Page 1

Level Two Technical Support for BBSM
Document ID: 15942
Introduction
Prerequisites
Requirements
Components Used
Conventions
Software Requirements
Software Application Description
BBSM End User Supported Ethernet Network Interface Cards
Troubleshooting
BBSM Users are Unable to Send or Receive E−Mail
IIS Proxy LAT Setup (BBSM 5.0 only)
PMS Does Not Post Charges
End Users Redirected to RadiusClearFail.asp
Regroom Problems
RME 19+7 − "Sorry, a network error has occurred" Error Message
Switches Are Unresponsive
URL Error Page
NetPro Discussion Forums − Featured Conversations
Related Information
Introduction
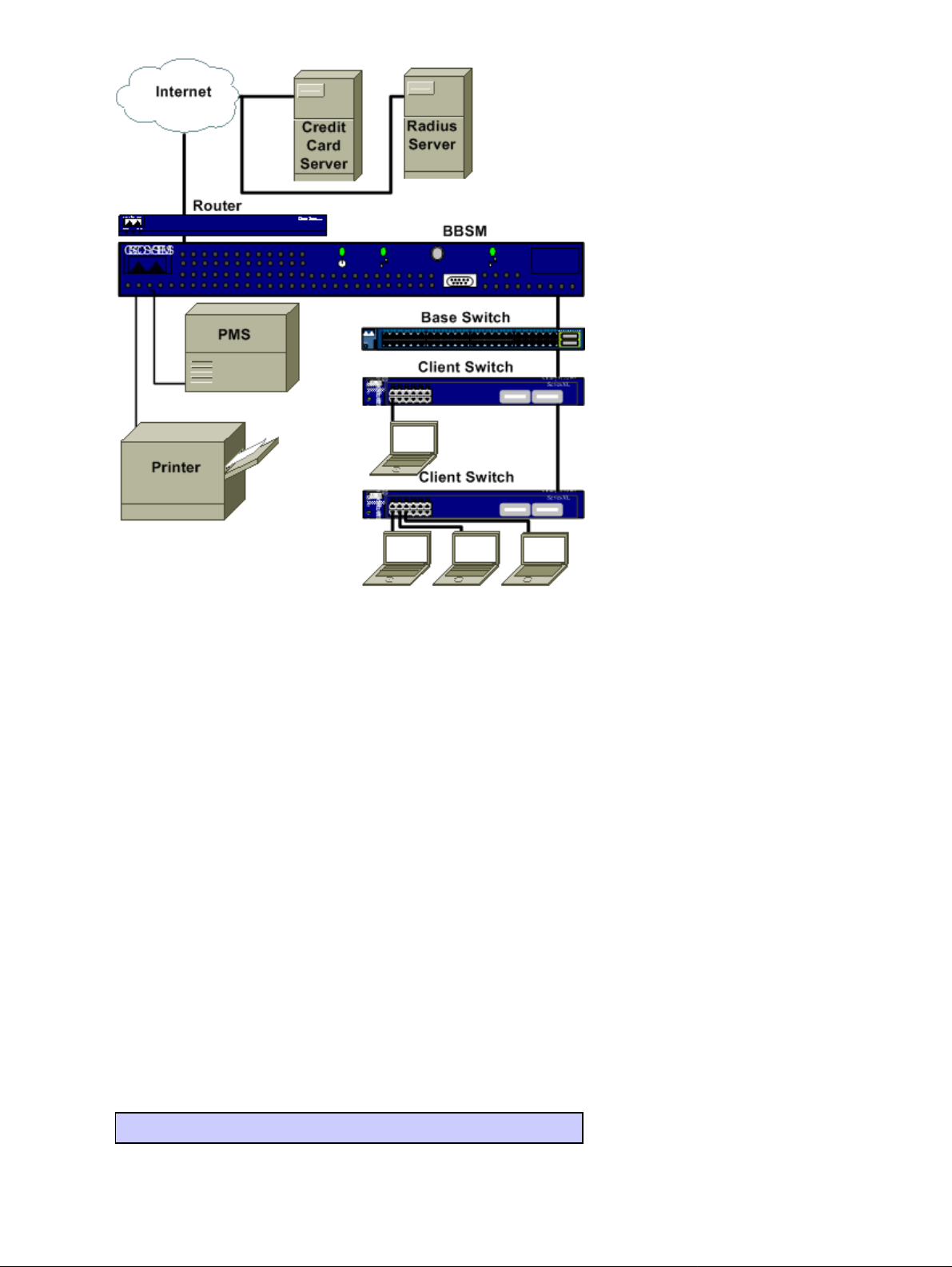
The Cisco Building Broadband Service Manager (BBSM) is a subscriber management software package for a
public local−area network (LAN) server that provides "an Internet Service Provider (ISP) in a box". For end
users in the network, Cisco BBSM provisions, tracks, and provides billing support for access to the Internet.
The BBSM software is provided on a server.
BBSM consists of a dedicated server, usually located at this site, as well as switches, routers, and cables to
connect each end user port to the server. The end user connects to the server when the user connects to an end
user port.
When a Web browser such as Internet Explorer or Netscape Communicator is opened, the browser
automatically searches for Internet access. The browser finds the BBSM Welcome page, which indicates a
connection to the BBSM server but not to the Internet.
At this point, the BBSM software has already identified the Media Access Control (MAC) address of the end
user's computer, queried all switches on the network in order to determine the location of the end user, and
assigned a temporary IP address to the end user's location. After you press the Connect button, the BBSM
software designates the end user port as active. If relevant, billing information is processed for that end port.
The end user now has a connection to the Internet.
This figure shows a typical BBSM configuration.
Cisco − Level Two Technical Support for BBSM
Page 2
Prerequisites
Requirements
There are no specific requirements for this document.
Components Used
This document is not restricted to specific software and hardware versions.
The information in this document was created from the devices in a specific lab environment. All of the
devices used in this document started with a cleared (default) configuration. If your network is live, make sure
that you understand the potential impact of any command.
Conventions
Refer to Cisco Technical Tips Conventions for more information on document conventions.
Software Requirements
Before you troubleshoot, verify that user equipment meets the basic requirements for BBSM:
BBSM Compatible Client Operating Systems/Versions
Cisco − Level Two Technical Support for BBSM
Page 3
Microsoft
Windows Me
Apple
Macintosh OS 9, X
Windows CE
Windows NT 4.0 Workstation
Windows NT 4.0 Server
Windows NT 4.0 Enterprise
Server
Windows 2000 Professional
Windows 2000 Server
Windows 2000 Advanced Server
Note: The configuration of advanced services such as Domain Name System (DNS), Interim−Interswitch
Signaling (IIS), and Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) on a server product can cause conflicts
that result in connection problems.
BBSM 5.0 Server Software
Linux
Red Hat Linux 6.1 − 7.1
Open BSD
Turbo Linux
Solaris
Versions 7 and 8
BEOS
BEOS Version 4.5 or higher
Windows 2000 Server CD•
Cisco BBSM 5.0 CD•
Microsoft Proxy Server 2.0 CD•
BBSM 5.1 Server Software
Windows 2000 Server CD•
Cisco BBSM 5.1 CD•
Microsoft Industry−Standard Architecture (ISA) Server•
Software Application Description
Software Applications
Provides plug and play (bridged network)•
AtNat
MSDE MSDE is the database used in order to store
necessary informtion for BBSM.
Redirects clients before authentication•
Provides Network Address Translation
•
(NAT) for static clients
Emulates Web proxy•
BBSM
Access
Cisco − Level Two Technical Support for BBSM
Allows billing methods and access policies
Page 4
Policy
IIS
Proxy 2.0
ISA Server
MSMQ
AtDial
Athdmn Sends billing information to the Property
DHCP
Server Provides non−static clients with IP addresses and
DNS Server
Release
Number
Provides Web services
Proxy support for BBSM 5.0
Proxy support for BBSM 5.1
Provides data transport between IIS and MSDE
Core Service of BBSM software
Management System (PMS) server
related information
Transcribes a fully−qualified domain name to an
IP address; for example, www.cisco.com
to198.133.219.25
X.Y designates the release numbers as such:
X indicates a core code change.•
Y indicates a new release or update to the
•
existing code.
Example 1:
BBSM 5.0 (Cisco Systems, Inc.
•
Windows 2000 version)
BBSM 4.5 (Cisco Systems, Inc.
•
Windows NT 4.0 version)
BBSM End User Supported Ethernet Network Interface Cards
All cards are standard Ethernet cards running at 10 Mbps or 10/100 Mbps. Apple uses a Farallon or IBM
network card that is built into the device.
BBSM supports Internet Explorer 4.0 and later and Netscape Communicator 4.0 and later as the client Web
browser.
BBSM Supported Ethernet and Wireless Network Cards
BBSM Supported Ethernet
Cards 10 Mbps or 10/100
Mbps
3COM
Farallon
Intel
Linksys
Megahertz
BBSM Supported Wireless
Cards IEEE 802.11b WiFi
Compliant
Cisco Aironet 340 or 350
3COM AirConnect
Apple AirPort
Breeze COM DS.11
Intel 2011
Cisco − Level Two Technical Support for BBSM
Page 5
Netgear
US Robotics ORiNOCO or Lucent or
Xircom
Linksys WPC11
Wavelan
Troubleshooting
This section lists the most common error messages and support steps to help resolve each. Error messages are
arranged alphabetically by topic.
For more details on BBSM and WEBConfig, consult the Cisco Building Broadband Service Manager
Software Configuration Guide (78−12742−01). For the most up−to−date information and caveats on BBSM,
consult the Cisco Building Broadband Service Manager 5.x Release Notes (OL−1044−01) available at
www.cisco.com under Aggregation Solutions in the Documentation area.
BBSM Users are Unable to Send or Receive E−Mail
Symptoms
Cause 1
Resolution1If the BBSM network provider has set up an
Users cannot send or receive e−mail with their
normal ISP account while connected to the BBSM
service. Users can either receive e−mail or not.
The user's ISP does not accept e−mail from
unrecognized sources or IP addresses. This does
not allow the the user's e−mail server to be used as
a SPAM gateway. Normally, the user's computer
receives its IP address from the ISP itself, so this
address is recognized as a valid source address.
When the user logs on to the BBSM network, the
user's computer receives its IP address from the
BBSM server. Therefore, the ISP sees this address
as foreign. When the user tries to send an e−mail
to this server, the server ignores the e−mail since
the server does not recognize the source IP address
as an address on its own network.
Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP) server in
order to resolve this problem, the IP address of that
server can be configured within BBSM. BBSM
then intercepts all SMTP packets and forwards the
packets to the IP address. This solution precludes
the need for users to reconfigure their e−mail
program. Set the SMTP forwarding address as
such:
From the desktop, navigate to BBSM
1.
Dashboard > WEBconfig > Server. You
can also access this from: http://<BBSM
IP:9488>/WEBconfig/server.asp
Enter the IP address of the SMTP server
2.
in the SMTP Forwarding IP Address
Cisco − Level Two Technical Support for BBSM
Page 6

field.
Click Update.3.
Cause 2 The user normally connects to the Internet through
their corporate network, which is behind a firewall.
Resolution2In this instance, users must tunnel into their
corporate network in order to receive e−mail. See
Resolution 1 in order to only allow the users to
send mail.
IIS Proxy LAT Setup (BBSM 5.0 only)
Proxy Local Address Tables (LAT) add routes to the RRAS tables. These LAT table settings are needed for
proper BBSM operation.
Clients are only able to connect with the
•
Proxy Server.
Clients are able to ping the external
•
Network Interface Card (NIC), but not the
Symptoms
internal NIC.
Clients are unable to access the Report
•
pages from the internal NIC, but can reach
the pages from the external NIC.
The client gets a Page cannot be
•
displayed error message with no proxy
setup in the browser.
Cause The LAT tables in IIS under Web Proxy are not set
up correctly.
Resolution
Click Start > Programs > Microsoft
1.
Proxy Server > Microsoft Management
Console.
In the left window, click + , the plus sign,
2.
next to BBSM.
Right−click Web Proxy and choose
3.
Properties.
With the Service tab selected, click the
4.
Local Address Table button.
Click the Construct Table button.5.
Uncheck the Add the private ranges box.6.
Make sure Load from NT Internal
7.
Routing Table and Load known address
ranges from all IP Interface cards are
both selected.
Click OK.8.
Click OK again in order to confirm
9.
changes to the LAT tables.
Make sure the ranges now include:
10.
Internal network IP addresses External
Cisco − Level Two Technical Support for BBSM
Page 7

network IP addresses.
Click OK in order to accept the new
11.
ranges.
Click Apply.12.
Click OK in order to close the LAT table.13.
Close the IIS Manager.14.
Note: If you are prompted to save console settings, select
No.
PMS Does Not Post Charges
Symptoms Billing is not posted to the Property Management
Systme (PMS).
Cause 1 The Athdmn service is not started. This service
must be set to start automatically.
In order to start the Athdmn service, click
1.
Resolution
1
Start > Settings > Control Panel >
Administrative Tools.
Double−click on Services.2.
Highlight athdmn.3.
Right−click and select Start.4.
Ideally, charges now start to post.5.
Cause 2
Resolution
2
Cause 3
Resolution
3
Cause 4
BBSM is not set up for PMS billing.
Go to WEBConfig > Sites page and place
1.
a check in the PMS Billing check box.
Choose the PMS protocol the hotel uses
2.
from the drop−down box.
Click Update.3.
The PMS is not connected to the BBSM server.
Verify that the BBSM server is connected
1.
to the PMS.
Verify that the correct communications
2.
(COM) port settings and PMS protocol are
used.
Open WEBConfig > WEBPMSTest and
3.
send a test charge to the PMS in order to
verify the connectivity.
Some PMSs require that a room is "checked in"
before the PMS accepts a charge for the folio. This
is most likely to occur during the final stages of an
installation.
Resolution4Have someone at the front desk temporarily check
the technician into the room. Once the PMS test is
successfully completed, the front desk can then
Cisco − Level Two Technical Support for BBSM
Page 8

"check out" the technician.
It is useful to request a print out of the BBSM
Note:
room charge for future use. The property staff can
then delete the charges to the guest folio created
by the test.
End Users Redirected to RadiusClearFail.asp
Symptoms The client gets redirected to the radiusclearfail.asp
screen over and over again.
Cause
Resolution
Remote Authentication Dial−In User Service
(RADIUS) is not correctly configured on the
BBSM server.
Verify that you can ping the RADIUS
1.
server(s) IP address from the BBSM
server.
Verify that the RADIUS server is
2.
configured with the same shared secret or
password as the WEBConfig RADIUS
server page.
Verify that the port setting on the BBSM
3.
WEBConfig > RADIUS server page is
set to the same port the RADIUS server
uses. The default RADIUS port is1645.
Verify that the RADIUS server is
4.
configured to accept RADIUS requests
from this site.
Verify that the user account is set up and is
5.
active on the RADIUS server.
Verify that the BBSM server uses the
6.
correct page set for the MDU/RADIUS
configuration.
Regroom Problems
Symptoms Immediately after a site regroom, the BBSM
network no longer functions correctly.
A regroom occurs when all IP addresses are
changed on a site. It is possible for this to occur
Cause
Resolution Verify the WEBConfig information and change
Cisco − Level Two Technical Support for BBSM
because the ISP has changed or more IP addresses
are needed. Therefore the ISP sent a new IP
scheme. If a regroom is performed incorrectly or
incompletely, problems occur.
this information if necessary:
Page 9

Open the BBSM Dashboard >
1.
WEBConfig.
Change all the address information on the
2.
relevant tabs for the DHCP scope and
switches.
Apply the changes, and then close the
3.
WEBConfig page.
Verify the DNS server address and change
4.
this information if necessary.
Note: See the URL Error Page Resolution
1 instructions, in this document.
Verify the Proxy Server LAT settings and
5.
change this information if necessary.
Note: See the IIS Proxy LAT Tables Setup
procedure in this document.
RME 19+7 − "Sorry, a network error has occurred" Error Message
Symptoms The user is unable to access the BBSM start page and receives
the RME 19+7 error message.
Cause 1
Resolution
1
Note: The port map could need to be updated if any changes were
Cause 2
The user attempts to connect to BBSM through an unsupported
switch or though a switch that has not been set up within
BBSM.
Verify that all switches on site are on the supported
1.
hardware list and are correctly set up in BBSM.
From the desktop, navigate to the BBSM Dashboard >
2.
WEBConfig > Switches.
You can also access this from http://<BBSM IP
Address:9488>WEBConfig/switches.asp.
Ping the IP address of all switches in order to verify
3.
connectivity.
Verify the correct configuration of the switches with
4.
Telnet.
Correct any information and add any necessary switch
5.
information to the WEBConfig pages.
Continue with Cause 2.6.
made to the switch information.
A previously generated port map has been corrupted. One or
more switches were added to this site, and the port map was not
updated or a port map was never generated for this site.
Resolution2Update or generate the port map with these instructions:
From the desktop, navigate to BBSM Dashboard >
1.
WEBConfig > Switches.
Cisco − Level Two Technical Support for BBSM
Page 10

Note:
You can also access this from
http://<BBSM_IP_Address:9488>/WEBConfig/switches.asp.
Disable any switches that do not need the port map
2.
updated.
Use the navigation buttons at the bottom of the port
3.
map page in order to scroll to the affected site.
Disable Clear Existing Port Map.4.
Click on the Port Map link at the top of the
5.
WEBConfig page.
Verify that all other data is correct based on the
6.
property settings.
Click Generate.7.
Re−enable all switches that were disabled in Step 2.8.
Attempt to connect a client in order to see whether the
9.
problem is resolved.
If the BBSM server is part of a Building Broadband Service
Director (BBSD) network, the port map can be restored if no
changes have occurred on site since the last valid backup was
performed. See the BBSD documentation on how to perform
this restoration.
Caution:
Cause 3 The SNMP read−write community string on the switch does not
Resolution
3 Change the SNMP read−write community string to match both
Cause 4
Resolution
4
Note:
If existing switches are not temporarily disabled durind a port
map update, the existing port map is erased and the entire
property has to be remapped.
match the BBSM server.
the server and the switch. Refer to the for more information.
A previously configured switch has lost its configuration.
Reconfigure the switch with the correct IP parameters. These
parameters can be obtained from an up−to−date copy of the
network diagram.
An on−site technician must perform this step.
Switches Are Unresponsive
One of these symptoms occurs:
Users are unable to receive a DHCP
•
Symptoms
address.
Support personnel cannot ping or telnet to
•
a switch.
All switches located downstream of a
•
common base switch are unreachable.
Cause All of these symptoms indicate that a network
switch was disconnected. The problem could be a
bad Ethernet cable, an unplugged Ethernet or
power cable, or the switch itself could
Cisco − Level Two Technical Support for BBSM
Page 11
malfunction. If a switch is merely mis−configured,
traffic still passes through. Thus, the client
receives a DHCP address, and switches located
downstream of the suspected switch are reachable
by support personnel.
Resolution Determine the most likely location of the failure
with utilities such as ping and Telnet as well as the
network diagram. Use this procedure:
Determine which switches do not respond
1.
to the ping utility.
Telnet into a visible switch, if available,
2.
and try to ping the non−responsive
switches again.
If the property has an IT staff willing to
3.
help:
Have the IT staff check the
a.
unresponsive switch(es) in order
to ensure that all power and
Ethernet cables are plugged
snuggly into their respective
sockets.
Ensure all applicable link lights on
b.
the switch are lit and note lights
that are not lit.
A link light that must be lit, but is
not, can indicate the presence of
the wrong type of cable.
Unplug the power cable in order to
c.
power cycle the switch. Wait five
to ten seconds, and plug the power
cable back into the switch.
Unplug the uplink cable from the
d.
suspected switch. Plug this uplink
cable into a laptop configured for
DHCP and try to get an IP
address.
If you cannot get an IP address,
the problem is most likely
upstream. If you can get an IP
address, the problem is most likely
downstream.
Configure the laptop with the IP
e.
address of the BBSM internal NIC
and plug it into the uplink port of
the suspected switch. Try to ping
the switch.
Cisco − Level Two Technical Support for BBSM
Page 12

Note 1:
Note: If the property does not
have an IT staff, or is unable or
unwilling to assist, a technician
must be sent to the property in
order to perform these tests.
If the problem with a switch or switches
4.
cannot be resolved, replace the switch(es).
Switch−to−switch and router−to−computer
connections require a crossover cable.
Switch−to−computer connections require a
straight−through cable.
Caution:
Note 2:
This diagram represents Straight−Through Cable Wiring:
If you replace switches or move cables, return the
same cables to the exact same port. If you do not,
the port map is invalidated.
The resolution to this problem could require a
technician on site to perform troubleshooting.
Check the network diagram in order to determine
which, if any, switches are downstream of the
suspected switch.
It is possible that the network diagram does not
reflect recent changes.
This diagram represents Crossover Cable Wiring:
Cisco − Level Two Technical Support for BBSM
Page 13

URL Error Page
Symptoms The user receives the you are connected
but... error message.
Cause 1 The DNS server is not set to obtain DNS
information from the Internet.
Enter the IP address of the ISP's DNS server:
Select Start > Programs >
1.
Administrative Tools > DNS.
Resolution
1
Cause 2 The DNS Service has cached bad information or
is not started.
Right−click on BBSM and select
2.
Properties.
Select the Forwarders tab.3.
Enter the IP address of the ISP's DNS
4.
server in the IP address box and click
Add.
Click OK.5.
Close the DNS window.6.
In order to restart the DNS Server:
Resolution
2
Cause 3 The Internet could be slow or the site could be
unresponsive.
Resolution Have the user try again later or try another site on
Cisco − Level Two Technical Support for BBSM
Select Start > Programs >
1.
Administrative Tools > Services.
Right−click on DNS Server.2.
Select Start or Restart.3.
Page 14
3 the Internet.
Cause 4 The Internet connection (T−1 or T−3) from the
ISP to the site could be down.
Resolution
4
Submit a trouble call with the ISP.
NetPro Discussion Forums − Featured Conversations
Networking Professionals Connection is a forum for networking professionals to share questions, suggestions,
and information about networking solutions, products, and technologies. The featured links are some of the
most recent conversations available in this technology.
NetPro Discussion Forums − Featured Conversations for Network Management
Network Infrastructure: Network Management
Virtual Private Networks: Network and Policy Management
Related Information
BBSM Glossary•
BBSM Technical Tips•
Technical Support & Documentation − Cisco Systems•
All contents are Copyright © 2006−2007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Important Notices and Privacy Statement.
Updated: Jul 13, 2007 Document ID: 15942
Cisco − Level Two Technical Support for BBSM
 Loading...
Loading...