Page 1

EM73P968
4-BIT MICRO-CONTROLLER FOR LCD PRODUCT
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
EM73P968 is an advanced single chip CMOS 4-bit one time programming (OTP) micro-controller. It contains
16K-byte ROM, 2.5K nibbles RAM, 4-bit ALU, 13-level subroutine nesting, 22-stage time base, two 12-bit timer/
counters for the kernel function. EM73P968 also contains 6 interrupt sources, 1 input port, 8 bidirection ports, Max
LCD display (52x5), built-in watch-dog-timer and high speed Timer/Counter.
An analog to digital (A/D) converter having 8-bit multipler analog input and 8-bit resolution. Serial peripheral
interface (SPI).
EM73P968 has plentiful operating modes (SLOW, IDLE, STOP) intended to reduce the power consumption.
FEATURES
Operation voltage : 2.2V ~ 6V.
Clock source : Dual clock system. Low-frequency oscillator is Crystal or RC oscillator (32K Hz,
Instruction set : 107 powerful instructions.
Instruction cycle time : Up to 2us for 4 MHz (high speed clock).
ROM capacity : 16K x 8 bits.
RAM capacity : 2.5K x 4 bits.
Input port : 1 port, P0(0..3), IDLE/STOP releasing function are available by mask option.
Output port : 9 pins (P17.0, P30, P31), P17.0, P30, P31 are shared with LCD pins.
Bidirection port : 9 ports (P1, P2, P4, P5, P6, P7, P8, P11, P15). IDLE/STOP releasing function are
12-bit timer/counter : Two 12-bit timer/counters are programmable for timer, event counter and pulse width
A/D converter : An analog to digital (A/D) converter having 8-bit multipler analog input and 8-bit
SPI : Serial peripheral interface.
Built-in watch-dog-timer : It is available by mask option.
Built-in time base counter : 22 stages.
Built-in high Speed Timer/Counter : Could be timer.
Subrountine nesting : Up to 13 levels.
Interrupt : External . . . . . 2 input interrupt sources.
LCD driver : 52 X 5 dots, 1/3 bias, 1/4 or 1/5 duty by mask option.
Power saving function : SLOW, IDLE, STOP operation mode.
Package type : Chip form.
Preliminary
connect an external resistor) by mask option and high-frequency oscillator is RC
(Connect an external resistor) or Crystall oscillator.
122 µs for 32768 Hz (low speed clock with frequency Double)
available by mask option for P8(0..3), P5 and P6 have high current sink.
measurement.
resolution.
Internal . . . . . . 2 Timer overflow interrupts, 1 time base interrupt.
1 high speed counter overflow interrupt.
QFP 128 pin.
APPLICATIONS
EM73P968 is suitable for application in family applicance, consumer products, hand held games, calculator and
the toy controller.
* This specification are subject to be changed without notice.
8.14.2001
1
Page 2
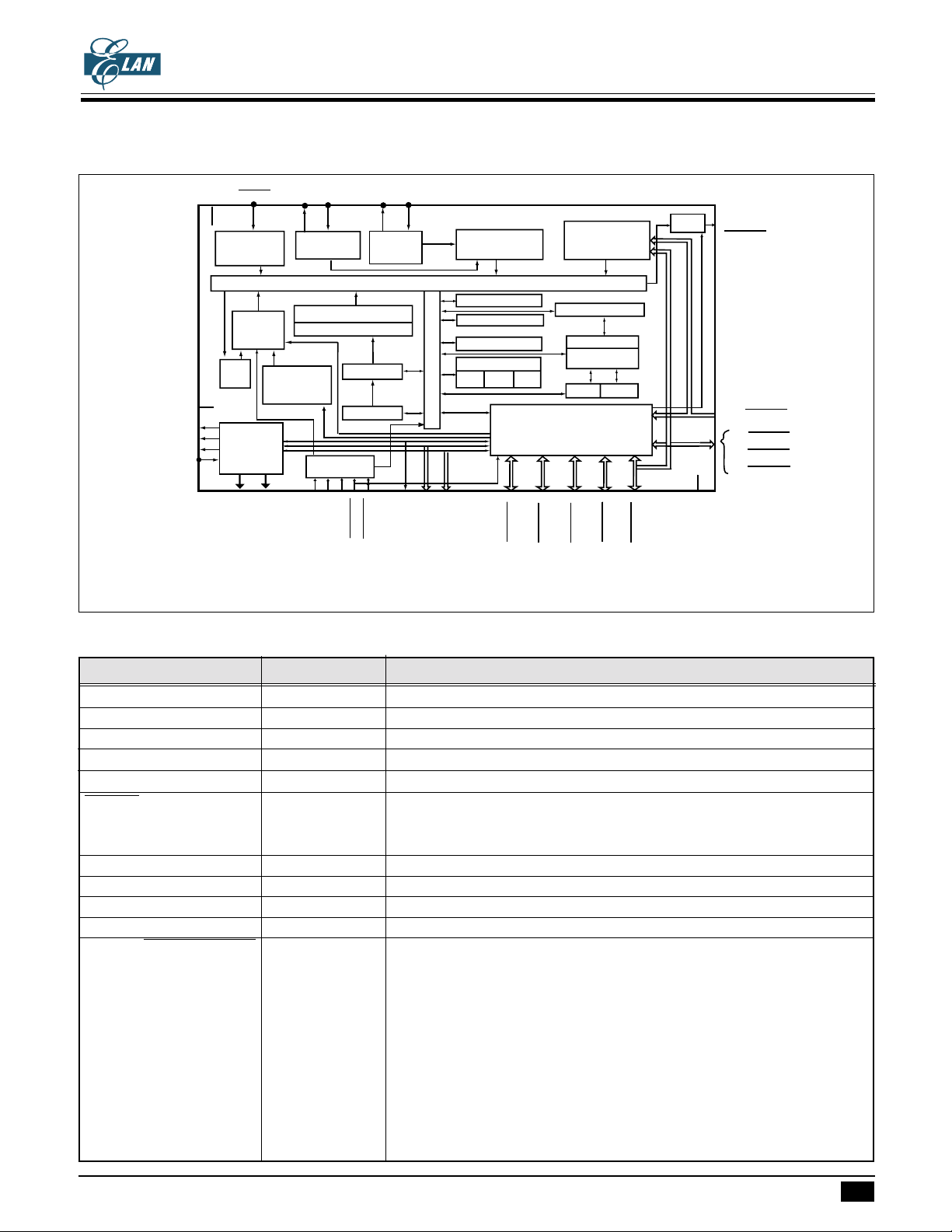
FUNCTION BLOCK DIAGRAM
EM73P968
4-BIT MICRO-CONTROLLER FOR LCD PRODUCT
Preliminary
TEST
V
RLC
LXIN
LXOUT
Clock
Generator
(slow)
System Control
Data Bus
ROM
PC
P17.0/COM4
P30/SEG(44~47)
(AIN 0~3)P6/WAKEUP
(AIN 4~7)P7/WAKEUP
Timing
Generator
Data pointer
ACC
ALU
Flag
ZCS
P31/SEG(48~51)
P1/WAKEUP
Stack pointer
HR
I/O Control
P11/WAKEUP
Sleep Mode
Control
Stack
RAM
LR
P15.2/WAKEUP
P15.3/WAKEUP
P8/WAKEUP
SPI
VSS
P15.0/P15.1/
WAKEUP
P0/WAKEUP
/WAKEUP
P2
/WAKEUP
P4
/WAKEUP
P5
Generator
(TA,TB)
XINXOUT
Clock
Instruction Decoder
Instruction Register
ADC
Vref
VAD
VADSS
RESET
VDD
Reset
Control
Interrupt
Control
Time
Timer/Counter
Base
V1
V2
V3
LCD
SEG0~SEG43
COM0~COM3
PIN DESCRIPTIONS
Symbol Pin-type Function
V
DD
V
SS
Vref ADC power (+)
V
AD
V
ADSS
RESET RESET-A System reset input signal, low active
XIN/RC
OSC OSC-A/OSC-H1 Crystal/RC clock source connecting pin
XOUT OSC-A Crystal connecting pin
LXIN OSC-B/OSC-H2 Crystal/RC connecting pin for low speed clock source
LXOUT OSC-B Crystal connecting pin for low speed clock source
P0(0..3)/WAKEUP(0..3) INPUT-K 4-bit input port with IDLE/STOP releasing function
Power supply (+)
Power supply (-)
ADC power (+)
ADC power (-)
mask option : none
pull-up
P0.0/ACLK : address counter clock for programming OTP.
P0.1/PGMB : program data to OTP cells for programming OTP.
P0.2/OEB : data output enable for programming OTP.
P0.3/DCLK : data in/out clock signal for programming OTP.
mask option 1 : wakeup disable
wakeup enable
mask option 2 : low current pull up
normal current pull up
high current pull up
none
* This specification are subject to be changed without notice.
8.14.2001
2
Page 3
EM73P968
4-BIT MICRO-CONTROLLER FOR LCD PRODUCT
Preliminary
PIN DESCRIPTIONS
Symbol Pin-type Function
P8.0(INT1)/WAKEUPA I/O-R1 2-bit bidirection I/O port with external interrupt sources input and IDLE/
/DIN STOP releasing function
P8.2(INT0)/WAKEUPC P8.0/DIN : data input for programming OTP
mask option 1 : wakeup disable
wakeup enable
mask option 2 : low current push pull
normal current push pull
high current push pull
none
P8.1(TRGB)/WAKEUPB, I/O-R1 2-bit bidirection I/O port with timer/counter A, B external input and
/DOUT IDLE/STOP releasing function
P8.3(TRGA)/WAKEUPD P8.1/DOUT : data output for programming OTP
mask option 1 : wakeup disable
wakeup enable
mask option 2 : low current push pull
normal current push pull
high current push pull
none
P6(0..3)/WAKEUP(20..23) I/O-R1 8-bit bidirection I/O port with IDLE/STOP releasing function.
AIN (0..3) Share with A/D analog input pin.
P7(0..3)/WAKEUP(24..27) mask option 1 : wakeup disable
AIN (4..7) wakeup enable
mask option 2 : low current push pull
normal current push pull
high current push pull
none
P4(0..3)/WAKEUP(12,15) I/O-R1 4-bit bidirection I/O port with IDLE/STOP releasing function
mask option 1 : wakeup disable
wakeup enable
mask option 2 : low current push pull
normal current push pull
high current push pull
none
* This specification are subject to be changed without notice.
8.14.2001
3
Page 4
EM73P968
4-BIT MICRO-CONTROLLER FOR LCD PRODUCT
Preliminary
PIN DESCRIPTIONS
Symbol Pin-type Function
P1(0..3)/WAKEUP(4..7) I/O-R1 18-bit bidirection I/O pins with IDLE/STOP releasing function
P2(0..3)/WAKEUP(8..11) mask option 1 : wakeup disable
P5(0..3)/WAKEUP(16..19) wakeup enable
P11(0..3)/ mask option 2 : low current push pull
WAKEUP(28..31) normal current push pull
P15.2/P15.3/ high current push pull
WAKEUP(34,35) none
P15.0/WAKEUP(32) 1-bit bidirection I/O pins with IDLE/STOP releasing function. Share with
SPI data input/output pin.
mask option 1 : wakeup disable
wakeup enable
mask option 2 : low current push pull
normal current push pull
high current push pull
none
P15.1/WAKEUP(33) I/O-R1 1-bit bidirection I/O pins with IDLE/STOP releasing function.Share with
SPI clock input/output pin.
mask option 1 : wakeup disable
wakeup enable
mask option 2 : low current push pull
normal current push pull
high current push pull
none
P17.0/COM4 Output-L 1-bit output pin with LCD common pin
mask option : LCD common pin
Push pull
Open-drain
P30(0..3)/SEG(51..48) Output-M 8-bit output pins are shared with LCD segment pin
P31(0..3)/SEG(47..44) mask option : LCD segment pin
Low current push pull
Normal current push pull
High current push pull
Open drain
COM0~COM3 LCD common output pins
SEG0~SEG43 LCD segment output pins
VRLC, V1, V2, V3 -- LCD bias voltage pins
TEST -- Test pin must be connected to VSS
VPP : high voltage (12V) power source for programming OTP
* This specification are subject to be changed without notice.
8.14.2001
4
Page 5
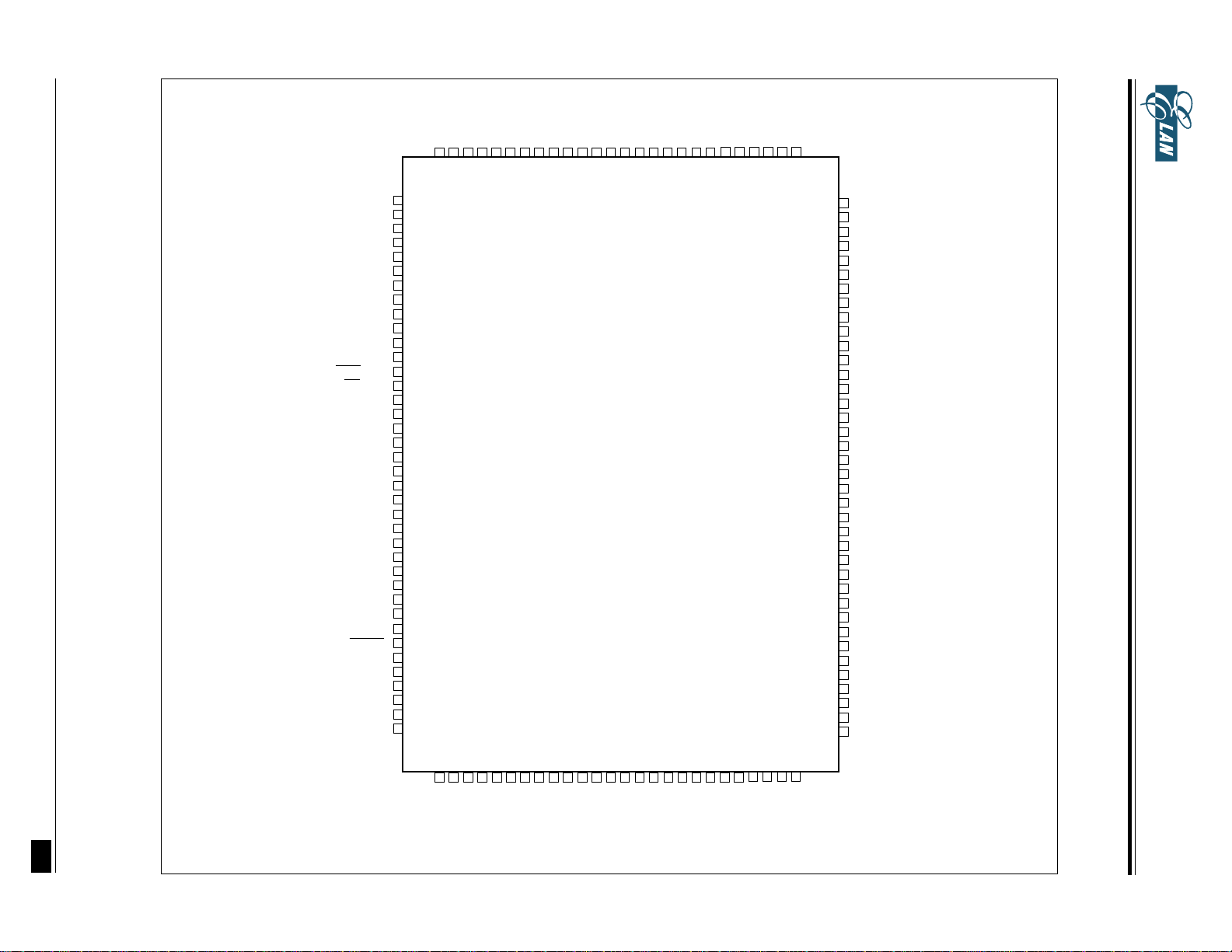
* This specification are subject to be changed without notice.
SEG40
SEG41
127
128
SEG38
SEG39
125
126
SEG36
SEG37
123
124
SEG34
SEG35
121
122
SEG32
SEG33
119
120
SEG30
SEG31
117
118
SEG29
SEG28
115
116
SEG26
SEG27
113
114
SEG24
SEG25
111
112
NC
110
NC
109
NC
108
NC
107
NC
106
NC
105
NC
104
PIN ASSIGNMENT
SEG23
103
8.14.2001
SEG42
SEG43
SEG44
SEG45
SEG46
SEG47
SEG48
SEG49
SEG50
SEG51
VPP
ACLK/P0.0
PGM/P0.1
OE/P0.2
DCLK/P0.3
P1.0
P1.1
P1.2
P1.3
P2.0
P2.1
P2.2
P2.3
P4.0
P4.1
P4.2
P4.3
P5.0
P5.1
P5.2
P5.3
RESET
P6.0
P6.1
P6.2
P6.3
P7.0
P7.1
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
49
48
47
46
45
44
43
42
41
40
39
XIN
VSS
P8.3
P8.2
DOUT/P8.1
DIN/P8.0
VAD
VREF
VADSS
P7.3
P7.2
EM73P968
QFP 128
55
54
53
52
51
50
VR1
LXOUT
VDDC
LXIN
VSS
XOUT
VDDI
62
61
60
59
58
57
56
NC
NC
NC
VR2
NC
NC
63
NC
64
NC
102
101
100
SEG22
SEG21
SEG20
99
SEG19
98
SEG18
97
SEG17
SEG16
96
95
SEG15
94
SEG14
93
SEG13
92
SEG12
91
SEG11
90
SEG10
89
SEG9
88
SEG8
87
SEG7
86
SEG6
85
SEG5
84
SEG4
83
SEG3
82
SEG2
81
SEG1
80
SEG0
79
COM4
78
COM3
77
COM2
76
COM1
75
COM0
74
P15.3
73
P15.2
72
P15.1
71
P15.0
70
P11.3
69
P11.2
68
P11.1
67
P11.0
66
VRLC
65
VR3
Preliminary
4-BIT MICRO-CONTROLLER FOR LCD PRODUCT
EM73P968
5
Page 6
4-BIT MICRO-CONTROLLER FOR LCD PRODUCT
Preliminary
FUNCTION DESCRIPTIONS
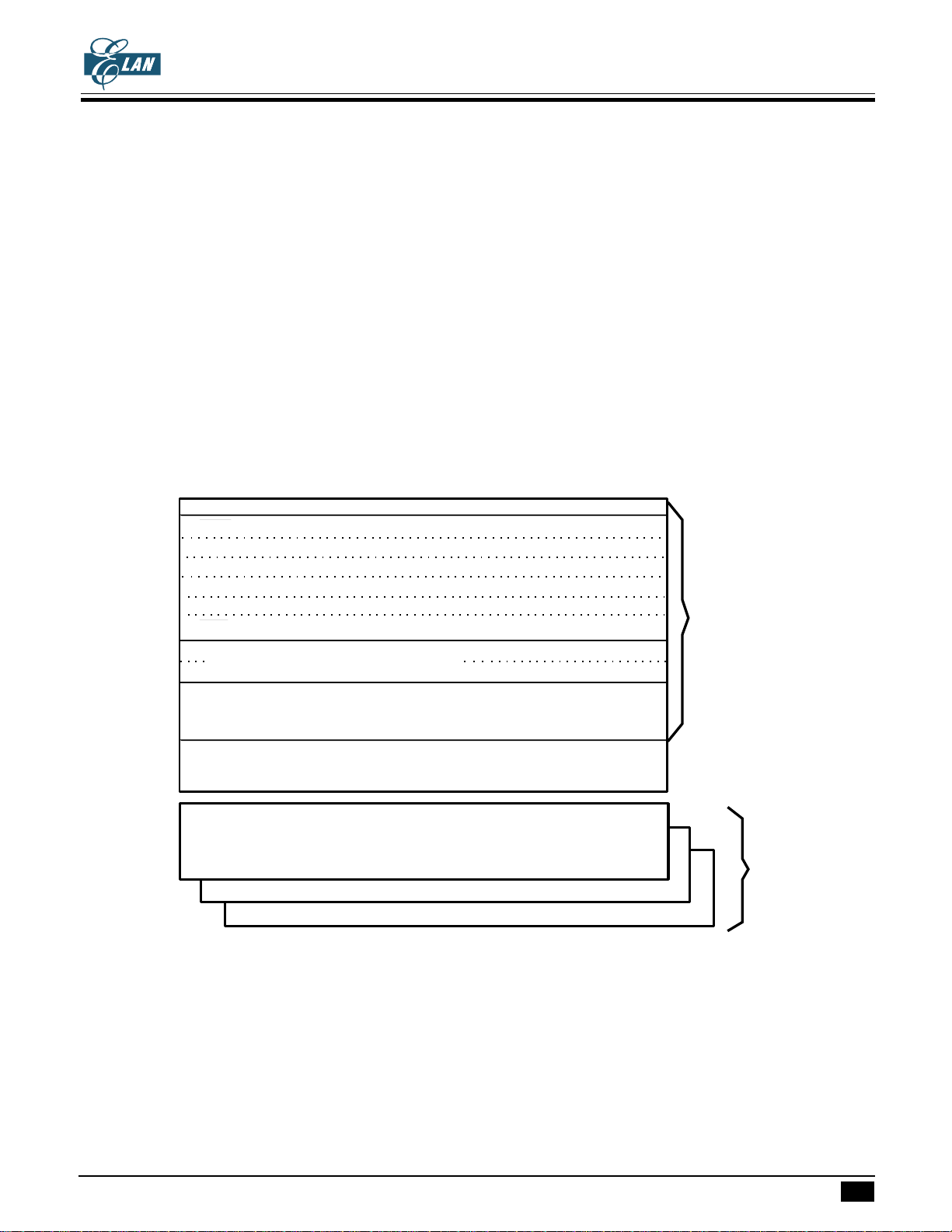
PROGRAM ROM ( 16K X 8 bits )
16 K x 8 bits program ROM contains user's program and some fixed data.
The basic structure of the program ROM may be categorized into 5 partitions.
1. Address 0000h : Reset start address.
2. Address 0002h - 000Ch : 6 kinds of interrupt service routine entry addresses.
3. Address 000Eh - 0086h : SCALL subroutine entry address, only available at 000Eh, 0016h, 001Eh, 0026h, 002Eh,
0036h, 003Eh, 0046h, 004Eh, 0056h, 005Eh, 0066h, 006Eh, 0076h, 007Eh, 0086h.
4. Address 0000h - 07FFh : LCALL subroutine entry address.
5. Address 0000h - 1FFFh : Except used as above function, the other region can be used as user's program and
data region.
address Bank 0 :
EM73P968
0000h
0002h
0004h
0006h
0008h
000Ah
000Ch
000Eh
0086h
.
.
.
07FFh
0800h
0FFFh
1000h
1FFFh
Reset start address
INT0 ; interrupt service routine entry address
HTCI / ADI
TRGA
TRGB
TBI
INT1
SCALL, subroutine call entry address
Bank 1
Bank 2
Bank 3
Subroutine call entry address
designated by [LCALL a]
instruction
Data table for
[LDAX],[LDAXI]
instruction
* This specification are subject to be changed without notice.
8.14.2001
6
Page 7
EM73P968
4-BIT MICRO-CONTROLLER FOR LCD PRODUCT
User's program and fixed data are stored in the program ROM. User's program is executed using the PC value
Preliminary
to fetch an instruction code.
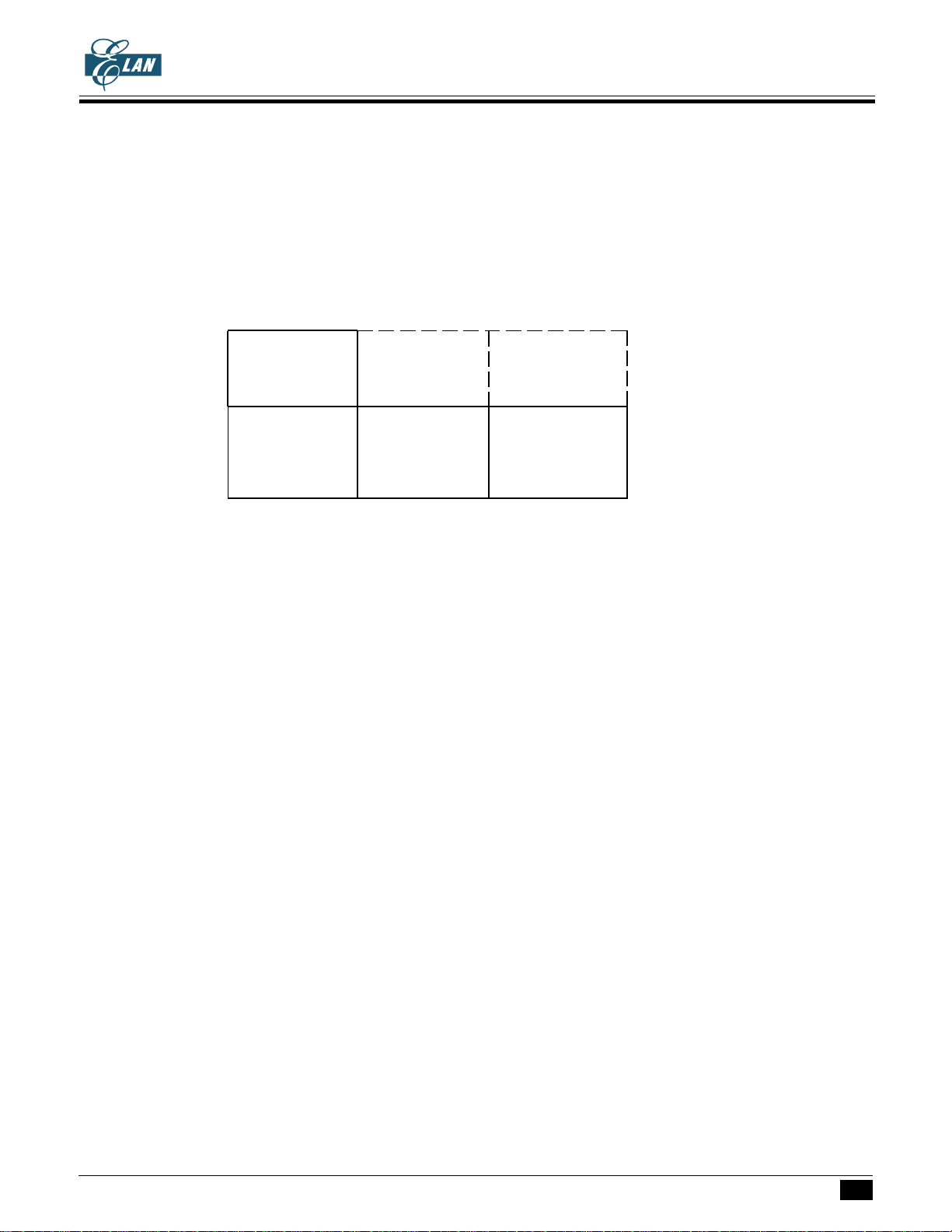
The 16Kx8 bits program ROM can be divided into 4 banks. There are 4Kx8 bits per bank.
The program ROM bank is selected by P3(1..0). The program counter is a 13-bit binary counter. The PC and
P3 are initialized to "0" during reset.
When P3(1..0)=00B, the bank0 and bank1 of program ROM will be selected. P3(1..0)=01B, the bank0 and
bank2 will be selected.
P3=xx00B
Address P3=xx11B P3=xx01B P3=xx10B
0000h
:
: Bank0 Bank0 Bank0
0FFFh
1000h
:
: Bank1 Bank2 Bank3
1FFFh
PROGRAM EXAMPLE:
BANK 0
START: :
:
:
LDIA #00H ; set program ROM to bank1
OUTA P3
B XA1
:
XA : :
:
LDIA #01H ; set program ROM to bank2
OUTA P3
B XB1
:
XB : :
:
LDIA #02H ; set program ROM to bank3
OUTA P3
B XC1
:
XC : :
:
BXD
XD : :
:
:
; - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -
BANK 1
XA1 : :
:
BXA
:
XA2 : :
* This specification are subject to be changed without notice.
8.14.2001
7
Page 8

EM73P968
4-BIT MICRO-CONTROLLER FOR LCD PRODUCT
B XA2
Preliminary
:
; - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -
BANK 2
XB1 : :
:
BXB
:
XB2 : :
B XB2
:
; - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -
BANK 3
XC1 : :
:
BXC
:
XC2 : :
B XC2
Fixed data can be read out by table-look-up instruction. Table-look-up instruction is requires the Data point
(DP) to indicate the ROM address in obtaining the ROM code data (Except bank 0) :
LDAX Acc
LDAXI Acc
←←
← ROM[DP]
←←
←←
← ROM[DP]
←←
L
,DP+1
H
DP is a 12-bit data register that stores the program ROM address as pointer for the ROM code data.
User has to initially load ROM address into DP with instructions "STADPL", and "STADPM, STADPH",
then to obtain the lower nibble of ROM code data by instruction "LDAX" and higher nibble by instruction
"LDAXI".
PROGRAM EXAMPLE: Read out the ROM code of address 1777h by table-look-up instruction.
LDIA #07h;
STADPL ; [DP]
STADPM ; [DP]
STADPH ; [DP]
:
LDL #00h;
LDH #03h;
LDAX ; ACC ← 6h
STAMI ; RAM[30] ← 6h
LDAXI ; ACC ← 5h
STAM ; RAM[31] ← 5h
;
ORG 1777h
DATA 56h;
← 07h
L
← 07h
M
← 07h, Load DP=777h
H
DATA RAM ( 2548-nibble )
A total 2548 - nibble data RAM is available from address 000 to 9FFh
Data RAM includes the zero page region, stacks and data areas.
* This specification are subject to be changed without notice.
8.14.2001
8
Page 9

EM73P968
4-BIT MICRO-CONTROLLER FOR LCD PRODUCT
Preliminary
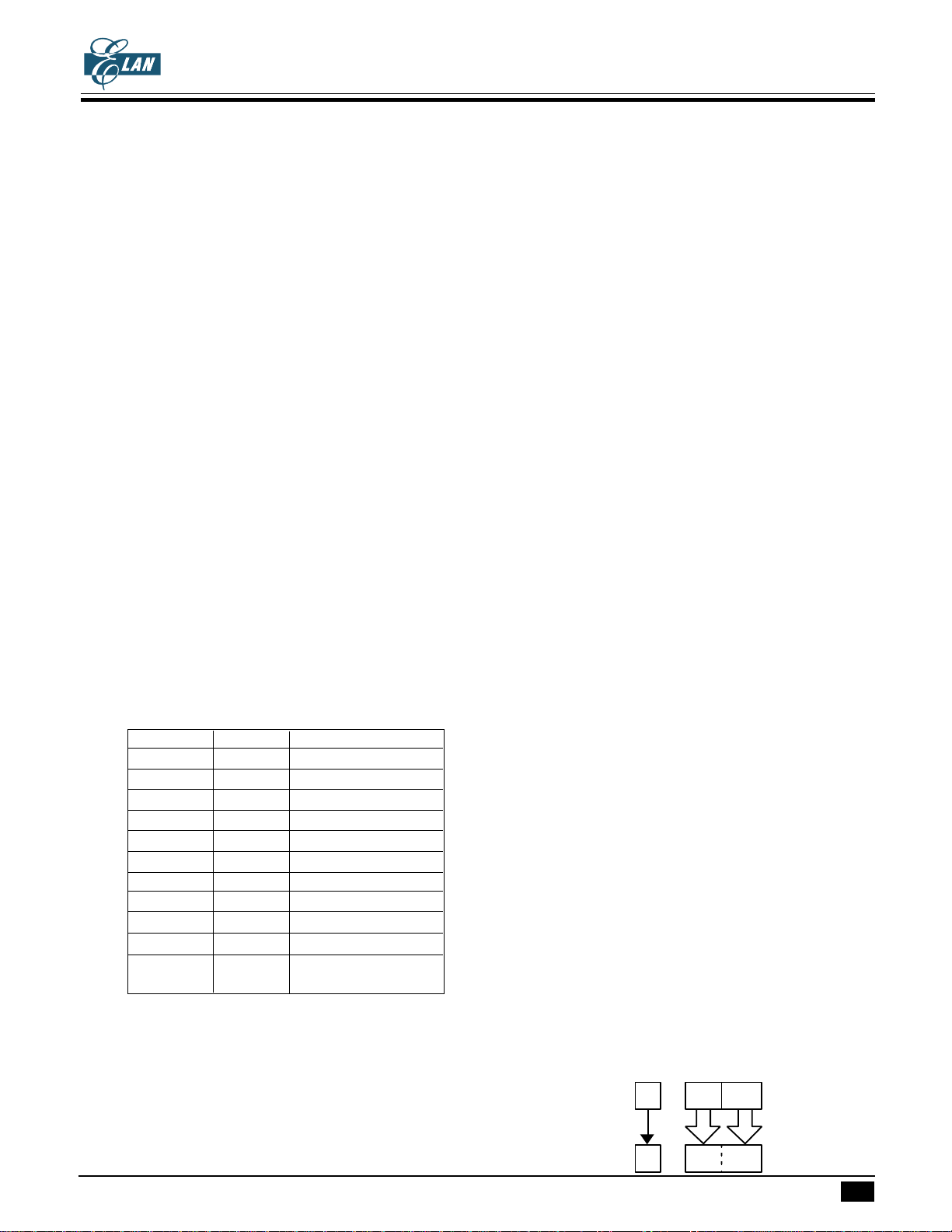
Bank 0 Address 0 1 2 3 4 56789ABCDEF
P9=0000B 000-00Fh ZERO PAGE
010-01Fh
020-02Fh COM0
030-03Fh COM1
040-04Fh COM2
050-05Fh COM3
060-06Fh COM4
070-07Fh
080-08Fh
090-09Fh
0A0-0AFh
0B0-0BFh
0C0-0CFh Level 0 Level 1 Level 2 Level 3
0D0-0DFh Level 4 Level 5 Level 6 Level 7
0E0-0EFh Level 8 Level 8 Level 10 Level 11
0F0-0FFh Level 12 TCA TCB DP SPW
Bank 1
P9=0001B 100-10Fh
:
:
1F0-1FFh
Bank 2
P9=0010B 200-20Fh
:
:
2F0-2FFh
Bank 3
P9=0011B 300-30Fh
:
:
3F0-3FFh
Bank 9
P9=1001B 900-90Fh
:
:
9F0-9FFh
:
:
:
:
:
:
:
* This specification are subject to be changed without notice.
8.14.2001
9
Page 10
EM73P968
4-BIT MICRO-CONTROLLER FOR LCD PRODUCT
Preliminary
ZERO- PAGE:
From 000h to 00Fh is the zero-page location. It is used as the zero-page address mode pointer for the
instruction of "STD #k,y; ADD #k,y; CLR y,b; CMP k,y".
PROGRAM EXAMPLE: To write immediate data "07h" to RAM [03] and to clear bit 2 of RAM [0Eh].
STD #07h, 03h ; RAM[03] ← 07h
CLR 0Eh,2 ; RAM[0Eh]
STACK:
There are 13 - level (maximum) stack levels that user can use for subroutine (including interrupt and CALL).
User can assign any level be the starting stack by providing the level number to stack pointer (SP).
When an instruction (CALL or interrupt) is invoked, before enter the subroutine, the previous PC address
is saved into the stack until returned from those subroutines, the PC value is restored by the data saved in stack.
DATA AREA:
← 0
2
Except the area used by user's application, the whole RAM can be used as data area for storing and loading
general data.
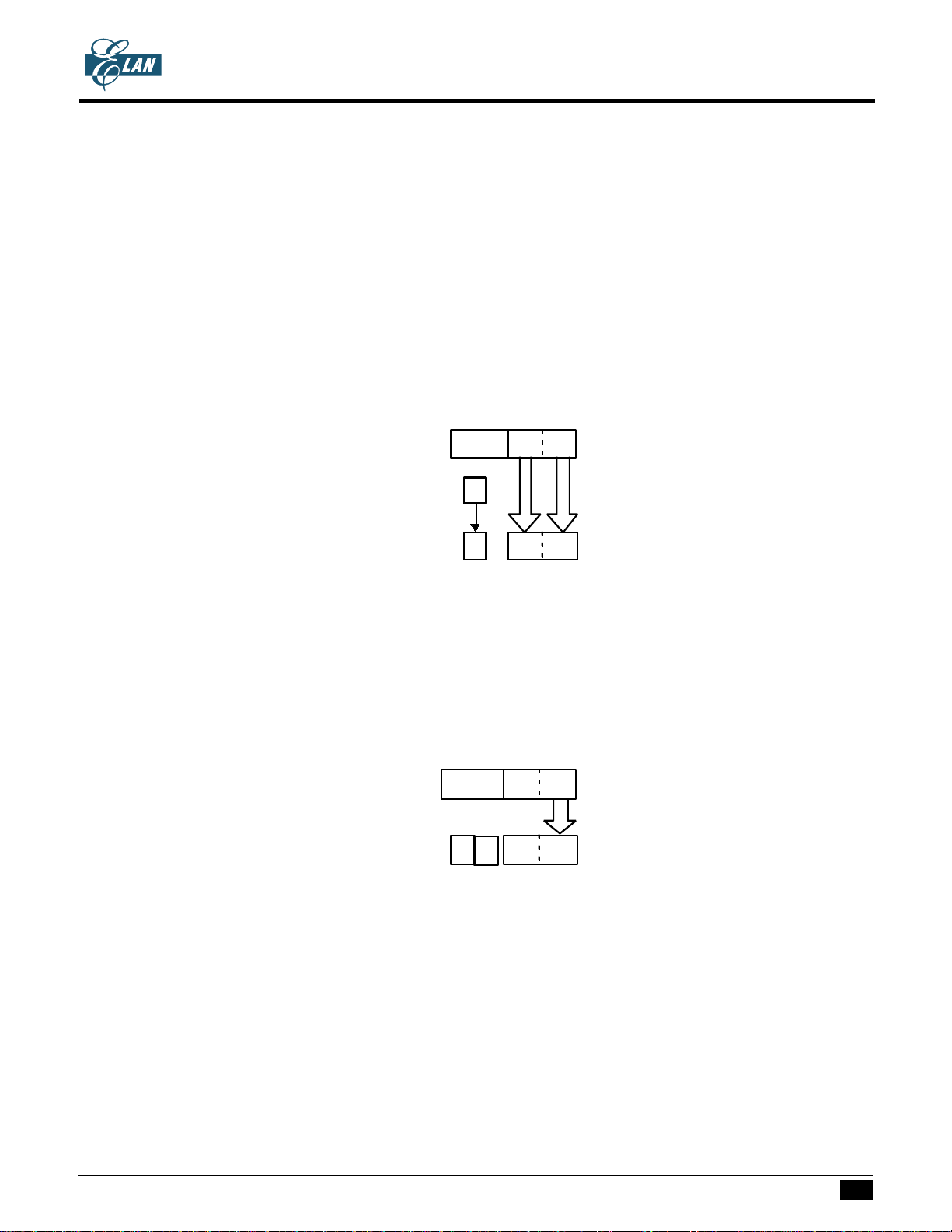
ADDRESSING MODE
The 2548 nibble data memory consists of ten banks (bank 0 ~ bank 9). There are 244x4 bits (address
000h~0F3h) in bank 0 and 2304x4 bits (address 100h ~ 9FF) in bank 1 ~ bank 9.
The bank is selected by P9.
P9(3..0) Initial value : 0 0 0 0
RBK Bank RAM address(hex)
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 ~ 0 F F
0 0 0 1 1 1 0 0 ~ 1 F F
0 0 1 0 2 2 0 0 ~ 2 F F
0 0 1 1 3 3 0 0 ~ 3 F F
0 1 0 0 4 4 0 0 ~ 4 F F
0 1 0 1 5 5 0 0 ~ 5 F F
0 1 1 0 6 6 0 0 ~ 6 F F
0 1 1 1 7 7 0 0 ~ 7 F F
1 0 0 0 8 8 0 0 ~ 8 F F
1 0 0 1 9 9 0 0 ~ 9 F F
1 0 1 0~ 0 0 0 0 ~ 0 F F
1 1 1 1
The Data Memory consists of three Address mode, namely -
(1) Indirect addressing mode:
The address in the bank is specified by the HL registers.
* This specification are subject to be changed without notice.
P9(3,2,1,0)
RAM address
HR LR
8.14.2001
10
Page 11
4-BIT MICRO-CONTROLLER FOR LCD PRODUCT
Preliminary
PROGRAM EXAMPLE: Load the data of RAM address "143h" to RAM address "032h".
OUT #0001B,P9 ; RAM bank1
LDL #3h ; LR← 3
LDH # 4h ; HR ← 4
LDAM ; Acc← RAM[134h]
OUT #0000B,P9 ; RAM bank0
LDL #2h ; LR← 2
LDH # 3h ; HR ← 3
STAM ; RAM[023h]← Acc
(2) Direct addressing mode:
The address in the bank is directly specified by 8 bits code of the second byte in the instruction field.
instruction field
xxxxxxxx
P9(3..0)
EM73P968
RAM address
PROGRAM EXAMPLE: Load the data of RAM address "143h" to RAM address "023h".
OUT #0001B,P9
LDA 43h ; Acc← RAM[143h]
OUT #0001B,P9
STA 23h ; RAM[023h]← Acc
(3) Zero-page addressing mode:
The zero-page is in the bank 0 (address 000h~00Fh). The address is the lower 4 bits code of the second byte
in the instruction field.
xxxxxxxx
instruction field
yyyy
RAM address
PROGRAM EXAMPLE: Write immediate "0Fh" to RAM address "005h".
STD #0Fh, 05h ; RAM[05h]← 0Fh
00 00
0000
yyyy
* This specification are subject to be changed without notice.
8.14.2001
11
Page 12

EM73P968
4-BIT MICRO-CONTROLLER FOR LCD PRODUCT
PROGRAM COUNTER (16K ROM)
Preliminary
Program counter ( PC ) is composed by a 13-bit counter, which indicates the next executed address for the
instruction of program ROM instruction.
For BRANCH and CALL instructions, PC is changed by instruction indicating. PC only can indicate the address
from 0000h-1FFFh. The bank number is decided by P3.
(1) Branch instruction:
SBR a
Object code: 00aa aaaa
Condition: SF=1; PC ← PC
( branch condition satisified )
12-6.a
PC Hold original PC value+1 aaaaaa
SF=0; PC← PC +1( branch condition not satisified )
PC Original PC value + 1
LBR a
Object code: 1100 aaaa aaaa aaaa
Condition: SF=1; PC ← PC
( branch condition satisified )
12.a
Hold
PC
a a a a a a aaaaaa
+2
SF=0; PC← PC +2( branch condition not satisified )
PC Original PC value + 2
SLBR a
Object code: 0101 0101 1100 aaaa aaaa aaaa (a:1000h~1FFFh)
0101 0111 1100 aaaa aaaa aaaa (a:0000h~0FFFh)
Condition: SF=1; PC ← a ( branch condition satisified )
PCaaaaaaaaaaaa a
SF=0 ; PC ← PC + 3 ( branch condition not satisified )
PC Original PC value + 3
(2) Subroutine instruction:
SCALL a
Object code: 1110 nnnn
Condition : PC ← a ; a=8n+6 ; n=1..Fh ; a=86h, n=0
PC00000aaaaa aaa
LCALL a
Object code: 0100 0aaa aaaa aaaa
Condition: PC ← a
* This specification are subject to be changed without notice.
8.14.2001
12
Page 13

EM73P968
4-BIT MICRO-CONTROLLER FOR LCD PRODUCT
Preliminary
PC00aaaaaaaaaa a
RET
Object code: 0100 1111
Condition: PC ← STACK[SP]; SP + 1
PC The return address stored in stack
RT I
Object code: 0100 1101
Condition : FLAG. PC ← STACK[SP]; EI ← 1; SP + 1
PC The return address stored in stack
(3) Interrupt acceptance operation:
When an interrupt is accepted, the original PC is pushed into stack and interrupt vector will be loaded into
PC. The interrupt vectors are as follows :
INT0 (External interrupt from P8.2)
PC00000000000 1 0
TRGH (High speed counter interrupt)
PC000000000010 0
TRGA (Timer A overflow interrupt)
PC0000000000 1 1 0
TRGB (Time B overflow interrupt)
PC00000000 0 1 0 0 0
TBI (Time base interrupt)
PC00000000 0 1 0 1 0
INT1 (External interrupt from P8.0)
PC00000000 0 1 1 0 0
(4) Reset operation:
PC00000000000 0 0
* This specification are subject to be changed without notice.
8.14.2001
13
Page 14

EM73P968
4-BIT MICRO-CONTROLLER FOR LCD PRODUCT
Preliminary
(5) Other operations:
For 1-byte instruction execution: PC + 1
For 2-byte instruction execution: PC + 2
For 3-byte instruction execution: PC + 3
ACCUMULATOR
Accumulator(ACC) is a 4-bit data register for temporary data storage. For the arithematic, logic and
comparative opertion.., ACC plays a role which holds the source data and result.
FLAGS
There are three kinds of flag, CF (Carry flag), ZF (Zero flag) and SF (Status flag), these three 1-bit flags
are included by the arithematic, logic and comparative .... operation.
All flags will be put into stack when an interrupt subroutine is served, and the flags will be restored after
RTI instruction is executed.
(1) Carry Flag ( CF )
The carry flag is affected by the following operations:
a. Addition : CF as a carry out indicator, under addition operation, when a carry-out occures, the CF is "1",
likewise, if the operation has no carry-out, CF is "0".
b. Subtraction : CF as a borrow-in indicator, under subtraction operation, when a borrow occures, the CF
is "0", likewise, if there is no borrow-in, the CF is "1".
c. Comparision : CF as a borrow-in indicator for Comparision operation as in the subtraction operation.
d. Rotation : CF shifts into the empty bit of accumulator for the rotation and holds the shift out data after
rotation.
e. CF test instruction : Under TFCFC instruction, the CF content is sent into SF then clear itself as "0".
Under TTSFC instruction, the CF content is sent into SF then set itself as "1".
(2) Zero Flag ( ZF )
ZF is affected by the result of ALU, if the ALU operation generates a "0" result, the ZF is "1", likewise, the
ZF is "0".
(3) Status Flag ( SF )
The SF is affected by instruction operation and system status.
a. SF is initiated to "1" for reset condition.
b. Branch instruction is decided by SF, when SF=1, branch condition is satisified, likewise, when SF = 0,
branch condition is unsatisified.
* This specification are subject to be changed without notice.
8.14.2001
14
Page 15
EM73P968
4-BIT MICRO-CONTROLLER FOR LCD PRODUCT
PROGRAM EXAMPLE:
Preliminary
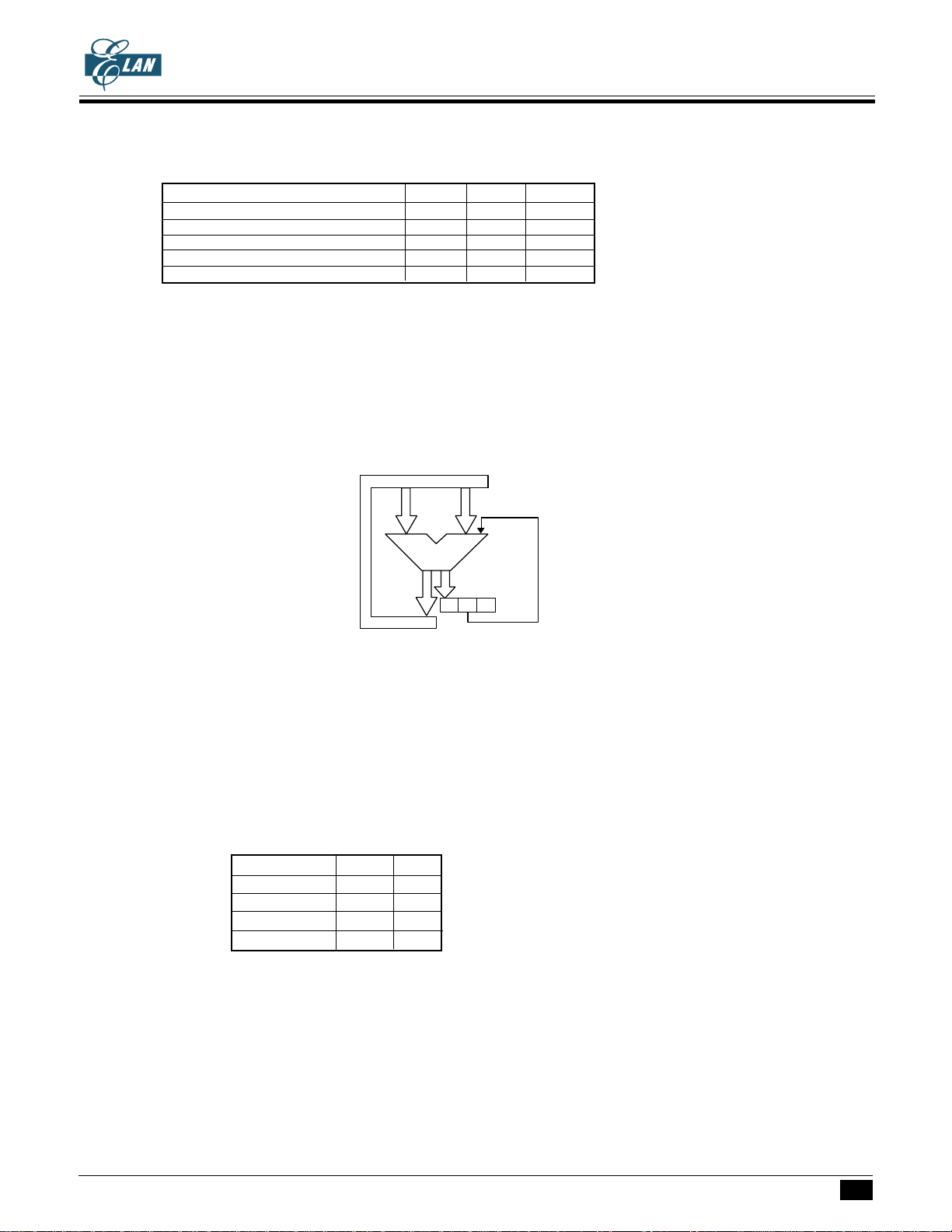
Check following arithematic operation for CF, ZF, SF
CF ZF SF
LDIA #00h; - 1 1
LDIA #03h; - 0 1
ADDA #05h; - 0 1
ADDA #0Dh; - 0 0
ADDA #0Eh; - 0 0
ALU
The arithematic operation of 4-bit data is performed in ALU unit. There are 2 flags that can be affected by
the result of ALU operation, ZF and SF. The operation of ALU is affected by CF only.
ALU STRUCTURE
ALU supported user arithematic operation functions, including Addition, Subtraction and Rotaion.
DATA BUS
ALU
ZF CF SF
ALU FUNCTION
(1) Addition:
ALU supports addition function with instructions ADDAM, ADCAM, ADDM #k, ADD #k,y .... .
The addition operation affects CF and ZF. Under addition operation, if the result is "0", ZF will be "1",
otherwise, ZF will be "0". When the addition operation has a carry-out, CF will be "1", otherwise, CF will
be "0".
EXAMPLE:
Operation Carry Zero
3+4=7 0 0
7+F=6 1 0
0+0=0 0 1
8+8=0 1 1
(2) Subtraction:
ALU supports subtraction function with instructions SUBM #k, SUBA #k, SBCAM, DECM... . The
subtraction operation affects CF and ZF. Under subtraction operation, if the result is negative, CF will
be "0", and a borrow out, otherwise, if the result is positive, CF will be "1". For ZF, if the result of subtraction
operation is "0", the ZF is "1", likewise, ZF is "1".
* This specification are subject to be changed without notice.
8.14.2001
15
Page 16
EM73P968
4-BIT MICRO-CONTROLLER FOR LCD PRODUCT
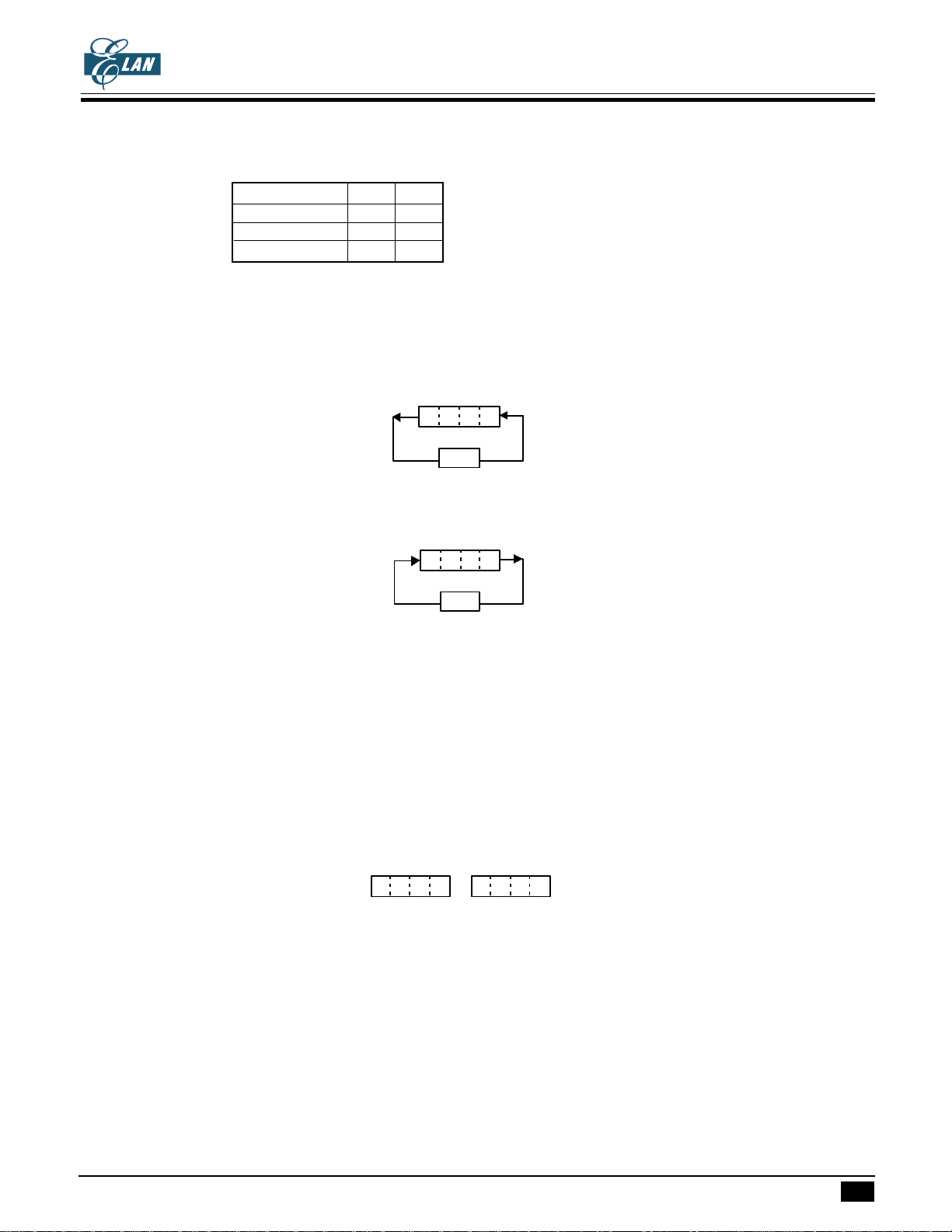
EXAMPLE:
Preliminary
Operation Carry Zero
8-4=4 1 0
7-F= -8(1000) 0 0
9-9=0 1 1
(3) Rotation:
Two types of rotation operation are available, one is rotation left, the other is rotation right.
RLCA instruction rotates Acc value counter-clockwise, shift the CF value into the LSB bit of Acc and hold
the shift out data in CF.
MSB LSB
ACC
CF
RRCA instruction operation rotates Acc value clockwise, shift the CF value into the MSB bit of Acc and
hold the shift out data in CF.
MSB LSB
ACC
CF
PROGRAM EXAMPLE: To rotate Acc clockwise (right) and shift a "1" into the MSB bit of Acc.
TTCFS; CF ← 1
RRCA; rotate Acc right and shift CF=1 into MSB.
HL REGISTER
HL register are two 4-bit registers, they are used as a pair of pointer for the RAM memoryaddress. They are
used as also 2 independent temporary 4-bit data registers. For certain instructions, L register can be a pointer
to indicate the pin number (Port4 only).
HL REGISTER STRUCTURE
3 2 1 0
H REGISTER
3 2 1 0
L REGISTER
HL REGISTER FUNCTION
(1) HL register is used as a temporary register for instructions : LDL #k, LDH #k, THA, THL, INCL, DECL,
EXAL, EXAH.
PROGRAM EXAMPLE:
LDL #05h;
LDH #0Dh;
Load immediate data "5h" into L register, "0Dh" into H register.
(2) HL register is used as a pointer for the address of RAM memory for instructions : LDAM, STAM, STAMI ..
PROGRAM EXAMPLE: Store immediate data "#0Ah" into RAM of address 35h.
* This specification are subject to be changed without notice.
8.14.2001
16
Page 17

EM73P968
4-BIT MICRO-CONTROLLER FOR LCD PRODUCT
Preliminary
LDL #5h;
LDH #3h;
STDMI #0Ah; RAM[35] ← Ah
(3) L register is used as a pointer to indicate the bit of I/O port for instructions : SELP, CLPL, TFPL,
(When LR = 0 indicate P4.0)
PROGRAM EXAMPLE: To set bit 0 of Port4 to "1"
LDL #00h;
SEPL ; P4.0 ← 1
STACK POINTER (SP)
Stack pointer is a 4-bit register that stores the present stack level number.
Before using stack, user must set the SP value first, CPU will not initiate the SP value after reset condition.
When a new subroutine is received, the SP is decreased by one automatically, likewise, if returning from a
subroutine, the SP is increased by one.
The data transfer between ACC and SP is done with instructions "LDASP" and "STASP".
DATA POINTER (DP)
Data pointer is a 12-bit register that stores the ROM address can indicating the ROM code data specified
by user (refer to data ROM).
CLOCK AND TIMING GENERATOR
The clock generator is supported by a dual clock system. The high-frequency oscillator is internal oscillator.
The low-frequency oscillator may be sourced from crystal, the working frequency is 32 KHz.
CLOCK GENERATOR STRUCTURE
There are two clock generator for system clock control unit, P14 is the status register that hold the CPU
status. P16, P19 and P22 are the command register for system clock mode control.
Mask option for choose Crystal or RC oscillator
XIN
XOUT
LXIN
LXOUT
High-frequency
generator
Low-frequency
generator
fc
System clock
fs
mode control
P14
P16
P19
P22
Mask option for choose Crystal or RC oscillator
LXIN/XIN
LXOUT/XOUT
Crystal connection or
(
Res=100K for high frequency osc
System control
Res
RC connection
/ Res=1M for slow frequency osc)
* This specification are subject to be changed without notice.
LXIN/XIN
LXOUT/XOUT
8.14.2001
17
Page 18

EM73P968
4-BIT MICRO-CONTROLLER FOR LCD PRODUCT
SYSTEM CLOCK MODE CONTROL
Preliminary
The system clock mode controller can start or stop the high-frequency and low-frequency clock oscillator
and switch between the basic clocks. EM73P968 has four operation modes (NORMAL, SLOW, IDLE and
STOP operation modes).
RESET
operation
Reset
Reset
I/O wakeup
Reset
Reset release
STOP
operation
mode
NORMAL
operation
mode
Command
Reset
(P16)
Command
High osc : stopped
Low osc : stopped
High osc : oscillating
Low osc : oscillating
Command
(P22)
(P22)
Command
Command
(P19)
I/O or internal timer wakeup
(P16)
SLOW
operation
mode
High osc : stopped
Low osc : oscillating
IDLE
(CPU
stops)
High osc : stopped
Low osc : oscillating
Operation Mode Oscillator System Clock Available function One instruction cycle
NORMAL High, Low frequency High frequency clock LCD, SPI, A/D, HTC. 8 / fc
SLOW Low frequency Low frequency clock LCD 4 / fs
IDLE Low frequency CPU stops LCD -
STOP None CPU stops All disable -
NORMAL OPERATION MODE
The 4-bit µc is in the NORMAL operation mode when the CPU is reseted. This mode is dual clock system
(high-frequency and low-frequency clocks oscillating). It can be changed to SLOW or STOP operation
mode with the command register (P22 or P16).
LCD display and high speed timer/counter are available for the NORMAL operation mode.
SLOW OPERATION MODE
The SLOW operation mode is single clock system (low-frequency clock oscillating). It can be changed to
the NORMAL operation mode with the command register (P22), STOP operation mode with P16 and IDEL
operation mode with P19.
LCD display is available for the SLOW operation mode.
* This specification are subject to be changed without notice.
8.14.2001
18
Page 19

EM73P968
4-BIT MICRO-CONTROLLER FOR LCD PRODUCT
P22 3210 Initial value : 0000
Preliminary
* SOM
SOM Low-frequency
000 2^3/LXIN RC solw to normal
001 2^4/LXIN RC solw to normal
010 2^11/LXIN X'tal slow to normal
011 2^12/LXIN X'tal slow to normal
1** normal to slow
P14
Port14 is the status register for CPU. P14.0 (CPU status) and. P14.2 (wakeup status) will be set to "1" when
CPU is wake-up by internal timer. P14.2 will be cleared to "0" when user out data to P14. INT2_S is low, the
program address "0004H" is the interrupt entry address of HTCI. INT2_S is high, the program address
"0004H" is the interrupt entry address of ADI.
32 10 Initial value : *000
INT2_S WKS SPI_F CPUS
SPI_F SPI_Flag CPUS CPU status
0 SPI register is empty 0 NORMAL operation mode
1 SPI register is full 1 SLOW operation
WKS Wakeup status
0 Wakeup not by internal timer
1 Wakeup by internal timer
IDLE OPERATION MODE
The IDLE operation mode suspends all CPU functions except the low-frequency clock oscillation and the
LCD driver. It keeps the internal status with low power consumption without stopping the slow clock
oscillator and LCD display.
LCD display is available for the IDLE operation mode. The IDLE operation mode will be wakeup and return
to the SLOW operation mode by the internal timing generator or I/O pins (P0(0..3)/WAKEUP 0..3, P1(0..3)/
WAKEUP 4..7, P2(0..3)/WAKEUP 8..11, P4(0..3)/WAKEUP 12..15, P5(0..3)/WAKEUP 16..19, P6(0..
3)/WAKEUP 20..23, P7(0..3)/WAKEUP 24..27, P8(0..3)/WAKEUPA..D, P11(0..3)/WAKEUP 28..31,
and P15(0..3)/WAKEUP 32..35).
P19 32 10 Initial value : 0000
IDME SIDR
IDME Enable IDLE mode SIDR Select IDLE releasing condition
0 1 Enable IDLE mode 0 0 P0,P1,P2,P4,P5,P6,P7,P8,P11,P15 pin input
* * no function 0 1 P0,P1,P2,P4,P5,P6,P7,P8,P11,P15 pin input and 1 sec
signal
1 0 P0,P1,P2,P4,P5,P6,P7,P8,P11,P15 pin input and 0.5 sec
signal
1 1 P0,P1,P2,P4,P5,P6,P7,P8,P11,P15 pin input and 15.625
ms signal
* This specification are subject to be changed without notice.
8.14.2001
19
Page 20

4-BIT MICRO-CONTROLLER FOR LCD PRODUCT
Preliminary
STOP OPERATION MODE
The STOP operation mode suspends system operation and holds the internal status immediately before the
suspension with low power consumption. This mode will be released by reset or I/O pins (P0(0..3)/
WAKEUP 0..3, P1(0..3)/WAKEUP 4..7, P2(0..3)/WAKEUP 8..11, P4(0..3)/WAKEUP 12..15, P5(0..3)/
WAKEUP 16..19, P6(0..3)/WAKEUP 20..23, P7(0..3)/WAKEUP 24..27, P8(0..3)/WAKEUPA..D, P11
(0..3)/WAKEUP 28..31, and P15(0..3)/WAKEUP 32..35).
LCD display and high speed timer/counter with melody output are disabled in STOP mode.
Initial value : 0000 P16 3 2 1 0
SWWT Set wake up
1 0 0 2^9/XIN for RC osc.
1 1 1 2^19/XIN for Crystal osc.
*
Stop wake up time (go to NORMAL)
*
*
1 0 1 2^10/XIN for RC osc.
*
1 1 0 2^18/XIN for Crystal osc.
*
EM73P968
GENERAL PURPOSE REGISTER (P10)
P10 is a 4-bit general purpose register which can be read, written and rested by all I/O instructions.
(including : INA, INM, OUT, OUTA, OUTM, SEP, CLP, TTP, TFP)
PROGRAM EXAMPLE:
CHIP ROM16K
;--------RAM define area-----------------
DSEG
ORG 10H
HLBUF: RES 2 ; HL buffer for in terrupt
P9BUF: RES 1 ; P9 (RAM bank) buffer for interrupt
:
;----------Interrupt subroutine--------------------
CSEG
ORG 004H
LBR HTCI
:
HTCI: OUTA P10 ; save Acc to general purpose register P10
INA P9
OUT #0000B,P9 10 instruction bytes
STA P9BUF ; save RAM bank to P9BUF
EXHL HLBUF ; save HL to HLBUF
:
:
EXHL HLBUF ; restore HLBUF to HL
LDA P9BUF ; resotre P9BUF to RAM bank 10 instruction bytes
OUTA P9
INA P10 ; restore register P10 to Acc
RTI
* This specification are subject to be changed without notice.
8.14.2001
20
Page 21

EM73P968
4-BIT MICRO-CONTROLLER FOR LCD PRODUCT
Preliminary
TIME BASE INTERRUPT (TBI)
The time base can be used to generate a single fixed frequency interrupt. Eight types of frequencies can be
selected with the "P25" setting.
P25 3 2 1 0
initial value : 0000
P25 NORMAL operation mode SLOW operation mode
0 0 x x Interrupt disable Interrupt disable
0 1 0 0 Interrupt frequency LXIN / 2
0 1 0 1 Interrupt frequency LXIN / 2
0 1 1 0 Interrupt frequency LXIN / 2
0 1 1 1 Interrupt frequency LXIN / 2
1 1 0 0 Interrupt frequency LXIN / 21 Hz Reserved
1 1 0 1 Interrupt frequency LXIN / 26 Hz Interrupt frequency LXIN / 26 Hz
1 1 1 0 Interrupt frequency LXIN / 28 Hz Interrupt frequency LXIN / 28 Hz
1 1 1 1 Interrupt frequency LXIN / 2
1 0 x x Reserved Reserved
3
Hz Reserved
15
Hz Interrupt frequency LXIN / 2
5
Hz Reserved
14
Hz Interrupt frequency LXIN / 2
10
Hz Interrupt frequency LXIN / 2
14
10
15
Hz
Hz
Hz
TIMER / COUNTER (TIMERA, TIMERB)
Timer/counters support three special functions:
1. Even counter
2. Timer.
3. Pulse-width measurement.
These three functions can be executed by 2 timer/counter independently.
With timerA, the counter data is saved in timer register TAH, TAM, TAL. User can set counter initial
value and read the counter value by instruction "LDATAH(M,L)" and "STATAH(M,L)". With timer B
register is TBH, TBM, TBL and the W/R instruction are "LDATBH (M,L)" and "STATBH (M,L)".
The basic structure of timer/counter is composed by two identical counter module, these two modules can
be set initial timer or counter value to the timer registers, P28 and P29 are the command registers for timerA
and timer B, user can choose different operation modes and internal clock rates by setting these two
registers. When timer/counter overflows, it will generate a TRGA(B) interrupt request to interrupt control
unit.
12 BIT COUNTER
INTERRUPT CONTROL
TRGA request
DATA BUS
TRGB request
12 BIT COUNTER
P8.3/
TRGA
internal clock
EVENT COUNTER CONTROL
TIMER CONTROL
PULSE-WIDTH MEASUREMENT
P28
CONTROL
TMSA IPSA
P29
* This specification are subject to be changed without notice.
EVENT COUNTER CONTROL
TIMER CONTROL
PULSE-WIDTH MEASUREMENT
CONTROL
TMSB IPSB
P8.1/
TRGB
internal clock
8.14.2001
21
Page 22

EM73P968
4-BIT MICRO-CONTROLLER FOR LCD PRODUCT
Preliminary
TIMER/COUNTER CONTROL
P8.1/TRGB, P8.3/TRGA are the external timer inputs for timerB and timerA, they are used in event
counter and pulse-width measurement mode.
Timer/counter command port: P28 is the command port for timer/counterA and P29 is for the timer/
counterB.
P28, P29 3210 Initial value : 0000
TMSA(B) IPSA(B)
TMSA(B) Mode selection
0 0 Stop
0 1 Event counter mode
1 0 Timer mode
1 1 Pulse width measurement mode
IPSA Clock rate selection IPSB Clock rate selection
NORMAL mode SLOW mode NORMAL mode SLOW mode
0 0 LXIN/23 HZ Reserved 0 0 Depend on high speed timer/counter
0 1 LXIN/27 HZ LXIN/27 HZ 0 1 LXIN/25 HZ LXIN/25 HZ
1 0 LXIN/211 HZ LXIN/211 HZ 1 0 LXIN/29 HZ LXIN/29 HZ
1 1 LXIN/215 HZ LXIN/215 HZ 1 1 LXIN/213 HZ LXIN/213 HZ
TIMER/COUNTER FUNCTION
Timer/counterA,B are programmable for timer, event counter and pulse width measurement mode. Each
timer/counter can execute any of these functions independently.
EVENT COUNTER MODE
Under event counter mode, the timer/counter is increased by one at any rising edge of P8.1/TRGB for timerB
(P8.3/TRGA for timer A). When timerB (timerA) counts overflow, it will provide an interrupt request
TRGB (TRGA) to interrupt control unit.
P8.1/TRGB (P8.3/TRGA)
TimerB (TimerA) value n n+1 n+2 n+3 n+4 n+5 n+6
PROGRAM EXAMPLE: Enable timerA with P28
LDIA #0100b;
OUTA P28 ; Enable timerA with event counter mode
* This specification are subject to be changed without notice.
8.14.2001
22
Page 23

EM73P968
4-BIT MICRO-CONTROLLER FOR LCD PRODUCT
Preliminary
TIMER MODE
Under timer mode, the timer/counter is increased by one at any rising edge of internal pulse. User can choose
up to 4 types of internal pulse rate by setting IPSB for timerB (IPSA for timerA).
When timer/counter counts overflow, an interrupt request will be sent to interrupt control unit.
Internal pulse
TimerB (TimerA )value
n n+1 n+2 n+3 n+4 n+5 n+6 n+7
PROGRAM EXAMPLE: To generate TRGA interrupt request after 60 ms with system clock LXlN=32KHz
LDIA #0100B ;
EXAE ; enable mask 2
EICIL 110111b ; interrupt latch ←0, enable EI
LDIA #0Ah;
STATAL;
LDIA #00h;
STATAM;
LDIA #0Fh;
STATAH;
LDIA #1000B;
OUTA P28 ; enable timerA with internal pulse rate: LXIN/23 Hz
NOTE: The preset value of timer/counter register is calculated as following procedure.
Internal pulse rate: LXIN/2
3
; LXIN = 32KHz
The time of timer counter count one = 23 /LXIN = 8/32768=0.244ms
The number of internal pulse to get timer overflow = 60 ms/0.244ms = 245.901= 0F6h
The preset value of timer/counter register = 1000h - 0F6h = F0Ah
PULSE WIDTH MEASUREMENT MODE
Under the pulse width measurement mode, the counter is incresed at the rising edge of internal pulse during
external timer/counter input (P8.1/TRGB, P8.3/TRGA) in high level, interrupt request is generated as soon as
timer/counter count overflow.
P8.1/TRGB(P8.3/TRGA)
Internal pulse
TimerB(TimerA) value
n n+1 n+2 n+3 n+4 n+5
PROGRAM EXAMPLE: Enable timerA by pulse width measurement mode.
LDIA #1100b ;
OUTA P28 ; Enable timerA with pulse width measurement mode.
* This specification are subject to be changed without notice.
8.14.2001
23
Page 24

EM73P968
4-BIT MICRO-CONTROLLER FOR LCD PRODUCT
Preliminary
HIGH SPEED TIMER/COUNTER
EM73P968 has one 8-bit high speed timer/counter (HTC). It supports two special functions : auto load timer
and melody output. The HTC is available for the NORMAL and SLOW operation mode.
The HTC can be set initial value and send counter value to counter registers (P12 and P13), P20 is the
command port for HTC, user can choose different operation mode and different internal clockrate by setting
the port. The timer/counter increase one at the rising edge of internal pulse. The HTC can generate an overflow
interrupt (HTCI) when it overflows. The HTCI cannot be generated when the HTC is in the melody mode
or disabled.
INTERRUPT FUNCTION
Six interrupt sources are available, 2 from external interrupt sources and 4 from internal interrupt sources.
Multiple interrupts are admitted according to their priority.
Type Interrupt source Priority Interrupt Interrupt Program ROM
Latch Enable condition entry address
External External interrupt (INT0) 1 IL5 EI=1 002h
Internal HTC interrupt (HTCI) 2 IL4 EI=1, MASK3=1 004h
Internal TimerA overflow interrupt (TRGA) 3 IL3 EI=1, MASK2=1 006h
Internal TimerB overflow interrupt (TRGB) 4 IL2 EI=1, MASK1=1 008h
Internal Time base interrupt(TBI) 5 IL1 00Ah
External External interrupt(INT1) 6 IL0 EI=1, MASK0=1 00Ch
INTERRUPT STRUCTURE
MASK0 MASK1 MASK1 MASK2 MASK3
HTCI/ADI
r4
IL3
Entry address generator
IL4
Reset by system reset and program
instruction
Reset by system reset and program
instruction
Set by program instruction
INT1
r0
IL0
r1
TBI
IL1
EI
TRGB
r2
TRGA
r3
IL2
Priority checker
INT0
r5
IL5
Interrupt request Interrupt entry address
* This specification are subject to be changed without notice.
8.14.2001
24
Page 25

EM73P968
4-BIT MICRO-CONTROLLER FOR LCD PRODUCT
Interrupt controller:
Preliminary
IL0-IL5 : Interrupt latch. Hold all interrupt requests from all interrupt sources. IL's can not
be set by program, but can be reset by program or system reset, so IL can only
decide which interrupt source can be accepted.
MASK0-MASK3 : Except INT0, MASK register may permit or inhibit all interrupt sources.
EI : Enable interrupt Flip-Flop may promit or inhibit all interrupt sources, when inter-
rupt occurs, EI is auto cleared to "0", after RTI instruction is executed, EI is auto
set to "1" again.
Priority checker : Check interrupt priority when multiple interrupts occur.
INTERRUPT OPERATION
The procedure of interrupt operation:
1. Push PC and all flags to stack.
2. Set interrupt entry address into PC.
3. Set SF = 1.
4. Clear EI to inhibit other interrupts occur.
5. Clear the IL with which interrupt source has already been accepted.
6. Excute interrupt subroutine from the interrupt entry address.
7. CPU accept RTI, restore PC and flags from stack. Set EI to accept other interrupt requests.
PROGRAM EXAMPLE: To enable interrupt of "INT0, TRGA"
LDIA #0100B ;
EXAE ; set mask register "1100b"
EICIL 010111B ; enable interrupt F.F. and clear IL3 and IL5
HIGH SPEED COUNTER
EM73P968 has one high speed counter for auto load timer mode. This function is available for the NORMAL
operation mode.
P20(3,2)
XIN
P20(1,0)
8-bit binary counter
P12
P13
Overflow
Reload
Data bus
HTCI interrupt
Timer/counter B
* This specification are subject to be changed without notice.
8.14.2001
25
Page 26

EM73P968
4-BIT MICRO-CONTROLLER FOR LCD PRODUCT
Preliminary
CONTROL OF HIGH SPEED COUNTER
The high speed counter is controlled by the command registers (P20) :
P20 3 2 1 0 Initial value : 0000
MODE RATE
MODE Selection of HTC mode
0 0 Disable HTC
0 1 Auto load timer mode
1 0 Reserved
1 1 Reserved
RATE Internal pulse rate /
( Hz ) Counter start request frequency
Auto load timer mode /
Melody mode internal pulse rate
0 0 CLK / 2
0 1 CLK / 2
1 0 CLK / 2
1 1 CLK / 2
Note : CLK is high frequency.
P12 and P13 are the 8-bit binary counter registers of the HTC. P12 is lower nibble register and P13 is higher
nibble register.
"
#
$
%
P13 P12
3 2 1 0 3 2 1 0 Initial value : 0000 0000
Higher nibble register Lower nibble register
The HTC can be set initial value and send counter value to counter registers (P13 and P12), and P20 are the
command ports for HTC, user can choose different operation mode and different internal clockrate. The
timer/counter increase one at the rising edge of internal pulse. The HTC can generate an overflow interrupt
(HTCI) when it overflows. The HTCI can not be generated when the HTC is disabled.
The value of 8-bit binary up counter can be presetted by P12 and P13. The value of registers can loaded into
the HTC when the counter starts counting or occurs overflow. If user write value to the registers before the
next overflow occurs, the preset value can be changed.
The preset value will be changed when users output the different data to P12 and P13.
The count value of HTC can be read from P12 and P13. The value is unstable when user read the value during
counting. Thus, user must disable the counter before reading the value.
* This specification are subject to be changed without notice.
8.14.2001
26
Page 27

EM73P968
4-BIT MICRO-CONTROLLER FOR LCD PRODUCT
FUNCTION OF HIGH SPEED COUNTER
Preliminary
The HTC has auto load timer mode.
The HTC is disabled when the CPU is reseted or in the SLOW/STOP/IDLE operation mode. Users
must enable it by self when the CPU is waked up.
Auto load timer mode
In this mode, there are four different internal pulse rates can be selected by P20. The HTC loads the
initial values by the counter registers (P12, P13) and increases at the rising edges of internal pulse generated
by the time base. The value of TCB increases one when the high speed counter overflows and generates
an overflow interrupt (TRGB) when the TCB overflows. This mode is only available for NORMAL operation
mode.
PROGRAM EXAMPLE :
LDIA #00H ; initial TCB & HTC register
STATBL
STATBM
STATBH
OUTA P13
OUTA P12
LDIA #1011B ; enable timer mode, internal pulse rate : CLK/2
OUTA P20
:
LDIA #00H ; disable timer mode
OUTA P20
INA P12 ; store the counter value to RAM[00] - RAM[04]
STA 00H
INA P13
STA 01H
LDATBL
STA 02H
LDATBM
STA 03H
LDATBH
STA 04H
7
* This specification are subject to be changed without notice.
8.14.2001
27
Page 28

EM73P968
g
h
4-BIT MICRO-CONTROLLER FOR LCD PRODUCT
Preliminary
ANALOG TO-DIGITAL CONVERTER (ADC)
The analog to - digital consists of an 8-bit analog multiplexer (P6, P7), one control register (P26), two data
register (P12,P13), and ADC with 8-bit resolution.
The ADC module utilizes successive approximation to convert the unknown analog signal to a digital value.
The result is fed to the P12,P13, Input channel are select by the analog input multiplexer the P17 register bits
SEL0, SEL1 and SEL2. The A/D converter is disable when the CPU is reset or in the STOP/IDLE/SLOW
operation mode. User must enable it by self when the CPU is NORMAL operation mode.
VAD
Vref
AIN0
AIN1
AIN2
AIN3
AIN4
AIN5
AIN6
AIN7
8-1 bit analo
Switc
1 2 3
SEL
3
INT2_S
0 1 3
P26
ADC
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7
P12, P13
V
ADSS (GND)
MUX
0 1
TR
DATA BUS
A/D channel control register
P17(BIT) 3 2 1 0 Initial value :0000
SYMBOL SEL2 SEL1 SEL0 COM4
SEL0~ SEL2: Analog Input select
A/D input share with P6 & P7.
Analog Input Select Input channel Share with pin
SEL2 SEL1 SEL0
0 0 0 AIN0 P6.0
0 0 1 AIN1 P6.1
0 1 0 AIN2 P6.2
0 1 1 AIN3 P6.3
1 0 0 AIN4 P7.0
1 0 1 AIN5 P7.1
1 1 0 AIN6 P7.2
1 1 1 AIN7 P7.3
* This specification are subject to be changed without notice.
8.14.2001
28
Page 29

EM73P968
4-BIT MICRO-CONTROLLER FOR LCD PRODUCT
ADC control register
P26(BIT) 3 2 1 0 Initial value : 0000
SYMBOL ADEN * F_RUN START
Port 26 is A/D control register , when P26.3 (ADEN) is high A/D converter enable , P26.3 is low A/D converter
disable , P26.1(F_RUN) is high, select A/D conversion is free run , P26.1(F_RUN) is slow , A/D could not
convert P26.0(START) is high , A/D converter is only one time.
A/D clock rate control register
P23(BIT) 3 2 1 0 Initial value : 0000
SYMBOL * * A/D rate select
A/D rate A/D clock rate
0 0 CLK / 2
0 1 CLK / 2
1 0 CLK / 2
1 1 CLK / 2
CLK=system clock (4M)
Preliminary
5
6
7
7
ADC Data Register (P12,P13)
When we use ADC , first ADC must get P12,P13 ,because P12,P13 share with SPI , ADC and HTC when
the A/D conversion is complete ,the result is load to the P12,P13, and the ADC can generate an interrupt (ADI),
the INT2_S ( P14.3) is set high.
* This specification are subject to be changed without notice.
8.14.2001
29
Page 30

4-BIT MICRO-CONTROLLER FOR LCD PRODUCT
Preliminary
PROGRAM EXAMPLE : input P6.0 an analog message to coverter
CHIP 16K
;---------------------- RAM define area ----------------------
DSEG 10H
ADCBUF: RES 2
;---------------------- interrupt subroutine ----------------------
CSEG
LBR START
ORG 004H
LBR ADI
;----------------------------------------------------------------------START:
LDIA #0001B ; A/D clock rate=60K
OUTA P23
LDIA #0001B
OUTA P18 ; P12,P13
LDIA #1001B
OUTA P26 ; ADC enable & ADC run one time
LDIA #0000B
OUTA P17 ; P6.0 input an analog
LOOP:
B LOOP ; wait the ADC interrupt to occur & interrupt Flag to be Set
(INT2 _S)
B LOOP
:
:
ADI:
INA P12
STA ADBUF
INA P13
STA ADBUF
RET
→ ADC
EM73P968
* This specification are subject to be changed without notice.
8.14.2001
30
Page 31

EM73P968
4-BIT MICRO-CONTROLLER FOR LCD PRODUCT
Preliminary
SERIAL PERIPHERAL INTERFACE (SPI)
The Serial Peripheral Interface (SPI) circuitry consists of two control register P18, P24 , one data register (P12,
P13) ,one shift register. The MSTR select the source of the serial clock from the internal or the external clock.
at the same time, only transfer can occur or receive can occur. The SPI is available for the NORMAL
operation mode.
Internal bus
SPI_F
MSTR
CLK0~1
SPI Control Register :
P24(Bit) 3 2 1 0
SYMBOL MSTR DORO CLKS1 CLKS0
CLKS0~CLKS1: SPI transmission clock rate select
This is the clock rate selection bits, on master mode, we have four Kinds of rate can select.
2
CTR0~1
2
CLOCK
GENERATOR
DCOL
SPIE
DORD
8- BIT Shift register
Output latch
8
SPI
reg
P12, P13
8
SDO
SDI
SCK
P15
Clock Rate P24(1,0 BIT)
CLKS1 CLKS0
Fc/2^5 0 0
Fc/2^6 0 1
Fc/2^7 1 0
Fc/2^8 1 1
DORD: Data transmission order
0: LSB first
the data in the 8-bit shift register is shifted in/out LSB first
1: MSB first
the data in the 8-bit shift register is shifted in/out LSB first
* This specification are subject to be changed without notice.
8.14.2001
31
Page 32

4-BIT MICRO-CONTROLLER FOR LCD PRODUCT
Preliminary
MSTR: master or slave mode select
0: Master mode
SPI is in master mode and SCK is configured as an output pin.
SPI clock source is internal clock.
1: slave mode
SPI is in slave mode and SCK is configured as an input pin.
SCK receives the serial clock externally.
P18(Bit) 3210
SYMBOL SPIE * CTR1 CTR0
SPIE: Serial Peripheral Interface Enable
1: Serial Peripheral Interface Enable
0: Serial Peripheral Interface disable
P12, P13 control table
CTR1 CTR0 Select resume
0 0 HTC counter
0 1 A/D converter
1 0 SPI shift data
1 1 Unused
EM73P968
SPI control bit:
SPI_F( P14.1): SPI control flag
when SPI register (P12, P13) is empty SPI_F clear 0
when SPI register (P12, P13) is full, SPI_F set 1
P3(Bit) 3 2 1 0
SYMBOL DCOL * ROM bank select
DCOL (P3.3): SPI control flag
When SPI shift register is empty DCOL clear 0.
When SPI shift register is full DCOL set 1.
SDO: Serial data out ( share with P15.0)
When MSTR set to 0 , SDO is an output pin, share with P15.0,
When the SPI is enable , data are shift out form SDO (P15.0)
SDI: Serial data out (share with P15.0)
When MSTR set to 1 , SDI is an input pin, share with P15.0,
When the SPI is enable , data are shift in form SDI (P15.0)
SCK: Serial Clock (share with P15.1)
The SCK pin for synchronization of both input and output data stream through SDI and SDO pins. When the
MSTR is set, SCK become an output and the Serial clock is supplied to the internal system. When the MSTR
is clear, SCK become an intput and the Serial clock is supplied to the external system. The clock speed in slave
mode is dependent upon the speed of the external system and has a maximum speed up till the internal system
clock.
* This specification are subject to be changed without notice.
8.14.2001
32
Page 33

EM73P968
4-BIT MICRO-CONTROLLER FOR LCD PRODUCT
Preliminary
SCK: Serial Clock (share with P15.1)
The SCK pin for synchronization of both input and output data stream through SDI and SDO pins. When the
MSTR is set, SCK become an output and the Serial clock is supplied to the internal system. When the MSTR
is clear, SCK become an intput and the Serial clock is supplied to the external system. The clock speed in slave
mode is dependent upon the speed of the external system and has a maximum speed up till the internal system
clock.
PROGRAM EXAMPLE :
transmission 16 bit (ABAB H) serial data LBS first, clock rate Fc/2^8 (Fc=4MHz)
LDIA #1010B
OUTA P18 ; enable SPI & P12,P13a SPI
LDIA #0011B
OUTA P24 ; transmission LBS first & Fc/2^8 clock rate
LDIA #0AH
OUTA P13 ; 0AH
LDIA #0BH
OUTA P12 ; 0BH → P12
SEP P14,1 ; SPI register (P12, P13) is full
NEXT:
TTP P14,1
B NEXT ; wait SPI register is empty and input next data (8 bits)
LDIA #0AH
OUTA P13 ; 0AH → P13
LDIA #0BH
OUTA P12 ; 0BH → P12
SEP P14,1
NEXT1:
TTP P14,1 ; wait SPI register is empty and input next data (8 bits)
B NEXT1
NEXT2:
TTP P3.3
B NEXT2 ; wait all data transfer over
LDIA #0
OUTA P18 ; SPI disable
→ P13,
* This specification are subject to be changed without notice.
8.14.2001
33
Page 34

SPI TIMING DIAGRAM
DATA OUTPUT TIMING
SCK
SDO
MSTR=0
DORD=0
SDO
MSTR=0
DORD=1
DATA
4-BIT MICRO-CONTROLLER FOR LCD PRODUCT
Preliminary
MSB BIT6 BIT5 BIT4
LSB BIT1
BIT2
BIT3
BIT3
IT4
BIT2 BIT1
BIT5 BIT6
EM73P968
LSB
SB
SAMPLE
SPI_F
DATA INPUT TIMING
SCK
SDO
MSTR=0
DORD=0
SDO
MSTR=0
DORD=1
DATA
SAMPLE
SPI_F
MSB BIT6 BIT5 BIT4
BIT3
BIT2 BIT1
LSB
LSB BIT1 BIT2 BIT3 BIT4 BIT5 BIT6 MSB
* This specification are subject to be changed without notice.
8.14.2001
34
Page 35

EM73P968
4-BIT MICRO-CONTROLLER FOR LCD PRODUCT
Preliminary
LCD DRIVER
EM73P968 can directly drive the liquid crystal display (LCD) and has 52 segment and 4 or 5 common output
pins by mask option. There are total 52x4 or 52x5 dots can be display. The VRLC pin is the LCD driver power
input, there is the voltage of (VCC-VRLC) to LCD.
P17.0 share with com 4. When the mask option select 1/4 duty, the P17.0 is an output pin and LCD have 4
common. When the mask option select 1/5 duty, the P17.0 is a LCD pin and LCD have 5 common.
LCD driver control command register (P27) :
Port27 3210 Initial value : 0000
LDC * * *
LDC LCD display control
0 LCD display disable
1 LCD display enable
* : Don't care.
Example :
LDIA #1000B ; enable LCD, reference voltage of LCD is 1.5V.
OUTA P27
:
LDIA #0000B ; disable LCD
OUTA P27
LCD RAM
20H-2CH
30H-3CH
40H-4CH
50H-5CH
60H-6CH
012345 6789
COM0
COM1
COM2
COM3
COM4
SEG0
SEG1
SEG2
SEG3
SEG4
SEG5
SEG6
SEG7
SEG8
SEG9
SEG10
SEG11
SEG12
SEG13
SEG14
SEG15
SEG16
SEG17
SEG18
SEG19
SEG20
SEG21
SEG22
SEG23
SEG24
SEG25
SEG26
SEG27
SEG28
SEG29
SEG30
SEG31
SEG32
SEG33
SEG34
SEG35
SEG36
ABCDEF
SEG37
SEG38
SEG39
SEG40
SEG41
SEG42
SEG43
SEG44
SEG45
SEG46
SEG47
SEG48
SEG49
SEG50
SEG51
* This specification are subject to be changed without notice.
8.14.2001
35
Page 36

4-BIT MICRO-CONTROLLER FOR LCD PRODUCT
Preliminary
Driving RAM SEG0 SEG1 SEG2 SEG3
Method address bit0 bit1 bit2 bit3
20H
1/5 1/4 30H
duty duty 40H
50H
- 60H
Driving RAM SEG4 SEG5 SEG6 SEG7
Method address bit0 bit1 bit2 bit3
21H
1/5 1/4 31H
duty duty 41H
51H
- 61H
:
:
EM73P968
Driving RAM SEG48 SE49 SEG50 SEG51
Method address bit0 bit1 bit2 bit3
2CH
1/5 1/4 3CH
duty duty 4CH
5CH
- 6CH
(2) 1/4 duty (1/3 bias)
COM0
COM1
COM2
COM3
SEG0
ON
OFF
Frame
V3
V2
V1
Vss
V3
V2
V1
Vss
V3
V2
V1
Vss
V3
V2
V1
Vss
V3
V2
V1
Vss
V3
V2
V1
Vss
-V1
-V2
-V3
V3
V2
V1
Vss
-V1
-V2
-V3
COM0
COM1
COM2
COM3
COM4
SEG0
SEG0-COM0
SEG0-COM1
(1) 1/5 duty (1/3 bias)
ON
OFF
Frame
V3
V2
V1
Vss
V3
V2
V1
Vss
V3
V2
V1
Vss
V3
V2
V1
Vss
V3
V2
V1
Vss
V3
V2
V1
Vss
V3
V2
V1
Vss
-V1
-V2
-V3
V3
V2
V1
Vss
-V1
-V2
-V3
SEG0-COM0
SEG0-COM1
* This specification are subject to be changed without notice.
8.14.2001
36
Page 37

EM73P968
4-BIT MICRO-CONTROLLER FOR LCD PRODUCT
Preliminary
WATCH-DOG-TIMER (WDT)
Watch-dog-timer can help user to detect the malfunction (runaway) of CPU and give system a timeup signal every
certain time. User can use the time up signal to give system a reset signal when system is fail.
This function is available by mask option. If the mask option of WDT is enabled, it will stop counting when CPU
is reseted or in the STOP operation mode.
The basic structure of Watch-Dog-Timer control is composed by a 4-stage binary counter and a control unit.
The WDT counter counts for a certain time to check the CPU status, if there is no malfunction happened, the
counter will be cleared and continue counting. Otherwise, if there is a malfunction happened, the WDT control
will send a WDT signal (low active) to reset CPU. The WDT checking period is assign by P21 (WDT command
port).
13
LXIN/2
counter clear request
WDT counter
0
12
WDT control
3
RESET pin
mask option
P21
WDT
command port
P21 is the control port of watch-dog-timer, and the WDT time up signal is connected to RESET.
Port 21 3210Initial value :0000
CWC * * WDT
CWC Clear watchdog timer counter
0 Clear counter then return to 1
1 Nothing
WDT Set watch-dog-timer detect time
0 3 x 213/LXIN = 3 x 213/32K Hz = 0.75 sec
13
1 7 x 2
/LXIN = 7 x 213/32K Hz = 1.75 sec
PROGRAM EXAMPLE
To enable WDT with 7 x 213/LXIN detection time.
LDIA #0001B
OUTA P21 ; set WDT detection time and clear WDT counter
:
:
* This specification are subject to be changed without notice.
8.14.2001
37
Page 38

EM73P968
4-BIT MICRO-CONTROLLER FOR LCD PRODUCT
Preliminary
RESETTING FUNCTION
When CPU in normal working condition and RESET pin is held in low level for three instruction cycles at least,
then CPU begins to initialize the whole internal states, when RESET pin changes to high level, CPU begins
to work in normal condition.
The CPU internal state during reset condition is as following table :
Hardware condition in RESET state Initial value
Program counter 0000h
Status flag 01h
Interrupt enable flip-flop ( EI ) 00h
MASK0 ,1, 2, 3 00h
Interrupt latch ( IL ) 00h
P3, 9, 10, 12, 13, 14, 16, 19, 20, 21, 22, 25, 00h
27, 28, 29
P0, 1, 2, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 11, 15, 17, 30, 31 0Fh
LXIN, XIN Start oscillation
The RESET pin is a hysteresis input pin and it has a pull-up resistor available by mask option.
The simplest RESET circuit is connect RESET pin with a capacitor to VSS and a diode to VDD.
RESET
* This specification are subject to be changed without notice.
8.14.2001
38
Page 39

EM73P968
4-BIT MICRO-CONTROLLER FOR LCD PRODUCT
Preliminary
EM73P968 I/O PORT DESCRIPTION :
Port Input function Output function Not e
0 E Input port, wakeup function
1 E Input port, wakeup function E Output port
2 E Input port, wakeup function E Output port
3 I ROM bank selection I ROM bank selection, P3.3 SPI use
4 E Input port, wakeup function E Output port
5 E Input port, wakeup function E Output port
6 E Input port, wakeup function E Output port
share with A/D input
7 E Input port, wakeup function E Output port
share with A/D input
8 E Input port, wakeup function, E Output port, P8.0(INT1), P8.1(TRGB),
external interrupt input P8.2(INT0), P8.3(TRGA)
9 I RAM bank selection I RAM bank selection
10 I General purpose register I General purpose register
11 E Input port, wakeup function E Output port
12 SPI input data register I High speed counter register share with SPI Low nibble
output data, A/D resolution data
13 SPI input data register I High speed counter register share with SPI High nibble
output data, A/D resolution data
14 I CPU status I CPU status, interrupt source selector
15 E Input port, wakeup function E Output port,
P15.0 input data with SPI, P15.0 output data with SPI,
P15.1 input clock with SPI P15.1 output clock with SPI
16 I STOP mode control register
17 I Output port P17.0/COM4
P17.1-P17.3 A/D control register
18 I Interrupt status register
P12, P13 control register
19 I IDLE mode control register
20 I HTC control register
21 I WDT control register
22 I NORMAL/SLOW mode control register
23 I ADC control register
24 SPI control register
25 I Timebase control register
26 A/D control register
27 I LCD control register
28 I Timer / counter A control register
29 I Timer / counter B control register
30 I Output port / SEG(51..48)
31 I Output port / SEG(47..44)
* This specification are subject to be changed without notice.
8.14.2001
39
Page 40

RESET PIN TYPE
TYPE RESET-A
EM73P968
4-BIT MICRO-CONTROLLER FOR LCD PRODUCT
Preliminary
RESET
OSCILLATION PIN TYPE
TYPE OSC-A TYPE OSC-B
XIN
XOUT
TYPE OSC-H1 (Low frequency) TYPE OSC-H2 (High frequency)
VDD
1Mohm
LXIN
mask option
Crystal
Osc.
RC Osc.
10Kohm
VDD
OSC
LXIN
Crystal
Osc.
LXOUT
RC Osc.
INPUT PIN TYPE
TYPE INPUT-K
input data
WAKEUP
mask option
negative
: mask option
edge
detector
I/O PIN TYPE
TYPE I/O-N TYPE I/O-O
: mask option
* This specification are subject to be changed without notice.
TYPE I/O-N
: mask option
path B
path A
Output
data
latch
Input
data
Output
data
Special function
output
8.14.2001
40
Page 41

4-BIT MICRO-CONTROLLER FOR LCD PRODUCT
Preliminary
TYPE I/O-Q TYPE I/O-R1
path B
path A
TYPE I/O-Q
Output
data
latch
EM73P968
Input
data
Output
data
: mask option
WAKEUP function
mask option
TYPE I/O-S TYPE I/O-Z
path B
path A
TYPE I/O-N
WAKEUP function
mask option
SEL
Output
data
latch
Special function
control input
Input
data
TYPE I/O-Q
Output
data
path B
path A
: mask option
OUTPUT-L OUTPUT-M
TYPE I/O-Q
Output
data
latch
Output
data
TYPE I/O
Output
data
latch
Output
data
latch
Special function
output
Input
data
S
R
Special function
output
Power-on
reset
Output
data
Output
data
: mask option
Special function
output
: mask option
Special function
output
Path A : For set and clear bit of port instructions, data goes through path A from output data latch to CPU.
Path B : For input and test instructions, data from output pin go through path B to CPU and the output data latch
will be set to high.
* This specification are subject to be changed without notice.
8.14.2001
41
Page 42

EM73P968
4-BIT MICRO-CONTROLLER FOR LCD PRODUCT
ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS
Preliminary
Items Sym. Ratings Conditions
Supply Voltage V
Input Voltage V
Output Voltage V
Power Dissipation P
Operating Temperature T
Storage Temperature T
DD
IN
O
D
OPR
STG
-0.5V to 6V
-0.5V to VDD+0.5V
-0.5V to VDD+0.5V
300mW T
-30oC to 70oC
-55oC to 125oC
OPR
=50oC
RECOMMANDED OPERATING CONDITIONS
Items Sym. Ratings Condition
Min. Max.
Supply Voltage V
Input Voltage V
schmitt circuit V
Operating Frequency F
Fs 32KHz LXIN, LXOUT (crystal osc)
DD
IH
IL
C
Normal 2.2V 4MHz by RC osc
Slow 2.2V
Idle 2.2V 6.0V
Stop 2.0V
0.80xVDD to V
0V to 0.20 to V
DD
DD
V
: 2.0~5.5V
DD
4MHz Osc
AD CONBERTER CHARACTERISTICS (V),=5.0V, V
=5.0V, V55=0V)
4-.
Characteristic Sym. Min. Max. Unit Condition
Resolution - 8 8 bit
Conversion range V
Quantization error
SS
V
AD
+1 LSB
Sampling rate 10 CLK V
A/D supply current AIDD1 - 1.0 mA ADEN=0
AIDD2 5 µA ADEN=1
Analog input impedance RAN 3 MΩ
Vref current AIref - 0.2 mA
VV
AD
DD
=5V
=5V
* This specification are subject to be changed without notice.
8.14.2001
42
Page 43

4-BIT MICRO-CONTROLLER FOR LCD PRODUCT
Preliminary
EM73P968
DC ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS (VDD=5±0.5V, VSS=0V, T
OPR
=25oC)
Parameters Sym. Min. Typ. Max. Unit Conditions
Supply current I
Hysteresis voltage V
Input I
DD_Xtal
I
DD_RC
HYS+
V
HYS-
IH
current - - ±1 µA Open-drain,V
High current I
High current 450 550 650 µA P0, I/O port acts as input(push-pull),
Normal current I
IL1
IL
Low current 20 24 28 µA P11,P15
Output V
OH
Voltage P15,P30,P31
V
OL
High current I
OH1
Normal current 45 55 65 µA
Low current 18 22 27 µA
High current IOH 400 450 500 µA P4~P8,
Normal current 45 55 65 µA P11,P15,P30,P31,
Low current 16 20 25 µA optional
Leakage current I
Input resistor R
Normal current 45 55 65 µA P17.0
LO - - 1 µA Open-drain,VDD=5.5V,Vo=5.5V
IN -- -KΩ RESET
High Frequency 20 30 % V
Variation R=100K
Low Frequency 20 30 % V
Variation R=1MΩ
Note : RESET pin must add to a pull-up resistor.
-1.5 2mAV
=5.5V,no load,NORMAL mode,
DD
Fc=4MHz, Fs=32KHz (crystal)
- 100 150 µA V
=5.5V,no load,SLOW mode,Fs=32KHz
DD
(crystal)
- 80 100 µA V
=5.5V,no load,RV
DD
Fs=32KHz (crystal)
-0.1 1µAV
=5.5V,STOP mode (crystal)
DD
- 650 1000 µA VDD=5.5V,no load,NORMAL mode,
Fc=4MHz,Fs=32KHz (RC, OSC)
- 80 120 µA V
=5.5V,no load,SLOW mode,Fs=32KHz
DD
(RC, OSC)
-4570µAV
=5.5V,no load,RV
DD
Fs=32KHz (RC, OSC)
-0.1 1µAV
0.50V
0.20V
DD
DD
- 0.75V
- 0.40V
V RESET,all I/O ports
DD
V
DD
=5.5V,STOP mode (RC, OSC)
DD
- - ±1 µA RESET,P0,VDD=5.5V,VIH=5.5/0V
=5.5V,VIH=5.5/0V
DD
11 14 18 mA P1,P2
50 60 80 µA P4~P8, optional,VDD=4.5V,VIL=0.2V
2.2 - - V VDD=4.5V,see IOH=typical. for P4~P8,P11,
--0.2VV
=4.5V,IOL=0.5mA,P1,P2, P4,P7,P8,
DD
P11,P15,P17.0,P30,P31
--1.0VV
=4.5V,IOL=16mA,P5,P6
DD
9 11 14 mA P1,P2 VDD=4.5V,VOH=2.2V
=2.2~5.5V+10% RC OSC
DD
+2%, fc=4MHz
=2.2~5.5V+10% RC OSC
DD
+2%, fs=32KHz
=68K,IDLE mode,
RLC
=68K,IDLE mode,
RLC
* This specification are subject to be changed without notice.
8.14.2001
43
Page 44

PAD DIAGRAM
SEG42
SEG43
SEG44/P31.3
SEG45/P31.2
SEG46/P31.1
SEG47/P31.0
SEG48/P30.3
SEG49/P30.2
SEG50/P30.1
SEG51/P30.0
VPP/TEST
ACLK/P0.0
PGM/P0.1
OE/P0.2
DCLK/P0.3
P1.0
P1.1
P1.2
P1.3
P2.0
P2.1
P2.2
P2.3
P4.0
P4.1
P4.2
P4.3
P5.0
P5.1
P5.2
P5.3
RESET
P6.0
P6.1
P6.2
P6.3
P7.0
P7.1
P7.2
4-BIT MICRO-CONTROLLER FOR LCD PRODUCT
Preliminary
SEG41
SEG40
SEG39
SEG38
SEG37
110 103
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
ELAN
37
38
39
40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57
SEG34
SEG33
SEG32
SEG36
SEG35
SEG31
(0,0)
EM73P968
SEG30
SEG29
SEG28
SEG27
SEG26
SEG25
979899100101102104105106107108109111112113114
96
95
94
93
92
91
90
89
88
87
86
85
84
83
82
81
80
79
78
77
76
75
74
73
72
71
70
69
68
67
66
65
64
63
62
61
60
59
58
EM73P968
SEG24
SEG23
SEG22
SEG21
SEG20
SEG19
SEG18
SEG17
SEG16
SEG15
SEG14
SEG13
SEG12
SEG11
SEG10
SEG9
SEG8
SEG7
SEG6
SEG5
SEG4
SEG3
SEG2
SEG1
SEG0
COM4
COM3
COM2
COM1
COM0
P15.3
P15.2
P15.1
P15.0
P11.3
P11.2
P11.1
P11.0
VRLC
VR3
P7.3
VADSS
VREF
VAD
P8.0/DIN
P8.2
P8.1/DOUT
P8.3
VSS
XIN
* This specification are subject to be changed without notice.
VDD
XOUT
VSS
LXIN
VDD
LXOUT
VR1
VR2
8.14.2001
44
Page 45

4-BIT MICRO-CONTROLLER FOR LCD PRODUCT
Preliminary
Pad No. Symbol X Y
1 SEG42 -935.0 2080.0
2 SEG43 -935.0 1960.0
3 SEG44/P31.3 -935.0 1845.0
4 SEG45/P31.2 -935.0 1730.0
5 SEG46/P31.1 -935.0 1615.0
6 SEG47/P31.0 -935.0 1505.0
7 SEG48/P30.3 -935.0 1395.0
8 SEG49/P30.2 -935.0 1285.0
9 SEG50/P30.1 -935.0 1175.0
10 SEG51/P30.0 -935.0 1065.0
11 VPP/TEST -935.0 955.0
12 P0.0/ACLK -935.0 847.5
13 P0.1/PGM -935.0 740.0
14 P0.2/OE -935.0 632.5
15 P0.3/DCLK -935.0 525.0
16 P1.0 -935.0 420.0
17 P1.1 -935.0 315.0
18 P1.2 -935.0 210.0
19 P1.3 -935.0 105.0
20 P2.0 -935.0 0.0
21 P2.1 -935.0 -105.0
22 P2.2 -935.0 -210.0
23 P2.3 -935.0 -315.0
24 P4.0 -935.0 -420.0
25 P4.1 -935.0 -525.0
26 P4.2 -935.0 -632.5
27 P4.3 -935.0 -740.0
28 P5.0 -935.0 -847.5
29 P5.1 -935.0 -955.0
30 P5.2 -935.0 -1065.0
31 P5.3 -935.0 -1175.0
32 RESET -935.0 -1285.0
33 P6.0 -935.0 -1395.0
34 P6.1 -935.0 -1505.0
35 P6.2 -935.0 -1615.0
36 P6.3 -935.0 -1730.0
37 P7.0 -935.0 -1845.0
38 P7.1 -935.0 -1960.0
39 P7.2 -935.0 -2080.0
40 P7.3 -935.0 -2200.0
EM73P968
* This specification are subject to be changed without notice.
8.14.2001
45
Page 46

4-BIT MICRO-CONTROLLER FOR LCD PRODUCT
Preliminary
Pad No. Symbol X Y
41 VADSS -815.0 -2200.0
42 VREF -700.0 -2200.0
43 VAD -590.0 -2200.0
44 P8.0/DIN -480.0 -2200.0
45 P8.1/DOUT -372.5 -2200.0
46 P8.2 -265.0 -2200.0
47 P8.3 -157.5 -2200.0
48 VSS -52.5 -2200.0
49 XIN 52.5 -2200.0
50 VDD 157.5 -2200.0
51 XOUT 265.0 -2200.0
52 VSS 372.5 -2200.0
53 LXIN 480.0 -2200.0
54 VDD 590.0 -2200.0
55 LXOUT 700.0 -2200.0
56 VR1 815.0 -2200.0
57 VR2 935.0 -2200.0
58 VR3 935.0 -2080.0
59 VRLC 935.0 -1960.0
60 P11.0 935.0 -1845.0
61 P11.1 935.0 -1730.0
62 P11.2 935.0 -1615.0
63 P11.3 935.0 -1505.0
64 P15.0 935.0 -1395.0
65 P15.1 935.0 -1285.0
66 P15.2 935.0 -1175.0
67 P15.3 935.0 -1065.0
68 COM0 935.0 -955.0
69 COM1 935.0 -847.5
70 COM2 935.0 -740.0
71 COM3 935.0 -632.5
72 COM4 935.0 -525.0
73 SEG0 935.0 -420.0
74 SEG1 935.0 -315.0
75 SEG2 935.0 -210.0
76 SEG3 935.0 -105.0
77 SEG4 935.0 0.0
78 SEG5 935.0 105.0
79 SEG6 935.0 210.0
80 SEG7 935.0 315.0
EM73P968
* This specification are subject to be changed without notice.
8.14.2001
46
Page 47

4-BIT MICRO-CONTROLLER FOR LCD PRODUCT
Preliminary
Pad No. Symbol X Y
81 SEG8 935.0 420.0
82 SEG9 935.0 525.0
83 SEG10 935.0 632.5
84 SEG11 935.0 740.0
85 SEG12 935.0 847.5
86 SEG13 935.0 955.0
87 SEG14 935.0 1065.0
88 SEG15 935.0 1175.0
89 SEG16 935.0 1285.0
90 SEG17 935.0 1395.0
91 SEG18 935.0 1505.0
92 SEG19 935.0 1615.0
93 SEG20 935.0 1730.0
94 SEG21 935.0 1845.0
95 SEG22 935.0 1960.0
96 SEG23 935.0 2080.0
97 SEG24 935.0 2200.0
98 SEG25 815.0 2200.0
99 SEG26 700.0 2200.0
100 SEG27 590.0 2200.0
101 SEG28 480.0 2200.0
102 SEG29 372.5 2200.0
103 SEG30 265.0 2200.0
104 SEG31 157.5 2200.0
105 SEG32 52.5 2200.0
106 SEG33 -52.5 2200.0
107 SEG34 -157.5 2200.0
108 SEG35 -265.0 2200.0
109 SEG36 -372.5 2200.0
110 SEG37 -480.0 2200.0
111 SEG38 -590.0 2200.0
112 SEG39 -700.0 2200.0
113 SEG40 -815.0 2200.0
114 SEG41 -935.0 2200.0
EM73P968
Unit : um
Chip size : 2130 x 4660um
Note : For PCB layout, IC substrate must be floated or connected to Vss.
* This specification are subject to be changed without notice.
8.14.2001
47
Page 48

PACKAGE DIMENSION
EM73P968
4-BIT MICRO-CONTROLLER FOR LCD PRODUCT
Preliminary
A
Symbol Min Normal Max
A 3.400
A2 2.540 2.720 2.900
A1 0.250 0.350 0.450
b 0.2(TYP)
c 0.15(TYP)
D 13.900 14.000 14.100
Hd 17.000 17.200 17.400
E 19.900 20.000 20.100
He 23.000 23.200 23.400
L 0.650 0.800 0.950
L1 1.400 1.600 1.800
e 0.5(bsc)
θ0 7
All dimensions are in millimeters.
* This specification are subject to be changed without notice.
8.14.2001
48
Page 49

EM73P968
4-BIT MICRO-CONTROLLER FOR LCD PRODUCT
INSTRUCTION TABLE
Preliminary
(1) Data Transfer
Mnemonic Object code ( binary ) Operation description Byte Cycle Flag
CZ S
LDA x 0110 1010 xxxx xxxx Acc←RAM[x] 2 2 - Z 1
LDAM 0101 1010 Acc ←RAM[HL] 1 1 - Z 1
LDAX 0110 0101 Acc←ROM[DP]
LDAXI 0110 0111 Acc←ROM[DP]
L
,DP+1 1 2 - Z 1
H
12-Z1
LDH #k 1001 kkkk HR←k11--1
LDHL x 0100 1110 xxxx xx00 LR←RAM[x],HR←RAM[x+1] 2 2 - - 1
LDIA #k 1101 kkkk Acc←k11-Z1
LDL #k 1000 kkkk LR←k11--1
STA x 0110 1001 xxxx xxxx RAM[x]←Acc 2 2 - - 1
STAM 0101 1001 RAM[HL]←Acc 1 1 - - 1
STAMD 0111 1101 RAM[HL]←Acc, LR-1 1 1 - Z C
STAMI 0111 1111 RAM[HL]←Acc, LR+1 1 1 - Z C'
STD #k,y 0100 1000 kkkk yyyy RAM[y]←k22--1
STDMI #k 1010 kkkk RAM[HL]←k, LR+1 1 1 - Z C'
THA 0111 0110 Acc←HR 1 1 - Z 1
TLA 0111 0100 Acc←LR 1 1 - Z 1
(2) Rotate
Mnemonic Object code ( binary ) Operation description Byte Cycle Flag
CZS
RLCA 0101 0000 ←CF←Acc← 11CZC'
RRCA 0101 0001 →CF→Acc→ 11CZC'
(3) Arithmetic operation
Mnemonic Object code ( binary ) Operation description Byte Cycle Flag
C ZS
ADCAM 0111 0000 Acc←Acc + RAM[HL] + CF 1 1 C Z C'
ADD #k,y 0100 1001 kkkk yyyy RAM[y]←RAM[y] + k 2 2 - Z C'
ADDA #k 0110 1110 0101 kkkk Acc←Acc+k 2 2 - Z C'
ADDAM 0111 0001 Acc←Acc + RAM[HL] 1 1 - Z C'
ADDH #k 0110 1110 1001 kkkk HR←HR+k 2 2 - Z C'
ADDL #k 0110 1110 0001 kkkk LR←LR+k 2 2 - Z C'
ADDM #k 0110 1110 1101 kkkk RAM[HL]←RAM[HL] +k 2 2 - Z C'
DECA 0101 1100 Acc←Acc-1 1 1 - Z C
DECL 0111 1100 LR←LR-1 1 1 - Z C
DECM 0101 1101 RAM[HL]←RAM[HL] -1 1 1 - Z C
INCA 0101 1110 Acc←Acc + 1 1 1 - Z C'
* This specification are subject to be changed without notice.
8.14.2001
49
Page 50

EM73P968
4-BIT MICRO-CONTROLLER FOR LCD PRODUCT
Preliminary
INCL 0111 1110 LR←LR + 1 1 1 - Z C'
INCM 0101 1111 RAM[HL]←RAM[HL]+1 1 1 - Z C'
SUBA #k 0110 1110 0111 kkkk Acc←k-Acc 2 2 - Z C
SBCAM 0111 0010 Acc←RAM[HLl - Acc - CF' 1 1 C Z C
SUBM #k 0110 1110 1111 kkkk RAM[HL]←k - RAM[HL] 2 2 - Z C
(4) Logical operation
Mnemonic Object code (binary) Operation description Byte Cycle Flag
CZS
ANDA #k 0110 1110 0110 kkkk Acc←Acc&k 2 2 - Z Z'
ANDAM 0111 1011 Acc←Acc & RAM[HL] 1 1 - Z Z'
ANDM #k 0110 1110 1110 kkkk RAM[HL]←RAM[HL]&k 2 2 - Z Z'
ORA #k 0110 1110 0100 kkkk Acc←Acc k 2 2 - Z Z'
ORAM 0111 1000 Acc ←Acc RAM[HL] 1 1 - Z Z'
ORM #k 0110 1110 1100 kkkk RAM[HL]←RAM[HL] k 2 2 - Z Z'
XORAM 0111 1001 Acc←Acc^RAM[HL] 1 1 - Z Z'
- -
- -
- -
(5) Exchange
Mnemonic Object code (binary) Operation description Byte Cycle Flag
CZS
EXA x 0110 1000 xxxx xxxx Acc↔RAM[x] 2 2 - Z 1
EXAH 0110 0110 Acc↔HR 1 2 - Z 1
EXAL 0110 0100 Acc↔LR 1 2 - Z 1
EXAM 0101 1000 Acc↔RAM[HL] 1 1 - Z 1
EXHL x 0100 1100 xxxx xx00 LR↔RAM[x],
HR↔RAM[x+1] 2 2 - - 1
(6) Branch
Mnemonic Object code (binary) Operation description Byte Cycle Flag
CZS
SBR a 00aa aaaa If SF=1 then PC←PC
12-6.a5-0
11--1
else null
LBR a 1100 aaaa aaaa aaaa If SF= 1 then PC←a else null 2 2 - - 1
SLBR a 0101 0101 1100 aaaa If SF=1 then PC←a else null 3 3 - - 1
aaaa aaaa (a:1000~1FFFh)
0101 0111 1100 aaaa
aaaa aaaa (a:0000~0FFFh)
(7) Compare
Mnemonic Object code (binary) Operation description Byte Cycle Flag
CZS
CMP #k,y 0100 1011 kkkk yyyy k-RAM[y] 2 2 C Z Z'
CMPA x 0110 1011 xxxx xxxx RAM[x]-Acc 2 2 C Z Z'
* This specification are subject to be changed without notice.
8.14.2001
50
Page 51

EM73P968
4-BIT MICRO-CONTROLLER FOR LCD PRODUCT
Preliminary
Mnemonic Object code ( binary ) Operation description Byte Cycle Flag
CZS
CMPAM 0111 0011 RAM[HL] - Acc 1 1 C Z Z'
CMPH #k 0110 1110 1011 kkkk k - HR 2 2 - Z C
CMPIA #k 1011 kkkk k - Acc 1 1 C Z Z'
CMPL #k 0110 1110 0011 kkkk k-LR 2 2 - Z C
(8) Bit manipulation
Mnemonic Object code ( binary ) Operation description Byte Cycle Flag
CZS
CLM b 1111 00bb RAM[HL]
CLP p,b 0110 1101 11bb pppp PORT[p]
CLPL 0110 0000 PORT[LR
CLR y,b 0110 1100 11bb yyyy RAM[y]
SEM b 1111 01bb RAM[HL]
SEP p,b 0110 1101 01bb pppp PORT[p]
SEPL 0110 0010 PORT[LR
SET y,b 0110 1100 01bb yyyy RAM[y]
TF y,b 0110 1100 00bb yyyy SF←RAM[y]
TFA b 1111 10bb SF←Acc
TFM b 1111 11bb SF←RAM[HL]
TFP p,b 0110 1101 00bb pppp SF←PORT[p]
TFPL 0110 0001 SF←PORT[LR
TT y,b 0110 1100 10bb yyyy SF←RAM[y]
TTP p,b 0110 1101 10bb pppp SF←PORT[p]
←011--1
b
←022--1
b
+4]LR
3-2
←022--1
b
←111--1
b
←122--1
b
+4]LR
3-2
←122--1
b
b
'11--*
b
b
←012--1
1-0
←112 --1
l-0
'22--*
'11--*
b
'22--*
b
+4]LR
3-2
'1 2--*
1-0
22--*
b
22--*
(9) Subroutine
Mnemonic Object code ( binary ) Operation description Byte Cycle Flag
CZS
LCALL a 0100 0aaa aaaa aaaa STACK[SP]←PC, 2 2 - - -
SP←SP -1, PC←a
SCALL a 1110 nnnn STACK[SP]←PC, 1 2 - - -
SP←SP - 1, PC←a, a = 8n + 6
(n =1∼15),0086h (n = 0)
RET 0100 1111 SP←SP + 1, PC←STACK[SP] 1 2 - - -
(10) Input/output
Mnemonic Object code ( binary ) Operation description Byte Cycle Flag
CZS
INA p 0110 1111 0100 pppp Acc←PORT[p] 2 2 - Z Z'
INM p 0110 1111 1100 pppp RAM[HL]←PORT[p] 2 2 - - Z'
OUT #k,p 0100 1010 kkkk pppp PORT[p]←k22--1
OUTA p 0110 1111 000p pppp PORT[p]←Acc 2 2 - - 1
OUTM p 0110 1111 100p pppp PORT[p]←RAM[HL] 2 2 - - 1
* This specification are subject to be changed without notice.
8.14.2001
51
Page 52

EM73P968
4-BIT MICRO-CONTROLLER FOR LCD PRODUCT
(11) Flag manipulation
Preliminary
Mnemonic Object code ( binary ) Operation description Byte Cycle Flag
CZS
TFCFC 0101 0011 SF←CF', CF←0110-*
TTCFS 0101 0010 SF←CF, CF←1111-*
TZS 0101 1011 SF←ZF 1 1 - - *
(12) Interrupt control
Mnemonic Object code ( binary ) Operation description Byte Cycle Flag
CZS
CIL r 0110 0011 11rr rrrr IL←IL & r 2 2 - - 1
DICIL r 0110 0011 10rr rrrr EIF←0,IL←IL&r 2 2 - - 1
EICIL r 0110 0011 01rr rrrr EIF←1,IL←IL&r 2 2 - - 1
EXAE 0111 0101 MASK↔Acc 1 1 - - 1
RTI 0100 1101 SP←SP+1,FLAG.PC 1 2 * * *
←STACK[SP],EIF ←1
(13) CPU control
Mnemonic Object code ( binary ) Operation description Byte Cycle Flag
CZS
NOP 0101 0110 no operation 1 1 - - -
(14) Timer/Counter & Data pointer & Stack pointer control
Mnemonic Object code ( binary ) Operation description Byte Cycle Flag
CZS
LDADPL 0110 1010 1111 1100 Acc←[DP]
LDADPM 0110 1010 1111 1101 Acc←[DP]
LDADPH 0110 1010 1111 1110 Acc←[DP]
L
M
H
22-Z1
22-Z1
22-Z1
LDASP 0110 1010 1111 1111 Acc←SP 2 2 - Z 1
LDATAL 0110 1010 1111 0100 Acc←[TA]
LDATAM 0110 1010 1111 0101 Acc←[TA]
LDATAH 0110 1010 1111 0110 Acc←[TA]
LDATBL 0110 1010 1111 1000 Acc←[TB]
LDATBM 0110 1010 1111 1001 Acc←[TB]
LDATBH 0110 1010 1111 1010 Acc←[TB]
STADPL 0110 1001 1111 1100 [DP]
STADPM 0110 1001 1111 1101 [DP]
STADPH 0110 1001 1111 1110 [DP]
←Acc 2 2 - - 1
L
←Acc 2 2 - - 1
M
←Acc 2 2 - - 1
H
L
M
H
L
M
H
22-Z1
22-Z1
22 -Z1
22-Z1
22-Z1
22-Z1
STASP 0110 1001 1111 1111 SP←Acc 2 2 - - 1
STATAL 0110 1001 1111 0100 [TA]
STATAM 0110 1001 1111 0101 [TA]
STATAH 0110 1001 1111 0110 [TA]
STATBL 0110 1001 1111 1000 [ TB]
STATBM 0110 1001 1111 1001 [TB]
STATBH 0110 1001 1111 1010 [TB]
* This specification are subject to be changed without notice.
←Acc 2 2 - - 1
L
←Acc 2 2 - - 1
M
←Acc 2 2 - - 1
H
←Acc 2 2 - - 1
L
←Acc 2 2 - - 1
M
←Acc 2 2 - - 1
H
8.14.2001
52
Page 53

4-BIT MICRO-CONTROLLER FOR LCD PRODUCT
Preliminary
**** SYMBOL DESCRIPTION
Symbol Description Symbol Description
HR H register LR L register
PC Program counter DP Data pointer
SP Stack pointer STACK[SP] Stack specified by SP
A
CC
CF Carry flag ZF Zero flag
SF Status flag EI Enable interrupt register
IL Interrupt latch MASK Interrupt mask
PORT[p] Port ( address : p ) ΤΑ Timer/counter A
ΤΒ Timer/counter B RAM[HL] Data memory (address : HL )
RAM[x] Data memory (address : x ) ROM[DP]
ROM[DP]
[DP]
M
[TA]L([TB]L) Low 4-bit of timer/counter A [TA]M([TB]M) Middle 4-bit of timer/counter A
[TA]H([TB]H) High 4-bit of timer/counter A LR
LR
3-2
PC
12-6
↔ Exchange + Addition
- Substraction & Logic AND
- -
#k 4-bit immediate data x 8-bit RAM address
y 4-bit zero-page address p 4-bit or 5-bit port address
b Bit address r 6-bit interrupt latch
Accumulator FLAG All flags
Low 4-bit of program memory
Low 4-bit of data pointer register
High 4-bit of data pointer register
High 4-bit of program memory [DP]
H
Middle 4-bit of data pointer register [DP]
L
L
H
(timer/counter B) register (timer/counter B) register
1-0
Contents of bit assigned by bit
(timer/counter B) register 1 to 0 of LR
Bit 3 to 2 of LR a
5-0
Bit 5 to 0 of destination address for
branch instruction
Bit 12 to 6 of program counter ← Transfer
Logic OR ^ Logic XOR
Inverse operation . Concatenation
EM73P968
* This specification are subject to be changed without notice.
8.14.2001
53
 Loading...
Loading...