Page 1

INTEGRATED CIRCUITS
SA7025
Low-voltage 1GHz fractional-N
synthesizer
Product specification 1996 Aug 6
IC17 Data Handbook
Page 2
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
SA70251GHz low-voltage Fractional-N synthesizer
DESCRIPTION
The SA7025 is a monolithic low power, high performance dual
frequency synthesizer fabricated in QUBiC BiCMOS technology.
Featuring Fractional-N division with selectable modulo 5 or 8
implemented in the Main synthesizer to allow the phase detector
comparison frequency to be five or eight times the channel spacing.
This feature reduces the overall division ratio yielding a lower noise
floor and faster channel switching. The phase detectors and charge
pumps are designed to achieve phase detector comparison
frequencies up to 5MHz. A triple modulus prescaler (divide by
64/65/72) is integrated on chip with a maximum input frequency of
1.04GHz. Programming and channel selection are realized by a
high speed 3-wire serial interface.
FEA TURES
•Operation up to 1.04GHz
•Fast locking by “Fractional-N” divider
•Auxiliary synthesizer
•Digital phase comparator with proportional and integral charge
pump output
•High speed serial input
•Low power consumption
•Programmable charge pump currents
•Supply voltage range 2.7 to 5.5V
•Excellent input sensitivity: V
RF_IN
= –20dBm
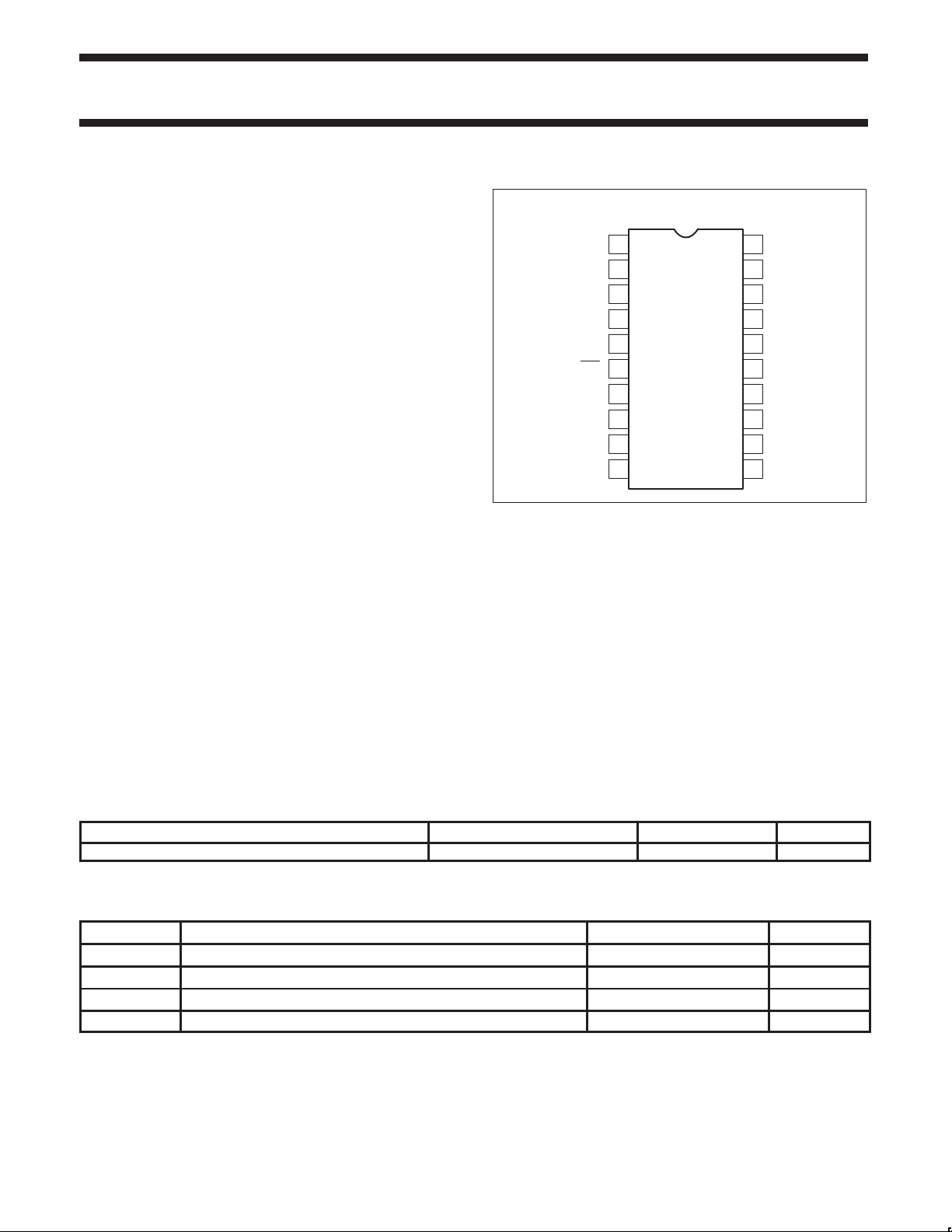
PIN CONFIGURATION
CLOCK
STROBE
1
DATA
2
3
V
4
SS
RF
5
IN
RF
6
IN
7
V
CCP
8
REF
IN
9
RA
AUX
10
IN
Figure 1. Pin Configuration
DK Package
V
20
DD
TEST
19
LOCK
18
17
RF
16
RN
15
V
DDA
PHP
14
PHI
13
12
V
SSA
PHA
11
SR00600
APPLICATIONS
•NADC (North American Digital Cellular)
•PDC (Personal Digital Cellular)
•Cellular radio
•Spread-spectrum receivers
ORDERING INFORMATION
DESCRIPTION TEMPERATURE RANGE ORDER CODE DWG #
20-Pin Plastic Shrink Small Outline Package (SSOP) –40 to +85°C SA7025DK SOT266-1
ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS
SYMBOL PARAMETER RATING UNITS
V Supply voltage, VDD, V
T
V
STG
T
IN
A
Voltage applied to any other pin -0.3 to (VDD + 0.3) V
Storage temperature range -65 to +150 °C
Operating ambient temperature range -40 to +85 °C
NOTE: Thermal impedance (θJA) = 117°C/W. This device is ESD sensitive.
DDA
, V
CCP
-0.3 to +6.0 V
1996 Aug 6 853-1786 17157
2
Page 3
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
SA70251GHz low-voltage Fractional-N synthesizer
PIN DESCRIPTIONS
Symbol Pin Description
CLOCK 1 Serial clock input
DATA 2 Serial data input
STROBE 3 Serial strobe input
V
SS
RF
IN
RF
IN
V
CCP
REF
RA 9 Auxiliary current setting; resistor to V
AUX
PHA 11 Auxiliary phase detector output
V
SSA
PHI 13 Integral phase detector output
PHP 14 Proportional phase detector output
V
DDA
RN 16 Main current setting; resistor to V
RF 17 Fractional compensation current setting; resistor to V
LOCK 18 Lock detector output
TEST 19 Test pin; connect to V
V
DD
4 Digital ground
5 Prescaler positive input
6 Prescaler negative input
7 Prescaler positive supply voltage. This pin supplies power to the prescaler and RF input buffer
8 Reference divider input
IN
SSA
10 Auxiliary divider input
IN
12 Analog ground
15 Analog supply voltage. This pin supplies power to the charge pumps, Auxiliary prescaler, Auxiliary and Reference
buffers.
SSA
SSA
DD
20 Digital supply voltage. This pin supplies power to the CMOS digital part of the device
1996 Aug 6
3
Page 4
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
SA70251GHz low-voltage Fractional-N synthesizer
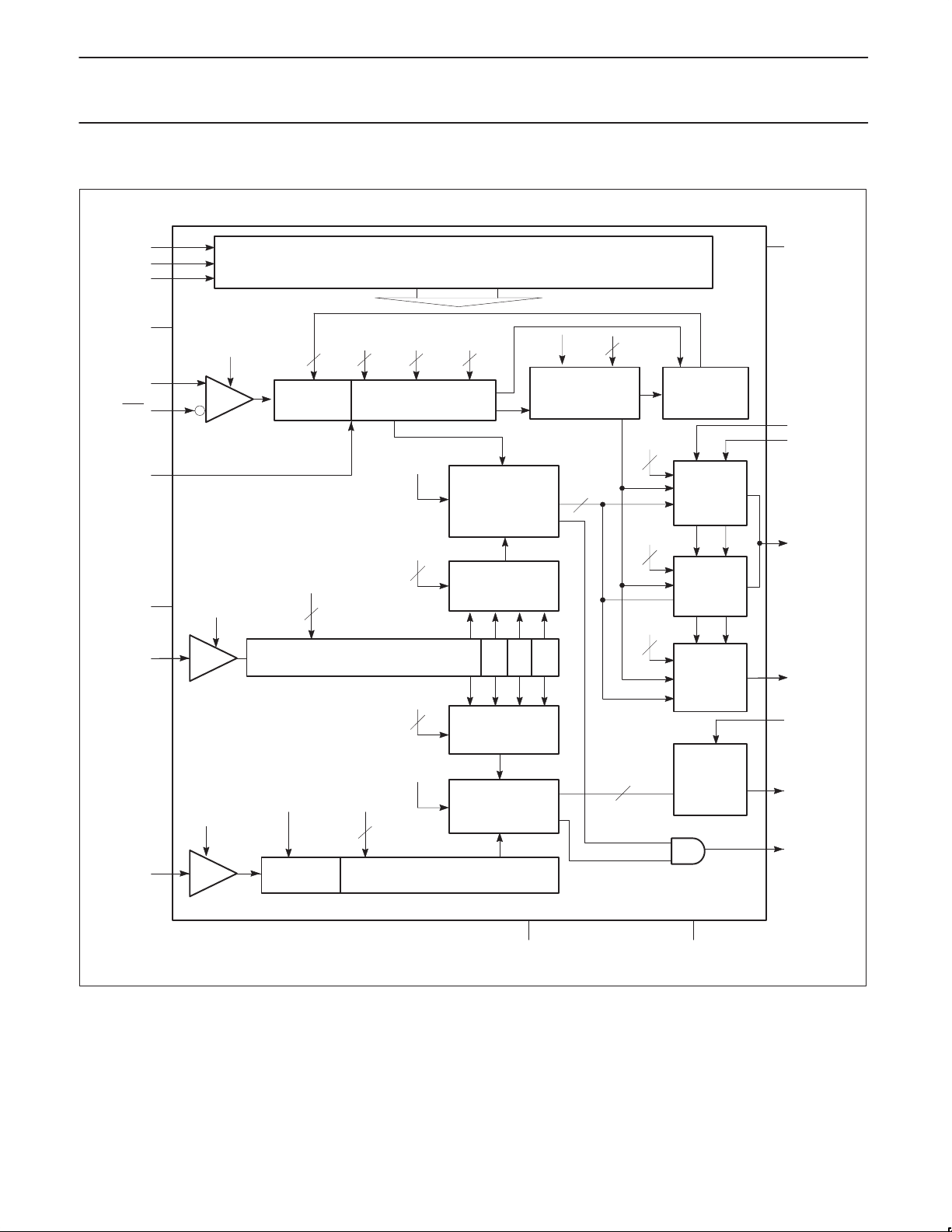
BLOCK DIAGRAM
CLOCK
DATA
STROBE
V
SS
RF
RF
TEST
V
CCP
REF
AUX
V
SERIAL INPUT + PROGRAM LATCHES
EM
IN
IN
EM+EA
FB
64/65/72
PRESCALER
NR
IN
EA
IN
PA NA
1/4
PRESCALER
PR NM1
2
12
REFERENCE DIVIDER ÷2 ÷2 ÷2
2
MAIN DIVIDERS
EM
SM
2
SA
2
EA
12
AUXILIARY DIVIDER
NM2
NM3
12 8
MAIN
PHASE
DETECTOR
MAIN
REFERENCE
SELECT
AUXILIARY
REFERENCE
SELECT
AUXILIARY
PHASE
DETECTOR
FMOD
FRACTIONAL
ACCUMULATOR
3
NF
FRD
CN
8
2
CL
2
CK
4
2
FB
PRESCALER
MODULUS
CONTROL
NORMAL
OUTPUT
CHARGE
PUMP
SPEED-UP
OUTPUT
CHARGE
PUMP
INTEGRAL
OUTPUT
CHARGE
PUMP
AUXILIARY
OUTPUT
CHARGE
PUMP
DD
RF
RN
PHP
PHI
RA
PHA
LOCK
1996 Aug 6
V
DDA
Figure 2. Block Diagram
4
V
SSA
SR00601
Page 5
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
SYMBOL
PARAMETER
TEST CONDITIONS
UNITS
|IRX|
ggyg
A
|I
|
Output current PHA
A
∆I
Output current matching PHA pump
A
|I
|
Output current PHP
A
∆I
g
A
|I
|
Output current PHP
mA
∆I
g
A
|I
|
Output current PHI
mA
∆I
Output current matching PHI pump
A
I
nA
SA70251GHz low-voltage Fractional-N synthesizer
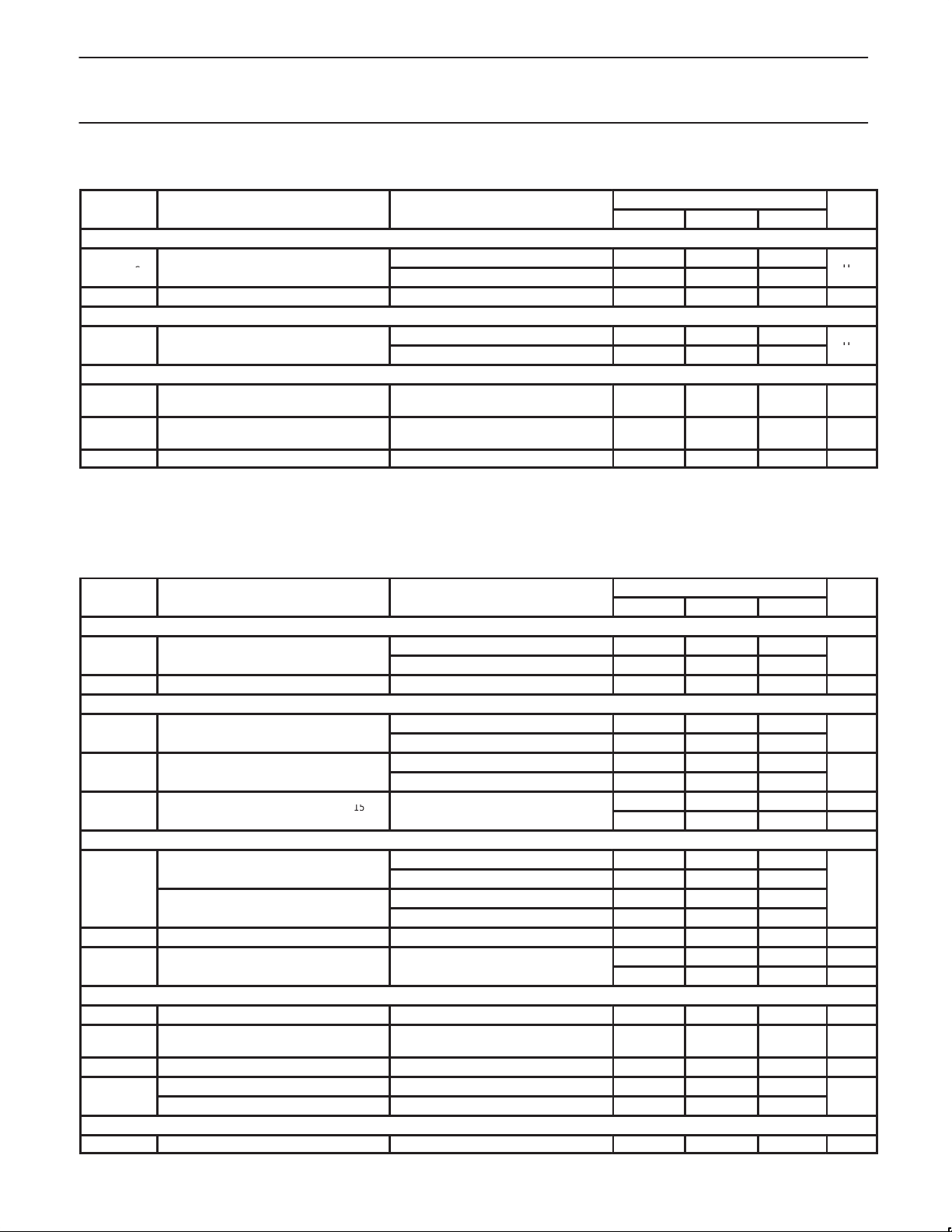
DC ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS
VDD = V
V
I
STANDBY
Operational supply currents: I = IDD + I
Digital inputs CLK, DATA, STROBE
Digital outputs LOCK
Charge pumps: V
V
Charge pump PHA
I
|I
Charge pump PHP, normal mode
PHP_N_M
Charge pump PHP, speed-up mode
I
PHP_S_M
Charge pump PHI, speed-up mode
Fractional compensation PHP, normal mode
PHP_F_N
DDA
SUPPLY
I
AUX
I
MAIN
I
TOTAL
V
IH
V
IL
V
OL
V
OH
PHOUT
PHA
PHP_A
PHP_A
PHA_M
PHP_N
I
PHP_N
I
PHP_N
PHP_S
PHP_S
I
PHP_S
PHI
I
PHI
I
PHI
PHI_M
= V
= 3V; TA = 25°C, unless otherwise specified.
CCP
LIMITS
MIN TYP MAX
Recommended operating conditions V
CCP
= VDD, V
DDA
≥ V
DD
2.7 5.5 V
Total standby supply currents EM = EA = 0, IRN = IRF = IRA = 0 50 500 µA
+ I
CCP
; IRN = 25µA, IRA = 25µA, (see Note 5)
DDA
Operational supply currents EM = 0, EA = 1 3.5 mA
Operational supply currents EM = 1, EA = 0 5.5 mA
Operational supply currents EM = EA = 1 7.5 mA
High level input voltage range 0.7xV
DD
Low level input voltage range 0 0.3xV
V
DD
DD
Output voltage LOW IO = 2mA 0.4 V
Output voltage HIGH IO = –2mA VDD–0.4 V
= 3V / IRX = 25µA or V
DDA
Setting current range for any setting resistor
Output voltage range 0.7 V
p
Relative output current variation PHA IRA = –62.5µA
|
p
1, 4, 6
VRF = V
p
Relative output current variation PHP IRN = –62.5µA
Output current matching PHP
normal mode
1, 4, 7
p
Relative output current variation PHP IRN = –62.5µA
Output current matching PHP
speed-up mode
1, 4, 8
p
Relative output current variation PHI IRN = –62.5µA
p
Fractional compensation output current
PHP vs F
RD
3
= 5V / IRX = 62.5µA, V
DDA
p
p
DDA
VRF = V
VRF = V
p
p
1, 9
DDA
DDA
VRN = V
in range, unless otherwise specified. (See Note 16)
PHX
2.7V < V
4.5V < V
IRA = –62.5µA; V
IRA = –25µA; V
V
= 3V, IRA = 25µA ±50
DDA
V
= 5V, IRA = 62.5µA ±65
DDA
IRN = –62.5µA; V
IRN = –25µA; V
V
= 3V, IRA = 25µA ±50
DDA
V
= 5V, IRA = 62.5µA ±65
DDA
IRN = –62.5µA; V
IRN = –25µA; V
V
= 3V, IRA = 25µA ±250
DDA
V
= 5V, IRA = 62.5µA ±300
DDA
IRN = –62.5µA; V
IRN = –25µA; V
V
= 3V, IRA = 25µA ±500
DDA
V
= 5V, IRA = 62.5µA ±600
DDA
, V
DDA
PHP
IRF = –62.5µA;FRD = 1 to 7
< 5.5V 25
DDA
< 5.5V 62.5
DDA
13
/2
DDA
/2 160 200 240
DDA
13
/2
DDA
/2 175 220 265
DDA
13
/2
DDA
/2 0.85 1.1 1.35
DDA
13
/2
DDA
/2 1.75 2.2 2.65
DDA
13
400 500 600
440 550 660
2.20 2.75 3.30
–625 –400 –250
= V
PHA
PHA
PHP
PHP
PHP
PHP
PHI
PHI
DDA
= V
= V
2, 13
= V
= V
2, 13
= V
= V
2, 13
= V
= V
2, 13
/2
2 6 %
2 6 %
2 6 %
4.4 5.5 6.6
2 8 %
IRF = –25µA;FRD = 1 to 7 –250 –180 –100
–0.8 V
DDA
V
V
µ
µ
µ
µ
µ
µ
µ
1996 Aug 6
5
Page 6
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
SYMBOL
PARAMETER
TEST CONDITIONS
UNITS
I
A
I
A
SYMBOL
PARAMETER
TEST CONDITIONS
UNITS
f
Input signal frequenc
GH
f
Input signal frequenc
MH
V
Input signal range, AC coupled
mV
Z
Reference divider input impedance
15
f
MH
Z
Auxiliary divider input impedance
t
ns
SA70251GHz low-voltage Fractional-N synthesizer
DC ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS (Continued)
LIMITS
MIN TYP MAX
Fractional compensation PHP, speed up mode
PHP_F_S
Fractional compensation output current
PHP vs F
RD
3
Pump leakage –20 20 nA
Fractional compensation PHI, speed up mode
PHI_F
Fractional compensation output current
PHI vs F
RD
3
Charge pump leakage currents, charge pump not active
I
PHP_L
I
PHI_L
I
PHA_L
Output leakage current PHP; normal
1
mode
Output leakage current PHI; normal
1
mode
Output leakage current PHA V
1, 10
1, 11
V
= V
DDA
, VRN = V
PHP
IRF = –62.5µA;FRD = 1 to 7
IRF = –25µA;FRD = 1 to 7 –1.35 –1.0 –0.5
V
= V
PHP
/2, VRN = V
DDA
IRF = –62.5µA;FRD = 1 to 7
IRF = –25µA;FRD = 1 to 7 –2.15 –1.6 –1.05
V
= 0.7 to V
PHP
V
= 0.7 to V
PHI
= 0.7 to V
PHA
DDA
DDA
DDA
DDA
13
DDA
13
–3.35 –2.0 –1.1
–5.4 –4.0 –2.6
– 0.8 0.1 10 nA
– 0.8 0.1 10 nA
– 0.8 0.1 10 nA
µ
µ
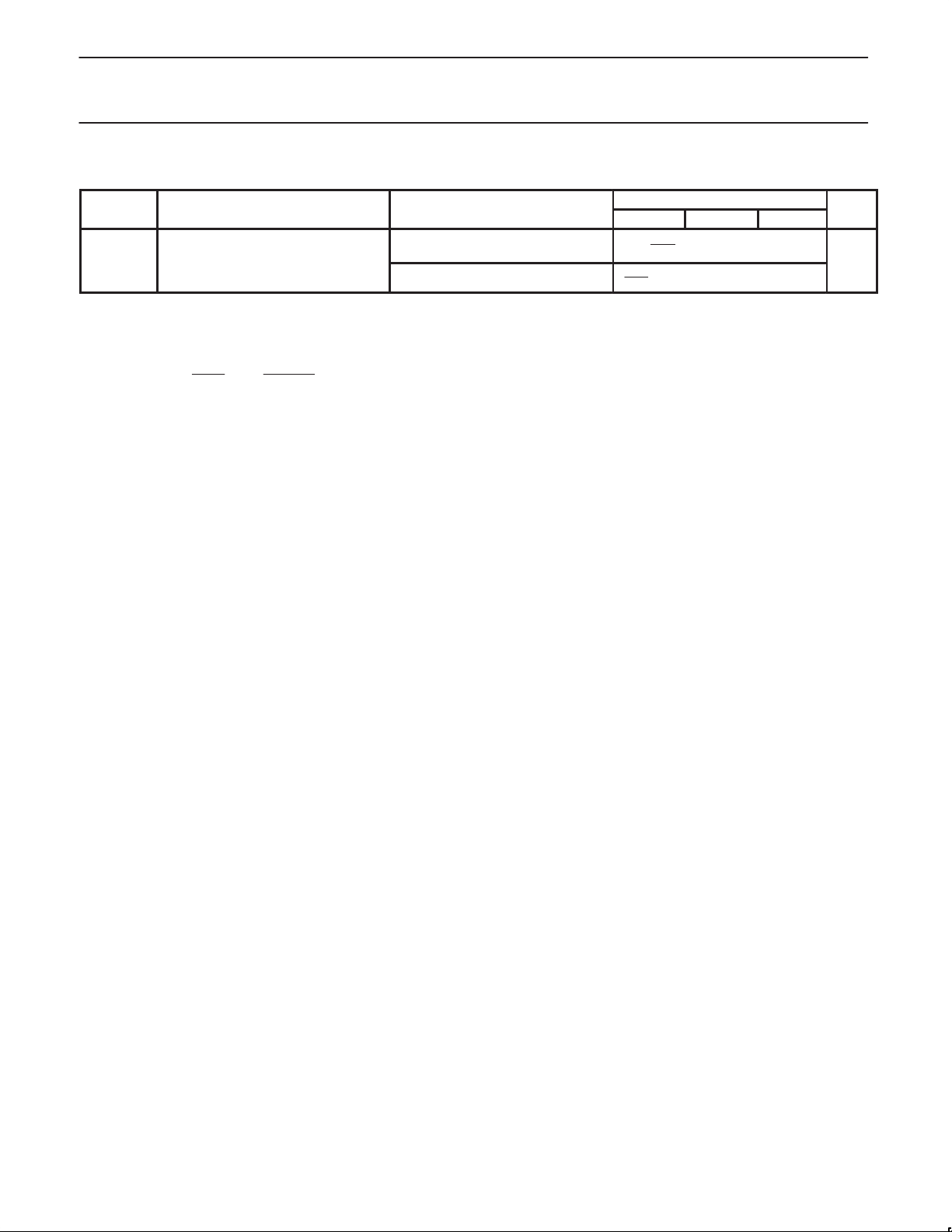
AC ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS
VDD = V
listed below are tested using automatic test equipment to assure consistent electrical characteristics. The limits do not represent the ultimate
performance limits of the device. Use of an optimized RF layout will improve many of the listed parameters.
Main divider
V
Reference divider (VDD = V
Auxiliary divider
V
Serial interface
f
In-Loop Performance17 V
RF_IN
RF_IN
REF_IN
REF_IN
REF_IN
AUX_IN
AUX_IN
AUX_IN
CLOCK
t
SU
t
H
W
R
MM
= V
DDA
= 3V; TA = 25°C; f
CCP
= 1GHz, input level = –20dBm; unless otherwise specified. Test Circuit, Figure 4. The parameters
RF_IN
LIMITS
MIN TYP MAX
p
y
Direct coupled input
1000pF input coupling 1.04
14
Input sensitivity 1040MHz –20 0 dBm
= 3V or VDD = 3V / V
DDA
p
p
y
p
p
p
DDA
= 5V)
2.7 < VDD and V
2.7 < VDD and V
2.7 < VDD and V
2.7 < VDD and V
< 5.5V 25
DDA
< 4.5V 30
DDA
< 5.5V 500
DDA
< 4.5V 300
DDA
100 kΩ
3 pF
Input signal frequency 0 50
PA = “0”, prescaler enabled 4.5V ≤ V
≤ 5.5V 0 150
DDA
Input signal frequency 0 30
PA = “1”, prescaler disabled 4.5V ≤ V
≤ 5.5V 0 40
DDA
Input signal range, AC coupled 200 mV
p
p
15
100 kΩ
3 pF
Clock frequency 10 MHz
Set-up time: DATA to CLOCK,
CLOCK to STROBE
30 ns
Hold time; CLOCK to DATA 30 ns
Pulse width; CLOCK 30
Pulse width; STROBE B, C, D, E words 30
= 5V, VDD = 2.7V
DDA
Main loop residual FM FVCO = 1030MHz 300 600 Hz
1.04
z
z
P-P
z
P-P
1996 Aug 6
6
Page 7
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
SYMBOL
PARAMETER
TEST CONDITIONS
UNITS
tSWPulse width STROBE
ns
SA70251GHz low-voltage Fractional-N synthesizer
AC ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS (continued)
LIMITS
MIN TYP MAX
;
A word, PR = ‘01’
A word, PR = ‘10’
NOTES:
1. When a serial input “A” word is programmed, the main charge pumps on PHP and PHI are in the “speed up mode” as long as STROBE = H.
When this is not the case, the main charge pumps are in the “normal mode”.
2. The relative output current variation is defined thus:
I
OUT
2
I
3. F
is the value of the 3 bit fractional accumulator.
RD
4. Monotonicity is guaranteed with C
OUT
5. Power supply current measured with V
Main comp frequency = 240kHz, Auxiliary comp frequency = 120kHz, CN = 160, CL = 0, CK = 0. Internal registers NM1 = 52, NM2 = 0,
|(I
(I
I1)
2
I1)|
2
N
; with V1 = 0.7V, V2 = V
= 0 to 255.
= V
CCP
= 3V, V
DD
DDA
– 0.8V (see Figure 3).
DDA
= 5V, f
= 915.99MHz, XTAL at 21.36MHz, AUX at 85.92MHz (PA = ‘0’),
RF IN
NM3 = 4, PR = ‘10’, SM = ‘00’, SA = ‘01’, NA = 179, NF = 5, FMOD = 8, NR = 89, PA = 0, IRN = IRA = IRF = 25µA, lock condition, normal
mode. Operational supply current = I
6. Specification condition: CN = 255
DDA
+ IDD + I
CCP
.
7. Specification conditions:
1) CN = 255; CL = 1, or
8. Typical output current | I
2) CN = 75; CL = 3
1) CN = 160; CL = 3; CK = 1, or
| = –IRN x CN x 2
PHI
(CL+1)
x CK/32:
2) CN = 160; CL = 2; CK = 2, or
3) CN = 160; CL = 1; CK = 4, or
4) CN = 160; CL = 0; CK = 8
9. Any RFD, CL = 1 for speed-up pump. The integral pump is intended for switching only and the fractional compensation is not guaranteed.
10.Specification conditions: F
11.Specification conditions:
1) F
2) F
12.The matching is defined by the sum of the P and the N pump for a given output voltage.
= 1 to 7; CL = 1.
RD
= 1 to 7; CL = 1; CK = 2, or
RD
= 1 to 7; CL = 2; CK = 1.
RD
13.Limited analog supply voltage range 4.5 to 5.5V.
14.For f
15.Guaranteed by design.
< 50MHz, low frequency operation requires DC-coupling and a minimum input slew rate of 32V/µs.
IN
16.Close in noise for the charge pumps is tested on a sample basis in a typical application in order to eliminate parts outside the normal
distribution.
17.F
= 14.4MHz, V
XTAL
XTAL
= 500mV
, comparison frequency = 200kHz, Loop bandwidth = 5kHz, Audio filter = 300Hz to 15kHz.
P-P
1
(NM2 65) t
f
VCO
1
[(NM2 65) (NM31) 72] t
f
VCO
W
W
1996 Aug 6
7
Page 8

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
SA70251GHz low-voltage Fractional-N synthesizer
CURRENT
I
2
I
1
CLOCK
DATA
STROBE
RF
RF
V
CCP
REF
AUX
V
1
I
2
I
1
V
2
VOLTAGE
SR00602
Figure 3. Relative Output Current Variation
100
22nF
V
DD
10µF
22nF
V
DD
1k
A
V
PH
P
V
PHI
1k
V
PH
A
150k
RN
RF
150k
10µF
CLOCK
1
DATA
2
STROBE
3
4
10K
22nF
22nF
10µF
50
50
22nF
22nF
IN
IN
IN
50
22nF
150k
IN
50
V
SS
SA7025
5
RF
IN
6
RF
IN
7
V
CCP
8
REF
IN
RA
9
10
AUX
IN
V
TEST
LOCK
V
DDA
PHP
V
SSA
PHA
DD
RF
RN
PHI
20
19
18
17
16
15
14
13
12
11
TEST
LOCK
1996 Aug 6
SR00603
Figure 4. Test Circuit
8
Page 9

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
SA70251GHz low-voltage Fractional-N synthesizer
AC TIMING CHARACTERISTICS
DATA
CLOCK
STROBE
CLOCK
STROBE (B, C, D, E) WORDS
D0 D1
t
t
SU
50%
t
W
50% 50%
H
Figure 5. Serial Input Timing Sequence
FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION
Serial Input Programming
The serial input is a 3-wire input (CLOCK, STROBE, DATA) to
program all counter ratios, DACs, selection and enable bits. The
programming data is structured into 24 or 32 bit words; each word
includes 1 or 4 address bits. Figure 5 shows the timing diagram of
the serial input. When the STROBE = L, the clock driver is enabled
and on the positive edges of the CLOCK the signal on DATA input is
clocked into a shift register. When the STROBE = H, the clock is
disabled and the data in the shift register remains stable.
Depending on the 1 or 4 address bits the data is latched into
different working registers or temporary registers. In order to fully
program the synthesizer, 4 words must be sent: D, C, B and A.
Figure 6 and Table 1 shows the format and the contents of each
word. The E word is for testing purposes only. The E (test) word is
reset when programming the D word. The data for CN and PR is
stored by the B word in temporary registers. When the A word is
loaded, the data of these temporary registers is loaded together with
the A word into the work registers which avoids false temporary
main divider input. CN is only loaded from the temporary registers
when a short 24 bit A0 word is used. CN will be directly loaded by
programming a long 32 bit A1 word. The flag LONG in the D word
determines whether A0 (LONG = “0”) or A1 (LONG = “1”) format is
applicable. The A word contains new data for the main divider.
Main Divider Synchronization
The A word is loaded only when a main divider synchronization
signal is also active in order to avoid phase jumps when
reprogramming the main divider. The synchronization signal is
generated by the main divider . The signal is active while the NM1
divider is counting down from the programmed value. The new A
word will be loaded after the NM1 divider has reached its terminal
count; also, at this time a main divider output pulse will be sent to
the main phase detector. The loading of the A word is disabled
while the NM2 or NM3 dividers are counting up to their programmed
D22,
D30
CLOCK ENABLED CLOCK
SHIFT IN DATA
STROBE
(A WORD)
D23,
D31
LAST CLOCK FIRST CLOCKFIRST CLOCK
t
SU
DISABLED
STORE DATA
t
SW
D0
t
SU
SR00604
values. Therefore, the new A word will be correctly loaded provided
that the STROBE signal has been at an active high value for at least
a minimum number of VCO input cycles at RF
t_strobe_min +
t_strobe_min +
1
(NM2@ 65) ) tWforPR + ‘01Ȁ
f
VCO
1
[NM2@ 65 ) (NM3) 1)@ 72] ) tWforPR + ‘10Ȁ
f
VCO
or RFIN.
IN
Programming the A word means also that the main charge pumps
on output PHP and PHI are set into the speed-up mode as long as
the STROBE is H.
Auxiliary Divider
The input signal on AUX_IN is amplified to logic level by a
single-ended CMOS input buffer, which accepts low level AC
coupled input signals. This input stage is enabled if the serial
control bit EA = “1”. Disabling means that all currents in the input
stage are switched off. A fixed divide by 4 is enabled if PA = “0”.
This divider has been optimized to accept a high frequency input
signal. If PA = “1”, this divider is disabled and the input signal is fed
directly to the second stage, which is a 12-bit programmable divider
with standard input frequency (40MHz). The division ratio can be
expressed as:
if PA = “0”: N = 4 x NA
if PA = “1”: N = NA; with NA = 4 to 4095
Reference Divider
The input signal on REF_IN is amplified to logic level by a
single-ended CMOS input buffer, which accepts low level AC
coupled input signals. This input stage is enabled by the OR
function of the serial input bits EA and EM. Disabling means that all
currents in the input stage are switched off. The reference divider
consists of a programmable divider by NR (NR = 4 to 4095) followed
by a three bit binary counter. The 2 bit SM register (see Figure 7)
determines which of the 4 output pulses is selected as the main
1996 Aug 6
9
Page 10

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
SA70251GHz low-voltage Fractional-N synthesizer
phase detector input. The 2 bit SA register determines the selection
of the auxiliary phase detector signal.
Main Divider
The differential inputs are amplified (to internal ECL logic levels) and
provide excellent sensitivity (–20dBm at 1GHz) making the prescaler
ideally suited to directly interface to a VCO as integrated on the
SA620 RF gain stage, VCO and mixer device. The internal triple
modulus prescaler feedback loop FB controls the selection of the
divide by ratios 64/65/72, and reduces the minimum system division
ratio below the typical value required by standard dual modulus
(64/65) devices.
This input stage is enabled when serial control bit EM = “1”.
Disabling means that all currents in the prescaler are switched off.
The main divider is built up by a 12 bit counter plus a sign bit.
Depending on the serial input values NM1, NM2, NM3, and the
prescaler select PR, the counter will select a prescaler ratio during a
number of input cycles according to Table 2 and Table 3.
The loading of the work registers NM1, NM2, NM3 and PR is
synchronized with the state of the main counter, to avoid extra
phase disturbance when switching over to another main divider ratio
as explained in the Serial Input Programming section.
At the completion of a main divider cycle, a main divider output
pulse is generated which will drive the main phase comparator.
Also, the fractional accumulator is incremented with NF. The
accumulator works modulo Q. Q is preset by the serial control bit
FMOD to 8 when FMOD = “1”. Each time the accumulator
overflows, the feedback to the prescaler will select one cycle using
prescaler ratio R2 instead of R1.
As shown above, this will increase the overall division ratio by 1 if
R2 = R1 + 1. The mean division ratio over Q main divider will then
be
NQ N
Programming a fraction means the prescaler with main divider will
divide by N or N + 1. The output of the main divider will be
modulated with a fractional phase ripple. This phase ripple is
proportional to the contents of the fractional accumulator FRD,
which is used for fractional current compensation.
NF
Q
Phase Detectors
The auxiliary and main phase detectors are a two D-type flip-flop
phase and frequency detector shown in Figure 8. The flip-flops are
set by the negative edges of output signals of the dividers. The
rising edge of the signal, L, will reset the flip-flops after both flip-flops
have been set. Around zero phase error this has the effect of
delaying the reset for 1 reference input cycle. This avoids
non-linearity or deadband around zero phase error. The flip-flops
drive on-chip charge pumps. A source current from the charge
pump indicates the VCO frequency will be increased; a sink current
indicates the VCO frequency will be decreased.
1996 Aug 6
10
Page 11

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
SA70251GHz low-voltage Fractional-N synthesizer
MSB
LAST IN FIRST IN
WORD
D31 D0
NM2
A1
0 NF NM1
NM3 NM2
D23
0 NF NM1
A0
1 0 0 0 CN CK CL PR
B
100 NA1
C
0000
NM3 NM2
P
A
NM2
0
D0
LSB
CN
PR = “01”
PR = “10”
101 NR0SM
D
1111
E
D23 D0
ADDRESS BITS TEST BITS
000
T1T
0
Figure 6. Serial Input Word Format
Current Settings
The SA7025 has 3 current setting pins: RA, RN and RF. The active
charge pump currents and the fractional compensation currents are
linearly dependent on the current connected between the current
setting pin and V
. The typical value R (current setting resistor)
SS
can be calculated with the formula:
R +
* 0.9 * 150 I
V
DDA
I
Ǹ
R
R
The current can be set to zero by connecting the corresponding pin
to V
.
DDA
Auxiliary Output Charge Pumps
The auxiliary charge pumps on pin PHA are driven by the auxiliary
phase detector and the current value is determined by the external
resistor RA at pin RA. The active charge pump current is typically:
F
E
M
A
O
D
| + 8@ I
L
O
N
G
SR00605
RA
E
SA
M
0
|I
PHA
Main Output Charge Pumps and Fractional
Compensation Currents
The main charge pumps on pin PHP and PHI are driven by the main
phase detector and the current value is determined by the current at
pin RN and via a number of DACs which are driven by registers of
the serial input. The fractional compensation current is determined
by the current at pin RF, the contents of the fractional accumulator
FRD and a number of DACs driven by registers from the serial input.
The timing for the fractional compensation is derived from the
reference divider. The current is on during 1 input reference cycle
before and 1 cycle after the output signal to the phase comparator.
Figure 9 shows the waveforms for a typical case.
1996 Aug 6
11
Page 12

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
SA70251GHz low-voltage Fractional-N synthesizer
Table 1. Function Table
Symbol Bits Function
NM1 12
NM2
8 if PR = “01”
4 if PR = “10”
NM3 4 if PR = “10”
PR 2 Prescaler type in use
NF 3 Fractional-N increment
FMOD 1 Fractional-N modulus selection flag
LONG 1 A word format selection flag
CN 8 Binary current setting factor for main charge pumps
CL 2 Binary acceleration factor for proportional charge pump current
CK 4 Binary acceleration factor for integral charge pump current
EM 1 Main divider enable flag
EA 1 Auxiliary divider enable flag
SM 2 Reference select for main phase detector
SA 2 Reference select for auxiliary phase detector
NR 12 Reference divider ratio
NA 12 Auxiliary divider ratio
PA 1
*Not including reset cycles and Fractional-N effects.
Number of main divider cycles when prescaler modulus = 64*
Number of main divider cycles when prescaler modulus = 65*
Number of main divider cycles when prescaler modulus = 72*
PR = “01”: modulus 2 prescaler (64/65)
PR = “10”: modulus 3 prescaler (64/65/72)
“1”: modulo 8
“0”: modulo 5
“0”: 24 bit A0 format
“1”: 32 bit A1 format
Auxiliary prescaler mode:
PA = “0”: divide by 4
PA = “1”: divide by 1
MAIN SELECT
SM = “00”
MAIN
PHASE
DETECTOR
AUXILIARY
PHASE
DETECTOR
REFERENCE
INPUT
DIVIDE BY NR ÷2
SM = “01”
SM = “10”
SM = “11”
÷2 ÷2
AUXILIARY SELECT
SA = “11”
SA = “10”
SA = “01”
SA = “00”
Figure 7. Reference Divider
Table 2. Prescaler Ratio
The total division ratio from prescaler to the phase detector may be expressed as:
if PR = “01” N = (NM1 + 2) x 64 + NM2 x 65
N’ = (NM1 + 1) x 64 + (NM2 + 1) x 65 (*)
if PR = “10” N = (NM1 + 2) x 64 + NM2 x 65 + (NM3 + 1) x 72
N’ = (NM1 + 1) x 64 + (NM2 + 1) x 65 + (NM3 + 1) x 72 (*)
(*) When the fractional accumulator overflows the prescaler ratio = 65 (64 + 1) and the total division ratio N’ = N + 1
SR00606
1996 Aug 6
12
Page 13

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
ǒ
Ǔ
ǒ
Ǔ
ǒ
Ǔ
ǒ
Ǔ
SA70251GHz low-voltage Fractional-N synthesizer
Table 3. PR Modulus
PR Modulus Prescaler Bit Capacity
NM1 NM2 NM3
01 2 12 8 –
10 3 12 4 4
When the serial input A word is loaded, the output circuits are in the
“speed-up mode” as long as the STROBE is H, else the “normal
mode” is active. In the “normal mode” the current output PHP is:
I
PHP_N
+ I
PHP
) I
PHP_comp
where:
CN @ I
|I
PHP
|I
PHP_comp
| +
RN
| + FRD@
:charge pump current
I
:fractional comp.
RF
current
128
The current in PHI is zero in “normal mode”.
In “speed-up mode” the current in output PHP is:
I
PHP_S
|I
PHP
+ I
| +
PHP
CN @ I
32
) I
RN
PHP_comp
CL)1
(2
) 1)
In “speed-up mode” the current in output PHI is:
+ I
I
PHI_S
PHI
) I
PHI_comp
where:
| +
|I
PHI
|I
PHI_comp
IRNCN
| +
32
IRFFRD
(2
128
CL)1
)CK
CL)1
(2
)CK
Figure 9 shows that for proper fractional compensation, the area of
the fractional compensation current pulse must be equal to the area
of the charge pump ripple output. This means that the current
setting on the input RN, RF is approximately:
I
RN
I
RF
+
(3 @ CN @ F
(Q @ f
VCO
)
)
where:
Q = fractional-N modulus
f
= f
VCO
F
INR
× N, input frequency of the prescaler
INM
= input frequency of the reference divider
PHI pump is meant for switching only. Current and compensation
are not as accurate as PHP.
|I
PHP_comp
| +
FRD @ I
128
RF
REF_IN
REF_IN
(2
CL)1
L
R
X
P
) 1)
REFERENCE
DIVIDER
AUX/MAIN
DIVIDER
L
“1”
DCQ
V
R
R
“1”
R
D
C
X
Q
DDA
P
N
V
SSA
P-TYPE
CHARGE PUMP
PH
N-TYPE
CHARGE PUMP
1996 Aug 6
N
I
P
H
SR00607
Figure 8. Phase Detector Structure with Timing
13
Page 14

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
SA70251GHz low-voltage Fractional-N synthesizer
REFERENCE R
MAIN N
VCO CYCLES
DETECTOR
OUTPUT
CONTENTS
ACCUM.
FRACTIONAL
COMPENSATION
CURRENT
OUTPUT ON
PHP, PHI
PULSE-WIDTH
MODULATION
TIME
N N N + 1 N N + 1
24130
mA
µA
PULSE-LEVEL
MODULATION
Figure 9. Waveforms for NF = 2, Fraction = 0.4
Lock Detect
The output LOCK is H when the auxiliary phase detector AND the
main phase detector indicates a lock condition. The lock condition
is defined as a phase difference of less than +1 cycle on the
reference input REF_IN. The lock condition is also fulfilled when the
relative counter is disabled (EM = “0” or respectively EA = “0”) for
the main, respectively auxiliary counter.
Test Modes
The lock output is selectable as f
and T0 of the E word control the selection (see Figures 6 and 10).
If T1 = T0 = Low, or if the E-word is not sent, the lock output is
configured as the normal lock output described in the Lock Detect
section.
If T1 = Low and T0 = High, the lock output is configured as f
The signal is the buffered output of the reference divider NR and the
3-bit binary counter SM. The f
and pulses high whenever the divider reaches terminal count from
the value programmed into the NR and SM registers. The f
signal can be used to verify the divide ratio of the Reference divider.
If T1 = High and T0 = Low, the lock output is configured as f
The signal is normally high and pulses low whenever the divider
reaches terminal count from the value programmed into the NA and
, f
, f
REF
AUX
signal appears as normally low
REF
and lock. Bits T1
MAIN
REF
REF
AUX
.
.
SR00608
PA registers. The f
signal can be used to verify the divide ratio
AUX
of the Auxiliary divider.
If T1 = High and T0 = High, the lock output is configured as f
The signal is the buffered output of the MAIN divider. The f
MAIN
MAIN
signal appears as normally high and pulses low whenever the
divider reaches terminal count from the value programmed into the
NM1, NM2 or NM3 registers. The f
signal can be used to verify
MAIN
the divide ratio of the MAIN divider and the prescaler.
.
1996 Aug 6
14
Page 15

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
SA70251GHz low-voltage Fractional-N synthesizer
Test Pin
The Test pin, Pin 19, is a buffered logic input which is exclusively
ORed with the output of the prescaler. The output of the XOR gate
is the input to the MAIN divider. The Test pin must be connected to
V
during normal operation as a synthesizer. This pin can be used
DD
as an input for verifying the divide ratio of the MAIN divider; while in
this condition the input to the prescaler, RF
V
through a 10kΩ resistor in order to place prescaler output into
CCP
, may be connected to
IN
a known state.
PIN FUNCTIONS
PIN
No.
1 CLOCK ––
2DATA––
3 STROBE ––
PIN
MNEMONIC
DC V EQUIVALENT CIRCUIT
1
V
DD
MAIN
DIVIDER
REF
DIVIDER
AUX
DIVIDER
φ
MAIN
φ
AUX
Figure 10. Test Mode Diagram
PIN
No.
PIN
MNEMONIC
DC V EQUIVALENT CIRCUIT
9 RA 1.35
16 RN 1.35
SM
T1
T0
9
SELECT
LOGIC
LOCK
V
DDA
SR00609
= 3V
19 TEST ––
5RF
2.1
IN
6RFIN2.1
8 REF
10 AUX
1.8
IN
1.8
IN
V
SS
V
= 3V
CCP
5
10
2.5k
2.5k
100k
V
SS
6
V
DDA
ENABLE
17 RF 1.35
11 PHA ––
13 PHI ––
14 PHP ––
= 3V
18 LOCK ––
V
SS
25µA
V
V
V
V
DDA
SSA
DD
SS
V
SSA
SR00610
11
18
Figure 11. Pin Functions
1996 Aug 6
15
Page 16

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
SA70251GHz low-voltage Fractional-N synthesizer
TYPICAL PERFORMANCE CHARACTERISTICS
11
V
= V
10
CCP
EM = EA = 1, Note5
9
8
I TOTAL (mA)
7
6
5
2.7 3.5 4.5 5.5
= V
DDA
DD
SUPPLY VOLTAGE (V)
t = –40°C
t = 25°C
t = 85°C
SR00611
Figure 12. Operational Supply Current vs Supply Voltage and
Temperature
7
V
= V
6
CCP
EA=0, EM=1, Note5
5
4
I TOTAL (mA)
3
2
1
2.7 3.5 4.5 5.5
= V
DDA
DD
SUPPLY VOLTAGE (V)
t = –40°C
t = 25°C
t = 85°C
SR00612
Figure 13. Auxiliary Operational Supply Current vs Supply
Voltage and Temperature
8.5
8
V
= V
CCP
EA=0, EM=1, Note5
7
6
5
4
2.7 3.5 4.5 5.5
I TOTAL (mA)
7.5
6.5
5.5
4.5
= V
DDA
DD
SUPPLY VOLTAGE (V)
t = –40°C
t = 25°C
t = 85°C
SR00614
Figure 15. Main Operational Supply Current vs Supply Voltage
and Temperature
3.5
VDD = 3V, V
Pin = –10dBm,
3
ref divider halted
2.5
2
I TOTAL (mA)
1.5
1
50 100 150
= 5V
DDA
AUXILIARY INPUT FREQUENCY (MHz)
t = –40°C
t = 25°C
t = 85°C
SR00615
Figure 16. Auxiliary Operational Supply Current vs Frequency
and Temperature
20
0
–20
INPUT POWER (dBm)
–40
TA = 25°C,
N = 3971.625
–60
500
550
600
650
700
VDD = V
CCP
750
800
FREQUENCY (MHz)
850
900
950
2.7V
3.5V
4.5V
5.5V
1000
1050
SR00613
1100
Figure 14. Main Divider Input Power vs frequency and Supply
1996 Aug 6
1150
16
20
0
t=–40°C
900
t=25°C
t=85°C
950
1000
1050
SR00616
–20
INPUT POWER (dBm)
–40
VDD = V
CCP
N=3971.625
–60
500
550
600
= 3V
650
700
FREQUENCY (MHz)
750
800
850
Figure 17. Main Divider Input Power vs Frequency and
Temperature
1100
1150
Page 17

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
SA70251GHz low-voltage Fractional-N synthesizer
TYPICAL PERFORMANCE CHARACTERISTICS (continued)
0
–5
–10
–15
–20
INPUT POWER (dBm)
–25
–30
10 15 20 25 30 35 40 45 50 55
FREQUENCY (MHz)
N=100
VDD/V
DDA
3/3V
3/5V
5/5V
SR00617
Figure 18. Reference Divider Minimum Input Power vs
frequency and Supply
0
VDD/V
DDA
3/3V
3/5V
5/5V
–10
–15
–5
T
=amb,
A
PA=1,
N=100
5
VDD= 3V,
0
V
= 5V,
DDA
N = 100
–5
–10
MINIMUM INPUT POWE (dBm)
–15
–20
10 15 20 25 30 35 40
FREQUENCY (dBm)
t = –40°C
t = 25°C
t = 85°C
SR00631
Figure 21. Reference Divider Minimum Input Power vs
Frequency and Temperature
–10
–15
VDD =3V,
V
=5V,
DDA
PA=1,
N=100
t = –40°C
t = 25°C
t = 85°C
–20
MINIMUM INPUT POWER (dBm)
–25
–30
30 50 70 90 110 130 150
FREQUENCY (MHz)
Figure 19. Auxiliary Divider Minimum Input Power vs
Frequency and Supply
0
VDD/V
T
= amb,
A
–5
PA=0,
N=25
–10
–15
–20
MINIMUM INPUT POWER (dBm)
–25
–30
50 100 150 200 250
FREQUENCY (MHz)
DDA
3/3V
3/5V
5/5V
Figure 20. Auxiliary Divider Minimum Input Power vs
Frequency and Supply
SR00618
–20
MINIMUM INPUT POWER (dBm)
–25
30 50 70 90
FREQUENCY (MHz)
Figure 22. Auxiliary Divider Minimum Input Power vs
Frequency and Temperature
0
VDD=3V,
V
=5V
DDA
PA=0,
–5
N=25
–10
–15
MINIMUM INPUT POWER (dBm)
–20
50 100 150 200
FREQUENCY (MHz)
t = –40°C
t = 25°C
t = 85°C
Figure 23. Auxiliary Divider Minumum Input Power vs
Frequency and Temperature
SR00632
SR00619
1996 Aug 6
17
Page 18

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
SA70251GHz low-voltage Fractional-N synthesizer
j1
j0.5
0
–j0.5
–j1
–j2
j2
1100
900
600
300
= VDD = 3V
V
CCP
T
= 25°C
A
R3 L4
2nH
1
50
1Ω
C2
0.1pF
R1
3000Ω
C1
0.85pF
Equivalent Input Impedance
SR00620
Figure 24. Typical RFIN Input Impedance
1996 Aug 6
18
Page 19

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
SA70251GHz low-voltage Fractional-N synthesizer
TOP SILK SCREEN
1996 Aug 6
TOP VIEW
BOTTOM VIEW
Figure 25. SA7025DK Demoboard Layout (NOT ACTUAL SIZE)
19
SR00621
Page 20

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
SA70251GHz low-voltage Fractional-N synthesizer
1996 Aug 6
SR00622
Figure 26. SA7025DK Application Circuit
20
Page 21

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
SA70251GHz low-voltage Fractional-N synthesizer
SSOP20: plastic shrink small outline package; 20 leads; body width 4.4 mm SOT266-1
1996 Aug 6
21
Page 22

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
SA7025Low-voltage 1GHz fractional-N synthesizer
DEFINITIONS
Data Sheet Identification Product Status Definition
Objective Specification
Preliminary Specification
Product Specification
Formative or in Design
Preproduction Product
Full Production
This data sheet contains the design target or goal specifications for product development. Specifications
may change in any manner without notice.
This data sheet contains preliminary data, and supplementary data will be published at a later date. Philips
Semiconductors reserves the right to make changes at any time without notice in order to improve design
and supply the best possible product.
This data sheet contains Final Specifications. Philips Semiconductors reserves the right to make changes
at any time without notice, in order to improve design and supply the best possible product.
Philips Semiconductors and Philips Electronics North America Corporation reserve the right to make changes, without notice, in the products,
including circuits, standard cells, and/or software, described or contained herein in order to improve design and/or performance. Philips
Semiconductors assumes no responsibility or liability for the use of any of these products, conveys no license or title under any patent, copyright,
or mask work right to these products, and makes no representations or warranties that these products are free from patent, copyright, or mask
work right infringement, unless otherwise specified. Applications that are described herein for any of these products are for illustrative purposes
only. Philips Semiconductors makes no representation or warranty that such applications will be suitable for the specified use without further testing
or modification.
LIFE SUPPORT APPLICA TIONS
Philips Semiconductors and Philips Electronics North America Corporation Products are not designed for use in life support appliances, devices,
or systems where malfunction of a Philips Semiconductors and Philips Electronics North America Corporation Product can reasonably be expected
to result in a personal injury. Philips Semiconductors and Philips Electronics North America Corporation customers using or selling Philips
Semiconductors and Philips Electronics North America Corporation Products for use in such applications do so at their own risk and agree to fully
indemnify Philips Semiconductors and Philips Electronics North America Corporation for any damages resulting from such improper use or sale.
Philips Semiconductors
811 East Arques Avenue
P.O. Box 3409
Sunnyvale, California 94088–3409
Philips Semiconductors and Philips Electronics North America Corporation
register eligible circuits under the Semiconductor Chip Protection Act.
Copyright Philips Electronics North America Corporation 1996
All rights reserved. Printed in U.S.A.
Telephone 800-234-7381
print code
Document order number:
 Loading...
Loading...