Page 1
MIC834 Micrel
MIC834
Comparator with Reference
Advance Information
General Description
The MIC834 is a micropower, precision voltage comparator
with an on-chip voltage reference.
The threshold is adjusted by the choice of two external
resistors. Voltage detection threshold is accurate to 1%.
Supply current is extremely low (1.5µA, typical), making it
ideal for portable applications.
The MIC834 is supplied in Micrel’s IttyBitty™ 5-lead SOT-235 package.
Ordering Information
Part Number Marking Accuracy Temperature Range Package
MIC834BM5 B12 1% –40°C to +85°C SOT-23-5
Features
• Optimized for PDAs, cellular telephones, pagers,
and other battery-powered devices
• Input and output can be pulled up to 6V
regardless of supply voltage
• High ±1% voltage threshold accuracy
• Built in hysteresis for noise suppression
• Extremely low 1.5µA typical supply current
• Immune to brief input transients
• 5-lead SOT-23 package
Applications
•PDAs
• Pagers
• Cordless phones
• Consumer electronics
• Embedded controllers
• Personal electronics
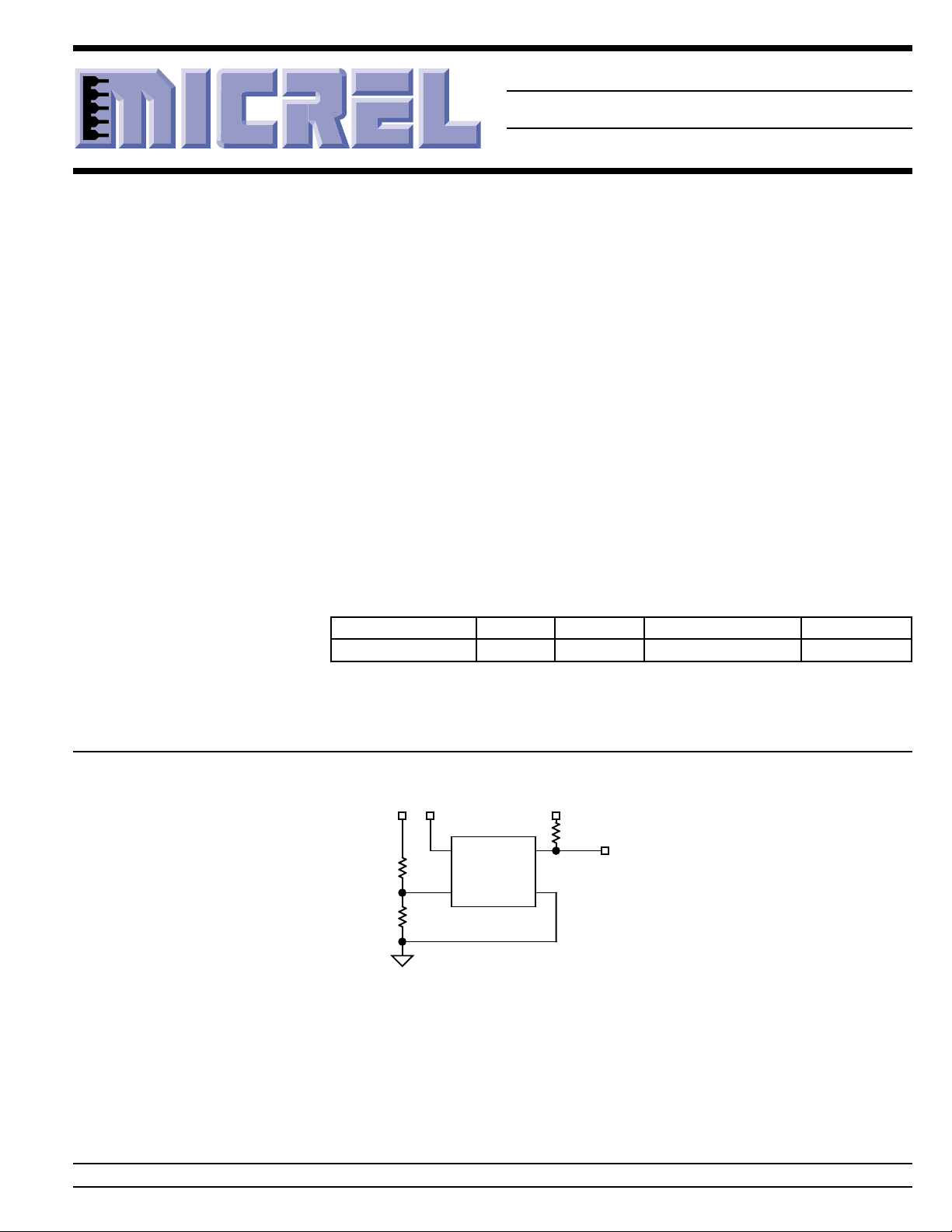
Typical Application
V
V
IN
DD
MIC834
R1
R2
IttyBitty™ is a trademark of Micrel, Inc.
Micrel, Inc. • 1849 Fortune Drive • San Jose, CA 95131 • USA • tel + 1 (408) 944-0800 • fax + 1 (408) 944-0970 • http://www.micrel.com
5
INP
April 2000 1 MIC834
OUTVDD
GND
V
PULL-UP
4
21
R
PU
V
V
V
1.5V ≤ V
V
OUT
= 1.24V
REF
= 6V
INP(max)
PULL-UP(max)
DD
= 6V
≤ 5.5V
Page 2
MIC834 Micrel
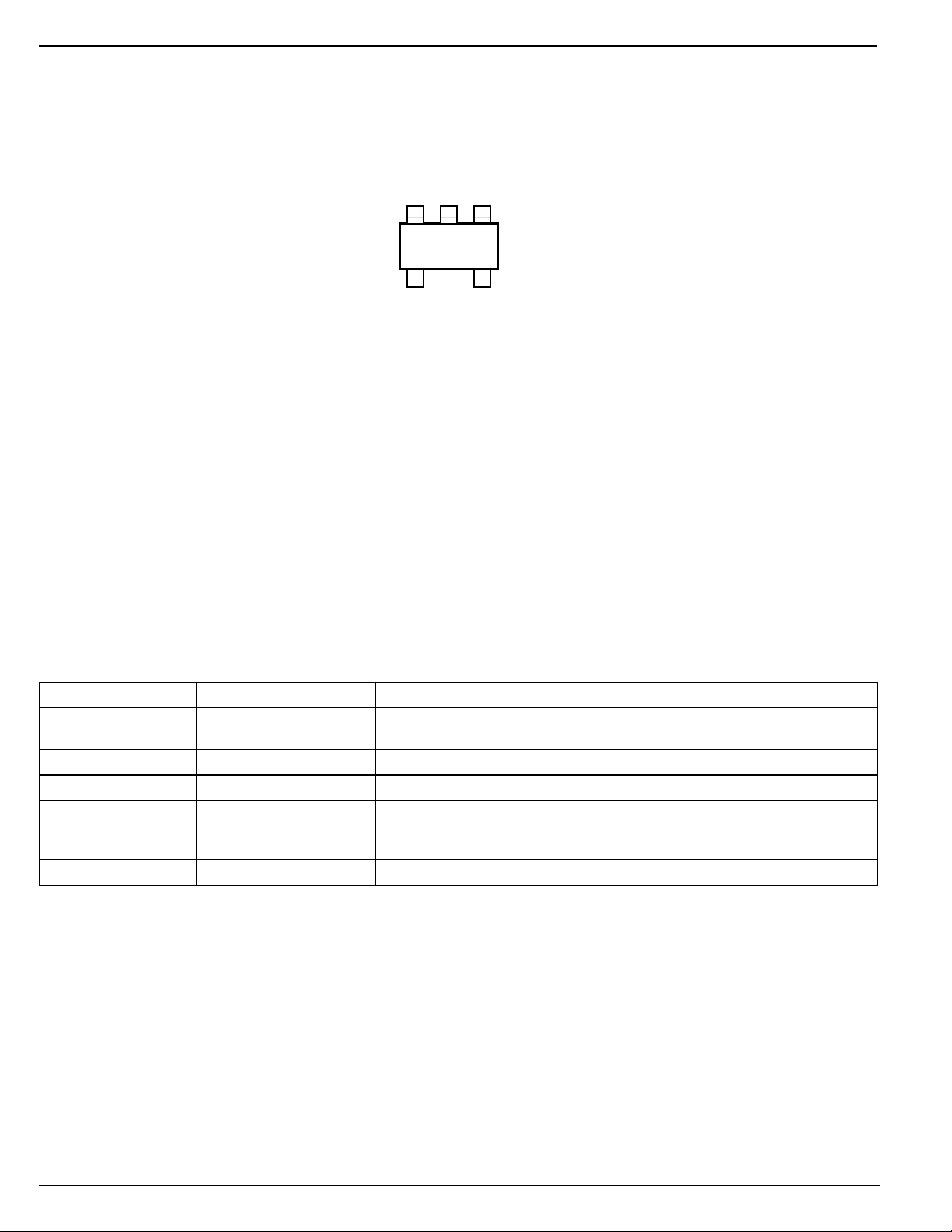
Pin Configuration
GND
2
INP
13
VDDOUT
NC
45
SOT-23-5 (M5)
Pin Description
Pin Number Pin Name Pin Function
1 INP Input: Analog input to the comparator. When V
2 GND Ground
3 NC No Connect
4 OUT Output: Active-high, open-drain output. This output is de-asserted when
5 VDD Power Supply (Input): Independent supply input for internal circuitry.
asserted to a logic-high level output.
V
INP<VREF
V
INP>VREF+VHYST.
, indicating a low voltage input. The output is asserted when
INP>VREF+VHYST
, V
OUT
is
MIC834 2 April 2000
Page 3
MIC834 Micrel
Absolute Maximum Ratings (Note 1)
Supply Voltage (V
Input Voltage (V
Output Current (I
Storage Temperature (TS) ....................... –65°C to +150°C
ESD Rating, Note 3 ......................................................2kV
) ..................................... –0.3V to +7V
DD
) ......................................................+7V
INP
).................................................20mA
OUT
Operating Ratings (Note 2)
Supply Voltage (V
Input Voltage (V
Ambient Temperature Range (T
Junction Temperature (TJ) ....................... Internally Limited
Package Thermal Resistance (θ
) .................................. +1.5V to +5.5V
DD
) ......................................... –0.3V to 6V
INP
) .............–40°C to +85°C
A
) ......................260°C/W
JA
Electrical Characteristics
1.5V ≤ VDD ≤ 5.5V; TA = +25°C, bold values indicate –40°C ≤ TA ≤ +85°C; unless noted
Symbol Parameter Condition Min Typ Max Units
I
DD
I
INP
V
REF
V
HYST
t
D
V
OUT
Note 1. Exceeding the absolute maximum rating may damage the device.
Note 2. The device is not guaranteed to function outside its operating rating.
Note 3. Devices are ESD sensitive. Handling precautions recommended. Human body model, 1.5k in series with 100pF.
Note 4. V
Note 5. VDD operating range is 1.5V to 5.5V. Output is guaranteed to be held low down to VDD = 1.2V.
Supply Current output not asserted 1.5 3 µA
Input Leakage Current 0.005 10 nA
Reference Voltage 1.228 1.240 1.252 V
Hysteresis Voltage, Note 4 10 23 35 mV
Propagation Delay V
Output Voltage-Low, Note 5 OUT de-asserted, I
= V
HTH
REF
+ V
HYST
.
= 1.352V to 1.128V 12 µs
INP
V
= 1.143V to 1.367V 8 µs
INP
= 1.6mA, VDD ≥ 1.6V 0.05 0.3 V
SINK
OUT de-asserted, I
= 100µA, VDD ≥ 1.2V, 0.005 0.4 V
SINK
Functional Diagram
V
HTH
V
V
IN
REF
(Note A)
0V
V
PULL-UP
V
OUT
0V
Note A. VIN here represents the attenuated input voltage, as applied to the INP pin; i.e., V
Note B. Brief transients are ignored by the MIC834. See “Applications Information.”
Note B
Note B
t
D
INP
t
D
.
April 2000 3 MIC834
Page 4

MIC834 Micrel
Block Diagram
V
V
IN
INP
TH
1
1.24V
Bandgap
Reference
2
GND
DD
VDD
5
High-Voltage
Detect
MIC834
OUT
4
Functional Description
The MIC834 monitors the input voltage and detects when it
is higher than a programmed level (plus V
tion asserts the active-high output. An external pull-up resistor is used to produce a logic-one output. When the input
voltage falls below the programmed threshold (V
the output stage is on.
Voltage Low Output
The voltage-low output (OUT) is an active-high, open-drain
output which sinks current when the MIC834 detects a low
input voltage.
). This condi-
HYST
INP<VREF
Trip Points
Input voltage is monitored by a comparator via a voltage
divider network. The divided voltage is compared to an
internal reference voltage. When the voltage at the input pin
INP exceeds the internal reference voltage (plus V
output is pulled high by an external resistor.
),
V
is typically 23mV, and is added to the programmed
HYST
threshold voltage for positive-going inputs. Decreasing inputs trip at the user-programmed threshold voltage.
The tolerance of the switching threshold on the falling edge
is equal to the tolerance of just the voltage reference. The
tolerance of the switching threshold on the rising edge is
equal to the tolerance of the voltage reference
tolerance of the hysteresis voltage.
HYST
plus
), the
the
MIC834 4 April 2000
Page 5

MIC834 Micrel
V
R1
IN
5
MIC834
OUTVDD
470k
V
4
OUT
Applications Information
Output
Since the MIC834 output is an open-drain MOSFET, most
applications will require a pull-up resistor. The value of the
INP
resistor should not be too large or leakage effects may
dominate. 470kΩ is the maximum recommended value. Note
R2
GND
21
that the output may be pulled up as high as 6V regardless of
the IC’s supply voltage. See “Electrical Characteristics.”
Programming the Threshold
The voltage threshold is calculated using:
R1 R2
+
VV
=
IN(lo) REF
R2
where:
V 1.240V
=
REF
In order to provide the additional criteria needed to solve for
the resistor values, the resistors can be selected such that
they have a given total value, that is, R1 + R2 = R
value such as 1MΩ for R
is a reasonable value because
TOTAL
TOTAL
. A
it draws minimum current but has no significant effect on
accuracy.
When working with large resistors, a small amount of leakage
current can cause voltage offsets that degrade system accuracy. The maximum recommended total resistance from V
to ground is 3MΩ. The accuracy of the resistors can be
chosen based upon the accuracy required by the system. The
inputs may be subjected to voltages as high as 6V steadystate without adverse effects of any kind regardless of the
IC’s supply voltage. This applies even if the supply voltage is
zero. This permits the situation in which the IC’s supply is
turned off, but voltage is still present on the inputs. See
Input Transients
The MIC834 is inherently immune to very short negativegoing “glitches.” Very brief transients may exceed the V
threshold without tripping the output.
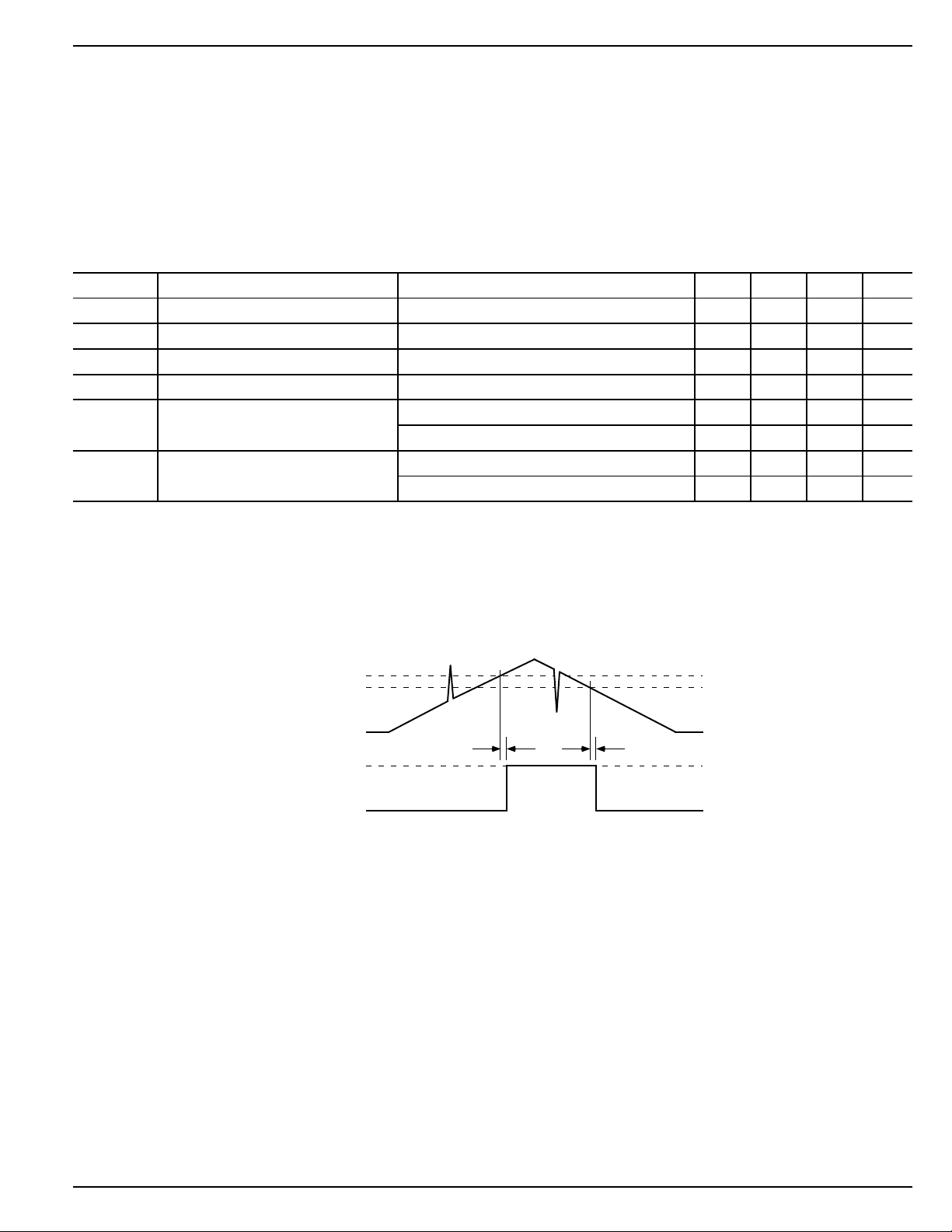
As shown in Figure 2, the narrower the transient, the deeper
the threshold overdrive that will be ignored by the MIC834.
The graph represents the typical allowable transient duration
for a given amount of threshold overdrive that will not generate an output.
IN
Figure 1. Example Circuit
Input Transient
140
120
100
80
60
40
20
0
MAX. TRANSIENT DURATION (µs)
1 10 100 1000
RESET COMP. OVERDRIVE, V
Response
REF–VLTH
(mV)
Figure 2. Input Transient Response
IN(lo)
“Electrical Characteristics.”
April 2000 5 MIC834
Page 6

MIC834 Micrel
Package Information
1.90 (0.075) REF
0.95 (0.037) REF
3.02 (0.119)
2.80 (0.110)
0.50 (0.020)
0.35 (0.014)
1.75 (0.069)
1.50 (0.059)
1.30 (0.051)
0.90 (0.035)
0.15 (0.006)
0.00 (0.000)
5-Pin SOT (M)
3.00 (0.118)
2.60 (0.102)
10°
0°
DIMENSIONS:
MM (INCH)
0.20 (0.008)
0.09 (0.004)
0.60 (0.024)
0.10 (0.004)
MIC834 6 April 2000
Page 7

MIC834 Micrel
April 2000 7 MIC834
Page 8

MIC834 Micrel
MICREL INC. 1849 FORTUNE DRIVE SAN JOSE, CA 95131 USA
TEL + 1 (408) 944-0800 FAX + 1 (408) 944-0970 WEB http://www.micrel.com
This information is believed to be accurate and reliable, however no responsibility is assumed by Micrel for its use nor for any infringement of patents or
other rights of third parties resulting from its use. No license is granted by implication or otherwise under any patent or patent right of Micrel Inc.
© 2000 Micrel Incorporated
MIC834 8 April 2000
 Loading...
Loading...