glossary 67
Page 70

M
MHz
Megahertz or one million cycles per second is a unit of frequency commonly
used to measure the operating speed of a computer processor or any other
electronic component.
Mirroring
The process of providing complete redundancy using two physical disks, by
maintaining an exact copy of one physical disk’s data on the second physical disk.
If one physical disk fails, the contents of the other physical disk can be used to
maintain the integrity of the system and to rebuild the failed physical disk.
N
NVDATA
This refers to non-volatile data. It is the configuration information that is part
of and is used by the controller firmware and is stored in the flash memory on
the controller.
O
Operating System
The software that runs a computer, including scheduling tasks, managing
storage, and handling communication with peripherals and performs basic
input/output functions, such as recognizing input from the keyboard, sending
output to the display screen, etc. is called an operating system.
P
PCI Express (PCI-E)
PCI Express (PCI-E) is an evolutionary upgrade to the existing Peripheral
Component Interconnect (PCI) bus. PCI-E is a serial connection that operates
more like a network than a bus. Instead of one bus that handles data from
multiple sources, PCI-E has a switch that controls several point-to-point serial
68 Glossary
Page 71

connections. These connections fan out from the switch, leading directly to the
devices where the data needs to go. Every device has its own dedicated
connection, so devices no longer share bandwidth like they do on a normal bus.
PHY
The interface required to transmit and receive data packets transferred across
the serial bus. Each PHY can form one side of the physical link in a connection
with a PHY on a different Dell-qualified SATA device. The physical link
contains four wires that form two differential signal pairs. One differential pair
transmits signals, while the other differential pair receives signals. Both
differential pairs operate simultaneously and allow concurrent data transmission
in both the receive and the transmit directions.
Physical Disk
A physical disk (also known as hard disk drive) consists of one or more rigid
magnetic discs rotating about a central axle, with associated read/write heads
and electronics. A physical disk is used to store information, (data), in
a non-volatile and randomly accessible memory space.
POST
POST, short for Power-On Self-Test is a process performed before the operating
system loads when the computer is turned on. The POST tests various system
components, such as RAM, the physical disks, and the keyboard.
R
RAID
Acronym for Redundant Array of Independent Disks (originally Redundant
Array of Inexpensive Disks). It is an array of multiple independent physical disks
managed together to yield higher reliability and/or performance exceeding that
of a single physical disk. The virtual disk appears to the operating system as a
single storage unit. I/O is expedited because several disks can be accessed
simultaneously. Redundant RAID levels provide data protection.
Glossary 69
Page 72

ROM
Read-only memory (ROM), also known as firmware, is an integrated circuit
programmed with specific data when it is manufactured. ROM chips are used
not only in computers, but in most other electronic items as well. Data stored in
these chips is nonvolatile i.e., it is not lost when the power is turned off.
Data stored in these chips is either unchangeable or requires a special operation
such as flashing to change.
RPM
RPM, short for "Red Hat Package Manager" is a package management system
primarily intended for Linux. RPM installs, updates, uninstalls, verifies and
queries software. RPM is the baseline package format of the Linux Standard
Base. Originally developed by Red Hat for Red Hat Linux, RPM is now used by
many Linux distributions. It has also been ported to some other operating
systems such as NetWare by Novell.
S
SAS
Serial-Attached SCSI, SAS, is a serial, point-to-point, enterprise-level device
interface that leverages the proven SCSI protocol set. The SAS interface
provides improved performance, simplified cabling, smaller connectors, lower
pin count, and lower power requirements when compared to parallel SCSI.
SATA
Serial Advanced Technology Attachment, a physical storage interface standard,
is a serial link that provides point-to-point connections between devices.
The thinner serial cables allow for better airflow within the system and permit
smaller chassis designs.
SCSI
SCSI stands for "Small Computer System Interface," a processor-independent
standard interface for system-level interfacing between a computer and
intelligent devices including hard-drives, floppy disks, CD-ROM, printer,
scanners and many more.
70 Glossary
Page 73

SCSIport
SCSIport driver is a Microsoft® driver for Windows® XP storage architecture,
delivering SCSI commands to the storage targets. The SCSIport driver works
well with storage using parallel SCSI.
Serial Architecture
Serial architectures have emerged to deliver higher performance by allowing
more bandwidth per device pathway than their parallel counterparts.
Serial architecture connections consist of a single pair of transmission signals
that contain an embedded clock for self-clocking, enabling clock speed to be
easily scaled. Serial bus architectures also support a network of dedicated
point-to-point device connections, versus the multi-drop architectures of
parallel buses, to deliver full bandwidth to each device, eliminate the need for
bus arbitration, reduce latency, and greatly simplify hot-plug and hot-swap
system implementations.
Serial Technology
Serial storage technology, specifically Serial ATA, Serial-Attached SCSI and
PCI Express, address the architectural limitations of their parallel counterparts
to deliver highly scalable performance. The technology draws its name from the
way it transmits signals - in a single stream, or serially, compared to multiple
streams for parallel. The main advantage of serial technology is that while it
moves data in a single stream, it wraps data bits into individual packets that are
transferred up to 30 times faster than parallel technology data.
SMART
Acronym for Self-Monitoring Analysis and Reporting Technology.
The self-monitoring analysis and reporting technology (SMART) feature
monitors the internal performance of all motors, heads, and drive electronics
to detect predictable drive failures. This feature helps monitor drive
performance and reliability, and protects the data on the drive. When problems
are detected on a drive, you can replace or repair the drive without losing any
data. SMART-compliant disks have attributes for which data (values) can be
monitored to identify changes in values and determine whether the values are
within threshold limits. Many mechanical failures and some electrical failures
display some degradation in performance before failure.
Glossary 71
Page 74

Storport
The Storport driver has been designed to replace SCSIport and work with
Windows 2003 and beyond. In addition, it offers better performance for storage
controllers, providing higher I/O throughput rates, improved manageability, and
an upgraded miniport interface.
Stripe Element
A stripe element is the portion of a stripe that resides on a single physical disk.
Striping
Disk striping writes data across all physical disks in a virtual disk. Each stripe
consists of consecutive virtual disk data addresses that are mapped in fixed-size
units to each physical disk in the virtual disk using a sequential pattern.
For example, if the virtual disk includes five physical disks, the stripe writes data
to physical disks one through five without repeating any of the physical disks.
The amount of space consumed by a stripe is the same on each physical disk.
The portion of a stripe that resides on a physical disk is a stripe element.
Striping by itself does not provide data redundancy.
W
Windows
Microsoft Windows is a range of commercial operating environments for
computers. It provides a graphical user interface (GUI) to access programs and
data on the computer.
X
XP
XP is a Microsoft Windows operating system. Released in 2001, it is built on the
Windows 2000 kernel, making it more stable and reliable than previous versions
of Windows. It includes an improved user interface and more mobility features,
such as plug and play features used to connect to wireless networks.
72 Glossary
Page 75

Index
B
BIOS, 35
Configuration Utility, 36
fault code messages, 35
POST messages, 35
C
Configuration Utility
functions performed, 36
navigating, 37
overview, 36
starting, 36
D
driver diskette, 24
drivers
installation, 23
Microsoft operating system
installation, 25
E
electrostatic discharge. See ESD
F
firmware
update utility, 55
updating, 55
I
installation
driver, 23
SAS 6/iR Adapter, 19
Integrated RAID
configuration, 37, 42
create new virtual disk, 38
creating IM, 43
creating IS, 42
Integrated Mirroring, 13
Integrated Striping, 12
manage array, 41
new virtual disk, 38
rebuilding virtual disk, 46
replacing virtual disk, 46
view virtual disk, 41
virtual disk activation, 45
virtual disk deletion, 46
virtual disk properties, 44
virtual disk synchronization, 45
ESD, 10
Index 73
Page 76

M
T
Manage Array, 41
P
PCI-E connector, 11
R
RAID, 11-12
RAID 0, 12
RAID 1, 12
Red Hat Enterprise Linux, 23
creating a driver diskette, 29
installing with the driver update
diskette, 30
S
safety instructions
for preventing ESD, 10
SAS 6/iR
BIOS, 35
features, 15
overview, 11
SAS 6/iR Adapter, 11
SAS 6/iR Adapter installation, 19
specifications, 15
troubleshooting, 49
troubleshooting, 49
BIOS boot order, 49
BIOS error messages, 52
Configuration Utility error
messages, 51
physical disk issues, 50
W
Windows, 23
drivers, 23
updating drivers, 28
SCSI
controller, 11
74 Index
Page 77

Page 78

Printed in the U.S.A.
www.dell.com | support.dell.com
Page 79

Page 80

Printed in Malaysia.
www.dell.com | support.dell.com
Page 81

Page 82

Printed in Brazil.
www.dell.com | support.dell.com
Page 83

Page 84

Printed in China.
Printed on recycled paper.
www.dell.com | support.dell.com
Page 85

Page 86

Printed in Ireland.
www.dell.com | support.dell.com
 Loading...
Loading...