Page 1
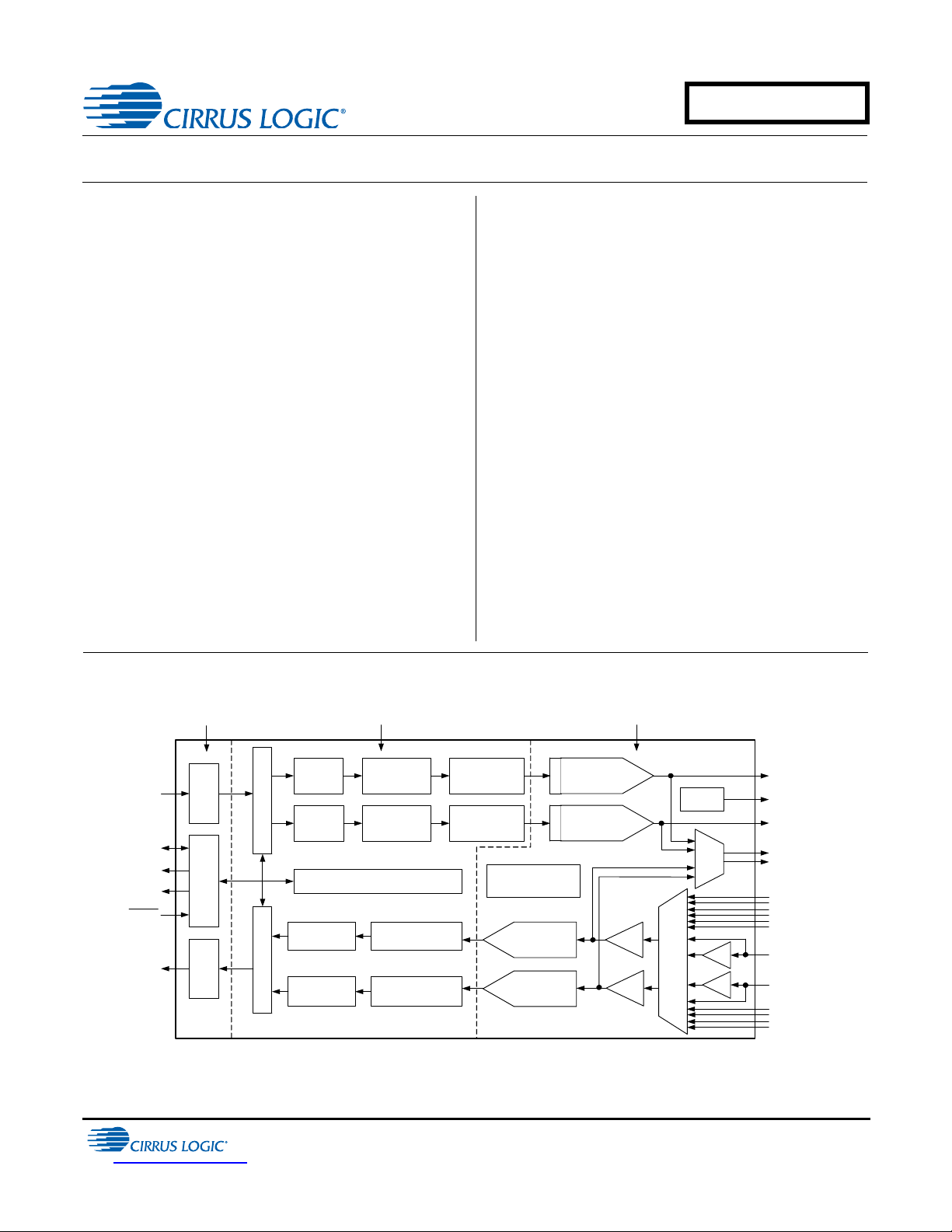
1.8 V to 5 V
Multibit
Modulator
Multibit
Modulator
Low-Latency
Anti-Alias Filter
Internal Voltage
Reference
Interpolation
Filter
Interpolation
Filter
Left DAC Output
Right DAC Output
Switched Capacito r
DAC and Filter
Multibit
Oversampling
ADC
Multibit
Oversampling
ADC
Low-Latency
Anti-Alias Filter
High Pass
Filter
High Pass
Filter
Stereo Input 1
Serial
Audio
Input
Serial
Audio
Output
3.3 V to 5 V 3.3 V to 5 V
Switched Capacito r
DAC and Filter
MUX
PGA
MUX
Volume
Control
Volume
Control
PCM Serial InterfacePCM Serial Interface
Mute
Control
Register Configuration
Level
Translator
Level Translator
Level
Translator
Reset
I2C/SPI
Control Data
Mute Control
Left Aux Output
Right Aux Output
Stereo Input 2
Stereo Input 3
Stereo Input 4 /
Mic Input 1 & 2
Stereo Input 5
Stereo Input 6
PGA
+32 dB
+32 dB
Interrupt
ADC Overflow
CS4245
104 dB, 24-Bit, 192 kHz Stereo Audio CODEC
D/A Features
Multi-bit Delta Sigma Modulator
104 dB Dynamic Range
-90 dB THD+N
Up to 192 kHz Sampling Rates
Single-Ended Analog Architecture
Volume Control with Soft Ramp
– 0.5 dB Step Size
– Zero Crossing, Click-Free Transitions
Popguard
– Minimizes the Effects of Output Transients
Filtered Line-Level Outputs
Selectable Serial Audio Interface Formats
– Left-Justified up to 24-bit
– I²S up to 24-bit
– Right-Justified 16-, 18-, 20-, and 24-bit
Selectable 50/15 µs De-Emphasis
Control Output for External Muting
®
Technology
A/D Features
Multi-bit Delta Sigma Modulator
104 dB Dynamic Range
-95 dB THD+N
Stereo 6:1 Input Multiplexer
Programmable Gain Amplifier (PGA)
– ± 12 dB Gain, 0.5 dB Step Size
– Zero Crossing, Click-Free Transitions
Stereo Microphone Inputs
– +32 dB Gain Stage
– Low-Noise Bias Supply
Up to 192 kHz Sampling Rates
Selectable Serial Audio Interface Formats
– Left-Justified up to 24-bit
– I²S up to 24-bit
High-Pass Filter or DC Offset Calibration
http://www.cirrus.com
Copyright Cirrus Logic, Inc. 2012
(All Rights Reserved)
AUG '12
DS656F3
Page 2

CS4245
System Features
Direct Interface with 1.8 V to 5 V Logic Levels
Optional Asynchronous Serial Port Operation
– Each Serial Port Supports Master or Slave
Operation
Selectable Auxiliary Analog Output
– Allows Analog Monitoring of Either the ADC
Input Signal after PGA or DAC Output
Signal
Internal Digital Loopback
Power-Down Mode
– Available for A/D, D/A, CODEC, Mic
Preamplifier
+3.3 V to +5 V Analog Power Supply
+3.3 V to +5 V Digital Power Supply
Supports I²C
Interfaces
Pin-Compatible with CS5345
®
and SPITM Control Port
General Description
The CS4245 is a h ighly integrated stereo audio
CODEC. The CS4245 performs stereo analog-to-digital
(A/D) and digital-to-analog (D/A) conversion of up to
24-bit serial values at sample rates up to 192 kHz.
A 6:1 stereo input multiplexer is included for s electing
between line-level or microphone-level inputs. The microphone input path includes a +32 dB gain stage and
a low-noise bias voltage supply. The PGA is available
for line or microphone inputs and provides gain/attenuation of 12 dB in 0.5 dB steps.
The output of the PGA is followed by an advanced 5thorder, multi-bit delta sigma modulator and digital filtering/decimation. Sampled data is transmitted by the
serial audio interface at rates from 4 kHz to 192 kHz in
either Slave or Master Mode.
The D/A converter is based on a 4th-order multi-bit delta
sigma modulator with an ultra-linear low-pass filter and
offers a volume control that operates with a 0.5 dB step
size. It in corporates selectable soft ramp and zero
crossing transition functions to eliminate clicks and
pops.
Standard 50/15 s de-emphasis is availa ble for a
44.1 kHz sample rate for compatibility with digital audio
programs mastered using the 50 /15 s pre-emphasis
technique.
Integrated level translators allow easy interfacing between the CS4245 and other devices operating over a
wide range of logic levels.
The CS4245 is available in a 48-pin LQFP package in
both Commercial (-10° to +70° C) and Automotive (-40°
to +105° C) grade. The CDB4245 Customer Demonstration board is also available for device evaluation and
implementation suggestions. Please see “Ordering In-
formation” on page 58 for complete details.
2 DS656F3
Page 3

TABLE OF CONTENTS
1. PIN DESCRIPTIONS ........................................................................................................................ 7
2. CHARACTERISTICS AND SPECIFICATIONS ...................................................................................... 9
SPECIFIED OPERATING CONDITIONS ............................................................................................. 9
ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS .......................................................................................................9
DAC ANALOG CHARACTERISTICS ................................................................................................. 10
DAC COMBINED INTERPOLATION & ON-CHIP ANALOG FILTER RESPONSE ............................ 11
ADC ANALOG CHARACTERISTICS ................................................................................................. 13
ADC ANALOG CHARACTERISTICS ................................................................................................. 15
ADC DIGITAL FILTER CHARACTERISTICS ..................................................................................... 16
AUXILIARY OUTPUT ANALOG CHARACTERISTICS ...................................................................... 17
AUXILIARY OUTPUT ANALOG CHARACTERISTICS ...................................................................... 18
AUXILIARY OUTPUT ANALOG CHARACTERISTICS ...................................................................... 19
DC ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS ............................................................................................. 20
DIGITAL INTERFACE CHARACTERISTICS ...................................................................................... 21
SWITCHING CHARACTERISTICS - SERIAL AUDIO PORT 1 .......................................................... 22
SWITCHING CHARACTERISTICS - SERIAL AUDIO PORT 2 .......................................................... 24
SWITCHING CHARACTERISTICS - CONTROL PORT - I²C FORMAT ............................................ 27
SWITCHING CHARACTERISTICS - CONTROL PORT - SPI FORMAT ........................................... 28
3. TYPICAL CONNECTION DIAGRAM ................................................................................................... 29
4. APPLICATIONS ................................................................................................................................... 30
4.1 Recommended Power-Up Sequence ............................................................................................. 30
4.2 System Clocking ............................................................................................................................. 30
4.2.1 Synchronous / Asynchronous Mode ...................................................................................... 30
4.2.2 Master Clock ......................................................................................................................... 30
4.2.3 Master Mode ......................................................................................................................... 32
4.2.4 Slave Mode ........................................................................................................................... 32
4.3 High-Pass Filter and DC Offset Calibration .................................................................................... 32
4.4 Analog Input Multiplexer, PGA, and Mic Gain ................................................................................34
4.5 Input Connections ........................................................................................................................... 34
4.6 Output Connections ........................................................................................................................ 34
4.7 Output Transient Control ................................................................................................................ 35
4.7.1 Power-Up .............................................................................................................................. 35
4.7.2 Power-Down .......................................................................................................................... 35
4.7.3 Serial Interface Clock Changes ............................................................................................. 35
4.8 Auxiliary Analog Output .................................................................................................................. 35
4.9 De-Emphasis Filter ......................................................................................................................... 35
4.10 Internal Digital Loopback .............................................................................................................. 36
4.11 Mute Control ................................................................................................................................. 36
4.12 Control Port Description and Timing ............................................................................................. 37
4.12.1 SPI Mode ............................................................................................................................. 37
4.12.2 I²C Mode .............................................................................................................................. 38
4.13 Interrupts and Overflow ................................................................................................................ 39
4.14 Reset ............................................................................................................................................ 40
4.15 Synchronization of Multiple Devices ............................................................................................. 40
4.16 Grounding and Power Supply Decoupling .................................................................................... 40
5. REGISTER QUICK REFERENCE ........................................................................................................ 41
6. REGISTER DESCRIPTION .................................................................................................................. 42
6.1 Chip ID - Register 01h .................................................................................................................... 42
6.2 Power Control - Address 02h ......................................................................................................... 42
6.2.1 Freeze (Bit 7) ......................................................................................................................... 42
6.2.2 Power-Down MIC (Bit 3) ........................................................................................................ 42
6.2.3 Power-Down ADC (Bit 2) .............................
CS4245
.......................................................................... 42
DS656F3 3
Page 4

CS4245
6.2.4 Power-Down DAC (Bit 1) ....................................................................................................... 43
6.2.5 Power-Down Device (Bit 0) ................................................................................................... 43
6.3 DAC Control - Address 03h ............................................................................................................ 43
6.3.1 DAC Functional Mode (Bits 7:6) ............................................................................................ 43
6.3.2 DAC Digital Interface Format (Bits 5:4) ................................................................................. 43
6.3.3 Mute DAC (Bit 2) ................................................................................................................... 43
6.3.4 De-Emphasis Control (Bit 1) .................................................................................................. 44
6.3.5 DAC Master / Slave Mode (Bit 0) ..........................................................................................44
6.4 ADC Control - Address 04h ............................................................................................................ 44
6.4.1 ADC Functional Mode (Bits 7:6) ............................................................................................ 44
6.4.2 ADC Digital Interface Format (Bit 4) ...................................................................................... 45
6.4.3 Mute ADC (Bit 2) ................................................................................................................... 45
6.4.4 ADC High-Pass Filter Freeze (Bit 1) ..................................................................................... 45
6.4.5 ADC Master / Slave Mode (Bit 0) ..........................................................................................45
6.5 MCLK Frequency - Address 05h .................................................................................................... 45
6.5.1 Master Clock 1 Frequency (Bits 6:4) ..................................................................................... 45
6.5.2 Master Clock 2 Frequency (Bits 2:0) ..................................................................................... 46
6.6 Signal Selection - Address 06h ...................................................................................................... 46
6.6.1 Auxiliary Output Source Select (Bits 6:5) .............................................................................. 46
6.6.2 Digital Loopback (Bit 1) ......................................................................................................... 46
6.6.3 Asynchronous Mode (Bit 0) ................................................................................................... 46
6.7 Channel B PGA Control - Address 07h .......................................................................................... 47
6.7.1 Channel B PGA Gain (Bits 5:0) ............................................................................................. 47
6.8 Channel A PGA Control - Address 08h .......................................................................................... 47
6.8.1 Channel A PGA Gain (Bits 5:0) ............................................................................................. 47
6.9 ADC Input Control - Address 09h ................................................................................................... 47
6.9.1 PGA Soft Ramp or Zero Cross Enable (Bits 4:3) .................................................................. 47
6.9.2 Analog Input Selection (Bits 2:0) ........................................................................................... 48
6.10 DAC Channel A Volume Control - Address 0Ah ........................................................................... 48
6.11 DAC Channel B Volume Control - Address 0Bh ........................................................................... 48
6.11.1 Volume Control (Bits 7:0) .................................................................................................... 48
6.12 DAC Control 2 - Address 0Ch ...................................................................................................... 49
6.12.1 DAC Soft Ramp or Zero Cross Enable (Bits 7:6) ................................................................ 49
6.12.2 Invert DAC Output (Bit 5) .................................................................................................... 49
6.12.3 Active High/Low (Bit 0) ........................................................................................................ 50
6.13 Interrupt Status - Address 0Dh ..................................................................................................... 50
6.13.1 ADC Clock Error (Bit 3) ....................................................................................................... 50
6.13.2 DAC Clock Error (Bit 2) ....................................................................................................... 50
6.13.3 ADC Overflow (Bit 1) ........................................................................................................... 50
6.13.4 ADC Underflow (Bit 0) ......................................................................................................... 50
6.14 Interrupt Mask - Address 0Eh ....................................................................................................... 50
6.15 Interrupt Mode MSB - Address 0Fh .............................................................................................. 51
6.16 Interrupt Mode LSB - Address 10h .........................................................................................
ARAMETER DEFINITIONS ................................................................................................................ 52
7. P
8. DAC FILTER PLOTS .................................................................................................................... 53
9. ADC FILTER PLOTS ......................................................................................................................... 55
10. PACKAGE DIMENSIONS .................................................................................................................. 57
11. THERMAL CHARACTERISTICS AND SPECIFICATIONS ............................................................. 57
12. ORDERING INFORMATION ..................................................................................................... 58
13. REVISION HISTORY .......................................................................................................................... 58
...... 51
4 DS656F3
Page 5

LIST OF FIGURES
Figure 1.DAC Output Test Load ................................................................................................................ 12
Figure 2.Maximum DAC Loading .............................................................................................................. 12
Figure 3.Master Mode Timing - Serial Audio Port 1 .................................................................................. 23
Figure 4.Slave Mode Timing - Serial Audio Port 1 .................................................................................... 23
Figure 5.Master Mode Timing - Serial Audio Port 2 .................................................................................. 25
Figure 6.Slave Mode Timing - Serial Audio Port 2 .................................................................................... 25
Figure 7.Format 0, Left-Justified up to 24-Bit Data ................................................................................... 26
Figure 8.Format 1, I²S up to 24-Bit Data ................................................................................................... 26
Figure 9.Format 2, Right-Justified 16-Bit Data.
Format 3, Right-Justified 24-Bit Data. ....................................................................................................... 26
Figure 10.Control Port Timing - I²C Format ............................................................................................... 27
Figure 11.Control Port Timing - SPI Format .............................................................................................. 28
Figure 12.Typical Connection Diagram ..................................................................................................... 29
Figure 13.Master Mode Clocking .............................................................................................................. 32
Figure 14.Analog Input Architecture .......................................................................................................... 34
Figure 15.De-Emphasis Curve .................................................................................................................. 36
Figure 16.Suggested Active-Low Mute Circuit .......................................................................................... 37
Figure 17.Control Port Timing in SPI Mode .............................................................................................. 38
Figure 18.Control Port Timing, I²C Write ................................................................................................... 38
Figure 19.Control Port Timing, I²C Read ................................................................................................... 39
Figure 20.De-Emphasis Curve .................................................................................................................. 44
Figure 21.DAC Single-Speed Stopband Rejection ................................................................................... 53
Figure 22.DAC Single-Speed Transition Band .......................................................................................... 53
Figure 23.DAC Single-Speed Transition Band .......................................................................................... 53
Figure 24.DAC Single-Speed Passband Ripple ........................................................................................ 53
Figure 25.DAC Double-Speed Stopband Rejection ..................................................................................53
Figure 26.DAC Double-Speed Transition Band ........................................................................................ 53
Figure 27.DAC Double-Speed Transition Band ........................................................................................ 54
Figure 28.DAC Double-Speed Passband Ripple ...................................................................................... 54
Figure 29.DAC Quad-Speed Stopband Rejection ..................................................................................... 54
Figure 30.DAC Quad-Speed Transition Band ........................................................................................... 54
Figure 31.DAC Quad-Speed Transition Band ........................................................................................... 54
Figure 32.DAC Quad-Speed Passband Ripple ......................................................................................... 54
Figure 33.ADC Single-Speed Stopband Rejection ................................................................................... 55
Figure 34.ADC Single-Speed Stopband Rejection ................................................................................... 55
Figure 35.ADC Single-Speed Transition Band (Detail) ............................................................................. 55
Figure 36.ADC Single-Speed Passband Ripple ........................................................................................ 55
Figure 37.ADC Double-Speed Stopband Rejection ..................................................................................55
Figure 38.ADC Double-Speed Stopband Rejection ..................................................................................55
Figure 39.ADC Double-Speed Transition Band (Detail) ............................................................................56
Figure 40.ADC Double-Speed Passband Ripple ...................................................................................... 56
Figure 41.ADC Quad-Speed Stopband Rejection ..................................................................................... 56
Figure 42.ADC Quad-Speed Stopband Rejection ..................................................................................... 56
Figure 43.ADC Quad-Speed Transition Band (Detail) ..............................................................................56
Figure 44.ADC Quad-Speed Passband Ripple ......................................................................................... 56
CS4245
LIST OF TABLES
Table 1. Speed Modes .............................................................................................................................. 30
Table 2. Common Clock Frequencies ....................................................................................................... 31
Table 3. Slave Mode MCLK Dividers ........................................................................................................ 31
Table 4. Slave Mode Serial Bit Clock Ratios ............................................................................................. 32
Table 5. Device Revision .......................................................................................................................... 42
DS656F3 5
Page 6

CS4245
Table 6. Freeze-able Bits .......................................................................................................................... 42
Table 7. Functional Mode Selection ......................................................................................................... 43
Table 8. DAC Digital Interface Formats .................................................................................................... 43
Table 9. De-Emphasis Control .................................................................................................................. 44
Table 10. Functional Mode Selection ........................................................................................................ 44
Table 11. ADC Digital Interface Formats .................................................................................................. 45
Table 12. MCLK 1 Frequency ................................................................................................................... 45
Table 13. MCLK 2 Frequency ................................................................................................................... 46
Table 14. Auxiliary Output Source Selection ............................................................................................. 46
Table 15. Example Gain and Attenuation Settings ................................................................................... 47
Table 16. PGA Soft Cross or Zero Cross Mode Selection ........................................................................ 48
Table 17. Analog Input Multiplexer Selection ............................................................................................ 48
Table 18. Digital Volume Control Example Settings ................................................................................. 49
Table 19. DAC Soft Cross or Zero Cross Mode Selection ........................................................................ 49
6 DS656F3
Page 7
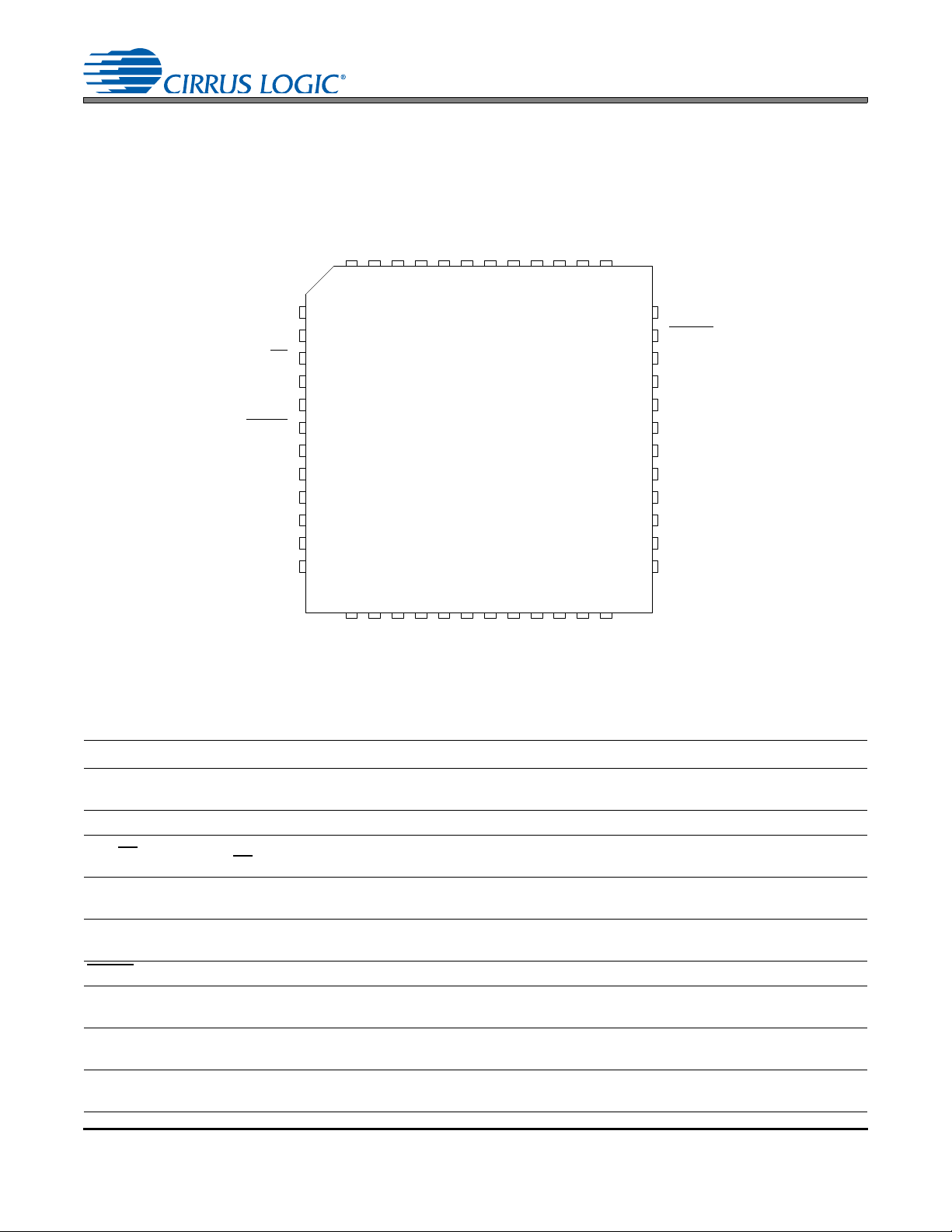
1. PIN DESCRIPTIONS
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24
48 47 46 45 44 43 42 41 40 39 38 37
36
35
34
33
32
31
30
29
28
27
26
25
VLSSDA/CDOUT
AGND
OVFL
SCL/CCLK
AD0/CS
AD1/CDIN
VLC
RESET
AIN3A
AIN3B
AIN2A
AIN2B
AIN1A
AIN1B
VA
AFILTB
VQ1
VQ2
FILT1+
FILT2+
AIN4A/MICIN1
AIN4B/MICIN2
AIN5A
AIN5B
AFILTA
MUTEC
AOUTB
AOUTA
AGND
AGND
VA
AUXOUTB
AUXOUTA
AIN6B
AIN6A
MICBIAS
INTVDDGND
MCLK1
LRCK1
SCLK1
SDOUT
MCLK2
LRCK2
SCLK2
SDIN
CS4245
CS4245
Pin Name # Pin Description
SDA/CDOUT 1
SCL/CCLK 2 Serial Control Port Clock (Input) - Serial clock for the serial control port.
AD0/CS
AD1/CDIN 4
VLC 5
RESET
AIN3A
AIN3B
AIN2A
AIN2B
AIN1A
AIN1B
DS656F3 7
Serial Control Data (Input/Output) - SDA is a data I/O in I²C Mode. CDOUT is the output data line for
the control port interface in SPI Mode.
Address Bit 0 (I²C) / Control Port Chip Select (SPI) (Input) - AD0 is a chip address pin in I²C Mode;
3
CS
Address Bit 1 (I²C) / Serial Control Data Input (SPI) (Input) - AD1 is a chip address pin in I²C Mode;
CDIN is the input data line for the control port interface in SPI Mode.
Control Port Power (Input) - Determines the required signal level for the control port interface. Refer
to the Recommended Operating Conditions for appropriate voltages.
6 Reset (Input) - The device enters a low power mode when this pin is driven low.
Stereo Analog Input 3 (Input) - The full-scale level is specified in the ADC Analog Characteristics
7, 8
specification table.
Stereo Analog Input 2 (Input) - The full-scale level is specified in the ADC Analog Characteristics
9, 10
specification table.
Stereo Analog Input 1 (Input) - The full-scale level is specified in the ADC Analog Characteristics
11, 1 2
specification table.
is the chip-select signal for SPI format.
Page 8

CS4245
AGND 13 Analog Ground (Input) - Ground reference for the internal analog section.
VA 14 Analog Power (Input) - Positive power for the internal analog section.
AFILTA 15 Antialias Filter Connection (Output) - Antialias filter connection for the channel A ADC input.
AFILTB 16 Antialias Filter Connection (Output) - Antialias filter connection for the channel B ADC input.
VQ1 17 Quiescent Voltage 1 (Output) - Filter connection for the internal quiescent reference voltage.
VQ2 18 Quiescent Voltage 2 (Output) - Filter connection for the internal quiescent reference voltage.
FILT1+ 19 Positive Voltage Reference 1 (Output) - Positive reference voltage for the internal sampling circuits.
FILT2+ 20 Positive Voltage Reference 2 (Output) - Positive reference voltage for the internal sampling circuits.
AIN4A/MICIN1
AIN4B/MICIN2
AIN5A
AIN5B
MICBIAS 25
AIN6A
AIN6B
AUXOUTA
AUXOUTB
VA 30 Analog Power (Input) - Positive power for the internal analog section.
AGND 31, 32 Analog Ground (Input) - Ground reference for the internal analog section.
AOUTA
AOUTB
MUTEC
VLS 36
SDIN 37 Serial Audio Data Input (Input) - Input for two’s complement serial audio data.
SCLK2 38 Serial Port 2 Serial Bit Clock (Input/Output) - Serial bit clock for serial audio interface 2.
LRCK2 39
MCLK2 40 Master Clock 2 (Input) - Optional asynchronous clock source for the DAC’s delta-sigma modulators.
SDOUT 41 Serial Audio Data Output (Output) - Output for two’s complement serial audio data.
SCLK1 42 Serial Port 1 Serial Bit Clock (Input/Output) - Serial bit clock for serial audio interface 1.
LRCK1 43
MCLK1 44
DGND 45 Digital Ground (Input) - Ground reference for the internal digital section.
VD 46 Digital Power (Input) - Positive power for the internal digital section.
INT 47 Interrupt (Output) - Indicates an interrupt condition has occurred.
OVFL 48 ADC Overflow (Output) - Indicates an ADC overflow condition is present.
Stereo Analog Input 4 / Micropho ne Inp ut 1 & 2 (Input) - The full-scale level is specified in the ADC
21, 22
Analog Characteristics specification table.
Stereo Analog Input 5 (Input) - The full-scale level is specified in the ADC Analog Characteristics
23, 24
specification table.
Microphone Bias Supply (Output) - Low-noise bias supply for external microphone. Electrical charac-
teristics are specified in the DC Electrical Characteristics specification table.
Stereo Analog Input 6 (Input) - Th
26, 27
specification table.
Auxiliary Analog Au dio Ou tput (Output) - Analog output from either the DAC, the PGA block, or high
28, 29
impedance. See “Auxiliary Output Source Select (Bits 6:5)” on page 46.
DAC Analog Audio Output (Output) - The full-scale output level is specified in the DAC Analog Char-
33, 34
acteristics specification table.
Mute Control (Output) - This pin is active during power-up initialization, reset, muting, when master
35
clock to left/right clock frequency ratio is incorrect, or power-down.
Serial Audio Interface Power (Input) - Determines the required signal level for the serial audio inter-
face. Refer to the Recommended Operating Conditions for appropriate voltages.
Serial Port 2 Left Right Clock (Input/Output) - Determines which channel, Left or Right, is currently
active on the serial audio input data line.
Serial Port 1 Left Right Clock (Input/Output) - Determines which channel, Left or Right, is currently
active on the serial audio output data line.
Master Clock 1 (Input) - Clock source for the ADC’s delta-sigma modulators. By default, this signal
also clocks the DAC’s delta-sigma modulators.
e full-scale level is specified in the ADC Analog Characteristics
8 DS656F3
Page 9
2. CHARACTERISTICS AND SPECIFICATIONS
SPECIFIED OPERATING CONDITIONS
AGND = DGND = 0 V; All voltages with respect to ground.
Parameters Symbol Min Nom Max Units
DC Power Supplies: Analog
Digital
Logic - Serial Port
Logic - Control Port
Ambient Operating Temperature (Power Applied) T
VA
VD
VLS
VLC
Notes: 1. Maximum of VA+0.25 V or 5.25 V, whichever is less.
ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS
AGND = DGND = 0 V All voltages with respect to ground. (Note 2)
Parameter Symbol Min Max Units
DC Power Supplies: Analog
Digital
Logic - Serial Port
Logic - Control Port
Input Current (Note 3)
Analog Input Voltage
Digital Input Voltage Logic - Serial Port
Logic - Control Port
Ambient Operating Temperature (Power Applied)
Storage Temperature
VLS
VLC
V
V
V
A
VA
VD
I
in
INA
IND-S
IND-C
T
A
T
stg
CS4245
3.13
3.13
1.71
1.71
-10 - +70 C
AGND-0.3 VA+0.3 V
5.0
3.3
3.3
3.3
-0.3
-0.3
-0.3
-0.3
- 10 mA
-0.3
-0.3
-50 +125 C
-65 +150 C
5.25
(Note 1)
5.25
5.25
+6.0
+6.0
+6.0
+6.0
VLS+0.3
VLC+0.3
V
V
V
V
V
V
V
V
V
V
2. Operation beyond these limits may result in permanent damage to the device.
Normal operation is not guaranteed at these extremes.
3. Any pin except s upplies. Transient currents of up to ±100 mA on the analog input pins will not cause
SCR latch-up.
DS656F3 9
Page 10
CS4245
DAC ANALOG CHARACTERISTICS
Test Conditions (unless otherwise specified): AGND = DGND = 0 V; VA = 3.13 V to 5.25 V; VD = 3.13 V to 5.25 V
or VA + 0.25 V, whichever is less; VLS = VLC = 1.71 V to 5.25 V; T
+85° C for Automotive; Output test signal: 997 Hz full-scale sine wave; Test load R
Figure 1), Fs = 48/96/192 kHz. Measurement Bandwidth 10 Hz to 20 kHz Synchronous mode; All Connections as
shown in Figure 12 on page 29.
Commercial Grade Automotive Grade
Parameter
Symbol Min Typ Max Min Typ Max Unit
Dynamic Performance for VA = 4.75 V to 5.25 V
Dynamic Range (Note 4)
18 to 24-Bit A-Weighted
unweighted
16-Bit A-Weighted
unweighted
Total Harmonic Distortion + Noise (Note 4)
18 to 24-Bit 0 dB
-20 dB
-60 dB
16-Bit 0 dB
-20 dB
-60 dB
THD+N
98
95
90
87
-
-
-
-
-
-
Dynamic Performance for VA = 3.13 V to 3.46 V
Dynamic Range (Note 4)
18 to 24-Bit A-Weighted
unweighted
16-Bit A-Weighted
unweighted
Total Harmonic Distortion + Noise (Note 4)
18 to 24-Bit 0 dB
-20 dB
-60 dB
16-Bit 0 dB
-20 dB
-60 dB
Interchannel Isolation (1 kHz) - 100 - - 100 - dB
THD+N
95
92
88
85
-
-
-
-
-
-
DC Accuracy
Interchannel Gain Mismatch - 0.1 0.25 - 0.1 0.25 dB
Gain Drift - 100 - - 100 - ppm/°C
Analog Output
Full Scale Output Voltage 0.60*VA 0.65*VA 0.70*VA 0.60*VA 0.65*VA 0.70*VA V
DC Current draw from an AOUT pin (Note 5) I
AC-Load Resistance (Note 6) R
Load Capacitance (Note 6) C
Output Impedance Z
OUT
L
L
OUT
--10--10A
3--3- -k
- - 100 - - 100 pF
-150- -150-
= -10° to +70° C for Commercial or -40° to
104
101
96
93
-90
-81
-41
-93
-73
-33
101
98
93
90
-87
-78
-38
-90
-70
-30
A
-
-
-
-
-84
-
-
-87
-
-
-
-
-
-
-79
-
-
-82
-
-
= 3 k, CL = 10 pF (see
L
96
93
88
85
-
-
-
-
-
-
93
90
86
83
-
-
-
-
-
-
104
101
96
93
-90
-81
-41
-93
-73
-33
101
98
93
90
-87
-78
-38
-90
-70
-30
-
-
-
-
-82
-
-
-85
-
-
-
-
-
-
-77
-
-
-80
-
-
dB
dB
dB
dB
dB
dB
dB
dB
dB
dB
dB
dB
dB
dB
dB
dB
dB
dB
dB
dB
pp
4. One-half LSB of triangular PDF dither added to data.
5. Guaranteed by design. The DC current draw represents the allowed current draw from the AOUT pin
due to typical leakage through the electrolytic DC blocking capacitors.
10 DS656F3
Page 11
CS4245
6. Guaranteed by design. See Figure 2. RL and CL reflect the recommended minimum resistance and
maximum capacitance required for the internal op-amp’s stability. C
internal output amp; increasing C
beyond 100 pF can cause the internal op-amp to become unstable.
L
affects the dominant pole of the
L
DAC COMBINED INTERPOLATION & ON-CHIP ANALOG FILTER RESPONSE
Parameter (Note 7,10) Symbol Min Typ Max Unit
Combined Digital and On-chip Analog Filter Response Single-Speed Mode
Passband (Note 7) to -0.1 dB corner
to -3 dB corner
Frequency Response 10 Hz to 20 kHz -0.175 - +0.01 dB
StopBand 0.5465 - - Fs
StopBand Attenuation (Note 8) 50 - - dB
Group Delay tgd - 10/Fs - s
De-emphasis Error (Note 9) Fs = 44.1 kHz - - +0.05/-0.25 dB
0
0
-
-
0.35
0.4992
Fs
Fs
Combined Digital and On-chip Analog Filter Response Double-Speed Mode
Passband (Note 7) to -0.1 dB corner
to -3 dB corner
Frequency Response 10 Hz to 20 kHz -0.15 - +0.15 dB
StopBand 0.5770 - - Fs
StopBand Attenuation (Note 8) 55 - - dB
Group Delay tgd - 5/Fs - s
0
0
-
-
0.22
0.501
Fs
Fs
Combined Digital and On-chip Analog Filter Response Quad-Speed Mode
Passband (Note 7) to -0.1 dB corner
to -3 dB corner
Frequency Response 10 Hz to 20 kHz -0.12 - 0 dB
StopBand 0.7 - - Fs
StopBand Attenuation (Note 8) 51 - - dB
Group Delay tgd - 2.5/Fs - s
0
0
-
-
0.110
0.469
Fs
Fs
7. Filter response is guaranteed by design.
8. For Single-Speed Mode, the Measurement Bandwidth is 0.5465 Fs to 3 Fs.
For Double-Speed Mode, the Measurement Bandwidth is 0.577 Fs to 1.4 Fs.
For Quad-Speed Mode, the Measurement Bandwidth is 0.7 Fs to 1 Fs.
9. De-emphasis is available only in Single-Speed Mode.
10. Response is clock dependent and will scale with Fs. Note that the amplitude vs. frequency plots of this
data (Figures 21 to 30) have been normalized to Fs and can be de-normalized by multiplying the X-axis
scale by Fs.
DS656F3 11
Page 12
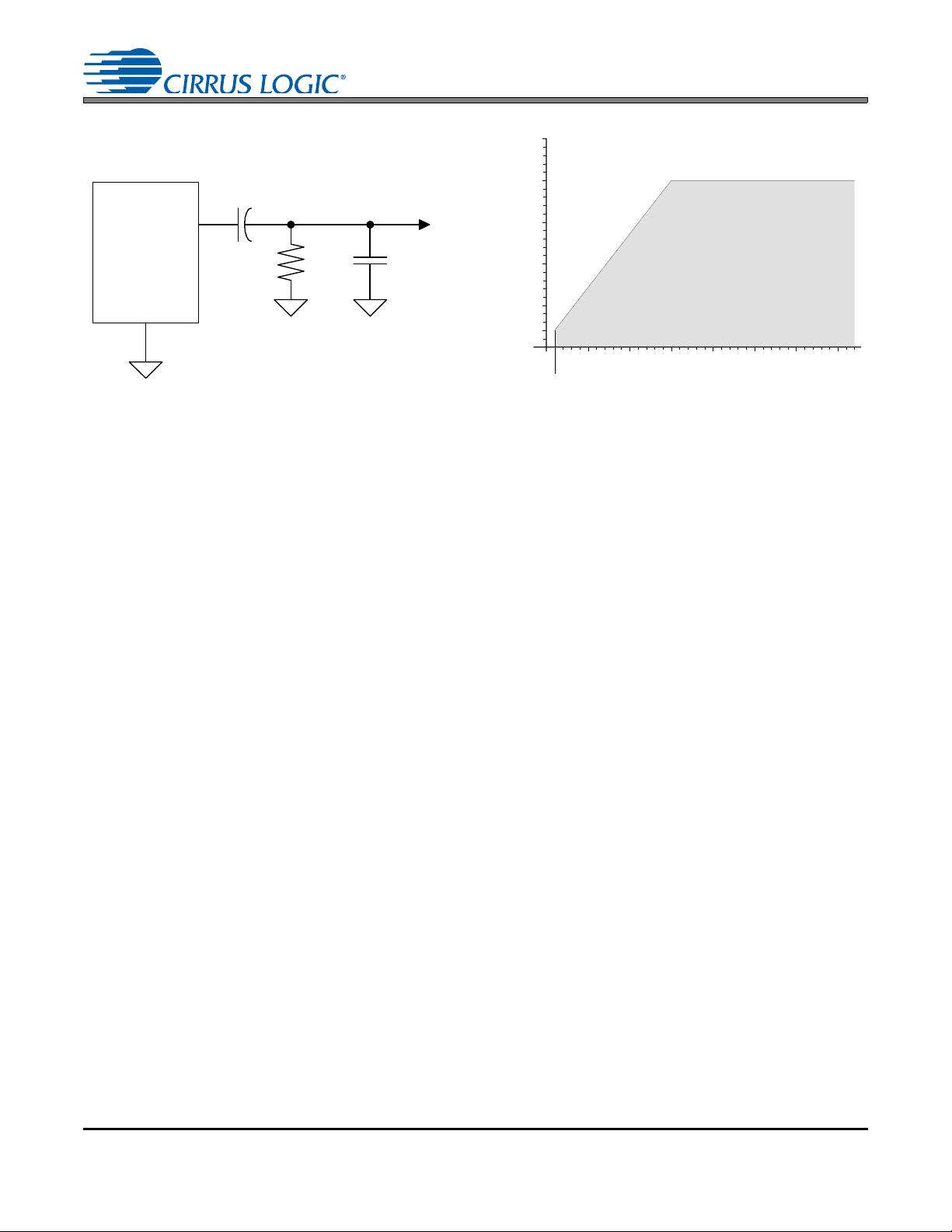
AOUTx
AGND
3.3µF
V
out
R
L
C
L
Figure 1. DAC Output Test Load Figure 2. Maximum DAC Loading
100
50
75
25
2.5
51015
Safe Operating
Region
Capacitive Load -- C (pF)
L
Resistive Load -- R (k)
L
125
3
20
CS4245
12 DS656F3
Page 13
CS4245
ADC ANALOG CHARACTERISTICS
Test conditions (unless otherwise specified): AGND = DGND = 0 V; VA = 3.13 V to 5.25 V; VD = 3.13 V to 5.25 V
or VA + 0.25 V, whichever is less; VLS = VLC = 1.71 V to 5.25 V; T
+85° C for Automotive; Input test signal: 1 kHz sine wave; measurement bandwidth is 10 Hz to 20 kHz;
Fs = 48/96/192 kHz. Synchronous mode; All connections as shown in Figure 12 on page 29.
Line-Level Inputs
Parameter Symbol Min Typ Max Unit
Dynamic Performance for VA = 4.75 V to 5.25 V
Dynamic Range
PGA Setting: -12 dB to +6 dB
A-weighted
unweighted
(Note 13) 40 kHz bandwidth unweighted
PGA Setting: +12 dB Gain
A-weighted
unweighted
(Note 13) 40 kHz bandwidth unweighted
Total Harmonic Distortion + Noise (Note 12)
PGA Setting: -12 dB to +6 dB
-1 dB
-20 dB
-60 dB
(Note 13) 40 kHz bandwidth -1 dB
PGA Setting: +12 dB Gain
-1 dB
-20 dB
-60 dB
(Note 13) 40 kHz bandwidth -1 dB
THD+N
Dynamic Performance for VA = 3.13 V to 3.46 V
Dynamic Range
PGA Setting: -12 dB to +6 dB
A-weighted
unweighted
(Note 13) 40 kHz bandwidth unweighted
PGA Setting: +12 dB Gain
A-weighted
unweighted
(Note 13) 40 kHz bandwidth unweighted
Total Harmonic Distortion + Noise (Note 12)
PGA Setting: -12 dB to +6 dB
-1 dB
-20 dB
-60 dB
(Note 13) 40 kHz bandwidth -1 dB
PGA Setting: +12 dB Gain
-1 dB
-20 dB
-60 dB
(Note 13) 40 kHz bandwidth -1 dB
THD+N
Line-Level Inputs
Parameter Symbol
Interchannel Isolation - 90 - dB
= -10° to +70° C for Commercial or -40° to
A
98
95
-
92
89
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
93
90
-
89
86
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
104
101
98
98
95
92
-95
-81
-41
-92
-92
-75
-35
-89
101
98
95
95
92
89
-92
-78
-38
-84
-89
-72
-32
-81
-89
-86
-86
-83
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
dB
dB
dB
dB
dB
dB
dB
dB
dB
dB
dB
dB
dB
dB
dB
dB
dB
dB
dB
dB
dB
dB
dB
dB
dB
dB
dB
dB
Commercial Grade
UnitMin Typ Max
DS656F3 13
Page 14
CS4245
DC Accuracy
Gain Error --10 %
Gain Drift - 100 - ppm/°C
Line-Level Input Characteristics
Full-scale Input Voltage 0.51*VA 0.57*VA 0.63*VA V
Input Impedance (Note 11) 6.12 6.8 7.48 k
Maximum Interchannel Input Impedance
Mismatch
-5-%
Line-Level and Microphone-Level Inputs
Commercial Grade
Parameter Symbol
DC Accuracy
Interchannel Gain Mismatch - 0.1 - dB
Programmable Gain Characteristics
Gain Step Size - 0.5 - dB
Absolute Gain Step Error - - 0.4 dB
11. Valid for the selected input pair.
pp
UnitMin Typ Max
14 DS656F3
Page 15
ADC ANALOG CHARACTERISTICS
(Continued)
Microphone-Level Inputs
Parameter Symbol Min Typ Max Unit
Dynamic Performance for VA = 4.75 V to 5.25 V
Dynamic Range
PGA Setting: -12 dB to 0 dB
A-weighted
unweighted
PGA Setting: +12 dB
A-weighted
unweighted
Total Harmonic Distortion + Noise (Note 12)
PGA Setting: -12 dB to 0 dB
-1 dB
-20 dB
-60 dB
PGA Setting: +12 dB
-1 dB
Dynamic Performance for VA = 3.13 V to 3.46 V
Dynamic Range
PGA Setting: -12 dB to 0 dB
A-weighted
unweighted
THD+N
77
74
65
62
77
74
CS4245
83
80
71
68
-
-
-
-
-80
-60
-20
-68
83
80
-74
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
dB
dB
dB
dB
dB
dB
dB
dB
dB
dB
PGA Setting: +12 dB
A-weighted
unweighted
Total Harmonic Distortion + Noise (Note 12)
PGA Setting: -12 dB to 0 dB
-1 dB
-20 dB
-60 dB
PGA Setting: +12 dB
-1 dB
Interchannel Isolation - 80 - dB
THD+N
65
62
71
68
-
-
-
-
-80
-60
-20
-68
-74
-
-
-
-
-
dB
dB
dB
dB
dB
dB
DC Accuracy
Gain Error - 5 -%
Gain Drift - 300 - ppm/°C
Microphone-Level Input Characteristics
Full-scale Input Voltage 0.013*VA 0.017*VA 0.021*VA V
Input Impedance (Note 14) -60-k
pp
12. Referred to the typical line-level full-scale input voltage
13. Valid for Double- and Quad-Speed Modes only.
14. Valid when the microphone-level inputs are selected.
DS656F3 15
Page 16
CS4245
ADC DIGITAL FILTER CHARACTERISTICS
Parameter (Notes 15, 17) Symbol Min Typ Max Unit
Single-Speed Mode
Passband (-0.1 dB) 0 - 0.4896 Fs
Passband Ripple - - 0.035 dB
Stopband 0.5688 - - Fs
Stopband Attenuation 70 - - dB
Total Group Delay (Fs = Output Sample Rate) t
gd
Double-Speed Mode
Passband (-0.1 dB) 0 - 0.4896 Fs
Passband Ripple - - 0.025 dB
Stopband 0.5604 - - Fs
Stopband Attenuation 69 - - dB
Total Group Delay (Fs = Output Sample Rate) t
gd
Quad-Speed Mode
Passband (-0.1 dB) 0 - 0.2604 Fs
Passband Ripple - - 0.025 dB
Stopband 0.5000 - - Fs
Stopband Attenuation 60 - - dB
Total Group Delay (Fs = Output Sample Rate) t
gd
High-Pass Filter Characteristics
Frequency Response -3.0 dB
-0.13 dB (Note 16)
Phase Deviation @ 20 Hz (Note 16) -10 -Deg
Passband Ripple -- 0dB
Filter Settling Time
-12/Fs - s
-9/Fs - s
-5/Fs - s
-120-
5
10
/Fs s
-
Hz
Hz
15. Filter response is guaranteed by design.
16. Response shown is for Fs = 48 kHz.
17. Response is clock-dependent and will scale with Fs. Note that the response plots (Figures 33 to 44) are
normalized to Fs and can be de-normalized by multiplying the X-axis scale by Fs.
16 DS656F3
Page 17
CS4245
AUXILIARY OUTPUT ANALOG CHARACTERISTICS
Test conditions (unless otherwise specified): AGND = DGND = 0 V; VA = 3.13 V to 5.25 V; VD = 3.13 V to 5.25 V
or VA + 0.25 V, whichever is less; VLS = VLC = 1.71 V to 5.25 V; T
+85° C for Automotive; Input test signal: 1 kHz sine wave; Measurement bandwidth: 10 Hz to 20 kHz;
Fs = 48/96/192 kHz; Synchronous mode; All connections as shown in Figure 12 on page 29.
VA = 4.75 V to 5.25 V
Commercial Grade Automotive Grade
Parameter Symbol
Dynamic Performance with PGA Output Selected, Line Level Input
Dynamic Range
PGA Setting: -12 dB to +6 dB
A-weighted
unweighted
PGA Setting: +12 dB Gain
A-weighted
unweighted
Total Harmonic Distortion + Noise (Note 19)
PGA Setting: -12 dB to +6 dB
-1 dB
-20 dB
-60 dB
PGA Setting: +12 dB Gain
-1 dB
-20 dB
-60 dB
THD+N
98
95
92
89
-
-
-
-
-
-
Dynamic Performance with PGA Output Selected, Mic Level Input
Dynamic Range
PGA Setting: -12 dB to 0 dB
A-weighted
unweighted
PGA Setting: +12 dB
A-weighted
unweighted
Total Harmonic Distortion + Noise (Note 19)
PGA Setting: -12 dB to 0 dB
-1 dB
-20 dB
-60 dB
PGA Setting: +12 dB
-1 dB
THD+N
77
74
65
62
-
-
-
-
Dynamic Performance with DAC Output Selected
Dynamic Range (Notes 18)
18 to 24-Bit A-weighted
unweighted
16-Bit A-Weighted
unweighted
Total Harmonic Distortion + Noise (Notes 18, 20)
18 to 24-Bit 0 dB
-20 dB
-60 dB
16-Bit 0 dB
-20 dB
-60 dB
THD+N
98
95
90
87
-
-
-
-
-
-
= -10° to +70° C for Commercial or -40° to
A
104
101
98
95
-80
-81
-41
-80
-75
-35
83
80
71
68
-74
-60
-20
-68
104
101
96
93
-80
-81
-41
-80
-73
-33
-74
-74
-68
-74
-74
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
96
93
90
87
75
72
63
60
96
93
88
85
104
101
98
95
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-80
-81
-41
-80
-75
-35
83
80
71
68
-74
-60
-20
-68
104
101
96
93
-80
-81
-41
-80
-73
-33
-
-
-
-
-72
-
-
-72
-
-
-
-
-
-
-66
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-72
-
-
-72
-
-
UnitMin Typ Max Min Typ Max
dB
dB
dB
dB
dB
dB
dB
dB
dB
dB
dB
dB
dB
dB
dB
dB
dB
dB
dB
dB
dB
dB
dB
dB
dB
dB
dB
dB
DS656F3 17
Page 18
AUXILIARY OUTPUT ANALOG CHARACTERISTICS
(Continued)
VA = 3.13 V to 3.46 V
Commercial Grade Automotive Grade
Parameter Symbol
Dynamic Performance with PGA Output Selected, Line Level Input
Dynamic Range
PGA Setting: -12 dB to +6 dB
A-weighted
unweighted
PGA Setting: +12 dB Gain
A-weighted
unweighted
Total Harmonic Distortion + Noise (Note 19)
PGA Setting: -12 dB to +6 dB
-1 dB
-20 dB
-60 dB
PGA Setting: +12 dB Gain
-1 dB
-20 dB
-60 dB
THD+N
Dynamic Performance with PGA Output Selected, Mic Level Input
Dynamic Range
PGA Setting: -12 dB to 0 dB
A-weighted
unweighted
PGA Setting: +12 dB
A-weighted
unweighted
Total Harmonic Distortion + Noise (Note 19)
PGA Setting: -12 dB to 0 dB
-1 dB
-20 dB
-60 dB
PGA Setting: +12 dB
-1 dB
THD+N
Dynamic Performance with DAC Output Selected
Dynamic Range (Notes 18)
18 to 24-Bit A-Weighted
unweighted
16-Bit A-Weighted
unweighted
Total Harmonic Distortion + Noise (Notes 18, 20)
18 to 24-Bit 0 dB
-20 dB
-60 dB
16-Bit 0 dB
-20 dB
-60 dB
THD+N
93
90
89
86
77
74
65
62
95
92
88
85
101
98
95
92
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-80
-78
-38
-80
-72
-32
83
80
71
68
-74
-60
-20
-68
101
98
93
90
-80
-78
-38
-80
-70
-30
-
-
-
-
-74
-
-
-74
-
-
-
-
-
-
-68
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-74
-
-
-74
-
-
91
88
87
84
75
72
63
60
93
90
86
83
CS4245
UnitMin Typ Max Min Typ Max
101
98
95
92
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-80
-78
-38
-80
-72
-32
83
80
71
68
-74
-60
-20
-68
101
98
93
90
-80
-78
-38
-80
-70
-30
-72
-72
-66
-72
-72
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
dB
dB
dB
dB
dB
dB
dB
dB
dB
dB
dB
dB
dB
dB
dB
dB
dB
dB
dB
dB
dB
dB
dB
dB
dB
dB
dB
dB
18. One-half LSB of triangular PDF dither added to data.
19. Referred to the typical Line-Level Full-Scale Input Voltage.
18 DS656F3
Page 19

CS4245
20. Referred to the typical DAC Full-Scale Output Voltage.
AUXILIARY OUTPUT ANALOG CHARACTERISTICS
(Continued)
VA = 3.13 V to 5.25 V
Commercial Grade Automotive Grade
Parameter Symbol
DC Accuracy with PGA Output Selected, Line Level Input
Interchannel Gain Mismatch - 0.1 - - 0.1 - dB
Gain Error - 5- -5- %
Gain Drift -
100 - - 100 - ppm/°C
DC Accuracy with PGA Output Selected, Mic Level Input
Interchannel Gain Mismatch - 0.3 - - 0.3 - dB
Gain Error Gain Drift - 300 - - 300 - ppm/°C
5- -5- %
DC Accuracy with DAC Output Selected
Interchannel Gain Mismatch - 0.1 - - 0.1 - dB
Gain Drift -
100 - - 100 - ppm/°C
Analog Output
Frequency Response 10 Hz to 20 kHz (Note 22) -0.1dB - +0.1dB -0.1dB - +0.1dB dB
Analog In to Analog Out Phase Shift (Note 21) - 180 - - 180 - deg
DC Current draw from an AUXOUT pin I
AC-Load Resistance R
Load Capacitance C
OUT
L
L
--1--1A
100 - - 100 - - k
- - 20 - - 20 pF
UnitMin Typ Max Min Typ Max
21. Valid only when PGA output is selected.
22. Guaranteed by design.
DS656F3 19
Page 20

CS4245
DC ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS
AGND = DGND = 0 V, all voltages with respect to ground. MCLK=12.288 MHz; Fs=48 kHz; Master Mode.
Parameter Symbol Min Typ Max Unit
Power Supply Current VA = 5 V
(Normal Operation) VA = 3.3 V
VD, VLS, VLC = 5 V
VD, VLS, VLC = 3.3 V
Power Supply Current VA = 5 V
(Power-Down Mode) (Note 23) VLS, VLC, VD=5 V
Power Consumption
(Normal Operation) VA, VD, VLS, VLC = 5 V
VA, VD, VLS, VLC = 3.3 V
(Power-Down Mode) VA, VD, VLS, VLC = 5 V
Power Supply Rejection Ratio (1 kHz) (Note 24) PSRR - 55 - dB
VQ Characteristics
Quiescent Voltage 1 VQ1 - 0.5 x VA - VDC
DC Current from VQ1 (Note 25) I
VQ1 Output Impedance Z
Quiescent Voltage 2 VQ2 - 0.5 x VA - VDC
DC Current from VQ2 (Note 25) I
VQ2 Output Impedance Z
FILT1+ Nominal Voltage FILT1+ - VA - VDC
FILT2+ Nominal Voltage FILT2+ - VA - VDC
Microphone Bias Voltage MICBIAS - 0.8 x VA - VDC
Current from MICBIAS I
I
I
I
I
I
I
Q1
Q1
Q2
Q2
MB
A
A
D
D
A
D
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-- 1A
-23 -k
-- 1A
-4.5 -k
-- 2mA
41
37
39
23
0.50
0.54
400
198
4.2
50
45
47
28
-
-
485
241
-
mA
mA
mA
mA
mA
mA
mW
mW
mW
23. Power-Down Mode is defines as RESET
= Low with all clock and data lines held static and no analog
input.
24. Valid with the recommended capacitor values on FILT1+, FILT2+, VQ1 and VQ2 as shown in the Typical Connection Diagram.
25. Guaranteed by design. The DC current draw represents the allowed current draw due to typical leakage
through the electrolytic de-coupling capacitors.
20 DS656F3
Page 21

CS4245
10
6
LRCK1
--------------------
DIGITAL INTERFACE CHARACTERISTICS
Test conditions (unless otherwise specified): AGND = DGND = 0 V; VLS = VLC = 1.71 V to 5.25 V.
Parameters (Note 26) Symbol Min Typ Max Units
High-Level Input Voltage
VL = 1.71 V Serial Port
Control Port
VL > 2.0 V Serial Port
Control Port
Low-Level Input Voltage Serial Port
Control Port
High-Level Output Voltage at I
= 2 mA Serial Port
o
Control Port
MUTEC
Low-Level Output Voltage at I
= 2 mA Serial Port
o
Control Port
MUTEC
Input Leakage Current I
V
IH
V
IH
V
IH
V
IH
V
IL
V
IL
V
OH
V
OH
V
OH
V
OL
V
OL
V
OL
in
Input Capacitance (Note 27) --1pF
Maximum MUTEC Drive Current - 3 - mA
Minimum OVFL Active Time - - s
0.8xVLS
0.8xVLC
0.7xVLS
0.7xVLC
-
-
VLS-1.0
VLC-1.0
VA- 1.0
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
0.2xVLS
0.2xVLC
-
-
-
0.4
0.4
0.4
--±10A
V
V
V
V
V
V
V
V
V
V
V
V
26. Serial Port signals include: MCLK1, MCLK2, SCLK1, SCLK2, LRCK1, LRCK2, SDIN, SDOUT.
Control Port signals include: SCL/CCLK, SDA/CDOUT, AD0/CS
, AD1/CDIN, RESET, INT, OVFL.
27. Guaranteed by design.
DS656F3 21
Page 22

CS4245
10
9
128Fs
---------------------
10
9
64Fs
------------------
10
9
64Fs
------------------
SWITCHING CHARACTERISTICS - SERIAL AUDIO PORT 1
Logic ‘0’ = DGND = AGND = 0 V; Logic ‘1’ = VL, C
Parameter Symbol Min Typ Max Unit
Sample Rate Single Speed Mode
Double Speed Mode
Quad Speed Mode
MCLK Specifications
MCLK1 Input Frequency fmclk 1.024 - 51.200 MHz
MCLK1 Input Pulse Width High/Low t
Master Mode
LRCK1 Duty Cycle - 50 - %
SCLK1 Duty Cycle - 50 - %
SCLK1 falling to LRCK1 edge t
SCLK1 falling to SDOUT valid t
Slave Mode
LRCK1 Duty Cycle 40 50 60 %
SCLK1 Period
Single-Speed Mode
= 20 pF. (Note 28)
L
Fs
Fs
Fs
clkhl 8--ns
slr
sdo
t
sclkw
4
50
100
-
-
-
50
100
200
kHz
kHz
kHz
-10 - 10 ns
0-36ns
-
-
ns
Double-Speed Mode
Quad-Speed Mode
SCLK1 Pulse Width High t
SCLK1 Pulse Width Low t
SCLK1 falling to LRCK1 edge t
SCLK1 falling to SDOUT valid t
28. See Figure 3 and Figure 4 on page 23.
t
sclkw
t
sclkw
sclkh
sclkl
sdo
-
-
-
-
ns
ns
30 - - ns
48 - - ns
slr
-10 - 10 ns
0-36ns
22 DS656F3
Page 23

slr
t
SDOUT
SCLK1
Output
LRCK1
Output
sdo
t
slr
t
SDOUT
SCLK1
Input
LRCK1
Input
sdo
t
sclkh
t
sclkl
t
sclkw
t
Figure 3. Master Mode Timing - Serial Audio Port 1
Figure 4. Slave Mode Timing - Serial Audio Port 1
CS4245
DS656F3 23
Page 24

CS4245
10
9
128Fs
---------------------
10
9
64Fs
------------------
10
9
64Fs
------------------
SWITCHING CHARACTERISTICS - SERIAL AUDIO PORT 2
Logic ‘0’ = DGND = AGND = 0 V; Logic ‘1’ = VL, CL = 20 pF. (Note 29)
Parameter Symbol Min Typ Max Unit
Sample Rate Single Speed Mode
Double Speed Mode
Quad Speed Mode
MCLK Specifications
MCLK2 Input Frequency fmclk 1.024 - 51.200 MHz
MCLK2 Input Pulse Width High/Low t
Master Mode
LRCK2 Duty Cycle - 50 - %
SCLK2 Duty Cycle - 50 - %
SCLK2 falling to LRCK edge t
SDIN valid to SCLK2 rising setup time t
SCLK2 rising to SDIN hold time t
Slave Mode
LRCK2 Duty Cycle 40 50 60 %
SCLK2 Period
Single-Speed Mode
Fs
Fs
Fs
clkhl 8--ns
slr
sdis
sdih
t
sclkw
4
50
100
-
-
-
50
100
200
kHz
kHz
kHz
-10 - 10 ns
16 - - ns
20 - - ns
-
-
ns
Double-Speed Mode
Quad-Speed Mode
SCLK2 Pulse Width High t
SCLK2 Pulse Width Low t
SCLK2 falling to LRCK2 edge t
SDIN valid to SCLK2 rising setup time t
SCLK2 rising to SDIN hold time t
29. See Figure 5 and Figure 6 on page 25.
t
sclkw
t
sclkw
sclkh
sclkl
sdis
sdih
-
-
-
-
ns
ns
30 - - ns
48 - - ns
slr
-10 - 10 ns
16 - - ns
20 - - ns
24 DS656F3
Page 25

sdis
t
slr
t
SCLK2
Output
LRCK2
Output
SDIN
sdih
t
sdis
t
slr
t
SCLK2
Input
LRCK2
Input
SDIN
sdih
t
sclkh
t
sclkl
t
sclkw
t
Figure 5. Master Mode Timing - Serial Audio Port 2
Figure 6. Slave Mode Timing - Serial Audio Port 2
CS4245
DS656F3 25
Page 26

CS4245
Figure 7. Format 0, Left-Justified up to 24-Bit Data
LRCK
SCLK
SDATA
+3 +2 +1+5 +4
-1 -2 -3 -4 -5
+3 +2 +1+5 +4
MSB
-1 -2 -3 -4
Channel A - Left
Channel B - Right
LSBLSBMSB
Figure 8. Format 1, I²S up to 24-Bit Data
LRCK
SCLK
SDATA
+3 +2 +1+5 +4
MSB
-1 -2 -3 -4 -5
+3 +2 +1+5 +4
-1 -2 -3 -4
Channel A - Left
Channel B - Right
LSB MSB LSB
LRCK
SCLK
SDATA
+5 +4 +3 +2 +1-1 -2 -3 -4 -5 +5 +4 +3 +2 +1-1 -2 -3 -4 -5+6-6 +6-6
Channel A - Left
Channel B - Right
MSB LSB MSB LSBLSB
Figure 9. Format 2, Right-Justified 16-Bit Data.
Format 3, Right-Justified 24-Bit Data.
26 DS656F3
Page 27

SWITCHING CHARACTERISTICS - CONTROL PORT - I²C FORMAT
t
buf
t
hdst
t
low
t
hdd
t
high
t
sud
Stop S tar t
SDA
SCL
t
irs
RST
t
hdst
t
rc
t
fc
t
sust
t
susp
Start
Stop
Repeated
t
rd
t
fd
t
ack
Figure 10. Control Port Timing - I²C Format
Inputs: Logic 0 = DGND = AGND = 0 V, Logic 1 = VLC, CL=30pF.
Parameter Symbol Min Max Unit
SCL Clock Frequency f
RESET
Rising Edge to Start t
Bus Free Time Between Transmissions t
Start Condition Hold Time (prior to first clock pulse) t
Clock Low time t
Clock High Time t
Setup Time for Repeated Start Condition t
SDA Hold Time from SCL Falling (Note 30) t
SDA Setup time to SCL Rising t
Rise Time of SCL and SDA (Note 31) t
Fall Time SCL and SDA (Note 31) t
Setup Time for Stop Condition t
Acknowledge Delay from SCL Falling t
hdst
high
sust
hdd
sud
rc
fc
susp
scl
irs
buf
low
, t
, t
ack
rd
fd
- 100 kHz
500 - ns
4.7 - µs
4.0 - µs
4.7 - µs
4.0 - µs
4.7 - µs
0-µs
250 - ns
-1µs
-300ns
4.7 - µs
300 1000 ns
CS4245
30. Data must be held for sufficient time to bridge the transition time, t
31. Guaranteed by design.
, of SCL.
fc
DS656F3 27
Page 28

SWITCHING CHARACTERISTICS - CONTROL PORT - SPI FORMAT
t
r2
t
f2
t
dsu
t
dh
t
sch
t
scl
CS
CCLK
CDIN
t
css
t
pd
CDOUT
t
csh
RST
t
srs
Figure 11. Control Port Timing - SPI Format
Inputs: Logic 0 = DGND = AGND = 0 V, Logic 1 = VLC, CL=30pF.
Parameter Symbol Min Max Units
CCLK Clock Frequency f
RESET Rising Edge to CS Falling t
CS High Time Between Transmissions t
CS
Falling to CCLK Edge t
CCLK Low Time t
CCLK High Time t
CDIN to CCLK Rising Setup Time t
CCLK Rising to DATA Hold Time (Note 32) t
CCLK Falling to CDOUT Stable t
Rise Time of CDOUT t
Fall Time of CDOUT t
Rise Time of CCLK and CDIN (Note 33) t
Fall Time of CCLK and CDIN (Note 33) t
sck
srs
csh
css
scl
sch
dsu
dh
pd
r1
f1
r2
f2
-6.0MHz
500 - ns
1.0 - s
20 - ns
66 - ns
66 - ns
40 - ns
15 - ns
-50ns
-25ns
-25ns
- 100 ns
- 100 ns
CS4245
32. Data must be held for sufficient time to bridge the transition time of CCLK.
33. For f
<1 MHz.
sck
28 DS656F3
Page 29
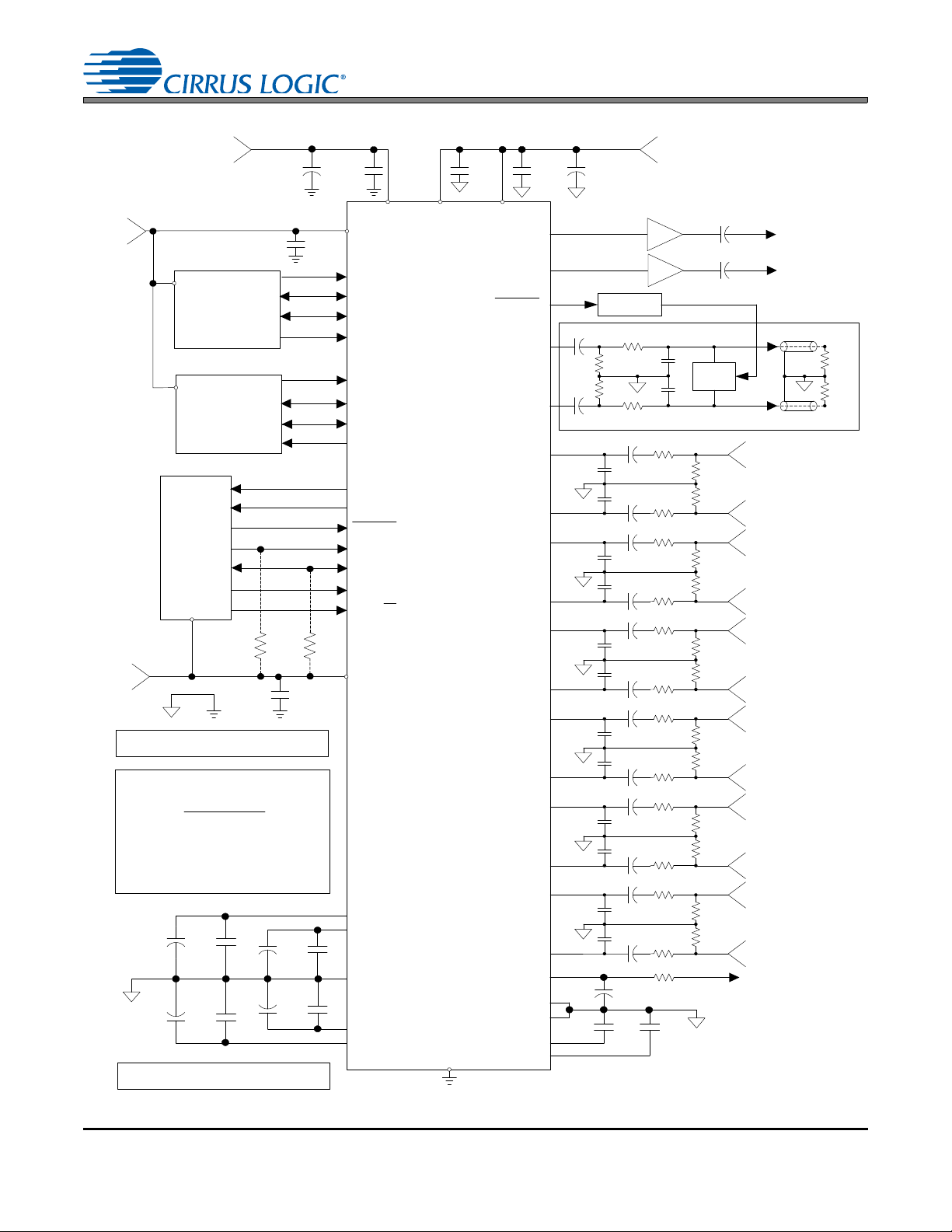
3. TYPICAL CONNECTION DIAGRAM
VLS
0.1 µF
+1.8V
to +5V
MUTEC
Mute
Drive
DGND
VLC
0.1 µF
+1.8V
to +5V
SCL/CCLK
SDA/CDOUT
AD1/CDIN
RESET
2 k
See Note 1
LRCK2
SDIN
AGND
AD0/CS
Note 1: Res istors are required for I²C control
port operation
Digital Audio
Playback
Micro-
Controller
MCLK2
SCLK2
* Capacitors must be C0G or equivalent
Digital Audio
Capture
LRCK1
SDOUT
MCLK1
SCLK1
AUXOUTA
AUXOUTB
2.2nF
AFILTA
AFILTB
OVFL
2.2nF
3.3 µF
3.3 µF
47 µF
0.1 µF
VQ1
FILT1+
10 µF
AGND
**
AOUTA
AOUTB
470
470
3.3 µF
C
Optional
Analog
Muting
2 k
3.3 µF
INT
47 µF
10 k
10 k
C
R
ext
R
ext
See Note 2
For best res ponse to F s/2 :
4704
470
ext
ext
RFs
R
C
This circuitry is intended for applications where
the CS4245 connects directly to an unbalanced
output of the design. For internal routing
applications please see the DAC Analog O utput
Characte ristics section for loa ding limitations .
Note 2 :
AIN1A
Left Analog Input 1
10 µF
10 µF
1800 pF
1800 pF
100 k
100 k
100
100
AIN1B
Right Analog Input 1
AIN2A
Left Analog Input 2
10 µF
10 µF
1800 pF
1800 pF
100 k
100 k
100
100
AIN2B
Right Analog Input 2
AIN3A
Left Analog Input 3
10 µF
10 µF
1800 pF
1800 pF
100 k
100 k
100
100
AIN3B
Right Analog Input 3
AIN4A/MICIN1
Left Analog Input 4
10 µF
10 µF
1800 pF
1800 pF
100 k
100 k
100
100
AIN4B/MICIN2
Right Analog Input 4
AIN5A
Left Analog Input 5
10 µF
10 µF
1800 pF
1800 pF
100 k
100 k
100
100
AIN5B
Right Analog Input 5
AIN6A
Left Analog Input 6
10 µF
10 µF
1800 pF
1800 pF
100 k
100 k
100
100
AIN6B
Right Analog Input 6
MICBIAS
AGND
0.1 µF
47 µF
0.1 µF
VQ2
FILT2+
10 µF
0.1 µF
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
0.1 µF
VA
10 µF
+3.3V to +5V
0.1 µF
10 µF
0.1 µF
VAVD
+3.3V to +5V
R
L
Note 3
Note 3: The value of RL is dictated by the
microphone carteridge.
CS4245
Figure 12. Typical Connection Diagram
CS4245
DS656F3 29
Page 30

4. APPLICATIONS
4.1 Recommended Power-Up Sequence
1. Hold RESET low until the power supply, MCLK1, MCLK2 (if used), LRCK1 and LRCK2 are stable. In
this state, the Control Port is reset to its default settings.
2. Bring RESET
trol port will be accessible.
3. The desired register settings can be loaded while the PDN bit remains set.
4. Clear the PDN bit to initiate the power-up sequence.
4.2 System Clocking
The CS4245 will operate at sampling frequencies from 4 kHz to 200 kHz. This range is divided into three
speed modes as shown in Table 1.
high. The device will remain in a low power state with the PDN bit set by default. The con-
Mode Sampling Frequency
Single-Speed 4-50 kHz
Double-Speed 50-100 kHz
Quad-Speed 100-200 kHz
Table 1. Speed Modes
CS4245
The CS4245 has two serial ports which may be operated synchronously or asynchronously. Serial port 1
consists of the SCLK1 and LRCK1 signals and clocks the serial audio output, SDOUT. Serial port 2 consists
of the SCLK2 and LRCK2 signals and clocks the serial audio input, SDIN.
Each serial port may be independently placed into Single, Double, or Quad Speed mode. The serial ports
may also be independently placed into Master or Slave mode.
4.2.1 Synchronous / Asynchronous Mode
By default, the CS4245 operates in Synchronous Mode with both serial ports synchronous to MCLK1. In
this mode, the serial ports may operate at different synchronous rates as set by the ADC_FM and
DAC_FM bits, and MCLK2 does not need to be provided (the MCLK2 pin may be left unconnected).
If the Asynch bit is set (see “Asynchronous Mode (Bit 0)” on page 46), the CS4245 will operate in asynchronous mode. The serial ports will operate asynchronously with Serial Port 1 clocked from MCLK1 and
Serial Port 2 clocked from MCLK2. In this mode, the serial ports may operate at different asynchronous
rates.
4.2.2 Master Clock
In Asynchronous Mode, MCLK1/LRCK1 and MCLK2/LRCK2 must maintain an integer ratio. In synchronous mode MCLK1/LRCK1 and MCLK1/LRCK2 must maintain an integer ratio. Some common ratios are
shown in Table 2.The LRCK frequency is equal to Fs, the frequency at which audio samples for each
channel are clocked into or out of the device. The ADC_FM and DAC_FM bits and the MCLK Freq bits
(See “MCLK Frequency - Address 05h” on page 45.) configure the device to generate the proper clocks
30 DS656F3
Page 31

CS4245
in Master Mode, and receive the proper clocks in Slave Mode. Table 2 illustrates several standard audio
sample rates and the required MCLK and LRCK frequencies.
LRCK
(kHz)
32
44.1
48
64
88.2
96
128
176.4
192
Mode
MCL
K (MHz)
64x 96x 128x 192x 256x 384x 512x 768x 1024x
- ---8.1920 12.2880 16.3840 24.5760 32.7680
- ---11.2896 16.9344 22.5792 33.8680 45.1584
- ---12.2880 18.4320 24.5760 36.8640 49.1520
- - 8.1920 12.2880 16.3840 24.5760 32.7680 - -
- - 11.2896 16.9344 22.5792 33.8680 45.1584 - -
- - 12.2880 18.4320 24.5760 36.8640 49.1520 - -
8.1920 12.2880 16.3840 24.5760 32.7680 - - - -
11.2896 16.9344 22.5792 33.8680 45.1584 - - - -
12.2880 18.4320 24.5760 36.8640 49.1520 - - - -
QSM
Table 2. Common Clock Frequencies
In both Master and Slave Mo
ratio to achieve a post-divider MCLK/LRCK ratio of 256x for SSM, 128x for DSM, or 64x for QSM. Table 3
lists the appropriate dividers.
MCLK/LRCK Ratio MCLK Dividers
64x --÷1
96x --÷1.5
128x -÷1÷2
192x -÷1.5÷3
256x ÷1 ÷2 ÷4
384x ÷1.5 ÷3 -
512x ÷2 ÷4 -
768x ÷3 - -
1024x ÷4 - -
Mode SSM
des, the external MCLK must be divided down based on the MCLK/LRCK
DSM QSM
DSM
SSM
Table 3. MCLK Dividers
DS656F3 31
Page 32

4.2.3 Master Mode
÷256
÷128
÷64
÷4
÷2
÷1
00
01
10
00
01
10
LRCK1
SCLK1
000
001
010
÷1
÷1.5
÷2
011
100
÷3
÷4
MCLK1
÷256
÷128
÷64
÷4
÷2
÷1
00
01
10
00
01
10
000
001
010
÷1
÷1.5
÷2
011
100
÷3
÷4
MCLK2
LRCK2
SCLK2
0
1
DAC_FM Bits
ADC_FM Bits
ASynch Bit
MCLK1 Freq Bits
MCLK2 Freq Bits
Figure 13. Master Mode Clocking
As a clock master, LRCK and SCLK will operate as outputs. The two serial ports may be independently
placed into Master or Slave mode. Each LRCK and SCLK is internally derived from its respective MCLK
with LRCK equal to Fs and SCLK equal to 64 x Fs as shown in Figure 13.
CS4245
4.2.4 Slave Mode
In Slave Mode, SCLK and LRCK operate as inputs. Each serial port may be independently placed into
Slave Mode. The Left/Right clock signal must be equal to the sample rate, Fs. If operating in Asynchronous Mode, LRCK1 must be synchronously derived from MCLK1 and LRCK2 must be synchronously derived from MCLK2. If operating in Synchronous Mode, LRCK1, and LRCK2 must be synchronously
derived from MCLK1. For more information on Synchronous and Asynchronous Modes, see “Synchro-
nous / Asynchronous Mode” on page 30.
For each serial port, the serial bit clock must be equal to 128x, 64x, 48x or 32x Fs, depending on the desired speed mode. If operating in Asynchronous Mode, the serial bit clock SCLK1 must be synchronously
derived from MCLK1 and SCLK2 must be synchronously derived from MCLK2. If operating in Synchronous Mode, SCLK1, and SCLK2 must be synchronously derived from MCLK1. Refer to Table 4 for re-
4.3 High-Pass Filter and DC Offset Calibration
32 DS656F3
quired serial bit clock to Left/Right clock ratios.
SCLK/LRCK Ratio 32x, 48x, 64x, 128x 32x, 48x, 64x 32x, 48x, 64x
When using operational amplifiers in the input circuitry driving the CS4245, a small DC offset may be driven
into the A/D converter. The CS4245 includes a high-pass filter after the decimator to remove any DC offset
which could result in recording a DC level, possibly yielding clicks when switching between devices in a multichannel system.
Single-Speed Double-Speed Quad-Speed
Table 4. Slave Mode Serial Bit Clock Ratios
Page 33

CS4245
The high-pass filter continuously subtracts a measure of the DC offset from the output of the decimation
filter. If the HPFFreeze bit (See “ADC High-Pass Filter Freeze (Bit 1)” on page 45.) is set during normal operation, the current value of the DC offset for the each channel is frozen and this DC offset will continue to
be subtracted from the conversion result. This feature makes it possible to perform a system DC offset calibration by:
1. Running the CS4245 with the high-pass filter enabled until the filter settles. See the ADC Digital Filter
Characteristics section for filter settling time.
2. Disabling the high-pass filter and freezing the stored DC offset.
A system calibration performed in this way will eliminate offsets anywhere in the signal path between the
calibration point and the CS4245.
DS656F3 33
Page 34

4.4 Analog Input Multiplexer, PGA, and Mic Gain
PGA
MUX
+32 dB
AIN1A
AIN2A
AIN3A
AIN4A/MICIN1
AIN5A
AIN6A
PGA
MUX
+32 dB
AIN1B
AIN2B
AIN3B
AIN4B/MICIN2
AIN5B
AIN6B
Analog Input
Selection Bi ts
Channel A
PGA Gain Bits
Channel B
PGA Gain Bits
Out to ADC
Channel A
Out to ADC
Channel B
Figure 14. Analog Input Architecture
The CS4245 contains a stereo 6-to-1 analog input multiplexer followed by a programmable gain amplifier
(PGA). The input multiplexer can select one of six possible stereo analog input sources and route it to the
PGA. Analog inputs 4A and 4B are able to insert a +32 dB gain stage before the input multiplexer, allowing
them to be used for microphone-level signals without the need for any external gain. The PGA stage provides 12 dB of gain or attenuation in 0.5 dB steps. Figure 14 shows the architecture of the input multiplexer, PGA, and microphone gain stages. .
CS4245
The “Analog Input Selection (Bits 2:0)” on page 48 outlines the bit settings n ecessary to control the input
multiplexer and mic gain. “Channel B PGA Control - Address 07h” on page 47 and “Channel A PGA Control
- Address 08h” on pa ge 47 outline the register settings necessary to control the PGA. By de fault, line-
level input 1 is selected, and the PGA is set to 0 dB.
4.5 Input Connections
The analog modulator samples the input at 6.144 MHz (MCLK=12.288 MHz). The digital filter will reject signals within the stopb and of the f ilter. However, there is no rejection for input signals which a re
6.144 MHz) the digital passband frequency, where n=0,1,2,... Refer to the Typical Connection Diagram
(n
for the recommended analog input circuit that will attenuate noise energy at 6.144 MHz. The use of capacitors which ha ve a large voltage coefficient (such as general-purpose ceramics) must be avoid ed since
these can degrade signal linearity. Any unused analog input pairs should be left unconnected.
4.6 Output Connections
The CS4245 DACs implement a switched-capacitor filter, followed by a continuous time low-pass filter. Its
response, combined with tha t of the digital interpolator, is sh own in Section 8. “DAC Filter Plots” on
page 53”. The recommended external analog circuitry is shown in the Typical Connection Diagram.
The CS4245 DAC does not include phase or amplitude compensation for an external filter. Therefore, the
DAC system phase and amplitude response is dependent on the external analog circuitry.
34 DS656F3
Page 35

4.7 Output Transient Control
The CS4245 uses Popguard® technology to minimize the effects of output transients during power-up and
power-down. This technique eliminates the audio transients commonly produced by single-ended, singlesupply converters when it is implemented with external DC-blocking capacitors connected in series with the
audio outputs. To make best use of this feature, it is necessary to understand its operation.
4.7.1 Power-Up
When the device is initially powered-up, the audio outputs AOUTA and AOUTB are clamped to VQ2,
which is initially low. After the PDN bit is released (set to ‘0’), the DAC outputs begin to ramp with VQ2
towards the nominal quiescent voltage. This ramp takes approximately 200 ms to complete. The gradual
voltage ramping allows time for the external DC-blocking capacitors to charge to VQ2, effectively blocking
the quiescent DC voltage. Audio output will begin after approximately 2000 sample periods.
4.7.2 Power-Down
To prevent audio transients at power-down, the DC-blocking capacitors must fully discharge before turning off the power. In order to do this, either the PDN bit should be set or the device should be reset about
250 ms before removing power. During this time, the voltage on VQ2 and the DAC outputs discharge
gradually to GND. If power is removed before this 250 ms time period has passed, a transient will occur
when the VA supply drops below that of VQ2. There is no minimum time for a power cycle; power may be
re-applied at any time.
CS4245
4.7.3 Serial Interface Clock Changes
When changing the DAC clock ratio or sample rate, it is recommended that zero data (or near zero data)
be present on SDIN for at least 10 LRCK samples before the change is made. During the clocking change,
the DAC outputs will always be in a zero data state. If non-zero serial audio input is present at the time of
switching, a slight click or pop may be heard as the DAC output automatically goes to its zero data state.
4.8 Auxiliary Analog Output
The CS4245 includes an auxiliary analog output through the AUXOUT pins. These pins can be configured
to output the analog input to the ADC as se lected with the input MUX and gained or attenuated with the
PGA, the analog output of the DAC, or alternatively they may be set to high-impedance. See “Section 6.6.1
“Auxiliary Output Source Select (Bits 6:5)” on page 46” for information on configuring the auxiliary analog
output.
The auxiliary analog output can source very little current. As current from the AUXOUT pins increases, distortion will increase. For this reason, a high input impedance buffer must be used on the AUXOUT pins to
achieve full performance. Refer to the table in “Auxiliary Output Analog Characteristics” on page 17 for acceptable loading conditions.
4.9 De-Emphasis Filter
The CS4245 includes on-chip digital de-emphasis optimized for a sample rate of 44.1 kHz. The filter response is shown in Figure 15. The frequency response of the de-emphasis curve scales proportionally with
changes in sample rate, Fs. Please see Section 6.3.4 “De-Emphasis Control (Bit 1)” on page 44 for de-em-
phasis control.
The de-emphasis feature is included to accommodate audio recordings that utilize 50/15 s pre-emphasis
equalization as a means of noise reduction.
DS656F3 35
Page 36

De-emphasis is only available in Single-Speed Mode.
Gain
dB
-10dB
0dB
Frequency
T2 = 15 µs
T1=50 µs
F1 F2
3.183 kHz 10.61 kHz
Figure 15. De-Emphasis Curve
4.10 Internal Digital Loopback
The CS4245 supports an internal digital loopback mode in which the output of the ADC is routed to the input
of the DAC. This mode may be activated by setting the LOOP bit in the Signal Selection register (See Sec-
tion 6.6 “Signal Selection - Address 06h” on page 46). To use this mode, the ADC and DAC must be oper-
ating at the same synchronous sample rate.
CS4245
When this bit is set, the status of the DAC_DIF[1:0] bits in register 03h will be disregarded by the CS4245.
Any changes made to the DAC_DIF[1:0] bits while the LOOP bit is set will have no impact on operation until
the LOOP bit is cleared, at which time the Digital Interface Format of the DAC will operate according to the
format selected by the DAC_DIF[1:0] bits. While the LOOP bit is set, data will be present on the SDOUT pin
in the format selected by the ADC_DIF bit in register 04h.
4.11 Mute Control
The MUTEC pin becomes active during power-up initialization, reset, and muting if the MCLK2 to LRCK2
ratio is incorrect in Asynchronous Mode or the MCLK1 to LRCK2 ratio is incorrect in Synchronous Mode,
and during power-down. The MUTEC
order to add off-chip mute capability.
Use of the M ute Control function is not mandatory, but recommended, for designs requiring the absolute
minimum in extraneous clicks and pops. Also, use of the Mute Control function can enable the system de-
pin is intended to be used as control for an external mute circuit in
36 DS656F3
Page 37

CS4245
LPF
+V
EE
-V
EE
560
Audio
Out
2 k
10 k
-V
EE
+V
A
MMUN2111LT1
AOUT
MUTEC
AC
Couple
47 k
Figure 16. Suggested Active-Low Mute Circuit
CS4245
signer to achieve idle channel noise/signal-to-noise ratios which are only limited by the external mute circuit.
The MUTEC
pin is an active-low CMOS driver. See Figure 16 for a suggested active-low mute circuit.
4.12 Control Port Description and Timing
The control port is used to access the registers, allowing the CS4245 to be configured for the desired operational modes and formats. The operation of the control port may be completely asynchronous with respect
to the audio sample rates. However, to avoid potential interference problems, the control port pins should
remain static if no operation is required.
The control port has two modes: SPI and I²C, with the CS4245 acting as a slave device. SPI Mode is selected if there is a high-to-low transition on the AD0/CS
Mode is selected by connecting the AD0/CS
selecting the desired AD0 bit address state.
4.12.1 SPI Mode
In SPI Mode, CS is the CS4245 chip-select signal; CCLK is the control port bit clock (input into the CS4245
from the microcontroller); CDIN is the input data line from the microcontroller; CDOUT is the output data
line to the microcontroller. Data is clocked in on the rising edge of CCLK and out on the falling edge.
Figure 17 shows the operation of the control port in SPI Mode. To write to a register, bring CS
first seven bits on CDIN form the chip address and must be 1001111. The eighth bit is a read/write indi-
), which should be low to write. The next eight bits form the Memory Address Pointer (MAP),
high) immediately after the MAP byte. To begin a read, bring CS low, send out the chip ad-
cator (R/W
which is set to the address of the register that is to be updated. The next eight bits are the data that will
be placed into the register designated by the MAP. During writes, the CDOUT output stays in the Hi-Z
state. It may be externally pulled high or low with a 47 k resistor, if desired.
To read a register, the MAP has to be set to the correct address by executing a partial write cycle which
finishes (CS
pin, after the RESET pin has been brought high. I²C
pin through a resistor to VLC or DGND, thereby permanently
low. The
DS656F3 37
Page 38

CS4245
MAP
MSB
LSB
DATA
byte 1
byte n
R/W
R/W
ADDRESS
CHIP
ADDRESS
CHIP
CDIN
CCLK
CS
CDOUT
MSB
LSB
MSB
LSB
1001111
1001111
MAP = Memory Address Pointer, 8 bits, MSB first
High Impedance
Figure 17. Control Port Timing in SPI Mode
4 5 6 7 24 25
SCL
CHIP ADDRESS (WRITE) MAP BYTE DATA
DATA +1
START
ACK
STOP
ACKACKACK
1 0 0 1 1 AD1 AD0 0
SDA
6 6 5 4 3 2 1 0 7 6 1 0 7 6 1 0 7 6 1 0
0 1 2 3 8 9 12 16 17 18 19 10 11 13 14 15 27 28
26
DATA +n
Figure 18. Control Port Timing, I²C Write
dress and set the read/write bit (R/W) high. The next falling edge of CCLK will clock out the MSB of the
addressed register (CDOUT will leave the high-impedance state).
For both read and write cycles, the memory address pointer will automatically increment following each
data byte in order to facilitate block reads and writes of successive registers.
4.12.2 I²C Mode
In I²C Mode, SDA is a bidirectional data line. Data is clocked into and out of the part by the clock, SCL.
There is no CS
be connected through a resistor to VLC or DGND as desired. The state of the pins is sensed while the
CS4245 is being reset.
The signal timings for a read and write cycle are shown in Figure 18 and Figure 19. A Start condition is
defined as a falling transition of SDA while the clock is high. A Stop condition is a rising transition while
the clock is high. All other transitions of SDA occur while the clock is low. The first byte sent to the CS4245
after a Start condition consists of a 7-bit chip address field and a R/W
The upper 5 bits of the 7-bit address field are fixed at 10011. To communicate with a CS4245, the chip
address field, which is the first byte sent to the CS4245, should match 10011 followed by the settings of
the AD1 and AD0. The eighth bit of the address is the R/W
the Memory Address Pointer (MAP) which selects the register to be read or written. If the operation is a
read, the contents of the register pointed to by the MAP will be output. Following each data byte, the memory address pointer will automatically increment to facilitate block reads and writes of successive registers. Each byte is separated by an acknowledge bit. The ACK bit is output from the CS4245 after each
input byte is read, and is input to the CS4245 from the microcontroller after each transmitted byte.
pin. Pins AD0 and AD1 form the two least-significant bits of the chip address and should
bit (high for a read, low for a write).
bit. If the operation is a write, the next byte is
38 DS656F3
Page 39

CS4245
SCL
CHIP ADDRESS (WRITE)
MAP BYTE
DATA
DATA +1
START
ACK
STOP
ACK
ACK
ACK
1 0 0 1 1 AD1 AD0 0
SDA
1 0 0 1 1 AD1 AD0 1
CHIP ADDRESS (READ)
START
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
7 0 7 0 7 0
NO
16 8 9 12 13 14 15 4 5 6 7 0 1 20 21 22 23 24
26 27 28
2 3 10 11 17 18 19 25
ACK
DATA + n
STOP
Figure 19. Control Port Timing, I²C Read
Since the read operation cannot set the MAP, an aborted write operation is used as a preamble. As shown
in Figure 19, the write operation is aborted after the acknowledge for the MAP byte by sending a stop con-
dition. The following pseudocode illustrates an aborted write operation followed by a read operation.
Send start condition.
Send 10011xx0 (chip address & write operation).
Receive acknowledge bit.
Send MAP byte.
Receive acknowledge bit.
Send stop condition, aborting write.
Send start condition.
Send 10011xx1 (chip address & read operation).
Receive acknowledge bit.
Receive byte, contents of selected register.
Send acknowledge bit.
Send stop condition.
4.13 Interrupts and Overflow
The CS4245 has a comprehensive interrupt capability. The INT output pin is intended to drive the interrupt
input pin on the host microcontroller. The INT pin may function as either an active high CMOS driver or an
active low open-drain driver (see “Active High/Low (Bit 0)” on page 50). When configured as active low
open-drain, the INT pin has no active pull-up transistor, allowing it to be used for wired-OR hook-ups with
multiple peripherals connected to the microcontroller interrupt input pin. In this configuration, an external
pull-up resistor must be placed on the INT pin for proper operation.
Many conditions can cause an interrupt, as listed in the interrupt status register descriptions (see “Interrupt
Status - Address 0Dh” on page 50). Each source may be masked off through mask register bits. In addition,
each source may be set to rising edge, falling edge, or level-sensitive. Combined with the option of levelsensitive or edge-sensitive modes within the microcontroller, many different configurations are possible, depending on the needs of the equipment designer.
The CS4245 also has a de dicated overflow output. The OVFL pin functions as active low open drain and
has no active pull-up transistor, thereby requiring an external pull-up resistor. The OVFL pin outputs an OR
of the ADCOverflow and ADCUnderflow conditions available in the Interrupt Status register; however, these
conditions do not need to be unmasked for proper operation of the OVFL pin.
DS656F3 39
Page 40

4.14 Reset
When RESET is low, the CS4245 enters a low-power mode and all internal states are reset, including the
control port and registers, the outputs are muted. When RESET
al, and the desired settings should be loaded into the control registers. Writing a 0 to the PDN bit in the Power Control register will then cause the part to leave the low-power state and begin operation.
The delta-sigma modulators settle in a matter of microseconds after the analog section is powered, either
through the application of power or by setting the RESET
much longer to reach a final value due to the presence of external capacitance on the FILT1+ and FILT2+
pins. During this voltage reference ramp delay, both SDOUT and DAC outputs will be automatically muted.
CS4245
is high, the control port becomes operation-
pin high. However, the voltage reference will take
It is recommended that RESET
operating condition to prevent power-glitch-related issues.
be activated if the analog or digital supplies drop below the recommended
4.15 Synchronization of Multiple Devices
In systems where multiple ADCs are required, care must be taken to achieve simultaneous sampling. To
ensure synchronous sampling, the mast er clocks and left/ right clocks must be the same f or all of the
CS4245s in the system. If only one master clock source is needed, one solution is to place one CS4245 in
Master Mode, and slave all of the other CS4245s to the one master. If multiple master clock sources are
needed, a possible solution would be to supply all cl ocks from the same external source and time the
CS4245 reset with the inactive edge of master clock. This will ensure that all converters begin sampling on
the same clock edge.
4.16 Grounding and Power Supply Decoupling
As with any high-resolution converter, the CS4245 requires careful attention to power supply and grounding
arrangements if its potential performance is to be realized. Figure 12 shows the recommended power arrangements, with VA connected to a clean supply. VD, which powers the digital filter, may be run from the
system logic supply (VLS or VLC) or may be po wered from the analog supply (VA) via a resistor. In this
case, no additional devices should be powered from VD. Power supply decoupling capacitors should be as
near to the CS4245 as possible, with the low value ceramic capacitor being the nearest. All signals, especially clocks, should be kept away from the FILT1+, FILT2+, VQ1 and VQ2 pins in order to avoid unwanted
coupling into the modulators. The FILT1+, FILT2+, VQ1 and VQ2 decoupling capacitors, particularly the
0.1 µF, must be positioned to minimize the electrical path from FILT1+ and FILT2+ and AGND. The CS4245
evaluation board demonstrates the optimum layout and power supply arrangements. To minimize digital
noise, connect the CS4245 digital outputs only to CMOS inputs.
40 DS656F3
Page 41

CS4245
5. REGISTER QUICK REFERENCE
This table shows the register names and their associated default values.
Addr Function 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
01h Chip ID PART3 PART2 PART1 PART0 REV3 REV2 REV1 REV0
110 0 0 0 0 1
02h Power Control Freeze Reserved Reserved Reserved PDN_MIC PDN_ADC PDN_DAC PDN
000 0 0 0 0 1
03h DAC Control 1 DAC_FM1 DAC_FM0 DAC_DIF1 DAC_DIF0 Reserved MuteDAC DeEmph DAC_M/S
000 0 1 0 0 0
04h ADC Control ADC_FM1 ADC_FM0 Reserved ADC_DIF Reserved MuteADC HPFFreeze ADC_M/S
000 0 0 0 0 0
05h MCLK
Frequency
06h Signal Selec-
tion
07h PGA Ch B
Gain Control
08h PGA Ch A
Gain Control
09h Analog Input
Control
0Ah DAC Ch A Vol-
ume Control
0Bh DAC Ch B Vol-
ume Control
0Ch DAC Control 2 DACSoft DACZero InvertDAC Reserved Reserved Reserved Reserved Active_H/L
0Dh Interrupt Status Reserved Reserved Reserved Reserved ADCClkErr DACClkErr ADCOvfl ADCUndrfl
0Eh Interrupt Mask Reserved Reserved Reserved Reserved ADCClkErrM DACClkErrM ADCOvflM ADCUndrflM
0Fh Interrupt Mode
MSB
10h Interrupt Mode
LSB
Reserved MCLK1
Freq2
000 0 0 0 0 0
Reserved AOutSel1 AOutSel0 Reserved Reserved Reserved LOOP ASynch
010 0 0 0 0 0
Reserved Reserved Gain5 Gain4 Gain3 Gain2 Gain1 Gain0
000 0 0 0 0 0
Reserved Reserved Gain5 Gain4 Gain3 Gain2 Gain1 Gain0
000 0 0 0 0 0
Reserved Reserved Reserved PGASoft PGAZero Sel2 Sel1 Sel0
000 1 1 0 0 1
Vol7 Vol6 Vol5 Vol4 Vol3 Vol2 Vol1 Vol0
000 0 0 0 0 0
Vol7 Vol6 Vol5 Vol4 Vol3 Vol2 Vol1 Vol0
000 0 0 0 0 0
110 0 0 0 0 0
000 0 0 0 0 0
000 0 0 0 0 0
Reserved Reserved Reserved Reserved ADCClkErr1 DACClkErr1 ADCOvfl1 ADCUndrfl1
000 0 0 0 0 0
Reserved Reserved Reserved Reserved ADCClkErr0 DACClkErr0 ADCOvfl0 ADCUndrfl0
000 0 0 0 0 0
MCLK1
Freq1
MCLK1
Freq0
Reserved MCLK2
Freq2
MCLK2
Freq1
MCLK2
Freq0
DS656F3 41
Page 42
CS4245
6. REGISTER DESCRIPTION
6.1 Chip ID - Register 01h
76543210
PART3 PART2 PART1 PART0 REV3 REV2 REV1 REV0
Function:
This register is Read-Only. Bits 7 through 4 are the part number ID, which is 1100b (0Ch), and the remaining
bits (3 through 0) indicate the device revision as shown in Table 5 below.
REV[2:0] Revision
001 A
010 B, C0
011 C1
Table 5. Device Revision
6.2 Power Control - Address 02h
76543210
Freeze Reserved Reserved Reserved PDN_MIC PDN_ADC PDN_DAC PDN
6.2.1 Freeze (Bit 7)
Function:
This function allows modifications to be made to certain control port bits without the changes taking effect
until the Freeze bit is disabled. To make multiple changes to these bits take effect simultaneously, set the
Freeze bit, make all changes, then clear the Freeze bit. The bits affected by the Freeze function are listed
in Table 6.
Name Register Bit(s)
MuteDAC 03h 2
MuteADC 04h 2
Gain[5:0] 07h 5:0
Gain[5:0] 08h 5:0
Vol[7:0] 0Ah 7:0
Vol[7:0] 0Bh 7:0
6.2.2 Power-Down MIC (Bit 3)
Function:
The microphone preamplifier block will enter a low-power state whenever this bit is set.
6.2.3 Power-Down ADC (Bit 2)
Function:
Table 6. Freeze-able Bits
The ADC pair will remain in a reset state whenever this bit is set.
42 DS656F3
Page 43

CS4245
6.2.4 Power-Down DAC (Bit 1)
Function:
The DAC pair will remain in a reset state whenever this bit is set.
6.2.5 Power-Down Device (Bit 0)
Function:
The device will enter a low-power state whenever this bit is set. The power-down bit is set by default and
must be cleared before normal operation can occur. The contents of the control registers are retained
when the device is in power-down.
6.3 DAC Control - Address 03h
76543210
DAC_FM1 DAC_FM0 DAC_DIF1 DAC_DIF0 Reserved MuteDAC DeEmph DAC_M/S
6.3.1 DAC Functional Mode (Bits 7:6)
Function:
Selects the required range of input sample rates.
DAC_FM1 DAC_FM0 Mode
0 0 Single-Speed Mode: 4 to 50 kHz sample rates
0 1 Double-Speed Mode: 50 to 100 kHz sample rates
1 0 Quad-Speed Mode: 100 to 200 kHz sample rates
11Reserved
Table 7. Functional Mode Selection
6.3.2 DAC Digital Interface Format (Bits 5:4)
Function:
The required relationship between LRCK, SCLK and SDIN for the DAC is defined by the DAC Digital Interface Format and the options are detailed in Table 8 and Figures 7-9.
DAC_DIF1 DAC_DIF0 Description Format Figure
0 0 Left Justified, up to 24-bit data (default) 0 7
0 1 I²S, up to 24-bit data 1 8
1 0 Right-Justified, 16-bit Data 2 9
1 1 Right-Justified, 24-bit Data 3 9
T able 8. DAC Digital Interface Formats
6.3.3 Mute DAC (Bit 2)
Function:
The DAC outputs will mute and the MUTEC
active high, it should be noted that the MUTEC
will be retained when this bit is set. The muting function is effected, similar to attenuation changes, by the
DACSoft and DACZero bits in the DAC Control 2 register.
pin will become active when this bit is set. Though this bit is
pin is active low. The common mode voltage on the outputs
DS656F3 43
Page 44

6.3.4 De-Emphasis Control (Bit 1)
Gain
dB
-10dB
0dB
Frequency
T2 = 15 µs
T1=50 µs
F1 F2
3.183 kHz 10.61 kHz
Figure 20. De-Emphasis Curve
Function:
The standard 50/15 s digital de-emphasis filter response, Figure 20, may be implemented for a sample
rate of 44.1 kHz when the DeEmph bit is configured as shown in Table 9. NOTE: De-emphasis is available
only in Single-Speed Mode.
DeEmph Description
0 Disabled (default)
1 44.1 kHz de-emphasis
Table 9. De-Emphasis Control
CS4245
6.3.5 DAC Master / Slave Mode (Bit 0)
Function:
This bit selects either master or slave operation for serial audio port 2. Setting this bit will select Master
Mode, while clearing this bit will select Slave Mode.
6.4 ADC Control - Address 04h
76543210
ADC_FM1 ADC_FM0 Reserved ADC_DIF Reserved MuteADC HPFFreeze ADC_M/S
6.4.1 ADC Functional Mode (Bits 7:6)
Function:
Selects the required range of output sample rates.
ADC_FM1 ADC_FM0 Mode
0 0 Single-Speed Mode: 4 to 50 kHz sample rates
0 1 Double-Speed Mode: 50 to 100 kHz sample rates
1 0 Quad-Speed Mode: 100 to 200 kHz sample rates
11Reserved
T a ble 10. Fu nctio nal Mod e Selection
44 DS656F3
Page 45
6.4.2 ADC Digital Interface Format (Bit 4)
Function:
The required relationship between LRCK1, SCLK1 and SDOUT is defined by the ADC Digital Interface
Format bit. The options are detailed in Table 11 and may be seen in Figure 7 and Figure 8.
ADC_DIF Description Format Figure
0 Left-Justified, up to 24-bit data (default) 0 7
1 I²S, up to 24-bit data 1 8
Table 11. ADC Digital Interface Formats
6.4.3 Mute ADC (Bit 2)
Function:
When this bit is set, the serial audio output of the both ADC channels is muted.
6.4.4 ADC High-Pass Filter Freeze (Bit 1)
Function:
When this bit is set, the internal high-pass filter is disabled. The current DC offset value will be frozen and
continue to be subtracted from the conversion result. See “High-Pass Filter and DC Offset Calibration” on
page 32.
CS4245
6.4.5 ADC Master / Slave Mode (Bit 0)
Function:
This bit selects either master or slave operation for serial audio port 1. Setting this bit selects Master
Mode, while clearing this bit selects Slave Mode.
6.5 MCLK Frequency - Address 05h
76543210
Reserved
MCLK1
Freq2
MCLK1
Freq1
MCLK1
Freq0
Reserved
MCLK2
Freq2
MCLK2
Freq1
MCLK2
Freq0
6.5.1 Master Clock 1 Frequency (Bits 6:4)
Function:
Sets the frequency of the supplied MCLK1 signal. See Table 12 for the appropriate settings.
MCLK1 Divider MCLK1 Freq2 MCLK1 Freq1 MCLK1 Freq0
÷1 000
÷1.5 001
÷2 010
÷3 011
÷4 100
Reserved 101
Reserved 11x
Table 12. MCLK 1 Frequency
DS656F3 45
Page 46

CS4245
6.5.2 Master Clock 2 Frequency (Bits 2:0)
Function:
These bits set the frequency of the supplied MCLK2 signal. See Table 13 for the appropriate settings.
MCLK2 Divider MCLK2 Freq2 MCLK2 Freq1 MCLK2 Freq0
÷1 000
÷1.5 001
÷2 010
÷3 011
÷4 100
Reserved 101
Reserved 11x
Table 13. MCLK 2 Frequency
6.6 Signal Selection - Address 06h
76543210
Reserved AOutSel1 AOutSel0 Reserved Reserved Reserved LOOP ASynch
6.6.1 Auxiliary Output Source Select (Bits 6:5)
Function:
These bits are used to select the analog output source. Please refer to Table 14.
AOutSel1 AO utSel0 Auxiliary Output Source
0 0 High Impedance
0 1 DAC Output
1 0 PGA Output
11 Reserved
Table 14. Auxiliary Output Source Selection
6.6.2 Digital Loopback (Bit 1)
Function:
When this bit is set, an internal digital loopback from the ADC to the DAC are enabled. Please refer to
“Internal Digital Loopback” on page 36.
6.6.3 Asynchronous Mode (Bit 0)
Function:
When this bit is set, the DAC and ADC may be operated at independent asynchronous sample rates derived from MCLK1 and MCLK2. When this bit is cleared, the DAC and ADC must operate at synchronous
sample rates derived from MCLK1.
46 DS656F3
Page 47

CS4245
6.7 Channel B PGA Control - Address 07h
76543210
Reserved Reserved Gain5 Gain4 Gain3 Gain2 Gain1 Gain0
6.7.1 Channel B PGA Gain (Bits 5:0)
Function:
See “Channel A PGA Gain (Bits 5:0)” on page 47.
6.8 Channel A PGA Control - Address 08h
76543210
Reserved Reserved Gain5 Gain4 Gain3 Gain2 Gain1 Gain0
6.8.1 Channel A PGA Gain (Bits 5:0)
Function:
Sets the gain or attenuation for the ADC input PGA stage. The gain may be adjusted from -12 dB to
+12 dB in 0.5 dB steps. The gain bits are in two’s complement with the Gain0 bit set for a 0.5 dB step.
Register settings outside of the ±12 dB range are reserved and must not be used. See Table 15 for example settings.
Gain[5:0] Setting
101000 -12 dB
000000 0 dB
011000 +12 dB
Table 15. Example Gain and Attenuation Settings
6.9 ADC Input Control - Address 09h
76543210
Reserved Reserved Reserved PGASoft PGAZero Sel2 Sel1 Sel0
6.9.1 PGA Soft Ramp or Zero Cross Enable (Bits 4:3)
Function:
Soft Ramp Enable
Soft Ramp allows level changes, both muting and attenuation, to be implemented by incrementally ramping, in 1/8 dB steps, from the current level to the new level at a rate of 1 dB per 8 left/right clock periods.
See Table 16.
Zero Cross Enable
Zero Cross Enable dictates that signal-level changes, either by attenuation changes or muting, will occur
on a signal zero crossing to minimize audible artifacts. The requested level change will occur after a timeout period between 512 and 1024 sample periods (10.7 ms to 21.3 ms at 48 kHz sample rate) if the signal
does not encounter a zero crossing. The zero cross function is independently monitored and implemented
for each channel. See Table 16.
Soft Ramp and Zero Cross Enable
Soft Ramp and Zero Cross Enable dictate that signal-level changes, either by attenuation changes or muting, will occur in 1/8 dB steps and be implemented on a signal zero crossing. The 1/8 dB level change will
DS656F3 47
Page 48

occur after a time-out period between 512 and 1024 sample periods (10.7 ms to 21.3 ms at 48 kHz sample rate) if the signal does not encounter a zero crossing. The zero cross function is independently monitored and implemented for each channel. See Table 16.
PGASoft PGAZeroCross Mode
0 0 Changes to affect immediately
0 1 Zero Cross enabled
1 0 Soft Ramp enabled
1 1 Soft Ramp and Zero Cross enabled (default)
Table 16. PGA Soft Cross or Zero Cross Mode Selection
6.9.2 Analog Input Selection (Bits 2:0)
Function:
These bits are used to select the input source for the PGA and ADC. Please see Table 17.
Sel2 Sel1 Sel0 PGA/ADC Input
0 0 0 Microphone-Level Inputs (+32 dB Gain Enabled)
0 0 1 Line-Level Input Pair 1
0 1 0 Line-Level Input Pair 2
0 1 1 Line-Level Input Pair 3
1 0 0 Line-Level Input Pair 4
1 0 1 Line-Level Input Pair 5
1 1 0 Line-Level Input Pair 6
1 1 1 Reserved
CS4245
Table 17. Analog Input Multiplexer Selection
6.10 DAC Channel A Volume Control - Address 0Ah
See 6.11 DAC Channel B Volume Control - Address 0Bh.
6.11 DAC Channel B Volume Control - Address 0Bh
76543210
Vol7 Vol6 Vol5 Vol4 Vol3 Vo l2 Vol1 Vol0
6.11.1 Volume Control (Bits 7:0)
Function:
The digital volume control allows the user to attenuate the signal in 0.5 dB increments from 0 to -127 dB.
The Vol0 bit activates a 0.5 dB attenuation when set, and no attenuation when cleared. The Vol[7:1] bits
activate attenuation equal to their decimal equivalent (in dB). Example volume settings are decoded as
48 DS656F3
Page 49

CS4245
shown in Table 18. The volume changes are implemented as dictated by the DACSoft and DACZeroCross bits in the DAC Control 2 register (see Section 6.12.1).
Binary Code Volume Setting
00000000 0 dB
00000001 -0.5 dB
00101000 -20 dB
00101001 -20.5 dB
11111110 -127 dB
11111111 -127.5 dB
Table 18. Digital Volume Control Example Settings
6.12 DAC Control 2 - Address 0Ch
76543210
DACSoft DACZero InvertDAC Reserved Reserved Reserved Reserved Active_H/L
6.12.1 DAC Soft Ramp or Zero Cross Enable (Bits 7:6)
Function:
Soft Ramp Enable
Soft Ramp allows level changes, both muting and attenuation, to be implemented by incrementally ramping, in 1/8 dB steps, from the current level to the new level at a rate of 1 dB per 8 left/right clock periods.
See Table 19.
Zero Cross Enable
Zero Cross Enable dictates that signal-level changes, either by attenuation changes or muting, will occur
on a signal zero crossing to minimize audible artifacts. The requested level change will occur after a timeout period between 512 and 1024 sample periods (10.7 ms to 21.3 ms at 48 kHz sample rate) if the signal
does not encounter a zero crossing. The zero cross function is independently monitored and implemented
for each channel. See Table 19.
Soft Ramp and Zero Cross Enable
Soft Ramp and Zero Cross Enable dictate that signal-level changes, either by attenuation changes or muting, will occur in 1/8 dB steps and be implemented on a signal zero crossing. The 1/8 dB level change will
occur after a time-out period between 512 and 1024 sample periods (10.7 ms to 21.3 ms at 48 kHz sample rate) if the signal does not encounter a zero crossing. The zero cross function is independently monitored and implemented for each channel. See Table 19.
DACSoft DACZeroCross Mode
0 0 Changes to affect immediately
0 1 Zero Cross enabled
1 0 Soft Ramp enabled
1 1 Soft Ramp and Zero Cross enabled (default)
Table 19. DAC Soft Cross or Zero Cross Mode Selection
6.12.2 Invert DAC Output (Bit 5)
Function:
When this bit is set, the output of the DAC is inverted.
DS656F3 49
Page 50

CS4245
6.12.3 Active High/Low (Bit 0)
Function:
When this bit is set, the INT pin functions as an active high CMOS driver.
When this bit is cleared, the INT pin functions as an active low open drain driver and will require an external pull-up resistor for proper operation.
6.13 Interrupt Status - Address 0Dh
76543210
Reserved Reserved Reserved Reserved ADCClkErr DACClkErr ADCOvfl ADCUndrfl
For all bits in this register, a ‘1’ means the associated interrupt condition has occurred at least once since
the register was last read. A ‘0’ me ans the associated interrupt condition has NOT occurred since the last
reading of the register. Status bits that are masked off in the associated mask register will always be ‘0’ in
this register. This register defaults to 00h.
6.13.1 ADC Clock Error (Bit 3)
Function:
Indicates the occurrence of an ADC clock error condition.
6.13.2 DAC Clock Error (Bit 2)
Function:
Indicates the occurrence of a DAC clock error condition.
6.13.3 ADC Overflow (Bit 1)
Function:
Indicates the occurrence of an ADC overflow condition.
6.13.4 ADC Underflow (Bit 0)
Function:
Indicates the occurrence of an ADC underflow condition.
6.14 Interrupt Mask - Address 0Eh
76543210
Reserved Reserved Reserved Reserved ADCClkErrM DACClkErrM ADCOvflM ADCUndrflM
Function:
The bits of this register serve as a mask for the Status sources found in the register “Interrupt Status - Ad-
dress 0Dh” on page 50. If a mask bit is set to 1, the error is unmasked, meaning that its occurrence will affect
the INT pin and the status register. If a mask bit is set to 0, the error is masked, meaning that its occurrence
will not affect the INT pin or the status register. The bit positions align with the corresponding bits in the Status register.
50 DS656F3
Page 51

CS4245
6.15 Interrupt Mode MSB - Address 0Fh
6.16 Interrupt Mode LSB - Address 10h
76543210
Reserved Reserved Reserved Reserved ADCClkErr1 DACClkErr1 ADCOvfl1 ADCUndrfl1
Reserved Reserved Reserved Reserved ADCClkErr0 DACClkErr0 ADCOvfl0 ADCUndrfl0
Function:
The two Inter rupt Mode registers form a 2-bit code for each Interrupt Status register function. There are
three ways to set the INT pin active in accordance with the interrupt condition. In the Rising-Edge Active
Mode, the INT pin becomes active on the arrival of the interrupt condition. In the Falling-Edge Active Mode,
the INT pin becomes active on the removal of the interrupt condition. In Level-Active Mode, the INT pin remains active during the interrupt condition.
00 - Rising edge active
01 - Falling edge active
10 - Level active
11 - Reserved
DS656F3 51
Page 52

7. PARAMETER DEFINITIONS
Dynamic Range
The ratio of the rms value of the signal to the rms sum of all other spectral components over the specified
bandwidth. Dynamic Range is a signal-to-noise ratio measurement over the specified bandwidth made with
a -60 dBFS signal. 60 dB is added to resulting measurement to refer the measurement to full scale. This
technique ensures that the distortion components are below the noise level and do not affect the measurement. This measurement technique has been accepted by the Au dio Engineering Society, AES17-1991,
and the Electronic Industries Association of Japan, EIAJ CP-307. Expressed in decibels.
Total Harmonic Distortion + Noise
The ratio of the rms value of the signal to the rms sum of all other spectral components over the specified
bandwidth (typically 10 Hz to 20 kHz), including distortion components. Expressed in decibels. Measured
at -1 and -20 dBFS as suggested in AES17-1991 Annex A.
Frequency Response
A measure of the amplitude response variation from 10 Hz to 20 kHz relative to the amplitude response at
1 kHz. Units in decibels.
Interchannel Isolation
A measure of crosstalk between the left and right channels. Measured for each channel at the converter's
output with no signal to the input under test and a full-scale signal applied to the other channel. Units in decibels.
CS4245
Interchannel Gain Mismatch
The gain difference between left and right channels. Units in decibels.
Gain Drift
The change in gain value with temperature. Units in ppm/°C.
52 DS656F3
Page 53

8. DAC FILTER PLOTS
Figure 21. DAC Single-Speed Stopband Rejection Figure 22. DAC Single-Speed Transition Band
0 0.05 0.1 0.15 0.2 0.25 0.3 0.35 0.4 0.45 0.5
-0.25
-0. 2
-0.15
-0. 1
-0.05
0
0.05
Frequency (normalized to Fs)
Amplitude dB
Figure 23. DAC Single-Speed Transition Band Figure 24. DAC Single-Speed Passband Ripple
0.45 0.46 0.47 0.48 0.49 0.5 0.51 0.52 0.53 0.54 0.5
5
-10
-9
-8
-7
-6
-5
-4
-3
-2
-1
0
Frequency (normalized to Fs)
Amplitude dB
Figure 25. DAC Double-Speed Stopband Rejection Figure 26. DAC Double-Speed Transition Band
CS4245
DS656F3 53
Page 54

0 0.05 0.1 0.15 0.2 0.25 0.3 0.35 0.4 0.45 0.5
-0. 2
-0. 1
0
0.1
0.2
0.3
0.4
0.5
0.6
0.7
0.8
Frequency (normalized to Fs)
Amplitude dB
0.45 0.46 0.47 0.48 0.49 0.5 0.51 0.52 0.53 0.54 0.55
-10
-9
-8
-7
-6
-5
-4
-3
-2
-1
0
1
Frequency (normalized to Fs)
Amplitude dB
Figure 27. DAC Double-Speed Transition Band Figur e 28. DAC Double-Speed Passband Ripple
Figure 29. DAC Quad-Speed Stopband Rejection Figure 30. DAC Quad-Speed Transition Band
0 0.05 0.1 0.15 0.2 0.25 0.3 0.35 0.4 0.45 0.5
-1. 5
-1
-0. 5
0
Frequency (normalized to Fs)
Amplitude dB
Figure 31. DAC Quad-Speed Transition Band Figure 32. DAC Quad-Speed Passband Ripple
CS4245
0
-10
-20
-30
-40
-50
Amplitude (dB)
-60
-70
-80
-90
-100
0 0.1 0.2 0.3 0.4 0.5 0.6 0.7 0.8 0.9 1
0
-5
-10
-15
-20
-25
Amplitude (dB)
-30
-35
-40
-45
-50
0.4 0.45 0.5 0.55 0.6 0.65 0.7
54 DS656F3
Frequency(normalized to Fs)
Frequency(normalized to Fs)
0
-10
-20
-30
Amplitude (dB)
-40
-50
-60
0.35 0.4 0.45 0.5 0.55 0.6 0.65 0.7 0.75
Frequency(normalized to Fs)
Page 55

9. ADC FILTER PLOTS
-140
-130
-120
-110
-100
-90
-80
-70
-60
-50
-40
-30
-20
-10
0
0.0 0.1 0 .2 0 .3 0.4 0.5 0 .6 0 .7 0 .8 0 .9 1.0
Frequency (normalized to Fs)
Amplitude (dB)
-140
-130
-120
-110
-100
-90
-80
-70
-60
-50
-40
-30
-20
-10
0
0.40 0.42 0.44 0.46 0.48 0.50 0.52 0.54 0.56 0.58 0.60
Frequency (normalized to Fs)
Amplitude (dB)
-10
-9
-8
-7
-6
-5
-4
-3
-2
-1
0
0.45 0.46 0.47 0.48 0.49 0.5 0.51 0.52 0.53 0.54 0.55
Frequency (normalized to Fs)
Amplitude (dB)
-0.10
-0.08
-0.06
-0.04
-0.02
0.00
0.02
0.04
0.06
0.08
0.10
0 0 .05 0.1 0 .15 0.2 0 .25 0.3 0.3 5 0.4 0 .45 0.5
Frequency (normalized to Fs)
Amplitude (dB)
-140
-130
-120
-110
-100
-90
-80
-70
-60
-50
-40
-30
-20
-10
0
0.0 0.1 0 .2 0 .3 0.4 0.5 0 .6 0 .7 0 .8 0.9 1.0
Frequency (normalized to Fs)
Amplitude (dB)
-140
-130
-120
-110
-100
-90
-80
-70
-60
-50
-40
-30
-20
-10
0
0.40 0.42 0.44 0.46 0.48 0.50 0.52 0.54 0.56 0.58 0.60
Frequency (normalized to Fs)
Amplitude (dB)
Figure 33. ADC Single-Speed Stopband Rejection Figure 34. ADC Single-Speed Stopband Rejection
CS4245
Figure 35. ADC Single-Speed Transition Band (Detail) Figure 36. ADC Single-Speed Passband Ripple
Figure 37. ADC Double-Speed Stopband Rejection Figure 38. ADC Double-Speed Stopband Rejection
DS656F3 55
Page 56

-10
-9
-8
-7
-6
-5
-4
-3
-2
-1
0
0.46 0.47 0.48 0.49 0.50 0.51 0.52
Frequency (normalized to Fs)
Amplitude (dB)
-0.10
-0.08
-0.06
-0.04
-0.02
0.00
0.02
0.04
0.06
0.08
0.10
0.00 0.05 0.10 0.15 0.20 0.25 0.30 0.35 0.40 0.45 0.50
Frequency (normalized to Fs)
Amplitude (dB)
-140
-130
-120
-110
-100
-90
-80
-70
-60
-50
-40
-30
-20
-10
0
0.0 0.1 0 .2 0 .3 0.4 0.5 0 .6 0 .7 0 .8 0.9 1.0
Frequency (normalized to Fs)
Amplitude (dB)
-140
-130
-120
-110
-100
-90
-80
-70
-60
-50
-40
-30
-20
-10
0
0.20 0.25 0.30 0.35 0.40 0.45 0.50 0.55 0.60 0.65 0.70 0.75 0.80 0.85
Frequency (normalized to Fs)
Amplitude (dB)
-10
-9
-8
-7
-6
-5
-4
-3
-2
-1
0
0.10 0.15 0.20 0.25 0.30 0.35 0.40 0.45 0.50
Frequency (normalized to Fs)
Amplitude (dB)
-0.10
-0.08
-0.06
-0.04
-0.02
0.00
0.02
0.04
0.06
0.08
0.10
0.00 0.03 0.05 0.08 0.10 0.13 0.15 0.18 0.20 0.23 0.25 0.28
Frequency (normalized to Fs)
Amplitude (dB)
Figure 39. ADC Double-Speed Transition Band (Detail) Figure 40. ADC Double -Speed Passband Ripple
CS4245
Figure 41. ADC Quad-Speed Stopband Rejection Figure 42. ADC Quad-Speed Stopband Rejection
Figure 43. ADC Quad-Speed Transition Band (Detail) Figure 44. ADC Quad-Speed Passband Ripple
56 DS656F3
Page 57

10.PACKAGE DIMENSIONS
48L LQFP PACKAGE DRAWING
E1
E
D1
D
1
e
L
B
A1
A
CS4245
INCHES MILLIMETERS
DIM MIN NOM MAX MIN NOM MAX
A --- 0.055 0.063 --- 1.40 1.60
A1 0.002 0.004 0.006 0.05 0.10 0.15
B 0.007 0.009 0.011 0.17 0.22 0.27
D 0.343 0.354 0.366 8.70 9.0 BSC 9.30
D1 0.272 0.28 0.280 6.90 7.0 BSC 7.10
E 0.343 0.354 0.366 8.70 9.0 BSC 9.30
E1 0.272 0.28 0.280 6.90 7.0 BSC 7.10
e* 0.016 0.020 0.024 0.40 0.50 BSC 0.60
L 0.018 0.24 0.030 0.45 0.60 0.75
* Nominal pin pitch is 0.50 mm *Controlling dimension is mm. *JEDEC Designation: MS022
0.000° 4° 7.000° 0.00° 4° 7.00°
11.THERMAL CHARACTERISTICS AND SPECIFICATIONS
Parameters Symbol Min Typ Max Units
Package Thermal Resistance (Note 1) 48-LQFP
Allowable Junction Temperature
1. JA is specified according to JEDEC specifications for multi-layer PCBs.
DS656F3 57
JA
JC
-
-
--125
48
15
-
-
°C/Watt
°C/Watt
C
Page 58

CS4245
12.ORDERING INFORMATION
Product Description Package Pb-Free Grade Temp Range Container Order #
CS4245
CS4245
CDB4245 CS4245 Evaluation Board No - - - CDB4245
24-bit, 192 kHz
Stereo Audio CODEC
24-bit, 192 kHz
Stereo Audio CODEC
48-LQFP Yes Commercial -10° to +70° C
48-LQFP Yes Automotive -40° to +105° C
Tray CS4245-CQZ
Tape & Reel CS4245-CQZR
Tray CS4245-DQZ
Tape & Reel CS4245-DQZR
13.REVISION HISTORY
Release Changes
– Removed the MAP auto-increment functional description from the Control Port Description and Timing section
beginning on page 37.
F1
F2
F3
– Added device revision information to the Chip ID - Register 01h description on page 42.
– Updated the VQ1 Output Impedance specification in the DC Electrical Characteristics table on page 20.
– Updated the Microphone Interchannel Isolation specification in the ADC Analog Characteristics table on page 15.
– Added Automotive Grade
– Changed MCLK1 and MCLK2 to input only in the Pin Descriptions table on page 7.
– Updated the DAC Analog Characteristics table on page 10.
– Updated the ADC Analog Characteristics table on page 13.
– Updated the Auxiliary Output Analog Characteristics table on page 17.
– Updated the DC Electrical Characteristics table on page 20.
– Updated the Digital Interface Characteristics table on page 21.
– Updated the Switching Characteristics - Serial Audio Port 1 table on page 22.
– Updated the Switching Characteristics - Control Port - SPI Format table on page 28.
– Updated the Typical Connection Diagram on page 29.
– Switched Channel B PGA Control - Address 07h on page 47 and Channel A PGA Control - Address 08h on
page 47.
– Added Table 3.
58 DS656F3
Page 59

CS4245
Contacting Cirrus Logic Support
For all product questions and inquiries, contact a Cirrus Logic Sales Representative.
To find the one nearest you, go to www.cirrus.com
IMPORTANT NOTICE
Cirrus Logic, Inc. and its subsidiaries (“Cirrus”) believe that the information contained in this document is accurate and reliable. However, the information is subject
to change without notice and is provided “AS IS” without warranty of any kind (express or implied). Customers are advised to obtain the latest version of relevant
information to verify, before placing orders, that information being relied on is current and complete. All products are sold subject to the terms and conditions of sale
supplied at the time of order acknowledgment, including those pertaining to warranty, indemnification, and limitation of liability. No responsibility is assumed by Cirrus
for the use of this information, including use of this information as the basis for manufacture or sale of any items, or for infringement of patents or other rights of third
parties. This document is the property of Cirrus and by furnishing this information, Cirrus grants no license, express or implied under any patents, mask work rights,
copyrights, trademarks, trade secrets or other intellectual property rights. Cirrus owns the copyrights associated with the information contained herein and gives consent for copies to be made of the information only for use within your organization with respect to Cirrus integrated circuits or other products of Cirrus. This consent
does not extend to other copying such as copying for general distribution, advertising or promotional purposes, or for creating any work for resale.
CERTAIN APPLICATIONS USING SEMICONDUCTOR PRODUCTS MAY INVOLVE POTENTIAL RISKS OF DEATH, PERSONAL INJURY, OR SEVERE PROPERTY OR ENVIRONMENTAL DAMAGE (“CRITICAL APPLICATIONS”). CIRRUS PRODUCTS ARE NOT DESIGNED, AUTHORIZED OR WARRANTED FOR USE
IN AIRCRAFT SYSTEMS, MILITARY A PPLICATIONS, PRODUCTS SURGICALLY IMPLANTED INTO THE BODY, AUTOMOTIVE SAFETY OR SECURITY DEVICES, LIFE SUPPORT PRODUCTS OR OTHER CRITICAL APPLICATIONS. INCLUSION OF CIRRUS PRODUCTS IN SUCH APPLICATIONS IS UNDERSTOOD
TO BE FULLY AT THE CUSTOMER’S RISK AND CIRRUS DISCLAIMS AND MAKES NO WARRANTY, EXPRESS, STATUTORY OR IMPLIED, INCLUDING THE
IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS FOR PARTICULAR PURPOSE, WITH REGARD TO ANY CIRRUS PRODUCT THAT IS USED
IN SUCH A MANNER. IF THE CUSTOMER OR CUSTOMER’S CUSTOMER USES OR PERMITS THE USE OF CIRRUS PRODUCTS IN CRITICAL APPLICATIONS, CUSTOMER AGREES, BY SUCH USE, TO FULLY INDEMNIFY CIRRUS, ITS OFFICERS, DIRECTORS, EMPLOYEES, DISTRIBUTORS AND OTHER
AGENTS FROM ANY AND ALL LIABILITY, INCLUDING ATTORNEYS’ FEES AND COSTS, THAT MAY RESULT FROM OR ARISE IN CONNECTION WITH
THESE USES.
Cirrus Logic, Cirrus, the Cirrus Logic logo designs, and Popguard are trademarks of Cirrus Logic, Inc. All other brand and product names in this document may be
trademarks or service marks of their respective owners.
I²C is a registered trademark of Philips Semiconductor.
SPI is a trademark of Motorola, Inc.
DS656F3 59
 Loading...
Loading...