Page 1

Data Sheet
Thermostatic Expansion Valves
Type TR6
The TR6 series is a hermetic design which is
developed with features especially for use in
applications such as:
• Residential air conditioning systems
• Split systems
• Roof top units
• Heat pumps
• Chillers
• Light commercial air conditioning systems
The TR6 design incorporates a forged brass
body with the entire power element, including
the capillary tube and bulb, fabricated from
stainless steel. All valves are designed with
balanced port which reduces the inuence
from varying condensing pressures. The valves
can be delivered with special connections and
ttings both at the inlet, outlet, and the
equalizer connection.
AI318728845972en-000401
Page 2

Thermostatic Expansion Valves, Type TR6
Features
• Compact size - hermetic design, straightway conguration with external equalization
• Refrigerants & rated capacities ranging up to
◦ R22/R407C: 23.6 kW / 6.7 TR
◦ R410A: 24.5 kW / 7 TR
• Laser-welded power element
◦ Longer diaphragm life
◦ High corrosion resistant
• Stainless steel capillary tube
◦ Tolerates more bending for easier installation and longer life
◦ High strength and vibration resistance
• Stainless steel bulb
◦ Self aligning
• Balance port design
• A complete program with and without internal check valve
• Internal check valve design with low pressure drop in reverse ow
• Adjustable or non-adjustable superheat, for customer specic factory setting
• Bleed function available
• Solder, chatle and aeroquip connections
• With external equalization
• UL listed, le SA7200
• Anti-hunt bulb charge
© Danfoss | Climate Solutions | 2021.02 AI318728845972en-000401 | 2
Page 3
Danfoss
R64-1822.12
A
B
C
D
E
A
BCD
E
TR6 with / without internal
check valve
RD Distributor
Compressor
Outdoor coil
DCL/DML
Danfoss
R64-1823.13
A
B
C
D
E
F
H
G
ABCDEFGHRD Distributor
Indoor coil
TR6 with internal check valve
4-way valve
Compressor
DCB/DMB
TR6 with internal check valve
Outdoor coil
Thermostatic Expansion Valves, Type TR6
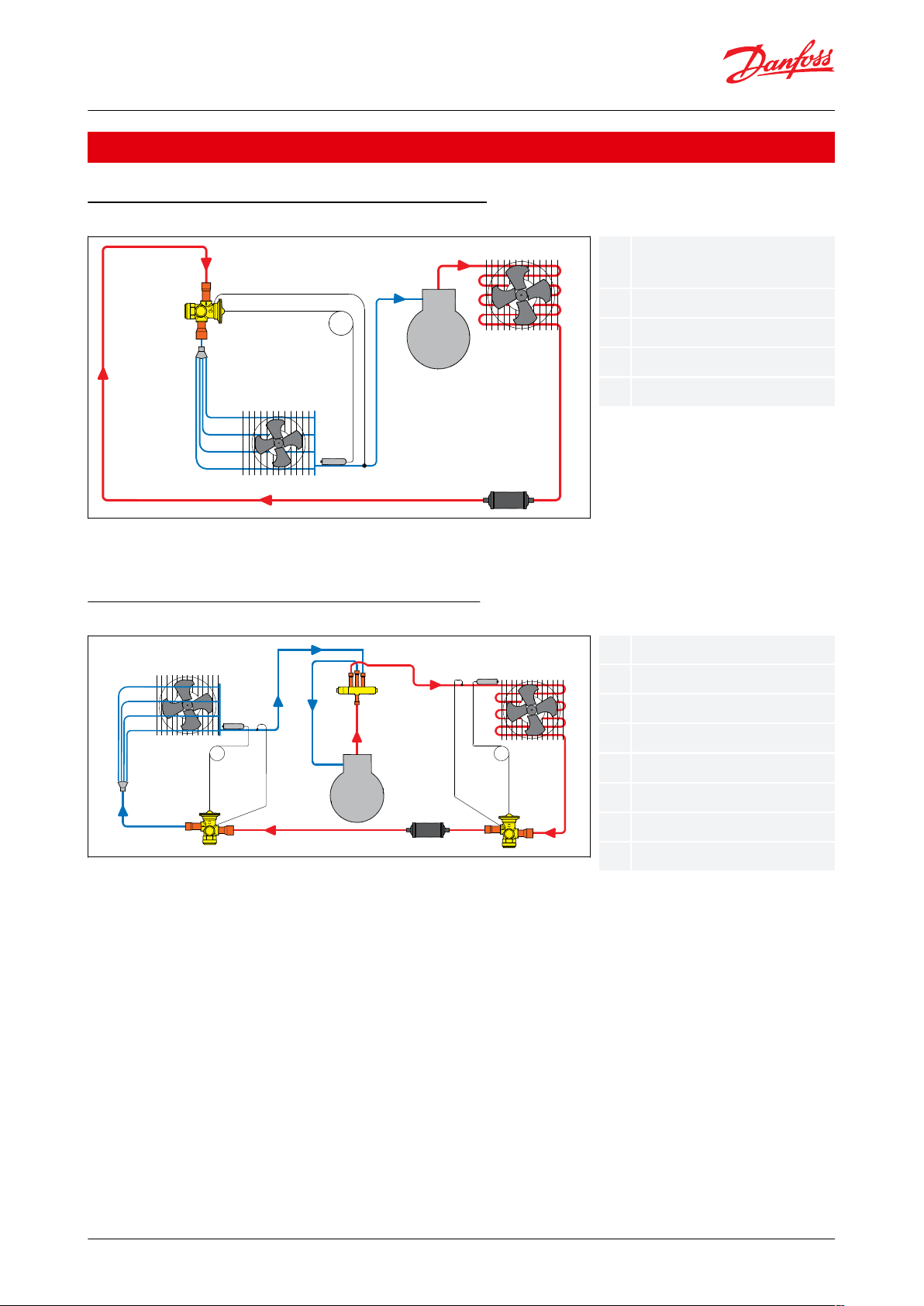
Application
Traditional air conditioning system, cooling only
Figure 1: Traditional air conditioning system, cooling only
Illustrates the diagram of a traditional air conditioning system where the TR6 is controlling liquid injection in one
direction only.
Traditional air conditioning / heat pump system
Figure 2: Traditional air conditioning / heat pump system
Illustrates a split air conditioning / heat pump system with two thermostatic expansion valves, one for cooling mode
and one for heating mode. The thermostatic expansion valves each has a built-in check valve, which has the
function of preventing ow in one direction and allowing the ow in the opposite direction. It means that one
thermostatic expansion valve is controlling liquid injection into the indoor coil while the other thermostatic
expansion valve is bypassing the metering device with the open check valve.
© Danfoss | Climate Solutions | 2021.02 AI318728845972en-000401 | 3
Page 4
Danfoss
R64-1824.13
A
B
C
D
E
F
ABCDEFRD Distributor
Indoor coil
TR6 without check valve
4-way valve
Compressor
Outdoor coil
Thermostatic Expansion Valves, Type TR6
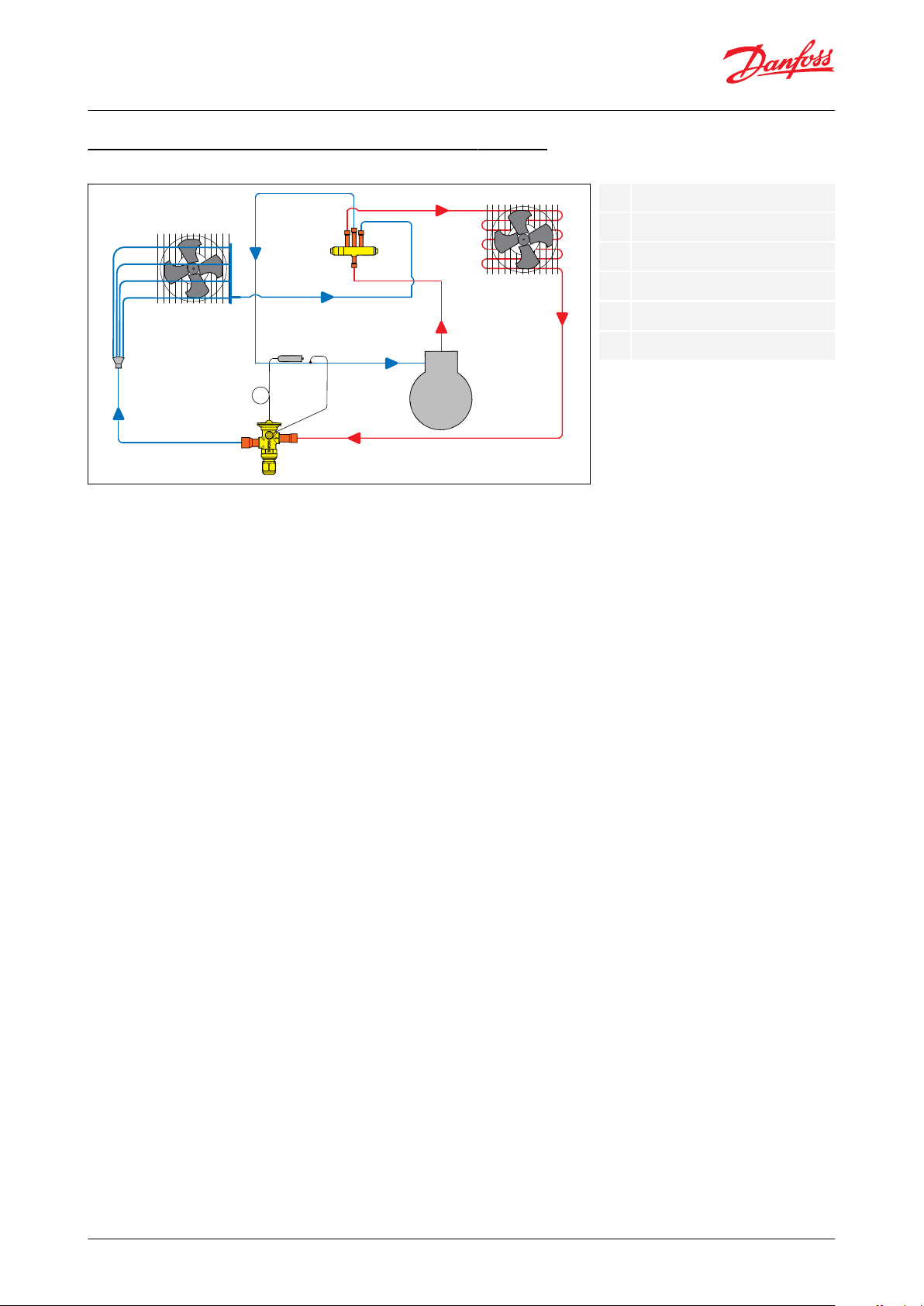
Simplied air conditioning / heat pump system (bi-ow)
Figure 3: Simplied air conditioning / heat pump system (bi-ow)
Illustrates a packaged air conditioning / heat pump system with a short distance between the indoor and outdoor
heat-exchangers. The two TR6 valves from g 6 can be replace by one TR6 valve without internal check valve,
making use of the bi-ow feature of this thermostatic expansion valve. The single valve is controlling the liquid
injection in both directions. The normal ow direction marked with an arrow on the valve body should be used for
the primary function, i.e. cooling or heating.
© Danfoss | Climate Solutions | 2021.02 AI318728845972en-000401 | 4
Page 5

Thermostatic Expansion Valves, Type TR6
Product specication
Technical data
Max. operating temperature
• Thermostatic element:
◦ R22 / R407C: max. 100°C / 212°F
◦ R410A: max. 100°C / 212°F
• Valve body:160 °C / 320 °F
Max. working pressure PS / MWP
49 bar / 711 psig
Valve program
Standard versions
Refrigerants:
R22 / R407C and R410A
Operating range:
-10 to 15°C / 15 to 60°F
Setting:
• Fixed setting:
◦ Static superheat in accordance with customers' specications
• Adjustable setting:
R22 / R407C
Factory static superheat of 4 K / 7.2 °F
R410A
Factory static superheart of 3 K / 5.4 °F
Packing
Single or Multipack
Industrial Pack for OEM specic valves only
Versions:
All valves are in straightway versions with or without internal check valve
Standard connections:
Inlet solder
Equalizer capillary tube ¼ in. are; 24.3 in. length
Capillary tube length: 800 mm / 31.5 in.
3
⁄8 in. ODF x Outlet solder 3⁄8 in. ODF
Options on request
Capillary tube lengths(approx.):
450 mm / 17.7 in.
975 mm / 38.4 in.
Options for Connections:
Inlet/Outlet:
Inlet: Solder ODM
© Danfoss | Climate Solutions | 2021.02 AI318728845972en-000401 | 5
3
⁄8 in., solder ODF 3⁄8 in., solder ODF ½ in., Chatle male 5⁄8 in. and aeroquip male 5⁄8 in.
Page 6

A
D
B
E
C
F
G
H
ABCDEFGHValve type
Code number
Evaporating temperature range in °C
Refrigerant
Rated capacity Qnom in Tons of refrigeration
Evaporating temperature range in °F
Max. working pressure in bar and psig
Date making (BC=Mexico, week 49, year 2017, weekday
D=Thursday)
X
Y
XYDp (psi)
Mass ow lb/h
Thermostatic Expansion Valves, Type TR6
Outlet: Solder ODF
female
5
⁄8 in., short and long tail.
3
⁄8 in., solder ODF ½ in., solder ODF 5⁄8 in., chatle female ¾ in., short and long tail, aeroquip
Equalizer:
Copper capillary tube size (approx.): Ø
1
⁄8 in.
Available congurations:
Solder ODM
1
⁄8 in., lengths 9.5 in., 16.9 in., 24.3 in., 31.7 in.
Solder ODF ¼ in., lengths 31.7 in. and 39.1 in.
Flare nut ¼ in., lengths 9.5 in., 16.9 in., 24.3 in., 31.7 in.
Identication
Figure 4: Main valve data example:
Essential valve data is given on the power element.
Check valve capacity
Figure 5: Internal check valve for orice bypass in reverse ow (ow rate as a function of pressure dierential)
TC= 32 °C / 90 °F
TI= 24 °C / 75 °F
Valve selection based on capacity calculation
As for extended capacity calculations and valve selection based on capacities and refrigerants, please refer to
Coolselector®2. Rated and extended capacities are calculated with the Coolselector®2 calculation engine to ARI
standards with the ASEREP equations based on laboratory measurements of selected valves.
Download Coolselector®2 for free at coolselector.danfoss.com.
© Danfoss | Climate Solutions | 2021.02 AI318728845972en-000401 | 6
Page 7

123456789
TR6 with xed setting
TR6 with adjustable setting
4
9
6
8
2
7
3
5
1
Bulb
Thermostatic element
Push pin seal
Balanced port
Check valve
Setting spindle for adjustment of static superheat
(SS)
Equalizer
Inlet connection
Outlet connection
Thermostatic Expansion Valves, Type TR6
Design and function
Table 1: Design and function
© Danfoss | Climate Solutions | 2021.02 AI318728845972en-000401 | 7
Page 8

SSOSOSH
Static superheat
Opening superheat at nominal/ rated capacity
SS + OS = Operating superheat
Danfoss
67U02.10
45.5 mm / 1.79 in.
46.3 mm / 1.82 in.
7.5 mm /
0.30 in.
35.5 mm /
1.40 in.
29.4 mm /
1.16 in.
Danfoss
67U03.10
47 mm / 1.85 in.
40.5 mm / 1.59 in.
Ø14.35 mm /
0.565 in.
22.7 mm /
0.89 in.
Thermostatic Expansion Valves, Type TR6
Figure 6: Static/opening superheat graph
The central push pin is sealed with a robust seal (pos. 3) that ensures maximum tightness and minimum friction
through the lifetime of the valve.
The balanced port (pos. 4) ensures minimal superheat changes when condensing pressure varies. This feature
makes the valve ideal for bi-ow operation.
Static superheat (SS) can be adjusted with the setting spindle (pos. 6).
Example
Static superheat
SS = 4 K / 7.2 °F (factory setting)
or according to customer specication
Opening superheat at nominal/ rated capacity OS = 4 K / 7.2 °F
Opening superheat is dened as the required superheat to open the valve to nominal capacity
Dimensions and weights
Fixed setting
Table 2: Fixed setting
Weight 0.305 kg, 0.672 lbs
© Danfoss | Climate Solutions | 2021.02 AI318728845972en-000401 | 8
Page 9

Danfoss
67U05.10
45.5 mm / 1.79 in.
46.3 mm / 1.82 in.
7.5 mm /
0.30 in.
43.1 mm / 1.70 in.
29.4 mm /
1.16 in.
Danfoss
67U06.10
47 mm / 1.85 in.
Ø14.35 mm /
0.565 in.
48.1 mm / 1.89 in.
22.9 mm /
0.90 in.
Thermostatic Expansion Valves, Type TR6
Adjustable setting
Table 3: Adjustable setting
Weight 0.361 kg; 0.795 lbs
© Danfoss | Climate Solutions | 2021.02 AI318728845972en-000401 | 9
Page 10

Danfoss
R64-1825.11
t
l
t
e
p
e
B
A
C
ABC
TR6
RD Distributor
Compressor
Valve type
Orice no.
Rated capacity
Connections solder ODF
Code no.
Multi pack
(1)
R410A
(2)
R407C
R22
Inlet x Out‐
let [in.]
Pressure
equalization
[in.]
[KW]
[TR]
[KW]
[TR]
[KW]
[TR]
TR63––9.8
2.8113.1
3⁄8 × 3⁄8
1⁄4
067L5855
TR64––13.8
3.9
15.5
4.4
3⁄8 × 3⁄8
1⁄4
067L5856
TR65––16.4
4.7
18.4
5.2
3⁄8 × 3⁄8
1⁄4
067L5857
TR66––17.4
4.9
19.6
5.6
3⁄8 × 3⁄8
1⁄4
067L5858
TR67––20.9623.8
6.8
3⁄8 × 3⁄8
1⁄4
067L5859
TR6311.3
3.2––––
3⁄8 × 3⁄8
1⁄4
067L5955
TR6415.9
4.5––––
3⁄8 × 3⁄8
1⁄4
067L5956
TR6519
5.4––––
3⁄8 × 3⁄8
1⁄4
067L5957
TR6620.2
5.8––––
3⁄8 × 3⁄8
1⁄4
067L5958
TR6724.57––––3⁄8 × 3⁄8
1⁄4
067L5959
Thermostatic Expansion Valves, Type TR6
Ordering
R22 / R407C and R410A
Figure 7: Adjustable setting
Table 4: R22 / R407C and R410A
(1)
(1)
Kit part numbers consist of a valve, bulb strap, insulation tape, installation guide, and the following connectors:
Kit part numbers consist of a valve, bulb strap, insulation tape, installation guide, and the following connectors:
1 Chatle female 3⁄4 in. connector
1 Chatle female 3⁄4 in. connector
1 Aeroquip female 5⁄8 in. connector
1 Aeroquip female 5⁄8 in. connector
1 Flare 3⁄8 in. connector
1 Flare 3⁄8 in. connector
(2)
(2)
The rated capacity is based on:
The rated capacity is based on:
Evaporating temperature te : 4.4 °C / 40 °F
Evaporating temperature te : 4.4 °C / 40 °F
Condensing temperature tc : 38 °C / 100 °F
Condensing temperature tc : 38 °C / 100 °F
Refrigerant temperature ahead of valve tl : 37 °C / 98 °F
Refrigerant temperature ahead of valve tl : 37 °C / 98 °F
Temperature range = -10 to 15 °C / 15 to 60 °F = 4 K / 7.2 °F
TR6 with xed superheat setting are available upon request.
Single pack = 1 valve kit in a box
Industrial pack = 12 pieces in one box
Sizing
Figure 8: Sizing
Example:
Refrigerant=R410A
© Danfoss | Climate Solutions | 2021.02 AI318728845972en-000401 | 10
Page 11

Thermostatic Expansion Valves, Type TR6
Evaporating temperature=(te=45 °F;pe=131 psig)
Condensing temperature =(tc=110 °F;pc=368 psi
Liquid line tl= 100 °F
pressure drop in liquid line, drier and distributor system Dp2+ Dp1=35 psi
Pressure drop in valve Dp = 368 - 131 - 35 = 202 psi
Subcooling Δtsub = tc – tl=10 °F
Evaporator capacity = 4.0 TR
Correction factor from table= 1.02
The corrected evaporator capacity then becomes 4.0 × 1.02 = 4.08 TR
As the selected valve must be equal to or slightly larger than the corrected evaporator capacity of 4.08 TR, the TR6
with orice 4 would be a suitable choice. Reference table below for rated capacities.
© Danfoss | Climate Solutions | 2021.02 AI318728845972en-000401 | 11
Page 12

File name
Document type
Document topic
Approval authority
067U9601 Vr.AB
Manufacturers Declaration
China RoHs
Danfoss
Thermostatic Expansion Valves, Type TR6
Certicates, declarations, and approvals
The list contains all certicates, declarations, and approvals for this product type. Individual code number may have
some or all of these approvals, and certain local approvals may not appear on the list.
Some approvals may change over time. You can check the most current status at danfoss.com or contact your local
Danfoss representative if you have any questions.
Table 5: Declaration for TR6
© Danfoss | Climate Solutions | 2021.02 AI318728845972en-000401 | 12
Page 13

Online support
Danfoss oers a wide range of support along with our products, including digital product information, software,
mobile apps, and expert guidance. See the possibilities below.
The Danfoss Product Store
The Danfoss Product Store is your one-stop shop for everything product related—no matter where
you are in the world or what area of the cooling industry you work in. Get quick access to essential
information like product specs, code numbers, technical documentation, certications, accessories,
and more.
Start browsing at store.danfoss.com.
Find technical documentation
Find the technical documentation you need to get your project up and running. Get direct access to
our ocial collection of data sheets, certicates and declarations, manuals and guides, 3D models
and drawings, case stories, brochures, and much more.
Start searching now at www.danfoss.com/en/service-and-support/documentation.
Danfoss Learning
Danfoss Learning is a free online learning platform. It features courses and materials specically
designed to help engineers, installers, service technicians, and wholesalers better understand the
products, applications, industry topics, and trends that will help you do your job better.
Create your Danfoss Learning account for free at www.danfoss.com/en/service-and-support/learning.
Get local information and support
Local Danfoss websites are the main sources for help and information about our company and
products. Find product availability, get the latest regional news, or connect with a nearby expert—all
in your own language.
Find your local Danfoss website here: www.danfoss.com/en/choose-region.
Coolselector®2 - nd the best components for you HVAC/R system
Coolselector®2 makes it easy for engineers, consultants, and designers to nd and order the best
components for refrigeration and air conditioning systems. Run calculations based on your operating
conditions and then choose the best setup for your system design.
Download Coolselector®2 for free at coolselector.danfoss.com.
Danfoss can accept no responsibility for possible errors in catalogues, brochures and other printed material. Danfoss reserves the right to alter its
products without notice. This also applies to products already on order provided that such alterations can be made without subsequential
changes being necessary in specications already agreed. All trademarks in this material are property of the respective companies. Danfoss and
the Danfoss logotype are trademarks of Danfoss A/S. All rights reserved.
© Danfoss | Climate Solutions | 2021.02 AI318728845972en-000401 | 13
 Loading...
Loading...