Daikin JEHCCU0050M1, JEHCCU0075L1, JEHCCU0088M1, JEHCCU0175L1, JEHCCU0150M1 Installation manuals
...
Installation Manual
Medium temperature application Low temperature application
JEHCCU0050M1 JEHCCU0075L1
JEHCCU0088M1 JEHCCU0175L1
JEHCCU0150M1 JEHCCU0175L3
JEHCCU0150M3 JEHCCU0225L1
JEHCCU0225M1 JEHCCU0225L3
JEHCCU0225M3 JEHCCU0350L3
JEHCCU0300M1 JEHCCU0400L3
JEHCCU0300M3 JEHCCU0725L3
JEHCCU0400M3 JEHCCU0825L3
JEHCCU0500M3
JEHCCU0600M3
JEHCCU0675M3
JEHCCU0825M3
JEHCCU1000M3
2
Important Note
Contents
1. Nomenclature 2
2. Safety and Health 2
3. Installation & commissioning 2
4. Service and Maintenance 4
5. Checklist 5
6. Trouble Shooting 5
7. Specifications 6
8. Outline Drawings 7
9. Electrical Data 9
10. Declaration of conformity 12
1. Nomenclature
JEHCCU 0150 M 1
JEHCCU 0150 M 1
1: Single Phase
1: Single Phase
3: Three Phase
3: Three Phase
Application
Application
M: Medium Temperature
M: Medium Temperature
L: Low Temperature
L: Low Temperature
Nominal Capacity in Horse Power
Nominal Capacity in Horse Power
0150: 1.5 HP
0150: 1.5 HP
J & E Hall Commercial Condensing Unit for Daikin
J & E Hall Commercial Condensing Unit for Daikin
2. Safety and Health
Only a qualified refrigeration engineer who is familiar
with refrigeration systems and components, including all
controls should perform the installation and start-up of
the system. To avoid potential injury, use care when
working around coil surfaces or sharp edges of metal
cabinets. All piping and electrical wiring should be
installed in accordance with all applicable codes,
ordinances and local by-laws.
• The electrical covers and condenser fan guard must
remain fitted at all times.
• Use of the condensing unit outside of design conditions
and application for which units were intended may be
unsafe and be detrimental to the unit, regardless short
or long term operation.
• The condensing units are not designed to withstand
loads or stresses from other equipment or personnel.
Such extraneous loads or stress may cause
failure/leak/injury.
• In some circumstances, a suction accumulator (not
supplied) component may be required, it offers
protection against refrigerant flood back during
operation. It helps protect against off-cycle migration by
adding internal free volume to the low side of the
system.
• Test must be conducted to ensure the amount of off-
cycle migration to the compressor does not exceed the
compressor’s charge limit.
• Wherever possible the system should be installed to
utilize a pump down configuration.
• After installation, the system should be allowed to run
for 3 – 4 hours. The oil level should be checked after 3
– 4 hours run time and topped up as necessary. The oil
level should be visible at least ½ - ¾ up the compressor
oil sight glass. For the details of the oil requirements,
please refer to page 4 in the installation &
commissioning section and page 4 in the service and
maintenance section.
3. Installation & Commissioning
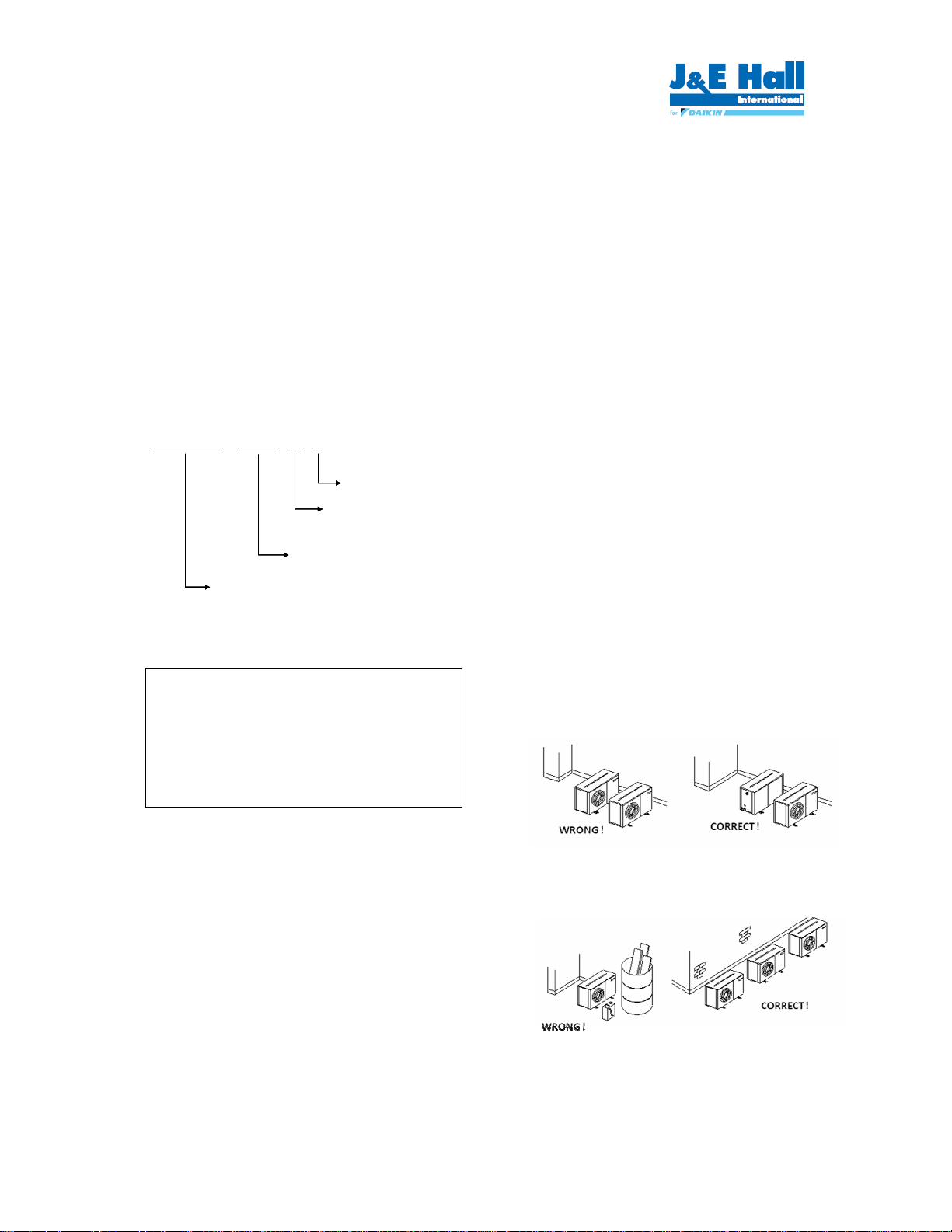
Unit site location
• In order to achieve maximum cooling capacity, the
installation location for condensing unit should be
carefully selected.
• Install the condensing unit in such a way so that hot air
distributed by the condensing unit cannot be drawn in
again (as in the case of short circuit of hot discharge
air). Allow sufficient space for maintenance around the
unit.
General Information
• Ensure the unit received is the correct model for the
intended application.
• Ensure refrigerant, voltage, are suitable for the
proposed application and environment.
• Installation and maintenance are to be performed only
by qualified personnel who are familiar with local codes
and regulations, and experienced with this type of
equipment.
• The condensing unit is delivered with a nitrogen holding
charge.
• The condensing unit contains moving machinery and
electrical power hazards. May cause severe injury or
death. Disconnect and shut off power before installation
or service of the equipment.
• Refrigerant release into the atmosphere is illegal.
Proper evacuation, handling and leak testing
procedures must be observed at all times.
• Units must be earthed and no maintenance work
should be attempted prior to disconnecting the
electrical supply.
• Ensure that there is no obstruction of air flow into or out
of the unit. Remove obstacles which block air intake or
discharge.
• The location must be well ventilated, so the unit can
draw in and distribute plenty of air thus lowering the
condensing temperature.
Rev 008/April 2009
All specifications are subjected to change by the manufacturer without prior notice
3
• To optimize the unit running conditions, the condenser
Important Note
coil must be cleaned at regular intervals.
Installation Clearance
• The installation location should allow sufficient space
for air flow and maintenance around the unit.
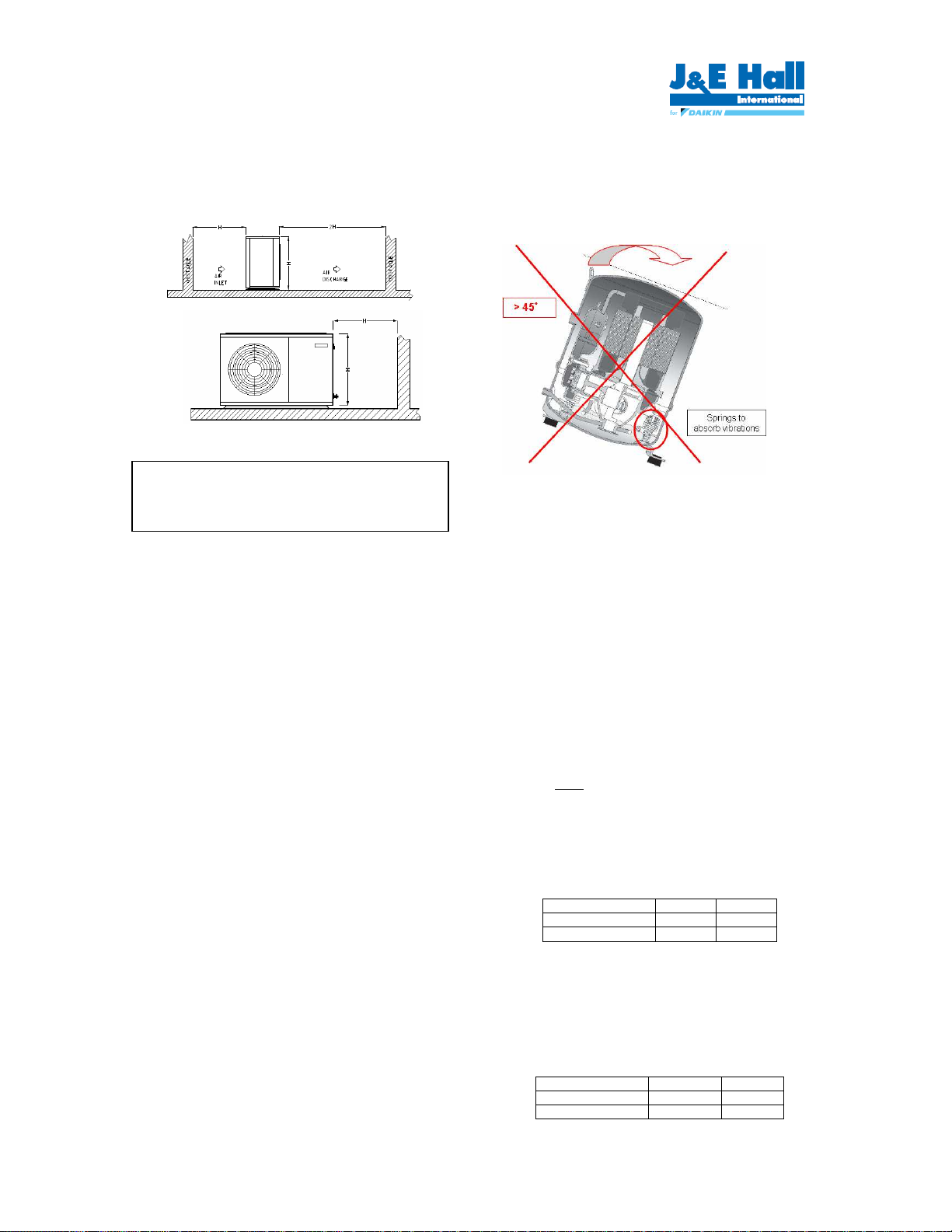
Compressor handling
To ensure compressor reliability, the condensing unit and
the compressor must not be tilt greater than an angle of 45°.
Otherwise, the compressor can fall from its 3 compressor
housing prings, which results in noisy vibrations during
operation.
Field Piping
Line sizing should only be determined by qualified
personnel. All local codes of practice must be observed
in the installation of refrigerant piping
To ensure satisfactory operation and performance, the
following points should be noted for field piping
arrangements,
• Pipework routes must be as simple and as short as
possible.
• Avoid low points on pipework where oil can
accumulate.
• Suction gas velocity must be sufficient to ensure good
oil return.
• Use only clean, dehydrated refrigeration grade copper
tube with large radius elbows.
• Braze without over filling to ensure there is no excess
solder into the tube.
• To prevent oxidation, blow nitrogen through pipework
when brazing.
• Install insulation on all suction lines.
• Adequately support all pipe work at a maximum of 2
meter intervals.
• In vertical pipework, the use of U-trap and double
suction risers is often required. These suction risers
must always be fitted with a U-trap at the bottom and a
P-trap at the top and never be higher than 4 meter
unless a second U-trap system is fitted.
• Recommend piping length less than 25m
Correct line sizing will minimize the pressure drop and
maintain sufficient gas velocity for proper oil return.
Leak detection
• Make sure that all manual valves are open
• Perform a leak test of the system using nitrogen mixed with
the refrigerant to be used
• Do not use CFC for leak testing the condensing unit which
will be used with HFC refrigerants
• The use of leak testing fluids is not recommended as this
may interact with the lubricants own additives
Pressure testing
• When running a pressure test, always use an inert, dry gas
such as Nitrogen
• The pressure differential between the high and low side
should not exceed 24 bar (350 psig)
• Maximum test pressures are :
25 bar (370 psig) on the Low Side
30 bar (480 psig) on the High Side
Safety pressure switch settings
The Danfoss KP17 HP/LP pressure switch fitted to condensing
units with auto reset for low pressure and manual reset for high
pressure is NOT factory preset. Be sure that the high pressure
setting does not exceed the receiver’s maximum service pressure.
High pressure safety
The high pressure safety switch is required to stop the compressor
should the discharge pressure exceed the values shown in the
following table. The high pressure switch can be set to lower
values depending on the application and the ambient conditions
Refrigerant R404A R134a
Cut Out (bar g) 28 22.6
Cut Out (psig) 405 325
Low pressure safety
The low pressure safety switch protects the compressor against
deep vacuum operation, a potential cause of failure due to internal
arching.
The low pressure safety cut should never be set below 0.1 bar (2
psig) as shown in the following table. For systems without pumpdown the LP switch signal contact shall be used to energize a low
pressure safety alarm
Refrigerant R404A R134a
Cut Out (bar g) 0.1 0.4
Cut In (bar g) 1.2 1.2
Rev 008/April 2009
All specifications are subjected to change by the manufacturer without prior notice

4
Important Note
Important Note
Important Note
Important Note
There must be no more than 12 compressor starts per
hour. A higher number reduces the service life of the
compressor. If necessary, use an anti-short-cycle timer in
the control circuit. A three minutes time out is required.
Fan speed controller*
The fan speed controller controls the speed of the
condenser.
It keeps the condensing pressure at a steady level by
changing the speed of the fan according to the required
condensing pressure.
1) Adjusting screw
2) Bellows
3) Range setting pointer (dual marking 11 and 19 bar)
4) Change over switch
5) Terminal board
6) ¼” flare with depression pin (7/16-20 UF)
Setting point can be increased by turning the adjusting
screw clockwise. Setting point can be decreased by turning
the adjusting screw counter clockwise. Adjustment should be
within the range indicated for the setting pointer.
With the Change over switch you can choose between two
settings:
Cut off: Fan motor stops when the pressure decreases
below the value Pmin.
Min. speed: Fan motor operates at the Minimum Speed
when the pressure decreases below the value Pmin.
F.V.S. = Full Voltage Set Point (pressure setting for
maximum speed)
E.P.B. = Effective Proportional Band
Pmin = (F.V.S. – E.P.B.)
* Except JEHCCU0050M1 / JEHCCU0088M1 /
JEHCCU0075L1
Vacuum - moisture removal
Warning! – Disconnect the mains electrical supply
before servicing or opening the unit
Moisture prevents proper functioning of the compressor
and the refrigeration system
Air and moisture reduce service life and increase
condensing pressure causing abnormally high discharge
temperatures likely to destroy the oil’s lubricating properties.
The risk of acid formation is also increased by air and
moisture and copper plating can be generated in this way.
All these phenomena can be cause mechanical and
electrical failure.
Ensure that a good quality vacuum pump is used to pull a
minimum vacuum of 250 microns (0.33 mbar)
Oil requirements
The polyoilester with the following characteristics must be
used:
Property Specification Test method
Viscosity at 40°C 31 – 33 cSt ASTM D 445
Viscosity at 100°C 5,6 cSt ASTM D 445
Density at 15,6 °C 0,97 g/ml
Colour 100
Pour point -45°C (max) ASTM D 97
Flash point 217°C ASTM D 93
Dielectric strength
at 25°C
Acid value (Tan) 0,15 mg KOH/g (max) ASTM D 974
The initial oil charge is 600 cm³
Example: polyoilester (POE) oil type 160PZ from Danfoss.
Commissioning of the Condensing Unit
Please make sure that all manual service valves are fully
open when starting the system for the first time.
This includes external shut off valves as well as liquid
receiver valve in the unit.
Characteristics of the oil
47 kV (min)
ASTM D
4052
ASTM D
1209
ASTM D
1816
4. Checklist
• Ensure crankcase heater is energized minimum
12 hours prior to start up and permanently
energized.
• Check all electrical connections.
• Check all electrical termination and circuits are
correct.
• Check compressor oil level.
• Ensure the high low pressure controls are
configured properly.
• Ensure fan motor and fan blades are installed
properly.
• Observed the system pressures during the
charging and initial operation process.
• Continue to charge the system until sight glass is
clear. Make sure that high pressure is > 12bar
when doing this charge adjustment operation.
• Check the compressor’s discharge and suction
pressure, ensure it’s within operating range.
• Check condenser fan, ensure warm air blowing off
the condenser coil.
Rev 008/April 2009
All specifications are subjected to change by the manufacturer without prior notice

5
• Check evaporator blower, ensure it’s discharging
cool air.
• Check evaporator superheat and adjust expansion
valve if necessary
5. Service and Maintenance
The condensing units are designed to give long life
operation with minimum maintenance. However, they should
be routinely checked and the following service schedule is
recommended under normal circumstances:
The removal of the top, side and front panels ensures that all
parts are accessible.
1. Compressor – Inspect at regular intervals
• Check for refrigerant leaks on all joints and fittings.
• Ensure that no abnormal noise or vibration is
detected during test run.
• Check the compressor oil levels and top up if
required. The oil level should be ½ to ¾ way up
the sight glass.
2. Condenser Fan Motor & Blade – Clean and inspect at
regular intervals
• Check for abnormal noise, vibration and fan
imbalance.
• Ensure that the fan motor is clean and spins
freely.
• Check that the condenser fan blade is clean and
free from restriction.
• Note: The Fan Motor is pre-lubricated and factory
sealed so no maintenance is necessary.
3. Condenser Coil – Clean and inspect at regular intervals
• Check and remove the dirt and debris between the
fins using a suitable chemical coil cleaner.
• Check and remove any obstacles which may
hinder the airflow through the condenser coil.
4. Power Supply – Inspect at regular intervals
• Check the running current and voltage for the
condensing unit.
• Check the electrical wiring and tighten the wires
Under normal circumstances:
onto the terminal blocks if necessary.
• Clean condenser coil every three months
• Carry out leak test every month
• Examine electrical cables and enclosures each
year
• Check and verify operation of all safety devices
every three months, ensure crankcase heater is
operational
• Check sight glass and operating conditions
• Check security of compressor mountings and the
bolts that hold down the unit each year
6. Trouble Shooting
This troubleshooting guide describes some common
condensing units failure. Consult qualified personnel before
any corrective actions are taken.
Failure Possible Causes
Fan does not work
Compressor does
not start
Insufficient cooling
• Improper wiring
• Fan motor faulty
• Improper wiring
• Defective contactor or coil
• System stopped because of
tripped of safety device.
• Defective start/run capacitor
• Compressor faulty
• Low refrigerant charge
• Condenser coil dirty
• Obstacle blocking air inlet/outlet
• Improper thermostat setting
Rev 008/April 2009
All specifications are subjected to change by the manufacturer without prior notice
 Loading...
Loading...