Carrier PCV015-060 User Manual

AQUAZONE™
50PCH,PCV015-060
Compact High-Efficiency Water Source Heat Pumps
®
with PURON
Refrigerant (R-410A)
Installation, Start-Up, and
Service Instructions
CONTENTS
Page
SAFETY CONSIDERATIONS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1,2
GENERAL . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2
INSTALLATION . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-24
Step 1 — Check Jobsite . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2
Step 2 — Check Unit . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2
• STORAGE
•PROTECTION
•INSPECT UNIT
Step 3 — Locate Unit. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
• FIELD CONVERSION OF DISCHARGE AIR
Step 4 — Mount the Unit . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
• HORIZONTAL UNITS
• VERTICAL UNITS
Step 5 — Check Duct System . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
• SO U N D AT T E NUATI O N
• EXISTING DUCT SYSTEM
Step 6 — Install Condensate Drain . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
• HORIZONTAL UNITS
• VERTICAL UNITS
• VENTING
Step 7 — Pipe Connections . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
• WATER LOOP APPLICATIONS
• GOUND LOOP APPLICATIONS
• INSTALLATION OF SUPPLY AND RETURN HOSE
KIT
Step 8 — Wire Field Power Supply . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
• POWER CONNECTION
• SUPPLY VOLTAGE
• 208-VOLT OPERATION
• 460-VOLT OPERATION
Step 9 — Wire Field Controls. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
• THERMOSTAT CONNECTIONS
• WATER FREEZE PROTECTION
• AIR COIL FREEZE PROTECTION
• ACCESSORY CONNECTIONS
• WATER SOLENOID VALVES
• WSHP OPEN WIRING
PRE-START-UP . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .24,25
System Checkout . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
PSC Blower Speed Selection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
FIELD SELECTABLE INPUTS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .26,27
Complete C Control Jumper Settings. . . . . . . . . . . 26
Complete C Control DIP Switches. . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
Deluxe D Control Jumper Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
Deluxe D Control DIP Switches . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
Deluxe D Control Accessory Relay
Configurations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27
Water Valve (Slow Opening) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27
Outside Air Damper (OAD) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27
START-UP . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27-33
Operating Limits . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27
Scroll Compressor Rotation. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
Unit Start-Up Cooling Mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
Page
Unit Start-Up Heating Mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
Unit Start-Up with WSHP Open Controls . . . . . . . . 31
Flow Regulation. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32
Flushing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32
Antifreeze . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 33
Cooling Tower/Boiler Systems . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 33
OPERATION. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 33-37
Power Up Mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 33
Units with Aquazone Complete C Control . . . . . . . 33
Units with Aquazone Deluxe D Control
Units with WSHP Open Multiple Protocol. . . . . . . . 34
COMPLETE C AND DELUXE D BOARD
SYSTEM TEST . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .37,38
Test Mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 37
WSHP Open Test Mode. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 37
Retry Mode. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 37
Aquazone Deluxe D Control LED Indicators . . . . . 37
SERVICE . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 38-40
Filters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 38
Water Coil . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 38
Condensate Drain Pans . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 38
Refrigerant System. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 38
Compressor . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 38
Fan Motors. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 38
Condensate Drain Cleaning . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 38
Air Coil Cleaning . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 38
Condenser Cleaning . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
Checking System Charge . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
Refrigerant Charging . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
Air Coil Fan Motor Removal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
Replacing the WSHP Open Controller’s
Battery . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40
TROUBLESHOOTING . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40-42
Thermistor . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40
Control Sensors. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40
WSHP Open Controller . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40
APPENDIX A — WSHP OPEN SCREEN
CONFIGURATION . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 43-48
50PCH,PCV START-UP CHECKLIST . . . . . CL-1, CL-2
IMPORTANT: Read the entire instruction manual before
starting installation.
. . . . . . . . . . 33
SAFETY CONSIDERATIONS
Installation and servicing of air-conditioning equipment can
be hazardous due to system pressure and electrical components. Only trained and qualified service personnel should
install, repair, or service air-conditioning equipment.
Untrained personnel can perform basic maintenance functions of cleaning coils and filters and replacing filters. All other
operations should be performed by trained service personnel.
When working on air-conditioning equipment, observe
precautions in the literature, tags and labels attached to the unit,
and other safety precautions that may apply.
Manufacturer reserves the right to discontinue, or change at any time, specifications or designs without notice and without incurring obligations.
Catalog No. 04-53500049-01 Printed in U.S.A. Form 50PC-1SI Pg 1 7-09 Replaces: New
Improper installation, adjustment, alteration, service, maintenance, or use can cause explosion, fire, electrical shock or other
conditions which may cause personal injury or property damage. Consult a qualified installer, service agency, or your distributor or branch for information or assistance. The qualified installer or agency must use factory-authorized kits or accessories
when modifying this product. Refer to the individual instructions packaged with the kits or accessories when installing.
Follow all safety codes. Wear safety glasses and work
gloves. Use quenching cloth for brazing operations. Have fire
extinguisher available. Read these instructions thoroughly and
follow all warnings or cautions attached to the unit. Consult
local building codes and the National Electrical Code (NEC)
for special installation requirements.
Understand the signal words — DANGER, WARNING,
and CAUTION. DANGER identifies the most serious hazards
which will result in severe personal injury or death. WARNING signifies hazards that could result in personal injury or
death. CAUTION is used to identify unsafe practices, which
would result in minor personal injury or product and property
damage.
Recognize safety information. This is the safety-alert
symbol ( ). When you see this symbol on the unit and in
instructions or manuals, be alert to the potential for personal
injury.
WARNING
Electrical shock can cause personal injury or death. Before
installing or servicing system, always turn off main power
to system. There may be more than one disconnect switch.
Turn off accessory heater power if applicable.
GENERAL
This Installation and Start-Up Instructions literature is for
Aquazone™ water source heat pump systems.
Water source heat pumps (WSHPs) are single-package horizontally and vertically mounted units with electronic controls
designed for year-round cooling and heating. Aquazone
WSHPs are available in the following unit configurations:
• PCH standard efficiency with horizontal airflow and
right, left or back discharge
• PCV standard efficiency with vertical airflow and top
discharge
IMPORTANT: The installation of water source heat pump
units and all associated components, parts, and accessories
which make up the installation shall be in accordance with
the regulations of ALL authorities having jurisdiction and
MUST conform to all applicable codes. It is the responsibility of the installing contractor to determine and comply
with ALL applicable codes and regulations.
INSTALLATION
Step 1 — Check Jobsite —
maintenance instructions are provided with each unit. Before
unit start-up, read all manuals and become familiar with the
unit and its operation. Thoroughly check out the system before
operation. Complete the inspections and instructions listed
below to prepare a unit for installation. See Table 1 for unit
physical data.
HORIZONTAL UNITS (50PCH) — Horizontal units are
designed for indoor installation only. Be sure to allow adequate
space around the unit for servicing. See Fig. 1 for overall unit
dimensions. Refer to Fig. 2 for an illustration of a typical horizontal installation.
VERTICAL UNITS (50PCV) — Vertical units are designed
for indoor installations. While vertical units are typically
Installation, operation and
installed in a floor-level closet or a small mechanical room,
the unit access guidelines for these units are very similar to
those described for horizontal units. See Fig. 3 for overall dimensions. Refer to Fig. 4 for an example of a typical vertical
installation.
CAUTION
To avoid equipment damage, do not use these units as a
source of heating or cooling during the construction
process. The mechanical components and filters used in
these units quickly become clogged with construction
dirt and debris which may cause system damage.
Step 2 — Check Unit — Upon receipt of shipment at
the jobsite, carefully check the shipment against the bill of
lading. Make sure all units have been received. Inspect the carton or crating of each unit, and inspect each unit for damage.
Ensure the shipping company makes proper notation of any
shortages or damage on all copies of the freight bill. Concealed
damage not discovered during unloading must be reported to
the shipping company within 15 days of receipt of shipment.
NOTE: It is the responsibility of the purchaser to file all
necessary claims with the shipping company.
1. Verify unit is correct model for entering water temperature of job.
2. Be sure that the location chosen for unit installation provides ambient temperatures maintained above freezing.
Well water applications are especially susceptible to
freezing.
3. Be sure the installation location is isolated from sleeping
areas, private offices and other acoustically sensitive
spaces.
NOTE: A sound control accessory package may be used
to help eliminate sound in sensitive spaces.
4. Check local codes to be sure a secondary drain pan is not
required under the unit.
5. Be sure unit is mounted at a height sufficient to provide
an adequate slope of the condensate lines. If an appropriate slope cannot be achieved, a field-supplied condensate
pump may be required.
6. Provide sufficient space for duct connection.
7. Provide adequate clearance for filter replacement and
drain pan cleaning. Do not allow piping, conduit, etc. to
block filter access.
8. Provide sufficient access to allow maintenance and
servicing of the fan and fan motor, compressor and coils.
Removal of the entire unit from the closet should not be
necessary.
9. Provide an unobstructed path to the unit within the closet
or mechanical room. Space should be sufficient to allow
removal of unit if necessary.
10. Provide ready access to water valves and fittings, and
screwdriver access to unit side panels, discharge collar,
and all electrical connections.
11. Where access to side panels is limited, pre-removal of the
control box side mounting screws may be necessary for
future servicing.
STORAGE — If the equipment is not needed immediately at
the jobsite, it should be left in its shipping carton and stored in a
clean, dry area of the building or in a warehouse. Units must be
stored in an upright position at all times. If carton stacking is
necessary, stack units a maximum of 3 high. Do not remove
any equipment from its shipping package until it is needed for
installation.
PROTECTION — Once the units are properly positioned on
the jobsite, cover them with either a shipping carton, vinyl film,
2
or an equivalent protective covering. Cap open ends of pipes
stored on the jobsite. This precaution is especially important in
areas where painting, plastering, or spraying of fireproof material, etc. is not yet complete. Foreign material that accumulates
within the units can prevent proper start-up and necessitate
costly clean-up operations.
Before installing any of the system components, be sure to
examine each pipe, fitting, and valve, and remove any dirt or
foreign material found in or on these components.
CAUTION
DO NOT store or install units in corrosive environments or
in locations subject to temperature or humidity extremes
(e.g., attics, garages, rooftops, etc.). Corrosive conditions
and high temperature or humidity can significantly reduce
performance, reliability, and service life. Always move
units in an upright position. Tilting units on their sides may
cause equipment damage.
INSPECT UNIT — To prepare the unit for installation, complete the procedures listed below:
1. Compare the electrical data on the unit nameplate with
ordering and shipping information to verify that the
correct unit has been shipped.
2. Verify that the unit is the correct model for the entering
water temperature of the job.
3. Do not remove the packaging until the unit is ready for
installation.
4. Verify that the refrigerant tubing is free of kinks or dents,
and that it does not touch other unit components.
5. Inspect all electrical connections. Be sure connections are
clean and tight at the terminals.
6. Loosen compressor bolts until the compressor rides freely
on springs. Remove shipping restraints.
7. Remove the four
1
/4 in. shipping bolts from compressor
support plate (two bolts on each side) to maximize vibration and sound alternation.
CAUTION
Failure to remove shipping brackets from spring-mounted
compressors will cause excessive noise and could cause
component failure due to added vibration.
8. Remove any blower support cardboard from inlet of the
blower.
9. Locate and verify any accessory kit located in compressor
section.
10. Remove any access panel screws that may be difficult to
remove once unit is installed.
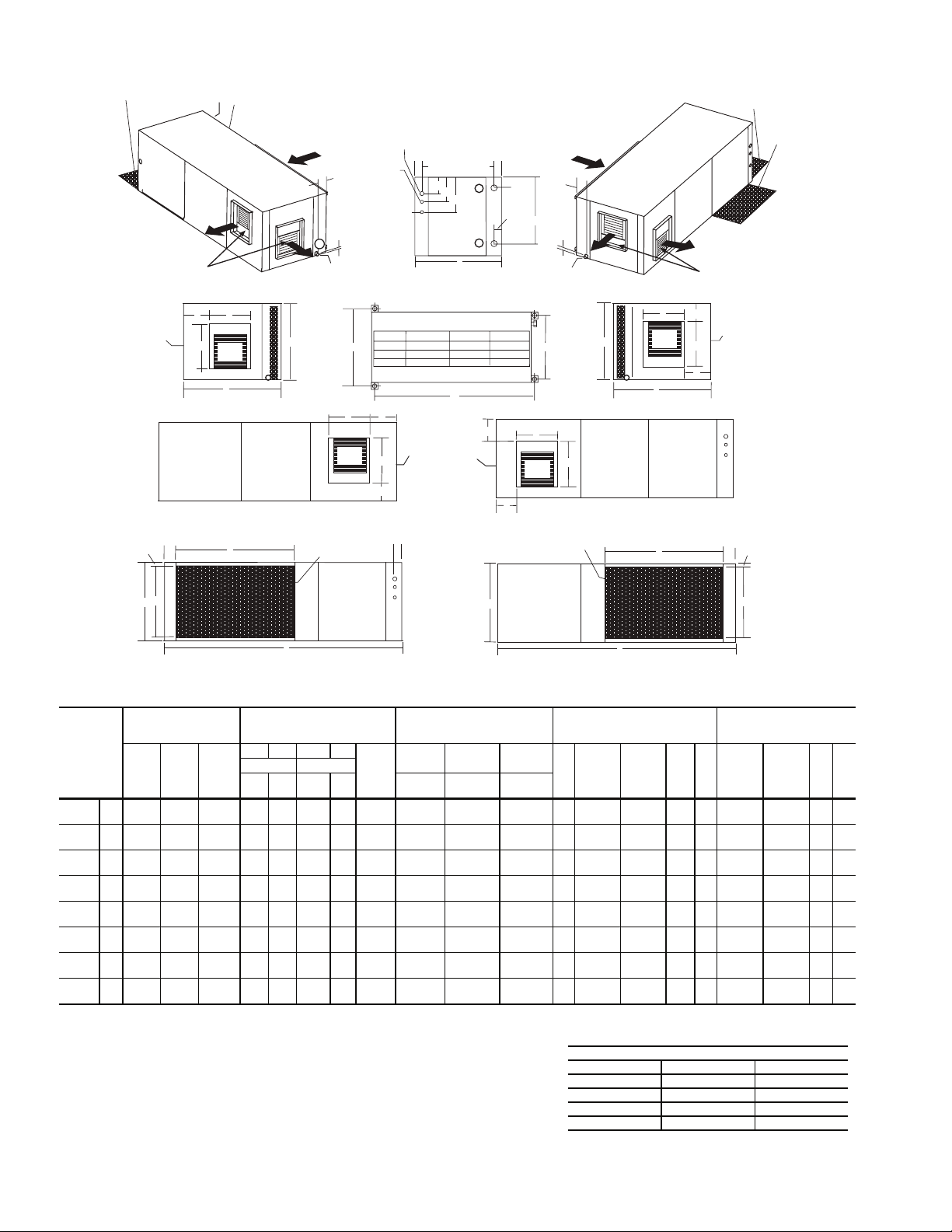
Table 1 — 50PCH,PCV Unit Physical Data
50PCH,PCV UNIT 015 018 024 030 036 042 048 060
COMPRESSOR (1 each) Rotary Scroll
REFRIGERANT TYPE R-410A
Factory Charge (oz) 32 43 43 47 50 70 74 82
FAN MOTOR AND BLOWER
Fan Motor Type/Speeds PSC/3
Fan Motor (hp)
Blower Wheel Size (Dia x W) (in.) 8 x 7 9 x 7 9 x 8 10 x 10 11 x 10
WATER CONNECTION SIZE IPT (in.)
HORIZONTAL
Air Coil Dimensions (H x W)(in.) 16 x 22 20 x 25 20 x 35
Standard Filter - (Qty) 1 in. Throwaway (1) 16 x 25 (1) 20 x 28 or
Weight (lb)
Operating 153 158 189 197 203 218 263 303
Packaged 158 163 194 202 209 224 270 310
Corner Weight (lb)*
Left-Front 53 55 62 67 75 81 98 103
Right-Front 36 37 40 41 47 50 60 64
Left-Back 34 35 39 40 44 48 58 61
Right-Back 30 31 33 34 37 39 47 75
VERTICAL
Air Coil Dimensions (H x W)(in.) 20 x 17.25 24 x 17.75 24 x 28.25
Standard Filter - (Qty) 1 in. Throwaway (1) 20 x 20 (1) 24 x 24 (1) 14 x 28, (1) 18 x 24
Weight (lb)
Operating 153 158 189 197 203 218 263 278
Packaged 158 163 194 202 209 224 270 285
LEGEND *Front is located at control box end.
IPT — Internal Pipe Thread
PSC — Permanent Split Capacitor
1
/
6
1
/
6
1
/
2
1
/
4
NOTES:
1. All units have grommet compressor mountings, and
2. Maximum water working pressure is 500 psig.
3
/
4
3
/4-in. electrical knockouts.
3
/
4
1
/
2
(2) 20 x 14
3
/
4
3
/
4
(1) 20 x 24,
(1) 20 x 14
1
1
/2-in. and
1
3
2 FT [610 MM] SERVICE
ACCESS
a50-8412
LEFT RETURN RIGHT RETURN
OPTIONAL 2 FT
CSP
SERVICE
FRONT
STRAIGHT
DISCHARGE
NOTE: CHOOSE EITHER
BACK OR STRAIGHT DISCHARGE
BSP
LEFT RETURN BACK DISCHARGE
FRONT
ACCESS
O
N
M
BLOWER
OUTLET
P
A
LEFT RETURN STRAIGHT DISCHARGE
[610 MM]
LEFT RETURN
3
CONDENSATE
BACK
DISCHARGE
AIR COIL SIDE
3 / 4" IPT
C
BSP — Blower Service Panel
CAP — Control Access Panel
CSP — Compressor Service Panel
IPT — Internal Pipe Thread
POWER SUPPLY
3 / 4" [19.1 MM] KNOCKOUT
1 / 2"
[12.7 MM]
KNOCKOUT
3.3"
[83.8 MM]
LOW VOLTAGE
1 / 2" [12.7 MM]
KNOCKOUT
0.7" [17.8 MM]
NOTE: BLOWER SERVICE PANEL REQUIRES 2 FT SERVICE ACCESS
1.1 [27.9 MM]
K
J
H
CAP
A
FRONT-VIEW
G
2
1
F
E
RIGHT RETURN
3.3"
[83.8 MM]
D
0.7"
[17.8 MM]
CONDENSATE
3 / 4" IPT
UNIT HANGER DETAIL
MODEL U V W
015-030 43.1 [109.5] 22.2 [56.4] 18.0 [45.7]
LEGEND
V
FRONT
036-042 47.1 [119.6] 22.2 [56.4] 18.0 [45.7]
048-060 54.1 [137.4] 26.2 [66.5] 22.0 [55.9]
N
O
BLOWER
OUTLET
BSP
M
L
U
L
BSP
W
N
M
BLOWER
OUTLET
O
RIGHT RETURN STRAIGHT DISCHARGE
DISCHARGE
BACK
DISCHARGE
C
RIGHT RETURN BACK DISCHARGE
NOTE: CHOOSE EITHER
BACK OR STRAIGHT DISCHARGE
P
N
BLOWER
OUTLET
M
AIR COIL SIDE
O
A
CSP
2 FT [610 MM] SERVICE
ACCESS
FRONT
OPTIONAL 2 FT
CSP
STRAIGHT
BSP
FRONT
[610 MM]
SERVICE
ACCESS
CSP
1.75 [44.5 MM]
FRONT
C
FRONT
T
R
C
QS
B
LEFT RETURN LEFT VIEW -
AIR COIL OPENING
AIR COIL
AIR COIL
RIGHT RETURN RIGHT VIEW -
AIR COIL OPENING
Q
B
S
T
R
50PCH015-060 UNITS
OVERALL CABINET
50PCH
UNIT
SIZE
015
018
024
030
036
042
048
060
NOTES:
1. While clear access to all removable panels is not required, installer should
take care to comply with all building codes and allow adequate clearance
for future field service.
2. Horizontal units shipped with filter bracket only. This bracket should be
removed for return duct connection.
3. Discharge flange and hanger brackets are factory installed.
4. Condensate is
5. Blower service panel requires 2 ft (610 mm) service access.
6. Blower service access is through back panel on straight (right or left) discharge units or through panel opposite air coil on back discharge units.
A
WidthBDepthCHeight
in. 20.1 43.1 17.0 15.1 1.4 3.2 1.4
cm 51.1 109.5 43.2 38.4 3.4 8.1 3.5 1.3 30.8 23.2 15.6 6.6 33.8 25.1 10.5 3.3 58.4 38.1 2.8 2.5
in. 20.1 43.1 17.0 15.1 1.4 4.1 1.4
cm 51.1 109.5 43.2 38.4 3.4 10.4 3.5 1.3 30.8 23.2 15.6 6.6 33.8 25.1 10.5 3.3 58.4 38.1 2.8 2.5
in. 20.1 43.1 18.3 15.1 1.4 4.4 1.4
cm 51.1 109.5 46.5 38.4 3.4 11.3 3.5 1.9 30.8 23.2 15.6 6.6 33.8 25.1 10.5 3.3 58.4 41.4 2.8 2.5
in. 20.1 43.1 18.3 15.1 1.4 3.1 1.4
cm 51.1 109.5 46.5 38.4 3.4 7.8 3.5 1.9 30.8 23.2 15.6 6.6 33.8 25.1 10.5 3.3 58.4 41.4 2.8 2.5
in. 20.1 47.1 21.0 15.1 1.4 5.3 1.4
cm 51.1 119.6 53.3 38.4 3.4 13.4 3.5 1.9 41.0 33.3 25.7 6.3 40.9 27.9 7.7 6.4 65.8 48.3 2.8 2.5
in. 20.1 47.1 21.0 15.1 1.4 4.4 1.4
cm 51.1 119.6 53.3 38.4 3.4 11.3 3.5 1.9 41.0 33.3 25.7 6.3 40.9 27.9 7.7 6.4 65.8 48.3 2.8 2.5
in. 24.1 54.1 21.0 15.1 1.4 4.4 1.4 1 16.1 13.1 10.1 3.7 16.1 13.7 4.1 1.3 35.9 19.0 1.1 1.0
cm 61.2 137.4 53.3 38.4 3.4 11.1 3.5 2.5 41.0 33.3 25.7 9.5 41.0 34.8 10.3 3.2 91.2 48.3 2.8 2.5
in. 24.1 54.1 21.0 15.1 1.4 3.8 1.4 1 16.1 13.1 10.1 1.7 18.1 13.7 4.1 1.3 35.9 19.0 1.1 1.0
cm 61.2 137.4 53.3 38.4 3.4 9.7 3.5 2.5 41.0 33.3 25.7 4.4 46.0 34.8 10.3 3.2 91.2 48.3 2.8 2.5
3
/4-in. (19.1 mm) IPT copper.
12 34
Loop In Loop Out
DE F G
WATER
CONNECTIONS
ELECTRICAL KNOCKOUTS
H
1
/2-in.
Size
(IPT)
Low
Vol ta ge
1
/
12.1 9.1 6.1 2.6 13.3 9.9 4.1 1.3 23.0 15.0 1.1 1.0
2
1
/
12.1 9.1 6.1 2.6 13.3 9.9 4.1 1.3 23.0 15.0 1.1 1.0
2
3
/
12.1 9.1 6.1 2.6 13.3 9.9 4.1 1.3 23.0 16.3 1.1 1.0
4
3
/
12.1 9.1 6.1 2.6 13.3 9.9 4.1 1.3 23.0 16.3 1.1 1.0
4
3
/
16.1 13.1 10.1 2.5 16.1 11.0 3.0 2.5 25.9 19.0 1.1 1.0
4
3
/
16.1 13.1 10.1 2.5 16.1 11.0 3.0 2.5 25.9 19.0 1.1 1.0
4
J
1
/2-in.
Low
Vol ta ge
3
Power
Supply
DISCHARGE CONNECTIONS
DUCT FLANGE
(± 0.10 in., ± 2.5 mm)
K
/4-in.
LMSupply
Height
Code Return Discharge
D or S Left Right
E or F Left Back
A or Z Right Left
B or C Right Back
N
Supply
Width
OPQReturn
AIRFLOW CONFIGURATION
RETURN CONNECTION
USING RETURN AIR
Depth
OPENING
R
Return
Height
ST
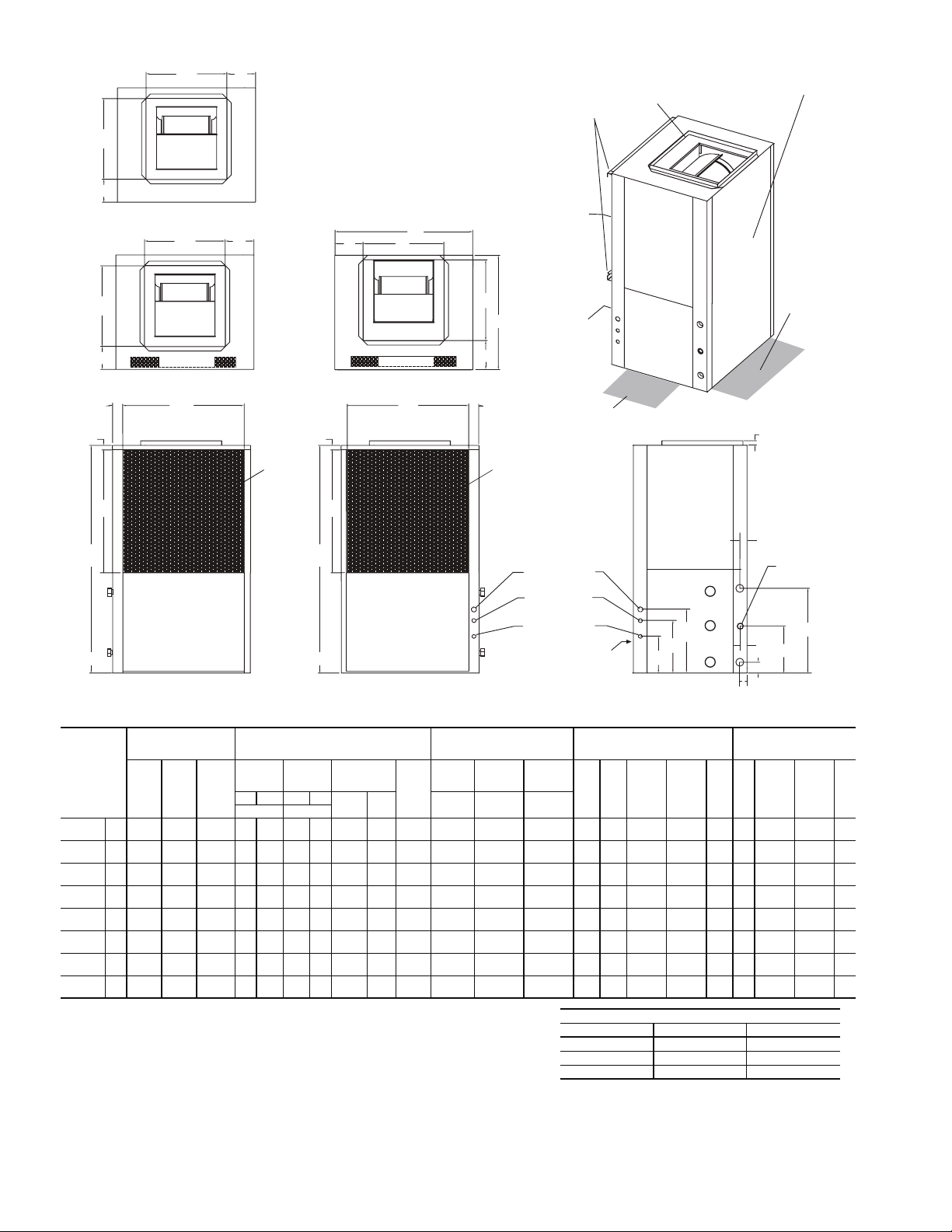
Fig. 1 — 50PCH Unit Dimensions
4
UNIT HANGER ISOLATION DETAIL
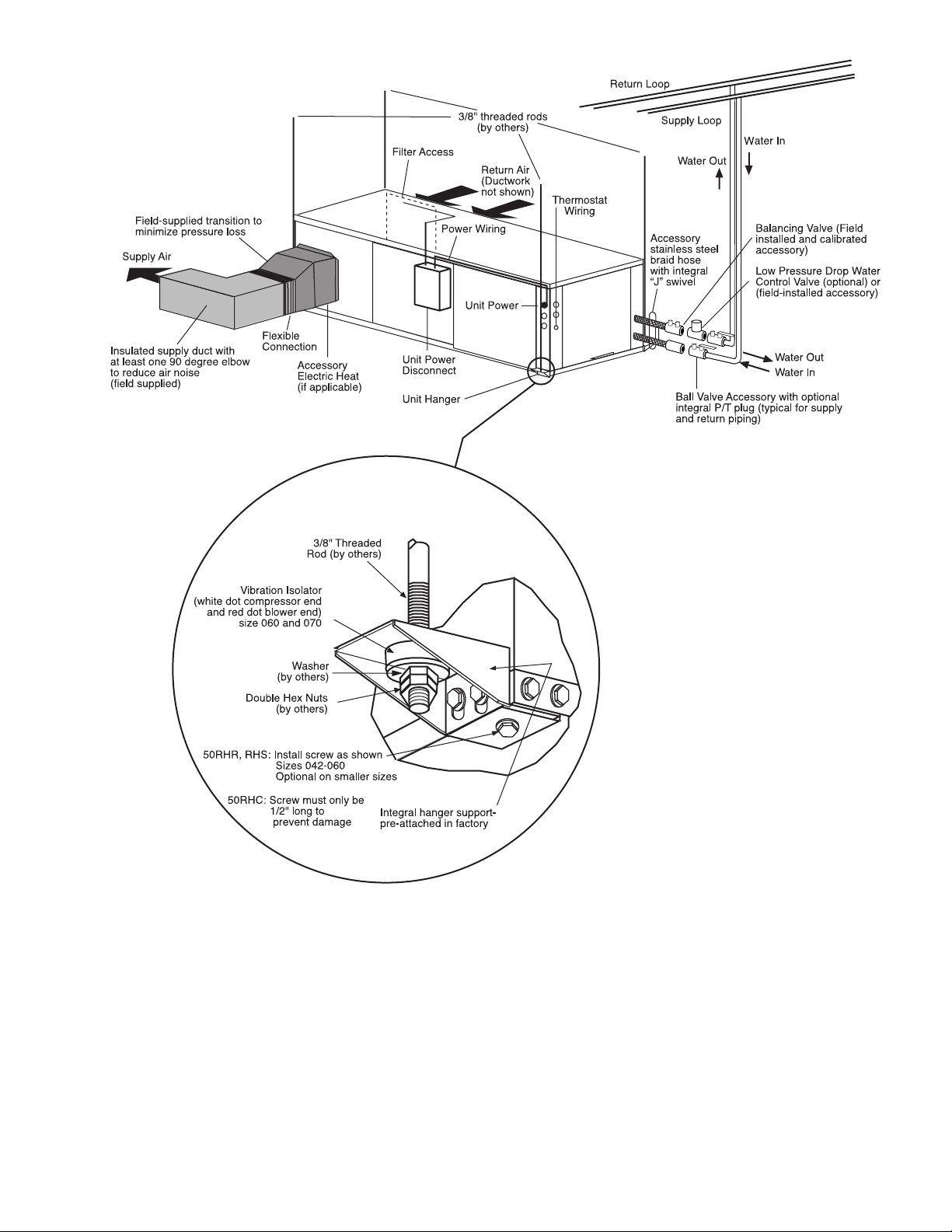
Fig. 2 — Typical Installation — 50PCH Units
5
P
O
N
ASP — Alternate Service Panel
BSP — Blower Service Panel
CAP — Control Access Panel
CSP — Compressor Service Panel
HV — High Voltage
IPT — Internal Pipe Thread
LV — Low Voltage
LEGEND
STANDARD FILTER BRACKET
FIELD INSTALLED
DISCHARGE FLANGE
ACCESS PANELS
Q
AIR COIL AND FRONT SIDE
a50-8413
TOP VIEW-FRONT RETURN
P
N
N
P
FRONT
O
Q
TOP VIEW-RIGHT RETURN
R
U
T
C
FRONT
RIGHT RETURN RIGHT VIEW
- AIR COIL OPENING
AIR COIL SIDE
S
U
AIR COIL
T
C
BACK
AIR COIL SIDE
TOP VIEW-LEFT RETURN
S
CSPCSP
LEFT RETURN LEFT VIEW
- AIR COIL OPENING
50PCV015-060 UNITS
OVERALL CABINET WATER CONNECTIONS ELECTRICAL KNOCKOUTS
50PCV
UNIT
SIZE
015
018
024
030
036
042
048
060
NOTES:
1. While clear access to all removable panels is not required, installer should take care to
comply with all building codes and allow adequate clearance for future field service.
2. Front and side access is preferred for service access. However, all components may be
serviced from the front access panel if side access is not available. (except on
50PCV009-030 and 041 sizes with front return).
3. Discharge flange is field installed.
4. Condensate is 3/4 in. (19.1 mm) IPT.
A
WidthBDepthCHeight
in. 21.5 21.5 39.0 1.9 1.4 13.8 1.4 8.1 1.4
cm 54.6 54.6 99.1 4.8 3.6 35.1 3.6 20.6 3.6 1.3 10.5 18.1 25.7 16.1 9.5 35.6 35.6 13.6 5.8 46.5 53.1 1.9
in. 21.5 21.5 39.0 1.9 1.4 12.9 1.4 8.1 1.4
cm 54.6 54.6 99.1 4.8 3.6 32.8 3.6 20.6 3.6 1.3 10.5 18.1 25.7 16.1 9.5 35.6 35.6 13.6 5.8 46.5 53.1 1.9
in. 21.5 21.5 40.0 1.9 1.4 13.8 1.4 8.1 1.4
cm 54.6 54.6 101.6 4.8 3.6 35.1 3.6 20.6 3.6 1.9 10.5 18.1 25.7 16.1 9.5 35.6 35.6 13.6 5.8 46.5 53.1 1.9
in. 21.5 21.5 40.0 1.9 1.4 15.2 1.4 8.1 1.43/
cm 54.6 54.6 101.6 4.8 3.6 38.6 3.6 20.6 3.6 1.9 10.5 18.1 25.7 16.1 9.5 35.6 35.6 13.6 5.8 46.5 53.1 1.9
in. 21.5 26.0 45.0 1.9 1.4 15.7 1.4 8.1 1.4
cm 54.6 66.0 114.3 4.8 3.6 39.9 3.6 20.6 3.6 1.9 10.5 18.1 25.7 16.1 9.5 35.6 35.6 13.1 5.8 57.9 60.7 1.9
in. 21.5 26.0 45.0 1.9 1.4 16.6 1.4 8.1 1.4
cm 54.6 66.0 114.3 4.8 3.6 42.0 3.6 20.6 3.6 1.9 10.5 18.1 25.7 16.1 9.5 35.6 35.6 13.1 5.8 57.9 60.7 1.9
in. 24.0 32.5 46.0 1 .9 1.4 16.6 1.4 8.1 1.4 1 4.1 7.1 10.1 6.9 7.3 16.0 18.0 5.1 2.3 29.3 22.5 0.7
cm 61.0 82.6 116.8 4.8 3.6 42.2 3.6 20.6 3.6 2.5 10.5 18.1 25.7 17.4 18.4 40.6 45.7 13.1 5.8 74.4 57.0 1.9
in. 24.0 32.5 46.0 1 .9 1.4 16.7 1.4 8.1 1.4 1 4.1 7.1 10.1 6.9 7.3 16.0 18.0 5.1 2.3 29.3 22.5 0.7
cm 61.0 82.6 116.8 4.8 3.6 42.4 3.6 20.6 3.6 2.5 10.5 18.1 25.7 17.4 18.4 40.6 45.7 13.1 5.8 74.4 57.0 1.9
12 3
DE FG
Loop In Loop Out
HI
Size
(IPT)
1
1
3
3
3
AIR COIL
B
BSP
ASP
O
FRONT
A
CSP
CAP
M
R
AIR COIL
POWER SUPPLY
3/4" [19.1 MM] HV
KNOCKOUT
LOW VOLTAGE
1/2" [12.7 MM] LV
KNOCKOUT
LOW VOLTAGE
1/2" [12.7 MM] LV
KNOCKOUT
FRONTBACK
J
1/2-in.
(1.3 cm)
Low
Vol ta ge
/
4.1 7.1 10.1 6.4 3.8 14.0 14.0 5.3 2.3 18.3 20.9 0.7
2
/
4.1 7.1 10.1 6.4 3.8 14.0 14.0 5.3 2.3 18.3 20.9 0.7
2
/
4.1 7.1 10.1 6.4 3.8 14.0 14.0 5.3 2.3 18.3 20.9 0.7
4
4.1 7.1 10.1 6.4 3.8 14.0 14.0 5.3 2.3 18.3 20.9 0.7
4
/
4.1 7.1 10.1 6.4 3.8 14.0 14.0 5.1 2.3 22.8 23.9 0.7
4
/
4.1 7.1 10.1 6.4 3.8 14.0 14.0 5.1 2.3 22.8 23.9 0.7
4
K
1/2-in.
(1.3 cm)
Low
Vol ta ge
3/4-in.
(1.3 cm)
Power
Supply
2 FT [610 MM]
SERVICE
ISOMETRIC
VIEW
BSP
CAP
L
CSP
DISCHARGE CONNECTION
DUCT FLANGE INSTALLED
L
(±0.10 in., ±2.5 mm)
MNOSupply
Code Return Discharge
F or H Front Top
L or M Left Top
G or R Right Top
K
J
FRONT-VIEW
P
Supply
Width
Depth
AIRFLOW CONFIGURATION
1.00 [25.4 MM]
G
2
3
I
1
D
E
RETURN CONNECTION
USING RETURN AIR
QRSReturn
Depth
OPTIONAL
2 FT [610 MM]
SERVICE
ACCESS
LEFT RTN
(RIGHT RTN
OPPOSITE
SIDE)
CONDENSATE
3/4" IPT
F
H
OPENING
Return
Height
T
U
Fig. 3 — 50PCV Unit Dimensions
6
Supply Air
Building
Flexible
Connection
Return
Air
Power
Thermostat
Wiring
Compressor
Access Panel
NOTE: Ball valve with integral pressure temperature plug recommended.
Loop
Water
Out
Water
In
Field-supplied
stainless steel
braid hose
with integral
“ J” swivel
Ball Valve with optional
integral P/T plug
(typical for supply and
return piping)
Balancing Valve
(field installed
and calibrated
accessory)
Low Pressure
Drop Water
Control Valve
(optional)
(field-installed
accessory)
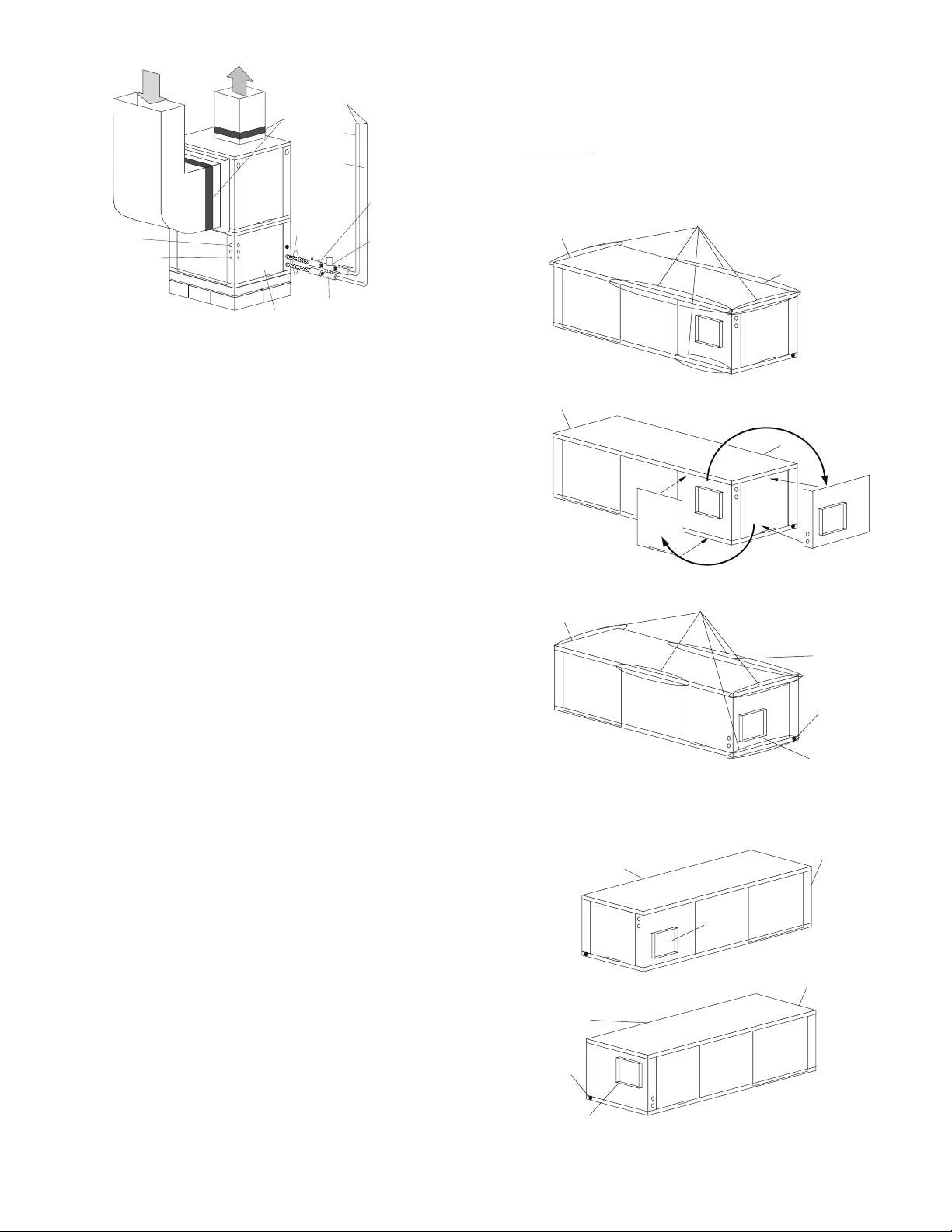
Fig. 4 — Typical Vertical Installation —
50PCV Units
Step 3 — Locate Unit — The following guidelines
should be considered when choosing a location for a WSHP:
• Units are for indoor use only.
• Locate in areas where ambient temperatures are between
40 F and 100 F and relative humidity is no greater than
75%.
• Provide sufficient space for water, electrical and duct
connections.
• Locate unit in an area that allows easy access and
removal of filter and access panels.
• Allow enough space for service personnel to perform
maintenance.
• Return air must be able to freely enter the space if unit
needs to be installed in a confined area such as a closet.
• Install the unit on a piece of rubber, neoprene or other
mounting pad material for sound isolation. The pad
should be at least
thickness. Extend the pad beyond all four edges of the
unit.
• Provide adequate clearance for filter replacement and
drain pan cleaning. Do not block filter access with piping, conduit or other materials. Refer to Fig. 1 and 3 for
dimensional data.
• Provide access for fan and fan motor maintenance and
for servicing the compressor and coils without removing
the unit.
• Provide an unobstructed path to the unit within the closet
or mechanical room. Space should be sufficient to allow
removal of the unit, if necessary.
• In limited side access installations, pre-removal of the
control box side mounting screws will allow control box
removal for future servicing.
• Provide access to water valves and fittings and screwdriver access to the unit side panels, discharge collar and
all electrical connections.
NOTE: Correct placement of the horizontal unit can play an
important part in minimizing sound problems. Since ductwork is normally applied to these units, the unit can be
placed so that the principal sound emission is outside the occupied space in sound-critical applications. A fire damper
may be required by the local code if a fire wall is penetrated.
FIELD CONVERSION OF DISCHARGE AIR — The discharge air of the 50PCH horizontal units can be converted
between side and back discharge in the field. The conversion
3
/8 in. [10 mm] to 1/2 in. [13 mm] in
process is the same for right and left return configurations. See
Fig. 5 and 6.
NOTE: It is not possible to convert return air between left or
right return models in the field due to refrigerant piping
changes.
Preparation
— The unit should be on the ground in a well lit
area for conversion. Hung units should be taken down to
ground level before converting.
Water
Connection End
Side Discharge
Water
Connection End
Water
Connection End
Back Discharge
Remove Screws
Return Air
Rotate
Return Air
Move to Side
Replace Screws
Return Air
Drain
Discharge Air
Fig. 5 — Conversion Left Return,
Side Discharge to Back Discharge
Water
Connection End
Water
Connection End
Return Air
Drain
Discharge Air
Return Air
Supply
Duct
Side Discharge
Back Discharge
Fig. 6 — Conversion Right Return,
Side Discharge to Back Discharge
7
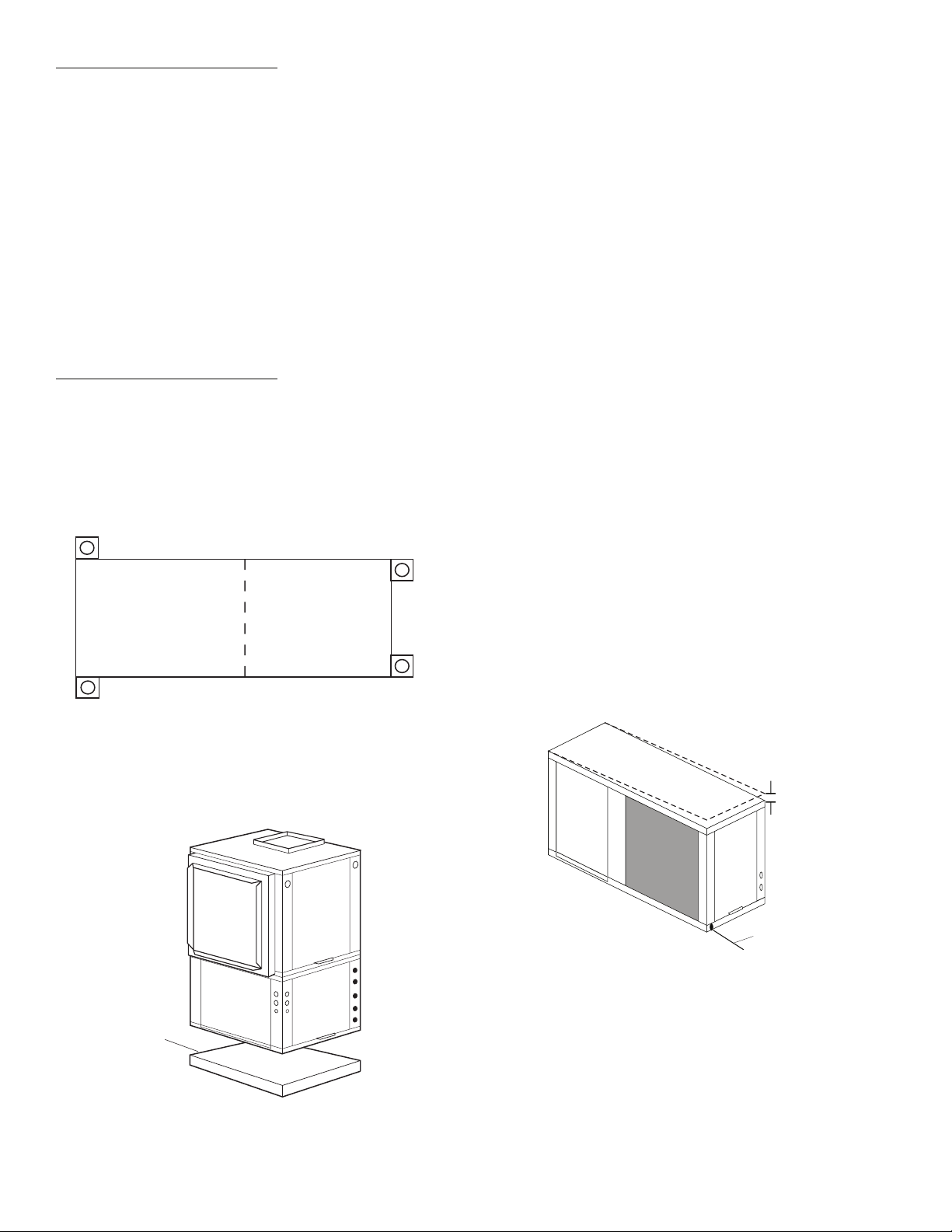
Side to Back Discharge Conversion
1. Remove screws to free the top and discharge panels. See
Fig. 5.
2. Remove the access panel and set aside.
3. Lift the discharge panel from side of unit and rotate it to
back using care not to damage blower wiring.
4. Check blower wire routing and connections for undue
tension or contact with sheet metal edges. Re-route if
necessary.
5. Check refrigerant tubing for contact with other components. Adjust if necessary.
6. Reinstall top panel using screws set aside in Step 1.
NOTE: Location for some screws at bottom of discharge panel
may have to be changed.
7. Manually spin fan wheel to check for obstructions.
Adjust for any obstruction found.
8. Replace access panel.
Back to Side Discharge Conversion
— Follow instructions
above for Side to Back Discharge Conversion, noting the
panels would be reversed.
Step 4 — Mount the Unit
HORIZONTAL UNITS (50PCH) — Horizontal units should be
mounted using the factory-installed hangers. Proper attachment
of hanging rods to building structure is critical for safety. See
Fig. 2 and 7. Rod attachments must be able to support the
weight of the unit. See Table 1 for unit operating weights.
a50-8489
COMPRESSOR
SECTION
Fig. 7 — Horizontal Hanger Bracket
(Factory Installed)
VERTICAL UNITS (50PCV) — Vertical units are available in
left or right return air configurations. See Fig. 3. Mount the unit
on a vibration absorption pad slightly larger than the entire base
to minimize vibration transmission. It is not necessary to mount
the unit on the floor. See Fig. 8.
AIR HANDLER
SECTION
NOTE: Some codes require the use of a secondary drain pan
under vertical units. Check local codes for more information.
Step 5 — Check Duct System — Size the duct sys-
tem to handle the design airflow quietly.
NOTE: Depending on the unit, the fan wheel may have a shipping support installed at the factory. This must be removed
before operating unit.
SOUND ATTENUATION — To eliminate the transfer of
vibration to the duct system, a flexible connector is recommended for both discharge and return air duct connections on
metal duct systems. The supply and return plenums should include internal duct liner of fiberglass or be made of duct board
construction to maximize sound attenuation of the blower.
Installing the WSHP unit to uninsulated ductwork in an unconditioned space is not recommended since it will sweat and
adversely affect the unit’s performance.
To reduce air noise, at least one 90-degree elbow could be
included in the supply and return air ducts, provided system
performance is not adversely impacted. The blower speed can
also be changed in the field to reduce air noise or excessive airflow, provided system performance is not adversely impacted.
EXISTING DUCT SYSTEM — If the unit is connected to
existing ductwork, consider the following:
• Verify that the existing ducts have the proper capacity to
handle the unit airflow. If the ductwork is too small,
install larger ductwork.
• Check existing ductwork for leaks and repair as
necessary.
NOTE: Local codes may require ventilation air to enter the
space for proper indoor air quality. Hard-duct ventilation may
be required for the ventilating air supply. If hard ducted ventilation is not required, be sure that a proper air path is provided
for ventilation air to unit to meet ventilation requirement of the
space.
Step 6 — Install Condensate Drain
HORIZONTAL UNITS (50PCH) — Slope the unit toward
the drain at a
sible to meet the required pitch, install a condensate pump at
the unit to pump condensate to building drain.
1
/4 in. drop at drain end. See Fig. 9. If it is not pos-
1/4” Pitch for
Drainage
Vibration
Absorption
Pad
Fig. 8 — 50PCV Units Mounted with
Vibration Absorption Pad
Pitch Toward
Drain
Drain Connection
Fig. 9 — Horizontal Unit Pitch
Horizontal units are not internally trapped, therefore an external trap is necessary. Install each unit with its own individual
trap and means to flush or blow out the condensate drain line.
Do not install units with a common trap or vent. For typical
condensate connections see Fig. 10.
NOTE: Never use a pipe size smaller than the connection.
VERTICAL UNITS (50PCV) — Each unit uses a condensate
hose inside all cabinets as a trapping loop, therefore an external
trap is not necessary. See Fig. 11.
8
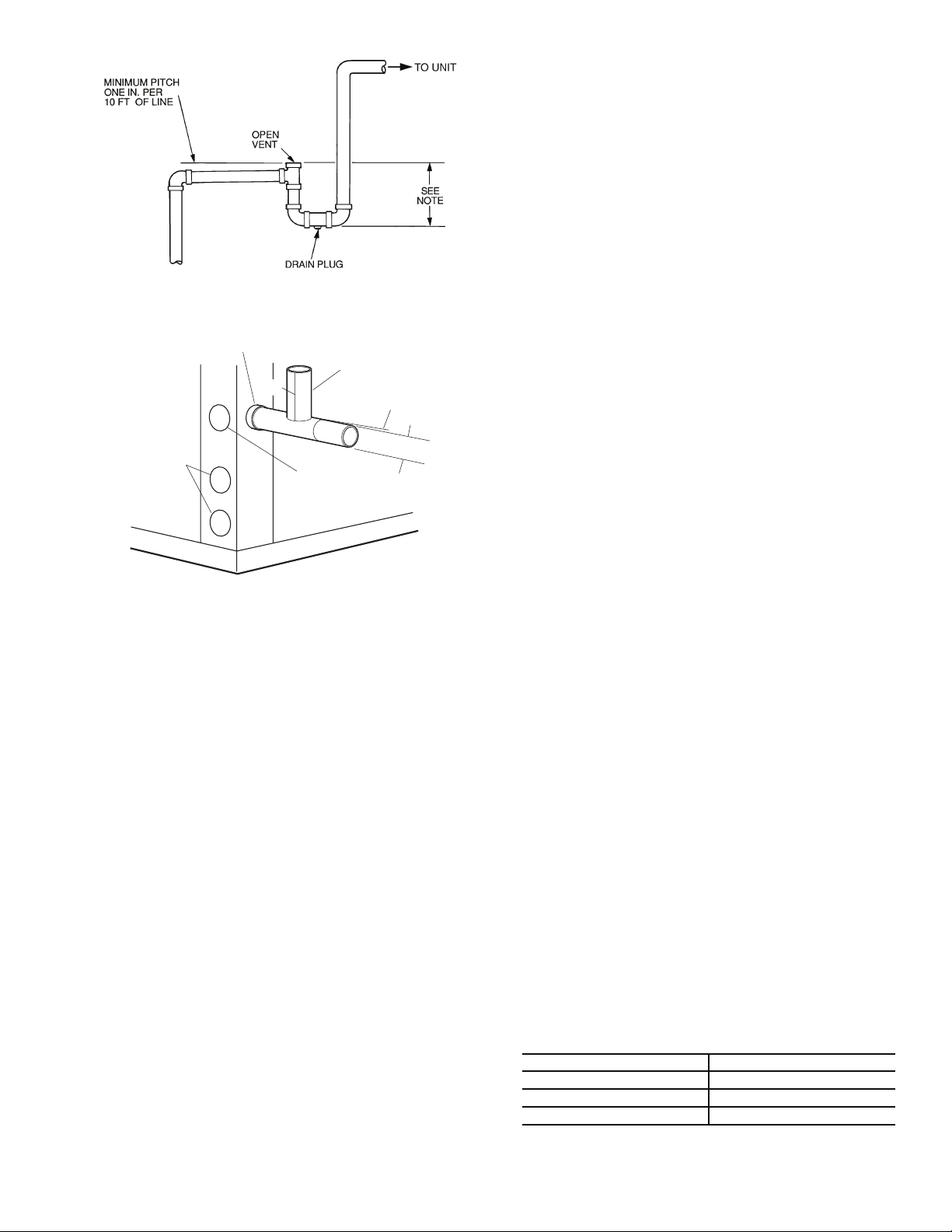
d
a50-6261tf
NOTE: Trap should be deep enough to offset maximum unit static
ifference. A 4-in. trap is recommended.
Fig. 10 — Trap Condensate Drain
3/4” Copper FPT/PVC
1/2”
Water
Connections
NOTE: Unit does not need to be sloped toward drain.
3/4” PVC
Vent
Alternate
Condensate
Location
1/4” per foot
slope to drain
1/2”
Fig. 11 — Vertical Condensate Connection
Each unit must be installed with its own individual vent and
means to flush or blow out the condensate drain line. Do not install units with a common trap or vent.
VENTING — Install a vent in the condensate line of any
application that may allow dirt or air to collect in the line. Consider the following:
• Always install a vent where an application requires a
long horizontal run.
• Always install a vent where large units are working
against higher external static pressure and to allow
proper drainage for multiple units connected to the same
condensate main.
• Be sure to support the line where anticipated sagging from
the condensate or when “double trapping” may occur.
• If condensate pump is present on unit, be sure drain con-
nections have a check valve to prevent back flow of con-
densate into other units.
Step 7 — Pipe Connections — Depending on the
application, there are 3 types of WSHP piping systems to
choose from: water loop, ground-water and ground loop. Refer
to Piping Section of Carrier System Design Manual for additional information.
All WSHP units use low temperature soldered female pipe
thread fittings for water connections to prevent annealing and
out-of-round leak problems which are typically associated with
high temperature brazed connections. Refer to Table 1 for connection sizes. When making piping connections, consider the
following:
• Use a backup wrench when making screw connections to
unit to prevent internal damage to piping.
• Insulation may be required on piping to avoid condensa-
tion in the case where fluid in loop piping operates at
temperatures below dew point of adjacent air.
• Piping systems that contain steel pipes or fittings may
be subject to galvanic corrosion. Dielectric fittings may
be used to isolate the steel parts of the system to avoid
galvanic corrosion.
WATER LOOP APPLICATIONS — Water loop applications
usually include a number of units plumbed to a common piping system. Maintenance to any of these units can introduce air
into the piping system. Therefore, air elimination equipment
comprises a major portion of the mechanical room plumbing.
The flow rate is usually set between 2.25 and 3 gpm per ton
of cooling capacity. For proper maintenance and servicing,
pressure-temperature (P/T) ports are necessary for temperature
and flow verification.
In addition to complying with any applicable codes, consid-
er the following for system piping:
• Piping systems using water temperatures below 50 F
require
1
/2-in. closed cell insulation on all piping surfaces
to eliminate condensation.
• Avoid all plastic to metal threaded fittings due to the
potential to leak. Use a flange fitted substitute.
• Teflon tape thread sealant is recommended to minimize
internal fouling of the heat exchanger.
• Use backup wrench. Do not overtighten connections.
• Route piping to avoid service access areas to unit.
• Flush the piping system prior to operation to remove dirt
and foreign materials from the system.
GROUND-LOOP APPLICATIONS — Temperatures between 25 and 110 F and a cooling capacity of 2.25 to 3 gpm of
flow per ton is recommended. In addition to complying with
any applicable codes, consider the following for system piping:
• Limit piping materials to only polyethylene fusion in the
buried sections of the loop.
• Do not use galvanized or steel fittings at any time due to
corrosion.
• Avoid all plastic to metal threaded fittings due to the potential to leak. Use a flange fitted substitute.
• Do not overtighten connections.
• Route piping to avoid service access areas to unit.
• Use pressure-temperature (P/T) plugs to measure flow of
pressure drop.
INSTALLATION OF SUPPLY AND RETURN HOSE
KIT — Follow these piping guidelines.
1. Install a drain valve at the base of each supply and return
riser to facilitate system flushing.
2. Install shutoff/balancing valves and unions at each unit to
permit unit removal for servicing.
3. Place strainers at the inlet of each system circulating
pump.
4. Select the proper hose length to allow slack between connection points. Hoses may vary in length by +2% to –4%
under pressure.
5. Refer to Table 2. Do not exceed the minimum bend radius
for the hose selected. Exceeding the minimum bend radius may cause the hose to collapse, which reduces water
flow rate. Install an angle adapter to avoid sharp bends
in the hose when the radius falls below the required
minimum.
NOTE: Piping must comply with all applicable codes.
Table 2 — Metal Hose Minimum Bend Radii
HOSE DIAMETER (in.) MINIMUM BEND RADII (in.)
1
/
2
3
/
4
15
21/
2
4
1
/
2
9
Insulation is not required on loop water piping except where
the piping runs through unheated areas or outside the building
or when the loop water temperature is below the minimum expected dew point of the pipe ambient. Insulation is required if
loop water temperature drops below the dew point.
IMPORTANT: Do not bend or kink supply lines or hoses.
Pipe joint compound is not necessary when Teflon threaded
tape is pre-applied to hose assemblies or when flared-end
connections are used. If pipe joint compound is preferred, use
compound only in small amounts on the male pipe threads of
the fitting adapters. Prevent sealant from reaching the flared
surfaces of the joint.
NOTE: When anti-freeze is used in the loop, assure that it is
compatible with Teflon tape or pipe joint compound employed.
Maximum allowable torque for brass fittings is 30 ft-lb. If a
torque wrench is not available, tighten finger-tight plus one
quarter turn. Tighten steel fittings as necessary.
Optional pressure-rated hose assemblies designed specifically for use with Carrier units are available. Similar hoses can
be obtained from alternate suppliers. Supply and return hoses
are fitted with swivel-joint fittings at one end to prevent kinking during installation.
CAUTION
Backup wrench is required when tightening water connections to prevent water line damage. Failure to use a backup
wrench could result in equipment damage.
Refer to Fig. 12 for an illustration of a supply/return hose
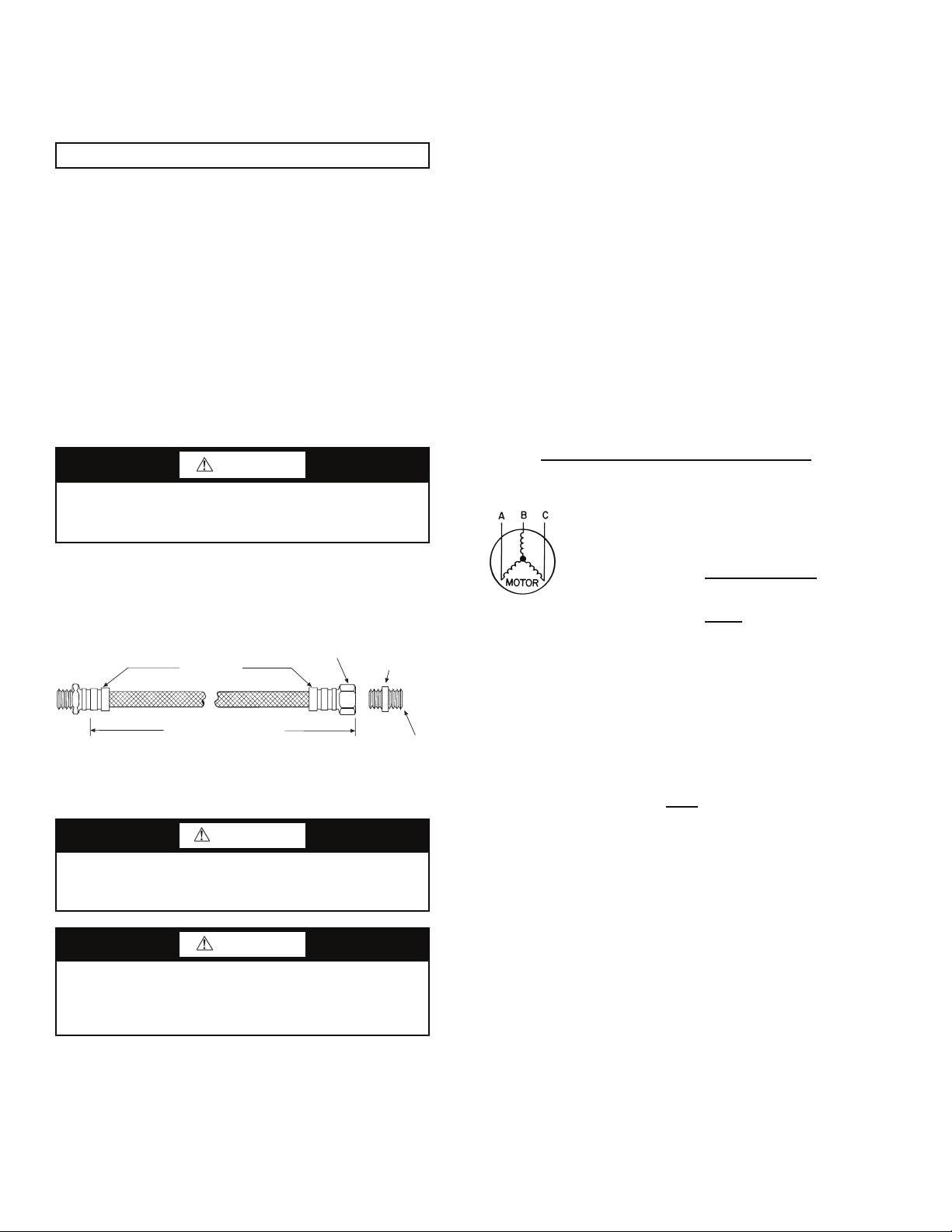
kit. Male adapters secure hose assemblies to the unit and risers.
Install hose assemblies properly and check them regularly to
avoid system failure and reduced service life.
A50-7734
Rib Crimped
Length
(2 ft Length Standard)
Fig. 12 — Supply/Return Hose Kit
Swivel
Brass
Fitting
Brass
Fitting
MPT
Refer to unit wiring diagrams Fig. 13-22 for a schematic of
the field connections, which must be made by the installing (or
electrical) contractor. Refer to Table 3 for fuse sizes.
Consult the unit wiring diagram located on the inside of the
compressor access panel to ensure proper electrical hookup.
The installing (or electrical) contractor must make the field
connections when using field-supplied disconnect.
Operating voltage must be the same voltage and phase as
shown in Table 3.
Make all final electrical connections with a length of flexible conduit to minimize vibration and sound transmission to
the building.
POWER CONNECTION — Make line voltage connection
by connecting the incoming line voltage wires to the L side
of the CC terminal as shown in Fig. 23. See Table 3 for correct wire and maximum overcurrent protection sizing.
SUPPLY VOLTAGE — Operating voltage to unit must be
within voltage range indicated on unit nameplate.
On 3-phase units, voltages under load between phases must
be balanced within 2%. Use the following formula to determine the percentage voltage imbalance:
% Voltage Imbalance
= 100 x
max voltage deviation from average voltage
average voltage
Example: Supply voltage is 460-3-60.
AB = 452 volts
BC = 464 volts
AC = 455 volts
Average Voltage =
452 + 464 + 455
3
1371
=
3
= 457
Determine maximum deviation from average voltage:
(AB) 457 – 452 = 5 v
(BC) 464 – 457 = 7 v
(AC) 457 – 455 = 2 v
Maximum deviation is 7 v.
Determine percent voltage imbalance.
Step 8 — Wire Field Power Supply
WARNING
To avoid possible injury or death due to electrical shock,
open the power supply disconnect switch and secure it in
an open position during installation.
CAUTION
Use only copper conductors for field-installed electrical
wiring. Unit terminals are not designed to accept other
types of conductors. Failure to follow this safety precaution
could lead to equipment damage.
All field installed wiring, including the electrical ground,
MUST comply with the National Electrical Code (NEC) as
well as applicable local codes. In addition, all field wiring must
conform to the Class II temperature limitations described in the
NEC.
% Voltage Imbalance = 100 x
7
457
= 1.53%
This amount of phase imbalance is satisfactory as it is
below the maximum allowable 2%.
Operation on improper line voltage or excessive phase
imbalance constitutes abuse and may cause damage to electrical components.
NOTE: If more than 2% voltage imbalance is present, contact
your local electric utility.
208-VOLT OPERATION — All 208-230 volt units are factory
wired for 208 volts. The transformers may be switched to
230-volt operation by switching the red (208 volt) wire with
the orange (230 volt) wire at the L1 terminal.
460-VOLT OPERATION — Units using 460-v and internal
secondary pump will require a neutral wire from the supply
side in order to feed accessory with 265-v.
10
a50-8490
Relay/Contactor Coil
Condensate Pan
Solenoid Coil
Temperature Switch
Thermistor
Ground
Wire Nut
anti-freeze solutions, cut JW3 jumper.
terminal to control box.
internal pump option.
remove BLU wire from fan motor speed trap “M” and connect to “H” for
high speed or “L” for low speed.
pump. Aquastat is rated for voltage up to 277 v.
6. 24-v alarm signal shown. For dry alarm contact, cut JW1 jumper and for
7. Transformer secondary ground via green wire with yellow stripe from “C”
8. Hot water generator pump only in models with hot water generation and
9. For auxiliary staging options, consult electric heat installation manual.
10. Fan motors factory wired for medium speed. For high or low speed,
11. Aquastat is with unit and must be wired in series with the hot leg to the
Field Line Voltage Wiring
Field Low Voltage Wiring
Printed Circuit Trace
Optional Wiring
LEGEND
LOC — Loss of Charge Pressure Switch
MV — Motorized Valve
MVES — Motorized Valve End Switch
NEC — National Electrical Code
P1 — Field Wiring Terminal Block
PSC — Permanent Split Capacitor
RV — Reversing Valve Coil
SW1 — DIP Switch, 2 Position
TRANS — Transformer
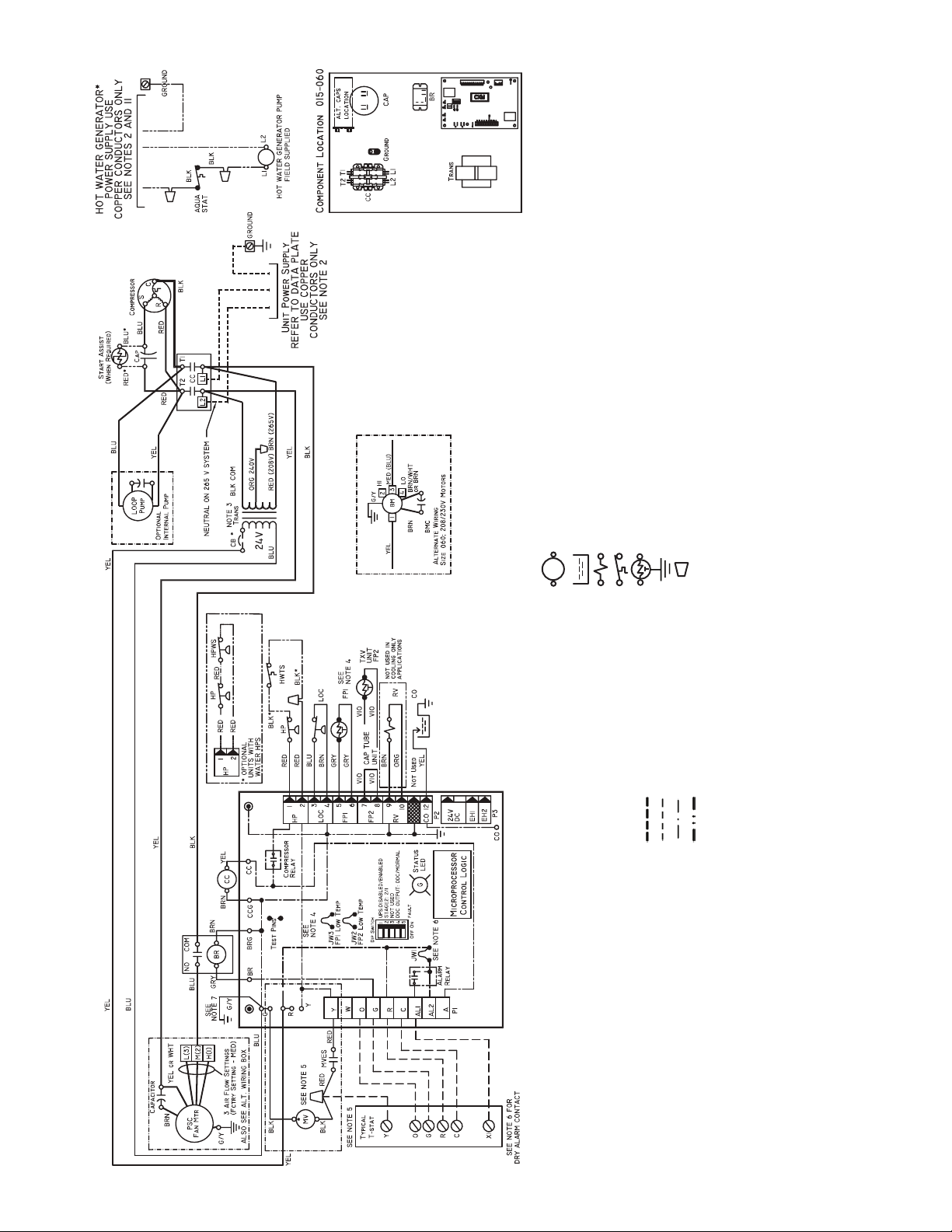
Fig. 13 — 50PCH,PCV Units with Complete C Controller, Single-Phase
Complete C
230 v operation, switch RED wire to ORG wire. Insulate open end of
RED lead. Transformer is energy limiting or may have circuit breaker.
freeze solutions, cut JW3 jumper.
tion instructions for wiring to the unit. Wire “Y” from thermostat to “Y”
Complete C when a motorized valve is not used. “O” terminal is not used
in cooling only applications. Thermostat wiring must be Class 1 and volt-
age rating equal to or greater than unit supply voltage.
1. Compressor and blower motor thermally protected internally.
2. All wiring to the unit must comply with NEC and local codes.
3. Transformer for 208/230 v will be connected for 208 v operation. For
4. FP1 thermistor provides freeze protection for water. When using anti-
AL — Alarm Relay Contacts
BM — Blower Motor
BMC — Blower Motor Capacitor
BR — Blower Relay
CAP — Compressor Capacitor
CB — Circuit Breaker
CC — Compressor Contactor
CO — Sensor, Condensate Overflow
FP1 — Sensor, Low Temperature Protection Water Coil
FP2 — Sensor, Low Temperature Protection Air Coil
HP — High-Pressure Switch
HPWS — High-Pressure Water Switch
HWTS — High Leaving Water Temperature Switch
JW1 — Jumper, Alarm
NOTES:
*Optional.
5. Typical heat pump thermostat wiring shown. Refer to thermostat installa-
11
a50-8491
Relay/Contactor Coil
Condensate Pan
Solenoid Coil
Thermistor
Ground
Wire Nut
Deluxe D
when motorized valve is not used. Thermostat wiring must be Class 1
and voltage rating equal to or greater than unit supply voltage. Heat/cool
thermostats not compatible with motorized water valve.
contact will be available between AL1 and AL2.
terminal to control box.
combination of speeds, attach black wire to the higher of the two desired
speed taps and the blue wire to the lower of the two desired speed taps.
6. 24-v alarm signal shown. For dry alarm contact, cut JW4 jumper and dry
7. Transformer secondary ground via green wire with yellow stripe from “C”
8. Blower motor is factory wired for medium and high speeds. For any other
12
Field Line Voltage Wiring
Field Low Voltage Wiring
Printed Circuit Trace
Optional Wiring
LEGEND
LOC — Loss of Charge Pressure Switch
MV — Motorized Valve
MVES — Motorized Valve End Switch
NEC — National Electrical Code
P1 — Field Wiring Terminal Block
RVS — Reversing Valve Solenoid
TRANS — Transformer
TXV — Thermostatic Expansion Valve
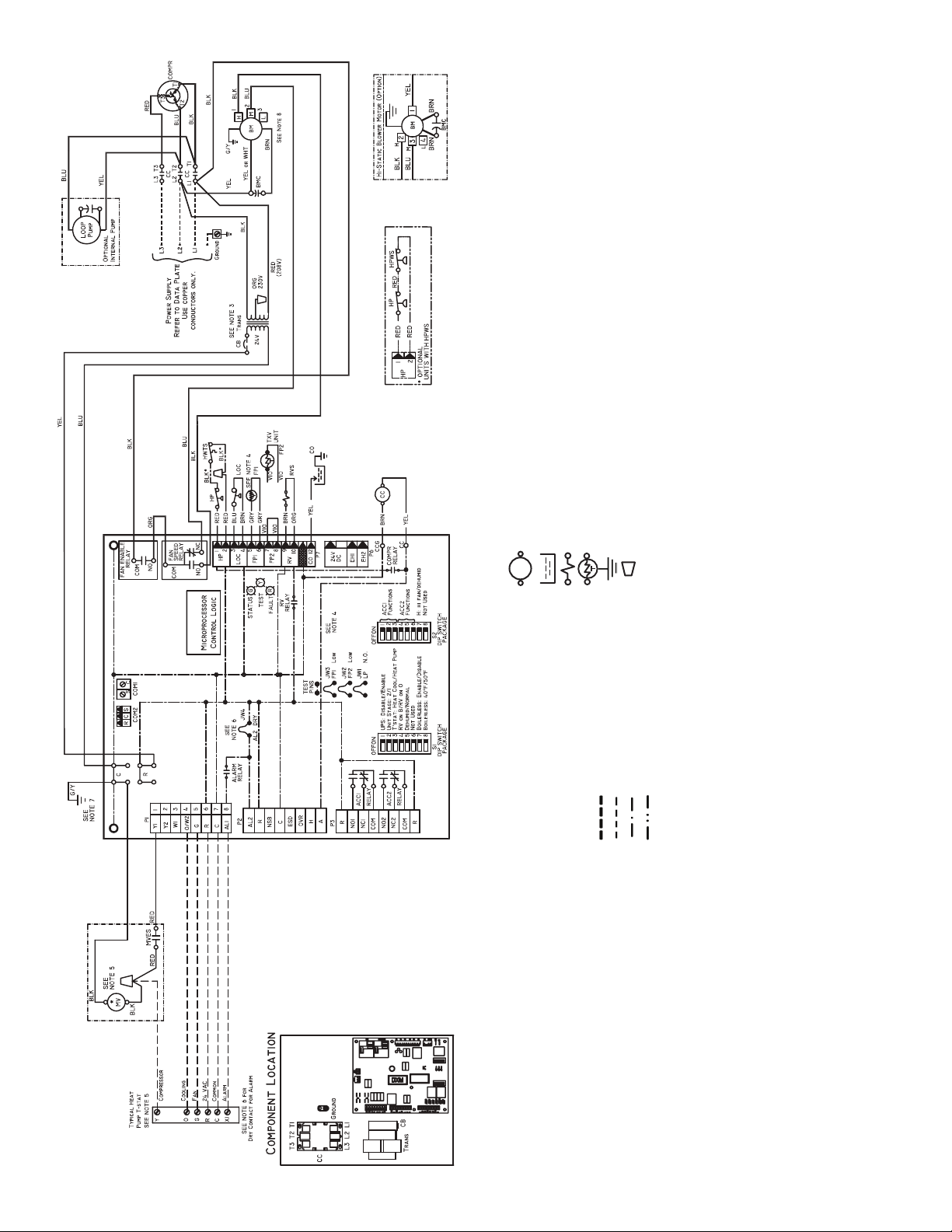
Fig. 14 — 50PCH,PCV Units with Deluxe D Controller, Three-Phase (208/230 V)
switch RED and ORG leads at L1 and insulate RED lead. Transformer is
energy limiting or may have circuit breaker.
freeze solutions, cut JW3 jumper.
tions for wiring to the unit. Wire “Y” from thermostat to “Y1” Deluxe D
1. Compressor thermally protected internally.
2. All wiring to the unit must comply with NEC and local codes.
3. Transformer is wired to 208-v RED lead for 208-3-60 units. For 230-3-60,
4. FP1 thermistor provides freeze protection for water. When using anti-
AL — Alarm Relay Contacts
BM — Blower Motor
BMC — Blower Motor Capacitor
CAP — Compressor Capacitor
CB — Circuit Breaker
CC — Compressor Contactor
CO — Sensor, Condensate Overflow
FP1 — Sensor, Low Temperature Protection Water Coil
FP2 — Sensor, Low Temperature Protection Air Coil
HP — High-Pressure Switch
HPWS — High-Pressure Water Switch
HWTS — High Leaving Water Temperature Switch
JW1 — Jumper, Alarm
*Optional.
NOTES:
5. Refer to microprocessor control, LON, or thermostat installation instruc-
a50-8492
Relay/Contactor Coil
Condensate Pan
Solenoid Coil
Thermistor
Ground
Wire Nut
contact will be available between AL1 and AL2.
terminal to control box.
other combination of speeds, attach black wire to the higher of the two
desired speed taps at the motor. Attach the blue wire to the lower of the
two desired speed taps.
nation of speeds is available.
Deluxe D
Field Line Voltage Wiring
Field Low Voltage Wiring
Printed Circuit Trace
6. 24-v alarm signal shown. For dry alarm contact, cut JW4 jumper and dry
7. Transformer secondary ground via green wire with yellow stripe from “C”
8. Blower motor is factory wired for medium and high speeds. For any
Optional Wiring
9. Blower motor is factory wired for high and low speeds. No other combi-
wire from the supply side in order to feed the accessory with 265-v.
10. The 460-v units using an internal secondary pump will require a neutral
13
LEGEND
LOC — Loss of Charge Pressure Switch
MV — Motorized Valve
MVES — Motorized Valve End Switch
NEC — National Electrical Code
P1 — Field Wiring Terminal Block
PB — Po wer Blo ck
RVS — Reversing Valve Solenoid
TRANS — Transformer
TXV — Thermostatic Expansion Valve
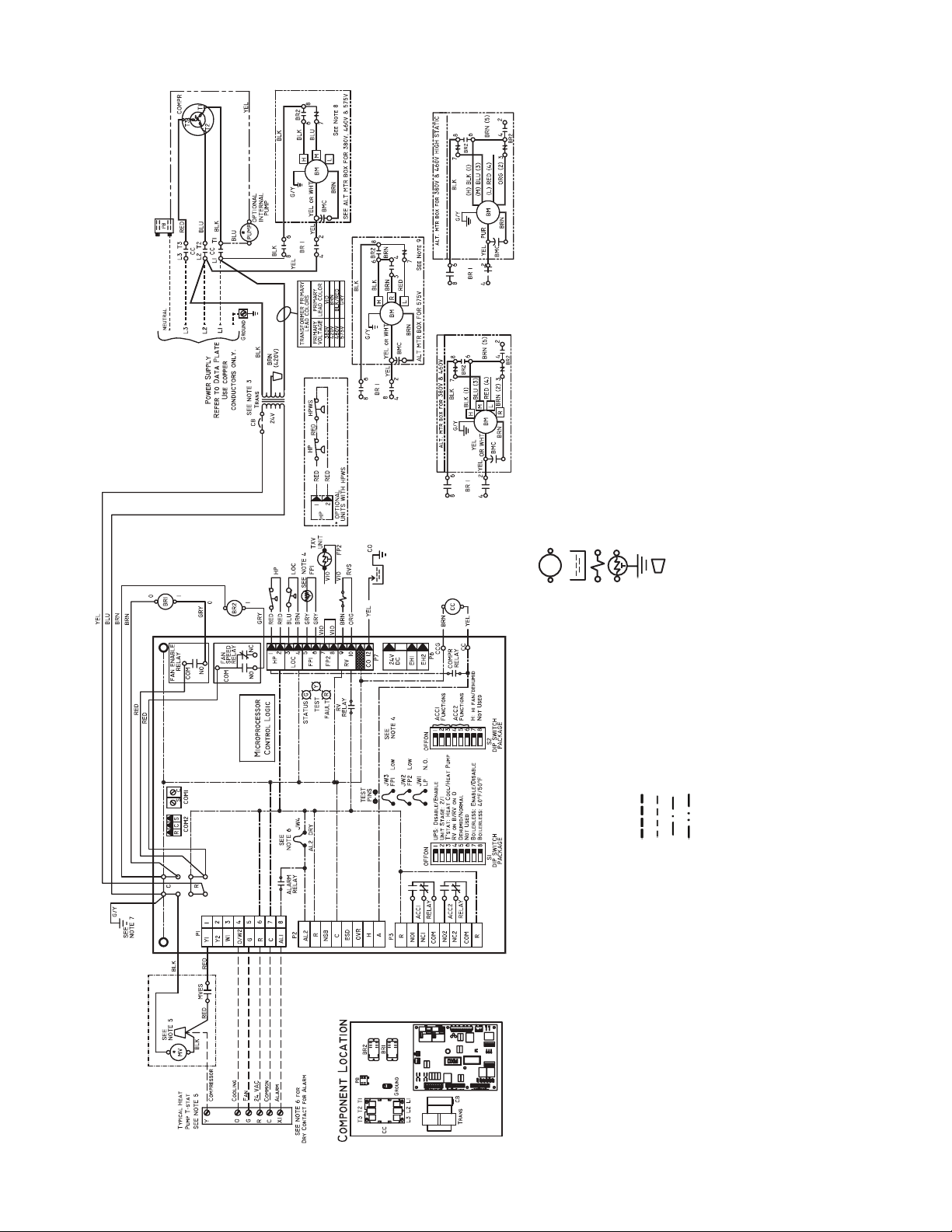
Fig. 15 — 50PCH,PCV Units with Deluxe D Controller, Three-Phase (460 V)
GRY lead for 575-3-60 units. Transformer is energy limiting or may have
circuit breaker.
using antifreeze solutions, cut JW3 jumper.
tions for wiring to the unit. Wire “Y” from thermostat to “Y1” Deluxe D
when motorized valve is not used. Thermostat wiring must be Class 1
and voltage rating equal to or greater than unit supply voltage. Heat/cool
thermostats not compatible with motorized water valve.
1. Compressor thermally protected internally.
2. All wiring to the unit must comply with NEC and local codes.
3. Transformer is wired to 460-v BLK/RED lead for 460-3-60 units or 575-v
4. FP1 thermistor provides low temperature protection for water. When
AL — Alarm Relay Contacts
BM — Blower Motor
BMC — Blower Motor Capacitor
BR — Blower Relay
CAP — Compressor Capacitor
CB — Circuit Breaker
CC — Compressor Contactor
CO — Sensor, Condensate Overflow
FP1 — Sensor, Low Temperature Protection Water Coil
FP2 — Sensor, Low Temperature Protection Air Coil
HP — High-Pressure Switch
HPWS — High-Pressure Water Switch
JW1 — Clippable Field Selection Jumper
*Optional.
NOTES:
5. Refer to microprocessor control, LON, or thermostat installation instruc-
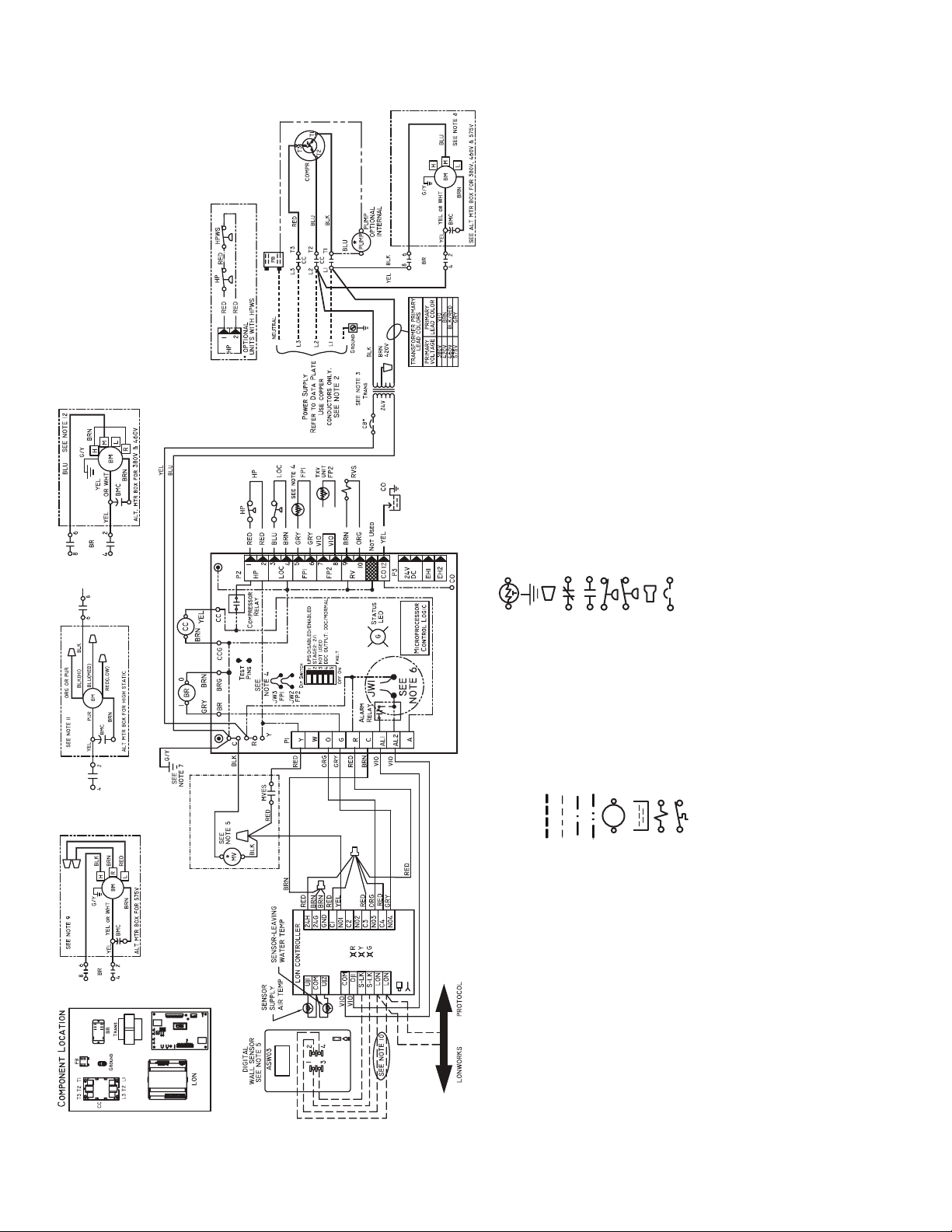
a50-8493
former is energy limiting or may have circuit breaker.
using antifreeze solutions, cut JW3 jumper.
instructions for wiring to the unit. Wire “N01” from LON to “Y1” Com-
plete C when a motorized valve is not used. Low voltage wiring must
be Class 1 and voltage rating equal to or greater than unit supply
voltage.
AL2.
terminal to control box.
remove BLU wire from fan motor speed tap “M” and connect to “H” for
high speed or “L” for low speed.
Connect BLK and BRN wires together.
wall sensor.
BLK wire from BR “6”. Connect BLK and ORG/PUR wire together.
Connect RED for low or BLU for medium to BR “6”.
BLU wire from medium tap and connect to low speed tap. For high
speed, remove BLU wire from exisiting speed tap and remove BRN
jumper wire from high speed tap. Connect BLU wire to high speed tap.
Tape off unconnected end of BRN jumper.
tral wire from the supply side in order to feed the accessory with 265-v.
1. Compressor and blower motor thermally protected internally.
2. All wiring to the unit must comply with NEC and local codes.
3. Transformer is wired to 460 v BLK/RED lead for 460-3-60 units. Trans-
4. FP1 thermistor provides low temperature protection for water. When
NOTES:
Complete C
5. Refer to microprocessor control, LON, or thermostat installation
Thermistor
Ground
Wire Nut
6. Factory cut JW1 jumper. Dry contact will be available between AL1 and
7. Transformer secondary ground via green wire with yellow strip from “C”
8. Fan motors are factory wired for medium speed. For high or low speed,
9. For low speed, remove BLK wire from BR “6” and replace with RED.
10. Optional LON wires. Only connect if LON connection is desired at the
11. For blower motors with leads. For medium or low speed, disconnect
12. Blower motor factory wired to medium speed. For low speed remove
Relay Contacts - N.C.
Relay Contacts - N.O.
Low Pressure Switch
High Pressure Switch
Splice Cap
Circuit Breaker
13. The 460-v units using an internal secondary pump will require a neu-
14
LEGEND
Field Line Voltage Wiring
Field Low Voltage Wiring
Printed Circuit Trace
Optional Wiring
Relay/Contactor Coil
Condensate Pan
Solenoid Coil
Temperature Switch
P1 — Field Wiring Terminal Block
RVS — Reversing Valve Solenoid
TRANS — Transformer
TXV — Thermostatic Expansion Valve
Fig. 16 — 50PCH,PCV Units with Complete C and LON Controller (460 V)
AL — Alarm Relay Contacts
BM — Blower Motor
BMC — Blower Motor Capacitor
BR — Blower Relay
CAP — Compressor Capacitor
CB — Circuit Breaker
CC — Compressor Contactor
CO — Sensor, Condensate Overflow
FP1 — Sensor, Low Temperature Protection, Water Coil
FP2 — Sensor, Low Temperature Protection, Air Coil
HP — High-Pressure Switch
HPWS — High-Pressure Water Switch
JW1 — Clippable Field Selection Jumper
LOC — Loss of Charge Pressure Switch
LON — Local Operating Network
MV — Motorized Valve
MVES — Motorized Valve End Switch
NEC — National Electrical Code
*Optional Wiring.

a50-8440
former is energy limiting or may have circuit breaker.
using antifreeze solutions, cut JW3 jumper.
tions for wiring to the unit. Wire “N01” from LON to “Y1” Deluxe D when
motorized valve is not used. Thermostat wiring must be Class 1 and
voltage rating equal to or greater than unit supply voltage.
AL2.
“C” terminal to control box.
other combination of speeds, attach black wire to the higher of the two
desired speed taps at the motor, and attach the blue wire to the lower of
the two desired speed taps.
nation is available.
wall sensor.
wire from the supply side in order to feed the accessory with 265-v.
1. Compressor and blower motor thermally protected internally.
2. All wiring to the unit must comply with NEC and local codes.
3. Transformer is wired to 460-v BLK/RED lead for 460-3-60 units. Trans-
4. FP1 thermistor provides low temperature protection for water. When
5. Refer to microprocessor control, LON, thermostat installation instruc-
6. Factory cut JW4 jumper. Dry contact will be available between AL1 and
7. Transformer secondary ground via green wire with yellow stripe from
8. Blower motor is factory wired for medium and high speeds. For any
9. Blower motor is factory wired for high and low speeds. No other combi-
10. Optional LON wires. Only connect if LON connection is desired at the
NOTES:
Thermistor
Ground
Wire Nut
Relay Contacts - N.C.
Relay Contacts - N.O.
Low Pressure Switch
High Pressure Switch
Splice Cap
Circuit Breaker
11. The 460-v units using an internal secondary pump will require a neutral
Deluxe D
Field Line Voltage Wiring
Field Low Voltage Wiring
Printed Circuit Trace
Optional Wiring
Relay/Contactor Coil
Condensate Pan
Solenoid Coil
Temperature Switch
LEGEND
P1 — Field Wiring Terminal Block
RVS — Reversing Valve Solenoid
TRANS — Transformer
TXV — Thermostatic Expansion Valve
Fig. 17 — 50PCH,PCV units with Deluxe D and LON Controller (460 V)
15
AL — Alarm Relay Contacts
BM — Blower Motor
BMC — Blower Motor Capacitor
BR — Blower Relay
CAP — Compressor Capacitor
CB — Circuit Breaker
CC — Compressor Contactor
CO — Sensor, Condensate Overflow
FP1 — Sensor, Low Temperature Protection, Water Coil
FP2 — Sensor, Low Temperature Protection, Air Coil
HP — High-Pressure Switch
HPWS — High-Pressure Water Switch
JW1 — Clippable Field Selection Jumper
LOC — Loss of Charge Pressure Switch
LON — Local Operating Network
MV — Motorized Valve
MVES — Motorized Valve End Switch
NEC — National Electrical Code
*Optional Wiring.
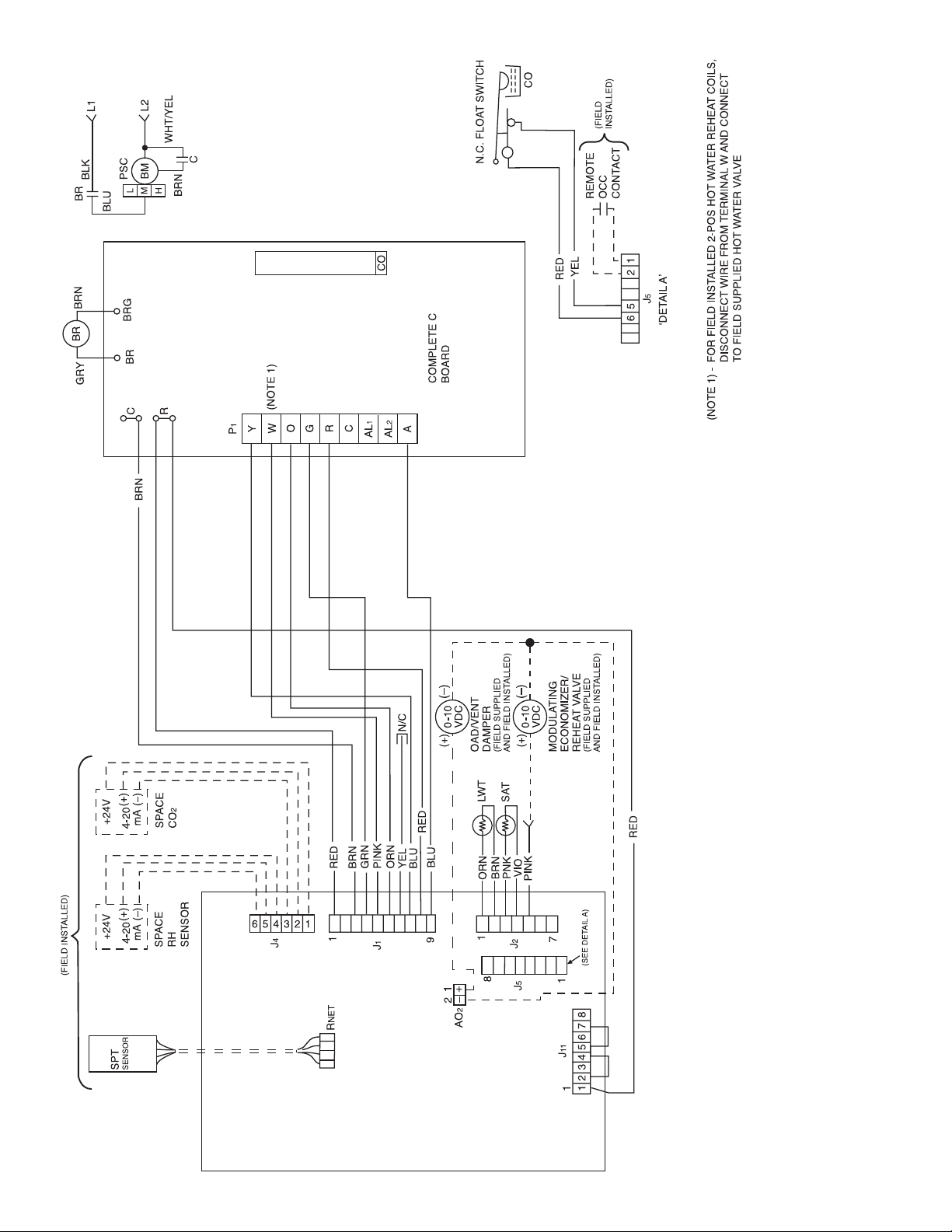
Fig. 18 — Units with Complete C and WSHP Open Multiple Protocol Controls
WHSP-OPEN
A50-8355
16
LEGEND
BM — Blower Motor
BR — Blower Relay
CO — Condensate Overflow
LWT — Leaving Water Temperature
N.C. — Normally Closed
OAD — Outside Air Damper
OCC — Occupancy Input Contact
RH — Relative Humidity
SAT — Supply Air Temperature
SPT — Space Temperature
 Loading...
Loading...