Page 1

OSPF Sham-Link Support for MPLS VPN
Feature History
Release Modification
12.2(8)T This feature was introduced.
This document describes how to configure and use a sham-link to connect Virtual Private Network
(VPN) client sites that run the Open Shortest Path First(OSPF) protocol and share backdoor OSPF links
in a Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) VPN configuration.
This document includes the following sections:
• Feature Overview, page 1
• Supported Platforms, page 8
• Supported Standards, MIBs, and RFCs, page 10
• Prerequisites, page 10
• Configuration Tasks, page 10
• Configuration Examples, page 12
• Command Reference, page 12
• Glossary, page 16
Feature Overview
Using OSPF in PE-CE Router Connections
In an MPLS VPN configuration, the OSPF protocol is one way you can connect customer edge (CE) routers
to service provider edge (PE) routers in the VPN backbone. OSPF is often used by customers that run OSPF
as their intrasite routing protocol, subscribe to a VPN service, and want to exchange routing information
between their sites using OSPF (during migration or on a permanent basis) over an MPLS VPN backbone.
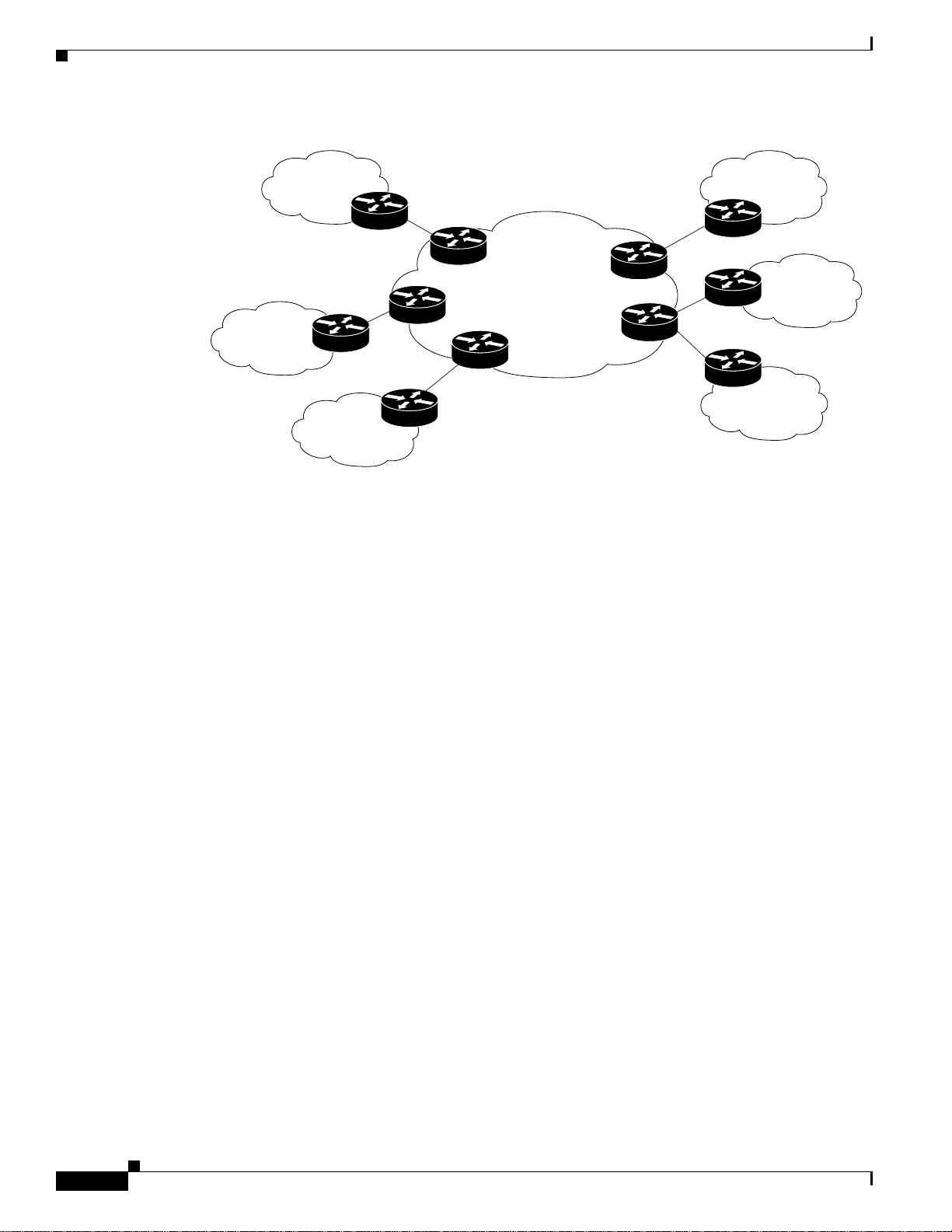
Figure 1 shows an example of how VPN client sites that run OSPF can connect over an MPLS VPN
backbone.
Cisco IOS Release 12.2(8)T
1
Page 2
Feature Overview
OSPF Sham-Link Support for MPLS VPN
Figure 1 OSPF Connectivity Between VPN Client Sites and an MPLS VPN Backbone
Area 1Area 1
MPLS VPN
Superbackbone
Area 0
Area 3
Area 2
Area 0
When OSPF is used to connect PE and CE routers, all routing information learned from a VPN site is placed
in the VPN routing and forwarding (VRF) instance associated with the incoming interface. The PE routers
that attach to the VPN use the Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) to distribute VPN routes to each other. A CE
router can then learn the routes to other sites in the VPN by peering with its attached PE router. The MPLS
VPN superbackbone provides an additional level of routing hierarchy to interconnect the VPN sites running
OSPF.
When OSPF routes are propagated over the MPLS VPN backbone, additional information about the prefix in
the form of BGP extended communities (route type, domain ID extended communities) is appended to the
BGP update. This community information is used by the receiving PE router to decide the type of link-state
advertisement (LSA) to be generated when the BGP route is redistributed to the OSPF PE-CE process. In this
way, internal OSPF routes that belong to the same VPN and are advertised over the VPN backbone are seen
as interarea routes on the remote sites.
For basic information about how to configure an MPLS VPN, refer to:
http://www.cisco.com/univercd/cc/td/doc/product/software/ios120/120newft/120t/120t5/vpn.htm
70390
Using a Sham-Link to Correct OSPF Backdoor Routing
Although OSPF PE-CE connections assume that the only path between two client sites is across the MPLS
VPN backbone, backdoor paths between VPN sites (shown in grey in Figure 2) may exist. If these sites
belong to the same OSPF area, the path over a backdoor link will always be selected because OSPF prefers
intraarea paths to interarea paths. (PE routers advertise OSPF routes learned over the VPN backbone as
interarea paths.) For this reason, OSPF backdoor links between VPN sites must be taken into account so that
routing is performed based on policy.
Cisco IOS Release 12.2(8)T
2
Page 3
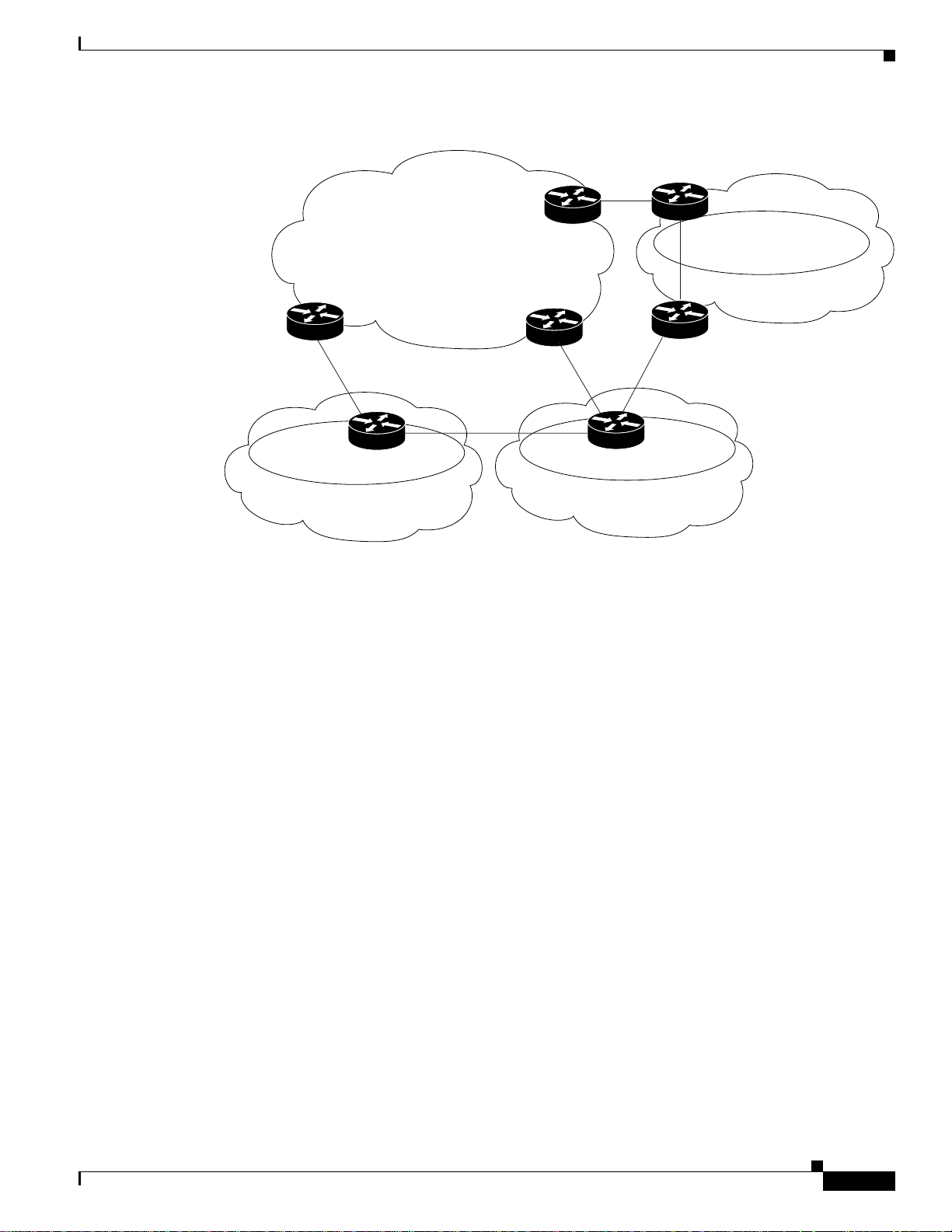
OSPF Sham-Link Support for MPLS VPN
Figure 2 Backdoor Paths Between OSPF Client Sites
MPLS VPN Backbone
PE-3
10.3.1.2
Winchester
10.3.1.7
Feature Overview
Area 1
PE-1
10.3.1.6
PE-2
Brighton
10.3.1.5
Area 1
Vienna
10.3.1.15
Stockholm
10.3.1.3
Area 1
For example, Figure 2 shows three client sites, each with backdoor links. Because each site runs OSPF within
the same Area 1 configuration, all routing between the three sites follows the intraarea path across the
backdoor links, rather than over the MPLS VPN backbone.
The following example shows BGP routing table entries for the prefix 10.3.1.7/32 in the PE-1 router in
Figure 2. This prefix is the loopback interface of the Winchester CE router. As shown in bold in this example,
the loopback interface is learned via BGP from PE-2 and PE-3. It is also generated through redistribution into
BGP on PE-1.
PE-1# show ip bgp vpnv4 all 10.3.1.7
BGP routing table entry for 100:251:10.3.1.7/32, version 58
Paths: (3 available, best #2)
Advertised to non peer-group peers:
10.3.1.2 10.3.1.5
Local
10.3.1.5 (metric 30) from 10.3.1.5 (10.3.1.5)
Origin incomplete, metric 22, localpref 100, valid, internal
Extended Community: RT:1:793 OSPF DOMAIN ID:0.0.0.100 OSPF
RT:1:2:0 OSPF 2
Local
10.2.1.38 from 0.0.0.0 (10.3.1.6)
Origin incomplete, metric 86, localpref 100, weight 32768,
valid, sourced, best
Extended Community: RT:1:793 OSPF DOMAIN ID:0.0.0.100 OSPF
RT:1:2:0 OSPF 2
Local
10.3.1.2 (metric 30) from 10.3.1.2 (10.3.1.2)
Origin incomplete, metric 11, localpref 100, valid, internal
Extended Community: RT:1:793 OSPF DOMAIN ID:0.0.0.100 OSPF
RT:1:2:0 OSPF 2
70391
Within BGP, the locally generated route (10.2.1.38) is considered to be the best route. However, as shown in
bold in the next example, the VRF routing table shows that the selected path is learned via OSPF with a next
hop of 10.2.1.38, which is the Vienna CE router.
Cisco IOS Release 12.2(8)T
3
Page 4

Feature Overview
OSPF Sham-Link Support for MPLS VPN
PE-1# show ip route vrf ospf 10.3.1.7
Routing entry for 10.3.1.7/32
Known via "ospf 100", distance 110, metric 86, type intra area
Redistributing via bgp 215
Advertised by bgp 215
Last update from 10.2.1.38 on Serial0/0/0, 00:00:17 ago
Routing Descriptor Blocks:
* 10.2.1.38, from 10.3.1.7, 00:00:17 ago, via Serial0/0/0
Route metric is 86, traffic share count is 1
This path is selected because:
• The OSPF intra-area path is preferred over the interarea path (over the MPLS VPN backbone)
generated by the PE-1 router.
• OSPF has a lower administrative distance (AD) than internal BGP (BGP running between routers in
the same autonomous system).
If the backdoor links between sites are used only for backup purposes and do not participate in the VPN
service, then the default route selection shown in the preceding example is not acceptable. To reestablish the
desired path selection over the MPLS VPN backbone, you must create an additionalOSPF intra-area (logical)
link between ingress and egress VRFs on the relevant PE routers. This link is called a sham-link.
A sham-link is required between any two VPN sites that belong to the same OSPF area and share an OSPF
backdoor link. If no backdoor link exists between the sites, no sham-link is required.
Figure 3 shows a sample sham-link between PE-1 and PE-2. A cost is configured with each sham-link and is
used to decide whether traffic will be sent over the backdoor path or the sham-link path. When a sham-link
is configured between PE routers, the PEs can populate the VRF routing table with the OSPF routes learned
over the sham-link.
Cisco IOS Release 12.2(8)T
4
Page 5
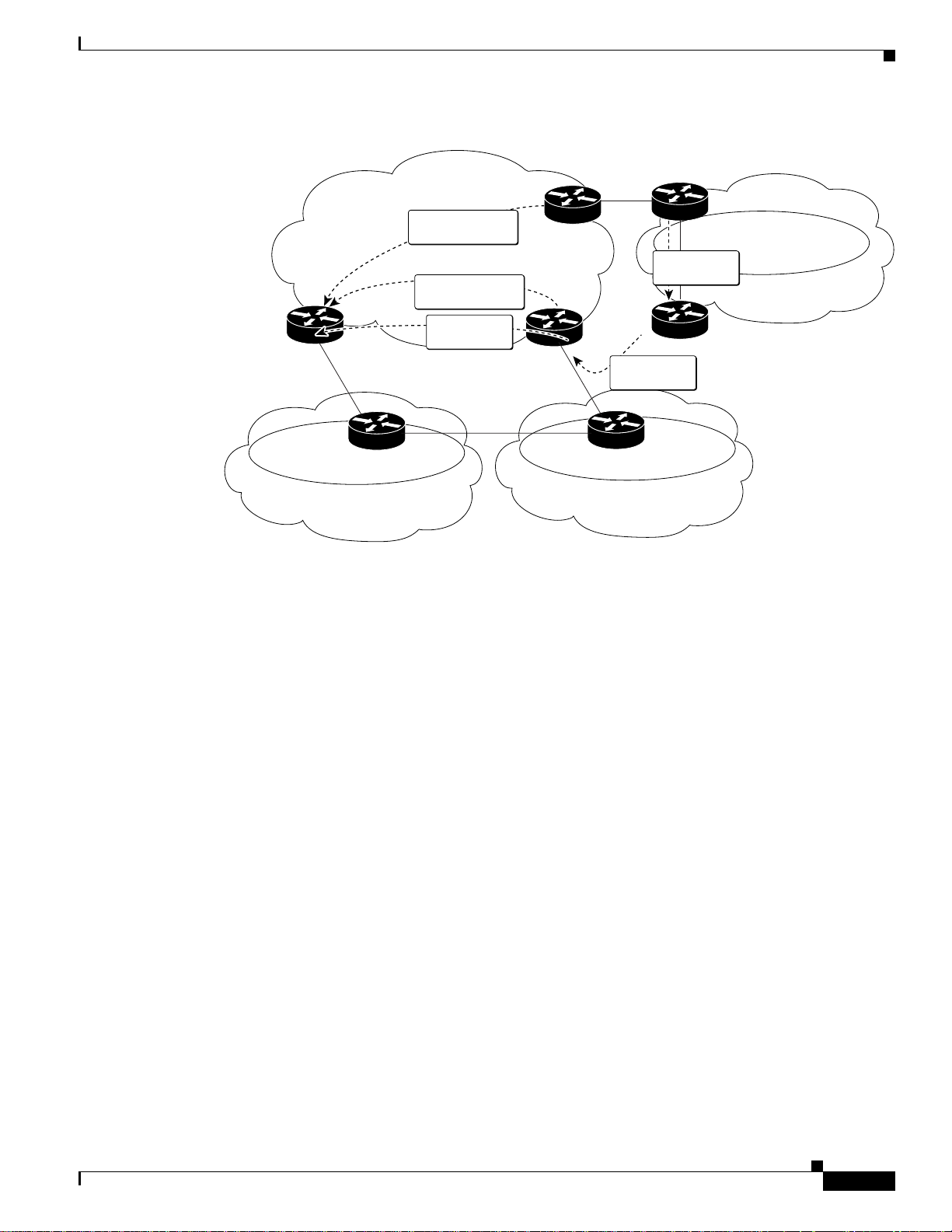
OSPF Sham-Link Support for MPLS VPN
Figure 3 Using a Sham-Link Between PE Routers to Connect OSPF Client Sites
PE-1
10.3.1.6
MPLS VPN Backbone
Net=10.3.1.7
Route-type 1:2:0
MP-BGP
Sham-linkSham-link
Net=10.3.1.7
Route-type 1:2:0
Net=10.3.1.7
Type-1 LSA
10.3.1.2
PE-2
10.3.1.5
PE-3
Net=10.3.1.7
Type-1 LSA
Net=10.3.1.7
Type-1 LSA
Winchester
10.3.1.7
Brighton
Feature Overview
Area 1
70392
Area 1
Vienna
10.3.1.15
Because the sham-link is seen as an intra-area link between PE routers, an OSPF adjacency is created and
database exchange (for the particular OSPF process) occurs across the link. The PE router can then flood
LSAs between sites from across the MPLS VPN backbone. As a result, the desired intra-area connectivity is
created.
The section, “Creating a Sham-Link”, describes how to configure a sham-link between two PE routers.
For more information about how to configure OSPF, refer to:
http://www.cisco.com/univercd/cc/td/doc/product/software/ios120/12cgcr/np1_c/1cprt1/1cospf.htm
Sham-Link Configuration Example
The example in this section is designed to show how a sham-link is used only to affect the OSPF intra-area
path selection of the PE and CE routers. The PE router also uses the information received from MP-BGP to
set the outgoing label stack of incoming packets, and to decide to which egress PE router to label switch the
packets.
Figure 4showsa sample MPLS VPN topology in which a sham-link configuration is necessary. A VPN client
hasthreesites,eachwithabackdoorlink.Twosham-linkshavebeenconfigured,onebetweenPE-1andPE-2,
and another between PE-2 and PE-3. A sham-link between PE-1 and PE-3 is not necessary in this
configuration because the Vienna and Winchester sites do not share a backdoor link.
Stockholm
10.3.1.3
Area 1
Cisco IOS Release 12.2(8)T
5
Page 6

Feature Overview
Figure 4 Sham-Link Example
MPLS VPN Backbone
Sham-link
PE-3
10.3.1.2
OSPF Sham-Link Support for MPLS VPN
Winchester
10.3.1.7
Area 1
PE-1
10.3.1.6
Sham-link
PE-2
Brighton
10.3.1.5
Area 1
Vienna
10.3.1.15
Stockholm
10.3.1.3
Area 1
The following example shows the forwarding that occurs between sites from the standpoint of how PE-1
views the 10.3.1.7/32 prefix, the loopback1 interface of the Winchester CE router in Figure 4.
PE-1# show ip bgp vpnv4 all 10.3.1.7
BGP routing table entry for 100:251:10.3.1.7/32, version 124
Paths: (1 available, best #1)
Local
10.3.1.2 (metric 30) from 10.3.1.2 (10.3.1.2)
Origin incomplete, metric 11, localpref 100, valid, internal,
best
Extended Community: RT:1:793 OSPF DOMAIN ID:0.0.0.100 OSPF
RT:1:2:0 OSPF 2
70393
PE-1# show ip route vrf ospf 10.3.1.7
Routing entry for 10.3.1.7/32
Known via "ospf 100", distance 110, metric 13, type intra area
Redistributing via bgp 215
Last update from 10.3.1.2 00:12:59 ago
Routing Descriptor Blocks:
10.3.1.2 (Default-IP-Routing-Table), from 10.3.1.7, 00:12:59 ago
The next example shows forwarding information in which the next hop for the route, 10.3.1.2, is the PE-3
router rather than the PE-2 router (which is the best path according to OSPF). The reason the OSPF route is
not redistributed to BGP on the PE is because the other end of the sham-link already redistributed the route
to BGP and there is no need for duplication. The OSPF sham-link is used only to influence intra-area path
selection. When sending traffic to a particular destination, the PE router uses the MP-BGP forwarding
information.
PE-1# show ip bgp vpnv4 all tag | begin 10.3.1.7
10.3.1.7/32 10.3.1.2 notag/38
PE-1# show tag-switching forwarding 10.3.1.2
Local Outgoing Prefix Bytes tag Outgoing Next Hop
tag tag or VC or Tunnel Id switched interface
31 42 10.3.1.2/32 0 PO3/0/0 point2point
Cisco IOS Release 12.2(8)T
6
Page 7

OSPF Sham-Link Support for MPLS VPN
PE-1# show ip cef vrf ospf 10.3.1.7
10.3.1.7/32, version 73, epoch 0, cached adjacency to POS3/0/0
0 packets, 0 bytes
tag information set
local tag: VPN-route-head
fast tag rewrite with PO3/0/0, point2point, tags imposed: {42 38}
via 10.3.1.2, 0 dependencies, recursive
next hop 10.1.1.17, POS3/0/0 via 10.3.1.2/32
valid cached adjacency
tag rewrite with PO3/0/0, point2point, tags imposed: {42 38}
If a prefix is learned across the sham-link and the path via the sham-link is selected as the best, the PE router
does not generate an MP-BGP update for the prefix. It is not possible to route traffic from one sham-link over
another sham-link.
In the following example, PE-2 shows how an MP-BGP update for the prefix is not generated. Although
10.3.1.7/32 has been learned via OSPF across the sham-link as shown in bold, no local generation of a route
into BGP is performed. The only entry within the BGP table is the MP-BGP update received from PE-3 (the
egress PE router for the 10.3.1.7/32 prefix).
PE-2# show ip route vrf ospf 10.3.1.7
Routing entry for 10.3.1.7/32
Known via "ospf 100", distance 110, metric 12, type intra area
Redistributing via bgp 215
Last update from 10.3.1.2 00:00:10 ago
Routing Descriptor Blocks:
* 10.3.1.2 (Default-IP-Routing-Table), from 10.3.1.7, 00:00:10 ago
Route metric is 12, traffic share count is 1
Feature Overview
Benefits
PE-2# show ip bgp vpnv4 all 10.3.1.7
BGP routing table entry for 100:251:10.3.1.7/32, version 166
Paths: (1 available, best #1)
Not advertised to any peer
Local
10.3.1.2 (metric 30) from 10.3.1.2 (10.3.1.2)
Origin incomplete, metric 11, localpref 100, valid, internal,
best
Extended Community: RT:1:793 OSPF DOMAIN ID:0.0.0.100 OSPF
RT:1:2:0 OSPF 2
The PE router uses the information received from MP-BGP to set the ongoing label stack of incoming
packets, and to decide to which egress PE router to label switch the packets.
Client Site Connection Across the MPLS VPN Backbone
A sham-link overcomes the OSPF default behavior for selecting an intra-area backdoor route between VPN
sites instead of an interarea (PE-to-PE) route. A sham-link ensures that OSPF client sites that share a
backdoor link can communicate over the MPLS VPN backbone and participate in VPN services.
Flexible Routing in an MPLS VPN Configuration
In an MPLS VPN configuration, the OSPF cost configured with a sham-link allows you to decide if OSPF
client site traffic will be routed over a backdoor link or through the VPN backbone.
Cisco IOS Release 12.2(8)T
7
Page 8

Supported Platforms
Restrictions
When OSPF is used as a protocol between PE and CE routers, the OSPF metric is preserved when routes
are advertised over the VPN backbone. The metric is used on the remote PE routers to select the correct
route. For this reason, you should not modify the metric value when OSPF is redistributed to BGP, and
when BGP is redistributed to OSPF. If you modify the metric value, routing loops may occur.
Related Features and Technologies
• MPLS
• OSPF
• BGP
Related Documents
• Cisco IOS Configuration Fundamentals Configuration Guide, Release 12.2
• Cisco IOS Configuration Fundamentals Command Reference, Release 12.2
• Cisco IOS IP Command Reference, Volume 2 of 3: Routing Protocols, Release 12.2
http://www.cisco.com/univercd/cc/td/doc/product/software/ios122/122cgcr/fiprrp_r/1rfospf.htm
• MPLS Virtual Private Networks
http://www.cisco.com/univercd/cc/td/doc/product/software/ios120/120newft/120t/120t5/vpn.htm
• Configuring OSPF
http://www.cisco.com/univercd/cc/td/doc/product/software/ios122/122cgcr/fipr_c/ipcprt2/1cfospf.
htm
• Configuring BGP
http://www.cisco.com/univercd/cc/td/doc/product/software/ios122/122cgcr/fipr_c/ipcprt2/1cfbgp.h
tm
• RFC 1163, A Border Gateway Protocol
• RFC 1164, Application of the Border Gateway Protocol in the Internet
• RFC 2283, Multiprotocol Extensions for BGP-4
• RFC 2328, Open Shortest Path First, Version 2
• RFC 2547, BGP/MPLS VPNs
OSPF Sham-Link Support for MPLS VPN
Supported Platforms
• Cisco 1400 series
• Cisco 1600
• Cisco 1600R
• Cisco 1710
• Cisco 1720
Cisco IOS Release 12.2(8)T
8
Page 9

OSPF Sham-Link Support for MPLS VPN
• Cisco 1721
• Cisco 1750
• Cisco 1751
• Cisco 2420
• Cisco 2600
• Cisco 2691
• Cisco 3620
• Cisco 3631
• Cisco 3640
• Cisco 3660
• Cico 3725
• Cisco 3745
• Cisco 7100
• Cisco 7200
• Cisco 7500
• Cisco 7700
• URM
• Cisco uBR7200
Supported Platforms
Determining Platform Support Through Cisco Feature Navigator
Cisco IOS software is packaged in feature sets that support specific platforms. To get updated
information regarding platform support for this feature, access Cisco Feature Navigator. Cisco Feature
Navigator dynamically updates the list of supported platforms as new platform support is added for the
feature.
Cisco Feature Navigator is a web-based tool that enables you to quickly determine which Cisco IOS
software images support a specific set of features and which features are supported in a specific
Cisco IOS image. You can search by feature or release. Under the release section, you can compare
releases side by side to display both the features unique to each software release and the features in
common.
To access Cisco Feature Navigator, you must have an account on Cisco.com. If you have forgotten or
lost your account information, send a blank e-mail to cco-locksmith@cisco.com. An automatic check
will verify that your e-mail address is registered with Cisco.com. If the check is successful, account
details with a new random password will be e-mailed to you. Qualified users can establish an account on
Cisco.com by following the directions at http://www.cisco.com/register.
Cisco Feature Navigator is updated regularly when major Cisco IOS software releases and technology
releases occur. For the most current information, go to the Cisco Feature Navigator home page at the
following URL:
http://www.cisco.com/go/fn
Cisco IOS Release 12.2(8)T
9
Page 10

Supported Standards, MIBs, and RFCs
Supported Standards, MIBs, and RFCs
Standards
No new or modified standards are supported by this feature.
MIBs
No new or modified MIBs are supported by this feature.
To obtain lists of supported MIBs by platform and Cisco IOS release, and to download MIB modules,
go to the Cisco MIB website on Cisco.com at the following URL:
http://www.cisco.com/public/sw-center/netmgmt/cmtk/mibs.shtml
RFCs
No new or modified RFCs are supported by this feature.
Prerequisites
OSPF Sham-Link Support for MPLS VPN
Before you can configure a sham-link in an MPLS VPN, you must first enable OSPF as follows:
• Create an OSPF routing process.
• Specify the range of IP addresses to be associated with the routing process.
• Assign area IDs to be associated with the range of IP addresses.
For more information on these OSPF configuration procedures, go to:
http://www.cisco.com/univercd/cc/td/doc/product/software/ios122/122cgcr/fiprrp_r/1rfospf.htm
Configuration Tasks
See the following sections for configuration tasks for the sham-link feature. Each task in the list is
identified as either required or optional.
• Creating a Sham-Link (required)
• Verifying Sham-Link Creation (optional)
Creating a Sham-Link
Before you create a sham-link between PE routers in an MPLS VPN, you must:
• Configure a separate /32 address on the remote PE so that OSPF packets can be sent over the VPN
backbone to the remote end of the sham-link. The /32 address must meet the following criteria:
–
Belong to a VRF.
–
Not be advertised by OSPF.
–
Be advertised by BGP.
You can use the /32 address for other sham-links.
• Associate the sham-link with an existing OSPF area.
10
Cisco IOS Release 12.2(8)T
Page 11

OSPF Sham-Link Support for MPLS VPN
To create a sham-link, use the following commands starting in EXEC mode:
Command Purpose
Step 1
Step 2
Step 3
Step 4
Step 5
Step 6
Step 7
Step 8
Step 9
Step 10
Step 11
Step 12
Step 13
Step 14
Step 15
Step 16
Router1# configure terminal
Router1(config)# interface loopback
interface-number
Router1(config-if)# ip vrf forwarding
vrf-name
Router1(config-if)# ip address
mask
Router1(config-if)# end
Router1(config)# end
Router2# configure terminal
Router2(config)# interface loopback
interface-number
Router2(config-if)# ip vrf forwarding
vrf-name
Router2(config-if)# ip address
mask
Router2(config-if)# end
Router1(config)# end
Router1(config)# router ospf
vrf
vrf-name
Router1(config-if)# area
sham-link
destination-address
Router2(config)# router ospf
vrf
Router2(config-if)# area
sham-link
destination-address
source-address
vrf-name
source-address
cost
cost
ip-address
ip-address
process-id
area-id
number
process-id
area-id
number
Configuration Tasks
Enters global configuration mode on the first PE router.
Creates a loopback interface to be used as an endpoint of the
sham-link on PE-1 and enters interface configuration mode.
Associates the loopback interface with a VRF. Removes the IP
address.
Reconfigures the IP address of the loopback interface on PE-1.
Returns to global configuration mode.
Returns to EXEC mode.
Enters global configuration mode on the second PE router.
Creates a loopback interface to be used as the endpoint of the
sham-link on PE-2 and enters interface configuration mode.
Associates the second loopback interface with a VRF. Removes
the IP address.
Reconfigures the IP address of the loopback interface on PE-2.
Returns to global configuration mode.
Returns to EXEC mode.
Configures the specified OSPF process with the VRF associated
with the sham-link interface on PE-1 and enters interface
configuration mode.
Configures the sham-link on the PE-1 interface within a specified
OSPF area and with the loopback interfaces specified by the IP
addresses as endpoints. cost number configures the OSPF cost for
sending an IP packet on the PE-1 sham-link interface.
Configures the specified OSPF process with the VRF associated
with the sham-link interface on PE-2 and enters interface
configuration mode.
Configures the sham-link on the PE-2 interface within a specified
OSPF area and with the loopback interfaces specified by the IP
addresses as endpoints. cost number configures the OSPF cost for
sending an IP packet on the PE-2 sham-link interface.
Verifying Sham-Link Creation
To verify that the sham-link was successfully created and is operational, use the show ip ospf
sham-links command in EXEC mode:
Router1# show ip ospf sham-links
Sham Link OSPF_SL0 to address 10.2.1.2 is up
Area 1 source address 10.2.1.1
Run as demand circuit
DoNotAge LSA allowed. Cost of using 40 State POINT_TO_POINT,
Cisco IOS Release 12.2(8)T
11
Page 12

Monitoring and Maintaining a Sham-Link
Timer intervals configured, Hello 10, Dead 40, Wait 40,
Hello due in 00:00:04
Adjacency State FULL (Hello suppressed)
Index 2/2, retransmission queue length 4, number of
retransmission 0
First 0x63311F3C(205)/0x63311FE4(59) Next
0x63311F3C(205)/0x63311FE4(59)
Last retransmission scan length is 0, maximum is 0
Last retransmission scan time is 0 msec, maximum is 0 msec
Link State retransmission due in 360 msec
Monitoring and Maintaining a Sham-Link
To monitor a sham-link, use the following show commands in EXEC mode:
Command Purpose
Router# show ip ospf sham-links
Router# show ip ospf data router
ip-address
Displays the operational status of all sham-links configured for a
router.
Displays information about how the sham-link is advertised as an
unnumbered point-to-point connection between two PE routers.
OSPF Sham-Link Support for MPLS VPN
Configuration Examples
The following example shows how to configure a sham-link between two PE routers:
Router1(config)# interface loopback 1
Router1(config-if)# ip vrf forwarding ospf
Router1(config-if)# ip address 10.2.1.1 255.255.255.255
!
Router2(config)# interface loopback 1
Router2(config-if)# ip vrf forwarding ospf
Router2(config-if)# ip address 10.2.1.2 255.255.255.255
!
Router1(config)# router ospf 100 vrf ospf
Router1(config-if)# area 1 sham-link 10.2.1.1 10.2.1.2 cost 40
!
Router2(config)# router ospf 100 vrf ospf
Router2(config-if)# area 1 sham-link 10.2.1.2 10.2.1.1 cost 40
Command Reference
This section documents new commands. All other commands used with this feature are documented in
the Cisco IOS Release 12.2 command reference publications.
• area sham-link cost
• show ip ospf sham-links
12
Cisco IOS Release 12.2(8)T
Page 13

OSPF Sham-Link Support for MPLS VPN
area sham-link cost
To configure a sham-link interface on a provider edge (PE) router in a Multiprotocol Label Switching
(MPLS) Virtual Private Network (VPN) backbone, use the area sham-link cost command in global
configuration mode. To remove the sham-link, use the no form of this command.
area area-id sham-link source-address destination-address cost number
no area area-id sham-link source-address destination-address cost number
area sham-link cost
Syntax Description
Defaults No default behavior or values.
Command Modes Global configuration
Command History
Usage Guidelines In the MPLS VPN environment, several VPN client sites can be connected in the same OSPF area. If
area-id ID number of the Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) area assigned to the
sham-link. Valid values: numeric value or valid IP address. There is no
default.
source-address IP address of the source PE router in the format: ip-address [mask].
destination-address IP address of the destination PE route in the format: ip-address [mask].
number OSPF cost to send IP packets over the sham-link interface.
Valid values are from 1 to 65535.
Release Modification
12.2(8)T This command was introduced.
these sites are connected over a backdoor link in addition to the VPN backbone, all traffic passes over
the backdoor link instead of over the VPN backbone. OSPF always selects intra-area routes over
interarea (external) routes.
To correct this default OSPF behavior in an MPLS VPN, use the area sham-link cost command to
configure a sham-link between two PEs to connect the sites through the MPLS VPN backbone. A
sham-link represents an intra-area (unnumbered point-to-point) connection between PEs. All other
routers in the area see the sham-link and use it to calculate intra-area shortest path first (SPF) routes to
the remote site.
Configurethe source and destination addresses of the sham-link as a host route mask (255.255.255.255)
on the PE routers that serve as the endpoints of the sham-link. The source and destination IP addresses
must belong to the VRF and be advertised by Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) to remote PE routers. The
sham-link endpoint addresses should not be advertised by OSPF.
Cisco IOS Release 12.2(8)T
13
Page 14

OSPF Sham-Link Support for MPLS VPN
area sham-link cost
Examples The following example shows how to configure a sham-link between two PE routers in an MPLS VPN
backbone by using the area sham-link cost command on each router:
Router1(config)# interface loopback 55
Router1(config-if)# ip vrf forwarding v1
Router1(config-if)# ip address 10.0.0.1 255.255.255.255
!
Router1(config)# router ospf 2 vrf v1
Router1(config-if)# log-adjacency-changes
Router1(config-if)# area 120 sham-link 10.0.0.1 10.44.0.1 cost 1
Router1(config-if)# redistribute bgp 1 subnets
Router1(config-if)# network 10.2.0.1 255.255.255.255 area 1
Router1(config-if)# network 10.120.0.0 0.255.255.255 area 120
Router1(config-if)# network 10.140.0.0 0.255.255.255 area 120
!
Router2(config)# interface loopback 44
Router2(config-if)# ip vrf forwarding v1
Router2(config-if)# ip address 44.0.0.1 255.255.255.255
!
Router2(config)# router ospf 2 vrf v1
Router2(config-if)# log-adjacency-changes
Router2(config-if)# area 120 sham-link 10.44.0.1 10.0.0.1 cost 1
Router2(config-if)# redistribute bgp 1 subnets
Router2(config-if)# network 10.2.0.1 255.255.255.255 area 1
Router2(config-if)# network 10.120.0.0 0.255.255.255 area 120
Router2(config-if)# network 10.140.0.0 0.255.255.255 area 120
!
14
Cisco IOS Release 12.2(8)T
Page 15

OSPF Sham-Link Support for MPLS VPN
show ip ospf sham-links
To display information about all sham-links configured for a provider edge (PE) router in the Virtual
Private Network (VPN) backbone, use the show ip ospf sham-links command in EXEC mode.
show ip ospf sham-links
Syntax Description This command has no arguments or keywords.
Defaults No default behavior or values.
Command Modes EXEC
show ip ospf sham-links
Command History
Release Modification
12.2(8)T This command was introduced.
Usage Guidelines Use this command to display Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) information about the sham-links
configured on a PE router.
Examples The following example shows sample output from the show ip ospf sham-links command for a PE
router in the VPN backbone:
Router1# show ip ospf sham-links
Sham Link OSPF_SL0 to address 10.44.0.1 is up
Area 120 source address 10.0.0.1
Run as demand circuit
DoNotAge LSA allowed., Cost of using 1
Transmit Delay is 1 sec, State POINT_TO_POINT,
Timer intervals configured, Hello 10, Dead 40, Wait 40, Retransmit 5
Hello due in 00:00:09
Adjacency State FULL (Hello suppressed)
Index 2/2, retransmission queue length 0, number of retransmission 27
First 0x0(0)/0x0(0) Next 0x0(0)/0x0(0)
Last retransmission scan length is 0, maximum is 2
Last retransmission scan time is 0 msec, maximum is 0 msec
Cisco IOS Release 12.2(8)T
15
Page 16

Glossary
Glossary
OSPF Sham-Link Support for MPLS VPN
BGP—Border Gateway Protocol. Interdomain routing protocol that exchanges reachability information
with other BGP systems. It is defined in RFC 1163.
CE router—customer edge router. A router that is part of a customer network and that interfaces to a
provider edge (PE) router. CE routers are not aware of associated VPNs.
CEF—Cisco Express Forwarding. An advanced Layer 3 IP switching technology. CEF optimizes
network performance and scalability for networks with large and dynamic traffic patterns.
OSPF—Open Shortest Path First protocol.
IGP—Interior Gateway Protocol. An Internet protocol used to exchange routing information within an
autonomous system. Examples of common IGPs include IGRP, OSPF, and RIP.
LSA—link-state advertisement. A broadcast packet used by link-state protocols. The LSA contains
information about neighbors and path costs and is used by the receiving router to maintain a routing
table.
MPLS—Multiprotocol Label Switching. Emerging industry standard upon which tag switching is
based.
PE router—provider edge router. A router that is part of a service provider network connected to a
customer edge (CE) router. All VPN processing occurs in the PE router.
SPF—shortest path first calculation.
VPN—Virtual Private Network. A secure IP-based network that shares resources on one or more
physical networks. A VPN contains geographically dispersed sites that can communicate securely over
a shared backbone.
VRF—VPN routing and forwarding instance. A VRF consists of an IP routing table, a derived
forwarding table, a set of interfaces that use the forwarding table, and a set of rules and routing protocols
that determine what goes into the forwarding table. In general, a VRF includes the routing information
that defines a customer VPN site that is attached to a PE router.
16
Cisco IOS Release 12.2(8)T
 Loading...
Loading...