
User Manual for Mellanox ConnectX®-3 10/40
Gigabit Ethernet Adapters for Dell PowerEdge
Servers
Rev 1.1
www.mellanox.com

Mellanox Technologies
350 Oakmead Parkway Suite 100
Sunnyvale, CA 94085
U.S.A.
www.mellanox.com
Tel: (408) 970-3400
Fax: (408) 970-3403
Mellanox Technologies, Ltd.
Beit Mellanox
PO Box 586 Yokneam 20692
Israel
www.mellanox.com
Tel: +972 (0)74 723 7200
Fax: +972 (0)4 959 3245
© Copyright 2014. Mellanox Technologies. All Rights Reserved.
Mellanox®, Mellanox logo, BridgeX®, ConnectX®, Connect-IB®, CORE-Direct®, InfiniBridge®, InfiniHost®,
InfiniScale®, MetroX®, MLNX-OS®, PhyX®, ScalableHPC®, SwitchX®, UFM®, Virtual Protocol Interconnect® and
Voltaire® are registered trademarks of Mellanox Technologies, Ltd.
ExtendX™, FabricIT™, Mellanox Open Ethernet™, Mellanox Virtual Modular Switch™, MetroDX™, TestX™,
Unbreakable-Link™ are trademarks of Mellanox Technologies, Ltd.
All other trademarks are property of their respective owners.
Dell and the DELL logo are trademarks of Dell Inc. Microsoft and Windows are trademarks of Microsoft Corporation. Linux
is a trademark of Linus Torvalds. Intel is a trademark of Intel Corporation. Magic Packet is a trademark of Advanced Micro
Devices, Inc. Red Hat is a trademark of Red Hat, Inc. PCI Express is a trademark of PCI-SIG. Any other trademarks or trade
names mentioned are the property of their respective owners.
NOTE:
THIS HARDWARE, SOFTWARE OR TEST SUITE PRODUCT (“PRODUCT(S)”) AND ITS RELATED
DOCUMENTATION ARE PROVIDED BY MELLANOX TECHNOLOGIES “AS-IS” WITH ALL FAULTS OF ANY
KIND AND SOLELY FOR THE PURPOSE OF AIDING THE CUSTOMER IN TESTING APPLICATIONS THAT USE
THE PRODUCTS IN DESIGNATED SOLUTIONS. THE CUSTOMER'S MANUFACTURING TEST ENVIRONMENT
HAS NOT MET THE STANDARDS SET BY MELLANOX TECHNOLOGIES TO FULLY QUALIFY THE
PRODUCTO(S) AND/OR THE SYSTEM USING IT. THEREFORE, MELLANOX TECHNOLOGIES CANNOT AND
DOES NOT GUARANTEE OR WARRANT THAT THE PRODUCTS WILL OPERATE W I TH THE HIGHEST
QUALITY. ANY EXPRESS OR IMPLIED WARRANTIES, INCLUDING, BUT NOT LIMITED TO, THE IMPLIED
WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY, FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE AND NONINFRINGEMENT
ARE DISCLAIMED. IN NO EVENT SHALL MELLANOX BE LIABLE TO CUSTOMER OR ANY THIRD PARTIES
FOR ANY DIRECT, INDIRECT, SPECIAL, EXEMPLARY, OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES OF ANY KIND
(INCLUDING, BUT NOT LIMITED TO, PAYMENT FOR PROCUREMENT OF SUBSTITUTE GOODS OR SERVICES;
LOSS OF USE, DATA, OR PROFITS; OR BUSINESS INTERRUPTION) HOWEVER CAUSED AND ON ANY
THEORY OF LIABILITY, WHETHER IN CONTRACT, STRICT LIABILITY, OR TORT (INCLUDING NEGLIGENCE
OR OTHERWISE) ARISING IN ANY WAY FROM THE USE OF THE PRODUCT(S) AND RELATED
DOCUMENTATION EVEN IF ADVISED OF THE POSS IBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGE.
Rev 1.1
2
Mellanox Technologies
Document Number: 4078

User Manual for Mellanox ConnectX®-3 10/40 Gigabit Ethernet Adapters for Dell PowerEdge Servers Rev 1.1
Restrictions and Disclaimers
The information contained in this document, including all instructions, cautions, and regulatory
approvals and certifications, is provided by the supplier and has not been independe ntly verified
or tested by Dell, except where specifically noted. Dell cannot be responsible for damage caused
as a result of either following or failing to follow these instructions. All statements or claims
regarding the properties, capabilities, speeds or qualifications of the part referenced in this document are made by the supplier and not by Dell. Dell specifically disclaims knowledge of the
accuracy, completeness or substantiation for any such statements. All questions or comments
relating to such statements or claims should be directed to the supplier.
Export Regulations
Customer acknowledges that these Products, which may include technology and software, are
subject to the customs and export control laws and regulations of the United States ("U.S.") and
may also be subject to the customs and export laws and regulations of the country in which the
Products are manufactured and/or received. Customer agrees to abide by those laws and regulations. Further, under U.S. law, the Products may not be sold, leased or otherwise transferred to
restricted end-users or to restricted countries. In addition, the Products may not be sold, leased or
otherwise transferred to, or utilized by an end-user engaged in activities related to weapons of
mass destruction, including without limitation, activities related to the design, development, production or use of nuclear weapons, materials, or facilities, missiles or the support of missile projects, and chemical or biological weapons.
Mellanox Technologies
3

Rev 1.1
Table of Contents
Restrictions and Disclaimers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .3
Export Regulations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .3
Table of Contents . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .4
List of Tables . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .8
List of Figures . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .9
Revision History . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .10
About this Manual . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .11
Intended Audience. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
Related Documentation. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
Document Conventions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
Technical Support . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
Chapter 1 Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
1.1 Functional Description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .12
1.2 Features . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .12
1.2.1 Single Root IO Virtualization (SR-IOV). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
1.2.2 Remote Direct Memory Access (RDMA) . . . . .
1.3 Supported Operating Systems/Distributions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .14
Chapter 2 Adapter Card Interfaces. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
2.1 I/O Interfaces . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .15
2.1.1 Ethernet QSFP+/ SFP+ Interface. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
2.1.2 LED Assignment. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
Chapter 3 Installing the Hardware . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
3.1 System Requirements . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .18
3.1.1 Hardware . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
3.1.2 Operating Systems/Distributions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
3.1.3 Software Stacks . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
3.1.4 Co-requisites . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
3.2 Safety Precautions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .18
3.3 Pre-installation Checklist . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .19
3.4 Installation Instructions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .19
3.4.1 For Adapters. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
3.4.2 For Mezzanine Cards. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
3.5 Connecting the Network Cables . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .20
3.5.1 Inserting a Cable into the Adapter Card. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
3.5.2 Removing a Cable from the Adapter Card . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
3.6 Identifying the Card in A System . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .20
3.6.1 On Linux. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
Chapter 4 Driver Installation and Configuration. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
4.1 Linux Driver . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .21
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
4
Mellanox Technologies

User Manual for Mellanox ConnectX®-3 10/40 Gigabit Ethernet Adapters for Dell PowerEdge Servers Rev 1.1
4.1.1 Installation Requirements. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
4.1.2 Downloading Mellanox OFED . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
4.1.3 Installing Mellanox OFED. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
4.1.3.1 Pre-installation Notes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
4.1.4 Installation Script . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
4.1.4.1 mlnxofedinstall Return Codes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
4.1.5 Installation Procedure. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
4.1.6 Installation Results . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
4.1.7 Post-installation Notes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
4.1.8 Uninstalling Mellanox OFED. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
4.2 Linux Driver Features . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .25
4.2.1 iSCSI Extensions for RDMA (iSER) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
4.2.2 iSER Initiator. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
4.2.3 Quality of Service (QoS) Ethernet . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
4.2.3.1 Mapping Traffic to Traffic Classes. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
4.2.3.2 Plain Ethernet Quality of Service Mapping . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
4.2.3.3 RoCE Quality of Service Mapping. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27
4.2.3.4 Raw Ethernet QP Quality of Service Mapping . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27
4.2.3.5 Map Priorities with tc_wrap.py/mlnx_qos . . . .
4.2.3.6 Quality of Service Properties. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
4.2.3.7 Quality of Service Tools . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27
4.2.4 Ethernet Time-Stamping. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32
4.2.4.1 Enabling Time Stamping. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32
4.2.4.2 Getting Time Stamping . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 35
4.2.4.3 Querying Time Stamping Capabilities via ethtool . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 36
4.2.5 RoCE Time Stamping. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 36
4.2.5.1 Query Capabilities. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 36
4.2.5.2 Creating Time Stamping Completion Queue. . .
4.2.5.3 Polling a Completion Queue . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 37
4.2.5.4 Querying the Hardware Time . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 38
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 37
4.2.6 Flow Steering . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 38
4.2.6.1 Enable/Disable Flow Steering. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 38
4.2.6.2 Flow Domains and Priorities . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
4.2.7 Single Root IO Virtualization (SR-IOV). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 41
4.2.7.1 System Requirements. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 41
4.2.7.2 Setting Up SR-IOV . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 41
4.2.7.3 Enabling SR-IOV and Para Virtualization on the Same Setup
4.2.7.4 Assigning a Virtual Function to a Virtual Machine
4.2.7.5 Uninstalling SR-IOV Driver . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 45
4.2.7.6 Configuring Pkeys and GUIDs under SR-IOV. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 46
4.2.7.7 Ethernet Virtual Function Configuration when Running SR-IOV. . . . . . . 47
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 44
. . . . . . . . 44
4.2.8 Ethtool . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 48
4.2.9 Ethernet Performance Counters. . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 50
4.3 VMware Driver . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .55
4.3.1 Installing and Running the Driver. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 55
4.3.1.1 Installing and Running the VIB Driver on ESXi-5.x . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 55
4.3.2 Installing and Running the offline_bundle Driver on ESXi-5.x . . . . . . . . . 57
4.3.3 Removing the VIB/offline_bundle Driver. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 57
Mellanox Technologies
5

Rev 1.1
4.4 Windows . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .57
4.4.1 Installation Requirements. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 58
4.4.1.1 Required Disk Space for Installation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 58
4.4.2 Software Requirements . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 58
4.4.2.1 Installer Privileges. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 58
4.4.3 Downloading Mellanox WinOF. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 58
4.4.4 Installing Mellanox WinOF . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 58
4.4.4.1 Attended Installation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 58
4.4.4.2 Unattended Installation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 59
4.4.5 Uninstalling Mellanox WinOF . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 59
4.4.6 Windows Performance Tuning . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 59
4.5 WinOF Features . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .59
4.5.1 Configuring Quality of Service (QoS) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 59
4.5.2 RDMA over Converged Ethernet . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 61
4.5.2.1 RoCE Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 61
4.5.2.2 Configuring Router (PFC only) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 63
4.5.3 Deploying Windows Server 2012 and 2012 R2 with SMB Direct. . . . . . . 63
4.5.3.1 Hardware and Software Prerequisites. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 63
4.5.3.2 SMB Configuration Verification . . . . . . . . . . .
4.5.3.3 Verifying SMB Connection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 64
4.5.3.4 Verifying SMB Events that Confirm RDMA Connection . . . . . . . . . . . . . 64
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 63
Chapter 5 Remote Boot. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 65
5.1 iSCSI Boot . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .65
5.1.1 RHEL6.4/RHEL6.5 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 65
5.1.1.1 Configuring the iSCSI Target Machine . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 65
5.1.1.2 Installing RHEL6.4/RHEL6.5 on a Remote Storage over iSCSI . . . . . . . 66
5.1.1.3 SAN-Booting the Diskless Client with FlexBoot . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 70
5.1.2 Booting Windows from an iSCSI Target. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 70
5.1.2.1 Configuring the WDS, DHCP and iSCSI Servers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 70
5.1.2.2 Configuring the Client Machine. . . . . . . . . . .
5.1.2.3 Installing iSCSI . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 72
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 71
5.1.3 SLES11 SP3. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 73
5.1.3.1 Configuring the iSCSI Target Machine . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 73
5.1.3.2 Configuring the DHCP Server. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 75
5.1.3.3 Installing SLES11 SP3 on a Remote Storage over iSCSI. . . . . . . . . . . . 75
5.1.3.4 Using PXE Boot Services for Booting the SLES
11 SP3 from the iSCSI Target 82
5.2 PXE Boot . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .82
5.2.1 SLES11 SP3. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 82
5.2.1.1 Configuring the PXE Server . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 82
Chapter 6 Firmware . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 84
Chapter 7 Troubleshooting. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 85
7.1 General . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .85
7.2 Linux . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .86
7.3 Windows . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .86
Chapter 8 Specifications. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 88
Chapter 9 Regulatory. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 91
6
Mellanox Technologies

User Manual for Mellanox ConnectX®-3 10/40 Gigabit Ethernet Adapters for Dell PowerEdge Servers Rev 1.1
9.1 Regulatory Statements . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .91
9.1.1 FCC Statements (USA) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 91
9.1.2 EN Statements (Europe) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 92
9.1.3 ICES Statements (Canada) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 92
9.1.4 VCCI Statements (Japan). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 92
9.1.5 KCC Certification (Korea). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 93
Appendix A Configuration for Mellanox Adapters through System Setup . . .94
Appendix B Safety Warnings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .108
Appendix C Avertissements de sécurité d’installation (Warnings in French) 110
Appendix D Sicherheitshinweise (Warnings in German) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .112
Appendix E Advertencias de seguridad para la instalación (Warnings in Spanish) 114
Mellanox Technologies
7

Rev 1.1
List of Tables
Table 1: Revision History Table . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .10
Table 2: Documents List . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1
1
Table 3: LED Assignment for 10GbE SFP+ Network Adapters . .
Table 4: LED Assignment for 40GbE QSFP+ Network Adapters . . . .
Table 5: install.sh Return Codes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .22
Table 6: Flow Specific Parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 7: ethtool Supported Options . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .49
Table 8: Port IN Counters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .5
Table 9: Port OUT Counters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .52
Table 10: Port VLAN Priority Tagging (where <i> is in the range 0…7)
Table 11: Port Pause (where <i> is in the range 0…7) . . . . . . .
Table 12: VPort Statistics (where <i>=<empty_string> is the
Table 13: SW Statistics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 14: Per Ring (SW) Statistics (where <i> is the ring I – per configuration) . . . . . . . . . . . . . .55
Table 15: Reserved IP Address Options . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .7 1
Table 16: Mellanox ConnectX-3 Dual 40GbE QSFP+ Network Adapter
Table 17: Mellanox ConnectX-3 Dual 10GbE SFP+ Network Adapter Specificat
Table 18: Mellanox ConnectX-3 Dual 10GbE KR Blade Mezzanine Card Specifications . . . . . . .90
Table 19: Ethernet Network Adapter Certifications
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .91
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .40
PF, and ranges 1…NumOfVf per VF) 53
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .15
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .16
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .52
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .53
54
Specifications . . . . . . . .88
ions . . . . . . . . . .89
1
8
Mellanox Technologies

User Manual for Mellanox ConnectX®-3 10/40 Gigabit Ethernet Adapters for Dell PowerEdge Servers Rev 1.1
List of Figures
Figure 1: Mellanox ConnectX-3 Dual Port 40GbE QSFP+ Network Adapter Full Height Bracket 16
Figure 2: Mellanox ConnectX-3 Dual Port 10GbE SFP+ Network Adapter Ful
l Height Bracket .17
Figure 3: Life Cycle Controller Main Configuration System Setup Menu
Figure 4: Main Configuration Page Options . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .95
Figure 5: Main ConfiguratioP page - iSCSI Configuration Figure 6: Main Configuration Page - iSCSI Configuration -
Figure 7: Main Configuration Page - iSCSI Configuration - iSCSI Target Parameters . . . . . . . .103
iSCSI General Parameters . . . . . . .101
iSCSI Initiator Parameters . . . . . . .102
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .94
Mellanox Technologies
9
Rev 1.1
Revision History
This document was printed on August 12, 2014.
Table 1 - Revision History Table
Date Rev
August 2014 1.1
Comments/Changes
• Added Section 4.2, “Linux Driver Features,” on page 25
• Added Section 4.5, “WinOF Features,” on page 59
• Added Section 5, “Remote Boot,” on page 65
• Added Appendix A, “Configuration for Mellanox Adapters
through System Setup,” on page 94
November 2013 1.0 Initial Release
10
Mellanox Technologies
User Manual for Mellanox ConnectX®-3 10/40 Gigabit Ethernet Adapters for Dell PowerEdge Servers Rev 1.1
About this Manual
This User Manual describes Mellanox Technologies ConnectX®-3 10/40 Gigabit Ethernet
Adapter and Cards for Dell PowerEdge Servers. It provides details as to the interfaces of the
board, specifications, required software and firmware for operating the board, and relevant documentation.
Intended Audience
This manual is intended for the installer and user of these cards.
The manual assumes the user has basic familiarity with Ethernet networks and architecture spec-
ifications.
Related Documentation
Table 2 - Documents List
IEEE Std 802.3 Specification This is the IEEE Ethernet specification
http://standards.ieee.org/getieee802
PCI Express 3.0 Specifications Industry Standard PCI Express 3.0 Base and
PCI_Express_CEM_r3.0
Document Conventions
This document uses the following conventions:
• MB and MBytes are used to mean size in mega Bytes. The use of Mb or Mbits (small b)
indicates size in mega bits.
• PCIe is used to mean PCI Express
Technical Support
Dell Support site: http://www.dell.com/support
Mellanox Technologies
11

1 Introduction
1.1 Functional Description
Mellanox Ethernet adapters utilizing IBTA RoCE technology provide efficient RDMA services,
delivering high performance to bandwidth and latency sensitive applications. Applications utilizing TCP/UDP/IP transport can achieve industry-leading throughpu t over 10 or 4 0GbE. The h ardware-based stateless offload and flow steering engines in Mellanox adapters reduce the CPU
overhead of IP packet transport, freeing more processor cycles to work on the application. Sockets acceleration software further increases performance for latency sensitive applications. This
User Manual relates to the following products:
• Mellanox ConnectX
Servers with full height bracket
• Mellanox ConnectX
Servers with low profile bracket
• Mellanox ConnectX
Edge Servers with full height bracket
• Mellanox ConnectX
Edge Servers with low profile bracket
• Mellanox ConnectX
Edge Servers
®
-3 Dual Port 40GbE QSFP Network Adapter for Dell PowerEdge
®
-3 Dual Port 40GbE QSFP Network Adapter for Dell PowerEdge
®
-3 Dual Port 10GbE DA/SFP+ Network Adapter for Dell Power-
®
-3 Dual Port 10GbE DA/SFP+ Network Adapter for Dell Power-
®
-3 Dual Port 10GbE KR Blade Mezzanine Card for Dell Power-
IntroductionRev 1.1
1.2 Features
The adapters and cards described in this manual support the following features:
• Low latency RDMA over Ethernet
• Traffic steering across multiple cores
• Intelligent interrupt coalescence
• Advanced Quality of Service
• Dual Ethernet ports
• CPU off-load of transport operations
• Application Offload
• End-to-end QoS and congestion control
•Ethernet
• IEEE 802.3ae 10 Gigabit Ethernet
• IEEE 802.3ba 40 Gigabit Ethernet supported on Mellanox ConnectX-3 Dual Port 40GbE QSFP+
Network Adapter only
• IEEE 802.3ad Link Aggregation and Failover
• IEEE 802.1Q, 802.1p VLAN tags and prior it y
• IEEE 802.1Qau Congestion Notification
• IEEE P802.1Qbb D1.0 Priority-based Flow Control
• Jumbo frame support (10KB)
12
Mellanox Technologies

User Manual for Mellanox ConnectX®-3 10/40 Gigabit Ethernet Adapters for Dell PowerEdge Servers Rev 1.1
• 128 MAC/VLAN addresses per port
• Wake on LAN (WoL) supported on Mellanox ConnectX-3 Dual Port 10GbE KR Blade Mezzanine
Card only
• PCI Express Interface
• PCIe Base 3.0 compliant, 1.1 and 2.0 compatible
• 2.5, 5.0, or 8. 0G T/s link rate x8
• Auto-negotiates to x8, x4, or x1
• Support for MSI/MSI-X mechanisms
• Hardware-based I/O V irtualization
• Single Root IOV (SR-IOV) - see Section 1.2.1, “Single Root IO Virtualization (SR-IOV),”
on page 14
• Address translation and protection
• Dedicated adapter resources
• Multiple queues per virtual machine
• Enhanced QoS for vNICs
• VMware NetQueue support
• Additional CPU Offloads
• RDMA over Converged Ethernet - see Section 1.2.2, “Remote Direct Memory Access
(RDMA),” on page 14
• TCP/UDP/IP stateless offload
• Intelligent interrupt coalescence
• FlexBoot™ Technology
• Remote boot over Ethernet
• iSCSI boot
• PXE boot
• Connectivity
• Interoperable with 1/10/40GbE switches
• QSFP+ connectors supported on Mellanox ConnectX-3 Dual Port 40GbE QSFP+ Network Adapter
only
• SFP+ connectors supported on Mellanox ConnectX-3 Dual Port 10GbE SFP+ Network Adapter
only
• Passive copper cable
• Powered connectors for optical and active cable support
• Management and Tools
• MIB, MIB-II, MIB-II Extensions, RMON, RMON 2
• Configur a ti on and diagnostic tools
• RoHS-R6 compliant
1.2.1 Single Root IO Virtualization (SR-IOV)
Single Root IO Virtualization (SR-IOV) is a technology that allows a physical PCIe device to
present itself multiple times through the PCIe bus. This technology enables multiple virtual
Mellanox Technologies
13

instances of the device with separate resources. Mellanox adapters are capable of exposing up to
126 virtual instances called Virtual Functions (VFs). These virtual functions can then be provisioned separately . Each VF can be seen as an addition device connected to the Physical Function.
It shares the same resources with the Physical Function, and its number of ports equals those of
the Physical Function. SR-IOV is commonly used in conjunction with an SR-IOV enabled hypervisor to provide virtual machines direct hardware access to network resources hence increasing
its performance.
1.2.2 Remote Direct Memory Access (RDMA)
Remote Direct Memory Access (RDMA) is the remote memory management capability that
allows server to server data movement directly between application memory without any CPU
involvement. RDMA over Converged Ethernet (RoCE) is a mechanism to provide this efficient
data transfer with very low latencies on loss-less Ethernet networks. With advances in data center
convergence over reliable Ethernet, ConnectX®-3 EN with RoCE use s the proven and efficient
RDMA transport to provide the platform for deploying RDMA technology in mainstream data
center application at 10GigE and 40GigE link-speed. ConnectX®-3 EN with its hardware offload
support takes advantage of this efficient RDMA transport (InfiniBand) services over Ethernet to
deliver ultra low latency for performance-critical and transaction intensive applications such as
financial, database, storage, and content delivery networks. RoCE encapsulates IB transport and
GRH headers in Ethernet packets bearing a dedicated ether type. While the use of GRH is
optional within InfiniBand subnets, it is mandatory when using RoCE. Applications written over
IB verbs should work seamlessly, but they require provisioning of GRH information when creating address vectors. The library and driver are modified to provide mapping from GID to MAC
addresses required by the hardware.
IntroductionRev 1.1
1.3 Supported Operating Systems/Distributions
• RedHat Enterprise Linux (RHEL)
• SuSe Linux Enterprise Server (SLES)
• OpenFabrics Enterprise Distribution (OFED)
• Microsoft Windows Server Family of Operating Systems
• VMware ESX
For the list of the specific supported operating systems and distributions, please refer to
the release notes for the applicable software downloads on the Dell support site:
www.dell.com/support.
http://
14
Mellanox Technologies
User Manual for Mellanox ConnectX®-3 10/40 Gigabit Ethernet Adapters for Dell PowerEdge Servers Rev 1.1
2 Adapter Card Interfaces
2.1 I/O Interfaces
Each adapter card includes the following interfaces:
• High speed port:
• QSFP+ for the 40GbE Network Adapters
• SFP+ for the 10GbE Network Adapters
• Backplane connection to the M1000e chassis for the 10GbE KR Blade Mezzanine Card
• PCI Express (PCIe) x8 edge connector
• I/O panel LEDs (does not apply with Mellanox ConnectX-3 Dual Port 10GbE KR Blade
Mezzanine Card)
2.1.1 Ethernet QSFP+/ SFP+ Interface
Note: This section does not apply to Mellanox ConnectX-3 Dual Port 10GbE KR Blade Mezzanine Card.
The network ports of the ConnectX-3 adapter cards are compliant with the IEEE 802.3 Ethernet
standards. The QSFP+ port has four Tx/Rx pairs of SerDes. T
SerDes. Ethernet traffic is transmitted through the cards' QSFP+ or SFP+ connectors.
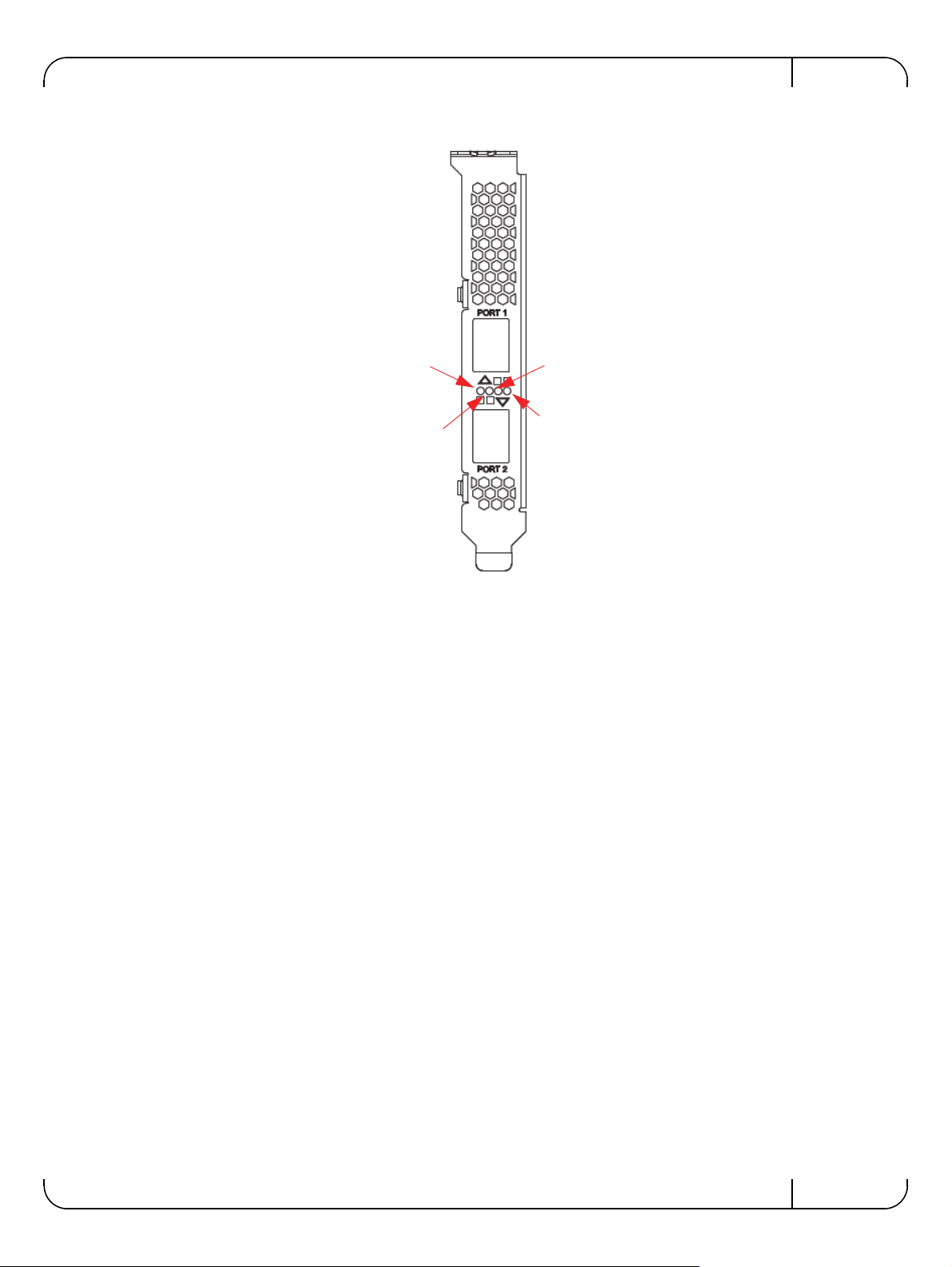
2.1.2 LED Assignment
There is a one bicolor link LED, green and yellow, and a green color activity LED located on the
I/O panel. Link LED color is determined by link speed. See Table 3 and Table 4 for different
LED functions.
Note: This section does not apply to Mellanox Connec
nine Card.
Table 3 - LED Assignment for 10GbE SFP+ Network Adapters
Link LED (Bicolor -
Green and Yellow)
Off Off
Yellow Off
Green Off
Yellow Blinking Green
he SFP+ port has one Tx/Rx pair of
tX-3 Dual Port 10GbE KR Blade Mezza-
Activity LED (Green) Function
No link present
1 Gb/s link is present
10 Gb/s link is present
Speed lower than the maximum is active
a
Green Blinking Green
a. 1 Gb/s Link Speed is only supported with 1 Gb/s optics. No 1 Gb/s optics are currently supported.
Maximum supported speed is active
Mellanox Technologies
15
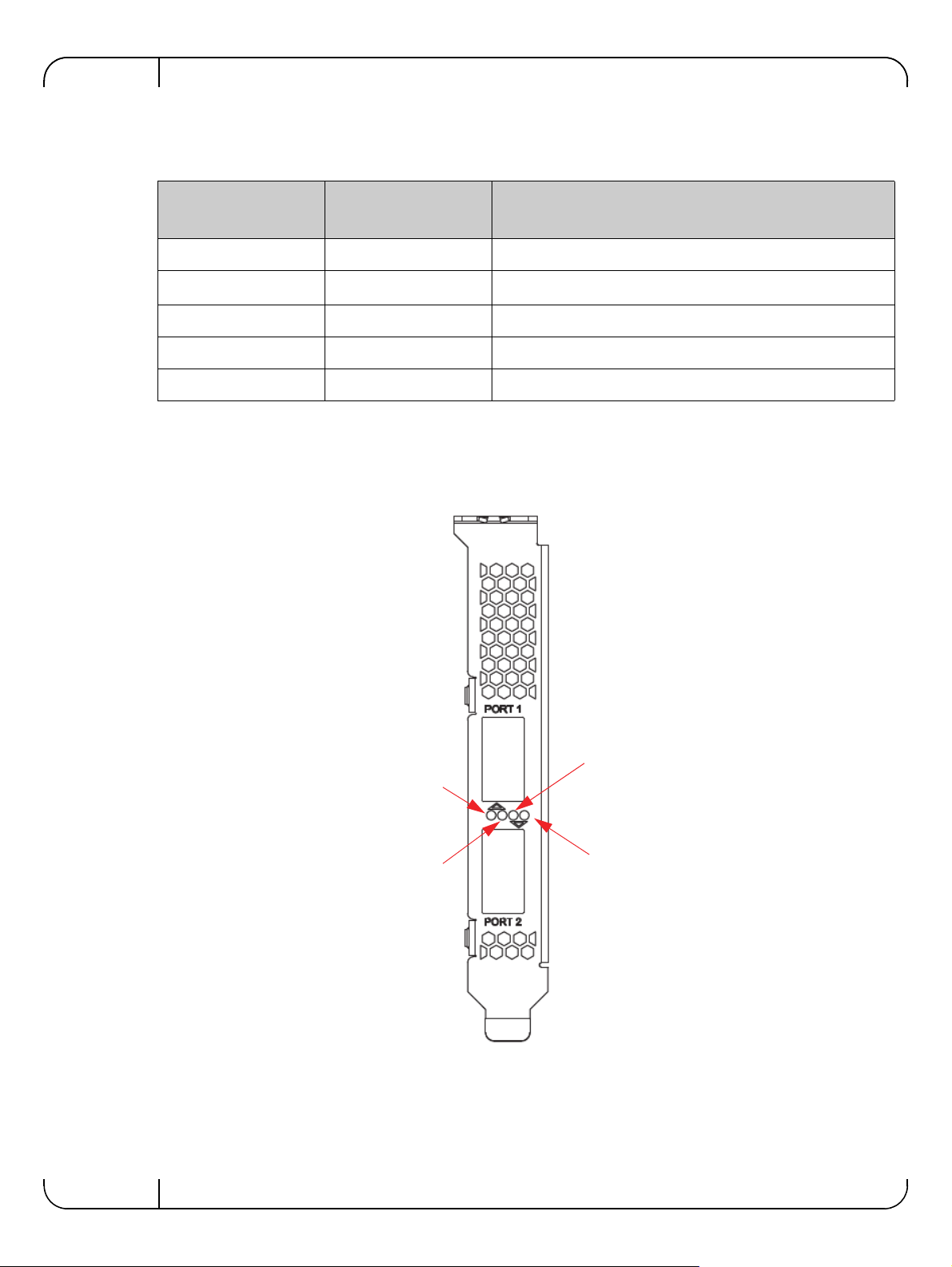
Table 4 - LED Assignment for 40GbE QSFP+ Network Adapters
Port 1 Activity
Port 2 Link
Port 2 Activity
Port 1 Link
Adapter Card InterfacesRev 1.1
Link LED (Bicolor -
Green and Yellow)
Off Off
Yellow Off
Green Off
Yellow Blinking Green
Green Blinking Green
a. 10 Gb/s Link Speed is only supported with the Mellanox Quad to Serial Small Form Factor Pluggable Adapter
(QSFP+ to SFP+ adapter or QSA). The QSA is not currently supported.
Activity LED (Green) Function
No link present
10 Gb/s link is present
40 Gb/s link is present
Speed lower than the maximum is active
Maximum supported speed is active
a
Figure 1: Mellanox ConnectX-3 Dual Port 40GbE QSFP+ Network Adapter Full Height Bracket
16
Mellanox Technologies
User Manual for Mellanox ConnectX®-3 10/40 Gigabit Ethernet Adapters for Dell PowerEdge Servers Rev 1.1
Port 2 Link
Port 2 Activity
Port 1 Link
Port 1 Activity
Figure 2: Mellanox ConnectX-3 Dual Port 10GbE SFP+ Network Adapter Full Height Bracket
Mellanox Technologies
17

3 Installing the Hardware
3.1 System Requirements
3.1.1 Hardware
Dell PowerEdge Server with an available PCI Express x8 slot for installing the card is required.
For the list of supported Dell PowerEdge Servers please refer to the release notes for the
applicable software and firmware downloads on the Dell support site:
www.dell.com/support.
3.1.2 Operating Systems/Distributions
Please refer to Section 1.3, “Supported Operating Systems/Distributions,” on page 14.
For the list of the specific supported operating systems and distributions, please refer to
the release notes for the applicable software downloads on the Dell support site:
www.dell.com/support.
Installing the HardwareRev 1.1
http://
http://
3.1.3 Software Stacks
Mellanox OpenFabric software package - MLNX_OFED for Linux.
3.1.4 Co-requisites
For full functionality including manageability support, minimum versions of Server BIOS, Integrated Dell Remote Access Controller (iDRAC), and Dell Lifecycle Controller are required.
For the list of co-requisites, please refer to the release notes for the applicable software
and firmware downloads on the Dell support site:
3.2 Safety Precautions
The adapter is being installed in a system that operates with voltages that can be lethal.
Before opening the case of the system, observe the following precautions to avoid
injury and prevent damage to system components.
1. Remove any metallic objects from your hands and wrists.
2. Make sure to use only insulated tools.
3. Verify that the system is p
4. It is required to use an ESD strap
http://www.dell.com/support.
owered off and is unplugged.
or other antistatic devices.
18
Mellanox Technologies

User Manual for Mellanox ConnectX®-3 10/40 Gigabit Ethernet Adapters for Dell PowerEdge Servers Rev 1.1
3.3 Pre-installation Checklist
1. Verify that your system meets the hardware and software requirements stated above.
2. Shut down your system if active.
3. After shutting down the system, turn of
4. Remove the card from its package. Please note that the ca
f power and unplug the cord.
rd must be placed on an antistatic
surface.
5. Check the card for visible signs of damage. Do
not attempt to install the card if damaged.
3.4 Installation Instructions
3.4.1 For Adapters
Refer to the manuals that were supplied with your system for instructions on installing add-in
cards.
1. Before installing the card, make
nected to the server. Please follow prop
2. Open the system case.
3. The adapter can be placed in an available slot.
sure that the system is off and the power cord is not con-
er electrical grounding procedures.
4. A lesser width adapter can be seated into a greater
adapter cannot be seated into a lesser width slot (x8 in a x4). Align the adapter connector edge
with the PCI Express connector slot.
5. Applying even pressure at both corner
firmly seated. When the adapter is properly seated, the adapter port connectors are aligned
with the slot opening, and the adapter faceplate is visible against the system chassis.
Do not use excessive force when seating the adapter, as this may damage the system or
the adapter.
6. Secure the adapter with the adapter clip
model.
Ensure that the adapters are seated correctly such that the QSFP+ or SFP+ ports of the
adapter are unobstructed.
7. Close the system case.
3.4.2 For Mezzanine Cards
Refer to the owner's manuals that were supplied with your Dell PowerEdge Blade Server for
instructions on installing blade mezzanine cards.
width slot (x4 in a x8), but a greater width
s of the adapter, insert the adapter into the slot until it is
or screw per the instructions provided with the server
1. Before installing the card, take the blade server out of the chassis
2. Open the system case.
3. The card can be placed in an available slot.
Mellanox Technologies
19

4. Expose the socket to be used for the new card. When replacing an existing card, remove the
card from the socket. Grab the card on the edge on the side with UPC number and pull up
while gently rocking the card back and forth. For a new installation remove the protective
cover enclosing the socket for the card.
5. Line up the blade mezzanine card so that the pins of the
server. Plug the card into the socket by placing your thumb over the Dell part number label
and pressing down until the card is fully seated.
Do not use excessive force when seating the card, as this may damage the system or
the adapter.
6. Secure the blade mezzanine card with the mezzanine card latch.
7. Close the system case.
3.5 Connecting the Network Cables
3.5.1 Inserting a Cable into the Adapter Card
1. Support the weight of the cable before connecting it to the adapter card. Do this by using a
cable holder or tying the cable to the rack.
Installing the HardwareRev 1.1
card are over the sockets in the blade
2. Determine the correct orientation of
the connector to the card before inserting the connector.
Do not try and insert the connector upside down. This may damage the adapter card.
3. Insert the connector into the adapter card. Be careful to insert
cage. Do not apply any torque, up or down, to the connector cage in the adapter card.
4. Make sure that the connector locks in place.
3.5.2 Removing a Cable from the Adapter Card
1. Pull on the latch release mechanism thereby unlatching the connector and pull the connector
out of the cage.
2. Do not apply torque to the connector when
removing it from the adapter card.
3. Remove any cable supports that were used to support the cable’s weight.
3.6 Identifying the Card in A System
3.6.1 On Linux
Get the device location on the PCI bus by running lspci and locating lines with the string “Mellanox Technologies”:
> lspci |grep -i Mellanox
27:00.0 Network controller: Mellanox Technologies MT27500 Family [ConnectX-3]
the connector straight into the
20
Mellanox Technologies

User Manual for Mellanox ConnectX®-3 10/40 Gigabit Ethernet Adapters for Dell PowerEdge Servers Rev 1.1
4 Driver Installation and Configuration
4.1 Linux Driver
For Linux, download and install the latest Linux Drivers for Mellanox ConnectX-3 Ethernet
adapters software package available on the Dell support site http://www.dell.com/support
driver installation instructions, please refer to Dell documentation via http://www.dell.com/sup-
port.
4.1.1 Installation Requirements
Required Disk Space for Installation
•100 MB
Software Requirements
• Linux operating system
For the list of supported operating system distributions and kernels, release notes for the
applicable software download on the Dell support site:
http://www.dell.com/support.
For
Ins
taller Privileges
• The installation requires administrator privileges on the target machine
4.1.2 Downloading Mellanox OFED
Step 1. Verify that the system has a Mellanox network adapter (NIC) installed by ensuring that you can
see ConnectX-3 in the display.
The following example shows a system with an installed Mellanox NIC:
host1# lspci -v | grep Mellanox
27:00.0 Network controller: Mellanox Technologies MT27500 Family [ConnectX-3]
Step 2. Download the software release to your host.
The software release name has the format
Step 3. Use the md5sum utility to confirm the file integrity of your software release. Run the following
command and compare the result to the value provided on the download page.
host1$ md5sum MLNX_OFED_LINUX-<ver>.tar.gz
4.1.3 Installing Mellanox OFED
The installation script, install.sh, performs the following:
• Discovers the currently installed kernel
• Uninstalls any software stacks that are part of the standard operating system distribution
or another vendor's commercial stack
• Installs the MLNX_OFED_LINUX binary RPMs (if they are available for the current
kernel)
MLNX_OFED_LINUX-<ver>.tar.gz
Mellanox Technologies
21
4.1.3.1 Pre-installation Notes
Driver Installation and ConfigurationRev 1.1
• The installation script removes all previous
installs the software release.
4.1.4 Installation Script
Within each distribution specific subdirectory there is an installation script called install.sh.
Its usage is described below. You will use it during the installation procedure described in
Section 4.1.5, “Installation Procedure,” on page 23.
4.1.4.1 mlnxofedinstall Return Codes
Table 5 lists the install.sh script return codes and their meanings.
Table 5 - install.sh Return Codes
Return Code Meaning
0 The Installation ended successfully
1 The installation failed
2 No firmware was found for the adapter device
22 Invalid parameter
28 Not enough free space
ly installed Mellanox OFED packages and
171 Not applicable to this system configuration. This can occur when the
required hardware is not present on the system.
172 Prerequisites are not met. For example, missing the required software
installed or the hardware is not configured correctly.
173
Failed to start the
mst driver
22
Mellanox Technologies

User Manual for Mellanox ConnectX®-3 10/40 Gigabit Ethernet Adapters for Dell PowerEdge Servers Rev 1.1
4.1.5 Installation Procedure
Step 1. Login to the installation machine as root.
Step 2. Copy the software release on your machine
For specific installation instructions, please refer to the applicable software download
on the Dell support site
Step 3. Un-tar the software release.
host1# tar -xvf MLNX_OFED_LINUX-<ver>.tar.gz
Step 4. Change directory to the distribution specific subdirectory.
host1# cd /MLNX_OFED_LINUX-<ver>/rhel6/rhel6.4
Step 5. Run the installation script (example).
../install.sh
This program will install the MLNX_OFED_LINUX package on your machine.
Note that all other Mellanox, OEM, OFED, or Distribution IB packages will be removed.
Do you want to continue?[y/N]:y
http://www.dell.com/support.
Installing mlnx-ofa_kernel RPM
Preparing... ##################################################
mlnx-ofa_kernel ##################################################
Installing kmod-mlnx-ofa_kernel RPM
Preparing... ##################################################
kmod-mlnx-ofa_kernel ##################################################
Installing mlnx-ofa_kernel-devel RPM
Preparing... ##################################################
mlnx-ofa_kernel-devel ##################################################
Installing user level RPMs:
Preparing... ##################################################
ofed-scripts ##################################################
Preparing... ##################################################
libibverbs ##################################################
Preparing... ##################################################
libibverbs-devel ##################################################
Preparing... ##################################################
libibverbs-devel-static ##################################################
Preparing... ##################################################
libibverbs-utils ##################################################
Preparing... ##################################################
libmlx4 ##################################################
Preparing... ##################################################
libmlx4-devel ##################################################
Preparing... ##################################################
libibumad ##################################################
Preparing... ##################################################
libibumad-devel ##################################################
Preparing... ##################################################
Mellanox Technologies
23

Driver Installation and ConfigurationRev 1.1
libibumad-static ##################################################
Preparing... ##################################################
libibmad ##################################################
Preparing... ##################################################
libibmad-devel ##################################################
Preparing... ##################################################
libibmad-static ##################################################
Preparing... ##################################################
librdmacm ##################################################
Preparing... ##################################################
librdmacm-utils ##################################################
Preparing... ##################################################
librdmacm-devel ##################################################
Preparing... ##################################################
perftest ##################################################
Device (02:00.0):
02:00.0 Ethernet controller: Mellanox Technologies MT27500 Family [ConnectX-
3]
Link Width: 8x
PCI Link Speed: Unknown
Installation finished successfully.
Step 6. The script adds the following lines to /etc/security/limits.conf for the userspace
components such as MPI:
* soft memlock unlimited
* hard memlock unlimited
These settings unlimit the amount of memory that can be pinned by a user space application. If
desired, tune the value unlimited to a specific amount of RAM.
4.1.6 Installation Results
Software
• The OFED package is installed under the /usr directory.
• The kernel modules are installed under:
• mlx4 driver:
/lib/modules/<kernel_version>/extra/mlnx-ofa_kernel/drivers/net/ethernet/mellanox/mlx4/
•RDS:
/lib/modules/`uname -r`/updates/kernel/net/rds/rds.ko
/lib/modules/`uname -r`/updates/kernel/net/rds/rds_rdma.ko
/lib/modules/`uname -r`/updates/kernel/net/rds/rds_tcp.ko
Kernel’s modules location may vary depending on the kernel’s configuration.
For example: /lib/modules/`uname -r`/extra/kernel/drivers/net/ethernet/mellanox/mlx4/
mlx4_core
24
• The script openibd is installed under /etc/init.d/. This script can be used to load and
unload the software stack.
Mellanox Technologies

User Manual for Mellanox ConnectX®-3 10/40 Gigabit Ethernet Adapters for Dell PowerEdge Servers Rev 1.1
• The installation process unlimits the amount of memory that can be pinned by a user
space application. See
Step 6.
• Man pages will be installed under /usr/share/man/
4.1.7 Post-installation Notes
• Most of the Mellanox OFED components can be configured or reconfigured after the
installation by modifying the relevant configuration files.
4.1.8 Uninstalling Mellanox OFED
Either use the distribution specific uninstall.sh script or use the script /usr/sbin/
ofed_uninstall.sh to uninstall the Mellanox OFED package. The ofed_uninstall.sh is part
of the ofed-scripts RPM.
4.2 Linux Driver Features
4.2.1 iSCSI Extensions for RDMA (iSER)
iSCSI Extensions for RDMA (iSER) extends the iSCSI protocol to RDMA. It permits data to be
transferred directly into and out of SCSI buffers without intermediate data copies.
4.2.2 iSER Initiator
The iSER initiator is controlled through the iSCSI interface available from the iscsi-initiator-utils
package.
Make sure iSCSI is enabled and properly configured on your system before proceeding with
iSER.
Targets settings such as
If targets are set to auto connect on boot, and targets are unreachable, it may take a long
time to continue the boot process if timeouts and max retries are set too high.
timeouts and retries are set the same as any other iSCSI targets.
Example for discovering and connecting targets over iSER:
iscsiadm -m discovery -o new -o old -t st -I iser -p <ip:port> -l
iSER also supports RoCE without any additional configuration required. To bond the RoCE
interfaces, set the
fail_over_mac option in the bonding driver.
4.2.3 Quality of Service (QoS) Ethernet
4.2.3.1 Mapping Traffic to Traffic Classes
Mapping traffic to TCs consists of several actions which are user controllable, some controlled
by the application itself and others by the system/network administrators.
Mellanox Technologies
25

The following is the general mapping traffic to Traffic Classes flow:
1. The application sets the required Type of Service (ToS).
2. The ToS is translated into a Socket
Priority (sk_prio).
Driver Installation and ConfigurationRev 1.1
3. The
sk_prio is mapped to a User Priority (UP) by the system administrator (some applica-
tions set
sk_prio directly).
4. The UP is mapped to TC by the network/system
5. TCs hold the actual QoS parameters
QoS can be applied on the following types of traf
among them:
• Plain Ethernet - Applications use regular inet sockets and the traffic passes via the kernel Ethernet driver
• RoCE - Applications use the RDMA API to transmit using QPs
• Raw Ethernet QP - Application use VERBs API to transmit using a Raw Ethernet QP
4.2.3.2 Plain Ethernet Quality of Service Mapping
Applications use regular inet sockets and the traf
The following is the Plain Ethernet QoS mapping flow:
1. The application sets the T
2. ToS is translated into the
TOS 0 <=> sk_prio 0
TOS 8 <=> sk_prio 2
TOS 24 <=> sk_prio 4
TOS 16 <=> sk_prio 6
oS of the socket using setsockopt (IP_TOS, value).
sk_prio using a fixed translation:
administrator.
fic. However, the general QoS flow may vary
fic passes via the kernel Ethernet driver.
3. The Socket Priority is mapped to the UP:
• If the underlying device is a VLAN device,
egress_map is used controlled by the vconfig
command. This is per VLAN mapping.
• If the underlying device is not a VLAN device, the
though
mlx4_en driver interprets this as a sk_prio to UP mapping.
tc manual states that the mapping is from the sk_prio to the TC number, the
Mapping the sk_prio to the UP is done by using
0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7
tc command is used. In this case, even
tc_wrap.py -i <dev name> -u
4. The the UP is mapped to the TC as configured by the mlnx_qos tool or by the lldpad daemon
if DCBX is used.
Socket applications can use setsockopt (SK_PRIO, value) to directly set the sk_prio
of the socket. In this case the ToS to
the application and the administrator to utilize more than the 4 values po ssible via ToS.
In case of VLAN interface, the UP obtained according to the above mapping is also used
in the VLAN tag of the traffic
sk_prio fixed mapping is not needed. This allows
26
Mellanox Technologies

User Manual for Mellanox ConnectX®-3 10/40 Gigabit Ethernet Adapters for Dell PowerEdge Servers Rev 1.1
4.2.3.3 RoCE Quality of Service Mapping
Applications use RDMA-CM API to create and use QPs.
The
following is the RoCE QoS mapping flow:
1. The application sets the ToS of the QP using the
RDMA_OPTION_ID_TOS, value).
(
2. ToS is translated into the Socket Priority (
TOS 0 <=> sk_prio 0
TOS 8 <=> sk_prio 2
TOS 24 <=> sk_prio 4
TOS 16 <=> sk_prio 6
sk_prio) using a fixed translation:
rdma_set_option option
3. The Socket Priority is mapped to the User P
riority (UP) using the tc command.
In case of a VLAN device, the parent real device is used
4. The the UP is mapped to the TC
as configured by the mlnx_qos tool or by the lldpad daemon
if DCBX is used.
With RoCE, there can only be 4 predefined ToS values for the purpose of QoS mapping.
4.2.3.4 Raw Ethernet QP Quality of Service Mapping
Applications open a Raw Ethernet QP using VERBs directly.
The
following is the RoCE QoS mapping flow:
1. The application sets the UP of the
Raw Ethernet QP during the INIT to RTR state transition of
the QP:
• Sets
qp_attrs.ah_attrs.sl = up
• Calls modify_qp with IB_QP_AV set in the mask
2. The UP is mapped to the TC as configure d by th e
DCBX is used
for the purpose of this mapping.
mlnx_qos tool or by the lldpad daemon if
When using Raw Ethernet QP mapping, the TOS/sk_prio to UP mapping is lost.
Performing the Raw Ethernet QP mapping forces the QP to transmit using the given UP.
If packets with VLAN tag are transmitted, UP in the VLAN tag will be overwritten with
the given UP.
4.2.3.5 Map Priorities with tc_wrap.py/mlnx_qos
Network flow that can be managed by QoS attributes is described by a User Priority (UP). A
sk_prio is mapped to UP which in turn is mapped into TC.
user's
• Indicating the UP
Mellanox Technologies
27

Driver Installation and ConfigurationRev 1.1
• When the user uses sk_prio, it is mapped into a UP by the ‘tc’ tool. This is done by the
tc_wrap.py tool which gets a list of <= 16 comma separated UP and maps the sk_prio to
the specified UP.
For example,
sk_prio 1 to UP 5.
tc_wrap.py -ieth0 -u 1,5 maps sk_prio 0 of eth0 device to UP 1 and
• Setting
The
• In RoCE,
• When creating QPs, the
set_egress_map in VLAN, maps the skb_priority of the VLAN to a vlan_qos.
vlan_qos is represents a UP for the VLAN device.
rdma_set_option with RDMA_OPTION_ID_TOS could be used to set the UP
sl field in ibv_modify_qp command represents the UP
• Indicating the TC
• After mapping the
skb_priority to UP, one should map the UP into a TC. This assigns
the user priority to a specific hardware traffic class. In order to do that,
be used.
ieth0 -p 0,0,0,0,1,1,1,1
mlnx_qos gets a list of a mapping between UPs to TCs. For example, mlnx_qos -
4.2.3.6 Quality of Service Properties
The different QoS properties that can be assigned to a TC are:
•
Strict Priority (see “Strict Priority”)
• Minimal Bandwidth Guarantee (ETS) (see “Minimal Bandwidth Guarantee (ETS)”)
• Rate Limit (see “Rate Limit”)
Strict Priority
When setting a TC's transmission algorithm to be 'strict', then this TC has absolute (strict) priority over other TC strict priorities coming before it (as determined by the TC number: TC 7 is
highest priority, TC 0 is lowest). It also has an absolute priority over non strict TCs (ETS).
This property needs to be used with care, as it may easily cause starvation of other TCs.
A higher strict priority TC is always given the first chance to transmit. Only if the highest strict
priority TC has nothing more to transmit, will the next highest TC be considered.
Non strict priority TCs will be considered last to transmit.
mlnx_qos should
maps UPs 0-3 to TC0, and Ups 4-7 to TC1.
28
This property is extremely useful for low latency low bandwidth traffic. Traffic that needs to get
immediate service when it exists, but is not of high volume to starve other transmitters in the system.
Minimal Bandwidth Guarantee (ETS)
After servicing the strict priority TCs, the amount of bandwidth (BW) left on the wire may be
split among other TCs according to a minimal guarantee policy.
If, for instance, TC0 is set to 80% guarantee and TC1 to 20% (the TCs sum must be 100), then
the BW left after servicing all strict priority TCs will be split according to this ratio.
Since this is a minimal guarantee, there is no maximum enforcement. This means, in the same
example, that if TC1 did not use its share of 20%, the reminder will be used by TC0.
Rate Limit
Rate limit defines a maximum bandwidth allowed for a TC. Please note that 10% deviation from
the requested values is considered acceptable.
Mellanox Technologies

User Manual for Mellanox ConnectX®-3 10/40 Gigabit Ethernet Adapters for Dell PowerEdge Servers Rev 1.1
4.2.3.7 Quality of Service Tools
mlnx_qos
mlnx_qos is a centralized tool used to configure QoS features of the local host. It communicates
directly with the driver thus does not require setting up a DCBX daemon on the system.
The
mlnx_qos tool enables the administrator of the system to:
• Inspect the current QoS mappings and configuration
The tool will also display maps configured by TC and
vconfig set_egress_map tools, in order to
give a centralized view of all QoS mappings.
• Set UP to TC mapping
• Assign a transmission algorithm to each TC (strict or ETS)
• Set minimal BW guarantee to ETS TCs
• Set rate limit to TCs
For unlimited ratelimit set the ratelimit to 0.
Usage:
mlnx_qos -i <interface> [options]
Options:
--version show program's version number and exit
-h, --help show this help message and exit
-p LIST, --prio_tc=LIST
maps UPs to TCs. LIST is 8 comma seperated TC numbers.
Example: 0,0,0,0,1,1,1,1 maps UPs 0-3 to TC0, and UPs
4-7 to TC1
-s LIST, --tsa=LIST Transmission algorithm for each TC. LIST is comma
seperated algorithm names for each TC. Possible
algorithms: strict, etc. Example: ets,strict,ets sets
TC0,TC2 to ETS and TC1 to strict. The rest are
unchanged.
-t LIST, --tcbw=LIST Set minimal guaranteed %BW for ETS TCs. LIST is comma
seperated percents for each TC. Values set to TCs that
are not configured to ETS algorithm are ignored, but
must be present. Example: if TC0,TC2 are set to ETS,
then 10,0,90 will set TC0 to 10% and TC2 to 90%.
Percents must sum to 100.
-r LIST, --ratelimit=LIST
Rate limit for TCs (in Gbps). LIST is a comma
seperated Gbps limit for each TC. Example: 1,8,8 will
limit TC0 to 1Gbps, and TC1,TC2 to 8 Gbps each.
-i INTF, --interface=INTF
Interface name
-a Show all interface's TCs
Mellanox Technologies
29
Get Current Configuration:
tc: 0 ratelimit: unlimited, tsa: strict
up: 0
skprio: 0
skprio: 1
skprio: 2 (tos: 8)
skprio: 3
skprio: 4 (tos: 24)
skprio: 5
skprio: 6 (tos: 16)
skprio: 7
skprio: 8
skprio: 9
skprio: 10
skprio: 11
skprio: 12
skprio: 13
skprio: 14
skprio: 15
up: 1
up: 2
up: 3
up: 4
up: 5
up: 6
up: 7
Driver Installation and ConfigurationRev 1.1
Set ratelimit. 3Gbps for tc0 4Gbps for tc1 and 2Gbps for tc2:
tc: 0 ratelimit: 3 Gbps, tsa: strict
up: 0
skprio: 0
skprio: 1
skprio: 2 (tos: 8)
skprio: 3
skprio: 4 (tos: 24)
skprio: 5
skprio: 6 (tos: 16)
skprio: 7
skprio: 8
skprio: 9
skprio: 10
skprio: 11
skprio: 12
skprio: 13
skprio: 14
skprio: 15
up: 1
up: 2
up: 3
up: 4
up: 5
up: 6
up: 7
30
Mellanox Technologies
 Loading...
Loading...