Page 1

Silicon NPN Epitaxial Planar
Application
VHF amplifier, mixer, local oscillator
Outline
TO-92 (2)
2SC535
1. Emitter
2. Collector
3. Base
3
2
1
Page 2

2SC535
Absolute Maximum Ratings (Ta = 25°C)
Item Symbol Ratings Unit
Collector to base voltage V
Collector to emitter voltage V
Emitter to base voltage V
Collector current I
Collector power dissipation P
CBO
CEO
EBO
C
C
Junction temperature Tj 150 °C
Storage temperature Tstg –55 to +150 °C
30 V
20 V
4V
20 mA
100 mW
2
Page 3

2SC535
Electrical Characteristics (Ta = 25°C)
Item Symbol Min Typ Max Unit Test conditions
Collector to base breakdown
V
(BR)CBO
voltage
Collector to emitter breakdown
V
(BR)CEO
voltage
Emitter to base breakdown
V
(BR)EBO
voltage
Collector cutoff current I
CBO
DC current transfer ratio hFE*
Base to emitter voltage V
Collector to emitter saturation
V
BE
CE(sat)
voltage
Gain bandwidth product f
T
Collector output capacitance Cob — 0.9 1.2 pF VCB = 10 V, IE = 0, f = 1 MHz
Power gain PG 17 20 — dB VCE = 6 V, IC = 1 mA,
Noise figure NF — 3.5 5.5 dB VCE = 6 V, IC = 1 mA,
Input admittance (typ) yie 1.3 + j5.3 mS VCE = 6 V, IC = 1 mA,
Reverse transfer admittance
yre –0.078 – j0.41 mS
(typ)
Foward transfer admittance
yfe 32 – j10 mS
(typ)
Output admittance (typ) yoe 0.08 + j0.82 mS
Note: 1. The 2SC535 is grouped by hFE as follows.
BC
60 to 120 100 to 200
30 — — V IC = 10 µA, IE = 0
20 — — V IC = 1 mA, RBE = ∞
4——VI
— — 0.5 µAV
1
60 — 200 VCE = 6 V, IC = 1 mA
= 10 µA, IC = 0
E
= 10 V, IE = 0
CB
— 0.72 — V VCE = 6 V, IC = 1 mA
— 0.17 — V IC = 20 mA, IB =4 mA
450 940 — MHz VCE = 6 V, IC = 5 mA
f = 100 MHz
f = 100 MHz, R
f = 100 MHz
= 50 Ω
g
3
Page 4
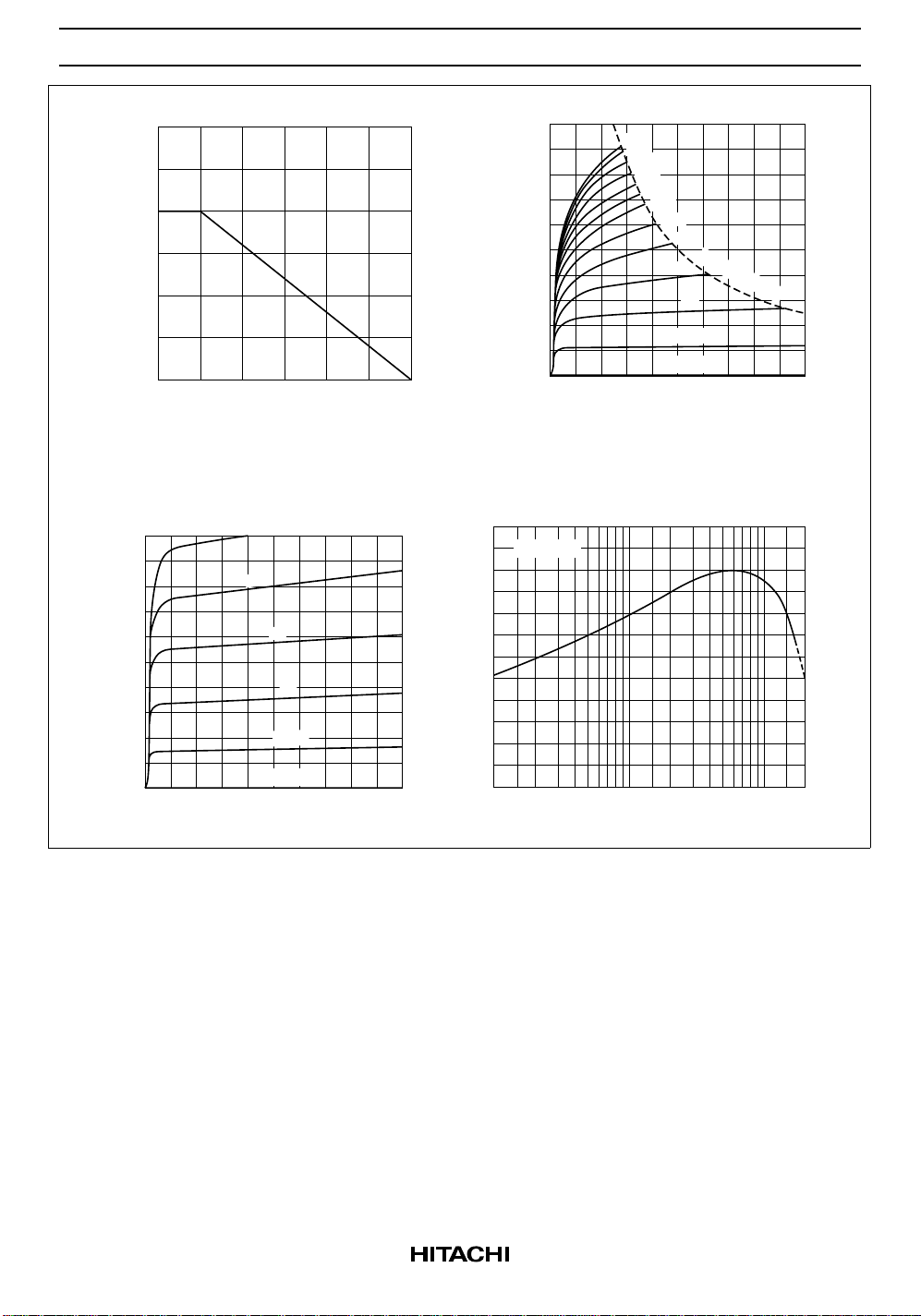
2SC535
Maximum Collector Dissipation Curve
150
(mW)
C
100
50
Collector power dissipation P
0 50 150100
Ambient Tmperature Ta (°C)
Typical Output Characteristics
5
4
(mA)
C
3
2
50
40
30
20
FE
(mA)
Collector Current I
120
VCE = 6 V
100
80
60
40
Typical Output Characteristics
20
16
C
12
8
300
275
250
225
200
175
150
125
75
100
P
C
50
4
25 µA
IB = 0
04 1612
Collector to Emitter Voltage VCE (V)
DC Current Transfer Ratio vs.
Collector Current
= 100 mW
208
1
Collector Current I
0 4 12 208
Collector to Emitter Voltage V
10µA
IB = 0
16
CE
(V)
20
DC Current Transfer ratio h
0
0.1 0.5 1050.2 2 201.0
Collector Current I
(mA)
C
4
Page 5

2SC535
Typical Transfer Cahracteristics (1)
20
VCE = 6 V
16
(mA)
C
12
8
4
Collector Current I
0
0.6 0.7
Base to Emitter Voltage V
(pF)
Typical Transfer Cahracteristics (2)
5
VCE = 6 V
4
(mA)
C
3
2
1
Collector Current I
0
BE
(V)
0.8
0.6 0.7
Base to Emitter Voltage V
BE
0.8
(V)
Collector Output Capacitance vs.
Collector to Base Voltage
1.5
f = 1 MHz
I
= 0
ob
1.3
E
1.1
0.9
0.7
Collector Output Capacitance C
0.5
0.3 101.0 303
Collector to Base Voltage V
CB
(V)
5
Page 6

2SC535
Gain Bandwidth Product vs.
Collector Current
1,000
800
(MHz)
T
VCE = 6 V
600
400
200
Gain Bandwidth Product f
0
0.1 0.5 2 100.2 1.0 5 20
Collector Current I
(mA)
C
Noise Figure vs. Collector Current
8
IC = 1 mA
f = 100 MHz
R
= 50 Ω
6
g
4
2
Noise figure NF (dB)
0
0.2 1.0 50.5 2 10
Collector Current I
(mA)
C
6
Page 7

Noise Figure vs. Signal Source Resistance
8
VCE = 6 V
I
f = 100 MHz
6
= 1 mA
C
8
6
Noise Figure vs. Collector to
Emitter Voltage
VCE = 6 V
f = 100 MHz
R
= 50 Ω
g
2SC535
4
2
Noise figure NF (dB)
0
20 100 50050 200 1,000
Signal Source Resistance R
(Ω)
g
100 MHz Power Gain Test Circuit
f = 100 MHz
R
= 100 Ω
g
IN
300 p
3 k
D.U.T.
500
V
0.01 µ
EE
10 p
max
0.01 µ
V
0.1 µ
0.01 µ
CC
OUT
= 550 Ω
R
l
Unit R : Ω
C : F
4
2
Noise figure NF (dB)
0
1521020
Collecter to Emitter Voltage V
CE
(V)
Input Admittance Characteristics
18
16
yie = gie + jb
VCE = 6 V
ie
14
(mS)
ie
12
f = 200 MHz
10
8
150
6
100
70
4
Input Suceptance b
2 mA
50
2
IC = 1 mA
50 MHz
5 mA
3 mA
70
100
150
200
02 8 146121841016
Input Conductance g
(mS)
ie
7
Page 8

2SC535
Reverse Transfer Admittance
Characteristics
Reverse Transfer Conductance g
–0.20
yre = gre + jb
VCE = 6 V
re
IC = 5 mA 3 21
Output Admittance Characteristics
2.4
2.0
(mS)
oe
1.6
1.2
0.8
yoe = goe + jb
VCE = 6 V
IC = 1 mA
oe
23 5
150
100
70
0.4
Output Suceptance b
50
0 0.1 0.60.40.30.2 0.5
Output Conductance goe (mS)
(mS)
re
f = 50 MHz
70
100
150
200
f = 200 MHz
0–0.04–0.16 –0.12 –0.08
–0.2
(mS)
re
(mS)
fe
–0.4
–0.6
–0.8
Reverse Transfer Suceptance b
–1.0
–100
–120
Forward Transfer Suceptance b
(mS)
ie
Input Admittance y
Forward Transfer Admittance
Characteristics
Forward Transfer Conductance gfe (mS)
020 6040 80 120100
–20
–40
yfe = gfe + jb
VCE = 6 V
IC = 1 mA
2 mA
fe
f = 50 MHz
5 mA
3 mA
200
150
70
100
–60
–80
Input Admittance vs. Collector
to Emitter Voltage
10
b
ie
5
y
= gie + jb
2
ie
IC = 1 mA
f = 100 MHz
ie
g
ie
1.0
0.5
1520210
Collector to Emitter Voltage V
CE
(V)
8
Page 9

Input Admittance vs. Collector Current
20
10
yie = gie + jb
VCE = 6 V
ie
f = 100 MHz
(mS)
5
ie
b
ie
2
1.0
0.5
Input Admittance y
g
ie
Reverse Transfer Admittance vs.
Collector to Emitter Voltage
–1.0 –0.1
(mS)
re
–5
y
= gre + jb
re
IC = 1 mA
–0.2
f = 100 MHz
–0.1
re
b
re
g
re
2SC535
–0.05
–0.02
–0.01
(mS)
re
0.2
0.1 0.5 2 100.2 1.0 5
Collector Current I
Reverse Transrer Admittance vs.
Collector Current
–1.0
(mS)
–0.5
re
–0.2
–0.1
yre = gre + jb
VCE = 6 V
f = 100 MHz
b
re
g
–0.05
–0.02
Reverse Transfer Suceptance b
–0.01
0.1 0.5 2 100.2 1.0 5
Collector Current I
Reverse Transfer Suceptance b
–0.05
–0.005
Reverse Transfer Conductance g
1520210
(mA)
C
Collector to Emitter Voltage V
CE
(V)
Forward Transfer Admittance vs.
Collector to Emitter Voltage
–0.1
re
–0.05
(mS)
re
–0.02
re
–0.01
–0.005
100
(mS)
ie
50
20
10
y
= gfe + jb
fe
IC = 1 mA
fe
f = 100 MHz
g
fe
–b
fe
–0.002
–0.001
Reverse Transfer Conductance g
Forward Transfer Admittance y
5
1520210
(mA)
C
Collector to Emitter Voltage V
CE
(V)
9
Page 10

2SC535
Forward Transrer Admittance vs.
Collector Current
100
(mS)
50
ie
20
yfe = gfe + jb
VCE = 6 V
f = 100 MHz
fe
–b
g
fe
fe
10
5
2
Forward Transrer Admittance y
1
0.1 0.5 2 100.2 1.0 5
Collector Current I
(mA)
C
(mS)
oe
2.0
1.0
(mS)
oe
0.5
0.2
Output Suceptance b
0.1
1520
Collector to Emitter Voltage V
Output Admittance vs. Collector Current
2.0
b
1.0
oe
0.5
Output Admittance vs. Collector
to Emitter Voltage
g
oe
b
oe
y
= goe + jb
eo
IC = 1 mA
oe
f = 100 MHz
210
(V)
CE
0.2
0.1
(mS)
oe
0.05
0.02
Output Conductance g
0.01
0.2
0.1
g
oe
0.05
Output Admittance y
0.02
0.1 0.5 2 100.2 1.0 5
Collector Current I
yoe = goe + jb
VCE = 6 V
f = 100 MHz
(mA)
C
oe
10
Page 11

Unit: mm
0.60 Max
0.45 ± 0.1
4.8 ± 0.3
1.27
2.54
0.7
5.0 ± 0.2
2.3 Max
12.7 Min
3.8 ± 0.3
0.5
Hitachi Code
JEDEC
EIAJ
(reference value)
Weight
TO-92 (2)
Conforms
Conforms
0.25 g
Page 12

Cautions
1. Hitachi neither warrants nor grants licenses of any rights of Hitachi’s or any third party’s patent,
copyright, trademark, or other intellectual property rights for information contained in this document.
Hitachi bears no responsibility for problems that may arise with third party’s rights, including
intellectual property rights, in connection with use of the information contained in this document.
2. Products and product specifications may be subject to change without notice. Confirm that you have
received the latest product standards or specifications before final design, purchase or use.
3. Hitachi makes every attempt to ensure that its products are of high quality and reliability. However,
contact Hitachi’s sales office before using the product in an application that demands especially high
quality and reliability or where its failure or malfunction may directly threaten human life or cause risk
of bodily injury, such as aerospace, aeronautics, nuclear power, combustion control, transportation,
traffic, safety equipment or medical equipment for life support.
4. Design your application so that the product is used within the ranges guaranteed by Hitachi particularly
for maximum rating, operating supply voltage range, heat radiation characteristics, installation
conditions and other characteristics. Hitachi bears no responsibility for failure or damage when used
beyond the guaranteed ranges. Even within the guaranteed ranges, consider normally foreseeable
failure rates or failure modes in semiconductor devices and employ systemic measures such as failsafes, so that the equipment incorporating Hitachi product does not cause bodily injury, fire or other
consequential damage due to operation of the Hitachi product.
5. This product is not designed to be radiation resistant.
6. No one is permitted to reproduce or duplicate, in any form, the whole or part of this document without
written approval from Hitachi.
7. Contact Hitachi’s sales office for any questions regarding this document or Hitachi semiconductor
products.
Hitachi, Ltd.
Semiconductor & Integrated Circuits.
Nippon Bldg., 2-6-2, Ohte-machi, Chiyoda-ku, Tokyo 100-0004, Japan
Tel: Tokyo (03) 3270-2111 Fax: (03) 3270-5109
URL NorthAmerica : http:semiconductor.hitachi.com/
For further information write to:
Hitachi Semiconductor
(America) Inc.
179 East Tasman Drive,
San Jose,CA 95134
Tel: <1> (408) 433-1990
Fax: <1>(408) 433-0223
Europe : http://www.hitachi-eu.com/hel/ecg
Asia (Singapore) : http://www.has.hitachi.com.sg/grp3/sicd/index.htm
Asia (Taiwan) : http://www.hitachi.com.tw/E/Product/SICD_Frame.htm
Asia (HongKong) : http://www.hitachi.com.hk/eng/bo/grp3/index.htm
Japan : http://www.hitachi.co.jp/Sicd/indx.htm
Hitachi Europe GmbH
Electronic components Group
Dornacher Stra§e 3
D-85622 Feldkirchen, Munich
Germany
Tel: <49> (89) 9 9180-0
Fax: <49> (89) 9 29 30 00
Hitachi Europe Ltd.
Electronic Components Group.
Whitebrook Park
Lower Cookham Road
Maidenhead
Berkshire SL6 8YA, United Kingdom
Tel: <44> (1628) 585000
Fax: <44> (1628) 778322
Hitachi Asia Pte. Ltd.
16 Collyer Quay #20-00
Hitachi Tower
Singapore 049318
Tel: 535-2100
Fax: 535-1533
Hitachi Asia Ltd.
Taipei Branch Office
3F, Hung Kuo Building. No.167,
Tun-Hwa North Road, Taipei (105)
Tel: <886> (2) 2718-3666
Fax: <886> (2) 2718-8180
Copyright ' Hitachi, Ltd., 1999. All rights reserved. Printed in Japan.
Hitachi Asia (Hong Kong) Ltd.
Group III (Electronic Components)
7/F., North Tower, World Finance Centre,
Harbour City, Canton Road, Tsim Sha Tsui,
Kowloon, Hong Kong
Tel: <852> (2) 735 9218
Fax: <852> (2) 730 0281
Telex: 40815 HITEC HX
 Loading...
Loading...