Page 1

Quick
Reference Guide
fx-CG10 PRIZM
The status bar will display messages and current status like battery
level, angle mode, fraction results, complex mode, or input/output
settings.
Select the desired icon by highlighting it and pressing lor just
press the number or letter in the lower right corner.
The function keys allow you to access the tab (soft key) menus that
will come up at the bottom of the screen. When an (>) appears
above the u key, selecting u will offer more on-screen choices.
The pkey displays every mode the calculator has. To select a
mode, you may $Nto the desired icon and press lor press
the number or letter in the lower right hand corner of the icon.
The dkey operates like the back arrow on a web browser; it will
take you back one screen each time you select it. The dkey will
not take you to the icon menu.
The Lkey activates any function displayed on or above the calculator buttons that is yellow. For example, to nd the square root of
number, you would need to press L, then s. L5gives
you access to on-screen color formatting.
The Okey will power the unit on. To turn the unit off, press the
yellow L key, then Okey.
The akey activates any function displayed on or above the
calculator buttons that is in red. For example, to type the letter A,
press a, then f.
The lkey executes operations. When data is entered, the l
button must be pressed to store the data.
Page 2

The following explains the meaning of each icon on the fx-CG10 icon menu
ICON
Menu
Name
RUN
MATRIX
STATISTICS
eACTIVITY
SPREAD-
SHEET
GRAPH
Description
This icon menu is used for general computations, including binary, octal, decimal, and hexadecimal
functions and matrices.
This icon menu is used to perform single-variable (standard deviation) and paired variable (regression)
statistical calculations, to perform test, to analyze data and to draw statistical graphs.
eActivity lets you input text, math expressions, and other data in a notebook-like interface.
Use this mode when you want to store text, formulas, or built-in application data in a le.
This icon menu is used for creating spreadsheets.
This icon menu is used to draw, store and calculate information of functions.
DYNAMIC
GRAPH
TABLE
RECURSION
CONIC
GRAPH
EQUATION
PROGRAM
This icon menu is used to store functions, to generate a numeric table of different solutions
as the values assigned to variables in a function change, and to draw graphs.
This icon menu is used to graph parabolas, circles, ellipses, and hyperbolas. You can input
a rectangular function, polar coordinate function or a parametric function for graphing.
This icon menu is used to solve linear equations with two through six unknowns, and high-order
equations from 2nd to 6th degree.
This icon menu is used to graph parabolas, circles, ellipses, and hyperbolas.
You can input a rectangular function, polar coordinate function or a arametric function for graphing.
This icon menu is used to solve linear equations with two through six unknowns, and high-order
equations from 2nd to 6th degree.
This icon menu is used to store programs in the program area and to run programs.
2
Getting Started with the fx-CG10
Page 3

The following explains the meaning of each icon on the fx-CG10 icon menu
ICON Menu Name Description
FINANCIAL
DATA
ANALYZER
LINK
LINK
MEMORY
SYSTEM
GEOMETRY
This icon menu is used to perform nancial calculations and to draw cash
ow and other types of graphs.
This icon menu is used to control the optionally available EA-200 Data Analyzer.
For information about this icon menu, download the E-CON2 manual from http://edu.casio.com.
This icon menu is used to transfer memory contents or back-up data to another unit or PC.
This icon is used to manage data stored in memory.
This icon menu is used to initialize memory, adjust contrast, reset memory, and to manage
other system settings.
This icon menu allows you to draw, analyze and animate geometric objects.
PICTURE
PLOT
Conversion
This icon menu allows you to plot points (that represents coordinates)
on screen and then perform various analysis of the data collected.
This icon menu allows you to perform unit conversions of length, area, volume, time, temperature,
velocity, mass, force/weight, pressure, energy/work, and power.
Getting Started with the fx-CG10
3
Page 4
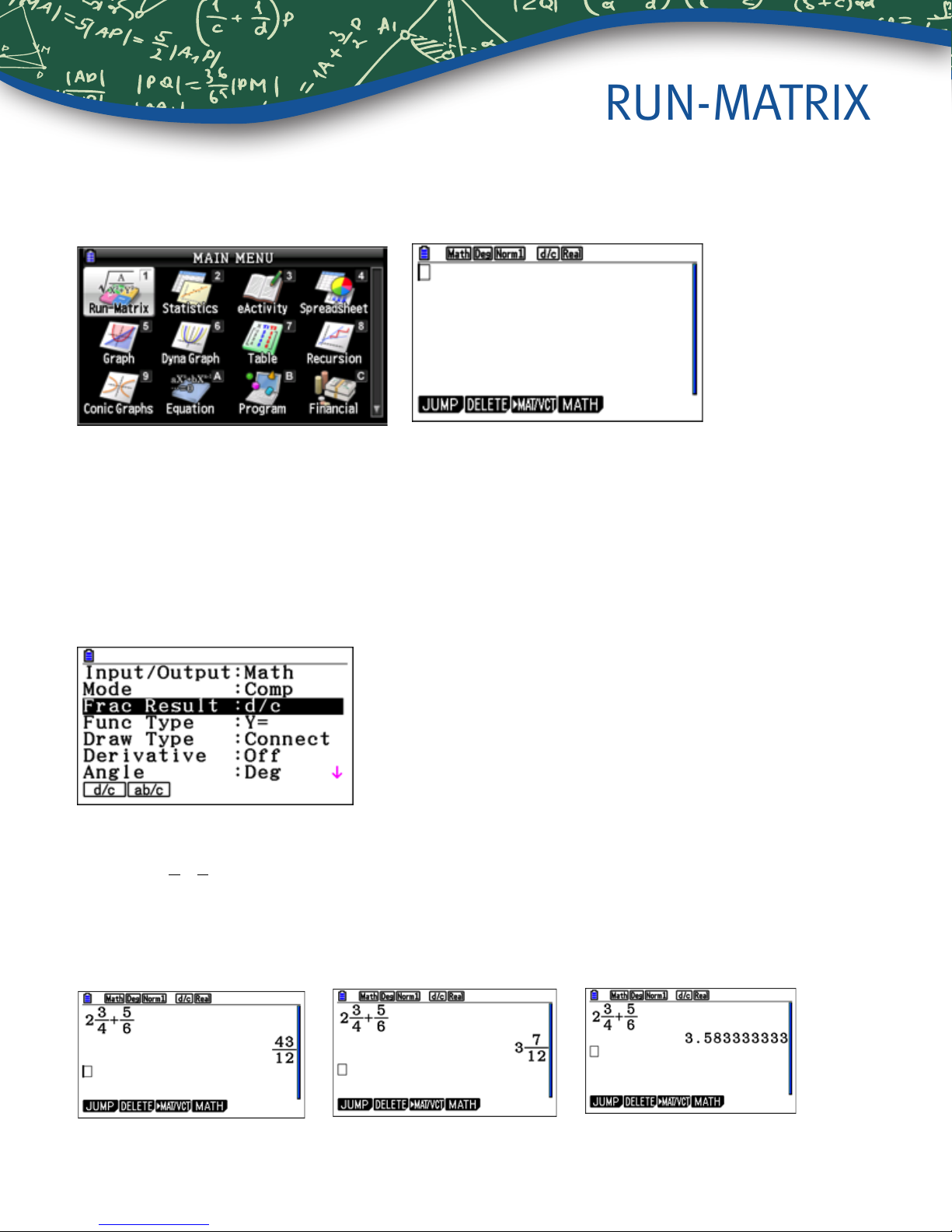
RUN-MATRIX
3
4
5
6
For basic calculations, like those that can be done on a scientic calculator, use the Run-Matrix menu.
From the Main Menu, press 1.
To select how certain commands and results will be interpreted or displayed, press Lp(SET UP). For Input/
Output, select Math for natural display of fractions, radicals and other expressions. For Frac Result, select d/c for a
fraction result as the default or ab/c for a mixed number as the default. For Angle, select Deg or Rad for degrees or
radians.
Note: the status bar at the top of the screen displays the selection for some of these options.
1. Evaluate
Press LzZ2$3$4$+z5$6l. To see the result as a mixed number,
press LxX. To see the result as a decimal, press x.
2
.
+
4
Getting Started with the fx-CG10
Page 5
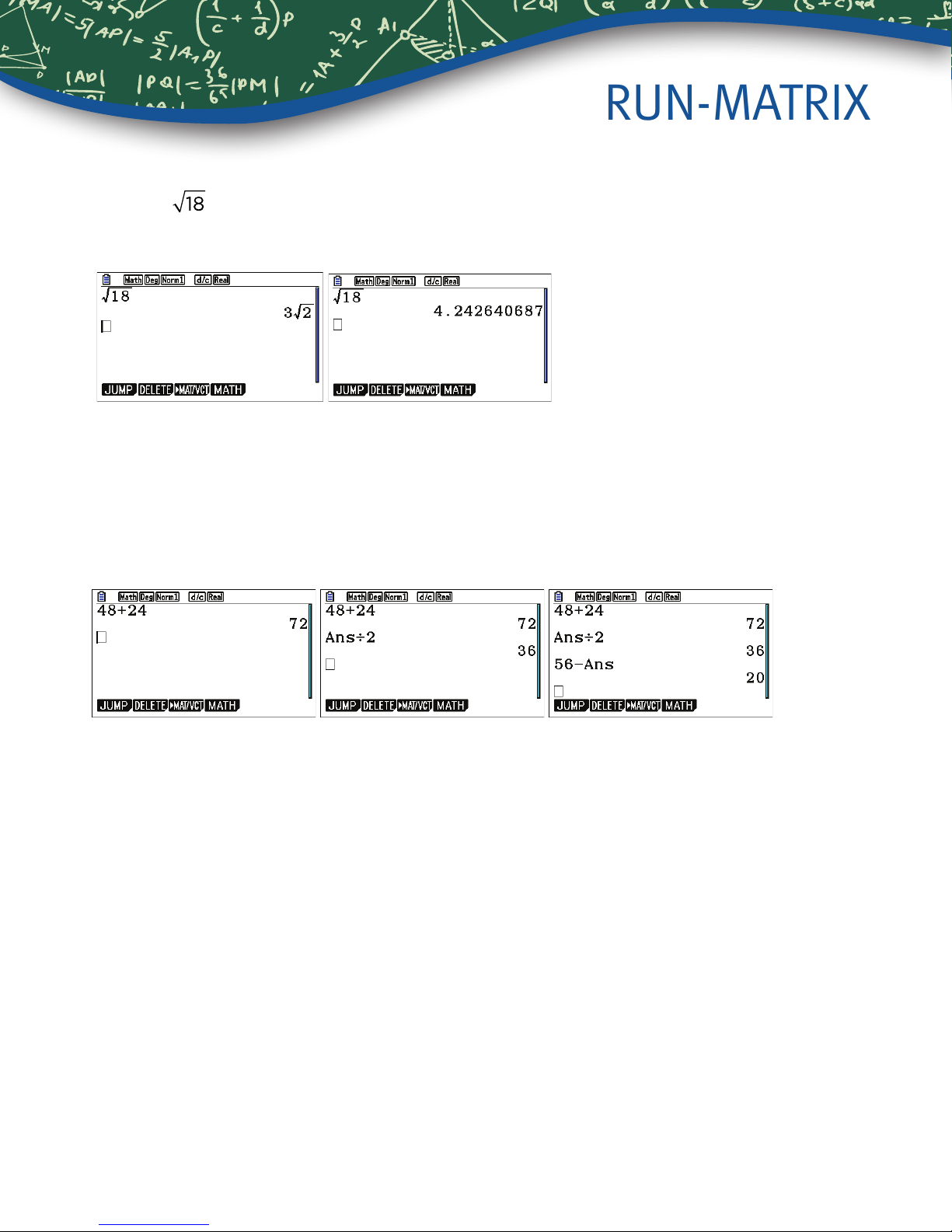
RUN-MATRIX
2. Simplify .
LsS18l. To see the result as a decimal, press x.
3. Add 48 and 24. Then, divide by 2. Finally, subtract from 56.
The purpose of this example is to demonstrate the Ans key. Ans represents the previous answer. Press
48+24l. Then, press M2l. Ans appears automatically when an operation symbol is
pressed. However, Ans has to be pressed for the subtraction part. Press 56-Ln(Ans)l.
Getting Started with the fx-CG10
5
Page 6

GRAPH
To construct graphs and use graphical analysis commands, use the Graph menu. From the Main Menu, press 5.
The rst screen is the function/relation editor. To select how certain results will be displayed, press Lp
(SET UP). The suggested selections for Coord, Grid, Axes and Label are shown. Scroll down to these selections.
To make a change, highlight the item and use the function button that appears directly below the desired tab. For
example, when Coord is highlighted, q(On) will turn coordinates on and w(Off) will turn coordinates off.
Press d to return to the editor.
The Math Club plans to sell t-shirts. Previous experience suggests that the number of t-shirts sold depends
on the price. A good model for the number sold, y, as a function of the price, x, is y = -2x + 40.
1. Construct a graph of this equation.
To construct a graph of this model, press n2f+40l. To select the view window, press
Le(V-Window). Change the values for the window, as shown, pressing l after each value. The values for
Scale determines the location for the marks on the axes and the gridlines. Press d to return to the editor.
To draw the graph, press u(DRAW). When a graph is displayed the +key can be used to zoom in,
the - key to zoom out, and$!BN to scroll.
6
Getting Started with the fx-CG10
Page 7
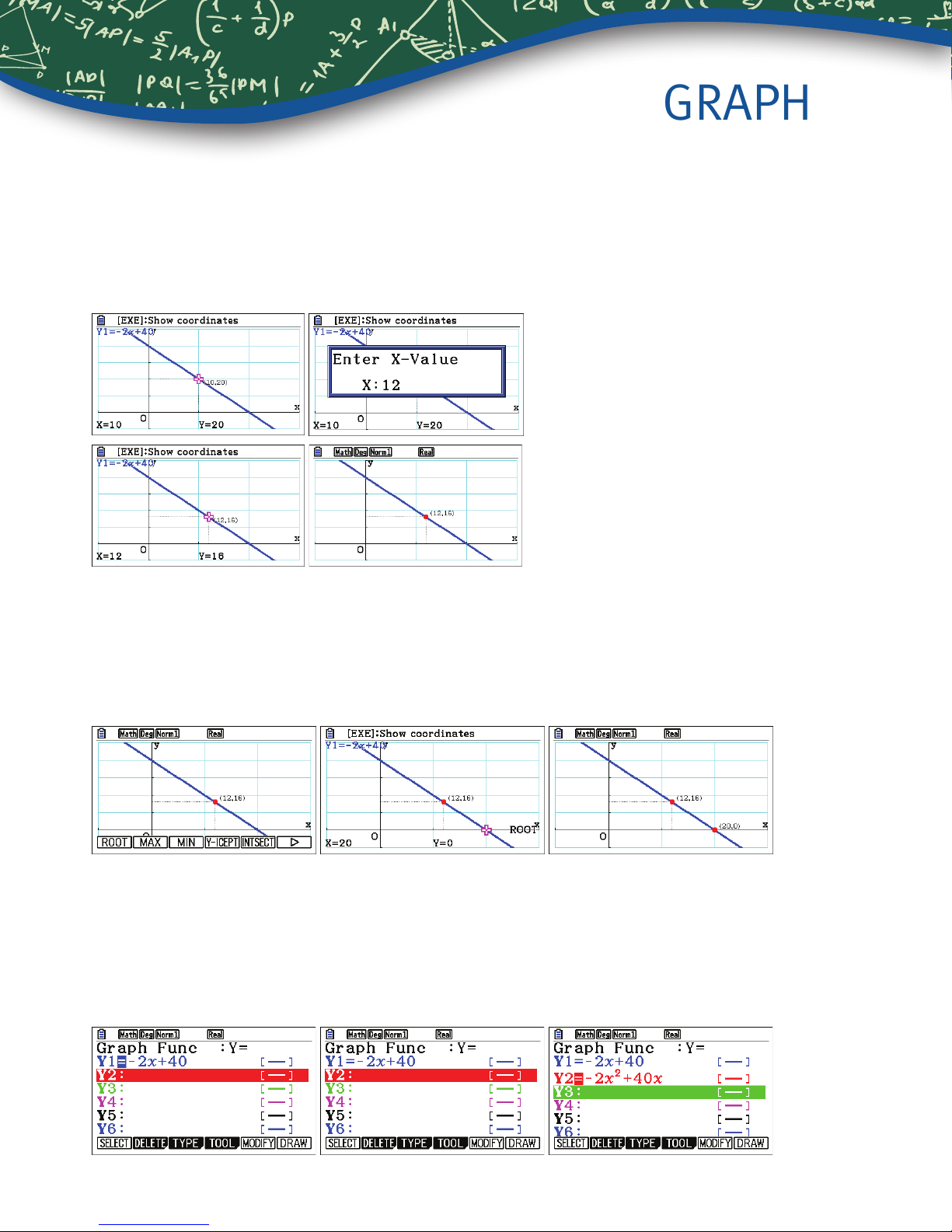
GRAPH
−2x + 40 = 0
−2x + 40
x−2x+40
−2x2+ 40 x
2. How many shirts would be sold at a price of $12 per t-shirt?
To trace on the graph, press Lq(Trace). Use $! to move the cursor. To select a specic value, type
the value, in this case 12. A dialogue box opens, press l. To mark a point and keep the coordinates on the
display, press l a second time.
3. There is a price that is too high, meaning no shirts are sold. At that point, the x-intercept of the graph (y = 0) and the
value of x is a root of the equation
To nd the root, press Ly(G-Solv)q(ROOT). The result, $20, is shown at the bottom of the screen. To mark
an intercept and keep the coordinates on the display, press l a second time.
4. If
or
To graph this function, rst, deselect the previous equation by pressing d, B so the cursor is on Y1,
then press q(SELECT)N. Note, the = sign is not highlighted. The cursor should now be on Y2.
Press n2fs+40fl.
shirts are sold at price, x, then the number of dollars collected for the sale is
.
.
( )
Getting Started with the fx-CG10
7
Page 8
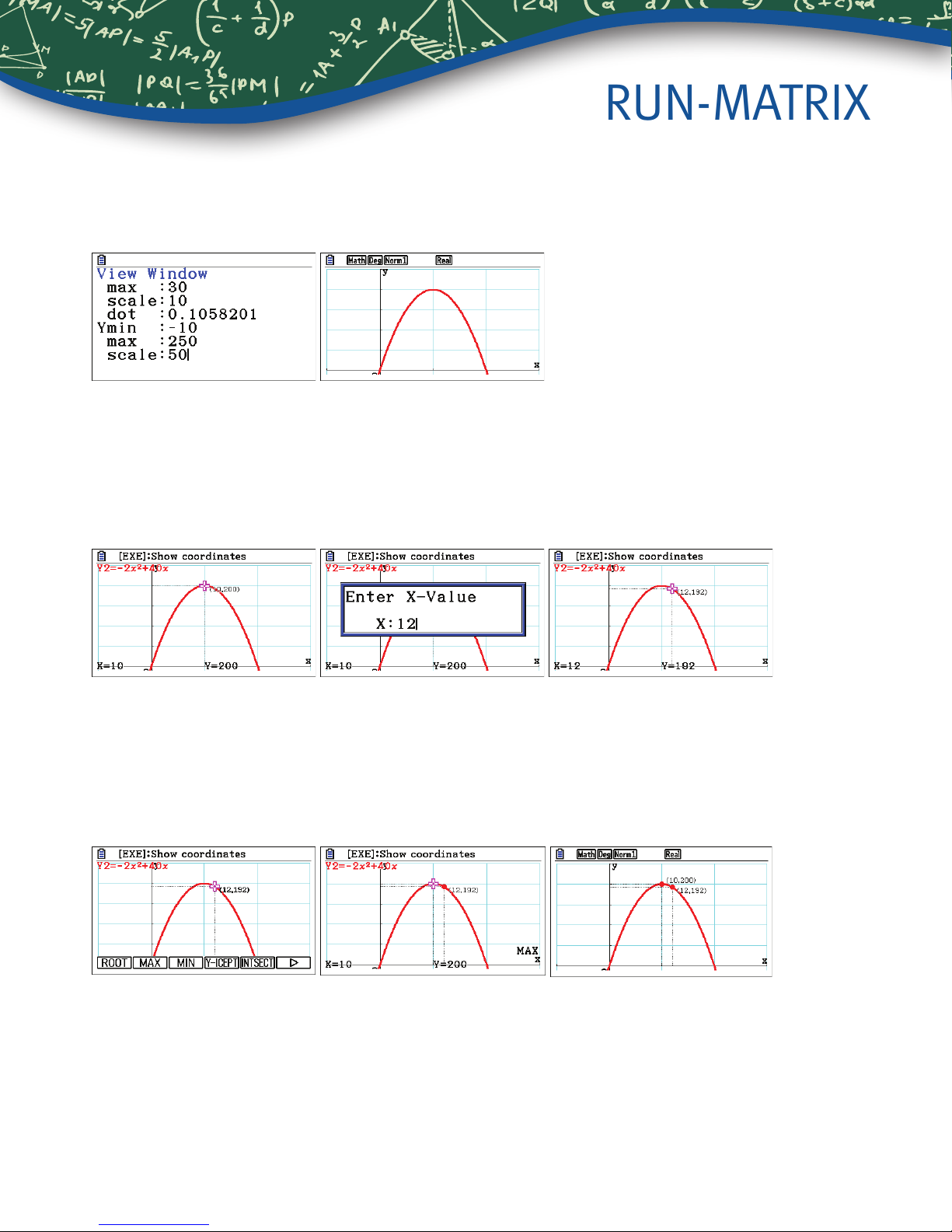
RUN-MATRIX
To select the view window, press Le(V-Window). Change the values for the window so that Ymax is 250 and
Yscale is 50. Press d to return to the editor. To draw the graph, press u(DRAW).
5. Compute the number of dollars earned, if each t-shirt is sold at $12.
To compute the number of dollars earned if shirts are sold for $12, press Lq(Trace). Type the value, in this
case 12. A dialogue box opens, pressl. The models predict that at a price of $12, 16 shirts will be sold
for a total of $192.
6. Determine the price that will give the greatest prot.
To determine the price that is predicted to make the most money, press Ly(G-Solv)w(MAX). The results,
$10 and $200, are shown at the bottom of the screen. To mark the point and keep the coordinates on the display,
press l a second time.
8
Getting Started with the fx-CG10
Page 9
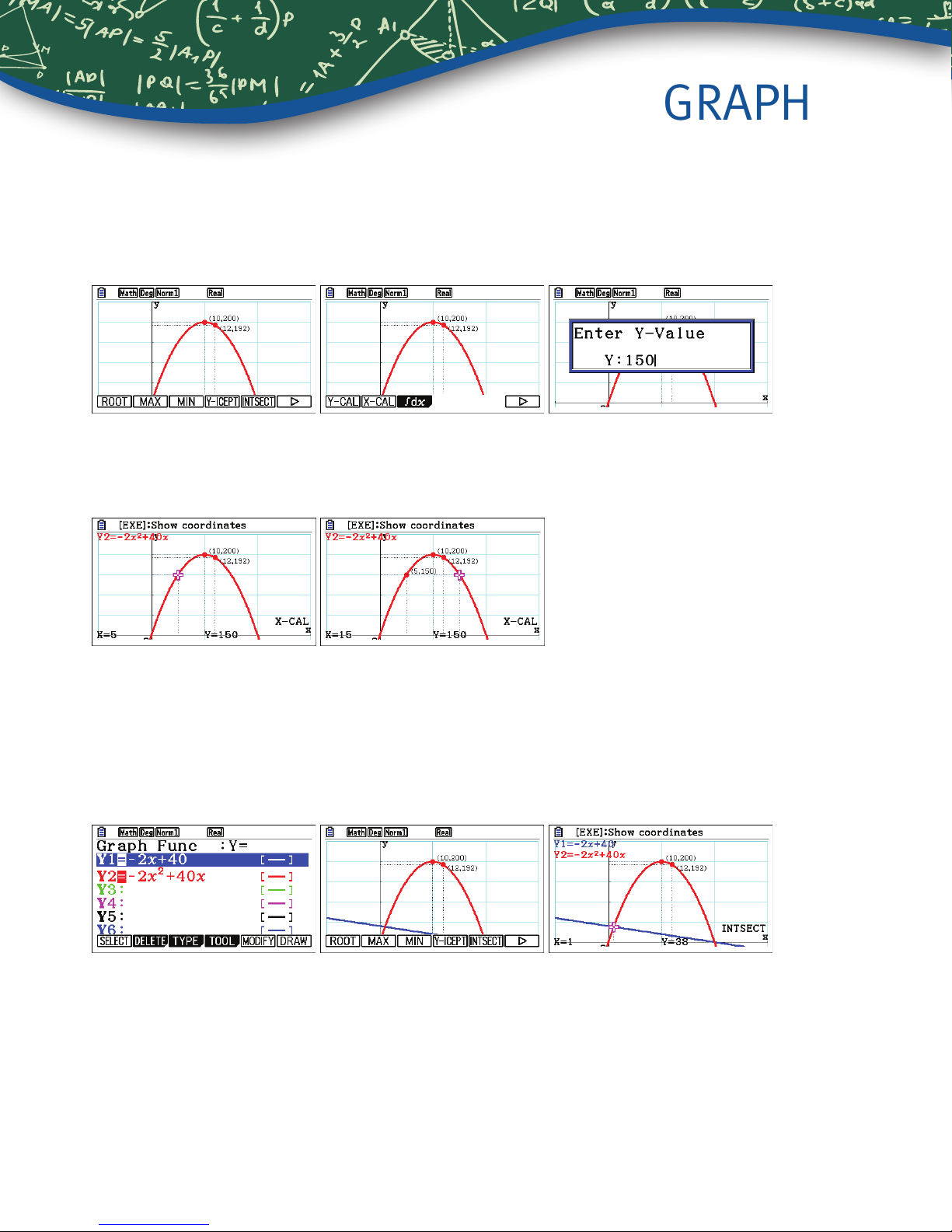
7. Determine the price of each t-shirt in order to collect $150.
()
()
GRAPH
To determine the price of each t-shirt, in order to collect a total of $150, press Ly(G-Solv)u
(X-CAL)150l. (The
There is another point where y = 150. Use $ to move to the next point. Press l to mark one or both of these
points. $150 can be earned by selling shirts at $5 or at $15.
8. Find the intersection of the equations in Y1 and Y2.
symbol moves to the next page of commands.)
w
Although it is not particularly meaningful in this example, a common problem is to nd the intersection point of two
graphs. Press d to return to the editor. Highlight Y1 and press q(SELECT). Now, both graphs will be drawn.
Press u(DRAW). To nd the intersection points for the two graphs, press y(G-Solv)y(INTSECT). 38 shirts
are sold at the price of $1, for a total of $38. (These graphs also intersect at (20, 0) where no shirts were sold.)
Getting Started with the fx-CG10
9
Page 10

TABLE
1. Construct a table of values that shows the price, number of shirts, and total dollars using increments of $0.50.
To construct tables, from the Main Menu, press 7. The equations for the functions appear if they have been
previously entered, including those entered in the Graph menu.
To set the initial value, end value and the increment, press y(SET). Enter the values for Start, End and Step. Press
l after entering each value, then press d. To display the table, press y(TABLE). Use N to scroll through
the table.
Note: values in the x-column can also be changed manually. Press any value desired, then press l. Here, the value
of 3 was changed to 7.
10
Getting Started with the fx-CG10
Page 11

GRAPH-MODIFY
y = Ax + B
1. Explore how the graph of the function
From the Main Menu, press 5. Use q(SELECT) to deselect any functions and N to move to a new line; in this
screen shot, it is Y3. Press r(TOOL)e(BUILT-IN). With Y=Ax+B, highlighted, press q(SELECT).
To use a standard window, press Le(V-Window)e(STANDRD)d.
changes for different values of A and B.
Press y(MODIFY). A graph is drawn based on values stored to A and B. Values for the variables are displayed in
the lower left portion of the screen. The active value is magenta, in this case, A. Press $ to increase A by the value
shown as Step. Press ! to decrease A. Alternately, press any number keys to change the value of A. A dialogue
box opens displaying the new desired value, then, press l. Notice, the previous graph is drawn in faint yellow. Use
NB to change the value of a different variable or the value for Step.
Getting Started with the fx-CG10
11
Page 12

EQUATION
−2x2+ 40 x = 150
-2x2+ 40 x -150 = 0
2
The equation
by transforming it to
Press pf(A). (It is not necessary to push a.) To solve polynomial equations, press w(POLY).
Press q(2) for a second degree polynomial.
Enter the 3 coefcients, pressing l after each one. Note, equations must be in standard form to solve. To solve,
press q(SOLVE). Both solutions are displayed. Note, when solutions are not rational, both a decimal and an exact
solution are displayed. The third screenshot displays the solutions to
was previously solved in the Graph menu. It can also be solved in the Equation menu
.
.
12
Getting Started with the fx-CG10
Page 13

EQUATION
a + 4b - 5c = 23
2. Solve the system
The Equation menu can also be used to solve linear systems. Within the Equation menu, press Ld(QUIT).
Press q(SIMUL) then w(3).
Enter all 12 values, pressing l after each one. To solve this system, press q (SOLVE).
2a -b + 6c = 5
{
3a + 7b + c = 32
Getting Started with the fx-CG10
13
Page 14

1. Construct the graph of the conic section .
From the Main Menu, press 9. Scroll down to the correct form and press l.
CONICS
Enter the correct values. Note, the exponents in the denominators, so A = 2, rather than 4. Also, note the minus signs
in the numerator, so H = 3 and K = -1. Press l after each value. As before, press Le(V-Window)
to change the values for the window, then press d. To draw the graph, press u(DRAW).
2. Find the asymptotes for the conic graph.
To draw the asymptotes, press Ly(G-Solv)y(ASYMPT). The slope for each line is also displayed.
14
Getting Started with the fx-CG10
Page 15

CONICS
3. Find and label the vertices and foci for the conic graph.
To label the coordinates of the vertices, press Ly(G-Solv)r(VERTEX). To label the coordinates of the foci,
press Ly(G-Solv)q(FOCUS). In each case, press $ to move to the second point. To mark points and keep
the coordinates on the display, press l a second time for either or both points.
Getting Started with the fx-CG10
15
Page 16

STATISTICS
1. Suppose one of the questions asked on a survey was “What type of pet do you have?”, and the results from
50 people are shown in this table. Construct a pie chart and a bar chart of these data.
Pet Category Dog Cat Fish Bird Other None
Frequency 14 12 9 6 4 5
From the Main Menu, press 2. The list editor opens. Enter the values in the table in List 1, pressing l after each
value.
To construct a graph, press q(GRAPH). Then, press u(SET). Scroll to Graph Type and select r(Pie).
If necessary, scroll to Data and change to List1. Display can be used to select percentages or counts with the chart.
Press d and q(GRAPH1). The color and shading of plots can be changed by using L5(FORMAT).
16
Getting Started with the fx-CG10
Page 17

STATISTICS
()
To change to a bar chart, press du(SET)Nu
To display the frequencies, press Lq(Trace).
2. The number of games won (out of 162) by a certain baseball team for the years 2002 – 2013 are shown in the
table. Construct a histogram and a boxplot for these data.
67 88 89 79 66 85
97 83 75 71 61 66
Enter these data in the list editor. To set StatGraph1 to a histogram, press q(GRAPH) and u(SET).
For Graph Type, select q(Hist).
e(Bar). Press dq(GRAPH1) to view the bar chart.
Press dq(GRAPH1). Select Start and Width values to determine the rectangles that will be plotted.
Press q(1-VAR) to see the statistical analysis of the data.
Getting Started with the fx-CG10
17
Page 18

STATISTICS
Press u(DRAW) to return to the plot. To display the frequencies, press Lq(Trace).
To change to a box-and-whisker plot (boxplot or median box plot), press du(SET). Scroll to Graph Type
and press w(MedBox). Press dq(GRAPH1). To display the minimum, maximum, and quartiles, press
Lq(Trace). Use $ to display the next value.
18
Getting Started with the fx-CG10
Page 19

RECURSION
1. Suppose $100.00 is deposited into a savings account with an interest rate of 4% compounded quarterly. How much
is in the account for each of the rst 8 quarters?
Because this is a discrete model, it can be modeled as a sequence. Although the menu says Recursion, it can be used
for both explicit and recursive sequences. From the Main Menu, press 8 to open the sequence editor. If the type is
not an, press e(TYPE)q(an). The account pays 1% per quarter so enter the formula as shown, using q(n) for n.
Press l.
To create a table of values, press y(SET). Select Start and End values and press l after entering each value. To
display the table, press u(TABLE).
This sequence can also be viewed as a graph. Before plotting the graph, set a window by pressing Le
(V-Window). Press d. To see the graph, press u(GPH-PLT). To trace on the graph, press Lq(Trace).
Getting Started with the fx-CG10
19
Page 20

RECURSION
1
2
The sequence can also be created as a recursive formula. Return to the editor using Ld(QUIT). To change
the type, press e(TYPE)w(a
value, press y(SET). For a0, enter 100l.
To see the table, press du(TABLE). To view a graph, press u(GPH-PLT).
n+1
) and edit the equation. To insert an, press w(an) then l. To specify the initial
2. How long will it take for the account to double in value to $200.00?
One good way to answer this question is to return to the Equation menu. Press pf(A). To enter the equation,
press e(SOLVER). If e(SOLVER) is not an option, press d until it is. To insert the =, press L.(=). Once
the equation is entered, press l or u(SOLVE). It will take 70 quarters or
years for the investment to double.
17
20
Getting Started with the fx-CG10
Page 21

FINANCIAL
Financial analysis can be done from the Finance menu (G).
1. Compute the amount in the account (from our previous example) after 8 quarters.
To compute the amount in the account after 8 quarters, use compound interest. For compound interest, press
w(COMPND). Enter the values, as shown, for n, I%, PV, and P/Y. PV is the present value, the initial amount.
P/Y is the number of payments per year. Remember to press l after entering each value.
To compute the future value, press y(FV). The negative sign is correct, as a reasonable interpretation is that $100
was deposited and $108.28 can be withdrawn. This value agrees with the previous result from the Recursion menu.
2. Determine how long it will take for the account to double in value to $200.00.
To determine how long it will take for the account to double in value to $200.00, press q(REPEAT). For FV, enter
n200l, then press q(n). This value agrees with the previous result from the Equation menu.
Getting Started with the fx-CG10
21
Page 22

CONIC GRAPHS
CONIC GRAPHS IMAGE BACKGOUND
1. What is an equation for a circle in the image?
From the Main Menu, press 9. To select a background, press Lp(SET UP). Scroll to Background and
press e(OPEN). Highlight the CASIO folder and press q(OPEN).
Scroll down to the g3p folder and press q(OPEN). Scroll down to Amusem~1.g3p and press q(OPEN).
Press d. Scroll down to the equation for the circle and press l. To change the color, press
L5(FORMAT)3(Red).
22
Getting Started with the fx-CG10
Page 23

Press q(MODIFY). Modify the coefcients to nd a good model.
CONIC GRAPHS
Getting Started with the fx-CG10
23
Page 24

PICTURE PLOT
As an alternate to Modify, the PRIZM™ fx-CG10 allows you to plot points on a image and use regression to nd
a model.
1. What is an equation for a line in the image?
From the Main Menu, press ((I). To open the image, press iq(FILE)q(OPEN)
Highlight the CASIO folder and press q(OPEN). Scroll down to the g3p folder and press q(OPEN).
Scroll down to Bridge.g3p and press q(OPEN). To plot points, press iw(Plot).
24
Getting Started with the fx-CG10
Page 25

PICTURE PLOT
()
Use the direction wheel to move the arrow to a point on the line. Press l to mark the point. Continue to mark
several additional points. When done, press d. To perform a regression, press u
For linear regression, press q(X) and select either form. Here w(a+bx) is used.
w(REG).
To save the result, press y(COPY). The display is improved if the graph is not blue, so scroll to Y2 and press l.
Press (DRAW) to view the equation of the line. The graph is drawn but as a thin blue line.
To draw the graph that was saved, press ir(DefG)u(DRAW).
Getting Started with the fx-CG10
25
Page 26

PICTURE PLOT
In a similar manner, a quadratic model can be used for another portion of the bridge.
26
Getting Started with the fx-CG10
Page 27

Notes
Getting Started with the fx-CG10
27
Page 28

See the complete line of Casio calculators
www.casioeducation.com
Getting Started with the fx-CG10
CCL3/15
 Loading...
Loading...