Page 1
DATA SHEET
MOS FIELD EFFECT TRANSISTOR
SWITCHING
N-CHANNEL POWER MOS FET
INDUSTRIAL USE
DESCRIPTION
2SK2498 is N-Channel MOS Field Effect Transistor designed for
high current switching applications.
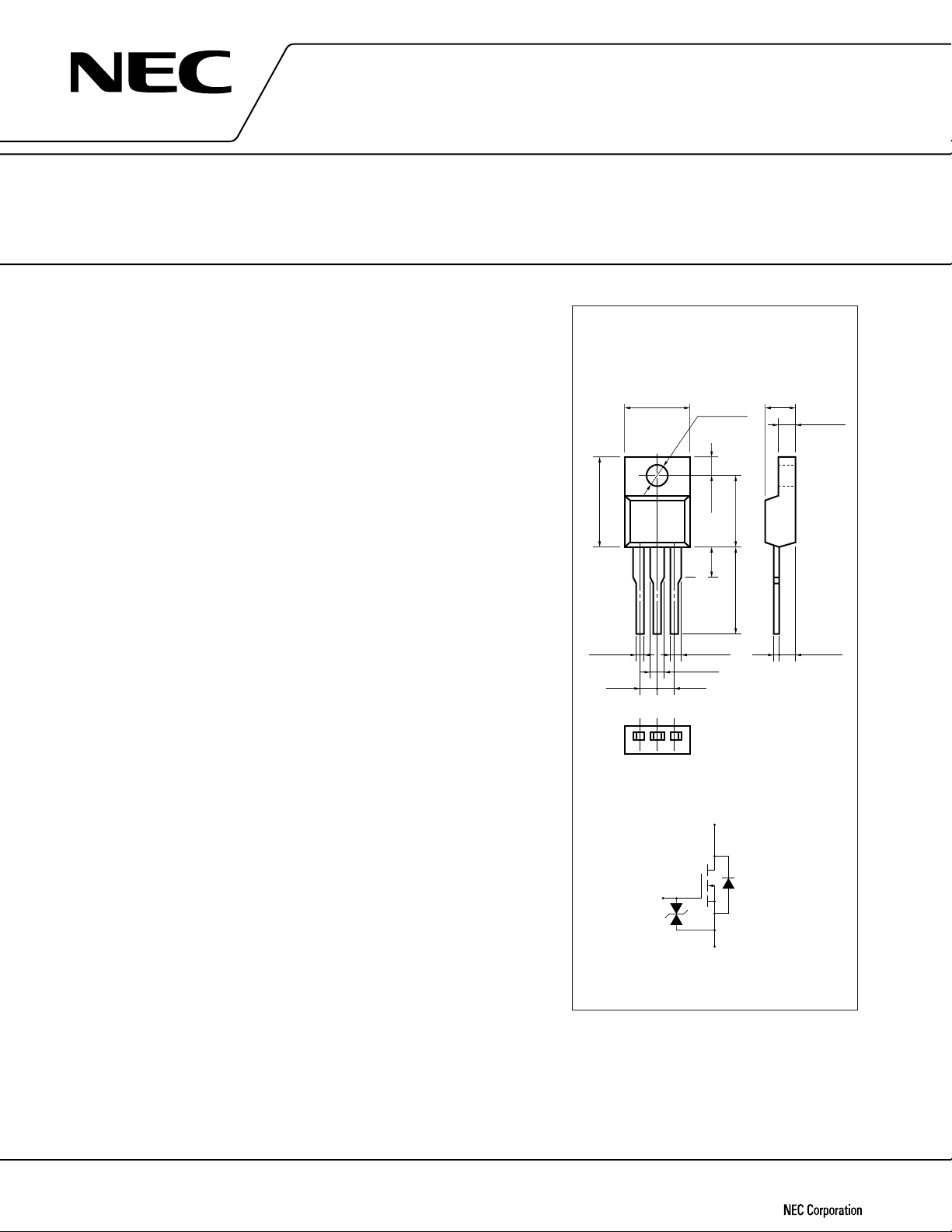
2SK2498
PACKAGE DIMENSIONS
(in millimeter)
FEATURES
• Super Low On-State Resistance
RDS (on)1 ≤ 9 mΩ (VGS = 10 V, ID = 25 A)
DS (on)2 ≤ 14 mΩ (VGS = 4 V, ID = 25 A)
R
• Low Ciss Ciss = 3400 pF TYP.
• High Avalanche Capability Ratings
• Isolate TO-220 Package
• Buit-in G-S Protection Diode
ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS (TA = 25 ˚C)
Drain to Source Voltage VDSS 60 V
Gate to Source Voltage VGSS ±20 V
Drain Current (DC) ID(DC) ±50 A
Drain Current (pulse)* I
Total Power Dissipation (Tc = 25 ˚C) PT1 35 W
Total Power Dissipation (TA = 25 ˚C) PT2 2.0 W
Channel Temperature T
Storage Temperature Tstg –55 to +150 ˚C
Single Avalanche Current** IAS 50 A
Single Avalanche Energy** E
* PW ≤ 10 µs, Duty Cycle ≤ 1 %
** Starting Tch = 25 ˚C, RG = 25 Ω, VGS = 20 V → 0
D(pulse) ±200 A
ch 150 ˚C
AS 250 mJ
10.0±0.3 4.5±0.2
15.0±0.3
0.7±0.1
2.54
123
MP-45F (ISOLATED TO-220)
Gate
3.2±0.2
3±0.14±0.2
1.5±0.2
2.54
Drain
2.7±0.2
12.0±0.213.5MIN.
2.5±0.11.3±0.2
0.65±0.1
1. Gate
2. Drain
3. Source
Body
Diode
Document No. D10044EJ1V0DS00 (1st edition)
Date Published July 1995 P
Printed in Japan
Gate Protection
Diode
Source
©
1995
Page 2
ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS (TA = 25 ˚C)
y Cy
CHARACTERISTIC SYMBOL MIN. TYP. MAX. UNIT TEST CONDITIONS
Drain to Source On-Resistance RDS (on)1 7.3 9.0 mΩ VGS = 10 V, ID = 25 A
RDS (on)2 11 14 mΩ VGS = 4 V, ID = 25 A
Gate to Source Cutoff Voltage VGS (off) 1.0 1.5 2.0 V VDS = 10 V, ID = 1 mA
Forward Transfer Admittance | yfs | 20 58 S VDS = 10 V, ID = 25 A
Drain Leakage Current IDSS 10
Gate to Source Leakage Current IGSS ±10 nA VGS = ±20 V, VDS = 0
Input Capacitance Ciss 3400 pF VDS = 10 V
Output Capacitance Coss 1600 pF VGS = 0
Reverse Transfer Capacitance Crss 770 pF f = 1 MHz
Turn-On Delay Time td (on) 55 ns ID = 25 A
Rise Time tr 360 ns VGS(on) = 10 V
Turn-Off Delay Time td (off) 480 ns VDD = 30 V
Fall Time tf 360 ns RG = 10 Ω
Total Gate Charge QG 152 nC ID = 50 A
Gate to Source Charge QGS 11 nC VDD = 48 V
Gate to Drain Charge QGD 60 nC VGS = 10 V
Body Diode Forward Voltage VF (S-D) 0.92 V IF = 50 A, VGS = 0
Reverse Recovery Time trr 105 ns IF = 50 A, VGS = 0
Reverse Recovery Charge Qrr 265
µ
A VDS = 60 V, VGS = 0
µ
C di/dt = 100 A/µs
2SK2498
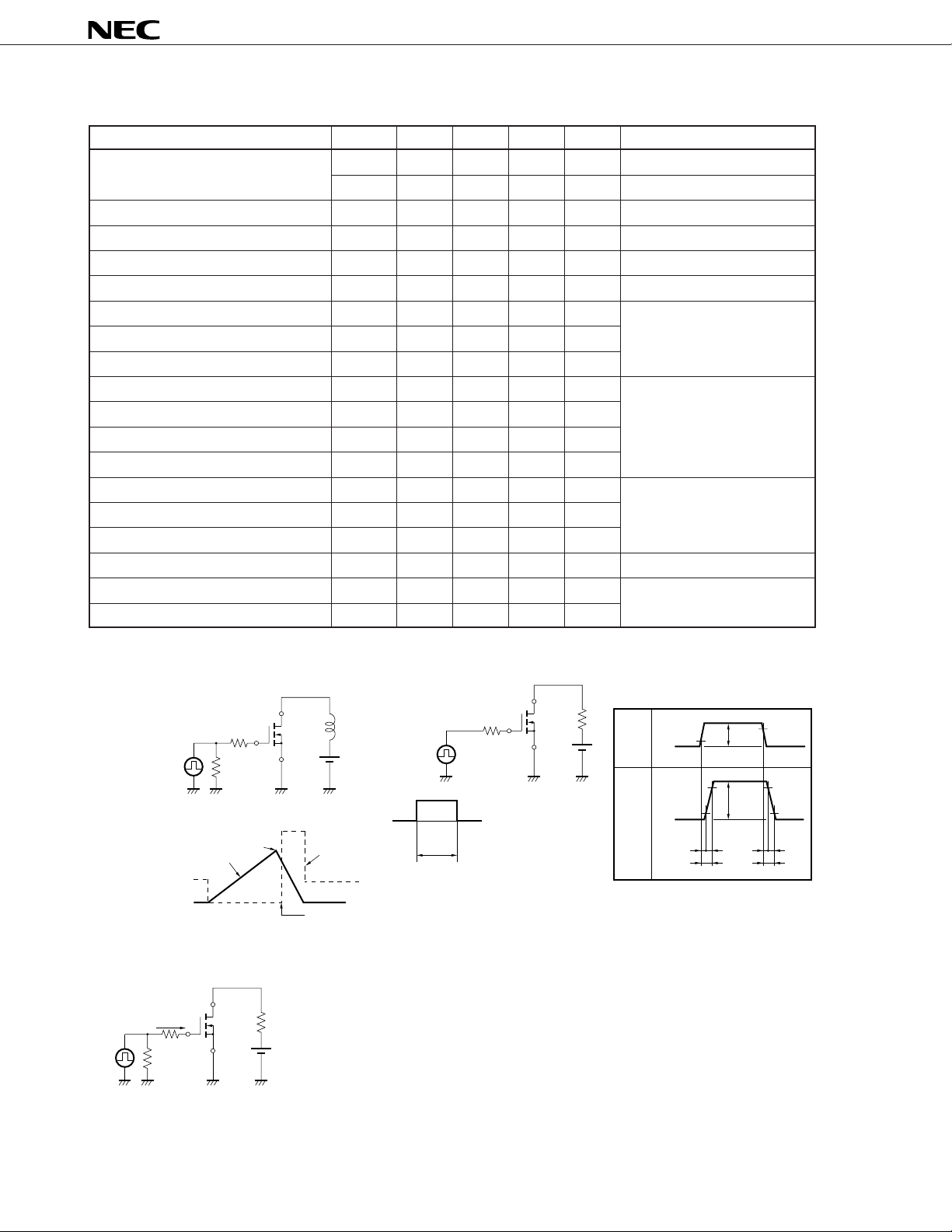
Test Circuit 1 Avalanche Capability Test Circuit 2 Switching Time
RG
G = 10 Ω
R
D.U.T.
V
GS
= 20 → 0 V
PG
G
= 25 Ω
R
V
DD
50 Ω
I
D
D.U.T.
I
AS
BV
DSS
Starting T
L
PG.
V
DD
VGS
0
t = 1 s
µ
Dut
t
cle ≤ 1 %
V
DS
ch
Test Circuit 3 Gate Charge
D.U.T.
I
G
PG.
= 2 mA
50 Ω
R
L
V
DD
R
VDD
L
VGS
Wave Form
ID
Wave Form
VGS
10 %
0
ID
90 %
10 %
0
td (on) tr td (off) tf
ton toff
90 %
GS (on)
V
90 %
ID
10 %
The application circuits and their parameters are for references only and are not intended for use in actual design-in's.
2
Page 3
TYPICAL CHARACTERISTICS (TA = 25 ˚C)
2SK2498
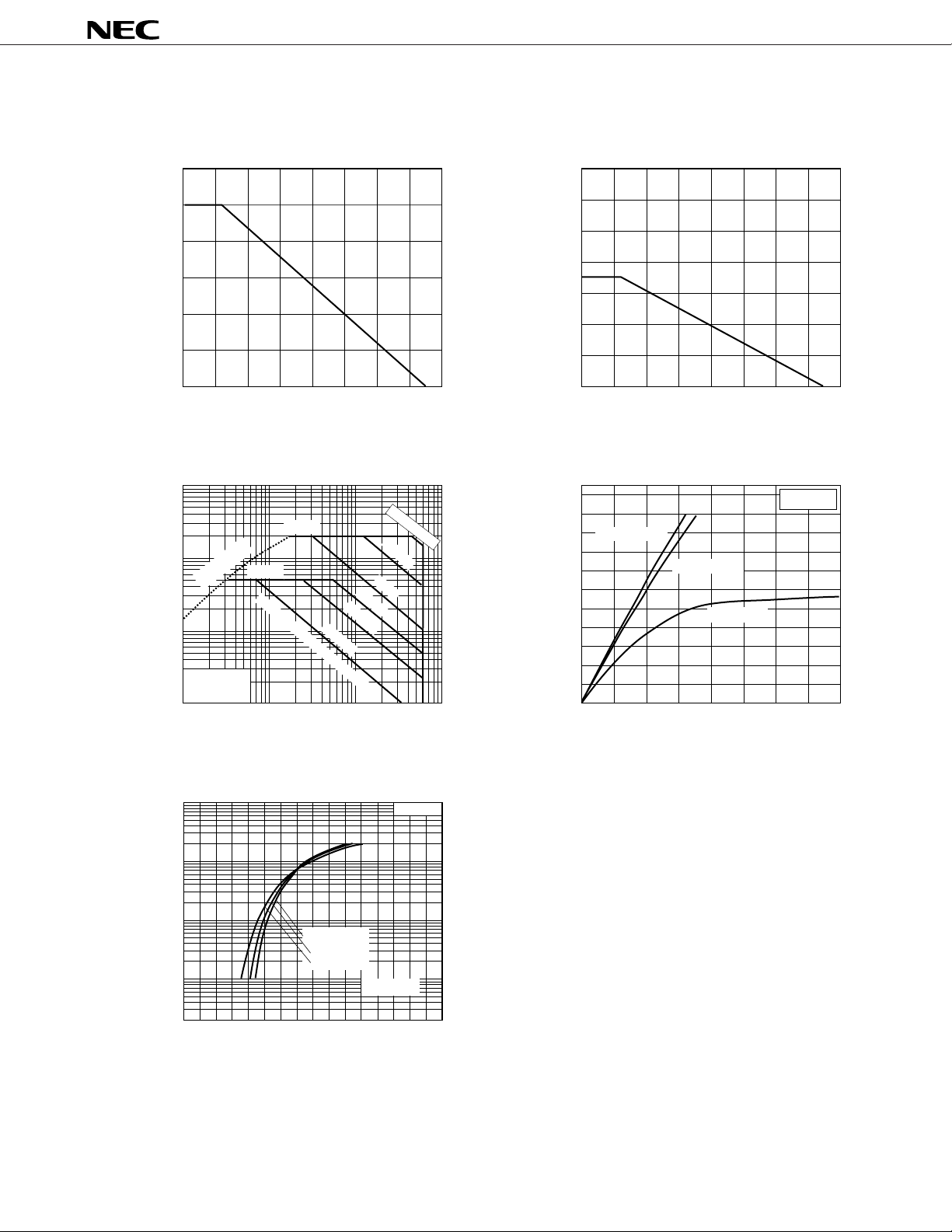
DERATING FACTOR OF FORWARD BIAS
SAFE OPERATING AREA
100
80
60
40
20
dT - Percentage of Rated Power - %
0
20 40 60 80 100 120 140 160
T
C - Case Temperature - ˚C
FORWARD BIAS SAFE OPERATING AREA
1000
ID(pulse)
100
10
R
DS(on)
(at V
Limited
= 10 V)
ID(DC)
GS
Power Dissipation Limited
DC
ID - Drain Current - A
TC = 25 ˚C
Single Pulse
1
0.1
1 10 100
V
DS - Drain to Source Voltage - V
10ms
100ms
PW=10 s
100 s
1 ms
TOTAL POWER DISSIPATION vs.
CASE TEMPERATURE
70
60
50
40
30
20
10
PT - Total Power Dissipation - W
0
20
40 60 80 100 120 140 160
T
C - Case Temperature - ˚C
DRAIN CURRENT vs.
DRAIN TO SOURCE VOLTAGE
Pulsed
200
µ
µ
160
VGS = 20 V
VGS = 10 V
120
80
VGS = 4 V
ID - Drain Current - A
40
0
1
V
DS - Drain to Source Voltage - V
2
3
4
FORWARD TRANSFER CHARACTERISTICS
1000
100
10
TA = –25 ˚C
25 ˚C
ID - Drain Current - A
125 ˚C
1
0
2
GS - Gate to Source Voltage - V
V
46
Pulsed
VDS = 10 V
8
3
Page 4

1 000
2SK2498
TRANSIENT THERMAL RESISTANCE vs. PULSE WIDTH
100
10
1
0.1
0.01
rth(t) - Transient Thermal Resistance - ˚C/W
0.001
100
µµ
FORWARD TRANSFER ADMITTANCE vs.
DRAIN CURRENT
1000
100
1 m 10 m 100 m 1 10 100 1 000 10
VDS = 10 V
Pulsed
PW - Pulse Width - s
Rth(ch-a) = 62.5 ˚C/W
Rth(ch-c) = 3.57 ˚C/W
Single Pulse
DRAIN TO SOURCE ON-STATE RESISTANCE vs.
GATE TO SOURCE VOLTAGE
30
Pulsed
20
10
|yfs | - Forward Transfer Admittance - S
1
1
10
I
D - Drain Current - A
DRAIN TO SOURCE ON-STATE
RESISTANCE vs. DRAIN CURRENT
30
20
V
GS = 4 V
10
VGS = 10 V
0
RDS(on) - Drain to Source On-State Resistance - mΩ
10
ID - Drain Current - A
100 1000
100 1000
Pulsed
10
0
RDS(on) - Drain to Source On-State Resistance - mΩ
V
GS - Gate to Source Voltage - V
ID = 25 A
10
GATE TO SOURCE CUTOFF VOLTAGE vs.
CHANNEL TEMPERATURE
2.0
1.5
1.0
0.5
0
VGS(off) - Gate to Source Cutoff Voltage - V
–50
0 50 100 150
ch - Channel Temperature - ˚C
T
20 30
VDS = 10 V
I
D = 1 mA
4
Page 5

2SK2498
DRAIN TO SOURCE ON-STATE RESISTANCE vs.
CHANNEL TEMPERATURE
20
15
VGS = 4 V
10
VGS = 10 V
5
0
–50
RDS(on) - Drain to Source On-State Resistance - mΩ
0
T
ch - Channel Temperature - ˚C
50
100 150
CAPACITANCE vs. DRAIN TO
SOURCE VOLTAGE
100 000
10 000
Ciss
D = 25 A
I
VGS = 0
f = 1 MHz
SOURCE TO DRAIN DIODE
FORWARD VOLTAGE
100
10
4 V
1
0.1
ISD - Diode Forward Current - A
0
0.5
V
SD - Source to Drain Voltage - V
SWITCHING CHARACTERISTICS
1 000
tf
100
VGS = 0
td(off)
1.0
Pulsed
1.5
tr
td(on)
1 000
Ciss, Coss, Crss - Capacitance - pF
100
0.1
1 10 100
V
DS - Drain to Source Voltage - V
REVERSE RECOVERY TIME vs.
DRAIN CURRENT
1000
100
10
trr - Reverse Recovery time - ns
1.0
0.1
1.0 10 100
I
D - Drain Current - A
Crss
Coss
di/dt =100 A/ s
GS = 0
V
µ
10
td(on), tr, td(off), tf - Switching Time - ns
1.0
0.1
1.0 10 100
I
D - Drain Current - A
DYNAMIC INPUT/OUTPUT CHARACTERISTICS
80
60
VDS
40
20
VDS - Drain to Source Voltage - V
0
50 100 150 200
Q
g - Gate Charge - nC
VDD = 30 V
VGS = 10 V
RG = 10 Ω
DD = 48 V
V
ID = 50 A
VGS
16
14
12
10
8
6
4
2
VGS - Gate to Source Voltage - V
0
5
Page 6

2SK2498
SINGLE AVALANCHE CURRENT vs.
INDUCTIVE LOAD
100
IAS = 50 A
E
AS
= 250 mJ
10
1.0
VDD = 30 V
IAS - Single Avalanche Current - A
VGS = 20 V → 0
RG = 25 Ω
0.1
10 100 1 m 10 m
µµ
L - Inductive Load - H
SINGLE AVALANCHE ENERGY
DERATING FACTOR
160
140
120
100
80
60
40
Energy Derating Factor - %
20
0
50 75 100 125 150
25
Starting T
ch - Starting Channel Temperature - ˚C
VDD = 30 V
R
G
= 25 Ω
V
GS
= 20 V → 0
I
AS
< 50 A
6
Page 7

2SK2498
REFERENCE
Document Name Document No.
NEC semiconductor device reliability/quality control system. TEI-1202
Quality grade on NEC semiconductor devices. IEI-1209
Semiconductor device mounting technology manual. IEI-1207
Semiconductor device package manual. IEI-1213
Guide to quality assurance for semiconductor devices. MEI-1202
Semiconductor selection guide. MF-1134
Power MOS FET features and application switching power supply. TEA-1034
Application circuits using Power MOS FET. TEA-1035
Safe operating area of Power MOS FET. TEA-1037
The diode connected between the gate and source of the transistor serves as a protector against ESD. When
this device is actually used, an additional protection circuit is externally required if a voltage exceeding the
rated voltage may be applied to this device.
7
Page 8

2SK2498
[MEMO]
No part of this document may be copied or reproduced in any form or by any means without the prior written
consent of NEC Corporation. NEC Corporation assumes no responsibility for any errors which may appear in this
document.
NEC Corporation does not assume any liability for infringement of patents, copyrights or other intellectual
property rights of third parties by or arising from use of a device described herein or any other liability arising
from use of such device. No license, either express, implied or otherwise, is granted under any patents,
copyrights or other intellectual property rights of NEC Corporation or others.
While NEC Corporation has been making continuous effort to enhance the reliability of its semiconductor devices,
the possibility of defects cannot be eliminated entirely. To minimize risks of damage or injury to persons or
property arising from a defect in an NEC semiconductor device, customer must incorporate sufficient safety
measures in its design, such as redundancy, fire-containment, and anti-failure features.
NEC devices are classified into the following three quality grades:
“Standard“, “Special“, and “Specific“. The Specific quality grade applies only to devices developed based on
a customer designated “quality assurance program“ for a specific application. The recommended applications
of a device depend on its quality grade, as indicated below. Customers must check the quality grade of each
device before using it in a particular application.
Standard: Computers, office equipment, communications equipment, test and measurement equipment,
audio and visual equipment, home electronic appliances, machine tools, personal electronic
equipment and industrial robots
Special: Transportation equipment (automobiles, trains, ships, etc.), traffic control systems, anti-disaster
systems, anti-crime systems, safety equipment and medical equipment (not specifically designed
for life support)
Specific: Aircrafts, aerospace equipment, submersible repeaters, nuclear reactor control systems, life
support systems or medical equipment for life support, etc.
The quality grade of NEC devices in “Standard“ unless otherwise specified in NEC's Data Sheets or Data Books.
If customers intend to use NEC devices for applications other than those specified for Standard quality grade,
they should contact NEC Sales Representative in advance.
Anti-radioactive design is not implemented in this product.
M4 94.11
8
 Loading...
Loading...