Page 1

Intel Active Management Technology v7.0
Administrator's Guide
Overview
Product Overview
Out of Box Experience
Operational Modes
Setup and Configuration Overview
Menus and Defaults
MEBx Settings Overview
ME General Settings
AMT Configuration
Intel Fast Call for Help
MEBx Defaults
ME General Settings
AMT Configuration
Setup and Configuration
Management
Intel AMT Web GUI
AMT Redirection (SOL/IDE-R)
AMT Redirection Overview
Intel Management and
Security Status Application
Intel Management and Security Status
Application
Troubleshooting
Troubleshooting
Methods Overview
Configuration Service - Using a USB Device
Configuration Service - USB Device Procedure
System Deployment
Operating System Drivers
If you purchased a DELL™ n Series computer, any references in this document to Microsoft® Windows® operating systems
are not applicable.
Information in this document is subject to change without notice.
© 2011 Dell Inc. All rights reserved.
Reproduction of these materials in any manner whatsoever without the written permission of Dell Inc. is strictly forbidden.
Trademarks used in this text: Dell™, the DELL logo, Dell Precision™, Precision ON™, ExpressCharge™, Latitude™, Latitude ON™, OptiPlex™, Vostro™,
and Wi- Fi Catcher™ are trademarks of Dell Inc. Intel®, Pentium®, Xeon®, Core™, Atom™, Centrino®, and Celeron® are registered trademarks or
trademarks of Intel Corporation in the U.S. and other countries. AMD® is a registered trademark and AMD Opteron™, AMD Phenom™, AMD
Sempron™, AMD Athlon™, ATI Radeon™, and ATI FirePro™ are trademarks of Advanced Micro Devices, Inc. Microsoft®, Windows®, MS - DOS®,
Windows Vista®, the Windows Vista start button, and Office Outlook® are either trademarks or registered trademarks of Microsoft Corporation in the
United States and/or other countries. Blu- ray Disc™; is a trademark owned by the Blu- ray Disc Association (BDA) and licensed for use on discs and
players. The Bluetooth® word mark is a registered trademark and owned by the Bluetooth® SIG, Inc. and any use of such mark by Dell Inc. is
under license. Wi - Fi® is a registered trademark of Wireless Ethernet Compatibility Alliance, Inc.
Other trademarks and trade names may be used in this publication to refer to either the entities claiming the marks and names or their products,
Dell Inc. disclaims any proprietary interest in trademarks and trade names other than its own.
March 2011 Rev. A00
Page 2
Product Overview
Intel Active Management Technology (Intel AMT) allows companies to manage their networked computers easily.
Discover computing assets on a network, regardless of whether the computer is turned On or Off – Intel AMT uses
information stored in the non-volatile system memory to access the computer. The computer can be accessed even
while it is powered Off (also called out-of-band or OOB access).
Remotely repair systems after operating system failures – In the event of a software or an operating system failure,
Intel AMT can be used to access the computer remotely for repair purposes. IT administrators can also detect system
problems easily with the assistance of Intel AMT's OOB event logging and alerting.
Protect networks from incoming threats while keeping software and virus protection up-to-date across the network.
Software Support
Several Independent Software Vendors (ISVs) are building software packages to work with Intel AMT features. Hence, this
provides IT administrators many options to remotely manage networked computer assets within a company.
Features and Benefits
Intel AMT
Features Benefits
Out-of-band (OOB) access
Remote troubleshooting and
recovery
Proactive alerting Decreases downtime and minimizes repair times.
Allows remote management of platforms regardless of system power or operating
system state.
Significantly reduces onsite visits, increasing the efficiency of IT technical staff.
New Features of Intel vPro Technology
Intel AMT 7.0
Host Based Provisioning : Easy deployment of AMT capable units by the customers.
Communication Proxy Support : Allow AMT communication to an external network (for example: IT outsourced to
offsite party)
MEFW Rollback
Enable downgrading of MEFW on vPro systems to enable customers to more easily lock on BIOS revisions.
AT-p 3.0
WWAN (3G) Support for AT-p (Ericsson wireless on NB only)
AT-p suspend / resume commands for temporary disablement
AT-p authentication on S3 resume (optional)
Add support for Desktop Workstations
Other New Features (related to MEFW)
Support for LAN ARP
Page 3

ME answers LAN ARP request (IPV4) & Neighbor Discovery packets (IPV6) by not waking and instead notifying the console
system in Sx.
New Win7 LAN requirement
Only for 5MB SKU and in Power Policy 2
Deep S4/S5
This is automatically disabled when AMT is provisioned in PP2.
Identify Protection Technology (IPT)
Enable One Time Password based secure login and web transactions via ME-based authentication.
Client System Requirements
The client system referred to in this document is based on the Intel 6 Series Chipset Family/Intel PCH platform, and is
managed by Intel Management Engine. The following firmware and software requirements are required for the installation and
setup before the Intel Management Engine can be configured and run on the client system.
An SPI flash device programmed with Intel AMT 7.0 flash image integrating BIOS, Intel Management Engine and GbE
component images.
BIOS set up with Intel AMT enabled, can access MEBx setup from F12 menu.
To enable all the Intel Management Engine features within Microsoft Operating System, the device drivers (Intel
MEI/SOL/LMS) must be installed and configured on the client system.
*
Information on this page provided by Intel.
NOTE: The Intel Management Engine BIOS Extension (MEBx) is an optional ROM module provided to Dell™ from Intel
that is included in the Dell BIOS. The MEBx has been customized for Dell computers.
Page 4

Out of Box Experience
The following materials are available with an Intel Active Management Technology (Intel AMT) computer:
Factory installation
Intel AMT 7.0 is shipped in the factory-default state from Dell factories.
Setup and Quick Reference Guide
Intel AMT overview
Backup media
Firmware and critical drivers are available on the Resource CD.
See the Administrator Guide for detailed information about Intel AMT available on support.dell.com\manuals
.
Page 5
Operational Modes
In Intel AMT 5.0 and earlier versions, there were two operational modes – SMB and Enterprise. In Intel AMT 6.0 and AMT 7.0,
their functionality has been integrated to provide the same functionality previously available in Enterprise mode.
The new configuration options are:
Manual Setup and Configuration (available for SMB customers)
Automatic Setup
Configuration
Setting
Enterprise Mode SMB Mode
TLS mode Enabled Disabled
Web UI Disabled Enabled Enabled
IDER/SOL/KVM
Redirection network
interface enabled
Legacy Redirection Mode
(Controls FW listening for
incoming redirection
connections)
NOTE: Customers may purchase TLS permanently disabled from the factory due to restrictions on encryption
technology in their country of delivery, therefore customers cannot re-enable TLS.
NOTE: KVM is supported only with integrated graphics CPU and system should be in integrated graphics mode.
Manual configuration can be performed using the following six steps:
1. Flash image with system BIOS and FW.
2. Enter the Intel MEBX via <F12> menu and enter default password admin and then change password.
3. Enter Intel ME General Settings menu.
4. Select Activate Network Access.
5. Select Y in the confirmation message.
6. Exit the Intel MEBx.
Intel AMT 5.0 and under Default
Disabled
Disabled
Enabled if feature enabled in
Intel® MEBX
Enabled if feature enabled in
Intel® MEBX
Intel AMT 6.0 / 7.0 (default
options)
Disabled, can be enabled at a
later time
Enabled, can be disabled at a
later time
Disabled (Need to set to
Enabled in order to work with
Legacy SMB consoles)
NOTE: You can also accomplish the activation through external means or through Operating System using Intel
Activator tool.
Page 6

Setup and Configuration Overview
The following is a list of important terms related to the Intel AMT setup and configuration.
Setup and configuration — The process that populates the Intel AMT-managed computer with usernames,
passwords, and network parameters that enable the computer to be administered remotely.
Configuration service — A third-party application that completes the Intel AMT provisioning.
Intel AMT WebUI — A Web browser-based interface for limited remote computer management.
You must set up and configure Intel AMT in a computer before using it. Intel AMT setup readies the computer for Intel AMT
mode and enables network connectivity. This setup is generally performed only once in the lifetime of a computer. When Intel
AMT is enabled, it can be discovered by management software over a network.
Once Intel AMT is set up in Enterprise mode, it is ready to initiate configuration of its own capabilities. When all required
network elements are available, simply connect the computer to a power source and the network, and Intel AMT automatically
initiates its own configuration. The configuration service (a third-party application) completes the process for you. Intel AMT is
then ready for remote management. This configuration typically takes only a few seconds. When Intel AMT is set up and
configured, you can reconfigure the technology as needed for your business environment.
Once Intel AMT is set up in SMB mode, the computer does not have to initiate any configuration across the network. It is set
up manually and is ready to use with the Intel AMT Web GUI.
Intel AMT Setup and Configuration States
The act of setting up and configuring Intel AMT is also known as provisioning. An Intel AMT capable computer can be in one
of three setup and configuration states:
Factory-default state
Setup state
Provisioned state
The Factory-Default State is a fully unconfigured state in which security credentials are not yet established and Intel AMT
capabilities are not yet available to management applications. In the factory-default state, Intel AMT has the factory-defined
settings.
The Setup State is a partially configured state in which Intel AMT has been set up with initial networking and transport layer
security (TLS) information: an initial administrator password, the provisioning passphrase (PPS), and the provisioning
identifier (PID). When Intel AMT has been set up, Intel AMT is ready to receive enterprise configuration settings from a
configuration service.
The Provisioned State is a fully configured state in which the Intel Management Engine (ME) has been configured with
power options, and Intel AMT has been configured with its security settings, certificates, and the settings that activate the
Intel AMT capabilities. When Intel AMT has been configured, the capabilities are ready to interact with management
applications.
Provisioning Methods
TLS-PKI
TLS-PKI is also known as "Remote Configuration". The SCS uses TLS-PKI (Public Key Infrastructure) certificates to securely
connect to an Intel AMT enabled computer. The certificates can be generated a few ways:
The SCS can connect using one of the default certificates pre-programmed on the computer, as detailed in the MEBx
interface section of this document.
The SCS can create a custom certificate, which can be deployed on the AMT computer by means of a desk-side visit
with a specially formatted USB thumb drive as detailed in the Configuration Service section of this document.
The SCS could use a custom certificate which was pre-programmed at the Dell factory through the Custom Factory
Integration (CFI) process.
TLS-PSK
TLS-PSK is also known as "One-Touch Configuration". The SCS uses PSK's (Pre-Shared Key's) to establish a secure
connection with the AMT computer. These 52-character keys can be created by the SCS, and then deployed on the AMT
Page 7

computer with a desk-side visit in one of two ways:
The key can be manually typed into the MEBx.
The SCS can create a list of custom keys, and put them onto a specially formatted USB thumb drive. Then each AMT
computer retrieves a custom key from the specially formatted USB thumb drive during BIOS boot as detailed in the
Configuration Service section of this document.
Page 8
MEBx Settings Overview
The Intel Management Engine BIOS Extension (MEBx) provides platform-level configuration options for you to configure the
behavior of Management Engine (ME) platform. Options include enabling and disabling individual features and setting power
configurations.
This section provides details about MEBx configuration options and constraints if any.
Access MEBx Configuration User Interface
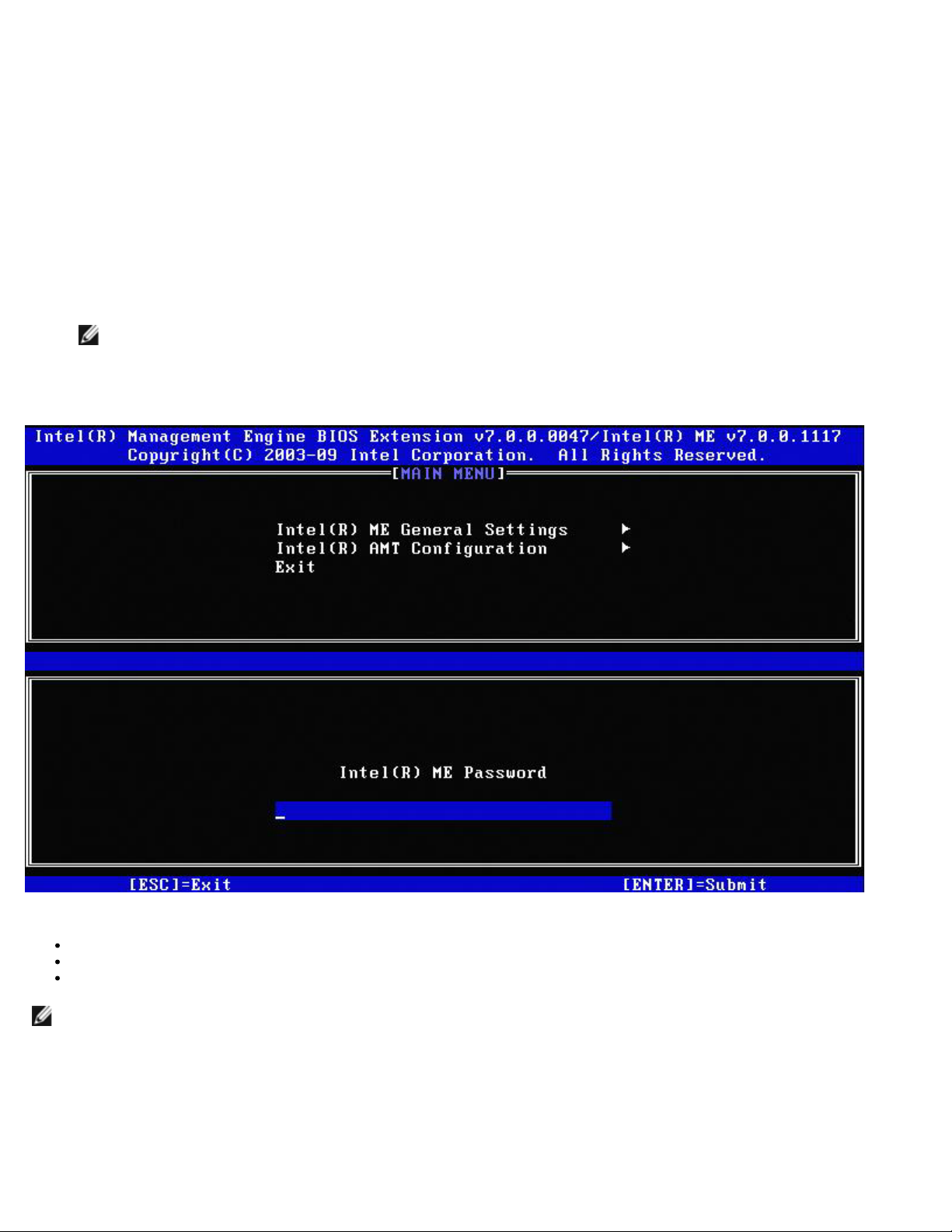
The MEBx configuration user interface can be accessed on a computer through the following steps:
1. Turn on (or restart) your computer.
2. When the DELL™ logo appears, press <F12> immediately and select MEBx.
NOTE: If you wait too long and the operating system logo appears, continue to wait until you see the Microsoft
Windows desktop. Then shut down your computer and try again.
3. Type the ME password. Press <Enter>. The default password is 'admin' and it can be altered by the user.
The MEBx screen appears as shown below.
The main menu presents three function selections:
Intel ME General Settings
Intel AMT Configuration
Exit
NOTE: Intel MEBx will display only detected options. If one or more of these options does not appear, verify that the
system supports the relevant missing feature.
Changing the Intel ME Password
The default password is admin and is the same on all newly deployed platforms. You must change the default password before
changing any feature configuration options.
Page 9

When an IT administrator first enters the Intel MEBx configuration menu with the default password, he or she must change
the default password before any feature can be used.
The new password must include the following elements:
Eight characters, no more than 32
One uppercase letter
One lowercase letter
A number
A special (Non-alphanumeric) character, such as !, $, or ; excluding the : " and , characters.)
NOTE: The underscore ( _ ) and spacebar are valid password characters but do NOT add to the password complexity.
NOTE: The password can be reset to the default setting (admin) by shutting down the system, removing AC and DC
power and performing a RTC reset.
*
Information on this page provided by Intel.
Page 10
ME General Settings
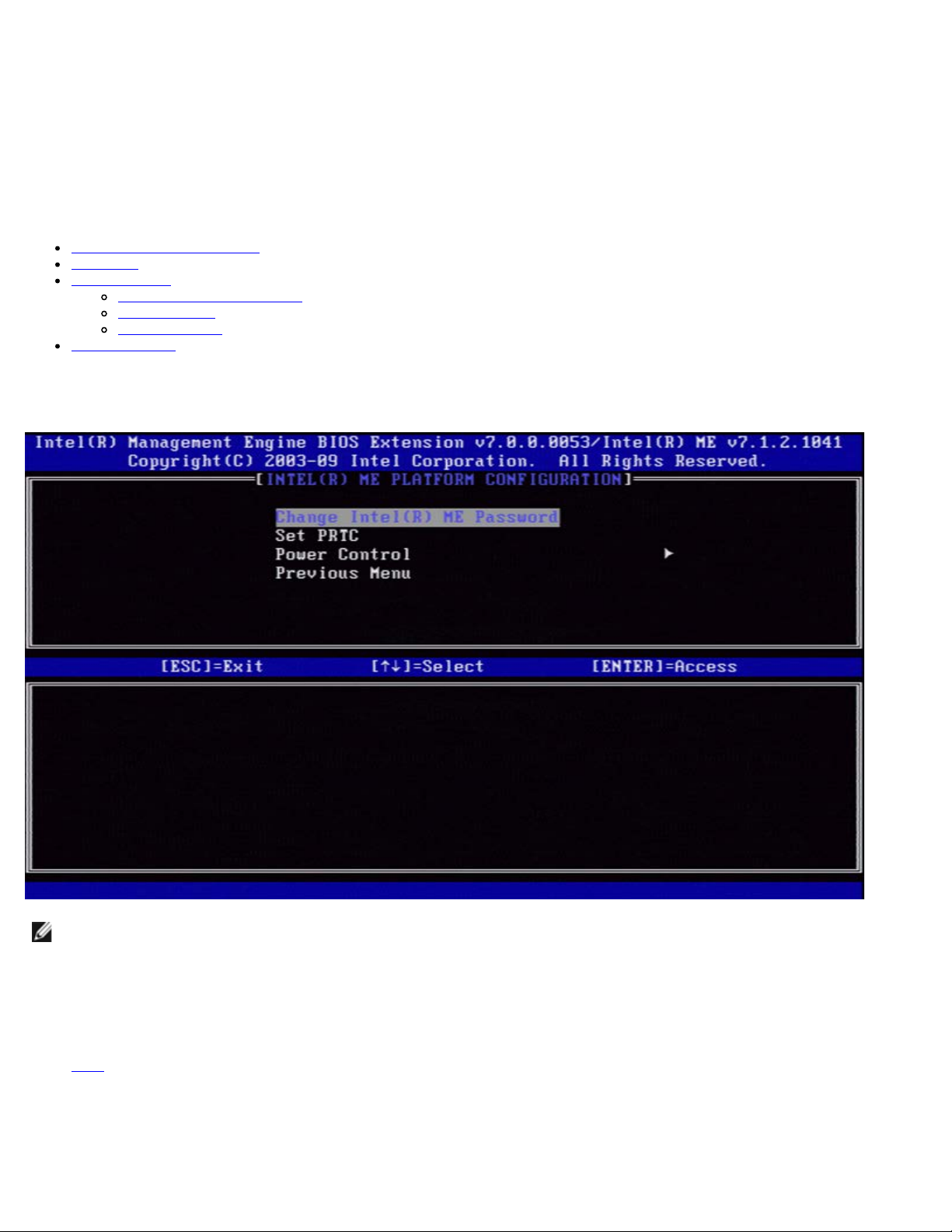
To reach the Intel Management Engine (ME) Platform Configuration page, follow these steps:
1. Under the Management Engine BIOS Extension (MEBx) main menu, select Intel ME General Settings. Press <Enter>.
2. The following message appears: "Acquiring General Settings configuration".
The Intel MEBX main menu changes to the Intel ME Platform Configuration page.
This page allows the IT administrator to configure the specific functionality of the Intel ME, such as password, power options,
and so on. The following are quick links to the various sections.
Change Intel ME Password
Set PRTC
Power Control
Intel ME ON in Host Sleep
Idle Time Out
Previous Menu
Previous Menu
Intel ME Platform Configuration
NOTE: The option of "Intel ME State Control" appearing in previous versions of MEBx has been removed in order to
avoid end users accidentally disable Intel ME. The option can now be offered by system BIOS.
Change Intel ME Password
1. At the Intel ME New Password prompt, type your new password. (The password policies and restrictions are available
.
here
2. At the Verify Password prompt, re-type your new password. Your password is now changed.
Page 11
Set PRTC
Under the Intel ME Platform Configuration menu select Set PRC and press <Enter>.
Valid date range: 1/1/2004 to 1/4/2021. Setting the PRTC value is used for virtually maintaining PRTC during the power-off
(G3) state.
Type PRTC in GMT (UTC) format (YYYY:MM:DD:HH:MM:SS) and press <Enter>.
Page 12
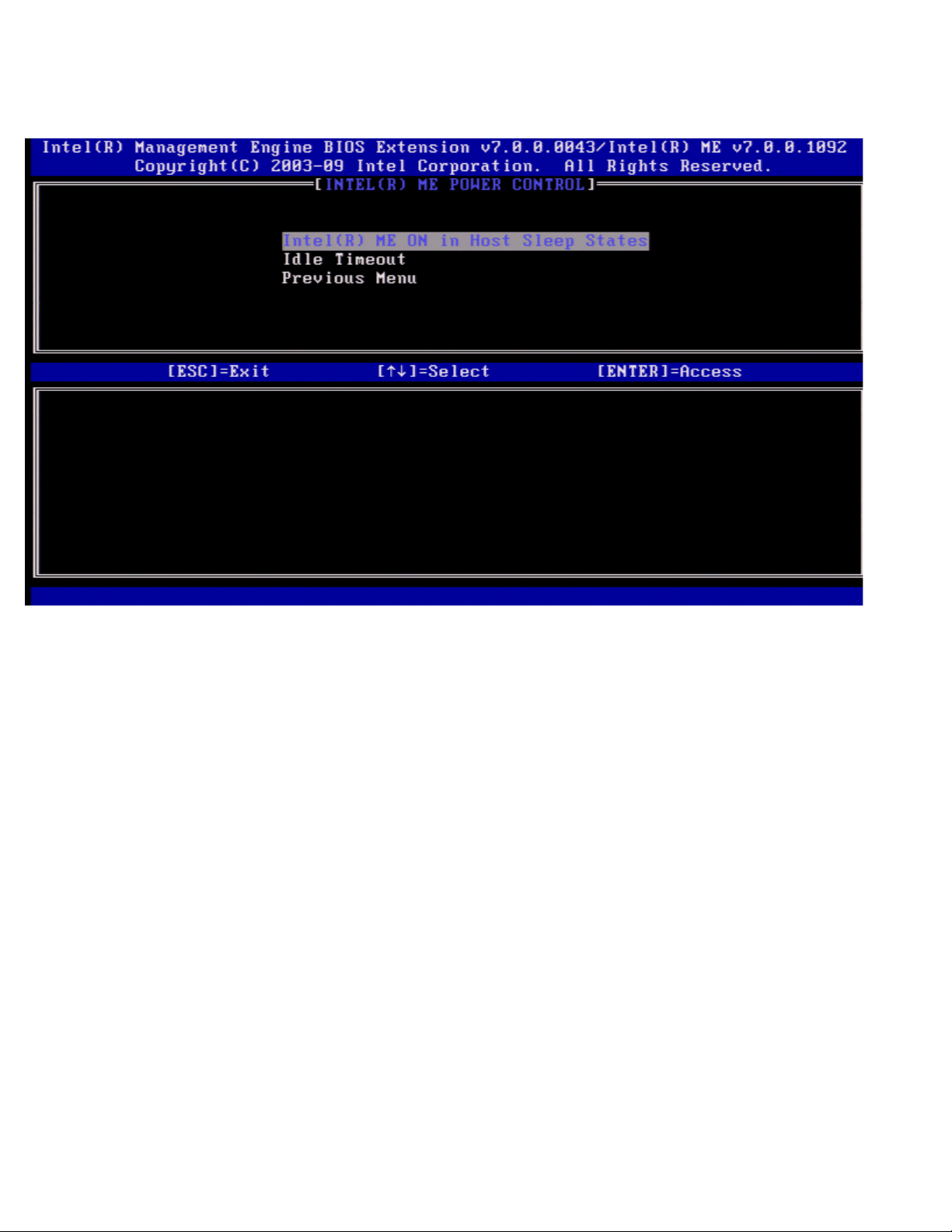
Power Control
Under the Intel ME Platform Configuration menu select Power Control and press <Enter>.
The Intel Power Control page appears.
To comply with ENERGY STAR* and EUP LOT6 requirements, the Intel ME can be turned off in various sleep states. The Intel
ME Power Control menu configures the Intel ME platform power related policies.
Intel ME ON in Host Sleep States
Under the Intel ME Power Control menu select Intel ME ON in Host Sleep States and press <Enter>.
Move the Up/Down arrow key to select the desired power policy and press <Enter>.
Page 13
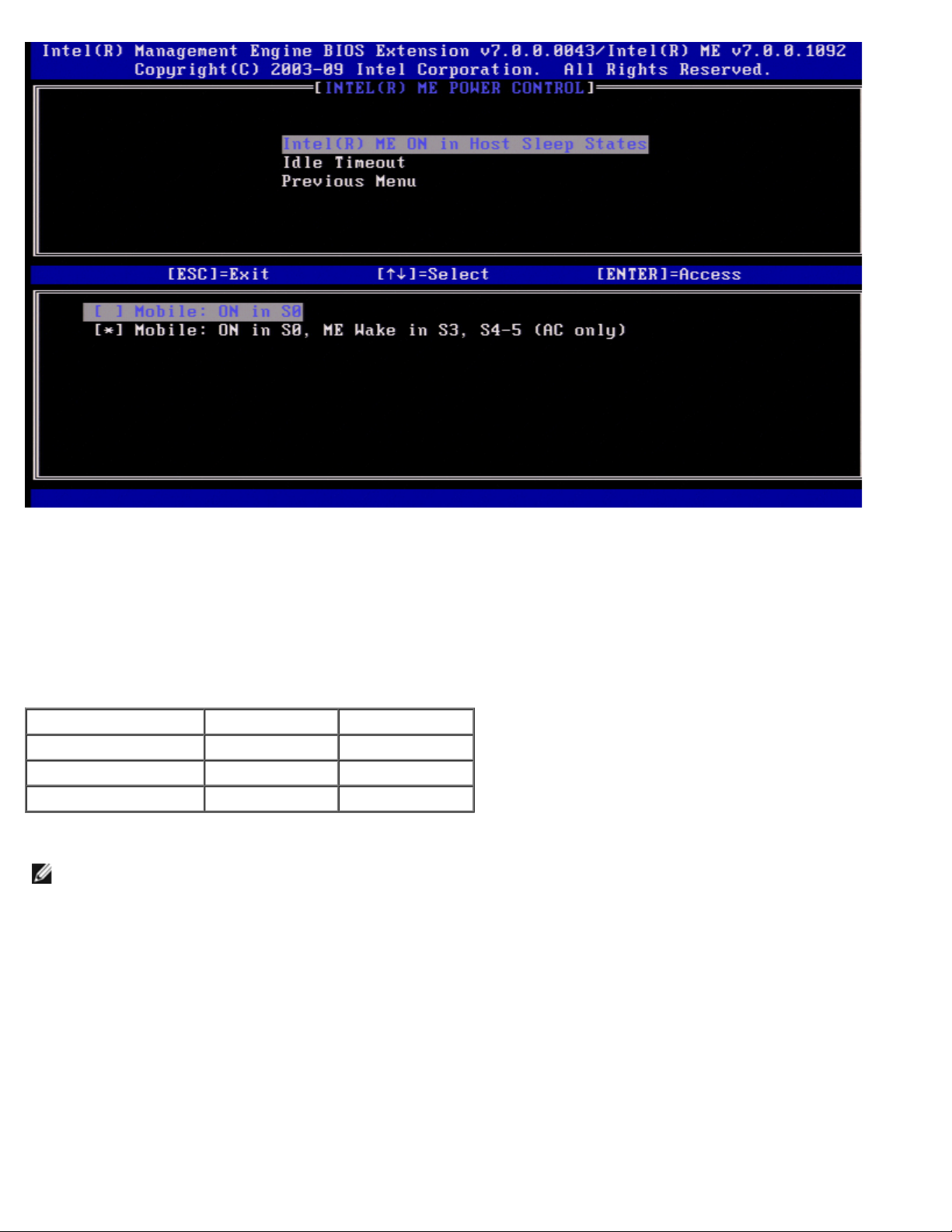
The end user administrator can select the desired power package to use depending on the system usage.
With Intel ME WoL, after the time-out timer expires, the Intel ME remains in the M-off state until a command is sent to the
ME. After this command has been sent, the Intel ME will transition to an M0 or M3 state and will respond to the next
command that is sent. A ping to the Intel ME will also cause the Intel ME to go into an M0 or M3 state.
The Intel ME takes a short time to transition from the M-off state to the M0 or M3 state. During this time, Intel AMT will not
respond to any Intel ME commands. When the Intel ME has reached the M0 or M3 state, the system will respond to Intel ME
commands.
The following table illustrates the details of the power packages.
Power Package 1 2
S0 ON ON
S3 OFF ON/ ME WoL
S4/S5 OFF ON/ ME WoL
Select the desired Power Policy and press <Enter>.
NOTE: Changing a system into the provisioning state will automatically switch to Power Package 2. This can later be
changed through WebUI, the management console, or MEBx.
Idle Time Out
Under the Intel ME Power Control menu select Idle Time Out and press <Enter>.
Page 14
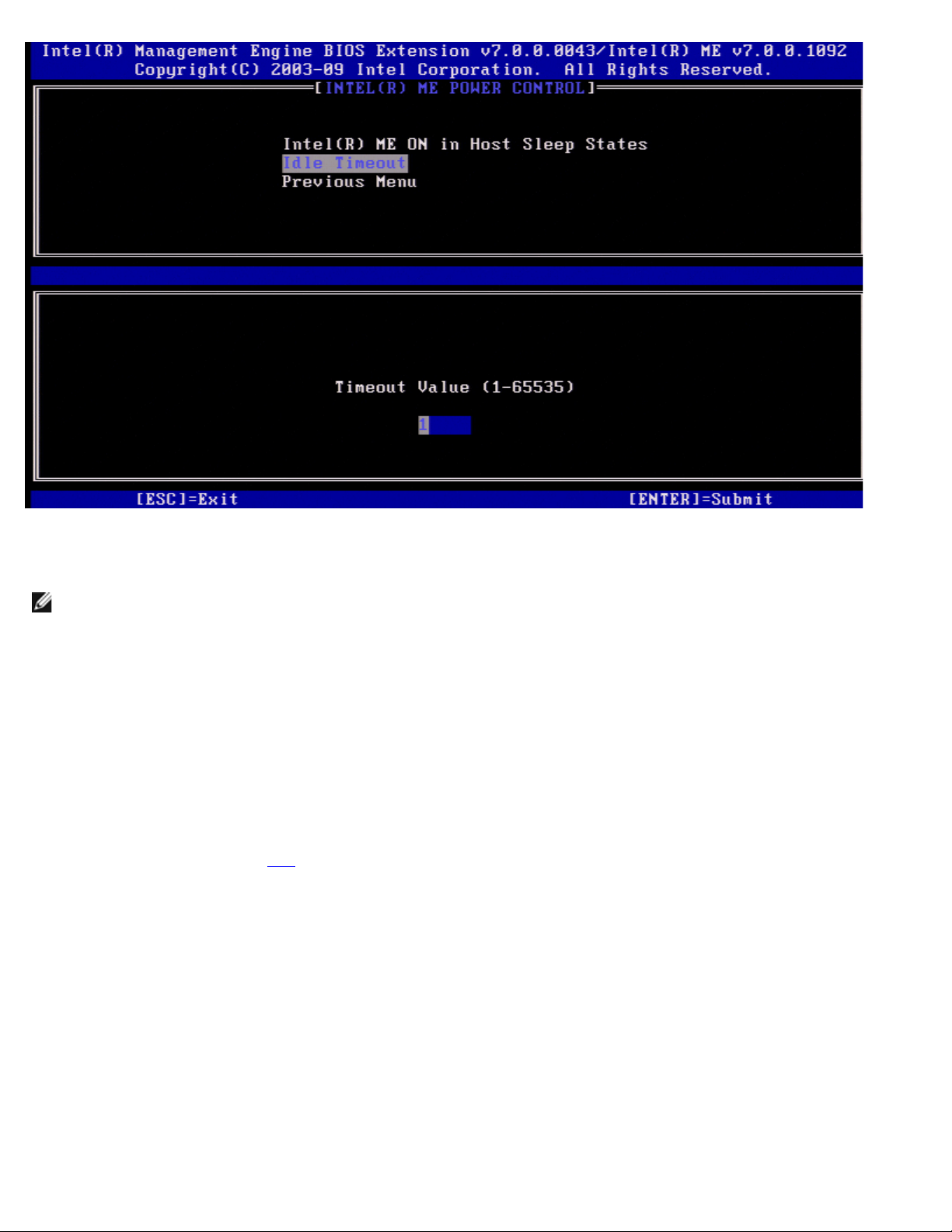
This setting is used to set time out value as to define the Intel ME idle timeout in M3 state. The value should be entered in
minutes. The value indicates the amount of time that the Intel ME is allowed remain idle in M3 before transitioning to the Moff state.
NOTE: If the Intel ME is in M0, it will NOT transition to M-off.
Previous Menu
Under the Intel ME Platform Configuration menu select Previous Menu and press <Enter>.
The Intel ME Platform Configuration page appears.
Previous Menu
Under the Intel ME Platform Configuration menu select Previous Menu and press <Enter>.
The Main Menu appears.
*
Information on this page provided by Intel.
Page 15
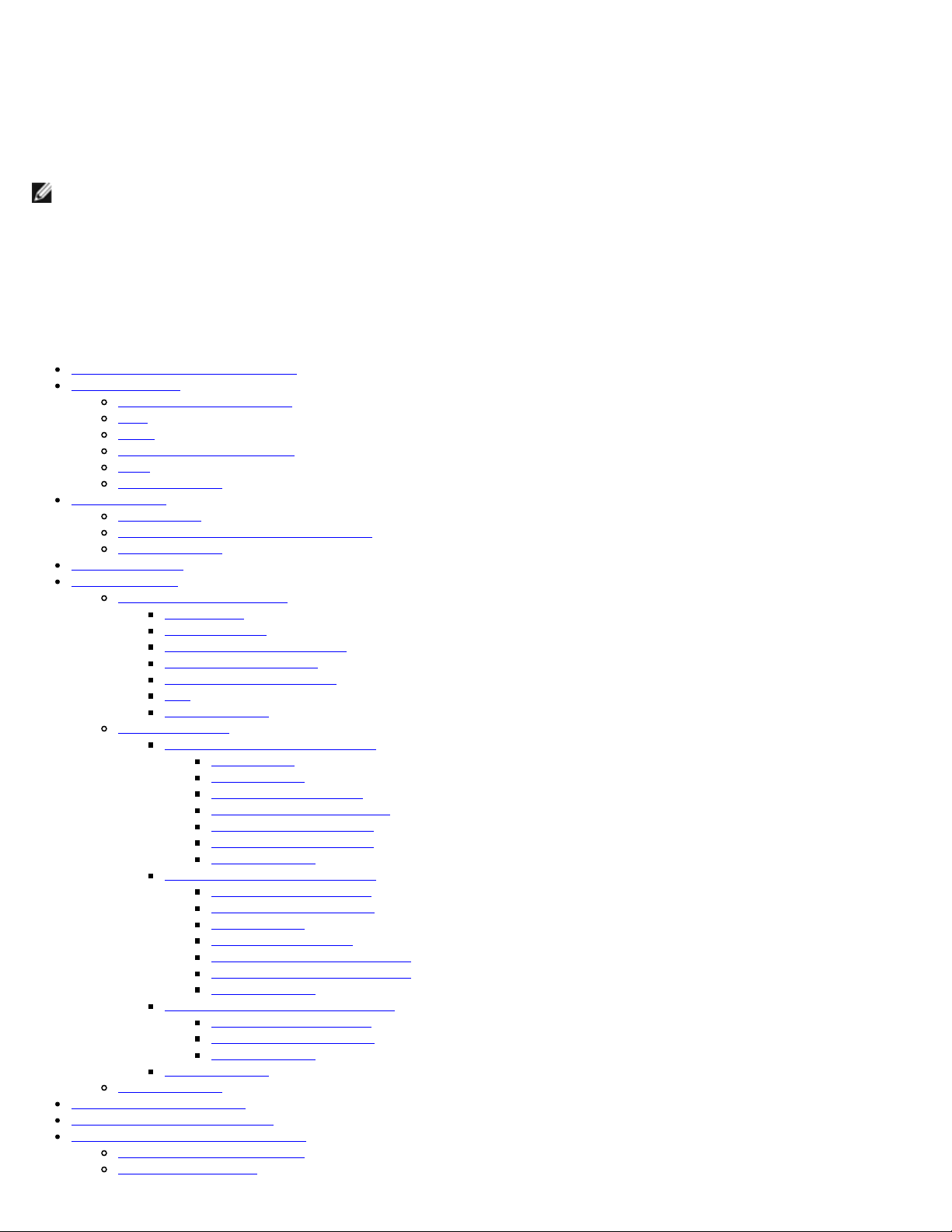
AMT Configuration
Provisioning Record
After you configure the Intel Management Engine (ME) feature, you must reboot before configuring the Intel AMT for a clean
system boot. The following image shows the Intel AMT configuration menu after a user selects the Intel AMT
Configuration option from the Management Engine BIOS Extension (MEBx) main menu. This feature allows you to
configure an Intel AMT capable computer to support the Intel AMT management features.
NOTE: You need to have a basic understanding of networking and computer technology terms, such as TCP/IP, DHCP,
VLAN, IDE, DNS, subnet mask, default gateway, and domain name. Explaining these terms is beyond the scope of this
document.
To navigate to the Intel AMT Configuration page, perform the following steps:
1. Under the Management Engine BIOS Extension (MEBx) main menu, select Intel AMT Configuration. Press
<Enter>. The Intel AMT Configuration screen appears.
The quick links displayed on the Intel AMT Configuration screen are:
Manageability Feature Selection
SOL/IDER/KVM
Username and Password
SOL
IDER
Legacy Redirection Mode
KVM
Previous Menu
User Consent
User Opt-in
Opt-in Configurable from remote IT
Previous Menu
Password Policy
Network Setup
Network Name Settings
Host Name
Domain Name
Shared / Dedicated FQDN
Dynamic DNS Update
Periodic Update Interval
TTL
Previous Menu
TCP/IP Settings
Wired LAN IPv4 Configuration
DHCP Mode
IPv4 Address
Subnet Mask Address
Default Gateway Address
Preferred DNS Address
Alternate DNS Address
Previous Menu
Wired LAN IPv6 Configuration
IPv6 Feature Selection
IPv6 Interface ID Type
IPv6 Address
IPv6 Default Router
Preferred DNS IPv6 Address
Alternate DNS IPv6 Address
Previous Menu
Wireless LAN IPv6 Configuration
IPv6 Feature Selection
IPv6 Interface ID Type
Previous Menu
Previous Menu
Previous Menu
Activate Network Access
Unconfigure Network Access
Remote Setup And Configuration
Current Provisioning Mode
Page 16
RCFG
Start Configuration
Previous Menu
Provisioning Server IPv4/IPv6
Provisioning Server FQDN
TLS PSK
Set PID and PPS
Delete PID and PPS
Previous Menu
TLS PKI
Remote Configuration
PKI DNS Suffix
Manage Hashes
Adding Customized Hash
Deleting a Hash
Changing the Active State
Viewing a Certificate Hash
Previous Menu
Previous Menu
Previous Menu
Manageability Feature Selection
1. Under the Intel AMT Configuration menu select Manageability Feature Selection and press <Enter>.
2. A message is displayed:
[Caution] Disabling reset network settings including network ACLs to factory default. System resets on
MEBx exit. Continue: (Y/N).
Press Y to change setting or N to cancel.
When the Manageability Feature Selection is enabled, the Intel ME manageability feature menu appears. If it is disabled, ME
manageability feature will not be displayed.
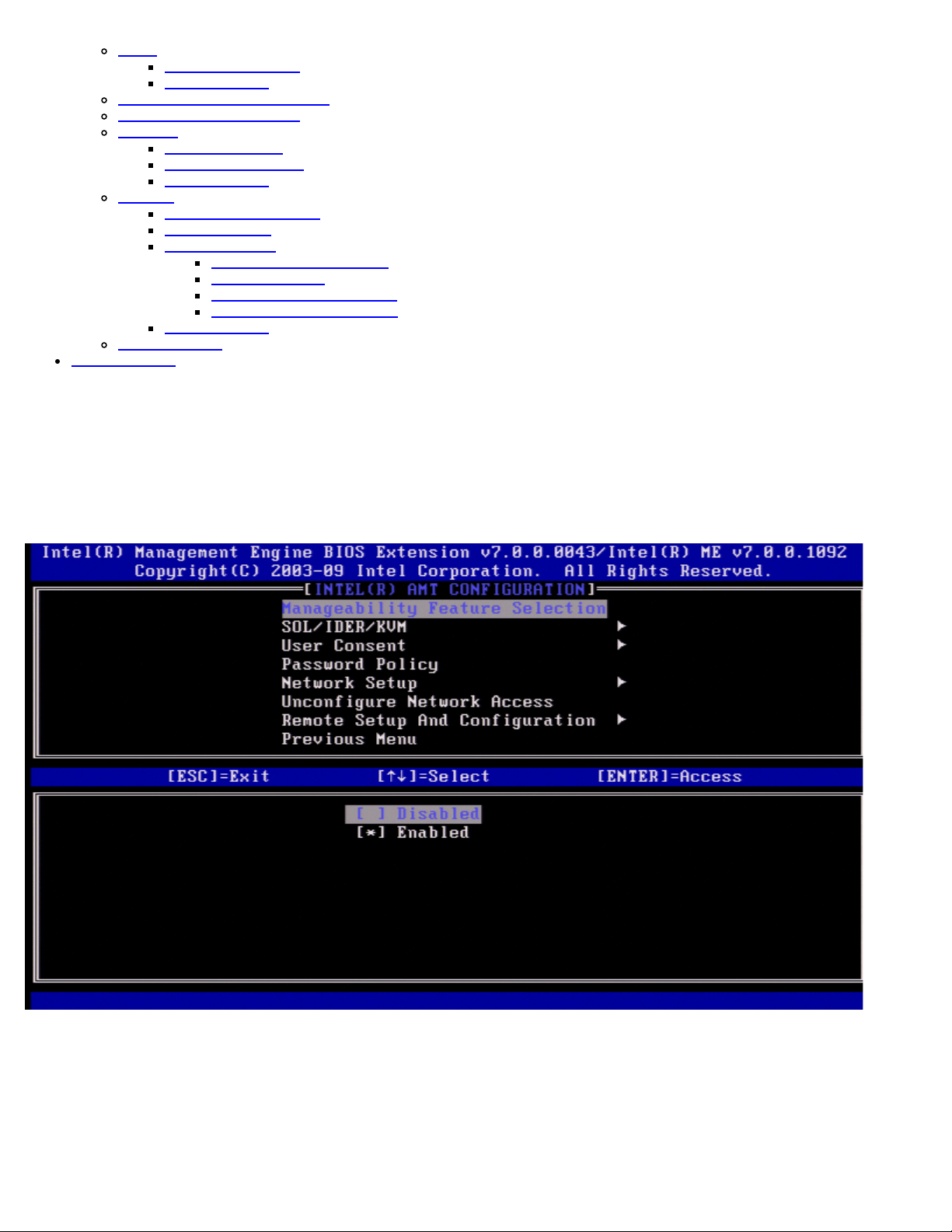
SOL/IDER/KVM
Under the Intel AMT Configuration page (with Intel AMT enabled) select SOL/IDER/KVM and press <Enter>.
The Intel AMT Configuration page changes to the SOL/IDER page.
Page 17
Username and Password
Under the SOL/IDER page select Username and Password and press <Enter>.
This option provides the user authentication for SOL/IDER session. If Kerberos* is used, this option should be set to
DISABLED. The user authentication is handled through Kerberos. If Kerberos is not used, the IT administrator has the choice
to enable or disable user authentication on SOL/IDER session.
Option Description
Enabled Username and Password is enabled
Disabled Username and Password is disabled.
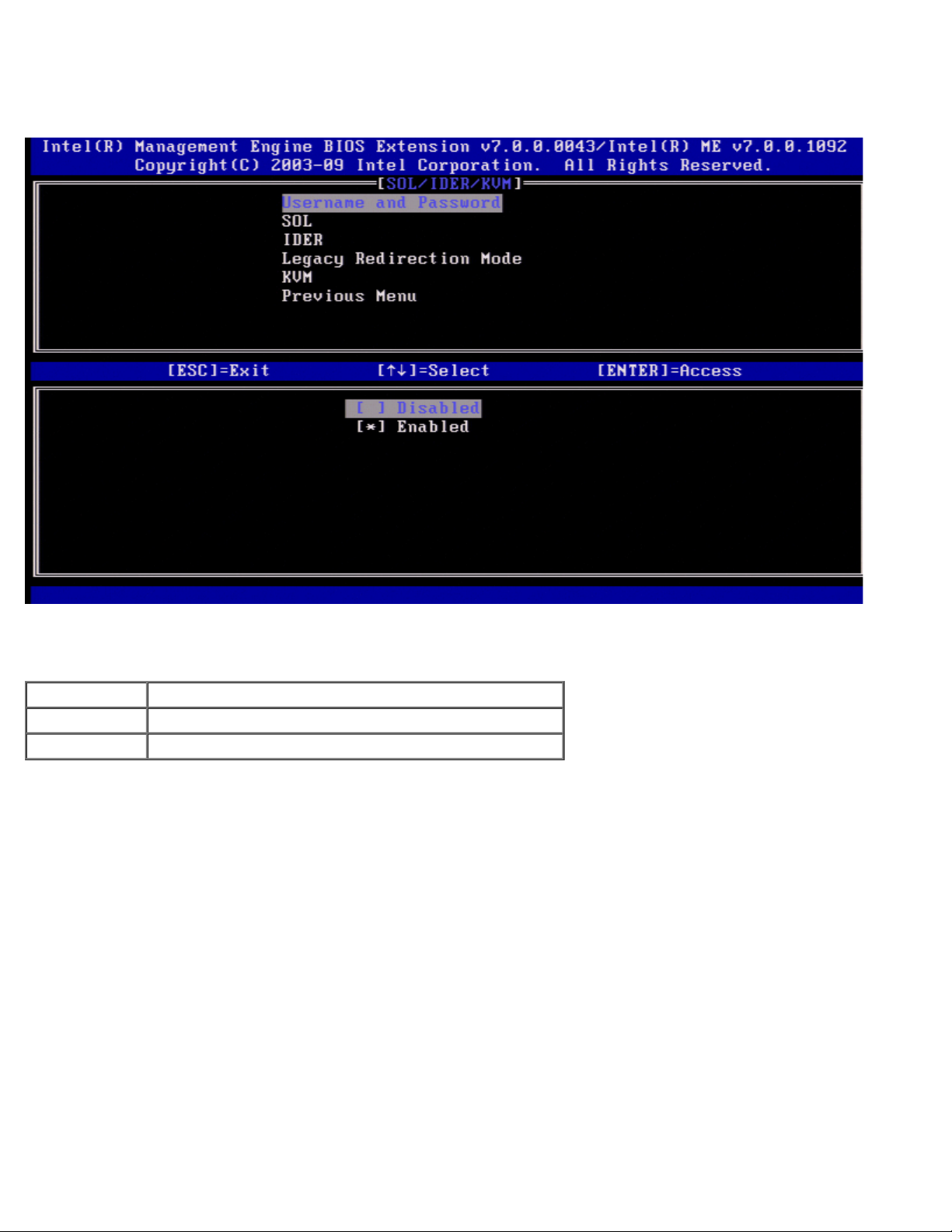
SOL
Under the SOL/IDER page select SOL and press <Enter>.
Page 18
SOL allows the console input/output of an Intel AMT managed client to be redirected to a management server console (if the
client system supports SOL). If the system does not support SOL, this value cannot enable it.
Option Description
Enabled SOL is enabled
Disabled SOL is disabled.
NOTE: Disabling SOL does not remove this feature but prevents it from being used.
IDER
Under the SOL/IDER page select IDER and press <Enter>.
Page 19
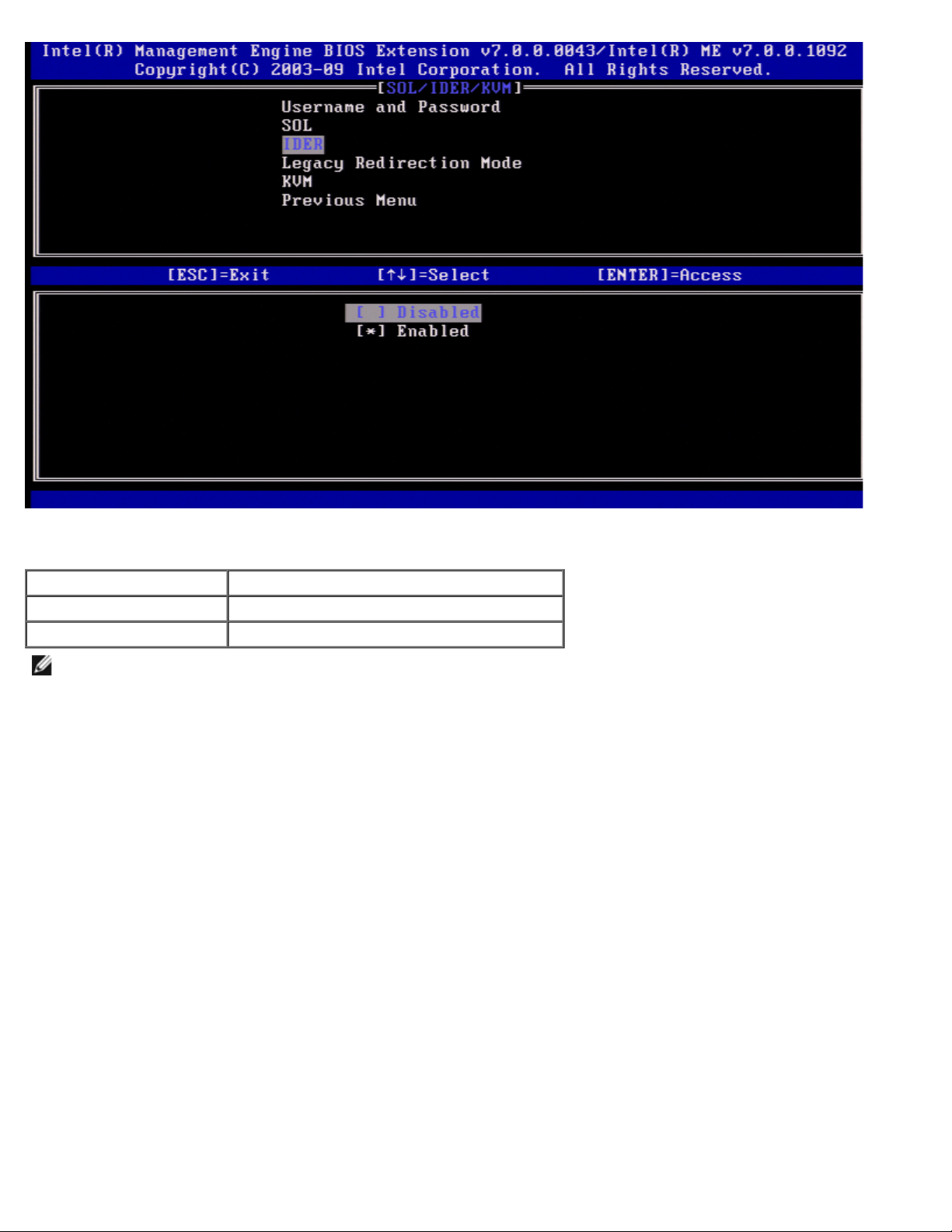
IDER allows an Intel AMT managed client to be booted by a management console from a remote disk image. If the client
system does not support IDER, this value cannot enable it.
Option Description
Enabled IDER is enabled
Disabled IDER is disabled.
NOTE: Disabling IDER does not remove this feature but prevents it from being used.
Legacy Redirection Mode
Under the SOL/IDER page select Legacy Redirection Mode and press <Enter>.
Page 20
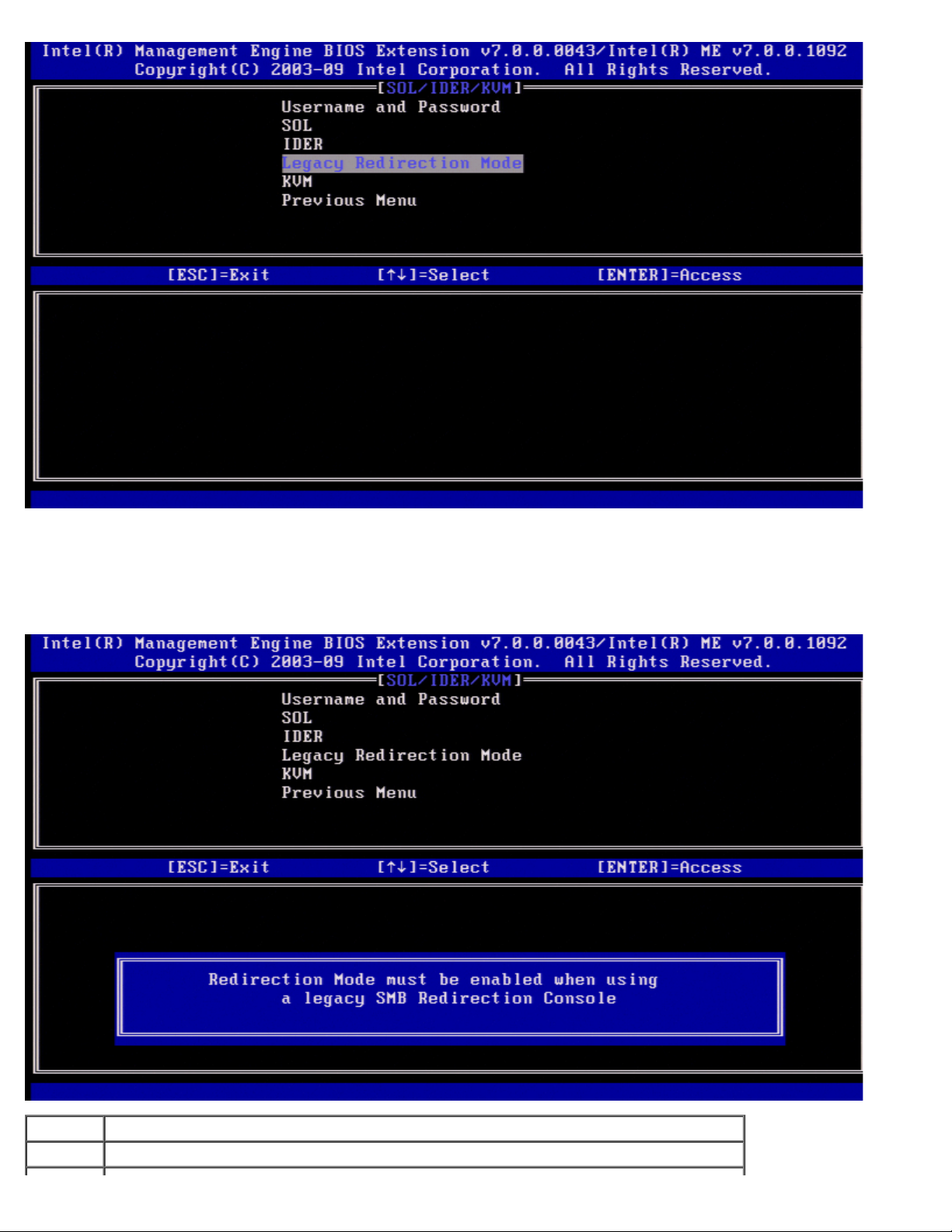
Legacy Redirection Mode controls how the redirection works. If set to disabled, the console needs to open the redirection
ports before each session. This is meant for Enterprise consoles and new SMB consoles that support opening the redirection
ports. The old SMB consoles (before Intel AMT 6.0) which do not support opening the redirection ports function need to
manually turn on the redirection port through this Intel MEBx option.
When selecting the mode, the following message appears.
Option Description
Disabled Legacy redirection Mode is disabled.(Default)
Page 21
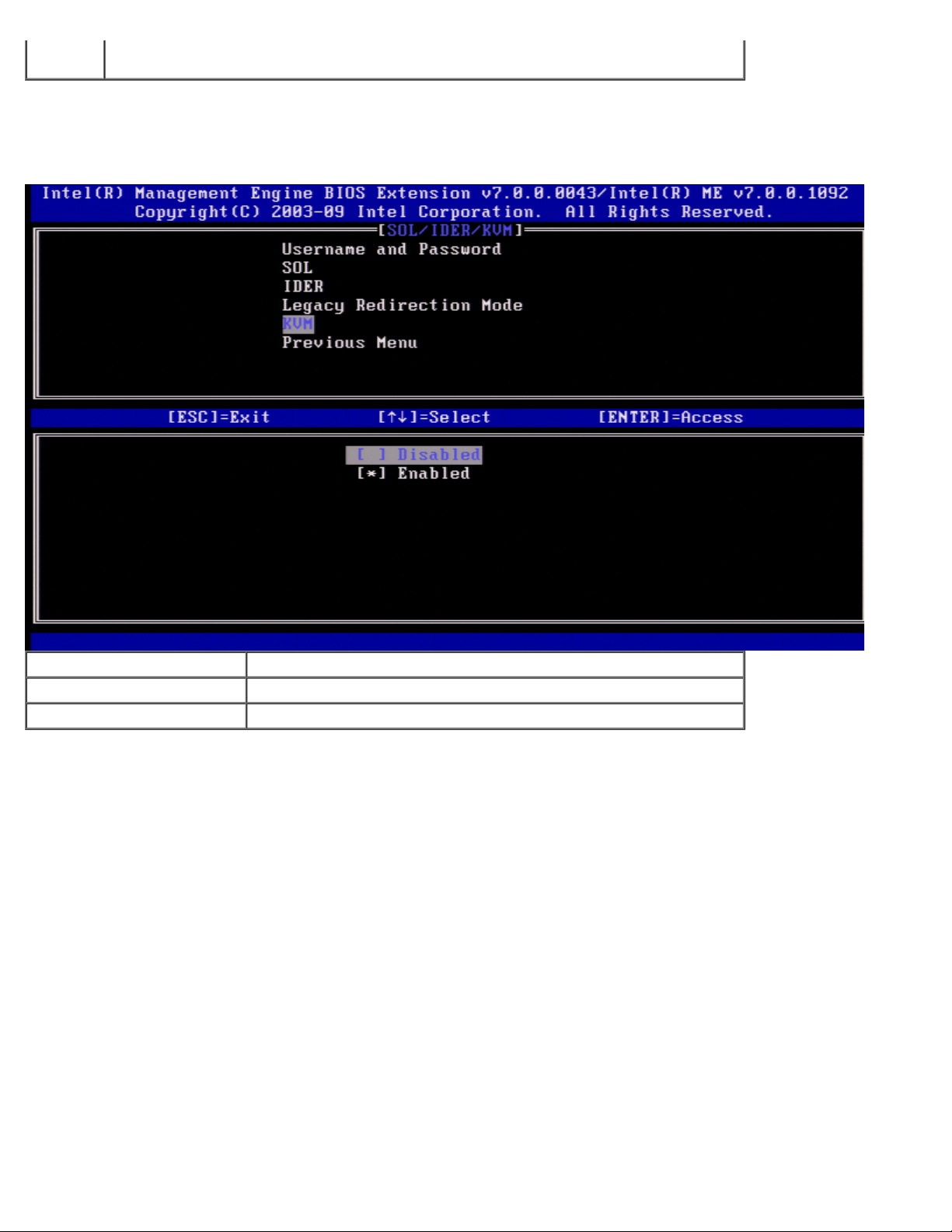
Enabled
The port is left open at all times when redirection is enabled in the Intel MEBx. SMB
consoles before Intel AMT 6.0 require this mode enabled for redirection sessions.
KVM
Under the SOL/IDER page select KVM and press <Enter>.
Option Description
Disabled KVM feature is disabled
Enabled KVM feature is enabled
Previous Menu
Under the SOL/IDER page select Previous Menu and press <Enter>.
The SOL/IDER page changes to the Intel AMT Configuration page.
User Consent
Under the Intel AMT Configuration page select User Consent and press <Enter>.
The User Consent Configuration screen appears.
Sets whether local user consent is required before remote computer can establish a KVM Remote Control session to the local
computer. Also sets whether the remote computer user can configure the KVM Opt-In Policy.
User Opt-in
Under the User Consent Configuration page select User Opt-in and press <Enter>.
Page 22
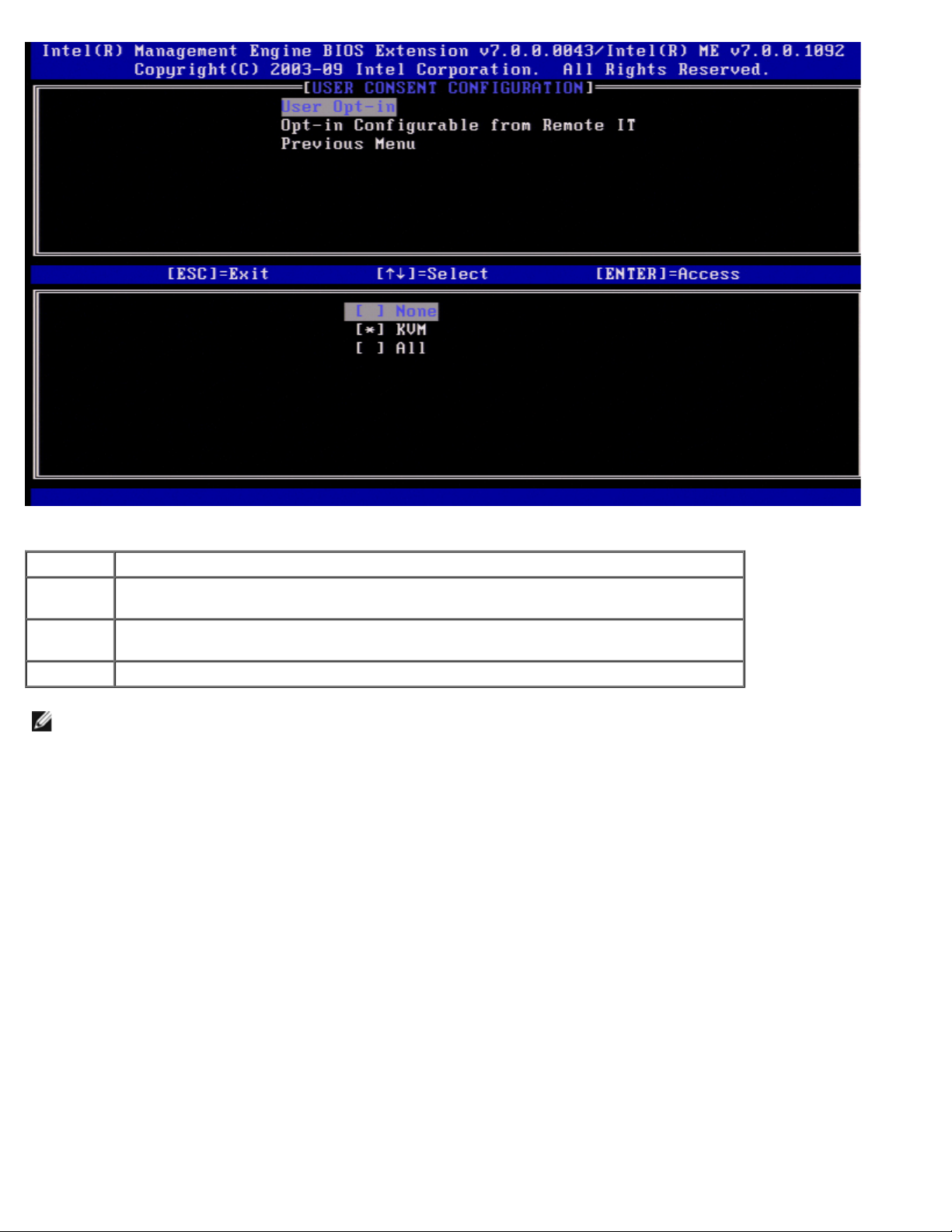
The following options can be selected:
Option Description
None
KVM
All Local User Consent is required for SOL, IDER and KVM
NOTE: When using Host Based Provisioning, Client mode will override this setting and behave as if the "ALL" option has
been selected. For more details on Host Based Provisioning and Client Mode, see the Activator++ User guide and the
UCT (User Consent Tool) user guide in the SDK kit.
Local User Consent is not required for a remote computer to establish KVM Remote
Control session.
Local User Consent is required for a remote computer to establish KVM Remote
Control session.
Opt-in Configurable from remote IT
Under the IKVM Configuration page select Opt-in Configurable from remote IT and press <Enter>.
This setting determines whether a remote computer's user can configure the Opt-In Policy when establishing a KVM Remote
Control session to this computer.
Page 23
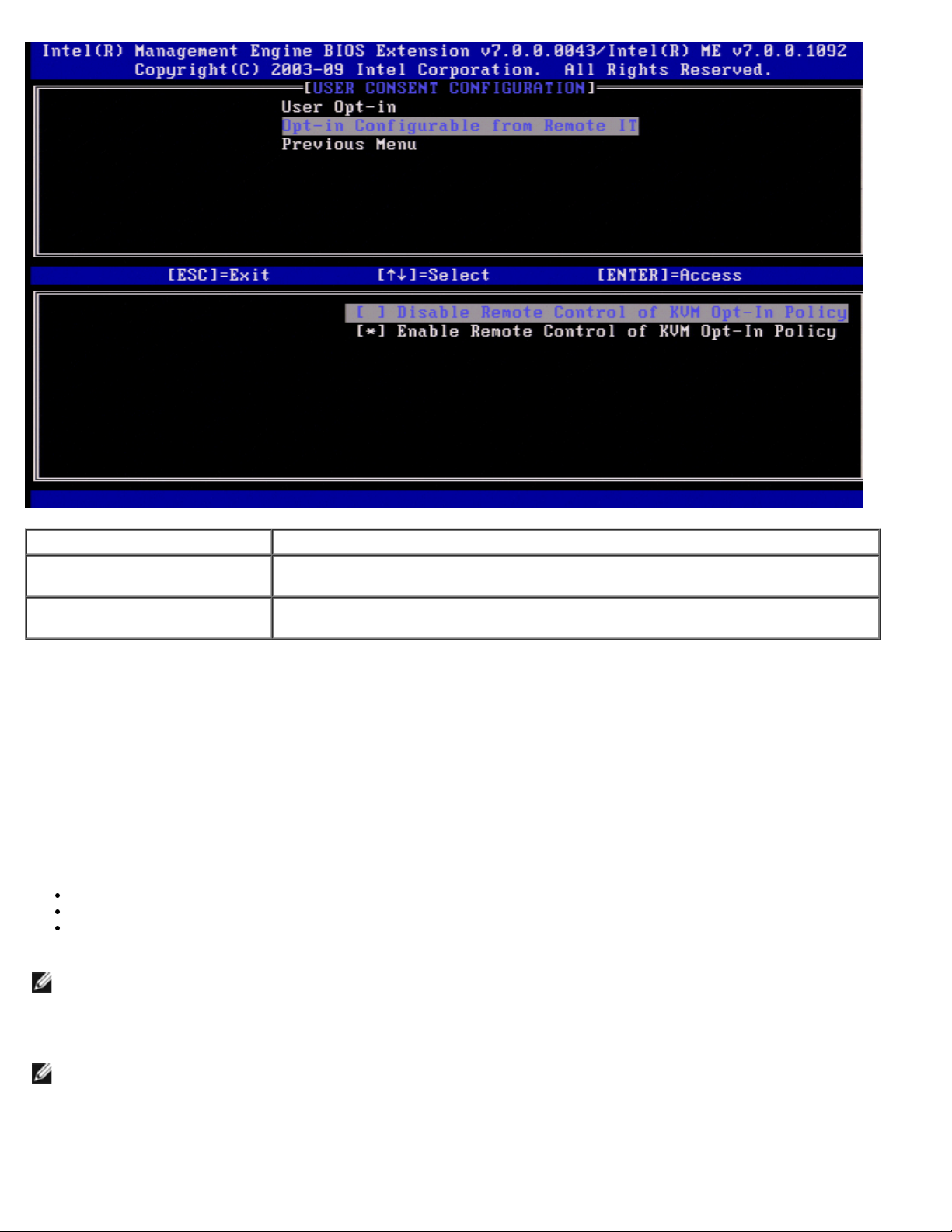
Option Description
Disable Remote Control of
KVM Opt-in Policy
Enable Remote Control of
KVM Opt-in Policy
Disables the remote user's ability to select User OPT-IN Policy. In this case only
the local user can control the opt-in policy.
Enables remote user's ability to select User OPT-IN Policy.
Previous Menu
Under the User Consent Configuration page select Previous Menu and press <Enter>.
The Intel AMT Configuration page appears.
Password Policy
Under the Intel AMT Configuration page select Password Policy and press <Enter>.
This option determines when the user is allowed to change the Intel MEBx password through the network.
There are two passwords for the firmware.
The Intel MEBx password is the password that is entered when a user is physically at the system.
The network password is the password that is entered when accessing an Intel ME enabled system through the
network.
NOTE: By default they are both the same until the network password is changed via the network. Once changed over
the network, the network password will always be kept separate from the local Intel MEBx password.
This option determines when the user is allowed to change the Intel MEBx password through the network.
NOTE: The Intel MEBx password can be changed via the Intel MEBx user interface.
Page 24
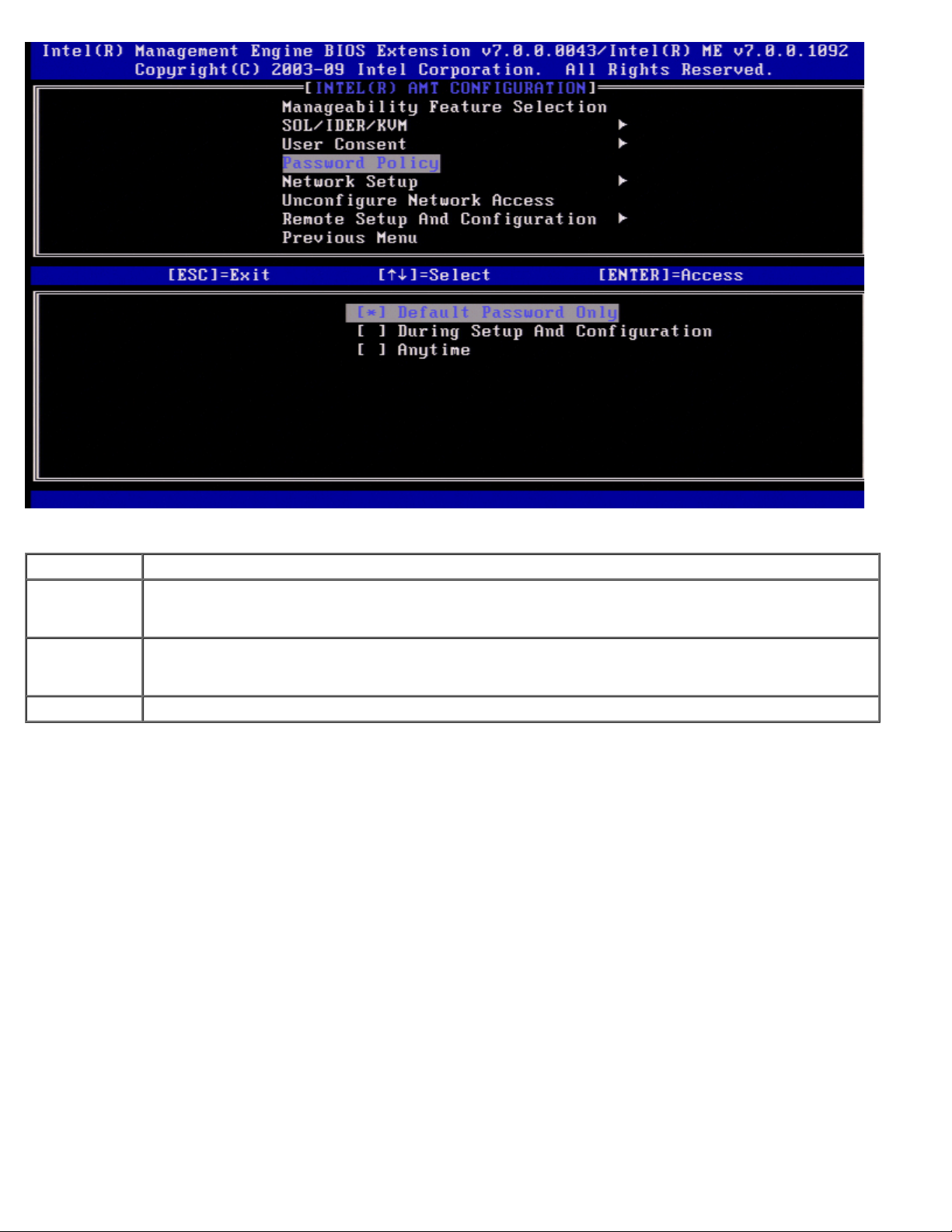
The options are:
Option Description
Default
Password
Only
During Setup
and
Configuration
Anytime The Intel MEBx password can be changed through the network interface at any time.
The Intel MEBx password can be changed through the network interface if the default password has
not been changed.
The Intel MEBx password can be changed through the network interface during the setup and
configuration process but at no other time. Once the setup and configuration process is complete, the
Intel MEBx password cannot be changed via the network interface.
Network Setup
Under the Intel ME Platform Configuration menu select Network Setup and press <Enter>.
The Intel ME Network Setup page appears.
Network Name Settings
Under the Intel ME Network Name Settings select Intel ME Network Name Settings and press <Enter>.
Page 25
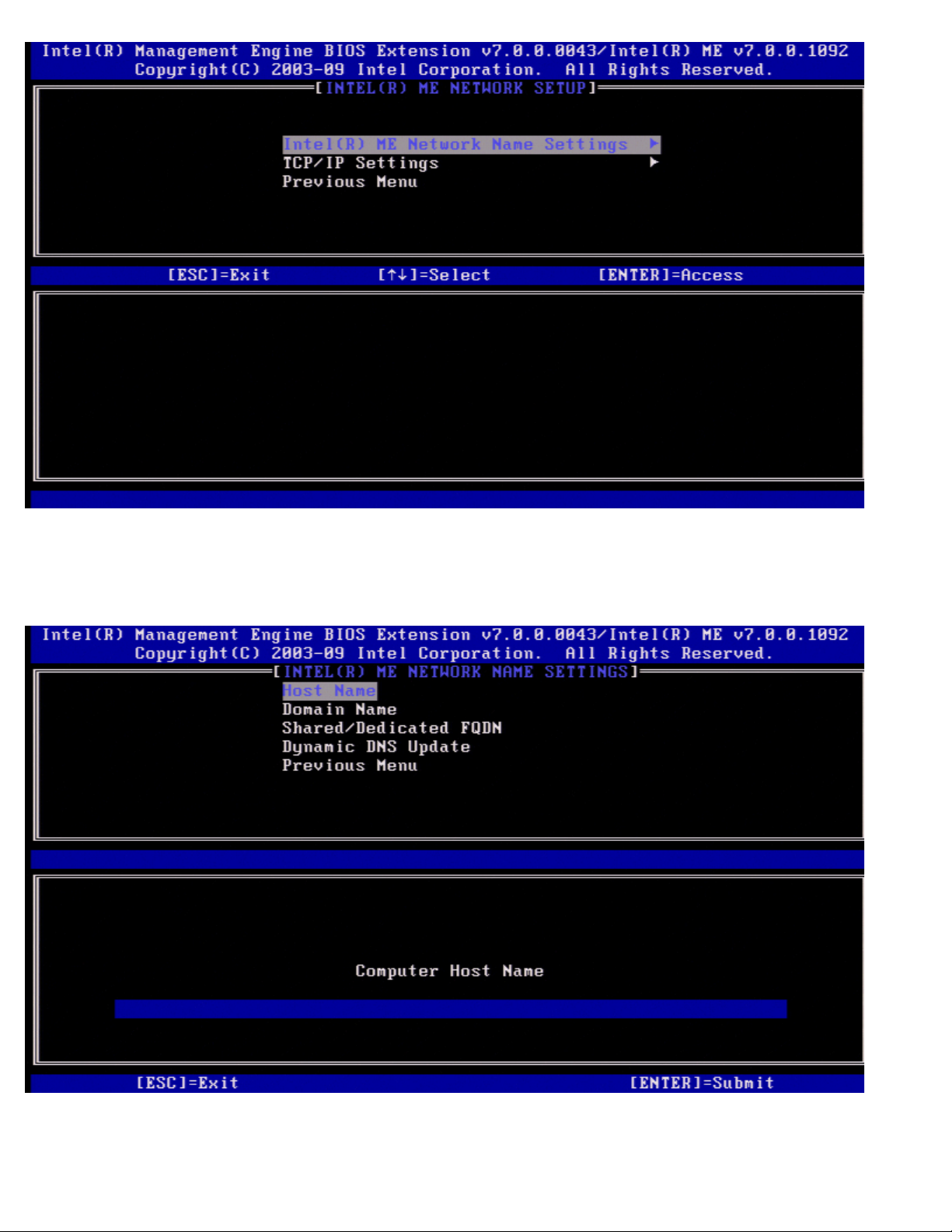
1. Host Name
Under the Intel ME Network Name Settings select Host Name and press <Enter>.
A host name can be assigned to the Intel AMT machine. This will be the hostname of the Intel AMT enabled system.
2. Domain Name
Page 26
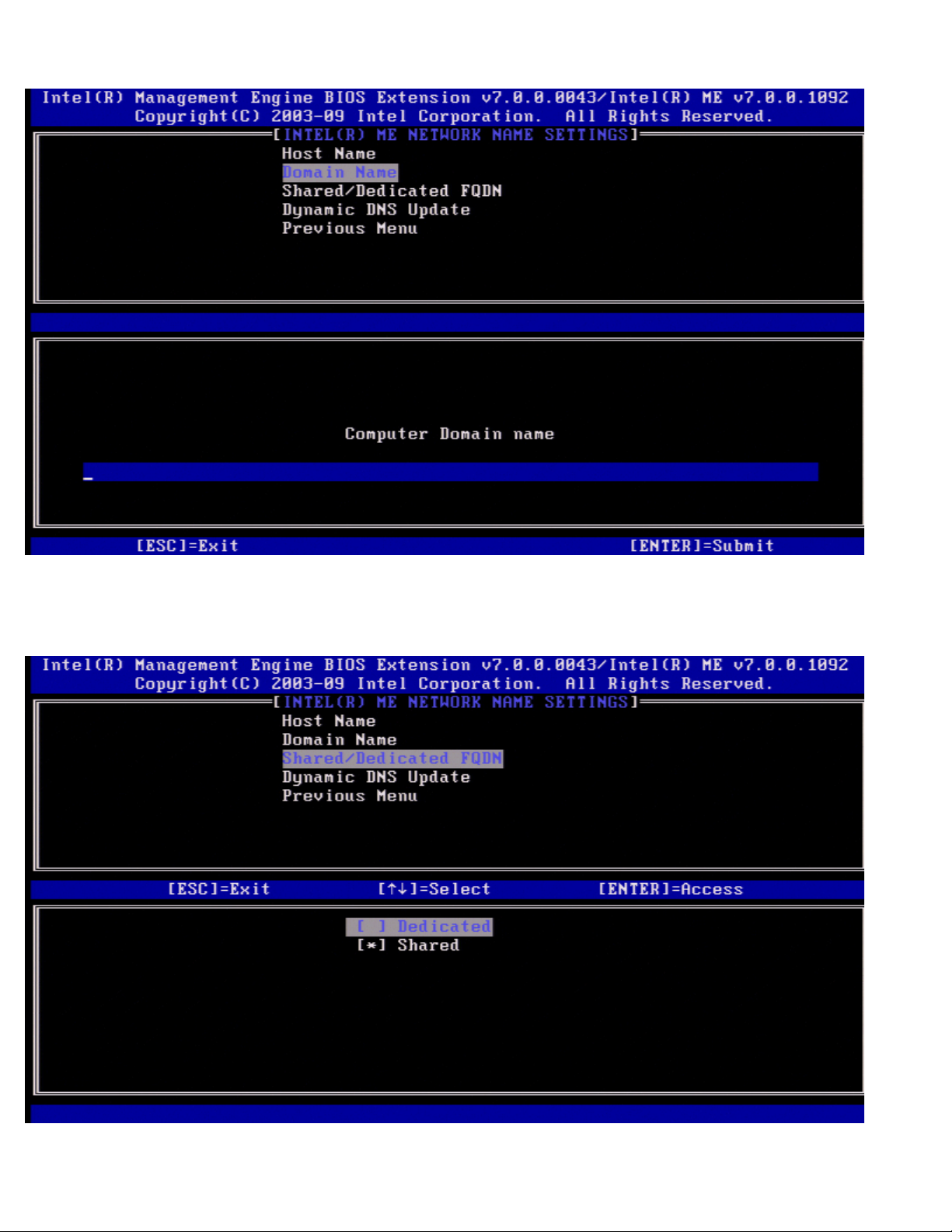
Under the Intel ME Network Name Settings select Domain Name and press <Enter>.
A domain name can be assigned to the Intel AMT machine.
3. Shared/Dedicated FQDN
Under the Intel ME Network Name Settings select Shared/Dedicated FQDN and press <Enter>.
This setting determines whether the Intel ME Fully Qualified Domain Name (FQDN) (HostName.DomainName) is shared with
the host and identical to the operating system machine name or dedicated to the Intel ME.
Page 27
Option Description
Dedicated The FQDN domain name is dedicated to ME
Shared The FQDN domain name is shared with the Host
4. Dynamic DNS Update
Under the Intel ME Network Name Settings select Dynamic DNS Update and press <Enter>.
If Dynamic DNS Update is enabled then the firmware will actively try to register its IP addresses and FQDN in DNS using the
Dynamic DNS Update protocol. If DDNS Update is disabled then the firmware will not make an attempt to update DNS using
DHCP option 81 or Dynamic DNS update. If the DDNS Update state (Enabled or Disabled) is not configured by the user, then
the firmware will assume its old implementation where the firmware used DHCP option 81 for DNS registration but did not
directly update DNS using the DDNS update protocol. For selecting "Enabled" for Dynamic DNS Update, it is required that the
Host Name and Domain Name are set.
Option Description
Enabled The Dynamic DNS Update Client in FW is enabled.
Disabled The Dynamic DNS Update Client in FW is disabled.
5. Periodic Update Interval
Under the Intel ME Network Name Settings select Periodic Update Interval and press <Enter>.
Type the desired internal and press <Enter>.
Page 28
NOTE: Periodic Update Interval option is only available when Dynamic DNS Update is enabled.
Defines the interval at which the firmware DDNS Update client will send periodic updates. It should be set according to
corporate DNS scavenging policy. Units are minutes. A value of 0 disables periodic update. The value set should be equal or
greater than 20 minutes. The default value for this property is 24 hours - 1440 minutes.
6. TTL
Under the Intel ME Network Name Settings select TTL and press <Enter>.
Type the desired time ( in seconds) and press <Enter>.
Page 29
NOTE: The TTL option is only available when Dynamic DNS Update is enabled.
This setting allows configuring the TTL time in seconds. This number should be greater than zero. If set to zero firmware uses
its internal default value which is 15 min or 1/3 of lease time for DHCP.
7. Previous Menu
Under the Intel ME Network Name Settings select Previous Menu and press <Enter>.
The Intel ME Network Name Settings menu changes to the Intel Network Setup page.
TCP/IP Settings
Under the Network Setup menu select TCP/IP Settings and press <Enter>.
The Intel Network Setup page appears.
The Intel Network Setup menu changes to the TCP/IP Settings page.
NOTE: The Intel MEBx has menus for Wireless IPv6, but no menu for wireless IPv4. When the Intel MEBx starts it will
check for the wireless interface to make the decision to display the wireless IPv6 menu or not.
Wired LAN IPv4 Configuration
Under the TCP/IP Settings select Wired LAN IPv4 Configuration and press <Enter>.
The Wired LAN IPv4 Configuration page appears.
Page 30
1. DHCP Mode
Under Wired LAN IPv4 Configuration select DHCP Mode and press <Enter>.
The Wired LAN IPv4 Configuration page appears.
Option Description
If DHCP mode is disabled, the following static TCP/IP settings are required for Intel
Disabled
Enabled If DHCP Mode is enabled, TCP/IP settings will be configured by a DHCP server.
DHCP mode enabled.
AMT. If a system is in static mode the system may require a second IP address. This
IP address, often called the Intel ME IP address may be different from the host IP
address.
Page 31

DHCP mode disabled.
2. IPv4 Address
Select IPv4 Address and press <Enter>.
Type the IPv4 Address in the address column and press <Enter>.
Page 32

3. Subnet Mask Address
Select Subnet Mask Address and press <Enter>.
Type the Subnet Mask Address in the address column and press <Enter>.
4. Default Gateway Address
Page 33

Select Default Gateway Address and press <Enter>.
Type the Default Gateway Address in the address column and press <Enter>.
5. Preferred DNS Address
Select Preferred DNS Address and press <Enter>.
Type the Preferred DNS Address in the address column and press <Enter>.
Page 34

6. Alternate DNS Address
Select Alternate DNS Address and press <Enter>.
Type the Alternate DNS Address in the address column and press <Enter>.
7. Previous Menu
Under the Wired LAN IPv4 Configuration select Previous Menu and press <Enter>.
The TCP/IP Settings menu appears.
Wired LAN IPv6 Configuration
Under the TCP/IP Settings select Wired LAN IPv6 Configuration and press <Enter>.
The Wired LAN IPv6 Configuration page appears.
The Intel ME IPv6 addresses are dedicated and not shared with the host operating system. To enable Dynamic DNS
registration for IPv6 addresses it is required to configure a dedicated FQDN.
Page 35

NOTE: The Intel ME network stack supports a multi-homed IPv6 interface. Each network interface can be configured
with the following IPv6 addresses:
1. One link local auto-configured address
2. Three auto-configured global addresses
3. One DHCPv6 configured address
4. One statically configured IPv6 address
1. IPv6 Feature Selection
Under the Wired LAN IPv6 Configuration select IPv6 Feature Selection and press <Enter>.
DISABLED, select 'Disabled' and press <Enter>. IPv6 Feature Selection disabled.
Page 36

ENABLED, select 'Enabled' and press <Enter>.
IPv6 Feature Selection enabled as more configuration allowed.
2. IPv6 Interface ID Type
Under the Wired LAN IPv6 Configuration select IPv6 Interface ID Type and press <Enter>.
The auto-configured IPv6 address consists of two parts, the IPv6 Prefix set by the IPv6 router is the first and the interface ID
is following part (64 bits each).
Option Description
Page 37

Random ID
Intel ID The IPv6 Interface ID is automatically generated using the MAC address.
Manual ID
The IPv6 Interface ID is automatically generated using a random number as described in RFC
3041. This is the default option.
The IPv6 Interface ID is configured manually. Selecting this type requires that the Manual
Interface ID is set with a valid value.
To select Manual ID
1. Select "Manual ID".
2. Press <Enter>. A new option of IPV6 Interface ID will be displayed below IPV6 Interface ID Type.
3. Select 'IPV6 Interface ID'.
4. Press <Enter>.
5. <Enter> preferred Manual ID.
Page 38

3. IPv6 Address
Under the Wired LAN IPv6 Configuration select IPv6 Address and press <Enter>.
Type the IPv6 Address and press <Enter>.
4. IPv6 Default Router
Under the Wired LAN IPv6 Configuration select IPv6 Default Router and press <Enter>.
Page 39

Type the IPv6 Default Router and press <Enter>.
5. Preferred DNS IPv6 Address
Under the Wired LAN IPv6 Configuration select Preferred DNS IPv6 Address and press <Enter>.
Type the Preferred DNS IPv6 Address and press <Enter>.
6. Alternate DNS IPv6 Address
Under the Wired LAN IPv6 Configuration select Alternate DNS IPv6 Address and press <Enter>.
Type the Alternate DNS IPv6 Address and press <Enter>.
Page 40

7. Previous Menu
Under the Wired LAN IPv6 Configuration select Previous Menu and press <Enter>.
The TCP/IP Settings menu appears.
Wireless LAN IPv6 Configuration
Under the TCP/IP Settings select Wireless LAN IPv6 Configuration and press <Enter>.
The Wireless LAN IPv6 Configuration page appears.
Page 41

1. IPv6 Feature Selection
Under the Wireless LAN IPv6 Configuration select IPv6 Feature Selection and press <Enter>.
2. IPv6 Interface ID Type
Under the Wired LAN IPv6 Configuration select IPv6 Interface ID Type and press <Enter>.
The auto-configured IPv6 address consists of two parts:
IPv6 Prefix (set by the IPv6 router)
Interface ID (64 bits each)
Option Description
Random ID
Intel ID The IPv6 Interface ID is automatically generated using the MAC address.
Manual ID
The IPv6 Interface ID is automatically generated using a random number as described in RFC
3041. This is the default option.
The IPv6 Interface ID is configured manually. Selecting this type requires that the Manual
Interface ID is set with a valid value.
Page 42

To select Manual ID:
1. Select Manual ID.
2. Press <Enter>. A new option of IPV6 Interface ID will be displayed below IPV6 Interface ID Type.
3. Select IPV6 Interface ID.
4. Press <Enter>.
5. Type the preferred Manual ID.
3. Previous Menu
Page 43

Under the Wireless LAN IPv6 Configuration select Previous Menu and press <Enter>.
The TCP/IP Settings menu appears.
Previous Menu
Under the TCP/IP Setting menu select Previous Menu and press <Enter>.
The Intel ME Network Setup menu appears.
Previous Menu
Under the Intel ME Network Setup menu select Previous Menu and press <Enter>.
The AMT Configuration menu appears.
Activate Network Access
Under the Intel AMT Configuration page select Activate Network Access and press <Enter>.
Press 'Y' to activate or press 'N' to cancel.
Activate Network Access causes the Intel ME to transition to the POST provisioning state if all required settings are
configured. Without Activating Network Access, ME will not be able to connect to the network.
NOTE: Power policy will change to PP2 after activating if the default power policy is set to PP1.
Unconfigure Network Access
Under the Intel ME Platform Configuration menu select Unconfigure Network Access and press <Enter>.
NOTE: This will cause Intel ME to transition to the PRE provisioning state.
Page 44

Select Y to unconfigure.
Select Full Unprovisioning and press <Enter>.
Option Description
Full Unprovision
The IPv6 Interface ID is automatically generated using a random number as
described in RFC 3041. This is the default.
Full unprovision will unprovision AMT and remove all the PID/PPS
Page 45

information or any new certificate information populated.
The IPv6 Interface ID is automatically generated using the MAC address.
Partial Unprovision
Unprovisioning in progress.
Partial Unprovisoin will unprovision AMT but will retain PID/PPD information
entered or any new certification information entered.
Remote Setup and Configuration
Under the Intel AMT Configuration select Remote Setup and Configuration and press <Enter>.
The Intel Automated Setup and Configuration page appears.
Page 46

Current Provisioning Mode
Under the Automated Setup and Configuration select Current Provisioning Mode and press <Enter>.
Current Provisioning Mode – Displays the current provisioning TLS Mode: None, PKI, or PSK.
Provisioning Record
Page 47

Under the Automated Setup and Configuration select Provisioning Record and press <Enter>.
Provisioning Record – Displays the system's provision PSK/PKI record data. If the data has not been entered, the Intel
MEBx displays a message stating "Provision Record not present".
If the data is entered, the Provision record will display as below:
Option Description
TLS
provisioning
mode
Provisioning IP The IP address of the setup and configuration server.
Date of
Provision
DNS
Hash Data Displays the 40-character certificate hash data (PKI only).
Hash Algorithm Describes the hash type. Currently only SHA1 is supported. (PKI only).
IsDefault
FQDN FQDN of the provisioning server mentioned in the certificate (PKI only).
Serial Number The 32-character string that indicates the Certificate Authority serial numbers.
Time Validity
Pass
Displays the current configuration mode of the system: None, PSK or PKI.
Displays the date and time of the provisioning in the format MM/DD/YYYY at HH:MM.
Indicates whether the "PKI DNS Suffix" was configured in Intel MEBx before remote
configuration took place or not. A value of 0 indicates that the DNS Suffix was not
configured and the firmware will rely on DHCP option 15 and compare this suffix to the
FQDN in the Configuration Server's client certificate. A value of 1 indicates that the DNS
Suffix was configured and the firmware matched it against the DNS Suffix in the
Configuration Server's client certificate. Host Initiated –Indicates whether the setup and
configuration process was initiated by the host: 'No' indicates that the setup and
configuration process was NOT host-initiated, 'Yes' indicates the setup and configuration
process was host-initiated (PKI only).
Displays 'Yes' if the Hash algorithm is the default algorithm selected. Displays 'No' if the
hash algorithm is NOT the default algorithm used (PKI only).
Indicates whether the certificate passed the time validity check.
RCFG
Page 48

Under the Intel Automated Remote Setup and Configuration menu select RCFG and press <Enter>.
The Intel Remote Configuration page appears.
Start Configuration
Under the Intel Remote Configuration menu select Start Configuration and press <Enter>.
If Remote Configuration is not activated, Remote configuration cannot occur.
To activate (enable) remote configuration, select Y.
Page 49

Previous Menu
Under the Intel Remote Configuration menu select Previous Menu and press <Enter>.
The Intel Automated Setup and Configuration page appears.
Provisioning Server IPv4/IPv6
Under the Intel Automated Setup and Configuration menu select Provisioning Server IPv4/IPv6 and press <Enter>.
1. Type provisioning server address and press <Enter>.
2. Type provisioning server port number and press <Enter>.
The port number (0 – 65535) of the Intel AMT provisioning server. The default port number is 9971.
Page 50

Provisioning Server FQDN
Under the Intel Automated Remote Setup and Configuration menu select Provisioning Server FQDN and press <Enter>.
Type the FQDN of the provisioning server and press <Enter>.
FQDN of the provisioning server mentioned in the certificate (PKI only). This is also the FQDN of the server that AMT
sends hello packets to for both PSK and PKI.
Page 51

TLS PSK
Under the Intel Automated Setup and Configuration menu select TLS PSK and press <Enter>.
The Intel TLS PSK Configuration page appears.
This submenu contains the settings for TLS PSK configuration settings
Set PID and PPS
Under the Intel TLS PSK Configuration menu select Set PID and PPS and press <Enter>.
Type the PID and press <Enter>.
Type the PPS and press <Enter>.
Page 52

Setting the PID/PPS will cause a partial unprovision if the setup and configuration is "In-process". The PID and PPS should be
Delete PID and PPS
entered in the dash format. (for example: PID: 1234-ABCD ; PPS: 1234-ABCD-1234-ABCD-1234-ABCD-1234-ABCD).
NOTE: A PPS value of '0000-0000-0000-0000-0000-0000-0000-0000' will not change the setup configuration state. If
this value is used, the setup and configuration state will remain 'Not-started'.
If an invalid entry is attempted, an error message will be displayed:
Page 53

Under the Intel TLS PSK Configuration menu select Delete PID and PPS and press <Enter>.
This option deletes the current PID and PPS stored in Intel ME. If the PID and PPS were not entered previously, the Intel
MEBx will return an error message.
To delete the PID and PPS entries, select Y, else N.
Previous Menu
Under the Intel TLS PSK Configuration menu select Previous Menu and press <Enter>.
The Intel Automated Setup and Configuration page appears.
TLS PKI
Under the Intel Automated Setup and Configuration menu select TLS PKI and press <Enter>.
The Intel Remote Configuration page appears.
Remote Configuration
Under the Intel Remote Configuration menu select Remote Configuration and press <Enter>.
Enabling/Disabling Remote configuration will cause a partial un-provision, if the setup and configuration server is "Inprocess".
Option Description
Disabled
Enabled
Remote configuration is disabled. Only 'Remote Configuration' and 'Previous Menu' items are
visible. To disable, select this option and press <Enter>.
Remote configuration is enabled, this will show additional fields. To enable, select this option
and press .
Page 54

PKI DNS Suffix
Under the Intel Remote Configuration menu select PKI DNS Suffix and press <Enter>.
Type the PKI DNS Suffix and press <Enter>. Key Value will be maintained in the EPS.
Manage Hashes
Page 55

Under the Intel Remote Configuration menu select Manage Hashes and press <Enter>.
Selecting this option will enumerate the hashes in the system and display the Hash Name and the active and default state. If
the system does not contain any hashes yet, Intel MEBx will display the following screen.
Answering 'Yes' will begin the process of adding customized hash. The Manage Certificate Hash screen provides keyboard
controls for managing the hashes on the system. The following keys are valid when in the Manage Certificate Hash menu.
Key Description
Escape Exits from the menu.
Insert Adds a customized certificate hash to the system.
Delete Deletes the currently selected certificate hash from the system.
+ Changes the active state of the currently selected certificate hash.
<Enter> Displays the details of the currently selected certificate hash.
Adding Customized Hash
Page 56

When the Insert key is pressed in the Manage Certificate Hash screen, the following screen is displayed.
To add a customized certificate hash: Type the hash name (up to 32 characters). When you press <Enter>, you are
prompted to select the algorithm of hash being used for PKI provisioning. Type Y if SHA1 is being used, otherwise enter N.
The supported hash algorithms are:
1. SHA1
2. SHA2-256
Page 57

3. SHA2-384
If SHA1 is not chosen, in the next screen you are prompted to select the option of supported SHA2 algorithm. Type Y if
SHA256 is being used, otherwise enter N.
When SHA256 is not chosen, in the next screen, type Y to select SHA2-384.
If N is entered, an error message will be shown to prompt the user to select one supported algorithm.
Page 58

After selecting desired Hash Algorithm, you are prompted to type the certificate hash value.
The Certificate hash value is a hexadecimal number (for SHA-1 it is 20 bytes for SHA-2 it is 32 bytes). If the value is not
entered in the correct format, the message "Invalid Hash Certificate Entered - Try Again" is displayed. When you press
<Enter>, you are prompted to set the active state of the hash.
Page 59

Your response sets the active state of the customized hash as follows:
Yes – The customized hash will be marked as active.
No (Default) – The customized hash will add to the EPS but will not be active.
Deleting a Hash
When the Delete is pressed in the Manage Certificate Hash screen, the following screen is displayed.
NOTE: A certificate hash that is set to Default cannot be deleted.
Page 60

This option allows deleting of the selected certificate hash.
Yes – Intel MEBx sends the firmware a message to delete the selected hash.
No – Intel MEBx does not delete the selected hash, and returns to Remote Configuration.
Changing the Active State
When the + is pressed in the Manage Certificate Hashes screen, the following screen is displayed as seen in the following
screen.
Answering Y toggles the active state of the currently selected certificate hash. Setting a hash as active indicates that the hash
is available for use during PSK provisioning.
Viewing a Certificate Hash
When <Enter> is pressed in the Manage Certificate Hash screen, the following screen is displayed.
Page 61

The details of the selected certificate hash are displayed to the user and include the following:
Hash Name
Certificate Hash Data
Active and Default States
Previous Menu
Under the Intel Remote Configuration menu select Previous Menu and press <Enter>.
The Intel Automated Setup and Configuration page appears.
Previous Menu
Under the Intel Automated Setup and Configuration menu select Previous Menu and press <Enter>.
The Intel AMT Configuration menu appears.
Previous Menu
Under the Intel AMT Configuration menu select Previous Menu and press <Enter>.
The Main Menu appears.
*
Information on this page provided by Intel.
Page 62

Intel Fast Call for Help
Intel Fast Call for help is available for VPro SKUs. An Intel Fast Call for help connection allows the end user to request
assistance if the VPro system is outside the corporate network.
NOTE: It is recommended that to press <F12> and select Fast Call for Help. It will only be available when the IT
administrator has configured the system to support it.
Requirements
Before an Intel Fast Call connection can be established from the Operating System the VPro system must have:
1. Environment detection enabled
2. Remote Connection policy
3. Management Presence Server (MPS)
Putting it all Together
To get the Intel Fast Call for help, system needs to be in provisioned stated. If the system supports Full VPro Intel Fast Call
for help will be available for use. If the system only supports Intel Standard Manageability Intel Fast call for help is not
enabled.
1. Before an Intel Fast Call for help can be started, environment detection must be enabled. This allows Intel AMT to
determine if the system is within the corporate network. This is configured through an ISV app.
2. A remote connection policy must be created before an Intel Fast call for help can be initiated. The policy for the BIOS
initiated call does not need to be configured, but another policy must exist before initiating a help call from the BIOS.
The BIOS must support the hot key that initiates the Intel Fast call for help.
3. A management presence server must exist to answer the Intel fast calls for help. The management presence server
resides in the DMZ zone.
When all of these conditions are satisfied the system is able to initiate an Intel Fast Call for help.
Initiating Intel Fast Call for Help
Once the feature has been fully configured, there are three methods for initiating an Intel Fast Call for help session. These
include:
At the Dell splash screen press <Ctrl><h>.
At the Dell splash screen press <F12> for the One Time Boot Menu.
Select the last option titled Intel Fast Call for Help.
From Windows:
1. Launch the Intel AMT privacy icon/application Intel Management Security Status.
2. Switch to the Intel AMT tab.
3. In the Remote Connectivity box, click Connect.
Page 63

ME General Settings
The table below lists the default settings for the Intel Management Engine BIOS Extension (MEBx) on general settings page.
Password
Password admin
Change Intel ME Password
Change Intel ME Password blank
SET PRTC
Set PRTC blank
Power Control
Power Control
Intel ME ON in Host Sleep
Idle Time Out 1
*Default setting
**May cause Intel AMT partial unprovision
1
Intel ME Platform State Control is only changed for Management Engine (ME) troubleshooting.
2
Un-provision setting only seen if the box is provisioned.
Mobile: ON is S0
Mobile: ON is S0, ME Wake in S3, S4-5 (AC only) *
Page 64

AMT Configuration
The table below lists the default settings for the Intel Management Engine BIOS Extension (MEBx) on AMT configuration page.
Manageability/Feature Selection
SOL/IDER
Username and Password
SOL
IDER
Legacy Redirection Mode
KVM
User Consent
User Opt-in
Opt-in Configurable from remote IT
NOTE: In order for KVM to work, the requirement must be an Intel i3/i5/i7/Celeron/Pentium CPU.
Disabled
Enabled *
Disabled
Enabled *
Disabled
Enabled *
Disabled
Enabled *
Disabled
Enabled *
None
KVM *
All
Disable Remote Control of KVM Opt-In Policy
Enable Remote Control of KVM Opt-In Policy *
Password Policy
Default Password Only *
Password Policy
During Setup and Configuration
Anytime
Network Setup
Network Name Settings
Host Name blank
Domain Name blank
Shared / Dedicated FQDN
Dynamic DNS Update
TCP/IP Settings
Wired LAN IPv4 Configuration
DHCP Mode
Dedicated
Shared *
Disabled *
Enabled
Disabled
Enabled *
Below configuration page will only available if enabled selected
Page 65

IPv4 Address 0.0.0.0
Subnet Mask Address 0.0.0.0
Default Gateway Address 0.0.0.0
Preferred DNS Address 0.0.0.0
Alternate DNS Address 0.0.0.0
Wired LAN IPv6 Configuration
Disabled *
IPv6 Feature Selection
Enabled
Below configuration page will only available if enabled selected
Random ID *
IPv6 Interface ID Type
Intel ID
Manual ID
IPv6 Address blank
IPv6 Default Router blank
Preferred DNS IPv6 Address blank
Alternate DNS IPv6 Address blank
Activate Network Access Y / N
Unconfigure Network Access Y / N
Remote Setup and Configuration
Current Provisioning Mode
Provisioning Record
RCFG
Start Configuration Y / N
Provisioning Server IPv4/IPv6 blank
Provisioning Server FQDN blank
TLS PSK
Set PID and PPS blank
Delete PID and PPS Y / N
TLS PKI
Remote Configuration
Disabled
Enabled *
PKI DNS Suffix blank
Manage Hashes
*Default setting
**May cause Intel AMT partial unprovision
1
Intel ME Platform State Control is only changed for Management Engine (ME) troubleshooting.
2
In Enterprise mode, DHCP automatically loads the domain name.
3
Un-provision setting only seen if the box is provisioned.
Page 66

Methods Overview
As discussed in the Setup and Configuration Overview section, the computer has to be configured before the Intel AMT
capabilities are ready to interact with management application. There are three methods to complete the provisioning process
(from least complex to most complex):
Configuration service — A configuration service allows you to complete the provisioning process from a GUI console
on their server with only one touch on each of the Intel AMT capable computers. The PPS and PID fields are completed
using a file created by the configuration service saved to a USB mass storage device.
MEBx interface — The IT administrator manually configures the Management Engine BIOS Extension (MEBx) settings
on each Intel AMT ready computer. The PPS and PID fields are completed by typing the 32 character and 8 character
alpha-numeric keys created by the configuration service into the MEBx interface.
TLS-PKI— Commonly referred to as Remote Configuration (RCFG) or Zero Touch Configuration (ZTC). This process
utilizes a certificate associated with the ProvisionServer. The associated certificate hash must be listed within the Intel
Management Engine BIOS Extension (MEBx).
*TLS-PKI refer as Transport Layer Security - Public Key Infrastructure*
Details on using these various methods are available in the next section.
Page 67

Using a USB Device
This section discusses Intel AMT setup and configuration using a USB storage device. You can set up and locally configure
password, provisioning ID (PID), and provisioning passphrase (PPS) information with a USB drive key. This is also called USB
provisioning. USB provisioning allows you to manually set up and configure computers without the problems associated with
manually typing in entries.
NOTE: USB provisioning only works if the MEBx password is set to the factory default of admin. If the password has
been changed, reset it to the factory default by clearing the CMOS.
The following is a typical USB drive key setup and configuration procedure. For a detailed walk-through using Altiris Dell
Client Manager (DCM), refer to the USB device procedure
1. Insert a USB drive key into the computer with a management console.
2. Request the local setup and configuration records from a setup and configuration server (SCS) through the console.
3. The SCS does the following:
1. Generates the appropriate passwords, PID, and PPS sets.
2. Stores this information in its database.
3. Returns the information to the management console.
4. The management console writes the password, PID, and PPS sets to a setup.bin file in the USB drive key.
5. Take the USB drive key to the staging area where new Intel AMT capable computers are located. Perform the following:
1. Unpack and connect the computers, if necessary.
2. Insert the USB drive key into a computer.
3. Turn on that computer.
6. The computer BIOS detects the USB drive key.
If found, the BIOS looks for a setup.bin file at the beginning of the drive key. Go to step 7.
If no USB drive key or setup.bin file is found, then restart the computer. Ignore the remaining steps.
7. The computer BIOS displays a message that automatic setup and configuration will occur.
1. The first available record in the setup.bin file is read into memory. The process accomplishes the following:
Validates the file header record.
Locates the next available record.
If the procedure is successful, the current record is invalidated so it cannot be used again.
2. The process places the memory address into the MEBx parameter block.
3. The process calls MEBx.
8. MEBx processes the record.
9. MEBx writes a completion message to the display.
10. Turn off the computer. The computer is now in the setup state and is ready to be distributed to users in an Enterprise
mode environment.
11. Repeat step 5 if you have more than one computer.
page.
Refer to the management console supplier for more information on USB drive key setup and configuration.
USB Drive Key Requirements
The USB drive key must meet the following requirements to be able to set up and configure Intel AMT:
It must be greater than 16 MB.
It must be formatted with the FAT16 or FAT32 file system.
The sector size must be 1 KB.
The USB drive key is not bootable.
The USB drive key AMT provisioning and not for any other purpose.
The USB key must not contain any other files whether hidden, deleted, or otherwise.
The setup.bin file must be the first file landed on the USB drive key (for Legacy BIOS or Wembley)
The setup.bin file must be in the top directory (for UEFI BIOS or RAM)
Page 68

USB Device Procedure
Dell Client Management (DCM) application is the default console package provided. This section provides the procedure to set
up and configure Intel AMT with the DCM package. As mentioned earlier in the document, several other packages are
available through third-party vendors.
The computer must be configured and seen by the DNS server before you begin this process. A USB storage device is also
required and must conform to the requirements listed on Using a USB Device
NOTE: The nature of management software is that it is not always dynamic or real time. You may have to repeat an
action multiple times to cause a result.
1. Format a USB device with the FAT16 file system and no volume label and then set it aside.
page.
2. Open the Altiris Dell Client Manager application by double-clicking the desktop icon or through the Start menu.
3. Select AMT Quick Start from the left navigation menu to open the Altiris Console.
Page 69

4. Click the <+> to expand the Intel AMT Getting Started section.
Page 70

5. Click the <+> to expand the Section 1. Provisioning section.
Page 71

6. Click the <+> to expand the Basic Provisioning (without TLS) section.
Page 72

7. Select Step 1. Configure DNS.
8. The notification server with an out-of-band management solution installed must be registered in DNS as
"ProvisionServer."
Page 73

9. Click Test on the DNS Configuration screen to verify that DNS has the ProvisionServer entry and that it resolves to
the correct Intel Setup and Configuration Server (SCS).
Page 74

10. The IP address for the ProvisionServer and Intel SCS are now visible.
Page 75

11. Select Step 2. Discovery Capabilities.
Page 76

12. Verify that the setting is Enabled. If Disabled, select the check box next to Disabled and click Apply.
Page 77

13. Select Step 3. View Intel AMT Capable Computers.
Page 78

14. Any Intel AMT capable computers on the network are visible in this list.
Page 79

15. Select Step 4. Create Profile.
Page 80

16. Click the plus symbol to add a new profile.
Page 81

17. On the General tab the administrator can modify the profile name and description along with the password. The
administrator sets a standard password for easy maintenance in the future. Select the manual radio button and type a
new password.
Page 82

18. The Network tab provides the option to enable ping responses, VLAN, WebUI, Serial over LAN, and IDE Redirection. If
you are configuring Intel AMT manually, all these settings are also available in the MEBx.
19. The TLS (Transport Layer Security) tab provides the ability to enable TLS. If enabled, several other pieces of
information are required including the certificate authority (CA) server name, CA common name, CA type, and
certificate template.
Page 83

20. The ACL (access control list) tab is used to review users already associated with this profile and to add new users and
define their access privileges.
21. The Power Policy tab has configuration options to select the sleep states for Intel AMT as well as an Idle Timeout
setting. It is recommended that Idle timeout is always set to 0 for optimal performance.
NOTE: The setting for the Power Policy tab can potentially impact a computer's ability to remain E-Star 4.0
compliant.
Page 84

22. Select Step 5. Generate Security Keys.
Page 85

23. Select the icon with the arrow pointing out to Export Security Keys to USB Key.
Page 86

24. Select the Generate keys before export radio button.
Page 87

25. Type the number of keys to generate (depends on the number of computers that need to be provisioned). The default
is 50.
26. The Intel ME default password is admin. Configure the new Intel ME password for the environment.
Page 88

27. Click Generate. Once the keys have been created, a link appears to the left of the Generate button.
28. Insert the previously formatted USB device into a USB connector on the ProvisioningServer.
Page 89

29. Click the Download USB key file link to download setup.bin file to the USB device. The USB device is recognized by
default; save the file to the USB device.
NOTE: If additional keys are needed in the future, the USB device must be reformatted before saving the
setup.bin file to it.
a. Click Save on the File Download dialog box.
b. Verify that the Save in: location is directed to the USB device. Click Save.
Page 90

c. Click Close in the Download complete dialog box.
30. The setup.bin file is now visible in the drive explorer window.
Page 91

31. Close the Export Security Keys to USB Key and drive explorer windows to return to the Altiris Console.
32. Insert the USB device and turn on the computer. The USB device is recognized immediately and you are prompted to
Continue with Auto Provisioning (Y/N)
33. Press <Y>.
Press any key to continue with system boot...
Page 92

34. Once complete, turn off the computer and move back to the management server.
35. Select Step 6. Configure Automatic Profile Assignments.
Page 93

36. Verify that the setting is enabled. In the Intel AMT 2.0+ dropdown, select the profile created previously. Configure the
other settings for the environment.
Page 94

37. Select Step 7. Monitor Provisioning Process.
Page 95

38. The computers for which the keys were applied are updated in the system list. At first the status is Unprovisioned,
then the system status changes to In provisioning, and finally it changes to Provisioned at the end of the process.
Page 96

39. Select Step 8. Monitor Profile Assignments.
Page 97

40. The computers for which profiles were assigned appear in the list. Each computer is identified by the FQDN, UUID,
and Profile Name columns.
Page 98

41. Once the computers are provisioned, they are visible under the Collections folder in All configured Intel AMT
computers.
Page 99

Page 100

System Deployment
Once you are ready to deploy a computer to a user, plug the computer into a power source and connect it to the network.
Use the integrated Intel 82566DM Network Interface Card (NIC). Intel Active Management Technology (Intel AMT) does not
work with any other NIC solution.
When the computer is turned on, the computer immediately looks for a Setup and Configuration Server (SCS). If the
computer finds this server, the Intel AMT capable computer sends a Hello message to the server.
NOTE: User must first activate network access either via MEBx or using Intel Activator.
DHCP and DNS must be available for the setup and configuration server search to automatically succeed. If DHCP and DNS
are not available, then the setup and configuration servers (SCS) IP address must be manually entered into the Intel AMT
capable computer's MEBx.
The Hello message contains the following information:
Provisioning ID (PID)
Universally Unique Identifier (UUID)
IP address
ROM and firmware (FW) version numbers
The Hello message is transparent to the end user.
1. In the AMT 7, in the OS, select IMSS.
2. Under the Advanced tab, select Extended System Details.
3. Click Intel ME Information.
If Provisioning Mode states "In Provisioning", the hello packets are being sent to provision server in the network. The SCS
uses the information in the Hello message to initiate a Transport Layer Security (TLS) connection to the Intel AMT capable
computer using a TLS Pre-Shared key (PSK) cipher suite if TLS is supported.
The SCS uses the PID to look up the provisioning passphrase (PPS) in the provisioning server database and uses the PPS and
PID to generate a TLS Pre-Master Secret. TLS is optional. For secure and encrypted transactions, use TLS if the infrastructure
is available. If you do not use TLS, then HTTP Digest is used for mutual authentication. HTTP Digest is not as secure as TLS.
The SCS logs into the Intel AMT computer with the username and password and provisions the following required data items:
New PPS and PID (for future setup and configuration)
TLS certificates
Private keys
Current date and time
HTTP Digest credentials
HTTP Negotiate credentials
The computer goes from the setup state to the provisioned state, and then Intel AMT is fully operational. Once in the
provisioned state, the computer can be remotely managed.
 Loading...
Loading...