Page 1

SA7026
1.3GHz low voltage fractional-N dual
frequency synthesizer
Objective specification
Supersedes data of 1998 Apr 06
1998 Oct 13
INTEGRATED CIRCUITS
Page 2

Philips Semiconductors Objective specification
SA70261.3GHz low voltage fractional-N dual synthesizer
2
1998 Oct 13
FEATURES
•Low phase noise
•Low power
•Fully programmable main and auxiliary dividers
•NORMAL & INTEGRAL charge pumps outputs
•Fast Locking Adaptive mode design
•Internal fractional spurious compensation
•Hardware and software power down
APPLICATIONS
•500–1300 MHz wireless equipment
•Cellular phones
•Portable battery-powered radio equipment.
General description
The SA7026 BICMOS device integrates programmable dividers,
charge pumps and a phase comparator to implement a
phase-locked loop. The device is designed to operate from 3 NiCd
cells, in pocket phones, with low current and nominal 3 V supplies.
The synthesizer operates at VCO input frequencies up to 1.3 GHz.
The synthesizer has fully programmable main, auxiliary and
reference dividers. All divider ratios are supplied via a 3-wire serial
programming bus.
Separate power and ground pins are provided to the analog and
digital circuits. The ground leads should be externally short-circuited
to prevent large currents flowing across the die and thus causing
damage. V
DDCP
could be greater than or equal to V
DD
.
The charge pump current (gain) is fixed by an external resistance at
pin R
SET (pin ). Only passive loop filters are used; the charge-pump
operates within a wide voltage compliance range to provide a wider
tuning range.
SR01649
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
LOCK
TEST
V
DD
GND
RFin+
RFin–
GND
CP
PHP
PHI
GND
CP
PON
STROBE
DATA
CLOCK
REF
in
+
REF
in
–
RSET
AUXin
V
DDCP
PHA
10
Figure 1. Pin Configuration
QUICK REFERENCE DA TA
SYMBOL PARAMETER CONDITIONS MIN. TYP. MAX. UNIT
V
DD
Supply voltage V
DD
2.7 – 5.5 V
V
DDCP
Analog supply voltage V
DDCP
≥ V
DD
2.7 – 5.5 V
I
DDCP+IDD
Supply current Main and Aux. on – 7.5 8.8 mA
I
DDCP+IDD
Total supply current in power-down mode – 1 – µA
f
VCO
Input frequency 500 – 1300 MHz
f
AUX
Input frequency 10 – 550 MHz
f
REF
Crystal reference input frequency 10 – 40 MHz
f
PC
Maximum phase comparator frequency – 4 MHz
T
amb
Operating ambient temperature –40 – +85 °C
ORDERING INFORMATION
PACKAGE
TYPE NUMBER
NAME DESCRIPTION VERSION
SA7026DK TSSOP20 Plastic thin shrink small outline package; 20 leads; body width 4.4 mm SOT360–1
Page 3

Philips Semiconductors Objective specification
SA70261.3GHz low voltage fractional-N dual synthesizer
1998 Oct 13
3
SR01496
CLOCK
DATA
STROBE
RFin+
RFin–
REF
in+
REF
in–
AUXin
TEST
LOAD SIGNALS
ADDRESS DECODER
2–BIT SHIFT
REGISTER
22–BIT SHIFT
REGISTER
CONTROL
LATCH
LATCH
MAIN DIVIDER
SM
REFERENCE
DIVIDER
2222
LATCH
AMP
AMP
15
16
6
5
19
18
17
12
2
LATCH
AUX DIVIDER
PHASE
DETECTOR
PHASE
DETECTOR
COMP
PUMP
BIAS
PUMP
CURRENT
SETTING
13
V
DDCP
GND
4
SA
103
GND
CP
V
DD
RSET
GND
CP
PHP
PHI
LOCK
PHA
PUMP
BIAS
14
7
8
9
1
11
PON
20
Figure 2. Block Diagram
PINNING
SYMBOL PIN DESCRIPTION
LOCK 1 Lock detect output
TEST 2 Test
V
DD
3 Digital supply
GND 4 Digital ground
RFin+ 5 RF positive input to main divider
RFin– 6 RF negative input to main divider
GND
CP
7 Charge pump ground
PHP 8 Main NORMAL chargepump
PHI 9 Main INTEGRAL chargepump
GND
CP
10 Charge Pump Ground
SYMBOL PIN DESCRIPTION
PHA 11 Auxiliary chargepump output
AUXin 12 Input to auxiliary divider
V
DDCP
13 Charge pump supply voltage
RSET 14 External resistor from this pin to ground
sets the chargepump current
REF
in–
15 Reference input
REF
in+
16 Reference input
CLOCK 17 Programming bus clock input
DATA 18 Programming bus data input
STROBE 19 Programming bus enable input
PON 20 Power down control
Page 4
Philips Semiconductors Objective specification
SA70261.3GHz low voltage fractional-N dual synthesizer
1998 Oct 13
4
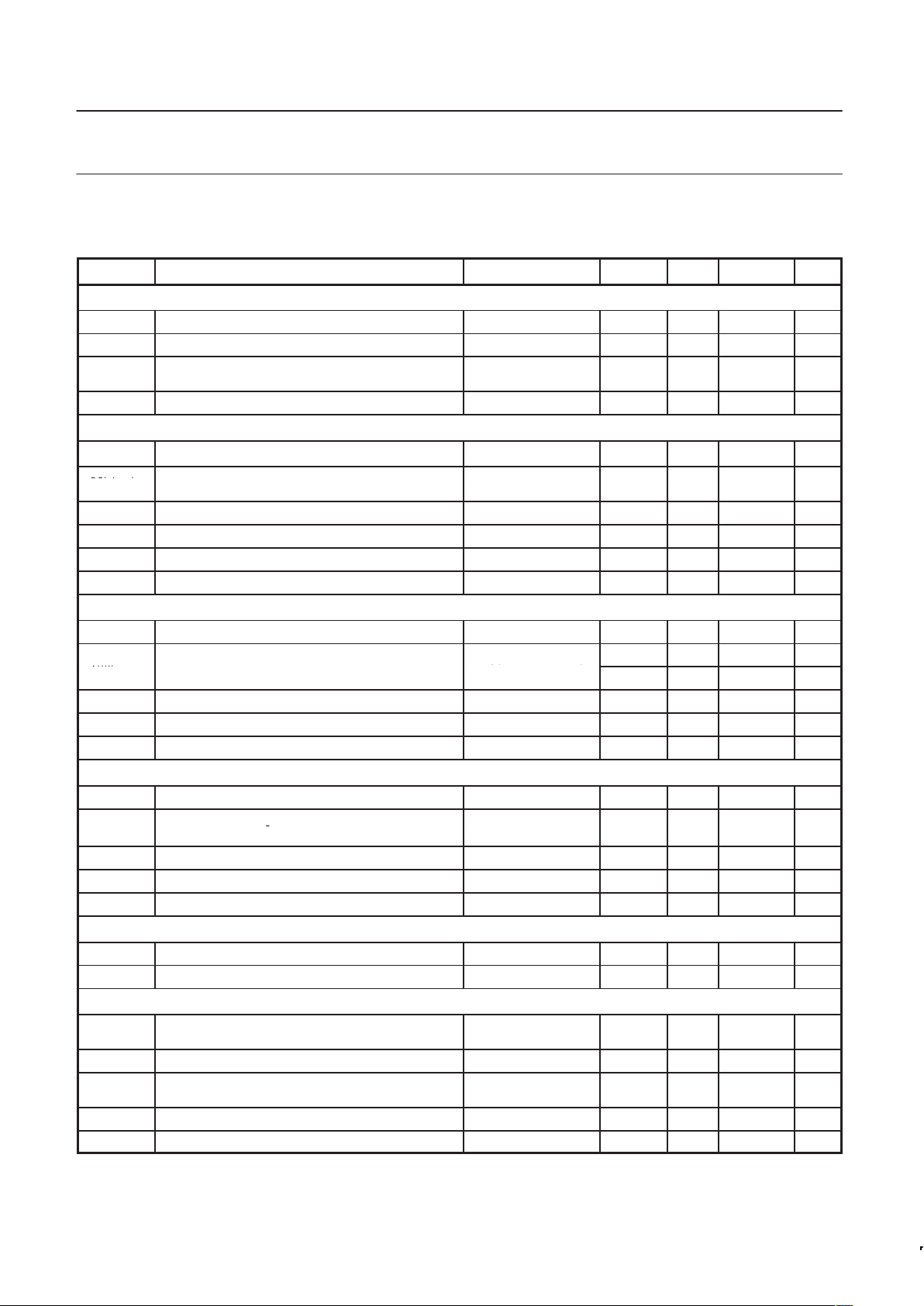
Characteristics
V
DDCP
= V
DD
= +3.0V, T
amb
= +25°C; unless otherwise specified.
SYMBOL
PARAMETER CONDITIONS MIN. TYP. MAX. UNIT
Supply; pins 3, 13
V
DD
Digital supply voltage 2.7 – 5.5 V
V
DDCP
Analog supply voltage V
DDCP
= V
DD
2.7 – 5.5 V
I
DDTotal
Synthesizer operational digital supply current V
DD
= +3.0 V
(with main and aux on)
– 7.5 8.8 mA
I
standby
Total supply current in power-down mode logic levels 0 or VDD – 1 TBD µA
RFin main divider input; pins 5, 6
p
–
f
VCO
VCO in ut frequency
500–1300
MHz
p
p
;
V
RFin(rms)
AC-coupled input signal level
R
s
= 50 Ω;
MAX. limit is
–
18–0
dBm
indicative
Z
IRFin
Input impedance (real part) f
VCO
= 2.0 GHz – TBD – kΩ
C
IRFin
Typical pin input capacitance indicative, not tested – TBD – pF
N
m
Main divider ratio 512 – 65535
f
PCmax
Maximum loop comparison frequency indicative, not tested – – 4 MHz
AUX reference divider input; pins 12
f
AUXin
Input frequency range 10 – 550 MHz
p
p
R
=50Ω; MAX. limit is
–18 – 0 dBm
V
AUXin
AC-coupled input signal level
Rs50Ω MAX. limit is
indicative
80 – 636 mVpp
Z
AUXin
Input impedance (real part) f
VCO
=500 MHz – TBD – kΩ
C
AUXin
Typical pin input capacitance indicative, not tested – TBD – pF
N
AUX
Auxiliary division ratio 128 – 16384
Reference divider input; pins 15, 16
f
REFin
Input frequency range from crystal 10 – 40 MHz
VRFin AC-coupled input signal level RS=50Ω; MAX. limit is 360 – 1300 mVpp
g
S
indicative
Z
REFin
Input impedance (real part) – TBD – kΩ
C
REFin
Typical pin input capacitance indicative, not tested – TBD – pF
R
REF
Reference division ratio SA=SM=”000” 4 – 1023
Charge pump current setting resistor input; pin 14
R
SET
External resistor from pin 3 to ground 6 7.5 24 kΩ
V
SET
Regulated voltage at pin 3 R
SET
=7.5 kΩ – 1.25 – V
Charge pump outputs (including fractional compensation pump); pins 8, 9, 11; R
SET
=7.5 kΩ, FC=80
Icp Chargepump current ratio to Iset CURRENT GAIN
I
PH/ISET
–15 +15 %
I
MATCH
Sink-to-source current matching Vph=1/2 V
DDCP
–10 +10 %
I
ZOUT
Output current variation versus V
ph
2
V
ph
in compliance
range
–10 +10 %
I
LPH
Charge pump off leakage current Vcp=1/2 V
CC
–10 +10 nA
V
ph
Charge pump voltage compliance 0.7 – V
DDCP
–0.8 V
Page 5

Philips Semiconductors Objective specification
SA70261.3GHz low voltage fractional-N dual synthesizer
1998 Oct 13
5
SYMBOL UNITMAX.TYP.MIN.CONDITIONSPARAMETER
Phase noise
C/N Synthesizer’s contribution to close-in-phase noise of
1300 MHz RF signal at 1 kHz offset.
fref=19.44MHz;
fcomp=240kHz
indicative, not tested
– –77 – dBc
Hz
Interface logic input signal levels; pins 3, 15, 16, 18, 19, 20
V
IH
HIGH level input voltage 0.7*V
DD
– VDD+0.3 V
V
IL
LOW level input voltage –0.3 – 0.3*V
DD
V
I
bias
Input bias current logic 1 or logic 0 –5 – +5 µA
Lock detect output signal (in push/pull mode); pin 1
V
OL
LOW level output voltage I
sink
= 2mA – – 0.4 V
V
OH
HIGH level output voltage I
source
= –2mA VDD–0.4 – – V
NOTES:
1. I
SET =
V
SET
R
SET
bias current for charge pumps.
2. The relative output current variation is defined thus:
I
OUT
I
OUT
2
.
(I2–I1)
I(I
2
I1)I
; with V1 0.7V, V2 V
DDCP
–0.8V (See Figure 3.)
I
2
I
1
I
2
I
1
V
1
V
2
CURRENT
VOLTAGE
SR00602
Figure 3. Relative Output Current Variation
Page 6

Philips Semiconductors Objective specification
SA70261.3GHz low voltage fractional-N dual synthesizer
1998 Oct 13
6
LIMITING VALUES
In accordance with the Absolute Maximum Rating System (IEC 134).
SYMBOL PARAMETER MIN. MAX. UNIT
V
DD
Digital supply voltage –0.3 +5.5 V
V
DDCP
Analog supply voltage –0.3 +5.5 V
∆V
DDCP–VDD
Difference in voltage between V
DDCP
and VDD (V
DDCP
≥ VDD) –0.3 +2.8 V
V
n
Voltage at pins 1, 2, 5, 6, 12, 15 to 20 –0.3 V
DD
+ 0.3 V
V
1
Voltage at pin 8, 9, 13 –0.3 V
DDCP
+ 0.3 V
∆V
GND
Difference in voltage between GNDCP and GND (these pins should
be connected together)
–0.3 +0.3 V
P
tot
Total power dissipation TBD mW
T
stg
Storage temperature –55 +125
C
T
amb
Operating ambient temperature –30 +85
C
T
j
Maximum junction temperature TBD
C
Handling
Inputs and outputs are protected against electrostatic discharge in
normal handling. However , to be totally safe, it is desirable to take
normal precautions appropriate to handling MOS devices.
THERMAL CHARACTERISTICS
SYMBOL PARAMETER VALUE UNIT
R
th j–a
Thermal resistance from junction to ambient in free air 120 K/W
Page 7

Philips Semiconductors Objective specification
SA70261.3GHz low voltage fractional-N dual synthesizer
1998 Oct 13
7
FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION
Main Fractional-N divider
The RFin input (pins 5 and 6) drive a pre-amplifier to provide the
clock to the first divider stage. For single ended operation, the signal
should be fed to one of the inputs while the other one is AC
grounded. The pre-amplifier has a high input impedance, dominated
by pin and pad capacitance. The circuit operates with signal levels
from –18dBm to +0dBm, and at frequencies as high as 2.5 GHz.
The divider consists of a fully programmable bipolar prescaler
followed by a CMOS counter. Divide ratios (512 to 65536) allow a
minimum phase comparison frequency of 25kHz at 2.5 GHz RF.
At the completion of a main divider cycle, a main divider output
pulse is generated which will drive the main phase comparator. Also,
the fractional accumulator is incremented by the value of NF. The
accumulator works with modulo Q set by FMOD. When the
accumulator overflows the overall division ratio N will be increased
by 1 to N + 1, the average division ratio over Q main divider cycles
(either 5 or 8) will be
Nfrac N
NF
Q
The output of the main divider will be modulated with a fractional
phase ripple. The phase ripple is proportional to the contents of the
fractional accumulator and is nulled by the fractional compensation
charge pump.
The reloading of a new programming word is synchronized to the
state of the main divider to avoid introducing a phase disturbance.
Auxiliary divider
The auxiliary divider consists of a divider with fully programmable
values between 128 and 16384. The AUXin input, pin 13, drives a
pre-amplifier to provide the clock to the first divider stage. The
AUXin negative input is internally connected to ground. The
pre-amplifier has a high input impedance, dominated by pin and pad
capacitance. The circuit operates with signal levels from –18dBm to
+0dBm (80 to 636 mVpp), and at frequencies as high as 550 MHz.
The divider consists of a fully programmable bipolar prescaler
followed by a CMOS counter. The divide ratios allow a minimum
phase comparison frequency of 25kHz at 550 MHz RF.
Reference divider
The reference divider consists of a divider with programmable
values between 4 and 1023 followed by a three bit binary counter.
The 3 bit SM (SA) register (see figure 4) determines which fo the 5
output pulses are selected as the main (auxiliary) phase detector
input.
Phase detector
The reference and main (aux) divider outputs are connected to a
phase/frequency detector that controls the charge pump. The pump
current is set by a an external resistor. The dead zone (caused by
finite time taken to switch the current sources on or off) is cancelled
by forcing the pumps ON for a minimum time at every cycle
(backlash time) providing improved linearity.
SR01415
DIVIDE BY R /2/2 /2 /2 /2
REFERENCE
INPUT
SM=”000”
SM=”001”
SM=”010”
SM=”011”
SM=”100”
SA=”100”
SA=”011”
SA=”010”
SA=”001”
SA=”000”
MAIN
PHASE
DETECTOR
AUXILIARY
PHASE
DETECTOR
Figure 4. Reference Divider
Page 8

Philips Semiconductors Objective specification
SA70261.3GHz low voltage fractional-N dual synthesizer
1998 Oct 13
8
SR01451
R
X
P
N
REF DIVIDER
AUX/MAIN
DIVIDER
D
Q
CLK
“1”
R
D
R
CLK
“1”
X
Q
N
P
τ
V
DDA
GND
PH
V
SSA
P–TYPE
CHARGE PUMP
N–TYPE
CHARGE PUMP
R
INR
INR
I
PH
Figure 5. Phase Detector Struction with Timing
Page 9

Philips Semiconductors Objective specification
SA70261.3GHz low voltage fractional-N dual synthesizer
1998 Oct 13
9
Main Output Charge Pumps and Fractional
Compensation Currents.
The main charge pumps on pins PHP and PHI are driven by the
main phase detector and the charge pump current values are
determined by the current at pin RSET. The fractional compensation
is derived from the current at RSET, the contents of the fractional
accumulator FRD and by the program value of the FDAC. The
timing for the fractional compensation is derived from the main
divider. See table of charge pump ratios.
Principle of Fractional Compensation
The fractional compensation is designed into the circuit as a means
of reducing or eliminating fractional spurs that predominate when the
accumulator rolls over and the main divider counts one extra RF
input cycle (+1, swallows a cycle). Since I
COMP
is the compensation
current and I
PUMP
is the pump current, for each charge pump,
I
PUMP_TOTAL
= I
PUMP
+ I
COMP
.
The theoretical values for FDAC are: 128 for FMOD = 1 (modulo 5)
and 80 for FMOD = 0 (modulo 8). Fractional division will cause the
pump to output a charge that is compensated for in order to reduce
fractional spurs. This compensation is done by sourcing a small
current, i
A
, see Figure 7, that is proportional to the fractional error
phase. Figure 6 shows that for proper fractional compensation, the
area of the fractional compensation current pulse must be equal to
the area of the charge pump ripple.
This means I
PUMP
*Q=I
COMP
*128, where Q equals fractional-N
modulus e.g., 2/5 for NF = 2 and FMOD = 1. The fractional
compensation current is derived from the main charge pump in that
it follows all the current scaling through external resistor setting, RN,
programming or speed-up operation. For a given pump,
I
COMP
= ( I
PUMP
/ 128 ) * ( FDAC / 5*128) * FRD
FRD is the fractional accumulator value.
SR01416
REFERENCE R
MAIN M
DIVIDE RATIO
DETECTOR
OUTPUT
ACCUMULATOR
FRACTIONAL
COMPENSATION
CURRENT
OUTPUT ON
PUMP
N N N+1 N N+1
241
3
0
PULSE
WIDTH
MODULATION
PULSE LEVEL
MODULATION
mA
µA
Figure 6. Waveforms for NF = 2, Fraction = 0.4
Fig 6. shows that for a proper fractional compensation, the area of the fractional
compensation current pulse must be equal to the area of the charge pump ripple output.
SR01682
f
RF
1930.140 MHz
MAIN DIVIDER
N = 8042
FRACTIONAL
ACCUMULATOR
f
REF
240 kHz
240.016 kHz i
A
i
C
LOOP FILTER
& VCO
Figure 7. Current Injection Concept
Page 10

Philips Semiconductors Objective specification
SA70261.3GHz low voltage fractional-N dual synthesizer
1998 Oct 13
10
Auxiliary Output Charge Pumps
The auxiliary charge pumps on pin PHA are driven by the auxiliary phase detector and the current value is determined by the external resistor
attached to pin R
set
.
Main and auxiliary chargepump currents
CP1
CP0 I
PHA
I
PHP
I
PHP–SU
I
PHI
0 0 1.5xlset 3xIset 15xlset 36xlset
0 1 0.5xlset 1xlset 5xlset 12xlset
1 0 1.5xlset 3xlset 15xlset 0
1 1 0.5xlset 1xlset 5xlset 0
NOTES
1. I
SET
=
Vset
/
Rset
: bias current for charge pumps.
2. CP1 is used to disable the PHI pump, I
PHP_SU
is the total current at pin PHP during speed up condition.
Lock Detect
The output LOCK maintains a logic ‘1’ when the auxiliary phase
detector ANDed with the main phase detector indicates a lock
condition. The lock condition for the main and auxiliary synthesizers
is defined as a phase difference of less than 1 period of the
frequency at the input REF
in+, –
. One counter can fulfill the lock
condition when the other counter is powered down. Out of lock (logic
’0’) is indicated when both counters are powered down.
Power-down mode
The power-down signal can be either hardware (PON) or software
(PD). The PON signal is exclusively ORed with the PD bits. If
PON = 0, then the part is powered up when PD = 1. PON can be
used to invert the polarity of the software bit PD. When the
synthesizer is reactivated after the power-down the main and
reference dividers are synchronized to avoid possibility of random
phase errors on power-up.
Page 11

Philips Semiconductors Objective specification
SA70261.3GHz low voltage fractional-N dual synthesizer
1998 Oct 13
11
Serial programming bus
The serial input is a 3-wire input (CLOCK, STROBE, DATA) to
program all counter divide ratios, fractional compensation DAC,
selection and enable bits. The programming data is structured into
24 bit words; each word includes 2 address bits. Figure 8 shows the
timing diagram of the serial input. When the STROBE goes active
HIGH, the clock is disabled and the data in the shift register remains
unchanged. Depending on the 2 address bits the data is latched into
different working registers or temporary registers. In order to fully
program the synthesizer, 3 words must be sent: C, B, and A. Table 1
shows the format and the contents of each word. The D word is for
testing purposes only. The data for the fractional compensation
DAC, FC is stored by the B word in temporary registers. When the A
word is loaded, the data of these temporary registers is loaded
together with the main divider ratio.
Serial bus timing characteristics. See Figure 8.
V
DD
= V
DDCP
=+3.0V; T
amb
= +25°C unless otherwise specified.
SYMBOL
PARAMETER MIN. TYP. MAX. UNIT
Serial programming clock; CLK
t
r
Input rise time – 10 40 ns
t
f
Input fall time – 10 40 ns
T
cy
Clock period 100 – – ns
Enable programming; STROBE
t
START
Delay to rising clock edge 40 – – ns
t
W
Minimum inactive pulse width 1/fcomp – – ns
T
SU;E
Enable set-up time to next clock edge 20 – – ns
Register serial input data; DATA
t
SU;DAT
Input data to clock set-up time 20 – – ns
t
HD;DAT
Input data to clock hold time 20 – – ns
Application information
SR01417
CLK
DATA
STROBE
MSB LSB ADDRESS
t
SU;DAT
t
HD;DAT
t
r
t
w
t
f
t
SU;E
t
START
T
cy
Figure 8. Serial Bus Timing Diagram
Page 12

Philips Semiconductors Objective specification
SA70261.3GHz low voltage fractional-N dual synthesizer
1998 Oct 13
12
Data format
Table 1. Format of programmed data
LAST IN MSB SERIAL PROGRAMMING FORMAT FIRST IN LSB
p23 p22 p21 p20 ../.. ../.. p1 p0
Table 2. A word, length 24 bits
LAST IN MSB LSB FIRST IN
Address fmod Fractional-N Main Divider ratio Spare
0 0 FM NF2 NF1 NF0 N15 N14 N13 N12 N11 N10 N9 N8 N7 N6 N5 N4 N3 N2 N1 N0 SK1 SK2
Default:
0 0 1 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 0
A word select Fixed to 00.
Fractional Modulus select FM 0 = modulo 8, 1 = modulo 5.
Fractional-N Increment NF2..0 Fractional N Increment values 000 to 111.
N-Divider N0..N15, Main divider values 512 to 65535 allowed for divider ratio.
Table 3. B word, length 24 bits
ADDRESS
REFERENCE DIVIDER LOCK PD FRACTIONAL COMPENSATION DAC
0 1 R9 R8 R7 R6 R5 R4 R3 R2 R1 R0 L1 L0 Main Aux FC7 FC6 FC5 FC4 FC3 FC2 FC1 FC0
Default:
0 0 0 1 0 1 0 0 0 1 0 0 1 1 0 1 0 1 0 0 0 0
B word select Fixed to 01
R-Divider R0..R9, Reference divider values 4 to 1023 allowed for divider ration.
Lock detect output L1 L0
0 0 Combined main, aux. lock detect signal present at the LOCK pin (push/pull).
0 1 Combined main, aux, lock detect signal present at the LOCK pin (open drain).
1 0 Main lock detect signal present at the LOCK pin.
1 1 Auxiliary loop lock detect signal present at the LOCK pin.
When auxiliary loop and main loop are in power down mode, the lock indicator is low.
Power down Main = 1: power to N-divider, reference divider, main charge pumps, Main = 0 to power down.
Aux = 1: power to Aux divider, reference divider, aux charge pump, Aux = 0 to power down.
Fractional Compensation FC7..0 Fractional Compensation charge pump current DAC, values 0 to 255. Recommended values: FC = 80 for
MOD 8; FC = 128 for MOD 5.
Table 4. C word, length 24 bits
Address Auxiliary Divider CP SM SA
1 0 A13 A12 A11 A10 A9 A8 A7 A6 A5 A4 A3 A2 A1 A0 CP1 CP0 SM2 SM1 SM0 SA2 SA1 SA0
Default
0 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 0 0 1 0 1 0 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 0
C word select Fixed to 10
A-Divider A0..A13, Auxiliary divider values 128 to 16384 allowed for divider ratio.
Charge pump current Ratio CP1, CP0: Charge pump current ratio, see table of charge pump currents.
Main comparison select SM comparison divider select for main phase detector.
Aux comparison select SA Comparison divider select for auxiliary phase detector.
Table 5. D word, length 24 bits
ADDRESS SYNTHESIZER TEST
BITS
SYNTHESIZER TEST BITS
1 1 0 – – – – –
Tspu
– – – – – – – – – – – – – – –
DEFAULT 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
Tspu: Speed up Forces the synthesizer charge pump in speed-up mode all the time.
NOTE: All test bits must be set to 0 for normal operation.
Page 13

1.3GHz low voltage dual fractional-N frequency
synthesizer
Philips Semiconductors Objective specification
SA7026
1998 Oct 13
13
TSSOP20: plastic thin shrink small outline package; 20 leads; body width 4.4 mm SOT360-1
Page 14

1.3GHz low voltage dual fractional-N frequency
synthesizer
Philips Semiconductors Objective specification
SA7026
1998 Oct 13
14
Definitions
Short-form specification — The data in a short-form specification is extracted from a full data sheet with the same type number and title. For
detailed information see the relevant data sheet or data handbook.
Limiting values definition — Limiting values given are in accordance with the Absolute Maximum Rating System (IEC 134). Stress above one
or more of the limiting values may cause permanent damage to the device. These are stress ratings only and operation of the device at these or
at any other conditions above those given in the Characteristics sections of the specification is not implied. Exposure to limiting values for extended
periods may affect device reliability.
Application information — Applications that are described herein for any of these products are for illustrative purposes only. Philips
Semiconductors make no representation or warranty that such applications will be suitable for the specified use without further testing or
modification.
Disclaimers
Life support — These products are not designed for use in life support appliances, devices or systems where malfunction of these products can
reasonably be expected to result in personal injury . Philips Semiconductors customers using or selling these products for use in such applications
do so at their own risk and agree to fully indemnify Philips Semiconductors for any damages resulting from such application.
Right to make changes — Philips Semiconductors reserves the right to make changes, without notice, in the products, including circuits, standard
cells, and/or software, described or contained herein in order to improve design and/or performance. Philips Semiconductors assumes no
responsibility or liability for the use of any of these products, conveys no license or title under any patent, copyright, or mask work right to these
products, and makes no representations or warranties that these products are free from patent, copyright, or mask work right infringement, unless
otherwise specified.
Philips Semiconductors
811 East Arques Avenue
P.O. Box 3409
Sunnyvale, California 94088–3409
Telephone 800-234-7381
Copyright Philips Electronics North America Corporation 1998
All rights reserved. Printed in U.S.A.
Data sheet
status
Objective
specification
Preliminary
specification
Product
specification
Product
status
Development
Qualification
Production
Definition
[1]
This data sheet contains the design target or goal specifications for product development.
Specification may change in any manner without notice.
This data sheet contains preliminary data, and supplementary data will be published at a later date.
Philips Semiconductors reserves the right to make chages at any time without notice in order to
improve design and supply the best possible product.
This data sheet contains final specifications. Philips Semiconductors reserves the right to make
changes at any time without notice in order to improve design and supply the best possible product.
Data sheet status
[1] Please consult the most recently issued datasheet before initiating or completing a design.
 Loading...
Loading...