Page 1
Cisco IOS DHCP Server
Feature Overview
Dynamic Host Control Protocol (DHCP) enables you to automatically assign reusable IP addresses
to DHCP clients. The Cisco IOS DHCP Server feature is a full DHCP server implementation that
assigns and manages IP addresses from specified address pools within the router to DHCP clients.
If the Cisco IOS DHCP Servercannot satisfy a DHCP request from its own database, it can forward
the request to one or more secondary DHCP servers defined by the network administrator.
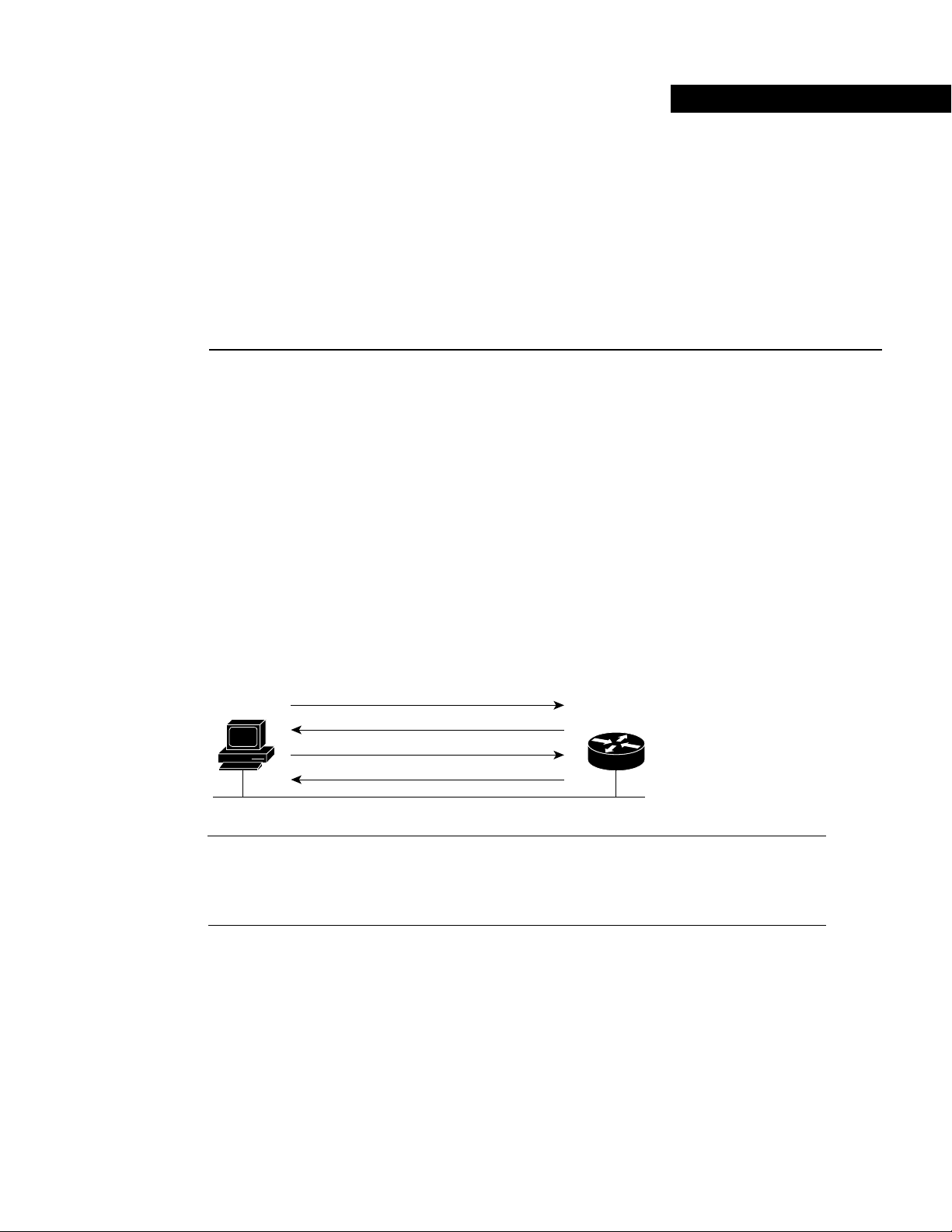
Figure 1 shows the basic steps that occur when a DHCP client requests an IP address from a DHCP
server. The client, Host A, sends a DHCPDISCOVER broadcast message to locate a Cisco IOS
DHCP Server. A DHCP server offers configuration parameters (such as an IP address, a MAC
address, a domain name, and a lease for the IP address) to the client in a DHSCPOFFER unicast
message.
Figure 1 DHCP Request for an IP Address from a DHCP Server
Host A
Note A DHCP client may receive offers from multiple DHCP servers and can accept any one of the
offers; however, the client usually accepts the first offer it receives. Additionally, the offer from the
DHCP server is not a guarantee that the IP address will be allocated to the client; however, the server
usually reserves the address until the client has had a chance to formally request the address.
The client returns a formal request for the offered IP address to the DHCP server in a
DHCPREQUEST broadcast message. The DHCP server confirms that the IP address has been
allocated to the client by returning a DHCPACK unicast message to the client.
DHCPDISCOVER (broadcast)
DHCPOFFER (unicast)
DHCPREQUEST (broadcast)
DHCPACK (unicast)
Cisco IOS
DHCP server
32369
Cisco IOS DHCP Server 1
Page 2

Benefits
Benefits
Note The formal request for the offered IP address (the DHCPREQUEST message) that is sent by
the client is broadcast so that all other DHCP servers that received the DHCPDISCOVERbroadcast
message from the client can reclaim the IP addresses that they offered to the client.
If the configuration parameters sent to the client in the DHCPOFFER unicast message by the DHCP
server are invalid (a misconfiguration error exists), the client returns a DHCPDECLINE broadcast
message to the DHCP server.
The DHCP server will send to the client a DHCPNAK denial broadcast message, which means the
offered configuration parameters have not been assigned, if an error has occurred during the
negotiationof the parameters or the client hasbeen slow in responding to the DHCPOFFER message
(the DHCP server assigned the parameters to another client) of the DHCP server.
The Cisco IOS DHCP Server feature offers the following benefits:
• Reduced Internet access costs
Using automatic IP address assignment at each remote site substantially reduces Internet access
costs. Static IP addresses are considerably more expensive to purchase than are automatically
allocated IP addresses.
• Reduced client configuration tasks and costs
Because DHCP is easy to configure, it minimizes operational overhead and costs associated with
device configuration tasks and eases deployment by nontechnical users.
• Centralized management
Because the DHCP server maintains configurations for several subnets, an administrator only
needs to update a single, central server when configuration parameters change.
Supported Platforms
This Cisco IOS DHCP Server feature is supported on the following routers and access servers:
• Catalyst 5000 family switches with an installed Route Switch Module
• Catalyst 6000 family switches with an installed MultiLayer Switch Feature Card
• Catalyst 8500 series
• Cisco 800 series
• Cisco 1000 series
• Cisco 1400 series
• Cisco 1600 series
• Cisco 1700 series (support for the Cisco 1700 series was added in Cisco IOS Release 12.0[2]T)
Release 12.0(1)T
2
• Cisco 2500 series
• Cisco 2600 series
• Cisco 3600 series
• Cisco 3800 series
Page 3

• Cisco MC3810 series
• Cisco 4000 series
• Cisco AS5100 access server
• Cisco AS5200 universal access server
• Cisco AS5300 universal access server
• Cisco 7000 series
• Cisco 7100 series
• Cisco 7200 series
• Cisco MGX 8800 with an installed Route Processor Module
• Cisco 12000 series
• Cisco uBR900 series
• Cisco uBR7200 series
Supported Standards, MIBs, and RFCs
Standards
No new or modified standards are supported by this feature.
MIBs
No new or modified MIBs are supported by this feature.
For descriptions of supported MIBs and how to use MIBs, see the Cisco MIB web site on CCO at
http://www.cisco.com/public/sw-center/netmgmt/cmtk/mibs.shtml.
RFCs
• RFC 951, Bootstrap Protocol (BOOTP)
• RFC 1542, Clarifications and Extensions for the Bootstrap Protocol
• RFC 2131, Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol
• RFC 2132, DHCP Options and BOOTP Vendor Extensions
Cisco IOS DHCP Server 3
Page 4

Prerequisites
Prerequisites
Before you configure the Cisco IOS DHCP Server feature, complete the following tasks:
• Identify an external File Transport Protocol (FTP), Trivial File Transfer Protocol (TFTP), or
remote copy protocol (rcp) server that you will use to store the DHCP bindings database.
• Identify the IP addresses that you will enable the DHCP server to assign, and the IP addresses
that you will exclude.
• Identify DHCP options for devices where necessary, including:
— Default boot image name
— Default router(s)
— Domain Name System (DNS) server(s)
— NetBIOS name server
• Decide on a NetBIOS node type (b, p, m, or h).
• Decide on a DNS domain name.
DHCP Configuration Task List
The DHCP server database is organized as a tree. The root of the tree is the address pool for natural
networks, branches are subnetwork address pools, and leaves are manual bindings to clients.
Subnetworks inherit network parameters and clients inherit subnetwork parameters. Therefore,
common parameters, for example the domain name, should be configured at the highest (network or
subnetwork) level of the tree.
Note Inherited parameters can be overridden. For example, if a parameter is defined in both the
natural network and a subnetwork, the definition of the subnetwork is used.
Address leases are not inherited. If a lease is not specified for an IP address, by default, the DHCP
server assigns a one-day lease for the address.
To configure the Cisco IOS DHCP Server feature, first configure a database agent or disable conflict
logging, then configure IP addresses that the DHCP server should not assign (excluded addresses)
and should assign (a pool of available IP addresses) to requesting clients. These configuration tasks
are explained in the following sections. Each task in the following list is identified as required or
optional.
• Configuring a DHCP Database Agent or Disabling DHCP Conflict Logging (Required)
• Excluding IP Addresses (Required)
• Configuring a DHCP Address Pool (Required)
Release 12.0(1)T
4
• Configuring Manual Bindings (Optional)
• Configuring a DHCP Server Boot File (Optional)
• Configuring the Number of Ping Packets (Optional)
• Configuring the Timeout Value for Ping Packets (Optional)
• Enabling the Cisco IOS DHCP Server Feature (Optional)
Page 5

Configuring a DHCP Database Agent or Disabling DHCP Conflict Logging
Configuring a DHCP Database Agent or Disabling DHCP Conflict
Logging
A DHCP database agent is any host, for example, an FTP, TFTP, or RCP server that stores the DHCP
bindings database. You can configure multiple DHCP database agents and you can configure the
interval between database updates and transfers for each agent. To configure a database agent and
database agent parameters, use the following command in global configuration mode:
Command Purpose
Router(config)# ip dhcp database url
[timeout seconds | write-delay seconds]
If you choose not to configure a DHCP database agent, disable the recording of DHCP address
conflicts on the DHCP server. To disable DHCP address conflict logging, use the following
command in global configuration mode:
Command Purpose
Router(config)# no ip dhcp conflict
logging
Configures the database agent and the interval between
database updates and database transfers.
Disables DHCP address conflict logging.
Excluding IP Addresses
The DHCP server assumes that all IP addresses in a DHCP address pool subnet are available for
assigning to DHCP clients. You must specify the IP address that the DHCP server should not assign
to clients. To do so, use the following command in global configuration mode:
Command Purpose
Router(config)# ip dhcp
excluded-address low-address
[high-address]
Specifies the IP addresses that the DHCP server should not
assign to DHCP clients.
Configuring a DHCP Address Pool
You can configure a DHCP address pool with a name that is a symbolic string (such as
“engineering”) or an integer (such as 0). Configuring a DHCP address pool also places you in DHCP
pool configuration mode—identified by the (config-dhcp)# prompt—from which you can configure
pool parameters (for example, the IP subnet number and default router list). To configure a DHCP
address pool, complete the required tasks in the following sections.
Configuring the DHCP Address Pool Name and Entering DHCP Pool
Configuration Mode
To configure the DHCP address pool name and enter DHCP pool configuration mode, use the
following command in global configuration mode:
Command Purpose
Router(config)# ip dhcp pool name Creates a name for the DHCP server address pool and places
you in DHCP pool configuration mode (identified by the
config-dhcp# prompt).
Cisco IOS DHCP Server 5
Page 6

DHCP Configuration Task List
Configuring the DHCP Address Pool Subnet and Mask
To configure a subnet and mask for the newly created DHCP address pool, which contains the range
of available IP addresses that the DHCP server may assign to clients, use the following command in
DHCP pool configuration mode:
Command Purpose
Router(config-dhcp)# network
network-number [mask | /prefix-length]
Note You can not configure manual bindings within the same pool that is configured with the
Specifies the subnet network number and mask of the DHCP
address pool.
The prefix length specifies the number of bits that comprise the
address prefix. The prefix is an alternative way of specifying
the network mask of the client. The prefix length must be
preceded by a forward slash (/).
network command. To configure manual bindings, see the “Configuring Manual Bindings” section.
Configuring the Domain Name for the Client
The domain name of a DHCP client places the client in the general grouping of networks that make
up the domain. To configure a domain name string for the client, use the following command in
DHCP pool configuration mode:
Command Purpose
Router(config-dhcp)# domain-name
domain
Specifies the domain name for the client.
Configuring the Domain Name System IP Servers for the Client
DHCP clients query DNS IP servers when they need to correlate host names to IP addresses. To
configure the DNS IP servers that are available to a DHCP client, use the following command in
DHCP pool configuration mode:
Command Purpose
Router(config-dhcp)# dns-server address
[address2 ... address8]
Specifies the IP address of a DNS server that is available to a
DHCP client. One IP address is required; however, you can
specify up to eight IP addresses in one command line.
Configuring the NetBIOS Windows Internet Naming Service IP Servers for the
Client
WindowsInternet Naming Service(WINS) is a name resolutionservice that Microsoft DHCP clients
use to correlate host names to IP addresses within a general grouping of networks. Toconfigure the
NetBIOS WINS servers that are available to a Microsoft DHCP client, use the following command
in DHCP pool configuration mode:
Release 12.0(1)T
6
Command Purpose
Router(config-dhcp)#netbios-name-server
address [address2 ... address8]
Specifies the NetBIOS WINS server that is available to a
Microsoft DHCP client. One address is required; however, you
can specify up to eight addresses in one command line.
Page 7

Configuring the NetBIOS Node Type for the Client
Configuring the NetBIOS Node Type for the Client
The NetBIOS node type for Microsoft DHCP clients can be one of four settings: broadcast,
peer-to-peer,mixed, or hybrid. Toconfigure the NetBIOS node type for a Microsoft DHCP,use the
following command in DHCP pool configuration mode:
Command Purpose
Router(config-dhcp)# netbios-node-type
type
Specifies the NetBIOS node type for a Microsoft DHCP client.
Configuring the Default Router for the Client
Aftera DHCP client has booted, the client begins sending packetsto its default router.The IP address
of the default router should be on the same subnet as the client. To configure a default router for a
DHCP client, use the following command in DHCP pool configuration mode:
Command Purpose
Router(config-dhcp)# default-router
address [address2 ... address8]
Specifies the IP address of the default router for a DHCP client.
One IP address is required, although you can specify up to
eight addresses in one command line.
Configuring the Address Lease Time
By default, each IP address assigned by a DHCP server comes with a one-day lease, which is the
amount of time that the address is valid. To change the lease value for an IP address, use the
following command in DHCP pool configuration mode:
Command Purpose
Router(config-dhcp)# lease {days
[hours][minutes] | infinite}
Configuring Manual Bindings
An address binding is a mapping between the IP address and Media Access Control (MAC) address
of a client. The IP address of a client can be assigned manually by an administrator or assigned
automatically from a pool by a DHCP server.
Manual bindings are IP addresses that have been manually mapped to the MAC addresses of hosts
that are found in the DHCP database. Manual bindings are stored in NVRAM on the DHCP server.
Manual bindings are just special address pools. There is no limit on the number of manual bindings
but you can only configure one manual binding per host pool.
Automatic bindings are IP addresses that have been automatically mapped to the MACaddresses of
hosts that are found in the DHCP database. Automatic bindings are stored on a remote host called a
database agent. The bindings are saved as text records for easy maintenance.
To configure a manual binding, first create a host pool, then specify the IP address and hardware
address of the client or client identifier. The hardware address is the MAC address. The client
identifier, which is required for Microsoft clients (instead of hardware addresses), is formed by
concatenating the media type and the MAC address of the client. Refer to the “Address Resolution
Protocol Parameters” section of RFC 1700, Assigned Numbers, for a list of media type codes.
Specifies the duration of the lease. The default is a a one-day
lease.
Cisco IOS DHCP Server 7
Page 8

DHCP Configuration Task List
Toconfigure manual bindings, use the following commands beginningin global configuration mode:
Step Command Purpose
1 Router(config)# ip dhcp pool name Creates a name for the a DHCP server address
2 Router(config-dhcp)# host address [mask |
3 Router(config-dhcp)# hardware-address
4 Router(config-dhcp)# client-name name (Optional) Specifies the name of the client using
/prefix-length]
hardware-address type
or
Router(config-dhcp)# client-identifier
unique-identifier
pool and places you in DHCP pool configuration
mode—identified by the (config-dhcp)# prompt.
Specifies the IP address and subnet mask of the
client.
The prefix length specifies the number of bits that
comprise the address prefix. The prefix is an
alternativeway of specifying the network mask of
the client. The prefix length must be preceded by
a forward slash (/).
Specifies a hardware address for the client.
Specifies the distinct identification of the client in
dotted-hexadecimal notation, for example,
01b7.0813.8811.66, where 01 represents the
Ethernet media type.
any standard ASCII character. The client name
should not include the domain name. For
example, the name mars should not be specified
as mars.cisco.com.
Configuring a DHCP Server Boot File
The boot file is used to store the boot image for the client. The boot image is generally the operating
system the client uses to load. Tospecifya boot file for the DHCP client, use the following command
in DHCP pool configuration mode:
Command Purpose
Router(config-dhcp)# bootfile filename Specifies the name of the file that is used as a boot image.
Configuring the Number of Ping Packets
By default, the DHCP server pings a pool address twice before assigning the address to a requesting
client. If the ping is unanswered, the DHCP server assumes (with a high probability) that the address
is not in use and assigns the address to the requesting client. To change the number of ping packets
the DHCP server should send to the pool address before assigning the address, use the following
command in global configuration mode:
Command Purpose
Router(config)# ip dhcp ping packets
number
Specifies the number of ping packets the DHCP server sends to
a pool address before assigning the address to a requesting client. The default is two packets.
Release 12.0(1)T
8
Page 9

Configuring the Timeout Value for Ping Packets
Configuring the Timeout Value for Ping Packets
By default, the DHCP server waits 500 milliseconds before timing out a ping packet. To change the
amount of time the server waits, use the following command in global configuration mode:
Command Purpose
Router(config)# ip dhcp ping timeout
milliseconds
Specifies the amount of time the DHCP server must wait
before timing out a ping packet. The default 500 milliseconds.
Enabling the Cisco IOS DHCP Server Feature
By default, the Cisco IOS DHCP Server feature is enabled on your router. If the feature is disabled,
use the following command in global configuration mode to reenable the Cisco IOS DHCP Server
feature on your router:
Command Purpose
Router(config)# service dhcp Enables the Cisco IOS DHCP Server feature on your router.
Use the no form of this command to disable the Cisco IOS
DHCP Server feature.
Monitoring and Maintaining the DHCP Server
To clear DHCP server variables, use the following commands in privileged EXEC mode, as needed:
Command Purpose
Router# clear ip dhcp binding address | * Deletes an automatic address binding from the DHCP
database. Specifying address clears the automatic binding for
a specific (client) IP address whereas specifying asterisk (*)
clears all automatic bindings.
Router# clear ip dhcp conflict address | * Clears an address conflict from the DHCP database. Specify-
ing address clears the conflict for a specific IP address
whereas specifying an asterisk (*) clears conflicts for all
addresses.
Router# clear ip dhcp server statistics Resets all DHCP server counters to 0.
To enable DHCP server debugging, use the following command in privileged EXEC mode, as
needed:
Command Purpose
Router# debug ip dhcp server {events |
packets | linkage}
Enables debugging on the DHCP server.
Cisco IOS DHCP Server 9
Page 10

Configuration Examples
To display DHCP server information, use the following commands in EXEC mode, as needed:
Command Purpose
Router> show ip dhcp binding [address] Displays a list of all bindings created on a specific DHCP
Router> show ip dhcp conflict [address] Displays a list of all address conflicts recorded by a specific
Router# show ip dhcp database [url] Displays recent activity on the DHCP database.
Router> show ip dhcp server statistics Displays count information about server statistics and mes-
Configuration Examples
This section provides the following configuration examples:
• DHCP Database Agent Configuration Example
• DHCP Address Pool Configuration Example
server.
DHCP server.
Note Use this command in privileged EXEC mode.
sages sent and received.
• Manual Bindings Configuration Example
DHCP Database Agent Configuration Example
The following example stores bindings on host 172.16.4.253. The file transfer protocol is FTP.The
server should wait 2 minutes (120 seconds) before writing database changes.
ip dhcp database ftp://user:password@172.16.4.253/router-dhcp write-delay 120
DHCP Address Pool Configuration Example
In the following example, three DHCP address pools are created: one in network 172.16.0.0, one in
subnetwork172.16.1.0,and one in subnetwork 172.16.2.0. Attributesfromnetwork172.16.0.0, such
as the domain name, DNS server, NetBIOS name server, and NetBIOS node type, are inherited in
subnetworks 172.16.1.0 and 172.16.2.0. In each pool, clients are granted 30-day leases and all
addresses in each subnetwork, except the excluded addresses, are available to the DHCP server for
assigning to clients. Table 1 lists the IP addresses for the devices in three DHCP address pools.
Table 1 DHCP Address Pool Devices
Pool 0 (Network 172.16.0.0) Pool 1 (Subnetwork 172.16.1.0) Pool 2 (Subnetwork 172.16.2.0)
Device IP Address Device IP Address Device IP Address
Default routers – Default routers 172.16.1.100
172.16.1.101
DNS server 172.16.1.102 — — — —
172.16.2.102
NetBIOS name server 172.16.1.103 — — — —
172.16.2.103
NetBIOS node type h-node — — — —
Default routers 172.16.2.100
172.16.2.101
Release 12.0(1)T
10
Page 11

ip dhcp database ftp://user:password@172.16.4.253/router-dhcp write-delay 120
ip dhcp excluded-address 172.16.1.100 172.16.1.103
ip dhcp excluded-address 172.16.2.100 172.16.2.103
!
ip dhcp pool 0
network 172.16.0.0 /16
domain-name cisco.com
dns-server 172.16.1.102 172.16.2.102
netbios-name-server 172.16.1.103 172.16.2.103
netbios-node-type h-node
!
ip dhcp pool 1
network 172.16.1.0 /24
default-router 172.16.1.100 172.16.1.101
lease 30
!
ip dhcp pool 2
network 172.16.2.0 /24
default-router 172.16.2.100 172.16.2.101
lease 30
Manual Bindings Configuration Example
The following example creates a manual binding for a client named Mars.cisco.com. The MAC
address of the client is 02c7.f800.0422 and the IP address of the client is 172.16.2.254.
ip dhcp pool Mars
host 172.16.2.254
hardware-address 02c7.f800.0422 ieee802
client-name Mars
Manual Bindings Configuration Example
Because attributes are inherited, the previous configuration is equivalent to the following:
ip dhcp pool Mars
host 172.16.2.254 mask 255.255.255.0
hardware-address 02c7.f800.0422 ieee802
client-name Mars
default-router 172.16.2.100 172.16.2.101
domain-name cisco.com
dns-server 172.16.1.102 172.16.2.102
netbios-name-server 172.16.1.103 172.16.2.103
netbios-node-type h-node
Cisco IOS DHCP Server 11
Page 12

Command Reference
Command Reference
This section documents new or modified commands. All other commands used with this feature are
documented in the Cisco IOS Release 12.0 command reference publications.
• bootfile
• clear ip dhcp binding
• clear ip dhcp conflict
• clear ip dhcp server statistics
• client-identifier
• client-name
• default-router
• dns-server
• domain-name
• hardware-address
• host
• ip dhcp conflict logging
• ip dhcp database
• ip dhcp excluded-address
• ip dhcp ping packets
• ip dhcp ping timeout
• ip dhcp pool
• ip dhcp relay information check
• ip dhcp relay information option
• ip dhcp relay information policy
• lease
• netbios-name-server
• netbios-node-type
• network (DHCP)
• next-server
• option
• service dhcp
• show ip dhcp binding
Release 12.0(1)T
12
• show ip dhcp conflict
• show ip dhcp database
• show ip dhcp server statistics
Page 13

Manual Bindings Configuration Example
In Cisco IOS Release 12.0(1)T or later, you can search and filter the output for show and more
commands. This functionality is useful when you need to sort through large amounts of output, or if
you want to exclude output that you do not need to see.
To use this functionality, enter a show or more command followed by the “pipe” character (|), one
of the keywords begin, include, or exclude, and an expression that you want to search or filter on:
command | {begin | include | exclude} regular-expression
Following is an example of the show atm vc command in which you want the command output to
begin with the first line where the expression “PeakRate” appears:
show atm vc | begin PeakRate
For more information on the search and filter functionality, refer to the Cisco IOS Configuration
Fundamentals Configuration Guide.
Cisco IOS DHCP Server 13
Page 14

Command Reference
bootfile
Syntax Description
Defaults
Command Modes
Tospecify the name of the defaultboot image for a Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP)
client, use the bootfile DHCP pool configuration command. Use the no form of this command to
delete the boot image name.
bootfile filename
no bootfile
filename Specifies the name of the file that is used as a boot image.
No default behavior or values.
DHCP pool configuration
Usage Guidelines
Examples
Related Commands
This command first appeared in Cisco IOS Release 12.0(1)T.
The following example specifies xllboot as the name of the boot file:
bootfile xllboot
ip dhcp pool
next-server
Release 12.0(1)T
14
Page 15

clear ip dhcp binding
To delete an automatic address binding from the Cisco IOS Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol
(DHCP) Server database, use the clear ip dhcp binding privileged EXEC command.
clear ip dhcp binding address | *
Syntax Description
address The address of the binding you want to clear.
* Clears all automatic bindings.
Command Modes
Privileged EXEC
Usage Guidelines
Typically, the address denotes the client’s IP address. If the asterisk (*) character is used as the
address parameter, DHCP clears all automatic bindings.
clear ip dhcp binding
Examples
Related Commands
Use the no ip dhcp pool global configuration command to delete a manual binding.
The following example deletes the address binding 10.12.1.99 from a DHCP server database:
clear ip dhcp binding 10.12.1.99
show ip dhcp binding
Cisco IOS DHCP Server 15
Page 16

Command Reference
clear ip dhcp conflict
To clear an address conflict from the Cisco IOS Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP)
Server database, use the clear ip dhcp conflict privileged EXEC command.
clear ip dhcp conflict address | *
Syntax Description
address The IP address of the host that contains the conflicting address you
* Clears all address conflicts.
Command Modes
Privileged EXEC
want to clear.
Usage Guidelines
Examples
Related Commands
This command first appeared in Cisco IOS Release 12.0(1)T.
The server detects conflicts using a ping session. The client detects conflicts using gratuitous
Address Resolution Protocol (ARP). If the asterisk (*) character is used as the address parameter,
DHCP clears all conflicts.
The following example shows an address conflict of 10.12.1.99 being deleted from the DHCP server
database:
clear ip dhcp conflict 10.12.1.99
show ip dhcp conflict
Release 12.0(1)T
16
Page 17

clear ip dhcp server statistics
To reset all Cisco IOS Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) Server counters, use the
clear ip dhcp server statistics privileged EXEC command.
clear ip dhcp server statistics
Syntax Description
This command has no arguments or keywords.
Command Modes
Privileged EXEC
Usage Guidelines
This command first appeared in Cisco IOS Release 12.0(1)T.
The show ip dhcp serverstatistics command displays DHCP counters. All counters are cumulative.
The counters will be initialized, or set to zero, with this command.
clear ip dhcp server statistics
Examples
Related Commands
The following example resets all DHCP counters to zero:
clear ip dhcp server statistics
show ip dhcp server statistics
Cisco IOS DHCP Server 17
Page 18

Command Reference
client-identifier
To specify a Microsoft Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) client’s unique identifier
(in dotted-hexadecimal notation), use the client-identifier DHCP pool configuration command. It is
valid for manual bindings only. Use the no form of this command to delete the client identifier.
client-identifier unique-identifier
no client-identifier
Syntax Description
unique-identifier The distinct identification of the client in dotted-hexadecimal notation,
Defaults
None
Command Modes
DHCP pool configuration
for example, 01b7.0813.8811.66.
Usage Guidelines
Examples
Related Commands
This command first appeared in Cisco IOS Release 12.0(1)T.
Microsoft DHCP clients require client identifiers instead of hardware addresses. The client identifier
is formed by concatenating the media type and the MAC address. For example, the Microsoft client
identifier for Ethernet address b708.1388.f166 is 01b7.0813.88f1.66, where 01 represents the
Ethernet media type. For a list of media type codes, refer to the “Address Resolution Protocol
Parameters” section of RFC 1700, Assigned Numbers.
The following example specifies the client identifier for Mac address b7.0813.8811.66 in
dotted-hexadecimal notation:
client-identifier 01b7.0813.8811.66
hardware-address
host
ip dhcp pool
Release 12.0(1)T
18
Page 19

client-name
Syntax Description
Defaults
client-name
To specify the name of a Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) client, use the
client-name DHCP pool configuration command. The client name should not include the domain
name. Use the no form of this command to remove the client name.
client-name name
no client-name
name Specifies the client’s name, using any standard ASCII character. The
client name should not include the domain name. For example, the
name mars should not be specified as mars.cisco.com.
None
Command Modes
Usage Guidelines
Examples
Related Commands
DHCP pool configuration
This command first appeared in Cisco IOS Release 12.0(1)T.
The following example specifies a string client1 that will be the name of the client:
client-name client1
host
ip dhcp pool
Cisco IOS DHCP Server 19
Page 20

Command Reference
default-router
To specify the default router list for a Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) client, use
the default-router DHCP pool configuration command. Use the no form of this command to
remove the default router list.
Syntax Description
address Specifies the IP address of a router. One IP address is required,
Defaults
None
Command Modes
DHCP pool configuration
default-router address [address2 ... address8]
no default-router
although you can specify up to eight addresses in one command line.
Usage Guidelines
Examples
Related Commands
This command first appeared in Cisco IOS Release 12.0(1)T.
The IP address of the router should be on the same subnet as the client subnet. You can specify up
to eight routers in the list. Routers are listed in order of preference (address1 is the most preferred
router, address2 is the next most preferred router, and so on).
The following example specifies 10.12.1.99 as the IP address of the default router:
default-router 10.12.1.99
ip dhcp pool
Release 12.0(1)T
20
Page 21

dns-server
Syntax Description
Defaults
dns-server
To specify the Domain Name System (DNS) IP servers available to a Dynamic Host Configuration
Protocol (DHCP) client, use the dns-server DHCP pool configuration command. Use the no form
of this command to remove the DNS server list.
dns-server address [address2 ... address8]
no dns-server
address Specifies the IP address of a DNS server. One IP address is required,
although you can specify up to eight addresses in one command line.
If DNS IP servers are not configured for a DHCP client, the client cannot correlate host names to IP
addresses.
Command Modes
Usage Guidelines
Examples
Related Commands
DHCP pool configuration
This command first appeared in Cisco IOS Release 12.0(1)T.
Servers are listed in order of preference (address1 is the most preferred server, address2 is the next
most preferred server, and so on).
The following example specifies 10.12.1.99 as the IP address of the domain name server of the
client:
dns-server 10.12.1.99
domain-name
ip dhcp pool
Cisco IOS DHCP Server 21
Page 22

Command Reference
domain-name
To specify the domain name for a Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) client, use the
domain-nameDHCP pool configuration command. Use the no form of this command to remove the
domain name.
Syntax Description
domain Specifies the client’s domain name string.
Defaults
None.
Command Modes
DHCP pool configuration
domain-name domain
no domain-name
Usage Guidelines
Examples
Related Commands
This command first appeared in Cisco IOS Release 12.0(1)T.
The following example specifies cisco.com as the domain name of the client:
domain-name cisco.com
dns-server
ip dhcp pool
Release 12.0(1)T
22
Page 23

hardware-address
To specify the hardware address of a Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) client, use
the hardware-address DHCP pool configuration command. It is valid for manual bindings only.
Use the no form of this command to remove the hardware address.
hardware-address hardware-address type
no hardware-address
Syntax Description
hardware-address Specifies the MAC address of the client’s hardware platform.
type Indicates the protocol of the hardware platform. Strings and values are
hardware-address
acceptable. The string options are:
• ethernet
• ieee802
The value options are:
• 1 10Mb Ethernet
• 6 IEEE 802
If no type is specified, the default protocol is Ethernet.
Defaults
Command Modes
Usage Guidelines
Examples
Related Commands
Ethernet is the default type if none is specified.
DHCP pool configuration
This command first appeared in Cisco IOS Release 12.0(1)T.
The following example specifies b708.1388.f166 as the MAC address of the client:
hardware-address b708.1388.f166
client-identifier
host
ip dhcp pool
Cisco IOS DHCP Server 23
Page 24

Command Reference
host
Syntax Description
Defaults
Tospecify the IP address and network mask for a manual binding to a Dynamic Host Configuration
Protocol (DHCP) client, use the host DHCP pool configuration command. Use the no form of this
command to remove the client’s IP address.
host address [mask | /prefix-length]
no host
address Specifies the IP address of the client.
mask (Optional) Specifies the network mask of the client.
/prefix-length (Optional) Specifies the number of bits that comprise the address
prefix. The prefix is an alternative way of specifying the network mask
of the client. The prefix length must be preceded by a forward slash (/).
None
Command Modes
Usage Guidelines
Examples
Related Commands
DHCP pool configuration
This command first appeared in Cisco IOS Release 12.0(1)T.
If the mask and prefix length are unspecified, DHCP examines its address pools. If no mask is found
in the pool database, the Class A, B, or C natural mask is used. This command is valid for manual
bindings only.
There is no limit on the number of manual bindings but you can only configure one manual binding
per host pool.
The following example specifies 10.12.1.99 as the client’s IP address and 255.255.248.0 as the
subnet mask:
host 10.12.1.99 255.255.248.0
client-identifier
hardware-address
ip dhcp pool
network (DHCP)
Release 12.0(1)T
24
Page 25

ip dhcp conflict logging
To enable conflict logging on a Cisco IOS Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) Server,
use the ip dhcp conflict logging global configuration command. Use the no form of this command
to disable conflict logging.
ip dhcp conflict logging
no ip dhcp conflict logging
Syntax Description
This command has no arguments or keywords.
Defaults
Conflict logging is enabled.
Command Modes
Global configuration
ip dhcp conflict logging
Usage Guidelines
Example
Related Commands
This command first appeared in Cisco IOS Release 12.0(1)T.
Cisco recommends using a DHCP server database agent to store automatic bindings. If you decide
not to use a DHCP server database agent to store automatic bindings, use the no ip dhcp conflict
logging command to disable the recording of address conflicts. By default, the Cisco IOS DHCP
Server records DHCP address conflicts in a log file.
The following example disables the recording of DHCP address conflicts:
no ip dhcp conflict logging
clear ip dhcp conflict
ip dhcp database
show ip dhcp conflicts
Cisco IOS DHCP Server 25
Page 26

Command Reference
ip dhcp database
You can configure a Cisco IOS Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) Server to save
automatic bindings on a remote host called a database agent. To configure a DHCP server database
agent and database agent parameters, use the ip dhcp database global configuration command. Use
the no form of this command to remove the database agent.
ip dhcp database url [timeout seconds | write-delay seconds]
no ip dhcp database url
Syntax Description
url Specifies the remote file used to store the automatic bindings.
timeout seconds (Optional) Specifies how long, in seconds, the DHCP server should
Following are the acceptable URL file formats:
• tftp://host/filename
• ftp://user:password@host/filename
• rcp://user@host/filename
wait before aborting a database transfer. Transfers that exceed the
timeout period are aborted. By default, DHCP waits 300 seconds
before aborting a database transfer. Infinity is defined as 0 seconds.
Defaults
Command Modes
Usage Guidelines
Example
write-delay seconds (Optional) Specifies how soon the DHCP server should send database
updates. By default, DHCP waits 300 seconds (5 minutes) before
sending database changes. The minimum delay is 60 seconds.
DHCP waits 300 seconds for both a write delay and a timeout.
Global configuration
This command first appeared in Cisco IOS Release 12.0(1)T.
Theadministrator may configure multiple database agents. Bindings are transferred by using the File
Transfer Protocol (FTP), Trivial File Transport Protocol (TFTP), or remote copy protocol (RCP).
The following example specifies the DHCP database transfer timeout value at 80 seconds:
ip dhcp database ftp://user:password@172.16.1.1/router-dhcp timeout 80
Release 12.0(1)T
26
The following example specifies the DHCP database update delay value at 100 seconds:
ip dhcp database tftp://172.16.1.1/router-dhcp write-delay 100
Page 27

Related Commands
ip dhcp database
show ip dhcp database
Cisco IOS DHCP Server 27
Page 28

Command Reference
ip dhcp excluded-address
To specify IP addresses that a Cisco IOS Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) Server
should not assign to DHCP clients, use the ip dhcp excluded-address global configuration
command. Use the no form of this command to remove the excluded IP addresses.
ip dhcp excluded-address low-address [high-address]
no ip dhcp excluded-address low-address [high-address]
Syntax Description
low-address The excluded IP address, or first IP address in an excluded address
high-address (Optional) The last IP address in the excluded address range.
Defaults
All IP pool addresses are assignable.
range.
Command Modes
Usage Guidelines
Example
Related Commands
Global configuration
This command first appeared in Cisco IOS Release 12.0(1)T.
The DHCP server assumes that all pool addresses may be assigned to clients. Use this command to
exclude a single IP address or a range of IP addresses.
The following example configures an excluded IP address range from 172.16.1.100 through
172.16.1.199:
ip dhcp excluded-address 172.16.1.100 172.16.1.199
ip dhcp pool
network (DHCP)
Release 12.0(1)T
28
Page 29

ip dhcp ping packets
To specify the number of packets a Cisco IOS Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP)
Server sends to a pool address as part of a ping operation, use the ip dhcp ping packets global
configuration command. Use the no form of this command to prevent the server from pinging pool
addresses.
ip dhcp ping packets count
no ip dhcp ping packets
Syntax Description
count Indicatesthe number of ping packets that are sent before assigning the
Defaults
Two packets
ip dhcp ping packets
address to a requesting client. The default value is two packets.
Command Modes
Usage Guidelines
Examples
Related Commands
Global configuration
This command first appeared in Cisco IOS Release 12.0(1)T.
The DHCP server pings a pool address before assigning the address to a requesting client. If the ping
is unanswered, the DHCP server assumes (with a high probability) that the address is not in use and
assigns the address to the requesting client.
The following example specifies five ping attempts by the DHCP server before ceasing any further
ping attempts:
ip dhcp ping packets 5
clear ip dhcp conflicts
ip dhcp ping timeout
show ip dhcp conflicts
Cisco IOS DHCP Server 29
Page 30

Command Reference
ip dhcp ping timeout
To specify how long a Cisco IOS Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) Server waits for
a ping reply from an address pool, use the ip dhcp ping timeout global configuration command. Use
the no form of this command to restore the default number of milliseconds (500) of the timeout.
ip dhcp ping timeout milliseconds
no ip dhcp ping timeout
Syntax Description
milliseconds The amount of time in milliseconds that the DHCP server waits for a
Defaults
500 milliseconds
ping reply before it stops attempting to reach a pool address for client
assignment. The maximum timeout is 10000 milliseconds
(10 seconds). The default timeout is 500 milliseconds.
Command Modes
Usage Guidelines
Examples
Related Commands
Global configuration
This command first appeared in Cisco IOS Release 12.0(1)T.
This command specifies how long to wait for a ping reply in milliseconds.
The following example specifies that the DHCP server will wait 800 milliseconds for a ping reply
before considering the ping a failure:
ip dhcp ping timeout 800
clear ip dhcp conflicts
ip dhcp ping packets
show ip dhcp conflicts
Release 12.0(1)T
30
Page 31

ip dhcp pool
Syntax Description
Defaults
Command Modes
ip dhcp pool
Toconfigure a Dynamic Host ConfigurationProtocol (DHCP) address pool on a Cisco IOS DHCP
Server and enter DHCP pool configuration mode, use the ip dhcp pool global configuration
command. Use the no form of this command to remove the address pool.
ip dhcp pool name
no ip dhcp pool name
name Can either be a symbolic string (such as “engineering”) or an integer
(such as 0).
DHCP address pools are not configured.
Global configuration
Usage Guidelines
Examples
Related Commands
This command first appeared in Cisco IOS Release 12.0(1)T.
During execution, the configuration mode changes to DHCP pool configuration mode, identified by
the (config-dhcp)# prompt. In this mode, the administrator can configure pool parameters, like the
IP subnet number and default router list.
The following example configures pool1 as the DHCP address pool:
ip dhcp pool pool1
host
ip dhcp excluded-address
network (DHCP)
Cisco IOS DHCP Server 31
Page 32

Command Reference
ip dhcp relay information check
To configure a Cisco IOS Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) Server to validate the
relay agent information option in forwarded BOOTREPLY messages, use the ip dhcp relay
information check global configuration command. Use the no form of this command to disable an
information check.
ip dhcp relay information check
no ip dhcp relay information check
Syntax Description
This command has no arguments or keywords.
Defaults
The DHCP server checks relay information. Invalid messages are dropped.
Command Modes
Global configuration
Usage Guidelines
Examples
Related Commands
This command first appeared in Cisco IOS Release 12.0(1)T.
This command is used by cable modem termination systems. By default, DHCP checks relay
information. Invalid messages are dropped.
The following example configures the DHCP server to check that the relay agent information option
in forwarded BOOTREPLY messages is valid:
ip dhcp relay information check
ip dhcp relay information option
ip dhcp relay information policy
Release 12.0(1)T
32
Page 33

ip dhcp relay information option
To configure a Cisco IOS Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) Server to insert the
DHCP relay agent information option in forwarded BOOTREQUEST messages, use the ip dhcp
relay information option global configuration command. Use the no form of this command to
disable inserting relay information to forwarded BOOTREQUEST messages.
ip dhcp relay information option
no ip dhcp relay information option
Syntax Description
This command has no arguments or keywords.
Defaults
The DHCP server does not insert relay information.
Command Modes
Global configuration
ip dhcp relay information option
Usage Guidelines
Examples
Related Commands
This command first appeared in Cisco IOS Release 12.0(1)T.
This command is used by cable modem termination systems. By default, DHCP does not insert relay
information.
The following example configures a DHCP server to insert the DHCP relay agent information option
in forwarded BOOTREQUEST messages:
ip dhcp relay information option
ip dhcp relay information check
ip dhcp relay information policy
Cisco IOS DHCP Server 33
Page 34

Command Reference
ip dhcp relay information policy
To configure a Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) relay agent’s information
reforwarding policy (what a DHCP relay agent should do if a message already contains relay
information), use the ip dhcp relay information policy global configuration command. Use the no
form of this command to restore the default relay information policy.
ip dhcp relay information policy {drop | keep | replace}
no ip dhcp relay information policy
Syntax Description
drop Directs the DHCP relay agent to discard messages with existing relay
information if the relay information option is already present.
keep Indicates that existing information is left unchanged on the DHCP
relay agent.
replace Indicates that existing information is overwritten on the DHCP relay
agent.
Defaults
Command Modes
Usage Guidelines
Examples
The DHCP server replaces existing relay information.
Global configuration
This command first appeared in Cisco IOS Release 12.0(1)T.
This command is used by cable modem termination systems. When a DHCP relay agent receives a
message from a another DHCP relay agent, relay information might already be present in the
message. By default, the relay information from the previous relay agent is replaced.
The following examples configure a DHCP relay agent to drop messages with existing relay
information, keep existing information, and replace existing information:
ip dhcp relay information policy drop
ip dhcp relay information policy keep
ip dhcp relay information policy replace
Related Commands
Release 12.0(1)T
34
ip dhcp relay information check
ip dhcp relay information option
Page 35

lease
Syntax Description
lease
To configure the duration of the lease for an IP address that is assigned from a Cisco IOS Dynamic
Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) Server to a DHCP client, use the lease DHCP pool
configuration command. Use the no form of this command to restore the default value.
lease {days [hours][minutes] | infinite}
no lease
days Specifies the duration of the lease in numbers of days.
hours (Optional) Specifies the number of hours in the lease. A days value
must be supplied before you can configure an hours value.
minutes (Optional) Specifies the number of minutes in the lease. A days value
and an hours value must be supplied before you can configure a
minutes value.
infinite Specifies the duration of the lease is unlimited.
Defaults
Command Modes
Usage Guidelines
Examples
One day
DHCP pool configuration
This command first appeared in Cisco IOS Release 12.0(1)T.
The following example shows a one-day lease:
lease 1
The following example shows a one-hour lease:
lease 0 1
The following example shows a one-minute lease:
lease 0 0 1
The following example shows an infinite (unlimited) lease:
lease infinite
Related Commands
ip dhcp pool
Cisco IOS DHCP Server 35
Page 36

Command Reference
netbios-name-server
To configure NetBIOS Windows Internet Naming Service (WINS) name servers that are available
to Microsoft Dynamic Host ConfigurationProtocol (DHCP) clients, use the netbios-name-server
DHCP pool configuration command. Use the no form of this command to remove the NetBIOS
name server list.
netbios-name-server address [address2...address8]
no netbios-name-server
Syntax Description
address Specifies the IP address of the NetBIOS WINS name server.
Defaults
None
Command Modes
DHCP pool configuration
Usage Guidelines
Examples
Related Commands
This command first appeared in Cisco IOS Release 12.0(1)T.
One IP address is required, although you can specify up to eight addresses in one command line.
Servers are listed in order of preference (address1 is the most preferred server, address2 is the next
most preferred server, and so on).
The following example specifies the IP address of a NetBIOS name server available to the client:
netbios-name-server 10.12.1.90
dns-server
domain-name
ip dhcp pool
netbios-node-type
Release 12.0(1)T
36
Page 37

netbios-node-type
Toconfigure the NetBIOS node type for Microsoft Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP)
clients, use the netbios-node-type DHCP pool configuration command. Use the no form of this
command to remove the NetBIOS node type.
netbios-node-type type
no netbios-node-type
Syntax Description
type Specifies the NetBIOS node type. Valid types are:
Defaults
None
netbios-node-type
• b-node Broadcast
• p-node Peer-to-peer
• m-node Mixed
• h-node Hybrid (recommended)
Command Modes
Usage Guidelines
Examples
Related Commands
DHCP pool configuration
This command first appeared in Cisco IOS Release 12.0(1)T.
The recommended type is h-node (hybrid).
The following example specifies the client’s NetBIOS type as hybrid:
netbios node-type h-node
ip dhcp pool
netbios-name-server
Cisco IOS DHCP Server 37
Page 38

Command Reference
network (DHCP)
To configure the subnet number and mask for a Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP)
address pool on a Cisco IOS DHCP Server, use the network DHCP pool configuration command.
Use the no form of this command to remove the subnet number and mask.
network network-number [mask | /prefix-length]
no network
Syntax Description
network-number The IP address of the DHCP address pool.
mask (Optional) The bit combination that renders which portion of the
/prefix-length (Optional) Specifies the number of bits that comprise the address
address of the DHCP address pool refers to the network or subnet and
which part refers to the host.
prefix. The prefix is an alternative way of specifying the network mask
of the client. The prefix length must be preceded by a forward slash (/).
Defaults
Command Modes
Usage Guidelines
Examples
None
DHCP pool configuration
This command first appeared in Cisco IOS Release 12.0(1)T.
This command is valid for DHCP subnetwork address pools only. If the mask or prefix length is not
specified, the class A, B, or C natural mask is used. The DHCP server assumes that all host addresses
are available. The system administrator can exclude subsets of the address space by using the ip
dhcp excluded-address command.
You can not configure manual bindings within the same pool that is configured with the network
command.
The following example configures 172.16.0.0/16 as the DHCP pool’ssubnetworknumber and mask:
network 172.16.0.0 /16
Related Commands
Release 12.0(1)T
38
host
ip dhcp excluded-address
ip dhcp pool
Page 39

next-server
Syntax Description
Defaults
next-server
To configure the next server in a Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) client’s boot
process, use the next-server DHCP pool configuration command. Use the no form of this command
to remove the boot server list.
next-server address [address2...address8]
no next-server address
address Specifies the IP address of the next server in the boot process, which is
typically a Trivial File Transfer Protocol (TFTP) server. One IP
address is required, although you can specify up to eight addresses in
one command line.
If the next-server command is not used to configure a boot server list, the DHCP server uses
inbound interface helper addresses as boot servers.
Command Modes
Usage Guidelines
Examples
Related Commands
DHCP pool configuration
This command first appeared in Cisco IOS Release 12.0(1)T.
You can specify up to eight servers in the list. Servers are listed in order of preference (address1 is
the most preferred server, address2 is the next most preferred server, and so on).
The following example specifies 10.12.1.99 as the IP address of the next server in the boot process:
next-server 10.12.1.99
bootfile
ip dhcp pool
ip helper-address
option
Cisco IOS DHCP Server 39
Page 40

Command Reference
option
Syntax Description
To configure Cisco IOS Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) Server options, use the
option DHCP pool configuration command. Use the no form of this command to remove the
options.
option code [instance number] {ascii string | hex string | ip address}
no option code [instance number]
code Specifies the DHCP option code.
instance number (Optional) Specifies a number from 0 to 255.
ascii string Specifies an NVT ASCII character string. ASCII character strings that
contain white space must be deliminated by quotation marks.
hex string Specifies dotted-hexadecimal data. Each byte in hexidecimal character
strings is two hexidecimal digits—each byte can be separated by a
period, colon, or white space.
Defaults
Command Modes
Usage Guidelines
Examples
ip address Specifies an IP address.
The default instance number is 0.
DHCP pool configuration
This command first appeared in Cisco IOS Release 12.0(1)T.
DHCP provides a framework for passing configuration information to hosts on a TCP/IP network.
Configuration parameters and other control information are carried in tagged data items that are
stored in the options field of the DHCP message. The data items themselves are also called options.
The current set of DHCP options are documented in RFC 2131, Dynamic Host Configuration
Protocol.
The following example configures DHCP option 19, which specifies whether the client should
configure its IP layer for packet forwarding. A value of 0 means disable IP forwarding; a value of 1
means enable IP forwarding. IP forwarding is enabled in the following example:
option 19 hex 01
Release 12.0(1)T
40
The following example configures DHCP option 72, which specifies the World Wide Web servers
for DHCP clients. World Wide Web servers 172.16.3.252 and 172.16.3.253 are configured in the
following example:
option 72 ip 172.16.3.252 172.16.3.253
Page 41

Related Commands
option
ip dhcp pool
Cisco IOS DHCP Server 41
Page 42

Command Reference
service dhcp
Syntax Description
Defaults
Command Modes
To enable the Cisco IOS Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) Server feature on your
router, use the service dhcp global configuration command. Use the no form of this command to
disable the Cisco IOS DHCP Server feature.
service dhcp
no service dhcp
This command has no keywords or arguments.
The feature is enabled.
Global configuration
Usage Guidelines
Examples
This command first appeared in Cisco IOS Release 12.0(1)T.
The following example enables DHCP services on the DHCP server:
service dhcp
Release 12.0(1)T
42
Page 43

show ip dhcp binding
To display address bindings on the Cisco IOS Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP)
Server, use the show ip dhcp binding EXEC command.
show ip dhcp binding [address]
Syntax Description
address (Optional) Specifies the IP address of the DHCP client for which
Defaults
None
Command Modes
EXEC
show ip dhcp binding
bindings will be displayed.
Usage Guidelines
Examples
This command first appeared in Cisco IOS Release 12.0(1)T.
If the address is not specified, all address bindings are shown. Otherwise, only the binding for the
specified client is displayed.
The following examples show the DHCP binding address parameters, including an IP address, an
associated MAC address, a lease expiration date, and the type of address assignment that have
occurred. Table 2 lists descriptions of the fields in each example.
Router> show ip dhcp binding 172.16.1.11
IP address Hardware address Lease expiration Type
172.16.1.11 00a0.9802.32de Feb 01 1998 12:00 AM Automatic
Router> show ip dhcp binding 172.16.3.254
IP address Hardware address Lease expiration Type
172.16.2.254 02c7.f800.0422 Infinite Manual
Table 2 show ip dhcp Field Descriptions
Field Description
IP address The IP address of the host as recorded on the DHCP server.
Hardware address The MAC address or client identifier of the host as recorded
on the DHCP server.
Lease expiration The lease expiration date of the IP address of the host.
Type The manner in which the IP address was assigned to the host.
Cisco IOS DHCP Server 43
Page 44

Command Reference
Related Commands
clear ip dhcp binding
Release 12.0(1)T
44
Page 45

show ip dhcp conflict
To display address conflicts found by a Cisco IOS Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP)
Server when addresses are offered to the client, use the show ip dhcp conflict EXEC command.
show ip dhcp conflict [address]
Syntax Description
address (Optional) Specifies the IP address of the conflict found.
Defaults
None
Command Modes
EXEC
show ip dhcp conflict
Usage Guidelines
Examples
This command first appeared in Cisco IOS Release 12.0(1)T.
The server detects conflicts using ping. The client detects conflicts using gratuitous Address
Resolution Protocol (ARP). If an address conflict is detected, the address is removed from the pool
and the address will not be assigned until an administrator resolves the conflict.
The following example displays the detection method and detection time for all IP addresses the
DHCPserver has offered that have conflicts with other devices. Table 3 lists descriptions of the fields
in the example.
Router> show ip dhcp conflict
IP address Detection Method Detection time
172.16.1.32 Ping Feb 16 1998 12:28 PM
172.16.1.64 Gratuitous ARP Feb 23 1998 08:12 AM
Table 3 show ip dhcp conflict Field Descriptions
Field Description
IP Address The IP address of the host as recorded on the DHCP server.
Detection Method The manner in which the IP address of the hosts were found
on the DHCP server. Can be a ping or a gratuitous ARP.
Detection time The time when the conflict was found.
Related Commands
clear ip dhcp conflict
ip dhcp ping packets
ip dhcp ping timeout
Cisco IOS DHCP Server 45
Page 46

Command Reference
show ip dhcp database
To display Cisco IOS Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) Server database agent
information, use the show ip dhcp database Privileged EXEC command.
show ip dhcp database [url]
Syntax Description
url (Optional) Specifies the remote file used to store automatic DHCP
Defaults
If a URL is not specified, all database agent records are shown. Otherwise, only information about
the specified agent is displayed.
bindings. Following are the acceptable URL file formats:
• tftp://host/filename
• ftp://user:password@host/filename
• rcp://user@host/filename
Command Modes
Usage Guidelines
Examples
Privileged EXEC
This command first appeared in Cisco IOS Release 12.0(1)T.
ThefollowingexampleshowsallDHCPserverdatabase agent information. Table 4 listsdescriptions
for each field in the example.
Router# show ip dhcp database
URL : ftp://user:password@172.16.4.253/router-dhcp
Read : Dec 01 1997 12:01 AM
Written : Never
Status : Last read succeeded. Bindings have been loaded in RAM.
Delay : 300 seconds
Timeout : 300 seconds
Failures : 0
Successes : 1
Table 4 show ip dhcp database Field Descriptions
Field Description
URL Specifies the remote file used to store automatic DHCP
bindings. Following are the acceptable URL file formats:
• tftp://host/filename
• ftp://user:password@host/filename
• rcp://user@host/filename
Release 12.0(1)T
46
Page 47

Related Commands
show ip dhcp database
Table 4 show ip dhcp database Field Descriptions (continued)
Field Description
Read The last time bindings were read from the file server.
Written The last time bindings were written to the file server.
Status Indication of whether the last read or write of host bindings
was successful.
Delay The amount of time to wait before updating the database.
Timeout The amount of time before the file transfer is aborted.
Failures The number of failed file transfers.
Successes The number of successful file transfers.
ip dhcp database
Cisco IOS DHCP Server 47
Page 48

Command Reference
show ip dhcp server statistics
To display Cisco IOS Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) Server statistics, use the
show ip dhcp server statistics EXEC command.
show ip dhcp server statistics
Syntax Description
This command has no arguments or keywords.
Defaults
None
Command Modes
EXEC
Usage Guidelines
This command first appeared in Cisco IOS Release 12.0(1)T.
Examples
The following example displays DHCP server statistics. Table 5 lists descriptions for each field in
the example.
Router> show ip dhcp server statistics
Memory usage 40392
Address pools 3
Database agents 1
Automatic bindings 190
Manual bindings 1
Expired bindings 3
Malformed messages 0
Message Received
BOOTREQUEST 12
DHCPDISCOVER 200
DHCPREQUEST 178
DHCPDECLINE 0
DHCPRELEASE 0
DHCPINFORM 0
Message Sent
BOOTREPLY 12
DHCPOFFER 190
DHCPACK 172
DHCPNAK 6
Release 12.0(1)T
48
Page 49

show ip dhcp server statistics
Table 5 show ip dhcp server statistics Field Descriptions
Field Description
Memory usage The number of bytes of RAM allocated by the DHCP server.
Address pools The number of configured address pools in the DHCP
database.
Database agents The number of database agents configured in the DHCP
database.
Automatic bindings The number of IP addresses that have been automatically
mapped to the MAC addresses of hosts that are found in the
DHCP database.
Manual bindings The number of IP addresses that have been manually mapped
to the MAC addresses of hosts that are found in the DHCP
database.
Expired bindings The number of expired leases.
Malformed messages The number of truncated or corrupted messages that were
received by the DHCP server.
Message The DHCP message type that was received by the DHCP
server.
Received The number of DHCP messages that were received by the
DHCP server.
Sent The number of DHCP messages that were sent by the DHCP
server.
Related Commands
clear ip dhcp server statistics
Cisco IOS DHCP Server 49
Page 50

Debug Commands
Debug Commands
This section describes the following new debug command:
• debug ip dhcp server
Release 12.0(1)T
50
Page 51

debug ip dhcp server
To enable Cisco IOS Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) Server debugging, use the
debug ip dhcp server privileged EXEC command. Use the no form of this command to disable
DHCP server debugging.
debug ip dhcp server {events | packets | linkage}
no debug ip dhcp server {events | packets | linkage}
Syntax Description
events Reports server events, like address assignments and database updates.
packets Decodes DHCP receptions and transmissions.
linkage Displays database linkage information (such as parent-child
Defaults
DHCP server debugging is not enabled.
debug ip dhcp server
relationships in a radix tree).
Usage Guidelines
Examples
This command first appeared in Cisco IOS Release 12.0(1)T.
The first example below shows a combination of DHCP server events and decoded receptions and
transmissions. The second example below shows database linkage information.
Router# debug ip dhcp server events
Router# debug ip dhcp server packets
DHCPD:DHCPDISCOVER received from client 0b07.1134.a029 through relay 10.1.0.253.
DHCPD:assigned IP address 10.1.0.3 to client 0b07.1134.a029.
DHCPD:Sending DHCPOFFER to client 0b07.1134.a029 (10.1.0.3).
DHCPD:unicasting BOOTREPLY for client 0b07.1134.a029 to relay 10.1.0.253.
DHCPD:DHCPREQUEST received from client 0b07.1134.a029.
DHCPD:Sending DHCPACK to client 0b07.1134.a029 (10.1.0.3).
DHCPD:unicasting BOOTREPLY for client 0b07.1134.a029 to relay 10.1.0.253.
DHCPD:checking for expired leases.
Router# debug ip dhcp server linkage
DHCPD:child pool:10.1.0.0 / 255.255.0.0 (subnet10.1)
DHCPD:parent pool:10.0.0.0 / 255.0.0.0 (net10)
DHCPD:child pool:10.0.0.0 / 255.0.0.0 (net10)
DHCPD:pool (net10) has no parent.
DHCPD:child pool:10.1.0.0 / 255.255.0.0 (subnet10.1)
DHCPD:parent pool:10.0.0.0 / 255.0.0.0 (net10)
DHCPD:child pool:10.0.0.0 / 255.0.0.0 (net10)
DHCPD:pool (net10) has no parent.
Related Commands
show ip dhcp bindings
show ip dhcp database
Cisco IOS DHCP Server 51
Page 52

Glossary
Glossary
address binding—A mapping between the client’s IP and hardware (MAC) addresses. The client’s
IP address may be configured by the administrator (manual address allocation) or assigned from a
poolby the DHCP server (automaticaddress allocation). The binding also contains a lease expiration
date. The default for the lease expiration date is one day.
address conflict—A duplication of use of the same IP address by two hosts. During address
assignment, DHCP checks for conflicts using ping and gratuitous ARP. If a conflict is detected, the
address is removed from the pool. The address will not be assigned until the administrator resolves
the conflict.
address pool—The range of IP addresses assigned by the DHCP server. Address pools are indexed
by subnet number.
client—Any host requesting configuration parameters.
database—A collection of address pools and bindings.
databaseagent—Anyhost storing the DHCP bindings database, for example,a TrivialFileTransfer
Protocol (TFTP) server.
DNS—Domain Name System. A system used in the Internet for translating names of network nodes
into addresses.
automatic address allocation—An address assignment method where a network administrator
obtains an IP address for a client for a finite period of time or until the client explicitly relinquishes
the address. Automatic allocation is particularly useful for assigning an address to a client that will
be connected to the network only temporarily or for sharing a limited pool of IP addresses among a
group of clients that do not need permanent IP addresses. Automatic allocation may also be a good
choice for assigning an IP address to a new client being permanently connected to a network where
IP addresses are sufficiently scarce that it is important to reclaim them when old clients are retired.
Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP)—A protocol that provides a mechanism for
allocating IP addresses dynamically so that addresses can be reused when hosts no longer need them.
manual address allocation—An address assignment method that allocates an administratively
assignedIP address to a host. Manual allocationallowsDHCP to be usedto eliminate the error-prone
process of manually configuring hosts with IP addresses.
server—Any host providing configuration parameters.
Release 12.0(1)T
52
 Loading...
Loading...