Page 1

MULTISYNCON-SCREENDISPLAY FOR MONITOR
.
CMOSSINGLECHIP OSDFOR MONITOR
.
BUILT IN 1 KBYTE RAM HOLDING:
- PAGES’DESCRIPTORS
- CHARACTER CODES
- USERDEFINABLE CHARACTERS
.
128 ALPHANUMERIC CHARACTERS OR
GRAPHIC SYMBOLS IN INTERNAL ROM
(12 x18 DOTMATRIX)
.
UP TO 26 USERDEFINABLE CHARACTERS
.
INTERNALHORIZONTALPLL(15TO120kHz)
.
PROGRAMMABLE VERTICAL HEIGHT OF
CHARACTER WITH A SLICEINTERPOLATOR
TO MEETMULTI-SYNCHREQUIREMENTS
.
PROGRAMMABLE VERTICAL AND HORIZONTALPOSITIONING
.
FLEXIBLESCREEN DESCRIPTION
.
CHARACTER BY CHARACTER COLOR SELECTION(UP TO 8 DIFFERENT COLORS)
.
PROGRAMMABLE BACKGROUND (COLOR,
TRANSPARENTORWITH SHADOWING)
.
CHARACTER BLINKING
.
2-WIRES ASYNCHRONOUS SERIAL MCU
INTERFACE (I
.
8 x 8BITS PWM DACOUTPUTS
.
SINGLEPOSITIVE5V SUPPLY
2
C PROTOCOL)
STV9422
STV9424
SHRINK 24
(Plastic Package)
ORDER CODE : STV9422
DESCRIPTION
The STV9422/24is an ONSCREEN DISPLAYfor
monitor.It is built as a slave peripheralconnected
to a host MCU via a serial I
display memory, controls all the display attributes
and generatespixels from the data read in its on
chip memory. The line PLL and a special slice
interpolator allow to have a display aspect which
doesnotdependon thelineandframefrequencies.
2
C interface allows MCU to make transparent in-
I
ternal accessto preparethe next pages duringthe
display of the current page. Togglefrom one page
to anotherby programmingonlyone register.
8 x 8 bits PWM DAC are available to provideDC
voltage control to otherperipherals.
The STV9422/24providestheuseraneasy to use
and cost effectivesolutiontodisplayalphanumeric
or graphicinformation onmonitorscreen.
October 1995
2
C bus. It includes a
DIP16
(Plastic Package)
ORDER CODE : STV9424
1/15
Page 2
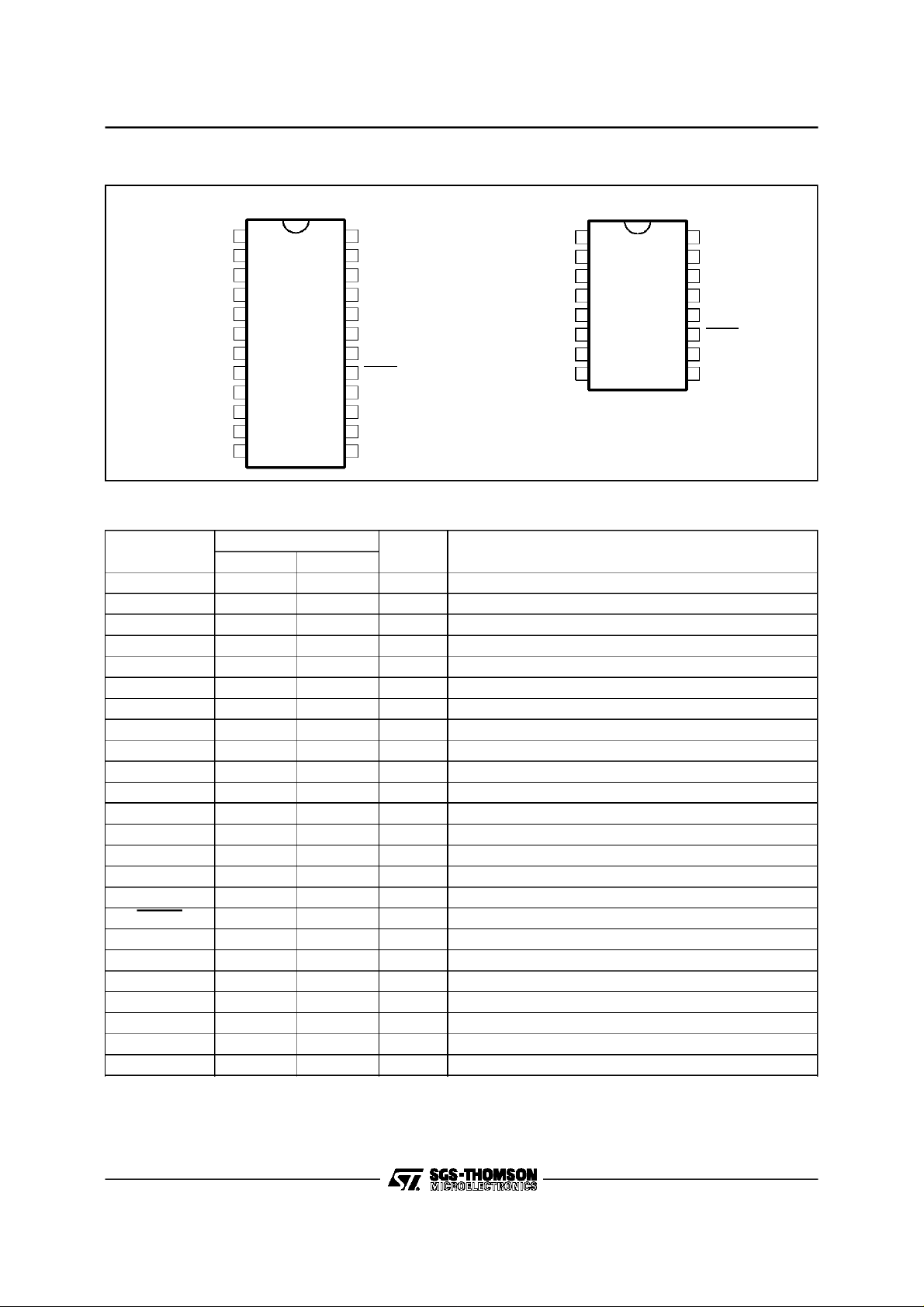
STV9422 - STV9424
PIN CONNECTIONS
PWM0
PWM1
FBLK
VSYNC
HSYNC
V
PXCK
CKOUT
XTAL OUT
XTALIN
PWM2
SDIP24 (STV9422)
1
2
3
4
5
6
DD
7
8
9
10
11
12
24
PWM7
23
PWM6
22
TEST
21
B
20
G
19
R
18
GND
17
RESET
16
SDA
15
SCL
14
PWM5
13
PWM4PWM3
XTAL OUT
DIP16 (STV9424)
FBLK
V-SYNC
H-SYNC
V
DD
PXCK
CKOUT
XTAL IN
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
PIN DESCRIPTION
Symbol
PWM0 1 - O DAC0 Output
PWM1 2 - O DAC1 Output
FBLK 3 1 O Fast Blanking Output
V-SYNC 4 2 I Vertical Sync Input
H-SYNC 5 3 I HorizontalSync Input
V
DD
PXCK 7 5 O Pixel Frequency Output
CKOUT 8 6 O Clock Output
XTAL OUT 9 7 O Crystal Output
XTAL IN 10 8 I Crystal or Clock Input
PWM2 11 - O DAC2 Output
PWM3 12 - O DAC3 Output
PWM4 13 - O DAC4 Output
PWM5 14 - O DAC5 Output
SCL 15 9 I Serial Clock
SDA 16 10 I/O Serial Input/output Data
RESET 17 11 I Reset Input (ActiveLow)
GND 18 12 S Ground
R 19 13 O Red Output
G 20 14 O Green Output
B 21 15 O Blue Output
TEST 22 16 I Reserved (grounded in Normal Operation)
PWM6 23 - O DAC6 Output
PWM7 24 - O DAC7 Output
Pin Number
SDIP24 DIP16
I/O Description
6 4 S +5V Supply
TEST
16
B
15
G
14
R
13
GND
12
RESET
11
SDA
10
SCL
9
9422-01.EPS / 9424-01.EPS
9422-01.TBL
2/15
Page 3
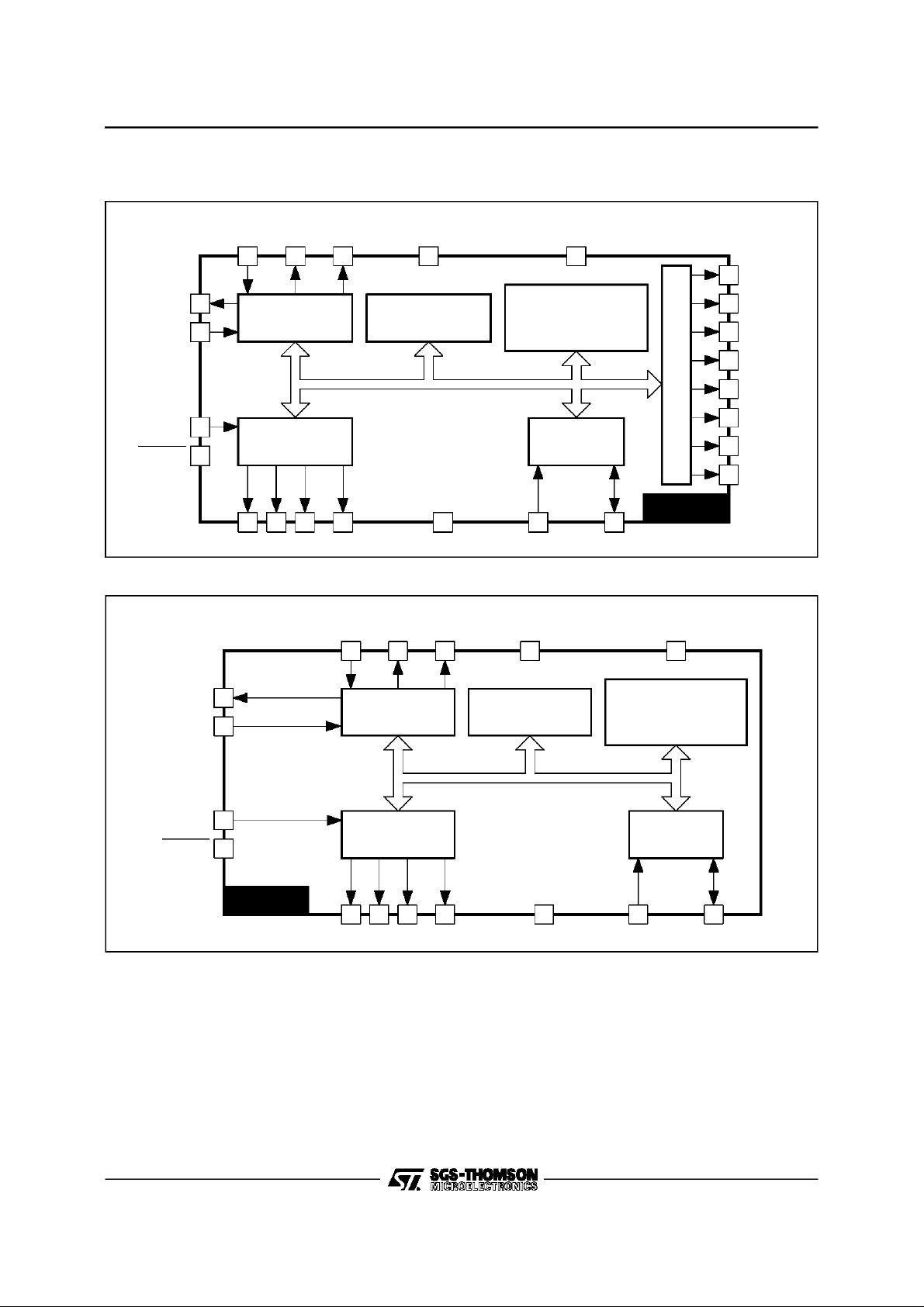
BLOCK DIAGRAMS
STV9422
XTALINXTAL
OUT PXCK TEST
V
DD
10 9 7 6 22
STV9422 - STV9424
24
PWM7
CKOUT
HSYNC
VSYNC
RESET
STV9424
8
5
4
17
CKOUT
HSYNC
HORIZONTAL
DIGITAL PLL
4KROM
(128 characters)
1K RAM
Page Descriptors +
User Defined Char.
Address/Data
DISPLAY
CONTROLLER
2
I C BUS
INTERFACE
19 20 21 3 18 15 16
R G B FBLK GND SCL SDA
XTALINXTAL
OUT
PXCK TEST
78
6
3
HORIZONTAL
DIGITAL PLL
V
DD
45
4KROM
(128 characters)
23
14
13
PWM
12
11
2
1
STV9422
16
1K RAM
Page Descriptors +
User Defined Char.
PWM6
PWM5
PWM4
PWM3
PWM2
PWM1
PWM0
9422-02.EPS
VSYNC
RES ET
2
11
STV9424
Address/Data
DISPLAY
CONTROLLER
1
1213 14 15
INTERFACE
910
R G B FBLK GND SCL
2
I C BUS
SDA
9424-02.EPS
3/15
Page 4

STV9422 - STV9424
ABSOLUTEMAXIMUM RATINGS
Symbol Parameter Value Unit
V
DD
V
IN
T
oper
T
stg
ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS
=5V,VSS=0V,TA=0 to70°C, F
(V
DD
Symbol Parameter Min. Typ. Max. Unit
SUPPLY
V
DD
I
DD
INPUTS
SCL, SDA, TEST, RESET, V-SYNC and H-SYNC
V
IL
V
IH
I
IL
OUTPUTS
R, G, B, FBLK, SDA, CKOUT, PXCK and PWMi(i = 0 to 7)
V
OL
V
OH
For R, G, Band FBLK outputs,see Figure 1.
Supply Voltage -0.3, +7.0 V
Input Voltage -0.3, +7.0 V
Operating Ambient Temperature 0, +70 °C
Storage Temperature -40, +125 °C
= 8 to 15MHz, TEST = 0 V,unless otherwisespecified)
XTAL
Supply Voltage 4.75 5 5.25 V
Supply Current - - 50 mA
Input LowVoltage 0.8 V
Input HighVoltage 0.8V
DD
Input LeakageCurrent -20 +20 µ
Output Low Voltage(IOL= 1.6mA) 0 0.4 V
Output HighVoltage (IOL= -0.1mA) 0.8V
DD
V
DD
9422-02.TBL
V
A
V
9422-03.TBL
Figure 1 : TypicalR, G, B OutputsCharacteristics
(V)
V
,
V
OH
V
OL
I (A)
10
-4
10
-3
10
-2
10
-1
5
2.5
0
V
10
OL OH
-5
9422-17.EPS
4/15
Page 5
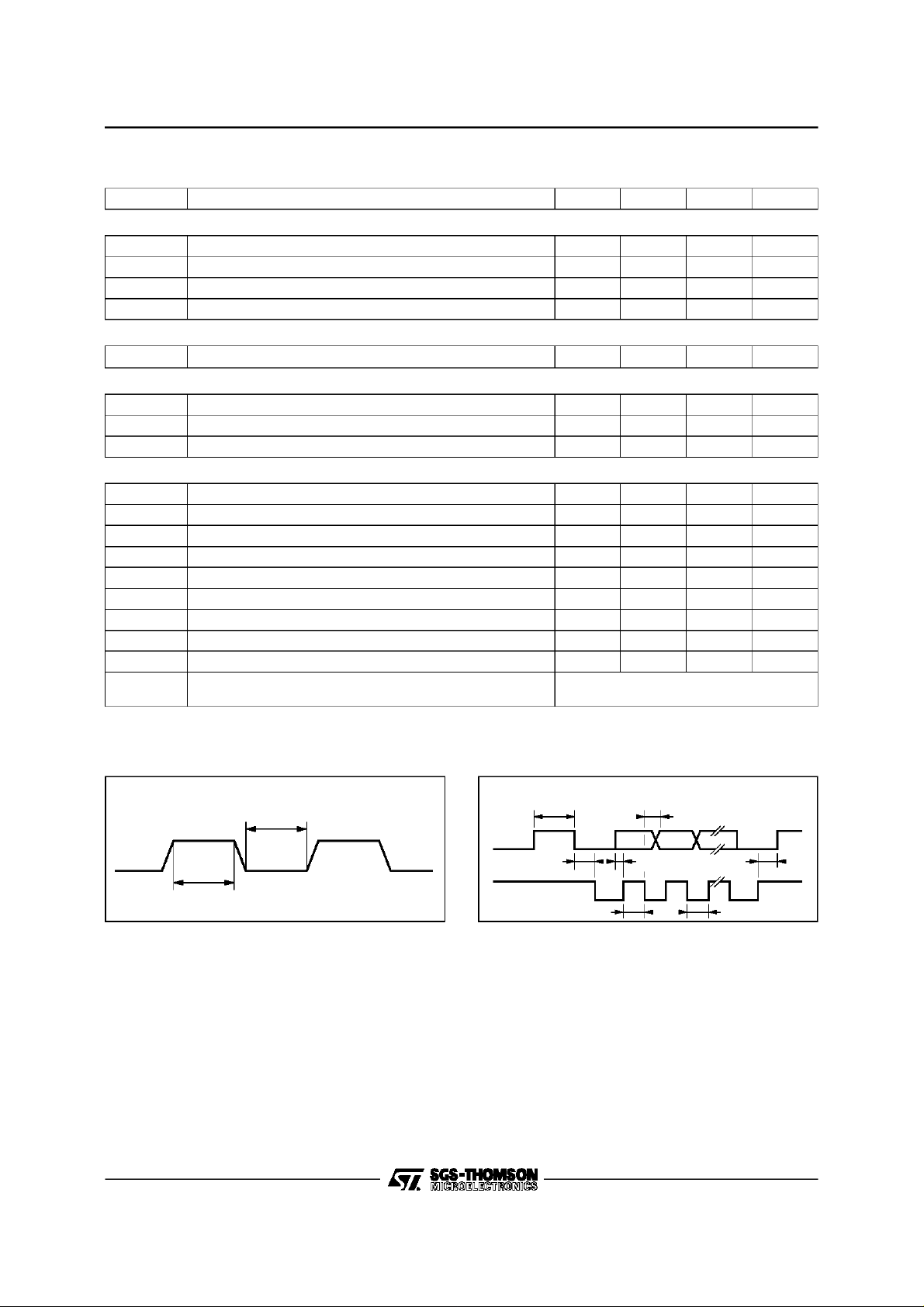
STV9422 - STV9424
TIMINGS
Symbol Parameter Min. Typ. Max. Unit
OSCILATOR INPUT : XTI (seeFigure 2)
t
WH
t
WL
f
XTAL
f
PXL
RESET
t
RES
R, G,B, FBLK (C
t
R
t
F
t
SKEW
2
I
C INTERFACE : SDA AND SCL (see Figure 3)
f
SCL
t
BUF
t
HDS
t
SUP
t
LOW
t
HIGH
t
HDAT
t
SUDAT
t
F
t
R
Note 1 : These parameters are not tested on each unit. They are measured during our internal qualification procedure which includes
Clock High Level 20 ns
Clock LowLevel 20 ns
Clock Frequency 6 15 MHz
Pixel Frequency 40 MHz
Reset Low LevelPulse 4
= 30pF)
LOAD
Rise Time (Note 1) 5 ns
Fall Time (Note 1) 5 ns
Skew between R, G,B, FBLK (Note 1) 5 ns
SCL Clock Frequency 0 1 MHz
Time the bus must be free between 2 access 500 ns
Hold Time forStart Condition 500 ns
Set upTime for Stop Condition 500 ns
The LowPeriod of Clock 400 ns
The High Periodof Clock 400 ns
Hold Time Data 0 ns
Set upTime Data 375 ns
Fall Time of SDA 20 ns
Rise Time of Both SCL and SDA
characterization on batches comming from corners of our processesand also temperaturecharacterization.
Depend on the pull-up resistor
and the loadcapacitance
µs
9422-04.TBL
Figure2
XTI
Figure 3
STOP START DATA STOP
t
t
WL
SDA
t
WH
SCL
9422-03.EPS
BUF
t
HDS
t
HIGH
t
SUDAT
t
HDAT
t
SUP
t
LOW
9422-04.EPS
5/15
Page 6

STV9422 - STV9424
FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION
The STV9422/24 display processor operation is
controlledby a host MCU via the I
fully programmablethrough 16 internal read/write
registers (8 for STV9424) and performs all the
display functions by generating pixels from data
stored in its internal memory. After the page downloading from the MCU, the STV9422/24refreshes
screen by its built in processor, without any MCU
control (access).In addition, the host MCU has a
direct access to the on chip 1Kbytes RAM during
the displayof thecurrentpageto make anyupdate
of itscontents.
With the STV9422/24, a page displayed on the
screenis madeof several strips which can beof 2
types : spacing or character and which are described by a table of descriptors and character
codes in RAM.Severalpagescan be downloaded
at thesametime in the RAMandthe choice of the
currentdisplaypage is made by programming the
CONTROLregister.
I - Serial Interface
The 2-wires serial interface is an I
be connectedto theI
2
C bus,a devicemust ownits
sl ave addr ess ; the sla ve addre ss of the
STV9422/24is BA(in hexadecimal).
A6 A5 A4 A3 A2 A1 A0 R/W
1011101
Figure 3 : STV9422/I2C Write Operation
2
C interface. It is
2
C interface.To
I.1 -Data Transferin Write Mode
The hostMCU canwritedatainto theSTV9422/24
registersor RAM.
Towritedataintothe STV9422/24,aftera start,the
MCUmust send(Figure 3) :
- First, the I
2
C addressslave byte with a lowlevel
for theR/Wbit,
- The two bytes of the internaladdress where the
MCU wants towrite data(s),
- The successivebytes of data(s).
All bytes are sent MS bit first and the write data
transferis closed by a stop.
I.2 -Data Transferin Read Mode
ThehostMCU can readdatafromtheSTV9422/24
registers,RAM or ROM.
To readdata from the STV9422/24(Figure 4),the
MCUmust send2 different I
Thefirstoneis madeofI
2
C sequences.
2
Cslave addressbytewith
R/W bit at low level and the 2 internal address
bytes.
2
The secondoneismade ofI
C slave addressbyte
with R/W bit at high level and all the successive
data bytes read at successive addresses starting
fromthe initialaddressgivenbythefirst sequence.
SCL
R/W
SDA
2
C Slave Address
I
SCL
D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0 D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0 D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
SDA
ACK ACKData Byte1 Data Byte 2 ACK Data Byte n Stop
A7 A6 A5 A4 A3 A2 A1 A0 - - A13 A12 A11 A10 A9 A8
ACK LSB Address ACK MSB Address ACKStart
Figure 4 : STV9422/I2C ReadOperation
SCL
R/W
SDA
I1C SlaveAddress
SCL
SDA R/W
I1C SlaveAddress
6/15
A7 A6 A5
ACK LSB Address ACK MSB Address ACKStart
D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
ACK ACK Data Byten ACKStart
A4 A3 A2 A1 A0
Data Byte1
- - A13 A12 A10 A10 A9 A8
D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
Stop
Stop
9422-05.AI
9422-06.EPS
Page 7

FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION (continued)
I.3 -AddressingSpace
STV9422/24registers,RAMandROMaremapped
in a 16Kbytesaddressing space. The mapping is
the following:
0000
03FF
0400
1FFF
2000
32FF
3300
3FFF
3FF0
3FFF
1024 bytes RAM
Empty Space
Character
Generator ROM
Empty Space
Internal
Registers
Descriptors character
codes user definable
characters
I.4 - RegisterSet
LINE DURATION
3FF0 VSP HSP LD5 LD4 LD3 LD2 LD1 LD0
* 0 0111111
VSP : V-SYNC active edge selection
= 0 : falling egde, = 1 : rising edge
HSP : H-SYNCactive edge selection
= 0 : falling egde, = 1 : rising edge
LD[5:0] : LINE DURATION
(numberof pixelperiod per line divided
by 12 ie.Unit = 12 pixel periods).
HORIZONTALDELAY
3FF1 DD7 DD6 DD5 DD4 DD3 DD2 DD1 DD0
*00001000
DD[7:0] : HORIZONTAL DISPLAY DELAY from
the H-SYNC reference falling edge to
st
the 1
pixel position of the character
strips.Unit = 3 pixel periods.
CHARACTERS HEIGHT
3FF2 - - CH5 CH4 CH3 CH2 CH1 CH0
*--010010
CH[5:0] : HEIGHT of the character strips in scan
lines. For each scan line,thenumberof
the slice which is displayedis givenby :
SLICE-NUMBER =
SCAN±LINE±NUMBER x 18
round
CH[5:0]
.
SCAN-LINE-NUMBER = Number of the
current scan line of thestrip.
STV9422 - STV9424
DISPLAYCONTROL
3FF3 OSD FBK FL1 FL0 - P8 P7 P6
* 0 0 0 0 -000
OSD : ON/OFF(if 0, R, G, B and FBLKare0 ).
FBK : Fast blankingcontrol :
= 1: FBLK=1,forcingblackwherethese
is no display,
= 0: FBLKis activeonlyduringcharacter
display.
FL[1:0] : Flashing mode :
- 00 : No flas hing . T he ch ara cter
attributeis ignored,
- 01 : 1/1 flashing (a dutycycle = 50%),
- 10 : 1/3 flashing,
- 11: 3/1 flashing.
P[8:6] : Address of the 1
current displayedpages.
P[13:9] and P[5:0]=0 ; up to 8 different
pages can be stored in the RAM.
LOCKINGCONDITION TIME CONSTANT
3FF4 FR AS2 AS1 AS0 - BS2 BS1 BS0
*0010-010
FR : Free Running;if = 1 PLLisdisabled and
the pixelfrequencykeepsits last value.
AS[2:0] : Phase constant during locking
conditions.
BS[2:0] : Frequen cy constant during locking
conditions.
CAPTUREPROCESS TIME CONSTANT
3FF5 - AF2 AF1 AF0 - BF2 BF1 BF0
*-011-011
AF[2:0] : Phase constant during the capture
process.
BF[2:0] : Frequency constant during the capture
process.
INITIALPIXELPERIOD
3FF6 PP7 PP6 PP5 PP4 PP3 PP2 PP1 PP0
*00101000
PP[7:0] : Valueto initialize the pixel period of the
PLL.
FREQUENCY MULTIPLIER
3FF7 - - - - FM3 FM2 FM1 FM0
* ----1010
FM[3:0] : Frequency multiplier of the crystal
frequency to reach the high frequency
used by the PLL to derive the pixel
frequency.
st
descriptor of the
7/15
Page 8

STV9422 - STV9424
FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION (continued)
The last fourth registersdescribedbelow are only
availablewith the STV9422 :
PULSE WIDTH MODULATOR0 (STV9422)
3FF8 V07 V06 V05 V04 V03 V02 V01 V00
* 00000000
V0[7:0] : Digital value of the 1stPWM D to A
converter(Pin1).
PULSE WIDTH MODULATOR1 (STV9422)
3FF9 V17 V16 V15 V14 V13 V12 V11 V10
* 00000000
V1[7:0] : Digitalvalueofthe2ndPWMDAC(Pin2).
PULSE WIDTH MODULATOR2 (STV9422)
3FFA V27 V26 V25 V24 V23 V22 V21 V20
* 00000000
V2[7:0] : Digital value of the 3rdPWM D AC
(Pin11).
PULSE WIDTH MODULATOR3 (STV9422)
3FFB V37 V36 V35 V34 V33 V32 V31 V30
* 00000000
V3[7:0] : Digital value of the 4thPWM DAC
(Pin12).
PULSE WIDTH MODULATOR4 (STV9422)
3FFC V47 V46 V45 V44 V43 V42 V41 V40
* 00000000
V4[7:0] : Digital value of the 5thPWM DAC
(Pin13).
PULSE WIDTH MODULATOR5 (STV9422)
3FFD V57 V56 V55 V54 V53 V52 V51 V50
* 00000000
V5[7:0] : Digital value of the 6thPWM DAC
(Pin14).
PULSE WIDTH MODULATOR6 (STV9422)
3FFE V67 V66 V65 V64 V63 V62 V61 V60
* 00000000
V6[7:0] : Digital value of the 7thPWM DAC
(Pin23).
PULSE WIDTH MODULATOR7 (STV9422)
3FFF V77 V76 V75 V74 V73 V72 V71 V70
* 00000000
V7[7:0] : Digital value of the 8thPWM DAC
(Pin24).
Note : * is power on reset value.
II -Descriptors
SPACING
MSB 0 - - - - - - LSB SL7 SL6 SL5 SL4 SL3 SL2 SL1 SL0
SL[7:0] : The number of the scan lines of the
spacingstrip (1 to 255).
CHARACTER
MSB 1 DE - ZY - - C9 C8
LSB C7 C6 C5 C4 C3 C2 C1 0
C[9:0] : The addressof the first character code of
the strip (even).
DE : Display enable :
- DE = 0, R= G = B =0 and FBLK = FBK
(displaycontrol register)on wholestrip,
- DE = 1, displayof the characters.
ZY : Zoom, ZY = 1 all the scan lines are
repeatedonce.
III - Code Format
MSB SET CHARACTER NUMBER
LSB BK3 BK2 BK1 BK0 FL RF GF BF
SET : The setCHARACTER NUMBER
- If SET= 0 : ROM character,
- If SET= 1 :
• If CHARACTER NUMBER is 0 to
25, a user redefinable character
(UDC) located in RAM at th e
address equal to :
38 x CHARACTER NUMBER,
• If CHARACTERNUMBER is 26 to
63, space character,
• If CHARACTERNUMBER>63, end
of line.
FL : Flashing attribute (the flashing mode
is defined in the DISPLAYCONTROL
register).
RF, GF, BF: Foregroundcolor.
BK[3:0] : Background :
- If BK3 = 0, BK[2:0] = background
color R, Gand B,
- If BK3 =1, shadowing :
• BK2 : vertivalshadowing,
• BK1 : horizontalshadowing.
(if BK2 = BK1= 0, the backgroundis
transparent).
8/15
Page 9

FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION (continued)
Figure 5 : Horizontal Timing
H-SYNC
R, G, B
STV9422 - STV9424
Character
Period
LD[5:0]
Fixed
DD[7:0]
Given by number
of characters of the strips
0123n+1n+2n+3n+4 LD-1LD01
= 4 (min) = 4n + 2
IV -Clock and Timing
ThewholetimingisderivedfromtheXTALINandthe
SYNCHRO (horizontal and vertival) input frequencies.TheXTALINinputfrequencycanbe anexternal
clockoracrystalsignalthankstoXTALIN/XTALOUT
pins. The value of this frequency can be chosen
between8 and15MHz,it isavailableon theCKOUT
pinand isusedbythePLLto generatea pixelclock
lockedon the horizontalsynchroinputsignal.
IV.1- Horizontal Timing(see Figure 5)
The number of pixel periods is given by the LINE
DURATION register and is equal to :
[LD[5:0] + 1 ] x 12.
(LD[5:0] : valueof theLINEDURATION register).
Thisvalueallowsto choose thehorizontalsizeofthe
characters.The horizontalleftmarginis givenbythe
HORIZONTALDELAYregisterandisequalto :
[DD[7:0] + 8] x 3x T
PXCK
(DD[7:0] : value of the DISPLAY DELAY register
and T
: pixelperiod).
PXCK
This value allows to choosethe horizontalposition
of the characters on the screen. The value of
DD[7:0] must beequal or greater than4 (theminimumvalueofthe horizontaldelayis 36xT
PXCK
=3
character periods).The length of the active area,
where R,G, B are different from 0, dependsonthe
number of charactersof the strips.
IV.2- D toATiming(STV9422)
The D to A converters of the STV9422 are pulse
width modulaterconverter.
f
The frequencyof the output signalis :
and theduty cycle is :
Vi[7:0]
256
percent.
XTAL
256
After a low pass filter, the average value of the
output is :
Vi [7:0]
256
⋅ V
DD
V - DisplayControl
Ascreenis composedofsuccessivescanlinesgathered in several strips. Each strip is defined by a
descriptorstored in memory.A table of descriptors
allows screen composition and differenttables can
bestored in memory atthe pageaddresses(8 possible≠ addresses).
Two types of strips are available:
- Spacing strip : its descriptor (see II) gives the
numberof black(FBK = 1inDISPLAYCONTROL
register)or transparent(FBK = 0)lines.
- Character strip : its descriptor gives the memory
address of the character codes correspondingto
the 1st displayed character. The characters and
attributes (see code format III) are defined by a
succession of codes stored in the RAM at addresses starting from the 1st one given by the
descriptor. A character strip can be displayed or
not by using the DE bit of its descriptor. A zoom
canbe madeon it by using the ZYbit.
Figure6 : PWM Timing
V1[7:0]
0
1
128
255
PWM1 Signal
t
XTAL
256.t
XTAL
9422-07.AI
9422-08.EPS
9/15
Page 10

STV9422 - STV9424
FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION (continued)
After the falling edge on V-SYNC, the first strip
descriptoris read at the top of the current table of
descriptors at the address given by P[9:0] (see
DISPLAYCONTROLregister).
If it is a spacing strip,SL[7:0] blackor transparent
scan lines are displayed.
If it is a character strip, during CH[5:0] x (I + ZY)
Figure7 :RelationbetweenScreen/AddressPage/CharacterCode in RAM
DISPLAY CONTROL Register
CSD FBK FL[1:0] P8 P7 P8
scan lines (CH[5:0] given by the CHARACTER
HEIGHTregister),thecharactercodesare read at
the addressesstarting fromthe1
descriptoruntil a endof line character or theendof
thescan line.
Thenextdescriptoris thenread andthesame processisrepeateduntilthenextfallingedgeonV-SYNC.
V-SYNC
st
onegivenbythe
2nd CHARACTER
STRIP CODES
OTHER
TABLE OF
DESCRIPTORS
OTHER
(UDC for example)
1st CHARACTER
STRIP CODES
3rd CHARACTER
SRTIP CODES
OTHER
(CODES OR
DESCRIPTORS)
RAM CODE
AND DESCRIPTORS
Figure8 :User Definable Character
ON THE SCREEN
36 Pixels (= 3 Characters)
123
36 Slices (= 2 Characters)
456
SPACING
ROW1
ROW2
SPACING
ROW3
SPACING
TABLE OF THE
DESCRIPTORS
Character Number
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
Character Number
TOP SPACING STRIP
1st CHARACTER STRIP
2nd CHARACTERSTRIP
SPACING STRIP
3rd CHARACTER STRIP
|
BOTTOM SPACING STRIP
SCREEN
IN THE RAM
(example for Character n°5)
Slice 0
Slice 1
Slice 2
Slice 3
Slice 4
Slice 5
Slice 6
Slice 7
Slice 8
Slice 9
Slice 10
Slice 11
Slice 12
Slice 13
Slice 14
Slice 15
Slice 16
Slice 17
Slice 18
: 0x01
: 0x00
: 0x08
: 0x0c
: 0x0e
: 0x0f
: 0x0f
: 0x0f
: 0x0f
: 0x0e
: 0x0c
: 0x00
: 0x00
: 0x00
: 0x00
: 0x00
: 0x00
: 0x00
: 0x00
Odd
Address
Slice 18 of thecharacter n°2
0xff =
only for verticalshadowing
(not displayed).
0xff
0x7f
0x3f
0x1f
0x1f
0x1f
0x1e
0x1e
0x3c
0x3c
0x78
0x78
0xf1
0x00
0x00
0x00
0x00
0x00
Even
Address
9422-09.EPS
9422-10.AI
10/15
Page 11

FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION (continued)
Table 1 : ROM Character Generator
CHARACTER NUMBERC(6:0)
C(6:4)
01234567
C(3:0)
0
1
2
3
4
5
STV9422 - STV9424
6
7
8
9
a
b
c
d
e
f
9422-11.EPS
11/15
Page 12

STV9422 - STV9424
FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION (continued)
VI -User Definable Character
The STV9422/24 allows the user to dynamically
define character(s)for hisownneeds (fora special
LOGO for example). Like the ROM characters, a
UDC is made ofa 12 pixelsx 18slicesdot matrix,
but one more slice is added for the vertical shadowing whenseveralUDCsaregatheredto makea
special greatcharacter (see Figure8).
In a UDC, each pixel is defined with a bit,1 refers
to foreground, and 0 to background color. Each
slice of a UDC uses 2 bytes :
add +1- - - - PX11 PX10 PX9 PX8
add
(even)
PX11istheleft mostpixel. Characterslice address:
SLICEADDRESS=38x(CHARACTERNUMBER)
+ (SLICENUMBER).
Where :
- CHARACTER NUMBER is the numbergiven by
the character code,
- SLICE NUMBER isthe number given bytheslice
interpolator (n° of the current slice of the strip :
1 < <18)
VII - ROM Character Generator
The STV9422/24includes a ROM charactergenerator which is made of 128 alphanumeric or
graphic characters (seeTable 1)
VIII -PLL
The PLL function of the STV9422/24provides the
internalpixelclocklockedon thehorizontalsynchro
signal and usedby the display processorto generate theR,G,B andfast blanckingsignals.Itismade
of 2 PLLs. The first one analogic (see Figure 9),
provides a high frequency signal locked on the
crystal frequency.Thefrequency multiplierisgiven
by :
N=2⋅(FM[3:0]+3)
Where FM[3:0] is the value of the FREQUENCY
MULTIPLIER register.
Figure 9 : Analogic PLL
PX7 PX6 PX5 PX4 PX3 PX2 PX1 PX0
N.F
XTAL
VCO
%N F
FILTRE
XTAL
The second PLL, full digital (see Figure 10), provides a pixel frequency locked on the horizontal
synchrosignal.The ratio between the frequencies
of these 2 signalsis :
M = 12 x (LD[5:0] + 1)
WhereLD[5:0]is the value of theLINEDURATION
register.
Figure 10 : Digital PLL
M.F
H-SYNC
N.F
XTAL
%D
%M F
ALGO
err(n)D(n)
VIII.1 - Programming of the PLLRegisters
FrequencyMultiplier
(@3FF7)
This register gives the ratio between the crystal
frequency and the high frequency of the signal
usedby the2
nd
PLLtoprovide,bydivision,thepixel
clock. The value of this high frequency must be
near to 200MHz (for example if the crystal is a
8MHz, the value of FM must be equal to 10) and
greaterthan 6x (pixel frequency).
Initial Pixel Period
(@3FF6)
This register allows to increase the speed of the
convergence of the PLL when the horizontal frequencychanges(new graphicstandart). The relationshipbetweenFM[3:0],PP[7:0],LD[5:0],F
and F
PP[7:0] = round
LockingCondition Time Constant
XTAL
is:
2 ⋅ (FM[3:0] + 3) ⋅ F
8 ⋅
12 ⋅ (LD[5:0] + 1) ⋅ F
XTAL
HSYNC
(@3FF4)
This register gives the constants AS[2:0] and
BS[2:0]usedbythealgopartofthePLL(seeFigure
10) to calculate, from the phase error, err(n), the
new value, D(n), of the division of the high frequencysignaltoprovidethe pixelclock. These two
constantsare usedonly in locking condition,which
is true,if thephase error is less than a fixedvalue
during at least, 4 scan lines. If the phase error
becomes greater than the fixed value, the PLL is
not in locking condition but in capture process. In
this case, the algo part of the PLL used the other
constants, AF[2:0] and BF[2:0], givenby the next
register.
CaptureProcess TimeConstant
(@3FF5)
The choice between these two time constants
(locking condition or capture process) allows to
decreasethecaptureprocesstimebychanging the
time response of the PLL.
9422-12.AI
H-SYNC
HSYNC
± 24
9422-13.AI
12/15
Page 13

FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION (continued)
VIII.2 -How to choose the value of the time
constant ?
The timeresponse of the PLL is given by itscharacteristicequationwhich is :
2
(x ± 1)
+(α+β)⋅(x±1)+β=0.
Where :
α=3⋅LD[5:0] ⋅ 2
A ± 11
and β=3⋅LD[5:0]⋅ 2
B ± 19
(LD[5:0] = value of the LINE DURATION register,
A = value of the 1st time constant, AF or AS and
B =value of the 2
d
timeconstant,BF or BS).
As you can see, the solution depend only on the
LINE DURATION and the TIME CONSTANTS
given by the I
If (α + β)
2
C registers.
2
± 4β ≥ 0 and 2α±β<4, the PLL is sta-
ble and its response is like this presented on
Figure11.
Figure 11 : Time Responseof the PLL/Charac-
teristic Equation Solutions (with
Real Solutions)
PLL
Frequency
f
1
f
0
t
Input
Frequency
f
1
If (α + β)
f
0
2
± 4β ≤ 0, the responseof the PLL is like
t
this presented on Figure12.
STV9422 - STV9424
In this case the PLL is stable if τ > 0.7 damping
coefficient).
Figure 12 : Time Responseof the PLL/Charac-
teristic Equation Solutions (with
ComplexSolutions)
PLL
.
9422-14.AI
Frequency
f
1
f
0
Input
Frequency
f
1
f
0
The Table 2 gives some good values for A and B
constants for different values of the LINE DURATION.
Summary
For a good working of the PLL:
- A and B time constants must be chosen among
values for which thePLL is stable,
- B mustbe equalorgreater than A and the difference between them must be less than 3,
- The greater(A,B) are, the faster the captureis.
Anoptimalchoiceforthemostofapplicationsmight
be :
- For locking condition: AS =0 and BS = 1,
- For capture process: AS =2 and BS = 4.
But for eachapplicationthetimeconstants can be
calculated by solving the characteristic equation
and choosing the best response.
t
t
9422-15.AI
Table 2 : ValidTime ConstantsExamples
B\A0123456
0YYYY YYYY YYYY YYYN YNNN NNNN NNNN
1 YYYY YYYY YYYY YYYN YNNN NNNN NNNN
2 NYYY YYYY YYYY YYYN YNNN NNNN NNNN
3 NNNY YYYY YYYY YYYN YNNN NNNN NNNN
4 NNNN NYYY
5 NNNN NNNY YYYY YYYN YNNN NNNN NNNN
6 NNNN NNNN NYYY YYYN YNNN NNNN NNNN
7 NNNN NNNN NNNY YYYN YNNN NNNN NNNN
Note : 1. Case of A[2:0] = 1 (001) and B[2:0]= 4(100) :
LD 16 32 48 63
Valid TimeConstants NYYY
(1)
YYYY YYYN YNNN NNNN NNNN
Value ofLINE DURATION Register (@ 3FF0) :
LD = 16 : LD[5:0] = 010000
LD = 32 : LD[5:0] = 100000
LD = 48 : LD[5:0] = 110000
LD = 63 : LD[5:0] = 111111
Tablemeaning :
N = No possible capture
Y = PLLcan lock
13/15
9422-05.TBL
Page 14

STV9422 - STV9424
PACKAGE MECHANICAL DATA (STV9424)
16 PINS - PLASTICDIP
PM-DIP16.WMF
Dimensions
Min. Typ. Max. Min. Typ. Max.
Millimeters Inches
a1 0.51 0.020
B 0.77 1.65 0.030 0.065
b 0.5 0.020
b1 0.25 0.010
D 20 0.787
E 8.5 0.335
e 2.54 0.100
e3 17.78 0.700
F 7.1 0.280
I 5.1 0.201
L 3.3 0.130
Z 1.27 0.050
DIP16.TBL
14/15
Page 15

PACKAGE MECHANICAL DATA (STV9422)
24 PINS - PLASTICSHRINKDIP
STV9422 - STV9424
PMSDIP24.WMF
Dimensions
Min. Typ. Max. Min. Typ. Max.
Millimeters Inches
a1 0.51 0.020
b 0.36 0.46 0.56 0.0142 0.0181 0.0220
b1 0.23 0.25 0.38 0.0090 0.0098 0.0150
b2 0.76 1.02 1.4 0.030 0.040 0.045
b3 0.76 1.02 1.4 0.030 0.040 0.045
D 22.61 22.86 23.11 0.890 0.90 0.910
E 7.62 8.64 0.30 0.340
e 1.778 0.070
e3 19.558 0.770
e4 7.62 0.300
F 6.10 6.40 6.86 0.240 0.252 0270
I 5.08 0.200
L 2.54 3.30 3.81 0.10 0.130 0.150
Informationfurnished is believed to be accurate and reliable.However, SGS-THOMSON Microelectronics assumes noresponsibility
for the consequences ofuse of such information norfor any infringement of patents or otherrights of third partieswhich may result
from its use.No licence isgranted byimplication or otherwiseunder anypatent or patent rightsof SGS-THOMSON Microelectronics.
Specifications mentioned in this publication are subject to change without notice. This publication supersedes and replaces all
informationpreviously supplied. SGS-THOMSONMicroelectronics products arenot authorized for use as critical components in life
support devices or systems without express written approvalof SGS-THOMSON Microelectronics.
1995 SGS-THOMSON Microelectronics - All Rights Reserved
Purchase of I
2
I
C Patent. Rights to use these components in a I2C system, is granted provided that the system conforms to
Australia - Brazil - China - France - Germany - Hong Kong -Italy -Japan -Korea - Malaysia - Malta - Morocco
The Netherlands - Singapore - Spain- Sweden - Switzerland- Taiwan - Thailand-United Kingdom - U.S.A.
2
C Components of SGS-THOMSON Microelectronics, conveys a license under the Philips
2
the I
C Standard Specifications as defined by Philips.
SGS-THOMSON Microelectronics GROUP OF COMPANIES
SDIP24.TBL
15/15
 Loading...
Loading...