Page 1

Data Sheet
Cisco Catalyst 4948 Series Switch
High-Performance, Rack-Optimized Server Switching
PRODUCT OVERVIEW
The Cisco® Catalyst® 4948 is a wire-speed, low-latency, Layer 2–4, 1 rack unit (RU) fixed-configuration switch for rack-optimized server switching.
Based on the proven Cisco Catalyst 4500 Series hardware and software architecture, the Cisco Catalyst 4948 Series offers exceptional performance
and reliability for low density, multilayer aggregation of high performance servers and workstations.
The Cisco Catalyst 4948 offers 48 ports of wire-speed 10/100/1000BASE-T with 4 alternative wired ports that can accommodate optional
1000BASE-X Small Form-Factor Pluggable (SFP) optics*. Exceptional reliability and serviceability are delivered with optional internal
AC or DC 1 + 1 hot-swappable power supplies and a hot-swappable fan tray with redundant fans (refer to Figures 1 and 2).
Figure 1. Cisco Catalyst 4948 Series Switch
Figure 2. Rear View of Cisco Catalyst 4948 with Dual Redundant Power Supplies and Removable Fan Tray
KEY FEATURES AND BENEFITS
Wire-Speed Performance for 10/1 00/1 000 Connectivity
The Cisco Catalyst 4948 delivers wire-speed throughput with low latency for data-intensive applications using a 96 Gbps switching fabric with a
72 Mpps forwarding rate in hardware for Layer 2–4 traffic. Switching performance is guaranteed regardless of the number of route entries or
Layer 3 and 4 services enabled. Hardware-based Cisco Express Forwarding routing architecture allows for increased scalability and performance.
* The Cisco Catalyst 4948 has 52 physical switching ports (48 10/100/1000 and 4 SFP) on the front panel. Up to 48 of these ports can be active at one time in
any combination.
All contents are Copyright © 1992–2006 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Important Notices and Privacy Statement.
Page 1 of 1
Page 2

Power Supply Redundancy for Nonstop Operation
The Cisco Catalyst 4948 provides reliability for critical applications with 1 + 1 redundant hot-swappable internal AC or DC power supplies. The
1 + 1 power supply design provides A-to-B failover when power supplies are connected to different circuits. AC and DC power supplies can be
mixed in the same unit for maximum deployment flexibility. The Cisco Catalyst 4948 also has a hot-swappable fan tray with four redundant fans
for additional serviceability and availability.
Robust Security
Multiple server communities can be securely established on a single Cisco Catalyst 4948. The switch can isolate different Layer 2 community traffic
simultaneously, while conserving IP address space. In an unlikely event that a server is compromised, the Cisco Catalyst 4948 can prevent man-inthe-middle and IP spoofing attacks to the rest of community with no change to the server configuration. Such attacks can be logged by the Cisco
Catalyst 4948 for auditing.
The Cisco Catalyst 4900 Series offers a rich set of integrated security features to proactively lock down your critical network infrastructure. It
reduces network security risks with a rich set of Network Admission Control (NAC) capabilities and 802.1x-based user authentication, authorization,
and accounting (AAA). The security policy enforcement is uncompromised with the wire-rate, dedicated access-control lists (ACLs) to fend off everincreasing virus and security attacks. The Cisco Catalyst 4900 Series offers powerful, easy-to-use tools to effectively prevent untraceable man-in-themiddle attacks, control plane resource exhaustion, IP spoofing, and flooding attacks, without any change to the end-user or host configurations.
Secure remote access, file transfers, and network management are accomplished with the Secure Shell (SSH Version 1 and Version 2) Protocol,
Secure Copy Protocol (SCP), and Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) v3, respectively.
Network Admission Control (NAC) is a foundational component of the Cisco Self-Defending Network strategy, improving the network’s ability
to automatically identify, prevent, and respond to security threats. NAC enables the Cisco Catalyst switches to collaborate with third-party solutions
for security-policy compliance and enforcement before a host is permitted to access the network.
NAC performs posture validation at the Layer 2 network edge for hosts with or without 802.1x enabled. Vulnerable and noncompliant hosts can be
isolated, given reduced network access or directed to remediation servers based on organizational policy. By ensuring that every host complies with
security policy, organizations can significantly reduce the damage caused by infected hosts. NAC is available through standard software upgrades or
Cisco SMARTnet contracts on Cisco Catalyst switches.
Comprehensive Management
The Cisco Catalyst 4948 includes a single, dedicated 10/100 console port and a single, dedicated 10/100 management port for offline disaster
recovery. Remote in-band management is available with SNMP, Telnet client, BOOTP, and Trivial File Transfer Protocol (TFTP). Support for
local or remote out-of-band management is delivered through a terminal or modem attached to the console interface. The management port helps
enable the Cisco Catalyst 4948 to reload a new image from a TFTP server within seconds.
The Cisco Catalyst 4948 delivers a comprehensive set of management tools to provide the visibility and control required for server switching.
Managed with Cisco Works solutions and embedded Cisco View, the Cisco Catalyst 4948 can be configured and managed to deliver device, VLAN,
traffic, and policy management. These Web-based management tools offer numerous services, including software deployment and quick isolation of
error conditions.
SOFTWARE CONFIGURATION OPTIONS
Table 1 gives descriptions of the software configuration options for the Cisco Catalyst 4948.
Important notices, privacy statements, and trademarks of Cisco Systems, Inc. can be found on cisco.com.
© 2006 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
Page 2 of 16
Page 3
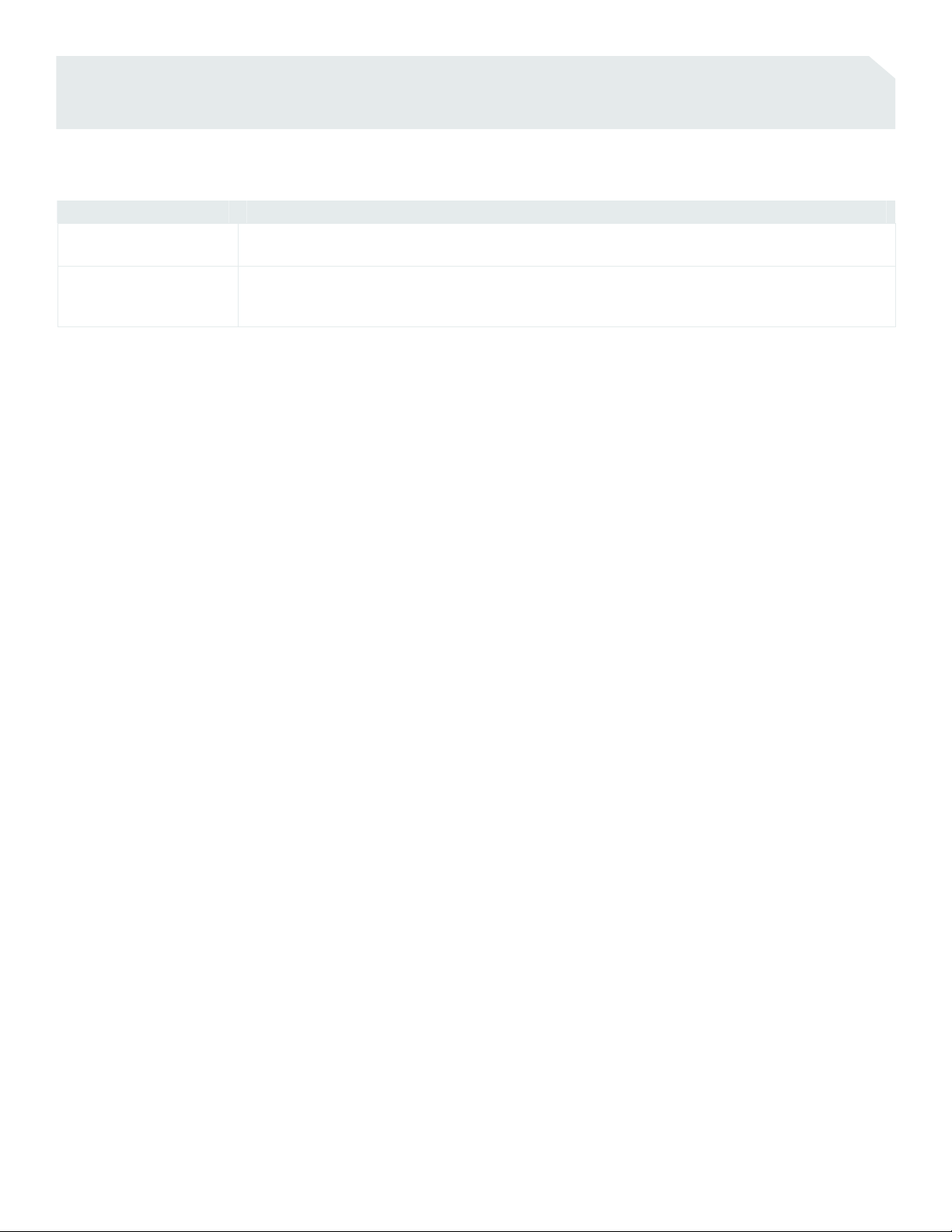
Table 1. Descriptions of Software Configuration Options for Cisco Catalyst 4948
Software Image Description
IP Base Image
Enterprise Services Image
TECHNICAL SPECIFICATIONS
Performance and Switching Specifications
• 96 Gbps nonblocking switch fabric
• 72 Mpps Layer 2 Forwarding (hardware)
• 72 Mpps Layer 3 and 4 forwarding—IP routing, Cisco Express Forwarding-based (hardware)
• Layer 2–4 hardware-based switch engine (application-specific integrated circuit [ASIC]-based)
• Unicast and multicast routing entries: 32,000
• Support for 2048 active VLANs and 4096 VLAN IDs per switch
• Layer 2 multicast addresses: 16,384
• MAC addresses: 32,768
• Policers: 512 ingress and 512 egress
• ACL or quality-of-service (QoS) entries: 32,000
• Uplinks: 4 alternatively wired SFP ports with (Gigabit EtherChannel) support
• Latency: 6 microseconds for 64-byte packets
• Switched virtual interfaces (SVIs): 2048
• STP instances: 1500
• Internet Group Management Protocol (IGMP) snooping entries: 8000
Standard Layer 3 image, including Routing Information Protocol Version 1 (RIPv1), RIPv2, static routes,
EIGRP stub.
Enhanced Layer 3 image, including Open Shortest Path First (OSPF), Intermediate System-to-Intermediate System
(IS-IS), and Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol (EIGRP), Border Gateway Protocol (BGP), Appletalk, and
Internetwork Packet Exchange (IPX). Also includes all IP Base Image features.
Layer 2 Features
• Layer 2 hardware forwarding at 72 Mpps
• Layer 2 switch ports and VLAN trunks
• IEEE 802. 1Q VLAN encapsulation
• Inter-Switch Link (ISL) VLAN encapsulation
• Dynamic Trunking Protocol (DTP)
• VLAN Trunking Protocol (VTP) and VTP domains
• Per-VLAN Spanning Tree Protocol (PVST+) and Per-VLAN Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol (PVRST)
• Spanning-tree PortFast and PortFast guard
• Spanning-tree UplinkFast and BackboneFast
• 802.1s
• 802.1w
• Spanning-tree root guard
• Cisco Discovery Protocol
• IGMP snooping v1, v2, and v3
• 802.3ad
• Cisco EtherChannel® technology, Cisco Fast EtherChannel technology, and Cisco Gigabit EtherChannel technology support
Important notices, privacy statements, and trademarks of Cisco Systems, Inc. can be found on cisco.com.
© 2006 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
Page 3 of 16
Page 4

• Port Aggregation Protocol (PAgP)
• Unidirectional Link Detection Protocol (UDLD) and aggressive UDLD on the SFP ports
• Q-in-Q in hardware
• Layer 2 protocol tunneling
• Jumbo frames on all ports (up to 9216 bytes)
• Baby giants (up to 1600 bytes)
• Hardware-based storm control (formally known as broadcast and multicast suppression)
• Community private VLANs (PVLANs)
• Forced 10/100 autonegotiation
• Web Content Communication Protocol Version 2 Layer 2 Redirect
• Private VLAN Promiscuous Trunk
Layer 3 Features
• Hardware-based IP Cisco Express Forwarding routing at 72 Mpps
• Static IP routing
• IP routing protocols: EIGRP, OSPF, RIP, RIP2
• BGPv4 and Multicast Border Gateway Protocol (MBGP)
• Hot Standby Router Protocol (HSRP)
• Software routing of IPX and AppleTalk
• IS-IS routing protocol
• IGMPv1, v2, and v3
• IGMP filtering on access and trunk ports
• IP Multicast routing protocols (Protocol Independent Multicast [PIM], Source Specific Multicast [S SM], and Distance Vector
• Multicast Routing Protocol [DVMRP])
• Pragmatic General Multicast (PGM)
• Cisco Group Management Protocol (GMP) server
• Full Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP) support
• ICMP Router Discovery Protocol
• Policy-based routing (PBR)
• Virtual Route Forwarding-lite (VRF-lite)
• IPv6 software switching support
• OSPF fast convergence
• EIGRP stub
• Virtual Router Redundancy Protocol (VRRP)
Sophisticated QoS and Traffic Management
• Per-port QoS configuration
• Per-port per VLAN QoS
• Support for four queues per port in hardware
• Strict priority queuing
• IP differentiated services code point (DSCP) and IP Precedence
• Classification and marking based on IP type of service (ToS) or DSCP
• Classification and marking based on full Layer 3 and 4 headers (IP only)
• Input and output policing based on Layer 3 and 4 headers (IP only)
© 2006 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
Important notices, privacy statements, and trademarks of Cisco Systems, Inc. can be found on cisco.com.
Page 4 of 16
Page 5

• Support for 512 policers on ingress and 512 policers on egress configured as aggregate or individual
• Shaping and sharing output queue management
• Dynamic Buffer Limiting (DBL): Advanced congestion avoidance
• No performance penalty for granular QoS functions
Predictable Performance
• 96 Gbps switching fabric
• Layer 2 hardware forwarding at 72 Mpps
• Layer 3 hardware-based IP Cisco Express Forwarding routing at 72 Mpps
• Layer 4 TCP or User Datagram Protocol (UDP) hardware-based filtering at 72 Mpps
• No performance penalty with advanced Layer 3 and 4 services enabled
• Software-based learning at a sustained rate of 500 hosts per second
• Support for 32,768 MAC addresses
• Support for 32,000 entries in routing table (shared between unicast and multicast)
• Support for 512 ingress policers and 512 egress policers
• Support for 32,000 ACL and QoS entries
• Scalability to 2048 virtual ports (VLAN port instances)
• Scalability to 8000 IGMP snooping entries
• Scalability to 1500 STP instances
• Bandwidth aggregation up to 16 Gbps through Cisco Gigabit EtherChannel technology
• Hardware-based wire-speed multicast management
• Hardware-based wire-speed ACLs
Comprehensive Management
• Manageable through CiscoWorks Windows network-management software on a per-port and per-switch basis, providing a common management
interface for Cisco routers, switches, and hubs
• Manageable through Cisco Network Assistant
• SNMPv1, v2, and v3 instrumentation, delivering comprehensive in-band management
• Command-line interface (CLI)-based management console to provide detailed out-of-band management
• Remote Monitoring (RMON) software agent to support four RMON groups (history, statistics, alarms, and events) for enhanced traffic
management, monitoring, and analysis
• Support for all nine RMON groups through the use of a Cisco SwitchProbe® analyzer (Switched Port Analyzer [SPAN]) port, which permits
traffic monitoring of a single port, a group of ports, or the entire switch from a single network analyzer or RMON probe
• Analysis support, including ingress port, egress port, and VLAN SPAN
• Layer 2 traceroute
• Remote SPAN (RSPAN)
• Smartports macros
• SPAN ACL filtering
• Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) client autoconfiguration
• IfIndex persistence
• HTTPS
• Time Domain Reflectometry (TDR)
• MAC Address Notification
Important notices, privacy statements, and trademarks of Cisco Systems, Inc. can be found on cisco.com.
© 2006 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
Page 5 of 16
Page 6

Advanced Security
• TACACS+ and RADIUS, which enable centralized control of the
• Standard and extended ACLs on all ports
• 802.1x user authentication (with VLAN assignment, port security, voice VLAN, and guest VLAN extension)
• 802.1x accounting
• 802. 1x authentication failure
• 802. 1x Private VLAN assignment
• 802. 1x Private Guest VLAN
• 802. 1x Radius-supplied time out
• Trusted boundary
• Router ACLs (RACLs) on all ports (no performance penalty)
• VLAN ACLs (VACLs)
• Port ACLs (PACLs)
• PVLANs on access and trunk ports
• DHCP snooping
• DHCP Option 82
• DHCP Option 82 insertion
• DHCP Option 82 pass through
• Port security
• Trunk port security
• Sticky port security
• SSHv1 and v2
• VLAN Management Policy Server (VMPS) client
• Unicast MAC filtering
• Unicast port flood blocking
• Dynamic Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) inspection switch and restrict unauthorized users from altering the configuration
• IP source guard
• Community PVLAN
• Control Plane Policing
• 802.1x Unidirectional Controlled Port
• Voice VLAN Sticky Port Security
• Secure Copy Protocol (SCP)
• 802.1x Inaccessible Authentication Bypass
• MAC Authentication Bypass
Traffic and Congestion Management
• Number of queues: four queues per port
• Type of buffers: Dynamic
Switch Architecture Specifications
• Packet buffering: Dynamic, 16 MB shared memory
• CPU speed: 266 MHz
• Flash memory: 64 MB
• Synchronous dynamic RAM (SDRAM): 256 MB
© 2006 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
Important notices, privacy statements, and trademarks of Cisco Systems, Inc. can be found on cisco.com.
Page 6 of 16
Page 7

Management
• CiscoWorks LAN Management Solution (LMS), including CiscoWorks Resource Manager Essentials
• CiscoView
• BGP4-MIB.my
• BRIDGE-MIB.my* (RFC 1493)
• CISCO-BULK-FILE-MIB.my
• CISCO-CDP-MIB.my
• CISCO-CLASS-BASED-QOS-MIB.my
• CISCO-CONFIG-COPY-MIB.my
• CISCO-CONFIG-MAN-MIB.my
• CISCO-ENTITY-ASSET-MIB.my
• CISCO-ENTITY-EXT-MIB.my
• CISCO-ENTITY-FRU-CONTROL-MIB.my
• CISCO-ENTITY-SENSOR-MIB.my
• CISCO-ENTITY-VENDORTYPE-OID-MIB.my
• CISCO-ENVMON-MIB.my
• CISCO-FLASH-MIB.my
• CISCO-FTP-CLIENT-MIB.my
• CISCO-HSRP-MIB.my
• CISCO-IETF-IP-MIB.my
• CISCO-IETF-IP-FORWARD-MIB.my
• CISCO-IETF-ISIS-MIB.my
• CISCO-IF-EXTENSION-MIB.my
• CISCO-IGMP-FILTER-MIB.my
• CISCO-IMAGE-MIB.my
• CISCO-IPMROUTE-MIB.my
• CISCO-L2-TUNNEL-CONFIG-MIB.my
• CISCO-L2L3-INTERFACE-CONFIG-MIB.my
• CISCO-LAG-MIB.my
• CISCO-MEMORY-POOL-MIB.my
• CISCO-NDE-MIB.my
• CISCO-PAGP-MIB.my
• CISCO-PAE-MIB.my
• CISCO-PING-MIB.my
• CISCO-PORT-SECURITY-MIB.my
• CISCO-PORT-STORM-CONTROL-MIB.my
• CISCO-PRIVATE-VLAN-MIB.my
• CISCO-PROCESS-MIB.my
• CISCO-PRODUCTS-MIB.my
• CISCO-RF-MIB.my
• CISCO-RMON-CONFIG-MIB.my
• CISCO-RTTMON-MIB.my
• CISCO-STP-EXTENSIONS-MIB.my
Important notices, privacy statements, and trademarks of Cisco Systems, Inc. can be found on cisco.com.
© 2006 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
Page 7 of 16
Page 8

• CISCO-SYSLOG-MIB.my
• CISCO-VLAN-IFTABLE-RELATIONSHIP-MIB.my
• CISCO-VLAN-MEMBERSHIP-MIB.my
• CISCO-VTP-MIB.my
• DOT3-MAU-MIB.my (RFC 3636)
• ENTITY-MIB.my
• ETHERLIKE-MIB.my
• EXPRESSION-MIB.my
• HC-RMON-MIB.my
• IEEE8021-PAE-MIB.my
• IEEE8023-LAG-MIB.my (802.3ad)
• IF-MIB.my
• IGMP-MIB.my
• IPMROUTE-MIB.my
• NOVELL-IPX-MIB.my
• NOVELL-RIP SAP-MIB.my
• OLD-CISCO-TS-MIB.my
• PIM-MIB.my
• RFC1213-MIB.my (MIB-II)
• RFC1243-MIB.my (APPLETALK MIB)
• RFC1253-MIB.my (OSPF-MIB)
• RMON-MIB.my (RFC 1757)
• RMON2-MIB.my (RFC 2021)
• SMON-MIB.my (Internet-Draft)
• SNMP-FRAMEWORK-MIB.my (RFC 2571)
• SNMP-MPD-MIB.my (RFC 2572)
• SNMP-NOTIFICATION-MIB.my (RFC 2573)
• SNMP-TARGET-MIB.my (RFC 2573)
• SNMP-USM-MIB.my (RFC 2574)
• SNMP-VACM-MIB.my (RFC 2575)
• SNMPv2-MIB.my
• TCP-MIB.my
• UDP-MIB.my
• RIP SNMP MIB
Industry Standards
• Ethernet: IEEE 802.3 and 10BASE-T
• Fast Ethernet: IEEE 802.3u and 100BASE-TX
• Gigabit Ethernet: IEEE 802.3z and 802.3ab
• IEEE 802. 1D Spanning Tree Protocol
• IEEE 802.1w rapid reconfiguration of spanning tree
• IEEE 802. 1s multiple VLAN instances of spanning tree
• IEEE 802.3 ad Link Aggregation Control Protocol (LACP)
• IEEE 802. 1p class-of-service (CoS) prioritization
© 2006 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
Important notices, privacy statements, and trademarks of Cisco Systems, Inc. can be found on cisco.com.
Page 8 of 16
Page 9

• IEEE 802.1Q VLAN
• IEEE 802. 1x user authentication
• 1000BASE-X (SFP)
• 1000BASE-SX
• 1000BASE-LX/LH
• 1000BASE-ZX
• RMON I and II standards
Indicator and Port Specifications
• Fan, PS1, PS2
• Power supply status: Green (operational)/red (faulty)
• System status: Green (operational)/red (faulty)
• Console: RJ-45 female
• SFP ports: Link
• Image management port: 10/100BASE-TX (RJ-45 female) data terminal equipment (DTE); green (good)/orange (disabled)/off (not connected)
Supported SFPs
Table 2 lists the SFPs supported by the Cisco Catalyst 4948.
Table 2. SFPs Supported by Cisco Catalyst 4948
SFP
Gigabit Ethernet SFP, LC connector LH transceiver
Gigabit Ethernet SFP, LC connector SX transceiver
Gigabit Ethernet SFP, LC connector ZX transceiver
Gigabit Ethernet SFP, RJ-45 connector, 10/100/1000BASE-T transceiver
Cisco Coarse Wavelength-Division Multiplexing (CWDM) SFP 1470 nm; Gigabit Ethernet and 1Ggigabit/2G FC (grey)
Cisco CWDM SFP 1490 nm; Gigabit Ethernet and FC (violet)
Cisco CWDM SFP 1510 nm; Gigabit Ethernet and FC (blue)
Cisco CWDM SFP 1530 nm; Gigabit Ethernet and 1G/2G FC (green)
Cisco CWDM SFP 1550 nm; Gigabit Ethernet and FC (yellow)
Cisco CWDM SFP 1570 nm; Gigabit Ethernet and FC (orange)
Cisco CWDM SFP 1590 nm; Gigabit Ethernet and FC (red)
Cisco CWDM SFP 1610 nm; Gigabit Ethernet and FC (brown)
Power Supply Specifications
The Cisco Catalyst 4948 offers a choice of 300 watt AC or DC power supplies. The switch can operate with one power supply present. When two
power supplies are installed, the switch shares the power load between the two supplies (refer to Table 3).
Important notices, privacy statements, and trademarks of Cisco Systems, Inc. can be found on cisco.com.
© 2006 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
Page 9 of 16
Page 10

Table 3. AC and DC Power Supply Specifications
Specification 300 Watt AC 300 Watt DC
Input Current
Output Current
Weight
Heat Dissipation
Switch Dimensions
• Width: 17.290 in. (43.9166 cm)
• Depth: 16.14 in. (40.9956 cm)
• Height: 1.712 in. (4.445 cm)
• Weight: 16.5 lb (7.48 kg) with one power supply
Software Requirements
The Cisco Catalyst 4948 High-Performance Edge Switch is supported only in Cisco IOS® Software and is not supported in the Cisco Catalyst OS
Software. The minimum software versions are as follows:
4A @ 100V
2A @ 240V
25A @12 VDC 25A @ 12 VDC
Weight 2.0 kg Weight 2.0 kg
1023 BTU/hr 1023 BTU/hr
8A @ -48 to -60V
• Cisco Catalyst 4948 supported in Cisco IOS Software Release 12.2(20)EWA or later
Environmental Conditions
• Operating temperature: 32 to 104ºF (0 to 40ºC)
• Storage temperature: –40 to 167ºF (–40 to 75ºC)
• Relative humidity: 10 to 90 percent, noncondensing
• Operating altitude: –60 to 2000m
REGULATORY STANDARDS COMPLIANCE
Table 4. Regulatory Standards Compliance for Cisco Catalyst 4948
Specification Description
Regulatory Compliance
Safety
Products bear CE Marking, indicating compliance with the 89/336/EEC and 73/23/EEC directives, which include the
following safety and EMC standards.
• UL 60950-1
• CAN/CSA-C22.2 No. 60950-1
• EN 60950-1
• IEC 60950-1
• AS/NZS 60950
• IEC 60825-1
• IEC 60825-2
• EN 60825-1
• EN 60825-2
• 21 CFR 1040
Important notices, privacy statements, and trademarks of Cisco Systems, Inc. can be found on cisco.com.
© 2006 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
Page 10 of 16
Page 11

Specification Description
EMC
Table 5 gives industry EMC, safety, and environmental standards for the Cisco Catalyst 4948.
• FCC Part 15 (CFR 47) Class A
• ICES-003 Class A
• EN55022 Class A
• CISPR22 Class A
• AS/NZS 3548 Class A
• VCCI Class A
• EN55024
• ETS300 386
• EN50082-1
• EN61000-3-2
• EN61000-3-3
Table 5. Industry EMC, Safety, and Environmental Standards for Cisco Catalyst 4948
Specification Description
Network Equipment Building Standards (NEBS)
• GR-63-Core NEBS Level 3
• GR-1089-Core NEBS Level 3
European Telecommunications Standards Institute (ETSI)
• ETS 300 019 Storage Class 1.1
• ETS 300 019 Transportation Class 2.3
• ETS 300 019 Stationary Use Class 3.1
Table 6 gives ordering information for the Cisco Catalyst 4948.
New Cisco IOS Software Packaging for the Cisco Catalyst 4900 Series
Cisco Systems® announces a new Cisco IOS Software package for the Cisco Catalyst 4900 Series, creating a new foundation for features and
functionality, and offering consistency across all Catalyst switches. The new Cisco IOS Software release train is designated as 12.2SG.
Prior Cisco IOS Software images for the Catalyst 4900 Series, formally known as “Basic L3” (SMI) and “Enhanced L3” (EMI) images, now map
to “IP Base” and “Enterprise Services,” respectively. Unless otherwise specified, all currently shipping Catalyst 4900 software features based on
Cisco IOS Software are supported in the 12.2(25)SG, IP Base image with a few points to note:
• The IP Base image will not support the following routing related features: BGP, EIGRP, OSPF, IS-IS, IPX, Apple Talk, Virtual Route Forwarding
[VRF]-lite, and Policy-Based Routing [PBR])
• The IP Base image will support EIGRP-Stub for Layer 3 routing on all Catalyst 4900 Series Supervisor Engines. For more information on
EIGRP¬Stub functionality, go to http://www.cisco.com/en/US/tech/tk365/technologies_white_paper0900aecd8023df6f.shtml
The Enterprise Services image supports all Catalyst 4900 Series software features based on Cisco IOS Software, including enhanced routing. Table 1
shows a more detailed description of the feature differences between the IP Base and Enterprise Services (ES) images.
Important notices, privacy statements, and trademarks of Cisco Systems, Inc. can be found on cisco.com.
© 2006 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
Page 11 of 16
Page 12

Table 6. Ordering Information for Cisco Catalyst 4948
Product Number Description
WS-C4948-S Cisco Catalyst 4948, IP Base software image (RIP, static routes), one AC power supply, fan tray
WS-C4948-E Cisco Catalyst 4948, Enterprise Services software image (IPX, Appletalk, OSPF, EIGRP, IS-IS, BGP), one AC power
supply, fan tray
WS-C4948 Cisco Catalyst 4948, optional software image, optional power supplies, fan tray
S49IPB-12231SG Cisco IOS Software for the Cisco Catalyst 4900 Series (IP Base image with EIGRP-stub support)
S49IPBK9-12231SG Cisco IOS Software for the Cisco Catalyst 4900 Series (IP Base image with Triple Data Encryption Standard [3DES] and
EIGRP-stub support)
S49ES-12231SG Cisco IOS Software for the Cisco Catalyst 4900 Series (Enterprise Services image)
S49ESK9-12231SG Cisco IOS Software for the Cisco Catalyst 4900 Series (Enterprise Services image with 3DES)
PWR-C49-300AC(=) Cisco Catalyst 4900 300-Watt AC power supply
PWR-C49-300AC/2 Cisco Catalyst 4900 300-Watt AC power supply, redundant
PWR-C49-300DC(=) Cisco Catalyst 4900 300-Watt DC power supply**
PWR-C49-300DC/2 Cisco Catalyst 4900 300-Watt DC power supply, redundant**
WS-X4991= Cisco Catalyst 4900 fan tray (spare)
C4948-ACC-KIT= Spare rack-mount and cable guide**
C4948-BKT-KIT= C4900 front and rear mount brackets**
Power Cable Options
CAB-7KAC AC Power Cord North America
CAB-7KACA AC Power Cord (Australia)
CAB-7KACE AC Power Cord (Europe)
CAB-7KACI AC Power Cord CD12 (Italy)
CAB-7KACR AC POWER CORD (Argentina)
CAB-7KACSA AC Power Cord (South Africa)
CAB-7KACU AC Power Cord (UK)
SFP Options
GLC-LH-SM= Gigabit Ethernet SFP, LC connector LH transceiver
GLC-SX-MM= Gigabit Ethernet SFP, LC connector SX transceiver
GLC-ZX-SM= Gigabit Ethernet SFP, LC connector ZX transceiver
GLC-BX-D= 1000BASE-BX10-D downstream bidirectional single fiber; with DOM
GLC-BX-U= 1000BASE-BX10-U upstream bidirectional single fiber; with DOM
CWDM-SFP-1470= Cisco CWDM SFP 1470 nm; Gigabit Ethernet and 1G/2G FC (gray)
CWDM-SFP-1490= Cisco CWDM SFP 1490 nm; Gigabit Ethernet and FC (violet)
CWDM-SFP-1510= Cisco CWDM SFP 1510 nm; Gigabit Ethernet and 1G/2G FC (blue)
CWDM-SFP-1530= Cisco CWDM SFP 1530 nm; Gigabit Ethernet and 1G/2G FC (green)
CWDM-SFP-1550= Cisco CWDM SFP 1550 nm; Gigabit Ethernet and 1G/2G FC (yellow)
CWDM-SFP-1570= Cisco CWDM SFP 1570 nm; Gigabit Ethernet and 1G/2G FC (orange)
Important notices, privacy statements, and trademarks of Cisco Systems, Inc. can be found on cisco.com.
© 2006 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
Page 12 of 16
Page 13

Product Number Description
CWDM-SFP-1590= Cisco CWDM SFP 1590 nm; Gigabit Ethernet and 1G/2G FC (red)
CWDM-SFP-1610= Cisco CWDM SFP 1610 nm; Gigabit Ethernet and 1G/2G FC (brown)
CSS5-CABLX-LCSC= Cisco CSS 11500 10-meter fiber single-mode LX LC-to-SC connectors
CSS5-CABSX-LC= Cisco CSS 11500 10-meter fiber multimode SX LC connectors
CSS5-CABSX-LCSC= Cisco CSS 11500 10-meter fiber multimode SX LC-to-SC connectors
CAB-SM-LCSC-1M 1 meter fiber single-mode LC-to-SC connectors
CAB-SM-LCSC-5M 5 meter fiber single-mode LC-to-SC connectors
** Orderable in October 2004.
WARRANTY
The warranty for the Cisco Catalyst 4948 is a one-year limited hardware warranty; it includes hardware replacement with a 10-day turnaround from
receipt of a return materials authorization (RMA).
CISCO TECHNICAL SUPPORT SERVICES—EXTENDING NETWORK INTELLIGENCE THAT PROTECTS YOUR NETWORK
INVESTMENT. NOW.
Cisco Technical Support Services help to ensure that your Cisco Systems® products operate efficiently, remain highly available, and benefit from
current system software to assist you in effectively managing your network service while controlling operational costs.
Cisco Technical Support Services provide significant benefits that go beyond what is offered under the Cisco warranty policy. Services available
under a Cisco SMARTnet® service contract that are not covered under a warranty include the following (also refer to Tables 7 and 8):
• Latest software updates
• Rapid replacement of hardware in next-day, four-hour, or two-hour dispatch options
• Ongoing technical support through Cisco Technical Assistance Center (TAC)
• Registered access to
Cisco.com
Table 7. Technical Support Services-Components
Service Feature Overview Benefit or Advantage
Software Support
Software support offers maintenance and minor and major updates for the licensed feature sets.
Downloading new maintenance releases, patches, or updates of Cisco IOS Software helps to enhance and
extend the useful life of Cisco devices. Through major software updates, it is possible to extend the life of
equipment and maximize application technology investments by:
• Increasing the performance of current functions
• Adding new functions that, in many cases, require no additional hardware investment
• Enhancing network or application availability, reliability, and stability
Cisco TAC Support
Cisco.com
With more than 1000 highly-trained customer support engineers, 390 CCIE® experts, and access to 13,000
research and development engineers, Cisco TAC complements your in-house staff with a high level of
knowledge in data, voice, and video communications networking technology. Its sophisticated call-routing
system quickly routes calls to the correct technology personnel. The Cisco TAC is available 24 hours a day,
365 days a year.
This award-winning Website provides 24-hour access to an extensive collection of online product and
technology information, interactive network management and troubleshooting tools, and knowledge transfer
resources that can help customers reduce costs by increasing staff self-sufficiency and productivity.
Important notices, privacy statements, and trademarks of Cisco Systems, Inc. can be found on cisco.com.
© 2006 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
Page 13 of 16
Page 14

Service Feature Overview Benefit or Advantage
Advance Hardware Replacement
Table 8. Technical Support Services-Competitive Differentiators
Feature Benefit or Advantage
Worldwide Virtual Lab
Cisco TAC Training
• Boot camps
This extensive lab of Cisco equipment and Cisco IOS Software versions provides an invaluable engineering resource and
knowledge base for training, product information, and recreation and testing of selected network issues to help decrease
time to resolution.
Cisco is committed to providing customers the latest in technology support. These Cisco TAC training programs assist
customers in case avoidance as well as providing knowledge transfer of Cisco networking expertise.
• Technical calls
• Technical forums
Advance Replacement and onsite field engineer options supply fast access to replacement hardware and
field resources for installing hardware, minimizing the risk of potential network downtime.
Cisco Live
Global Logistics
Cisco IOS Software
This powerful suite of Internet-enabled tools with firewall-friendly features consists of secure, encrypted Java applets that
can turn a simple phone call into an interactive collaboration session, allowing a customer and Cisco TAC support
engineer to work together more effectively.
With 10,000 onsite field engineers and a $2.3 billion investment in inventory, Cisco delivers award-winning, worldwide
hardware replacement support from 650 depots, covering 120 countries.
Cisco IOS Software employs 100 discrete technologies with more than 2000 features. Each year 400 new features are
added. This software is installed in more than 10 million devices and is running on more than 10,000 networks worldwide.
It operates on the world’s largest IPv6 and VoIP networks and in all major service provider networks worldwide.
FOR MORE INFORMATION
To learn more about how you can take advantage of Cisco Technical Support Services, talk to your Cisco representative or visit Cisco Technical
Support Services at: http://www.cisco.com/en/US/products/svcs/ps3 034/ps2827/serv_group_home.html
For additional information about the Cisco Catalyst 4948, visit: http://www.cisco.com/go/catalyst4500
For additional information about Cisco products, contact:
• United States and Canada: 800 553-NETS (6387)
• Europe: 32 2 778 4242
• Australia: 612 9935 4107
• Other: 408 526-7209
• http://www.cisco.com
Important notices, privacy statements, and trademarks of Cisco Systems, Inc. can be found on cisco.com.
© 2006 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
Page 14 of 16
Page 15

Corporate Headquarters
Cisco Systems, Inc.
170 West Tasman Drive
San Jose, CA 95134-1706
USA
www.cisco.com
Tel: 408 526-4000
800 553-NETS (6387)
Fax: 408 526-4100
European Headquarters
Cisco Systems International BV
Haarlerbergpark
Haarlerbergweg 13-19
1101 CH Amsterdam
The Netherlands
www-europe.cisco.com
Tel: 31 0 20 357 1000
Fax: 31 0 20 357 1100
Americas Headquarters
Cisco Systems, Inc.
170 West Tasman Drive
San Jose, CA 95134-1706
USA
www.cisco.com
Tel: 408 526-7660
Fax: 408 527-0883
Asia Pacific Headquarters
Cisco Systems, Inc.
168 Robinson Road
#28-01 Capital Tower
Singapore 068912
www.cisco.com
Tel: +65 6317 7777
Fax: +65 6317 7799
Cisco Systems has more than 200 offices in the following countries and regions. Addresses, phone numbers, and fax numbers are listed on
the Cisco Website at
www.cisco.com/go/offices.
Argentina • Australia • Austria • Belgium • Brazil • Bulgaria • Canada • Chile • China PRC • Colombia • Costa Rica • Croatia • Cyprus
Czech Republic • Denmark • Dubai, UAE • Finland • France • Germany • Greece • Hong Kong SAR • Hungary • India • Indonesia • Ireland • Israel
Italy • Japan • Korea • Luxembourg • Malaysia • Mexico • The Netherlands • New Zealand • Norway • Peru • Philippines • Poland • Portugal
Puerto Rico • Romania • Russia • Saudi Arabia • Scotland • Singapore • Slovakia • Slovenia • South Africa • Spain • Sweden • Switzerland • Taiwan
Thailand • Turkey • Ukraine • United Kingdom • United States • Venezuela • Vietnam • Zimbabwe
Copyright 2006 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. CCSP, CCVP, the Cisco Square Bridge logo, Follow Me Browsing, and StackWise are trademarks of Cisco Systems, Inc.;
Changing the Way We Work, Live, Play, and Learn, and iQuick Study are service marks of Cisco Systems, Inc.; and Access Registrar, Aironet, BPX, Catalyst, CCDA, CCDP, CCIE,
CCIP, CCNA, CCNP, Cisco, the Cisco Certified Internetwork Expert logo, Cisco IOS, Cisco Press, Cisco Systems, Cisco Systems Capital, the Cisco Systems logo, Cisco Unity,
Enterprise/Solver, EtherChannel, EtherFast, EtherSwitch, Fast Step, FormShare, GigaDrive, GigaStack, HomeLink, Internet Quotient, IOS, IP/TV, iQ Expertise, the iQ logo, iQ Net
Readiness Scorecard, LightStream, Linksys, MeetingPlace, MGX, the Networkers logo, Networking Academy, Network Registrar, Packet, PIX, Post-Routing, Pre-Routing, ProConnect,
RateMUX, ScriptShare, SlideCast, SMARTnet, The Fastest Way to Increase Your Internet Quotient, and TransPath are registered trademarks of Cisco Systems, Inc. and/or its affiliates in
the United States and certain other countries.
All other trademarks mentioned in this document or Website are the property of their respective owners. The use of the word partner does not imply a partnership relationship between
Cisco and any other company. (0601R)
Printed in the USA C78-340096-00 03/06
Important notices, privacy statements, and trademarks of Cisco Systems, Inc. can be found on cisco.com.
© 2006 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
Page 15 of 16
Page 16

Important notices, privacy statements, and trademarks of Cisco Systems, Inc. can be found on cisco.com.
© 2006 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
Page 16 of 16
 Loading...
Loading...