Multipurpose Units
EWYD 4Z
MultiPurpose Units
D-EOMZC00204-18_01EN
Operation Manual
1/48
REV
01
Date
May 2018
Supersedes
D-EOMZC00204-18_00EN
EWYD4Z - Multipurpose Unit
D-EOMZC00204-18_01EN
OPERATING MANUAL

Multipurpose Units
D-EOMZC00204-18_01EN
Operation Manual
2/48
EWYD 4Z
MultiPurpose Units
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 SAFETY CONSIDERATIONS ....................................................................................................................................... 4
1.1 General ..................................................................................................................................................................................... 4
1.2 Avoid electrocution.................................................................................................................................................................... 4
1.3 Safety Devices .......................................................................................................................................................................... 4
2 GENERAL DESCRIPTION ............................................................................................................................................ 5
2.1 Basic Information ...................................................................................................................................................................... 5
2.2 Abbreviations used ................................................................................................................................................................... 5
2.3 Controller Operating Limits ....................................................................................................................................................... 5
2.4 Controller Architecture .............................................................................................................................................................. 5
2.5 Communication Modules........................................................................................................................................................... 6
3 USING THE CONTROLLER ......................................................................................................................................... 7
3.1 General Recommendation ........................................................................................................................................................ 7
3.2 Navigating ................................................................................................................................................................................. 7
3.3 Passwords ................................................................................................................................................................................ 8
3.4 Editing ...................................................................................................................................................................................... 8
3.5 Basic Control System Diagnostic .............................................................................................................................................. 8
3.6 Controller maintenance ............................................................................................................................................................. 9
3.7 Optional Remote User Interface ................................................................................................................................................ 9
3.8 Embedded Web Interface ....................................................................................................................................................... 10
4 WORKING WITH THIS UNIT ...................................................................................................................................... 12
4.1 Unit Setup ............................................................................................................................................................................... 12
4.1.1 Control Source .............................................................................................................................................................. 12
4.1.2 Operating Mode ............................................................................................................................................................. 12
4.1.3 Temperature Settings .................................................................................................................................................... 12
4.1.4 Pumps settings .............................................................................................................................................................. 13
4.1.5 Alarm Settings ................................................................................................................................ ............................... 13
4.1.6 Power Conservation ...................................................................................................................................................... 13
4.1.6.1 Demand Limit ..................................................................................................................................... 13
4.1.6.2 Current Limit (Optional) ...................................................................................................................... 14
4.1.6.3 Setpoint Reset .................................................................................................................................... 14
4.1.6.4 Setpoint Reset by OAT Reset ............................................................................................................ 14
4.1.6.5 Setpoint Reset by External 4-20 mA Signal ....................................................................................... 15
4.1.6.6 Setpoint Reset by Evaporator Return Temperature ........................................................................... 15
4.1.7 Date/Time ...................................................................................................................................................................... 15
4.1.7.1 Date,Time and UTC Settings ............................................................................................................. 15
4.1.7.2 Quiet Mode Scheduling ...................................................................................................................... 15
4.1.8 Scheduler ...................................................................................................................................................................... 15
4.2 Unit/Circuit Start-up................................................................................................................................................................. 15
4.2.1 Prepare the unit to start ................................................................................................................................................. 16
4.2.1.1 Unit Enable ......................................................................................................................................... 16
4.2.2 Unit Status ..................................................................................................................................................................... 16
4.2.3 Circuits Enable .............................................................................................................................................................. 17
4.2.4 Circuit Status ................................................................................................................................ ................................. 17
4.2.5 Circuit Preventions ........................................................................................................................................................ 18
4.2.5.1 High Water Temperature Limit ........................................................................................................... 18
4.2.5.2 Low Evaporating Pressure ................................................................................................................. 18
4.2.5.3 High Condensing Pressure ................................................................................................................ 18
4.2.5.4 High Vfd Current ................................................................................................................................ 19
4.2.5.5 High Discharge Temperature ............................................................................................................. 19
5 TROUBLESHOOTING ................................................................................................................................................ 20
5.1 Unit Alerts ................................ ................................................................................................................................ ............... 20
5.1.1 Bad Current Limit Input .................................................................................................................................................. 20
5.1.2 Bad Demand Limit Input ................................................................................................................................................ 20
5.1.3 Bad Leaving Water Temperature Reset Input ................................................................................................................ 21
5.1.4 Condenser Pump #1 Failure .......................................................................................................................................... 21
5.1.5 Condenser Pump #2 Failure .......................................................................................................................................... 21
5.1.6 Energy Meter Communication Fail ................................................................................................................................. 21
5.1.7 Evaporator Pump #1 Failure .......................................................................................................................................... 22
5.1.8 Evaporator Pump #2 Failure .......................................................................................................................................... 22
5.1.9 External Event ............................................................................................................................................................... 22
5.1.10 Fan Alarm Module Communication Fail ......................................................................................................................... 23
5.1.11 Heat Recovery Entering Water Temperature sensor fault .............................................................................................. 23
5.1.12 Heat Recovery Leaving Water Temperature sensor fault ............................................................................................... 23
5.1.13 Heat Recovery Water Temperatures inverted ................................................................................................................ 24

Multipurpose Units
EWYD 4Z
MultiPurpose Units
D-EOMZC00204-18_01EN
Operation Manual
3/48
5.1.14 Rapid Recovery Module Communication Fail ................................................................................................................ 24
5.1.15 Switch Box Temperature sensor fault ............................................................................................................................ 24
5.2 Unit Pumpdown Stop Alarms .................................................................................................................................................. 25
5.2.1 Condenser Entering Water Temperature (EWT) sensor fault ......................................................................................... 25
5.2.2 Condenser Leaving Water Temperature (LWT) sensor fault .......................................................................................... 25
5.2.3 Evaporator Entering Water Temperature (EWT) sensor fault ......................................................................................... 25
5.2.4 Evaporator Water Temperatures inverted ...................................................................................................................... 26
5.2.5 Outside Air Temperature (OAT) Lockout ................................................................................................ ........................ 26
5.2.6 Outside Air Temperature sensor fault alarm................................................................................................ ................... 26
5.3 Unit Rapid Stop Alarms ........................................................................................................................................................... 26
5.3.1 Condenser Water Freeze alarm ..................................................................................................................................... 26
5.3.2 Condenser Water Flow Loss alarm ................................................................................................................................ 27
5.3.3 Emergency Stop ............................................................................................................................................................ 27
5.3.4 Evaporator Flow Loss alarm ......................................................................................................................................... 27
5.3.5 Evaporator Leaving Water Temperature (LWT) sensor fault .......................................................................................... 28
5.3.6 Evaporator Water Freeze alarm ..................................................................................................................................... 28
5.3.7 External alarm ............................................................................................................................................................... 28
5.3.8 Gas Leakage Alarm ....................................................................................................................................................... 29
5.3.9 Heat Recovery Water Freeze Protect alarm ................................................................................................................... 29
5.3.10 OptionCtrlrCommFail ..................................................................................................................................................... 29
5.3.11 Power Fault ................................................................................................................................................................... 29
5.3.12 PVM alarm .................................................................................................................................................................... 30
5.4 Circuit Alerts ........................................................................................................................................................................... 30
5.4.1 Economizer Pressure Sensor fault ................................................................................................................................. 30
5.4.2 Economizer Temperature Sensor fault ........................................................................................................................... 31
5.4.3 Failed Pumpdown .......................................................................................................................................................... 31
5.4.4 Fan Fault ....................................................................................................................................................................... 32
5.4.5 Gas Leakage Sensor fault ............................................................................................................................................. 32
5.4.6 CxCmp1 MaintCode01 .................................................................................................................................................. 32
5.4.7 CxCmp1 MaintCode02 .................................................................................................................................................. 32
5.4.8 Power Loss.................................................................................................................................................................... 33
5.5 Circuit Pumpdown Stop Alarms ............................................................................................................................................... 33
5.5.1 Discharge Temperature Sensor fault ............................................................................................................................. 33
5.5.2 Gas Leakage fault ......................................................................................................................................................... 33
5.5.3 High Compressor Vfd Temperature fault ................................................................................................ ........................ 34
5.5.4 Liquid Temperature Sensor fault .................................................................................................................................... 34
5.5.5 Low Compressor Vfd Temperature fault ........................................................................................................................ 34
5.5.6 Low Oil Level fault ......................................................................................................................................................... 35
5.5.7 Low Discharge Superheat fault ...................................................................................................................................... 35
5.5.8 Oil Pressure Sensor fault ............................................................................................................................................... 35
5.5.9 Suction Temperature Sensor fault ................................................................................................................................. 36
5.6 Circuit Rapid Stop Alarms ....................................................................................................................................................... 36
5.6.1 Compressor Extension Communication Error ................................................................................................................ 36
5.6.2 EXV Driver Extension Communication Error .................................................................................................................. 36
5.6.3 Compressor VFD Fault .................................................................................................................................................. 37
5.6.4 Compressor VFD OverTemp ......................................................................................................................................... 37
5.6.5 Condensing Pressure sensor fault ................................................................................................................................. 37
5.6.6 Economizer EXV Driver Error ........................................................................................................................................ 38
5.6.7 Economizer EXV Motor Not Connected ......................................................................................................................... 38
5.6.8 Evaporating Pressure sensor fault ................................................................................................................................. 38
5.6.9 EXV Driver Error ............................................................................................................................................................ 39
5.6.10 EXV Motor Not Connected (TZ B, MP) .......................................................................................................................... 39
5.6.11 Fail Start Low Pressure ................................................................................................................................................. 39
5.6.12 Fan VFD Over Current................................................................................................................................................... 39
5.6.13 High Discharge Temperature Alarm ............................................................................................................................... 40
5.6.14 High Motor Current Alarm .............................................................................................................................................. 40
5.6.15 High Motor Temperature Alarm ..................................................................................................................................... 41
5.6.16 High Oil Pressure Differential Alarm .............................................................................................................................. 41
5.6.17 High Pressure alarm ...................................................................................................................................................... 41
5.6.18 Low Pressure alarm ....................................................................................................................................................... 42
5.6.19 Low Pressure Ratio Alarm ............................................................................................................................................. 42
5.6.20 Maximum Number of Restart Alarm ............................................................................................................................... 43
5.6.21 Mechanical High Pressure Alarm ................................................................................................................................... 43
5.6.22 Mechanical Low Pressure Alarm.................................................................................................................................... 44
5.6.23 No Pressure At Start Alarm............................................................................................................................................ 44
5.6.24 No Pressure Change At Start Alarm .............................................................................................................................. 44
5.6.25 Overvoltage Alarm ......................................................................................................................................................... 45
5.6.26 Undervoltage Alarm ....................................................................................................................................................... 45
5.6.27 VFD Communication Failure .......................................................................................................................................... 46
6 OPTIONS .................................................................................................................................................................... 47
6.1 Energy Meter including Current Limit (Optional) ...................................................................................................................... 47

Multipurpose Units
D-EOMZC00204-18_01EN
Operation Manual
4/48
EWYD 4Z
MultiPurpose Units
RISK OF ELECTROCUTION: Even when the main circuit breaker or isolator is switched off, certain circuits may
still be energized, since they may be connected to a separate power source.
RISK OF BURNS: Electrical currents cause components to get hot either temporarily or permanently. Handle
power cable, electrical cables and conduits, terminal box covers and motor frames with great care.
ATTENTION: In accordance with the operating conditions the fans can be cleaned periodically. A fan can start at
any time, even if the unit has been shut down.
The emergency stop causes all motors to stop, but does not switch off power to the unit. Do not service or
operate on the unit without having switched off the main switch.
Do not operate on a faulty fan before the main switch has been shut off. Overtemperature protection is autoreset, therefore a fan may restart automatically if temperature conditions allow it.
Direct intervention on the power supply can cause electrocution, burns or even death. This action must be
performed only by trained persons.
1 SAFETY CONSIDERATIONS
1.1 General
Installation, start-up and servicing of equipment can be hazardous if certain factors particular to the installation are not
considered: operating pressures, presence of electrical components and voltages and the installation site (elevated plinths
and built-up up structures). Only properly qualified installation engineers and highly qualified installers and technicians,
fully trained for the product, are authorized to install and start-up the equipment safely.
During all servicing operations, all instructions and recommendations, which appear in the installation and service
instructions for the product, as well as on tags and labels fixed to the equipment and components and accompanying parts
supplied separately, must be read, understood and followed.
Apply all standard safety codes and practices.
Wear safety glasses and gloves.
Use the proper tools to move heavy objects. Move units carefully and set them down gently.
1.2 Avoid electrocution
Only personnel qualified in accordance with IEC (International Electrotechnical Commission) recommendations may be
permitted access to electrical components. It is particularly recommended that all sources of electricity to the unit be shut
off before any work is begun. Shut off main power supply at the main circuit breaker or isolator.
IMPORTANT: This equipment uses and emits electromagnetic signals. Tests have shown that the equipment
conforms to all applicable codes with respect to electromagnetic compatibility.
1.3 Safety Devices
Each unit is equipped with safety devices of three different kinds:
Emergency Stop
Overcurrent/Overload Protections
Overtemperature Protections
Phase reversal, under/over voltage, ground fault protections
Phase reversal, under/over voltage, ground fault protections
Freezing protection
High Pressure Protection
Low Pressure Protection
Mechanical High Pressure Switch
Relief Safety Valve
Inverter fault auto diagnostic

Multipurpose Units
EWYD 4Z
MultiPurpose Units
D-EOMZC00204-18_01EN
Operation Manual
5/48
A/C
Air Cooled
CEWT
Condenser Entering Water Temperature
CLWT
Condenser Leaving Water Temperature
CP
Condensing Pressure
CSRT
Condensing Saturated Refrigerant Temperature
DSH
Discharge Superheat
DT
Discharge Temperature
E/M
Energy Meter Module
EEWT
Evaporator Entering Water Temperature
ELWT
Evaporator Leaving Water Temperature
EP
Evaporating Pressure
ESRT
Evaporating Saturated Refrigerant Temperature
EXV
Electronic Expansion Valve
HMI
Human Machine Interface
MOP
Maximum operating pressure
SSH
Suction SuperHeat
ST
Suction Temperature
UC
Unit controller (Microtech III)
W/C
Water Cooled
2 GENERAL DESCRIPTION
2.1 Basic Information
Microtech® III is a system for controlling single or dual-circuit air/water-cooled liquid chillers. Microtech® III controls
compressor start-up necessary to maintain the desired heat exchanger leaving water temperature. In each unit mode it
controls the operation of the condensers to maintain the proper condensation process in each circuit.
Safety devices are constantly monitored by Microtech® III to ensure their safe operation. Microtech® III also gives access
to a Test routine covering all inputs and outputs. All Microtech® III controls can work in accordance with three independent
modes:
Local mode: the unit is controlled by commands from the user interface.
Remote mode: the unit is controlled by remote contacts (volt-free contacts).
Network mode: the unit is controlled by commands from a BAS system. In this case, a data communication cable
is used to connect the unit to the BAS.
When the Microtech® III system operates autonomously (Local or Remote mode) it retains all of its own control capabilities
but does not offer any of the features of the Network mode. In this case monitoring of the unit operational data is still
allowed.
2.2 Abbreviations used
In this manual, the refrigeration circuits are called circuit #1 and circuit #2. The compressor in circuit #1 is labelled Cmp1.
The other in circuit #2 is labelled Cmp2. The following abbreviations are used:
2.3 Controller Operating Limits
Operation (IEC 721-3-3):
Temperature -40...+70 °C
Restriction LCD -20… +60 °C
Restriction Process-Bus -25….+70 °C
Humidity < 90 % r.h (no condensation)
Air pressure min. 700 hPa, corresponding to max. 3,000 m above sea level
Transport (IEC 721-3-2):
Temperature -40...+70 °C
Humidity < 95 % r.h (no condensation)
Air pressure min. 260 hPa, corresponding to max. 10,000 m above sea level.
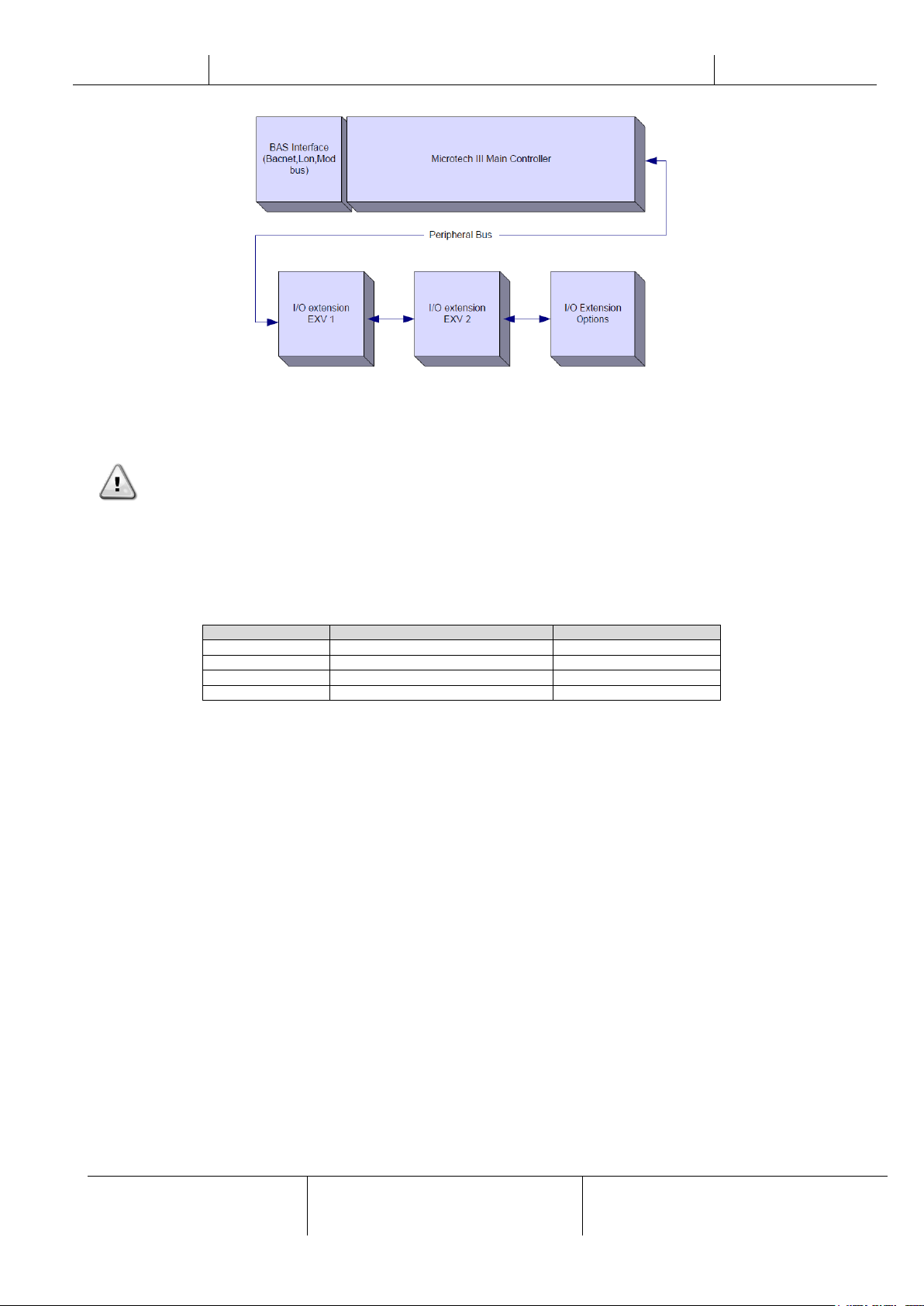
2.4 Controller Architecture
The overall controller architecture is the following:
One MicroTech III main controller
I/O extensions as needed depending on the configuration of the unit
Communications interface(s) as selected
Peripheral Bus is used to connect I/O extensions to the main controller.
Multipurpose Units
D-EOMZC00204-18_01EN
Operation Manual
6/48
EWYD 4Z
MultiPurpose Units
CAUTION: Maintain the correct polarity when connecting the power supply to the boards, otherwise the peripheral
bus communication will not operate and the boards may be damaged.
Module
Siemens Part Number
Usage
BacNet/IP
POL908.00/MCQ
Optional
Lon
POL906.00/MCQ
Optional
Modbus
POL902.00/MCQ
Optional
BACnet/MSTP
POL904.00/MCQ
Optional
All boards are supplied from a common 24 Vac source. Extension boards can be directly powered by the Unit Controller.
All boards can be also supplied by a 24Vdc source.
2.5 Communication Modules
Any of the following modules can be connected directly to the left side of the main controller to allow a BAS or other remote
interface to function. Up to three can be connected to the controller at a time. The controller should automatically detect
and configure itself for new modules after booting up. Removing modules from the unit will require manually changing the
configuration.
Multipurpose Units
EWYD 4Z
MultiPurpose Units
D-EOMZC00204-18_01EN
Operation Manual
7/48
Alarm status (from any page it links with the page with alarm list, alarm log and alarm snapshot if available)
Back to Main Page
Back to the previous level (it can be the Main Page)
M a i n M e n u 1 /
11
E n t e r P a s s w o r d
U n i t S t a t u s = O f f : U n i t S W
A c t i v e S e t p t = 7 . 0 °
C
M a i n M e n u 1 / E n t e r P a s s w o r d
U n i t S t a t u s =
O f f : U n i t S W A c t i v e S e t p t = 7 . 0 °
C
A
B
C
UC
A
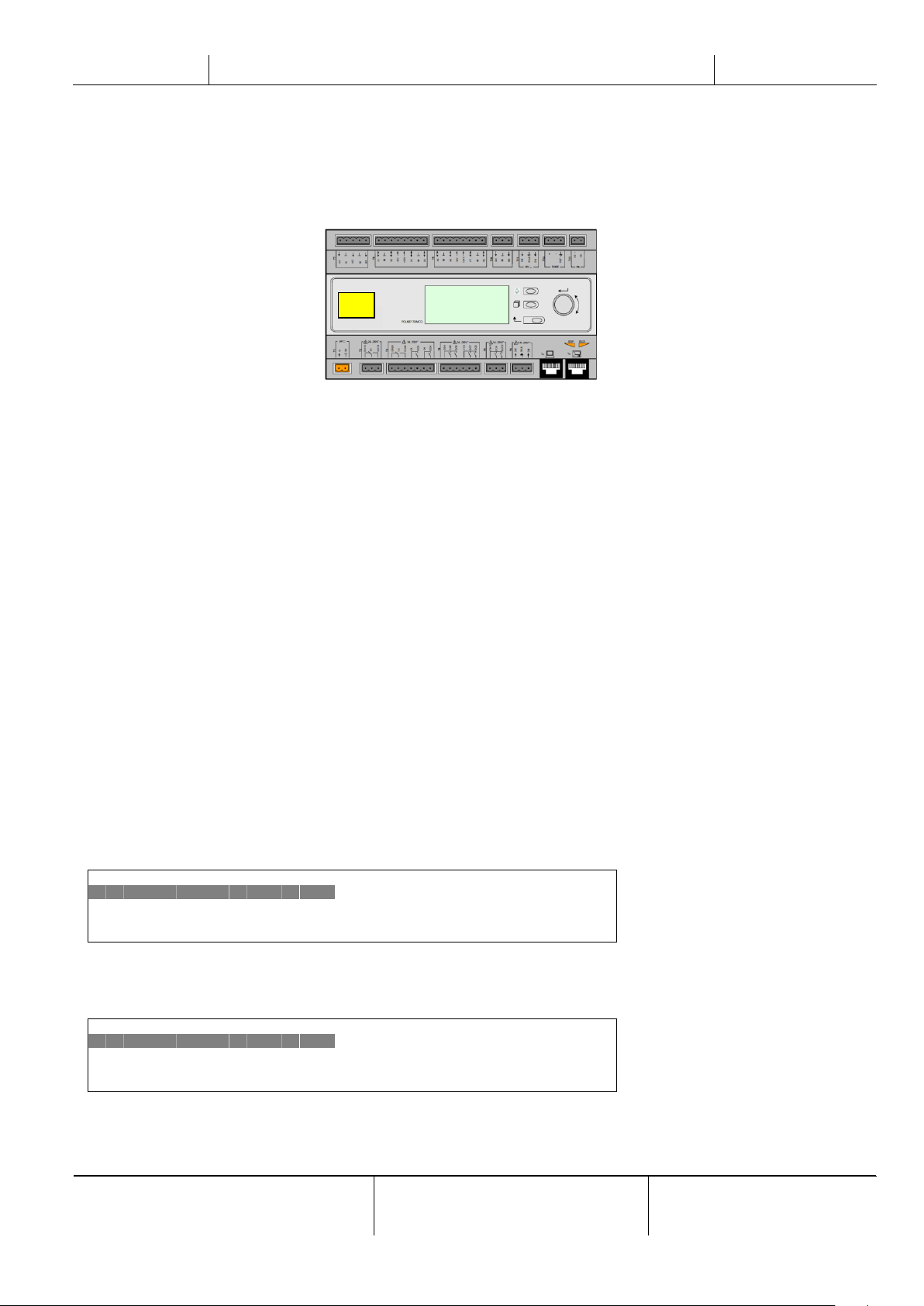
3 USING THE CONTROLLER
The control system consists of a unit controller (UC) equipped with a set of extension modules that implement additional
features. All boards communicate via an internal peripheral bus with the UC. The Microtech III continuously manages the
information received from the various pressure and temperature probes installed on the compressors and communicated
to the unit .The UC incorporates a program that controls the unit.
The standard HMI consists of an inbuilt display (A) with 3 buttons (B) and a push’n’roll control (C).
The keypad/display (A) consists of a 5-line by 22 character display. The function of the three buttons (B) is described
below:
The push’n’roll command (C) is used to scroll between the different menu pages, settings and data available on the HMI
for the active password level. Rotating the wheel allows to navigate between lines on a screen (page) and to increase and
decrease changeable values when editing. Pushing the wheel acts as an Enter Button and will jump from a link to the next
set of parameters.
3.1 General Recommendation
Before switching on the unit read the following recommendations:
When all the operations and all the settings have been carried out, close all the switchbox panels
The switchbox panels can only be opened by trained personnel
When the UC requires to be accessed frequently the installation of a remote interface is strongly recommended
Evaporator, compressors and related inverters are protected from freezing by electrical heaters. These heaters
are supplied through unit main supply and temperature controlled by thermostat or by the unit controller. Also the
LCD display of the unit controller may be damaged by extremely low temperatures. For this reason, it is strongly
recommended to never power off the unit during winter, especially in cold climates.
3.2 Navigating
When power is applied to the control circuit, the controller screen will be active and display the Home screen, which can
also be accessed by pressing the Menu Button. The navigating wheel is the only navigating device necessary, although
the MENU, ALARM, and BACK buttons can provide shortcuts as explained previously.
An example of the HMI screens is shown in the following picture.
A bell ringing in the top right corner will indicate an active alarm. If the bell doesn’t move it means that the alarm has been
acknowledged but not cleared because the alarm condition hasn’t been removed. A LED will also indicate where the alarm
is located between the unit or circuits.
The active item is highlighted in contrast, in this example the item highlighted in Main Menu is a link to another page. By
pressing the push’n’roll, the HMI will jump to a different page. In this case the HMI will jump to the Enter Password page.
Multipurpose Units
D-EOMZC00204-18_01EN
Operation Manual
8/48
EWYD 4Z
MultiPurpose Units
E n t e r P a s s w o r d 2 /
2
E n t e r P W * * *
*
USER
5321
MAINTENANCE
2526
E n t e r P a s s w o r d 2 /
2
E n t e r P W 5 * *
*
BSP LED
Mode
Solid Green
Application running
Solid Yellow
Application loaded but not running (*) or BSP Upgrade mode active
Solid Red
Hardware Error (*)
Flashing Green
BSP startup phase. The controller needs time for starting.
Flashing Yellow
Application not loaded (*)
Flashing Yellow/Red
Fail safe mode (in case that the BSP upgrade was interrupted)
Flashing Red
BSP Error (software error*)
Flashing Red/Green
Application/BSP update or inizialization
BSP LED
Mode
BUS LED
Mode
Solid Green
BSP running
Solid Green
Communication running, I/O working
Solid Red
Hardware Error (*)
Solid Red
Communication down (*)
3.3 Passwords
The HMI structure is based on access levels that means that each password will disclose all the settings and parameters
allowed to that password level. Basic informations about the status including the active alarm list, active setpoint and
controlled water temperature can be accessed without the need to enter the password. The user UC handles two level of
passwords:
The following information will cover all data and settings accessible with the maintenance password. User
password will disclose a subset of the settings explained in chapter Errore. L'origine riferimento non è stata trovata..
In the Enter Password screen, the line with the password field will be highlighted to indicate that the field on the right can
be changed. This represents a setpoint for the controller. Pressing the push’n’roll the individual field will be highlighted to
allow an easy introduction of the numeric password. By changing all fields, the 4 digits password will be entered and, if
correct, the additional settings available with that password level will be disclosed.
The password will time out after 10 minutes and is cancelled if a new password is entered or the control powers down.
Entering an invalid password has the same effect as continuing without a password.
Once a valid password has been entered, the controller allows further changes and access without requiring the user to
enter a password until either the password timer expires or a different password is entered. The default value for this
password timer is 10 minutes. It is changeable from 3 to 30 minutes via the Timer Settings menu in the Extended Menus.
3.4 Editing
The Editing Mode is entered by pressing the navigation wheel while the cursor is pointing to a line containing an editable
field. Once in the edit mode pressing the wheel again causes the editable field to be highlighted. Turning the wheel
clockwise while the editable field is highlighted causes the value to be increased. Turning the wheel counter-clockwise
while the editable field is highlighted causes the value to be decreased. The faster the wheel is turned, the faster the value
is increased or decreased. Pressing the wheel again cause the new value to be saved and the keypad/display to leave the
edit mode and return to the navigation mode.
A parameter with an “R” is read only; it is giving a value or description of a condition. An “R/W indicates a read and/or write
opportunity; a value can be read or changed (providing the proper password has been entered).
3.5 Basic Control System Diagnostic
MicroTech III controller, extension modules and communication modules are equipped with two status LED (BSP and BUS)
to indicate the operational status of the devices. The BUS LED indicates the status of the communication with the controller.
The meaning of the two status LED is indicated below.
Main Controller (UC)
(*) Contact Service.
Extension modules
Multipurpose Units
EWYD 4Z
MultiPurpose Units
D-EOMZC00204-18_01EN
Operation Manual
9/48
Flashing Red
BSP Error (*)
Solid Yellow
Communication running but parameter from the application
wrong or missing, or uncorrect factory calibration
Flashing Red/Green
BSP upgrade mode
BSP LED
Mode
Solid Green
BPS running, communication with controller
Solid Yellow
BSP running, no communication with controller (*)
Solid Red
Hardware Error (*)
Flashing Red
BSP Error (*)
Flashing Red/Green
Application/BSP update
BUS LED
LON
Bacnet MSTP
Bacnet IP
Modbus
Solid Green
Ready for
Communication. (All
Parameter loaded,
Neuron configured).
Doesn't indicate a
communication with other
devices.
Ready for
Communication. The
BACnet Server is started.
It doesn't indicate an
active communication
Ready for
Communication. The
BACnet Server is started.
It doesn't indicate an
active communication
All Communication
running
Solid
Yellow
Startup
Startup
Startup. The LED stays
yellow until the module
receives a IP Address,
therefore a link must be
established.
Startup, or one configured
channel not
communicating to the
Master
Solid Red
No Communication to
Neuron (internal error,
could be solved by
downloading a new LON
application)
BACnet Server down.
Automatically a restart
after 3 seconds are
initiated.
BACnet Server down.
Automatic restart after 3
seconds is initiated.
All configured
Communications down.
Means no communication
to the Master. The timeout
can be configured. In case
that the timeout is zero the
timeout is disabled.
Flashing
Yellow
Communication not
possible to the Neuron.
The Neuron must be
configured and set online
over the LON Tool.
Communication modules
BSP LED (same for all modules)
(*) Contact Service.
BUS LED
3.6 Controller maintenance
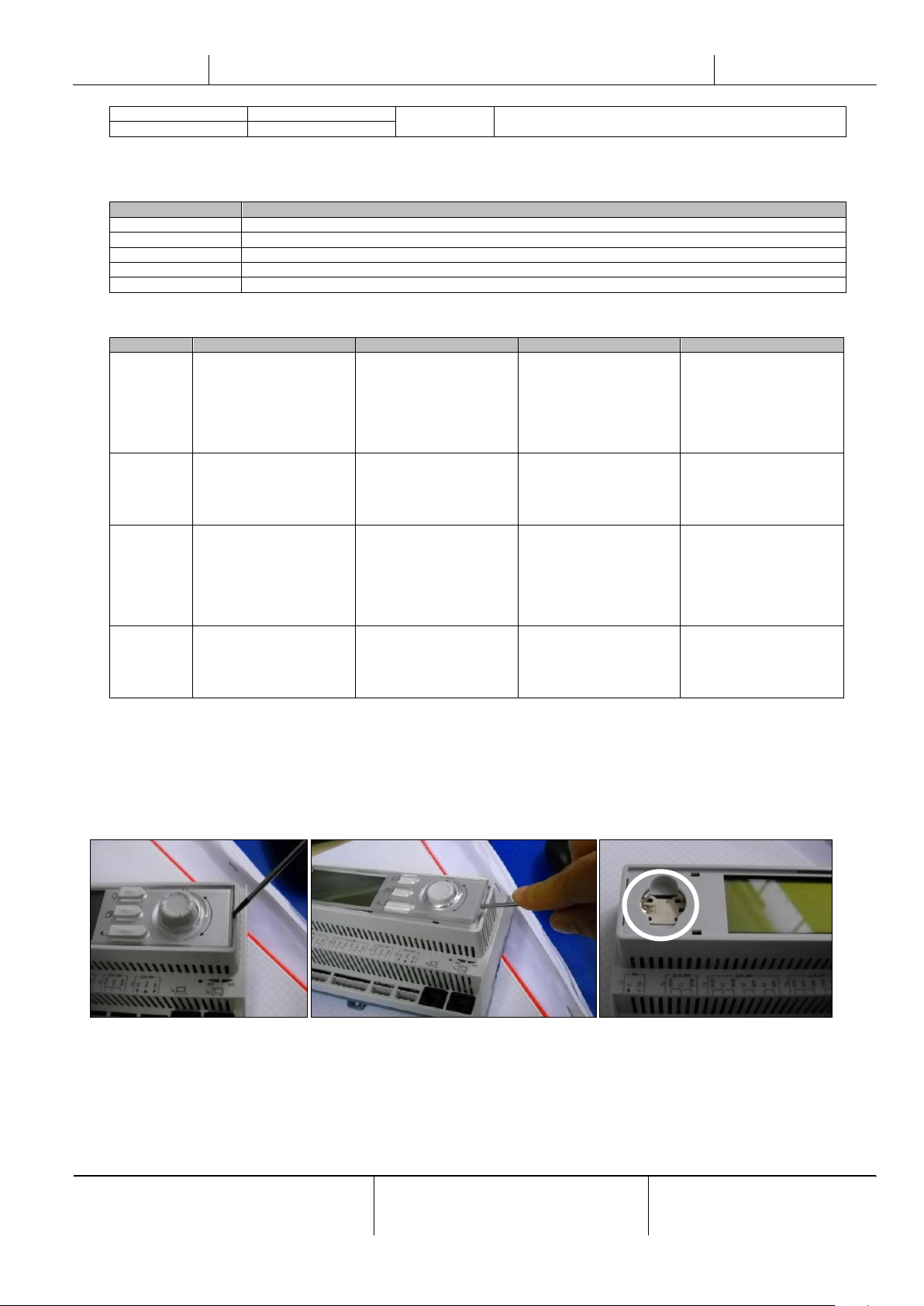
The controller requires to maintain the installed battery. Every two years it’s required to replace the battery. Battery model
is: BR2032 and it is produced by many different vendors.
To replace the battery remove the plastic cover of the controller display using a screw driver as shown in the following
pictures:
Be careful to avoid damages to the plastic cover. The new battery shall be placed in the proper battery holder which is
highlighted in the picture, respecting the polarities indicated into the holder itself.
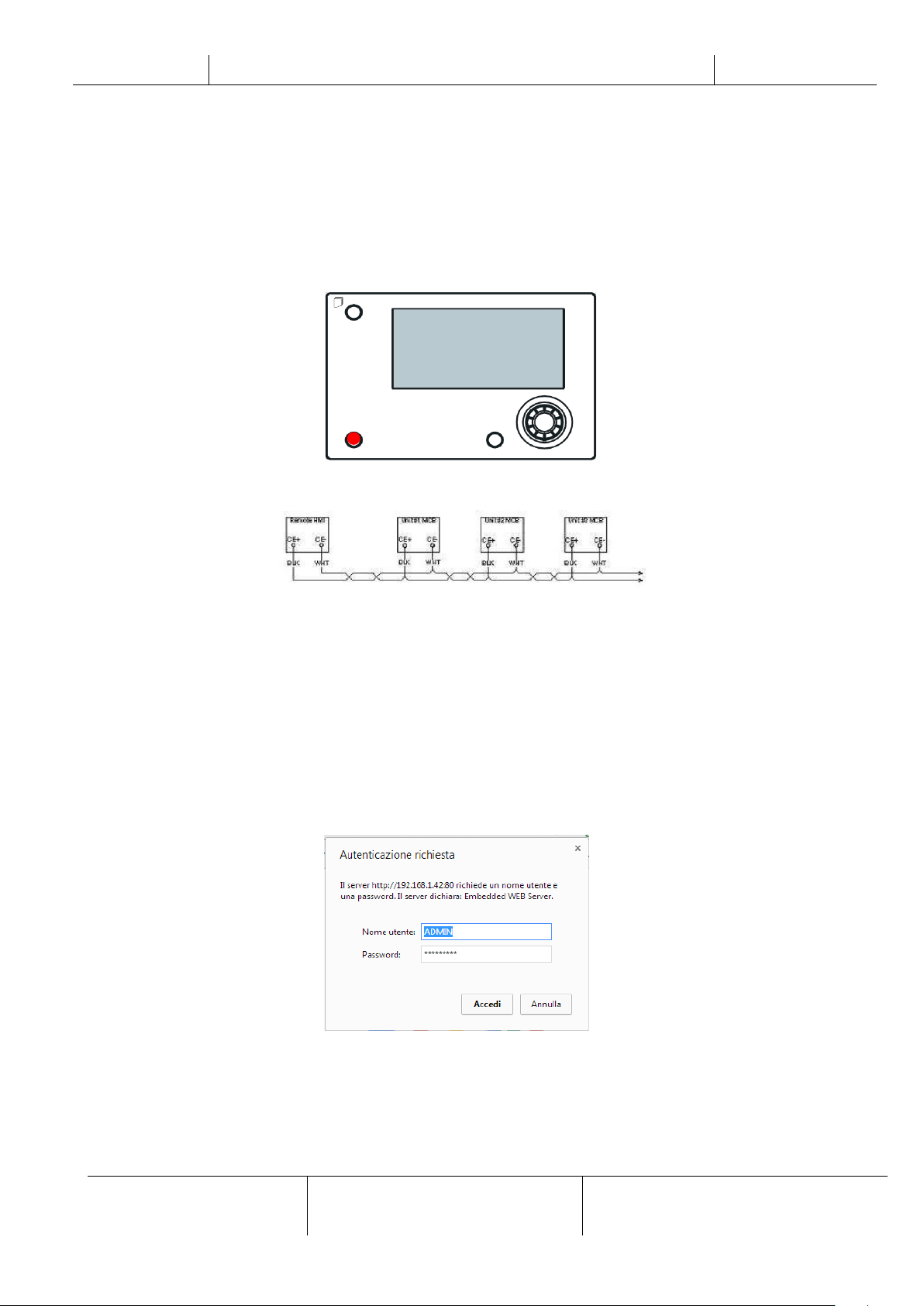
3.7 Optional Remote User Interface
As an option an external Remote HMI can be connected on the UC. The Remote HMI offers the same features as the
inbuilt display plus the alarm indication done with a light emitting diode located below the bell button.
Multipurpose Units
D-EOMZC00204-18_01EN
Operation Manual
10/48
EWYD 4Z
MultiPurpose Units
MicroTech® III
The Remote can be ordered with the unit and shipped loose as a field installed option. It can also be ordered
any time after chiller shipment and mounted and wired on the job as explained on the following page. The remote panel
is powered from the unit and no additional power supply is required.
All viewing and setpoint adjustments available on the unit controller are available on the remote panel. Navigation is
identical to the unit controller as described in this manual.
The initial screen when the remote is turned on shows the units connected to it. Highlight the desired unit and press the
wheel to access it. The remote will automatically show the units attached to it, no initial entry is required.
The Remote HMI can be extended up to 700m using the process bus connection available on the UC. With a daisy-chain
connection as below, a single HMI can be connected to up to 8 units. Refer to the specific HMI manual for details.
3.8 Embedded Web Interface
The MicroTech III controller has an embedded web interface that can be used to monitor the unit when connected to a
local network. It is possible to configure the IP addressing of the MicroTech III as a fixed IP of DHCP depending on the
network configuration.
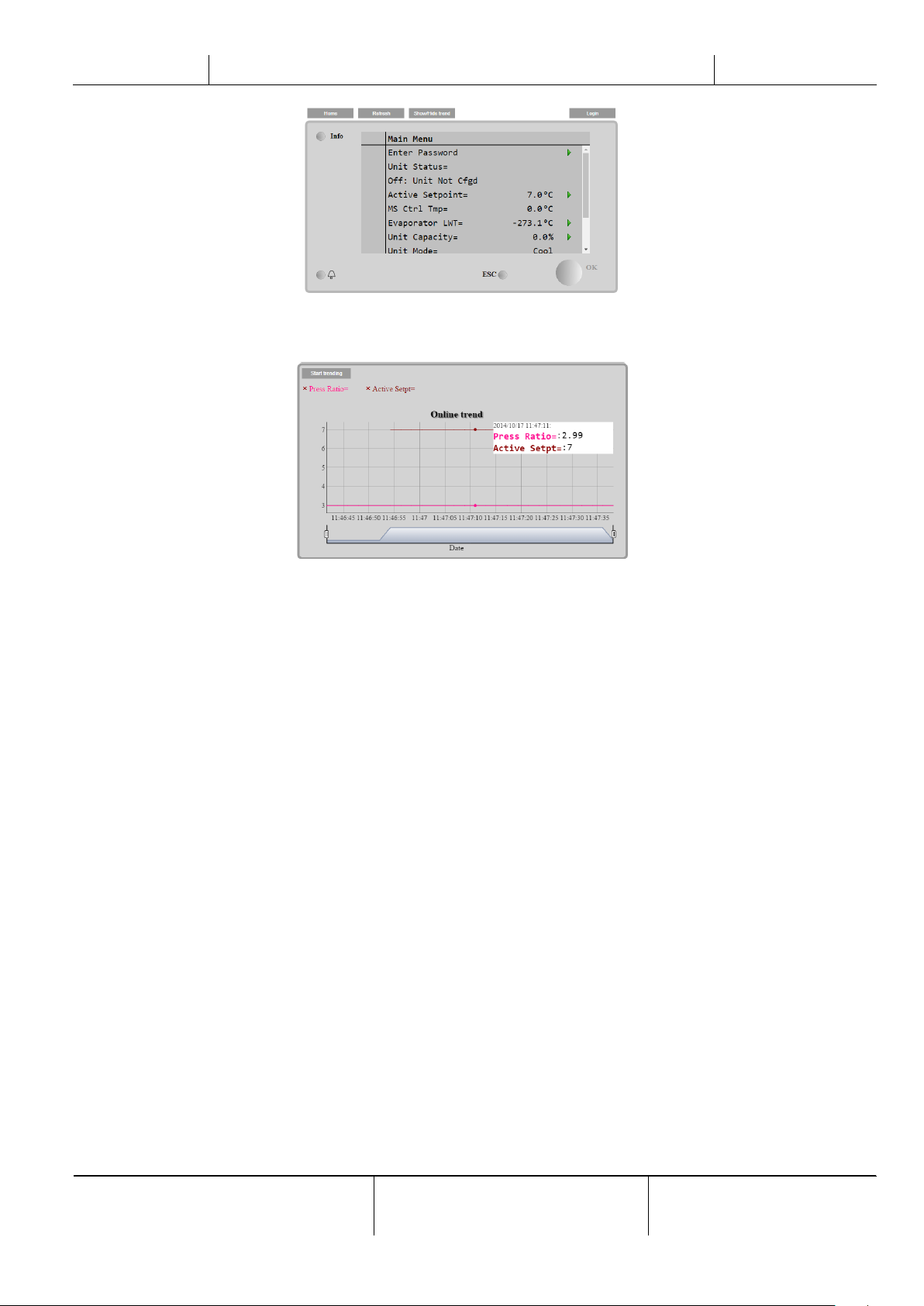
With a common web browser a PC can connect with the unit controller entering the IP address of the controller or the host
name, both visible in the “About Chiller” page accessible without entering a password.
When connected, it will be required to enter a user name and a password. Enter the following credential to get access to
the web interface:
User Name: ADMIN
Password: SBTAdmin!
The Main Menu page will be displayed. The page is a copy of the onboard HMI and follows the same rules in terms of
access levels and structure.
Multipurpose Units
EWYD 4Z
MultiPurpose Units
D-EOMZC00204-18_01EN
Operation Manual
11/48
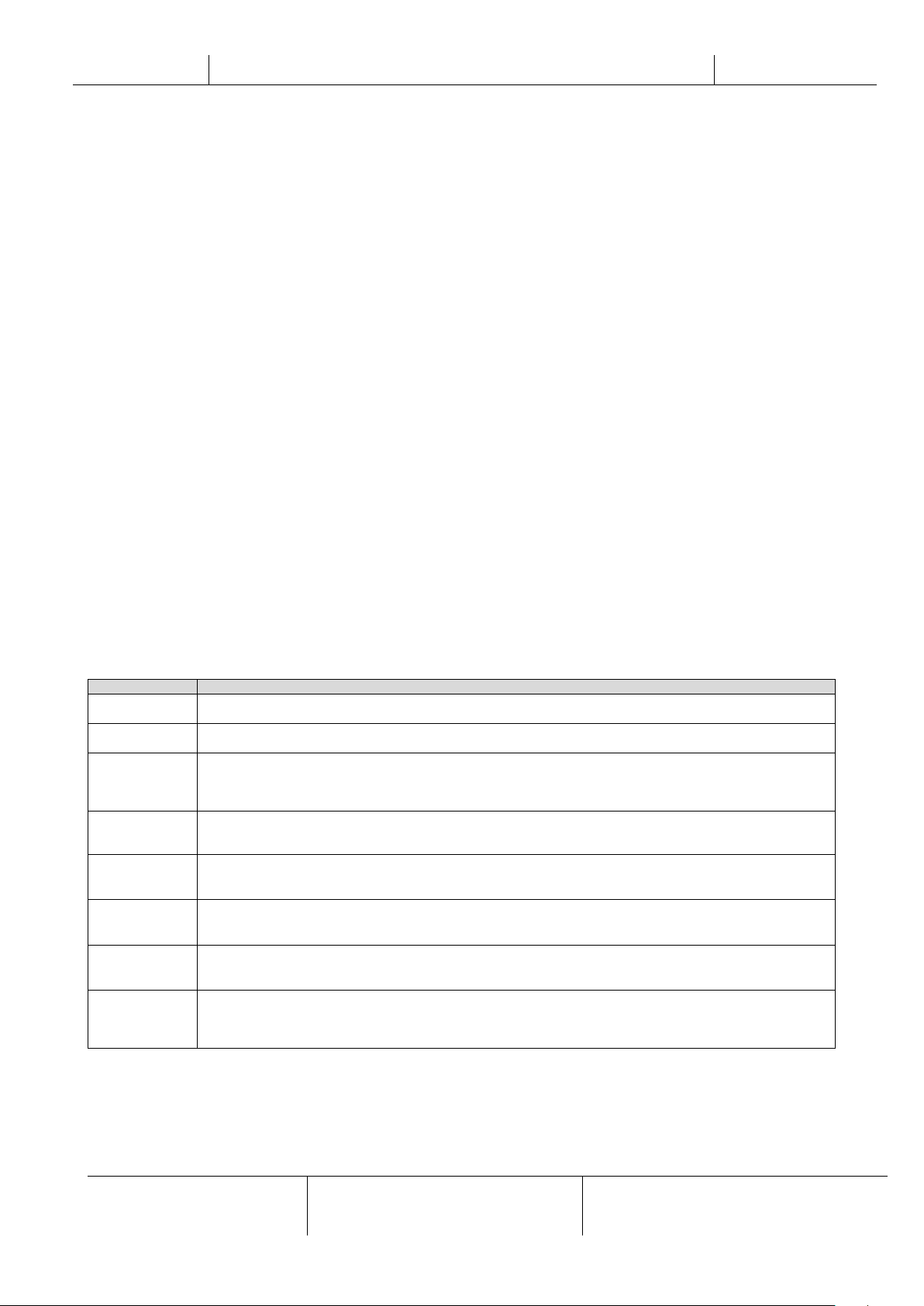
In addition it allows to trend log a maximum of 5 different quantities. It’s required to click on the value of the quantity to
monitor and the following additional screen will become visible:
Depending on the web browser and its version the trend log feature may not be visible. It’s required a web browser
supporting HTML 5 like for example:
Microsoft Internet Explorer v.11,
Google Chrome v.37,
Mozilla Firefox v.32.
These software are only an example of the browser supported and the versions indicated have to be intended as minimum
versions.
Multipurpose Units
D-EOMZC00204-18_01EN
Operation Manual
12/48
EWYD 4Z
MultiPurpose Units
Local
Unit is enabled by local switches placed into the switchbox, chiller mode (cool, cool w/glycol, ice), LWT setpoint and capacity
limit are determined by local settings in the HMI.
Network
Unit is enable by a remote switch, chiller mode, LWT setpoint and capacity limit are determined by an external BMS. This
function requires:
Remote enable connection to a BMS (unit on/off switch must be in remote)
Communication module and its connection to a BMS.
Mode
Description
Cool
Set if only chilled water temperature up to 4°C is required. No glycol is generally needed in the water circuit, unless
ambient temperature may reach low values.
Cool w/Glycol
Set if only chilled water temperature below 4°C is required. This operation requires proper glycol/water mixture in
the evaporator water circuit.
Cool/Ice
w/Glycol
Set in case only a dual cool/ice mode is required. This setting implies an operation with double setpoint which is
activated through a customer supplied switch, according to the following logic:
Switch OFF: The chiller will work in cooling mode with the Cool LWT 1 being as the Active Setpoint.
Switch ON: The chiller will work in ice mode with the Ice LWT as the Active Setpoint.
Ice w/Glycol
Set if only ice storage is required. The application requires the compressors to operate at full load until the ice bank
is completed, and then to stop for at least 12 hours. In this mode the compressor(s) will not operate at part load,
but will work only in on/off mode.
MultiPurpose
Set in case a contemporary cool/heat mode is required. This setting implies an operation with double functioning,
with the Cool LWT 1 as the cooling Active Setpoint and
with the Heat LWT 1 as the heating Active Setpoint.
MultiPurpose
w/Glycol
Set in case a contemporary cool/heat mode is required. This setting implies an operation with double functioning,
with the Cool LWT 1 as the cooling Active Setpoint and
with the Heat LWT 1 as the heating Active Setpoint.
MultiPurpose/Ice
w/Glycol
Set in case a contemporary cool/heat mode is required. This setting implies an operation with double functioning,
with the Ice LWT as the cooling Active Setpoint and
with the Heat LWT 1 as the heating Active Setpoint.
Test
Enables the Manual Control of the unit. The manual test feature helps in debugging and checking the operational
status of sensors and actuators. This feature is accessible only with the maintenance password in the main menu.
To activate the test feature is required to disable the Unit from the Q0 switch and change the available mode to
Test (see section 4.2.1).
4 WORKING WITH THIS UNIT
This section contains a guide on how to deal with the everyday usage of the unit. Next sections describe how to perform
routine tasks on the unit, such as:
Unit Setup
Unit/Circuit start-up
Alarm handling
BMS Control
Battery replacement
4.1 Unit Setup
Before starting up the unit, some basic settings need to be set by the customer according to the application.
Control Source
Available Modes
Temperature Settings
Alarm Settings
Pump Settings
Power Conservation
Date/Time
Scheduler
4.1.1 Control Source
This function allows to select which source should be used for unit control. The following sources are available:
4.1.2 Operating Mode
The following operating modes can be selected through the Available modes setpoint.
4.1.3 Temperature Settings
Setpoint range is limited according to the selected operating mode. The controller includes:
two set points in cooling mode (either standard cool or cool w/glycol)
two set points in heating mode
one set point in ice mode
Multipurpose Units
EWYD 4Z
MultiPurpose Units
D-EOMZC00204-18_01EN
Operation Manual
13/48
Operating Mode
Double Setpoint
Input
Scheduler
LWT Setpoint
Default
Range
Cool
OFF
Off, On Setpoint 1
Cool LWT 1
7.0°C
4.0°C 15.0°C
ON
On Setpoint 2
Cool LWT 2
7.0°C
4.0°C 15.0°C
Ice
N/A
N/A
Ice LWT
-4.0°C
-8.0°C 4.0°C
Heat
OFF
Off, On Setpoint 1
Heat LWT 1
45.0°C
30.0°C 60.0°C(*)
ON
On Setpoint 2
Heat LWT 2
45.0°C
30.0°C 60.0°C(*)
#1 Only
Set to this in case of single pump or twin pump with only #1 operational (f.e. in case of maintenance on #2)
#2 Only
Set to this in case of twin pump with only #2 operational (f.e. in case of maintenance on #1)
Auto
Set for automatic pump start management. At each chiller start, the pump with the least number of hours will be activated.
#1 Primary
Set to this in case of twin pump with #1 running and #2 as a backup
#2 Primary
Set to this in case of twin pump with #2 running and #1 as a backup
Parameter
Description
Low Press Hold
Set the minimum refrigerant pressure of the unit. It is generally recommended to set to a value whose saturated
temperature is 8 to 10°C below the minimum active setpoint. This will allow a safe operation and a proper control
of compressor suction superheat.
Low Press Unload
Set lower than the hold threshold enough to allow a suction pressure recovery from fast transients without
unloading the compressor. A 20 kPa differential is generally appropriate for most applications.
Evap Water Frz
Stops the unit in case the leaving temperature falls below a given threshold. To allow a safe operation of the
chiller, this setting must be adequate to the minimum temperature allowed by the mixture water/glycol present in
the evaporator water circuit.
Cond Water Frz
Stops the unit in case the leaving temperature falls below a given threshold. To allow a safe operation of the
chiller, this setting must be adequate to the minimum temperature allowed by the mixture water/glycol present in
the condenser water circuit.
When glycol is used in the plant, always disconnect antifreeze electric heater.
The above setpoints are activated according to Operating mode, Double Setpoint or Scheduler selection. If the Time
Scheduler is enabled the Double Setpoint input state will be ignored by the controller.
The table below lists the LWT Setpoint being activated according to the operation mode, the double setpoint switch status
and the scheduler state. The table also reports the defaults and the range allowed for each setpoint.
(*) 30.0°C 65.0 for HT unit type
The LWT setpoint can be overridden in case the setpoint reset or the quiet mode are activated.
4.1.4 Pumps settings
The UC can manages one or two water pumps for both evaporator and, for W/C units, condenser. Number of pumps and
their priority can be set from the HMI. The following options are available to control the pump(s):
4.1.5 Alarm Settings
If glycol is present in the water circuits, factory defaults values for the Alarm Limits listed below must be adjusted:
4.1.6 Power Conservation
4.1.6.1 Demand Limit
Demand limit function allows the unit to be limited to a specified maximum load. Capacity limit level is defined with an
external 4-20 mA signal and linear relationship. 4 mA indicate maximum capacity available whereas 20 mA indicates
minimum capacity available.
With demand limit function is not possible shutdown the unit but only unload it until minimum admissible capacity. Demand
limit related setpoints available through this menu are listed in the table below.
Multipurpose Units
D-EOMZC00204-18_01EN
Operation Manual
14/48
EWYD 4Z
MultiPurpose Units
Parameter
Description
Unit Capacity
Displays current unit capacity
Demand Limit En
Enables demand limit
Demand Limit
Displays active demand limit
Parameter
Description
Setpoint Reset
Set the Setpoint Reset mode (None, 4-20 mA, Return, OAT)
Max Reset
Max Setpoint Reset (valid for all active modes)
Start Reset DT
Used on Setpoint Reset by Evaporator DT
Max Reset OAT
See Setpoint Reset by OAT Reset
Strt Reset OAT
See Setpoint Reset by OAT Reset
Capacity Limit
[%]
Minimum
Capacity
Maximum
Capacity
20
4
Demand Limit
[mA]
Current
Limit [A]
Current Limit
Setpoint
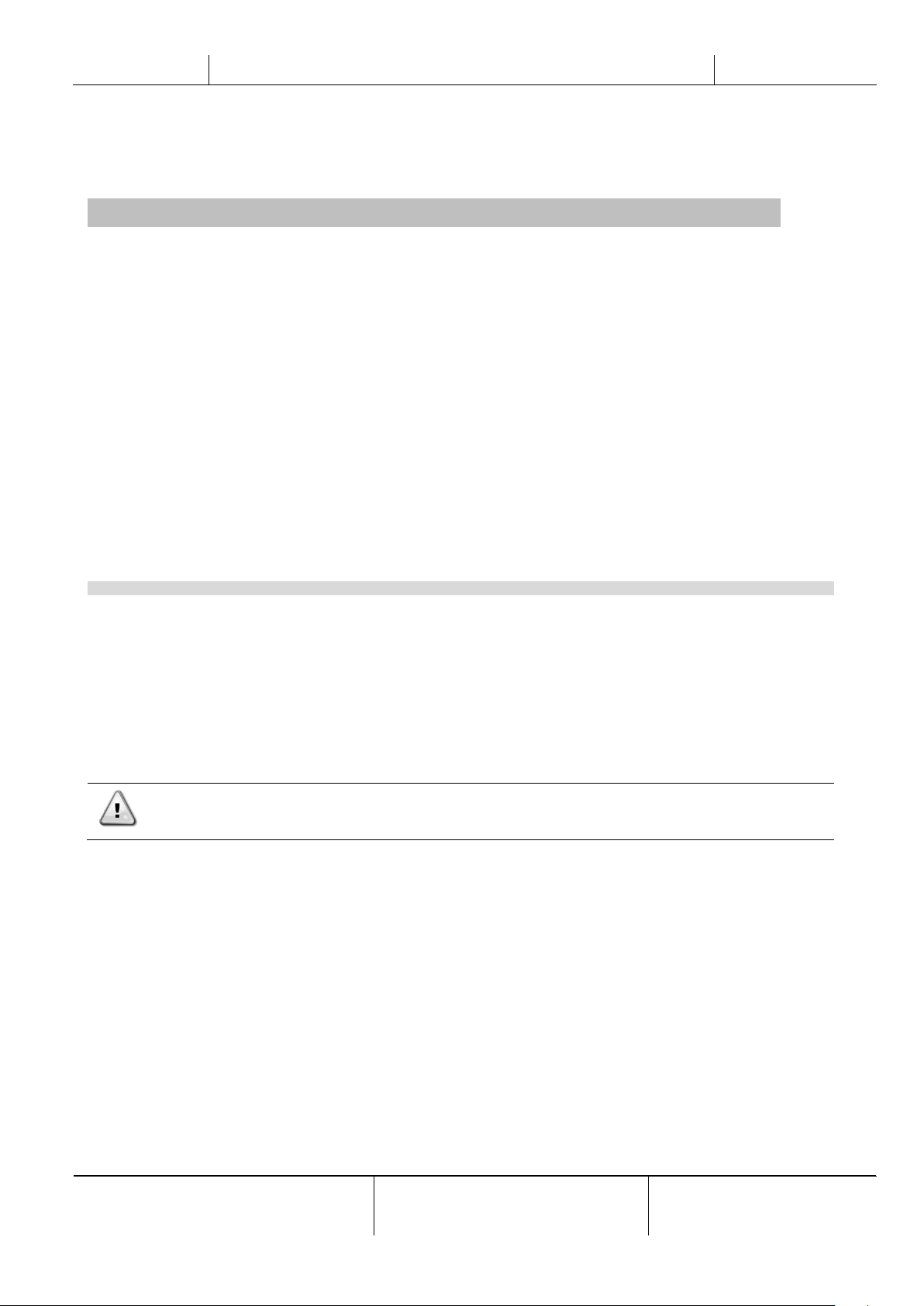
4.1.6.2 Current Limit (Optional)
Current limit function allows to control unit power consumption taking current drawn below a specific limit. Starting from
the Current Limit Setpoint defined through the HMI or BAS communication, user can decrease the real limit using an
external 4-20mA signal as indicate in the graph below. With 20 mA real current limit is set to Current Limit Setpoint, whereas
with 4 mA signal the unit is unloaded until minimum capacity.
Flexible
Current
4.1.6.3 Setpoint Reset
The setpoint reset function overrides the water temperature setpoints selected through the interface, when certain
circumstances occur. This feature helps in reducing energy consumption optimizing comfort as well. Three different control
strategies can be selected:
Setpoint Reset by Outside Air Temperature (OAT)
Setpoint Reset by an external signal (4-20mA)
Setpoint Reset by Evaporator ΔT (Return)
The following setpoints are available through this menu:
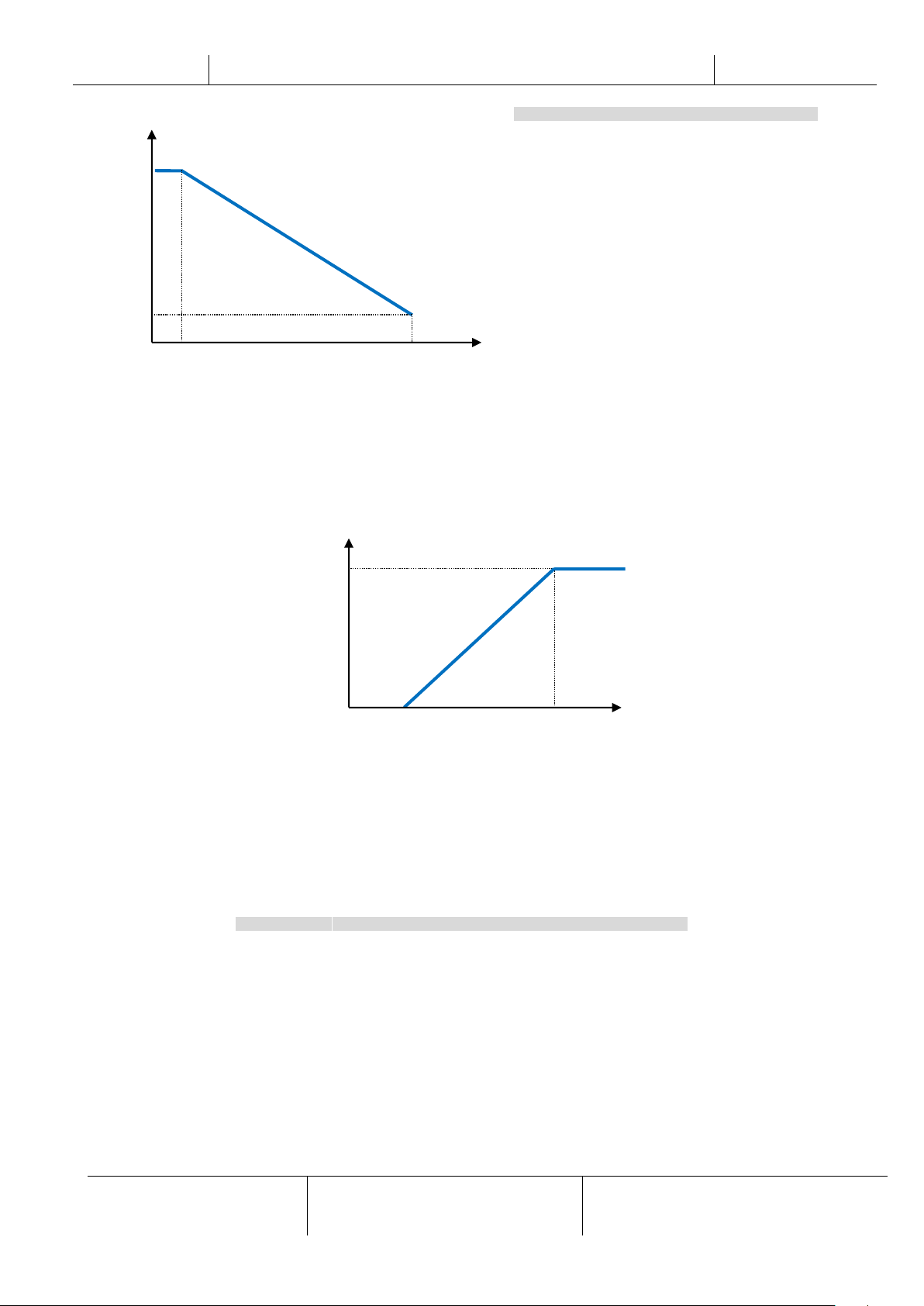
4.1.6.4 Setpoint Reset by OAT Reset
The active setpoint is calculated applying a correction which is a function of ambient temperature (OAT). As temperature
drops below the Start Reset OAT (SROAT), Cool LWT setpoint is gradually increased until OAT reaches the Max Reset
OAT value (MROAT). Beyond this value, the Cool LWT setpoint is increased by the Max Reset (MR) value. As temperature
grow over the Start Reset OAT (SROAT), Heat LWT setpoint is gradually reduced until OAT reaches the Max Reset OAT
value (MROAT). Above this value, the Heat LWT setpoint is decreased by the Max Reset (MR) value.
Multipurpose Units
EWYD 4Z
MultiPurpose Units
D-EOMZC00204-18_01EN
Operation Manual
15/48
The Return Reset may affect negatively the chiller operation when operated with variable flow. Avoid to use this
strategy in case of inverter water flow control.
The Quiet Mode may affect negatively chiller efficiency due to the increased condenser setpoint
Parameter
Default
Range
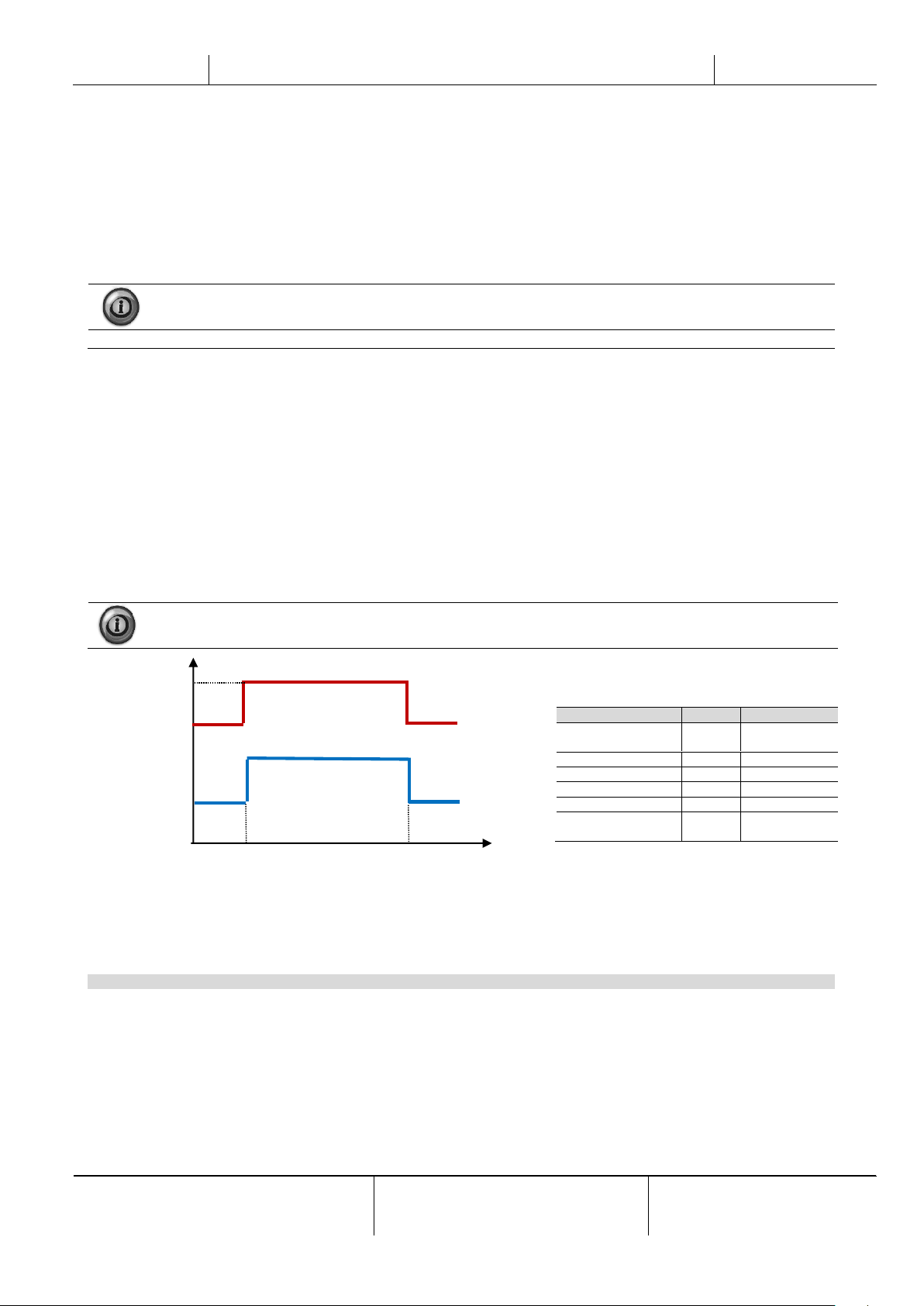
Quiet Mode
Disable
Disable,
Enable
QM Start Hr (QMS)
21h
0…24h
QM Start Min
0min
0...60min
QM End Hr (QME)
6h
0…24h
QM End Min
0min
0…60min
QM Cond Offset
(CO)
5°C
0…10°C
Parameter
Description
Off
Unit Off
On Setpoint 1
Unit On and Cool LWT 1 is the active setpoint
On Setpoint 2
Unit On and Cool LWT 2 is the active setpoint
0
QME
Evap T
LWT SP
LWT SP + MR
QMS
time
CP SP
CP SP + CO
Cond Press
4.1.6.5 Setpoint Reset by External 4-20 mA Signal
The active setpoint is calculated applying a correction based on an external 4-20mA signal. 4 mA corresponds to 0°C
correction, while 20 mA corresponds to a correction of the active setpoints as set in Max Reset (MR).
4.1.6.6 Setpoint Reset by Evaporator Return Temperature
The active cooling setpoint is calculated applying a correction that depends on the evaporator entering (return) water
temperature. The active heating setpoint is calculated applying a correction that depends on the condenser entering
(return) water temperature.
4.1.7 Date/Time
4.1.7.1 Date,Time and UTC Settings
Date, time and UTC settings are available in the HMI.
4.1.7.2 Quiet Mode Scheduling
The Quiet Mode can be used to reduce chiller noise in certain hours of the day when noise reduction is more important
than cooling operation, like for example in night time. When Quiet Mode is activated, the LWT setpoint is increased by the
maximum setpoint reset (MR) described in the chapter “Setpoint Reset”, thus forcing a capacity limitation to the unit without
losing control on chilled water temperature. Also, condenser temperature target is increased by a value set in “QM Cond
Offset”. In this way condenser fans are forced to reduce speed without losing control on condensation. Quiet mode is timer
enabled.
4.1.8 Scheduler
Unit On/Off can be managed automatically through the function Time Scheduler enabled when the parameter Unit Enable
is set to Scheduler Errore. L'origine riferimento non è stata trovata.. For each day of the week user can define six time
slots and choose for each time slot one of following mode:
4.2 Unit/Circuit Start-up
In this section, starting and stopping sequence of the unit will be described. status will be briefly described to allow a better
understanding of what is going on into the chiller control.

Multipurpose Units
D-EOMZC00204-18_01EN
Operation Manual
16/48
EWYD 4Z
MultiPurpose Units
Switch Enable
Software Enable
BMS
Enable
Unit Status
Q0
State
Chiller Enable
(KeyPad Enable set
point)
Control Source
(set point)
BAS
request
0
X X X X DISABLED
LOCAL X Disable
X X DISABLED
LOCAL X X
Network
DISABLE
DISABLED
LOCAL X Enable
Local
X
ENABLED
LOCAL X Enable
Network
ENABLE
ENABLED
REMOTE
Open X X X DISABLED
REMOTE X Disable
X X DISABLED
REMOTE
Closed
Enable
Network
DISABLE
DISABLED
REMOTE
Closed
Enable
Local
X
ENABLED
REMOTE
Closed
Enable
Network
ENABLE
ENABLED
Local
With the Q0 switch in this position the unit is enabled. Pump will start if all other enable signals are
set to enable and at least one compressor is available to run
Disable
With the Q0 switch in this position the unit is disabled. Pump will not start in normal operational
condition. Compressor are kept disabled independently from the status of the individual enable
switches.
Remote
With the Q0 switch in this position the unit can be enabled using the additional connections available
on the connection terminals. A closed loop will identify an enable signal, this can come from a
remote switch or a timer by example.
Overall Status
Status text
Description
Off:
Keypad Disable
The Unit has been disabled by keypad. Check with your local maintenance if it can be
enabled.
Loc/Rem Switch
The Local/Remote enable switch is set to disable. Turn it to Local to enable the unit to start
its starting sequence.
4.2.1 Prepare the unit to start
4.2.1.1 Unit Enable
The unit starts only if all the enable setpoints/signals are active:
Unit Switch Enable (signal) = Enable
Keypad Enable (setpoint) = Enable
BMS Enable (setpoint) = Enable
Switch Enable
Each unit is equipped with a Main selector installed outside the front panel of the unit switchbox. As shown in the pictures
below, for TZ and TZ B units three different positions can be selected: Local, Disable, Remote:
Keypad Enable
The Keypad enable setpoint is not accessible by user password level. If it is set to “Disable”, contact your local maintenance
service to check if it can be changed to Enable.
BMS Enable
The last enable signal is coming through the high level interface, that is from a Building Management System. The unit can
be enabled/disabled from a BMS connected to the UC using a communication protocol. In order to control the unit over
the network, the Control Source setpoint must be turned in “Network” (default is Local) and Network En Sp must be
“Enable”(Errore. L'origine riferimento non è stata trovata.). If disabled, check with your BAS company how the
chiller is operated.
4.2.2 Unit Status
One of the texts strings listed in the table below will inform, on the HMI, about the Unit Status.

Multipurpose Units
EWYD 4Z
MultiPurpose Units
D-EOMZC00204-18_01EN
Operation Manual
17/48
Overall Status
Status text
Description
BAS Disable
Unit is disabled by BAS/BMS system. Check with the BAS company how to start the unit.
Master Disable
Unit is disabled by the Master Slave function
Scheduler Disabled
Unit is disabled by the time scheduler.
Unit Alarm
A unit alarm is active. Check the alarm list to see what is the active alarm inhibiting the unit
to start and check if the alarm can be cleared. Refer to section 5. before proceeding.
Test Mode
Unit mode set to Test. This mode is activated to check operability of onboard actuators and
sensors. Check with the local maintenance if the Mode can be reverted to the one
compatible with unit application (View/Set Unit – Set-Up – Available Modes).
All Cir Disabled
No circuit is available to run. All circuits can be disabled by their individual enable switch or
can be disabled by a component safety condition active or can be disabled by keypad or
can be all in alarms. Check the individual circuit status for further details.
Ice Mode Tmr
This status can be shown only if the unit can work in Ice Mode. The unit is off because the
Ice setpoint has been satisfied. Unit will remain off until the Ice Timer has expired.
OAT Lockout
The unit cannot run because the Oustide Air Temperature is below the limit foreseen for the
condenser temperature control system installed in this Unit. If the Unit has to run anyway
check with your local maintenance how to proceed.
Auto
Unit is in Auto control. The pump is running and at least one compressor is running.
Auto:
Evap Recirc
Unit is running the evaporator pump to equalize the water temperature in the evaporator.
Wait For Flow
Unit pump is running but the flow signal still indicate a lack of flow through the evaporator.
Wait For Load
Unit is in standby because the thermostat control satisfied the active setpoint.
Unit Cap Limit
Demand limit has been hit. Unit capacity will not further increase.
Current Limit
Maximum current has been hit. Unit capacity will not further increase.
Noise Reduction
Unit is running with the Quiet Mode activated. Active setpoint may differ from what has been
set as cooling setpoint.
Max Pulldn
Unit thermostat control is limiting the unit capacity because the water temperature is
dropping at a rate that could exceed the active setpoint.
Pumpdn
Unit is shutting down.
Switch Enable
Software Enable
Circuit Status
Q1/Q2
State
Circuit Enable
(KeyPad Enable set point)
0
Disabled X DISABLED
0
Disabled X DISABLED
1
Enabled
Disable
DISABLED
1
Enabled
Enable
ENABLED
4.2.3 Circuits Enable
As for the unit enable, the circuits can start only if all the enable setpoints/signals are active:
Circuit Switch Enable (signal) = Enable
Keypad Enable (setpoint) = Enable
4.2.4 Circuit Status
One of the texts strings listed in the table below will inform, on the HMI, about the Circuit Status.

Multipurpose Units
D-EOMZC00204-18_01EN
Operation Manual
18/48
EWYD 4Z
MultiPurpose Units
Overall Status
Status
Description
Off:
Ready
Circuit is off waiting for a stage up signal from thermostat control
Stage Up Delay
Circuit is off waiting for the stage up delay to expire.
Cycle Timer
Circuit is off waiting for the compressor cycle timer to expire
BAS Disable
Circuit is off by BAS signal. Check with the BAS company how to start the unit.
Keypad Disable
Circuit is off by the local or remote HMI. Check with your local maintenance if it can be
enabled.
Circuit Switch
Circuit is off by Enable switch. Turn the Enable switch to 1 to allow the circuit start up
procedure to start
Oil Heating
Circuit is off because the oil temperature is too low to guarantee a proper lubrication of
compressor. Heating resistor is activated to eliminate this temporary condition. It’s
suggested to power up the unit in advance to avoid this limiting condition.
Alarm
A circuit alarm is active. Check the alarm list to see what is the active alarm inhibiting the
circuit to start and check if the alarm can be cleared. Refer to section 5.before proceeding.
Test Mode
Circuit mode set to Test. This mode is activated to check operability of onboard circuit
actuators and sensors. Check with the local maintenance if the Mode can be reverted to
Enable.
Max Comp Starts
Compressor starts exceed the maximum number of starts per hour.
VFD Heating
Inverter on compressor cannot start because of low internal temperature. Heating resistor
is activated to eliminate this temporary condition. It’s suggested to power up the unit in
advance to avoid this limiting condition.
Maintenance
A component needs to be replaced or maintained. Refer to section 5.before proceeding.
EXV
Preopen
EXV prepositioning before compressor starts.
Run:
Pumpdown
Circuit is shutting down because of thermostat control or pumpdown alarm or because the
enable switch has been turned to off.
Normal
Circuit is running within the expected operational conditions.
Disch SH Low
Discharge superheat is below the acceptable value. This is a temporary condition that
should disappear after few minutes of operation.
Evap Press Low
Circuit is running with low evaporator pressure. This could be due to a transitory condition
or a lack of refrigerant. Check with the local maintenance if corrective actions are required.
Circuit is protected by preventive logic.
Cond Press High
Circuit is running with high condenser pressure. This could be due to a transitory condition
or high ambient temperature or problems with the condenser fans. Check with the local
maintenance if corrective actions are required. Circuit will be protected by preventive logic.
High LWT Limit
Circuit is running with a high water temperature. This is a temporary condition that will limit
the maximum compressor capacity. Reduction of the water temperature will allow the
compressor to reach the full capacity.
High VFD Amps
Inverter current is higher than the maximum allowed current. Preventive logic will protect the
inverter.
Symptom
Cause
Solution
Unit maximum capacity equal to 80%
Leaving Evaporator water temperature
higher than 25°C or Leaving Condenser
water temperature higher than 60°C
Wait until the water temperature drops
below 25°C
4.2.5 Circuit Preventions
4.2.5.1 High Water Temperature Limit
The only prevention that can activate at unit level will limit the maximum unit capacity to 80% when the leaving water
temperature exceeds 25°C in cooling or 60°C in heating. This condition will be displayed at circuit level to indicate the
capacity limitation.
4.2.5.2 Low Evaporating Pressure
When the circuit is running and the evaporating pressure drops below the safety limits the circuit control logic reacts at two
different levels in order to recover the normal running conditions.
If the evaporating pressure drops below the Low Pressure Hold limit, compressor is inhibited to increase its running
capacity. This condition is indicated on the controller display in the circuit status as “ Run: Evap Press Low”. The status is
automatically cleared when the evaporating pressure rise above the Low Pressure Hold limit by 14 kPa.
If the evaporating pressure drops below the Low Pressure Unld limit, compressor is unloaded in order to recover the normal
operating conditions. This condition is indicated on the controller display in the circuit status as “Ru n: Evap Press Low”.
The status is automatically cleared when the evaporating pressure rise above the Low Pressure Hold limit by 14 kPa.
See section 5.6.18 to troubleshoot this problem.
4.2.5.3 High Condensing Pressure
When the circuit is running and the condensing pressure rises above the safety limits the circuit control logic reacts at two
different levels in order to recover the normal running conditions.

Multipurpose Units
EWYD 4Z
MultiPurpose Units
D-EOMZC00204-18_01EN
Operation Manual
19/48
Safe Operation Area
Evap. Sat. Temp.
Cond. Sat.
Temp.
Hi Press Trip
Hi Press Hold
Hi Press Unload
The two different levels, called High Pressure Hold and High Pressure Unload limits, are calculated by the controller from
the maximum condenser pressure allowed by the compressor envelope. This value depends from evaporating pressure
as reported in the figure below.
If the condensing pressure rises above the High Pressure Hold limit, compressor is inhibited to increase its running
capacity. This condition is indicated on the controller display in the circuit status as “Run: Cond Press High”. The limit is
calculated in terms of saturated condensing temperature; the status is automatically cleared when the saturated
condensing temperature rises above the High Pressure Hold limit by 5.6°C.
If the condensing pressure rises above the High Pressure Unload limit, compressor is unloaded in order to recover the
normal operating conditions. This condition is indicated on the controller display in the circuit status as “Run: Cond Press
High”. The status is automatically cleared when the saturated condensing temperature rises above the High Pressure Hold
limit by 5.6°C. See section 5.6.17 to troubleshoot this problem.
4.2.5.4 High Vfd Current
When the compressor is running and its output current rises above the safety limits the circuit control logic reacts at two
different levels in order to recover the normal running conditions. Safety limits are calculated by the controller based on
the selected compressor type.
If the running current rises above the Running Current Hold limit (101% of RLA), compressor is inhibited to increase its
running capacity. This condition is indicated on the controller display in the circuit status as “Run: High VFD Amps”.
If the condensing pressure rises above the Running Current Unload limit (105% of RLA), compressor is unloaded in order
to recover the normal operating conditions. This condition is indicated on the controller display in the circuit status as “Run:
High VFD Amps”. The status is automatically cleared when the running amps falls below the hold limit.
4.2.5.5 High Discharge Temperature
When the compressor is running and its discharge temperature rises above the safety limits the circuit control logic reacts
at two different levels in order to recover the normal running conditions.
If the discharge temperature rises above the Discharge Temperature Hold limit (95°C), compressor is inhibited to increase
its running capacity. This condition is indicated on the controller display in the circuit status as “Run: High Discharge Temp”.
If the discharge temperature rises above the Discharge Temperature Unload limit (100°C), compressor is unloaded in order
to recover the normal operating conditions. This condition is indicated on the controller display in the circuit status as “Run:
High Discharge Temp”. The status is automatically cleared when the discharge temperature falls below the hold limit.

Multipurpose Units
D-EOMZC00204-18_01EN
Operation Manual
20/48
EWYD 4Z
MultiPurpose Units
Allowed
Not allowed
Not foreseen
Symptom
Cause
Solution
Unit status is Run.
Bell icon is moving on controller’s display.
Flexible Current Limit function cannot be
used.
String in the alarm list:
BadCurrentLimitInput
String in the alarm log:
BadCurrentLimitInput
String in the alarm snapshot
BadCurrentLimitInput
Flexible current limit input out of range.
For this warning out of range is considered
to be a signal less than 3mA or more than
21mA.
Check for values of input signal to the unit
controller. It has to be in the allowed mA
range.
Check for electrical shielding of wirings.
Check for right value of the unit’s controller
output in case input signal is into allowed
range.
Reset
Notes
Local HMI
Network
Auto
Automatically clears when the signal
returns in the allowed range.
Symptom
Cause
Solution
Unit status is Run.
Bell icon is moving on controller’s display.
Demand Limit function cannot be used.
String in the alarm list:
BadDemandLimitInput
String in the alarm log:
BadDemandLimitInput
String in the alarm snapshot
BadDemandLimitInput
Demand limit input out of range
For this warning out of range is considered
to be a signal less than 3mA or more than
21mA.
Check for values of input signal to the unit
controller. It has to be in the allowed mA
range;
Check for electrical shielding of wirings.
Check for right value of the unit’s
controller output in case input signal is
into allowed range.
Reset
Notes
Local HMI
Network
Auto
Automatically clears when the signal
returns in the allowed range.
5 TROUBLESHOOTING
The UC protects the unit and the components from operating in abnormal conditions. Protections can be divided in
preventions and alarms. Alarms can then be divided in pump-down and rapid stop alarms. Pump-down alarms are activated
when the system or sub-system can perform a normal shutdown in spite of the abnormal running conditions. Rapid stop
alarms are activated when the abnormal running conditions require an immediate stop of the whole system or sub-system
to prevent potential damages.
The UC displays the active alarms in a dedicated page and keep an history of the last 50 entries divided between alarms
and acknowledges occurred. Time and date for each alarm event and of each alarm acknowledge are stored.
The UC also stores alarm snapshot of each alarm occurred. Each item contains a snapshot of the running conditions right
before the alarm has occurred. Different sets of snapshots are programmed corresponding to unit alarms and circuit alarms
holding different information to help the failure diagnosis.
In the following sections it will also be indicated how each alarm can be cleared between local HMI, Network (by any of the
high level interfaces Modbus, Bacnet or Lon) or if the specific alarm will clear automatically. The following symbols are
used:
5.1 Unit Alerts
5.1.1 Bad Current Limit Input
This alarm is generated when the Flexible Current Limit option has been enabled and the input to the controller is out of
the admitted range.
5.1.2 Bad Demand Limit Input
This alarm is generated when the Demand Limit option has been enabled and the input to the controller is out of the
admitted range.

Multipurpose Units
EWYD 4Z
MultiPurpose Units
D-EOMZC00204-18_01EN
Operation Manual
21/48
Symptom
Cause
Solution
Unit status is Run.
Bell icon is moving on controller’s display.
LWT Reset function cannot be used.
String in the alarm list:
BadSetPtOverrideInput
String in the alarm log:
BadSetPtOverrideInput
String in the alarm snapshot
BadSetPtOverrideInput
LWT reset input signal is out of range.
For this warning out of range is considered
to be a signal less than 3mA or more than
21mA.
Check for values of input signal to the
unit controller. It has to be in the allowed
mA range.
Check for electrical shielding of wirings.
Check for right value of the unit’s
controller output in case input signal is
into allowed range.
Reset
Notes
Local HMI
Network
Auto
Automatically clears when the signal
returns in the allowed range.
Symptom
Cause
Solution
Unit could be ON.
Bell icon is moving on controller’s display.
Backup pump is used or stop of all circuits
in case of pump #2 failure.
String in the alarm list:
CondPump1Fault
String in the alarm log:
CondPump1Fault
String in the alarm snapshot
CondPump1Fault
Pump #1 may not be operating.
Check for problem in electrical wiring of
the pump #1.
Check that electrical breaker of pump #1
is tripped.
If fuses are used to protect the pump,
check the integrity of fuses.
Check for problem in wiring connection
between pump starter and unit controller.
Check the water pump filter and the water
circuit for obstructions.
Flow Switch doesn’t operate properly
Check flow switch connection and
calibration.
Reset
Notes
Local HMI
Network
Auto
Symptom
Cause
Solution
Unit could be ON.
Bell icon is moving on controller’s display.
Backup pump is used or stop of all circuits
in case of pump #1 failure.
String in the alarm list:
CondPump2Fault
String in the alarm log:
CondPump2Fault
String in the alarm snapshot
CondPump2Fault
Pump #1 may not be operating.
Check for problem in electrical wiring of
the pump #1.
Check that electrical breaker of pump #1
is tripped.
If fuses are used to protect the pump,
check the integrity of fuses.
Check for problem in wiring connection
between pump starter and unit controller.
Check the water pump filter and the water
circuit for obstructions.
Flow Switch doesn’t operate properly
Check flow switch connection and
calibration.
Reset
Notes
Local HMI
Network
Auto
Symptom
Cause
Solution
5.1.3 Bad Leaving Water Temperature Reset Input
This alarm is generated when the Setpoint Reset option has been enabled and the input to the controller is out of the
admitted range.
5.1.4 Condenser Pump #1 Failure
This alarm is generated if the pump is started but the flow switch is not able to close within the recirculate time. This can
be a temporary condition or may be due to a broken flowswitch, the activation of circuit breakers, fuses or to a pump
breakdown.
5.1.5 Condenser Pump #2 Failure
This alarm is generated if the pump is started but the flow switch is not able to close within the recirculate time. This can
be a temporary condition or may be due to a broken flowswitch, the activation of circuit breakers, fuses or to a pump
breakdown.
5.1.6 Energy Meter Communication Fail
This alarm is generated in case of communication problems with the energy meter.

Multipurpose Units
D-EOMZC00204-18_01EN
Operation Manual
22/48
EWYD 4Z
MultiPurpose Units
Bell icon is moving on controller’s display.
String in the alarm list:
EnergyMtrCommFail
String in the alarm log:
EnergyMtrCommFail
String in the alarm snapshot
EnergyMtrCommFail
Module has no power supply
Refer to the datasheet of the specific
component to see if it is correctly
powered
Wrong cabling with the Unit Controller
Check if the polarity of the connections is
respected.
Modbus parameters not properly set
Referring to the datasheet of the specific
component to see if the modbus
parameters are set correctly:
Address = 20
Baud Rate =19200 kBs
Parity = None
Stop bits =1
Module is broken
Check if the display shows something
and the power supply is present.
Reset
Notes
Local HMI
Network
Auto
Automatically clears when the
communication is re-established.
Symptom
Cause
Solution
Unit could be ON.
Bell icon is moving on controller’s display.
Backup pump is used or stop of all circuits
in case of pump #2 failure.
String in the alarm list:
EvapPump1Fault
String in the alarm log:
EvapPump1Fault
String in the alarm snapshot
EvapPump1Fault
Pump #1 may not be operating.
Check for problem in electrical wiring of
the pump #1.
Check that electrical breaker of pump #1
is tripped.
If fuses are used to protect the pump,
check the integrity of fuses.
Check for problem in wiring connection
between pump starter and unit controller.
Check the water pump filter and the water
circuit for obstructions.
Flow Switch doesn’t operate properly
Check flow switch connection and
calibration.
Reset
Notes
Local HMI
Network
Auto
Symptom
Cause
Solution
Unit could be ON.
Bell icon is moving on controller’s display.
Backup pump is used or stop of all circuits
in case of pump #1 failure.
String in the alarm list:
EvapPump2Fault
String in the alarm log:
EvapPump2Fault
String in the alarm snapshot
EvapPump2Fault
Pump #2 may not be operating.
Check for problem in electrical wiring of
the pump #2.
Check that electrical breaker of pump #2
is tripped.
If fuses are used to protect the pump,
check the integrity of fuses.
Check for problem in wiring connection
between pump starter and unit controller.
Check the water pump filter and the
water circuit for obstructions.
Flow Switch doesn’t operate properly
Check flow switch connection and
calibration.
Reset
Notes
Local HMI
Network
Auto
5.1.7 Evaporator Pump #1 Failure
This alarm is generated if the pump is started but the flow switch is not able to close within the recirculate time. This can
be a temporary condition or may be due to a broken flowswitch, the activation of circuit breakers, fuses or to a pump
breakdown.
5.1.8 Evaporator Pump #2 Failure
This alarm is generated if the pump is started but the flow switch is not able to close within the recirculate time. This can
be a temporary condition or may be due to a broken flowswitch, the activation of circuit breakers, fuses or to a pump
breakdown.
5.1.9 External Event
This alarm indicates that a device, whose operation is linked with this unit, is reporting a problem on the dedicated input.

Multipurpose Units
EWYD 4Z
MultiPurpose Units
D-EOMZC00204-18_01EN
Operation Manual
23/48
Symptom
Cause
Solution
Unit status is Run.
Bell icon is moving on controller’s display.
String in the alarm list:
UnitExternalEvent
String in the alarm log:
UnitExternalEvent
String in the alarm snapshot
UnitExternalEvent
There is an external event that has caused
the opening, for at least 5 seconds, of the
digital input on the controller board.
Check for reasons of external event and
if it can be a potential problem for a
correct chiller operation.
Reset
Notes
Local HMI
Network
Auto
The alarm is automatically cleared when
the problem is solved.
NOTE: What above applies in case of configuration of the external fault digital input as Event
Symptom
Cause
Solution
Bell icon is moving on controller’s display.
String in the alarm list:
FanMdlCommFail
String in the alarm log:
FanMdlCommFail
String in the alarm snapshot
FanMdlCommFail
Module has no power supply
Check the power supply from the
connector on the side of the module.
Check if LEDs are both green.
Check if the connector on the side is tightly
inserted in the module
Module address is not properly set
Check if module’s address is correct
referring to the wiring diagram.
Module is broken
Check if LED are on and both green. If
BSP LED is solid red replace the module
Check if power supply is ok but LEDs are
both off. In this case replace the module
Reset
Notes
Local HMI
Network
Auto
Symptom
Cause
Solution
Unit status is Off.
All circuits are stopped with a normal
shutdown procedure.
Bell icon is moving on controller’s display.
String in the alarm list:
UnitAlHREwtSen
String in the alarm log:
UnitAlHREwtSen
String in the alarm snapshot
UnitAlHREwtSen
Sensor is broken.
Check for sensor integrity according table
and allowed kOhm (k) range.
Check correct sensors operation
Sensor is shorted.
Check if sensor is shorted with a resistance
measurement.
Sensor is not properly connected (open).
Check for absence of water or humidity on
electrical contacts.
Check for correct plug-in of the electrical
connectors.
Check for correct sensors wiring also
according electrical scheme.
Reset
Notes
Local HMI
Network
Auto
Symptom
Cause
Solution
Heat Recovery is Off
Bell icon is moving on controller’s display.
String in the alarm list:
UnitAlHRLvgSen
String in the alarm log:
UnitAlHRLvgSen
String in the alarm snapshot
UnitAlHRLvgSen
Sensor is broken.
Check for sensor integrity.
according table and allowed kOhm (k)
range.
Check correct sensors operation
Sensor is shorted.
Check if sensor is shorted with a resistance
measurement.
Sensor is not properly connected (open).
Check for absence of water or humidity on
electrical contacts.
5.1.10 Fan Alarm Module Communication Fail
This alarm is generated in case of communication problems with the FAC module.
5.1.11 Heat Recovery Entering Water Temperature sensor fault
This alarm is generated any time that the input resistance is out of an acceptable range.
5.1.12 Heat Recovery Leaving Water Temperature sensor fault
This alarm is generated any time that the input resistance is out of an acceptable range.

Multipurpose Units
D-EOMZC00204-18_01EN
Operation Manual
24/48
EWYD 4Z
MultiPurpose Units
Check for correct plug-in of the electrical
connectors.
Check for correct sensors wiring also
according electrical scheme.
Reset
Notes
Local HMI
Network
Auto
Symptom
Cause
Solution
Bell icon is moving on controller’s display.
Bell icon is moving on controller’s display.
String in the alarm list:
Unit HRInvAl
String in the alarm log:
Unit HRInvAl
String in the alarm snapshot
Unit HRInvAl
Entering and leaving water temperature
sensors are inverted.
Check cabling of the sensors on the unit
controller.
Check offset of the two sensors with the
water pump running
Entering and leaving water pipes are
reversed
Check if the water flows in counter flow
respect to refrigerant.
Water pump operate reverse.
Check if the water flows in counter flow
respect to refrigerant.
Reset
Notes
Local HMI
Network
Auto
Symptom
Cause
Solution
Bell icon is moving on controller’s display.
String in the alarm list:
RpdRcvryCommFail
String in the alarm log:
RpdRcvryCommFail
String in the alarm snapshot
RpdRcvryCommFail
Module has no power supply
Check the power supply from the
connector on the side of the module.
Check if LEDs are both green.
Check if the connector on the side is tightly
inserted in the module
Module address is not properly set
Check if module’s address is correct
referring to the wiring diagram.
Module is broken
Check if LED are on and both green. If
BSP LED is solid red replace the module
Check if power supply is ok but LEDs are
both off. In this case replace the module
Reset
Notes
Local HMI
Network
Auto
Symptom
Cause
Solution
Unit status is On
Bell icon is moving on controller’s display.
Bell icon is moving on controller’s display.
String in the alarm list:
SwitchBoxTempSen
String in the alarm log:
SwitchBoxTempSen
String in the alarm snapshot
SwitchBoxTempSen
Sensor is broken.
Check for sensor integrity.
according table and allowed kOhm (k)
range.
Check correct sensors operation
Sensor is shorted.
Check if sensor is shorted with a
resistance measurement.
Sensor is not properly connected (open).
Check for absence of water or humidity on
electrical contacts.
Check for correct plug-in of the electrical
connectors.
Check for correct sensors wiring also
according electrical scheme.
Reset
Notes
Local HMI
Network
Auto
5.1.13 Heat Recovery Water Temperatures inverted
This alarm is generated any time that the heat recovery entering water temperature is lower than the leaving by 1°C and
at least one compressor is running.
5.1.14 Rapid Recovery Module Communication Fail
This alarm is generated in case of communication problems with the RRC module.
5.1.15 Switch Box Temperature sensor fault
This alarm is generated any time that the input resistance is out of an acceptable range.

Multipurpose Units
EWYD 4Z
MultiPurpose Units
D-EOMZC00204-18_01EN
Operation Manual
25/48
Symptom
Cause
Solution
Unit status is Off.
All circuits are stopped with a normal
shutdown procedure.
Bell icon is moving on controller’s display.
String in the alarm list:
UnitOffCndEntWTempSen
String in the alarm log:
UnitOffCndEntWTempSen
String in the alarm snapshot
UnitOffcndEntWTempSen
Sensor is broken.
Check for sensor integrity.
according table and allowed kOhm (k)
range.
Check correct sensors operation
Sensor is shorted.
Check if sensor is shorted with a
resistance measurement.
Sensor is not properly connected (open).
Check for absence of water or humidity on
electrical contacts.
Check for correct plug-in of the electrical
connectors.
Check for correct sensors wiring also
according electrical scheme.
Reset
Notes
Local HMI
Network
Auto
Symptom
Cause
Solution
Unit status is Off.
All circuits are stopped with a normal
shutdown procedure.
Bell icon is moving on controller’s display.
String in the alarm list:
UnitOffCndLvgWTempSen
String in the alarm log:
UnitOffCndLvgWTempSen
String in the alarm snapshot
UnitOffcndLvgWTempSen
Sensor is broken.
Check for sensor integrity.
according table and allowed kOhm (k)
range.
Check correct sensors operation
Sensor is shorted.
Check if sensor is shorted with a
resistance measurement.
Sensor is not properly connected (open).
Check for absence of water or humidity on
electrical contacts.
Check for correct plug-in of the electrical
connectors.
Check for correct sensors wiring also
according electrical scheme.
Reset
Notes
Local HMI
Network
Auto
Symptom
Cause
Solution
Unit status is Off.
All circuits are stopped with a normal
shutdown procedure.
Bell icon is moving on controller’s display.
String in the alarm list:
UnitOffEvpEntWTempSen
String in the alarm log:
UnitOffEvpEntWTempSen
String in the alarm snapshot
UnitOffEvpEntWTempSen
Sensor is broken.
Check for sensor integrity.
according table and allowed kOhm (k)
range.
Check correct sensors operation
Sensor is shorted.
Check if sensor is shorted with a
resistance measurement.
Sensor is not properly connected (open).
Check for absence of water or humidity on
electrical contacts.
Check for correct plug-in of the electrical
connectors.
Check for correct sensors wiring also
according electrical scheme.
Reset
Notes
Local HMI
Network
5.2 Unit Pumpdown Stop Alarms
5.2.1 Condenser Entering Water Temperature (EWT) sensor fault
This alarm is generated any time the input resistance is out of an acceptable range.
5.2.2 Condenser Leaving Water Temperature (LWT) sensor fault
This alarm is generated any time the input resistance is out of an acceptable range.
5.2.3 Evaporator Entering Water Temperature (EWT) sensor fault
This alarm is generated any time the input resistance is out of an acceptable range.

Multipurpose Units
D-EOMZC00204-18_01EN
Operation Manual
26/48
EWYD 4Z
MultiPurpose Units
Symptom
Cause
Solution
Unit status is Off.
All circuits are stopped with a normal
shutdown precedure.
Bell icon is moving on controller’s display.
String in the alarm list:
UnitOffEvpWTempInvrtd
String in the alarm log:
UnitOffEvpWTempInvrtd
String in the alarm snapshot
UnitOffEvpWTempInvrtd
Entering and leaving water temperature
sensors are inverted.
Check cabling of the sensors on the unit
controller.
Check offset of the two sensors with the
water pump running
Entering and leaving water pipes are
reversed
Check if the water flows in counter flow
respect to refrigerant.
Water pump operate reverse.
Check if the water flows in counter flow
respect to refrigerant.
Reset
Notes
Local HMI
Network
Auto
Symptom
Cause
Solution
Unit Status is OAT Lockout.
All circuits are stopped with a normal
shutdown procedure.
Bell icon is moving on controller’s display.
String in the alarm list:
StartInhbtAmbTempLo
String in the alarm log:
StartInhbtAmbTempLo
String in the alarm snapshot
StartInhbtAmbTempLo
Outside ambient temperature is lower than
value set into unit’s controller.
Check the minimum outside ambient
temperature value set into the unit’s
controller.
Check if this value is in accordance with
chiller application, therefore check about
the proper application and utilization of the
chiller.
Improper operation of Outside Ambient
Temperature sensor.
Check for proper operation of OAT sensor
according information about kOhm (k)
range related to temperature values.
Reset
Notes
Local HMI
Network
Auto
It clears automatically with a 2.5°C of
hysteresis.
Symptom
Cause
Solution
Unit status is Off.
All circuits are stopped with a normal
shutdown precedure.
Bell icon is moving on controller’s display.
String in the alarm list:
UnitOffAmbTempSen
String in the alarm log:
UnitOffAmbTempSen
String in the alarm snapshot
UnitOffAmbTempSen
Sensor is broken.
Check for sensor integrity.
Check correct sensors operation
according table and allowed kOhm (k)
range.
Sensor is shorted.
Check if sensor is shorted with a
resistance measurement.
Sensor is not properly connected (open).
Check for absence of water or humidity on
electrical contacts.
Check for correct plug-in of the electrical
connectors.
Check for correct sensors wiring also
according electrical scheme.
Reset
Notes
Local HMI
Network
Auto
Symptom
Cause
Solution
5.2.4 Evaporator Water Temperatures inverted
This alarm is generated any time the entering water temperature is lower than the leaving by 1°C and at least one
compressor is running since 90 seconds.
5.2.5 Outside Air Temperature (OAT) Lockout
This alarm prevents the unit to start if the outside air temperature is too low. Purpose is to prevent low pressure trips at
startup. The limit depends on the fan regulation that is installed on the unit. By default this value is set to 10°C.
5.2.6 Outside Air Temperature sensor fault alarm
This alarm is generated any time the input resistance is out of an acceptable range.
5.3 Unit Rapid Stop Alarms
5.3.1 Condenser Water Freeze alarm
This alarm is generated to indicate that the water temperature (entering or leaving) has dropped below a safety limit.
Control tries to protect the heat exchanger starting the pump and letting the water circulate.

Multipurpose Units
EWYD 4Z
MultiPurpose Units
D-EOMZC00204-18_01EN
Operation Manual
27/48
Unit status is Off.
All circuits are stopped immediately.
Bell icon is moving on controller’s display.
String in the alarm list:
UnitOffCondWaterTmpLo
String in the alarm log:
UnitOffCondWaterTmpLo
String in the alarm snapshot
UnitOffCondWaterTmpLo
Water flow too low.
Increase the water flow.
Inlet temperature to the evaporator is too
low.
Increase the inlet water temperature.
Flow switch is not working or no water flow.
Check the flow switch and the water pump.
Refrigerant temperature become too low (<
-0.6°C).
Check the water flow and filter. No good
heat exchange condition into the
evaporator.
Sensors readings (entering or leaving) are
not properly calibrated
Check the water temperatures with a
proper instrument and adjust the offsets
Wrong freeze limit setpoint
The freeze limit has not been changed as
a function of glycol percentage.
Reset
Notes
Local HMI
Network
Auto
It’s required to check if the condenser has
any damage due to this alarm.
Symptom
Cause
Solution
Unit status is Off.
All circuits are stopped immediately.
Bell icon is moving on controller’s display.
String in the alarm list:
UnitOffCondWaterFlow
String in the alarm log:
UnitOffCondWaterFlow
String in the alarm snapshot
UnitOffCondWaterFlow
No water flow sensed for 3 minutes
continuously or water flow too low.
Check the water pump filler and the water
circuit for obstructions.
Check the flow switch calibration and
adapt to minimum water flow.
Check if pump impeller can rotate freely
and has no damages.
Check pumps protection devices (circuit
breakers, fuses, inverters, etc.)
Check if water filter is clogged.
Check flow switch connections.
Reset
Notes
Local HMI
Network
Auto
Before resetting the Emergency Stop button please verify that the harmful condition has been removed.
Symptom
Cause
Solution
Unit status is Off.
All circuits are stopped immediately.
Bell icon is moving on controller’s display.
String in the alarm list:
UnitOffEmergencyStop
String in the alarm log:
UnitOffEmergencyStop
String in the alarm snapshot
UnitOffEmergencyStop
Emergency stop button has been pushed.
Turning counterclockwise the emergency
stop button, the alarm should be cleared.
Reset
Notes
Local HMI
Network
Auto
Please see note on the top.
Symptom
Cause
Solution
Unit status is Off.
All circuits are stopped immediately.
Bell icon is moving on controller’s display.
String in the alarm list:
UnitOffEvapWaterFlow
No water flow sensed for 3 minutes
continuously or water flow too low.
Check the water pump filler and the water
circuit for obstructions.
Check the flow switch calibration and
adapt to minimum water flow.
5.3.2 Condenser Water Flow Loss alarm
This alarm is generated in case of flow loss to the chiller to protect the unit against Mechanical High Pressure trips.
5.3.3 Emergency Stop
This alarm is generated any time the Emergency Stop button is activated.
5.3.4 Evaporator Flow Loss alarm
This alarm is generated in case of flow loss to the chiller to protect the unit against freezing.

Multipurpose Units
D-EOMZC00204-18_01EN
Operation Manual
28/48
EWYD 4Z
MultiPurpose Units
String in the alarm log:
UnitOffEvapWaterFlow
String in the alarm snapshot
UnitOffEvapWaterFlow
Check if pump impeller can rotate freely
and has no damages.
Check pumps protection devices (circuit
breakers, fuses, inverters, etc.)
Check if water filter is clogged.
Check flow switch connections.
Reset
Notes
Local HMI
Network
Auto
Symptom
Cause
Solution
Unit status is Off.
All circuits are stopped with a normal
shutdown procedure.
Bell icon is moving on controller’s display.
String in the alarm list:
UnitOffLvgEntWTempSen
String in the alarm log:
UnitOffLvgEntWTempSen
String in the alarm snapshot
UnitOffEvpLvgWTempSen
Sensor is broken.
Check for sensor integrity.
according table and allowed kOhm (k)
range.
Check correct sensors operation
Sensor is shorted.
Check if sensor is shorted with a
resistance measurement.
Sensor is not properly connected (open).
Check for absence of water or humidity on
electrical contacts.
Check for correct plug-in of the electrical
connectors.
Check for correct sensors wiring also
according electrical scheme.
Reset
Notes
Local HMI
Network
Auto
Symptom
Cause
Solution
Unit status is Off.
All circuits are stopped immediately.
Bell icon is moving on controller’s display.
String in the alarm list:
UnitOffEvapWaterTmpLo
String in the alarm log:
UnitOffEvapWaterTmpLo
String in the alarm snapshot
UnitOffEvapWaterTmpLo
Water flow too low.
Increase the water flow.
Inlet temperature to the evaporator is too
low.
Increase the inlet water temperature.
Flow switch is not working or no water flow.
Check the flow switch and the water pump.
Sensors readings (entering or leaving) are
not properly calibrated.
Check the water temperatures with a
proper instrument and adjust the offsets
Wrong freeze limit setpoint.
The freeze limit has not been changed as
a function of glycol percentage.
Reset
Notes
Local HMI
Network
Auto
It’s required to check if the evaporator has
any damage due to this alarm.
Symptom
Cause
Solution
Unit status is Off.
All circuits are switched off with the normal
shutdown procedure.
Bell icon is moving on controller’s display.
String in the alarm list:
UnitOffExternalAlarm
String in the alarm log:
UnitOffExternalAlarm
String in the alarm snapshot
UnitOffExternalAlarm
There is an external event that has caused
the opening, for at least 5 seconds, of the
port on the controller board.
Check causes of the external event or
alarm.
Check electrical wiring from unit controller
to the external equipment in case of any
external events or alarms have been
occurred.
5.3.5 Evaporator Leaving Water Temperature (LWT) sensor fault
This alarm is generated any time that the input resistance is out of an acceptable range.
5.3.6 Evaporator Water Freeze alarm
This alarm is generated to indicate that the water temperature (entering or leaving) has dropped below a safety limit.
Control tries to protect the heat exchanger starting the pump and letting the water circulate.
5.3.7 External alarm
This alarm is generated to indicate that an external device whose operation is linked with this unit operation. This external
device could be a pump or an inverter.

Multipurpose Units
EWYD 4Z
MultiPurpose Units
D-EOMZC00204-18_01EN
Operation Manual
29/48
Reset
Notes
Local HMI
Network
Auto
NOTE: What above applies in case of configuration of the external fault digital input as Alarm.
Symptom
Cause
Solution
Unit status is Off.
All circuits are stopped immediately.
Bell icon is moving on controller’s display.
String in the alarm list:
UnitOffGasLeakage
String in the alarm log:
UnitOffGasLeakage
String in the alarm snapshot
UnitOffGasLeakage
Refrigerant leakage
Locate the leakage with a sniffer and fix the
leakage
Leak detector is not properly powered
Check the power supply of the leak
detector.
Leak detector is not properly connected to
the controller.
Check the connection of the detector with
reference to the wiring diagram of the unit.
Leak detector is broken
Replace the leak detector.
Leak detector is not required/needed
Check the configuration on the unit
controller and disable this option.
Reset
Notes
Local HMI
Network
Auto
Symptom
Cause
Solution
Unit status is Off.
All circuits are stopped immediately.
Bell icon is moving on controller’s display.
String in the alarm list:
UnitOff HRFreeze
String in the alarm log:
UnitOff HRFreeze
String in the alarm snapshot
UnitOff HRFreeze
Water flow too low.
Increase the water flow.
Inlet temperature to the heat recovery is
too low.
Increase the inlet water temperature.
Sensors readings (entering or leaving) are
not properly calibrated
Check the water temperatures with a
proper instrument and adjust the offsets
Reset
Notes
Local HMI
Network
Auto
Symptom
Cause
Solution
Unit status is Off.
All circuits are stopped immediately.
Bell icon is moving on controller’s display.
String in the alarm list:
OptionCtrlrCommFail
String in the alarm log:
OptionCtrlrCommFail
String in the alarm snapshot
OptionCtrlrCommFail
Module has no power supply
Check the power supply from the
connector on the side of the module.
Check if LEDs are both green.
Check if the connector on the side is tightly
inserted in the module
Module address is not properly set
Check if module’s address is correct
referring to the wiring diagram.
Module is broken
Check if LED are on and both green. If
BSP LED is solid red replace the module
Check if power supply is ok but LEDs are
both off. In this case replace the module
Reset
Notes
Local HMI
Network
Auto
5.3.8 Gas Leakage Alarm
This alarm is generated when the external leak detector(s) detects a refrigerant concentration higher that a threshold. To
clear this alarm is required to clear the alarm either locally and, if needed, on the leak detector itself.
5.3.9 Heat Recovery Water Freeze Protect alarm
This alarm is generated to indicate that the heat recovery water temperature (entering or leaving) has dropped below a
safety limit. Control tries to protect the heat exchanger starting the pump and letting the water circulate.
5.3.10 OptionCtrlrCommFail
This alarm is generated in case of communication problems with the AC module.
5.3.11 Power Fault
This alarm is generated when the main power is Off and the unit controller is powered by the UPS.

Multipurpose Units
D-EOMZC00204-18_01EN
Operation Manual
30/48
EWYD 4Z
MultiPurpose Units
Resolution of this fault requires a direct intervention on the power supply of this unit. Direct intervention on the
power supply can cause electrocution, burns or even death. This action must be performed only by trained
persons. In case of doubts contact your maintenance company.
Symptom
Cause
Solution
Unit status is Off.
All circuits are stopped immediately. Bell
icon is moving on controller’s display.
String in the alarm list:
Power Fault
String in the alarm log:
Power Fault
String in the alarm snapshot
Power Fault
Loss of one phase.
Check voltage level on each of the phases.
Not correct sequence connection of
L1,L2,L3.
Check sequence of L1, L2, L3 connections
according indication on chiller’s electrical
scheme.
Voltage level on the unit’s panel is not in the
allowed range (±10%).
Check that voltage level on each phases is
into the allowed range that is indicated on
the chiller label.
Is important to check the voltage level on
each phases not only with chiller not
running, but mainly with chiller running
from minimum capacity up to full load
capacity. That's because voltage drop can
occur from a certain unit cooling capacity
level, or because of certain working
condition (i.e. high values of OAT);
In these cases the issue can be related
with the sizing of power cables.
There is a short-circuit on the unit.
Check for correct electrical isolation
condition of each unit’s circuit with a
Megger tester.
Reset
Notes
Local HMI
Network
Auto
Resolution of this fault requires a direct intervention on the power supply of this unit.
Direct intervention on the power supply can cause electrocution, burns or even death. This action must be
performed only by trained persons. In case of doubts contact your maintenance company.
Symptom
Cause
Solution
Unit status is Off.
All circuits are stopped immediately. Bell
icon is moving on controller’s display.
String in the alarm list:
UnitOffPhaveVoltage
String in the alarm log:
UnitOffPhaveVoltage
String in the alarm snapshot
UnitOffPhaveVoltage
Loss of one phase.
Check voltage level on each of the phases.
Not correct sequence connection of
L1,L2,L3.
Check sequence of L1, L2, L3 connections
according indication on chiller’s electrical
scheme.
Voltage level on the unit’s panel is not in
the allowed range (±10%).
Check that voltage level on each phases is
into the allowed range that is indicated on
the chiller label.
Is important to check the voltage level on
each phases not only with chiller not
running, but mainly with chiller running
from minimum capacity up to full load
capacity. That's because voltage drop can
occur from a certain unit cooling capacity
level, or because of certain working
condition (i.e. high values of OAT);
In these cases the issue can be related
with the sizing of power cables.
There is a short-circuit on the unit.
Check for correct electrical isolation
condition of each unit’s circuit with a
Megger tester.
Reset
Notes
Local HMI
Network
Auto
5.3.12 PVM alarm
This alarm is generated in case of problems with the power supply to the chiller.
5.4 Circuit Alerts
5.4.1 Economizer Pressure Sensor fault
This alarm is generated to indicate that the sensor is not reading properly.

Multipurpose Units
EWYD 4Z
MultiPurpose Units
D-EOMZC00204-18_01EN
Operation Manual
31/48
Symptom
Cause
Solution
Circuit status is On.
Economizer is Off.
Bell icon is moving on controller’s display.
String in the alarm list:
Cx EcoPressSen
String in the alarm log:
Cx EcoPressSen
String in the alarm snapshot
Cx EcoPressSen
Sensor is broken.
Check for sensor integrity.
Check correct sensors operation according
information about mVolt (mV) range related
to pressure values in kPa.
Sensor is shorted.
Check if sensor is shorted with a resistance
measurement.
Sensor is not properly connected (open).
Check for correct installation of the sensor
on refrigerant circuit pipe. The transducer
must be able to sense the pressure through
the valve’s needle.
Check for absence of water or humidity on
sensor electrical contacts.
Check for correct plug-in of the electrical
connectors.
Check for correct sensors wiring also
according electrical scheme.
Reset
Notes
Local HMI
Network
Auto
Symptom
Cause
Solution
Circuit status is On.
Economizer is Off.
Bell icon is moving on controller’s display.
String in the alarm list:
Cx EcoTempSen
String in the alarm log:
Cx EcoTempSen
String in the alarm snapshot
Cx EcoTempSen
Sensor is shorted.
Check for sensor integrity.
Check correct sensors operation according
information about kOhm (k) range related
to temperature values.
Sensor is broken.
Check if sensor is shorted with a resistance
measurement.
Sensor is not good connected (open).
Check for correct installation of the sensor
on refrigerant circuit pipe.
Check for absence of water or humidity on
sensor electrical contacts.
Check for correct plug-in of the electrical
connectors.
Check for correct sensors wiring also
according with electrical scheme.
Reset
Notes
Local HMI
Network
Auto
Symptom
Cause
Solution
Circuit status is Off.
No indications on the screen
String in the alarm list:
-String in the alarm log:
Cx Failed Pumpdown
String in the alarm snapshot
Cx Failed Pumpdown
EEXV is not closing completely, therefore
there’s “short-circuit” between high
pressure side with low pressure side of the
circuit.
Check for proper operation and full closing
position of EEXV. Sight glass should not
show refrigerant flow after the valve is
closed.
Check LED on the top of the valve, C LED
should be solid green. If both LED are
blinking alternately the valve motor is not
properly connected.
Evaporating pressure sensor is not
working properly.
Check for proper operation of evaporating
pressure sensor.
Compressor on circuit is internally
damaged with a mechanical problems for
example on internal check-valve, or on
internal spirals or vanes.
Check compressors on circuits.
Reset
Notes
Local HMI
Network
Auto
5.4.2 Economizer Temperature Sensor fault
This alarm is generated to indicate that the sensor is not reading properly.
5.4.3 Failed Pumpdown
This alarm is generated to indicate that the circuit hadn’t been able to remove all the refrigerant from the evaporator. It
automatically clear as soon as the compressor stops just to be logged in the alarm history. It may not be recognized from
BMS because the communication latency can give enough time for the reset. It may not even be seen on the local HMI.

Multipurpose Units
D-EOMZC00204-18_01EN
Operation Manual
32/48
EWYD 4Z
MultiPurpose Units
Symptom
Cause
Solution
Circuit status is On.
The compressor keep operating as
normal.
Bell icon is moving on controller’s display.
String in the alarm list:
Cx FanAlm
String in the alarm log:
Cx FanAlm
String in the alarm snapshot
Cx FanAlm
At least one of the fan has some problems
In case of on/off fan check the
thermal magnetic circuit breaker of each
fan. The fan could absorbs too much
current
In case of fan with VFD check the alarm
output of the and message error provided
by each fan VFD
Reset
Notes
Local HMI
Network
Auto
Symptom
Cause
Solution
Circuit status is On.
Bell icon is moving on controller’s display.
String in the alarm list:
Cx GasLeakSen
String in the alarm log:
Cx GasLeakSen
String in the alarm snapshot
Cx GasLeakSen
Sensor is broken.
Check for sensor integrity.
Check correct sensors operation according
information about mVolt (mV) range related
to ppm values.
Sensor is shorted.
Check if sensor is shorted with a resistance
measurement.
Sensor is not properly connected (open).
Check for correct installation of the sensor.
Check for absence of water or humidity on
sensor electrical contacts.
Check for correct plug-in of the electrical
connectors.
Check for correct sensors wiring also
according electrical scheme.
Reset
Notes
Local HMI
Network
Auto
Symptom
Cause
Solution
Circuit status is On.
The compressor keep operating as
normal.
Bell icon is moving on controller’s display.
String in the alarm list:
CxCmp1 MainCode01
String in the alarm log:
CxCmp1 MainCode01
String in the alarm snapshot
CxCmp1 MainCode01
The inverter cooling valve in the inverter,
may require a verification or a
replacement.
Contact your service organization to get
the problem solved.
Reset
Notes
Local HMI
Network
Auto
Symptom
Cause
Solution
Circuit status is On.
The compressor keep operating as normal.
Bell icon is moving on controller’s display.
String in the alarm list:
CxCmp1 MainCode02
String in the alarm log:
CxCmp1 MainCode02
String in the alarm snapshot
The capacitors in the inverter, may require
a verification or a replacement.
Contact your service organization to get
the problem solved.
5.4.4 Fan Fault
This alarm indicates that at least one of the fans could has some problems
5.4.5 Gas Leakage Sensor fault
This alarm is generated to indicate that the sensor is not reading properly.
5.4.6 CxCmp1 MaintCode01
This alarm indicates that a component in the inverter may require verification or even a replacement.
5.4.7 CxCmp1 MaintCode02
This alarm indicates that a component in the inverter may require verification or even a replacement.

Multipurpose Units
EWYD 4Z
MultiPurpose Units
D-EOMZC00204-18_01EN
Operation Manual
33/48
CxCmp1 MainCode02
Reset
Notes
Local HMI
Network
Auto
Resolution of this fault requires a direct intervention on the power supply of this unit.
Direct intervention on the power supply can cause electrocution, burns or even death. This action must be
performed only by trained persons. In case of doubts contact your maintenance company.
Symptom
Cause
Solution
Circuit status is On.
The controller brings the compressor to
the minimum speed and then normal
operation is recovered (default 1200rmp)
Bell icon is moving on controller’s display.
String in the alarm list:
Cx FanAlm
String in the alarm log:
Cx FanAlm
String in the alarm snapshot
Cx FanAlm
Chiller main power supply had a down
peak which caused the trip.
Check if main power supply is within the
acceptable tolerance for this chiller
Reset
Notes
Local HMI
Network
Auto
Symptom
Cause
Solution
Circuit status is Off.
The circuit is switched off with the normal
shutdown procedure.
Bell icon is moving on controller’s display.
String in the alarm list:
CxCmp1 OffDischTmpSen
String in the alarm log:
CxCmp1 OffDischTmpSen
String in the alarm snapshot
CxCmp1 OffDischTmpSen
Sensor is shorted.
Check for sensor integrity.
Check correct sensors operation according
information about kOhm (k) range related
to temperature values.
Sensor is broken.
Check if sensor is shorted with a
resistance measurement.
Sensor is not properly connected (open).
Check for correct installation of the sensor
on refrigerant circuit pipe.
Check for absence of water or humidity on
sensor electrical contacts.
Check for correct plug-in of the electrical
connectors.
Check for correct sensors wiring also
according with electrical scheme.
Reset
Notes
Local HMI
Network
Auto
Symptom
Cause
Solution
Circuit status is Off.
Gas leakage in the compressors box .
Switch off the unit and perform a gas
leakage test.
5.4.8 Power Loss
This alarm indicates that a short under voltage on main power supply, that does not turn off the unit, has occurred.
5.5 Circuit Pumpdown Stop Alarms
5.5.1 Discharge Temperature Sensor fault
This alarm is generated to indicate that the sensor is not reading properly.
5.5.2 Gas Leakage fault
This alarm indicates a gas leakage in the compressor box.

Multipurpose Units
D-EOMZC00204-18_01EN
Operation Manual
34/48
EWYD 4Z
MultiPurpose Units
The circuit is switched off with the
shutdown procedure performing a deep
pumpdown of the circuit.
Bell icon is moving on controller’s display.
String in the alarm list:
Cx OffGasLeakage
String in the alarm log:
Cx OffGasLeakage
String in the alarm snapshot
Cx OffGasLeakage
Gas Leakage in the plant room.
Check if there are leakage on the unit with
a detector eventually starting suction fans
to change the air in the room.
Gas leakage sensor fault.
Put the sensor in open air and check that
the alarm can be cleared. In case replace
the sensor or disable the option before
getting a new part.
Reset
Notes
Local HMI
Network
Auto
Symptom
Cause
Solution
Circuit status is Off.
The circuit is switched off with the normal
shutdown procedure.
Bell icon is moving on controller’s display.
String in the alarm list:
CxCmp1 VfdOverTemp
String in the alarm log:
CxCmp1 VfdOverTemp
String in the alarm snapshot
CxCmp1 VfdOverTemp
Cooling solenoid valve is not operating
properly.
Check electrical connection of the solenoid
valve.
Check refrigerant charge. Low refrigerant
charge can cause overheating of the Vfd
electronic.
Check for obstructions in the pipe.
Vfd Heater not properly connected.
Check if Vfd heater is switched off when
the Vfd temperature increases.
Check if the contactor that commands the
Vfd heater can switch propertly.
Reset
Notes
Local HMI
Network
Auto
Symptom
Cause
Solution
Circuit status is Off.
The circuit is switched off with the normal
shutdown procedure.
Bell icon is moving on controller’s display.
String in the alarm list:
CxCmp1 OffLiquidTempSen
String in the alarm log:
CxCmp1 OffLiquidTempSen
String in the alarm snapshot
CxCmp1 OffLiquidTempSen
Sensor is shorted.
Check for sensor integrity.
Check correct sensors operation
according information about kOhm (k)
range related to temperature values.
Sensor is broken.
Check if sensor is shorted with a
resistance measurement.
Sensor is not properly connected (open).
Check for correct installation of the sensor
on refrigerant circuit pipe.
Check for absence of water or humidity on
sensor electrical contacts.
Check for correct plug-in of the electrical
connectors.
Check for correct sensors wiring also
according with electrical scheme.
Reset
Notes
Local HMI
Network
Auto
Symptom
Cause
Solution
Circuit status is Off.
The circuit is switched off with the normal
shutdown procedure.
Bell icon is moving on controller’s display.
String in the alarm list:
CxCmp1 VfdLowTemp
String in the alarm log:
Cooling solenoid valve is not operating
properly. It’s always open when
compressor runs.
Check electrical connection of the solenoid
valve.
Check operation of the valve to see if it can
close properly.
5.5.3 High Compressor Vfd Temperature fault
This alarm is generated to indicate that the Vfd temperature is too high to allow the compressor to run.
5.5.4 Liquid Temperature Sensor fault
This alarm is generated to indicate that the sensor is not reading properly.
5.5.5 Low Compressor Vfd Temperature fault
This alarm is generated to indicate that the Vfd temperature is too low to allow the compressor to run safely.

Multipurpose Units
EWYD 4Z
MultiPurpose Units
D-EOMZC00204-18_01EN
Operation Manual
35/48
CxCmp1 VfdLowTemp
String in the alarm snapshot
CxCmp1 VfdLowTemp
Check operating cycles of the valve. It has
a limited number of cycles.
Vfd heater is not working.
Check if the Vfd heater is powered.
Check if the Vfd heater is commanded on
when Vfd temperature is low.
Reset
Notes
Local HMI
Network
Auto
Symptom
Cause
Solution
Circuit status is Off.
The circuit is switched off with the normal
shutdown procedure.
Bell icon is moving on controller’s display.
String in the alarm list:
CxCmp1 OffOilLevelLo
String in the alarm log:
CxCmp1 OffOilLevelLo
String in the alarm snapshot
CxCmp1 OffOilLevelLo
Oil Level switch not operating correctly.
Check the cabling between switch and
controller feedback and power
Check if switch operates correctly.
Check if digital input of the controller
operates correctly.
Check the oil charge
Verify if there is enough oil inside the
circuit.
Reset
Notes
Local HMI
Network
Auto
Symptom
Cause
Solution
Circuit status is Off.
The circuit is switched off with the
shutdown procedure.
Bell icon is moving on controller’s display.
String in the alarm list:
CxCmp1 OffDishSHLo
String in the alarm log:
CxCmp1 OffDishSHLo
String in the alarm snapshot
CxCmp1 OffDishSHLo
EEXV is not working correctly.
It’s not opening enough or it’s moving in
the opposite direction.
Check if pump-down can be finished for
pressure limit reached;
Check expansion valve movements.
Check connection to the valve driver on the
wiring diagram.
Measure the resistance of each winding, it
has to be different from 0 Ohm.
Reset
Notes
Local HMI
Network
Auto
x 2 attempts (W/C only)
Symptom
Cause
Solution
Circuit status is Off.
The circuit is switched off with the normal
shutdown procedure.
Bell icon is moving on controller’s display.
String in the alarm list:
CxCmp1 OffOilFeedPSen
String in the alarm log:
CxCmp1 OffOilFeedPSen
String in the alarm snapshot
CxCmp1 OffOilFeedPSen
Sensor is broken.
Check for sensor integrity.
Check correct sensors operation according
information about mVolt (mV) range related
to pressure values in kPa.
Sensor is shorted.
Check if sensor is shorted with a resistance
measurement.
Sensor is not properly connected (open).
Check for correct installation of the sensor
on refrigerant circuit pipe. The transducer
must be able to sense the pressure through
the valve’s needle.
Check for absence of water or humidity on
sensor electrical contacts.
5.5.6 Low Oil Level fault
This alarm indicates that the oil level inside the oil separator has become too low to allow for a safe operation of the
compressor.
This switch may not be installed on the unit because in regular operations the oil separation is always granted.
5.5.7 Low Discharge Superheat fault
This alarm indicates that the unit has worked for too long with low discharge super heat.
5.5.8 Oil Pressure Sensor fault
This alarm is generated to indicate that the sensor is not reading properly.

Multipurpose Units
D-EOMZC00204-18_01EN
Operation Manual
36/48
EWYD 4Z
MultiPurpose Units
Check for correct plug-in of the electrical
connectors.
Check for correct sensors wiring also
according electrical scheme.
Reset
Notes
Local HMI
Network
Auto
Symptom
Cause
Solution
Circuit status is Off.
The circuit is switched off with the normal
shutdown procedure.
Bell icon is moving on controller’s display.
String in the alarm list:
CxCmp1 OffSuctTempSen
String in the alarm log:
CxCmp1 OffSuctTempSen
String in the alarm snapshot
CxCmp1 OffSuctTempSen
Sensor is shorted.
Check for sensor integrity.
Check correct sensors operation according
information about kOhm (k) range related
to temperature values.
Sensor is broken.
Check if sensor is shorted with a
resistance measurement.
Sensor is not good connected (open).
Check for correct installation of the sensor
on refrigerant circuit pipe.
Check for absence of water or humidity on
sensor electrical contacts.
Check for correct plug-in of the electrical
connectors.
Check for correct sensors wiring also
according with electrical scheme.
Reset
Notes
Local HMI
Network
Auto
Symptom
Cause
Solution
Circuit status is Off.
All circuits are stopped immediately.
Bell icon is moving on controller’s display.
String in the alarm list:
Cx OffCmpCtrlrComFail
String in the alarm log:
Cx OffCmpCtrlrComFail
String in the alarm snapshot
Cx OffCmpCtrlrComFail
Module has no power supply
Check the power supply from the
connector on the side of the module.
Check if LEDs are both green.
Check if the connector on the side is tightly
inserted in the module
Module address is not properly set
Check if module’s address is correct
referring to the wiring diagram.
Module is broken
Check if LED are on and both green. If
BSP LED is solid red replace the module
Check if power supply is ok but LEDs are
both off. In this case replace the module
Reset
Notes
Local HMI
Network
Auto
Symptom
Cause
Solution
Circuit status is Off.
All circuits are stopped immediately.
Bell icon is moving on controller’s display.
String in the alarm list:
Cx OffEXVCtrlrComFail
String in the alarm log:
Cx OffEXVCtrlrComFail
String in the alarm snapshot
Cx OffEXVCtrlrComFail
Module has no power supply
Check the power supply from the
connector on the side of the module.
Check if LEDs are both green.
Check if the connector on the side is tightly
inserted in the module
Module address is not properly set
Check if module’s address is correct
referring to the wiring diagram.
Module is broken
Check if LED are on and both green. If
BSP LED is solid red replace the module
Check if power supply is ok but LEDs are
both off. In this case replace the module
5.5.9 Suction Temperature Sensor fault
This alarm is generated to indicate that the sensor is not reading properly.
5.6 Circuit Rapid Stop Alarms
5.6.1 Compressor Extension Communication Error
This alarm is generated in case of communication problems with the CCx module.
5.6.2 EXV Driver Extension Communication Error
This alarm is generated in case of communication problems with the EEXVx module.

Multipurpose Units
EWYD 4Z
MultiPurpose Units
D-EOMZC00204-18_01EN
Operation Manual
37/48
Reset
Notes
Local HMI
Network
Auto
Symptom
Cause
Solution
Circuit status is Off.
The compressor does not load anymore,
circuit is immediately stopped.
Bell icon is moving on controller’s display.
String in the alarm list:
CxCmp1 OffVfdFault
String in the alarm log:
CxCmp1 OffVfdFault
String in the alarm snapshot
CxCmp1 OffVfdFault
Inverter is operating in an unsafe condition
and for this reason the inverter must be
stopped.
Check the alarm snapshot to identify the
alarm code from the inverter. Contact your
service organization to get the problem
solved.
Reset
Notes
Local HMI
Network
Auto
Symptom
Cause
Solution
Circuit status is Off.
The circuit is stopped.
Bell icon is moving on controller’s display.
String in the alarm list:
CxCmp1 OffVfdOverTemp
String in the alarm log:
CxCmp1 OffVfdOverTemp
String in the alarm snapshot
CxCmp1 OffVfdOverTemp
Insufficient motor cooling
Check refrigerant charge.
Check if operational envelope of the unit is
respected.
Check operation of the cooling solenoid
valve
Motor temperature sensor could not
operate properly.
Check the readings of the motor
temperature sensor and check the Ohmic
value. A correct reading should be around
hundreds of Ohm at ambient temperature.
Check the electrical connection of the
sensor with the electronic board.
Reset
Notes
Local HMI
Network
Auto
Symptom
Cause
Solution
Circuit status is Off.
The circuit is stopped.
Bell icon is moving on controller’s display.
String in the alarm list:
CxCmp1 CondPressSen
String in the alarm log:
CxCmp1 CondPressSen
String in the alarm snapshot
CxCmp1 CondPressSen
Sensor is broken.
Check for sensor integrity.
Check correct sensors operation
according information about mVolt (mV)
range related to pressure values in kPa.
Sensor is shorted.
Check if sensor is shorted with a
resistance measurement.
Sensor is not properly connected (open).
Check for correct installation of the sensor
on refrigerant circuit pipe. The transducer
must be able to sense the pressure
through the valve’s needle.
Check for absence of water or humidity
on sensor electrical contacts.
Check for correct plug-in of the electrical
connectors.
Check for correct sensors wiring also
according electrical scheme.
Reset
Notes
Local HMI
Network
Auto
5.6.3 Compressor VFD Fault
This alarm indicates an abnormal condition that forced the inverter to stop.
5.6.4 Compressor VFD OverTemp
This alarm indicates that the Inverter temperature has exceeded a safety limits and the inverter has to be stopped in order
to avoid damages to components.
5.6.5 Condensing Pressure sensor fault
This alarm indicates that the condensing pressure transducer is not operating properly.

Multipurpose Units
D-EOMZC00204-18_01EN
Operation Manual
38/48
EWYD 4Z
MultiPurpose Units
Symptom
Cause
Solution
Circuit is stopped if the discharge
temperature reach the high limit value.
Bell icon is moving on controller’s display.
String in the alarm list:
Cx EcoEXVDrvError
String in the alarm log:
Cx OffEcoEXVDrvError
String in the alarm snapshot
Cx OffEcoEXVDrvError
Hardware Error
Contact your service organization to get
the problem solved.
Reset
Notes
Local HMI
Network
Auto
Symptom
Cause
Solution
Circuit is stopped if the discharge
temperature reach the high limit value.
Bell icon is moving on controller’s display.
String in the alarm list:
Cx EcoEXVMotor
String in the alarm log:
Cx EcoEXVMotor
String in the alarm snapshot
Cx EcoEXVMotor
Valve not connected.
Referring to the wiring diagram check if the
valve is correctly connected to the module.
Reset
Notes
Local HMI
Network
Auto
Symptom
Cause
Solution
Circuit status is Off.
The circuit is stopped.
Bell icon is moving on controller’s display.
String in the alarm list:
CxCmp1 EvapPressSen
String in the alarm log:
CxCmp1 EvapPressSen
String in the alarm snapshot
CxCmp1 EvapPressSen
Sensor is broken.
Check for sensor integrity.
Check correct sensors operation according
information about mVolt (mV) range
related to pressure values in kPa.
Sensor is shorted.
Check if sensor is shorted with a
resistance measurement.
Sensor is not properly connected (open).
Check for correct installation of the sensor
on refrigerant circuit pipe. The transducer
must be able to sense the pressure
through the valve’s needle.
Check for absence of water or humidity on
sensor electrical contacts.
Check for correct plug-in of the electrical
connectors.
Check for correct sensors wiring also
according electrical scheme.
Reset
Notes
Local HMI
Network
Auto
5.6.6 Economizer EXV Driver Error
This alarm indicates an abnormal condition of the Economizer EXV Driver.
5.6.7 Economizer EXV Motor Not Connected
This alarm indicates an abnormal condition of the Economizer EXV Driver.
5.6.8 Evaporating Pressure sensor fault
This alarm indicates that the evaporating pressure transducer is not operating properly.

Multipurpose Units
EWYD 4Z
MultiPurpose Units
D-EOMZC00204-18_01EN
Operation Manual
39/48
Symptom
Cause
Solution
Circuit status is Off.
Circuit is immediately stopped.
Bell icon is moving on controller’s display.
String in the alarm list:
Cx OffEXVDrvError
String in the alarm log:
Cx OffEXVDrvError
String in the alarm snapshot
Cx OffEXVDrvError
Hardware Error
Contact your service organization to get
the problem solved.
Reset
Notes
Local HMI
Network
Auto
Symptom
Cause
Solution
Circuit status is Off.
Circuit is immediately stopped.
Bell icon is moving on controller’s display.
String in the alarm list:
Cx OffEXVMotor
String in the alarm log:
Cx OffEXVMotor
String in the alarm snapshot
Cx OffEXVMotor
Valve not connected.
Referring to the wiring diagram check if the
valve is correctly connected to the module.
Reset
Notes
Local HMI
Network
Auto
Symptom
Cause
Solution
Circuit status is Off.
The circuit is stopped.
Bell icon is moving on controller’s display.
String in the alarm list:
Cx OffStartFailEvpPrLo
String in the alarm log:
Cx OffStartFailEvpPrLo
String in the alarm snapshot
Cx OffStartFailEvpPrLo
Ambient temperature is too low or water
temperature is too low
Check the operating envelope for this unit.
Circuit refrigerant charge is too low
Check refrigerant charge.
Check for gas leakage with a sniffer.
Reset
Notes
Local HMI
Network
Auto
Symptom
Cause
Solution
Circuit status is Off.
The circuit is stopped.
The ambient temperature is too high.
Check the unit selection to see if the unit
can operate at full load.
5.6.9 EXV Driver Error
This alarm indicates an abnormal condition of the EXV Driver.
5.6.10 EXV Motor Not Connected (TZ B, MP)
This alarm indicates an abnormal condition of the EXV Driver.
5.6.11 Fail Start Low Pressure
This alarm indicates that at the compressor start the evaporating pressure or condensing pressure is below a minimum
fixed limit at compressor start.
5.6.12 Fan VFD Over Current
This alarm indicates that the Inverter current has exceeded a safety limits and the inverter has to be stopped in order to
avoid damages to components.

Multipurpose Units
D-EOMZC00204-18_01EN
Operation Manual
40/48
EWYD 4Z
MultiPurpose Units
Bell icon is moving on controller’s display.
String in the alarm list:
CxCmp1 OffVfdOverCurr
String in the alarm log:
CxCmp1 OffVfdOverCurr
String in the alarm snapshot
CxCmp1 OffVfdOverCurr
Check if all fans are operating properly and
are able to keep the condensing pressure
at the proper level.
Clean condenser coils to allow a lower
condensing pressure.
Reset
Notes
Local HMI
Network
Auto
When this alarm occurs compressor’s crankcase and discharge pipes may become very hot. Be careful
when getting in contact with the compressor and discharge pipes in this condition.
Symptom
Cause
Solution
Circuit status is Off.
The compressor does not load anymore or
even unload, circuit is stopped.
Bell icon is moving on controller’s display.
String in the alarm list:
CxCmp1 OffDischTmpHi
String in the alarm log:
CxCmp1 OffDischTmpHi
String in the alarm snapshot
CxCmp1 OffDischTmpHi
Liquid Injection solenoid valve is not
operating properly.
Check the electrical connection between
the controller and the liquid injection
solenoid valve.
Check if the solenoid coil operates properly
Check if the digital output operates
correctly.
Liquid injection orifice is small.
Check if when the liquid injection solenoid
is activated the temperature can be
controlled between the limits.
Check that the liquid injection line is not
obstructed by observing the discharge
temperature when it is activated.
Discharge temperature sensor could not
operate properly.
Check for proper operation of the
discharge temperature
Reset
Notes
Local HMI
Network
Auto
Symptom
Cause
Solution
Circuit status is Off.
The compressor does not load anymore or
even unload, circuit is stopped.
Bell icon is moving on controller’s display.
String in the alarm list:
CxCmp1 OffMtrAmpsHi
String in the alarm log:
CxCmp1 OffMtrAmpsHi
String in the alarm snapshot
CxCmp1 OffMtrAmpsHi
The ambient temperature is too high or
condenser water temperature is higher
than the limit set on the unit.
Check the unit selection to see if the unit
can operate at full load.
Check if all fans are operating properly and
are able to keep the condensing pressure
at the proper level.
Clean condenser coils to allow a lower
condensing pressure
Check if condenser pump is operating
correctly, giving enough water flow.
Clean condenser water heat exchanger.
The wrong compressor model has been
selected.
Check the compressor model for this unit.
Reset
Notes
Local HMI
Network
Auto
5.6.13 High Discharge Temperature Alarm
This alarm indicates that the temperature at the discharge port of the compressor exceeded a maximum limit which may
cause damages to the mechanical parts of the compressor.
5.6.14 High Motor Current Alarm
This alarm indicates that the compressor absorbed current is exceeding a predefined limit.

Multipurpose Units
EWYD 4Z
MultiPurpose Units
D-EOMZC00204-18_01EN
Operation Manual
41/48
Symptom
Cause
Solution
Circuit status is Off.
The compressor does not load anymore or
even unload, circuit is stopped.
Bell icon is moving on controller’s display.
String in the alarm list:
CxCmp1 OffMotorTempHi
String in the alarm log:
CxCmp1 OffMotorTempHi
String in the alarm snapshot
CxCmp1 OffMotorTempHi
Insufficient motor cooling.
Check refrigerant charge.
Check if operational envelope of the unit is
respected.
Motor temperature sensor could not
operate properly.
Check the readings of the motor
temperature sensor and check the Ohmic
value. A correct reading should be around
hundreds of Ohm at ambient temperature.
Check the electrical connection of the
sensor with the electronic board.
Reset
Notes
Local HMI
Network
Auto
Symptom
Cause
Solution
Circuit status is Off.
The circuit is stopped.
Bell icon is moving on controller’s display.
String in the alarm list:
CxCmp1 OffOilPrDiffHi
String in the alarm log:
CxCmp1 OffOilPrDiffHi
String in the alarm snapshot
CxCmp1 OffOilPrDiffHi
Oil filter is clogged.
Replace oil filter.
Oil Pressure Transducer is reading
incorrectly.
Check Oil Pressure Transducer readings
with a gauge.
Condensing Pressure Transducer is
reading incorrectly.
Check Condensing Pressure Transducer
readings with a gauge.
Reset
Notes
Local HMI
Network
Auto
Symptom
Cause
Solution
Circuit status is Off.
The compressor does not load anymore or
even unload, circuit is stopped.
Bell icon is moving on controller’s display.
String in the alarm list:
CxCmp1 OffCndPressHi
String in the alarm log:
CxCmp1 OffCndPressHi
String in the alarm snapshot
CxCmp1 OffCndPressHi
One or more condenser fans do not
operate properly .
Check if fans protections have been
activated.
Check that the fans can turn freely.
Check that there is not any obstacle to the
free ejection of the air blown.
Condenser pump may not be operating
correctly
Check if the pump can run and give the
required water flow.
Dirty or partially blocked condenser coil .
Remove any obstacle;
Clean the condenser coil using soft brush
and blower.
Dirty condenser heat exchanger
Clean the condenser heat exchanger.
Inlet air temperature of the condenser is
too high .
The air temperature measured at the inlet
of the condenser may not exceed the limit
indicated in the operational range (working
envelope) of the chiller.
Check the location where the unit is
installed and check that there are no any
short circuit of the hot-air blown from the
fans of the same unit, or even from fans of
next chillers (Check IOM for proper
installation).
5.6.15 High Motor Temperature Alarm
This alarm indicates that the motor temperature has exceeded the maximum temperature limit for safe operations.
5.6.16 High Oil Pressure Differential Alarm
This alarm indicates that the oil filter is clogged and needs to be replaced.
5.6.17 High Pressure alarm
This alarm is generated in case the Condensing saturated temperature rise above the Maximum condensing saturated
temperature and the control is not able to compensate to this condition. The maximum condenser saturated temperature
is 68.5°C but it can decrease when the evaporator saturated temperature become negative.
In case of water cooled chillers operating at high condenser water temperature, if the Condensing saturated temperature
exceeds the Maximum condenser saturated temperature, the circuit is only switched off without any notification on the
screen as this condition is considered acceptable in this range of operation.

Multipurpose Units
D-EOMZC00204-18_01EN
Operation Manual
42/48
EWYD 4Z
MultiPurpose Units
Entering water temperature at condenser
is too high .
Check the cooling tower operation and
settings.
Check the three way valve operation and
settings.
One or more condenser
fan turning in wrong
direction .
Check for correct phases sequence (L1,
L2, L3) in the electrical connection of the
fans.
Excessive charge of
refrigerant into the unit.
Check liquid sub-cooling and suction
super-heat to control indirectly the correct
charge of refrigerant.
If necessary recover all the refrigerant to
weight the entire charge and to control if
the value is in line with kg indication on unit
label.
Condensing pressure transducer could not
operate properly.
Check for proper operation of the high
pressure sensor.
Wrong unit configuration .
Check that the unit has been configured for
high condenser temperature applications.
Reset
Notes
Local HMI
Network
Auto
Symptom
Cause
Solution
Circuit status is Off.
The compressor does not load anymore or
even unload, circuit is stopped
immediately.
Bell icon is moving on controller’s display.
String in the alarm list:
CxCmp1 OffEvpPressLo
String in the alarm log:
CxCmp1 OffEvpPressLo
String in the alarm snapshot
CxCmp1 OffEvpPressLo
Transitory condition like a fan staging .
Wait until the condition is recovered by
EXV control
Refrigerant charge is low.
Check sight glass on liquid line to see if
there is flash gas.
Measure sub-cooling to see if the charge is
correct.
Protection limit not set to fit customer
application.
Check the evaporator approach and the
corresponding water temperature to
evaluate the low pressure hold limit.
High Evaporator Approach.
Clean the evaporator
Check the quality of the fluid that flows into
heat exchanger.
Check the glycol percentage and type
(ethilenic or propilenic)
Water flow into water heat exchanger is too
low.
Increase the water flow.
Check that evaporator water pump is
operating correctly providing the required
water flow.
Evaporating pressure transducer is not
working properly.
Check the sensor for proper operation and
calibrate the readings with a gauge.
EEXV is not working correctly.
It’s not opening enough or it’s moving in
the opposite direction.
Check if pump-down can be finished for
pressure limit reached;
Check expansion valve movements.
Check connection to the valve driver on the
wiring diagram.
Measure the resistance of each winding, it
has to be different from 0 Ohm.
Water temperature is low
Increase inlet water temperature.
Check the low pressure safeties settings.
Reset
Notes
Reset
Local HMI
Network
Auto
Symptom
Cause
Solution
Circuit status is Off.
The circuit is stopped.
Bell icon is moving on controller’s display.
String in the alarm list:
CxCmp1 OffPrRatioLo
Compressor is not able to develop the
minimum compression.
Check fan setpoint and settings, it could be
too low .
Check compressor absorbed current and
discharge superheat. Compressor can be
damaged.
5.6.18 Low Pressure alarm
This alarm is generated in case the evaporating pressure drops below the Low Pressure Unload and the control is not able
to compensate to this condition.
5.6.19 Low Pressure Ratio Alarm
This alarm indicates that the ratio between evaporating and condensing pressure is below a limit which depends on
compressor speed and guarantees the proper lubrication to compressor.

Multipurpose Units
EWYD 4Z
MultiPurpose Units
D-EOMZC00204-18_01EN
Operation Manual
43/48
String in the alarm log:
CxCmp1 OffPrRatioLo
String in the alarm snapshot
CxCmp1 OffPrRatioLo
Check the correct operation of suction /
delivery pressure sensors.
Check the internal relief valve didn’t
opened during previous operation (check
the unit history).
Note:
If the difference between delivery and
suction pressure exceed 22bar, the
internal relief valve open and need to be
replaced.
Inspect the gate rotors / screw rotor for
possible damages.
Check if the cooling tower or three way
valves are operating correctly and properly
set.
Reset
Notes
Local HMI
Network
Auto
Symptom
Cause
Solution
Circuit status is Off.
The circuit is stopped.
Bell icon is moving on controller’s display.
String in the alarm list:
Cx OffNbrRestarts
String in the alarm log:
Cx OffNbrRestarts
String in the alarm snapshot
Cx OffNbrRestarts
Ambient temperature is too low
Check the operating envelope for this unit.
Reset
Notes
Local HMI
Network
Auto
Symptom
Cause
Solution
Circuit status is Off.
The compressor does not load anymore or
even unload, circuit is stopped.
Bell icon is moving on controller’s display.
String in the alarm list:
CxCmp1 OffMechPressHi
String in the alarm log:
CxCmp1 OffMechPressHi
String in the alarm snapshot
CxCmp1 OffMechPressHi
One or more condenser fans do not
operate properly .
Check if fans protections have been
activated.
Check that the fans can turn freely.
Check that there is not any obstacle to the
free ejection of the air blown.
Condenser pump may not be operating
correctly
Check if the pump can run and give the
required water flow.
Dirty or partially blocked condenser coil .
Remove any obstacle;
Clean the condenser coil using soft brush
and blower.
Dirty condenser heat exchanger
Clean the condenser heat exchanger.
Inlet air temperature of the condenser is
too high .
The air temperature measured at the inlet
of the condenser may not exceed the limit
indicated in the operational range (working
envelope) of the chiller .
Check the location where the unit is
installed and check that there are no any
short circuit of the hot-air blown from the
fans of the same unit, or even from fans of
next chillers (Check IOM for proper
installation).
One or more condenser
fan turning in wrong
direction.
Check for correct phases sequence (L1,
L2, L3) in the electrical connection of the
fans.
5.6.20 Maximum Number of Restart Alarm
This alarm indicates that for three consecutive times after the compressor start the evaporating pressure is under a
minimum limit for too much time
5.6.21 Mechanical High Pressure Alarm
This alarm is generated when the condenser pressure rises above the mechanical high pressure limit causing this device
to open the power supply to all the auxiliary relays. This causes an immediate shutdown of compressor and all the other
actuators in this circuit.

Multipurpose Units
D-EOMZC00204-18_01EN
Operation Manual
44/48
EWYD 4Z
MultiPurpose Units
Entering water temperature at condenser
is too high .
Check the cooling tower operation and
settings.
Check the three way valve operation and
settings.
Mechanical high pressure switch is
damaged or not calibrated.
Check for proper operation of the high
pressure switch.
Reset
Notes
Local HMI
Network
Auto
Reset of this alarm requires a manual
action on the high pressure switch.
Symptom
Cause
Solution
Circuit status is Off.
The compressor does not load anymore or
even unload, circuit is stopped.
Bell icon is moving on controller’s display.
String in the alarm list:
CxCmp1 OffMechPressLo
String in the alarm log:
CxCmp1 OffMechPressLo
String in the alarm snapshot
CxCmp1 OffMechPressLo
Refrigerant charge is low.
Check sight glass on liquid line to see if
there is flash gas.
Measure sub-cooling to see if the charge
is correct.
High Evaporator Approach.
Clean the evaporator
Check the quality of the fluid that flows into
heat exchanger.
Check the glycol percentage and type
(ethilenic or propilenic)
Water flow into water heat exchanger is
too low.
Increase the water flow.
Check that evaporator water pump is
operating correctly providing the required
water flow.
Evaporating pressure transducer is not
working properly.
Check the sensor for proper operation and
calibrate the readings with a gauge.
EEXV is not working correctly.
It’s not opening enough or it’s moving in
the opposite direction.
Check if pump-down can be finished for
pressure limit reached;
Check expansion valve movements.
Check connection to the valve driver on the
wiring diagram.
Measure the resistance of each winding, it
has to be different from 0 Ohm.
Reset
Notes
Local HMI
Network
Auto
Symptom
Cause
Solution
Circuit status is Off.
The compressor does not start
Bell icon is moving on controller’s display.
String in the alarm list:
Cx OffNoPressAtStart
String in the alarm log:
Cx OffNoPressAtStart
String in the alarm snapshot
Cx OffNoPressAtStart
Evaporator or condenser pressure are
below 35kPa
Check transducers calibration with an
appropriate gauge.
Check transducers cabling and readout.
Check refrigerant charge and set it to the
proper value.
Reset
Notes
Local HMI
Network
Auto
Symptom
Cause
Solution
Circuit status is Off.
The circuit is stopped.
Compressor cannot start
Check if the start signal is properly
connected to the inverter.
5.6.22 Mechanical Low Pressure Alarm
This alarm is generated when the evaporating pressure drops below the mechanical low pressure limit causing this device
to open. This causes an immediate shutdown of compressor to prevent from freezing.
5.6.23 No Pressure At Start Alarm
This alarm is used to indicate a condition where the pressure at the evaporator or at the condenser is lower than 35kPa,
so the circuit is potentially empty of refrigerant.
5.6.24 No Pressure Change At Start Alarm
This alarm indicates that the compressor is not able to start or to create a certain minimum variation of the evaporating or
condensing pressures after start.

Multipurpose Units
EWYD 4Z
MultiPurpose Units
D-EOMZC00204-18_01EN
Operation Manual
45/48
Bell icon is moving on controller’s display.
String in the alarm list:
Cx OffNoPressChgStart
String in the alarm log:
Cx OffNoPressChgStart
String in the alarm snapshot
Cx OffNoPressChgStart
Compressor is turning in wrong direction.
Check correct phases sequence to the
compressor (L1, L2, L3) according to the
electrical scheme.
Inverter is not properly programmed with
the right direction of rotation
Refrigerant circuit is empty of refrigerant.
Check circuit pressure and presence of
refrigerant.
Not proper operation of evaporating or
condensing pressure transducers.
Check proper operation of evaporating or
condensing pressure transducers.
Reset
Notes
Local HMI
Network
Auto
Resolution of this fault requires a direct intervention on the power supply of this unit.
Direct intervention on the power supply can cause electrocution, burns or even death. This action must be
performed only by trained persons. In case of doubts contact your maintenance company.
Symptom
Cause
Solution
Circuit status is Off.
The circuit is stopped.
Bell icon is moving on controller’s display.
String in the alarm list:
Cx OffOverVoltage
String in the alarm log:
Cx OffOverVoltage
String in the alarm snapshot
Cx OffOverVoltage
Chiller main power supply had an up peak
which caused the trip.
Check if main power supply is within the
acceptable tolerance for this chiller
Main power supply setting on the
Microtech III is not suitable with the power
supply in use .
Measure the power supply to the chiller
and select the proper value on the
Microtech III HMI.
Reset
Notes
Local HMI
Network
Auto
The alarm clears automatically when the
voltage is reduced to an acceptable limit.
Resolution of this fault requires a direct intervention on the power supply of this unit.
Direct intervention on the power supply can cause electrocution, burns or even death. This action must be
performed only by trained persons. In case of doubts contact your maintenance company.
Symptom
Cause
Solution
Circuit status is Off.
The circuit is stopped.
Bell icon is moving on controller’s display.
String in the alarm list:
Cx OffUnderVoltage
String in the alarm log:
Cx OffUnderVoltage
String in the alarm snapshot
Cx OffUnderVoltage
Chiller main power supply had a down
peak which caused the trip.
Check if main power supply is within the
acceptable tolerance for this chiller
Main power supply setting on the
Microtech III is not suitable with the power
supply in use .
Measure the power supply to the chiller
and select the proper value on the
Microtech III HMI.
Reset
Notes
Local HMI
Network
Auto
The alarm clears automatically when the
voltage is increased to an acceptable limit.
5.6.25 Overvoltage Alarm
This alarm indicates that chiller supply voltage exceeded the maximum limit which allows proper operations of the
components. This is estimated looking at the DC voltage on the inverter which depends of course from the main power.
5.6.26 Undervoltage Alarm
This alarm indicates that chiller supply voltage exceeded the minimum limit which allows proper operations of the
components.

Multipurpose Units
D-EOMZC00204-18_01EN
Operation Manual
46/48
EWYD 4Z
MultiPurpose Units
Symptom
Cause
Solution
Circuit status is Off.
The compressor does not load anymore,
circuit is immediately stopped.
Bell icon is moving on controller’s display.
String in the alarm list:
CxCmp1 OffVfdCommFail
String in the alarm log:
CxCmp1 OffVfdCommFail
String in the alarm snapshot
CxCmp1 OffVfdCommFail
RS485 network is not properly cabled.
Check the continuity of the RS485 network
with the unit off. There should be continuity
from the main controller to the last inverter
as indicated on the wiring diagram.
Modbus communication is not running
properly.
Check inverter addresses and addresses
of all the additional devices in the RS485
network (for example the energy meter).
All the addresses must be different.
Modbus interface card can be faulty
Check with your service organization to
evaluate this possibility and eventually
replace the board.
Reset
Notes
Local HMI
Network
Auto
The alarm clears automatically when the
communication is re-established.
5.6.27 VFD Communication Failure
This alarm indicates a communication problem with the inverter.

Multipurpose Units
EWYD 4Z
MultiPurpose Units
D-EOMZC00204-18_01EN
Operation Manual
47/48
Energy Meter Settings (Nemo D4-L / Nemo D4-Le)
Password (Down+Enter)
1000 Connection
3-2E
three phase Aron System
Address
020
Baud
19.2
kbps
Par
None
parity bit
Time Out
3
sec Password 2
2001 CT ratio
see CT label
current transformer ratio (i.e if CT is 600:5, set to 120)
VT ratio
1
no voltage transformers (unless 690V chiller)
Unit Current
Displays the unit current
Current Limit
Displays the active current limit (which can be given by an external signal if unit is in network mode)
Current Lim Sp
Set the current limit setpoint (if unit is in local mode)
6 OPTIONS
6.1 Energy Meter including Current Limit (Optional)
An energy meter can be optionally installed on the unit. The energy meter is connected through Modbus to the unit
controller, which can display all relevant electrical data such as:
Line to Line Voltage (per phase and average)
Line Current (per phase and average)
Active Power
Cos Phi
Active Energy
More details are described in chapter Errore. L'origine riferimento non è stata trovata.. All these data can be also
accessed from a BMS by connecting it to a communication module. See the communication module manual for details on
the device and parameter settings.
Both the energy meter device and the unit controller need to be properly set. The instructions below detail how to set the
energy meter. Refer to the specific instructions of the energy meter for more detail on the operation of the device.
Once the energy meter has been configured, do the following steps in the unit controller:
From Main Menu, go to View/Set Unit Commission Unit Configuration Unit
Set Energy Mtr = Nemo D4-L or Nemo D4-Le
The energy meter option integrates the current limit function, which allows the unit to limit its capacity in order not to exceed
a pre-defined current setpoint. This setpoint can be set in the unit display or can be changed from an external 4-20 mA
signal.
The current limit must be set according to the following instructions:
From Main Menu, go to View/Set Unit Power Conservation
The following settings related to current limit option are available into the menu:

Multipurpose Units
D-EOMZC00204-18_01EN
Operation Manual
48/48
EWYD 4Z
MultiPurpose Units
The present publication is drawn up by of information only and does not constitute an offer binding upon Daikin Applied
Europe S.p.A.. Daikin Applied Europe S.p.A. has compiled the content of this publication to the best of its knowledge. No
express or implied warranty is given for the completeness, accuracy, reliability or fitness for particular purpose of its content,
and the products and services presented therein. Specification are subject to change without prior notice. Refer to the data
communicated at the time of the order. Daikin Applied Europe S.p.A. explicitly rejects any liability for any direct or indirect
damage, in the broadest sense, arising from or related to the use and/or interpretation of this publication. All content is
copyrighted by Daikin Applied Europe S.p.A..
DAIKIN APPLIED EUROPE S.p.A.
Via Piani di Santa Maria, 72 - 00040 Ariccia (Roma) - Italia
Tel: (+39) 06 93 73 11 - Fax: (+39) 06 93 74 014
http://www.daikinapplied.eu
 Loading...
Loading...