Page 1

97&%
3,3&
3&,,QWHJUDWHG3HULSKHUDO&RQWUROOHU
3&&RPSOLDQW3&,WR,6$%ULGJH
ZLWK$&3,'LVWULEXWHG'0$3OXJDQG3OD\
0DVWHU0RGH3&,,'(&RQWUROOHUZLWK8OWUD'0$
86%&RQWUROOHU.H\ERDUG&RQWUROOHUDQG57&
5HYLVLRQ
0D\
9,$7(&+12/2*,(6,1&
Page 2

&RS\ULJKW1RWLFH
&RS\ULJKW 9,$ 7HFKQRORJLHV ,QFRUSRUDWHG 3ULQWHG LQ WKH 8QLWHG 6WDWHV $//5
1R SDUW RI WKLV GRFXPHQW PD\ EH UHSURGXFHG WUDQVPLWWHG WUDQVFULEHG VWRUHG LQ D UHWULHYDO V\VWHP RU WUDQVODWHG LQWR
DQ\ ODQJXDJH LQ DQ\ IRUP RU E\ DQ\ PHDQV HOHFWURQLF PHFKDQLFDO PDJQHWLF RSWLFDO FKHPLFDO PDQXDO RU RWKHUZLVH
ZLWKRXW WKH SULRU ZULWWHQ SHUPLVVLRQ RI 9,$ 7HFKQRORJLHV ,QFRUSRUDWHG
7KH 97& 97&$ DQG 97&% PD\ RQO\ EH XVHG WR LGHQWLI\ SURGXFWV RI 9,$ 7HFKQRORJLHV
LV D UHJLVWHUHG WUDGHPDUN RI 9,$ 7HFKQRORJLHV ,QFRUSRUDWHG
70
36
3HQWLXP3UR
:LQGRZV
3&,
9(6$ LV D WUDGHPDUN RI WKH 9LGHR (OHFWURQLFV 6WDQGDUGV $VVRFLDWLRQ
$OO WUDGHPDUNV DUH WKH SURSHUWLHV RI WKHLU UHVSHFWLYH RZQHUV
LV D UHJLVWHUHG WUDGHPDUN RI ,QWHUQDWLRQDO %XVLQHVV 0DFKLQHV &RUS
70
*7/70DQG $3,&70DUH UHJLVWHUHG WUDGHPDUNV RI ,QWHO &RUS
70
70
LV D UHJLVWHUHG WUDGHPDUN RI WKH 3&, 6SHFLDO ,QWHUHVW *URXS
DQG 3OXJ DQG 3OD\70DUH UHJLVWHUHG WUDGHPDUNV RI 0LFURVRIW &RUS
,*+765(6(59('
'LVFODLPHU1RWLFH
1R OLFHQVH LV JUDQWHG LPSOLHG RU RWKHUZLVH XQGHU DQ\ SDWHQW RU SDWHQW ULJKWV RI 9,$ 7HFKQRORJLHV 9,$ 7HFKQRORJLHV
PDNHV QR ZDUUDQWLHV LPSOLHG RU RWKHUZLVH LQ UHJDUG WR WKLV GRFXPHQW DQG WR WKH SURGXFWV GHVFULEHG LQ WKLV GRFXPHQW
7KH LQIRUPDWLRQ SURYLGHG E\ WKLV GRFXPHQW LV EHOLHYHG WR EH DFFXUDWH DQG UHOLDEOH WR WKH SXEOLFDWLRQ GDWH RI WKLV
GRFXPHQW +RZHYHU 9,$ 7HFKQRORJLHV DVVXPHV QR UHVSRQVLELOLW\ IRU DQ\ HUURUV LQ WKLV GRFXPHQW )XUWKHUPRUH 9,$
7HFKQRORJLHV DVVXPHV QR UHVSRQVLELOLW\ IRU WKH XVH RU PLVXVH RI WKH LQIRUPDWLRQ LQ WKLV GRFXPHQW DQG IRU DQ\ SDWHQW
LQIULQJHPHQWV WKDW PD\ DULVH IURP WKH XVH RI WKLV GRFXPHQW 7KH LQIRUPDWLRQ DQG SURGXFW VSHFLILFDWLRQV ZLWKLQ WKLV
GRFXPHQW DUH VXEMHFW WR FKDQJH DW DQ\ WLPH ZLWKRXW QRWLFH DQG ZLWKRXW REOLJDWLRQ WR QRWLI\ DQ\ SHUVRQ RI VXFK FKDQJH
2IILFHV
86$ 2IILFH 7DLSHL 2IILFH
%UDQGLQ &RXUW WK )ORRU 1R
)UHPRQW &$ &KXQJ&KHQJ 5RDG +VLQ7LHQ
86$ 7DLSHL 7DLZDQ 52&
7HO 7HO
)D[ )D[
2QOLQH6HUYLFHV
+RPH 3DJH KWWSZZZYLDFRPWZ
)73 6HUYHU IWSYLDFRPWZ
%%6
Page 3
9,$7HFKQRORJLHV,QF
R
EVISION HISTORY
Document Release Date Revision Initials
Revision 0.1 10/13/96 Initial release for 586A DH
Revision 0.5 12/23/96
reprinted
1/8/97
to fix
Acrobat
PDF file
size
problem
Incorrect
Change
Revision 1.0 5/13/97 • Overview Changes: Added System Block Diagram
Update to reflect 586B:
• Updated pin definitions:
Pins 18,31,33,58,60,131,133 (removed EXTSMI2-7 & DACEN)
Pins 77-78,80-83,85-86 (added GPI8-15 and GPO8-15)
Pins 94,87-88,92,136 (changed to GPIO0-4 and added alternate functions)
Pins 90,106,137 (added MIRQ0, MIRQ1, and MIRQ2 functions)
Pins 91,93,103,107 (changed to PWRBTN#, RI#, VDD-5VSB, PWRON)
Pins 113-114,116-119,121-122 (added GPI, GPO, and EXTSMI functions)
Fixed doc error DACK0-7 pin names changed to active low (DACK0-7#)
Removed options: IRQ12 (pin 137), strap (pin 48), RTCAS (pin 94)
• Updated register definitions
Removed VIA-specific port A8/A9 registers
Updated function 0 Rx5-4[3], Rx7-6[13], Rx41[0-4,6-7], Rx42[4-7], Rx44,
Rx46[2-4], Rx47[3], Rx48[3], Rx4A[4-6], Removed Rx50 (MDRQ)
Rx55[7-4] change PIRQD# to MIRQ1, Rx56 swap A/B, Rx57 swap C/D
Added 58-5B for PnP, XD, KBC/RTC config; added 60-6F for DDMA ctrl
Removed power mgmt regs 80-94 & added function 3 ACPI Power Mgmt
• Straps: moved 95-96 to 5A, allow RW after powerup, removed strap XD3
• Expanded CMOS RAM: added ports 72-75 & table 5 CMOS Reg Summary
• Added Power Management Subsystem Overview
• Incorporated App Note #53 APM-Compliant Pwr Mgmt Model of 82C586A
• Added AC Timing Section with IDE Interface Timing Diagrams & Specs
• Pin Function Changes:
Pin 90 added alternate function "POS" output
Pin 106 added alternate function "IRQ8#" input
Pin 137 added alternate function "SDDIR" output
• Register Definition Changes:
Fixed typos: Port 75 note, Fn0 Rx48[3], Rx55-57[7:0]; Fn1 Rx4[7]; Fn2
Rx3C-3D; Fn3 Rx26[9], Rx2F, Rx62-63, Table 7
Added missing register: Function 0 Rx59[3] MIRQ Pin Config Register
Function 0 PCI-to-ISA Bridge
Rx08[7:0] (changed) Revision Code Register
Rx2C[31:0] (new) Subsystem ID Register (read)
Rx41[0] (changed) ISA Test Mode Register
Rx46[7:5] and Rx48[5:4] (new) Misc Control Registers 1 and 3
Rx5C[0] (new) DMA Control Register
Rx70[31:0] (new) Subsystem ID Register (write)
Function 1 IDE Controller
Rx43[7] (new) FIFO Configuration Register
Rx44[1:0] (new) Misc Control Register 1
Function 3 Power Management
Rx04[0] (moved to Rx41[7]) Command Register
Rx08[7:0] (changed) Revision ID Register
Rx10[4:1], Rx14 (changed) Processor Control and Processor Level 2
Rx20[31:0] (moved to Rx48) I/O Base Address Register
Power Management I/O
Rx40[6:5] (new) GPIO Direction Control Register
• Electrical Spec Changes: Added PCI Cycle Timing
• Mechanical Spec Changes: Added marking specs for 3040E/F, 3041 silicon
(3041 only silicon)
(3041 only silicon)
(3040F and 3041 silicon)
(3040F and 3041 silicon)
(3040F and 3041 silicon)
(3040F and 3041 silicon)
(3041 only silicon)
VT82C586B
DH
DH
Revision 1.0 May 13, 1997 -i- Revision History
Page 4

9,$7HFKQRORJLHV,QF
T
ABLE OF CONTENTS
VT82C586B
REVISION HISTORY........................................................................................................................................................................I
TABLE OF CONTENTS..................................................................................................................................................................II
LIST OF FIGURES..........................................................................................................................................................................III
LIST OF TABLES ...........................................................................................................................................................................IV
OVERVIEW.......................................................................................................................................................................................3
PINOUTS............................................................................................................................................................................................4
REGISTERS.....................................................................................................................................................................................14
EGISTER OVERVIEW
R
ONFIGURATION SPACE
C
EGISTER DESCRIPTIONS
R
.................................................................................................................................................................14
I/O .......................................................................................................................................................20
............................................................................................................................................................21
Legacy I/O Ports...................................................................................................................................................................21
Keyboard Controller Registers..............................................................................................................................................................22
DMA Controller I/O Registers..............................................................................................................................................................24
Interrupt Controller Registers ............................................................................................................................................................... 25
Timer / Counter Registers .....................................................................................................................................................................25
CMOS / RTC Registers......................................................................................................................................................................... 26
PCI to ISA Bridge Registers (Function 0) ..........................................................................................................................27
PCI Configuration Space Header.......................................................................................................................................................... 27
ISA Bus Control.................................................................................................................................................................................... 27
Plug and Play Control........................................................................................................................................................................... 30
Distributed DMA Control..................................................................................................................................................................... 32
Miscellaneous ....................................................................................................................................................................................... 32
Enhanced IDE Controller Registers (Function 1)..............................................................................................................33
PCI Configuration Space Header.......................................................................................................................................................... 33
IDE-Controller-Specific Confiiguration Registers................................................................................................................................ 35
IDE I/O Registers..................................................................................................................................................................................37
Universal Serial Bus Controller Registers (Function 2)....................................................................................................38
PCI Configuration Space Header.......................................................................................................................................................... 38
USB-Specific Configuration Registers..................................................................................................................................................39
USB I/O Registers................................................................................................................................................................................. 39
Power Management Registers (Function 3)........................................................................................................................40
PCI Configuration Space Header.......................................................................................................................................................... 40
Power Management-Specific PCI Configuration Registers .................................................................................................................. 41
Power Management Subsystem Overview ............................................................................................................................................43
Power Management I/O-Space Registers..............................................................................................................................................46
ELECTRICAL SPECIFICATIONS...............................................................................................................................................55
BSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS
A
HARACTERISTICS
DC C
IMING SPECIFICATIONS
AC T
................................................................................................................................................................55
.................................................................................................................................................55
......................................................................................................................................................56
PACKAGE MECHANICAL SPECIFICATIONS........................................................................................................................63
Revision 1.0 May 13, 1997 -ii- Table of Contents
Page 5

9,$7HFKQRORJLHV,QF
L
IST OF FIGURES
FIGURE 1. PC SYSTEM CONFIGURATION USING THE VT82C586B ................................................................................. 3
FIGURE 2. PIN DIAGRAM.............................................................................................................................................................4
FIGURE 3. STRAP OPTION CIRCUIT....................................................................................................................................... 31
FIGURE 4. POWER MANAGEMENT SUBSYSTEM BLOCK DIAGRAM........................................................................... 43
FIGURE 5. ULTRADMA-33 IDE TIMING - DRIVE INITIATING DMA BURST FOR READ COMMAND.................... 58
FIGURE 6. ULTRADMA-33 IDE TIMING - DRIVE INITIATING BURST FOR WRITE COMMAND............................58
FIGURE 7. ULTRADMA-33 IDE TIMING - PAUSING A DMA BURST ...............................................................................59
FIGURE 8. ULTRADMA-33 IDE TIMING - DRIVE TERMINATING DMA BURST DURING READ COMMAND......60
FIGURE 9. ULTRADMA-33 IDE TIMING - DRIVE TERMINATING DMA BURST DURING WRITE COMMAND ...60
FIGURE 10. ULTRADMA-33 IDE TIMING - HOST TERMINATING DMA BURST DURING READ COMMAND......61
FIGURE 11. ULTRADMA-33 IDE TIMING - HOST TERMINATING DMA BURST DURING WRITE COMMAND...61
FIGURE 12. ULTRADMA-33 IDE TIMING - PIO CYCLE......................................................................................................62
FIGURE 13. MECHANICAL SPECIFICATIONS - 208-PIN PLASTIC FLAT PACKAGE..................................................63
VT82C586B
Revision 1.0 May 13, 1997 -iii- List of Figures
Page 6

9,$7HFKQRORJLHV,QF
L
IST OF TABLES
TABLE 1. PIN DESCRIPTIONS.....................................................................................................................................................5
TABLE 2. SYSTEM I/O MAP....................................................................................................................................................... 14
TABLE 3. REGISTERS..................................................................................................................................................................14
TABLE 4. KEYBOARD CONTROLLER COMMAND CODES ..............................................................................................23
TABLE 5. CMOS REGISTER SUMMARY.................................................................................................................................26
TABLE 6. SCI/SMI/RESUME CONTROL FOR PM EVENTS.................................................................................................44
TABLE 7. SUSPEND RESUME EVENTS AND CONDITIONS ...............................................................................................44
TABLE 8. AC CHARACTERISTICS - PCI CYCLE TIMING..................................................................................................56
TABLE 9. AC CHARACTERISTICS - ULTRADMA-33 IDE BUS INTERFACE TIMING.................................................. 57
VT82C586B
Revision 1.0 May 13, 1997 -iv- List of Tables
Page 7

9,$7HFKQRORJLHV,QF
VT82C586B
VT82C586B PIPC
PCI I
WITH
M
ASTER MODE
USB C
• PC97 Compliant PCI to ISA Bridge
ONTROLLER
−
Integrated ISA Bus Controller with integrated DMA, timer, and interrupt controller
−
Integrated Keyboard Controller with PS2 mouse support
−
Integrated DS12885-style Real Time Clock with extended 256 byte CMOS RAM and Day/Month Alarm for ACPI
−
Integrated USB Controller with root hub and two function ports
−
Integrated master mode enhanced IDE controller with enhanced PCI bus commands and UltraDMA-33 extensions
−
PCI-2.1 compliant with delay transaction
−
Eight double-word line buffer between PCI and ISA bus
−
One level of PCI to ISA post-write buffer
−
Supports type F DMA transfers
−
Distributed DMA support for ISA legacy DMA across the PCI bus
−
Fast reset and Gate A20 operation
−
Edge trigger or level sensitive interrupt
−
Flash EPROM, 2MB EPROM and combined BIOS support
−
Programmable ISA bus clock
−
Supports external IOAPIC interface for symmetrical multiprocessor configurations
NTEGRATED PERIPHERAL CONTROLLER
PC97 C
ACPI, D
OMPLIANT
ISTRIBUTED
PCI IDE C
, K
EYBOARD CONTROLLER, AND REAL TIME CLOCK
PCI-TO-ISA B
DMA, P
RIDGE
LUG AND PLAY
ONTROLLER WITH ULTRA
,
DMA-33,
• Inter-operable with VIA and other Host-to-PCI Bridges
−
Combine with VT82C585VPX/587VP for a complete 75MHz 6x86 / PCI / ISA system (Apollo VPX)
−
Combine with VT82C595 for a complete Pentium / PCI / ISA system (Apollo VP2)
−
Combine with VT82C685/687 for a complete Pentium-Pro /PCI / ISA system (Apollo P6)
−
Combine with VIA Apollo-AGP and Apollo Pro chipsets for new high-performance / enhanced-functionality systems
−
Inter-operable with other Intel or non-Intel Host-to-PCI bridges for a complete PC97 compliant PCI/ISA system
• Enhanced Master Mode PCI IDE Controller with Extension to UltraDMA-33
−
Dual channel master mode PCI supporting four Enhanced IDE devices
−
Transfer rate up to 33MB/sec to cover PIO mode 4, multi-word DMA mode 2 drives, and UltraDMA-33 interface
−
Sixteen levels (doublewords) of prefetch and write buffers
−
Interlaced commands between two channels
−
Bus master programming interface for SFF-8038i rev.1.0 and Windows-95 compliant
−
Full scatter gather capability
−
Support ATAPI compliant devices including DVD devices
−
Support PCI native and ATA compatibility modes
−
Complete software driver support
Revision 1.0 May 13, 1997 -1- Features
Page 8

9,$7HFKQRORJLHV,QF
Universal Serial Bus Controller
•
−
USB v.1.0 and Intel Universal HCI v.1.1 compatible
−
Eighteen level (doublewords) data FIFO with full scatter and gather capability
−
Root hub and two function ports
−
Integrated physical layer transceivers with over-current detection status on USB inputs
−
Legacy keyboard and PS/2 mouse support
Sophisticated PC97-Compatible Power Management
•
−
Supports both ACPI (Advanced Configuration and Power Interface) and legacy (APM) power management
−
ACPI v1.0 Compliant (all required features plus extensions for most efficient desktop power management)
−
APM v1.2 Compliant
−
Supports soft-off (suspend to disk) and power-on suspend with hardware automatic wake-up
−
One idle timer, one peripheral timer and one general purpose timer, plus 24/32-bit ACPI compliant timer
−
Dedicated input pin for external modem ring indicator for system wake-up
−
Enhanced integrated real time clock (RTC) with date alarm, month alarm, and century field
−
Normal, doze, sleep, suspend and conserve modes
−
System event monitoring with two event classes
−
Five multi-purpose I/O pins plus support for up to 16 general purpose input ports and 16 output ports
−
I2C serial bus support for JEDEC-compatible DIMM identification and on-board-device power control
−
Seven external event input ports with programmable SMI condition
−
Primary and secondary interrupt differentiation for individual channels
−
Clock throttling control
−
Multiple internal and external SMI sources for flexible power management models
VT82C586B
Plug and Play Controller
•
−
PCI interrupts steerable to any interrupt channel
−
Three steerable interrupt channels for on-board plug and play devices
−
Microsoft Windows 95
Pin-compatible upgrade from VT82C586 and VT82C586A for existing designs
•
Built-in Nand-tree pin scan test capability
•
0.5um mixed voltage, high speed and low power CMOS process
•
Single chip 208 pin PQFP
•
TM
and plug and play BIOS compliant
Revision 1.0 May 13, 1997 -2- Features
Page 9
9,$7HFKQRORJLHV,QF
O
VERVIEW
VT82C586B
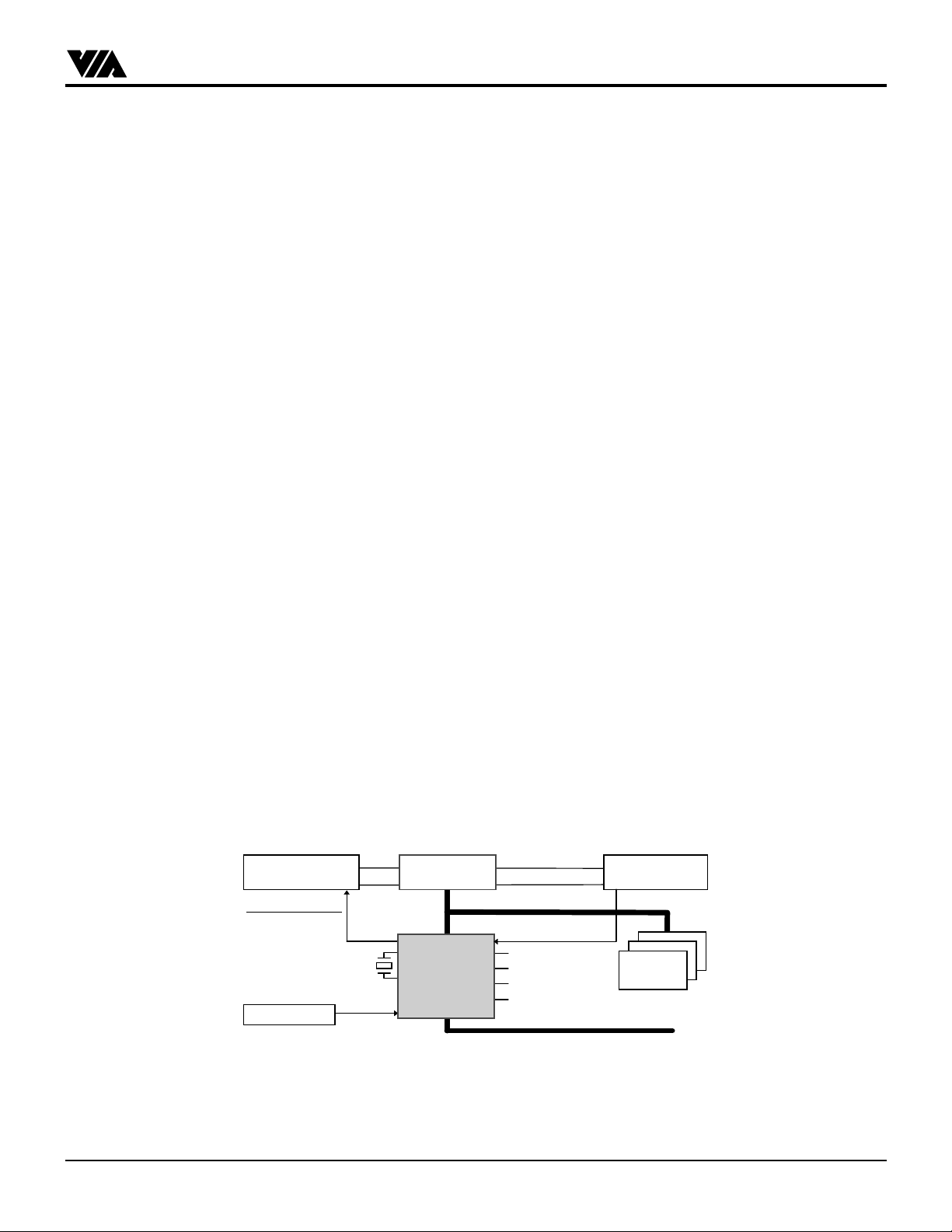
The VT82C586B PIPC (PCI Integrated Peripheral Controller) is a high integration, high performance and high compatibility
device that supports Intel and non-Intel based processor to PCI bus bridge functionality to make a complete Microsoft PC97compliant PCI/ISA system. In addition to complete ISA extension bus functionality, the VT82C586B includes standard intelligent
peripheral controllers:
a) Master mode enhanced IDE controller with dual channel DMA engine and interlaced dual channel commands. Dedicated
FIFO coupled with scatter and gather master mode operation allows high performance transfers between PCI and IDE
devices. In addition to standard PIO and DMA mode operation, the VT82C586B also supports the emerging UltraDMA-33
standard to allow reliable data transfer rates up to 33MB/sec throughput. The IDE controller is SFF-8038i v1.0 and
Microsoft Windows-95 compliant.
b) Universal Serial Bus controller that is USB v1.0 and Universal HCI v1.1 compliant. The VT82C586B includes the root hub
with two function ports with integrated physical layer transceivers. The USB controller allows hot plug and play and
isochronous peripherals to be inserted into the system with universal driver support. The controller also implements legacy
keyboard and mouse support so that legacy software can run transparently in a non-USB-aware operating system
environment.
c) Keyboard controller with PS2 mouse support.
d) Real Time Clock with 256 byte extended CMOS. In addition to the standard ISA RTC functionality, the integrated RTC also
includes the date alarm and other enhancements for compatibility with the ACPI standard.
e) Notebook-class power management functionality that is compliant with ACPI and legacy APM requirements. Two types of
sleep states (soft-off and power-on-suspend) are supported with hardware automatic wake-up. Additional functionality
includes event monitoring, CPU clock throttling (Intel processor pr otocol), modular power control, hardware- and software-
based event handling, general purpose IO, chip select and external SMI.
f) Distributed DMA capability for support of ISA legacy DMA over the PCI bus.
g) Plug and Play controller that allows complete steerability of all PCI interrupts to any interrupt channel. Three ad ditional
steerable interrupt channels are provided to allow plug and play and reconfigurability of on-board peripherals for W indows
95 compliance.
h) External IOAPIC support for Intel-compliant symmetrical multiprocessor systems.
The VT82C586B also enhances the functionality of the standard ISA peripherals. The integrated interrupt controller supports both
edge and level triggered interrupts channel by channel. The integrated DMA controller supports type F DMA in addition to
standard ISA DMA modes. Compliant with the PCI-2.1 specification, the VT82C586B supports delayed transactions so that
slower ISA peripherals do not block the traffic of the PCI bus. Special circuitry is built in to allow concurrent operation without
causing dead lock even in a PCI-to-PCI bridge environment The chip also includes eight levels (doublewords) of line buffers from
the PCI bus to the ISA bus to further enhance overall system performance.
CPU / Cache
Sideband Signals:
Init / CPUreset
IRQ / NMI
SMI / StopClk
FERR / IGNNE
Boot ROM
CA
CD
RTC
Crystal
North Bridge
VT82C586B
208PQFP
MA/RAS/CAS
MD
PCI
I2C (Module ID)
USB
KBC
IDE
GPIO, Power Control, Reset
ISA
System Memory
Expansion
Cards
Figure 1. PC System Configuration Using the VT82C586B
Revision 1.0 May 13, 1997 -3- Overview
Page 10
9,$7HFKQRORJLHV,QF
GND
AD3
AD2
AD1
156
155
154
153
IOIOIO
VDD-PCI
AD4
AD5
AD6
AD7
CBE0#
AD8
AD9
AD10
GND
AD11
AD12
AD13
AD14
VDD-PCI
AD15
CBE1#
PAR
SERR#
STOP#
GND
DEVSEL#
TRDY#
IRDY#
FRAME#
CBE2#
AD16
VDD-PCI
AD17
AD18
AD19
GND
AD20
AD21
AD22
AD23
IDSEL
CBE3#
AD24
AD25
GND
VDD-PCI
AD26
AD27
AD28
AD29
AD30
AD31
PIRQD#
PIRQC#
PIRQB#
GND
157
IO
158
IO
159
IO
160
IO
161
IO
162
IO
163
IO
164
IO
165
166
IO
167
IO
168
IO
169
IO
170
171
IO
172
IO
173
IO
174
I
175
IO
176
177
IO
178
IO
179
IO
180
IO
181
IO
182
IO
183
184
IO
185
IO
186
IO
187
188
IO
189
IO
190
IO
191
IO
192
I
193
IO
194
IO
195
IO
196
197
198
IO
199
IO
200
IO
201
IO
202
IO
203
IO
204
I
205
I
206
I
207
208
I
I
O
O
12345678910111213141516171819202122232425262728293031323334353637383940414243444546474849
P
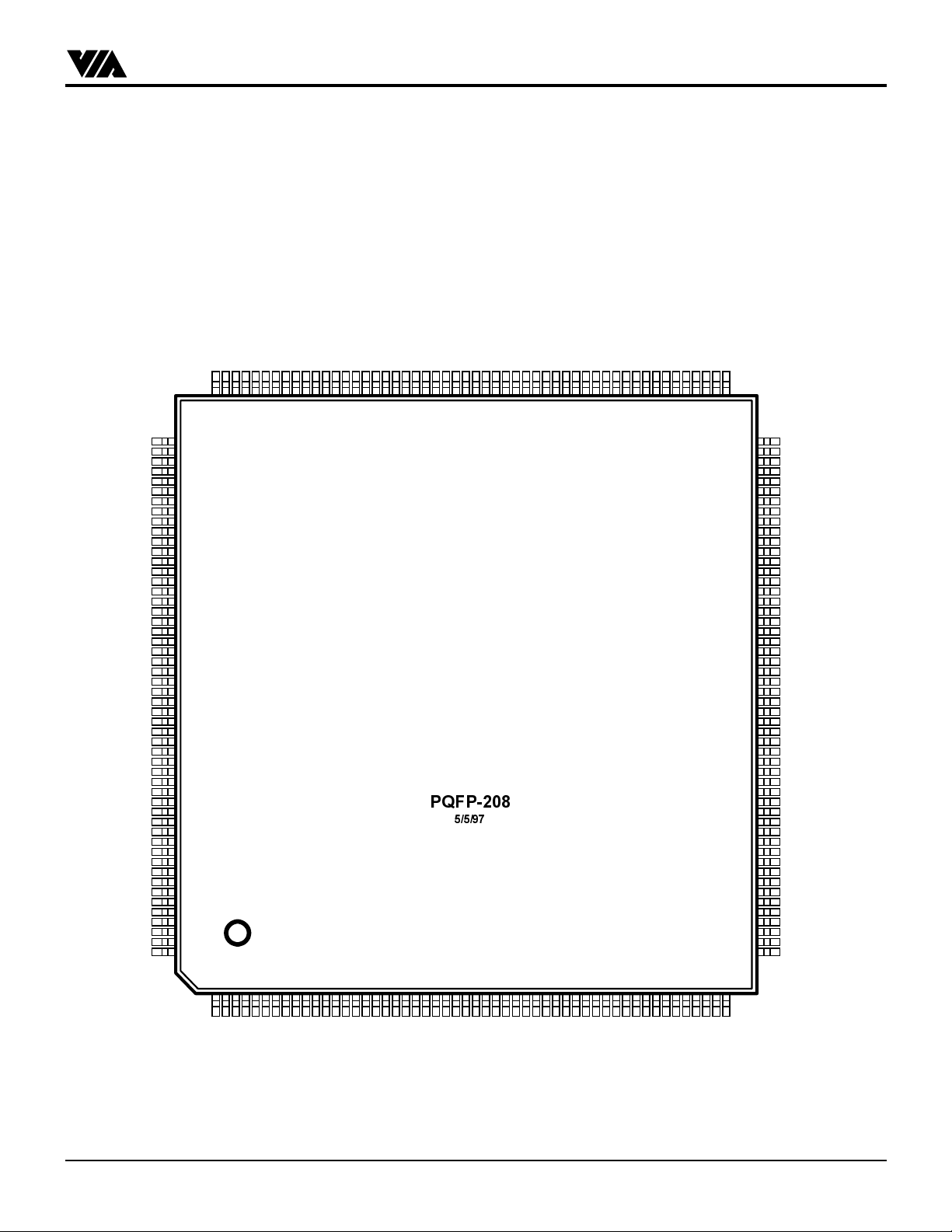
INOUTS
Figure 2. Pin Diagram
(EXTSMI3#)
(Strap)
(Strap)
(Strap)
(IRQ12)
VDD5
XD1
XD0
XDIR
MSDT
115
114
113
112
111
IOOIOIOIO
(GPI1) (GPO1)
(GPI0) (GPO0)
(EXTSMI0#)
‡ (POS) (MIRQ0)
(GPI15) (GPO15)
(GPI14) (GPO14)
(GPI13) (GPO13)
(GPI12) (GPO12)
(GPI11) (GPO11)
(GPI10) (GPO10)
(GPI9) (GPO9)
(GPI8) (GPO8)
AD0
PREQ#
PGNT#
SMI#
STPCLK#
A20M
NMI
INTR
VDD3
INIT
CPURST
152
151
150
149
148
147
146
145
144
143
OIOOOOOOOOO
IO
142
97&%
FERR#
GND
IGNNE#
PWRGD
141
140
139
138
I
(MIRQ2)
(EXTSMI4#)
(KBCS#)
(Strap)
MASTER#
GPIO4
ROMCS#
SPKR
DACK7#
DRQ7
137
136
135
134
133
132
OIO
IO
IOOIO
† (SDDIR)
(GPO_WE)
DACK6#
DRQ6
IRQ14
IRQ15
IRQ11
131
130
129
128
127
IIIII
(Strap) (EXTSMI7#)
(Strap) (EXTSMI6#)
(Strap) (EXTSMI5#)
(Strap) (EXTSMI4#)
IRQ10
IOCS16#
MEMW#
MEMR#
XD7
XD6
GND
XD5
XD4
126
125
124
123
122
121
120
119
I
IOIOIOIOIOIOIOIOIO
118
(GPI7) (GPO7)
(GPI6) (GPO6)
(GPI5) (GPO5)
(GPI4) (GPO4)
(GPI_RE#) (EXTSMI3#)
(Data) (I2CD2) (EXTSMI2#)
(Clock) (I2CD1) (EXTSMI1#)
XD3
XD2
117
116
(GPI3) (GPO3)
(GPI2) (GPO2)
3&,,QWHJUDWHG
3HULSKHUDO&RQWUROOHU
34)3
Note: Pin names in parentheses (...) indicate alternate function
‡ 3040 Rev F and Later Revisions
† 3041 Rev A and Later Revisions
III
I
O
O
O
OIO
IO
IO
IOIOIOIOIOIOIOIOIO
IO
I
OOO
O
IOIOIOIOIOIOIO
IO
I
I
(KA20G)
(KBRC#)
(IRQ1)
(MIRQ1) (IRQ8#) ‡
(RTCCS#)
KEYLOCK
KBDT
KBCK
PWRON
109
108
107
O
IO
OIO
50
RTCX2
106
105
I
O
I
104
103
I
102
101
100
I
99
IO
98
IO
97
IO
96
IO
95
O
94
I
93
IO
92
I
91
IO
90
I
89
IO
88
IO
87
IO
86
IO
85
84
IO
83
IO
82
IO
81
IO
80
79
IO
78
IO
77
I
76
I
75
I
74
I
73
I
72
I
71
IO
70
IO
69
68
IO
67
IO
66
IO
65
IO
64
IO
63
IO
62
I
61
O
60
I
59
O
58
I
57
O
56
O
55
O
54
53
O
51
52
MSCK
110
(IRQ8#)
O
VT82C586B
RTCX1
VDD-5VSB
VBAT
AGND
AVDD
USBCLK
USBDATA1USBDATA1+
USBDATA0USBDATA0+
GPIO0
RI#
GPIO3
PWRBTN#
APICCS#
DRDYB#
GPIO2
GPIO1
SD15
SD14
GND
SD13
SD12
SD11
SD10
VDD5
SD9
SD8
MEMCS16#
IRQ3
IRQ4
IRQ5
IRQ6
IRQ7
LA17/DA0
LA18/DA1
GND
LA19/DA2
LA20/DCS1A#
LA21/DCS3A#
LA22/DCS1B#
LA23/DCS3B#
SBHE#
IRQ9
DACK0#
DRQ0
DACK5#
DRQ5
SOE#
DIOWB#
DIORB#
VDD5
TC
DRQ3
DACK3#
DD8/SA8
REFRESH#
BALE
VDD5
DACK2#
DD7/SA7
DD6/SA6
GND
DD4/SA4
DD3/SA3
DD2/SA2
DD5/SA5
DDRQB
DDRQA
DD1/SA1
DD0/SA0
DDACKA#
GND
DIORA#
DIOWA#
DRDYA#
DDACKB#
PIRQA#
PCICLK
PCIRST#
RSTDRV
OSC
DRQ2
IOCHCK#
SMEMW#
IOCHRDY
IOR#
GND
IOW#
BCLK
SMEMR#
AEN
DRQ1
SA16
VDD5
DACK1#
DD15/SA15
GND
DD14/SA14
DD13/SA13
DD9/SA9
DD12/SA12
DD11/SA11
DD10/SA10
Revision 1.0 May 13, 1997 -4- Pinouts
Page 11
9,$7HFKQRORJLHV,QF
Table 1. Pin Descriptions
CPU Interface
Signal Name Pin No. I/O Signal Description
CPURST 142 O
INTR 145 O
NMI 146 O
INIT 143 O
STPCLK# 148 O
SMI# 149 O
FERR# 141 O
IGNNE# 139 O
CPU Reset.
CPU Interrupt.
interrupt request is pending and needs service.
Non-Maskable Interrupt.
CPU. The VT82C586B generates an NMI when either SERR# or IOCHK# is
asserted.
Initialization.
on the PCI bus or if a soft reset is initiated by the register
Stop Clock.
different Power-Management events.
System Management Interrupt.
in response to different Power-Management events.
Numerical Coprocessor Error.
the CPU.
Ignore Numeric Error.
The VT82C586B asserts CPURST to reset the CPU during power-up.
INTR is driven by the VT82C586B to signal the CPU that an
The VT82C586B asserts INIT if it detects a shut-down special cycle
STPCLK# is asserted by the VT82C586B to the CPU in response to
VT82C586B
NMI is used to force a non-maskable interrupt to the
SMI# is asserted by the VT82C586B to the CPU
This signal is tied to the coprocessor error signal on
This pin is connected to the “ignore error” pin on the CPU.
Revision 1.0 May 13, 1997 -5- Pinouts
Page 12
9,$7HFKQRORJLHV,QF
PCI Bus Interface
Signal Name Pin No. I/O Signal Description
PCLK 2 I
FRAME# 181 B
AD[31:0] 204-199, 196-
195, 192-189,
187-185, 183,
172, 170-167,
165-163, 161-
158, 155-152
C/BE[3:0]# 194, 182, 173,
162
IRDY# 180 B
TRDY# 179 B
STOP# 176 B
DEVSEL# 178 B
PAR 174 B
SERR# 175 I
IDSEL 193 I
PIRQA-D# 1, 207-205 I
PREQ# 151 O
PGNT# 150 I
PCI Clock.
Frame.
that one more data transfer is desired by the cycle initiator.
B
Address/Data Bus.
with FRAME# assertion and data is driven or received in following cycles.
B
Command/Byte Enable.
enables corresponding to supplied or requested data are driven on following clocks.
Initiator Ready.
Target Ready.
Stop.
Device Select.
positive or subtractive decoding.
Parity.
System Error.
error condition. Upon sampling SERR# active, the VT82C586B can be programmed
to generate an NMI to the CPU.
Initialization Device Select.
read and write cycles.
PCI Interrupt Request
INTD# pins as follows:
PCI Slot 1 INTA# INTB# INTC# INTD#
PCI Slot 2 INTB# INTC# INTD# INTA#
PCI Slot 3 INTC# INTD# INTA# INTB#
PCI Slot 4 INTD# INTA# INTB# INTC#
PCI Request.
PCI Grant.
VT82C586B.
PCLK provides timing for all transactions on the PCI Bus.
Assertion indicates the address phase of a PCI transfer. Negation indicates
Asserted when the initiator is ready for data transfer.
Asserted when the target is ready for data transfer.
Asserted by the target to request the master to stop the current transaction.
The VT82C586B asserts this signal to claim PCI transactions through
A single parity bit is provided over AD[31:0] and C/BE[3:0]#.
SERR# can be pulsed active by any PCI device that detects a system
This signal goes to the North Bridge to request the PCI bus.
This signal is driven by the North Bridge to grant PCI access to the
VT82C586B
The standard PCI address and data lines. The address is driven
The command is driven with FRAME# assertion. Byte
IDSEL is used as a chip select during configuration
. These pins are typically connected to the PCI bus INTA#-
PIRQA# PIRQB#
PIRQC# PIRQD#
Revision 1.0 May 13, 1997 -6- Pinouts
Page 13
9,$7HFKQRORJLHV,QF
ISA Bus Control
Signal Name Pin No. I/O Signal Description
SA[15:0] /
DD[15:0]
SA16 19 B
LA23/DCS3B#,
LA22/DCS1B#,
LA21/DCS3A#,
LA20/DCS1A#,
LA[19:17] /
DA[2:0]
SD[15:8] /
GPI[15:8] /
GPO[15:8]
SBHE# 62 B
IOR# 12 B
IOW# 11 B
MEMR# 123 B
MEMW# 124 B
SMEMR# 10 O
SMEMW# 9 O
BALE 35 O
IOCS16# 125 I
MEMCS16# 76 I
IOCHCK# 5 I
IOCHRDY 8 I
20-25, 27-28,
36-38, 40-44
63-67, 69-70 B
86-85, 83-80,
78-77
B
System Address Bus / IDE Data Bus
System Address Bus
Multifunction Pins
ISA Bus Cycles:
Address: The LA[23:17] address lines are bi-directional. These address lines allow
accesses to physical memory on the ISA bus up to 16MBytes.
PCI IDE Cycles:
Chip Select: DCS1A# is for the ATA command register block and corresponds to
CS1FX# on the primary IDE connector. DCS3A# is for the ATA command register
block and corresponds to CS3FX# on the primary IDE connector. DCS1B# is for the
ATA command register block and corresponds to CS17X# on the primary IDE
connector. DCS3B# is for the ATA command register block and corresponds to
CS37X# on the primary IDE connector.
Disk Address: DA[2:0] are used to indicate which byte in either the ATA command
block or control block is being accessed.
B
System Data.
the ISA bus. These pins also function as
GPIO3_CFG bit is low (pin 92 becomes GPI_RE# for enabling external inputs onto
the SD pins using an external buffer). These pins also function as
Outputs
of an external latch).
System Byte High Enable.
transferred on the upper byte (SD[15:8]) of the data bus. SBHE# is negated during
refresh cycles.
I/O Read.
data on to the ISA data bus.
I/O Write.
latch data from the ISA data bus.
Memory Read.
onto the ISA data bus.
Memory Write.
from the ISA data bus.
Standard Memory Read.
1MB, which indicates that it may drive data onto the ISA data bus
Standard Memory Write.
1MB, which indicates that it may latch data from the ISA data bus.
Bus Address Latch Enable.
VT82C586B to indicate that the address (SA[19:0], LA[23:17] and the SBHE#
signal) is valid
16-Bit I/O Chip Select.
indicate that they support 16-bit I/O bus cycles.
Memory Chip Select 16.
low to indicate they support 16-bit memory bus cycles.
I/O Channel Check.
uncorrectable error has occurred for a device or memory on the ISA Bus.
I/O Channel Ready.
additional time (wait states) is required to complete the cycle.
SD[15:8] provide the high order byte data path for devices residing on
15-8 if the GPIO4_CFG bit is low (pin 136 becomes GPO_WE for control
IOR# is the command to an ISA I/O slave device that the slave may drive
IOW# is the command to an ISA I/O slave device that the slave may
MEMR# is the command to a memory slave that it may drive data
MEMW# is the command to a memory slave that it may latch data
VT82C586B
General Purpose Inputs
SBHE# indicates, when asserted, that a byte is being
SMEMR# is the command to a memory slave, under
SMEMW# is the command to a memory slave, under
BALE is an active high signal asserted by the
This signal is driven by I/O devices on the ISA Bus to
ISA slaves that are 16-bit memory devices drive this line
When this signal is asserted, it indicates that a parity or an
Devices on the ISA Bus negate IOCHRDY to indicate that
15-8 if the
General Purpose
Revision 1.0 May 13, 1997 -7- Pinouts
Page 14
9,$7HFKQRORJLHV,QF
ISA Bus Control (continued)
Signal Name Pin No. I/O Signal Description
REFRESH# 29 B
AEN 15 O
IRQ15, 14, 119, 7-3
DRQ7-5, 3-0 132, 130, 57,
DACK7:5, 3-0# 133, 131, 58,
TC 32 O
MASTER# (see below) I
SPKR /
Power-up Strap
128-129, 127-
126, 61, 71-75
30, 7, 16, 59
31, 33, 18, 60
134 B
Refresh.
an input REFRESH# is driven by 16-bit ISA Bus masters to indicate refresh cycle.
Address Enable.
misinterpreting DMA cycles as valid I/O cycles.
I
Interrupt Request.
ISA Bus I/O devices with a mechanism for asynchronously interrupting the CPU.
I
DMA Request.
VT82C586B’s DMA controller.
O
Acknowledge.
been granted.
Terminal Count.
indicator.
ISA Master Request.
Multifunction Pin
As an output REFRESH# indicates when a refresh cycle is in progress. As
AEN is asserted during DMA cycles to prevent I/O slaves from
The DRQ lines are used to request DMA services from the
The DACK# output lines indicate a request for DMA service has
Normal Operation:
Power-up Strapping:
VT82C586B
The IRQ signals provide both system board components and
The VT82C586B asserts TC to DMA slaves as a terminal count
(see below pin 137)
Speaker Drive.
0/1 = Fixed/flexible IDE I/O base
The SPKR signal is the output of counter 2.
Revision 1.0 May 13, 1997 -8- Pinouts
Page 15
9,$7HFKQRORJLHV,QF
On Board Plug and Play
Signal Name Pin No. I/O Signal Description
MIRQ0 /
APICCS# /
POS (3040F)
MIRQ1 /
KEYLOCK /
IRQ8# (3040F)
MIRQ2 /
MASTER# /
SDDIR (3041A)
90 I
106 I
137 I
Multifunction Pin
O
O
O
MIRQ0.
APICCS#
implementations.
POS.
was introduced in rev F of the 3040 silicon and is not available in earlier chips.
Rx59[3] Rx59[0]
Multifunction Pin
I
MIRQ1.
I
KEYLOCK.
IRQ8#.
revision F of the 3040 silicon and is not available in earlier chips.
Rx48[4] Rx59[1]
Rx5A[2] Rx48[4]
Multifunction Pin
I
MIRQ2.
MASTER#.
control for the IDE interface DD / SA transceivers (see SOE#).
SDDIR.
interface DD / SA transceivers (see SOE#) separate from MASTER#. This
function was introduced in revision A of the 3041 silicon and not available in
earlier chips.
Rx48[5] Rx59[2]
Steerable interrupt request input for on-board devices.
. Chip select for external IOAPIC chip for symmetric multiprocessor
Power-On Suspend Status Output (see Function 0 Rx59 bit-3). This function
0 0 MIRQ0 (input)
0 1 APICCS# (output)
1 0 -illegal1 1 POS (output)
Steerable interrupt request input for on-board devices.
Keyboard lock input.
Interrupt input for external RTC. This function was introduced in
0 0 MIRQ1 (input)
0 1 KEYLOCK (input)
1 0 -illegal1 1 IRQ8# (input) (see also Rx5A[2] and table below). With
0 0 External RTC - IRQ8# input on pin 104
0 1 External RTC - IRQ8# input on pin 106
1 x Internal RTC - IRQ8# input not required
Steerable interrupt request input for on-board devices.
ISA Master Request indicator. This pin also serves as the direction
This pin may be programmed to serve as a direction control for the IDE
0 0 MASTER# (input)
0 1 MIRQ2 (input)
1 0 -illegal1 1 SDDIR (output)
VT82C586B
(see PCI Configuration Register Function 0 Rx59[3,0])
Pin Function
(see PCI Configuration Register Function 0 Rx59[1] & Rx48[4])
Pin Function
this setting, Rx57[3:0] must be set to 0 (MIRQ1 routing)
Pin Function
(see PCI Configuration Register Function 0 Rx59[2] & Rx48[5])
Pin Function
Revision 1.0 May 13, 1997 -9- Pinouts
Page 16
9,$7HFKQRORJLHV,QF
UltraDMA-33 Enhanced IDE Interface
Signal Name Pin No. I/O Signal Description
DRDYA# /
DDMARDYA#
/ DSTROBEA
DRDYB# /
DDMARDYB#
/ DSTROBEB
DIORA# /
HDMARDYA#
/ HSTROBEA
DIORB# /
HDMARDYB#
/ HSTROBEB
DIOWA# /
STOPA
DIOWB# /
STOPB
SOE# 56 O
DDRQA 45 I
DDRQB 46 I
DDACKA# 47 O
DDACKB# 48 O
49 I
89 I
50 O
54 O
51 O
55 O
EIDE Mode:
UltraDMA Mode:
EIDE Mode:
UltraDMA Mode:
EIDE Mode:
UltraDMA Mode:
EIDE Mode:
UltraDMA Mode:
EIDE Mode:
UltraDMA Mode:
EIDE Mode:
UltraDMA Mode:
System Address Transceiver Output Enable.
enables of the 245 transceivers that interface the DD[15:0] signals to SA[15:0]. The
transceiver direction controls are driven by MASTER# with DD[15-0] connected to
the “A” side of the transceivers and SA[15-0] connected to the “B” side.
Device DMA Request A.
Device DMA Request B.
Device DMA Acknowledge A.
Device DMA Acknowledge B.
VT82C586B
I/O Channel Ready A.
Device DMA Ready A
The device may assert DDMARDY# to pause output transfers
Device Strobe A
The device may stop DSTROBE to pause input data transfers
I/O Channel Ready B.
Device DMA Ready B
The device may assert DDMARDY# to pause output transfers
Device Strobe B
The device may stop DSTROBE to pause input data transfers
Device I/O Read A.
Host DMA Ready A
The host may assert HDMARDY# to pause input transfers
Host Strobe A
The host may stop HSTROBE to pause output data transfers
Device I/O Read B.
Host DMA Ready B
The host may assert HDMARDY# to pause input transfers
Host Strobe B
The host may stop HSTROBE to pause output data transfers
Device I/O Write A.
. Primary channel stop transfer: asserted by the host prior
Stop A
to initiation of an UltraDMA burst; negated by the host before
data is transferred in an UltraDMA burst. Assertion of STOP by
the host during or after data transfer in UltraDMA mode signals
the termination of the burst.
Device I/O Write B.
. Secondary channel stop transfer: asserted by the host
Stop B
prior to initiation of an UltraDMA burst; negated by the host
before data is transferred in an UltraDMA burst. Assertion of
STOP by the host during or after data transfer in UltraDMA mode
signals the termination of the burst.
Primary channel DMA request
Secondary channel DMA request
. Primary channel output data strobe (both edges)
. Secondary channel output strobe (both edges)
Primary channel DMA acknowledge
Secondary channel DMA acknowledge
Primary channel device ready indicator
. Primary channel output flow control
. Primary channel input data strobe (both edges)
Secondary channel device ready
. Secondary channel output flow control
. Secondary channel input strobe (both edges)
Primary channel device read strobe
. Primary channel input flow control
Secondary channel device read strobe
. Secondary channel input flow control
Primary channel device write strobe
Secondary channel device write strobe
This signal controls the output
Note: Refer to the ISA bus interface pin descriptions for remaining IDE interface pin descriptions (the IDE address, data, and
drive select pins are multiplexed with the ISA bus LA and SA pins). Also, the MASTER# pin description may be found
in the "On Board Plug and Play" pin group (DD / SA transceiver direction control).
Revision 1.0 May 13, 1997 -10- Pinouts
Page 17
9,$7HFKQRORJLHV,QF
XD Interface
Signal Name Pin No. I/O Signal Description
XD7-0,
EXTSMI7-3#,
GPI7-0,
GPO7-0,
Power-up Straps
XDIR 112 O
ROMCS# /
KBCS#
122
121
119
118
117
116
114
113
135 O
B
Multifunction Pins
X-bus Data Bus.
External SMI Inputs.
General Purpose Inputs.
General Purpose Outputs.
Power-up Strap Option Inputs.
XD0: 0/1 - Disable/enable internal KBC
XD1: 0/1 - Disable/enable internal PS/2 Mouse
XD2: 0/1 - Disable/enable internal RTC
XD4~XD7: RP13~RP16 for internal KBC
X-Bus Data Direction.
transceiver that buffers the X-Bus data and ISA-Bus data (the output enable of the
transceiver should be grounded). SD0-7 connect to the “A” side of the transceiver
and XD0-7 connect to the “B” side. XDIR high indicates that SD0-7 drives XD0-7.
Multifunction Pin. ROM Chip Select / Keyboard Controller Chip Select.
ISA memory cycle:
ISA I/O cycle:
VT82C586B
For connection to external X-Bus devices (e.g. BIOS ROM)
External SCI/SMI ports.
GPIO3_CFG bit low (pin 92 = GPI_RE#)
GPIO4_CFG bit low (pin 136 = GPO_WE)
(see Configuration Register Offset 5Ah)
XDIR is tied directly to the direction control of a 74F245
ROMCS#.
KBCS#.
Chip Select to the BIOS ROM.
Chip Select to the external keyboard controller.
General Purpose I/O
Signal Name Pin No. I/O Signal Description
GPIO0 /
EXTSMI0#
GPIO1 /
EXTSMI1# /
I2CD1 (Clock)
GPIO2 /
EXTSMI2# /
I2CD2 (Data)
GPIO3 /
EXTSMI3# /
GPI_RE#
GPIO4 /
EXTSMI4# /
GPO_WE
94 B
87 B
88 B
92 B
136 B
General Purpose I/O 0
This pin sits on the VDD-5VSB power plane and is available even under soft-off
state.
General Purpose I/O 1
Can be used along with pin 88 as an I
defined as clock).
General Purpose I/O 2
Can be used along with pin 87 as an I
defined as data).
Multifunction Pin
GPIO3 Configuration bit high:
external SCI/SMI capability.
GPIO3 Configuration bit low:
Connects to the output enable (OE# pin) of the external 244 buffers whose data pins
connect to SD15-8 and XD7-0 for GPI15-0.
Multifunction Pin
GPIO4 Configuration bit high:
external SCI/SMI capability.
GPIO4 Configuration bit low:
Connects to the latch enable (LE pin) of the external 373 latches whose data pins
connect to SD15-8 and XD7-0 for GPO15-0.
: General Purpose I/O with external SCI/SMI capability.
: General Purpose I/O with external SCI/SMI capability.
: General Purpose I/O with external SCI/SMI capability.
(per GPIO3 Configuration Bit: Function 3 Rx40 bit-6)
(per GPIO4 Configuration Bit: Function 3 Rx40 bit-7)
2
C pair (by software convention this pin is
2
C pair (by software convention this pin is
General Purpose I/O 3
Read Enable for General Purpose Inputs
General Purpose I/O 4
Write Enable for General Purpose Outputs
: General Purpose I/O with
: General Purpose I/O with
:
:
Revision 1.0 May 13, 1997 -11- Pinouts
Page 18
9,$7HFKQRORJLHV,QF
Universal Serial Bus Interface
Signal Name Pin No. I/O Signal Description
USBDATA0+ 95 B
USBDATA0- 96 B
USBDATA1+ 97 B
USBDATA1- 98 B
USBCLK 99 I
USB Port 0 Data +
USB Port 0 Data USB Port 1 Data +
USB Port 1 Data USB Clock.
Clock input for Universal Serial Bus interface
Keyboard Interface
Signal Name Pin No. I/O Signal Description
KBCK /
KA20G
KBDT /
KBRC#
MSCK / IRQ1 110 B
MSDT / IRQ12 111 B
A20M 147 O
KEYLOCK /
MIRQ1 /
IRQ8#
108 B
109 B
106 I
Multifunction Pin.
Internal KBC enabled:
Internal KBC disabled:
Multifunction Pin.
Internal KBC enabled:
Internal KBC disabled:
Multifunction Pin.
PS/2 mouse enabled:
PS/2 mouse disabled and internal KBC disabled:
IRQ 1 input from external KBC.
Multifunction Pin.
PS/2 mouse enabled:
PS/2 mouse disabled:
A20 Mask.
Keyboard Lock.
(For reference only - see pin 106 description in "Onboard Plug and Play" section)
Direct connect A20 mask on CPU.
Keyboard lock signal for internal keyboard controller.
VT82C586B
Function depends on enable/disable of internal KBC.
Keyboard Clock.
Gate A20:
Function depends on enable/disable of internal KBC.
Keyboard Data.
Keyboard Reset:
Function depends on enable/disable of internal KBC.
Mouse Clock.
Function depends on enable/disable of internal KBC.
Mouse Data.
Interrupt Request 12.
Clock to keyboard interface.
Gate A20 output from external KBC
Data to keyboard interface.
Reset input from external KBC.
Clock to PS/2 mouse interface.
Interrupt Request 1.
Data to PS/2 mouse interface.
IRQ 12 input from external KBC
Internal Real Time Clock
Signal Name Pin No. I/O Signal Description
RTCX1 /
IRQ8#
RTCX2 /
RTCCS#
VBAT 102 I
Revision 1.0 May 13, 1997 -12- Pinouts
104 I
105 O
Multifunction Pin
Internal RTC enabled:
Internal RTC disabled:
Rx5A[2] Rx48[4]
0 0 External RTC - IRQ8# input on pin 104
0 1 External RTC - IRQ8# input on pin 106
1 x Internal RTC - IRQ8# input not required
Multifunction Pin
Internal RTC enabled:
Internal RTC disabled:
RTC Battery.
Battery input for internal RTC
RTC Crystal Input
Interrupt Request 8
Pin Function
RTC Crystal Output
External RTC Chip Select
: 32.768Khz crystal or oscillator input.
: IRQ8 input from external RTC
: 32.768Khz crystal output
Page 19
9,$7HFKQRORJLHV,QF
Resets and Clocks
Signal Name Pin No. I/O Signal Description
PWRGD 138 I
PCIRST# 3 O
RSTDRV 4 O
BCLK 14 O
OSC 6 I
Power Good.
PCI Reset.
generate PCIRST# during power-up or from the control register.
Reset Drive.
Bus Clock.
Oscillator.
Connected to the POWERGOOD signal on the Power Supply.
An active low reset signal for the PCI bus. The VT82C586B will
RSTDRV is the reset signal to the ISA bus.
ISA bus clock.
OSC is the 14.31818 MHz clock signal. It is used by the internal Timer.
Power Management
Signal Name Pin No. I/O Signal Description
PWRBTN# 91 I
PWRON 107 O
RI# 93 I
Power Button.
Power Supply Control.
Ring Indicator.
to be re-activated by a received phone call. Input referenced to VDD-5VSB.
Referenced to VDD-5VSB.
May be connected to external modem circuitry to allow the system
Power and Ground
VT82C586B
Powered by VDD-5VSB.
Signal Name Pin No. I/O Signal Description
VDD5 17, 34, 53, 79,
115
VDD-5VSB 103 P
VDD3 144 P
VDD_PCI 157, 171, 184,
198
AVDD 100 P
AGND 101 P
GND 13, 26, 39, 52,
68, 84, 120,
140, 156, 166,
177, 188, 197,
208
P
Power Supply.
switch on the power supply is turned on and the PWRON signal is conditioned high.
Power Supply.
is turned off. If the "soft-off" state is not implemented, then this pin can be
connected to VDD5.
Power Supply.
circuitry.
P
PCI Voltage.
USB Differential Output Power Source
USB Differential Output Ground
P
Ground
4.75 to 5.25V. This supply is turned on only when the mechanical
Always available unless the mechanical switch of the power supply
This pin should be connected to the same voltage as the CPU I/O
3.3 or 5V.
Revision 1.0 May 13, 1997 -13- Pinouts
Page 20
9,$7HFKQRORJLHV,QF
VT82C586B
R
EGISTERS
Register Overview
The following tables summarize the configuration and I/O
registers of the VT82C586B. These tables also document the
power-on default value (“Default”) and access type (“Acc”) for
each register. Access type definitions used are RW
(Read/Write), RO (Read/Only), “—” for reserved / used
(essentially the same as RO), and RWC (or just WC) (Read /
Write 1’s to Clear individual bits). Registers indicated as RW
may have some read/only bits that always read back a fixed
value (usually 0 if unused); registers designated as RWC or
WC may have some read-only or read write bits (see individual
register descriptions for details).
Detailed register descriptions are provided in the following
section of this document. All offset and default values are
shown in hexadecimal unless otherwise indicated
Table 2. System I/O Map
Port Function Actual Port Decoding
00-1F Master DMA Controller 0000 0000 000x nnnn
20-3F Master Interrupt Controller 0000 0000 001x xxxn
40-5F Timer / Counter 0000 0000 010x xxnn
60-6F Keyboard Controller 0000 0000 0110 xnxn
(60h) KBC Data 0000 0000 0110 x0x0
(61h) Misc Functions & Spkr Ctrl 0000 0000 0110 xxx1
(64h) KBC Command / Status 0000 0000 0110 x1x0
70-77 RTC/CMOS/NMI-Disable 0000 0000 0111 0nnn
78-7F -available for system use- 0000 0000 0111 1xxx
80 -reserved- (debug port) 0000 0000 1000 0000
81-8F DMA Page Registers 0000 0000 1000 nnnn
90-91 -available for system use- 0000 0000 1001 000x
92 System Control 0000 0000 1001 0010
93-9F -available for system use- 0000 0000 1001 nnnn
A0-BF Slave Interrupt Controller 0000 0000 101x xxxn
C0-DF Slave DMA Controller 0000 0000 110n nnnx
E0-FF -available for system use- 0000 0000 111x xxxx
100-CF7 -available for system useCF8-CFB PCI Configuration Address 0000 1100 1111 10xx
CFC-CFF PCI Configuration Data 0000 1100 1111 11xx
D00-FFFF -available for system use-
Table 3. Registers
Legacy I/O Registers
Port Master DMA Controller Registers Default Acc
00 Channel 0 Base & Current Address RW
01 Channel 0 Base & Current Count RW
02 Channel 1 Base & Current Address RW
03 Channel 1 Base & Current Count RW
04 Channel 2 Base & Current Address RW
05 Channel 2 Base & Current Count RW
06 Channel 3 Base & Current Address RW
07 Channel 3 Base & Current Count RW
08 Status / Command RW
09 Write Request
0A Write Single Mask
0B Write Mode
0C Clear Byte Pointer FF
0D Master Clear
0E Clear Mask
0F Read / Write Mask RW
Port Master Interrupt Controller Regs Default Acc
20 Master Interrupt Control — *
21 Master Interrupt Mask — *
20 Master Interrupt Control Shadow —
21 Master Interrupt Mask Shadow —
* RW if shadow registers are disabled
Timer/Counter Registers Default Acc
Port
40 Timer / Counter 0 Count RW
41 Timer / Counter 1 Count RW
42 Timer / Counter 2 Count RW
43 Timer / Counter Control
Port Keyboard Controller Registers Default Acc
60 Keyboard Controller Data RW
61 Misc Functions & Speaker Control RW
64 Keyboard Ctrlr Command / Status RW
Port CMOS / RTC / NMI Registers Default Acc
70 CMOS Memory Address & NMI Disa
71 CMOS Memory Data (128 bytes) RW
72 CMOS Memory Address RW
73 CMOS Memory Data (256 bytes) RW
74 CMOS Memory Address RW
75 CMOS Memory Data (256 bytes) RW
NMI Disable is port 70h (CMOS Memory Address) bit-7.
RTC control occurs via specific CMOS data locations (0-0Dh).
Ports 72-73 may be used to access all 256 locations of CMOS.
Ports 74-75 may be used to access CMOS if the internal RTC is
disabled.
WO
WO
WO
WO
WO
WO
RW
RW
WO
WO
Revision 1.0 May 13, 1997 -14- Register Overview
Page 21
9,$7HFKQRORJLHV,QF
VT82C586B
Port DMA Page Registers Default Acc
87 DMA Page - DMA Channel 0 RW
83 DMA Page - DMA Channel 1 RW
81 DMA Page - DMA Channel 2 RW
82 DMA Page - DMA Channel 3 RW
8F DMA Page - DMA Channel 4 RW
8B DMA Page - DMA Channel 5 RW
89 DMA Page - DMA Channel 6 RW
8A DMA Page - DMA Channel 7 RW
Port System Control Registers Default Acc
92 System Control RW
Port Slave Interrupt Controller Regs Default Acc
A0 Slave Interrupt Control — *
A1 Slave Interrupt Mask — *
A0 Slave Interrupt Control Shadow —
A1 Slave Interrupt Mask Shadow —
* RW accessible if shadow registers are disabled
RW
RW
Slave DMA Controller Registers Default Acc
Port
C0 Channel 0 Base & Current Address RW
C2 Channel 0 Base & Current Count RW
C4 Channel 1 Base & Current Address RW
C6 Channel 1 Base & Current Count RW
C8 Channel 2 Base & Current Address RW
CA Channel 2 Base & Current Count RW
CC Channel 3 Base & Current Address RW
CE Channel 3 Base & Current Count RW
D0 Status / Command RW
D2 Write Request
D4 Write Single Mask
D6 Write Mode
D8 Clear Byte Pointer FF
DA Master Clear
DC Clear Mask
DE Read / Write Mask RW
WO
WO
WO
WO
WO
WO
Revision 1.0 May 13, 1997 -15- Register Overview
Page 22

9,$7HFKQRORJLHV,QF
PCI Function 0 Registers - PCI-to-ISA Bridge
Configuration Space PCI-to-ISA Bridge Header Registers
Offset PCI Configuration Space Header Default Acc
1-0 Vendor ID 1106 RO
3-2 Device ID 0586 RO
5-4 Command 000F
7-6 Status 0200
8 Revision ID nn RO
9 Programming Interface 00 RO
A Sub Class Code 01 RO
B Base Class Code 06 RO
C -reserved- (cache line size) 00 —
D -reserved- (latency timer) 00 —
E Header Type 80 RO
F Built In Self Test (BIST) 00 RO
10-27 -reserved- (base address registers) 00 —
28-2B -reserved- (unassigned) 00 —
2F-2C Subsystem ID Read 00 RO
30-33 -reserved- (expan. ROM base addr) 00 —
34-3B -reserved- (unassigned) 00 —
3C -reserved- (interrupt line) 00 —
3D -reserved- (interrupt pin) 00 —
3E -reserved- (min gnt) 00 —
3F -reserved- (max lat) 00 —
Configuration Space PCI-to-ISA Bridge-Specific Registers
Offset ISA Bus Control Default Acc
40 ISA Bus Control 00 RW
41 ISA Test Mode 00 RW
42 ISA Clock Control 00 RW
43 ROM Decode Control 00 RW
44 Keyboard Controller Control 00 RW
45 Type F DMA Control 00 RW
46 Miscellaneous Control 1 00 RW
47 Miscellaneous Control 2 00 RW
48 Miscellaneous Control 3 01 RW
49 -reserved- 00 —
4A IDE Interrupt Routing 04 RW
4B -reserved- 00 —
4C DMA / Master Mem Access Control 1 00 RW
4D DMA / Master Mem Access Control 2 00 RW
4F-4E DMA / Master Mem Access Control 3 0300 RW
RW
WC
VT82C586B
Offset Plug and Play Control Default Acc
50 -reserved- (do not program) 24 RW
51-53 -reserved- 00 —
54 PCI IRQ Edge / Level Selection 00 RW
55 PnP Routing for External MIRQ0-1 00 RW
56 PnP Routing for PCI INTB-A 00 RW
57 PnP Routing for PCI INTD-C 00 RW
58 PnP Routing for External MIRQ2 00 RW
59 MIRQ Pin Configuration 04 RW
5A XD Power-On Strap Options † RW
5B Internal RTC Test Mode 00 RW
5C DMA Control 00 RW
5F-5D -reserved- 00 —
† Power-up default value depends on external strapping
Distributed DMA Default Acc
Offset
61-60 Channel 0 Base Address / Enable 0000 RW
63-62 Channel 1 Base Address / Enable 0000 RW
65-64 Channel 2 Base Address / Enable 0000 RW
67-66 Channel 3 Base Address / Enable 0000 RW
69-68 -reserved- 0000 —
6B-6A Channel 5 Base Address / Enable 0000 RW
6D-6C Channel 6 Base Address / Enable 0000 RW
6F-6E Channel 7 Base Address / Enable 0000 RW
Offset Miscellaneous Default Acc
70 Subsystem ID Write 00 WO
71-7F -reserved- 00 —
Revision 1.0 May 13, 1997 -16- Register Overview
Page 23

9,$7HFKQRORJLHV,QF
VT82C586B
PCI Function 1 Registers - IDE Controller
Configuration Space IDE Header Registers
Offset PCI Configuration Space Header Default Acc
1-0 Vendor ID 1106 RO
3-2 Device ID 0571 RO
5-4 Command 0080 RO
7-6 Status 0280
8 Revision ID nn RO
9 Programming Interface 85
A Sub Class Code 01 RO
B Base Class Code 01 RO
C -reserved- (cache line size) 00 —
D Latency Timer 00 RW
E Header Type 00 RO
F Built In Self Test (BIST) 00 RO
13-10 Base Address - Pri Data / Command 000001F0 RO
17-14 Base Address - Pri Control / Status 000003F4 RO
1B-18 Base Address - Sec Data / Command 00000170 RO
1F-1C Base Address - Sec Control / Status 00000374 RO
23-20 Base Address - Bus Master Control 0000CC01
24-2F -reserved- (unassigned) 00 —
30-33 -reserved- (expan ROM base addr) 00 —
34-3B -reserved- (unassigned) 00 —
3C Interrupt Line 0E RW
3D Interrupt Pin 00 RO
3E Minimum Grant 00 RO
3F Maximum Latency 00 RO
RW
RW
RW
Configuration Space IDE-Specific Registers
Offset Configuration Space IDE Registers Default Acc
40 Chip Enable 08 RW
41 IDE Configuration 02 RW
42 -reserved- (do not program) 09
43 FIFO Configuration 3A RW
44 Miscellaneous Control 1 68 RW
45 Miscellaneous Control 2 00 RW
46 Miscellaneous Control 3 C0 RW
4B-48 Drive Timing Control
4C Address Setup Time FF RW
4D -reserved- (do not program) 00
4E Sec Non-1F0 Port Access Timing FF RW
4F Pri Non-1F0 Port Access Timing FF RW
53-50 UltraDMA33 Extd Timing Control 03030303 RW
54-5F -reserved- 00 —
61-60 Primary Sector Size 0200 RW
62-67 -reserved- 00 —
69-68 Secondary Sector Size 0200 RW
70-FF -reserved- 00 —
I/O Registers - IDE Controller
These registers are compliant with the SFF 8038 v1.0 standard.
Refer to that specification for additional information.
Offset
IDE I/O Registers Default Acc
0 Primary Channel Command 00 RW
1 -reserved- 00 —
2 Primary Channel Status 00 WC
3 -reserved- 00 —
4-7 Primary Channel PRD Table Addr 00 RW
8 Secondary Channel Command 00 RW
9 -reserved- 00 —
A Secondary Channel Status 00 WC
B -reserved- 00 —
C-F Secondary Channel PRD Table Addr 00 RW
A8A8A8A8
RW
RW
RW
Revision 1.0 May 13, 1997 -17- Register Overview
Page 24

9,$7HFKQRORJLHV,QF
VT82C586B
PCI Function 2 Registers - USB Controller
Configuration Space USB Header Registers
Offset PCI Configuration Space Header Default Acc
1-0 Vendor ID 1106 RO
3-2 Device ID 3038 RO
5-4 Command 0000
7-6 Status 0200
8 Revision ID nn RO
9 Programming Interface 00 RO
A Sub Class Code 03 RO
B Base Class Code 0C RO
C Cache Line Size 00 RO
D Latency Timer 16
E Header Type 00 RO
F BIST 00 RO
10-1F -reserved- 00 —
23-20 Base Address 00000301
24-3B -reserved- 00 —
3C Interrupt Line 00
3D Interrupt Pin 04
3E-3F -reserved- 00 —
RW
WC
RW
RW
RW
RO
I/O Registers - USB Controller
Offset USB I/O Registers Default Acc
1-0 USB Command 0000 RW
3-2 USB Status 0000
5-4 USB Interrupt Enable 0000 RW
7-6 Frame Number 0000 RW
B-8 Frame List Base Address 00000000 RW
C Start Of Frame Modify 40 RW
11-10 Port 1 Status / Control 0080
13-12 Port 2 Status / Control 0080
WC
WC
WC
Configuration Space USB-Specific Registers
Offset USB Control Default Acc
40 Miscellaneous Control 1 00
41 Miscellaneous Control 2 00
42-43 -reserved- 00 RO
44-45 -reserved- (test only, do not program)
46-47 -reserved- (test) RO
48-5F -reserved- 00 —
60 Serial Bus Release Number 10 RO
61-BF -reserved- 00 —
C1-C0 Legacy Support 2000
C2-FF -reserved- 00 —
RW
RW
RW
RW
Revision 1.0 May 13, 1997 -18- Register Overview
Page 25

9,$7HFKQRORJLHV,QF
VT82C586B
PCI Function 3 Registers - Power Management
Configuration Space Power Management Header Registers
Offset PCI Configuration Space Header Default Acc
1-0 Vendor ID 1106 RO
3-2 Device ID 3040 RO
5-4 Command 0000 RO
7-6 Status 0280
8 Revision ID nn RO
9 Programming Interface
A Sub Class Code
B Base Class Code
C Cache Line Size 00 RO
D Latency Timer 00 RO
E Header Type00RO
F BIST 00 RO
10-3F -reserved- 00 —
† The default values for these registers may be changed by
writing to offsets 61-63h (see below).
Configuration Space Power Management-Specific Registers
Offset Power Management Default Acc
40 Pin Configuration 00 RW
41 General Configuration 00 RW
42 SCI Interrupt Configuration 00 RW
43 -reserved- 00 —
45-44 Primary Interrupt Channel 0000 RW
47-46 Secondary Interrupt Channel 0000 RW
4B-48 I/O Base Address (256 Bytes) 0000 0001 RW
4F-4C -reserved- 00
53-50 GP Timer Control 0000 0000 RW
54-60 -reserved- 00
61 Write value for Offset 9 (Prog Intfc) 00
62 Write value for Offset A (Sub Class) 00
63 Write value for Offset B (Base Class) 00
64-FF -reserved- 00
WC
RO
RO
RO
—
—
WO
WO
WO
—
I/O Space Power Management- Registers
Offset Basic Control / Status Registers Default Acc
1-0 Power Management Status 0000 WC
3-2 Power Management Enable 0000 RW
5-4 Power Management Control 0000 RW
7-6 -reserved- 00
B-8 Power Management Timer 0000 0000 RW
F-C -reserved- 00
Offset Processor Registers Default Acc
13-10 Processor Control 0000 0000 RW
14 Processor LVL2 00
15 Processor LVL3 00
1F-16 -reserved- 00
Offset General Purpose Registers Default Acc
21-20 General Purpose Status 0000
23-22 General Purpose SCI Enable 0000 RW
25-24 General Purpose SMI Enable 0000 RW
27-26 General Purpose Power Supply Ctrl 0200 RW
Offset Generic Registers Default Acc
29-28 Global Status 0000
2B-2A Global Enable 0000 RW
2D-2C Global Control 00 RW
2E -reserved- 00
2F SMI Command 00 RW
33-30 Primary Activity Detect Status 0000 0000
37-34 Primary Activity Detect Enable 0000 0000 RW
3B-38 GP Timer Reload Enable 0000 0000 RW
3F-3C -reserved- 00
Offset General Purpose I/O Registers Default Acc
41-40 GPIO Direction Control 0000 RW
43-42 GPIO Port Output Value 0000 RW
45-44 GPIO Port Input Value input
47-46 GPO Port Output Value 0000 RW
49-48 GPI Port Input Value input
FF-4A -reserved- 00
—
—
RO
RO
—
WC
WC
—
WC
—
RO
RO
—
Revision 1.0 May 13, 1997 -19- Register Overview
Page 26

9,$7HFKQRORJLHV,QF
Configuration Space I/O
Mechanism #1
These ports respond only to double-word accesses. Byte or
word accesses will be passed on unchanged.
Port CFB-CF8 - Configuration Address ......................... RW
31 Configuration Space Enable
0 Disabled .................................................default
1 Convert configuration data port writes to
configuration cycles on the PCI bus
30-24 Reserved
23-16 PCI Bus Number
Used to choose a specific PCI bus in the system
15-11 Device Number
Used to choose a specific device in the system
10-8 Function Number
Used to choose a specific function if the selected
device supports multiple functions
7-2 Register Number
Used to select a specific DWORD in the device’s
configuration space
1-0 Fixed
........................................ always reads 0
........................................ always reads 0
VT82C586B
Port CFF-CFC - Configuration Data .............................. RW
Refer to PCI Bus Specification Version 2.1 for further details
on operation of the above configuration registers.
Revision 1.0 May 13, 1997 -20- Configuration Space I/O
Page 27

9,$7HFKQRORJLHV,QF
VT82C586B
Register Descriptions
Legacy I/O Ports
This group of registers includes the DMA Controllers,
Interrupt Controllers, and Timer/Counters as well as a number
of miscellaneous ports originally implemented using discrete
logic on original PC/AT motherboards. All of the registers
listed are integrated on-chip. These registers are implemented
in a precise manner for backwards compatibility with previous
generations of PC hardware. These registers are listed for
information purposes only. Detailed descriptions of the
actions and programming of these registers are included in
numerous industry publications (duplication of that
information here is beyond the scope of this document). All of
these registers reside in I/O space.
Port 61 - Misc Functions & Speaker Control ................. RW
7 Reserved
6 IOCHCK# Active
This bit is set when the ISA bus IOCHCK# signal is
asserted. Once set, this bit may be cleared by setting
bit-3 of this register. Bit-3 should be cleared to
enable recording of the next IOCHCK#. IOCHCK#
generates NMI to the CPU if NMI is enabled.
5 Timer/Counter 2 Output
This bit reflects the output of Timer/Counter 2
without any synchronization.
4 Refresh Detected
This bit toggles on every rising edge of the ISA bus
REFRESH# signal.
3 IOCHCK# Disable
0 Enable IOCHCK# assertions..................default
1 Force IOCHCK# inactive and clear any
2 Reserved
1 Speaker Enable
0 Disable ...................................................default
1 Enable Timer/Ctr 2 output to drive SPKR pin
0 Timer/Counter 2 Enable
0 Disable ...................................................default
1 Enable Timer/Counter 2
........................................ always reads 0
.................................................RO
.....................................RO
..................................................RO
..............................................RW
“IOCHCK# Active” condition in bit-6
........................................RW, default=0
....................................................RW
.....................................RW
Port 92h - System Control ................................................ RW
7-6 Hard Disk Activity LED Status
0 Off ....................................................default
1-3 On
5-4 Reserved
3 Power-On Password Bytes Inaccessable
2 Reserved
1 A20 Address Line Enable
0 A20 disabled / forced 0 (real mode) ...... default
1 A20 address line enabled
0 High Speed Reset
0 Normal
1 Briefly pulse system reset to switch from
........................................always reads 0
..default=0
........................................always reads 0
protected mode to real mode
Revision 1.0 May 13, 1997 -21- Register Descriptions
Page 28

9,$7HFKQRORJLHV,QF
VT82C586B
Keyboard Controller Registers
The keyboard controller handles the keyboard and mouse
interfaces. Two ports are used: port 60 and port 64. Reads
from port 64 return a status byte. Writes to port 64h are
command codes (see command code list following the register
descriptions). Input and output data is transferred via port 60.
A “Control” register is also available. It is accessable by
writing commands 20h / 60h to the command port (port 64h);
The control byte is written by first sending 60h to the
command port, then sending the control byte value. The
control register may be read by sending a command of 20h to
port 64h, waiting for “Output Buffer Full” status = 1, then
reading the control byte value from port 60h.
Traditional (non-integrated) keyboard controllers have an
“Input Port” and an “Output Port” with specific pins dedicated
to certain functions and other pins available for general
purpose I/O. Specific commands are provided to set these pins
high and low. All outputs are “open-collector” so to allow
input on one of these pins, the output value for that pin would
be set high (non-driving) and the desired input value read on
the input port. These ports are defined as follows:
Bit Input Port
0 P10 - Keyboard Data In B0 B8
1 P11 - Mouse Data In B1 B9
2 P12 - Turbo Pin (PS/2 mode only) B2 BA
3 P13 - user-defined B3 BB
4 P14 - user-defined B6 BE
5 P15 - user-defined B7 BF
6 P16 - user-defined – –
7 P17 - undefined – –
Bit Output Port
0 P20 - SYSRST (1=execute reset) – –
1 P21 - GATEA20 (1=A20 enabled) – –
2 P22 - Mouse Data Out B4 BC
3 P23 - Mouse Clock Out B5 BD
4 P24 - Keyboard OBF Interrupt (IRQ1) – –
5 P25 - Mouse OBF Interrupt (IRQ 12) – –
6 P26 - Keyboard Clock Out – –
7 P27 - Keyboard Data Out – –
Bit Test Port Lo Code
0 T0 - Keyboard Clock In – –
1 T1 - Mouse Clock In – –
Note: Command code C0h transfers input port data to the
output buffer. Command code D0h copies output port values
to the output buffer. Command code E0h transfers test input
port data to the output buffer.
Port 60 - Keyboard Controller Input Buffer ................. WO
Only write to port 60h if port 64h bit-1 = 0 (1=full).
Port 60 - Keyboard Controller Output Buffer ................ RO
Only read from port 60h if port 64h bit-0 = 1 (0=empty).
Lo Code Hi Code
Lo Code Hi Code
Hi Code
Port 64 - Keyboard / Mouse Status .................................. RO
0 Keyboard Output Buffer Full
0 Keyboard Output Buffer Empty.............default
1 Keyboard Output Buffer Full
1 Input Buffer Full
0 Input Buffer Empty................................ default
1 Input Buffer Full
2 System Flag
0 Power-On Default.................................. default
1 Self Test Successful
3 Command / Data
0 Last write was data write .......................default
1 Last write was command write
4 Keylock Status
0 Locked
1Free
5 Mouse Output Buffer Full
0 Mouse output buffer empty....................default
1 Mouse output buffer holds mouse data
6 General Receive / Transmit Timeout
0 No error ................................................. default
1 Error
7 Parity Error
0 No parity error (odd parity received)..... default
1 Even parity occurred on last byte received
from keyboard / mouse
KBC Control Register .......... (R/W via Commands 20h/60h)
7 Reserved
6 PC Compatibility
0 Disable scan conversion
1 Convert scan codes to PC format; convert 2-
5 Mouse Disable
0 Enable Mouse Interface .........................default
1 Disable Mouse Interface
4 Keyboard Disable
0 Enable Keyboard Interface .................... default
1 Disable Keyboard Interface
3 Keyboard Lock Disable
0 Enable Keyboard Inhibit Function.........default
1 Disable Keyboard Inhibit Function
2 System Flag
This bit may be read back as status register bit-2
1 Mouse Interrupt Enable
0 Disable mouse interrupts .......................default
1 Generate interrupt on IRQ12 when mouse data
0 Keyboard Interrupt Enable
0 Disable Keyboard Interrupts.................. default
1 Generate interrupt on IRQ1 when output buffer
........................................always reads 0
byte break sequences to 1-byte PC-compatible
break codes............................................ default
................................................default=0
comes in output bufer
has been written.
Revision 1.0 May 13, 1997 -22- Register Descriptions
Page 29

9,$7HFKQRORJLHV,QF
Port 64 - Keyboard / Mouse Command .......................... WO
This port is used to send co mmands to the keyboard / mouse
controller. The command codes recognized by the
VT82C586B are listed n the table below.
Note: The VT82C586B Keyboard Controller is compatible
with the VIA VT82C42 Industry-Standard Keyboard
Controller except that due to its integrated nature, many of the
input and output port pins are not available externally for use
as general purpo se I/O pins (even though P 13-P16 are set on
power-up as strapping options). In other words, many of the
commands below are provided and “work”, but otherwise
perform no useful function (e. g., commands that set P12-P 17
high or low). Also note that setting P10-11, P22-23, P26-27,
and T0-1 high or lo w directly serves no useful purpose, sinc e
these bits are used to implement the keyboard and mouse ports
and are directly controlled by keyboard controller logic.
Table 4. Keyboard Controller Command Codes
VT82C586B
Code Keyboard Command Code Description
20h Read Control Byte (next byte is Control Byte)
60h Write Control Byte (next byte is Control Byte)
9xh Write low nibble (bits 0-3) to P10-P13
A1h Output Keyboard Controller Version #
A4h Test if Password is installed
(always returns F1h to indicate not installed)
A7h Disable Mouse Interface
A8h Enable Mouse Interface
A9h Mouse Interface Test (puts test results in port 60h)
(value: 0=OK, 1=clk stuck low, 2=clk stuck high,
3=data stuck lo, 4=data stuck hi, FF=general error)
AAh KBC self test (returns 55h if OK, FCh if not)
ABh Keyboard Interface Test (see A9h Mouse Test)
ADh Disable Keyboard Interface
AEh Enable Keyboard Interface
AFh Return Version #
B0h Set P10 low
B1h Set P11 low
B2h Set P12 low
B3h Set P13 low
B4h Set P22 low
B5h Set P23 low
B6h Set P14 low
B7h Set P15 low
B8h Set P10 high
B9h Set P11 high
BAh Set P12 high
BBh Set P13 high
BCh Set P22 high
BDh Set P23 high
BEh Set P14 high
BFh Set P15 high
Code Keyboard Command Code Description
C0h Read input port (read P10-17 input data to
the output buffer)
C1h Poll input port low (read input data on P11-13
repeatably & put in bits 5-7 of status
C2h Poll input port high (same except P15-17)
C8h Unblock P22-23 (use before D1 to change
active mode)
C9h Reblock P22-23 (protection mechanism for D1)
CAh Read mode (output KBC mode info to port 60
output buffer (bit-0=0 if ISA, 1 if PS/2)
D0h Read Output Port (copy P10-17 output port values
to port 60)
D1h Write Output Port (data byte following is written to
keyboard output port as if it came from keyboard)
D2h Write Keyboard Output Buffer & clear status bit-5
(write following byte to keyboard)
D3h Write Mouse Output Buffer & set status bit-5 (write
following byte to mouse; put value in mouse input
buffer so it appears to have come from the mouse)
D4h Write Mouse (write following byte to mouse)
E0h Read test inputs (T0-1 read to bits 0-1 of resp byte)
Exh Set P23-P21 per command bits 3-1
Fxh Pulse P23-P20 low for 6usec per command bits 3-0
All other codes not listed are undefined.
Revision 1.0 May 13, 1997 -23- Register Descriptions
Page 30

9,$7HFKQRORJLHV,QF
VT82C586B
DMA Controller I/O Registers
Ports 00-0F - Master DMA Controller
Channels 0-3 of the Master DMA Controller control System
DMA Channels 0-3. There are 16 Master DMA Controller
registers:
I/O Address Bits 15-0 Register Name
0000 0000 000x 0000 Ch 0 Base / Current Address RW
0000 0000 000x 0001 Ch 0 Base / Current Count RW
0000 0000 000x 0010 Ch 1 Base / Current Address RW
0000 0000 000x 0011 Ch 1 Base / Current Count RW
0000 0000 000x 0100 Ch 2 Base / Current Address RW
0000 0000 000x 0101 Ch 2 Base / Current Count RW
0000 0000 000x 0110 Ch 3 Base / Current Address RW
0000 0000 000x 0111 Ch 3 Base / Current Count RW
0000 0000 000x 1000 Status / Command RW
0000 0000 000x 1001 Write Request WO
0000 0000 000x 1010 Write Single Mask WO
0000 0000 000x 1011 Write Mode WO
0000 0000 000x 1100 Clear Byte Pointer F/F WO
0000 0000 000x 1101 Master Clear WO
0000 0000 000x 1110 Clear Mask WO
0000 0000 000x 1111 R/W All Mask Bits RW
Note that not all bits of the address are decoded.
The Master DMA Controller is compatible with the Intel 8237
DMA Controller chip. Detailed descriptions of 8237 DMA
Controller operation can be obtained from the Intel Peripheral
Components Data Book and numerous other industry
publications.
Ports C0-DF - Slave DMA Controller
Channels 0-3 of the Slave DMA Controller control System
DMA Channels 4-7. There are 16 Slave DMA Controller
registers:
I/O Address Bits 15-0 Register Name
0000 0000 1100 000x Ch 0 Base / Current Address RW
0000 0000 1100 001x Ch 0 Base / Current Count RW
0000 0000 1100 010x Ch 1 Base / Current Address RW
0000 0000 1100 011x Ch 1 Base / Current Count RW
0000 0000 1100 100x Ch 2 Base / Current Address RW
0000 0000 1100 101x Ch 2 Base / Current Count RW
0000 0000 1100 110x Ch 3 Base / Current Address RW
0000 0000 1100 111x Ch 3 Base / Current Count RW
0000 0000 1101 000x Status / Command RW
0000 0000 1101 001x Write Request WO
0000 0000 1101 010x Write Single Mask WO
0000 0000 1101 011x Write Mode WO
0000 0000 1101 100x Clear Byte Pointer F/F WO
0000 0000 1101 101x Master Clear WO
0000 0000 1101 110x Clear Mask WO
0000 0000 1101 111x Read/Write All Mask Bits WO
Note that not all bits of the address are decoded.
The Slave DMA Controller is compatible with the Intel 8237
DMA Controller chip. Detailed description of 8237 DMA
controller operation can be obtained from the Intel Peripheral
Components Data Book and numerous other industry
publications.
Ports 80-8F - DMA Page Registers
There are eight DMA Page Registers, one for each DMA
channel. These registers provide bits 16-23 of the 24-bit
address for each DMA channel (bits 0-15 are stored in
registers in the Master and Slave DMA Controllers). They are
located at the following I/O Port addresses:
I/O Address Bits 15-0 Register Name
0000 0000 1000 0111 Channel 0 DMA Page (M-0).........RW
0000 0000 1000 0011 Channel 1 DMA Page (M-1).........RW
0000 0000 1000 0001 Channel 2 DMA Page (M-2).........RW
0000 0000 1000 0010 Channel 3 DMA Page (M-3).........RW
0000 0000 1000 1111 Channel 4 DMA Page (S-0)..........RW
0000 0000 1000 1011 Channel 5 DMA Page (S-1)..........RW
0000 0000 1000 1001 Channel 6 DMA Page (S-2)..........RW
0000 0000 1000 1010 Channel 7 DMA Page (S-3) .........RW
Revision 1.0 May 13, 1997 -24- Register Descriptions
Page 31

9,$7HFKQRORJLHV,QF
VT82C586B
Interrupt Controller Registers
Ports 20-21 - Master Interrupt Controller
The Master Interrupt Controller controls system interrupt
channels 0-7. Two registers control the Master Interrupt
Controller. They are:
I/O Address Bits 15-0 Register Name
0000 0000 001x xxx0 Master Interrupt Control RW
0000 0000 001x xxx1 Master Interrupt Mask RW
Note that not all bits of the address are decoded.
The Master Interrupt Controller is compatible with the Intel
8259 Interrupt Controller chip. Detailed descriptions of 8259
Interrupt Controller operation can be obtained from the Intel
Peripheral Components Data Book and numerous other
industry publications.
Ports A0-A1 - Slave Interrupt Controller
The Slave Interrupt Controller controls system interrupt
channels 8-15. The slave system interrupt controller also
occupies two register locations:
I/O Address Bits 15-0 Register Name
0000 0000 101x xxx0 Slave Interrupt Control RW
0000 0000 101x xxx1 Slave Interrupt Mask RW
Note that not all address bits are decoded.
The Slave Interrupt Controller is compatible with the Intel
8259 Interrupt Controller chip. Detailed descriptions of 8259
Interrupt Controller operation can be obtained from the Intel
Peripheral Components Data Book and numerous other
industry publications.
Interrupt Controller Shadow Registers
The following shadow registers are enabled by setting bit 4 of
Rx47 to 1 (offset 47h in the PCI-ISA Bridge function 0
register group). If the shadow registers are enabled, they are
read back at the indicated I/O port instead of the standard
interrupt controller registers (writes to the interrupt controller
register ports are directed to the standard interrupt controller
registers).
Port 20 - Master Interrupt Control Shadow ................... RO
7-5 Reserved
4 OCW3 bit 5
3 OCW2 bit 7
2 ICW4 bit 4
1 ICW4 bit 1
0 ICW1 bit 3
Port 21 - Master Interrupt Mask Shadow ....................... RO
7-5 Reserved
4-0 T7-T3 of Interrupt Vector Address
Port A0 - Slave Interrupt Control Shadow ..................... RO
7-5 Reserved
4 OCW3 bit 5
3 OCW2 bit 7
2 ICW4 bit 4
1 ICW4 bit 1
0 ICW1 bit 3
Port A1 - Slave Interrupt Mask Shadow ........................ RO
7-5 Reserved
4-0 T7-T3 of Interrupt Vector Address
Timer / Counter Registers
........................................always reads 0
........................................always reads 0
........................................always reads 0
........................................always reads 0
Ports 40-43 - Timer / Counter Registers
There are 4 Timer / Counter registers:
I/O Address Bits 15-0 Register Name
0000 0000 010x xx00 Timer / Counter 0 Count RW
0000 0000 010x xx01 Timer / Counter 1 Count RW
0000 0000 010x xx10 Timer / Counter 2 Count RW
0000 0000 010x xx11 Timer / Counter Cm d Mode WO
Note that not all bits of the address are decoded.
The Timer / Counters are compatible with the Intel 8254
Timer / Counter chip. Detailed descriptions of 8254 Timer /
Counter operation can be obtained from the Intel Peripheral
Components Data Book and numerous other industry
publications.
Revision 1.0 May 13, 1997 -25- Register Descriptions
Page 32

9,$7HFKQRORJLHV,QF
CMOS / RTC Registers
Port 70 - CMOS Address ................................................. WO
7 NMI Disable
0 Enable NMI Generation. NMI is asserted on
1 Disable NMI Generation ........................default
6-0 CMOS Address
Port 71 - CMOS Data........................................................ RW
7-0 CMOS Data
Note: Ports 70-71 may be accessed if Rx5A bit-2 is set to
one to select the internal RTC. If Rx5A bit-2 is set to
zero, accesses to ports 70-71 will be directed to an
external RTC.
.........................................................WO
encountering IOCHCK# on the ISA bus or
SERR# on the PCI bus.
(lower 128 bytes).......................WO
(128 bytes)
Offset Description
00 Seconds
01 Seconds Alarm
02 Minutes
03 Minutes Alarm
04 Hours
05 Hours Alarm
06 Day of the Week
07 Day of the Month
08 Month
09 Year
VT82C586B
Binary Range BCD Range
00-3Bh 00-59h
00-3Bh 00-59h
00-3Bh 00-59h
00-3Bh 00-59h
am 12hr: 01-1Ch 01-12h
pm 12hr: 81-8Ch 81-92h
24hr: 00-17h 00-23h
am 12hr: 01-1Ch 01-12h
pm 12hr: 81-8Ch 81-92h
24hr: 00-17h 00-23h
Sun=1: 01-07h 01-07h
01-1Fh 01-31h
01-0Ch 01-12h
00-63h 00-99h
Port 72 - CMOS Address .................................................. RW
7-0 CMOS Address
Port 73 - CMOS Data........................................................ RW
7-0 CMOS Data
Note: Ports 72-73 may be accessed if Rx5A bit-2 is set to
one to select the internal RTC. If Rx5A bit-2 is set to
zero, accesses to ports 72-73 will be directed to an
external RTC.
Port 74 - CMOS Address .................................................. RW
7-0 CMOS Address
Port 75 - CMOS Data........................................................ RW
7-0 CMOS Data
Note: Ports 74-75 may be accessed only if Function 0 Rx5B
bit-1 is set to one to enable the internal RTC SRAM
and if Rx48 bit-3 (Port 74/75 Access Enable) is set to
one to enable port 74/75 access.
Note: Ports 70-71 are compatible with PC industry-
standards and may be used to access the lower 128
bytes of the 256-byte on-chip CMOS RAM. Ports
72-73 may be used to access the full extended 256byte space. Ports 74-75 may be used to access the
full on-chip extended 256-byte space in cases where
the on-chip RTC is disabled.
Note: The system Real Time Clock (RTC) is part of the
“CMOS” block. The RTC control registers are
located at specific offsets in the CMOS data area (00Dh and 7D-7Fh). Detailed descriptions of CMOS /
RTC operation and programming can be obtained
from the VIA VT82887 Data Book or numerous
other industry publications. For reference, the
definition of the RTC register locations and bits are
summarized in the following table:
(256 bytes).................................RW
(256 bytes)
(256 bytes).................................RW
(256 bytes)
0A Register A
7 UIP
6-4 DV2-0
3-0 RS3-0
0B Register B
7 SET
6PIE
5 AIE
4 UIE
3 SQWE
2DM
1 24/12
0 DSE
0C Register C
7 IRQF
6PF
5AF
4UF
3-0 0
0D Register D
7 VRT
6-0 0
0E-7C Software-Defined Storage Registers
Offset Extended Functions
7D Date Alarm
7E Month Alarm
7F Century Field
80-FF Software-Defined Storage Registers
Update In Progress
Divide (010=ena osc & keep time)
Rate Select for Periodic Interrupt
Inhibit Update Transfers
Periodic Interrupt Enable
Alarm Interrupt Enable
Update Ended Interrupt Enable
No function (read/write bit)
Data Mode (0=BCD, 1=binary)
Hours Byte Format (0=12, 1=24)
Daylight Savings Enable
Interrupt Request Flag
Periodic Interrupt Flag
Alarm Interrupt Flag
Update Ended Flag
Unused (always read 0)
Reads 1 if VBAT voltage is OK
Unused (always read 0)
Binary Range BCD Range
01-1Fh 01-31h
01-0Ch 01-12h
13-14h 19-20h
Table 5. CMOS Register Summary
(111 Bytes)
(128 Bytes)
Revision 1.0 May 13, 1997 -26- Register Descriptions
Page 33

9,$7HFKQRORJLHV,QF
VT82C586B
PCI to ISA Bridge Registers (Function 0)
All registers are located in the function 0 PCI configuration
space of the VT82C586B. These registers are accessed
through PCI configuration mechanism #1 via I/O address
CF8/CFC.
PCI Configuration Space Header
Offset 1-0 - Vendor ID = 1106h ......................................... RO
Offset 3-2 - Device ID = 0586h .......................................... RO
Offset 5-4 - Command ....................................................... RW
15-4 Reserved
3 Special Cycle Enable
2 Bus Master
1 Memory Space
0 I/O Space
† If the test bit at offset 46 bit-4 is set, access to the above
indicated bits is reversed: bit-3 above becomes read only
(reading back 1) and bits 0-1 above become read / write (with
a default of 1).
Offset 7-6 - Status ........................................................... RWC
15 Detected Parity Error
14 Signalled System Error
13 Signalled Master Abort
12 Received Target Abort
11 Signalled Target Abort
10-9 DEVSEL# Timing
8 Data Parity Detected
7 Fast Back-to-Back
6-0 Reserved
Offset 8 - Revision ID = nn ................................................ RO
7-0 ID for VT82C586 = 0xh
ID for VT82C586A = 2xh
ID for VT82C586B = 3xh (3040 OEM Silicon)
ID for VT82C586B = 4xh (3041 Production Sil.)
Offset 9 - Program Interface = 00h ................................... RO
Offset A - Sub Class Code = 01h ....................................... RO
Offset B - Class Code = 06h ............................................... RO
........................................ always reads 0
.....Normally RW†, default = 1
........................................ always reads 1
.................. Normally RO†, reads as 1
...................... Normally RO†, reads as 1
....................write one to clear
...................... always reads 0
.................write one to clear
..................write one to clear
...................... always reads 0
....................fixed at 01 (medium)
.......................... always reads 0
.............................. always reads 0
........................................ always reads 0
ISA Bus Control
Offset 40 - ISA Bus Control ............................................. RW
7 ISA Command Delay
0 Normal................................................... default
1 Extra
6 Extended ISA Bus Ready
0 Disable................................................... default
1 Enable
5 ISA Slave Wait States
0 4 Wait States..........................................default
1 5 Wait States
4 Chipset I/O Wait States
0 2 Wait States..........................................default
1 4 Wait States
3 I/O Recovery Time
0 Disable................................................... default
1 Enable
2 Extend-ALE
0 Disable................................................... default
1 Enable
1 ROM Wait States
0 1 Wait State ........................................... default
1 0 Wait States
0 ROM Write
0 Disable................................................... default
1 Enable
Offset 41 - ISA Test Mode ................................................ RW
7 Bus Refresh Arbitration
6 XRDY Test Mode
5 Port 92 Fast Reset
0 Disable................................................... default
1 Enable
4 A20G Emulation
3 Double DMA Clock
0 Disable (DMA Clock = ½ ISA Clock)...default
1 Enable (DMA Clock = ISA Clock)
2 SHOLD Lock During INTA
1 Refresh Request Test Mode
0 Refresh Test Mode ..................... (3041 silicon only)
0 Disable ISA Refresh .............................. default
1 Enable ISA Refresh
Note: This bit should always be set to one in the
OEM 3040 silicon.
(do not program).............default=0
(do not program) default=0
(do not program)...........default=0
(do not program) def=0
(do not program).def=0
Offset E - Header Type = 80h ............................................ RO
7-0 Header Type Code .........
Offset F - BIST = 00h ......................................................... RO
Offset 2F-2C - Subsystem ID ............................................. RO
Revision 1.0 May 13, 1997 -27- Register Descriptions
80h (Multifunction Device)
Page 34

9,$7HFKQRORJLHV,QF
VT82C586B
Offset 42 - ISA Clock Control. ......................................... RW
7 Latch IO16#
0 Enable (recommended setting)...............default
1 Disable
6 Reserved
5 Master Request Test Mode
4 Reserved
3 ISA CLOCK Select Enable
2-0 ISA Bus Clock Select
000 PCICLK/3 ..............................................default
001 PCICLK/2
010 PCICLK/4
011 PCICLK/6
100 PCICLK/5
101 PCICLK/10
110 PCICLK/12
111 OSC/2
Note: Procedure for ISA CLOCK switching:
1) Set bit 3 to 0; 2) Change value of bit 2-0; 3) Set bit 3 to 1
Offset 43 - ROM Decode Control .................................... RW
Setting these bits enables the indicated address range to be
included in the ROMCS# decode:
7 FFFE0000h-FFFEFFFFh
6 FFF80000h-FFFDFFFFh
5 000E8000h-000EFFFFh
4 000E0000h-000E7FFFh
3 000D8000h-000DFFFFh
2 000D0000h-000D7FFFh
1 000C8000h-000CFFFFh
0 000C0000h-000C7FFFh
Offset 44 - Keyboard Controller Control ........................ RW
7 KBC Timeout Test
6-4 Reserved
3 Mouse Lock Enable
2-1 Reserved
0 Reserved
Offset 45 - Type F DMA Control ..................................... RW
7 ISA Master / DMA to PCI Line Buffer
6 DMA type F Timing on Channel 7
5 DMA type F Timing on Channel 6
4 DMA type F Timing on Channel 5
3 DMA type F Timing on Channel 3
2 DMA type F Timing on Channel 2
1 DMA type F Timing on Channel 1
0 DMA type F Timing on Channel 0
(no defined function)................. default = 0
(do not program) . def=0
(no defined function)................. default = 0
0 ISA Clock = PCICLK/4 .........................default
1 ISA Clock selected per bits 2-0
(if bit-3 = 1)
.......................... default=0
......................... default=0
............................ default=0
............................ default=0
........................... default=0
............................ default=0
........................... default=0
............................. default=0
(do not program)....... default = 0
(do not program)........................ default = 0
0 Disabled .................................................default
1 Enabled
(do not program)........................ default = 0
(no function).............................. default = 0
.... default=0
........... default=0
........... default=0
........... default=0
........... default=0
........... default=0
........... default=0
........... default=0
Offset 46 - Miscellaneous Control 1 ................................ RW
7 PCI Master Write Wait States .(3041 Silicon Only)
0 0 Wait States..........................................default
1 1 Wait State
6 Gate INTRQ...............................(3041 Silicon Only)
0 Disable................................................... default
1 Enable
5 Flush Line Buffer for Int or DMA IOR Cycle........
...............................(3041 Silicon Only)
0 Disable................................................... default
1 Enable
4 Config Command Reg Rx04 Access (Test Only)
0 Normal: Bits 0-1=RO, Bit 3=RW......... default
1 Test Mode: Bits 0-1=RW, Bit-3=RO
3 Reserved
2 Reserved
1 PCI Burst Read Interruptability
0 Post Memory Write Enable
The Post Memory Write function is automatically
enabled when Delay Transaction (see Rx47 bit-6
below) is enabled, independent of the state of this bit.
Offset 47 - Miscellaneous Control 2 ................................ RW
7 CPU Reset Source
6 PCI Delay Transaction Enable
The "Post Memory Write" function is automatically
enabled when this bit is enabled, independent of the
state of Rx46 bit-0 above.
5 EISA 4D0/4D1 Port Enable
4 Interrupt Controller Shadow Register Enable
3 Reserved (always program to 0)
Note: Always mask this bit. This bit may read back
2 Write Delay Transaction Time-Out Timer Enable
1 Read Delay Transaction Time-Out Timer Enable
0 Software PCI Reset
(do not program)........................default = 0
(no function) ..............................default = 0
0 Allow burst reads to be interrupted........default
1 Don’t allow PCI burst reads to be interrupted
0 Disable................................................... default
1 Enable
0 Use CPURST as CPU Reset..................default
1 Use INIT as CPU Reset
0 Disable................................................... default
1 Enable
0 Disable (ignore ports 4D0-1)................. default
1 Enable (ports 4D0-1 per EISA specification)
0 Disable................................................... default
1 Enable
..............default = 0
as either 0 or 1 but must always be
programmed with 0.
0 Disable................................................... default
1 Enable
0 Disable................................................... default
1 Enable
......write 1 to generate PCI reset
Revision 1.0 May 13, 1997 -28- Register Descriptions
Page 35

9,$7HFKQRORJLHV,QF
VT82C586B
Offset 48 - Miscellaneous Control 3 ................................. RW
7-6 Reserved
5 MASTER# Pin Function (Pin 137)... (3041 Silicon)
0 "Input" Mode (Pin 137 = MASTER#) ...default
1 "Output" Mode (Pin 137 = SDDIR)
4 IRQ8# Input Source.........(3040F and 3041 Silicon)
0 IRQ8# input on RTCX1 pin 104............default
1 IRQ8# input on KEYLOCK pin 106
3 Extra RTC Port 74/75 Enable
0 Disable ...................................................default
1 Enable
2 Integrated USB Controller Disable
0 Enable.....................................................default
1 Disable
1 Integrated IDE Controller Disable
0 Enable.....................................................default
1 Disable
0 512K PCI Memory Decode
0 Use Rx4E[15-12] to select top of PCI memory
1 Use contents of Rx4E[15-12] plus 512K as top
Offset 4A - IDE Interrupt Routing .................................. RW
7 Wait for PGNT Before Grant to ISA Master /
DMA
0 Disable ...................................................default
1 Enable
6 Bus Select for Access to I/O Devices Below 100h
0 Access ports 00-FFh via XD bus............default
1 Access ports 00-FFh via SD bus (applies to
5-4 Reserved (do not program)
3-2 IDE Second Channel IRQ Routing
00 IRQ14
01 IRQ15.....................................................default
10 IRQ10
11 IRQ11
1-0 IDE Primary Channel IRQ Routing
00 IRQ14.....................................................default
01 IRQ15
10 IRQ10
11 IRQ11
........................................ always reads 0
See also Rx5A[2] - internal/external RTC:
Rx5A[2]Rx48[4]
0 0 Ext RTC, IRQ8# in pin 104
0 1 Ext RTC, IRQ8# in pin 106
1 x Int RTC, no IRQ8# in req'd
of PCI memory.......................................default
(must be set to 1)
external devices only; internal devices such as
the mouse controller are not effected)
Pin Function
..................... default = 0
4C - ISA DMA/Master Memory Access Control 1 ........ RW
7-0 PCI Memory Hole Bottom Address
These bits correspond to HA[23:16] ............default=0
4D - ISA DMA/Master Memory Access Control 2 ........ RW
7-0 PCI Memory Hole Top Address
These bits correspond to HA[23:16] ............default=0
Note: Access to the memory defined in the PCI memory
hole will not be forwarded to PCI. This function is
disabled if the top address less than or equal to the
bottom address.
4F-4E - ISA DMA/Master Memory Access Control 3 ... RW
15-12 Top of PCI Memory
0000 1M ....................................................default
0001 2M
... ...
1111 16M
Note: All ISA DMA / Masters that access addresses higher
than the top of PCI memory will not be directed to the
PCI bus.
11 Forward E0000-EFFFF Accesses to PCI
10 Forward A0000-BFFFF Accesses to PCI
9 Forward 80000-9FFFF Accesses to PCI
8 Forward 00000-7FFFF Accesses to PCI
7 Forward DC000-DFFFF Accesses to PCI
6 Forward D8000-DBFFF Accesses to PCI
5 Forward D4000-D7FFF Accesses to PCI
4 Forward D0000-D3FFF Accesses to PCI
3 Forward CC000-CFFFF Accesses to PCI
2 Forward C8000-CBFFF Accesses to PCI
1 Forward C4000-C7FFF Accesses to PCI
0 Forward C0000-C3FFF Accesses to PCI
for ISA DMA/Master accesses
(HA[23:16])
........def=0
.......def=0
........ def=1
........ def=1
......def=0
...... def=0
....... def=0
....... def=0
.....def=0
...... def=0
....... def=0
....... def=0
Revision 1.0 May 13, 1997 -29- Register Descriptions
Page 36

9,$7HFKQRORJLHV,QF
Plug and Play Control
VT82C586B
Offset 50 - Reserved (Do Not Program) .......................... RW
7-0 Reserved
Offset 54 - PCI IRQ Edge / Level Select .......................... RW
7-4 Reserved
The following bits all default to “level” triggered (0)
3 PIRQA# Invert (edge) / Non-invert (level)
2 PIRQB# Invert (edge) / Non-invert (level)
1 PIRQC# Invert (edge) / Non-invert (level)
0 PIRQD# Invert (edge) / Non-invert (level)
Note: PIRQA-D# normally connect to PCI interrupt pins
INTA-D# (see pin definitions for more information).
Note: The definitions of the fields of the following three
registers were incorrectly documented in some earlier
revisions of this document. The silicon has not changed
and the following definition should be used for all silicon
revisions:
Offset 55 - PNP IRQ Routing 1 ........................................ RW
These bits control routing for external IRQ inputs MIRQ0-1.
7-4 PIRQD# Routing
3-0 MIRQ0 Routing
Offset 56 - PNP IRQ Routing 2 ........................................ RW
7-4 PIRQA# Routing
3-0 PIRQB# Routing
Offset 57 - PNP IRQ Routing 3 ........................................ RW
7-4 PIRQC# Routing
3-0 MIRQ1 Routing
Note: these bits must be set to 0 if Rx48[4]=1 and
Rx59[1]=1 (input IRQ8# on MIRQ1 pin 106)
.......................................... default = 04h
........................................ always reads 0
.......(1/0)
.......(1/0)
.......(1/0)
.......(1/0)
(see PnP IRQ routing table)
(see PnP IRQ routing table)
(see PnP IRQ routing table)
(see PnP IRQ routing table)
(see PnP IRQ routing table)
(see PnP IRQ routing table)
Offset 58 - PNP IRQ Routing 4 ....................................... RW
These bits control routing for external IRQ input MIRQ2.
7-4 Reserved
3-0 MIRQ2 Routing
PnP IRQ Routing Table
0000 Disabled................................................. default
0001 IRQ1
0010 Reserved
0011 IRQ3
0100 IRQ4
0101 IRQ5
0110 IRQ6
0111 IRQ7
1000 Reserved
1001 IRQ9
1010 IRQ10
1011 IRQ11
1100 IRQ12
1101 Reserved
1110 IRQ14
1111 IRQ15
Offset 59 - MIRQ Pin Configuration .............................. RW
7-4 Reserved
3 Power-On Suspend Status Output Enable (Pin 90)
0 Disable POS Status Output.................... default
1 Enable POS Status output on pin 90. Alternate
2 MIRQ2 / MASTER# Selection (Pin 137)
0 MIRQ2................................................... default
1 MASTER#
1 MIRQ1 / KEYLOCK Selection (Pin 106)
0 MIRQ1................................................... default
1 KEYLOCK
0 MIRQ0 / APICCS# Selection (Pin 90)
0 MIRQ0................................................... default
1 APICCS#
........................................always reads 0
(see PnP IRQ routing table)
........................................always reads 0
..(3040 Rev F and 3041 Silicon Only))
functions of pin 90 are APICCS# and MIRQ0
if this bit is not set (see bit-0 below).
Revision 1.0 May 13, 1997 -30- Register Descriptions
Page 37

9,$7HFKQRORJLHV,QF
VT82C586B
Offset 5A - XD Power-On Strap Options ........................ RW
The bits in this register are latched from pins XD7-0 at powerup but are read/write accessible so may be changed after
power-up to change the default strap setting:
7 Keyboard RP16
6 Keyboard RP15
5 Keyboard RP14
4 Keyboard RP13
3 Reserved
2 Internal RTC Enable
0 Disable
1 Enable
1 Internal PS2 Mouse Enable
0 Disable
1 Enable
0 Internal KBC Enable
0 Disable
1 Enable
Note: External strap option values may be set by connecting
the indicated external pin to a 4.7K ohm pullup (for
1) or driving it low during reset with a 7407 TTL
open collector buffer (for 0) as shown in the
suggested circuit below:
.............................latched from XD7
............................latched from XD6
............................latched from XD5
............................latched from XD4
....................................... always reads 0
....................latched from XD2
..........latched from XD1
....................latched from XD0
Offset 5B - Internal RTC Test Mode .............................. RW
7-3 Reserved
2 RTC Reset Enable
1 RTC SRAM Access Enable
0 Disable................................................... default
1 Enable
This bit is set if the internal RTC is disabled but it is
desired to still be able to access the internal RTC
SRAM via ports 74-75. If the internal RTC is
enabled, setting this bit does nothing (the internal
RTC SRAM should be accessed at either ports 70/71
or 72/73.
0 RTC Test Mode Enable
Offset 5C - DMA Control (3041 Silicon Only) ............... RW
7-1 Reserved
0 DMA Line Buffer Disable
0 DMA cycles can be to/from line buffer .......def
1 Disable DMA Line Buffer
........................................always reads 0
(do not program)..........default=0
(do not program) .default=0
........................................always reads 0
9&&
5(6(7
9&&
Figure 3. Strap Option Circuit
.
;'
Revision 1.0 May 13, 1997 -31- Register Descriptions
Page 38

9,$7HFKQRORJLHV,QF
VT82C586B
Distributed DMA Control
Offset 61-60 - Distributed DMA Ch 0 Base / Enable ...... RW
15-4 Channel 0 Base Address Bits 15-4
3 Channel 0 Enable
0 Disable ...................................................default
1 Enable
2-0 Reserved
Offset 63-62 - Distributed DMA Ch 1 Base / Enable ...... RW
15-4 Channel 1 Base Address Bits 15-4
3 Channel 1 Enable
0 Disable ...................................................default
1 Enable
2-0 Reserved
Offset 65-64 - Distributed DMA Ch 2 Base / Enable ...... RW
15-4 Channel 2 Base Address Bits 15-4
3 Channel 2 Enable
0 Disable ...................................................default
1 Enable
2-0 Reserved
Offset 67-66 - Distributed DMA Ch 3 Base / Enable ...... RW
15-4 Channel 3 Base Address Bits 15-4
3 Channel 3 Enable
0 Disable ...................................................default
1 Enable
2-0 Reserved
........................................ always reads 0
........................................ always reads 0
........................................ always reads 0
........................................ always reads 0
.......... default = 0
.......... default = 0
.......... default = 0
.......... default = 0
Miscellaneous
Offset 73-70 - Subsystem ID (3041 Silicon Only) ........... WO
31-0 Subsystem ID and Subsystem Vendor ID
Write Only. Always reads back 0.
Contents may be read at offset 2C.
Offset 6B-6A - Distributed DMA Ch 5 Base / Enable .... RW
15-4 Channel 5 Base Address Bits 15-4
3 Channel 5 Enable
0 Disable ...................................................default
1 Enable
2-0 Reserved
Offset 6D-6C - Distributed DMA Ch 6 Base / Enable .... RW
15-4 Channel 6 Base Address Bits 15-4
3 Channel 6 Enable
0 Disable ...................................................default
1 Enable
2-0 Reserved
Offset 6F-6E - Distributed DMA Ch 7 Base / Enable ..... RW
15-4 Channel 7 Base Address Bits 15-4
3 Channel 7 Enable
0 Disable ...................................................default
1 Enable
2-0 Reserved
........................................ always reads 0
........................................ always reads 0
........................................ always reads 0
.......... default = 0
.......... default = 0
.......... default = 0
Revision 1.0 May 13, 1997 -32- Register Descriptions
Page 39

9,$7HFKQRORJLHV,QF
VT82C586B
Enhanced IDE Controller Registers (Function 1)
This Enhanced IDE controller interface is fully compatible
with the SFF 8038i v.1.0 specification. There are two sets of
software accessible registers -- PCI configuration registers and
Bus Master IDE I/O registers. The PCI configuration registers
are located in the function 1 PCI configuration space of the
VT82C586B. The Bus Master IDE I/O registers are defined in
the SFF8038i v1.0 specification.
PCI Configuration Space Header
Offset 1-0 - Vendor ID (1106h=VIA) ................................ RO
Offset 3-2 - Device ID (0571h=IDE Controller) ............... RO
Offset 5-4 - Command ....................................................... RW
15-10 Reserved
9 Fast Back to Back Cycles
8 SERR# Enable
7 Address Stepping
VIA recommends that this bit always be set to 1 to
provide additional address decode time to IDE
devices.
6 Parity Error Response
5 VGA Palette Snoop
4 Memory Write & Invalidate
3 Special Cycles
2 Bus Master
S/G operation can be issued only when the “Bus
Master” bit is enabled.
1 Memory Space
0 I/O Space
When the “I/O Space” bit is disabled, the device will
not respond to any I/O addresses for both compatible
and native mode.
Offset 7-6 - Status ........................................................... RWC
15 Detected Parity Error
14 Signalled System Error
13 Received Master Abort
12 Received Target Abort
11 Signalled Target Abort
10-9 DEVSEL# Timing
8 Data Parity Detected
7 Fast Back to Back
6-0 Reserved
Offset 8 - Revision ID ......................................................... RO
0-7 Revision Code for IDE Controller Logic Block
........................................ always reads 0
..........fixed at 0 (disabled)
............................fixed at 0 (disabled)
...................... default=1
...............fixed at 0 (disabled)
....................fixed at 0 (disabled)
.....fixed at 0 (disabled)
.............................fixed at 0 (disabled)
............................... default=0 (disabled)
............................fixed at 0 (disabled)
............................... default=0 (disabled)
................................ default=0
.............................. default=0
.............................. default=0
.............................. default=0
..............................Fixed at 0
..................default = 01 (medium)
.................................. default=0
......................................Fixed at 1
........................................ always reads 0
(enabled)
Offset 9 - Programming Interface ................................... RW
7 Master IDE Capability
6-4 Reserved
3 Programmable Indicator - Secondary
0 Fixed (mode is determined by bit-2)
1 Supports both modes (may be set to either
2 Channel Operating Mode - Secondary
0 Compatibility Mode ............default if SPKR=0
1 Native PCI Mode ................default if SPKR=1
The default value for this bit is determined at powerup as strapped by the SPKR pin (pin 134) ): 0 =
fixed IDE addressing, 1 = flexible IDE addressing.
See figure 2 for strap circuit.
1 Programmable Indicator - Primary
0 Fixed (mode is determined by bit-2)
1 Supports both modes (may be set to either
0 Channel Operating Mode - Primary
0 Compatibility Mode.............default if SPKR=0
1 Native PCI Mode ................default if SPKR=1
The default value for this bit is determined at powerup as strapped by the SPKR pin (pin 134) ): 0 =
fixed IDE addressing, 1 = flexible IDE addressing.
See figure 2 for strap circuit.
Compatibility Mode (fixed IRQs and I/O addresses):
Command Block Control Block
Channel Registers
Pri 1F0-1F7 3F6 14
Sec 170-177 376 15
Native PCI Mode (registers are programmable in I/O space)
Command Block Control Block
Channel Registers
Pri BA @offset 10h BA @offset 14h
Sec BA @offset 18h BA @offset 1Ch
Command register blocks are 8 bytes of I/O space
Control registers are 4 bytes of I/O space (only byte 2 is used)
Offset A - Sub Class Code (01h) ....................................... RO
Offset B - Base Class Code (01h) ...................................... RO
Offset D - Latency Timer (Default=0) ............................. RW
Offset E - Header Type (00h) ............................................ RO
Offset F - BIST (00h) ......................................................... RO
........................................always reads 0
mode by writing bit-2)
mode by writing bit-0)
...........fixed at 1 (Supported)
......fixed at 1
..........fixed at 1
Registers IRQ
Registers
Revision 1.0 May 13, 1997 -33- Register Descriptions
Page 40

9,$7HFKQRORJLHV,QF
VT82C586B
Offset 13-10 - Pri Data / Command Base Address.......... RW
pecifies an 8 byte I/O address space.
S
31-16 Reserved
15-3 Port Address
2-0 Fixed at 001b
Offset 17-14 - Pri Control / Status Base Address............ RW
Specifies a 4 byte I/O address space of which only the third
byte is active (i.e., 3F6h for the default base address of 3F4h).
31-16 Reserved
15-2 Port Address
1-0 Fixed at 01b
Offset 1B-18 - Sec Data / Command Base Address ........ RW
pecifies an 8 byte I/O address space.
S
31-16 Reserved
15-3 Port Address
2-0 Fixed at 001b
Offset 1F-1C - Sec Control / Status Base Address .......... RW
Specifies a 4 byte I/O address space of which only the third
byte is active (i.e., 376h for the default base address of 374h).
31-16 Reserved
15-2 Port Address
1-0 Fixed at 01b
..........................................always read 0
.......................................default=01F0h
..................................................... fixed
..........................................always read 0
.......................................default=03F4h
....................................................... fixed
..........................................always read 0
...................................... default=0170h
..................................................... fixed
..........................................always read 0
...................................... default=0374h
....................................................... fixed
Offset 3C - Interrupt Line (0Eh) ..................................... RW
Offset 3D - Interrupt Pin (00h) ......................................... RO
7-0 Interrupt Routing Mode
00h Legacy mode interrupt routing...............default
01h Native mode interrupt routing
Offset 3E - Min Gnt (00h) ................................................. RO
Offset 3F - Max Latency (00h).......................................... RO
Offset 23-20 - Bus Master Control Regs Base Address .. RW
Specifies a 16 byte I/O address space compliant with the
8038i rev 1.0
31-16 Reserved
15-4 Port Address
3-0 Fixed at 0001b
specification.
..........................................always read 0
....................................... default=CC0h
.................................................. fixed
SFF-
Revision 1.0 May 13, 1997 -34- Register Descriptions
Page 41

9,$7HFKQRORJLHV,QF
VT82C586B
IDE-Controller-Specific Confiiguration Registers
Offset 40 - Chip Enable ..................................................... RW
7-2 Reserved
1 Primary Channel Enable
0 Secondary Channel Enable
Offset 41 - IDE Configuration .......................................... RW
7 Primary IDE Read Prefetch Buffer
0 Disable ...................................................default
1 Enable
6 Primary IDE Post Write Buffer
0 Disable ...................................................default
1 Enable
5 Secondary IDE Read Prefetch Buffer
0 Disable ...................................................default
1 Enable
4 Secondary IDE Post Write Buffer
0 Disable ...................................................default
1 Enable
3 Reserved (read write)
2 Reserved (read write)
1 Reserved (read write)
0 Reserved (read write)
Offset 42 - Reserved (Do Not Program) .......................... RW
Offset 43 - FIFO Configuration ....................................... RW
7 PREQ# Asserted Till DDACK# De-Asserted ..........
0 Disabled .................................................default
1 Enabled
6-5 FIFO Configuration Between the Two Channels
00 16 0
01 8 8......................................default
10 8 8
11 0 16
4 Reserved
3-2 Threshold for Primary Channel
00 1
01 3/4
10 1/2 .....................................................default
11 1/4
1-0 Threshold for Secondary Channel
00 1
01 3/4
10 1/2 .....................................................default
11 1/4
............................ always reads 000001b
........ default = 0 (disabled)
.... default = 0 (disabled)
.......
do not change
.......
do not change
.......
do not change
.......
do not change
.............................. (3041 Silicon Only)
Primary Secondary
........................................ always reads 1
, default=0
, default=1
, default=1
, default=0
Offset 44 - Miscellaneous Control 1 ................................ RW
7 Reserved
6 Master Read Cycle IRDY# Wait States
0 0 wait states
1 1 wait state............................................. default
5 Master Write Cycle IRDY# Wait States
0 0 wait states
1 1 wait state............................................. default
4 FIFO Output Data 1/2 Clock Advance
0 Disabled................................................. default
1 Enabled
3 Bus Master IDE Status Register Read Retry
Retry bus master IDE status register read when
master write operation for DMA read is not complete
0 Disabled
1 Enabled.................................................. default
2 Reserved
1 B-Channel Threshold Value 0 (3041 Silicon Only)
0 Disabled................................................. default
1 Enabled
0 A-Channel Threshold Value 0 (3041 Silicon Only)
0 Disabled................................................. default
1 Enabled
Offset 45 - Miscellaneous Control 2 ................................ RW
7 Reserved
6 Interrupt Steering Swap
0 Don’t swap channel interrupts ...............default
1 Swap interrupts between the two channels
5-0 Reserved
Offset 46 - Miscellaneous Control 3 ................................ RW
7 Primary Channel Read DMA FIFO Flush
1 = Enable FIFO flush for read DMA when interrupt
asserts primary channel. ...............default=1 (enabled)
6 Secondary Channel Read DMA FIFO Flush
1 = Enable FIFO flush for Read DMA when interrupt
asserts secondary channel............Default=1 (enabled)
5 Primary Channel End-of-Sector FIFO Flush
1 = Enable FIFO flush at the end of each sector for
the primary channel....................Default=0 (disabled)
4 Secondary Channel End-of-Sector FIFO Flush
1 = Enable FIFO flush at the end of each sector for
the secondary channel.................Default=0 (disabled)
3-2 Reserved
1-0 Max DRDY Pulse Width
Maximum DRDY# pulse width after the cycle count.
Command will deassert in spite of DRDY# status to
avoid system ready hang.
00 No limitation.......................................... default
01 64 PCI clocks
10 128 PCI clocks
11 192 PCI clocks
........................................always reads 0
........................................always reads 0
........................................always reads 0
........................................always reads 0
........................................always reads 0
Revision 1.0 May 13, 1997 -35- Register Descriptions
Page 42

9,$7HFKQRORJLHV,QF
VT82C586B
Offset 4B-48 - Drive Timing Control ............................... RW
The following fields define the Active Pulse Width and
Recovery Time for the IDE DIOR# and DIOW# signals:
31-28 Primary Drive 0 Active Pulse Width
27-24 Primary Drive 0 Recovery Time
23-20 Primary Drive 1 Active Pulse Width
19-16 Primary Drive 1 Recovery Time
15-12 Secondary Drive 0 Active Pulse Width
11-8 Secondary Drive 0 Recovery Time
7-4 Secondary Drive 1 Active Pulse Width
3-0 Secondary Drive 1 Recovery Time
The actual value for each field is the encoded value in the field
plus one and indicates the number of PCI clocks.
Offset 4C - Address Setup Time ....................................... RW
7-6 Primary Drive 0 Address Setup Time
5-4 Primary Drive 1 Address Setup Time
3-2 Secondary Drive 0 Address Setup Time
1-0 Secondary Drive 1 Address Setup Time
For each field above:
00 1T
01 2T
10 3T
11 4T .....................................................default
Offset 4E - Secondary Non-1F0 Port Access Timing ...... RW
7-4 DIOR#/DIOW# Active Pulse Width
3-0 DIOR#/DIOW# Recovery Time
The actual value for each field is the encoded value in
the field plus one and indicates the number of PCI
clocks.
Offset 4F - Primary Non-1F0 Port Access Timing` ........ RW
7-4 DIOR#/DIOW# Active Pulse Width
3-0 DIOR#/DIOW# Recovery Time
The actual value for each field is the encoded value in
the field plus one and indicates the number of PCI
clocks.
......def=1010b
.............def=1000b
......def=1010b
.............def=1000b
..def=1010b
.........def=1000b
..def=1010b
.........def=1000b
.......def=1111b
..............def=1111b
.......def=1111b
..............def=1111b
Offset 53-50 - UltraDMA33 Extended Timing Control . RW
31 Pri Drive 0 UltraDMA33-Mode Enable Method
0 Enable by using “Set Feature” command.....def
1 Enable by setting bit-6 of this register
30 Pri Drive 0 UltraDMA33-Mode Enable
0 Disable................................................... default
1 Enable UltraDMA33-Mode Operation
29 Pri Drive 0 Transfer Mode
0 Based on UltraDMA33 DMA mode......default
1 Based on UltraDMA33 PIO Mode
28-26 Reserved
25-24 Pri Drive 0 Cycle Time
02T
13T
24T
3 5T .................................................... default
23 Pri Drive 1 UltraDMA33-Mode Enable Method
22 Pri Drive 1 UltraDMA33-Mode Enable
21 Pri Drive 1 Transfer Mode
20-18 Reserved
17-16 Pri Drive 1 Cycle Time
15 Sec Drive 0 UltraDMA33-Mode Enable Method
14 Sec Drive 0 UltraDMA33-Mode Enable
13 Sec Drive 0 Transfer Mode
12-10 Reserved
9-8 Sec Drive 0 Cycle Time
7 Sec Drive 1 UltraDMA33-Mode Enable Method
6 Sec Drive 1 UltraDMA33-Mode Enable
5 Sec Drive 1 Transfer Mode
4-2 Reserved
1-0 Sec Drive 1 Cycle Time
Each byte defines UltraDMA33 operation for the indicated
drive. The bit definitions are the same within each byte.
Offset 61-60 - Primary Sector Size .................................. RW
15-12 Reserved
11-0 Number of Bytes Per Sector
........................................always reads 0
........................................always reads 0
........................................always reads 0
........................................always reads 0
........................................always reads 0
........................ read only
........................ read only
........................ read only
........................ read only
................default=200h
Offset 69-68 - Secondary Sector Size .............................. RW
15-12 Reserved
11-0 Number of Bytes Per Sector
Revision 1.0 May 13, 1997 -36- Register Descriptions
........................................always reads 0
................default=200h
Page 43

9,$7HFKQRORJLHV,QF
IDE I/O Registers
These registers are compliant with the SFF 8038I v1.0
standard. Refer to the SFF 8038I v1.0 specification for further
details.
Offset 0 - Primary Channel Command
Offset 2 - Primary Channel Status
Offset 4-7 - Primary Channel PRD Table Address
Offset 8 - Secondary Channel Command
Offset A - Secondary Channel Status
Offset C-F - Secondary Channel PRD Table Address
VT82C586B
Revision 1.0 May 13, 1997 -37- Register Descriptions
Page 44

9,$7HFKQRORJLHV,QF
VT82C586B
Universal Serial Bus Controller Registers (Function 2)
This USB host controller interface is fully compatible with
UHCI specification v1.1. There are two sets of software
accessible registers: PCI configuration registers and USB I/O
registers. The PCI configuration registers are located in the
function 2 PCI configuration space of the VT82C586B. The
USB I/O registers are defined in the UHCI v1.1 specification.
PCI Configuration Space Header
Offset 1-0 - Vendor ID ....................................................... RO
0-7 Vendor ID
Offset 3-2 - Device ID ......................................................... RO
0-7 Device ID
Offset 5-4 - Command ....................................................... RW
15-8 Reserved
7 Address Stepping
6 Reserved
5 Reserved
4 Memory Write and Invalidate
3 Reserved
2 Bus Master
1 Memory Space
0 I/O Space
Offset 7-6 - Status ........................................................... RWC
15 Reserved
14 Signalled System Error
13 Received Master Abort
12 Received Target Abort
11 Signalled Target Abort
10-9 DEVSEL# Timing
00 Fast
01 Medium ......................................default (fixed)
10 Slow
11 Reserved
8-0 Reserved
................. (1106h = VIA Technologies)
(3038h = VT82C586B USB Controller)
........................................ always reads 0
...................... default=0 (disabled)
(parity error response)..................fixed at 0
(VGA palette snoop) ....................fixed at 0
. default=0 (disabled)
(special cycle monitoring)............fixed at 0
............................... default=0 (disabled)
........................... default=0 (disabled)
............................... default=0 (disabled)
(detected parity error).......... always reads 0
.............................. default=0
.............................. default=0
.............................. default=0
.............................. default=0
........................................ always reads 0
Offset 8 - Revision ID (nnh) .............................................. RO
7-0 Silicon Revision Code (0 indicates first silicon)
Offset 9 - Programming Interface (00h) .......................... RO
Offset A - Sub Class Code (03h) ....................................... RO
Offset B - Base Class Code (0Ch) ..................................... RO
Offset 0D - Latency Timer ............................................... RW
7-0 Timer Value
Offset 0E - Header Type (00h) .......................................... RO
Offset 23-20 - USB I/O Register Base Address ............... RW
31-16 Reserved
15-5 USB I/O Reg ister Base Address.
the base of the 32-byte USB I/O Register block,
corresponding to AD[15:5]
4-0 00001b
Offset 3C - Interrupt Line (00h) ...................................... RW
7-4 Reserved
3-0 USB Interrupt Routing
0000 Disabled................................................. default
0001 IRQ1
0010 Reserved
0011 IRQ3
0100 IRQ4
0101 IRQ5
0110 IRQ6
0111 IRQ7
1000 IRQ8
1001 IRQ9
1010 IRQ10
1011 IRQ11
1100 IRQ12
1101 IRQ13
1110 IRQ14
1111 IRQ15 (see note below)
Note: Some software incorrectly sets this register to 0FFh to
disable USB interrupts. A value of 0FFh will program the
USB interrupt to interrupt controller channel 15 and cause the
secondary IDE channel to work improperly.
..........................................default = 16h
........................................always reads 0
Port Address for
........................................always reads 0
........................default = 16h
Offset 3D - Interrupt Pin (04h) ......................................... RO
Revision 1.0 May 13, 1997 -38- Register Descriptions
Page 45

9,$7HFKQRORJLHV,QF
VT82C586B
USB-Specific Configuration Registers
Offset 40 - Miscellaneous Control 1 ................................. RW
7 PCI Memory Command Option
0 Support Memory-Read-Line, Memory-Read-
Multiple, and Memory-Write-and-Invalidate....
.....................................................default
1 Only support Memory Read, Memory Write
Commands
6 Babble Option
0 Automatically disable babbled port when EOF
babble occurs..........................................default
1 Don’t disable babbled port
5 PCI Parity Check Option
0 Disable PERR# generation.....................default
1 Enable parity check and PERR# generation
4 Reserved
3 USB Data Length Option
0 Support TD length up to 1280................default
1 Support TD length up to 1023
2 USB Power Management
0 Disable USB power management...........default
1 Enable USB power management
1 DMA Option
0 16 DW burst access................................default
1 8 DW burst access
0 PCI Wait States
0 Zero wait ................................................default
1 One wait
........................................ always reads 0
USB I/O Registers
These registers are compliant with the UHCI v1.1 standard.
Refer to the UHCI v1.1 specification for further details.
Offset 1-0 - USB Command
Offset 3-2 - USB Status
Offset 5-4 - USB Interrupt Enable
Offset 7-6 - Frame Number
Offset B-8 - Frame List Base Address
Offset 0C - Start Of Frame Modify
Offset 11-10 - Port 1 Status / Control
Offset 13-12 - Port 2 Status / Control
Offset 1F-14 - Reserved
Offset 41 - Miscellaneous Control 2 ................................. RW
7-3 Reserved
2 Trap Option
0 Set trap 60/64 status bits without checking
1 Set trap 60/64 status bits only when trap 60/64
1 A20gate Pass Through Option
0 Pass through A20GATE command sequence
1 Don’t pass through Write I/O port 64 (ff)
0 Reserved
Offset 60 - Serial Bus Release Number ............................. RO
7-0 Release Number
Offset C1-C0 - Legacy Support ......................................... RO
15-0 UHCI v1.1 Compliant
........................................ always reads 0
enable bits ..............................................default
enable bits are set.
defined in UHCI.....................................default
........................................ always reads 0
.............................. always reads 10h
................ always reads 2000h
Revision 1.0 May 13, 1997 -39- Register Descriptions
Page 46

9,$7HFKQRORJLHV,QF
Power Management Registers (Function 3)
This section describes the ACPI (Advanced Configuration and
Power Interface) Power Management system of the
VT82C586B. This system supports both ACPI and legacy
power management functions and is compatible with the APM
v1.2 and ACPI v0.9 specifications.
PCI Configuration Space Header
VT82C586B
Offset 1-0 - Vendor ID ....................................................... RO
0-7 Vendor ID
Offset 3-2 - Device ID ......................................................... RO
0-7 Device ID
Offset 5-4 - Command ....................................................... RW
15-8 Reserved
7 Address Stepping
6 Reserved
5 Reserved
4 Memory Write and Invalidate
3 Reserved
2 Bus Master
1 Memory Space
0 I/O Space
0 Disable ........ always reads 0 in 3040F and later
1 Enable
Note: In 3040E and earlier silicon, this bit could be
set to 1 to allow access to the Power Management I/O
Register Block (the quadword at offset 20 was used in
that silicon to set the base address for this register
block). Beginning with 3040F silicon, the function of
this bit was moved to offset 41 bit-7 and the base
address register for the PM I/O register block was
moved from to offset 48.
Offset 7-6 - Status ........................................................... RWC
15 Detected Parity Error
14 Signalled System Error
13 Received Master Abort
12 Received Target Abort
11 Signalled Target Abort
10-9 DEVSEL# Timing
00 Fast
01 Medium ..................................... default (fixed)
10 Slow
11 Reserved
8 Data Parity Detected
7 Fast Back to Back
6-0 Reserved
................. (1106h = VIA Technologies)
................(3040h = ACPI Power Mgmt)
........................................ always reads 0
........................................fixed at 0
(parity error response)..................fixed at 0
(VGA palette snoop) ....................fixed at 0
...................fixed at 0
(special cycle monitoring)............fixed at 0
.................................................fixed at 0
.............................................fixed at 0
.................................................fixed at 0
........................ always reads 0
...................... always reads 0
...................... always reads 0
...................... always reads 0
...................... always reads 0
.......................... always reads 0
.............................. always reads 1
........................................ always reads 0
Offset 8 - Revision ID (nnh) .............................................. RO
7-4 Silicon Version Code
0 OEM Version ("3040 Silicon")
1 Production Version ("3041 Silicon")
2-F -reserved for future use-
3-0 Silicon Revision Code
OEM Version
0 Revision E ("3040E")
1 Revision F ("3040F")
2-F -reserved for future use-
Production Version
0 Revision A ("3041" or "3041A")
1-F -reserved for future useProgramming and pin differences between the above silicon
versions and revisions are indicated in this document in the
appropriate section. Marking specifications corresponding to
the above versions and revisions are also included in the
Mechanical Specifications section of this document.
Offset 9 - Programming Interface (00h) .......................... RO
The value returned by this register may be changed by writing
the desired value to PCI Configuration Function 3 offset 61h.
Offset A - Sub Class Code (00h) ....................................... RO
The value returned by this register may be changed by writing
the desired value to PCI Configuration Function 3 offset 62h.
Offset B - Base Class Code (00h) ...................................... RO
The value returned by this register may be changed by writing
the desired value to PCI Configuration Function 3 offset 63h.
Offset 0D - Latency Timer ............................................... RW
7-0 Timer Value
Offset 0E - Header Type (00h) .......................................... RO
Offset 23-20 - I/O Register Base Address (3040E only) . RW
31-16 Reserved
15-8 Power Management I/O Register Base Address.
Port Address for the base of the 256-byte Power
Management I/O Register block, corresponding to
AD[15:8]. The "I/O Space" bit at offset 5-4 bit-0
enables access to this register block.
7-0 00000001b
..........................................default = 16h
........................................always reads 0
Revision 1.0 May 13, 1997 -40- Register Descriptions
Page 47

9,$7HFKQRORJLHV,QF
VT82C586B
Power Management-Specific PCI Configuration Registers
Offset 40 - Pin Configuration (C0h) ................................ RW
7 GPIO4 Configuration
0 Define pin 136 as GPO_WE
1 Define pin 136 as GPIO4 .......................default
6 GPIO3 Configuration
0 Define pin 92 as GPI_RE#
1 Define pin 92 as GPIO4 .........................default
5-0 Reserved
Offset 41 - General Configuration (00h) ......................... RW
7 3040E and earlier: Reserved
7 3040F and later: I/O Enable for ACPI I/O Base
0 Disable access to ACPI I/O block ..........default
1 Allow access to Power Management I/O
6 ACPI Timer Reset
0 Disable ...................................................default
1 Enable
5-4 Reserved
3 ACPI Timer Count Select
0 24-bit Timer ...........................................default
1 32-bit Timer
2 PCI Frame Activation in C2 as Resume Event
0 Disable ...................................................default
1 Enable
1 Clock Throttling Clock Selection
0 32 usec (512 usec cycle time).................default
1 1 msec (16 msec cycle time)
0 Reserved
Offset 42 - SCI Interrupt Configuration (00h) ............... RW
7-4 Reserved
3-0 SCI Interrupt Assignment
0000 Disabled .................................................default
0001 IRQ1
0010 Reserved
0011 IRQ3
0100 IRQ4
0101 IRQ5
0110 IRQ6
0111 IRQ7
1000 IRQ8
1001 IRQ9
1010 IRQ10
1011 IRQ11
1100 IRQ12
1101 IRQ13
1110 IRQ14
1111 IRQ15
........................................ always reads 0
Register Block (see offset 4B-48 to set the
base address for this register block). The
definitions of the registers in the Power
Management I/O Register Block are included
later in this document, following the Power
Management Subsystem overview.
(Do Not Program)...................... default = 0
(Do Not Program)...................... default = 0
........................................ always reads 0
Offset 45-44 - Primary Interrupt Channel (0000h) ....... RW
15 1/0 = Ena/Disa IRQ15 as Primary Intrpt Channel
14 1/0 = Ena/Disa IRQ14 as Primary Intrpt Channel
13 1/0 = Ena/Disa IRQ13 as Primary Intrpt Channel
12 1/0 = Ena/Disa IRQ12 as Primary Intrpt Channel
11 1/0 = Ena/Disa IRQ11 as Primary Intrpt Channel
10 1/0 = Ena/Disa IRQ10 as Primary Intrpt Channel
9 1/0 = Ena/Disa IRQ9 as Primary Intrpt Channel
8 1/0 = Ena/Disa IRQ8 as Primary Intrpt Channel
7 1/0 = Ena/Disa IRQ7 as Primary Intrpt Channel
6 1/0 = Ena/Disa IRQ6 as Primary Intrpt Channel
5 1/0 = Ena/Disa IRQ5 as Primary Intrpt Channel
4 1/0 = Ena/Disa IRQ4 as Primary Intrpt Channel
3 1/0 = Ena/Disa IRQ3 as Primary Intrpt Channel
2 Reserved
1 1/0 = Ena/Disa IRQ1 as Primary Intrpt Channel
0 1/0 = Ena/Disa IRQ0 as Primary Intrpt Channel
Offset 47-46 - Secondary Interrupt Channel (0000h) .... RW
15 1/0 = Ena/Disa IRQ15 as Secondary Intr Channel
14 1/0 = Ena/Disa IRQ14 as Secondary Intr Channel
13 1/0 = Ena/Disa IRQ13 as Secondary Intr Channel
12 1/0 = Ena/Disa IRQ12 as Secondary Intr Channel
11 1/0 = Ena/Disa IRQ11 as Secondary Intr Channel
10 1/0 = Ena/Disa IRQ10 as Secondary Intr Channel
9 1/0 = Ena/Disa IRQ9 as Secondary Intr Channel
8 1/0 = Ena/Disa IRQ8 as Secondary Intr Channel
7 1/0 = Ena/Disa IRQ7 as Secondary Intr Channel
6 1/0 = Ena/Disa IRQ6 as Secondary Intr Channel
5 1/0 = Ena/Disa IRQ5 as Secondary Intr Channel
4 1/0 = Ena/Disa IRQ4 as Secondary Intr Channel
3 1/0 = Ena/Disa IRQ3 as Secondary Intr Channel
2 Reserved
1 1/0 = Ena/Disa IRQ1 as Secondary Intr Channel
0 1/0 = Ena/Disa IRQ0 as Secondary Intr Channel
Offset 4B-48 - I/O Register Base Address (3040F and later
silicon; see Offset 23-20 for 3040E and earlier) ............ RW
31-16 Reserved
15-8 Power Management I/O Register Base Address.
Port Address for the base of the 256-byte Power
Management I/O Register block, corresponding to
AD[15:8]. The "I/O Space" bit at offset 41 bit-7
(offset 5-4 bit-0 in 3040E and earlier silicon) enables
access to this register block. The definitions of the
registers in the Power Management I/O Register
Block are included later in this document, following
the Power-Management-Specific PCI Configuration
register descriptions and the Power Management
Subsystem overview.
7-0 00000001b
........................................always reads 0
........................................always reads 0
........................................always reads 0
Revision 1.0 May 13, 1997 -41- Register Descriptions
Page 48

9,$7HFKQRORJLHV,QF
VT82C586B
Offset 53-50 - GP Timer Control (0000 0000h) .............. RW
31-30 Conserve Mode Timer Count Value
00 1/16 second ............................................default
01 1/8 second
10 1 second
11 1 minute
29 Conserve Mode Status
This bit reads 1 when in Conserve Mode
28 Conserve Mode Enable
Set to 1 to enable Conserve Mode (not used in
desktop applications).
27-26 Secondary Event Timer Count Value
00 2 milliseconds.........................................default
01 64 milliseconds
10 ½ second
11 by EOI + 0.25 milliseconds
25 Secondary Event Occurred Status
This bit reads 1 to indicate that a secondary event has
occurred (to resume the system from suspend) and the
secondary event timer is counting down.
24 Secondary Event Timer Enable
0 Disable ...................................................default
1 Enable
23-16 GP1 Timer Count Value
15-8 GP0 Timer Count Value
7 GP1 Timer Start
On setting this bit to 1, the GP1 timer loads the value
defined by bits 23-16 of this register and starts
counting down. The GP1 timer is reloaded at the
occurrence of certain peripheral events enabled in the
GP Timer Reload Enable Register (Power
Management I/O Space Offset 38h). If no such event
occurs and the GP1 timer counts down to zero, then
the GP1 Timer Timeout Status bit is set to one (bit-3
of the Global Status register at Power Management
Register I/O Space Offset 28h). Additionally, if the
GP1 Timer Timeout Enable bit is set (bit-3 of the
Global Enable register at Power Management
Register I/O Space Offset 2Ah), then an SMI is
generated.
6 GP1 Timer Automatic Reload
This bit is set to one to enable the GP1 timer to reload
automatically after counting down to 0.
5-4 GP1 Timer Base
00 Disable ...................................................default
01 32 usec
10 1 second
11 1 minute
(base defined by bits 5-4)
(base defined by bits 1-0)
3 GP0 Timer Start
On setting this bit to 1, the GP0 timer loads the value
defined by bits 15-8 of this register and starts
counting down. The GP0 timer is reloaded at the
occurrence of certain peripheral events enabled in the
GP Timer Reload Enable Register (Power
Management I/O Space Offset 38h). If no such event
occurs and the GP0 timer counts down to zero, then
the GP0 Timer Timeout Status bit is set to one (bit-2
of the Global Status register at Power Management
Register I/O Space Offset 28h). Additionally, if the
GP0 Timer Timeout Enable bit is set (bit-2 of the
Global Enable register at Power Management
Register I/O Space Offset 2Ah), then an SMI is
generated.
2 GP0 Timer Automatic Reload
This bit is set to one to enable the GP0 timer to reload
automatically after counting down to 0.
1-0 GP0 Timer Base
00 Disable................................................... default
01 1/16 second
10 1 second
11 1 minute
Offset 61 - Programming Interface Read Value ............ WO
7-0 Rx09 Read Value
The value returned by the register at offset 9h (Programming
Interface) may be changed by writing the desired value to this
location.
Offset 62 - Sub Class Read Value .................................... WO
7-0 Rx0A Read Value
The value returned by the register at offset 0Ah (Sub Class
Code) may be changed by writing the desired value to this
location.
Offset 63 - Base Class Read Value ................................... WO
7-0 Rx0B Read Value
The value returned by the register at offset 0Bh (Base Class
Code) may be changed by writing the desired value to this
location.
Revision 1.0 May 13, 1997 -42- Register Descriptions
Page 49

9,$7HFKQRORJLHV,QF
VT82C586B
Power Management Subsystem Overview
The power management function of the VT82C586B is
indicated in the following block diagram:
*3
'HYLFH
,GOH
7LPHU
3ULPDU\
(YHQWV
*3
*OREDO
6WDQGE\
7LPHU
3:5%71
*3,2
5,
86%
UHVXPH
/HJDF\ 2QO\ (YHQW /RJLF
$&3, /HJDF\ (YHQW /RJLF
$&3, /HJDF\ *HQHULF &RQWURO )HDWXUHV
$&3, /HJDF\ )L[HG &RQWURO )HDWXUHV
$&3, 2QO\ (YHQW /RJLF
8VHU
,QWHUIDFH
%XV
0DVWHU
+DUGZDUH
(YHQWV
57&
30 7LPHU
6&,B(1
'HF
60, (YHQWV
6&,60, (YHQWV
:DNHXS (YHQWV
60, $UELWHU
6&, $UELWHU
6OHHS:DNH
6WDWH
0DFKLQH
&38
673&/.
&RQWURO
3RZHU
3ODQH
&RQWURO
60,
6&,
Figure 4. Power Management Subsystem Block Diagram
Refer to ACPI Specification v0.9 and APM specification v1.2
for additional information.
Power Plane Management
There are three power planes inside the VT82C586B. The
scheme is optimal for systems with ATX power supplies,
although it also works using non-ATX power supplies. The
key feature of the ATX power supply is that two sets of power
sources are available: the first set is always on unless turned
off by the mechanical switch. Only one voltage (5V) is
available for this set. The second set includes the normal 5V
and 12V and is controlled by an input signal PWRON as well
as the mechanical switch. This set of voltages is available only
when both the mechanical switch is on and the PWRON signal
is high. The power planes powered by the above two sets of
supplies are referred to as VDD-5VSB and VDD-5V (also
called VDD5), respectively. In addition to the two power
planes, a third plane is powered by the combination of 5VSB
and VBAT for the integrated real time clock. Most of the
circuitry inside the VT82C586B is powered by VDD-5V. The
amount of logic powered by VDD-5VSB is very small and
remains functional as long as the mechanical switch of the
power supply is turned on. The main function of this logic is
to control the power supply of the VDD-5V plane.
General Purpose I/O Ports
As ACPI compliant hardware, the VT82C586B includes
PWRBTN# (pin 91) and RI# (pin 93) pins to implement power
button and ring indicator functionality. In addition, a PWRON
pin (pin 107) is also available to control the VDD-5V power
plane by VDD-5VSB powered logic. Furthermore, the
VT82C586B offers many general purpose I/O ports with the
following capabilities:
2
C support
• I
• Three GPIO ports without external logic in addition to
2
C port. Five GPIO ports are available if I2C
the I
functionality is not used. Every port can be used inp uts,
outputs or I/O with external SCI/SMI capabilities.
• Sixteen GPI and sixteen GPO pins using external
buffers (244 buffers for input and 373 latches for output).
Pins 87, 88 and 94 of the VT82C586B are dedicated general
purpose I/O pins that can be used as inputs, outputs or I/O with
external SMI capability. In particular, pins 87 and 88 can be
used to implement a software-implemented I
2
C port for system
configuration and genera l purpose peripheral communication.
Pins 92 and 136 can be configured either as dedicated general
purpose I/O pins or as control signals for external buffers for
implementing up to sixteen GPI and sixteen GPO ports. The
GPI and GPO ports are connected to the SD15-8 and XD7-0.
The configuration is determined in the GPIO4_CFG and
CPIO3_CFG bits of the PIN_CFG register:
GPIO4_CFG: default to 1 to define pin 136 as GPIO4;
set to 0 to redefine the pin as GPO_WE latch enable.
GPIO3_CFG: default to 1 to define pin 92 as GPIO3; set
to 0 to redefine the pin as GPI_RE# buffer enable.
Revision 1.0 May 13, 1997 -43- Register Descriptions
Page 50

9,$7HFKQRORJLHV,QF
Power Management Events
VT82C586B
Three types of power management events are supported:
1)
ACPI-required Fixed Events
and PM1a_EN registers. These events can trigger either
SCI or SMI depending on the SCI_EN bit:
• PWRBTN# Triggering
• RTC Alarm
• ACPI Power Management Timer Carry (always SCI)
• BIOS Release (always SCI)
2)
ACPI-aware General Purpose Function Events
in the GP_STS and GP_SCI_EN, and GP_SMI_EN
registers. These events can trigger either SCI or SMI
depending on the setting of individual SMI and SCI
enable bits:
• EXTSMI triggering (refer to Table 2)
• USB Resume
• RI# Indicator
3)
Generic Global Events
GBL_EN registers. These registers are mainly used for
SMI:
• GP0 and GP1 Timer Time Out
• Secondary Event Timer Time Out
• Occurrence of Primary Events
(defined in register PACT_STS and PACT_EN)
• Legacy USB accesses (keyboard and mouse).
Once enabled, each of the EXTSMI inputs triggers an SCI or
SMI at either the rising or the falling transition of the
corresponding input pin signal. Software can check the status
of the input pins via register EXTSMI_VAL and take proper
actions.
Among many possible actions, the SCI and SMI routine can
change the processor state by programming the P_BLK
registers. The routine can also set the SLP_EN bit to put the
system into one of the two suspend states:
1)
Suspend to Disk (or Soft-Off):
plane is turned off while VDD-5VSB and VDD-RTC
planes remain on.
2)
Power-On-Suspend:
processor is put in the C3 state.
In either suspend state, there is minimal interface between
powered and non-powered planes.
All power planes remain on but the
defined in the PM1a_STS
defined
defined in the GBL_STS and
The VDD-5V power
The VT82C586B allows the following events to wake up the
system from the two suspend states and from the C2 state to
the normal working state (processor in C0 state):
•
Activation of External Inputs:
and other EXTSMI pins (see table below)
•
RTC Alarm and ACPI Power Management Timer
table below)
•
USB Resume Event
•
Interrupt Events
register setting)
•
ISA Master or DMA Events
independent of any register setting)
The VT82C586B also provides very flexible SCI/SMI steering
and the PWRON control for these events:
(see table below)
(always resume independent of any
PWRBTN#, RI#, GPIO0
(see
(always resume
Table 6. SCI/SMI/Resume Control for PM Events
Event Global
SCI/SMI
Control
PWRBTN# SCI_EN bit N
RI# N
RTC Alarm N
GPIO0
(EXTSMI0)
External SCI/SMI
(non-GPIO0)
ACPI PM Timer Always SCI N N
USB Resume N N
Please refer to the table below on the availability of resume
events in each type of suspend state.
N
N
Individual
Enable Bits
for SCI &
SMI
YY
Y
YY
Y
Separate
Control for
PWRON
Resume
Y
N
N
Y
Table 7. Suspend Resume Events and Conditions
Input Trigger Power Plane Soft Off Power-On
Suspend
PWRBTN# VDD-5VSB Y Y
RI# VDD-5VSB Y Y
RTC Alarm VBAT Y Y
GPIO0
(EXTSMI0)
External SCI/SMI
(non-GPIO0)
ACPI PM Timer VDD-5V
USB Resume VDD-5V
PCI/ISA
Interrupts
PCI/ISA
Master/DMA
VDD-5VSB Y Y
VDD-5V
VDD-5V
VDD-5V
N
N
N
NN
NN
Y
Y
Y
Revision 1.0 May 13, 1997 -44- Register Descriptions
Page 51

9,$7HFKQRORJLHV,QF
VT82C586B
Legacy Power Management Timers
In addition to the ACPI power management timer, the
VT82C586B includes the following four legacy power
management timers:
GP0 Timer
GP1 Timer
reload
Secondary Event Timer
Conserve Mode Timer
The normal sequence of operations for a general purpose timer
(GP0 or GP1) is to
1) First program the time base and timer value of the initial
count (register GP_TIM_CNT).
2) Then activate counting by setting the GP0_START or
GP1_START bit to one: the timer will start with the
initial count and count down towards 0.
3) When the timer counts down to zero, an SMI will be
generated if enabled (GP0TO_EN and GP1TO_EN in the
GBL_EN register) with status recorded (GP0TO_STS and
GP1TO_STS in the GBL_STS register).
4) Each timer can also be programmed to reload the initial
count and restart counting automatically after counting
down to 0. This feature is not used in standard VIA
BIOS.
The GP0 and GP1 timers can be used just as the general
purpose timers described above. However, they can also be
programmed to reload the initial count by system primary
events or peripheral events thus used as primary event (global
standby) timer and peripheral timer, respectively. The
secondary event timer is solely used to monitor secondary
events.
System Primary and Secondary Events
Primary system events are distinguished in the P RI_ACT _ST S
and PRI_ACT_EN registers:
Bit Event
7
Keyboard Access
6
Serial Port Access
5
Parallel Port Access
4
Video Access
3
IDE/Floppy Access
2
Reserved
1
Primary Interrupts
0
ISA Master/DMA Activity
Each category can be enabled as a primary event by setting the
corresponding bit of the PRI_ACT_EN register to 1. If
: general purpose timer with primary event
: general purpose timer with peripheral event
: to monitor secondary events
: not used in desktop applications
Trigger
I/O port 60h
I/O ports 3F8h-3FFh, 2F8h-2FFh,
3E8h-3EFh, or 2E8h-2EFh
I/O ports 378h-37Fh or 278h-27Fh
I/O ports 3B0h-3DFh or memory
A/B segments
I/O ports 1F0h-1F7h, 170h-177h,
or 3F5h
Each channel of the interrupt
controller can be programmed to
be a primary or secondary
interrupt
enabled, the occurrence of the primary event reloads the GP0
timer if the PACT_GP0_EN bit is also set to 1. T he cause of
the timer reload is recorded in the corresponding bit of
PRI_ACT_STS register while the timer is reloaded. If no
enabled primary event occurs during the count down, the GP0
timer will time out (count down to 0) and the system can be
programmed (setting the GP0TO_EN bit in the GBL_EN
register to one) to trigger an SMI to switch the system to a
power down mode.
The VT82C586B distinguishes two kinds of interrupt requests
as far as power management is concerned: the primary and
secondary interrupts. Like other primary events, the
occurrence of a primary interrupt demands that the system be
restored to full processing capability. Secondary interrupts,
however, are typically used for housekeeping tasks in the
background unnoticeable to the user. The VT82C586B allows
each channel of interrupt request to be declared as either
primary, secondary, or ignorable in the PIRQ_CH and
SIRQ_CH registers. Secondary interrupts are the only system
secondary events defined in the VT82C586B.
Like primary events, primary interrupts can be made to reload
the GP0 timer by setting the PIRQ_EN bit to 1. Secondary
interrupts do not reload the GP0 timer. Therefore the GP0
timer will time out and the SMI routine can put the system into
power down mode if no events other than secondary interrupts
are happening periodically in the background.
Primary events can be programmed to trigger an SMI (setting
of the PACT_EN bit). Typically, this SMI triggering is turned
off during normal system operation to avoid degrading system
performance. Triggering is turned on by the SMI routine
before entering the power down mode so that the system may
be returned to normal operation at the occurrence of primary
events. At the same time, the GP0 timer is reloaded and the
count down process is restarted.
Peripheral Events
Primary and secondary events define system events in general
and the response is typically expressed in terms of system
events. Individual peripheral events can also be monitored by
the VT82C586B through the GP1 timer. The follo wing four
categories of perip heral events are distinguished (via register
GP_RLD_EN):
Bit-7
Bit-6
Bit-4
Bit-3
The four categories are subsets of the primary events as
defined in PRI_ACT_EN and the occurrence of these events
can be checked through a common register PRI_ACT_STS.
As a peripheral timer, GP1 can be used to monitor one (or
more than one) of the above four device types by programming
the corresponding bit to one and the other bits to zero. Time
out of the GP1 timer indicates no activity of the corresponding
device type and appropriate action can be taken as a result.
Keyboard Access
Serial Port Access
Video Access
IDE/Floppy Access
Revision 1.0 May 13, 1997 -45- Register Descriptions
Page 52

9,$7HFKQRORJLHV,QF
Power Management I/O-Space Registers
Basic Power Management Control and Status
VT82C586B
Offset 1-0 - Power Management Status ........................ RWC
The bits in this register are set only by hardware and can be
reset by software by writing a one to the desired bit position.
15 Wakeup Status
This bit is set when the system is in the suspend state
and an enabled resume event occurs. Upon setting
this bit, the system automatically transitions from the
suspend state to the normal working state (from C3 to
C0 for the processor).
14-12 Reserved
11 Power Button Override Status
This bit is set when the PWRBTN# input pin is
continuously asserted for more than 4 seconds. The
setting of this bit will reset the PB_STS bit and
transition the system into the soft off state.
10 RTC Status
This bit is set when the RTC generates an alarm (on
assertion of the RTC IRQ signal).
9 Reserved
8 Power Button Status
This bit is set when the PWRBTN# signal is asserted
LOW. If the PWRBTN# signal is held LOW for
more than four seconds, this bit is cleared, the
PBOR_STS bit is set, and the system will transition
into the soft off state.
7-6 Reserved
5 Global Status
This bit is set by hardware when BIOS_RLS is set
(typically by an SMI routine to release control of the
SCI/SMI lock). When this bit is cleared by software
(by writing a one to this bit position) the BIOS_RLS
bit is also cleared at the same time by hardware.
4 Bus Master Status
This bit is set when a system bus master requests the
system bus. All PCI master, ISA master and ISA
DMA devices are included.
3-1 Reserved
0 Timer Carry Status
The bit is set when the 23
bit ACPI power management timer changes.
(WAK_STS) ................... default = 0
........................................ always reads 0
(PBOR_STS). def=0
(RTC_STS)........................... default = 0
........................................ always reads 0
(PB_STS)............... default = 0
........................................ always reads 0
(GBL_STS)........................ default = 0
(BM_STS) ................. default = 0
........................................ always reads 0
(TMR_STS)............. default = 0
rd
(31st) bit of the 24 (32)
Offset 3-2 - Power Management Enable ......................... RW
The bits in this register correspond to the bits in the Power
Management Status Register at offset 1-0.
15 Reserved
14-12 Reserved
11 Reserved
10 RTC Enable
This bit may be set to trigger either an SCI or an SMI
(depending on the setting of the SCI_EN bit) to be
generated when the RTC_STS bit is set.
9 Reserved
8 Power Button Enable
This bit may be set to trigger either an SCI or an SMI
(depending on the setting of the SCI_EN bit) to be
generated when the PB_STS bit is set.
7-6 Reserved
5 Global Enable
This bit may be set to trigger either an SCI or an SMI
(depending on the setting of the SCI_EN bit) to be
generated when the GBL_STS bit is set.
4 Reserved
3-1 Reserved
0 ACPI Timer Enable
This bit may be set to trigger either an SCI or an SMI
(depending on the setting of the SCI_EN bit) to be
generated when the TMR_STS bit is set.
........................................always reads 0
........................................always reads 0
........................................always reads 0
(RTC_EN)............................default = 0
........................................always reads 0
(PB_EN) ...............default = 0
........................................always reads 0
(GBL_EN).........................default = 0
........................................always reads 0
........................................always reads 0
(TMR_EN)..............default = 0
Revision 1.0 May 13, 1997 -46- Register Descriptions
Page 53

9,$7HFKQRORJLHV,QF
VT82C586B
Offset 5-4 - Power Management Control ........................ RW
15-14 Reserved
13 Sleep Enable
This is a write-only bit; reads from this bit always
return zero. Writing a one to this bit causes the
system to sequence into the sleep (suspend) state
defined by the SLP_TYP field.
12-10 Sleep Type
000 Soft Off (also called Suspend to Disk). The
010 Power On Suspend. All power planes remain
0x1 Reserved
1xx Reserved
In either sleep state, there is minimal interface
between powered and non-powered planes so that the
effort for hardware design may be well managed.
9-3 Reserved
2 Global Release
This bit is set by ACPI software to indicate the
release of the SCI / SMI lock. Upon setting of this
bit, the hardware automatically sets the BIOS_STS
bit. The bit is cleared by hardware when the
BIOS_STS bit is cleared by software. Note that the
setting of this bit will cause an SMI to be generated if
the BIOS_EN bit is set (bit-5 of the Global Enable
register at offset 2Ah).
1 Bus Master Reload
This bit is used to enable the occurrence of a bus
master request to transition the processor from the C3
state to the C0 state.
0 SCI Enable
Selects the power management event to generate
either an SCI or SMI:
0 Generate SMI
1 Generate SCI
Note that certain power management events can be
programmed individually to generate an SCI or SMI
independent of the setting of this bit (refer to the
General Purpose SCI Enable and General Purpose
SMI Enable registers at offsets 22 and 24). Also,
TMR_STS & GBL_STS always generate SCI and
BIOS_STS always generates SMI.
........................................ always reads 0
(SLP_EN)...................... always reads 0
(SLP_TYP)
VDD5 power plane is turned off while the
VDD-5VSB and VDD-RTC (VBAT) planes
remain on.
on but the processor is put into the C3 state.
........................................ always reads 0
(GBL_RLS) ..................... default = 0
(BMS_RLD)............. default = 0
(SCI_EN)............................... default = 0
Offset 0B-08 - Power Management Timer ...................... RW
31-24 Extended Timer Value (ETM_VAL)
This field reads back 0 if the 24-bit timer option is
selected (Rx41 bit-3).
23-0 Timer Value (TMR_VAL)
This read-only field r eturns the running count of the
power management timer. This is a 24/32-bit counter
that runs off a 3.579545 MHz clock, and counts while
in the S0 (working) system state. The timer is reset to
an initial value of zero during a reset, and then
continues counting until the 14.31818 MHz input to
the chip is stopped. If the clock is restarted without a
reset, then the counter will continue counting from
where it stopped.
Revision 1.0 May 13, 1997 -47- Register Descriptions
Page 54

9,$7HFKQRORJLHV,QF
Processor Power Management Registers
VT82C586B
Offset 13-10 - Processor Control ...................................... RW
31-5 Reserved
4 Throttling Enable (THT_EN)
3040 Silicon:
reading the "Processor Level 2" (P_LVL2) port:
0 No clock thro ttling. Reads from the Processor
1 Reading the "Processor Level 2" port enables
3041 Silicon:
3-1 Throttling Duty Cycle (THT_DTY)
This 3-bit field determines the duty cycle of the
STPCLK# signal when the system is in throttling
mode (the "Throttling Enable" bit is set to one and , in
3040 silicon, the "Processor Level 2" register is
read). The duty cycle indicates the percentage of
time the STPCLK# signal is asserted while the
Throttling Enable bit is set. The field is decoded as
follows:
000 Reserved
001 0-12.5%
010 12.5-25%
011 25-37.5%
100 37.5-50%
101 50-62.5%
110 62.5-75%
111 75-87.5%
0 Reserved
........................................ always reads 0
.
This bit determines the effect of
Level 2 register are ignored.
clock throttling by modulating the STPCLK#
signal with a duty cycle determined bits 3-1 of
this register.
Setting this bit starts clock throttling
(modulating the STPCLK# signal) regardless
of the CPU state (i.e., it is not necessary to
read the "Processor Level 2" port to start clock
throttling). The throttling duty cycle is
determined by bits 3-1 of this register.
........................................ always reads 0
Offset 14 - Processor Level 2 (P_LVL2) .......................... RO
7-0 Level 2
3040 Silicon:
processor in the C2 clock state if the Throttling
Enable bit (Function 3 Rx10 bit-4) is set.
3041 Silicon:
processor into the Stop Clock state (the VT82C586B
asserts STPCLK# to suspend the processor). Wake
up from Stop Clock state is by interrupt (INTR, SMI,
PWRBTN#, RTC wakeup, or pin toggle SCI).
Reads from this register return all zeros; writes to this register
have no effect.
Offset 15 - Processor Level 3 (P_LVL3) .......................... RO
7-0 Level 3
Reads from this register put the processor in the C3
clock state with the STPCLK# signal asserted.
silicon:
interrupt (INTR, SMI, PWRBTN#, RTC wakeup, or
pin toggle SCI).
Reads from this register return all zeros; writes to this register
have no effect.
........................................always reads 0
Reads from this register put the
Reads from this register put the
........................................always reads 0
3041
wake up from Stop Clock state is by
Revision 1.0 May 13, 1997 -48- Register Descriptions
Page 55

9,$7HFKQRORJLHV,QF
General Purpose Power Management Registers
VT82C586B
Offset 21-20 - General Purpose Status (GP_STS) ....... RWC
15-10 Reserved
9 USB Resume Status (USB_STS)
This bit is set when a USB peripheral generates a
resume event.
8 Ring Status (RI_STS)
This bit is set when the RI# input is asserted low.
7 EXTSMI7 Toggle Status (EXT7_STS)
This bit is set when the EXTSMI7# pin is toggled.
6 EXTSMI6 Toggle Status (EXT6_STS)
This bit is set when the EXTSMI6# pin is toggled.
5 EXTSMI5 Toggle Status (EXT5_STS)
This bit is set when the EXTSMI5# pin is toggled.
4 EXTSMI4 Toggle Status (EXT4_STS)
This bit is set when the EXTSMI4# pin is toggled.
3 EXTSMI3 Toggle Status (EXT3_STS)
This bit is set when the EXTSMI3# pin is toggled.
2 EXTSMI2 Toggle Status (EXT2_STS)
This bit is set when the EXTSMI2# pin is toggled.
1 EXTSMI1 Toggle Status (EXT1_STS)
This bit is set when the EXTSMI1# pin is toggled.
0 EXTSMI0 Toggle Status (EXT0_STS)
This bit is set when the EXTSMI0# pin is toggled.
Note that the above bits correspond one for one with the bits
of the General Purpose SCI Enable and General Purpose SMI
Enable registers at offsets 22 and 24: an SCI or SMI is
generated if the corresponding bit of the General Purpose SCI
or SMI Enable registers, respectively, is set to one.
The above bits are set by hardware only and can only be
cleared by writing a one to the desired bit.
........................................ always reads 0
Offset 23-22 - General Purpose SCI Enable ................... RW
15-10 Reserved
9 Enable SCI on setting of the USB_STS bit
8 Enable SCI on setting of the RI_STS bit
7 Enable SCI on setting of the EXT7_STS bit
6 Enable SCI on setting of the EXT6_STS bit
5 Enable SCI on setting of the EXT5_STS bit
4 Enable SCI on setting of the EXT4_STS bit
3 Enable SCI on setting of the EXT3_STS bit
2 Enable SCI on setting of the EXT2_STS bit
1 Enable SCI on setting of the EXT1_STS bit
0 Enable SCI on setting of the EXT0_STS bit
These bits allow generation of an SCI using a separate set of
conditions from those used for generating an SMI.
Offset 25-24 - General Purpose SMI Enable .................. RW
15-10 Reserved
9 Enable SMI on setting of the USB_STS bit
8 Enable SMI on setting of the RI_STS bit
7 Enable SMI on setting of the EXT7_STS bit
6 Enable SMI on setting of the EXT6_STS bit
5 Enable SMI on setting of the EXT5_STS bit
4 Enable SMI on setting of the EXT4_STS bit
3 Enable SMI on setting of the EXT3_STS bit
2 Enable SMI on setting of the EXT2_STS bit
1 Enable SMI on setting of the EXT1_STS bit
0 Enable SMI on setting of the EXT0_STS bit
These bits allow generation of an SMI using a separate set of
conditions from those used for generating an SCI.
Offset 27-26 - Power Supply Control .............................. RW
15-11 Reserved
10 Ring PS Control (RI_PS_CTL)
This bit enables the setting of the RI_STS bit to turn
on the VDD_5V power plane by setting PWRON = 1.
9 Power Button Control (PB_CTL)
This bit is used to control the setting of the P B_STS
bit to resume the system from suspend (turn on the
VDD_5V power plane by setting PWRON = 1).
8 RTC PS Control (RTC_PS_CTL)
This bit enables the setting of the RTC_STS bit to
resume the system from suspend (turn on the
VDD_5V power plane by setting PWRON = 1).
7-1 Reserved
0 EXTSMI0 Toggle PS Control (E0_PS_CTL)
This bit enables the setting of the EXT0_ST S bit to
resume the system from suspend (turn on the
VDD_5V power plane by setting PWRON = 1).
........................................always reads 0
.... def=0
.......def=0
..def=0
..def=0
..def=0
..def=0
..def=0
..def=0
..def=0
..def=0
........................................always reads 0
... def=0
......def=0
..def=0
..def=0
..def=0
..def=0
..def=0
..def=0
..def=0
..def=0
........................................always reads 0
...................... def=0
.................. def=1
.................. def=0
........................................always reads 0
def=0
Revision 1.0 May 13, 1997 -49- Register Descriptions
Page 56

9,$7HFKQRORJLHV,QF
Generic Power Management Registers
VT82C586B
Offset 29-28 - Global Status .......................................... RWC
15-7 Reserved
6 Software SMI Status (SW_SMI_STS)
This bit is set when the SMI_CMD port (offset 2F) is
written.
5 BIOS Status (BIOS_STS)
This bit is set when the GBL_RLS bit is set to one
(typically by the ACPI software to release control of
the SCI/SMI lock). When this bit is reset (by writing
a one to this bit position) the GBL_RLS bit is reset at
the same time by hardware.
4 Legacy USB Status (LEG_USB_STS)
This bit is set when a legacy USB event occurs.
3 GP1 Timer Time Out Status (GP1TO_STS)
This bit is set when the GP1 timer times out.
2 GP0 Timer Time Out Status (GP0TO_STS)
This bit is set when the GP0 timer times out.
1 Secondary Event Timer Time Out Status
(STTO_STS)
This bit is set when the secondary event timer times
out.
0 Primary Activity Status (PACT_STS)
This bit is set at the occurrence of any enabled
primary system activity (see the Primary Activity
Detect Status register at offset 30h and the Primary
Activity Detect Enable register at offset 34h). After
checking this bit, software can check the status bits in
the Primary Activity Detect Status register at offset
30h to identify the specific source of the primary
event. Note that setting this bit can be enabled to
reload the GP0 timer (see bit-0 of the GP Timer
Reload Enable register at offset 38).
........................................ always reads 0
............def=0
................................def=0
............def=0
..def=0
..def=0
.....................................................def=0
............def=0
Offset 2B-2A - Global Enable .......................................... RW
15-7 Reserved
6 Software SMI Enable (SW_SMI_EN)
This bit may be set to trigger an SMI to be generated
when the SW_SMI_STS bit is set.
5 BIOS Enable (BIOS_EN)
This bit may be set to trigger an SMI to be generated
when the BIOS_STS bit is set.
4 Legacy USB Enable (LEG_USB_EN)
This bit may be set to trigger an SMI to be generated
when the LEG_USB_STS bit is set.
3 GP1 Timer Time Out Enable (GP1TO_EN)
This bit may be set to trigger an SMI to be generated
when the GP1TO_STS bit is set.
2 GP0 Timer Time Out Enable (GP0TO_EN)
This bit may be set to trigger an SMI to be generated
when the GP0TO_STS bit is set.
1 Secondary Event Timer Time Out Enable
(STTO_EN)
This bit may be set to trigger an SMI to be generated
when the STTO_STS bit is set.
0 Primary Activity Enable (PACT_EN)
This bit may be set to trigger an SMI to be generated
when the PACT_STS bit is set.
........................................always reads 0
............def=0
.................................def=0
.............def=0
..def=0
..def=0
......................................................def=0
............def=0
Note that SMI can be generated based on the setting of any of
the above bits (see the offset 2Ah Global Enable register bit
descriptions in the right hand column of this page).
The bits in this register are set by hardware only and can only
be cleared by writing a one to the desired bit position.
Revision 1.0 May 13, 1997 -50- Register Descriptions
Page 57

9,$7HFKQRORJLHV,QF
VT82C586B
Offset 2D-2C - Global Control (GBL_CTL) ................... RW
15-9 Reserved
8 SMI Active (INSMI)
7-5 Reserved
4 SMI Lock (SMIIG)
3 Reserved
2 Power Button Triggering
Set to one to avoid the situation where PB_STS is set
to wake up the system then reset again by
PBOR_STS to switch the system into the soft-off
state. Must be set to 0 for ACPI v0.9 compliance.
1 BIOS Release (BIOS_RLS)
This bit is set by legacy software to indicate release
of the SCI/SMI lock. Upon setting of this bit,
hardware automatically sets the GBL_STS bit. This
bit is cleared by hardware when the GBL_STS bit
cleared by software.
Note that if the GBL_EN bit is set (bit-5 of the Power
Management Enable register at offset 2), then setting
this bit causes an SCI to be generated (because setting
this bit causes the GBL_STS bit to be set).
0 SMI Enable (SMI_EN)
........................................ always reads 0
0 SMI Inactive...........................................default
1 SMI Active. If the SMIIG bit is set, this bit
needs to be written with a 1 to clear it before
the next SMI can be generated.
........................................ always reads 0
0 Disable SMI Lock ..................................default
1 Enable SMI Lock (SMI low to gate for the
next SMI).
........................................ always reads 0
0 SCI/SMI generated by PWRBTN# low level
1 SCI/SMI generated by PWRBTN# rising edge
0 Disable all SMI generation
1 Enable SMI generation
Offset 2F - SMI Command (SMI_CMD) ............. 3041: RW
............... 3040: WO, always reads 0 (Read at Func 3 Rx47)
7-0 SMI Command
Writing to this port sets the SW_SMI_ST S bit. Note
that if the SW_SMI_EN bit is set (see bit-6 of the
Global Enable register at offset 2Ah), then an SMI is
generated.
Revision 1.0 May 13, 1997 -51- Register Descriptions
Page 58

9,$7HFKQRORJLHV,QF
VT82C586B
Offset 33-30 - Primary Activity Detect Status ............. RWC
These bits correspond to the Primary Activity Detect Enable
bits in offset 37-34.
31-8 Reserved
7 Keyboard Controller Access Status..... (KBC_STS)
Set if the keyboard controller is accessed via I/O port
60h.
6 Serial Port Access Status....................... (SER_STS)
Set if the serial port is accessed via I/O ports 3F83FFh, 2F8-2FFh, 3E8-3EFh, or 2E8-2Efh (COM1-4,
respectively).
5 Parallel Port Access Status....................(PAR_STS)
Set if the parallel port is accessed via I/.O ports 27827Fh or 378-37Fh (LPT2 or LPT1).
4 Video Access Status.................................(VID_STS)
Set if the video port is accessed via I/O ports 3B03DFh or memory space A0000-BFFFFh.
3 IDE / Floppy Access Status ....................(IDE_STS)
Set if the IDE or floppy devices are accessed via I/O
ports 1F0-1F7h, 170-177h or 3F5h.
2 Reserved
1 Primary Interrupt Activity Status......(PIRQ_STS)
Set on the occurrence of a primary interrupt (enabled
via the "Primary Interrupt Channel" register at
Function 3 PCI configuration register offset 44h).
0 ISA Master / DMA Activity Status......(DRQ_STS)
Set on the occurrence of ISA master or DMA activity.
..........................................always read 0
............................................... default=0
Offset 37-34 - Primary Activity Detect Enable............... RW
These bits correspond to the Primary Activity Detect Status
bits in offset 33-30.
31-8 Reserved
7 Keyboard Controller Status Enable ..... (KBC_EN)
6 Serial Port Status Enable........................(SER_EN)
5 Parallel Port Status Enable ....................(PAR_EN)
4 Video Status Enable .................................(VID_EN)
3 IDE / Floppy Status Enable .....................(IDE_EN)
2 Reserved
1 Primary INTR Status Enable...............(PIRQ_EN)
0 ISA Master / DMA Status Enable.........(DRQ_EN)
......................................... always read 0
0 Don't set PACT_STS if KBC_STS is set..... def
1 Set PACT_STS if KBC_STS is set
0 Don't set PACT_STS if SER_STS is set......def
1 Set PACT_STS if SER_STS is set
0 Don't set PACT_STS if PAR_STS is set .....def
1 Set PACT_STS if PAR_STS is set
0 Don't set PACT_STS if VID_STS is set......def
1 Set PACT_STS if VID_STS is set
0 Don't set PACT_STS if IDE_STS is set ......def
1 Set PACT_STS if IDE_STS is set
....................................................default
0 Don't set PACT_STS if PIRQ_STS is set....def
1 Set PACT_STS if PIRQ_STS is set
0 Don't set PACT_STS if DRQ_STS is set ....def
1 Set PACT_STS if DRQ_STS is set
Note: The bits above correspond to the bits of the Primary
Activity Detect Enable register at offset 34 (see right
hand column of this page): if the corresponding bit is
set in that register, setting of the above bits will cause
the PACT_STS bit to be set (bit-0 of the Global
Status register at offset 28). Setting of PACT_STS
may be set up to enable a "Primary Activity Event":
an SMI will be generated if PACT_EN is set (bit-0 of
the Global Enable register at offset 2Ah) and/or the
GP0 timer will be reloaded if the "GP0 Timer Reload
on Primary Activity" bit is set (bit-0 of the GP Timer
Reload Enable register at offset 38 on this page).
Note: Bits 3-7 above also correspond to bits 3-7 of the GP
Timer Reload Enable register at offset 38 (see right
hand column of this page): if the corresponding bit is
set in that register, setting the bit in this register will
cause the GP1 timer to be reloaded.
All bits of this register are set by hardware only and may only
be cleared by writing a one to the desired bit. All bits default
to 0.
Note: Setting of any of the above bits also sets the
PACT_STS bit (bit-0 of offset 28) which causes the
GP0 timer to be reloaded (if PACT_GP0 _EN is set)
or generates an SMI (if PACT_EN is set).
Offset 3B-38 - GP Timer Reload Enable ......................... RW
All bits in this register default to 0 on power up.
31-8 Reserved
7 Enable GP1 Timer Reload on KBC Access
1 = setting of KBC_STS causes GP1 timer to reload.
6 Enable GP1 Timer Reload on Serial Port Access
1 = setting of SER_STS causes GP1 timer to reload.
5 Reserved
4 Enable GP1 Timer Reload on Video
1 = setting of VID_STS causes GP1 timer to reload.
3 Enable GP1 Timer Reload on IDE/Floppy Access
1 = setting of IDE_STS causes GP1 timer to reload.
2-1 Reserved
0 Enable GP0 Timer Reload on Primary Activity
1 = setting of PACT_STS causes GP0 timer to reload.
Primary activities are enabled via the Primary
Activity Detect Enable register (offset 37-34) with
status recorded in the Primary Activity Detect Status
register (offset 33-30).
......................................... always read 0
......................................... always read 0
Access
......................................... always read 0
Revision 1.0 May 13, 1997 -52- Register Descriptions
Page 59

9,$7HFKQRORJLHV,QF
General Purpose I/O Registers
VT82C586B
Offset 40 - GPIO Direction Control (GPIO_DIR) .......... RW
7 Reserved
6 SMI/SCI Event Disable on GPIO3/GPIO4
5 Interrupt Resume from Power-On Suspend
4 GPIO4_DIR
If Rx40[7]=0 (PCI Configuration function 3 offset
40h GPIO4_CFG bit), pin 136 is the GPO_WE
output, independent of the state of this bit.
3 GPIO3_DIR
If Rx40[6]=0 (PCI Configuration function 3 offset
40h GPIO3_CFG bit), pin 92 is the GPI_RE# output,
independent of the state of this bit.
2 GPIO2_DIR
1 GPIO1_DIR
0 GPIO0_DIR
..........................................always read 0
0 Enable GPIO3/GPIO4 to cause SCI/SMI
Events.....................................................default
1 GPIO3/GPIO4 will only cause SCI/SMI
Events during Power-On-Suspend (POS) mode
0 Enable (resume on interrupt from POS)...... def
1 Disable (ignore interrupts during POS)
0 Pin 136 is GPIO4 input ..........................default
1 Pin 136 is GPIO4 output (if Rx40 bit-7 = 1)
0 Pin 92 is GPIO3 input ............................default
1 Pin 92 is GPIO3 output (if Rx40 bit-6 = 1)
0 Pin 88 is GPIO2 / I2CD1 input ..............default
1 Pin 88 is GPIO2 / I2CD1 output
0 Pin 87 is GPIO1 / I2CD2 input ..............default
1 Pin 87 is GPIO1 / I2CD2 output
0 Pin 94 is GPIO0 input ............................default
1 Pin 94 is GPIO0 output
Offset 42 - GPIO Port Output Value (GPIO_VAL) ...... RW
7-5 Reserved
4 GPIO4_VAL
Write output value for the GPIO4 pin if the port is
available (GPIO4_CFG = 1 in PCI Config Register
function 3 offset 40h). The input state of the GPIO4
pin may be read from register EXTSMI_VAL bit-4.
3 GPIO3_VAL
Write output value for the GPIO3 pin if the port is
available (GPIO3_CFG = 1 in PCI Config Register
function 3 offset 40h). The input state of the GPIO3
pin may be read from register EXTSMI_VAL bit-3.
2 GPIO2_VAL
Write output value for the GPIO2 (I2CD2) pin. T he
input state of the GPIO2 pin may be read from
register EXTSMI_VAL bit-2.
1 GPIO1_VAL
Write output value for the GPIO1 (I2CD1) pin. T he
input state of the GPIO1 pin may be read from
register EXTSMI_VAL bit-1.
0 GPIO0_VAL
Write output value for the GPIO0 pin. The input
state of the GPIO0 pin may be read from register
EXTSMI_VAL bit-0.
Offset 44 - GPIO Port Input Value (EXTSMI_VAL) ..... RO
Depending on the configuration, up to 8 external SCI/SMI
ports are available as indicated below. The state of these
inputs may be read in this register.
7 EXTSMI7# Input Value
GPIO3_CFG=0: EXTSMI7# on XD7 (pin 122)
GPIO3_CFG=1: EXTSMI7# function not available
6 EXTSMI6# Input Value
GPIO3_CFG=0: EXTSMI6# on XD6 (pin 121)
GPIO3_CFG=1: EXTSMI6# function not available
5 EXTSMI5# Input Value
GPIO3_CFG=0: EXTSMI5# on XD5 (pin 119)
GPIO3_CFG=1: EXTSMI5# function not available
4 EXTSMI4# Input Value
GPIO4_CFG=0:
GPIO4_CFG=1: EXTSMI4# on GPIO4 (pin 136)
3 EXTSMI3# Input Value
GPIO3_CFG=0: EXTSMI3# on XD3 (pin 117)
GPIO3_CFG=1: EXTSMI3# on GPIO3 (pin 92)
2 EXTSMI2# Input Value
1 EXTSMI1# Input Value
0 EXTSMI0# Input Value
Note: GPIO3_CFG and GPIO4_CFG are located in PCI
Configuration Register function 3 offset 40h.
........................................always reads 0
GPIO3_CFG=0: EXTSMI4# on XD4 (pin 118)
GPIO3_CFG=1: EXTSMI4# function not avail
(on GPIO2 pin 88)
(on GPIO1 pin 87)
(on GPIO0 pin 94)
Revision 1.0 May 13, 1997 -53- Register Descriptions
Page 60

9,$7HFKQRORJLHV,QF
VT82C586B
Offset 47-46 - GPO Port Output Value (GPO_VAL) ..... RW
Reads from this register return the last value written (held on
chip).
15-8 GPO15-8 Value.
GPO port connected to SD15-8. This port is
available only if the GPIO4_CFG bit is zero to define
pin 136 as GPO_WE.
7-0 GPO7-0 Value.
GPO port connected to XD7-0. This port is availab le
only if the GPIO4_CFG bit is zero to define pin 136
as GPO_WE.
GPIO4_CFG is in PCI Config Register function 3 offset 40h.
Output port value for the external
Output port value for the external
Offset 49-48 - GPI Port Input Value (GPI_VAL) ........... RO
Reads from this register are ignored (and return a value of 0).
15-8 GPI15-8 Value.
GPI port connected to SD15-8. T his por t is availab le
only if the GPIO3_CFG bit is zero to define pin 92 as
GPI_RE#.
7-0 GPI7-0 Value.
port connected to XD7-0. This port is available only
if the GPIO3_CFG bit is zero to define pin 92 as
GPI_RE#.
GPIO3_CFG is in PCI Config Register function 3 offset 40h.
Input port value for the external
Input port value for the external GPI
Revision 1.0 May 13, 1997 -54- Register Descriptions
Page 61

9,$7HFKQRORJLHV,QF
Absolute Maximum Ratings
Parameter Min Max Unit
Ambient operating temperature 0 70
Storage temperature -55 125
Input voltage -0.5 5.5 Volts
Output voltage (VDD = 5V) -0.5 5.5 Volts
E
LECTRICAL SPECIFICATIONS
VT82C586B
o
C
o
C
Output voltage (VDD = 3.1 - 3.6V) -0.5 V
Note: Stress above the conditions listed may cause permanent damage to the
device. Functional operation of this device should be restricted to the
conditions described under operating conditions.
DC Characteristics
TA-0-70oC, VDD=5V+/-5%, GND=0V
Symbol Parameter Min Max Unit Condition
V
IL
V
IH
V
OL
V
OH
I
IL
I
OZ
I
CC
Input low voltage -0.50 0.8 V
Input high voltage 2.0 VDD+0.5 V
Output low voltage - 0.45 V IOL=4.0mA
Output high voltage 2.4 - V IOH=-1.0mA
Input leakage current - +/-10 uA 0<VIN<V
Tristate leakage current - +/-20 uA 0.45<V
Power supply current - 80 mA
+ 0.5 Volts
DD
DD
OUT<VDD
Revision 1.0 May 13, 1997 -55- Electrical Specifications
Page 62

9,$7HFKQRORJLHV,QF
AC Timing Specifications
T
AD[31:0] Setup Time to PCLK Rising 7 ns
S
T
FRAME#,TRDY#,IRDY# Setup Time to PCLK Rising 7 ns
S
T
CBE[3:0]#, STOP#,DEVSEL# Setup Time to PCLK Rising 7 ns
S
T
PGNT# Setup Time to PCLK Rising 12 ns
S
T
AD[31:0] Hold Time from PCLK Rising 0 ns
H
T
FRAME#,TRDY#,IRDY# Hold Time from PCLK Rising 0 ns
H
T
CBE[3:0]#, STOP#,DEVSEL# Hold Time from PCLK Rising 0 ns
H
T
PGNT# Hold Time from PCLK Rising 0 ns
H
T
AD[31:0] Valid Delay from PCLK Rising (address phase) 2 11 ns 0pf on min, 50pf on max
VD
T
AD[31:0] Valid Delay from PCLK Rising (data phase) 2 11 ns 0pf on min, 50pf on max
VD
T
FRAME#,TRDY#,IRDY# Valid Delay from PCLK Rising 2 11 ns 0pf on min, 50pf on max
VD
T
CBE[3:0]#, STOP#,DEVSEL# Valid Delay from PCLK Rising 2 11 ns 0pf on min, 50pf on max
VD
T
PREQ# Valid Delay from PCLK Rising 2 12 ns 0pf on min, 50pf on max
VD
VT82C586B
Table 8. AC Characteristics - PCI Cycle Timing
Parameter Min Max Unit Notes
T
FRAME#,TRDY#,IRDY# Float Delay from PCLK Rising 28 ns 0pf on min, 50pf on max
FD
T
CBE[3:0]#, STOP#,DEVSEL# Float Delay from PCLK Rising 28 ns 0pf on min, 50pf on max
FD
Revision 1.0 May 13, 1997 -56- Electrical Specifications
Page 63

9,$7HFKQRORJLHV,QF
VT82C586B
Table 9. AC Characteristics - UltraDMA-33 IDE Bus Interface Timing
Symbol Description Timing Unit
T
T
T
T
T
T
T
T
T
T
T
T
T
T
T
T
T
T
T
T
T
T
T
T
T
T
T
T
T
T
T
T
ENV1
DS1
DH1
ENV2
DVS2
DVH2
DVS2
DVH2
RFS
RP
LI4
LI4
ZA4
DVS4
DVH4
LI5
LI5
MIL5
DVS5
DVH5
MIL6
ZA6
LI5
MIL5
2
3
4
5
WDS
WDH
RDS
RDH
Envelope time for read initial 29.3 ns
Data setup time for read initial 1.1 ns
Data hold time for read initial (rise) 2.3 ns
Envelope time for write initial (rise) 29.3 ns
Data setup time for write initial (fall) 42.2 ns
Data hold time for write initial (fall) 17.8 ns
Data setup time for write initial 42.0 ns
Data hold time for write initial 17.2 ns
READY to final STROBE time 21.3 ns
READY to Pause time 180.0 ns
Limited interlock time (to STOP) 95.1 ns
Limited interlock time (to Host DMARDY) 125.3 ns
Delay time required for output drives turning on 102.0 ns
Data setup time for read terminating 55.3 ns
Data hold time for read terminating 31.6 ns
Limited interlock time (to STOP) 125.3 ns
Limited interlock time (to Host STROBE) 95.2 ns
Limited interlock time with minimum 120.6 ns
Data setup time for write terminating 57.7 ns
Data hold time for write terminating 31.8 ns
Limited interlock time with minimum 155.8 ns
Delay time required for output drives turning on 68.5 ns
Limited interlock time 65.2 ns
Limited interlock time with minimum 90.6 ns
Delay time of PCLK to DCS3,1# 4.8 ns
Delay time of PCLK to DA[2:0] 5.3 ns
Delay time of PCLK to DIOW# 9.3 ns
Delay time of PCLK to DIOR# 9.2 ns
Data setup time during PIO write 85.5 ns
Data hold time during PIO write 31.7 ns
Data setup time during PIO read 0.4 ns
Data hold time during PIO read 2.1 ns
Revision 1.0 May 13, 1997 -57- Electrical Specifications
Page 64

9,$7HFKQRORJLHV,QF
VT82C586B
DDRQ (Drive)
UI
T
DDACK# (Host)
STOP (Host)
HDMARDY# (Host)
T
ENV1
DSTROBE (Drive)
T
LI1
T
DS1
Data
T
DH1
Figure 5. UltraDMA-33 IDE Timing - Drive Initiating DMA Burst for Read Command
DDRQ (Drive)
T
UI
DDACK# (Host)
T
ENV2
STOP (Host)
DDMARDY# (Drive)
T
UI
HSTROBE (Host)
DDMARDY# (Drive)
HSTROBE (Host)
T
DVH2
Data
T
DVS2
Figure 6. UltraDMA-33 IDE Timing - Drive Initiating Burst for Write Command
Revision 1.0 May 13, 1997 -58- Electrical Specifications
Page 65

9,$7HFKQRORJLHV,QF
DDRQ (Drive)
DDACK# (Host)
For Write:
DDMARDY# (Drive)
HSTROBE (Host)
VT82C586B
T
RFS
For Read:
STOP (Host)
HDMARDY# (Host)
Figure 7. UltraDMA-33 IDE Timing - Pausing a DMA Burst
T
RP
Revision 1.0 May 13, 1997 -59- Electrical Specifications
Page 66

9,$7HFKQRORJLHV,QF
)
)
)
DDRQ (Drive
DDACK# (Host)
STOP (Host
HDMARDY# (Host
VT82C586B
T
LI4
T
CRC
DVS4
T
DVH4
Data
T
ZA4
Figure 8. UltraDMA-33 IDE Timing - Drive Terminating DMA Burst During Read Command
DDRQ (Drive)
DDACK# (Host)
T
STOP (Host)
LI5A
DDMARDY# (Host)
HSTROBE (Host)
T
LI5B
Data
Figure 9. UltraDMA-33 IDE Timing - Drive Terminating DMA Burst During Write Command
Revision 1.0 May 13, 1997 -60- Electrical Specifications
T
MLI5
T
CRC
DVS5
T
DVH5
Page 67

9,$7HFKQRORJLHV,QF
T
MLI6
VT82C586B
DDRQ# (Drive)
T
DDACK# (Host)
ZA6
STOP (Host)
HDMARDY# (Host)
Data
Figure 10. UltraDMA-33 IDE Timing - Host Terminating DMA Burst During Read Command
CRC
DDRQ (Drive)
DDACK# (Host)
T
MIL7
STOP (Host)
T
HSTROBE# (Host)
Data
Figure 11. UltraDMA-33 IDE Timing - Host Terminating DMA Burst During Write Command
Revision 1.0 May 13, 1997 -61- Electrical Specifications
LI7
T
DVS7
CRC
T
DVH7
Page 68

9,$7HFKQRORJLHV,QF
DCS3# / DCS1#
DA [2:0]
DIOW#
DD Write
DIOR#
DD Read
VT82C586B
T
2
T
3
T
WDS
T
4
T
WDH
T
5
T
T
RDS
RDH
Figure 12. UltraDMA-33 IDE Timing - PIO Cycle
Revision 1.0 May 13, 1997 -62- Electrical Specifications
Page 69

9,$7HFKQRORJLHV,QF
P
ACKAGE MECHANICAL SPECIFICATIONS
VT82C586B
7<3
7<3
97&%
66%
<<::997$,:$1
0
//5//////
0
Y = Date Code Year
W = Date Code Week
V = Chip Version
CD = OEM Version
CE = Production Version
R = Revision Code
L = Lot Code
0$;
R
a
Figure 13. Mechanical Specifications - 208-Pin Plastic Flat Package
Revision 1.0 May 13, 1997 -63- Package Mechanical Specifications
 Loading...
Loading...