Page 1

Intel® Active Management Technology v5.0
Administrator's Guide
Overview
Product Overview
Operational Modes
Setup and Configuration Overview
Provisioning Methods
Menus and Defaults
MEBx Settings Overview
ME Configuration Menu
AMT Configuration Menu
Intel Fast Call for Help
MEBx Defaults
Setup and Configuration
Methods Overview
Configuration Service--Using a USB Device
Configuration Service--USB Device Procedure
MEBx Interface--Enterprise Mode
MEBx Interface--SMB Mode
System Deployment
Operating System Drivers
Management
Intel AMT Web GUI
AMT Redirection (SOL/IDE-R)
AMT Redirection Overview
Troubleshooting
Troubleshooting
If you purchased a DELL™ n Series computer, any references in this document to Microsoft
are not applicable.
Information in this document is subject to change without notice.
© 2008 Dell Inc. All rights reserved.
Reproduction of these materials in any manner whatsoever without the written permission of Dell Inc. is strictly forbidden.
Trademarks used in this text: Dell, Latitude, and the DELL logo are trademarks of Dell Inc.; Intel is a registered trademark of Intel Corporation in
the U.S. and other countries; Microsoft and Windows are either trademarks or registered trademarks of Microsoft Corporation in the United States
and/or other countries.
Other trademarks and trade names may be used in this document to refer to either the entities claiming the marks and names or their products.
Dell Inc. disclaims any proprietary interest in trademarks and trade names other than its own.
October 2008 Rev. A00
®
Windows® operating systems
Page 2
Back to Contents Page
Overview
Intel® Active Management Technology (Intel AMT) allows companies to easily manage their networked computers.
Discover computing assets on a network regardless of whether the computer is turned on or off – Intel AMT uses
information stored in nonvolatile system memory to access the computer. The computer can even be accessed while it
is powered off (also called out-of-band or OOB access).
Remotely repair systems even after operating system failures – In the event of a software or operating system failure,
Intel AMT can be used to access the computer remotely for repair purposes. IT administrators can also detect computer
system problems easily with the assistance of Intel AMT's out-of-band event logging and alerting.
Protect networks from incoming threats while easily keeping software and virus protection up to date across the
network.
Software Support
Several independent software vendors (ISVs) are building software packages to work with Intel AMT features. This provides IT
administrators many options when it comes to remotely managing the networked computer assets within their company.
Features and Benefits
Intel AMT
Features Benefits
Out-of-band (OOB) access
Remote troubleshooting and recovery Significantly reduces desk side visits, increasing the efficiency of IT technical staff
Proactive alerting Decreases downtime and minimizes repair times
Remote hardware and software asset
tracking
Third-party nonvolatile storage
Allows remote management of platforms regardless of system power or operating
system state
Increases speed and accuracy over manual inventory tracking, reducing asset
accounting costs
Increases speed and accuracy over manual inventory tracking, reducing asset
accounting cost
*
Information on this page provided by Intel.
The Intel® Management Engine BIOS Extension (MEBx) is an optional ROM module provided to Dell™ from Intel that is
included in the Dell BIOS. The MEBx has been customized for Dell computers.
Back to Contents Page
Page 3

Back to Contents Page
Operational Modes
Intel® AMT can be set up for either Enterprise or Small and Medium Business operational modes (also called provisioning
models). Both operational modes support dynamic and static IP networking.
If you use dynamic IP networking (DHCP), the Intel AMT host name and the operating system host name must match. You
must also configure both the operating system and Intel AMT to use DHCP as well.
If you use static IP networking, the Intel AMT IP address must be different from the operating system's IP address.
Additionally, the Intel AMT hostname must be different from the operating system's hostname.
Enterprise mode – This mode is for large organizations. This is an advanced networking mode that supports
Transport Layer Security (TLS) and requires a configuration service. Enterprise mode allows IT administrators to set up
and configure Intel AMT securely for remote management. The Dell™ computer is defaulted to Enterprise mode when it
leaves the factory. The mode can be changed during the setup and configuration process.
Small Medium Business (SMB) mode – This mode is a simplified operational mode that does not support TLS and
does not require a setup application. SMB mode is for customers who do not have independent software vendor (ISV)
management consoles or the necessary network and security infrastructures to use encrypted TLS. In SMB mode, Intel
AMT setup and configuration is a manual process completed through the Intel ME BIOS Extension (MEBx). This mode is
the easiest to implement since it does not require much infrastructure, but it is the least secure since all network traffic
is not encrypted.
Intel AMT Configuration sets up all other Intel AMT options not covered in Intel AMT Setup, such as enabling the computer for
Serial-Over-LAN (SOL) or IDE-Redirect (IDE-R).
You can change the settings modified in the configuration phase many times over the course of a computer's life span. You
can make changes to the computer locally or through a management console.
Back to Contents Page
Page 4

Back to Contents Page
Setup and Configuration Overview
The following is a list of important terms related to the Intel® AMT setup and configuration.
Setup and configuration — The process that populates the Intel AMT-managed computer with usernames,
passwords, and network parameters that enable the computer to be administered remotely.
Provisioning — The act of setting up and configuring Intel AMT.
Configuration service — A third-party application that completes the Intel AMT provisioning.
Intel AMT WebGUI — A Web browser-based interface for limited remote computer management.
You must set up and configure Intel AMT on a computer before using it. Intel AMT setup readies the computer for Intel AMT
mode and enables network connectivity. This setup is generally performed only once in the lifetime of a computer. When Intel
AMT is enabled, it can be discovered by management software over a network.
Once Intel AMT is set up in Enterprise mode, it is ready to initiate configuration of its own capabilities. When all required
network elements are available, simply connect the computer to a power source and the network, and Intel AMT automatically
initiates its own configuration. The configuration service (a third-party application) completes the process for you. Intel AMT is
then ready for remote management. This configuration typically takes only a few seconds. When Intel AMT is set up and
configured, you can reconfigure the technology as needed for your business environment.
Once Intel AMT is set up in SMB mode, the computer does not have to initiate any configuration across the network. It is set
up manually and is ready to use with the Intel AMT Web GUI.
Intel AMT Setup and Configuration States
The act of setting up and configuring Intel AMT is also known as provisioning. An Intel AMT capable computer can be in one
of three setup and configuration states:
Factory-default state
Setup state
Provisioned state
The factory-default state is a fully unconfigured state in which security credentials are not yet established and Intel AMT
capabilities are not yet available to management applications. In the factory-default state, Intel AMT has the factory-defined
settings.
The setup state is a partially configured state in which Intel AMT has been set up with initial networking and transport layer
security (TLS) information: an initial administrator password, the provisioning passphrase (PPS), and the provisioning
identifier (PID). When Intel AMT has been set up, Intel AMT is ready to receive enterprise configuration settings from a
configuration service.
The provisioned state is a fully configured state in which the Intel Management Engine (ME) has been configured with power
options, and Intel AMT has been configured with its security settings, certificates, and the settings that activate the Intel AMT
capabilities. When Intel AMT has been configured, the capabilities are ready to interact with management applications.
Back to Contents Page
Page 5

Back to Contents Page
Provisioning Methods
The act of setting up and configuring Intel® AMT is known as provisioning. There are three methods of provisioning a
computer:
Small Business
Enterprise TLS-PKI
Enterprise TLS-PSK
Transport Layer Security (TLS) is a protocol that provides secure communications on the Internet for such things as web
browsing, e-mail, Internet faxing, instant messaging and other data transfers. TLS was a legacy method of configuring Intel
AMT on an isolated network separate from the corporate network. A setup and configuration server (SCS) requires a
secondary network connection to a certification authority (an entity which issues digital certificates) for TLS configuration.
Initially the computers are shipped in the factory-default state with Intel AMT ready for configuration and provisioning. These
computers must go through Intel AMT setup in order to go from the factory-default state to the setup state. Once the
computer is in the setup state, you can continue to configure it manually or connect it to a network where it connects with an
SCS and begin Enterprise Mode Intel AMT configuration.
Small Business Mode
Small business mode is remains the same as from AMT v3.0 and basically means no security. Small business setup consists of
just three steps:
1. Set the host name
2. Configure the TCP/IP settings
3. Set Provisioning Mode to "Small Business"
Enterprise Mode
TLS-PKI and TLS-PSK Intel AMT setup and configuration is usually performed in a company's IT department. The following are
required:
Setup and configuration server
Network and security infrastructure
Intel AMT capable computers in the factory-default state are given to the IT department, which is responsible for Intel AMT
setup and configuration. The IT department can use the methods described below to input Intel AMT setup information, after
which the computers are in Enterprise Mode and in the In-Setup phase. An SCS must generate PID and PPS sets.
The Intel AMT configuration must occur over a network. The network can be encrypted using the Transport Layer Security
Pre-Shared Key (TLS-PSK) protocol. Once the computers connect to an SCS, Enterprise Mode Configuration occurs.
Enterprise TLS-PKI
Enterprise TLS-PKI is also known as "Remote Configuration". The SCS uses TLS-PKI (Public Key Infrastructure) certificates to
securely connect to an Intel AMT enabled computer. The certificates can be generated a few ways:
The SCS can connect using one of the default certificates pre-programmed on the computer, as detailed in the MEBx
interface section of this document.
The SCS can create a custom certificate, which can be deployed on the AMT computer by means of a desk-side visit
with a specially formatted USB thumb drive as detailed in the Configuration Service section of this document.
The SCS could use a custom certificate which was pre-programmed at the Dell factory through the Custom Factory
Integration (CFI) process.
Enterprise TLS-PSK
Enterprise TLS-PSK is also known as "One-Touch Configuration". The SCS uses PSK's (Pre-Shared Key's) to establish a secure
connection with the AMT computer. These 52-character keys can be created by the SCS, and then deployed on the AMT
Page 6

computer with a desk-side visit in one of two ways:
The key can be manually typed into the MEBx.
The SCS can create a list of custom keys, and put them onto a specially formatted USB thumb drive. Then each AMT
computer retrieves a custom key from the specially formatted USB thumb drive during BIOS boot as detailed in the
Configuration Service section of this document.
Back to Contents Page
Page 7
Back to Contents Page
MEBx Settings Overview
The Intel® Management Engine BIOS Extension (MEBx) provides platform-level configuration options for you to configure the
behavior of Management Engine (ME) platform. Options include enabling and disabling individual features and setting power
configurations.
This section provides details about MEBx configuration options and constraints, if any.
All the ME Platform Configuration setting changes are not cached in MEBx. They are committed to ME non-volatile memory
(NVM) until you exit MEBx. Hence, if MEBx crashes, the changes made until that point are NOT going to be committed to ME
NVM.
Access MEBx Configuration User Interface
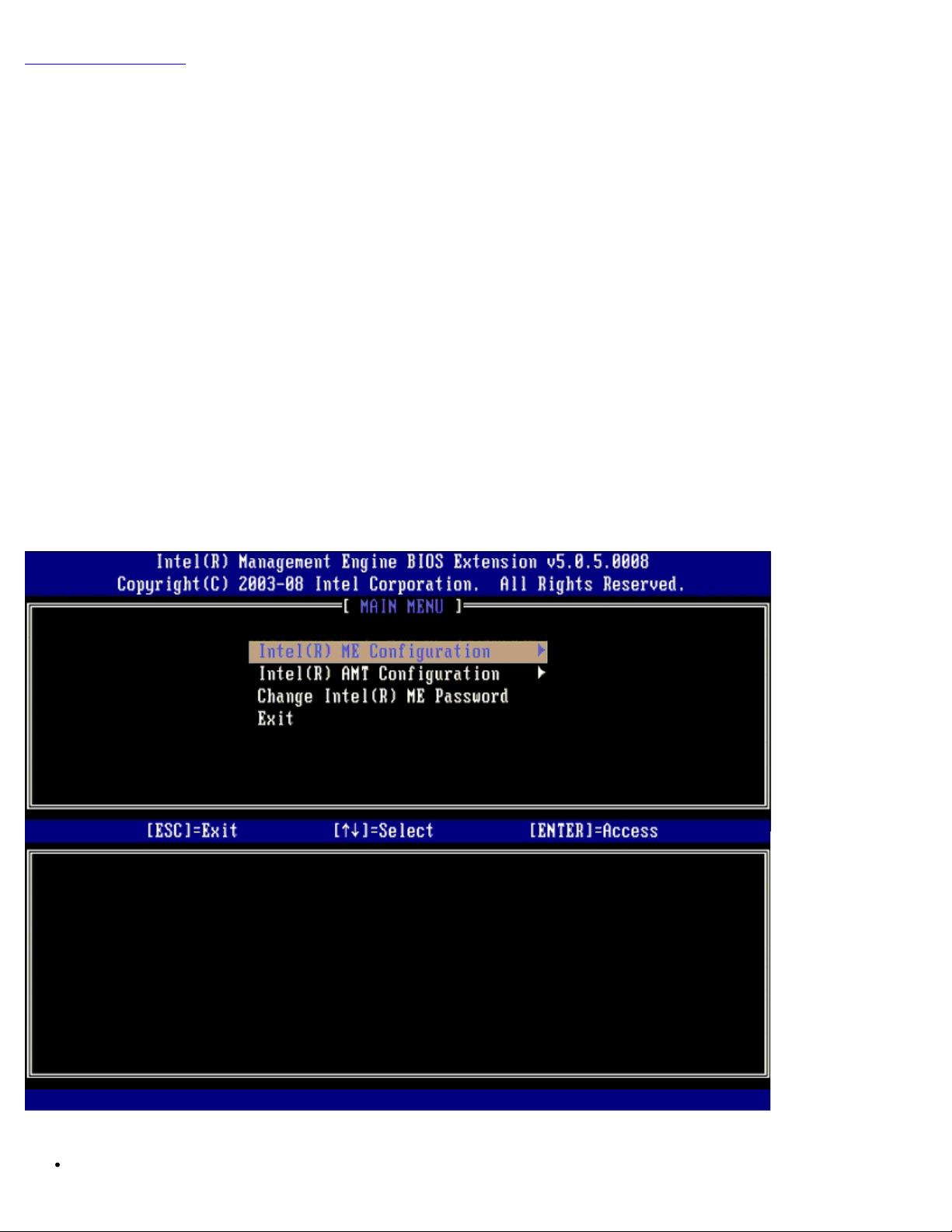
The MEBx configuration user interface can be accessed on a computer through the following steps:
1. Turn on (or restart) your computer.
2. When the blue DELL™ logo appears, press <Ctrl><p> immediately.
If you wait too long and the operating system logo appears, continue to wait until you see the Microsoft® Windows®
desktop. Then shut down your computer and try again.
3. Type the ME password. Press <Enter>.
The MEBx screen appears as shown below.
The main menu presents three function selections:
Intel ME Configuration
Page 8

Intel AMT Configuration
Change Intel ME Password
The Intel ME Configuration and Intel AMT Configuration menus are discussed on the following pages. First, the password must
be changed in order to proceed through these menus.
Changing the Intel ME Password
The default password is admin and is the same on all newly deployed platforms. You must change the default password before
changing any feature configuration options.
The new password must include the following elements:
Eight characters, no more than 32
One uppercase letter
One lowercase letter
A number
A special (nonalphanumeric) character, such as !, $, or ; excluding the :, ", and , characters.)
The underscore ( _ ) and spacebar are valid password characters but do NOT add to the password complexity.
*
Information on this page provided by Intel.
Back to Contents Page
Page 9
Back to Contents Page
ME Configuration Menu
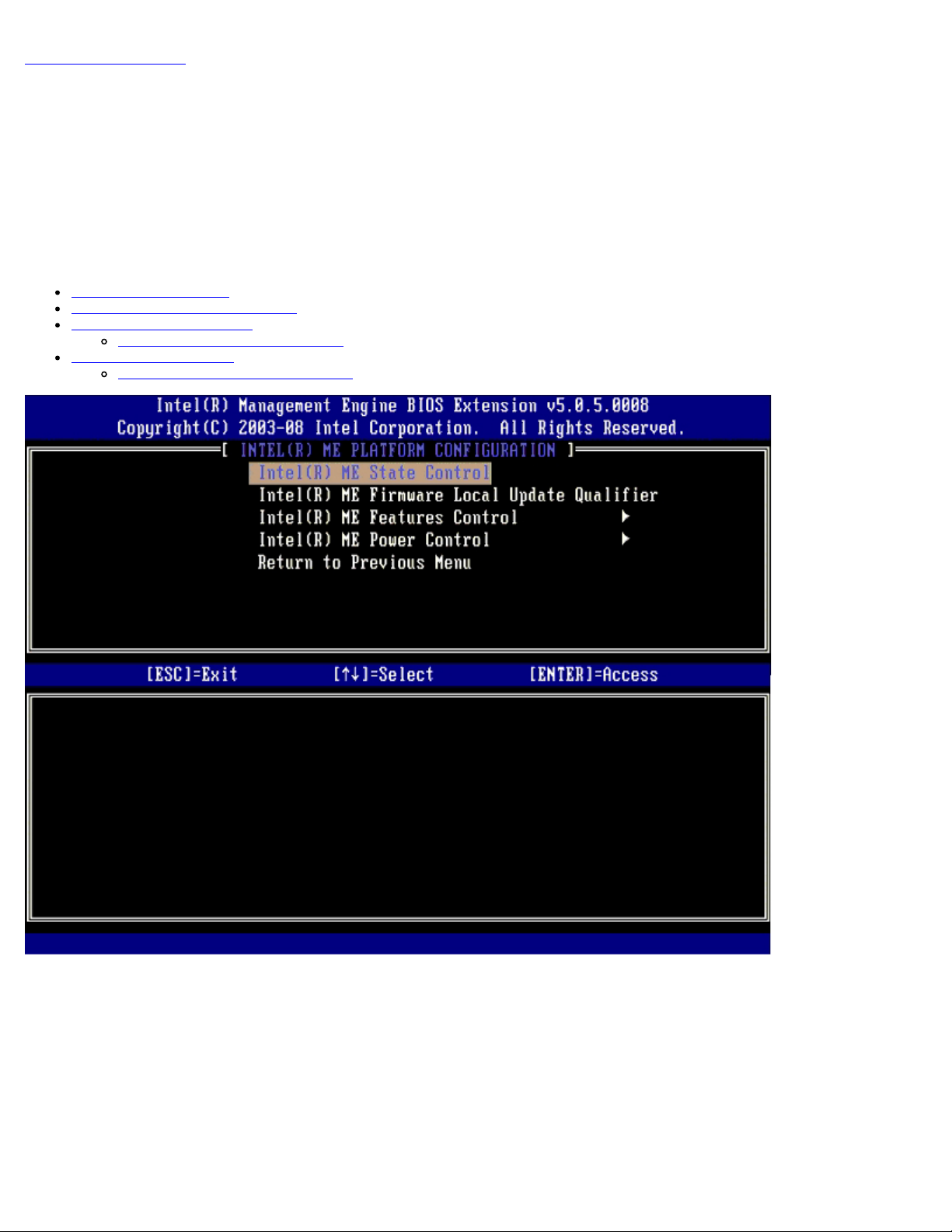
To reach the Intel® Management Engine (ME) Platform Configuration page, follow these steps:
1. Under the Management Engine BIOS Extension (MEBx) main menu, select ME Configuration. Press <Enter>.
2. The following message appears:
System resets after configuration changes. Continue: (Y/N)
3. Press <Y>.
The ME Platform Configuration page opens. This page allows you to configure the specific functions of the ME such as
features, power options, and so on. Below are quick links to the various sections.
Intel ME State Control
Intel ME Firmware Local Update
Intel ME Features Control
Manageability Feature Selection
Intel ME Power Control
Intel ME ON in Host Sleep States
Intel ME State Control
When the ME State Control option is selected on the ME Platform Configuration menu, the ME State Control menu
appears. You can disable ME to isolate the ME computer from main platform until the end of the debugging process.
Page 10
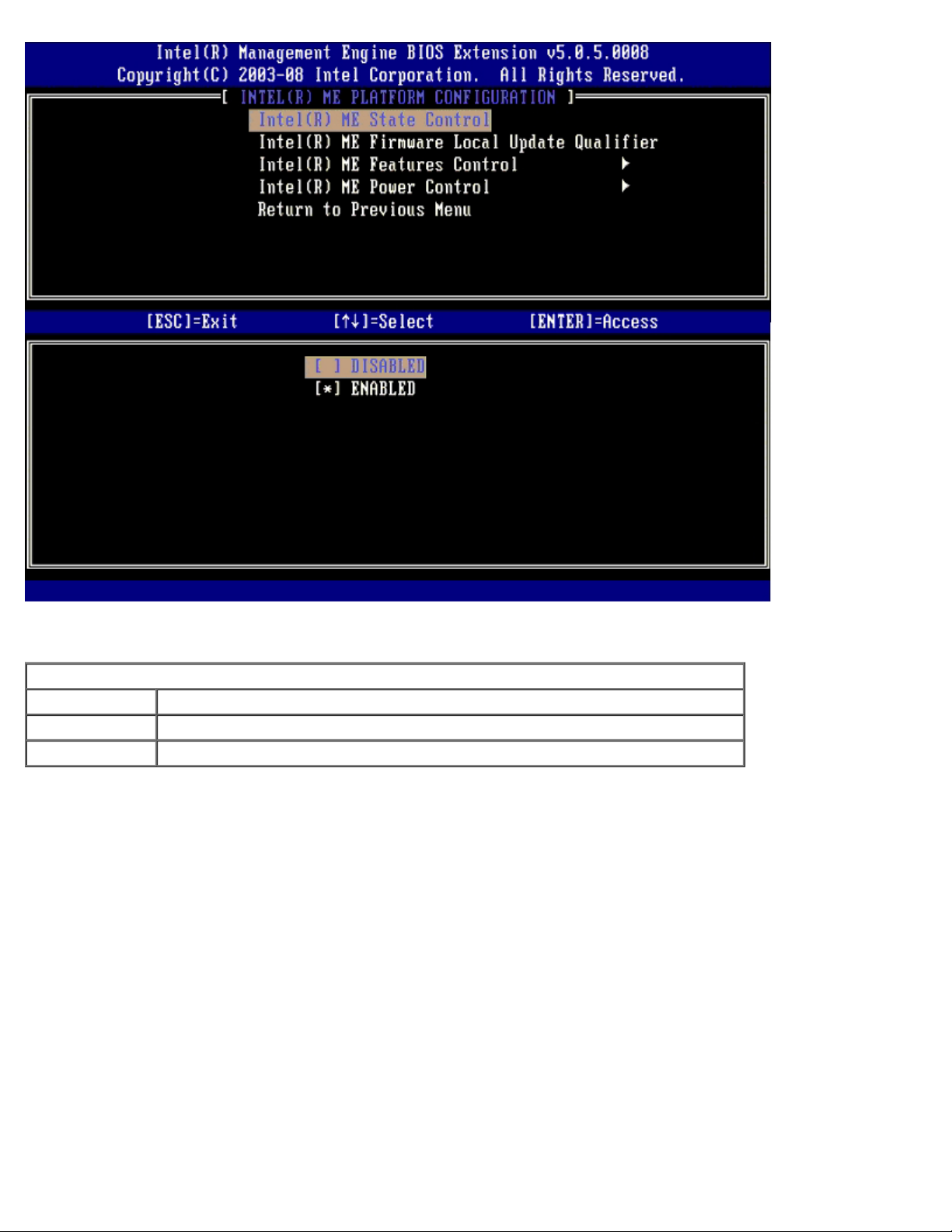
When enabled, the ME State Control option lets you disable ME to isolate the ME computer from the main platform while
debugging a field malfunction. The table below illustrates the details of the options.
ME Platform State Control
Option Description
Enabled Enable the Management Engine on the platform
Disabled Disable the Management Engine on the platform
In fact, the ME is not really disabled with the Disabled option. Instead, it is paused at the very early stage of its booting so
the computer has no traffic originating from the ME on any of its busses, ensuring that you can debug a computer problem
without worrying about any role the ME might have played in it.
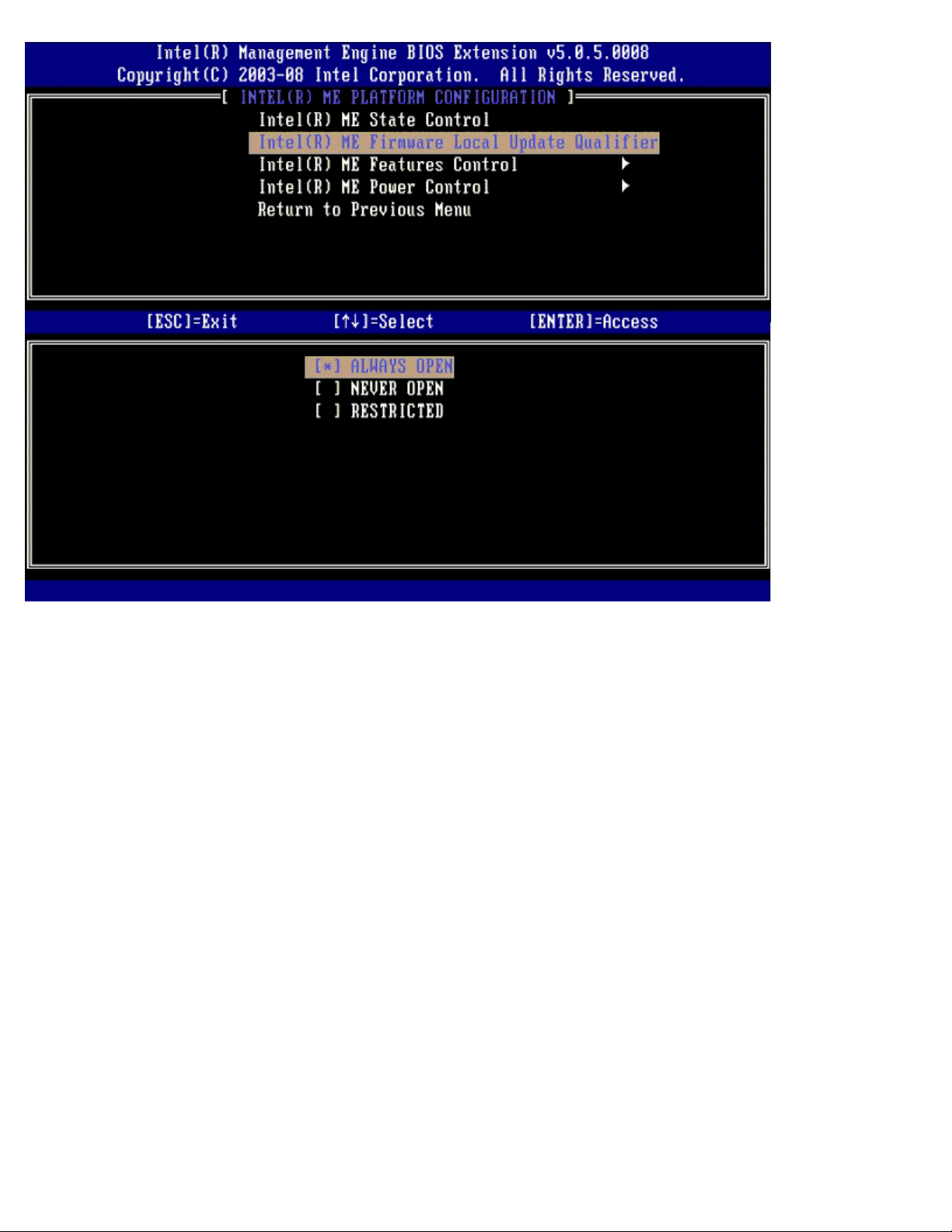
Intel ME Firmware Local Update Qualifier
This option on the ME Platform Configuration menu sets the policy for allowing the MEBx to be updated locally. The default
setting is Alway Open. The other settings available are Never Open and Restricted.
Page 11
Intel ME Features Control
The ME Features Control menu contains the following configuration selection.
Manageability Feature Selection
When you select the Manageability Feature Selection option on the ME Features Control menu, the ME Manageability
Feature menu appears.
Page 12
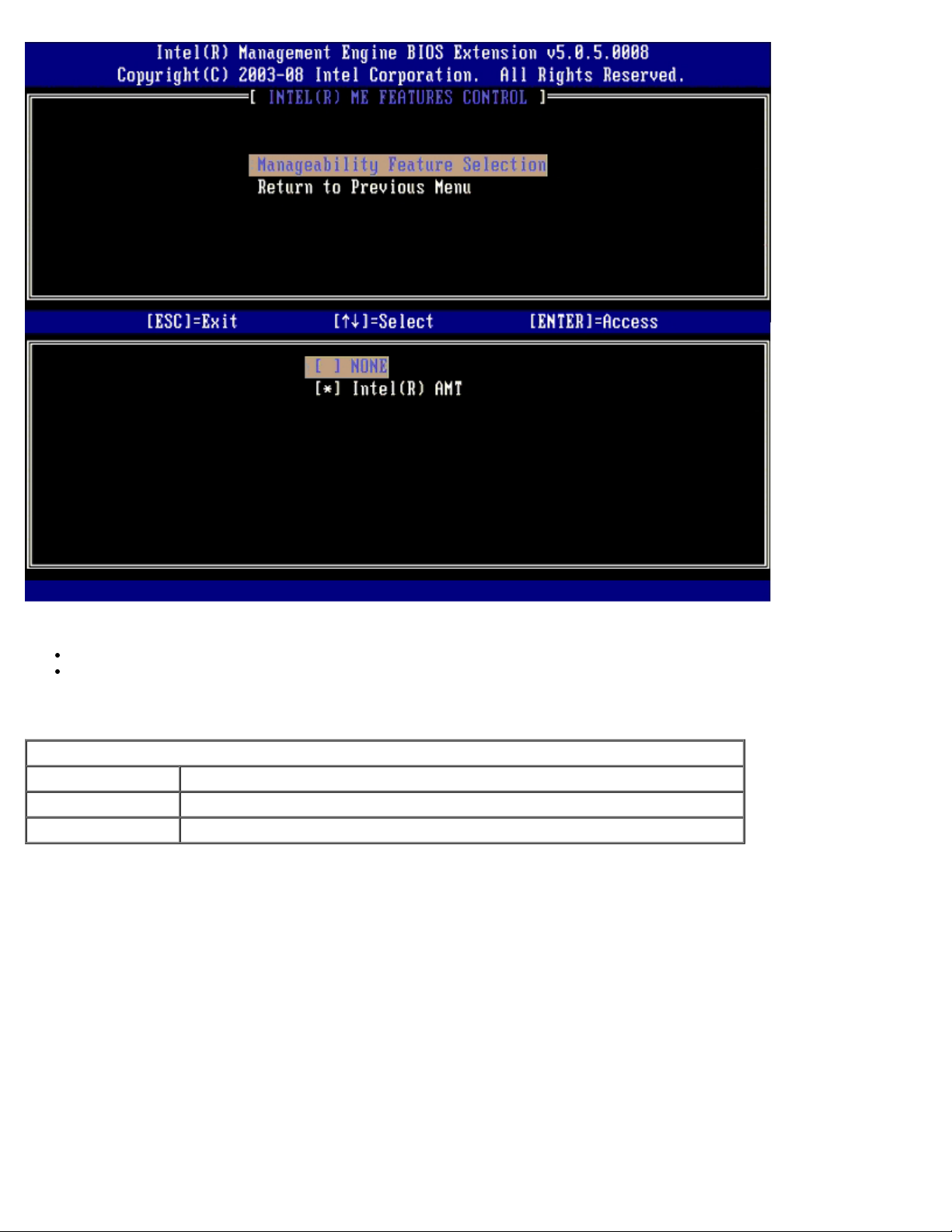
You can use this option to determine which manageability feature is enabled.
None — Choosing this option means that manageability will not be enabled. .
Intel AMT/Intel Standard Manageability — Intel Active Management Technology (Intel AMT). If the system does
not meet the minimum system requirements for Intel AMT, only Intel Standard Manageability will be selectable.
The table below explains these options.
Management Feature Select Option
Option Description
None Manageability Feature is not selected
Intel AMT Intel AMT manageability feature is selected
When the option is changed from Intel AMT to None, a warning message is displayed. If the user accepts the change from
Intel AMT to None, Intel AMT will go through a full un-provision. If the None option is selected, there is no manageability
feature provided by the Intel ME system, so management applications are not be able to use the Intel ME. However, Intel ME
is still enabled (the Intel ME firmware is still running).
Intel ME Power Control
To comply with ENERGY STAR requirements, the Intel Management Engine can be turned off in various sleep states. Intel ME
Power Control menu configures Intel ME platform power policies.
ME On in Host Sleep States
When the ME ON in Host Sleep States option is selected on the ME Power Control menu, the ME in Host Sleep States
menu loads.
Page 13
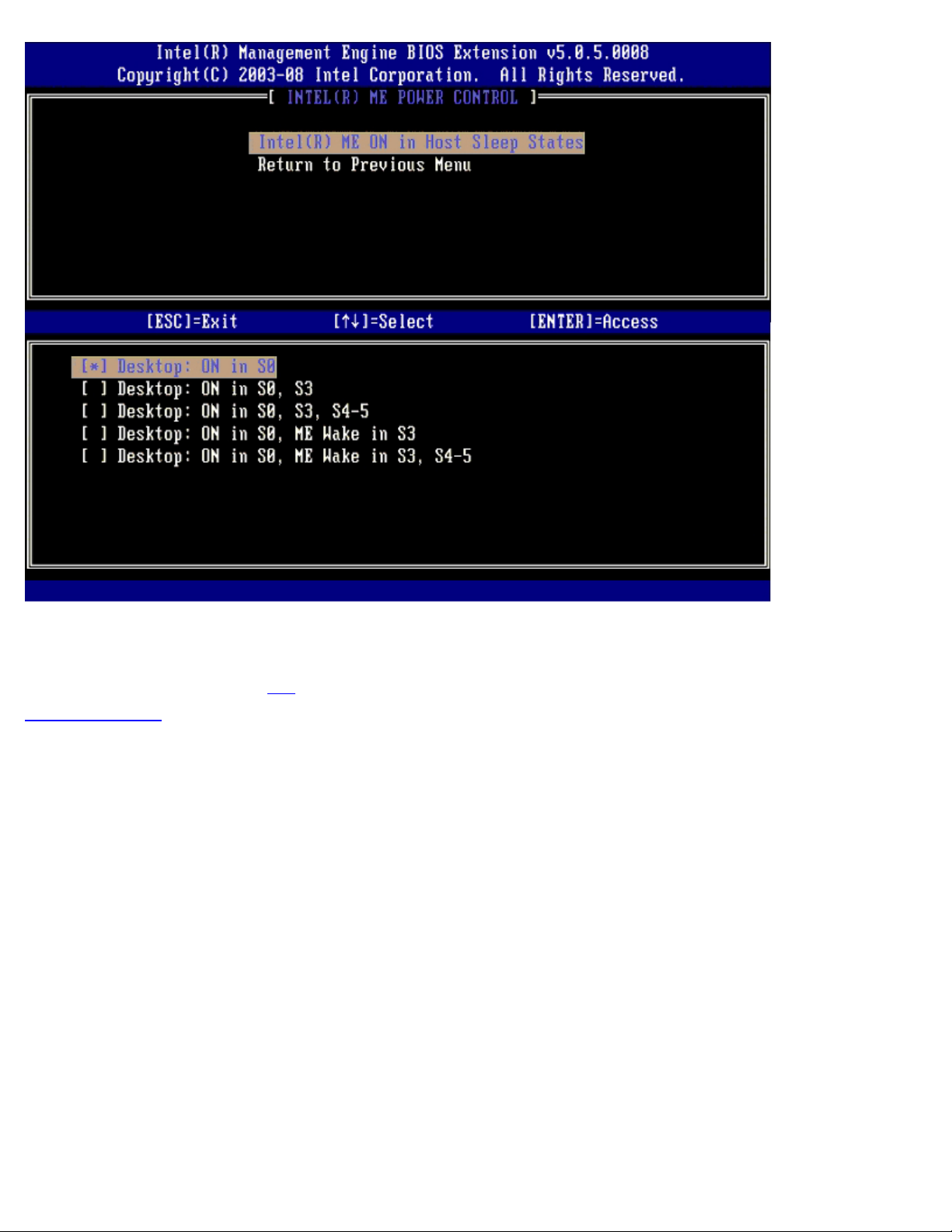
The power package selected determines when the ME is turned ON. The default power package is Desktop: ON in S0. The
end user administrator can choose which power package is used depending on computer usage. The power package selection
page can be seen above.
*
Information on this page provided by Intel.
Back to Contents Page
Page 14
Back to Contents Page
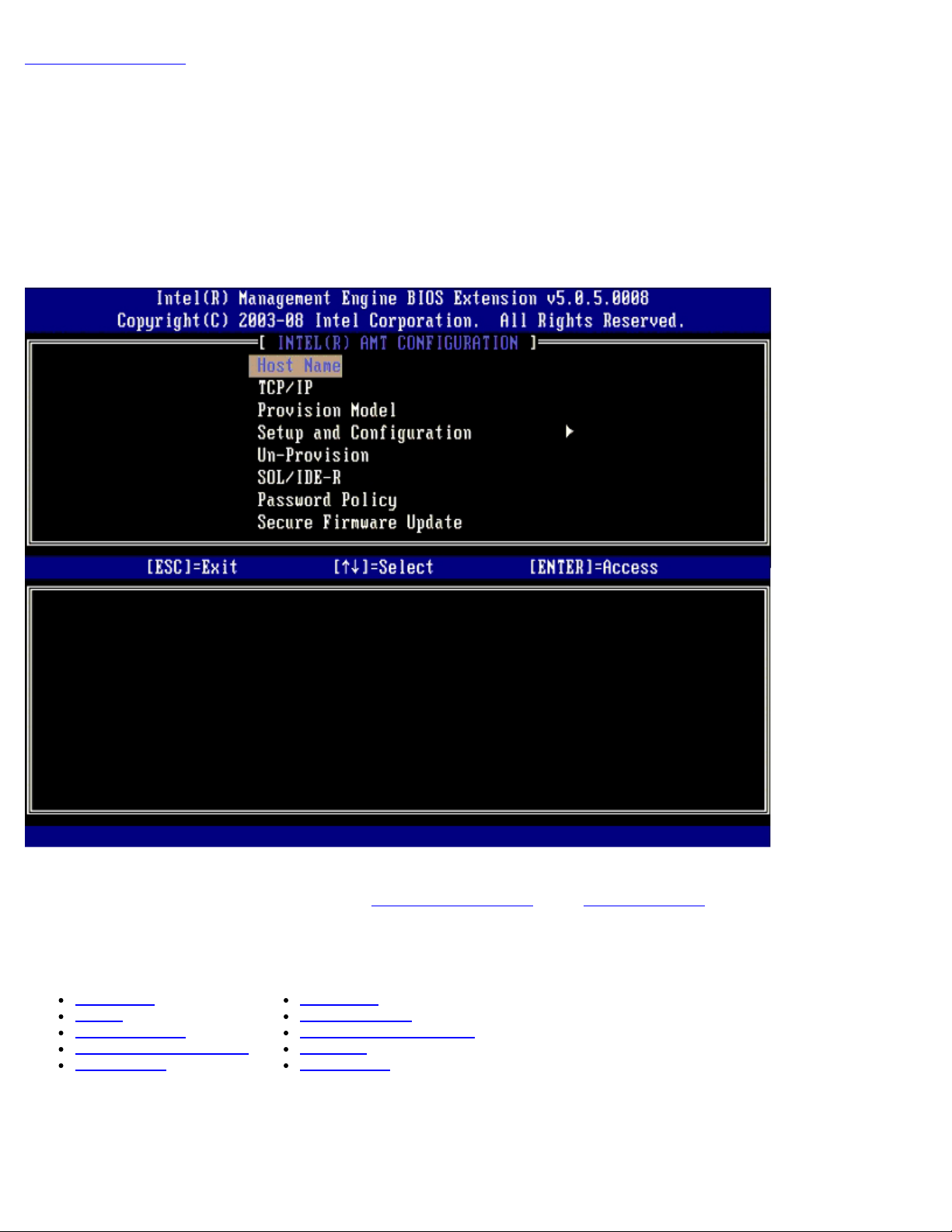
AMT Configuration Menu
After you completely configure the Intel® Management Engine (ME) feature, you must reboot before configuring the Intel AMT
for a clean system boot. The image below shows the Intel AMT configuration menu after a user selects the Intel AMT
Configuration option from the Management Engine BIOS Extension (MEBx) main menu. This feature allows you to
configure an Intel AMT capable computer to support the Intel AMT management features.
You need to have a basic understanding of networking and computer technology terms, such as TCP/IP, DHCP, VLAN, IDE,
DNS, subnet mask, default gateway, and domain name. Explaining these terms is beyond the scope of this document.
The Intel AMT Configuration page contains the user-configurable options listed below.
For images of these menu options, refer to the "Enterprise Mode Setup
" and "SMB Mode Setup" pages of this document.
Menu Options
Host Name
TCP/IP
Provision Model
Setup and Configuration
Un-Provision
Host Name
SOL/IDE-R
Password Policy
Secure Firmware Update
Set PRTC
Idle Timeout
Page 15

A hostname can be assigned to the Intel AMT capable computer. This is the host name of the Intel AMT-enabled computer. If
Intel AMT is set to DHCP, the host name MUST be identical to the operating system machine name.
TCP/IP
Allows you to change the following TCP/IP configuration of Intel AMT.
DHCP Mode – ENABLE** / DISABLED
If DHCP Mode is enabled, TCP/IP settings are configured by a DHCP server.
If a system is in static mode the system may require a second IP address. This IP address, often called the ME IP address
may be different from the host IP address.
IP address – Internet address of the Intel Management Engine.
Subnet mask – The subnet mask used to determine what subnet IP address belongs to.
Default Gateway address – The default gateway of the Intel Management Engine.
Preferred DNS address – Preferred domain name server address.
Alternate DNS address – Alternate domain name server address.
Domain name – Domain name of the Intel Management Engine.
Provision Model
The following provisioning models are available:
Provisioning Mode – Enterprise** / Small Business
This allows you to select between small business and enterprise mode. Enterprise mode may have different security
settings than Small Business mode. Because of the different security settings, each of these modes requires a different
process to complete the setup and configuration process.
Setup and Configuration
The menu contains the parameters for the setup and configuration server. This menu also contains the security settings for
PSK and PKI configurations.
Page 16
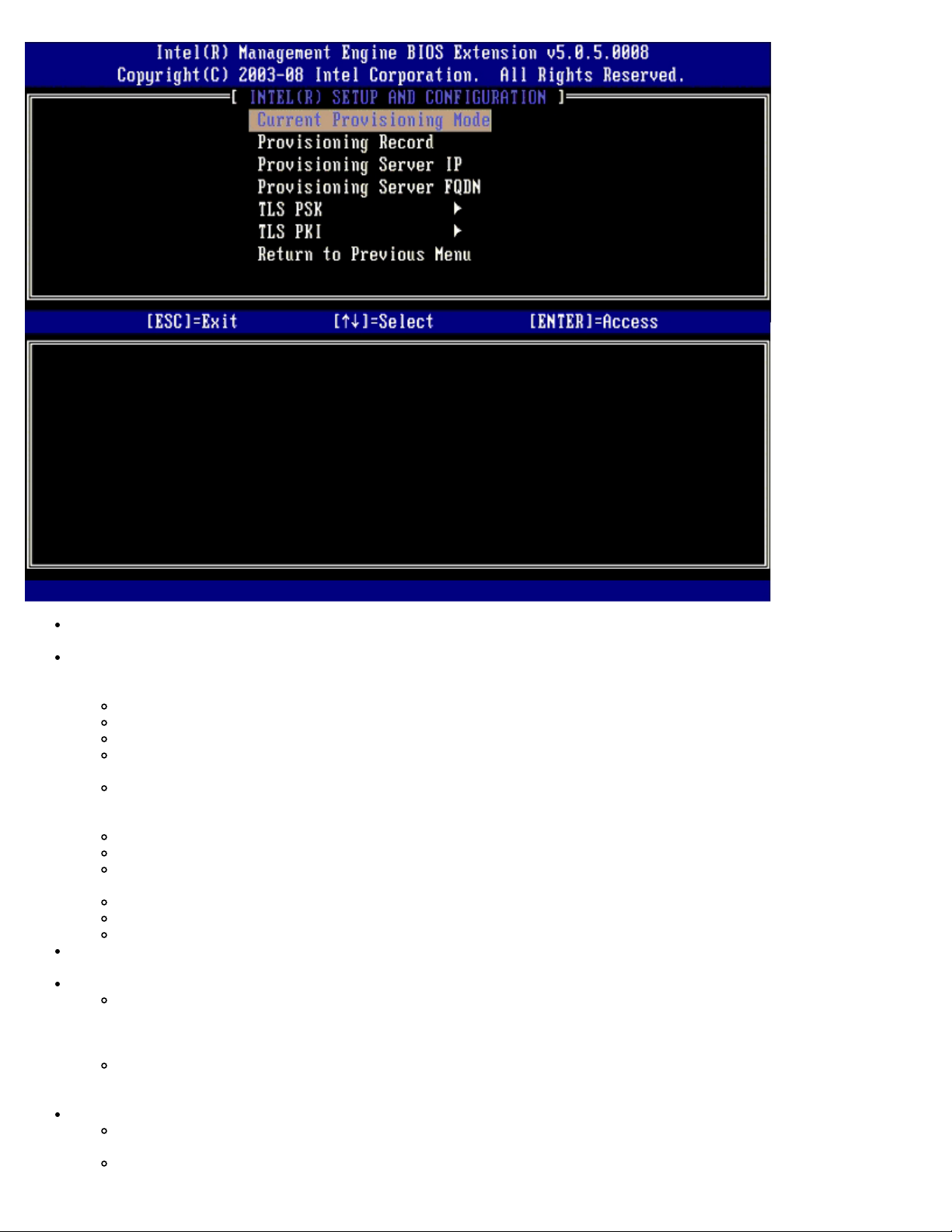
Current Provisioning Mode – Displays the current provisioning TLS Mode: None, PKI, or PSK. This configuration is
only shown in Enterprise Provision Model.
Provisioning Record – Displays the provision PSK/PKI record data of the computer. If the data has not been entered,
the MEBX displays a message that states "Provision Record not present". If the data is entered, the Provision Record
displays the following:
TLS provisioning mode – Displays the current configuration mode of the computer: None, PSK or PKI.
Provisioning IP – The IP of the setup and configuration server.
Date of Provision – Displays the date and time of the provisioning in the format MM/DD/YYYY at HH:MM.
DNS – Displays if Secure DNS is being used or not. 0 indicates DNS is not in use, 1 indicates secure DNS is
being used (PKI only).
Host Initiated – Displays if the setup and configuration process was initiated by the host: 'No' indicates the
setup and configuration process was not host initiated; 'Yes' indicates the setup and configuration process was
host initiated (PKI only).
Hash Data – Displays the 40 character certificate hash data (PKI only).
Hash Algorithm – Describes the hash type. Currently only SHA1 is supported (PKI only).
IsDefault – Displays 'Yes' if the Hash algorithm is the default algorithm selected. Displays 'No' if the hash
algorithm is not the default algorithm used (PKI only).
FQDN – FQDN of the provisioning server mentioned in certificate (PKI only).
Serial Number – The 32 character that indicate the Certificate Authority serial numbers.
Time Validity Pass – Indicates whether the certificate passed the time validity check.
Provisioning Server IP – The IP address and port number (0 – 65535) for an Intel AMT provisioning server. This
configuration is only shown for the enterprise provision model. The default port number is 9971.
TLS PSK – Contains the settings for TLS PSK configuration settings.
Set PID and PPS – Sets the provisioning identifier (PID) and provisioning passphrase (PPS). Enter the PID and
PPS in the dash format. (Ex. PID: 1234-ABCD ; PPS: 1234-ABCD-1234-ABCD-1234-ABCD-1234-ABCD) NOTE A PPS value of ' '0000-0000-0000-0000-0000-0000-0000-0000' does not change the setup configuration state.
If this value is used the setup and configuration state stays as 'Not-started'.
Delete PID and PPS – Deletes the current PID and PPS stored in ME. If there is no PID and PPS entered, the
MEBX returns an error message. Using this option does NOT set the setup and configuration process parameter
to "Not Started." This option sets the setup and configuration process parameter to "In Process."
TLS PKI – Contains the settings for the TLS PKI configuration settings.
Remote Configuration Enable/Disable – Disables or enables remote configuration. If this option is not
enabled, remote configuration cannot occur.
Manage Certificate Hashes – Displays the list of hashes that are currently stored and the current status. To
Page 17
change the active status of the certificate press the <+> key. To delete the hash press the <del> key. To add
another key press the <ins> key.
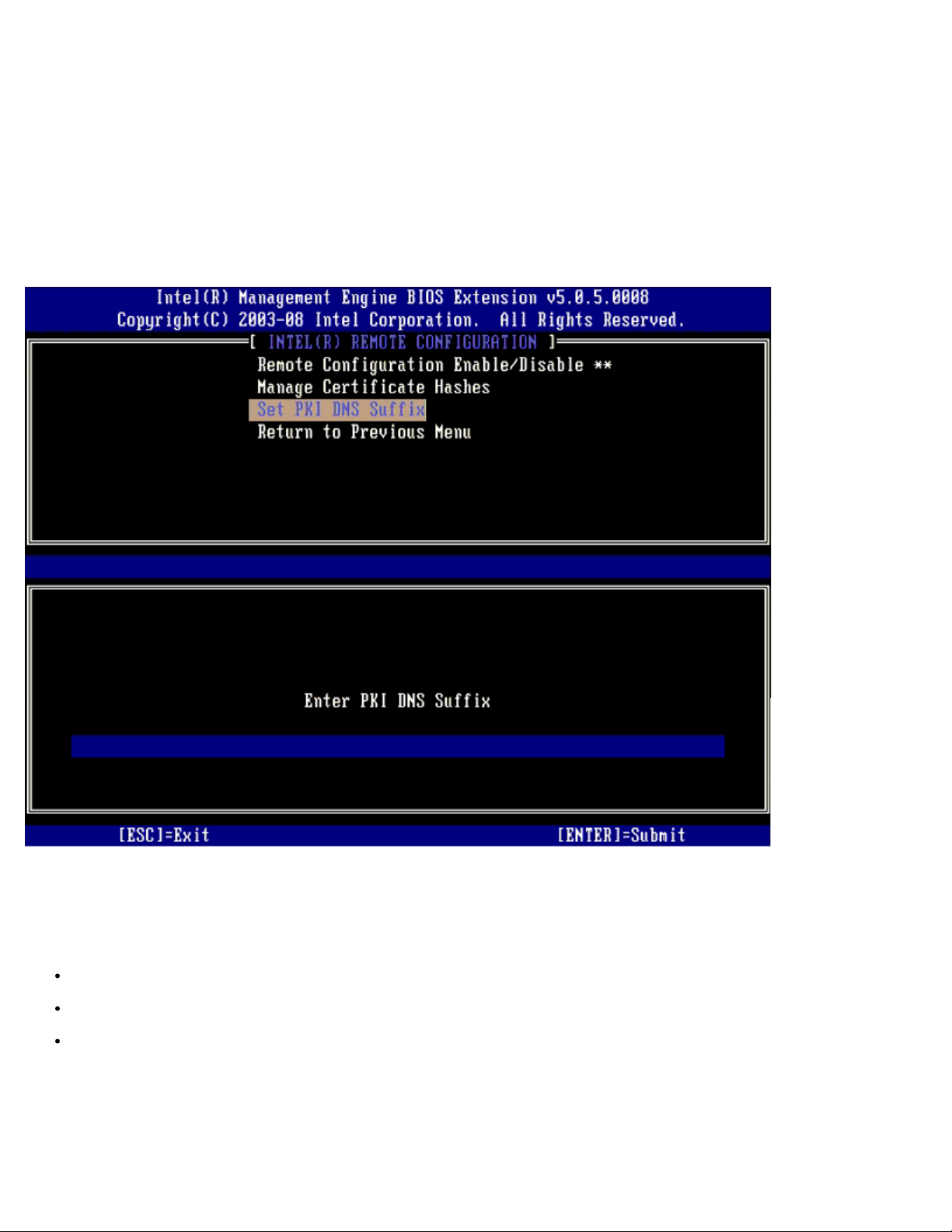
Set FQDN – Sets the fully qualified domain name for the computer.
Set PKI DNS suffix – Sets the PKI DNS suffix.
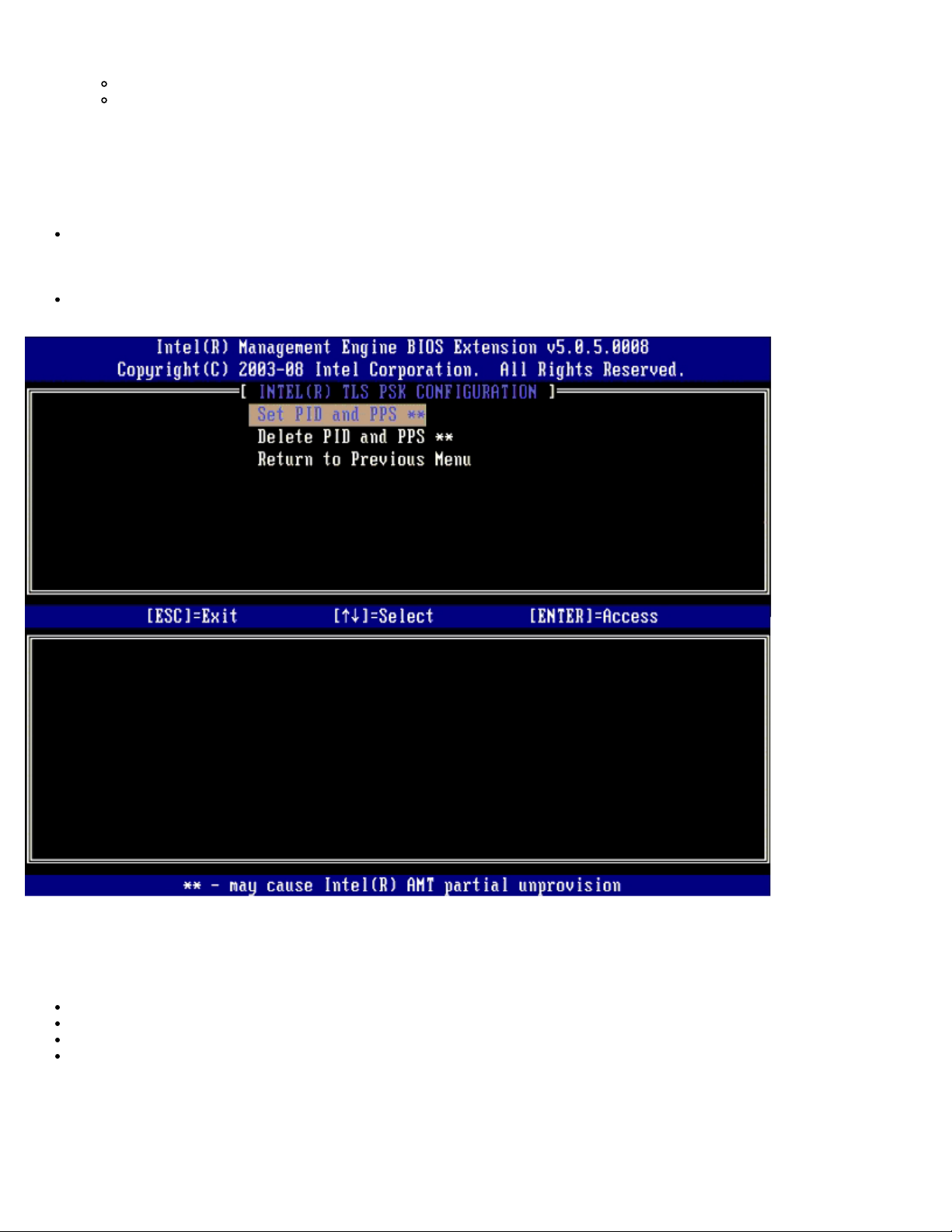
TLS PSK
The submenu contains the settings for TLS PSK configuration settings. Setting or deleting the PID/PPS causes a partial unprovision if the setup and configuration is "In-process".
Set PID and PPS – Sets the PID and PPS. Enter the PID and PPS in the dash format. (Ex. PID: 1234-ABCD ; PPS:
1234-ABCD-1234-ABCD-1234-ABCD-1234-ABCD) A PPS value of '0000-0000-0000-0000-0000-0000-0000-0000'
does not change the setup configuration state. If this value is used the setup and configuration state stays as "Notstarted."
Delete PID and PPS – Deletes the current PID and PPS stored in ME. If there is no PID and PPS entered, the MEBX
returns an error message.
TLS PKI – Remote Configuration Settings
The remote configuration options are contained under the TLS PKI sub menu. There are four remote configuration items:
Remote Configuration Enable/Disable
Manage Certificate Hashes
Set FQDN
Set PKI DNS Suffix
Page 18
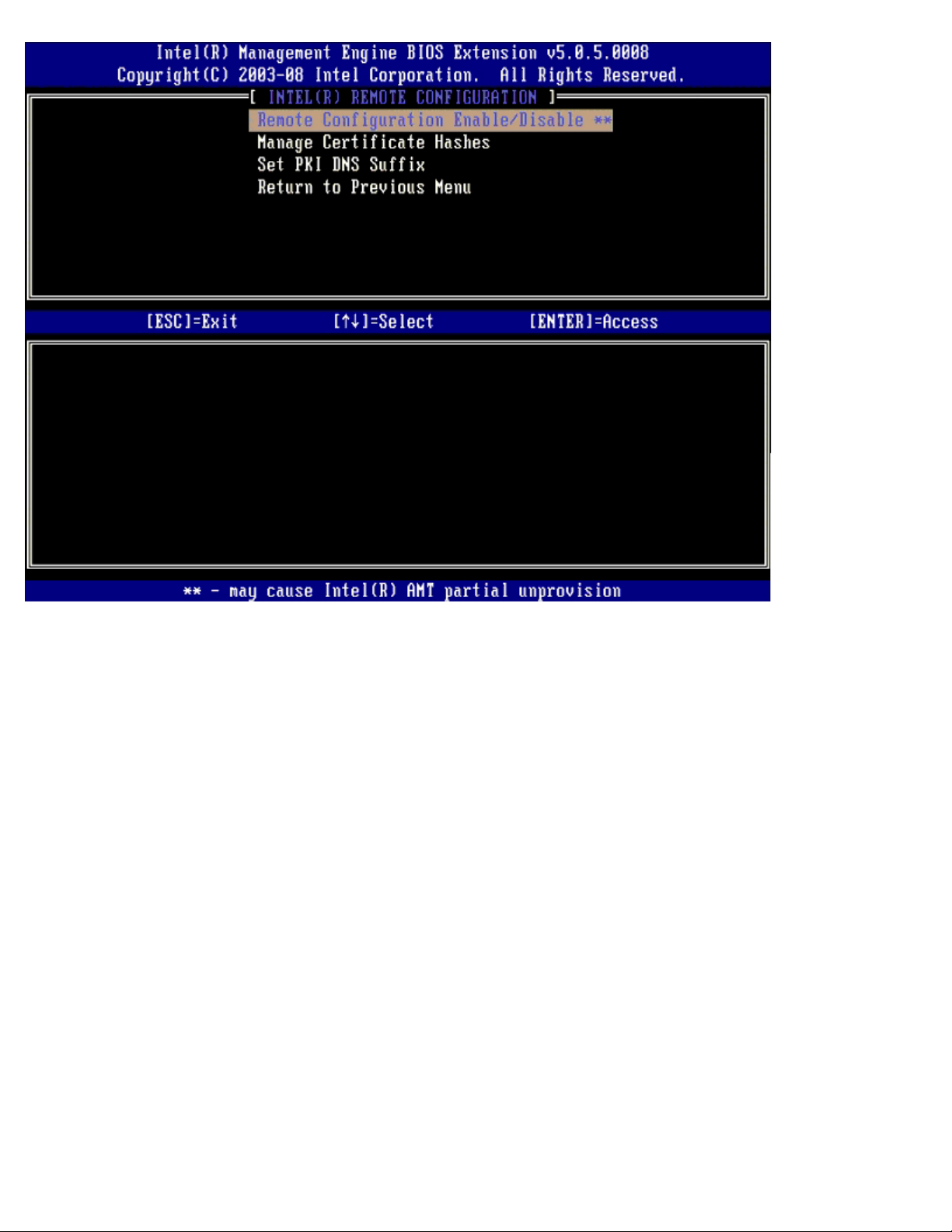
Remote Configuration Enable/Disable
The selectable options are Enable and Disable. If Remote Configuration is disabled, the menu options underneath are still
displayed, but cannot be used until Remote Configuration is enabled.
This option cannot be modified once the setup and configuration process is in process. This parameter can only be modified
while the computer is in the factory default or un-provisioned state.
Enabling/disabling remote configuration causes a partial un-provision if the setup and configuration is In-process.
Manage Certificate Hashes
Select the Manage Certificate Hashes option under the Remote Configuration menu to display the Manage Certificate
Hashes menu. Five default hashes are available from the factory. Hashes can be deleted or added as needed.
Page 19
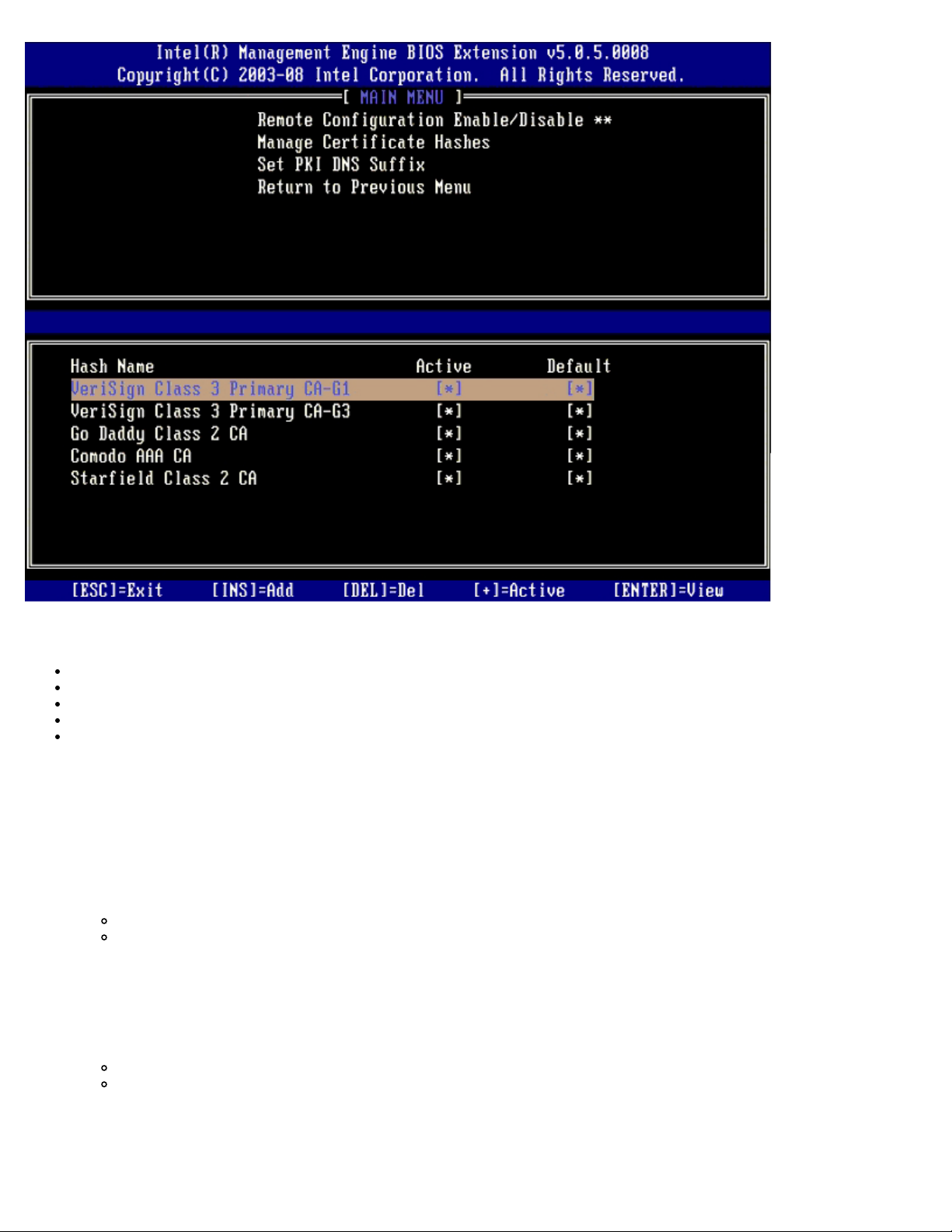
The Manage Certificate Hash screen has several keyboard controls available to you to manage the hashes on the computer.
The following keys are valid when in the Manage Certificate Hash menu:
Escape key – Exits from the menu
Insert key – Adds a customized certificate hash to the computer
Delete key – Deletes the currently selected certificate hash from the computer
<+> key – Changes the active state of the currently selected certificate hash
Enter key – Displays the details of the currently selected certificate hash
Adding a Customized Hash
1. Press <Insert> in the Manage Certificate Hash screen. A text field is displayed requesting the hash name.
2. You must enter the hash name. The hash name must be a maximum of 32 characters. Upon pressing <Enter> you are
prompted to enter the certificate hash value.
3. The certificate hash value is a 20 byte hexadecimal number. You must enter the hash data in the correct format or the
message Invalid Hash Certificate Entered - Try Again is displayed. Upon pressing <Enter> you are asked
about setting the active state of the hash.
4. This query allows for setting the active state of the customized hash.
Yes – The customized hash is be marked as active.
No (Default) – VA_Hash is be maintained within EPS.
Deleting a Hash
1. Press <Delete> in the Manage Certificate Hash screen to display the
Delete this certificate hash? (Y/N)
prompt.
2. This option allows deleting of the selected certificate hash.
Yes – MEBx shall send the message to FW to delete the selected hash.
No – MEBx shall not delete the selected hash and returns to the Remote Configuration.
Changing the Active State
Press the <+> key in the Manage Certificate Hash screen to display the
Page 20
Change the active state of this hash? (Y/N)
prompt. Answering yes to this question toggles the active state of the currently selected certificate hash. Setting a hash as
active indicates that the hash is available to use during PSK provisioning.
Viewing a Certificate Hash
Press <Enter> in the Manage Certificate Hash screen. The details of the selected certificate hash are displayed to include:
the hash name, the certificate hash data, and the active and default states.
Set PKI DNS Suffix
When the Set PKI DNS Suffix option is selected under the Remote Configuration menu, you are prompted to enter the
PKI DNS Suffix of the Provisioning Server. The Key Value is maintained in EPS.
Un-provision
The Un-Provision option allows you to reset the Intel AMT configuration to factory defaults. There are three types of unprovision:
Partial Un-provision – This option resents all the Intell AMT settings to their default values, but will not change
the PID/PPS or the MEBx password.
Full Un-provision – This option resets all of the Intel AMT settings to their default values. If a PID/PPS value is
present, both values are erased. The MEBx password is not changed.
CMOS clear – This un-provision option is not available in the MEBx. This option clears all values to their default values.
If a PID/PPS is present, both values are lost. The MEBx password resets to the default value (admin). To invoke this
option, you need to clear the CMOS (i.e. system board jumper).
Page 21
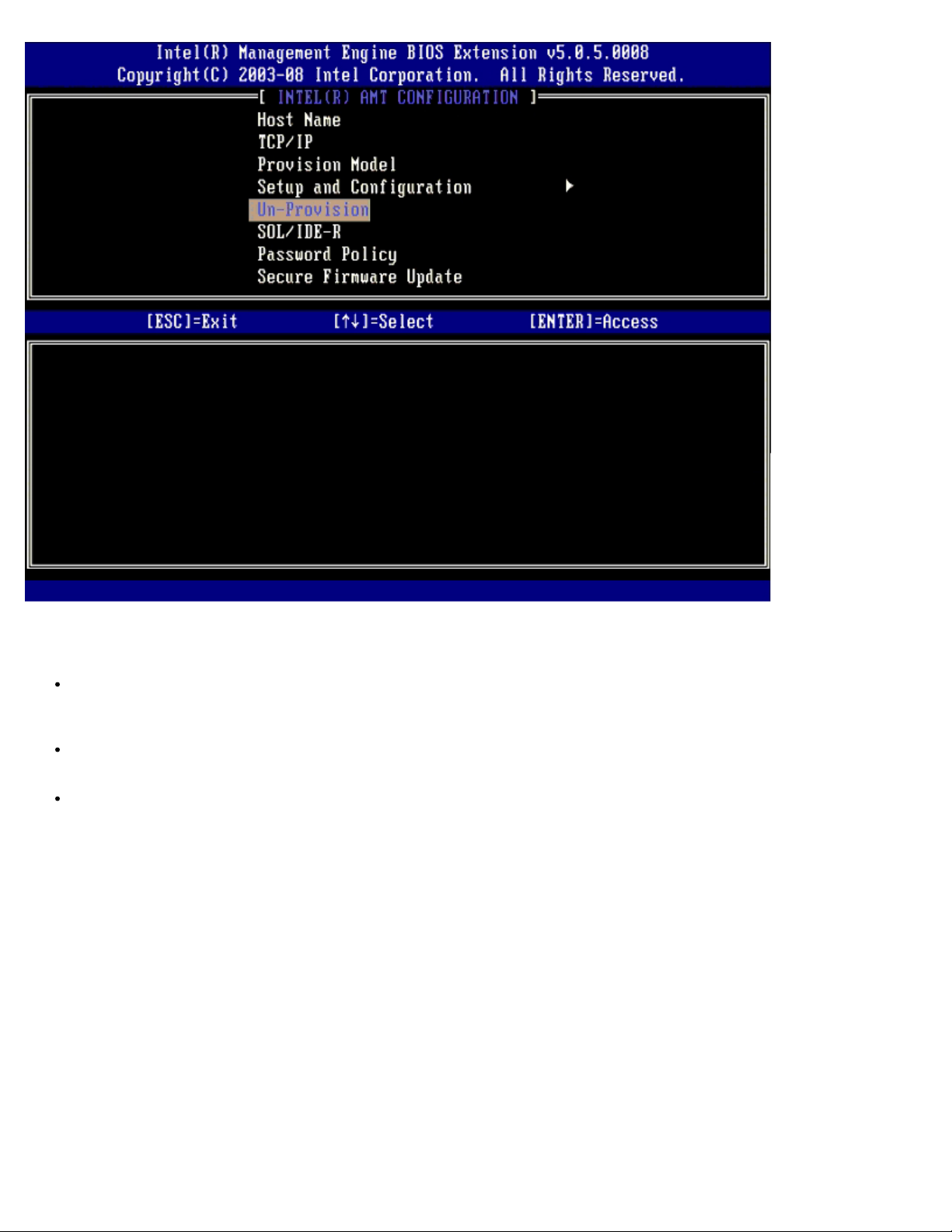
SOL/IDE-R
Username and Password – DISABLED** / ENABLED
This option provides the user authentication for SOL/IDER session. If the Kerberos protocol is used, set this option to
Disabled and set the user authentication through Kerberos. If Kerberos is not used, you have the choice to enable or
disable user authentication on the SOL/IDER session.
Serial-Over-LAN (SOL) – DISABLED** / ENABLED
SOL allows the Intel AMT managed client console input/output to be redirected to the management server console (if
the client system supports SOL). If the system does not support SOL, this value cannot enable it.
IDE Redirection (IDE-R) – DISABLED** / ENABLED
IDE-R allows the Intel AMT managed client to be booted from remote disk images at the management console. If the
client system does not support IDE-R, this value cannot enable it.
Page 22
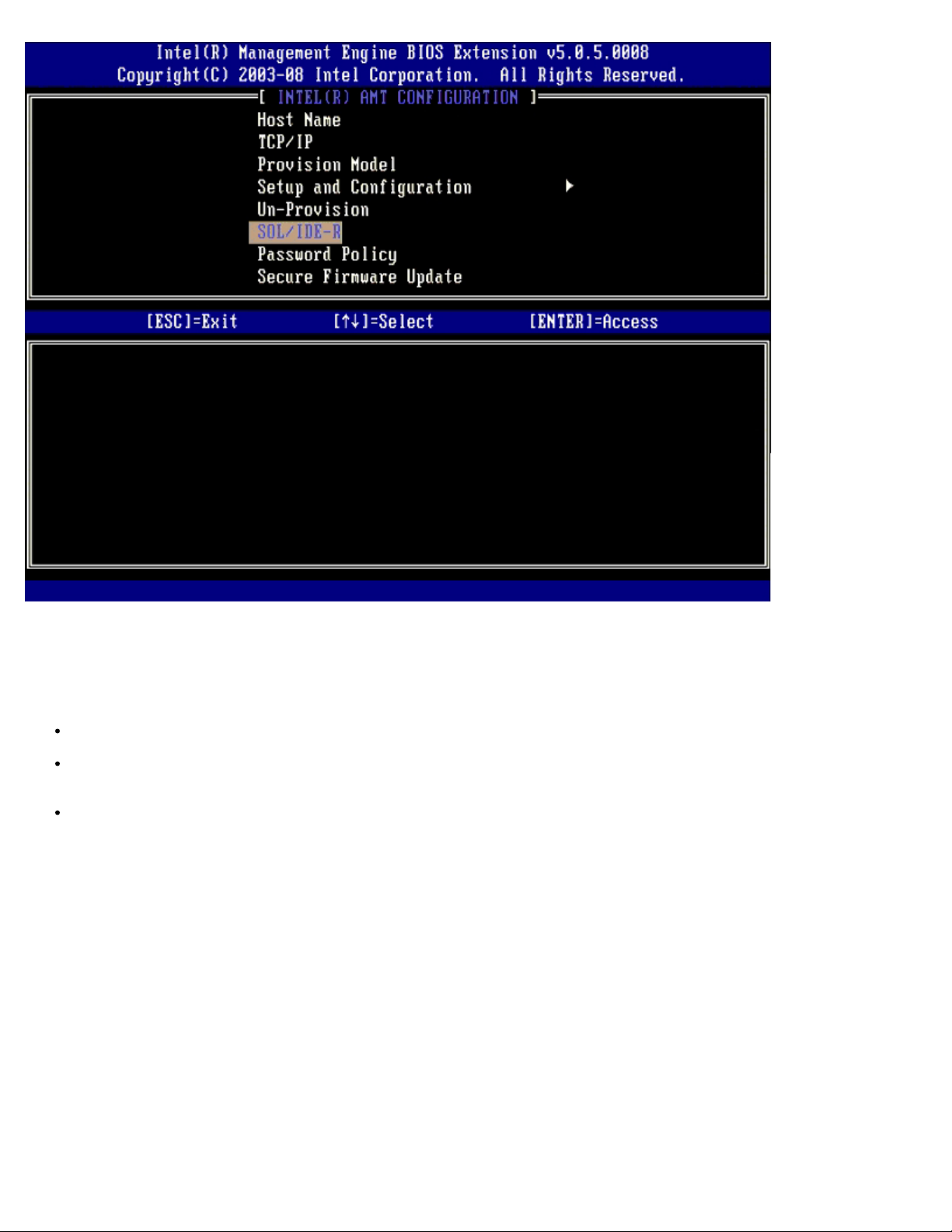
Password Policy
This option determines when the user is allowed to change the MEBx password through the nework. Note: The MEBx
password can always be changed via the MEBx user interface. The options are:
Default Password Only – The MEBx password can be changed through the network interface if the default password
has not been changed yet.
During Setup and Configuration – The MEBX password can be changed through the network interface during the
setup and configuration process but at no other time. Once the setup and configuration process is complete, the MEBx
password cannot be changed via the network interface.
Anytime – The MEBX password can be changed through the network interface at any time.
Page 23
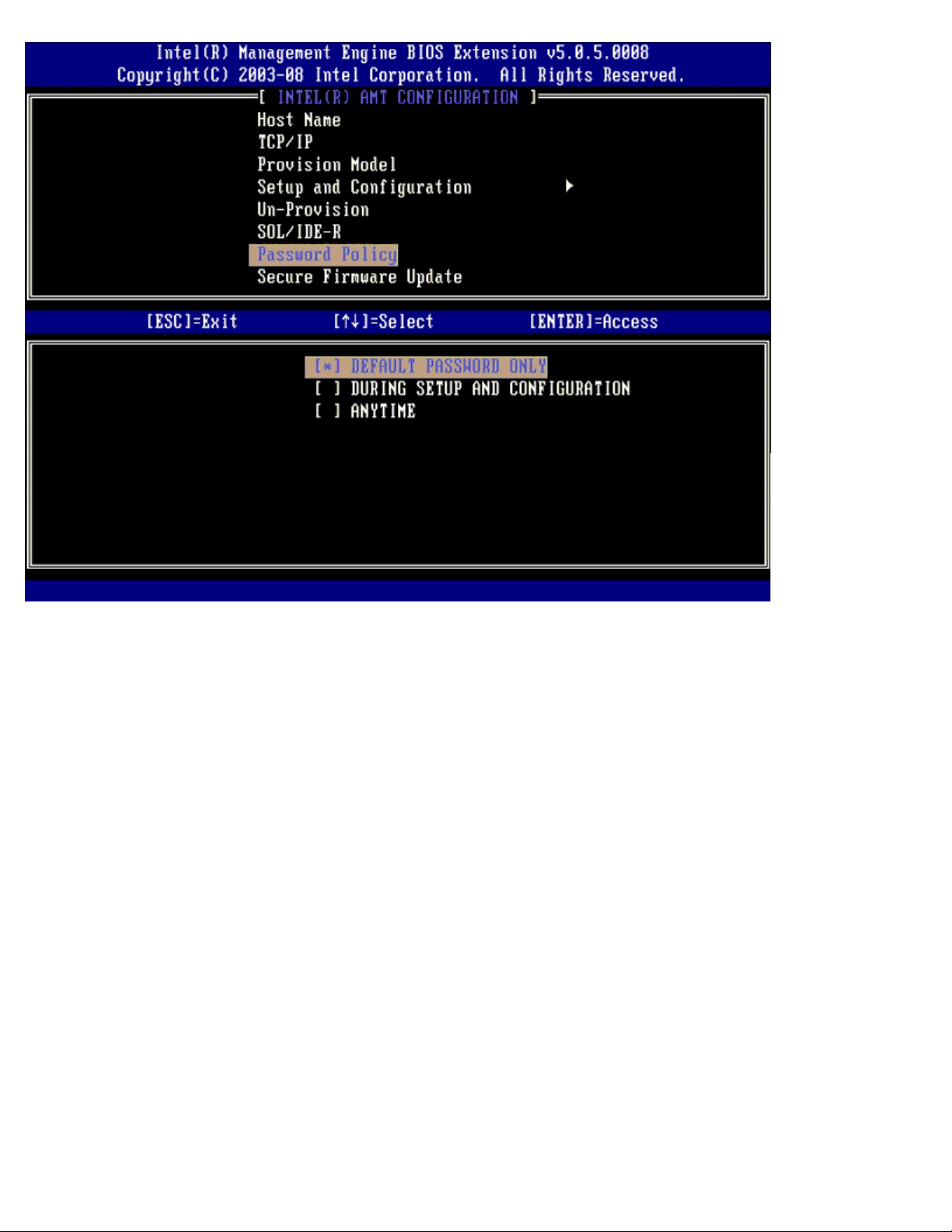
Secure Firmware Update
This option allows you to enable/disable secure firmware updates. Secure firmware update requires an administrator user
name and password. If the administrator user name and password are not supplied, the firmware cannot be updated.
When the secure firmware update feature is enabled, you are able to update the firmware using the secure method.
Secure firmware updates pass through the LMS driver. If secure and local firmware update is disabled, the user must enable
secure firmware update or local firmware update to allow the firmware updates.
Page 24
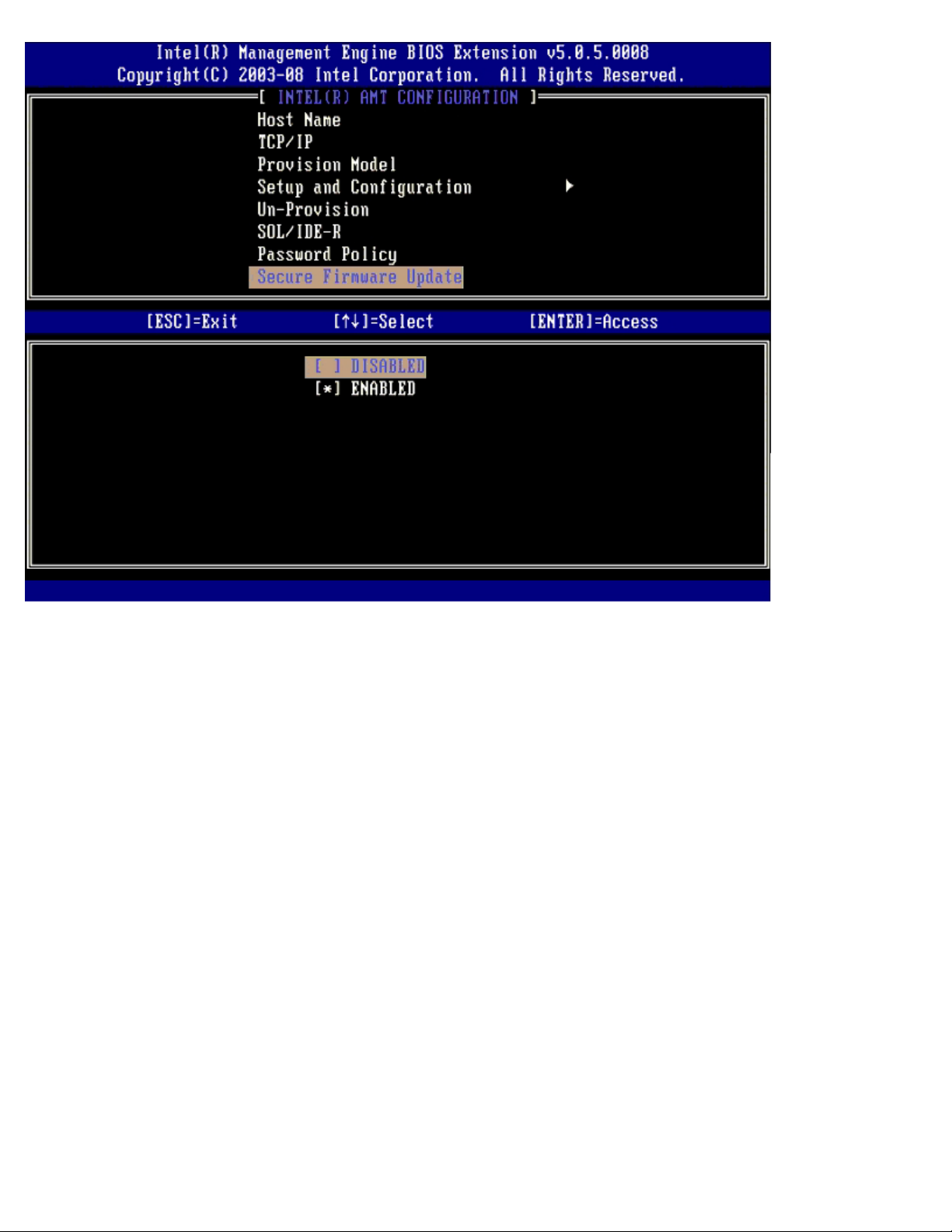
Set PRTC
Enter PRTC in GMT (UTC) format (YYYY:MM:DD:HH:MM:SS). Valid date range is 1/1/2004 – 1/4/2021. Setting PRTC value is
used for virtually maintaining PRTC during power off (G3) state. This configuration is only displayed for the Enterprise
Provision Model.
Page 25
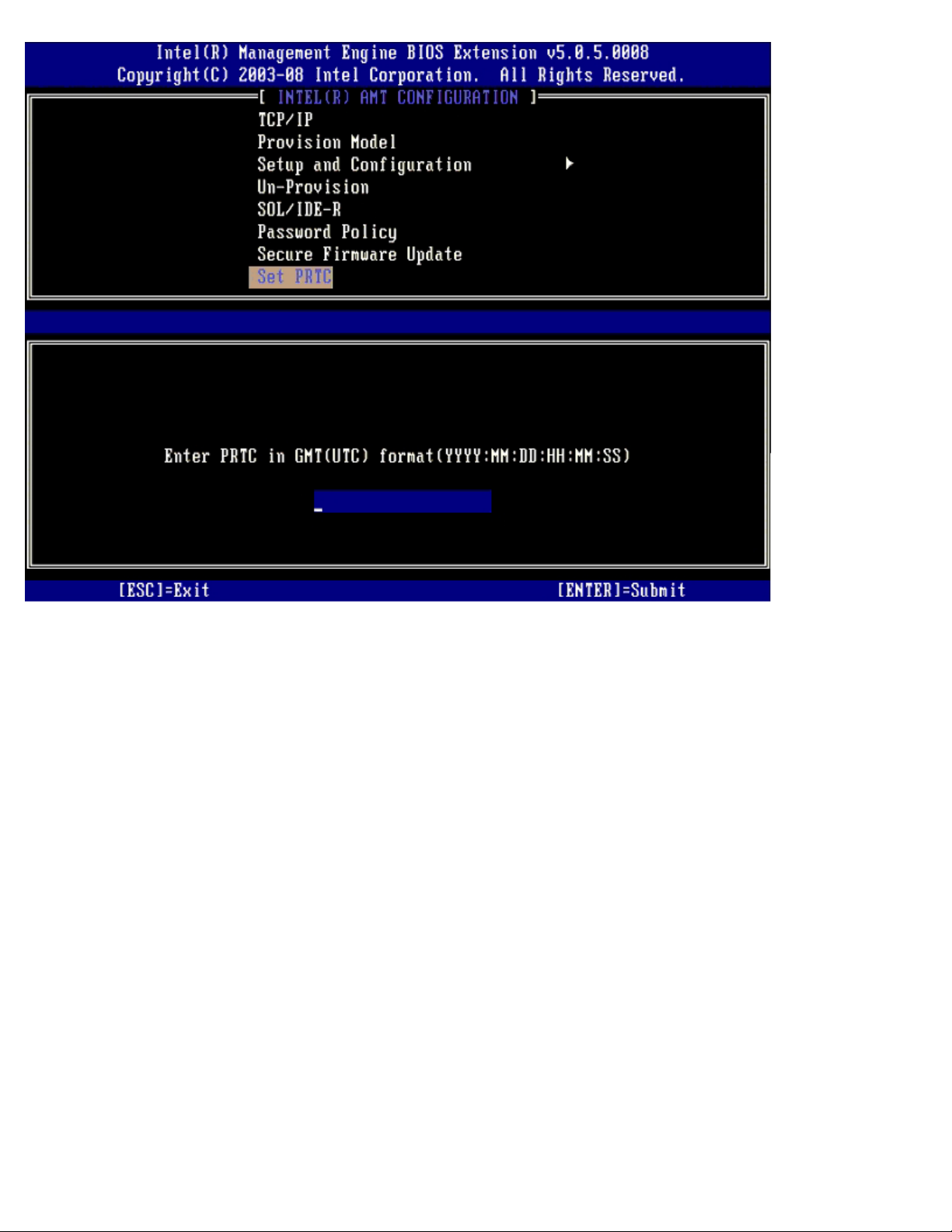
Idle Timeout
This setting is used to enable the Intel ME Wake on LAN feature and to define the Intel ME idle timeout in M1 state. The value
should be entered in minutes. The value indicates the amount of time that the Intel ME is allowed to remain idle in M1 before
transitioning to the M-off state. If the Intel ME is M0, it will not transition to M-off.
Page 26
Intel AMT in DHCP Mode Settings Example
The table below shows a basic field settings example for the Intel AMT Configuration menu page to configure the computer
in DHCP mode.
Intel AMT Configurations Example in DHCP Mode
Intel AMT Configuration Parameters Values
Intel AMT Configuration Select and press <Enter>.
Host Name
Example: IntelAMT
This is the same as the operating system machine name.
Set the parameters as follows:
TCP/IP
Provision Model
SOL/IDE-R
Remote FW Update Enabled
Save and exit MEBx and then boot the computer to the Windows® operating system.
Enable Network interface
Enable DHCP Mode
Set a domain name (e.g., amt.intel.com)
Intel AMT 4.0 Mode
Small Business
Enable SOL
Enable IDE-R
Intel AMT in Static Mode Settings Example
Page 27
The table below shows a basic field settings example for the Intel AMT Configuration menu page to configure the computer
in static mode. The computer requires two MAC addresses (GBE MAC address and Manageability MAC Address) to operate in
static mode. If there is no Manageability MAC address, Intel AMT cannot be set in static mode.
Intel AMT Configurations Example in Static Mode
Intel AMT Configuration Parameters Values
Intel AMT Configuration Select and press <Enter>
Host Name Example: IntelAMT
Set the parameters as follows:
Enable Network interface
Disable DHCP Mode
Set an IP address (e.g., 192.168.0.15)
TCP/IP
Set a subnet mask (e.g., 255.255.255.0)
The default gateway address is optional
The preferred DNS address is optional
The Alternate DNS address is optional
Set the domain name (e.g., amt.intel.com)
Provision Model
Small Business
Enable SOL
Intel AMT 4.0 Mode
SOL/IDE-R
Enable IDE-R
Remote FW Update Enabled
Save and exit MEBx and then boot computer to the Windows operating system.
*
Information on this page provided by Intel.
Back to Contents Page
Page 28

Back to Contents Page
Intel® Fast Call
Intel® Fast Call for help is a feature that is available for VPro SKUs. An Intel Fast Call for help connection allows the end user
to request assistance if the VPro system is outside the corporate network. If the BIOS allows an Intel Fast Call for help
connection the user can press the hot key/button (<Ctrl><h>) while the system is loading to initiate an Intel Fast Call
connection.
Requirements
Before an Intel Fast Call connection can be established from the Operating System the VPro system must have:
1. Environment detection enabled
2. Remote Connection policy
3. Management Presence Server (MPS)
Putting it all Together
There are no settings in the MEBX to enable/disable Intel Fast Call for help. If the system supports Full VPro Intel Fast Call for
help will be available for use. If the system only supports Intel Standard Manageability Intel Fast call for help is not enabled.
1. Before an Intel Fast Call for help can be started, environment detection must be enabled. This allows Intel AMT to
determine if the system is within the corporate network. This is configured through an ISV app.
2. A remote connection policy must be created before an Intel Fast call for help can be initiated. The policy for the BIOS
initiated call does not need to be configured, but another policy must exist before initiating a help call from the BIOS.
The BIOS must support the hot key that initiates the Intel Fast call for help.
3. A management presence server must exist to answer the Intel fast calls for help. The management presence server
resides in the DMZ zone. The management presence server.
When all of these conditions are satisfied the system is able to initiate an Intel Fast Call for help.
Initiating Intel Fast Call for Help
Once the feature has been fully configured, there are three methods for initiating an Intel Fast Call for help session. These
include:
At the Dell splash screen press <Ctrl><h>.
At the Dell splash screen press <F12> for the One Time Boot Menu.
Select the last option titled Intel Fast Call for Help.
From Windows:
1. Launch the Intel AMT privacy icon/application Intel Management Security Status.
2. Switch to the Intel AMT tab.
3. In the Remote Connectivity box, click Connect.
*
Information on this page provided by Intel
Back to Contents Page
.
Page 29

Back to Contents Page
Setup and Configuration Methods Overview
As discussed in the Setup and Configuration Overview section, the computer has to be configured before the Intel AMT
capabilities are ready to interact with management application. There are two methods to complete the provisioning process
(in order from least complex to most complex):
Configuration service — A configuration service allows you to complete the provisioning process from a GUI console
on their server with only one touch on each of the Intel AMT capable computers. The PPS and PID fields are completed
using a file created by the configuration service saved to a USB mass storage device.
MEBx interface — The IT administrator manually configures the Management Engine BIOS Extension (MEBx) settings
on each Intel AMT ready computer. The PPS and PID fields are completed by typing the 32 character and 8 character
alpha-numeric keys created by the configuration service into the MEBx interface.
Details on using these various methods are available in the next few sections.
Back to Contents Page
Page 30

Back to Contents Page
Configuration Service--Using a USB Device
This section discusses Intel® AMT setup and configuration using a USB storage device. You can set up and locally configure
password, provisioning ID (PID), and provisioning passphrase (PPS) information with a USB drive key. This is also called USB
provisioning. USB provisioning allows you to manually set up and configure computers without the problems associated with
manually typing in entries.
USB provisioning only works if the MEBx password is set to the factory default of admin. If the password has been changed,
reset it to the factory default by clearing the CMOS.
The following is a typical USB drive key setup and configuration procedure. For a detailed walk-through using Altiris® Dell™
Client Manager (DCM), refer to the USB device procedure
1. An IT technician inserts a USB drive key into a computer with a management console.
2. The technician requests local setup and configuration records from a setup and configuration server (SCS) through the
console.
3. The SCS does the following:
1. Generates the appropriate passwords, PID, and PPS sets
2. Stores this information in its database
3. Returns the information to the management console
4. The management console writes the password, PID, and PPS sets to a setup.bin file in the USB drive key.
5. The technician takes the USB drive key to the staging area where new Intel AMT capable computers are located. The
technician then does the following:
1. Unpacks and connects computers, if necessary
2. Inserts the USB drive key into a computer
3. Turns on that computer
6. The computer BIOS detects the USB drive key.
If found, the BIOS looks for a setup.bin file at the beginning of the drive key. Go to step 7.
If no USB drive key or setup.bin file is found, then restart the computer. Ignore the remaining steps.
7. The computer BIOS displays a message that automatic setup and configuration will occur.
1. The first available record in the setup.bin file is read into memory. The process accomplishes the following:
Validates the file header record
Locates the next available record
If the procedure is successful, the current record is invalidated so it cannot be used again
2. The process places the memory address into the MEBx parameter block
.
3. The process calls MEBx.
8. MEBx processes the record.
9. MEBx writes a completion message to the display.
10. The IT technician turns off the computer. The computer is now in the setup state and is ready to be distributed to
users in an Enterprise mode environment.
11. Repeat step 5 if you have more than one computer.
page.
Refer to the management console supplier for more information on USB drive key setup and configuration.
USB Drive Key Requirements
The USB drive key must meet the following requirements to be able to set up and configure Intel AMT:
It must be greater than 16 MB.
It must be formatted with the FAT16 file system.
The sector size must be 1 KB.
The USB drive key is not bootable.
The setup.bin file must be the first file landed on the USB drive key. The USB key must not contain any other files
whether hidden, deleted, or otherwise.
Back to Contents Page
Page 31

Back to Contents Page
USB Device Procedure
The default console package provided is the Dell!" Client Management (DCM) application. This section provides the procedure
to set up and configure Intel® AMT with the DCM package. As mentioned earlier in the document, several other packages are
available through third-party vendors.
The computer must be configured and seen by the DNS server before you begin this process. Also, a USB storage device is
required and must conform to the requirements listed in Configuration Service--Using a USB Device
The nature of management software is that it is not always dynamic or real time. In fact, sometimes if you tell a computer to
do something, such as to reboot, you may just have to do it again before it will work.
1. Format a USB device with the FAT16 file system and no volume label and then set it aside.
.
2. Open the Altiris® Dell Client Manager application by double clicking the desktop icon or through the Start menu.
3. Select AMT Quick Start from the left navigation menu to open the Altiris Console.
Page 32

4. Click the <+> to expand the Intel AMT Getting Started section.
Page 33

5. Click the <+> to expand the Section 1. Provisioning section.
Page 34

6. Click the <+> to expand the Basic Provisioning (without TLS) section.
Page 35

7. Select Step 1. Configure DNS.
The notification server with an out-of-band management solution installed must be registered in DNS as
"ProvisionServer."
Page 36

8. Click Test on the DNS Configuration screen to verify that DNS has the ProvisionServer entry and that it resolves to
the correct Intel setup and configuration server (SCS).
Page 37

The IP address for the ProvisionServer and Intel SCS are now visible.
Page 38

9. Select Step 2. Discovery Capabilities.
Page 39

10. Verify that the setting is Enabled. If Disabled, click the check box next to Disabled and click Apply.
Page 40

11. Select Step 3. View Intel AMT Capable Computers.
Page 41

Any Intel AMT capable computers on the network are visible in this list.
Page 42

12. Select Step 4. Create Profile.
Page 43

13. Click the plus symbol to add a new profile.
Page 44

On the General tab the administrator can modify the profile name and description along with the password. The
administrator sets a standard password for easy maintenance in the future. Select the manual radio button and
enter a new password.
Page 45

The Network tab provides the option to enable ping responses, VLAN, WebUI, Serial over LAN, and IDE
Redirection. If you are configuring Intel AMT manually, all these settings are also available in the MEBx.
The TLS (Transport Layer Security) tab provides the ability to enable TLS. If enabled, several other pieces of
information are required including the certificate authority (CA) server name, CA common name, CA type, and
certificate template.
The ACL (access control list) tab is used to review users already associated with this profile and to add new
users and define their access privileges.
Page 46

The Power Policy tab has configuration options to select the sleep states for Intel AMT as well as an Idle
Timeout setting. It is recommended that Idle timeout is always set to 0 for optimal performance.
The setting for the Power Policy tab can potentially impact a computer's ability to remain E-Star 4.0 compliant.
14. Select Step 5. Generate Security Keys.
Page 47

15. Select the icon with the arrow pointing out to Export Security Keys to USB Key.
Page 48

16. Select the Generate keys before export radio button.
Page 49

17. Enter the number of keys to generate (depends on the number of computers that need to be provisioned). The default
is 50.
18. The Intel ME default password is admin. Configure the new Intel ME password for the environment.
19. Click Generate. Once the keys have been created, a link appears to the left of the Generate button.
Page 50

20. Insert the previously formatted USB device into a USB connector on the Provisioning Serverr.
21. Click the Download USB key file link to download setup.bin file to the USB device. The USB device is recognized by
default; save the file to the USB device.
If additional keys are needed in the future, the USB device must be reformatted before saving the setup.bin file
to it.
Page 51

a. Click Save in the File Download dialog box.
b. Verify the Save in: location is directed to the USB device. Click Save.
Page 52

c. Click Close in the Download complete dialog box.
The setup.bin file is now visible in the drive Explorer window.
22. Close the Export Security Keys to USB Key and drive explorer windows to return to the Altiris Console.
23. Take the USB device to the computer, insert the device, and turn on the computer. The USB device is recognized
immediately and you are prompted to
Continue with Auto Provisioning (Y/N)
Press <y>.
Page 53

Press any key to continue with system boot...
24. Once complete, turn off the computer and move back to the management server.
25. Select Step 6. Configure Automatic Profile Assignments.
Page 54

26. Verify that the setting is enabled. In the Intel AMT 2.0+ dropdown, select the profile created previously. Configure the
other settings for the environment.
Page 55

27. Select Step 7. Monitor Provisioning Process.
Page 56

The computers for which the keys were applied begin to appearing in the system list. At first the status is
Unprovisioned, then the system status changes to In provisioning, and finally it changes to Provisioned at
the end of the process.
Page 57

28. Select Step 8. Monitor Profile Assignments.
Page 58

The computers for which profiles were assigned appear in the list. Each computer is identified by the FQDN,
UUID, and Profile Name columns.
Page 59

Once the computers are provisioned, they are visible under the Collections folder in All configured Intel AMT
computers.
Page 60

Back to Contents Page
Page 61

Back to Contents Page
MEBx Interface--Enterprise Mode Setup
The Intel® Management Engine BIOS Extension (MEBx) is an optional ROM module that Intel provides to Dell™ to be included
in the Dell BIOS. The MEBx has been customized for Dell computers.
Enterprise mode (for large corporate customers) requires a setup and configuration server (SCS). An SCS runs an application
over a network that performs Intel AMT setup and configuration. The SCS is also known as a provisioning server as seen in
the MEBx. An SCS is typically provided by independent software vendors (ISVs) and is contained within the ISV management
console product. Consult with the management console supplier for more information.
Follow the steps below to set up and configure Intel AMT in the Enterprise mode.
ME Configuration
To enable Intel Management Engine (ME) on the target platform:
1. Press <Ctrl><p> at the Dell logo screen to enter the MEBx screens.
2. Type admin in the Intel ME Password field. Press <Enter>. Passwords are case sensitive.
You must change the default password before making changes to the MEBx options.
3. Select Change Intel ME Password. Press <Enter>. Type the new password twice for verification.
The new password must include the following elements:
Eight characters
One uppercase letter
Page 62

One lowercase letter
A number
A special (nonalphanumeric) character, such as !, $, or ; excluding the :, ", and , characters.)
The underscore ( _ ) and spacebar are valid password characters but do NOT add to the password complexity.
4. Change the password to establish Intel AMT ownership. The computer then goes from the factory-default state to the
setup state.
5. Select Intel ME Configuration, and then press <Enter>.
ME Platform Configuration allows you to configure ME features such as power options, firmware update capabilities,
and so on.
Page 63

6. Press <y> when the following message appears:
System resets after configuration change. Continue (Y/N).
Page 64

Intel ME State Control is the next option. The default setting for this option is Enabled. Do not change this setting
to Disabled. If you want to disable Intel AMT, change the Manageability Feature Selection option to None in step
9.
Page 65

7. Select Intel ME Firmware Local Update Qualifier. Press <Enter>.
8. Then select either Always Open, Never Open, or Restricted. Press <Enter>.
The default setting for this option is Always Open.
Page 66

9. Select Intel ME Features Control, and then press <Enter>.
Page 67

Manageability Feature Selection is the next option. This feature sets the platform management mode. The default
setting is Intel AMT.
Selecting the None option disables all remote management capabilities.
Page 68

10. Select Return to Previous Menu, and then press <Enter>.
Page 69

11. Select Intel ME Power Control, and then press <Enter>.
Page 70

Intel ME ON in Host Sleep States is the next option. The default setting is Mobile: ON in S0.
Page 71

12. Select Return to Previous Menu, and then press <Enter>.
Page 72

13. Select Return to Previous Menu, and then press <Enter>.
Page 73

14. Exit the MEBx Setup and save the ME configuration.
The computer displays an Intel ME Configuration Complete message and then restarts. After the ME configuration is
complete, you can configure the Intel AMT settings.
Intel AMT Configuration
To enable Intel AMT Configuration settings on the target platform, perform the following steps:
1. At the initial boot screen, press <Ctrl><p> to re-enter the MEBx screens as seen in step 1
Engine for Enterprise Mode."
2. When a prompt for the password appears, enter the new Intel ME password.
3. Select Intel AMT Configuration, and then press <Enter>.
of "Enabling Management
Page 74

4. Select Host Name, and then press <Enter>.
5. Type in a unique name for this Intel AMT machine, and then press <Enter>.
Spaces are not accepted in the host name. Make sure there is not a duplicate host name on the network. Host names
can be used in place of the computer's IP for any applications requiring the IP address.
Page 75

6. Select TCP/IP, and then press <Enter>.
7. Press <n>when the following message appears:
[DHCP Enable] Disable DHCP (Y/N)
Page 76

8. Type the domain name into the Domain name field.
Page 77

9. Select Provision Model from the menu, and then press <Enter>.
10. Choose between an Enterprise or Small Business configuration. The default setting is Enterprise.
Page 78

11. Select Setup and Configuration from the menu, and then press <Enter>.
Page 79

12. Select Current Provisioning Mode to display the current mode, and then press <Enter>.
The current provisioning mode is displayed. Press <Enter> or <Esc> to exit.
Page 80

13. Select Provisioning Record from the menu, and then press <Enter>.
The screen displays the provision PSK/PKI record data of the computer. If the data has not been entered, the MEBX
displays a message that states
Provision Record not present
If the data is entered, the Provision Record displays one of several messages
.
Page 81

14. Select Provisioning Server from the menu, and then press <Enter>.
Page 82

15. Type the provisioning server IP in the Provisioning server address field and press <Enter>.
The default setting is 0.0.0.0. This default setting works only if the DNS server has an entry that can resolve the
provision server to the IP of the provisioning server.
Page 83

16. Type the port number in the Port number field and press <Enter>.
The default setting is 0. If left at the default setting of 0, the Intel AMT attempts to contact the provisioning server on
port 9971. If the provisioning server is listening on a different port, enter it here.
Page 84

17. Select Provisioning Server FQDN from the menu, and then press <Enter>.
Page 85

18. Type the fully qualified domain name (FQDN) for the provisioning server and press <Enter>.
Page 86

19. Select TLS PSK from the menu, and then press <Enter>.
Page 87

20. Set PID and PPS is the next option.
The PID and PPS can be input manually or by using a USB key once the SCS generates the codes.
This option is for entering the provisioning ID (PID) and provisioning passphrase (PPS). PIDs are eight characters and
PPS are 32 characters. There are dashes between every set of four characters, so including dashes, PIDs are nine
characters and PPS are 40 characters. An SCS must generate these entries.
Page 88

Skip the Delete PID and PPS option. This option returns the computer to factory defaults. See the "Return to Default"
section for more information about unprovisioning.
21. Select Return to Previous Menu, and then press <Enter>.
Page 89

22. Select TLS PKI from the menu, and then press <Enter>.
Page 90

23. Select Remote Configuration Enable/Disable from the menu, and then press <Enter>.
This option is Enabled by default and can be Disabled if the network infrastructure does not support a Certificate
Authority (CA).
Page 91

Manage Certificate Hashes option is the next option. Four hashes are configured by default. Hashes can be
deleted or added per customer needs.
Page 92

24. Select Set PKI DNS Suffix from the menu. Press <Enter>.
25. Type the PKI DNS Suffix in the text field and press <Enter>.
Page 93

26. Select Return to Previous Menu, and press <Enter>.
Page 94

27. Select Return to Previous Menu, and then press <Enter>.
This returns you to the Intel AMT Configuration menu.
Page 95

Skip the Un-Provision option. This option returns the computer to factory defaults. See the "Return to Default"
section for more information about unprovisioning.
Page 96

28. Select SOL/IDE-R, and then press <Enter>.
Page 97

29. Press <y> when the following message appears:
[Caution] System resets after configuration changes. Continue: (Y/N)
Page 98

For User Name & Password, select Enabled and then press <Enter>.
This option allows you to add users and passwords from the WebGUI. If the option is disabled, then only the
administrator has MEBx remote access.
Page 99

For Serial Over LAN (SOL/IDE-R), select Enabled and then press <Enter>.
Page 100

For IDE Redirection, select Enabled and then press <Enter>.
 Loading...
Loading...