Page 1

Authors
Deploying FCoE (FIP Snooping) on
Dell PowerConnect 10G Switches:
M8024-k, 8024 and 8024F
A Dell Deployment Guide
Network Enabled Solutions Team,
Kevin Locklear
Contributor
Kili Land
Page 2

Deploying FCoE (FIP Snooping) on Dell PowerConnect 10G Switches: M8024-k, 8024, and 8024F
This document is for informational purposes only and may contain typographical errors and
technical inaccuracies. The content is p rovided as is, without express or implied warranties of any
kind.
© 2011 - 2012 Dell Inc. All rights reserved. Dell and its affiliates cannot be responsible for errors or
omissions in typography or p h otography. Dell, the Dell logo, PowerConnect and PowerEdge are
trademarks of Dell Inc. Intel and Xeon are registered trademarks of Intel Corporation in the U.S. and
other countries. Microsoft, Windows, and Windows Server are either trademarks or registered
trademarks of Microsoft Corporation in the United States and/or other countries. Other trademarks and
trade names may be used in this document to refer to either the e n tities claiming the marks and names
or their products. Dell disclaims proprietary interest in the marks and names of others.
March 2012| Rev 2.0
2
Page 3

Deploying FCoE (FIP Snooping) on Dell PowerConnect 10G Switches: M8024-k, 8024, and 8024F
Contents
Introduction ........................................................................................................... 6
Basic Terminology .................................................................................................... 6
FIP snooping ........................................................................................................ 6
FIP snooping bridge (FSB) ........................................................................................ 6
FCF ................................................................................................................... 6
PFC ................................................................................................................... 7
NPIV .................................................................................................................. 7
NPV................................................................................................................... 7
VSAN ................................................................................................................. 7
Configuration scenarios ............................................................................................. 8
Important notes prior to deployment .......................................................................... 9
Scenario 1: Deploying the Dell PowerConnect 8024 Series FSB in a Cisco 5000 Series Switch (NPIV )
environment .......................................................................................................... 10
Configuring the Dell PowerConnect M8024-k,8024, and 8024F for FIP Snooping ....................... 13
Configuring the Cisco 5000 series switch with firmware ver 5. x for a single connection from the
Dell PowerConnect M8024-k or 8024()(F) ..................................................................... 17
Basic Validation for the Pow e r Connect M8024-k configuration ........................................... 23
Basic Troubleshooting Areas .................................................................................... 28
Scenario 2: Configuring Mult ip le Uplinks into LAG for Cisco Nexus 5000 Series Switch (NPIV)
Environment .......................................................................................................... 30
Configuring the Cisco Nexus 50 00 series switch with firmware ver 5.x for a multiple link LAG (link
aggregation) connection at the Top-of-Rack. ................................................................ 31
Configuring the M8024-k,8024, and 8024F for FIP Snoop in g ............................................... 33
Scenario 3: Configuring Mult ip le Uplinks into LAG for Cisco Nexus 5000 Series Switch (NPV mode)
Environment .......................................................................................................... 35
Configuring the Cisco Nexus 50 00 series switch with firmware ver 5.0(3)N2(2a) in NPV mode for a
multiple link LAG (link aggregation) connection from the Dell PowerConnect M8024-k or 8024()(F)
...................................................................................................................... 36
Configuring the Dell PowerConnect M8024-k,8024,and 8024F for FIP Snooping with Cisco Nexus
5000 series switch in NPV mode. ............................................................................... 37
ETS Behavior and CoS configur ations on the PowerConnect 8024 series switches ..................... 37
Updating firmware .................................................................................................. 39
Command-line interface method ............................................................................... 39
Web interface method ........................................................................................... 41
Appendix A – Full CLI examples ................................................................................... 45
M8024-k CLI example ............................................................................................. 45
3
Page 4

Deploying FCoE (FIP Snooping) on Dell PowerConnect 10G Switches: M8024-k, 8024, and 8024F
Cisco Nexus 5548UP CLI example .............................................................................. 52
Appendix B - Network Switch Versions ........................................................................... 56
References ............................................................................................................ 56
About Dell ............................................................................................................ 56
Figures
Figure 1. Dell PowerConnect™ M8024-k Switch (10G Ethernet) .............................................. 6
Figure 2. Dell PowerConnect™ 8024F (10G Ethernet) ......................................................... 6
Figure 3. General overview of deployment ...................................................................... 8
Figure 4. Disabling simple mode .................................................................................. 9
Figure 5. Simple 1-link connection between devices ......................................................... 10
Figure 6. General Overview of the whole configuration and planning procedure ........................ 11
Figure 7. Overview of parallel configurati on ................................................................... 12
Figure 8. Example commands for Dell PowerConnect M8024-k (can be copied and pasted) ........... 13
Figure 9. Configuration overview of Dell PowerConnect M8024-k .......................................... 16
Figure 10. Sample CLI for Cisco Nexus 5020 ( can be copied and pasted) ................................... 17
Figure 11. Sample CLI for Cisco Nexus 5548 ( can be copied and pasted) ................................... 18
Figure 12. Cisco Nexus 5000 series configuration sequence ................................................... 20
Figure 13. M1000e Chassis Management Controller -> Server Overview -> Properties -> WWN/MAC
information for Blade Serv e r 3’ s “B” fabric CNA port 2 (B2). ............................................ 21
Figure 14. Example of show interface brief command ......................................................... 22
Figure 15. show spanning-tree summary co mmand showing current configuration with ports states .. 23
Figure 16. show flogi database comman d sh owing devices that have compl e ted fabric login .......... 23
Figure 17. Example of show zoneset active command ......................................................... 23
Figure 18. Show interface status results ......................................................................... 24
Figure 19. show spanning-tree blockedports command ........................................................ 25
Figure 20. Show fip-snooping command which gives a brief status on available ENode’s, and FCF’s .. 25
Figure 21. show lldp dcbx interface all ........................................................................... 26
Figure 22. Show lldp dcbx interface te1/0/20 detail .......................................................... 27
Figure 23. Multiple port link (LAG) configuration between switches and storage ......................... 30
Figure 24. Multiple port link (LAG) Cisco 5020 configuration (can be copied and pasted) ............... 31
Figure 25. Multiple port uplink (LAG) M8024-k configuration (can be copied and pasted) ............... 33
Figure 26. Multiple link configuration between switches and storage ....................................... 35
Figure 27. Multiple port link Cisco 5020 configuration (can be copied and pasted) ....................... 36
Figure 28. CoS settings to establish min imum bandwidth for FCoE qu e ue .................................. 37
Figure 29. Fabric separation as preferred method for management of networks and storage .......... 38
4
Page 5

Deploying FCoE (FIP Snooping) on Dell PowerConnect 10G Switches: M8024-k, 8024, and 8024F
5
Page 6

Deploying FCoE (FIP Snooping) on Dell PowerConnect 10G Switches: M8024-k, 8024, and 8024F
Introduction
The PowerConnect™ M8024-k, 8024 and 8024F switches are now DCB/DCBx capable with a
downloadable update. Starting with firmware 4.2, the latest PowerConnect™ 10 Gigabit switches can
now be used as an FCoE Transit Switch (FIP Snooping Bridge, T11, BB-5). With this new firmware
implementation Converged Network Adapters (CNAs) can be used in the rack-mount or blade server to
enable access to Fibre Channel networks and their storage.
NOTE: The PowerConnect™ M8024 (predecessor to th e M 8024-k) does not support the FIP Snooping
capability and will not be suppo r t e d for any of the described scenarios.
This document provides an easy t o use guide for configuring FIP Snooping on the Dell
PowerConnect™ M8024-k Blade Switch (Figure 1), and the PowerConnect™ 8024F
Dell PowerConnect™ M8024-k Switch (10G Ethernet) Figure 1.
(Figure 2).
Dell PowerConnect™ 8024F (10G Ethernet) Figure 2.
Basic Terminology
FIP snooping
With FIP snooping enabled on the PowerConnect™ 8024 model switches, FIP logins, solicitations, and
advertisements are monitor e d . In this monitoring or snoopin g p rocess the switch gathers information
pertaining to the ENode and FCF ad d r esses. With this information the switch will then place filters that
only allow access to ENode devices that have logged-in successfully. This enables the FCoE VLAN to
deny all other traffic except this lossless FCoE storage traffic.
The filtering process also secures the end-to-end path between the ENode device and the FCF. The
ENode will only be able to talk with the FCF in which it has logged into.
FIP snooping bridge (FSB)
With a switch configured to per forming FIP snooping the industry term for this switch is FSB or FIP
snooping bridge. It is perfo r ming FIP snooping as described in th e pr e vious term.
FCF
FCoE forwarders (FCFs) act as an Ethernet and FC switch combine d . All typical termination functions
that would occur on a FC switch occur on the FCF. FCF’s give VF_Ports and VE_Ports for their virtual FC
interfaces.
6
Page 7
Deploying FCoE (FIP Snooping) on Dell PowerConnect 10G Switches: M8024-k, 8024, and 8024F
PFC
Priority Flow Control (PFC), or Per-Priority Pause is d e fined in the IEEE 802.1Qbb standar d . PFC is flow
control based on priority settings and adds additional information to the standard pause frame. The
additional fields added to the p ause frame allow devices to pause traffic on a specific priority instead
of pausing all traffic. (IEEE, 2009) Pause frames will be initiated by the FCF in most cases when its
receive buffers are starting to reach a congested point. With PFC traffic is paused instead of dropped
and retransmitted. This provides the lossless network behavior necessary for FC packets to be
encapsulated and passed along the Ethernet paths.
NPIV
N-port identifier virtualization which enables multiple N-port fabric logins at the same time on the
same physical FC link (Cisco Systems, Inc., 2011).This term is in reference to t he Cisco Nexus 5000
series switches implementation of NPIV .
NPV
N-port virtualizer is a FC aggregation method which passes tr affic through to end devices, w hile
eliminating the need to use a domain ID for this device (Cisco Systems, Inc., 2011). This term is also in
reference to configuration settings on the Cisco Nexus 5000 series switches.
VSAN
Virtual SAN is a logical partitioning of physical connections to provide for fabric or SAN separation.
Note: The Dell M 100 0e Server Chassis includes a console redirect feature that allows you to manage
each PowerConnect M8024-k module from a single serial c onnection to the chassis. For mo r e
information about console r e d ir ect, see the Dell Blade Server CMC User's Guide
at http://support.dell.com/support/edocs/software/smdrac3/cmc/index.htm
.
7
Page 8
Deploying FCoE (FIP Snooping) on Dell PowerConnect 10G Switches: M8024-k, 8024, and 8024F
Configuration scenarios
The following sections will present very basic examples of deploying the 10G switches for FIP Snooping
and will provide step-by-step explanations of the CLI commands as a guide. The GUI d oe s n ot currently
support configurations for FIP Snooping. Consult the table of contents above for a list of examples
covered in this document.
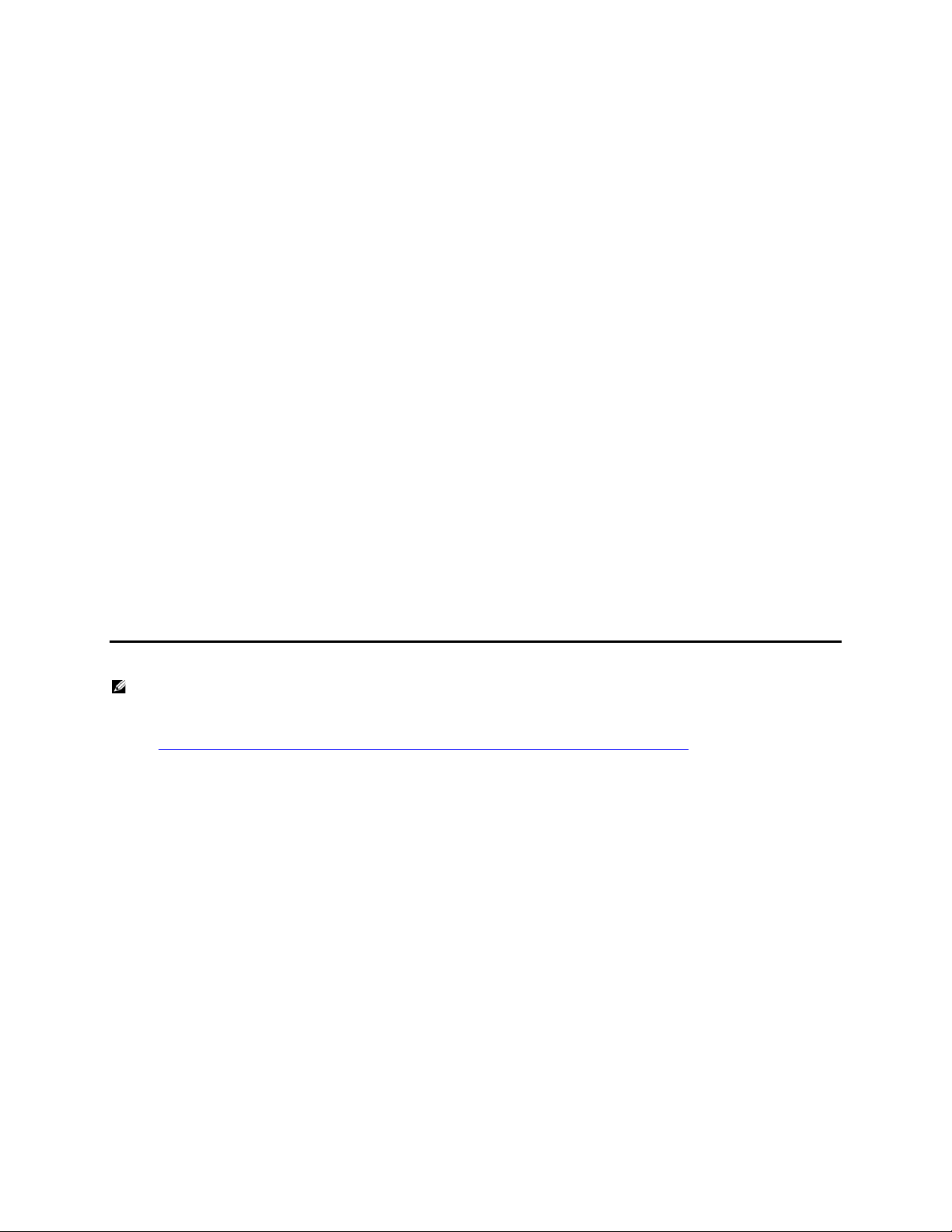
General overview of deployment Figure 3.
The following suggested co nfigurations used to deploy t his solution is done in a sequential order for
reading but as Figure 3 represents this is more of a simultaneous process. There are dependencies that
will be occuring during the configuration that will rely on other parts of the process. Storage
configuration is not covered in any depth due to the possibilit y for various supported storage devices as
part of the whole solution.
8
Page 9
Deploying FCoE (FIP Snooping) on Dell PowerConnect 10G Switches: M8024-k, 8024, and 8024F
configure
Important notes prior to deployment
No Simple Mode
Each of the following scenarios in this document assume that the PowerConnect™ 8024 model switch
being used is in normal Switch Mode (not Simple Mode) and is using firmware version 4.2.x.x or later.
NOTE: If Simple Mode is enabled it will need to be disabled prior to impl ementing the deployment
covered in this document. FCoE is not supported with the PowerConnect 8024 model switches in
Simple Mode. The CLI command in the example may be used for disabling Simple Mode, but please
consult the User Guide for more information on specifics of Simple Mode.
Disabling simple mode Figure 4.
no mode simple
_________________________________________________________________________________________
Non-FIP-aware switches
If a Non-FIP-Aware switch is introduced anywhere in the data path FCoE will not be supported and
can’t be expected to work as designed. The Dell PowerConnect M8024-k and 8024F are considered nonFIP-aware switches until they have t h e 4.2 or greater firmware installed. See updating firmware
section for instructions on p e r forming this update.
_________________________________________________________________________________________
Stacking
Stacking is not recommended in an FCoE environment with the Dell PowerConnect 8024 Model
Switches. If the switches are st acked the configuration should be changed to disable stacking . Please
refer to the Dell PowerConnect 8024 4.2 firmware user’s guid e for further details on disabli ng or
changing stacking ports. If th e configuration is used in this manner lossless Ethernet and reliability can
not be guaranteed.
Dell PowerConnect 4.2 or greater firmware on M8024-k or 8024F
As mentioned in the non-FIP-aware bullet the Dell PowerConnect Switches will not support FCoE or FIP
snooping without 4.2 or great e r firmware. See updating firmware
________________________________________________________________________________________
section to perform this update.
9
Page 10
Deploying FCoE (FIP Snooping) on Dell PowerConnect 10G Switches: M8024-k, 8024, and 8024F
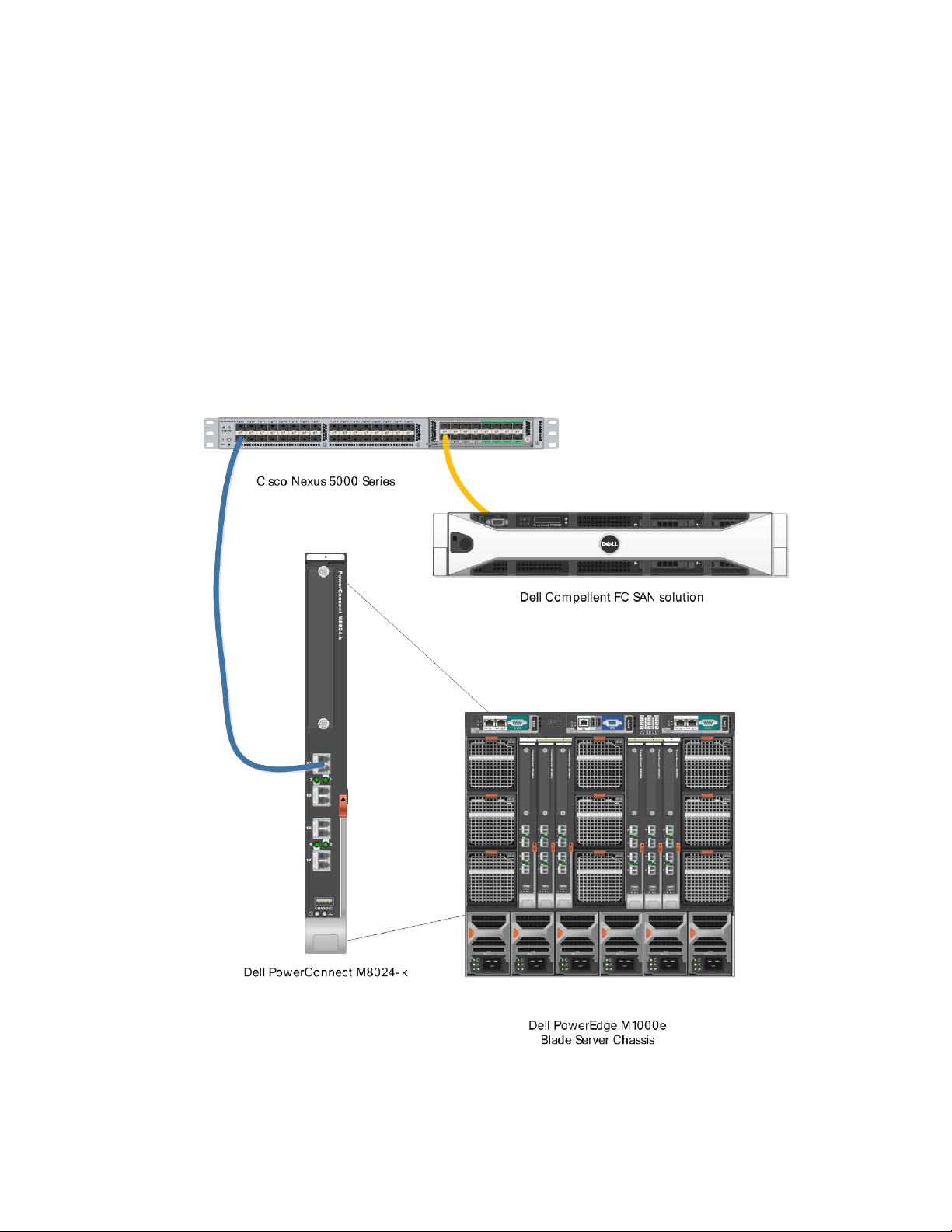
Scenario 1: Deploying the Dell PowerCo nnect 8024 Series FSB in a Cisco 5000 Series Switch (NPIV) environment
This first example is a basic, single connection between devices example using the Dell PowerConnect
M8024-k. This configuration is being shown for the purposes of simplification and potentially easing into
the progression of a more in-dep th setup. It is also easier to use a simple configuration such as this
setup to aid in troubleshooting of the initial install. In a typical business environment most
configurations will be scaled to include several connections between servers and storage . The scenarios
following this one will show some of these larger configurations. Note that this configuration will also
work in the rack server environment with Dell PowerConnect 8024F switch
Simple 1-link connection between devices Figure 5.
10
Page 11
Deploying FCoE (FIP Snooping) on Dell PowerConnect 10G Switches: M8024-k, 8024, and 8024F
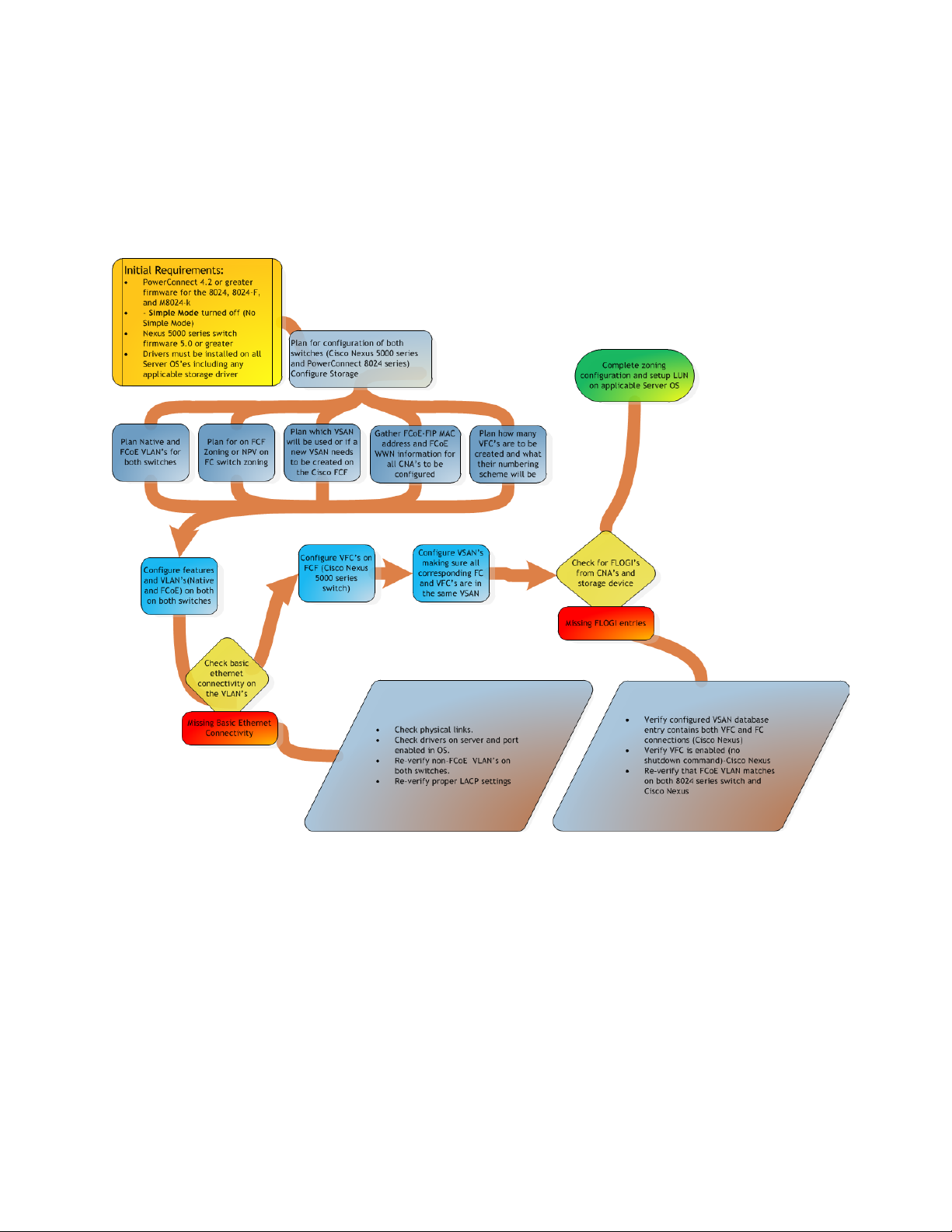
The flowchart in Figure 8 is a general overview of how the deployment will occur. This inclu d e s t he
basic planning that will need to take place in order for most of t he steps in the rest of the document to
fall into place.
General Overview of the whole configuration and planning procedure Figure 6.
11
Page 12
Deploying FCoE (FIP Snooping) on Dell PowerConnect 10G Switches: M8024-k, 8024, and 8024F
Figure 9 is a graphical represe n tation of how many of the configuration pieces are considered parallel
settings. Most of the configuration will depend heavily on configurations being comple ted in more than
just one place.
Overview of parallel configuration Figure 7.
In many of the business environments where this configuration will be installed there w ill be different
administrators for the diffe r e nt areas of the infrastructure. In other words there may be a LAN
infrastructure administrator, a storage or SAN administrator, and potentially a server administrator.
These different team member s will have to work together for a successful deployment of al l the
involved parts. In an M1000e bladeserver environment it may be the server admin that deploys t he
blade servers, operatings systems, net work adapter drivers, and very p ossibly configures the blade IOM
networking switches. If differ e n t admins are involved as described these tasks can be done in par allel
to enable a quicker deployment.
It is important to understand ce r tain checks or validations al on g the way may rely on configurat ions
being completed in a different part of the infrastructure.
12
Page 13

configure
Deploying FCoE (FIP Snooping) on Dell PowerConnect 10G Switches: M8024-k, 8024, and 8024F
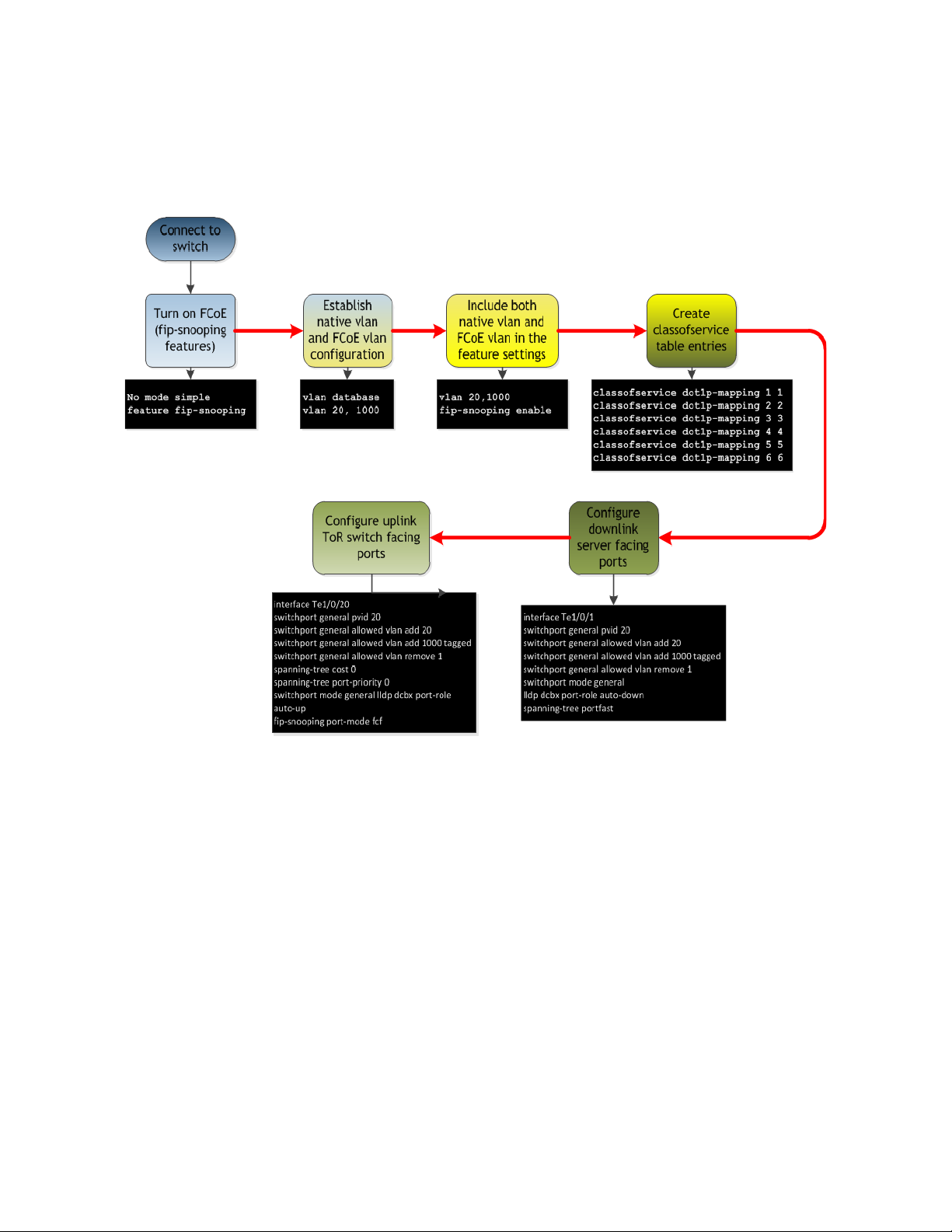
Configuring the Dell PowerConnect M8024-k,8024, and 8024F for FIP Snooping
The Dell PowerConnect 8024 model switches will monitor FIP packets and will establish the proper
filtering, and priorities f or the FCoE traffic that is passed t h rough the configured links. To see an
example of the full configuration see Appendix-A
Command-Line Interface Method
Example commands for Dell PowerConnect M8024-k (can be copied and pasted) Figure 8.
no mode simple
vlan database
vlan 20,1000
exit
hostname "mySwitch"
vlan database
vlan 20,1000
exit
feature fip-snooping
vlan 20,1000
fip-snooping enable
exit
interface out-of-band
ip address 192.168.10.1 255.255.255.0 192.168.10.254
exit
classofservice dot1p-mapping 1 1
classofservice dot1p-mapping 2 2
classofservice dot1p-mapping 3 3
classofservice dot1p-mapping 4 4
classofservice dot1p-mapping 5 5
classofservice dot1p-mapping 6 6
exit
interface Te1/0/1
switchport general pvid 20
switchport general allowed vlan add 20
switchport general allowed vlan add 1000 tagged
switchport general allowed vlan remove 1
switchport mode general
lldp dcbx port-role auto-down
spanning-tree portfast
exit
interface Te1/0/20
switchport general pvid 20
switchport general allowed vlan add 20
switchport general allowed vlan add 1000 tagged
switchport general allowed vlan remove 1
spanning-tree cost 0
spanning-tree port-priority 0
switchport mode general lldp dcbx port-role auto-up
fip-snooping port-mode fcf
exit
- M8024-K Example.
CAUTION: The “copy running-configuration startup-configuration” command should be issued after
several impacting steps so that the switch will retain the configuration settings put into place on
the next boot.
Routed VLAN’s can’t have FIP-snooping enabled. VLAN 1 may be set for routing and this must be
changed in the VLAN database if it is going to be used as the native VLAN or PVID.
13
Page 14

Deploying FCoE (FIP Snooping) on Dell PowerConnect 10G Switches: M8024-k, 8024, and 8024F
Step by Step explanation of CLI example
o Configure – this brings the prompt into the configuration interface
o no mode simple – puts switch into normal mode
o vlan database - moves down into the VLAN dat ab ase interface
vlan 20 – add VLAN 20 to u se d for untagged traffic or as the nat ive VLAN
vlan 1000 - add VLAN 1000 to the VLAN database, this will be the FCoE VLAN
exit – exit the current level of the inte r face configuration
o hostname “mySwitch” – set the hostname of the switch in this example “mySwitch”
o feature fip-snooping - this turns on the fip-snooping capab ility of the switch
o vlan 20,1000 – this moves the interface into vlan 20,1000
fip-snooping enable – this enables the fip-snooping capabilities on these p ar t icular
VLAN’s. Both must be included for the initial TLV negotiation to establish the FCoE
VLAN
exit – exit interfa ce configuration
o interface out-of-band – move into the interface out-of-band configuration inte rfa ce
ip address 192.168. 100.1 255.255.255.0 192.168.100.254 – this sets the out-of-
band management interface IP address, subnet, and gateway for the switch
exit – exit the interface configuration
o classofservice dot1p-mapping x x – establishes dire ct C oS mapping for the priorities (must be
in place for certain CNA’s
o interface te1/0/1 – this moves into the interface te1/0/1 configuration
switchport general pvid 20 – establishes the native VLAN as 20, you must r emove VLAN
1 in order for this to function correctly
switchport general allowed vlan add 20 - adds VLAN 20 the trunk as an untagged VLAN
switchport general allowed vlan add 1000 tagged – this sets up a trunk with a tagged
VLAN of 1000 (the FCoE VLAN), and includes the native VLAN as untagged if general
mode is enabled.
switchport general allowed remove vlan 1 – this removes vlan 1 which would typically
be the native vlan otherwise.
switchport mode general – this enables the port for general mode
lldp dcbx port-role auto-down – sets t h e DCBx port-role to be auto-down for an ENode
connection
spanning-tree portfast – sets the ports to a portfast b e h av ior since these are internal-
facing server ports.
exit – exits the interfa ce conf igu r ati on
14
Page 15

Deploying FCoE (FIP Snooping) on Dell PowerConnect 10G Switches: M8024-k, 8024, and 8024F
o interface te1/0/20 – this moves into the interface te1/0/20 configuration
switchport general pvid 20 – establishes the native VLAN as 20, you must r emove VLAN
1 in order for this to function correctly
switchport general allowed vlan add 20 - adds VLAN 20 the trunk as an untagged VLAN
switchport general allowed vlan add 1000 tagged - – this sets up a trunk with a
tagged VLAN of 1000 (the FCoE V LAN), and includes the native VL AN as untagged if
general mode is enabled.
switchport general allowed remove vlan 1 – this removes vlan 1 which would typically
be the native vlan otherwise.
switchport mode general – this enables the port for mode general
spanning-tree cost 0 – sets spanning tree cost to 0
spanning-tree port-priority 0 – sets this ports priority t o 0 so t hat it has the lowest
spanning tree priority in ca se a loop is created elsewhere on th e switch
lldp dcbx port-role auto-up – sets the DCBx port-role to be auto-up which dynamically
sets the configuration-source for an FCF connection
fip-snooping port-mode fcf – enables the port for fip-snooping fr om an FCF connection
exit - exits the interfa ce conf igu r ati on
exit – exits from con figuration mode
Critical steps: The “copy running-configuration startup-configuration” command should be issued
after important steps so that the switch will retain the configuration settings when the switch is
next rebooted or if a power los s occurs. It is also a good practice to copy a well-validated working
configuration to a separate location such as the management station for the networks, and have a
backup-configuration saved local to the switch.
Further explanation of key points:
• The spanning-tree settings in this example are established to keep the port from being
potentially blocked by spanning-tree. This could occur because anothe r cable is plugged into a
port with a lower priority, causing a loop. When the uplink port is set to 0 it will have the
lowest priority and therefore most likely not end up in a blocked state.
• A second key se tting to note is “switchport ge n e ral allowed vlan remove 1”. T his command
must be entered if you are choosing to use a different PVID or n at iv e V LAN. A port cannot have
two native VLANs. In this example the configuration is set to use VLAN 20 since typically the
recommendation is to have regular untagged traffic on a different VLAN other than just 1 for
segregation of the network. In addition when the FCF sends information to the fip-snooping
bridge (FSB) or M8024-k in this case, the M8024-k is receiving the initial information for
negotiation on its untagged vlan (vlan 20 in this case). Once the initial negotiations have
occurred properly the FCoE t r af fic will traverse the FCoE VLAN ( in this case VLAN 1000).
• The last configuration line “fip-snooping port-mod e fcf” is also ke y to this configuration. This
line establishes where the FCF is attached to the switch. With this setting the port is
configured to make Fibre Channel aware of the conne ct ion via this port to the forwarde r . The
previous line “lldp dcbx port-role auto-up“, is setting this port to be aware of DCBx T LV ’s, he
difference being the fip-snooping configurati on line points to the port for using fip-snooping
tohe FCF, and the lldp configur ation points to the point for doin g DCBx negotiations.
15
Page 16
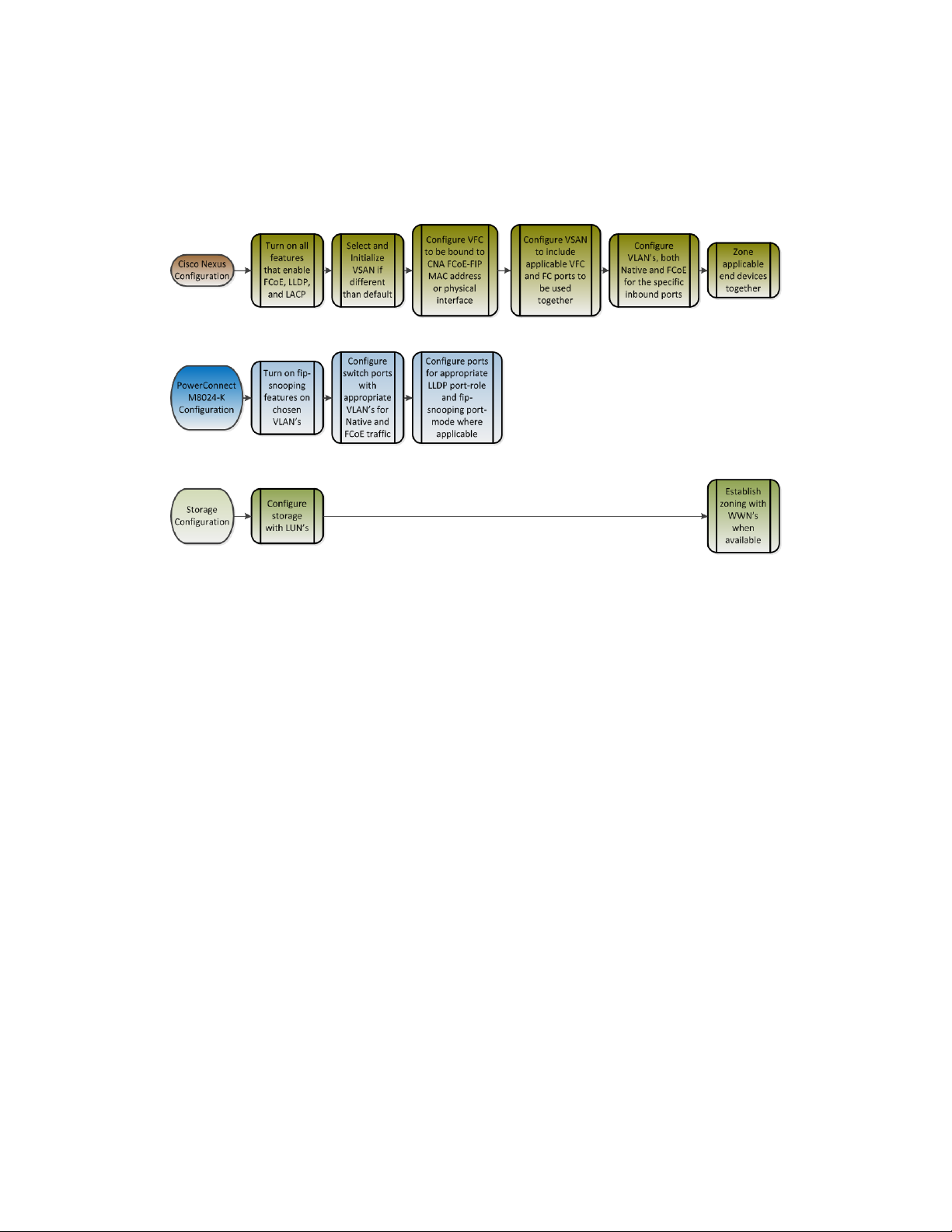
Deploying FCoE (FIP Snooping) on Dell PowerConnect 10G Switches: M8024-k, 8024, and 8024F
Configuration overview of Dell PowerConnect M8024-k Figure 9.
16
Page 17

feature fcoe
Deploying FCoE (FIP Snooping) on Dell PowerConnect 10G Switches: M8024-k, 8024, and 8024F
Configuring the Cisco 5000 series switch with firmware ver 5.x for a single connection from the Dell PowerConnect M8024-k or 8024()(F)
The CLI commands below are necessary for an un-configured Cisco 5020. The CLI will show additional
lines that are either default or can’t be changed and are not added f or t his example. The CLI will also
show the lines in a different order after they have been entered.
example will have a copy of the f u ll configuration for a 5548UP for reference.
Command-Line Interface Method
Sample CLI for Cisco Nexus 5020 (can be copied and pasted) Figure 10.
feature npiv
feature telnet
feature lacp
feature lldp
system default switchport trunk mode auto
vlan 20
vlan 1000
fcoe vsan 2
vsan database
vsan 2
vsan 2 interface vfc1
vsan 2 interface fc2/1
interface vfc1
bind interface Ethernet1/1
no shutdown
interface fc2/1
switchport trunk mode auto
no shutdown
interface Ethernet1/1
switchport mode trunk
switchport trunk native vlan 20
switchport trunk allowed vlan 1000
zone name blade1 vsan 2
member interface fc2/1
member pwwn xx:xx:xx:xx:xx:xx:xx:xx
zoneset name set1 vsan 2
member blade1
zoneset activate name set1 vsan 2
Appendix-A Cisco Nexus 5548UP CLI
17
Page 18

feature fcoe
Deploying FCoE (FIP Snooping) on Dell PowerConnect 10G Switches: M8024-k, 8024, and 8024F
The following CLI commands are necessary for an un-configured C isco Nexus 5548UP or Cisco Nexus
5596. The full CLI will show additional lines that are either default or can’t be changed and are not
added for this example. The CLI will also show the lines in a different order after th ey have been
entered. Appendix-A Cisco Nexus 5548UP CLI e xample
will have a copy of the full con f iguration.
Command-Line Interface Method
Sample CLI for Cisco Nexus 5548 (can be copied and pasted) Figure 11.
feature npiv
feature telnet
feature lacp
system default switchport trunk mode auto
system qos
service-policy type qos input fcoe-default-in-policy
service-policy type queuing input fcoe-default-in-policy
service-policy type queuing output fcoe-default-out-policy
service-policy type network-qos fcoe-default-nq-policy
vlan 20
vlan 1000
fcoe vsan 2
vsan database
vsan 2
vsan 2 interface vfc1
vsan 2 interface fc2/1
interface vfc1
bind interface Ethernet1/1
no shutdown
interface fc2/1
switchport trunk mode auto
no shutdown
interface Ethernet1/1
switchport mode trunk
switchport trunk native vlan 20
switchport trunk allowed vlan 1000
zone name blade1 vsan 2
member interface fc2/1
member pwwn xx:xx:xx:xx:xx:xx:xx:xx
zoneset name set1 vsan 2
member blade1
zoneset activate name set1 vsan 2
Note that the provided Cisco commands should be referenced in the Nexus 5000 Series NX-OS
SAN Switching Configuration Guide. The CLI entries above only cover the areas that must be added
to enable FCoE capabilities on th e p ar ticular ports being used of a Cisco Nexus 5020 and Nexus
5548. This topic will be covered after the Step by Step explanation of the CLI example.
18
Page 19

Deploying FCoE (FIP Snooping) on Dell PowerConnect 10G Switches: M8024-k, 8024, and 8024F
Step by Step explanation of the CLI example
Configure – t his brings you into the configu r ation interface.
o feature FCOE – enables the feature for FCOE as long as the licensing and FC modules are
installed.
o feature NPIV – enables the FC ports to accept multiple logins (Necessary for Compell e n t).
o feature LACP – enables the switch to be able to use port-channel groups in a LACP mode.
o feature LLDP – enables the switch to use LLDP which is needed for DCBx negotiations. Some
switch versions will have this on by default and the entry will not be needed.
o system qos
o service-policy type qos input fcoe-default-in-policy
service-policy type queuing input fcoe-default-in-policy
service-policy type queuing output fcoe-default-out-policy
service-policy type network-qos fcoe-default-nq-policy
- these are qos settings that are in place by default on the 5010 and 5020 Cisco Nexu s
switches. These settings will have to be input for the 5548 and 5596 Cisco Nexus
switches.
o system default switchport trunk mode auto – sets trunk mode to auto for FC port s; optionally
this can be set to off, or on if needed.
o vlan 20 – this is the VLAN to be used for the Native VLAN.
o vlan 1000 - this is the VLAN being used for FCoE in this example
fcoe vsan 2 – this establishes the previous VLAN 1000 as an FCoE VLAN in VSAN 2.
o vsan database – enter into the vsan database interface.
vsan 2 – initializes VS AN 2
vsan 2 interface vfc1 – set inte r f ace vfc1 to be part of VSAN 2
vsan 2 interface fc2/1 – set interface fc2/1 to be part of VSAN 2
o interface vfc1 – selects virtual fc interface vfc1 (vfc1 is an example an d can be a different
number based on the admin’s choice at configuration time).
Bind interface Ethernet1/1 – this binds interface Ethernet 1/1 to the virtual fc
interface which in this case is vfc1. This is one form of binding t he VFC. The other form
would be to bind the VFC to the FCoE FIP MAC address of the CNA being use d . Examples
of this will be included later in the document.
no shutdown – turns the virtual interface on since default is shutdown.
o Interface fc2/1 – selects the fc2/1 interface (which will t ypically be the first fibre channe l port
on the Nexus 5020.
no shutdown – turns the fc2/1 interface on since default is shutdown.
o interface Ethernet 1/1 – selects interface Ethernet 1/1
switchport mode trunk – set switchport mode to trunk for the 2 VLAN’s.
switchport trunk al lowed vlan 1000 – add allowed VLAN 1000 to the trunk.
19
Page 20

Deploying FCoE (FIP Snooping) on Dell PowerConnect 10G Switches: M8024-k, 8024, and 8024F
o Zone name blade1 vsan 2 – this will set the name for your zone (blade1 can be any chosen
name); vsan 2 will match the v san you have created.
Member interface fc2/1 - this adds the fc2/1 interface as a memb e r of the zone.
member pwwn xx:xx:xx:xx:xx:xx:xx:xx – adds the port WWN of the ENode device to
the zone. (insert the port WWN of the device being used).
o zoneset name set1 vsan 2 – move into the zoneset int e r face (in this case the name is set1 but
could be any name and the VSAN number is based on the FCoE VLAN being used.
member blade1 – this includes the blade1 zone into this zoneset.
o zoneset activate name set1 vsan 2 – activates the zoneset containing these zones.
Further explanation of key points:
• In order for devices to communicate end-to-end they must participate in the same VSAN. In this
sample configuration the VFC is b ou nd to either the FCoE FIP MAC Add r ess of the Converged
Network Adapter in the blade server or an actual interface that would be a connection from
the modular switch (in this case M8024-K) connecting the blade servers. The recommended
configuration for this is to bind to the FCoE FIP MAC address of the CNA.
However, as an easy setup step it is possible to b in d a VFC to the physical interface or portchannel in order to determine which FCoE FIP MAC addresses will present from the CNA’s.
These can be noted and then matched with the M1000e’s CMC -> Server Overview -> WWN/MAC
Summary that can be seen in Figure 15 on the next page. This is applicable only to the M8024-k
modular switch with blade ser v e rs. For the rack-mounted 8024 switches the CNA’s would need
to be verified on the servers th e mselves. This verification can be done through each adapters
driver properties in the dif f e r e n t operating systems.
Cisco Nexus 5000 series configuration sequence Figure 12.
20
Page 21

Deploying FCoE (FIP Snooping) on Dell PowerConnect 10G Switches: M8024-k, 8024, and 8024F
M1000e Chassis Management Controller -> Server Overview -> Properties -> Figure 13.
WWN/MAC information for Blade Server 3’s “B” fabric CNA port 2 (B2).
21
Page 22

Deploying FCoE (FIP Snooping) on Dell PowerConnect 10G Switches: M8024-k, 8024, and 8024F
Basic Validation for the Cisco Nexus 5000 series switch configuration
With connections made via fib e r optic cable or direct connect cab le (twin-ax) the basic connectivit y on
the port between the two switches can be verified. These cables or SFP+ transceivers must only be
Cisco-branded products for the Cisco Nexus to link properly. T he following command is used to give a
port status overview:
SHOW INTERFACE BRIEF. This example has been shortened from the actual results
but will display the results of active ports and VFC interfaces. Verify that the ports which are e xp e cted
to have links show up correctly.
Example of show interface brief command Figure 14.
Demo5548-1# show interface brief
------------------------------------------------------------------------------Interface Vsan Admin Admin Status SFP Oper Oper Port
Mode Trunk Mode Speed Channel
Mode (Gbps)
------------------------------------------------------------------------------fc1/31 2 auto auto up swl F 4 -fc1/32 2 auto auto up swl F 4 --
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------Ethernet VLAN Type Mode Status Reason Speed Port
Interface Ch #
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------Eth1/1 20 eth trunk up none 10G(D) 2
Eth1/2 20 eth trunk up none 10G(D) 2
Eth1/3 1 eth access up none 10G(D) -Eth1/4 1 eth access down SFP not inserted 10G(D) -Eth1/5 1 eth access down SFP not inserted 10G(D) -Eth1/6 1 eth access down SFP not inserted 10G(D) –
*rest of the ports removed for sizing
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------Port-channel VLAN Type Mode Status Reason Speed Protocol
Interface
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------Po2 20 eth trunk up none a-10G(D) lacp
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------Port VRF Status IP Address Speed MTU
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------mgmt0 -- up 172.25.188.100 1000 1500
------------------------------------------------------------------------------Interface Vsan Admin Admin Status SFP Oper Oper Port
Mode Trunk Mode Speed Channel
Mode (Gbps)
------------------------------------------------------------------------------vfc1 2 F on trunking -- TF auto -vfc3 2 F on down -- -- -vfc4 2 F on trunking -- TF auto -vfc5 2 F on down -- -- -vfc6 2 F on trunking -- TF auto -vfc7 2 F on down -- -- -vfc8 2 F on trunking -- TF auto -- TF auto --
22
Page 23

Deploying FCoE (FIP Snooping) on Dell PowerConnect 10G Switches: M8024-k, 8024, and 8024F
Demo-5020-1# show spanning-tree summary
Demo-5020-1# show flogi database
Demo-5020-1# show zoneset active
Check the spanning tree configuration. Blocking ports should be understood and when they show in this
entry it should be the number expected. Otherwise it could be that an unintentional cable loop has
been created that will need to be resolved. Type :
SHOW SPANNING-TREE SUMMARY
show spanning-tree summary command showing current configuration with Figure 15.
ports states
Switch is in rapid-pvst mode
Root bridge for: VLAN0001
Port Type Default is disable
Edge Port [PortFast] BPDU Guard Default is disabled
Edge Port [PortFast] BPDU Filter Default is disabled
Bridge Assurance is enabled
Loopguard Default is disabled
Pathcost method used is short
Name Blocking Listening Learning Forwarding STP Active
---------------------- -------- --------- -------- ---------- ---------VLAN0001 0 0 0 1 1
---------------------- -------- --------- -------- ---------- ---------1 vlan 0 0 0 1 1
Next, verify that negotiations have happened properly between the FCF and end devices, in this case
the Cisco Nexus 5020 is the FCF. Type :
SHOW FLOGI DATABASE
show flogi database command showing devices that have completed fabric login Figure 16.
----------------------------------------------------------------------INTERFACE VSAN FCID PORT NAME NODE NAME
-----------------------------------------------------------------------
fc2/1 2 0xc6000c 20:04:00:20:c2:10:ab:cd 10:00:00:20:c2:10:ab:cd
vfc1 2 0xc60009 20:01:14:fe:b5:07:12:34 20:00:14:fe:b5:07:12:34
Total number of flogi = 2.
At this point the VFC and FC interfaces should be populated in the FLOGI database. This command is
showing the devices that have done a valid FLOGI (fabric login) t o the Cisco Nexus switch. The VFC
should show the expected port and node WWN of the CNA being used in the server.
The following command will show the status of the zones that have been put into place. The asterisks
will indicate devices that have an established session (hav e n e g otiated and logged in) with the Cisc o
Nexus 5020. Type :
SHOW ZONESET ACTIVE. This command will show the current activated zoneset and all
the participating zones with their individual members.
Example of show zoneset active command Figure 17.
zoneset name set1 vsan 2
zone name blade1 vsan 2
* fcid 0xc6000c [interface fc2/1 swwn 20:00:00:05:73:ab:12:34]
* fcid 0xc60009 [pwwn 20:01:14:fe:b5:07:12.34]
Basic Validation for the PowerConnect M8024-k configuration
23
Page 24

Deploying FCoE (FIP Snooping) on Dell PowerConnect 10G Switches: M8024-k, 8024, and 8024F
With all cables in place between the switches and the FC/FCoE SAN, use the following commands to
validate your configuration.
First check general status of t he ports, and links by using:
SHOW INTERFACE ST ATUS
Show interface status results Figure 18.
PowerConnectM8024-k#show interfaces status
Port Name Duplex Speed Neg Link Flow Control
State Status
--------- ------------------------- ------ ------- ---- ------ -----------Te1/0/1 N/A Unknown Auto Down Inactive
Te1/0/2 N/A Unknown Auto Down Inactive
Te1/0/3 Full 10000 Auto Up Inactive
Te1/0/4 N/A Unknown Auto Down Inactive
Te1/0/5 Full 10000 Auto Up Inactive
Te1/0/6 N/A Unknown Auto Down Inactive
Te1/0/7 Full 10000 Auto Up Inactive
Te1/0/8 N/A Unknown Auto Down Inactive
Te1/0/9 N/A Unknown Auto Down Inactive
Te1/0/10 N/A Unknown Auto Down Inactive
Te1/0/11 Full 10000 Auto Up Active
Te1/0/12 Full 10000 Auto Up Inactive
Te1/0/13 N/A Unknown Auto Down Inactive
Te1/0/14 N/A Unknown Auto Down Inactive
Te1/0/15 N/A Unknown Auto Down Inactive
Te1/0/16 N/A Unknown Auto Down Inactive
Te1/0/17 N/A Unknown Auto Down Inactive
Te1/0/18 N/A Unknown Auto Down Inactive
Te1/0/19 Full 10000 Off Up Inactive
Te1/0/20 Full 10000 Off Up Inactive
Oob Type Link
State
--- ------------------------------ ----oob Out-Of-Band Up
Port Type Link
State
----- ------------------------------ ------Po1 Link Aggregate Down
Po2 Link Aggregate Up
• - Po3-127 removed from example for spacing
Po128 Link Aggregate Down
Flow Control:Enabled
24
Page 25

Deploying FCoE (FIP Snooping) on Dell PowerConnect 10G Switches: M8024-k, 8024, and 8024F
PowerConnectM8024-k#show fip-snooping
With the
SHOW SPANNING-TREE BLOCKEDPORTS command the status of ports that may be impacted by
spanning tree can be checked. This is also a good point to make sure that the spanning-tree behaviors
are as expected, such as Priorit y, which switch is root, etc.
show spanning-tree blockedports command Figure 19.
PowerConnectM8024-k#show spanning-tree blockedports
Spanning tree Enabled (BPDU flooding : Disabled) mode rstp
CST Regional Root: 80:00:5C:26:0A:AD:0C:39
Regional Root Path Cost: 0
###### MST 0 Vlan Mapped: 1, 20, 1000
ROOT ID
Priority 32768
Address 5C26.0AAD.0C39
This Switch is the Root.
Hello Time 2 Sec Max Age 20 sec Forward Delay 15 sec
Interfaces
Name State Prio.Nbr Cost Sts Role RestrictedPort
------ -------- --------- --------- ---- ----- --------------
On the PowerConnect M8024-k, 8024 or 8024F the sessions can be check e d b y using:
SHOW FIP-SNOOPING. This will show the VLAN’s that are snooped and configured, along with how many
FCF’s, and ENode devices that are available. If there is no entry or “0” FCF’s or ENode’s after ru n ning
this command there is possibly a missed step in the configurati on. Proceeding beyond this point will not
be possible until this confi guration error is corrected.
Show fip-snooping command which gives a brief status on available ENode’s, Figure 20.
Global Mode: Enabled
FCoE VLAN List: 20,1000
FCFs: 1
ENodes: 1
Sessions: 2
Max VLANs: 8
Max FCFs in VLAN: 4
Max ENodes: 72
Max Sessions: 1024
and FCF’s
25
Page 26

Deploying FCoE (FIP Snooping) on Dell PowerConnect 10G Switches: M8024-k, 8024, and 8024F
Te1/0/20 Enabled Auto-up Auto 22706 22865 0 0
The following command wil l show a set of vital information on the DCBX configuration. Type:
LLDP DCBX INTERFA CE ALL
. The important things to note with this command are that the configuration
SHOW
source selected is “True” and t h at the configuration source port is configured as expected to be the
uplink to the top-of-rack FCF switch. It can also be noted that ports that are expected to b e passing
DCBX traffic should have coun t e r statistics listed here.
show lldp dcbx interface all Figure 21.
PowerConnectM8024-k#show lldp dcbx interface all
Is configuration source selected............... True
Configuration source port...................... Te1/0/19
DCBX DCBX DCBX unknown
Interface Status Role Version Tx Rx Errors TLV
---------- -------- ------------- --------- ----- ----- ------ ------Te1/0/1 Enabled Auto-down Auto 0 0 0 0
Te1/0/2 Enabled Auto-down Auto 0 0 0 0
Te1/0/3 Enabled Auto-down Auto 22710 22562 1 0
Te1/0/4 Enabled Auto-down Auto 0 0 0 0
Te1/0/5 Enabled Auto-down Auto 22420 22151 0 0
Te1/0/6 Enabled Auto-down Auto 0 0 0 0
Te1/0/7 Enabled Auto-down Auto 22451 22292 0 0
Te1/0/8 Enabled Auto-down Auto 33 0 0 0
Te1/0/9 Enabled Auto-down Auto 22 35 0 0
Te1/0/10 Enabled Auto-down Auto 0 0 0 0
Te1/0/11 Enabled Auto-down Auto 17175 0 0 0
Te1/0/12 Enabled Auto-down Auto 17179 17310 0 0
Te1/0/13 Enabled Auto-down Auto 0 0 0 0
Te1/0/14 Enabled Auto-down Auto 0 0 0 0
Te1/0/15 Enabled Auto-down Auto 0 0 0 0
Te1/0/16 Enabled Auto-down Auto 0 0 0 0
Te1/0/17 Enabled Manual Auto 0 0 0 0
Te1/0/18 Enabled Manual Auto 0 0 0 0
Te1/0/19 Enabled Auto-up Auto 22707 22861 0 0
The highlighted port lines show the ports that are actively taking part in FCoE traffic. The role shown
by each of the server facing ports should always be auto-down, while the role for the uplinks to the
FCF should be auto-up or configuration source. The re should be both DCBX Tx counters as well as DCBX
Rx counters to show that the negotiations actually occurred with the particular devices.
26
Page 27

Deploying FCoE (FIP Snooping) on Dell PowerConnect 10G Switches: M8024-k, 8024, and 8024F
The following command wil l show a set of vital information on the DCBX configuration. Type:
LLDP DCBX INTERFA CE TE
1/0/20 DETAIL. This command will show more specific detail about the
SHOW
configuration that has been negotiated between the devices. In this example port te1/0/20 is used as it
is one of the uplink ports into the top-of-rack FCF switch.
Some key items in these results will be “true” for peer is configuration sour ce, “Auto-up” for autoconfiguration port role and local configuration PFC(3) En/Will/Error configured as Y /Y/N. As an
additional note you should al so see PFC enable vector: 3:1, this shows that priority queue 3 is set as
“strict” and will be lossless.
Show lldp dcbx interface te1/0/20 detail Figure 22.
27
Page 28

Deploying FCoE (FIP Snooping) on Dell PowerConnect 10G Switches: M8024-k, 8024, and 8024F
Finally, after these validation steps, go into the disk management interface of the server. If the SAN is
configured appropriately the server will have an available LUN to use for storage.
Basic Troubleshooting Areas
Problem Potential Problem Area Potential Fix
Basic Connectivity Between CNA and
8024 Series switch is not present (ping
between devices)
Cable is not connected or is failing
The OS on the server is not
configured to have the network card
enabled or active
The driver for the applicable OS is
not loaded
Internal server facing ports on the
M8024-k may not be enabled (no
shutdown)
External or regular ports on the 8024
series switch or Cisco Nexus 5000
series switch may not be enabled (no
shutdown)
Untagged or Native VLAN's are not
configured appropriately. If PVID is
changed on 8024 series, VLAN 1 must
be removed
Connect or Change cable and
reconnect
Check adapter settings in the OS and
verify ports turned on or enabled
Load driver and ensure both Ethernet
and storage device drivers are in
place for CNA (if applicable)
Determine which internal ports
should be enabled and configure the
ports on with the "no shutdown"
command
Determine which external ports
should be enabled and configure the
ports on with the "no shutdown"
command
Configure Native VLAN's
appropriately. See PowerConnect
8024 CLI section or Cisco Nexus 5000
series CLI section for detail on this.
ENode's or FCF entries are not present
on the PowerConnect 8024 series switch
ENode's or FCF entries are not present
on the PowerConnect 8024 series switchcontinued -
See above basic connectivity
problems see above
Applicable FCoE or storage driver is
not configured in the server OS for
the CNA
CNA may not be configured as willing
(will negotiate values with the FCF
switch)
PowerConnect 8024 may not have
appropriate firmware in place, it
must be 4.2.0.4 or greater
Cisco Nexus 5000 series switch may
not have the supported firmware in
place. Must be 5.0(2)N1(1) or
greater
Feature FCoE may not be configured
on Cisco Nexus 5000 series switch
fip-snooping may not be enabled on
the native and FCoE VLAN on the
Dell PowerConnect 8024 series
switch
This could be an indication that the
storage side of the CNA driver has not
been fully installed.
Some CNA's have the option to
configure the DCB settings manually.
This will potentially cause
misbehavior due to the DCBX
negotiations not occurring as
expected.
Download and install firmware
4.2.0.4 or greater see upgrade
firmware section
Download and install latest Cisco
firmware.
Ensure FCoE feature is configured on
Nexus 5000 Series switch
See PowerConnect 8024 CLI section
for explanation of enabling both
VLAN's for fip-snooping
28
Page 29

Deploying FCoE (FIP Snooping) on Dell PowerConnect 10G Switches: M8024-k, 8024, and 8024F
Verify above section on ENode’s or
Storage license for Cisco Nexus may
Check licenses on Cisco Nexus and
Cisco Nexus may be configured for
Check configuration of Cisco Nexus. If
Problem Potential Problem Area Potential Fix
Ensure that VFC's are created that
will be applicable to the connection.
This can be bound to the FCoE-FIP
MAC of the CNA or to the physical
interface of the Cisco Nexus 5000
Series switch
Check VFC entries applicable to the
connection and make sure "no
shutdown" is part of the configuration
for that interface
The same tagged VLAN should pass
FCoE traffic from the PowerConnect
8024 series switch to the Cisco Nexus
5000 series switch. Configure this
VLAN appropriately - see CLI
explanation sections
Configure feature LACP on the Cisco
Nexus, and make sure the applicable
port-channel is put into the
configuration - see CLI explanation
sections for further detail
See PowerConnect 8024 CLI section
for explanation of applying this
configuration
See CNA documentation for
applicable partition settings for FCoE
use
The VFC entries may not be present
on the Cisco Nexus 5000 series
switch
The VFC entry may not be enable (no
shutdown)
The FCoE VLAN may not match on
both sides (PowerConnect 8024 and
Cisco Nexus 5000 series tagged VLAN
entries matched to the FCoE
feature)
LACP feature may not be enabled on
Cisco Nexus 5000 series switch for
applicable LAG's between the two
switches
Configuration classofservice dot1pmapping may not be in place on the
PowerConnect switch
CNA’s that have NPAR capabilities
may not have the partitions
configured appropriately for FCoE
FLOGI entries for CNA's are not present
on Cisco Nexus 5000 series switch
FLOGI entries for FC devices are not
present on Cisco Nexus 5000 series
switch
See above basic connectivity
problems see above
FCF present on PowerConnect 8024
series switch
Cable is not connected or is failing
not be installed.
End storage device is not powered
on Power on Storage device
Storage device is not configured to
communicate with FCF or FC switch
FC port on Cisco Nexus not
configured
NPV which allows for the logins to
occur on FC switch further
downstream
see above
Connect or Change cable and
reconnect
install if necessary
Configure storage device to have
applicable settings
Configure FC ports for particular
storage device and turn on (no
shutdown)
configured for NPV check for FLOGI
logins on the FC switch that the Cisco
Nexus is connected to.
29
Page 30

Deploying FCoE (FIP Snooping) on Dell PowerConnect 10G Switches: M8024-k, 8024, and 8024F
Scenario 2: Configuring Multiple Uplinks into LAG for Cisco Nexus 5000 Series Switch (NPIV) Environment
Multiple port link (LAG) configuration between switches and storage Figure 23.
30
Page 31

Deploying FCoE (FIP Snooping) on Dell PowerConnect 10G Switches: M8024-k, 8024, and 8024F
Configuring the Cisco Nexus 5000 series sw it c h w it h firmware ver 5.x for a multiple link LAG (link aggregation) connection at the Top-of-Rack.
The typical scenario in a busin ess environment consists of more than one connection or uplink. The
following illustrations and examples describe a two link LAG from an M8024-k to the Cisco Nexus 5020.
Command-Line Interface Method
Multiple port link (LAG) Cisco 5020 configuration (can be copied and pasted) Figure 24.
31
Page 32

Deploying FCoE (FIP Snooping) on Dell PowerConnect 10G Switches: M8024-k, 8024, and 8024F
Step by Step explanation of CLI example (only covering the differences from the single port configuration)
o interface vfc1 – selects virtual fc interface vfc1 (vfc1 is an example and can be a different number based on choice
at configuration time)
bind interface port-channel1 – this binds interface port-channel1 to the virtual fc interface which in this case
is vfc1.
no shutdown – turns the virtual interface on since default is shutdown
o interface fc2/2 – selects the fc2/2 interface (this is an additional FC port for the 2 connections
no shutdown – turns the fc2/1 interface on since default is shutdown
o interface Ethernet 1/1 – selects interface Ethernet 1/1
switchport mode trunk – set switchport mode to trunk for the 2 VLAN’s
switchport trunk native vlan 20 – add native VLAN 20 to the trunk
switchport trunk al lowed vlan 1000 – add allowed VLAN 1000 to the trunk
channel-group 1 mode active – this in t erface is part of a port channel 1
o interface Ethernet 1/2 – selects interface Ethernet 1/2
switchport mode trunk – set switchport mode to trunk for the 2 VLAN’s
switchport trunk native vlan 20 – add native VLAN 20 to the trunk
switchport trunk al lowed vlan 1000 – add allowed VLAN 1000 to the trunk
channel-group 1 mode active – this in t erface is part of port channel 1
o zone name blade1 vsan 2 – this will set the name for your zone (blade1 can be any chosen name), vsan
2 will match the vsan you have created.
member interface fc2/1 - this adds the fc2/1 interface as a member of the zone.
member pwwn xx:xx:xx:xx:xx:xx:xx:xx – adds the port WWN of the ENode device to the zone
(this should match the CNA of the se r ver being used, in this case bl ad e 2).
o zone name blade2 vsan 2 – this will set the name for your zone (blade1 can be any chosen name), vsan
2 will match the vsan you have created.
member interface fc2/2 - this adds the fc2 /1 interface as a member of the zone.
member pwwn xx:xx:xx:xx:xx:xx:xx:xx – adds the port WWN of the ENode device to the zone
(this should match the CNA of the se r ver being used, in this case bl ad e 2).
o zoneset name set1 vsan 2 – move into the zoneset in t e r f ace (in this case the name is set1 but could be
any name and the VSAN number is based on the FCoE VLAN being used.
member blade1 – this includes the blade1 zone into this zoneset
member blade2 – this includes the blade2 zone into this zoneset
o zoneset activate name set1 vsan 2 – activates the zoneset containing these zones.
32
Page 33

Deploying FCoE (FIP Snooping) on Dell PowerConnect 10G Switches: M8024-k, 8024, and 8024F
Configuring the M8024-k,8024, and 8024F for FIP Snooping
This is an example of the necessary CLI commands for 8024 model switches configured with two links in
a LAG or port-channel uplinked t o the Cisco 5020. This provides m or e b andwidth and fail-over
capability which would be mor e typical in the larger scale infrastructure typically used.
Command-Line Interface Method
Multiple port uplink (LAG) M8024-k configuration (can be copied and pasted) Figure 25.
33
Page 34

Deploying FCoE (FIP Snooping) on Dell PowerConnect 10G Switches: M8024-k, 8024, and 8024F
Step by Step explanation of Dell PowerConnect M8024-k CLI example with multiple port (LAG) uplink (this only covers the differences from the single port configuration).
o interface te1/0/19 – this moves into the interface te1/0/19 configuration
channel-group 1 mode active – adds this interface to the channel-group 1
lldp dcbx port-role auto-up – sets the DCBX port-role to be auto-up for an FCF connection
exit - exit the interface configuration
o interface te1/0/20 – this moves into the interface te1/0/20 configuration
channel-group 1 mode active – adds this interface to the channel-group 1
lldp dcbx port-role auto-up – sets the DCBX port-role to be auto-up for an FCF connection
exit - exit the interface configuration
o interface port-channel 1 – this moves into the interface te1/0/20 configuration
switchport general allowed vlan ad d 1 000 tagged - – this sets up a trunk with a tagged VLAN of
1000 (the FCoE VLAN), and includes the native VLAN as untagged if general mode is enabled.
switchport mode general – this enables the port for mode general
fip-snooping port-mode fcf – enables the port for fip-snooping from an FCF connection
exit - exit the interface configuration
o exit – exit from configuration mode
Validation
Follow the same validation steps as mentioned with the single link steps to ensure that this
configuration is working correctly. The ideal method for troubleshooting or validation is to take one
link at a time.
34
Page 35

Deploying FCoE (FIP Snooping) on Dell PowerConnect 10G Switches: M8024-k, 8024, and 8024F
Scenario 3: Configuring Multiple Uplinks into LAG for Cisco Nexus 5000 Series Switch (NPV mode) Environment
Multiple link configuration between switches and storage Figure 26.
35
Page 36

Deploying FCoE (FIP Snooping) on Dell PowerConnect 10G Switches: M8024-k, 8024, and 8024F
Configuring the Cisco Nexus 5000 series switch with firmware ver 5.0(3)N2(2a) in NPV mode for a multiple link LAG (link aggregation) connection from the Dell PowerConnect M8024-k or 8024()(F)
The typical scenario in a busin ess environment consists of more than one connection or uplink. The
following pictures and examp le s d escribe a two link LAG from an M8024-k to the Cisco 5020.
Command-Line Interface Method
Multiple port link Cisco 5020 configuration (can be copied and pasted) Figure 27.
36
Page 37

Deploying FCoE (FIP Snooping) on Dell PowerConnect 10G Switches: M8024-k, 8024, and 8024F
! Default priority is 0 (CoS queue 0). Untagged frames receive the default priority
Step by Step explanation of CLI example for the Cisco Nexus 5000 Series using NPV (only covering the differences from the single port configuration)
o feature NPV– enables the NPV feature which turns off zoning. The FC side of the Nexus 5000 series
switch effectively turns in to just a FC gateway (just passing FC out to another switch). When this
feature is enabled the Cisco Ne xus 5000 series switch will have to do a full reload because it is
completely changing the way it deals with the FC packet behavior. Be prepared for this reload
because it may impact a currently running network environment.
Configuring the Dell PowerConnect M8024-k,8024,and 8024F for FIP Snooping with Cisco Nexus 5000 series switch in NPV mode.
The configuration will be the same as previously mentioned in the single or multiple port
configurations. The simplicity of the PowerConnect 8024 se ries switch setup for FIP Snoo p ing is one of
the great advantages to using this in an FCoE network.
ETS Behavior and CoS configurations on the PowerConnect 8024 series switches
The 8024 family devices will pass ETS information between end devices and the FCF but local settings
are not changed in the 8024 series switches. This proce ss allows for a best effort appr oach in the
default configuration. This will be sufficient for the typical business usage model but for more in-depth
settings the following CoS settings can be set in order to apply exact minimum thresholds for the
queues that will be used for FCoE or iSCSI. These minimum thresholds are a guaranteed minimum
bandwidth for the queues involved, in this case priority queue 3 for FCoE or 4 for iSCSI. The following
example is applicable to the FCoE class of service queue 3 settings. (These settings can also be found in
the appendix in the full CLI example
.)
CoS settings to establish minimum bandwidth for FCoE queue Figure 28.
treatment.
!
interface range te1/0/1-16
! Set CoS queue 3 to strict priority (not WRED) per 802.1Qaz
cos-queue strict 3
! Reserve 50% bw for CoS queue 3
cos-queue min-bandwidth 0 0 0 50 0 0 0
exit
interface te1/0/20
! Set CoS queue 3 to strict priority (not WRED) per 802.1Qaz (traffic selection class 0)
cos-queue strict 3
! Reserve 50% bw for CoS queue 3 - other queues are best effort.
! This bandwidth is shared with other queues if not used
cos-queue min-bandwidth 0 0 0 50 0 0 0
Exit
NOTE: In the above example the first setting is made on inte r faces te1/0/1 through 16. These are
all the internal server-facing ports on the M8024-k modular switch. The settings for te1/0/20 are
based on this port being an uplink from the M8024-k modular switch to the Cisco Nexus 500 0 se ries
switch. As mentioned above the full configuration with these settings in place can be seen in
the Appendix A – M8024-k CLI example
.
37
Page 38

Deploying FCoE (FIP Snooping) on Dell PowerConnect 10G Switches: M8024-k, 8024, and 8024F
Further notes on ETS / CoS behavior settings
Careful consideration should be taken when establishing the strict priority queues and managing
bandwidth reservations. It FCoE and iSCSI are configured on t h e same switch and these settings are
used to configured both CoS queues it is possible to choke the bandwidth being allowed for regular LAN
traffic. As a suggested meth od limiting the queues for these p r iorities to 30 or 40 percent would keep
this from occurring. The pre fe r r ed method for configuration is fabric separation or in simpler term s;
separating the two storage typ e s onto different switches for ease of management and bandwidth
control.
Fabric separation as preferred method for management of networks and Figure 29.
storage
38
Page 39

Deploying FCoE (FIP Snooping) on Dell PowerConnect 10G Switches: M8024-k, 8024, and 8024F
PowerConnectM8024-k #show version
1 4.1.0.9 4.1.0.6 image1 image1
Updating firmware
NOTE:. Be sure to check the Release Notes and any special instructions that may have come wit h
new firmware updates. It is important to follow instructions found in those documents if t hey
deviate from this white paper.
Steps for upgrading the firmwar e on a stack of switches are similar to upgrading the firmware on a
single switch. After downloading a new image to the Master by using the File Download page in the
Web UI or the copy command in the CLI, the downloaded image is distributed to all member units of
the stack. The instructions below will guide you through these steps.
Command-line interface method
To find the firmware version t h e switch is using, enter the follow ing command: show version
Image Descriptions
image1 : default image
image2 :
Images currently available on Flash
unit image1 image2 current-active next-active
----- ------------ ------------ ----------------- -----------------
The commands below demonstrate how to copy the firmware file down to the switch via a TFTP se r ver.
The switch will need access to the TFTP server on the network and the firmware file will need to be
present in the download folder of the TFTP server. Perform the follow in g command from the CLI
interface. Press Y when prompted.
Be patient as this procedure may take a few minutes
39
Page 40

Deploying FCoE (FIP Snooping) on Dell PowerConnect 10G Switches: M8024-k, 8024, and 8024F
boot system image2
show version
console#update bootcode
Perform another show version com mand to confirm that the new firmware has been downloaded to
the switch. Notice that the firmware w as copied into the inactive image for each member.
console#
Images currently available on Flash
unit image1 image2 current-active next-active
----- ------------ ------------ ----------------- ----------------1 4.1.0.9 4.2.0.4 image1 image1
The current-active column now shows the same v alues as the next-active column. T h e next step is to
activate the image that contains the new firmware. In this example, the switch will need image2
activated. Perform the fol lowing commands.
console#
Activating image image2 ..
Images currently available on Flash
unit image1 image2 current-active next-active
----- ------------ ------------ ----------------- ----------------1 4.1.0.9 4.2.0.4 image1 image2
Notice that the next-active column now shows different values than the current-active column.
Before performing the following update bootcode command, read the Release Notes and any special
instructions for updating t h e f irmware release. It is generally required that you update boot code only
on major releases of the firmw are, whereas minor releases w ill not require the update to bootcode. It
is recommended to only run t his command if required. Press Y when prompted.
Update bootcode and reset (Y/N)?Y
Issuing boot code update command... Validating boot code from image...CRC
Valid.
Updating and rebooting the switch will take a few minutes. If the bootcode is not r e q uired, then a
simple reload command will need to be performed. After reload, the firmware upgrade is complete.
40
Page 41

Deploying FCoE (FIP Snooping) on Dell PowerConnect 10G Switches: M8024-k, 8024, and 8024F
show version
To validate, login to the swit ch and perform a show version command. For t he example given the
following is displayed.
console#
Images currently available on Flash
unit image1 image2 current-active next-active
----- ------------ ------------ ----------------- ----------------1 4.1.0.9 4.2.0.4 image2 image2
While downgrading to a previous firmware is supported, all features and functions that were not p ar t
of the previous firmware will be lost, including those features and functions that were introduced in
the current firmware in use. Firmware version 4.2 or later must be active on all switches or st ack
members in order for stackin g and DCB to work. Do not downgrade a switch or stack to firmware
version 4.1.x.x or earlier.
Web interface method
Find the firmware versions that the st ack members are using.
1. Select System > File Managemen t > Active Images.
2. Look in the Current-Active column to find which images are enabled
3. Since image2 is active, look in t he Image 2 Version column to see what version each stack
member is at. These firmware ve rsions being used should be the same across all stack member
units.
The commands below demonstrate how to copy the firmware file down to the switch via a TFTP se r ver.
The switch will need access to the TFTP server on the network and the firmware file will need to be
present in the download folder of the TFTP server. If other methods are preferable over TFTP please
see the User’s Guide. Perform the following steps:
1. Select System > File Management > File Download.
2. Select Firmware for the File Type and TFTP for the Transfer Mode.
41
Page 42

Deploying FCoE (FIP Snooping) on Dell PowerConnect 10G Switches: M8024-k, 8024, and 8024F
3. Enter the IP address of the TFTP server into the Server Address field, and enter the name of
the Firmware file into the Source File Name field.
4. If not in the root directory of th e T FT P server, enter the path of the firmware file.
5. Click Apply.
The dialog box below will appear after a short period stating that the transfer is complete.
6. Click Close.
7. Select System > File Management > Active Images.
Notice that the firmware (i.e. 4.2. 0.4) was copied into the inactive image for each member.
42
Page 43

Deploying FCoE (FIP Snooping) on Dell PowerConnect 10G Switches: M8024-k, 8024, and 8024F
Also notice that the switch still has the same Current-Active image as before.
8. Under the Next-Active column, select the new image (i.e. image2) for the switch or stack.
9. Click Apply.
The Current-Active column should now show t h e opposite values as what is in t he Next-Active
column. A reload is required to active the firmware.
10. Select System > General > Reset. Choose “All” in the Switch ID menu.
11. Click Apply.
12. After the stack resets, verify the new fi r mware has become active.
13. Select System > File Management > Active Images again.
43
Page 44

Deploying FCoE (FIP Snooping) on Dell PowerConnect 10G Switches: M8024-k, 8024, and 8024F
Notice that the new firmware (i.e. 4.2.0.4) is now the Current-Active image for each member.
While downgrading to a previou s firmware is supported, al l features and functions that were not part
of the previous firmware will be lost, including those features and functions that were introduced in
the current firmware in use. Firmware version 4.2 or later must be active for the DCB or stacking
features to work correctly. Do not downgrade the switch to f irmware version 4.1.x.x or earlier.
44
Page 45

Deploying FCoE (FIP Snooping) on Dell PowerConnect 10G Switches: M8024-k, 8024, and 8024F
Appendix A – Full CLI examples
M8024-k CLI example
show running-config
!Current Configuration:
!System Description "PowerConnect M8024-k, 4.2.1.3, VxWorks 6.6"
!System Software Version 4.2.1.3
!Cut-through mode is configured as disabled
!System Operational Mode "Normal"
!
configure
no mode simple
vlan database
vlan 20,1000
exit
slot 1/0 2 ! PCM8024-k
feature fip-snooping
vlan 20,1000
fip-snooping enable
exit
stack
member 1 1 ! PCM8024-k
exit
no logging console
username "root" password e6e66b8981c1030d5650da159e79539a privilege 15
encrypted
line console
exec-timeout 0
exit
classofservice dot1p-mapping 1 1
classofservice dot1p-mapping 2 2
classofservice dot1p-mapping 3 3
classofservice dot1p-mapping 4 4
classofservice dot1p-mapping 5 5
classofservice dot1p-mapping 6 6
!
interface Te1/0/1
cos-queue min-bandwidth 0 0 0 50 0 0 0
cos-queue strict 3
shutdown
spanning-tree port-priority 0
mtu 2500
switchport mode general
switchport general pvid 20
switchport general allowed vlan add 20
switchport general allowed vlan add 1000 tagged
switchport general allowed vlan remove 1
lldp dcbx port-role auto-down
exit
45
Page 46

Deploying FCoE (FIP Snooping) on Dell PowerConnect 10G Switches: M8024-k, 8024, and 8024F
!
interface Te1/0/2
cos-queue min-bandwidth 0 0 0 50 0 0 0
cos-queue strict 3
shutdown
spanning-tree port-priority 0
mtu 2500
switchport mode general
switchport general pvid 20
switchport general allowed vlan add 20
switchport general allowed vlan add 1000 tagged
switchport general allowed vlan remove 1
lldp dcbx port-role auto-down
exit
!
interface Te1/0/3
cos-queue min-bandwidth 0 0 0 50 0 0 0
cos-queue strict 3
mtu 2500
switchport mode general
switchport general pvid 20
switchport general allowed vlan add 20
switchport general allowed vlan add 1000 tagged
switchport general allowed vlan remove 1
lldp dcbx port-role auto-down
exit
!
interface Te1/0/4
cos-queue min-bandwidth 0 0 0 50 0 0 0
cos-queue strict 3
shutdown
spanning-tree port-priority 0
mtu 2500
switchport mode general
switchport general pvid 20
switchport general allowed vlan add 20
switchport general allowed vlan add 1000 tagged
switchport general allowed vlan remove 1
lldp dcbx port-role auto-down
exit
!
interface Te1/0/5
cos-queue min-bandwidth 0 0 0 50 0 0 0
cos-queue strict 3
spanning-tree port-priority 0
mtu 2500
switchport mode general
switchport general pvid 20
switchport general allowed vlan add 20
switchport general allowed vlan add 1000 tagged
switchport general allowed vlan remove 1
lldp dcbx port-role auto-down
46
Page 47

Deploying FCoE (FIP Snooping) on Dell PowerConnect 10G Switches: M8024-k, 8024, and 8024F
exit
!
interface Te1/0/6
cos-queue min-bandwidth 0 0 0 50 0 0 0
cos-queue strict 3
shutdown
spanning-tree port-priority 0
mtu 2500
switchport mode general
switchport general pvid 20
switchport general allowed vlan add 20
switchport general allowed vlan add 1000 tagged
switchport general allowed vlan remove 1
lldp dcbx port-role auto-down
exit
!
interface Te1/0/7
cos-queue min-bandwidth 0 0 0 50 0 0 0
cos-queue strict 3
spanning-tree port-priority 0
mtu 2500
switchport mode general
switchport general pvid 20
switchport general allowed vlan add 20
switchport general allowed vlan add 1000 tagged
switchport general allowed vlan remove 1
lldp dcbx port-role auto-down
exit
!
interface Te1/0/8
cos-queue min-bandwidth 0 0 0 50 0 0 0
cos-queue strict 3
spanning-tree port-priority 0
mtu 2500
switchport mode general
switchport general pvid 20
switchport general allowed vlan add 20
switchport general allowed vlan add 1000 tagged
switchport general allowed vlan remove 1
lldp dcbx port-role auto-down
exit
!
interface Te1/0/9
cos-queue min-bandwidth 0 0 0 50 0 0 0
cos-queue strict 3
spanning-tree port-priority 0
mtu 2500
switchport mode general
switchport general pvid 20
switchport general allowed vlan add 20
switchport general allowed vlan add 1000 tagged
switchport general allowed vlan remove 1
47
Page 48

Deploying FCoE (FIP Snooping) on Dell PowerConnect 10G Switches: M8024-k, 8024, and 8024F
lldp dcbx port-role auto-down
exit
!
interface Te1/0/10
cos-queue min-bandwidth 0 0 0 50 0 0 0
cos-queue strict 3
shutdown
spanning-tree port-priority 0
mtu 2500
switchport mode general
switchport general pvid 20
switchport general allowed vlan add 20
switchport general allowed vlan add 1000 tagged
switchport general allowed vlan remove 1
lldp dcbx port-role auto-down
exit
!
interface Te1/0/11
cos-queue min-bandwidth 0 0 0 50 0 0 0
cos-queue strict 3
spanning-tree port-priority 0
mtu 2500
switchport mode general
switchport general pvid 20
switchport general allowed vlan add 20
switchport general allowed vlan add 1000 tagged
switchport general allowed vlan remove 1
lldp dcbx port-role auto-down
exit
!
interface Te1/0/12
cos-queue min-bandwidth 0 0 0 50 0 0 0
cos-queue strict 3
spanning-tree port-priority 0
mtu 2500
switchport mode general
switchport general pvid 20
switchport general allowed vlan add 20
switchport general allowed vlan add 1000 tagged
switchport general allowed vlan remove 1
lldp dcbx port-role auto-down
exit
!
interface Te1/0/13
cos-queue min-bandwidth 0 0 0 50 0 0 0
cos-queue strict 3
shutdown
spanning-tree port-priority 0
mtu 2500
switchport mode general
switchport general pvid 20
switchport general allowed vlan add 20
48
Page 49

Deploying FCoE (FIP Snooping) on Dell PowerConnect 10G Switches: M8024-k, 8024, and 8024F
switchport general allowed vlan add 1000 tagged
switchport general allowed vlan remove 1
lldp dcbx port-role auto-down
exit
!
interface Te1/0/14
cos-queue min-bandwidth 0 0 0 50 0 0 0
cos-queue strict 3
shutdown
spanning-tree port-priority 0
mtu 2500
switchport mode general
switchport general pvid 20
switchport general allowed vlan add 20
switchport general allowed vlan add 1000 tagged
switchport general allowed vlan remove 1
lldp dcbx port-role auto-down
exit
!
interface Te1/0/15
cos-queue min-bandwidth 0 0 0 50 0 0 0
cos-queue strict 3
shutdown
spanning-tree port-priority 0
mtu 2500
switchport mode general
switchport general pvid 20
switchport general allowed vlan add 20
switchport general allowed vlan add 1000 tagged
switchport general allowed vlan remove 1
lldp dcbx port-role auto-down
exit
!
interface Te1/0/16
cos-queue min-bandwidth 0 0 0 50 0 0 0
cos-queue strict 3
shutdown
spanning-tree port-priority 0
mtu 2500
switchport mode general
switchport general pvid 20
switchport general allowed vlan add 20
switchport general allowed vlan add 1000 tagged
switchport general allowed vlan remove 1
lldp dcbx port-role auto-down
exit
!
interface Te1/0/17
cos-queue min-bandwidth 0 0 0 50 0 0 0
cos-queue strict 3
shutdown
spanning-tree port-priority 0
49
Page 50

Deploying FCoE (FIP Snooping) on Dell PowerConnect 10G Switches: M8024-k, 8024, and 8024F
mtu 2500
switchport mode general
switchport general pvid 20
switchport general allowed vlan add 20
switchport general allowed vlan add 1000 tagged
switchport general allowed vlan remove 1
exit
!
interface Te1/0/18
cos-queue min-bandwidth 0 0 0 50 0 0 0
cos-queue strict 3
shutdown
spanning-tree port-priority 0
mtu 2500
switchport mode general
switchport general pvid 20
switchport general allowed vlan add 20
switchport general allowed vlan add 1000 tagged
switchport general allowed vlan remove 1
exit
!
interface Te1/0/19
channel-group 2 mode active
cos-queue min-bandwidth 0 0 0 50 0 0 0
cos-queue strict 0 3
spanning-tree port-priority 0
mtu 2500
switchport general allowed vlan add 20
switchport general allowed vlan add 1000 tagged
switchport general allowed vlan remove 1
lldp dcbx port-role auto-up
exit
!
interface Te1/0/20
channel-group 2 mode active
cos-queue min-bandwidth 0 0 0 50 0 0 0
cos-queue strict 0 3
spanning-tree port-priority 0
mtu 2500
switchport general allowed vlan add 20
switchport general allowed vlan add 1000 tagged
switchport general allowed vlan remove 1
lldp dcbx port-role auto-up
exit
!
interface port-channel 2
cos-queue min-bandwidth 0 0 0 50 0 0 0
cos-queue strict 3
spanning-tree port-priority 0
switchport mode general
switchport general pvid 20
switchport general allowed vlan add 20
50
Page 51

Deploying FCoE (FIP Snooping) on Dell PowerConnect 10G Switches: M8024-k, 8024, and 8024F
switchport general allowed vlan add 1000 tagged
switchport general allowed vlan remove 1
mtu 2500
fip-snooping port-mode fcf
exit
!
interface port-channel 3
mtu 2500
exit
!
interface port-channel 4
mtu 2500
exit
Skipped port-channel 5 through 126 for space
interface port-channel 127
mtu 2500
exit
!
interface port-channel 128
mtu 2500
exit
enable password f611e082a05f5562f1d0d2bbcef2b5bf encrypted
exit
console#
51
Page 52

Deploying FCoE (FIP Snooping) on Dell PowerConnect 10G Switches: M8024-k, 8024, and 8024F
Cisco Nexus 5548UP CLI example
Technet5548-1# show running-config
!Command: show running-config
!Time: Tue Feb 14 22:47:07 2012
version 5.0(3)N2(2a)
feature fcoe
feature telnet
cfs ipv4 distribute
feature lacp
feature lldp
username admin password 5 $1$0bcPjaAd$t3MSaSb34/4QiOx/il5VM0 role
network-admin
ip domain-lookup
hostname Technet5548-1
class-map type qos class-fcoe
class-map type queuing class-fcoe
match qos-group 1
class-map type queuing class-all-flood
match qos-group 2
class-map type queuing class-ip-multicast
match qos-group 2
class-map type network-qos class-fcoe
match qos-group 1
class-map type network-qos class-all-flood
match qos-group 2
class-map type network-qos class-ip-multicast
match qos-group 2
system qos
service-policy type qos input fcoe-default-in-policy
service-policy type queuing input fcoe-default-in-policy
service-policy type queuing output fcoe-default-out-policy
service-policy type network-qos fcoe-default-nq-policy
slot 1
port 31-32 type fc
snmp-server user admin network-admin auth md5
0x18e86ba84d1d511fcb6fe4b5e02dc408 priv
0x18e86ba84d1d511fcb6fe4b5e02dc408 loca
lizedkey
snmp-server enable traps entity fru
vrf context management
ip route 0.0.0.0/0 172.25.188.254
vlan 1
vlan 20
name NATIVE_VLAN
52
Page 53

Deploying FCoE (FIP Snooping) on Dell PowerConnect 10G Switches: M8024-k, 8024, and 8024F
vlan 1000
fcoe vsan 2
name FCoE_VLAN
vsan database
vsan 2
interface port-channel2
switchport mode trunk
switchport trunk native vlan 20
switchport trunk allowed vlan 1000
interface vfc3
bind mac-address 14:fe:b5:8e:5b:f2
no shutdown
interface vfc4
bind mac-address 14:fe:b5:8e:5b:f0
no shutdown
interface vfc5
bind mac-address 14:fe:b5:8e:5c:09
no shutdown
interface vfc6
bind mac-address 14:fe:b5:8e:5c:0b
no shutdown
interface vfc7
bind mac-address 14:fe:b5:8e:5c:26
no shutdown
interface vfc8
bind mac-address 14:fe:b5:8e:5c:24
no shutdown
vsan database
vsan 2 interface vfc3
vsan 2 interface vfc4
vsan 2 interface vfc5
vsan 2 interface vfc6
vsan 2 interface vfc7
vsan 2 interface vfc8
vsan 2 interface fc1/31
vsan 2 interface fc1/32
feature npv
feature npiv
interface fc1/31
switchport trunk mode on
no shutdown
53
Page 54

Deploying FCoE (FIP Snooping) on Dell PowerConnect 10G Switches: M8024-k, 8024, and 8024F
interface fc1/32
switchport trunk mode on
no shutdown
interface Ethernet1/1
interface Ethernet1/2
interface Ethernet1/3
interface Ethernet1/4
interface Ethernet1/5
interface Ethernet1/6
interface Ethernet1/7
interface Ethernet1/8
interface Ethernet1/9
interface Ethernet1/10
interface Ethernet1/11
interface Ethernet1/12
interface Ethernet1/13
interface Ethernet1/14
interface Ethernet1/15
interface Ethernet1/16
interface Ethernet1/17
interface Ethernet1/18
interface Ethernet1/19
interface Ethernet1/20
interface Ethernet1/21
interface Ethernet1/22
interface Ethernet1/23
interface Ethernet1/24
54
Page 55

Deploying FCoE (FIP Snooping) on Dell PowerConnect 10G Switches: M8024-k, 8024, and 8024F
interface Ethernet1/25
interface Ethernet1/26
switchport mode trunk
switchport trunk native vlan 20
switchport trunk allowed vlan 1000
interface Ethernet1/27
switchport mode trunk
switchport trunk native vlan 20
switchport trunk allowed vlan 1000
interface Ethernet1/28
switchport mode trunk
switchport trunk native vlan 20
switchport trunk allowed vlan 1000
interface Ethernet1/29
switchport mode trunk
switchport trunk native vlan 20
switchport trunk allowed vlan 1000
channel-group 2 mode active
interface Ethernet1/30
switchport mode trunk
switchport trunk native vlan 20
switchport trunk allowed vlan 1000
channel-group 2 mode active
interface mgmt0
ip address 172.25.188.100/16
line console
line vty
boot kickstart bootflash:/n5000-uk9-kickstart.5.0.3.N2.2a.bin
boot system bootflash:/n5000-uk9.5.0.3.N2.2a.bin
interface fc1/31
switchport mode NP
interface fc1/32
switchport mode NP
55
Page 56

Deploying FCoE (FIP Snooping) on Dell PowerConnect 10G Switches: M8024-k, 8024, and 8024F
Appendix B - Network Switch Versions
Version information for the network switches used in creating this document are as follows:
Network switch
Software version
Dell PowerConnect™
M8024k
4.2.0.1, 4.2.0.2,
4.2.0.3, 4.2.0.4, 4.2. 1.3
Switch Firmware Versions Table 1.
Dell PowerConnect™
8024/8024F
4.2.0.1, 4.2.0.2, 4.2. 0.3,
4.2.0.4, 4.2.1.3
Cisco 5020
5.0(3)N2(2a),
5.0(3)N1(1b)
References
Fibre Channel over Ethernet Initialization Protocol,
Cisco,
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/prod/collateral/switches/ps9441/ps9670/white_paper_c11-
560403.html
T11/08-264v0 FCoE: Increasing FCoE Robustne ss using FIP Snooping and FPMA,
T11, http://www.t11.org/ftp/t11/pub/fc/bb-5/08-264v0.pdf
T11/09-291v0 FIP VLAN discovery updates, T11,
http://www.t11.org/ftp/t11/pub/fc/bb-5/09-291v1.pdf
IEEE. (2008, November 24). 802.1Qaz/D0.2. Draft Standard f or Local and Metropolitan Area Networks –
Virtual.
IEEE. (2009, Feb 9). 802.1Qbb/D1.0. Draft Standard for Local an d Metropolitan Area Network s – Virtual.
Cisco Systems, Inc. (2011). Cisco Nexus 5000 Series NX-OS SAN Switching Configuration Guide, Release
5.0(3)N2(1). San Jose: Cisco Systems, Inc.
About Dell
Dell (NASDAQ: DELL) is a leading technology provider to commercial and public enterprises around the
world.
56
 Loading...
Loading...