Page 1

S3C7295/P7295 PRODUCT OVERVIEW
1 PRODUCT OVERVIEW
OVERVIEW
The S3C7295 single-chip CMOS microcontroller has been designed for high performance using Samsung's
newest 4-bit CPU core, SAM47 (Samsung Arrangeable Microcontrollers).
With an up-to-704-dot LCD direct drive capability, and flexible 8-bit timer/counter, the S3C7295 offers an
excellent design solution for a mid-end LCD game.
Up to 8 pins of the 80-pin QFP package can be dedicated to I/O. Six vectored interrupts provide fast response to
internal and external events. In addition, the S3C7295's advanced CMOS technology provides for low power
consumption.
OTP
The S3C7295 microcontroller is also available in OTP (One Time Programmable) version, S3P7295. S3P7295
microcontroller has an on-chip 16K-byte one-time-programable EPROM instead of masked ROM.
The S3P7295 is comparable to S3C7295, both in function and in pin configuration.
1-1
Page 2

PRODUCT OVERVIEW S3C7295/P7295
FEATURES
Memory
• 256 × 4-bit RAM (excluding LCD display RAM)
• 16,384 × 8-bit ROM
8 I/O Pins
• I/O: 8 pins
LCD Controller/Driver
• 44 segments and 16 common terminals
(8, 12 and 16 common selectable)
• Internal resistor circuit for LCD bias
• Voltage doubler
• All dot can be switched on/off
8-bit Basic Timer
• 4 interval timer functions
• Watch-dog timer
8-bit Timer/Counter
• Programmable 8-bit timer
• Arbitrary clock output (TCLO0)
• Inverted clock output (TCLO0)
Memory-Mapped I/O Structure
• Data memory bank 15
Power-Down Modes
• Idle mode (only CPU clock stops)
• Stop mode (main system oscillation stops)
• Sub system clock stop mode
Oscillation Sources
• Crystal, ceramic, or RC for main system clock
• Crystal oscillator for subsystem clock
• Main system clock frequency: 4.19 MHz
(typical)
• Subsystem clock frequency: 32.768 kHz
• CPU clock divider circuit (by 4, 8, or 64)
Instruction Execution Times
• 0.95, 1.91, 15.3 µs at 4.19 MHz (main)
• 122 µs at 32.768 kHz (subsystem)
Operating Temperature
• – 40 °C to 85 °C
Watch Timer
• Time interval generation: 0.5 s, 3.9 ms
at 32768 Hz
• Four frequency outputs to BUZ pin and BUZ pin
• Clock source generation for LCD
Interrupts
• Two internal vectored interrupts
• Four external vectored interrupts
• Two quasi-interrupts
1-2
Operating Voltage Range
• 2.2 V to 3.4 V (0.4 MHz to 4.19 MHz)
Package Type
• 80-pin QFP or pellet
Page 3
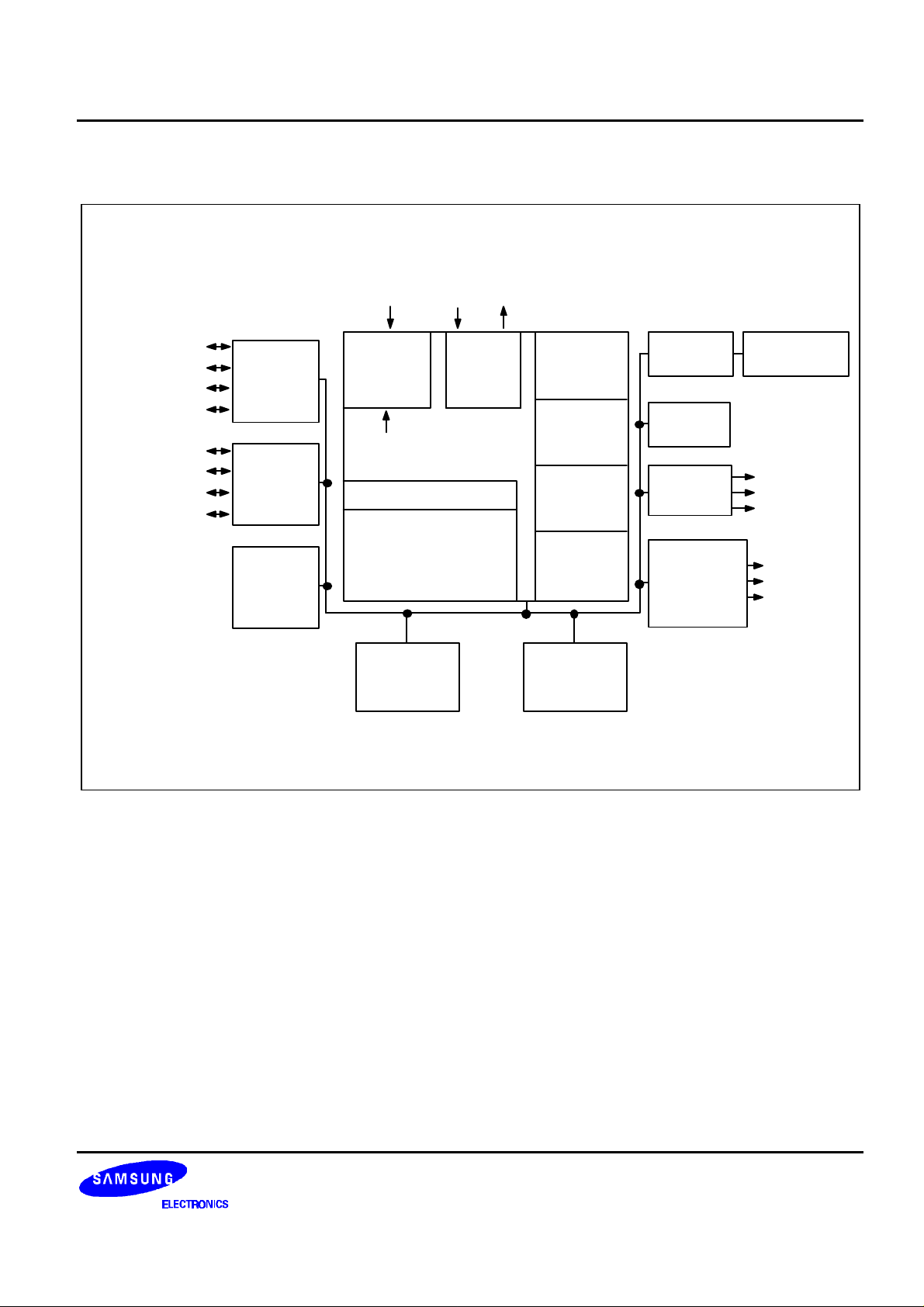
S3C7295/P7295 PRODUCT OVERVIEW
BLOCK DIAGRAM
Xin
RESET
XTin
Xout
XTout
P0.3/BUZ/K3
P0.2/CLO/ /K2
P0.1/ /K1
P0.0/TCLO0/K0
BUZ
TCLO0
P1.3/INT
P1.2/INT2
P1.1/INT1
P1.0/INT0
I/O PORT 0
I/O PORT 1
8-BIT
TIMER/
COUNTER
INTERRUPT
CONTROL
BLOCK
INTERNAL
INTERRUPT
INSTRUCTION DECODER
ARITHMETIC
AND
LOGIC UNIT
256 x 4-BIT
DATA
MEMORY
CLOCK
INSTRUCTION
REGISTER
PROGRAM
COUNTER
PROGRAM
STATUS
WORD
STACK
POINTER
16K BYTES
PROGRAM
MEMORY
BASIC
TIMER
WATCH
TIMER
VOLTAGE
DOUBLER
LCD
DRIVER/
CONTROLLER
WATCH-DOG
TIMER
BIAS
CA
CB
SEG0-SEG43
COM0-COM15
VLC0
Figure 1-1. S3C7295 Simplified Block Diagram
1-3
Page 4

PRODUCT OVERVIEW S3C7295/P7295
PIN ASSIGNMENTS
SEG40
SEG39
SEG38
SEG37
SEG36
SEG35
SEG34
SEG33
SEG32
SEG31
SEG30
SEG29
SEG28
SEG27
SEG26
SEG25
80
79
78
77
76
75
74
73
72
71
70
69
68
67
66
65
SEG41
SEG42
SEG43
P1.3/INT4
P1.2/INT2
P1.1/INT1
P1.0/INT0
P0.3/BUZ/K3
P0.2/CLO/ BUZ/K2
P0.1/TCLO0/K1
P0.0/TCLO0/K0
VDD
VSS
Xout
Xin
TEST
XTin
XTout
RESET
CA
CB
VLC0
BIAS
COM15
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
S3C7295
(TOP VIEW)
64
63
62
61
60
59
58
57
56
55
54
53
52
51
50
49
48
47
46
45
44
43
42
41
SEG24
SEG23
SEG22
SEG21
SEG20
SEG19
SEG18
SEG17
SEG16
SEG15
SEG14
SEG13
SEG12
SEG11
SEG10
SEG9
SEG8
SEG7
SEG6
SEG5
SEG4
SEG3
SEG2
SEG1
1-4
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38 3940
COM14
COM13
COM12
COM11
COM9
COM10
COM8
COM7
COM6
COM5
COM4
COM3
COM2
COM1
COM0
SEG0
Figure 1-2. S3C7295 80-QFP Pin Assignment Diagram
Page 5
S3C7295/P7295 PRODUCT OVERVIEW
PIN DESCRIPTIONS
Table 1-1. S3C7295 Pin Descriptions
Pin Name Pin
Type
P0.0
P0.1
P0.2
P0.3
P1.0
P1.1
P1.2
P1.3
INT0, INT1 I/O External interrupts. The triggering edge for INT0
INT2 I/O Quasi-interrupt with detection of rising or falling
INT4 I/O External interrupt with detection of rising or falling
BUZ I/O 2 kHz, 4 kHz, 8 kHz or 16 kHz frequency output for
BUZ
CLO I/O Clock output 9
TCLO0
TCLO0 I/O Timer/counter 0 clock output 11 P0.0/K0
COM0–COM15 O LCD common signal output H-6 39–24 –
SEG0–SEG43 O LCD segment signal output H-6 40–80,
I/O 4-bit I/O port.
1-bit and 4-bit read/write and test are possible.
Individual pins are software configurable as input or
output.
Individual pins are software configurable as open-
drain or push-pull output.
Individual pull-up resistors are software assignable;
pull-up resistors are automatically disabled for
output pins.
I/O Same as port 0. E-1 7
and INT1 is selectable.
edges
edges.
buzzer sound.
I/O Inverted BUZ signal 9 P0.2/CLO/K2
I/O Inverted Timer/counter 0 clock output 10 P0.1/K1
Description Circuit
Type
E-1 11
Number Share Pin
TCLO0/K0
10
9
8
6
5
4
7, 6 P1.0, P1.1
5 P1.2
4 P1.3
8 P0.3/K3
1–3
TCLO0/K1
CLO/BUZ/K2
BUZ/K3
INT0
INT1
INT2
INT4
P0.2/BUZ/K2
–
1-5
Page 6
PRODUCT OVERVIEW S3C7295/P7295
Table 1-1. S3C7295 Pin Descriptions (Continued)
Pin Name Pin
Type
Description Circuit
Type
Number Share Pin
K0–K3 I/O External interrupt (triggering edge is selectable) E-1 11–8 P0.0–P0.3
V
DD
V
SS
RESET
– Power supply – 12 –
– Ground – 13 –
I Reset input (active low) B 19 –
CA, CB – Capacitor terminal for voltage doubling – 20, 21 –
VCL0 – LCD power supply input – 22 –
BIAS O Doubling voltage level output – 23 –
X
in, Xout
– Crystal, ceramic or RC oscillator pins for system
– 15, 14 –
clock
XT
in, XTout
TEST I
NOTE: Pull-up resistors for all I/O ports are automatically disabled if they are configured to output mode.
– Crystal oscillator pins for subsystem clock – 17, 18 –
Test input (must be connected to VSS)
– 16 –
1-6
Page 7

S3C7295/P7295 PRODUCT OVERVIEW
PIN CIRCUIT DIAGRAMS
V
VDD
PNE
VDD
DD
PULL-UP
RESISTOR
P-CHANNEL
IN
N-CHANNEL
Figure 1-3. Pin Circuit Type A
V
DD
DATA
OUTPUT
DISABLE
V
LC0
V
LC1
P-CH
N-CH
SCHMITT TRIGGER
RESISTOR
ENABLE
Figure 1-5. Pin Circuit Type E-1
I/O
PULL-UP
RESISTOR
IN
SCHMITT TRIGGER
Figure 1-4. Pin Circuit Type B
V
LC2
SEG/COM DATA
V
LC3
V
LC4
V
SS
Figure 1-6. Pin Circuit Type H-6
OUT
1-7
Page 8

S3C7295/P7295 ELECTRICAL DATA
13 ELECTRICAL DATA
OVERVIEW
In this section, information on S3C7295 electrical characteristics is presented as tables and graphics.
The information is arranged in the following order:
Standard Electrical Characteristics
— Absolute maximum ratings
— D.C. electrical characteristics
— Main system clock oscillator characteristics
— Subsystem clock oscillator characteristics
— I/O capacitance
— A.C. electrical characteristics
— Operating voltage range
Miscellaneous Timing Waveforms
— A.C timing measurement point
— Clock timing measurement at X
— Clock timing measurement at XT
— TCL timing
— Input timing for RESET
— Input timing for external interrupts
— Serial data transfer timing
Stop Mode Characteristics and Timing Waveforms
— RAM data retention supply voltage in stop mode
— Stop mode release timing when initiated by RESET
— Stop mode release timing when initiated by an interrupt request
in
in
13-1
Page 9

ELECTRICAL DATA S3C7295/P7295
Table 13-1. Absolute Maximum Ratings
(TA = 25 °C)
Parameter Symbol Conditions Rating Units
Supply Voltage
Input Voltage
Output Voltage
Output Current High
V
I
DD
V
V
O
OH
– – 0.3 to + 4.5 V
Ports 0, 1 – 0.3 to VDD + 0.3 V
I
– – 0.3 to VDD + 0.3 V
One I/O pin active – 15 mA
All I/O pins active – 30
Output Current Low
I
OL
One I/O pin active + 30 (Peak value) mA
(note)
+ 15
Total for pins 0, 1 + 100 (Peak value)
(note)
+ 60
Operating Temperature
Storage Temperature
T
A
T
stg
– – 40 to + 85
– – 65 to + 150
°
C
°
C
NOTE: The values for Output Current Low ( IOL ) are calculated as Peak Value × Duty .
Table 13-2. D.C. Electrical Characteristics
(T
= – 40 °C to + 85 °C, VDD = 2.2 V to 3.4 V)
A
Parameter Symbol Conditions Min Typ Max Units
Input High
V
IH1
Ports 0, 1, and RESET
0.8V
DD
–
V
DD
Voltage
Input Low
V
IH2
V
IL1
Xin, X
, and XT
out
in
Ports 0, 1, and RESET
VDD – 0.1 V
– –
0.2V
DD
DD
Voltage
Output High
Voltage
V
IL2
V
OH
Xin, X
, and XT
out
in
VDD = 2.2 V to 3.4 V
IOH = – 1 mA
VDD – 1.0
0.1
– – V
Ports 0, 1
Output Low
Voltage
V
OL
V
= 2.2 V to 3.4 V
DD
IOL = 5 mA
– – 1.0 V
Ports 0, 1
V
V
13-2
Page 10

S3C7295/P7295 ELECTRICAL DATA
Table 13-2. D.C. Electrical Characteristics (Continued)
(T
= – 40 °C to + 85 °C, VDD = 2.2 V to 3.4 V)
A
Parameter Symbol Conditions Min Typ Max Units
Input High
Leakage
Current
Input Low
Leakage
Current
Output High
Leakage
I
LIH1
I
LIH2
I
LIL1
I
LIL2
I
LOH
VI = V
DD
All input pins except those
specified below for I
VI = V
DD
Xin, X
V
= 0 V
I
and XT
out
LIH2
in
All input pins except RESET
X
, X
out
= 0 V
and XT
DD
in
and XT
out
in
in
V
I
RESET, Xin, X
VO = V
All output pins
– – 3 µA
20
– – – 3 µA
– 20
– – 3 µA
Current
Output Low
Leakage
I
LOL
VO = 0 V
All output pins
– – – 3 µA
Current
Pull-Up
Resistor
LCD Voltage
R
R
R
LCD1
L1
L2
V
= 0 V; V
I
DD
Ports 0, 1
V
= 0 V; V
I
DD
Ta = + 25 °C
= 3V
= 3V; RESET
50 100 200
200 450 800
50 100 150
kΩ
kΩ
Dividing
Resistor
V
Voltage Drop
(1)
DD-COMi
R
LCD2
V
DC
Ta = + 25 °C
V
= 3.0 V
LCD
– 15 µA per common pin
25 50 75
– – 120 mV
(i = 0–15)
V
LCD-
SEGx
V
DS
V
LCD
= 3.0 V
– – 120
– 15 µA per common pin
Voltage Drop
(x = 0–43)
Middle Output
Voltage
(2)
V
V
V
V
V
LC0
LC1
LC2
LC3
LC4
V
LC0 =
5.0 V V
-0.2 V
LC0
0.8V
LC0
0.6V
LC0
0.4V
LC0
0.2V
LC0
LC0
-0.2 0.8V
-0.2 0.6V
-0.2 0.4V
-0.2 0.2V
LC0
LC0
LC0
LC0
V
LC0
0.8V
0.6V
0.4V
0.2V
+0.2
LC0
LC0
LC0
LC0
V
+0.2
+0.2
+0.2
+0.2
NOTES:
1. RLCD1 is LCD voltage dividing resistor when LCON.2 = "0", and RLCD2 when LCON.2 = "1".
2. It is middle output voltage when 1/16 duty and 1/5 bias.
13-3
Page 11

ELECTRICAL DATA S3C7295/P7295
Table 13-2. D.C. Electrical Characteristics (Concluded)
(T
= – 40 °C to + 85 °C, VDD = 2.2 V to 3.4 V)
A
Parameter Symbol Conditions Min Typ Max Units
Supply
Current
(1)
I
DD1
V
= 3V ± 10%
DD
4.19 MHz (PCON=3H) crystal oscillator
– 1.3 3.0 mA
C1 = C2 = 22 pF
I
DD2
Idle mode; VDD = 3 V ± 10%
0.4 1.0
4.19 MHz (PCON=3H) crystal oscillator
C1 = C2 = 22 pF
(2)
V
I
DD3
= 3 V ± 10%
DD
– 15 30 µA
32 kHz crystal oscillator
(2)
I
DD4
Idle mode; V
= 3 V ± 10%
DD
5 15
32 kHz crystal oscillator
I
DD5
Stop mode; VDD = 3 V ± 10%
SCMOD=0000B,
0.5 3
XTin=0V
Stop mode; VDD = 3 V ± 10%
NOTES:
SCMOD=0100B 0.2 2
1. Current in the following circuits are not included; on-chip pull-up resistors, internal LCD voltage dividing resistors,
voltage doubler, and output port drive currents.
2. Data includes power consumption for subsystem clock oscillation.
3. When the system clock control register, SCMOD, is set to 1001B, main system clock oscillation stops and the
subsystem clock is used.
13-4
Page 12

S3C7295/P7295 ELECTRICAL DATA
Table 13-3. Main System Clock Oscillator Characteristics
(TA = – 40 °C to + 85 °C, VDD = 2.2 V to 3.4 V)
Oscillator Clock
Configuration
Ceramic
Xin Xout
Oscillator
C1 C2
Crystal
Xin Xout
Oscillator
C1 C2
External
Xin Xout
Clock
Parameter Test Condition Min Typ Max Units
Oscillation frequency
(1)
Stabilization time
(2)
Stabilization occurs
– 0.4 – 4.19 MHz
– – 4 ms
when VDD is equal to
the minimum
oscillator voltage
range; VDD = 3.0 V
Oscillation frequency
(1)
Stabilization time
(2)
Xin input frequency
VDD = 3.0 V
(1)
– 0.4 – 4.19 MHz
– – 10 ms
– 0.4 – 4.19 MHz
Xin input high and low
– 83.3 – 1250 ns
level width (tXH, tXL)
RC
Xin Xout
Frequency
VDD = 3 V
0.4 – 1.5 MHz
Oscillator
R
NOTES:
1. Oscillation frequency and X
2. Stabilization time is the interval required for oscillator stabilization after a power-on occurs, or when stop mode is
terminated.
input frequency data are for oscillator characteristics only.
in
13-5
Page 13

ELECTRICAL DATA S3C7295/P7295
Table 13-4. Recommended Oscillator Constants
(TA = – 40 °C to + 85 °C, VDD = 2.2 V to 3.4 V)
Manufacturer Series
Number
TDK
FCRM5
FCRMC5
CCRMC3
NOTES:
1. Please specify normal oscillator frequency.
2. On-chip C: 30pF built in.
3. On-chip C: 38pF built in.
Frequency Range Load Cap (pF) Oscillator Voltage
(1)
3.58 MHz–4.2 MHz 33 33 2.2 3.4 Leaded Type
3.58 MHz–4.2 MHz
3.58 MHz–4.2 MHz
Table 13-5. Subsystem Clock Oscillator Characteristics
(TA = – 40 °C to + 85 °C, V
Oscillator Clock
= 2.2 V to 3.4 V)
DD
Parameter Test Condition Min Typ Max Units
Configuration
Crystal
XTin XTout
Oscillation frequency
Oscillator
Range (V)
C1 C2 MIN MAX
(2) (2)
(3) (3)
(1)
– 32 32.768 35 kHz
2.2 3.4 On-chip C
2.2 3.4 On-chip C
Remarks
Leaded Type
SMD Type
C1 C2
External
XTin XTout
Stabilization time
(2)
XTin input frequency
VDD = 2.2 V to 3.4 V
(1)
– 1.0 3 s
– 32 – 100 kHz
Clock
XTin input high and low
level width (t
NOTES:
1. Oscillation frequency and XT
2. Stabilization time is the interval required for oscillating stabilization after a power-on occurs.
input frequency data are for oscillator characteristics only.
in
XTL
, t
XTH
)
– 5 – 15 µs
13-6
Page 14

S3C7295/P7295 ELECTRICAL DATA
Table 13-6. Input/Output Capacitance
(TA = 25 °C, V
DD
= 0 V )
Parameter Symbol Condition Min Typ Max Units
C
C
IN
OUT
f = 1 MHz; Unmeasured pins
are returned to V
SS
– – 15 pF
– – 15 pF
Input
Capacitance
Output
Capacitance
I/O Capacitance
C
IO
– – 15 pF
Table 13-7. Voltage Doubler Output
(TA = -40 °C to + 85 °C, V
= 2.2 V to 3.4 V)
DD
Parameter Symbol Condition Min Typ Max Units
Voltage Doubler
Vbias
= 2.2 V to 3.4 V
DD
–
2 V
DD
– V
V
Output
Table 13-8. A.C. Electrical Characteristics
(TA = – 40 °C to + 85 °C, V
= 2.2 V to 3.4 V)
DD
Parameter Symbol Conditions Min Typ Max Units
Instruction Cycle
(note)
Time
t
CY
V
= 2.2 V to 3.4 V
DD
0.95 – 64 µs
With subsystem clock (fxt) 114 122 125
Interrupt Input
High, Low Width
RESET Input Low
f
INTH,
f
INTL
t
RSL
INT0–INT2, INT4
10 – –
K0–K3
Input 10 – –
Width
NOTE: Unless otherwise specified, Instruction Cycle Time condition values assume a main system clock ( fx ) source.
13-7
Page 15

ELECTRICAL DATA S3C7295/P7295
CPU CLOCK
1.05 MHz 4.2 MHz
15.6 kHz
1 2 3 4 5 6 7
2.2V
SUPPLY VOLTAGE (V)
CPU CLOCK = 1/n x oscillator frequency (n = 4, 8, 64)
Main OSC frequency (Divided by 4)
Figure 13-1. Standard Operating Voltage Range
Table 13-9. RAM Data Retention Supply Voltage in Stop Mode
(TA = – 40 °C to + 85 °C)
Parameter Symbol Conditions Min Typ Max Unit
Data retention supply voltage
Data retention supply current
Release signal set time
Oscillator stabilization wait
(1)
time
NOTES:
1. During oscillator stabilization wait time, all CPU operations must be stopped to avoid instability during oscillator
start-up.
2. Use the basic timer mode register (BMOD) interval timer to delay execution of CPU instructions during the wait time.
V
DDDR
I
DDDR
t
SREL
t
WAIT
– 2.2 – 3.4 V
V
DDDR
= 2.2 V
– 0 – – µs
Released by RESET
Released by interrupt –
– 0.1 10 µA
–
17
2
/ fx
(2)
– ms
–
13-8
Page 16

S3C7295/P7295 ELECTRICAL DATA
TIMING WAVEFORMS
V
DD
RESET
t
SREL
RESET
~
~
~
~
EXECUTION OF
STOP INSTRUCTION
OPERATION
STOP MODE
DATA RETENTION MODE
V
DDDR
INTERNAL
Figure 13-2. Stop Mode Release Timing When Initiated by RESETRESET
IDLE MODE
~
~
STOP MODE
IDLE MODE
t
WAIT
NORMAL MODE
NORMAL MODE
~
V
DD
EXECUTION OF
STOP INSTRUCTION
POWER-DOWN MODE TERMINATING SIGNAL
(INTERRUPT REQUEST)
~
DATA RETENTION MODE
Figure 13-3. Stop Mode Release Timing When Initiated by Interrupt Request
V
DDDR
t
SREL
t
WAIT
13-9
Page 17

ELECTRICAL DATA S3C7295/P7295
0.8 V
0.2 V
DD
DD
MEASUREMENT
POINTS
0.8 V
0.2 V
DD
DD
Figure 13-4. A.C. Timing Measurement Points (Except for Xin and XTin)
1 / f
x
t
XL
X
in
t
XH
VDD -0.5 V
0.4 V
XT
Figure 13-5. Clock Timing Measurement at X
1 / f
xt
t
XTL
in
t
XTH
Figure 13-6. Clock Timing Measurement at XT
in
VDD - 0.5 V
0.4 V
in
13-10
Page 18

S3C7295/P7295 ELECTRICAL DATA
t
RSL
RESET
0.2 V
DD
Figure 13-7. Input Timing for RESETRESET Signal
INT0, 1, 2, 4, K0 to K3
t
INTL
0.8 V
0.2 V
DD
DD
t
INTH
Figure 13-8. Input Timing for External Interrupts
13-11
Page 19

ELECTRICAL DATA S3C7295/P7295
NOTES
13-12
Page 20

S3C7295/P7295 ELECTRICAL DATA
CHARACTERISTIC CURVES
NOTE
The characteristic values shown in the following graphs are based on actual test measurements.
They do not, however, represent guaranteed operating values.
(TA = 25 °C, fx = 4.2 MHz)
5.0
4.5
I
, CPU Clock = fx/4
4.0
3.5
3.0
(mA)
DD1
DD2
, I
DD1
I
2.5
2.0
1.5
1.0
0.5
I
, CPU Clock = fx/64
DD1
I
DD2
0
2.7 4.0 4.5 6.0
VDD (V)
Figure 13-11. I
DD1
, I
DD2
VS. V
DD
13-13
Page 21

ELECTRICAL DATA S3C7295/P7295
(TA = 25 °C, fx = 32.768 kHz)
50
45
40
35
30
(µA)
25
DD3, 4, 5
20
I
15
10
5
0
2.0
2.5
3.0 3.5 4.0
Figure 13-12. I
DD3
VDD (V)
, I
DD4
I
DD3
I
DD4
I
DD5
4.5 5.0 5.5 6.0 6.5
, I
VS. V
DD5
DD
13-14
Page 22

S3C7295/P7295 ELECTRICAL DATA
(TA = 25 °C, CPU CLOCK = fx/4)
4.5
4.0
3.5
VDD = 6.0 V
3.0
2.5
(mA)
1
DD
2.0
I
1.5
1.0
0.5
0
0.5
1.0 1. 5 2.0
2.5 3.0 3.5 4. 0 4.5
VDD = 4.5 V
Main System Clock Frequency (MHz)
Figure 13-13. I
VS. Main System Clock Frequency
DD1
(TA = 25 °C)
1.6
1.4
VDD = 6.0 V
1.2
1.0
(mA)
2
0.8
DD
I
0.6
0.4
0.2
0
0.5
1.0 1.5 2.0
2.5 3. 0 3.5 4.0 4.5
VDD = 4.5 V
Mai n System Clock Frequency (MHz)
Figure 13-13. I
VS. Main System Clock Frequency
DD2
13-15
Page 23

ELECTRICAL DATA S3C7295/P7295
(TA = 25 °C, Ports 0, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7)
–25.0
–22.5
–20.0
–17.5
–15.0
(mA)
–12.5
OH
I
–10.0
–7.5
–5.0
–2.5
VDD = 4.5 V
0
0.5
1.0 1.5 2.0
2.5 3.0 3.5 4.0 4.5 5.0
VDD = 6.0 V
5.5 6.0
VOH (V)
Figure 13–15. IOH VS. VOH (P0, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7)
13-16
Page 24

S3C7295/P7295 ELECTRICAL DATA
(TA = 25 °C, Ports 8, 9)
–25.0
–22.5
–20.0
–17.5
–15.0
(mA)
–12.5
OH
I
–10.0
–7.5
–5.0
–2.5
VDD = 4.5 V
0
0.5
1.0 1.5 2.0
2.5 3.0 3.5 4.0 4.5 5.0
VDD = 6.0 V
5.5 6.0
VOH (V)
Figure 13–16. IOH VS. VOH (P8, 9)
13-17
Page 25

ELECTRICAL DATA S3C7295/P7295
(TA = 25 °C, Ports 0, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7)
55.0
50.0
45.0
40.0
VDD = 6.0 V
35.0
(mA)
30.0
OL
I
25.0
20.0
15.0
10.0
5.0
VDD = 4.5 V
0
0.5
1.0 1.5 2.0
2.5 3.0 3.5 4.0 4.5 5.0
5.5 6.0
VOL (V)
Figure 13–17. IOL VS. VOL (P0, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7)
13-18
Page 26

S3C7295/P7295 ELECTRICAL DATA
(TA = 25 °C, Ports 8, 9)
55.0
50.0
45.0
40.0
VDD = 6.0 V
35.0
(mA)
30.0
OL
I
25.0
20.0
15.0
10.0
5.0
VDD = 4.5 V
0
0.5
1.0 1.5 2.0
2.5 3.0 3.5 4.0 4.5 5.0
5.5 6.0
VOL (V)
Figure 13–18. IOL VS. VOL (P8, 9)
13-19
Page 27

S3C7295/P7295 MECHANICAL DATA
14 MECHANICAL DATA
OVERVIEW
The S3C7295/P7295 is available in a 80-QFP-1420 package.
23.90 ± 0.30
17.90 ± 0.30
14.00 ± 0.20
#80
0.80
#1
20.00
± 0.20
80-QFP-1420C
0.35 + 0.10
0.15 MAX
(0.80)
0-8
+ 0.10
- 0.05
0.15
0.10 MAX
0.80 ± 0.20
0.05 MIN
2.65
± 0.10
3.00 MAX
0.80
± 0.20
NOTE: Dimensions are in millimeters.
Figure 14-1. 80-QFP-1420C Package Dimensions
14-1
Page 28

S3C7295/P7295 S3P7295 OTP
15 S3P7295 OTP
OVERVIEW
The S3P7295 single-chip CMOS microcontroller is the OTP (One Time Programmable) version of the S3C7295
microcontroller. It has an on-chip OTP ROM instead of masked ROM. The EPROM is accessed by serial data
format.
The S3P7295 is fully compatible with the S3C7295, both in function and in pin configuration. Because of its
simple programming requirements, the S3P7295 is ideal for use as an evaluation chip for the S3C7295.
15-1
Page 29

S3P7295 OTP S3C7295/P7295
SEG40
SEG39
SEG38
SEG37
SEG36
SEG35
SEG34
SEG33
SEG32
SEG31
SEG30
SEG29
SEG28
SEG27
SEG26
SEG25
80
79
78
77
76
75
74
73
72
71
70
69
68
67
66
65
SEG41
SEG42
SEG43
P1.3/INT4
P1.2/INT2
P1.1/INT1
P1.0/INT0
P0.3/BUZ/K3
P0.2/CLO/
SDAT / P0.1/
SCLK /P0.0/TCLO0/K0
RESETRESET / RESET
/K2
BUZ
/K1
TCLO0
VDD/VDD
VSS/VSS
Xout
Xin
VPP/TEST
XTin
XTout
CA
CB
VLC0
BIAS
COM15
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
S3P7295
(TOP VIEW)
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38 3940
64
63
62
61
60
59
58
57
56
55
54
53
52
51
50
49
48
47
46
45
44
43
42
41
SEG24
SEG23
SEG22
SEG21
SEG20
SEG19
SEG18
SEG17
SEG16
SEG15
SEG14
SEG13
SEG12
SEG11
SEG10
SEG9
SEG8
SEG7
SEG6
SEG5
SEG4
SEG3
SEG2
SEG1
COM14
COM13
COM12
COM11
Figure 15-1. S3P7295 Pin Assignments (80-QFP Package)
15-2
COM9
COM10
COM8
COM7
COM6
COM5
COM4
COM3
COM2
COM1
COM0
SEG0
Page 30

S3C7295/P7295 S3P7295 OTP
Table 15-1. Descriptions of Pins Used to Read/Write the EPROM
Main Chip During Programming
Pin Name Pin Name Pin No. I/O Function
P0.1 SDAT 10 I/O Serial data pin. Output port when reading and
input port when writing. Can be assigned as a
Input/push-pull output port.
P0.0 SCLK 11 I/O Serial clock pin. Input only pin.
TEST
VPP(TEST)
16 I Power supply pin for EPROM cell writing
(indicates that OTP enters into the writing
mode). When 12.5 V is applied, OTP is in
writing mode and when 5 V is applied, OTP is in
reading mode. (Option)
RESET RESET
VDD/V
SS
VDD/V
SS
19 I Chip initialization
12/13 I Logic power supply pin. VDD should be tied to
+5 V during programming.
Table 15-2. Comparison of S3P7295 and S3C7295 Features
Characteristic S3P7295 S3C7295
Program Memory 16 Kbyte EPROM 16 Kbyte mask ROM
Operating Voltage (VDD)
OTP Programming Mode
2.2 V to 3.4 V 2.2 V to 3.4 V
VDD = 5 V, VPP(TEST)=12.5V
Pin Configuration 80 QFP 80 QFP
EPROM Programmability User Program 1 time Programmed at the factory
OPERATING MODE CHARACTERISTICS
When 12.5 V is supplied to the VPP(TEST) pin of the S3P7295, the EPROM programming mode is entered.
The operating mode (read, write, or read protection) is selected according to the input signals to the pins listed in
Table 15–3 below.
Table 15-3. Operating Mode Selection Criteria
V
DD
V
(TEST) REG/MEM Address
PP
R/W Mode
(A15–A0)
5 V 5 V 0 0000H 1 EPROM read
12.5 V 0 0000H 0 EPROM program
12.5 V 0 0000H 1 EPROM verify
12.5 V 1 0E3FH 0 EPROM read protection
NOTE: "0" means Low level; "1" means High level.
15-3
Page 31

S3P7295 OTP S3C7295/P7295
Table 15-4. D.C. Electrical Characteristics
(T
= – 40 °C to + 85 °C, VDD = 2.2 V to 3.4 V)
A
Parameter Symbol Conditions Min Typ Max Units
V
Supply
Current (1)
IDD1
= 3V ± 10%
DD
4.19 MHz (PCON=3H) crystal oscillator
– 1.3 3.0 mA
C1 = C2 = 22 pF
IDD2
Idle mode; VDD = 3 V ± 10%
0.4 1.0
4.19 MHz (PCON=3H) crystal oscillator
C1 = C2 = 22 pF
V
IDD3 (2)
= 3 V ± 10%
DD
– 15 30 µA
32 kHz crystal oscillator
IDD4 (2)
Idle mode; V
= 3 V ± 10%
DD
5 15
32 kHz crystal oscillator
IDD5
Stop mode; VDD = 3 V ± 10%
SCMOD=0000B,
0.5 3
XTin=0V
Stop mode; VDD = 3 V ± 10%
SCMOD=0100B 0.2 2
NOTES:
1. Data includes power consumption for subsystem clock oscillation.
2. When the system clock control register, SCMOD, is set to 1001B, main system clock oscillation stops and the
subsystem clock is used.
3. Current in the following circuits are not included; on-chip pull-up resistors, internal LCD voltage dividing resistors,
voltage doubler, and output port drive currents.
CPU CLOCK
1.05 MHz 4.2 MHz
15.6 kHz
1 2 3 4 5 6 7
2.2V
SUPPLY VOLTAGE (V)
CPU CLOCK = 1/n x oscillator frequency (n = 4, 8, 64)
Main OSC frequency (Divided by 4)
Figure 15-2. Standard Operating Voltage Range
15-4
 Loading...
Loading...