Page 1

42EM
EN
FR
DE
IT
ES
NL
DUCTED FAN COIL UNITS
Installation instructions
VENTILO-CONVECTEURS GAINABLES
Manuel d’installation
VENTILATOR-KONVEKTOREN MIT
KANALANSCHLUSS
Installationanweisungen
UNITÀ FAN COIL CANALIZZATE
Manuale d’installazione
UNIDAD DE FAN COIL CON CONDUCTOS
Manual de instalación
VENTILATORCONVECTOR VOOR
KANAALAANSLUITING
Montagehandleiding
Page 2

ENGLISH FRANCAIS DEUTSCH
CONTENTS
1 - PRECAUTIONS ................................................ 7
1.1 - Operating limits ................................................ 7
1.2 - Clearances required .........................................7
1.3 - Receiving a shipment - installation methods 7
1.4 - Supply voltage................................................... 7
2 - SAFETY CONSIDERATIONS ....................... 7
2.1 - General .............................................................. 7
2.2 - Protection against electrocution ..................... 7
2.3 - General installation conditions ....................... 8
2.4 - Caution for the control of the 42EM .............8
2.5 - Conformity ........................................................ 8
3 - INSTALLATION OF THE UNIT ...................
3.1 - Installing the unit in the false ceiling .............8
3.2 - Installation procedure ...................................... 8
3.3 - Removal procedure .......................................... 9
4 - COMPONENTS .................................................9
4.1 - Fan motor assembly ......................................... 9
4.2 - Water coil .........................................................10
4.3 - Duct connection spigots ................................ 10
4.4 - Optional filter and filter access ..................... 10
4.5 - Fresh air controller ......................................... 10
4.6 - Optional water flow control valves .............. 11
4.7 - Flexible pipe option .......................................12
4.8 - Optional electric heater ................................ 12
5 - CODIFICATION ..............................................
TABLE DES MATIÈRES
1 - PRECAUTIONS .............................................. 13
1.1 - Limites d’utilisation ....................................... 13
1.2 - Réservation pour maintenance ..................... 13
1.3 - Réception - Lieu d’implantation ..................13
1.4 - Tension d’alimentation................................... 13
2 - CONSIDERATIONS DE SECURITE ......... 13
2.1 - Généralités ...................................................... 13
2.2 - Protection contre les électrocutions ............. 13
2.3 - Préconisation générale d’installation ........... 14
2.4 - Préconisation concernant la régulation .......14
2.5 - Conformité ...................................................... 14
8
3 - INSTALLATION DE L’UNITE ....................
3.1 - Coordination entre unité et faux plafond ........14
3.2 - Procédure d’installation................................. 14
3.3 - Procédure de démontage ............................... 15
4 - COMPOSANTS ................................................ 15
4.1 - Motoventilateurs ............................................15
4.2 - Batterie à eau .................................................. 16
4.3 - Viroles de raccordement ................................ 16
4.4 - Option filtre à air et accès ............................. 16
4.5 - Régulateur de débit d’air neuf ...................... 16
4.6 - Option vannes de régulation du débit
d’eau ................................................................ 17
4.7 - Option flexible ................................................ 18
4.8 - Option batterie électrique ............................ 18
12
5 - CODIFICATION ..............................................
INHALT
1 - BESTIMMUNGEN .......................................... 19
1.1 - Betriebs-Grenzwerte ...................................... 19
1.2 - Erforderlicher freier Raum ........................... 19
1.3 - Erhalt der Sendung - Installations-
methoden ........................................................ 19
1.4 - Versorgungsspannung .................................... 19
2 - SICHERHEITSMASSNAHMEN..................19
2.1 - Allgemeines .....................................................19
2.2 - Schutz gegen elektrische Schläge .................19
2.3 - Allgemeine Installationsbedingungen ......... 20
2.4 - Warnung für die Atmosphera-Regelung ..... 20
2.5 - Konformität .....................................................20
14
3 - INSTALLATION DES GERÄTS ..................
3.1 - Installation des Geräts in der Zwischen-
decke ...............................................................20
3.2 - Installationsvorgang ....................................... 20
3.3 - Ausbauverfahren ............................................ 21
4 - BAUTEILE .......................................................
4.1 - Ventilator-Motor-Baugruppe ........................ 21
4.2 - Wasserregister ................................................. 22
4.3 - Kanalanschluss-Stutzen ................................. 22
4.4 - Wahlweiser Filter und Filterzugang .............. 22
4.5 - Außenluftregler ..............................................22
4.6 - Wahlweise Wasserregelventile ...................... 23
4.7 - Flexible Rohrleitungen (Option) .................24
4.8 - Wahlweise Elektroheizung ........................... 24
18
5 - GERÄTECODES ............................................
20
21
24
ITALIANO ESPAÑOL
INDICE
1 - PRECAUZIONI ............................................... 25
1.1 - Limiti di funzionamento ................................ 25
1.2 - Spazi necessari ................................................ 25
1.3 - Ricevimento delle unità e modalità
d’installazione ....................................................25
1.4 - Tensione di alimentazione .............................25
2 - CONSIDERAZIONI SULLA SICUREZZA .25
2.1 - Generalità ........................................................ 25
2.2 - Precauzioni contro le folgorazioni ............... 26
2.3 - Raccomandazioni per l’installazione ...........26
2.4 - Precauzione per il controllo .......................... 26
2.5 - Conformità ...................................................... 26
3 - INSTALLAZIONE DEI 42EM ......................26
3.1 - Installazione del 42EM in un controsoffitto ..26
3.2 - Procedura di installazione ............................. 27
3.3 - Procedura di smontaggio ............................... 27
4 - COMPONENTI ................................................ 28
4.1 - Assieme motoventilante ................................ 28
4.2 - Batteria ad acqua ............................................ 28
4.3 - Collari di collegamento del canale ............... 29
4.4 - Filtro (optional) e suo accesso ...................... 29
4.5 - Regolatore del flusso d’aria esterna ............. 29
4.6 - Valvole di controllo della portata d’acqua
(optional) ........................................................ 30
4.7 - Tubi flessibili optional .................................... 30
4.8 - Batteria elettrica di riscaldamento
(optional) ....................................................... 30
5 - CODIFICA ........................................................ 31
INDICE
1 - PRECAUCIONES ...........................................32
1.1 - Límites de funcionamiento............................ 32
1.2 - Espacio para el mantenimiento .................... 32
1.3 - Recepción de un envío - métodos de
instalación ....................................................... 32
1.4 - Tensión de alimentación ................................ 32
2 - CONSIDERACIONES DE SEGURIDAD ...
2.1 - Generalidades ................................................. 32
2.2 - Precauciones contra la electrocución ........... 33
2.3 - Recomendaciones para la instalación .......... 33
2.4 - Precaución con el control de la 42EM ......... 33
2.5 - Conformidad ................................................... 33
3 - INSTALACIÓN DE LA 42EM ......................
3.1 - Instalación de la unidad en falso techo ........ 33
3.2 - Procedimiento de instalación ........................ 34
3.3 - Procedimiento de desmontaje ...................... 34
4 - COMPONENTES ............................................34
4.1 - Conjunto motor/ventilador ...........................34
4.2 - Batería de agua ............................................... 35
4.3 - Tomas de conexión de conductos ................. 35
4.4 - Filtro (opción) y acceso al filtro .................... 36
4.5 - Aire de renovación ......................................... 36
4.6 - Válvulas de control del caudal de agua
(opción) ........................................................... 36
4.7 - Opción de tubo flexible ................................. 37
4.8 - Calentador eléctrico (opción) ...................... 37
5 - CODIFICACIÓN .............................................
NEDERLANDS
INHOUD
1 - VOORZORGSMAATREGELEN ................ 39
1.1 - Bedrijfslimieten ..............................................39
1.2 - Benodigde vrije ruimte .................................. 39
1.3 - Ontvangen van een zending - montage-
methoden ........................................................ 39
1.4 - Voedingsspanning ........................................... 39
2 - VEILIGHEID ...................................................
32
2.1 - Algemeen ........................................................39
2.2 - Voorkomen van elektrische schokken ......... 39
2.3 - Algemene aanbevelingen voor de montage ..40
2.4 - Waarschuwing voor de regeling van de 42EM . 40
2.5 - Conformiteit .................................................... 40
3 - MONTAGE VAN DE 42EM UNIT ...............
33
3.1 - Montage van de unit boven het verlaagd
plafond ............................................................ 40
3.2 - Montageprocedure ......................................... 40
3.3 - Demontage ...................................................... 41
4 - COMPONENTEN ...........................................41
4.1 - Ventilatormotor .............................................. 41
4.2 - Waterbatterij ...................................................
4.3 - Kanaalaansluitingen ....................................... 42
4.4 - Optioneel filter en toegang tot het filter ...... 42
4.5 - Verselucht ........................................................42
4.6 - Waterregelkleppen (optie) ............................ 43
4.7 - Flexibele waterslangen (optie) .....................44
4.8 - Elektrisch verwarmingselement (optie) .....44
5 - CODERING ......................................................
38
39
40
42
44
2
Page 3
5 mm
1
A
B
C
A
C
B
A B C
42EM T0 50 680 250
42EM T1 50 850 250
42EM T2 50 1250 250
42EM T3 50 1250 250
2
3
4
5
8
9
A B C
42EM T0 250 680 250
42EM T1 220 850 250
42EM T2 220 1250 250
42EM T3 220 1250 250
9b
6
9a
10
10a
10a
7
11
3
Page 4
L
12
H
g
C
g
N
N
N
L
L
1
2
3
4
5
6
16
16a
12a
16b
13
14
12b
12c
17
17a
17a
14b
14a
14c
15a
15
15b
4
Page 5
61
42EM 0.5/1.0/2.1/2.2/2.3
18
Hot
42EM 3.1/3.2/3.3
19
L
Cold
4-w V
Out
In
2-w V
R
Out
In
L
Air
In
Out
Air
Out
In
In
Out
Air
R
Hot
In
Out
Out
In
In
Out
Cold
Air
Out
In
Out
In
5
Page 6
ENGLISH FRANCAIS DEUTSCH
Figure titles and legends:
1 Clearance without return air plenum
2 Clearance with return air plenum
3 Electrical danger pictogram
4 Caution hand hazard pictogram
5 General danger pictogram
6 Lifting unit for installation in a false ceiling
7/8 Levelling the unit
9 Condensate drain pipe
9a 20 mm/m fall in horizontal pipe run
9b 50 mm siphon
10 Several units connected to one condensate collector
10a 20 mm/m fall
11 Fresh air controller modification
12 Fan assembly removal
12a Removing fan access panel
12b Position of torx screws
12c Slide assembly down
13 Capacitor assembly
14 Fan speed controller
14a Low speed connector - red wire
14b Medium speed connector - grey wire
14c High speed connector - black wire
L Live
15 Optional fan speed terminal block
15a Customer connection
15b Motor
16 Wiring 42EM sizes 2 and 3
16a Motor
16b Auto-transformer
17 Electric heater removal
17a Location of screws
18 Coil inlet/outlet positions, sizes 0.5, 1 and 2
19 Coil inlet/outlet positions, size 3
In Water in
Out Water out
R Right-hand connections
L Left-hand connections
Hot Hot water, 4-pipe version (two 1/2” gas nuts)
Cold Cold water (two 1/2” gas nuts)
4-w V Four-way valves
2-w V Two-way valves
Air Air flow direction
Figures et légendes:
1 Dégagements sans plenum de reprise
2 Dégagements avec plenum de reprise
3 Pictogramme “Danger électrique”
4 Pictogramme “Attention à vos mains”
5 Pictogramme “Danger général”
6 Levage et installation en faux plafond
7/8 Mise à niveau de l’unité
9 Tuyauterie d’évacuation des condensats
9a Pente de 20 mm/m
9b Siphon de 50 mm
10 Raccordements d’unités multiples à un même
collecteur d’évacuation
10a Pente de 20 mm/m
11 Modification du régulateur d’air neuf
12 Démontage du motoventilateur
12a Démonter le panneau d’accès
12b Position des vis Torx
12c Glisser l’ensemble vers le bas
13 Assemblage condensateur
14 Réglage des vitesses
14a Borne petite vitesse - fil rouge
14b Borne moyenne vitesse - fil gris
14c Borne grande vitesse - fil noir
L Phase
15 Câblage vitesse optional
15a Raccordement client
15b Moteur
16 Câblage 42EM tailles 2 et 3
16a Moteur
16b Autotransformateur
17 Démontage de la batterie électrique
17a Position des vis
18 Positions entrées-sorties d’eau, tailles 0.5, 1 et 2
19 Positions entrées-sorties d’eau, taille 3
In Entrée d’eau
Out Sortie d’eau
R Servitude droite
L Servitude gauche
Hot Eau chaude version 4 tubes (2 écrous
tournant 1/2”)
Cold Eau froide (2 écrous tournant 1/2”)
4-w V Vanne 4 voies
2-w V Vanne 2 voies
Air Air
Abbildungen und Legende:
1 Erforderlicher freier Raum ohne Rückluftplenum
2 Erforderlicher freier Raum mit Rückluftplenum
3 Piktogramm “Elektrische Gefahr”
4 Piktogramm “Gefahr für die Hände”
5 Piktogramm “Allgemeine Gefahr”
6 Einbau in die Zwischendecke: Anheben des Geräts
7/8 Nivellierung des Geräts
9 Kondensatablauf-Rohr
9a 20 mm/m Neigung, horizontale Leitung
9b Siphon 50 mm
10 Anschluss mehrerer Geräte an 1 Kondensatwanne
10a 20 mm/m Neigung
11 Modifikation des Außenluftreglers
12 Ventilatorbaugruppen-Ausbauverfahren
12a Ventilator-Zugangsblech entfernen
12b Position der Torx-Schrauben
12c Baugruppe nach unten schieben
13 Kondensator-Austauschvorgang
14 Ventilator-Drehzahlregler
14a Klemme niedrige Drehzahl - rotes Kabel
14b Klemme mittlere Drehzahl - graues Kabel
14c Klemme hohe Drehzahl - schwarzes Kabel
L Stromführendes Kabel
15 Wahlweiser Ventilatordrehzahl-Klemmblock
15a Kundenanschluss
15b Motor
16 Verdrahtung 42EM Größen 2 und 3
16a Motor
16b Auto-Transformator
17 Elektroheizungs-Ausbauvorgang
17a Position der Schrauben
18 Wasserein- und -austritt, Größen 0.5, 1 und 2
19 Wasserein- und -austritt, Größe 3
In Wassereintritt
Out Wasseraustritt
R Anschlüsse rechts
L Anschlüsse links
Hot Warmwasser, 4-Leiter-Version (zwei 1/2”-
Gasgewinde-Muttern)
Cold Kaltwasser (zwei 1/2”-Gasgewinde-Muttern)
4-w V Vierwegeventil
2-w V Zweiwegeventil
Air Luftströmungsrichtung
ITALIANO ESPAÑOL
Titoli e Legenda delle Figure:
1 Spazi necessari sensa plenum di ripresa
2 Spazi necessari con plenum di ripresa
3 Ideogramma Pericolo Elettrico
4 Ideogramma Pericolo per le Mani
5 Ideogramma Pericolo Generale
6 Sollevamento dell’unità per installazione in controsoffitto
7/8 Livellamento dell’apparecchio
9 Linea di scarico della condensa
9a Pendenza di almeno 20 mm/m nei tratti orizzontali
9b Sifone con profondità di almeno 50 mm
10 Collegamento di più unità ad un unico collectore
10a Pendenza di almeno 20 mm/m
11 Modificazione del regolatore del flusso d’aria esterna
12 Smontaggio dell’assieme motoventilante
12a Smontaggio del pannello d’accesso al ventilatore
12b Posizione da viti torx
12c Estrarre l’assieme dal basso
13 Condensatore
14 Regolatore della velocità del ventilatore
14a Morsetto per bassa velocità - cavo rosso
14b Morsetto per media velocità - cavo grigio
14c Morsetto per alta velocità - cavo nero
L Sotto tensione
15 Morsettiera per le velocità optional del ventilatore
15a Collegamento a cura del cliente
15b Motore
16 Collegamenti elettrici per 42EM grandezze 2 e 3
16a Motore
16b Autotrasformatore
17 Sostituzione della batteria elettrica
17a Posizioni dei viti
18 Posizioni di ingresso/uscita dell’acqua dalla batteria,
grandezze 0.5, 1 e 2
19 Posizioni di ingresso/uscita dell’acqua dalla batteria,
grandezza 3
In Ingresso dell’acqua
Out Uscita dell’acqua
R Attacchi destri
L Attacchi sinistri
Hot Acqua calda, versione per distribuzione a 4 tubi
Cold Acqua refrigerata
(due dadi con filettatura da 1/2” gas)
4-w V Valvola a quattro vie
2-w V Valvola a due vie
Air Flusso d’aria
(due dadi con filettatura da 1/2” gas)
Títulos de figuras y leyendas:
1 Espacio necesario sin plenum de aire de retorno
2 Espacio necesario con plenum de aire de retorno
3 Pictograma Peligro de descarga eléctrica
4 Pictograma: Peligro para las manos
5 Pictograma Peligro general
6 Elevación de la unidad para instalación en un falso
techo
7/8 Nivelación de la unidad
9 Tubo de drenaje de condensado
9a Caída de 20 mm/m en recorrido horizontal
9b Sifón de 50 mm
10 Varias unidades conectadas a un colector común
10a Caída de 20 mm/m
11 Modificación del controlador de aire de renovación
12 Desmontaje del conjunto del ventilador
12a Desmontaje del panel de acceso al ventilador
12b Posición de los tornillos torx
12c Deslizar el conjunto hacia abajo
13 Condensador
14 Controlador de velocidad del ventilador
14a Terminal velocidad baja - cable rojo
14b Terminal velocidad media - cable gris
14c Terminal velocidad alta - cable negro
L Activo
15 Bloque de terminales de velocidad del ventilador
opcional
15a Conexión del cliente
15b Motor
16 Cableado de 42EM tamaños 2 y 3
16a Motor
16b Autotransformador
17 Sustitución del calentador eléctricol
17a Posición de los tornillos
18 Posiciones de entrada/salida de la batería, tamaños
0.5, 1 y 2
19 Posiciones de entrada/salida de la batería, tamaño 3
In Entrada del agua
Out Salida del agua
R Conexiones por la derecha
L Conexiones por la izquierda
Hot Agua caliente, versión de 4 tubos (dos tuercas
Cold Agua fría (dos tuercas de gas de 1/2 pulg.)
4-w V Válvula de 4 vías
2-w V Válvula de 2 vías
Air Dirección del caudal de aire
de gas de 1/2 pulg.)
NEDERLANDS
Titels van afbeeldingen en verklaringen:
1 Benodigde vrije ruimte zonder retourluchtplenum
2 Benodigde vrije ruimte met retourluchtplenum
3 Symbool Gevaar voor elektrische schokken
4 Symbool Gevaar door bewegende delen
5 Symbool Algemeen gevaar
6 Tillen van de unit voor montage in verlaagd plafond
7/8 Op afschot plaatsen van de unit
9 Condensaatafvoerleiding
9a Afschot van 20 mm/m over het horizontale
9b Sifon van 50 mm
10 Meerdere units aangesloten op 1 condensaat-
10a Afschot van 20 mm/m
11 Instellen van de verselucht regelaar
12 Demontage van de ventilator
12a Verwijder het toegangspaneel
12b Plaats van de torx schroeven
12c Schuif de ventilator omlaag
13 Condensator
14 Regelaar ventilatorsnelheid
14a Laag toerental - rode kabel
14b Middelste toerental - grijze kabel
14c Hoog toerental - zwarte kabel
L Fase
15 Klemmenstrook ventilatorsnelheid (optie)
15a Externe aansluiting
15b Motor
16 Bedrading voor 42EM typen 2 en 3
16a Motor
16b Transformator
17 Vervangen van het elektrisch verwarmingselement
17a Plaats van de schroeven
18 Plaats van de batterij intrede/uitrede, typen 0.5, 1 en 2
19 Plaats van de batterij intrede/uitrede, type 3
In Waterintrede
Out Wateruittrede
R Aansluitingen rechterzijde
L Aansluitingen linkerzijde
Hot Warm water, 4-pijps uitvoering (twee wartels
Cold Koud water (twee wartels 1/2” gas)
4-w V Vierwegklep
2-w V Tweewegklep
Air Stromingsrichting van de lucht
leidingdeel
opvangbak
1/2” gas)
6
Page 7

1 - PRECAUTIONS
1.3 - Receiving a shipment - installation methods
1.1 - Operating limits
1.1.1 - Cooling mode
Minimum supply air temperature 12°C when the unit is
installed where the ambient temperature is 27°C dry bulb
with 65% relative humidity.
1.1.2 - Heating mode
Max. supply air temperature = 60°C to avoid damage of
the discharge spigots. To avoid all risks of stratification,
Carrier recommends to keep the supply air temperature
below 35°C.
1.1.3 - Operating environment
The 42EM has been designed for indoor application in
‘urban’ conditions having a non-corrosive, dust-free and
non-marine environment.
The concentrations of the following chemicals must not be
exceeded in any event:
• SO2 < 0.02 ppm
• H2S < 0.02 ppm
• NO, NO2 < 1 ppm
• NH3 < 6 ppm
• N2O < 0.25 ppm
Do not install a unit where flammable gases or products of
an acidic or alkaline character may be present. The copper/
aluminium coil or components inside the unit could suffer
irreparable corrosion damage in their presence.
1.1.4 - Recommended coil water quality
At installation handover, and then periodically every year,
it is advised to analyse the water for bacteria (detection of
ferro-bacteria, H2S-producing and sulphate-reducing
bacteria) and chemicals (in order to avoid problems due to
corrosion and scaling).
The water circuit must include all the necessary elements for
the treatment of the water: filters, additives, intermediate
exchangers, purges, drains, isolating valves, etc., according
to the analysis results.
The results must be in accordance with the values shown
below:
• Total hardness in mmol/l: 1 < mmol/l < 1.5
• Chloride [CL-] < 10 mg/litre
• Sulphate [SO
• Nitrate [NO
2-
] < 30 mg/litre
4
-
] = 0 mg/litre
3
• Dissolved iron: < 0.5 mg/litre
• Dissolved oxygen: 4 < [O2] < 9 mg/litre
• Carbon dioxide [CO2] < 30 mg/litre
• Resistivity: 20 Ohm·m < Resistivity
< 50 Ohm·m
• pH: 6.9 < pH < 8
1.2 - Clearances required
Without return air plenum: Fig. 1
With return air plenum: Fig. 2
When receiving a shipment, check the condition of the goods
and report any damage in transit to the shipping company.
Do not unpack the units until just before they are due to
be installed, and make sure they are as close as possible to
the installation site when unpacking them. Do not place
heavy articles of any sort on them.
1.4 - Supply voltage 230 V ± 10% - 50 Hz
Check that the supply voltage and frequency correspond
to the values of the unit to be installed.
WARNING: Failure to take proper account of the above
advice and unauthorised modification of the electrical
connections will render the Carrier warranty on the product
null and void.
2 - SAFETY CONSIDERATIONS
WARNING: Switch off the main electrical power supply
to the unit and accessories (if installed) before doing any
work on the unit.
2.1 - General
Installing, commissioning and servicing of the various components (unit, control system, hot and cold water system,
air distribution system) can be dangerous unless certain
aspects of the installation, such as the presence of mains
electricity and hot or cold water in the air conditioning
equipment, are taken into account. Only specially trained
and qualified technicians and installers who have been
fully trained on the product concerned are authorised to
install, commission and service this equipment.
During servicing work, it is essential to apply all recommendations and instructions given in service leaflets, on labels
or in the instructions delivered with the equipment, and to
comply with any other relevant instructions.
Definition of the pictograms used:
• Electrical danger - Fig. 3
• Caution hand hazard - Fig. 4
• General danger - Fig. 5
Comply with all safety rules and regulations currently in
force. Wear eye protectors and work gloves. Take care when
moving or positioning equipment.
2.2 - Protection against electrocution
Only electricians qualified to the level recommended by the
IEC (International Electrotechnical Commission) in its
standard IEC 364, corresponding to Europe HD 384, France
NFC 15 100 and UK IEE Wiring Regulations, may have
access to electrical components. In particular it is obligatory
to disconnect all power supplies to the unit and its accessories
before carrying out any work. Disconnect the main power
supply with an isolating device (not supplied by Carrier).
7
Page 8

IMPORTANT: The components, which make up the
different control loops described in this manual include
electronic items. As such, they may generate or be harmed
by electromagnetic interference unless they are installed
and used in accordance with these instructions. The
components making up these control systems conform to
the requirements of electromagnetic compatibility in
residential, commercial and light industrial areas. They
also comply with the low-voltage directive.
2.3 - General installation conditions
IMPORTANT: The Carrier numeric controller, power
module, or in general units fitted with controls loops must
have an isolating device upstream (for example a doublepole circuit breaker). If necessary, an easily operated
emergency stop device (such as a punch-button switch) must
cut off the power to all equipment. These safety devices
shall be sized and installed in accordance with IEC
Recommendation 364, corresponding to Europe HD 384,
France NFC 15 100 and UK IEE Wiring Regulations.
These devices are not supplied by Carrier.
In general terms the following rules must be applied:
Upstream over-voltage protection
Unit without electric heater T2A
Standard unit sizes 0.5/1.0/2.1/3.1 with electric heater T10A
Standard unit sizes 2.2/2.3/3.2/3.3 with electric heater T16A
• Units must be provided with over-voltage protection
upstream (not supplied by Carrier).
• The power disconnection device must be clearly labelled
to identify which items of equipment are connected to it.
• The wiring of the components which make up the
different control systems and the communication buses
must be carried out in accordance with the latest rules
and regulations by professional installers.
• The power supply cable must be doubly insulated and
fixed using a cable clamp. A hole is provided for this
purpose in the plastic Carrier controller housing. The
cable must be clamped on the outer insulation.
• The control loop components must be installed in an
environment, which conforms to their index of protection (IP).
• The maximum level of pollution is normally pollutant
(level 2) and installation category II.
• The low-voltage wiring (communication bus) must be
kept physically separate from the power wiring.
• In order to avoid interference with the communication
links:
- Keep low-voltage wiring away from power cables
and avoid using the same cable run (a maximum of
300 mm in common with the 230 V a.c., 30 A cable).
- Do not pass low-voltage wires through loops in
the power cables.
- Do not connect heavy inductive loads to the same
electrical supply (circuit breaker) used by the
controllers, power modules or speed controllers.
- Use the screened cable type recommended by
Carrier and make sure all cables are connected to
the controllers and power modules.
2.4 - Caution for the control of the Atmosphera
IMPORTANT: It is not permitted to connect several
Atmosphera units to the same control device (wall thermostat, electronic NTC controller, HDB controller, etc.)
2.5 - Conformity
This equipment has been declared to be in conformity with
the main requirements of the following directives:
• Electromagnetic compatibility: 2004/108/EEC,
• Low-voltage directive: 2006/95/EEC.
3 - INSTAllATION OF THE UNIT
3.1 - Installing the unit in the false ceiling
The positioning of the unit must not create an obstacle that
may lead to an unequal distribution and/or return flow of the
air. The ceiling must be sufficiently even to allow a simple
installation without danger from the unit. The supporting
structure must be able to carry the unit weight and prevent
deformation, breaks or vibrations during operation.
INSTALLATION PRECAUTIONS: During the installation
process, remove all debris and construction material from
the ducts to prevent any damage to the unit.
3.2 - Installation procedure
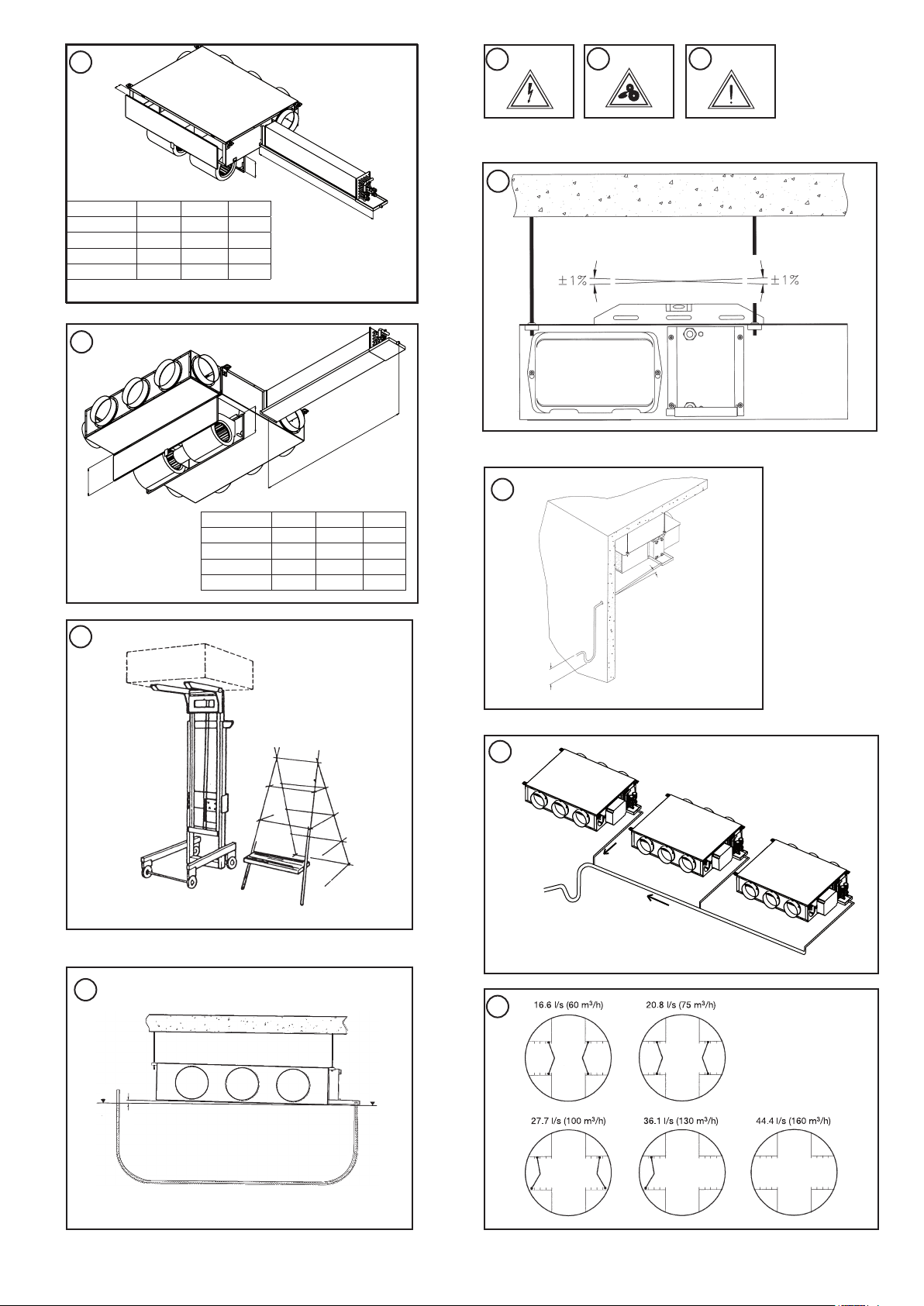
• Position the 42EM close to where it is to be installed
in the ceiling void. For installation in a false ceiling use
a hydraulic lift and a folding ladder to make the task
easier (Fig. 6).
• Check that the clearances around the unit are sufficient
to allow easy maintenance. Please refer to the diagram
that shows the service clearances.
• Mark the position of the threaded hangers on the
ceiling (if several units need to be installed, it may be
advisable to produce a drilling template). The method
of fixing the threaded hangers (not supplied by Carrier)
depends on the ceiling type (maximum diameter of
the threaded hangers is 10 mm). Once the threaded
hangers are fixed to the ceiling, tighten the first nuts.
WARNING: When moving the units, do not use water
pipes, condensate drain pan, valves or flexible pipes to lift
them.
Lift the unit and align it on the threaded hangers, insert
the second nuts and tighten them slightly.
NOTE: At this point do not tighten the nuts fully and do
not clamp the unit up to the ceiling (leave a space between
the ceiling and the unit). The nuts will be adjusted finally,
when the unit has been connected to the pipework and
ducts and levelled.
8
Page 9

Level the unit (Fig. 7).
Adjust the hanger nuts so that the unit is inclined 0.5%
towards the condensate drain pan. In the other direction
(air flow direction) the unit must be perfectly level (Fig. 8).
Condensate drain pipe (Fig. 9): Use a flexible pipe with an
inside diameter of 16 mm and provide a constant fall of 20
mm/m (9a) over the whole horizontal pipe run. Install a 50
mm (minimum) siphon (9b) to prevent gases and odours
from flowing back into the ceiling void.
If several units are connected to a common collector, a device
must be installed (Fig. 10). Before operating the unit, ensure
that the water flows into the internal condensate drain pan by
pouring some water into it. If problems are detected, check
the drain pipe slope and look for possible obstructions. In
all cases the connection duct(s) at the unit outlet must be
insulated to prevent any condensate formation on the walls.
NOTE: The pressure losses of these ducts must be compatible with the unit performance. The duct must be as smooth
as possible. Avoid sharp bends. Check that there are no
leaks or kinks, and that there is no dirt or installation
debris inside the ducts. Debris within the ducts might
damage the fan wheel and the damper in the air diffusers.
When installation is complete - i.e. when the 42EM is
attached to the ceiling, air ducts are complete, water manifolds are in position with stop valves ready on the connection stubs, and electrical installation is prepared - then
connect the water pipes (Carrier recommends the use of
flexible water pipes that can be supplied as an accessory).
Each flexible pipe has a 1/2" gas screw connector, depending on the model. Ensure that a gasket (not supplied by
Carrier) is installed between the screw connector and the
stop valve.
When all units are installed, open the stop valves on the
manifolds, bleed and then pressurize the circuits. To bleed
the coils, slightly loosen the bleed screws. The installation
can then be started.
NOTE: Do not switch on the power until all connections
are made and earthed.
3.3 - Removal procedure
Switch off the unit power supply at the isolator provided
for the purpose during installation (isolator not supplied
by Carrier).
• Disconnect the power supply and connection cables.
• Close the isolating valves on the manifolds.
• Disconnect the flexible water pipes by unscrewing the
gas connectors.
WARNING: Since the flexible water pipes do not have
drain valves, a receiver must be provided to allow the
cooling coil to be drained.
• Disconnect the supply air ducts.
• Disconnect the flexible condensate drain pipe. Drain
the siphon into a suitable vessel.
• Support the unit lightly and release it by unscrewing
the four nuts on the threaded hangers. Lower the unit
carefully.
4 - COMPONENTS
4.1 - Fan motor assembly
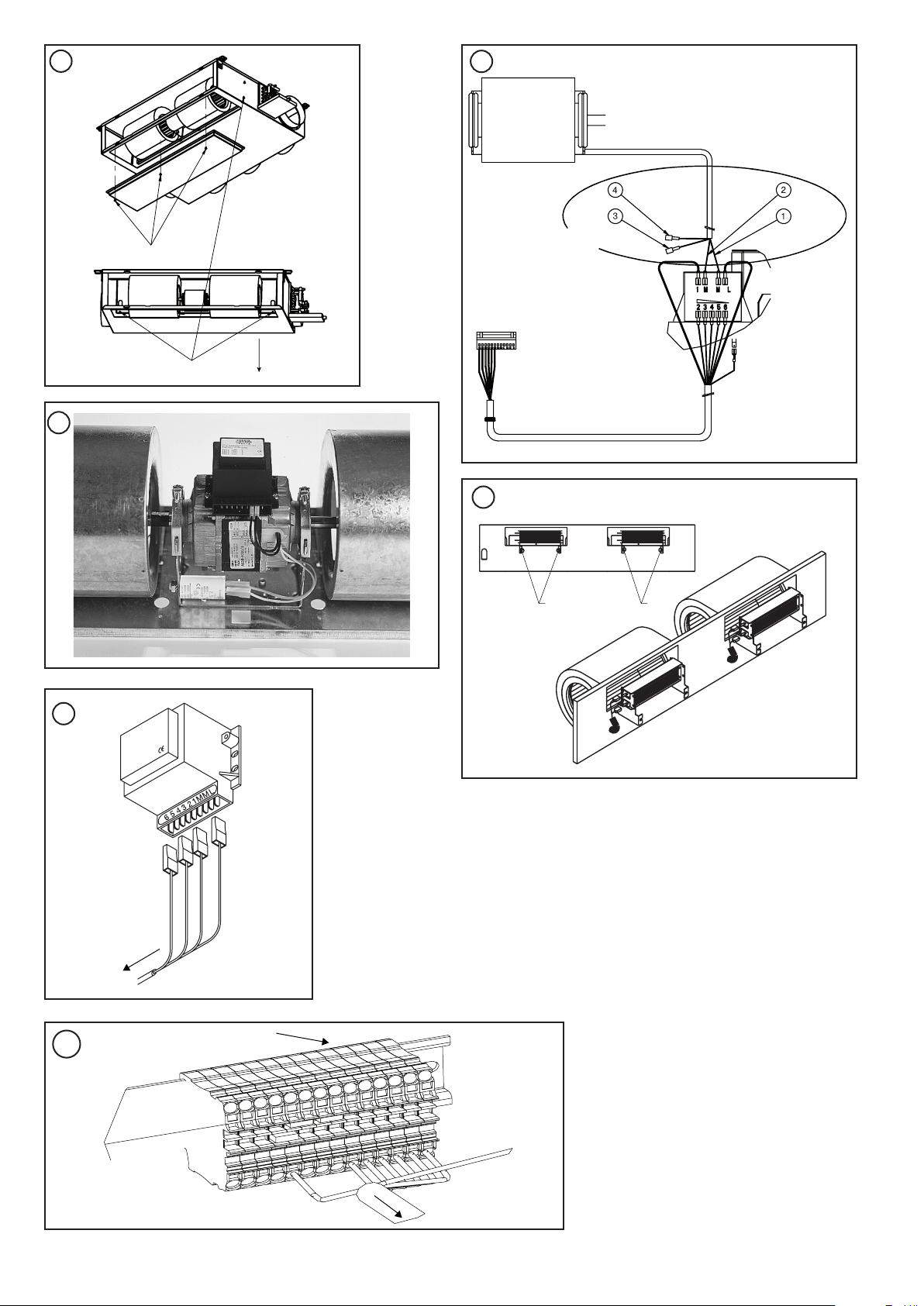
4.1.1 - Fan assembly removal procedure
WARNING: Disconnect the power supply to the Atmosphera
before carrying out any work on the unit.
Identify and note the wired fan speeds. If the fan develops
a fault the whole assembly must be removed and replaced
(Fig. 12).
• Remove the filter.
• Remove the fan access panel (12a).
• Disconnect the fan assembly power supply cables
(power and control wiring for variable-speed motor).
• If necessary remove the controller (fixed with screws)
to gain access to the maintenance screws of the panel
supporting the fan.
• The fan assembly and its panel are held in place by
four torx screws (T20) (12b). Remove these screws,
then push in the two tabs on each side below the panel
that supports the assembly and slide it down (12c).
• Remove the fan motor assembly.
NOTE: Be careful not to touch the fan blades during
the removal process to avoid unbalancing the fans.
• For units with the electric heater option, disconnect
the power supply cable to the heater. Withdraw the
cable through the cable gland.
• Unscrew the electric heaters.
• Replacement of the fan motor assembly is by the
reversal of the above procedure.
WARNING: The electrical connections to the fan motor
must be made in accordance with the labels on the connector block.
For the variable-speed motor carefully separate the power
wiring cable from the control wiring cable and pull them
apart as far as possible.
4.1.2 - Capacitor replacement procedure (Fig. 13)
• Disconnect the power supply to the Atmosphera before
carrying any work on the unit.
• Remove the filter.
• Remove the fan motor assembly access panel.
• Remove the capacitor that is attached to the motor
chassis assembly.
• Disconnect the capacitor by withdrawing the flat spade
connectors from the back of the capacitor.
• Replacement of the capacitor assembly is by the reversal
of the above procedure.
4.1.3 - Fan wiring
42EM 0.5/1.0 wiring (multi-speerd version)
The fan motor has 6 speeds, provided by an auto-transformer,
offering the installer greater flow control flexibility. Three
speeds must be selected to allow connection of the fan
motor in accordance with the applicable electromechanical
or electronic regulations (minimum speed: terminal 6,
maximum speed: terminal 1).
9
Page 10

• 42EM units equipped with factory-installed Carrier
controller: Fig. 14.
• Units without electronic control: access to six selectable
fan speeds from outside at the optional terminal block:
Fig. 15 (15a = customer connection, 15b = motor).
ATTENTION: Carefully observe the direction indicated
by the arrow on the valves, based on the connection side
and the valve type.
4.3 - Duct connection spigots
Wiring for 42EM 2.1/2.2/2.3 and 42EM 3.1/3.2/3.3: Fig. 16
42EM size 2.1 42EM size 2.2 42EM size 2.3
42EM size 3.1 42EM size 3.2 42EM size 3.3
Neutral (com)
Phase connected
Not connected
Not connected
Wiring legend:
Minimum speed = Terminal 6 Medium speed = Grey wire (14b)
Maximum speed = Terminal 1 High speed = Black wire (14c)
Low speed = Red wire (14a) L = Live
White White White
1
Red Blue Black
2
Blue Red Red
3
Black Black Blue
4
4.2 - Water coil
4.2.1 - Coil removal procedure
WARNING: Disconnect the power supply to the Atmosphera
before carrying out any work on the unit.
• Close the isolating valves on the manifolds.
• Unscrew the union nuts to disconnect the flexible
water pipes.
• Remove the valve actuators taking care to identify the
cooling and heating valves.
• Disconnect the flexible condensate drain pipe which is
held in place by a collar (the collar is not supplied by
Carrier).
• Remove the two-way or four-way water flow control
valve bodies. Depending how the Atmosphera is configured, the four-way valve coupling may be fitted with
a heating/cooling changeover switch, if so do not
remove it.
• Remove the 4 torx screws (T20) and slide out the coil
and drain pan assembly.
• Replacement is by the reversal of the procedure described above. Ensure that all gaskets are changed (new
gaskets fitted) and that the inlet and outlet connections
to the coil are made correctly using an appropriate
sealing compound applied to the valve body.
• Bleed all air from the coil during refilling.
ATTENTION: It is advisable to tighten the valve body to
the coils with caution (15 N·m is sufficient) to ensure they
are not damaged.
These are manufactured from high density plastic with a
VO fire rating, more or less equivalent to class M1 (French
standard). They are encased inside the unit. The ducts
should be fixed to these spigots using circular collars or
adhesive. Screws and rivets should not be used.
WARNING: In order to guarantee good air tightness, the
duct should overlap the whole of the spigot.
Make sure that the maximum supply air temperature does
not exceed 60°C.
Do not lift or support the unit using the spigots, place loads
on the spigots or damage the spigots during installation or
operation.
4.4 - Optional filter and filter access
4.4.1 - Description
The Carrier Atmosphera is fitted with a 85% gravimetric
filter (G3), according to standard EN 779. Medium fire
rating M1, metal wire frame.
Different filter access options are available to suit different
site requirements:
• Unit with non-ducted return air: Access is from the
rear of the unit.
• Unit with ducted return air: Access is from below.
4.4.2 - Air filter replacement
Air filters should be changed regularly. Filter life depends on
the rate at which the filter becomes clogged, which depends
upon the cleanliness of the working environment.
If clogged filters are not changed they can increase the air
pressure drop, trapped dust particles may be given off and
entrained in the air supply, and the general performance of
the Atmosphera may be degraded (as the air flow reduces).
NOTE: When installing an Atmosphera in a ceiling void,
check that no T-bars will obstruct filter access and removal.
4.5 - Fresh air controller
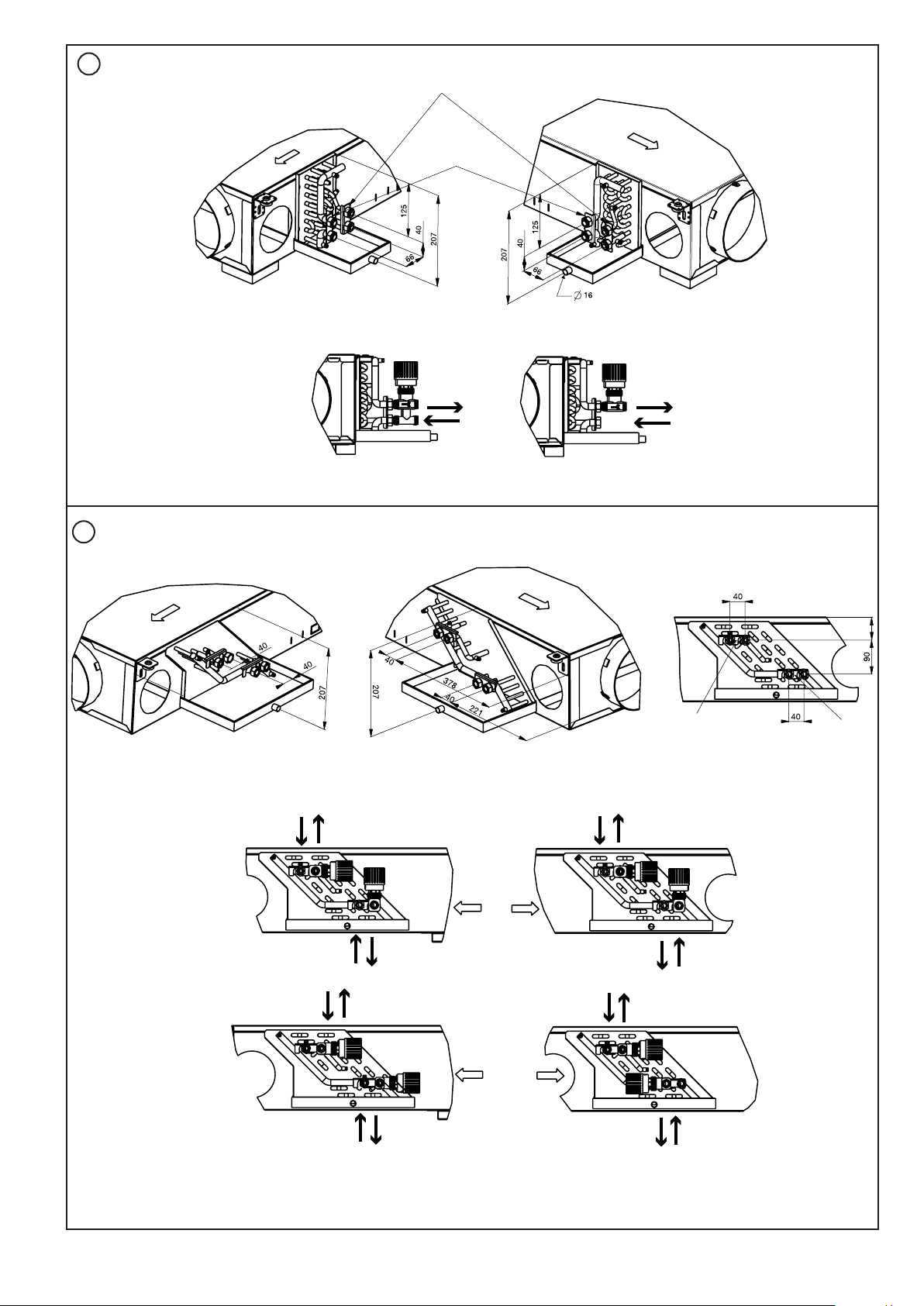
NOTE: It is possible to change the coil connection on site
by changing the condensate pan and coil assembly in the
guides.
For Size 3 the water inlet and outlet need to be reversed
to achieve the published performance.
4.2.2 - Coil inlet/outlet positions
Water inlets/outlets, sizes 0.5, 1 and 2: Fig. 18.
Water inlets/outlets, size 3: Fig. 19.
10
4.5.1 - Fresh air controller with constant air volume
The 42EM Atmosphera can be fitted with a constant fresh
air flow controller allowing the introduction of fresh air and
the air change rate to be controlled.
The following range of fresh air controllers is available:
Option a: 8.3 l/s (30 m3/h) (-10%; +20%)
Option b: 16.6 l/s (60 m3/h) (-10%; +20%)
Page 11

Options a and b: the diameter of the spigot housing the
fresh air flow controller is 125 mm.
The 16.6 1/s (60 m3/h) fresh air controller may be modified
on site by relocating or removing two plastic restrictors in
order to increase the maximum constant fresh air flow
capacity to 44.4 1/s (160 m3/h). A label on the 42EM shows
how to adjust the two plastic restrictors (Fig. 11).
Modification procedure
• Disconnect the fresh air duct from the spigot on the
Atmosphera.
• Remove or reposition the two plastic restrictors,
following the fresh air flow controller.
• Reconnect the fresh air duct to the spigot.
IMPORTANT: If the Atmosphera is fitted with a return
air temperature sensor, the constant fresh air flow rate
must not exceed 50% of the supply air flow delivered by
the unit at minimum speed.
NOTE: To operate correctly, the 8.3 l/s (30 m3/h) constant
fresh air flow controller requires a differential pressure in
the range 50 Pa to 200 Pa. The 16.6 l/s (60 m3/h) constant
fresh air controller requires a differential pressure in the
range 70 to 200 Pa.
4.5.2 - Fresh air controller with variable air volume
The 42EM Atmosphera can be equipped with an optional
variable fresh air flow controller from 0 to 55 l/s (0 to 200
m3/h).
This is connected to the numeric Carrier controller and
can regulate the fresh air intake in two ways:
• either using a fixed rate set by the installer that can be
reconfigured as required
• or based on the CO2 level; in this case it is connected
to a CO2 sensor via the Carrier numeric controller
(the CO2 sensor is located opposite the fresh air inlet).
NOTE: With the variable fresh air flow controller the
upstream pressure in the fresh air duct must be 180 Pa.
4.6 - Optional water flow control valves
These valves are two-way or four-way type, with a body
designed to withstand a 16 bar operating pressure.
4.6.1 - Electrothermal actuator (on/off)
The actuator is a 230 V a.c. on/off type.
To enable the installation to be filled with water, the
water circuits to be equalised and the units to be purged,
the actuators must be connected to the power supply to
open the valves via a command from the wall thermostats
or from the BMS.
4.6.2 - Actuator replacement procedure
The actuators on both the chilled water and the hot water
valves may be replaced if either develops a fault.
• Disconnect the power supply to the unit before carrying
out any work on a unit.
• Disconnect the actuator power supply cable.
- 230 V on/off type actuator used with the Carrier
numeric controller: Disconnect the actuator
power supply cable fitted with a quick connector.
- 230 V on/off actuator used with an electronic
thermostat: Remove the plastic protection cover
held in place with two screws. Disconnect the
actuator power supply cable connected to the
quick connector. This can be done by pressing
down the spring tongue using a screwdriver and
pulling out the wire from the appropriate terminal.
• Uncouple the faulty actuator. Refitting is by the reversal
of the procedure described above.
WARNING: Ensure that the actuator is firmly screwed to
the valve body (maximum torque 15 N·m).
4.6.3 - Valve body replacement procedure
• Disconnect the power supply before carrying out any
work on a unit.
• Close the isolating valves on the manifolds.
• Unscrew the union nuts to disconnect the flexible water
pipes.
• Remove the valve actuators taking care to identify the
cooling and heating valves.
• Disconnect the flexible condensate drain pipe which is
held in place by a collar (the collar is not supplied by
Carrier).
• Remove the two-way or four-way water flow control
valve bodies. Depending how the Atmosphera is configured, the four-way valve coupling may be fitted with
a heating/cooling changeover switch, if so do not
remove it.
• Remove the 4 torx screws (T20) and slide out the coil
and drain pan assembly.
• Fit the new valve body to the coil (fit new gaskets).
• Refit the coil and condensate assembly.
• Reconnect the flexible condensate drain pipe which is
held in place by a collar (the collar is not supplied by
Carrier).
• Refit the valve actuators taking care to ensure that
they are correctly fixed to the valve body.
• Reconnect the flexible water pipes by tightening the
union nuts. Retighten all the water connections and
ensure that all gaskets have been changed and correctly
fitted (maximum torque 15 N·m).
• Open the isolating valves on the manifolds and purge
all air from the system.
• Check that there are no leaks and reconnect the power
to the Atmosphera.
WARNING: When replacing a valve always ensure that
the direction of flow through the valve is as shown by the
arrow on the valve body. If the direction of flow is wrong,
the valve body will deteriorate rapidly.
11
Page 12
W
4.7 - Flexible pipe option
Minimum bending radius:
• non-insulated pipes 72 mm
• insulated pipes 106 mm.
4.8 - Optional electric heater
Electric heater replacement procedure:
• Remove the filter.
• Remove the fan motor assembly access panel.
• Identify and note the fan speeds wired to the autotransformer terminal block. Disconnect the power
supply cable.
• Remove the fan motor assembly.
WARNING: Disconnect the power supply before carrying
out any work on the unit.
If the electric heater develops a fault, it must be replaced;
this requires the removal of the fan motor assembly: Fig. 17
(17a = screw).
CAUTION: Do not touch the live metal heater elements
when the electric heater is connected to the power supply.
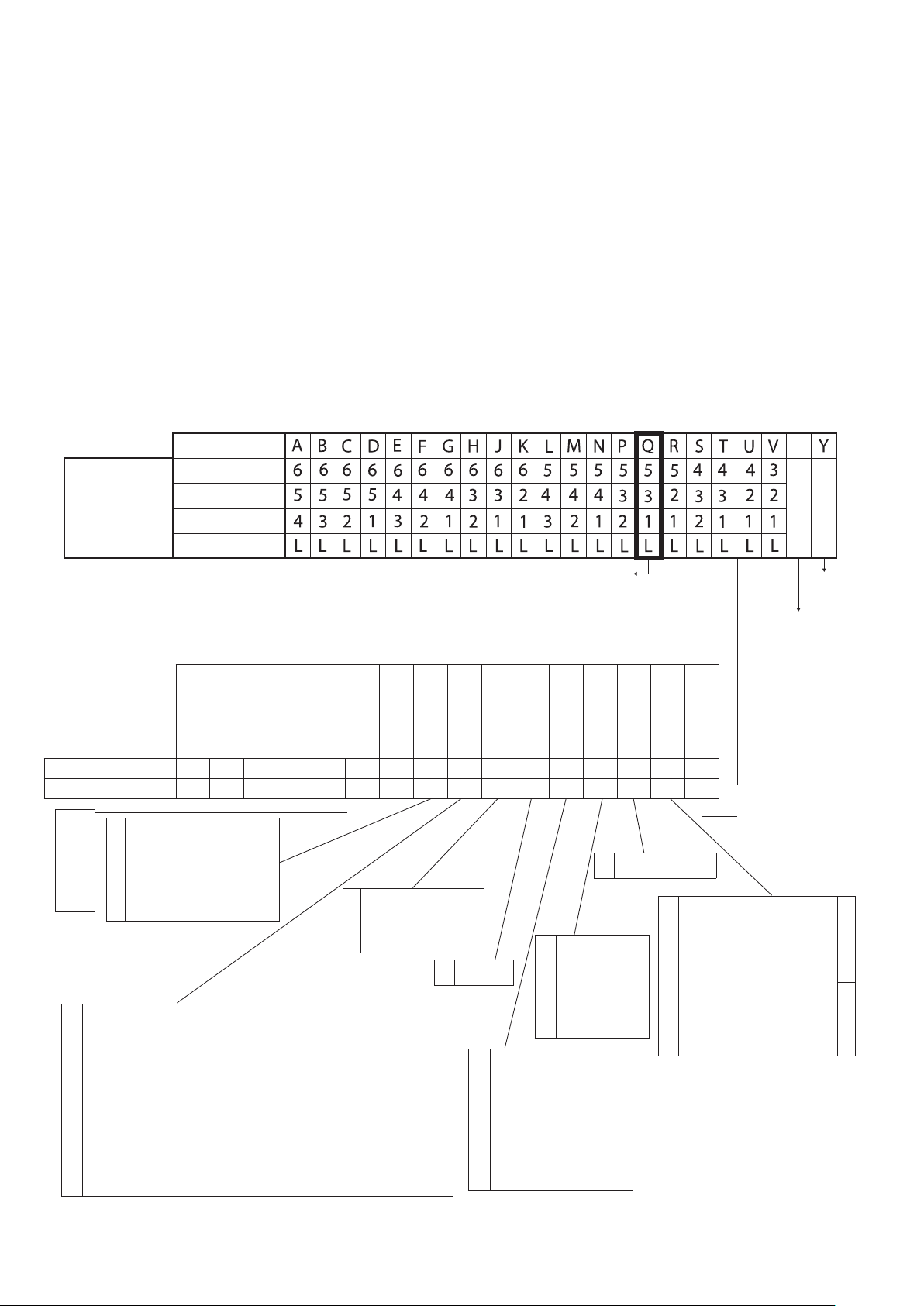
5 - CODIFICATION
Fan motor speed wiring
Codification (last digit)
or option 600
Red wire
Grey wire
Fan set
Black wire
Wire marked L
Terminal marking (standard wiring), option 600 not selected
NOTE: Terminal 1 = highest speed, Terminal 6 = lowest speed.
NOTE: Be careful not to touch the fan blades during
the removal process to avoid unbalancing the fans.
• Disconnect the electric heater power supply cables
and remove them through the cable conduit.
• Unscrew the defective heater(s) and replace it (them).
• Replacement of the fan motor assembly is by the
reversal of the above procedure.
Six wired
speeds
Variable-speed
LEC motor
Product type Size
Modification
Product reference
Digit
0 5
1 0
2 1
2 2
2 3
3 1
3 2
3 3
A 2 pipes right
B 2 pipes left
C 4 pipes right
D 4 pipes left
E 2 pipes/2 wires, right, low pressure
F 2 pipes/2 wires left, low pressure
G 2 pipes/2 wires, right, high pressure
H 2 pipes/2 wires left, high pressure
B Modular unit with 2 supply air spigots
C Modular unit with 3 supply air spigots
G Modular unit with 1 supply air spigot at the end (in-line configuration)
H Modular unit with 1 supply air spigot at the side (opposite coil)
J Modular unit with 4 supply air spigots
K Modular unit with 5 supply air spigots
M Return air plenum 1 spigot and modular unit 1 supply air spigot (in-line configuration)
N Return air plenum 1 spigot and modular unit 1 supply air spigot (U-shape configuration)
P Return air plenum 2 spigots and modular unit 2 supply air spigots
Q Return air plenum 3 spigots and modular unit 3 supply air spigots
R Return air plenum 4 spigots and modular unit 4 supply air spigots
S Return air plenum 5 spigots and modular unit 5 supply air spigots
T Compact unit with 1 return air spigot and 1 supply air spigot
U Compact unit with 2 return air spigots and 2 supply air spigots
V Compact unit with 3 return air spigots and 3 supply air spigots
4 2 E M N N C A A A A A A A A A
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16
{
- None
C 2-way valve
D 4-way valve
J 2-way valve + flexible piping
K 4-way valve + flexible piping
code
Coils
Supply and
return air plenum
Valves
Valve motors
0 None
A 230 V on/off
- None
A NTC
B HDB
D NTC + IAQ board
E Terminal block with plastic cover
F E + relay
G E + relay + fuse holder
K NTC + fuse holder
L NTC + IAQ board + fuse holder
M HDB + fuse holder
R E + fuse holder
Control
Sensors
A G3 rear access
B G3 access from below
- None
A Return air sensor
B Supply air sensor
C Change-over sensor
D A + B
E A + B + C
F A + C
G B + C
Filter and access
Fresh air
Motor wiring
- None
A 125 mm ø fresh air spigot only
B 8.3 l/s (30 m3/h)
C 16.6-44.4 l/s (21/28/36) 60-160 m3/h
(75/100/130)
E Motorised fresh air valve adapter ø
125 mm
J 125 mm ø fresh air spigot only
K 8.3 l/s (30 m3/h)
L 16.6-44.4 l/s (21/28/36) 60-160 m3/h
(75/100/130)
N Motorised fresh air valve adapter ø
125 mm
RIGHT
LEFT
12
Page 13

1 - PRECAUTIONS
1.3 - Réception - Lieu d’implantation
1.1 - Limites d’utilisation
1.1.1 - Mode froid
Température mini de soufflage 12°C lorsque l’appareil est
installé dans une ambiance de 27°C BS (bulbe sec) et 65%
HR (humidité relative).
1.1.2 - Mode chaud
La température de soufflage ne doit pas excéder 60°C sous
peine de détérioration des supply air spigots. Carrier
recommande de ne pas dépasser la température de 35°C
au soufflage pour éviter tout risque de stratification, cause
d’inconfort.
1.1.3 - Environnement d’utilisation
L’Atmosphera 42EM a été conçu pour fonctionner dans une
atmosphère intérieure “urbaine” non corrosive, non empoussiérée, dans un environnement non marin. Les teneurs
en composants chimiques ci-dessous ne doivent en aucun cas
être dépassées :
• SO2 < 0.02 ppm
• H2S < 0.02 ppm
• NO, NO2 < 1 ppm
• NH3 < 6 ppm
• N2O < 0.25 ppm
Ne pas installer l’unité dans des atmosphères comportant
des gaz inflammables, ou des produits acides ou alcalins. La
batterie en cuivre/aluminium et les composants internes
pourraient subir une corrosion irrémédiable.
1.1.4 - Qualité de l’eau recommandée pour les batteries à eau
A la réception de l’installation, puis périodiquement tous les
ans, il est conseillé de réaliser une analyse bactériologique
(détection des ferro-bactéries, des bactéries productrices
de H2S et réductrices des sulfates) et chimique de l’eau
(afin d’éviter les problèmes d’entartrage et de corrosion).
Le circuit d’eau doit inclure les éléments nécessaires au
traitement de l’eau : filtres, additifs, échangeurs intermédiaires, purges, évents, vanne d’isolement etc... en fonction
des résultats de l’analyse.
Dès réception, vérifier l’état du matériel, déceler tout dommage éventuel dû au transport et adresser toute plainte à ce
sujet par écrit au transporteur. Ne déballer qu’au moment de
l’installation finale, le plus près possible du lieu d’implantation, et ne pas placer d’outils lourds sur l’emballage dans la
période d’attente.
1.4 - Tension d’alimentation 230 V ± 10% - 50 Hz
Vérifier que la tension et la fréquence de l’alimentation
correspondent à celles nécessaires à l’unité à installer.
ATTENTION: Carrier suspend l’effet de la garantie si ces
points ne sont pas respectés, ou si des modifications
électriques ont été apportées aux raccordements d’origine.
2 - CONSIDERATIONS DE SECURITE
NOTE: Avant toute intervention sur l’unité, couper l’alimentation électrique générale de l’unité et des accessoires
éventuels.
2.1 - Généralités
L’installation, la mise en service et les opérations d’entretien
des différents composants du système (unité, système de
régulation, réseaux d’eau chaude, eau froide, aéraulique)
peuvent être dangereuses si l’on ne tient pas compte de
certains facteurs propres à l’installation tels que la présence de
la tension secteur et la présence d’eau chaude ou d’eau froide
dans le matériel de traitement d’air. Seuls des installateurs
et des techniciens spécialement formés et qualifiés, ayant
reçu une formation approfondie sur le produit concerné,
sont autorisés à installer, à mettre en service et à entretenir
ce matériel.
Lors de toute intervention, il convient d’appliquer toutes
les recommandations et instructions qui figurent dans les
notices d’entretien, sur les étiquettes ou dans les instructions
accompagnant l’ensemble du matériel, ainsi que toutes les
autres consignes de sécurité applicables.
Les résultats d’analyse doivent correspondre aux valeurs
mentionnées ci-dessous :
• Dureté totale en mmol/l 1 < mmol/l < 1.5
• Chlorure CL-] < 10 mg/l
• Sulfate [SO
• Nitrate [NO
2-
] < 30 mg/l
4
-
] = 0 mg/l
3
• Fer dissous < 0,5 mg/l
• Oxygène dissous 4 < [O
] < 9 mg/l
2
• Gaz carbonique [CO2] < 30 mg/l
• Résistivité 20 Ohm·m < Résistivité
< 50 Ohm·m
• pH 6.9 < pH < 8
1.2 - Réservation pour maintenance
Sans plenum de reprise: Fig. 1
Avec plenum de reprise: Fig. 2
Définition des pictogrammes utilisés:
• Danger électrique: Fig. 3.
• Attention à vos mains: Fig. 4.
• Danger général: Fig. 5.
Respecter tous les réglements et codes de sécurité en vigueur.
Porter des lunettes de sécurité et des gants de travail.
Manipuler avec précaution les matériels lors des opérations
de manutention et de pose.
2.2 - Protection contre les électrocutions
Seul le personnel qualifié au sens des recommandations de
la norme CEI 364 (Commission Electrique Internationale)
équivalent à Europe HD 384, France NFC 15 100 ou UK
IEE Wiring Regulation, doit avoir accès aux composants
électriques. Il est en particulier obligatoire de couper
l’ensemble des alimentations électriques de l’unité avant
toute intervention. Couper l’alimentation principale à l’aide
du dispositif de sectionnement (hors fourniture Carrier).
13
Page 14

IMPORTANT: Les composants constituant les différents
systèmes de régulation proposés, comportent de l’électronique. A ce titre, ils peuvent générer des perturbations
électromagnétiques ou être perturbés s’ils ne sont pas
installés et utilisés conformément aux présentes instructions.
Les composants constituant ces boucles de régulation sont
conformes aux exigences de compatibilité électromagnétique
pour les environnements résidentiels, commerciaux et de
l’industrie légère. Ils sont également conformes à la
directive basse tension.
2.3 - Préconisation générale d’installation
IMPORTANT: Les régulateurs doivent posséder en amont
un dispositif de sectionnement (disjoncteur bipolaire par
exemple). En cas de nécessité, un dispositif d’arrêt d’urgence
(interrupteur de type coup de poing par exemple) accessible
doit permettre la mise hors tension de tous les appareils.
Ils devront être dimensionnés et installés selon la recommandation CEI 364 équivalente à Europe HD 384, France
NFC 15 100 ou UK IEE Wiring Regulation. Ces dispositifs
sont hors fourniture Carrier.
D’une manière générale les règles suivantes doivent être
observées:
Protection amont contre les surintensités
Appareil sans batterie électrique T2A
Appareil standard tailles 0.5 / 1.0 / 2.1 / 3.1 avec batterie électrique T10A
Appareil standard tailles 2.2 / 2.3 / 3.2 / 3.3 avec batterie électrique T16A
2.4 - Préconisation concernant la régulation de
l’Atmosphera
IMPORTANT: Il est interdit de raccorder plusieurs
Atmosphera sur un même organe de régulation (thermostat mural, régulation électronique NTC, HDB, etc...)
2.5 - Conformité
Ce matériel a été déclaré conforme aux exigences
essentielles des directive suivantes :
• Compatibilité électromagnétique : 2004/108/CEE.
• Directive basse tension : 2006/95/CEE.
3 - INSTAllATION DE l’UNITE
3.1 - Coordination entre unité et faux plafond
L’emplacement ne doit présenter aucun obstacle susceptible
de provoquer une répartition et/ou une reprise d’air inégale.
Le plafond doit être suffisamment plat pour permettre une
installation simple et sans danger de l’unité.
La structure portante doit pouvoir supporter le poids de
l’unité et empêcher les déformations, les ruptures ou les
vibrations pendant le fonctionnement.
PRECAUTIONS D’INSTALLATION: Lors de l’installation de l’unité, s’assurer qu’aucun débris de construction
resté dans les gaines ne puisse venir endommager l’unité.
• Les appareils devront comporter une protection amont
contre les courants de fuite à la terre (différentiel hors
fourniture Carrier).
• Un repérage clair doit être effectué sur le dispositif de
sectionnement afin de repérer les appareils qui lui sont
connectés.
• Le câblage des composants constituant les différents
systèmes de régulation ainsi que des bus de communication doit être effectué conformément aux règles de
l’art par des installateurs professionnels.
• Le câble d’alimentation doit être muni d’une double
isolation et maintenu par le cavalier anti-traction prévu
à cet effet, ou l’attache-câble livré avec le régulateur
numérique Carrier. Le câble d’alimentation doit être
maintenu sur le double isolant.
• Les composants constituant ces différentes boucles de
régulation doivent être installés dans un environnement
en conformité avec leur indice de protection (IP).
• Le niveau de pollution maximum est normalement
polluant (niveau 2) et la catégorie d’installation II.
• Le câblage basse tension (Bus de Communication)
doit être physiquement séparé du câblage de puissance.
• Afin d’éviter les interférences avec les câbles de liaison
- Séparer les câbles basse tension des câbles de
puissance, éviter d’utiliser le même chemin de
câble (300 mm commun maximum avec le câble
230 V a.c., 30 A).
- Ne pas passer des câbles basse tension dans des
boucles de câbles de puissance.
- Ne pas raccorder de charges inductives impor-
tantes sur la même source électrique (disjoncteur)
servant à l’alimentation des équipements des
régulateurs ou des modules de puissance.
- Utiliser le type de câble blindé préconisé par
Carrier et maintenir les câbles reliés aux régulateurs et aux modules de puissance.
3.2 - Procédure d’installation
• Positionner l’Atmosphera au sol, à l’endroit où il doit
être installé dans le faux plafond. Pour une installation
en faux plafond, un élévateur et une échelle pliante
conviennent à une installation aisée des unités: Fig. 6.
• Vérifier que les dégagements autour de l’appareil sont
suffisants pour permettre une maintenance aisée. Se
reporter aux plans “réservations pour maintenance”.
• Marquer la position des tiges filetées au plafond (il
peut être judicieux de confectionner un gabarit de
perçage dans le cas ou l’on a plusieurs unités à installer). Le mode de fixation des tiges filetées, hors fourniture Carrier, dépend de la nature du plafond, (diamètre maximum de la tige filetée 10 mm). Une fois les
tiges filetées encrées au plafond, visser les premiers
écrous.
ATTENTION: Ne jamais lever l’unité en utilisant les
tubulures apparentes, les vannes/flexibles, les faisceaux
électriques, ou le bac à condensats.
Lever l’unité et l’engager dans les tiges filetées, placer les
écrous et les serrer convenablement.
NOTE : Ne pas serrer à fond les écrous à ce stade et ne
pas brider l’appareil à la dalle (laisser un espace entre la
dalle et l’appareil). Le réglage des écrous sera effectué
après le raccordement des tuyauteries ou flexibles et la
mise à niveau de l’unité.
14
Page 15

Mise à niveau: Fig. 7.
Régler à présent la position de l’appareil, de manière à
incliner l’unité de 0.5% vers l’évacuation des condensats.
Dans l’autre direction (sens de l’air) l’appareil devra être
parfaitement de niveau: Fig. 8.
4 - COMPOSANTS
4.1 - Motoventilateurs
4.1.1 - Procédure de démontage du motoventilateur
Tuyauterie d’évacuation des condensats: Fig. 9. Utiliser un
tuyau flexible ø intérieur 16 mm et réaliser une pente de 20
mm/m (9a), sans accident de parcours, remontée, etc.
Prévoir un siphon de 50 mm (9b) au moins pour éviter la
remontée de gaz ou d’odeurs d’égouts dans le faux plafond.
En cas de raccordements d’unités multiples à un même
collecteur d’évacuation, un dispositif est à prévoir: Fig. 10.
Avant de mettre l’unité en marche, vérifier que l’eau s’écoule
convenablement dans le bac à condensats interne en versant
de l’eau dedans. Si tel n’est pas le cas, vérifier que le tuyau
présente l’inclinaison requise et rechercher les causes
potentielles du problème rencontré. Les gaines de raccordement (en sortie d’air de l’appareil) devront être calorifugées
afin d’éviter toute formation de condensation sur les parois.
NOTE: Les pertes de charge de ces gaines doivent être
compatibles avec les performances de l’appareil. La gaine
doit être la plus tendue possible. Éviter les coudes courts.
Vérifier que les gaines ne présentent pas de fuite d’air et
qu’elles ne soient pas écrasées.Veillez également à la
propreté intérieure des gaines pour éviter des entraînements
de débris de construction.
Lorsque l’installation est prête, à savoir l’unité 42EM fixée
au plafond, les raccordements aérauliques réalisés, les
collecteurs hydrauliques posés avec les vannes d’arrêt en
attente sur les piquages, l’installation électrique préparée,
connecter la partie hydraulique (Carrier préconise l’utilisation de flexibles hydrauliques qui peuvent être fournis en
accessoires). Chaque flexible est muni d’un écrou tournant
1/2” gaz suivant le modèle. Ne pas oublier d’intercaler un
joint entre l’écrou tournant et la vanne d’arrêt (joint hors
fourniture Carrier).
ATTENTION: Avant toute intervention sur ce produit, il est
impératif de sectionner l’alimentation électrique de l’unité.
Repérer et noter les vitesses câblées. Dans le cas d’un dysfonctionnement du motoventilateur, l’ensemble complet
du motoventilateur devra être démonté et remplacé: Fig. 12.
• Retirer le filtre.
• Démonter le panneau d’accès au motoventilateur (12a).
• Déconnecter les câbles d’alimentation du
motoventilateur (puissance et contrôle pour moteur à
vitesse variable).
• Retirer si nécessaire le régulateur (fixé par vis) afin
d’accéder aux vis de maintien de la cloison supportant
le ventilateur.
• L’ensemble motoventilateur avec sa cloison est fixé à
l’unité par 4 vis à empreinte étoile T20 Torx (12b).
Dévisser ces vis puis rabattre les 2 languettes (de
chaque côté en-dessous de la cloison) supportant
l’ensemble et faire glisser l’ensemble motoventilateur
vers le bas (12c).
• Démonter l’ensemble motoventilateur.
NOTE: Veiller à ne pas toucher les turbines lors du
démontage du motoventilateur, l’équilibrage en serait
affecté.
• Dans le cas d’une option batterie électrique, déconnecter les câbles d’alimentation des batteries électriques. Faire passer ces câbles à travers le passe-fils
prévu à cet effet.
• Dévisser les batteries électriques.
• Remplacer le motoventilateur et procéder au remontage en appliquant la procédure en sens inverse.
Lorsque toutes les unités sont installées, ouvrir les vannes
d’arrêt situées sur les collecteurs, purger les circuits, puis
mettre en pression. Pour purger les batteries, desserrer légèrement les vis de purge. L’installation peut alors fonctionner.
NOTE: Ne mettre sous tension que lorsqu’ils sont tous
raccordés et mis à la terre.
3.3 - Procédure de démontage
Couper l’alimentation électrique de l’appareil, à partir
du disjoncteur (hors fourniture Carrier) prévu à cet effet
lors de l’installation.
• Déconnecter les câbles d’alimentation et raccordement.
• Fermer les vannes d’isolement situées sur les collecteurs.
• Déconnecter les flexibles hydrauliques en dévissant
les écrous tournants.
ATTENTION: Les flexibles hydrauliques n’étant pas
munis de clapets, prévoir un récipient permettant de
vidanger la batterie.
• Déconnecter les gaines de soufflage.
• Déconnecter le tuyau flexible d’évacuation des condensats, vidanger le siphon dans un récipient.
• Soulever légèrement l’unité, dévisser les 4 écrous situés
sur les tiges filetées. Descendre l’unité.
ATTENTION: Lors de la connexion du câble d’alimentation du motoventilateur respecter les indications
mentionnées sur le connecteur.
Dans le cas de moteur à vitesse variable, veiller à séparer
le câble puissance du câble contrôle et de les éloigner au
maximum.
4.1.2 - Procédure de remplacement du condensateur: Fig. 13
• Sectionner l’alimentation électrique de l’appareil
avant toute intervention.
• Retirer le filtre.
• Démonter le panneau d’accès au motoventilateur
• Démonter le condensateur qui est fixé sur le châssis
du support moteur.
• Déconnecter le condensateur en retirant les cosses
plates situées à l’arrière du condensateur.
• Remplacer le condensateur, et procéder au remontage
en appliquant la procédure en sens inverse.
4.1.3 - Câblage ventilateur
Câblage EM 0.5 et 1.0 (version multi-vitesses):
Le motoventilateur dispose de 6 vitesses réalisées à partir
d’un autotransformateur procurant ainsi à l’installateur
une grande souplesse de réglage des débits.
15
Page 16

Un choix de 3 vitesses parmi 6 disponibles devra être
effectué de façon à permettre le raccordement du
motoventilateur aux régula-tions électromécaniques ou
électroniques commercialisées. (vitesse minimum: borne 6,
vitesse maximum: borne 1).
• Unités 42EM équipées de régulateur Carrier monté
d’usine: Fig. 14.
• Unités sans régulation électronique : accès au choix
des 6 vitesses de l’extérieur, sur bornier en option:
Fig. 15 (15a = raccordement client, 15b = moteur).
Câblage EM 2.1/2.2/2.3 et EM 3.1/3.2/3.3 : Fig. 16.
42EM taille 21 42EM taille 22 42EM taille 23
42EM taille 31 42EM taille 32 42EM taille 33
Neutre (com)
Phase connectée
Non connecté
Non connecté
Légende câblage:
vitesse minimum = borne 6 moyenne vitesse = fil gris (14b)
vitesse maximum = borne 1 grande vitesse = fil noir (14c)
petite vitesse = fil rouge (14a) L = Phase
blanc blanc blanc
1
rouge bleu noir
2
bleu rouge rouge
3
noir noir bleu
4
4.2 - Batterie à eau
4.2.1 - Procédure de démontage de la batterie à eau:
ATTENTION: Avant toute intervention, il est impératif
de sectionner l’alimentation électrique de l’appareil.
• Fermer les vannes d’isolement situées sur les collecteurs.
• Déconnecter les flexibles hydrauliques en dévissant
les écrous tournants.
• Démonter les servomoteurs en prenant garde de
repérer la vanne froide et la vanne chaude.
• Déconnecter le tuyau flexible d’évacuation des condensats maintenu par un collier hors fourniture Carrier.
• Démonter les corps de vanne 2 voies ou 4 voies de
régulation de débit d’eau. Selon configuration de
l’Atmosphera, le coupling de la vanne 4 voies pourra
être muni d’un inverseur chaud/froid, ne pas le
démonter.
• Démonter l’ensemble bac à condensats/batterie, cet
ensemble est fixé par 4 vis à empreinte étoile T20 (Torx).
• Après intervention sur l’ensemble bac/batterie,
procéder au remontage de l’ensemble en appliquant
la procédure en sens inverse, en s’assurant que tous
les joints ont été changés (joints neufs mis en place) et
que l’étanchéité des raccordements entrée/sortie de la
batterie ait été réalisée à l’aide d’une pâte à joint
adaptée au montage des corps de vanne.
• Bien purger la batterie lors de la remise en eau.
4.2.2 - Positions entrées-sorties d’eau
Entrées-sorties d’eau tailles 0.5, 1 et 2: Fig. 18.
Entrées-sorties d’eau taille 3: Fig. 19.
ATTENTION: Bien respecter le sens indiqué par une
flèche sur les vannes en fonction de la servitude et du type
de vanne.
4.3 - Viroles de raccordement
Elles sont réalisées avec un plastique chargé, et présentent
un classement au feu V0, sensiblement équivalent au
classement M1. Elles sont emboitées par l’intérieur de
l’unité. Les gaines ne doivent être ni vissées ni rivetées sur
les viroles mais fixées par un collier ou de l’adhésif.
ATTENTION: Lors de la mise en place des gaines, veiller
à recouvrir la totalité de la surface des viroles, afin
d’assurer la meilleure étanchéité possible.
Veiller à ce que la température maximum de soufflage
d’air n’excède pas 60 °C.
Veiller à ne pas manutentionner l’appareil par les viroles, à
ne pas entreposer de charges sur celles-ci, et à ne pas les
endommager avec des outils ou lors de l’installation.
4.4 - Option filtre à air et accès
4.4.1 - Description
L’Atmosphera Carrier est équipé d’un filtre non régénérable selon la norme EN 779.
Classement au feu du média M1, cadre fil métallique.
Le dégagement du filtre pourra être réalisé de différentes
manières en fonction de la configuration de l’appareil :
• Appareil reprise en vrac : Accès par l’arrière.
• Appareil reprise gainée : Accès par le dessous.
4.4.2 - Remplacement du filtre à air
Il convient de changer régulièrement le filtre. La durée de
vie d’un filtre est fonction de son encrassement qui varie
selon ses conditions d’utilisation.
Si l’on ne change pas un filtre encrassé, sa perte de charge
augmente, il peut rejeter de la poussière emmagasinée et
remettre en cause les performances de l’Atmosphera
(diminution du débit d’air).
NOTE: Lors de l’installation de l’Atmosphera, veiller à
ce qu’aucun “T” porteur du faux plafond n’empêche le
retrait du filtre.
4.5 - Régulateur de débit d’air neuf
ATTENTION: Il est préconisé de serrer les corps de
vannes sur les batteries avec précaution (15 N·m sont
suffisants) afin de ne pas les détériorer.
NOTE: Il est possible de changer la servitude de la
batterie sur site en permuttant l’ensemble bac + batterie
montée en tiroir. Dans le cas d’une unité “taille 3”, il faut
inverser l’entrée et la sortie d’eau pour conserver les
performances annoncées.
16
4.5.1 - Régulateur de débit d’air neuf à débit constant
L’Atmosphera peut être doté d’un régulateur de débit
d’air neuf constant, permettant de contrôler l’introduction
et le renouvellement d’air.
Gamme de régulateurs de débit d’air neuf disponible :
Option a: 30 m3/h ou 8,3 l/s (-10% / +20%)
Option b: 60 m3/h ou 16,6 l/s (-10% / +20%)
Page 17

Options a et b : la virole recevant le régulateur est en
plastique, diamètre de raccordement 125 mm.
Le régulateur d’air neuf 60 m3/h (16,6 l/s) peut être modifié
sur site par déplacement ou retrait de deux restrictions
plastique afin de porter sa capacité jusqu’à un débit d’air
neuf constant maximum de 160 m3/h (44,4 l/s). Une étiquette
collée sur le 42EM indique comment modifier le réglage
des deux restrictions en plastique: Fig. 11.
Procédure de modification:
• Déconnecter la gaine d’air neuf de la virole
• Enlever les 2 restrictions ou les déplacer, suivant le
régulateur utilisé
• Reconnecter la gaine d’air neuf à la virole
IMPORTANT: Lorsque l’Atmosphera est muni d’une sonde
de température de reprise d’air, le débit d’air neuf constant
ne devra pas excéder 50 % du débit d’air soufflé par
l’appareil en vitesse minimale.
4.6.2 - Procédure de remplacement des servomoteurs
Les servomoteurs des vannes d’eau chaude et/ou glacée
peuvent être remplacés si un quelconque défaut est repéré.
• Avant toute intervention, il est impératif de sectionner
l’alimentation électrique de l’appareil.
• Déconnecter le câble d’alimentation du servomoteur:
- Servomoteur TOR 230 V utilisé avec le régulateur
numérique Carrier:
Déconnecter le câble d’alimentation du servo-
moteur muni d’un connecteur rapide.
- Servomoteur TOR 230 V utilisé avec le thermostat
électronique:
Démonter le capot de protection plastique
maintenu par 2 vis.
Déconnecter le câble d’alimentation du servomoteur raccordé au connecteur rapide ; pour cela
appuyer avec un tournevis sur la languette ressort
de la borne considérée et retirer le fil.
• Désaccoupler le servomoteur et procéder au remontage en appliquant la procédure en sens inverse.
NOTE: Le fonctionnement du régulateur de débit d’air neuf
constant 30 m3/h (8,3 l/s) nécessite une pression différentielle comprise entre 50 Pa et 200 Pa quant au régulateur
de débit d’air neuf constant 60 m3/h (16,6 l/s), il nécessite
une pression différentielle comprise entre 70 Pa et 200 Pa.
4.5.2 - Régulateur de débit d’air neuf à débit variable
L’Atmosphera 42EM peut être doté (en option) d’un
régulateur de débit d’air neuf à débit variable de 0 à 55 l/s
(0 à 200 m3/h).
Celui-ci est raccordé à la régulation numérique Carrier et
peut réguler le débit d’apport d’air neuf de deux manières
• soit un débit fixé par l’installeur et reparamétrable à
volonté,
• soit en fonction d’un taux de CO2, dans ce cas, il est
asservi à une sonde de CO2 par l’intermédiaire de la
régulation numérique Carrier (la sonde CO2 est située
à l’opposé de l’entrée d’air neuf).
NOTE: Dans le cas du régulateur de débit d’air neuf à
débit variable, il est nécessaire que la pression amont
dans la gaine d’air neuf soit de 180 Pa.
4.6 - Option vannes de régulation du débit d’eau
Les vannes de type 2 voies ou 4 voies, ont un corps conçu
pour résister à une pression de service de 16 bars.
4.6.1 - Servomoteur électrothermique TOR
Le servomoteur est de type TOR 230 V a.c.
Pour permettre la mise en eau de l’installation, l’équilibrage hydraulique des réseaux et la purge des unités, il sera
nécessaire d’alimenter électriquement les servomoteurs
pour demander l’ouverture des vannes, soit par l’intermédiaire des thermostats muraux, soit par la GTC.
ATTENTION: Serrer le servomoteur sur le corps de
vanne avec un couple maxi de 15 N·m.
4.6.3 - Procédure de remplacement des corps de vannes
• Avant toute intervention, il est impératif de sectionner
l’alimentation électrique de l’appareil.
•
Fermer les vannes d’isolement situées sur les collecteurs.
• Déconnecter les flexibles hydrauliques en dévissant
les écrous tournants.
• Désaccoupler les servomoteurs en prenant garde de
repérer la vanne froide et la vanne chaude.
• Déconnecter le tuyau flexible d’évacuation des condensats maintenu par un collier hors fourniture Carrier.
• Démonter les corps de vanne 2 voies ou 4 voies de
régulation de débit d’eau. Selon configuration de
l’appareil, le coupling de la vanne 4 voies pourra être
muni d’un inverseur chaud/froid, ne pas le démonter.
• Démonter l’ensemble bac à condensats/batterie, cet
ensemble est fixé par 4 vis à empreinte étoile T20 (Torx).
• Installer un nouveau corps de vanne sur la batterie
(mettre des joints neufs).
• Remonter l’ensemble bac à condensats/batterie.
• Connecter le tuyau flexible d’évacuation des condensats maintenu par un collier hors fourniture Carrier.
• Remettre en place les servomoteurs en veillant à ce
qu’ils soient correctement serrés sur le corps de vanne.
• Reconnecter les flexibles hydrauliques en revissant les
écrous tournants. Resserrer toutes les connexions
hydrauliques, et s’assurer que tous les joints ont été
changés et remis en place (couple de serrage: 15 N·m).
• Ouvrir les vannes d’isolement situées sur les collecteurs et purger la batterie.
• Mettre sous tension l’appareil après s’être assuré
qu’aucune fuite n’est survenue.
ATTENTION: Lors du montage du nouveau corps de
vanne, vérifier que le sens de passage du fluide indiqué
par une flèche sur le corps de vanne soit respecté. En cas de
montage en sens inverse, le corps de vanne sera détérioré.
17
Page 18

W
4.7 - Option flexible
Veillez à respecter les rayons de courbures suivants:
• Flexible non isolé : 72 mm,
• Flexible isolé : 106 mm.
4.8 - Option batterie électrique
Procédure de remplacement de la batterie électrique:
• Retirer le filtre.
• Démonter le panneau d’accès au motoventilateur.
• Repérer et noter les vitesses câblées sur le bornier de
l’autotransformateur. Déconnecter le câble d’alimentation du motoventilateur.
• Démonter l’ensemble motoventilateur.
ATTENTION: Avant toute intervention, il est impératif
de sectionner l’alimentation électrique de l’unité.
Dans le cas d’un dysfonctionnement de la batterie électrique celle-ci devra être remplacée, pour cela l’ensemble
motoventilateur devra être démonté: Fig. 17 (17a = vis).
NOTE: Veiller à ne pas toucher les turbines lors du
démontage du motoventilateur.
• Déconnecter les câbles d’alimentation des batteries
électriques. Faire passer ces câbles à travers le passefils prévu à cet effet.
• Dévisser la (ou les) batterie(s) défectueuse(s) et la (ou
IMPORTANT: Lorsque la batterie électrique est alimentée,
ne pas toucher les éléments métalliques qui sont sous
tension.
les) remplacer par une (ou des) nouvelle(s) batterie(s).
• Procéder au remontage de l’ensemble motoventilateur/
batteries en appliquant la procédure en sens inverse.
5 - CODIFICATION
Codification câblage vitesse
Codification (dernier
digit) ou option 600
Fil rouge
Faisceau ventilateur
Fil gris
Fil noir
Fil repère L
Repérage des bornes (câblage standard) option 600 non sélectionnée
ATTENTION: borne 1 = vitesse maximale, borne 6 = vitesse minimale.
6 vitesses
câblées
moteur “LEC”
vitesse variable
Type de produit Taille
Indice de
Référence produit
Digit
0 5
1 0
2 1
2 2
2 3
3 1
3 2
3 3
A 2 tubes droite
B 2 tubes gauche
C 4 tubes droite
D 4 tubes gauche
E 2 tubes / 2 fils droite BP
F 2 tubes / 2 fils gauche BP
G 2 tubes / 2 fils droite HP
H 2 tubes / 2 fils gauche HP
B Unité modulaire avec 2 viroles de soufflage
C Unité modulaire avec 3 viroles de soufflage
G Unité modulaire avec 1 virole de soufflage en bout (configuration en ligne)
H Unité modulaire avec 1 virole de soufflage latérale (opposée batterie)
J Unité modulaire avec 4 viroles de soufflage
K Unité modulaire avec 5 viroles de soufflage
M Plenum de reprise 1 virole et unité modulaire 1 virole au soufflage (configuration en ligne)
N Plenum de reprise 1 virole et unité modulaire 1 virole au soufflage (configuration en U)
P Plenum de reprise 2 viroles et unité modulaire 2 viroles au soufflage
Q Plenum de reprise 3 viroles et unité modulaire 3 viroles au soufflage
R Plenum de reprise 4 viroles et unité modulaire 4 viroles au soufflage
S Plenum de reprise 5 viroles et unité modulaire 5 viroles au soufflage
T Unité compacte avec 1 virole de reprise et 1 virole de soufflage
U Unité compacte avec 2 viroles de reprise et 2 viroles de soufflage
V Unité compacte avec 3 viroles de reprise et 3 viroles de soufflage
4 2 E M N N C A A A A A A A A A
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16
{
- Sans
C V2V
D V4V
J V2V + flexibles
K V4V + flexibles
modification
Batteries
0 Sans
A TOR 230 V
Return air plenum
et soufflage
Vannes
Moteurs de
vannes
Régulation
- Sans
A Sonde de reprise
B Sonde de soufflage
C Sonde change over
D A + B
E A + B + C
F A + C
G B + C
- Sans
A NTC
B HDB
D NTC + carte IAQ
E Bornier avec capot plastique
F E + relais
G E + relais + porte fusible
K NTC + porte fusible
L NTC + carte IAQ + porte fusible
M HDB + porte fusible
R E + porte fusible
Sondes
Filtre et accès
Air neuf
A G3 accès arrière
B G3 accès dessous
- Sans
A Virole d’air neuf dia. 125 mm seule
B 8,3 l/s (30 m3/h)
C 16,6-44,4 l/s (21/28/36) 60-160 m3/h
E Adaptateur pour vanne d’air neuf
J Virole d’air neuf dia. 125 mm seule
K 8,3 l/s (30 m3/h)
L 16,6-44,4 l/s (21/28/36) 60-160 m3/h
N Adaptateur pour vanne d’air neuf
Câblage moteur
(75/100/130)
motorisée dia. 125 mm
(75/100/130)
motorisée dia. 125 mm
DROITE
GAUCHE
18
Page 19

1 - BESTIMMUNGEN
1.3 - Erhalt der Sendung - Installationsmethoden
1.1 - Betriebs-Grenzwerte
1.1.1 - Kühlbetrieb
Mindest-Zulufttemperatur 12°C, wenn das Gerät bei einer
Umgebungs-Trockenkugeltemperatur von 27°C und 65%
relativer Feuchte installiert ist.
1.1.2 - Heizbetrieb
Die Luftausblastemperatur darf 60°C nicht überschreiten,
da sonst die Ausblastutzen beschädigt werden können. Um
das Risiko der Schichtenbildung und das damit verbundene
Unbehagen zu vermeiden, empfiehlt Carrier, die Zulufttemperatur unter 35°C zu halten.
1.1.3 - Betriebsumgebung
Die 42EM-Geräte sind zur Innenaufstellung in städtischen
Bedingungen in einer nicht korrosiven, staubfreien Umgebung ausgelegt, und nicht für Meeresluft.
Die Konzentrationen der folgenden Chemikalien dürfen
nie überschritten werden:
• SO2 < 0,02 ppm
• H2S < 0,02 ppm
• NO, NO2 < 1 ppm
• NH3 < 6 ppm
• N2O < 0,25 ppm
Die Geräte nicht an einem Ort aufstellen, wo entflammbare
Gase und Säuren oder alkaline Substanzen vorhanden sein
können. Der Kupfer-/Aluminium-Wärmetauscher bzw. die
Kunststoffteile im Gerät können sonst irreparable Korrosionsschäden erleiden.
1.1.4 - Empfohlene Register-Wasserqualität
Bei der Übergabe nach der Installation und dann regelmäßig
einmal jährlich sollte das Wasser auf Bakterien (Erkennung
von Eisen-Bakterien, H2S-erzeugenden und sulfatreduzierenden Bakterien) und Chemikalien analysiert werden (um
Korrosions- und Zunderbildungs-Probleme zu vermeiden).
Der Wasserkreislauf muss alle erforderlichen Elemente
zur Wasserbehandlung umfassen: Filter, Additive, ZwischenWärmetauscher, Entlüftungen, Abläufe, Absperrventile usw.,
entsprechend den Analyse-Ergebnissen.
Die Ergebnisse müssen den nachstehenden Werten
entsprechen:
• Gesamthärte in mmol/l: 1 < mmol/l < 1,5
• Chlorid [CL-] < 10 mg/Liter
• Sulphat [SO
• Nitrat [NO
2-
] < 30 mg/Liter
4
-
] = 0 mg/Liter
3
• Gelöstes Eisen: < 0,5 mg/Liter
• Gelöster Sauerstoff: 4 < [O2] < 9 mg/Liter
• Kohlendioxyd [CO2] < 30 mg/Liter
• Resistivität: 20 Ohm·m < Resistivität
< 50 Ohm·m
• pH: 6,9 < pH < 8
1.2 - Erforderlicher freier Raum
Nach Erhalt den Zustand der Ausrüstung prüfen und eventuelle Transportschäden dem Spediteur schriftlich mitteilen.
Die Ausrüstung erst direkt vor der Installation und so nahe
wie möglich beim Einbauort auspacken. Keine schweren
Objekte auf die Verpackung stellen.
1.4 - Versorgungsspannung 230 V ± 10% - 50 Hz
Sicherstellen, dass die Versorgungsspannung und -frequenz
den Werten des zu installierenden Geräts entsprechen.
WARNUNG: Werden die obigen Anleitungen nicht befolgt
oder nicht zugelassene Änderungen der elektrischen
Anschlüsse vorgenommen, wird die Garantie ungültig.
2 - SICHERHEITSMASSNAHMEN
HINWEIS: Ehe irgendwelche Arbeiten am Gerät vorgenommen werden, immer die Stromversorgung zum Gerät
und zu eventuellen Zubehörteilen abtrennen.
2.1 - Allgemeines
Installation, Inbetriebnahme und Wartung der verschiedenen Bauteile der unterschiedlichen Regelkreise können
gefährlich sein, wenn bestimmte Installationsaspekte, wie
z.B. Vorhandensein vom Netzstrom und Warm- oder Kaltwasser in den Klimaanlagen unberücksichtigt bleiben. Nur
speziell geschulte und qualifizierte Techniker und Installateure, die für das jeweilige Produkt geschult sind, dürfen
diese Anlagen installieren, in Betrieb nehmen und warten.
Bei Wartungsarbeiten müssen unbedingt alle Empfehlungen
und Anleitungen in Wartungsheften, auf Etiketten oder in
den mit den Geräten gelieferten Anleitungen beachtet und
alle anderen relevanten Anleitungen befolgt werden.
Definition der verwendeten Piktogramme:
• Elektrische Gefahr - Abb. 3
• Gefahr für die Hände - Abb. 4
• Allgemeine Gefahr - Abb. 5
Alle geltenden Sicherheitsregeln und -maßnahmen befolgen.
Augenschutz und Arbeitshandschuhe tragen. Beim Bewegen
und Positionieren der Geräte vorsichtig vorgehen.
2.2 - Schutz gegen elektrische Schläge
Nur Elektriker, die wie in der Norm IEC 364 (entspricht
der europäischen Norm HD 384, der französischen Norm
NFC 15 100 und den britischen Verdrahtungs-Bestimmungen UK IEE) der IEC (Internationale Elektrotechnische
Kommission) beschrieben für das entsprechende Niveau
qualifiziert sind, dürfen Zugang zu elektrischen Bauteilen
haben. Speziell müssen alle elektrischen Stromversorgungen
zum Gerät und seinen Zubehörteilen abgetrennt werden,
ehe irgendwelche Arbeiten durchgeführt werden. Die
Netzstromversorgung mit einer Trennvorrichtung (bauseits
beizustellen) abtrennen.
Ohne Rückluftplenum: Abb. 1
Mit Rückluftplenum: Abb. 2
19
Page 20

WICHTIG: Die Bauteile der verschiedenen in diesem
Prospekt beschriebenen Regelkreise umfassen Elektronikteile. Diese können elektromagnetische Störungen erzeugen
oder durch solche beschädigt werden, wenn sie nicht entsprechend diesen Anleitungen installiert und verwendet
werden. Die Bauteile dieser Regelsysteme entsprechen den
Erfordernissen der elektromagnetischen Verträglichkeit in
Wohnhäusern, kommerziellen und Leichtindustriebereichen.
Sie entsprechen auch der Niederspannungs-Direktive.
2.3 - Allgemeine Installationsbedingungen
WICHTIG: Regler, Strommodul, Regelkreise mit Drehzahlregler oder allgemein Geräte mit Regelkreisen müssen
stromaufwärts eine Trennvorrichtung enthalten (z.B. doppelpoliger Schutzschalter). Falls erforderlich muss eine leicht
zu betätigende Notstopvorrichtung (z.B. ein Druckschalter)
den Strom zur gesamten Ausrüstung unterbrechen. Diese
Sicherheitsvorrichtungen müssen entsprechend der IECEmpfehlung 364 (entspricht in Europa HD 384, in Frankreich NFC 15 100 und in Großbritannien UK IEE) dimensioniert und installiert werden. Diese Vorrichtungen werden
nicht von Carrier geliefert.
2.4 - Warnung für die Atmosphera-Regelung
WICHTIG: Es ist nicht erlaubt, mehrere AtmospheraGeräte an denselben Regler (Wandthermostat, NTCElektronikregler, HDB-Regler, usw.) anzuschließen.
2.5 - Konformität
Diese Ausrüstung gilt als konform mit den Haupterfordernissen der nachstehenden Direktiven:
• Elektromagnetische Verträglichkeit: 2004/108/EEC,
• Niederspannungs-Direktive: 2006/95/EEC.
3 - INSTAllATION DES GERÄTS
3.1 - Installation des Geräts in der Zwischendecke
Das Gerät so anbringen, dass es kein Hindernis darstellt, das
zu ungleichem Zu- und/oder Rückluftstrom führt. Die Decke
muss gleichmäßig genug sein, um eine leichte Installation
ohne Gefahr vom Gerät zu gestatten. Die Trägerstruktur
muss das Gerätegewicht aufnehmen können und Deformierungen, Brüche oder Schwingungen im Betrieb verhindern.
Allgemein gelten folgende Bestimmungen:
Überspannungsschutz stromaufwärts
Gerät ohne Elektroheizung T2A
Standardgrößen 42EM 0.5/1.0/2.1/3.1 mit Elektroheizung T10A
Standardgrößen 42EM 2.2/2.3/3.2/3.3 mit Elektroheizung T16A
• Die Geräte müssen mit Überspannungsschutz stromaufwärts versehen sein (bauseits beizustellen).
• Die Strom-Trennvorrichtung muss klar beschriftet sein
und angeben, welche Geräteteile angeschlossen sind.
• Die Verdrahtung der Bauteile der verschiedenen Regelsysteme und die Kommunikationbusse müssen entsprechend den neuesten Regeln und Bestimmungen von
professionellen Installateuren vorgenommen werden.
• Das Stromversorgungskabel muss doppelt isoliert und
mit einer entsprechenden Kabelklemme oder einer
mit dem Regler gelieferten Kabelklemme befestigt
werden. Das Kabel muss an die äußere Isolierung
geklemmt werden.
• Die Regelkreis-Bauteile müssen in einer Umgebung
installiert werden, die ihrem Schutzindex (IP) entspricht.
• Das maximale Verunreinigungsniveau ist normalerweise Verunreinigung (Ebene 2) und Installationskategorie II.
• Die Niederspannungsverdrahtung (Kommunikationsbus)
von der Betriebsstromverdrahtung getrennt verlegen.
• Um Störungen mit den Kommunikationverbindungen
zu vermeiden:
- Die Niederspannungsverdrahtung von den Be-
triebsstromkabeln fern halten und nicht denselben
Kabelverlauf verwenden (maximal 300 mm
gemeinsam mit dem 230-V-WS-, 30-A-Kabel).
- Niederspannungskabel nicht durch Schleifen in
den Betriebsstromkabeln führen.
- Schwere Induktivlasten nicht an die gleiche Strom-
versorgung (Trennschalter) anschließen wie die
für die Regler, Strommodule oder Drehzahlregler.
- Den von Carrier empfohlenen abgeschirmten
Kabeltyp verwenden und sicherstellen, dass alle
Kabel an die Regler und Strommodule angeschlossen sind.
VORSICHTSMASSNAHMEN BEI DER INSTALLATION: Beim Installationsvorgang alle Baumaterialien
aus den Kanälen entfernen, um eine Gerätebeschädigung
zu vermeiden.
3.2 - Installationsvorgang
• Das 42EM-Gerät nahe dem Installationsort in der
Zwischendecke positionieren. Um die Installation in
einer Zwischendecke zu erleichtern, ein HydraulikHebezeug und eine Trittleiter verwenden (Abb. 6).
• Sicherstellen, das die Freiräume um das Gerät ausreichen, um leichte Wartung zu gestatten. Siehe Diagramm mit den Wartungs-Freiräumen.
• Die Position der Gewindestangen an der Decke
markieren (sollen mehrere Geräte installiert werden,
kann eine Bohrschablone ratsam sein). Die Befestigungsmethode der Gewindestangen (nicht von Carrier
geliefert) hängt vom Deckentyp ab (Maximaldurchmesser der Gewindestangen ist 10 mm). Wenn die
Gewindestangen an der Decke befestigt worden sind,
die ersten Muttern anziehen.
WARNUNG: Bei der Geräteinstallation nicht die Wasserleitungsanschlüsse, Kondensatablaufstutzen, Ventile oder
flexiblen Leitungen als Griff benutzen.
Das Gerät anheben und auf den Gewindestanden nivellieren, die zweiten Muttern anbringen und leicht anziehen.
HINWEIS: Die Muttern jetzt noch nicht ganz anziehen und
das Gerät nicht an der Decke befestigen (zwischen Decke
und Gerät freien Raum lassen). Die Muttern werden endgültig justiert, wenn das Gerät an die Leitungen und Kanäle
angeschlossen und nivelliert worden ist.
Nivellierung des Geräts (Abb. 7)
Die Gewindestangen-Muttern justieren, so dass das Gerät
0,5% zur Kondensatwanne hin geneigt ist. In der anderen
Richtung (Luftströmungs-Richtung) muss das Gerät ganz
eben sein (Abb. 8).
20
Page 21

Kondensatablauf-Rohr (Abb. 9): Ein flexibles Rohr mit
einem Innendurchmesser von 16 mm verwenden und ein
konstantes Gefälle von 20 mm/m (9a) über den gesamten
horizontalen Leitungsverlauf vorsehen. Einen mindestens
50 mm (9b) tiefen Siphon vorsehen, um zu verhindern, dass
Gase und Gerüche in den Deckenraum zurückströmen.
Werden mehrere Geräte an einen gemeinsamen Sammler
angeschlossen, einen Siphon installieren (Abb. 10).
4 - BAUTEIlE
4.1 - Ventilator-Motor-Baugruppe
4.1.1 - Ventilatorbaugruppen-Ausbauverfahren
WARNUNG: Ehe irgendwelche Arbeiten am Gerät
vorgenommen werden, die Stromversorgung abtrennen.
Vor dem Gerätebetrieb sicherstellen, dass das Wasser in die
interne Kondensat-Ablaufwanne fließt, indem etwas Wasser
in die Wanne geschüttet wird. Bei Problemen die AblaufrohrNeigung und auf mögliche Behinderungen prüfen.
In allen Fällen ist (sind) der (die) Anschlusskanal (-kanäle)
am Geräteauslass zu isolieren, um Kondensatbildung an
den Wänden zu vermeiden.
HINWEIS: Der Druckverlust in den Kanälen muss mit der
Geräteleistung kompatibel sein. Der Kanal muss innen so
glatt wie möglich sein. Starke Biegungen vermeiden. Sicherstellen, dass die Kanäle keine Luftlecks oder Knicke haben.
Sicherstellen, dass sich kein Schmutz oder Baumaterial in
den Kanälen befindet, das sonst mechanische SystemBauteile, wie z.B. das Ventilator-Laufrad und die Diffusorklappen-Stellmotoren beschädigt werden können.
Nach Abschluss der Installation - d.h. wenn das Gerät an der
Decke befestigt ist, die Luftkanäle fertiggestellt sind, die Wassersammler mit Absperrventilen an den Anschlussstutzen
in ihrer Lage sind und die Elektroinstallation vorbereitet
worden ist - die Wasserleitungen anschließen (Carrier empfiehlt die Verwendung flexibler Leitungen, die als Zubehör
geliefert werden können). Alle flexiblen Leitungen haben
einen 1/2"-Gasgewinde-Anschluss, abhängig vom Modell.
Die Dichtscheibe (nicht von Carrier geliefert) zwischen
dem Schraubanschluss und dem Absperrventil installieren.
Die verdrahteten Ventilatordrehzahlen kennzeichnen und
notieren. Tritt am Ventilator ein Defekt auf, die gesamte
Baugruppe entfernen und austauschen (Abb. 12).
• Den Filter entfernen.
• Das Ventilator-Zugangsblech entfernen (12a).
• Die Stromversorgungskabel von der VentilatormotorBaugruppe abtrennen (Betriebs- und Steuerstromkabel
für Motor mit variabler Drehzahl).
• Falls erforderlich den Regler entfernen (mit Schrauben
befestigt), um Zugang zu den Wartungsschrauben der
Ventilator-Trägerplatte zu erhalten.
• Die Ventilatorbaugruppe und die Trennwand sind mit
vier Torx-Schrauben (T20) (12b) befestigt. Diese
Schrauben entfernen, dann die beiden Ansätze an beiden Seiten unter der Ventilator-Trägerplatte herunterdrücken und die Baugruppe nach unten schieben (12c).
• Die Ventilatormotor-Baugruppe entfernen.
HINWEIS: Beim Ausbau die Ventilatorschaufeln nicht
berühren, da die Ventilatoren sonst unwuchtig werden
können.
• Bei Geräten mit der Elektroheizungs-Option das Stromversorgungskabel zur Heizung abtrennen. Das Kabel
durch die Kabelführung herausziehen.
• Die Elektroheizungen losschrauben.
• Der Wiedereinbau der Ventilatormotor-Baugruppe
erfolgt in umgekehrter Reihenfolge.
Sind alle Geräte installiert worden, Absperrventile an den
Sammlern öffnen, Kreisläufe entlüften und dann unter Druck
setzen. Zur Entlüftung der Register die Entlüftungsschrauben
leicht lösen. Das System kann in Betrieb genommen werden.
HINWEIS: Den Strom erst einschalten, wenn alle
Anschlüsse abgeschlossen und geerdet worden sind.
3.3 - Ausbauverfahren
Den Strom zum Gerät am dafür bei der Installation eingebauten Trennschalter abtrennen (Trennschalter nicht von
Carrier geliefert).
• Die Stromversorgung und Anschlusskabel abtrennen.
• Die Absperrventile an den Sammlern schließen.
• Die flexiblen Wasserleitungen durch Losschrauben
der Gasanschlüsse abtrennen.
WARNUNG: Da die flexiblen Wasserleitungen keine
Ablaufventile haben, muss ein Behälter zum Entleeren
des Kühlregisters vorgesehen werden.
• Die Zuluftkanäle abtrennen.
• Die flexible Kondensatablaufleitung abtrennen. Den
Siphon in ein geeignetes Gefäß entleeren.
• Das Gerät leicht stützen und durch Lösen der vier
Muttern an den Gewindestangen demontieren und
dann vorsichtig absenken.
WARNUNG: Die Elektroanschlüsse an den Ventilatormotor
müssen den Schildern an der Anschlussleiste entsprechen.
Beim Motor mit variabler Drehzahl vorsichtig das Betriebsstromkabel von Steuerstromkabel abtrennen und sie so
weit wie möglich auseinanderziehen.
4.1.2 - Kondensator-Austauschvorgang (Abb. 13)
• Ehe irgendwelche Arbeiten am Gerät vorgenommen
werden, die Stromversorgung abtrennen.
• Den Filter entfernen.
• Das Ventilatormotor-Baugruppen-Zugangsblech
entfernen.
• Den Kondensator entfernen, der an der MotorchassisBaugruppe befestigt ist.
• Den Kondensator durch Herausziehen der Flachanschlüsse hinten am Kondensator abtrennen.
• Der Wiedereinbau der Kondensator-Baugruppe erfolgt
in umgekehrter Reihenfolge.
4.1.3 - Ventilatorverdrahtung
42EM 0.5- und 1.0-Verdrahtung (mehrstufige Ausführung)
Der Ventilatormotor umfasst sechs Drehzahlen und einen
automatischen Transformator, was dem Installateur eine
größere Flexibilität bei der Luftleistungs-Regelung bietet.
Drei Drehzahlen müssen gewählt werden, damit der Anschluss des Ventilatormotors den geltenden elektromechanischen bzw. elektronischen Bestimmungen entspricht
(Mindestdrehzahl: Klemme 6, Maximaldrehzahl: Klemme 1).
21
Page 22

• 42EM-Geräte mit werkseitig installiertem CarrierRegler: Abb. 14.
• Geräte ohne Elektronikregelung: Zugriff zu sechs wählbaren Ventilatorstufen von außen am wahlweisen
Klemmblock: Abb. 15 (15a = Kundenanschluss, 15b =
Motor).
Verdrahtung für 42EM 2.1/2.2/2.3 und 42EM 3.1/3.2/3.3:
Abb. 16
42EM Größe 2.1 Größe 2.2 Größe 2.3
Größe 3.1 Größe 3.2 Größe 3.3
Nullleiter (gemeinsam)
Phase angeschlossen
Nicht angeschlossen
Nicht angeschlossen
Legende Verdrahtung:
Mindestdrehzahl = Klemme 6 Mittlere Drehzahl = graues Kabel (14b)
Maximaldrehzahl = Klemme 1 Hohe Drehzahl = schwarzes Kabel (14c)
Niedrige Drehzahl = rotes Kabel (14a) L = stromführendes Kabel
Weiß Weiß Weiß
1
Rot Blau Schwarz
2
Blau Rot Rot
3
Schwarz Schwarz Blau
4
4.2 - Wasserregister
4.2.1 - Register-Austauschvorgang
ACHTUNG: Die durch den Pfeil auf dem Ventil angezeigte
Richtung beachten, die von der Anschlussseite und dem
Ventiltyp abhängt.
4.3 - Kanalanschluss-Stutzen
Diese sind aus hochdichtem Kunststoff mit Brandschutzklasse VO gefertigt, was mehr oder weniger M1 (französische
Norm) entspricht. Sie befinden sich im Gerät. Die Kanäle
sollten mit runden Manschetten oder Haftstoff an diesen
Stutzen befestigt werden. Es sollten keine Schrauben und
Nieten verwendet werden.
WARNUNG: Um gute Leckfestigkeit zu garantieren, sollte
der Kanal über die gesamte Stutzenlänge gehen.
Sicherstellen, dass die maximale Zulufttemperatur 60°C
nicht übersteigt.
Das Gerät nicht an den Stutzen heben oder abstützen,
keine Lasten auf auf sie legen und sie bei der Installation
und im Betrieb nicht beschädigen.
WARNUNG: Ehe irgendwelche Arbeiten am Gerät
vorgenommen werden, die Stromversorgung abtrennen.
• Die Absperrventile an den Sammlern schließen.
• Die Anschlussmuttern lösen, um die flexiblen Wasserleitungen abzutrennen.
• Die Ventil-Stellmotoren entfernen und dabei die Kühlund Heizventile kennzeichnen.
• Die flexible Kondensatablaufleitung abtrennen, die
durch eine Manschette gehalten wird (die Manschette
wird nicht von Carrier geliefert).
• Die Zwei- oder Vierwege-Wasserregelventile entfernen.
Je nach Konfiguration des Atmosphera-Geräts kann
der Vierwegeventil-Anschluss mit einem Heiz-/KühlUmschalter versehen sein. Ist dies der Fall, den Umschalter nicht entfernen.
• Die vier Torx-Schrauben (T20) entfernen und die
Register- und Ablaufwannen-Baugruppe herausschieben.
• Der Wiedereinbau erfolgt in umgekehrter Reihenfolge.
Sicherstellen, dass alle Dichtungen ausgetauscht werden (neue Dichtungen einbauen) und dass die Ein- und
Austrittsanschlüsse an das Register korrekt vorgenommen werden und die korrekte Dichtmasse am Ventil
verwendet wird.
• Die Luft aus dem Register beim Neufüllen entlüften.
ACHTUNG: Die Ventile vorsichtig an den Registern befestigen (15 N·m reicht aus), damit sie nicht beschädigt
werden.
4.4 - Wahlweiser Filter und Filterzugang
4.4.1 - Beschreibung
Das Carrier Atmosphera-Gerät ist mit einem G3-Filter
(85%, gravimetrisch) nach der Norm EN 779 ausgestattet.
Brandschutzklasse mittel M1 mit Metallrahmen.
Es werden verschiedene Filterzugangs-Optionen für die
jeweiligen Bedingungen am Einsatzort geboten:
• Gerät mit Rückluftführung ohne Kanal: Der Zugang
ist von der Geräte-Rückseite.
• Gerät mit Rückluftführung mit Kanal: Der Zugang ist
von der Geräte-Unterseite.
4.4.2 - Luftfilteraustausch
Die Luftfilter regelmäßig austauschen. Die Filter-Lebensdauer hängt von der Filter-Verschmutzungsrate ab, was wiederum von der Sauberkeit der Betriebsumgebung abhängt.
Werden verschmutzte Filter nicht ausgewechselt, kann sich
der Luft-Druckverlust erhöhen, aufgenommene Staubpartikel können abgegeben und in die Zuluft aufgenommen werden, und die allgemeine Leistung des Atmosphera-Geräts
kann beeinträchtigt werden (da die Luftleistung sinkt).
HINWEIS: Bei der Installation eines Atmosphera-Geräts
über der Zwischendecke sicherstellen, dass keine T-Balken
den Filterzugang und -austausch behindern.
4.5 - Außenluftregler
HINWEIS: Die Registeranschlüsse können bauseits durch
Umbau der Kondensatwanne und Registerbaugruppe in
den Führungen geändert werden.
Bei Größe 3 müssen Wasserein- und -austritt umgekehrt
werden, um die veröffentlichte Leistung zu erhalten.
4.2.2 - Registerein-/-austritts-Positionen
Wasserein- und -austritt, Größen 0.5, 1 und 2: Abb. 18.
Wasserein- und -austritt, Größe 3: Abb. 19.
22
4.5.1 - Konstant-Außenluftstrom-Regler
Das 42EM-Gerät kann mit einem Konstant-AußenluftstromRegler versehen werden, der Zuführung von Außenluft
und Regelung der Luftwechsel-Rate gestattet.
Nachstehende Regler sind erhältlich:
Option a: 8,3 l/s (30 m3/h) (-10%; +20%)
Option b: 16,6 l/s (60 m3/h) (-10%; +20%)
Page 23

Optionen a und b: Der Stutzendurchmesser zur Aufnahme
des Außenluftreglers ist 125 mm.
Der 16,6-l/s- oder 60-m3/h-Außenluftregler kann bauseitig
durch Versetzen oder Entfernen der beiden KunststoffBegrenzer modifiziert werden, um die Konstant-Außenluftleistung auf maximal 44,4 l/s oder 160 m3/h zu erhöhen. Ein
Etikett am 42EM-Gerät zeigt, wie die Kunststoff-Begrenzer
justiert werden können (Abb. 11).
Änderungsverfahren
• Den Außenluftkanal vom Stutzen am 42EM-Gerät
abtrennen.
• Die beiden Kunststoff-Begrenzer nach dem Außenluftregler entfernen oder versetzen.
• Den Außenluftkanal wieder an den Stutzen anschließen.
WICHTIG: Ist das 42EM-Gerät mit einem RückluftTemperatursensor ausgestattet, darf die Konstant-Außenluftleistung 50% der vom Gerät bei Mindestdrehzahl
gelieferten Luftleistung nicht überschreiten.
ANMERKUNG: Für korrekten Betrieb erfordert der 8,3-l/soder 30-m3/h-Konstant-Außenluftstromregler einen Differenzdruck im Bereich von 50 Pa bis 200 Pa. Der 16,6-l/soder 60-m3/h-Konstant-Außenluftstromregler erfordert
einen Differenzdruck im Bereich von 70 Pa bis 200 Pa.
4.5.2 - Variabler Außenluftregler
Das 42EM-Gerät kann mit einem wahlweisen variablen
Außenluftregler von 0 bis 55 l/s (0 bis 200 m3/h) versehen
werden.
Dieser wird an den numerischen Carrier-Regler angeschlossen und kann die Außenluft auf zwei Weisen regeln:
• entweder unter Benutzung einer vom Installateur festgelegten Rate, die wie erforderlich neu konfiguriert
werden kann
• oder basierend auf dem CO2-Pegel - in diesem Fall
wird er über den numerischen Carrier-Regler an einen
CO2-Sensor angeschlossen (der CO2-Sensor befindet
sich gegenüber dem Außenluft-Eintritt).
HINWEIS: Für den variablen Außenluftregler muss der
Druck stromaufwärts vom Außenluftkanal 180 Pa betragen.
4.6 - Wahlweise Wasserregelventile
Dies sind Zwei- oder Vierwegeventile, die einem Betriebsdruck von 16 bar standdhalten.
4.6.1 - Thermoelektrischer Stellmotor (ein/aus)
Der Stellmotor ist ein 230V WS-Ein-/Aus-Motor.
Um das System mit Wasser zu füllen, müssen die Wasserkreisläufe ausgeglichen und die Geräte entleert werden. Die
Stellmotoren müssen an die Stromversorgung angeschlossen
werden, um die Ventile über einen Befehl vom Wandthermostaten oder von der zentralen Leittechnik zu öffnen.
4.6.2 - Stellmotor-Austauschvorgang
Die Stellmotoren der Warm- und Kaltwasserventile können
ausgetauscht werden, wenn ein Defekt auftritt.
• Ehe irgendweche Arbeiten am Gerät vorgenommen
werden, die Stromversorgung zum Gerät abtrennen.
• Das Stromversorgungskabel vom Stellmotor abtrennen.
- 230-V-Ein-/Aus-Stellmotor für den numerischen
Carrier-Regler: Das Stromversorgungskabel mit
Schnellanschluss vom Stellmotor abtrennen.
- 230-V-Ein-/Aus-Stellmotor für einen elektronischen
Thermostaten: Den Kunststoff-Schutzdeckel entfernen, der von zwei Schrauben in seiner Lage gehalten wird. Das Stellmotor-Stromversorgungskabel abtrennen, das an den Schnellanschluss angeschlossen ist. Dazu mit einem Schraubenzieher den
gefederten Ansatz herunterdrücken und den Draht
von der jeweiligen Klemme abziehen.
• Den defekten Stellmotor abtrennen. Der Wiedereinbau
erfolgt in umgekehrter Reihenfolge.
WARNUNG: Sicherstellen, dass der Stellmotor fest in das
Ventil eingeschraubt ist (maximales Drehmoment 15 N·m).
4.6.3 - Ventil-Austauschvorgang
• Ehe irgendwelche Arbeiten am Gerät vorgenommen
werden, die Stromversorgung abtrennen.
• Die Absperrventile an den Sammlern schließen.
• Die Anschlussmuttern lösen, um die flexiblen Wasserleitungen abzutrennen.
• Die Ventil-Stellmotoren entfernen und dabei die Kühlund Heizventile kennzeichnen.
• Die flexible Kondensatablaufleitung abtrennen, die
durch eine Manschette gehalten wird (die Manschette
wird nicht von Carrier geliefert).
• Die Zwei- oder Vierwege-Wasserregelventile entfernen.
Je nach Konfiguration des Atmosphera-Geräts kann
der Vierwegeventil-Anschluss mit einem Heiz-/KühlUmschalter versehen sein. Ist dies der Fall, den Umschalter nicht entfernen.
• Die vier Torx-Schrauben (T20) entfernen und die Register- und Ablaufwannen-Baugruppe herausschieben.
• Das neue Ventil am Register anbringen (neue Dichtungen einsetzen).
• Die Register- und Kondensat-Baugruppe wieder einbauen.
• Die flexible Kondensatablauf-Leitung wieder anschließen, die durch eine Manschette gehalten wird (die
Manschette wird nicht von Carrier geliefert).
• Die Ventil-Stellmotoren wieder einbauen und sicherstellen, dass sie korrekt am Ventil befestigt sind.
• Die flexiblen Wasserleitungen wieder durch Anziehen
der Anschlussmuttern anschließen. Alle Wasseranschlüsse wieder anziehen und sicherstellen, dass alle
Dichtungen ausgetauscht und korrekt eingesetzt
wurden (maximales Drehmoment 15 N·m).
• Die Absperrventile an den Sammlern öffnen und das
System entlüften.
• Sicherstellen, dass keine Lecks vorhanden sind und
den Strom wieder an das Gerät anschließen.
WARNUNG: Beim Austausch eines Ventils immer sicherstellen, dass die Strömungsrichtung durch das Ventil dem
Pfeil auf dem Ventilkörper entspricht. Ist die Strömungsrichtung falsch, wird das Ventil rasch beeinträchtigt.
23
Page 24

W
4.7 - Flexible Rohrleitungen (Option)
Mindest-Biegeradius:
• Nicht isolierteRohrleitungen, 72 mm
• Isolierte Rohrleitungen, 106 mm.
4.8 - Wahlweise Elektroheizung
Elektroheizungs-Austauschvorgang:
• Den Filter entfernen.
• Das Ventilator-Zugangsblech entfernen.
• Die an den Auto-Transformator-Klemmblock verdrahteten Ventilatordrehzahlen kennzeichnen und notieren.
Das Stromversorgungskabel abtrennen.
• Die Ventilatormotor-Baugruppe entfernen.
WARNUNG: Ehe irgendwelche Arbeiten am Gerät
vorgenommen werden, die Stromversorgung abtrennen.
HINWEIS: Beim Ausbau die Ventilatorschaufeln nicht
berühren, da die Ventilatoren sonst unwuchtig werden
können.
Weist die Elektroheizung einen Defekt auf, muss sie ausgetauscht werden. Dazu muss die Ventilatormotor-Baugruppe
ausgebaut werden: Abb. 17 (17a = Schraube).
• Die Stromversorgungskabel zur Heizung abtrennen.
Die Kabel durch die Kabelführung herausziehen.
• Die defekte(n) Heizung(en) losschrauben und austau-
ACHTUNG: Keine stromführenden Metall-Heizelemente
berühren, wenn die Elektroheizung an die Stromversorgung
angeschlossen ist.
schen.
• Der Wiedereinbau der Ventilatormotor-Baugruppe
erfolgt in umgekehrter Reihenfolge.
5 - GERÄTECODES
Ventilatormotordrehzahl-Verdrahtung
Code (letzte Stelle)
oder Option 600
Rotes Kabel
Graues Kabel
Ventilator-
Einstellung
Schwarzes Kabel
Kabelbezeichnung L
Klemmenmarkierung (Standardverdrahtung), Option 600 nicht gewählt
HINWEIS: Klemme 1 = höchste Drehzahl, Klemme 6 = niedrigste Drehzahl
Sechs verdrahtete
Drehzahlen
LEC-Motor mit
variabler Drehzahl
Produkttyp Größe
Änderungscode
Produktbezug
Stelle
0 5
1 0
2 1
2 2
2 3
3 1
3 2
3 3
B Modulares Gerät mit 2 Zuluftstutzen
C Modulares Gerät mit 3 Zuluftstutzen
G Modulares Gerät mit 1 Zuluftstutzen am Ende (In-Line-Konfiguration)
H Modulares Gerät mit 1 seiticher Zuluftstutzen (dem Register gegenüber)
J Modulares Gerät mit 4 Zuluftstutzen
K Modulares Gerät mit 5 Zuluftstutzen
M Rückluft-Plenum 1 Stutzen und modulares Gerät 1 Zuluftstutzen (In-Line-Konfiguration)
N Rückluft-Plenum 1 Stutzen und modulares Gerät 1 Zuluftstutzen (U-förmige Konfiguration)
P Rückluft-Plenum 2 Stutzen und modulares Gerät 2 Zuluftstutzen
Q Rückluft-Plenum 3 Stutzen und modulares Gerät 3 Zuluftstutzen
R Rückluft-Plenum 4 Stutzen und modulares Gerät 4 Zuluftstutzen
S Rückluft-Plenum 5 Stutzen und modulares Gerät 5 Zuluftstutzen
T Kompaktes Gerät mit 1 Rückluftstutzen und 1 Zuluftstutzen
U Kompaktes Gerät mit 2 Rückluftstutzen und 2 Zuluftstutzen
V Kompaktes Gerät mit 3 Rückluftstutzen und 3 Zuluftstutzen
A 2 Leiter rechts
B 2 Leiter links
C 4 Leiter rechts
D 4 Leiter links
E 2 Leiter/2 Kabel, rechts, Niederdruck
F 2 Leiter/2 Kabel links, Niederdruck
G 2 Leiter/2 Kabel, rechts, Hochdruck
H 2 Leiter/2 Kabel links, Hochdruck
4 2 E M N N C A A A A A A A A A
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16
{
- Keine
C 2-Weg-Ventil
D 4-Weg-Ventil
J 2-Weg-Ventil + flexible Leitungen
K 4-Weg-Ventil + flexible Leitungen
Register
Zu- und
Rückluft-Plenum
Ventile
Ventilmotoren
- Keine
0 Keine
A 230 V Ein/Aus
- Keine
A NTC
B HDB
D NTC + IAQ-Platine
E Klemmblock m. Kunststoffdeckel
F E + Relais
G E + Relais + Sicherungshalter
K NTC + Sicherungshalter
L NTC + IAQ-Platine + Sicherungshalter
M HDB + Sicherungshalter
R E + Sicherungshalter
A Rückluftsensor
B Zuluftsensor
C Umschaltsensor
D A + B
E A + B + C
F A + C
G B + C
Regelung
Sensoren
Filter und
A G3 Zugang von hinten
B G3 Zugang von unten
Zugang
Außenluft
Motorver-
drahtung
- Keine
A Nur 125 mm ø Außenluftstutzen
B 8,3 l/s (30 m3/h)
C 16,6-44,4 l/s (21/28/36) 60-160 m3/h
(75/100/130)
E 125 mm ø Adapter, motorisiertes
Außenluftventil
J Nur 125 mm ø Außenluftstutzen
K 8,3 l/s (30 m3/h)
L 16,6-44,4 l/s (21/28/36) 60-160 m3/h
(75/100/130)
N 125 mm ø Adapter, motorisiertes
Außenluftventil
RECHTS
LINKS
24
Page 25

1 - PRECAUZIONI
1.2 - Spazi necessari
1.1 - Limiti di funzionamento
1.1.1 - Modalità di raffreddamento:
Minima temperatura di uscita aria 12°C, se l’unità è installata in locali aventi temperatura di 27°C al bulbo secco ed
umidità relativa del 65%.
1.1.2 - Modalità di riscaldamento:
Per evitare danni ai canali di mandata la temperatura d’uscita
aria non deve essere superiore ai 60°C. Per evitare rischi di
stratificazione si suggerisce di contenere entro i 35°C la
temperatura d’uscita aria.
1.1.3 - Ambiente di funzionamento
I moduli 42EM sono stati progettati per installazione in
ambienti chiusi in condizioni di atmosfera ‘urbana’ non
marina ed avente caratteristiche di non corrosività e di non
polverosità. Per nessun motivo devono essere superate le
seguenti concentrazioni di fattori inquinanti nell’aria in cui
il modulo deve operare:
• SO2 < 0,02 ppm
• H2S < 0,02 ppm
• NO, NO2 < 1 ppm
• NH3 < 6 ppm
• N2O < 0,25 ppm
L’unità non deve venire installata in posizioni caratterizzate
dalla presenza di gas infiammabili o di sostanze a carattere
acido o alcalino. In caso contrario le batterie in rame/alluminio ed i componenti interni degli apparecchi potrebbero
subire gravi ed irreparabili danni da corrosione.
1.1.4 - Raccomandazioni per la qualità dell’acqua circolante
nelle batterie
Si consiglia di fare eseguire un’analisi dell’acqua circolante
nella batteria focalizzata sulla la ricerca dell’eventuale presenza di batteri (rilevamento dei ferrobatteri e dei microrganismi che possono produrre H2S o ridurre chimicamente i
solfati) e sulla composizione chimica dell’acqua stessa in
modo da prevenire l’instaurazione di fenomeni di corrosione
di incrostazione dell’interno dei tubi.
Il circuito dell’acqua deve essere dotato di tutti i componenti
come per esempio sistemi di spurgo e di drenaggio, valvole
di intercettazione, etc. che i risultati delle analisi eseguite
fanno ritenere necessari per un opportuno trattamento
delle acque. Il sistema di trattamento dell’acqua deve
risultare tale da garantire il rispetto dei seguenti parametri
chimico - fisici:
• Durezza totale in mmol/l: 1 < mmol/l < 1,5
• Cloruri [CL-] < 10 mg/litro
• Solfati [SO
• Nitrati [NO
2-
] < 30 mg/litro
4
-
] = 0 mg/litro
3
• Ferro Dissolto: < 0,5 mg/litro
• Ossigeno Dissolto: 4 < [O2] < 9 mg/litro
• Anidride Carbonica [CO2] < 30 mg/litro
• Resistività: 20 Ohm·m < Resistività
< 50 Ohm·m
• pH: 6,9 < pH < 8
Senza plenum di ripresa: Fig. 1
Con plenum di ripresa: Fig. 2
1.3 - Ricevimento delle unità e modalità d’installazione
Al momento del ricevimento occorre anche controllare che
le unità non abbiano subito danni durante il trasporto; ogni
danno eventualmente scoperto deve venire immediatamente
contestato per iscritto allo spedizioniere. Le unità devono
rimanere nell’imballaggio fino al momento del loro montaggio. La rimozione dell’imballaggio deve venire in un luogo
che sia più vicino possibile a quello d’installazione. Le unità
non devono gravate di alcun peso.
1.4 - Tensione di alimentazione 230 V ± 10% - 50 Hz
Accertarsi che la tensione e la frequenza disponibili per
l’alimentazione corrispondano a quelle necessarie all’unità
che si sta installando.
ATTENZIONE: La mancata considerazione dei consigli
sopra riportati e/o ogni eventuale modifica al circuito
elettrico non preventivamente autorizzata da Carrier
fanno automaticamente decadere ogni forma di garanzia
dell’apparecchio.
2 - CONSIDERAZIONI SUllA SICUREZZA
ATTENZIONE: Prima di intraprendere qualsiasi operazione su l’unità e/o i suoi accessori è indispensabile interrompere il collegamento della linea elettrica d’alimentazione.
2.1 - Generalità
L’installazione, il commissioning ed ogni operazione di servizio dei componenti che costituiscono i circuiti di controllo
possono rivelarsi pericolosi, a meno che non venga tenuto
debitamente conto di alcune caratteristiche dell’impianto,
come la presenza di tensioni di rete e di acqua refrigerata
o calda nelle apparecchiature di climatizzazione. Quindi
l’esecuzione delle operazioni di installazione, commissioning
e servizio sono riservate solo a personale specializzato e
qualificato che sia stato specificatamente addestrato per
questo prodotto.
Durante l’esecuzione delle operazioni di servizio è essenziale porre in atto tutte le istruzioni e tutte le raccomandazioni che sono contenute nei bollettini di servizio, nelle
etichette apposte sulle apparecchiature o sulle istruzioni
che le corredano, nonché ogni altra istruzione specifica
Significato degli ideogrammi usati
• Pericolo Elettrico - Fig. 3
• Attenzione: Pericolo per le mani - Fig. 4
• Pericolo Generale - Fig. 5
Porre in atto tutte le norme ed i regolamenti di sicurezza
correntemente in vigore. Indossare occhiali antinfortunistici
e guanti di protezione. Fare attenzione durante la movimentazione ed il posizionamento delle apparecchiature.
25
Page 26

2.2 - Precauzioni contro le folgorazioni
L’accesso ai componenti elettrici è di esclusiva pertinenza
di elettricisti qualificati al livello raccomandato dalla IEC
(International Electrotechnical Commission) nella sua
Norma IEC 364, che corrisponde alla Norma Europea HD
384, alla Norma Francese NFC 15 100 ed allo Wiring Regulation Britannico. In particolare, prima dell’esecuzione di
qualsiasi lavoro è obbligatorio interrompere tutte le linee
elettriche di alimentazione all’unità e ad ogni suo accessorio.
Scollegare inoltre la linea di alimentazione generale aprendone il sezionatore (non di fornitura Carrier).
IMPORTANTE: Tutti i componenti che costituiscono i vari
circuiti di controllo descritti in questo manuale comprendono delle parti elettroniche. Quindi tali componenti, se
non vengono installati ed usati rispettando queste istruzioni,
possono generare interferenze elettromagnetiche o risultare
ad esse sensibili. Ognuno dei componenti che costituiscono
questi sistemi di controllo è comunque conforme alle
prescrizioni in fatto di compatibilità elettromagnetiche
per usi in aree residenziali, commerciali e caratterizzate
dalla presenza di piccole industrie. Essi sono anche conformi alla direttiva per bassa tensione.
• I componenti del circuito di controllo devono venire
installati in ambienti che siano in sintonia con il loro
indice di protezione. Il livello massimo tollerabile
corrisponde a quello di Livello 2, mentre la categoria
di installazione corrisponde alla II.
• I cavi di collegamento a bassa tensione (cioè quelli del
bus di comunicazione) debbono venire mantenuti
fisicamente separati dai cavi di alimentazione.
• Per evitare interferenze con i collegamenti di comunicazione:
- I cavi a bassa tensione ed i cavi di alimentazione
debbono correre lontani gli uni dagli altri ed
all’interno di canaline separate (nel caso di cavi
per corrente alternata da 230 V c.a. e 30 A sono
consentiti 300 mm al massimo in comune).
- I cavi a bassa tensione non devono transitare
entro spire dei cavi di alimentazione.
- Non collegare mai notevoli carichi induttivi ai cir-
cuiti di alimentazione (a valle del magnetotermico
di sezionamento) che servono regolatori e moduli
di alimentazione.
- Usare solo i cavi schermati raccomandati dalla
Carrier ed accertarsi che siano tutti debitamente
ai regolatori ed ai moduli di alimentazione.
2.3 - Raccomandazioni generali per l’installazione
IMPORTANTE: Il regolatore Carrier, il modulo di alimentazione o più genericamente le unità nelle quali sia
installato un circuito di controllo devono avere un dispositivo di isolamento installato a monte (come per esempio
un interruttore magnetotermico bipolare). Se necessario,
occorre anche prevedere un dispositivo ad azionamento
rapido (come per esempio un interruttore a pulsante) che, in
caso di necessità, permetta permetta di interrompere l’alimentazione a tutte le apparecchiature. Tali dispositivi di
sicurezza devono essere conformi ai dettami della Raccomandazione IEC 364, che corrisponde alla Norma Europea
HD 384, alla Norma Francese NFC 15 100 ed allo Wiring
Regulation Britannico. I dispositivi in questione non sono
di fornitura Carrier.
In termini generali è indispensabile rispettare le seguenti
regole:
Protezione a monte contro gli eccessivi innalzamenti della tensione
Unità prive di elettroriscaldatore T2A
Unità standard 42EM 0.5/1.0/2.1/3.1 dotate di elettroriscaldatore T10A
Unità standard 42EM 2.2/2.3/3.2/3.3 dotate di elettroriscaldatore T16A
• Le unità devono essere dotate di una protezione (non
di fornitura Carrier) contro gli eccessivi innalzamenti
della tensione che deve essere installata monte.
• Il dispositivo di apertura del circuito di alimentazione
deve essere chiaramente etichettato in modo che risulti
possibile identificare quali delle parti dell’apparecchiatura siano ad esso collegate.
• I collegamenti elettrici dei componenti che costituiscono i vari sistemi di controllo ed i bus di comunicazione
devono venire eseguiti da installatori professionisti,
rispettando le norme ed i regolamenti più recenti.
• Il cavo di alimentazione deve essere dotato di doppio
isolamento e debitamente fissato tramite un’apposita
fascetta. Nell’alloggiamento in plastica del regolatore
numerico Carrier è previsto un foro a tal scopo. Il cavo
deve essere fascettato all’isolamento esterno.
2.4 - Precauzione per il controllo delle unità
Atmosphera
IMPORTANTE: Non è consentito collegare più unità
Atmosphera allo stesso dispositivo di controllo (termostato
a parete, regolatore elettronico NTC, regolatore HDB, etc.).
2.5 - Conformità
Questi apparecchi sono risultati conformi che le principali
prescrizioni della direttiva, grazie al rispetto delle seguenti
norme:
• Compatibilità elettromagnetica: 2004/108/EEC,
• Direttiva per bassa tensione: 2006/95/EEC.
3 - INSTAllAZIONE DEI VENTIlCONVETTORI 42EM
3.1 - Installazione del ventilconvettore in un controsoffitto
Il ventilconvettore deve essere posizionato in modo che la
distribuzione dell’aria in ambiente possa avvenire uniformemente e che non vi siano ostacoli sulla ripresa e/o sulla
mandata dell’aria stessa. Il controsoffitto deve avere caratteristiche tali da consentire una facile installazione e da
salvaguardare l’integrità dell’apparecchio. In particolare la
struttura di supporto deve essere in grado di reggere il peso
dell’apparecchio e di prevenire deformazioni, rotture e/o
la manifestazione di vibrazioni durante il funzionamento.
PRECAUZIONI PER LA SICUREZZA: Mano a mano
che procedono i lavori di installazione occorre rimuovere
tutti i detriti e gli scarti di lavorazione in modo che nulla
possa danneggiare gli apparecchi.
26
Page 27

3.2 - Procedura di installazione
• Il ventilconvettore 42EM deve venire portato in prossimità della posizione nella quale verrà inserito nel
controsoffitto. Per le operazioni di installazione si
suggerisce di usare un muletto idraulico per il sollevamento dell’apparecchio ed una scala pieghevole per
l’operatore (Fig. 6).
• Controllare innanzitutto che tutt’attorno al ventilconvettore vi siano gli spazi necessari a consentire un
facile esecuzione delle operazioni di manutenzione. A
tal proposito vogliate consultare il disegno che riporta
gli spazi di rispetto che sono necessari per le necessità
di servizio.
• Contrassegnare sulla soletta le posizioni in cui dovranno
essere eseguiti i fori per l’inserimento dei tiranti
filettati di sospensione (se si dovessero installare più
apparecchi potrebbe essere utile costruirsi una dima
per sveltire il lavoro). Il metodo di fissaggio dei tiranti
filettati (che non sono di fornitura Carrier) dipende
dalla natura della soletta, ma il diametro massimo dei
tiranti corrisponde a 10 mm. Una volta fissati i tiranti
alla soletta, avvitare un primo dado su ciascuno di essi.
ATTENZIONE: Gli attacchi idraulici, gli attacchi di
scarico della condensa, le valvole o i tubi flessibili non
devono mai venire usati come maniglie per la movimentazione degli apparecchi.
Sollevare l’apparecchio, allinearlo ai tiranti filettati, inserire il
secondo dado su ciascuno di essi e serrare leggermente i dadi.
NOTE: A questo punto si deve evitare di serrare a fondo i
dadi per completare il fissaggio dell’apparecchio alla
soletta (tra il filo inferiore della soletta e l’apparecchio deve
comunque essere lasciato dello spazio libero). Il serraggio
a fondo dei dadi dovrò infatti essere eseguito solo dopo che
l’apparecchio sia stato collegato alle tubazioni ed ai canali
e che sia stato debitamente livellato.
In tutti i casi i canali di collegamento con l’apparecchio
devono venire isolati in modo da prevenire la formazione
di condensa sulle loro pareti esterne.
NOTA: Le perdite di carico dei canali e della griglia o del
diffusore devono essere compatibili con le prestazioni del
ventilconvettore. Il canale deve avere un andamento il più
uniforme possibile. In particolare occorre evitare di imporre
brusche variazioni di direzione ed impedire che all’interno
dei canali possa rimanere della sporcizia o degli sfridi di
lavorazione. La presenza di sporcizia e/o di sfridi di lavorazione all’interno dei canali può provocare danni alle giranti
dei ventilatori e/o alle serrande dei diffusori dell’aria.
Una volta completata l installazione - cioè quando il ventilconvettore è stato debitamente fissato alla soletta, è stato
completato il collegamento dei canali, gli attacchi idraulici
sono in posizione con le valvole di intercettazione installate
su di essi ed i collegamenti elettrici già preparati - si può
eseguire il collegamento delle tubazioni di adduzione
dell’acqua (a tal proposito Carrier raccomanda l’uso dei
flessibili disponibili come accessori). Ciascuno di tali flessibili ha, a seconda del modello, un attacco filettato 1/2” gas.
Occorre anche accertarsi che tra ciascuna valvola di intercettazione ed il rispettivo attacco filettato sia state installata
una guarnizione (non di fornitura Carrier).
Una volta installati tutti i ventilconvettori, occorre aprire le
valvole di intercettazione poste sugli attacchi, poi riempire
d’acqua il circuito alla pressione prevista ed infine allentare
infine leggermente le viti di sfiato per consentire l’uscita
dell’aria rimasta intrappolata nelle batterie. A questo punto
l’impianto può venire avviato.
NOTA: L’impianto non deve venire posto sotto tensione
prima dell’esecuzione di tutti i collegamenti elettrici e di
messa a terra.
3.3 - Procedura di smontaggio
Livellamento dell’apparecchio (Fig. 7)
Regolare i dadi dei tiranti di sospensione in modo che
l’apparecchio abbia una pendenza dello 0,5% in direzione
dell’attacco di scarico della condensa. Nell’altra direzione
(che è quella del flusso d’aria) l’apparecchio deve invece
risultare perfettamente livellato (Fig. 8).
Linea di scarico della condensa (Fig. 9): La linea di scarico
della condensa deve essere realizzato utilizzando un tubo
un flessibile con diametro interno di 16 mm e conferendole
nei tratti orizzontali una pendenza continua di almeno
20 mm/m (9a) in direzione del flusso. Per prevenire la
risalita nel controsoffitto di gas maleodoranti, nella linea di
scarico della condensa deve essere inserito un sifone con
profondità di almeno 50 mm (9b).
Quando gli scarichi della condensa di più unità confluiscono
in un collettore comune, il sifone può essere unico e venire
installato così come si vede nella in Fig. 10.
La funzionalità del sistema di scarico della condensa deve
essere verificata prima della messa in funzione dell’apparecchio. La verifica può essere eseguita immettendo
dell’acqua nella bacinella di scarico ed accertandone il
regolare deflusso. Se si rilevasse qualche problema di
deflusso occorrerebbe controllare la pendenza e ricercare
eventuali ostruzioni della linea di drenaggio.
Interrompere la linea di alimentazione del ventilconvettore
agendo sul sezionatore previsto a tal scopo su di essa
durante l’installazione (il sezionatore non è di fornitura
Carrier).
• Interrompere la linea di alimentazione ed i cavi di
collegamento.
• Scollegare i cavi di alimentazione e di collegamento.
• Scollegare i flessibili di adduzione acqua svitando gli
attacchi a vite.
ATTENZIONE: Poiché i flessibili non sono dotati di
valvoline di drenaggio occorre predisporre un recipiente
per la raccolta dell’acqua che uscirà dalla batteria.
• Scollegare i canali di mandata.
• Scollegare la linea di drenaggio flessibile e drenare il
sifone in un recipiente appositamente predisposto.
• Reggere il ventilconvettore e liberarlo dall’ancoraggio
allentando i dadi posti sui tiranti di sospensione.
Abbassare infine delicatamente l’apparecchio.
27
Page 28

4 - COMPONENTI
4.1 - Assieme motoventilante
4.1.1 - Smontaggio dell’assieme motoventilante
ATTENZIONE: Prima di intraprendere qualsiasi operazione su un’unità Atmosphera è indispensabile interrompere
il collegamento della linea elettrica d’alimentazione.
Identificare ed annotare le velocità per le quali il ventilatore
è collegato alla morsettiera. Quando si manifesta un guasto
al ventilatore è necessario smontare e sostituire l’intero
assieme motoventilante comportandosi come qui di seguito
precisato (Fig. 12).
• Smontare il filtro.
• Smontare il pannello d’accesso al ventilatore (12a).
• Scollegare i cavi di alimentazione (di alimentazione e
di controllo se il motore fosse a velocità variabile)
dell’assieme motoventilante.
• Se necessario, asportare il regolatore (che è fissato con
delle viti) in modo da potere avere accesso alle viti di
manutenzione del pannello che regge il ventilatore.
• L’assieme motoventilante ed il suo pannello sono mantenuti in posizione da quattro viti torx (T20) (12b).
Togliere queste viti, premere le due linguette che si
trovano entrambi i lati al di sotto del pannello che
regge l’assieme ed estrarre l’assieme dal basso (12c).
• Smontare l’assieme motoventilante.
NOTA: Durante il processo di smontaggio occorre
prestare attenzione ad evitare di toccare le pale del
ventilatore in quanto in caso contrario si rischierebbe
di compromettere la bilanciatura dei ventilatori.
• Se le unità sono dotate di batteria elettrica di riscaldamento optional occorre scollegare anche l’alimentazione di tale batteria. Recuperare in seguito il cavo
sfilandolo attraverso il foro passacavo.
• Svitare le batterie elettriche di riscaldamento.
• Il rimontaggio dell’assieme motoventilante deve
avvenire ponendo in atto all’inverso la procedura che
è stata sopra delineata.
ATTENZIONE: I collegamenti elettrici del motore del
ventilatore devono venire realizzati così come è indicato
sulle etichette apposte sul blocco del connettore.
Quando il motore è a velocità variabile occorre separare
con cura i cavi di alimentazione da quelli di controllo e poi
distanziarli il più possibile.
4.1.2 - Sostituzione del condensatore (Fig. 13)
• Interrompere il collegamento della linea elettrica d’alimentazione dell’unità Atmosphera prima di intraprendere qualsiasi lavoro sull’unità stessa.
• Smontare il filtro.
• Smontare il pannello d’accesso al ventilatore.
• Smontare il condensatore che è posto sull’assieme del
telaio del motore.
• Scollegare il condensatore estraendo i terminali a
linguetta dal lato posteriore del condensatore.
• Smontare il condensatore guasto e poi montare il condensatore di ricambio seguendo una procedura inversa
a quella sopra precisata.
4.1.3 - Collegamenti elettrici del ventilatore
Collegamenti elettrici di 42EM 0.5/1.0 (a più velocità)
Il motore del ventilatore, che è dotato di un autotrasformatore, può ruotare a sei velocità differenti e garantisce quindi
all’installatore la massima flessibilità in fatto di controllo
della portata. Di esse solo tre devono venire collegate per
consentire il collegamento del motore in conformità con le
norme localmente vigenti per le applicazioni elettroniche
ed elettromeccaniche (velocità massima: sul morsetto 1,
velocità minima: sul morsetto 6).
• Le unità fan coil 42EM sono dotate di sistema di controllo Carrier installato in fabbrica: vedere la Fig. 14.
• Unità prive di sistema di controllo elettronico: accesso
a sei velocità di rotazione del ventilatore, selezionabili
dall’esterno in corrispondenza della morsettiera per le
velocità optional del ventilatore: Fig. 15 (15a = collegamenti eseguiti dal cliente, 15b = motore).
Collegamenti elettrici per le unità 42EM 2.1/2.2/2.3 e
42EM 3.1/3.2/3.3: Fig. 16
42EM Grandezza 2.1 Grandezza 2.2 Grandezza 2.3
Grandezza 3.1 Grandezza 3.2 Grandezza 3.3
Neutro (com)
Collegamento
della fase
Non collegato
Non collegato
Legenda dei collegamenti:
Velocità Min. = Morsetto 6 Media Velocità = Cavo Grigio (14b)
Velocità Max. = Morsetto 1 Alta Velocità = Cavo Nero (14c)
Bassa Velocità = Cavo Rosso (14a) L = Sotto tensione
Bianco Bianco Bianco
1
Rosso Blu Nero
2
Blu Rosso Rosso
3
Nero Nero Blu
4
4.2 - BATTERIA AD ACQUA
4.2.1 - Smontaggio della batteria ad acqua
ATTENZIONE: Prima di intraprendere qualsiasi operazione su un’unità Atmosphera è indispensabile interrompere
il collegamento della linea elettrica d’alimentazione.
• Chiudere le valvole di intercettazione che si trovano
sugli attacchi del collettore.
• Allentare i dadi di collegamento e scollegare i tubi
flessibili di adduzione dell’acqua.
• Smontare i servomotori delle valvole avendo cura di
identificare preventivamente la valvola del circuito di
raffreddamento e quella del circuito di riscaldamento.
• Scollegare il tubo flessibile di drenaggio della condensa
che è mantenuto in posizione da un collare (tale collare
non è di fornitura Carrier).
• Smontare i corpi delle valvole a due o a quattro vie
che controllano il flusso dell’acqua. A seconda della
configurazione dell’unità Atmosphera il giunto della
valvola a tre vie può essere o non essere dotato di
commutatore di raffreddamento/riscaldamento. Se
presente, tale commutatore non deve venire smontato.
• Togliere le quattro viti torx (T20) e poi estrarre l’assieme
della batteria e della bacinella di raccolta della condensa.
• Il rimontaggio deve avvenire ponendo in atto all’inverso
la procedura che è stata sopra delineata. Accertarsi
che siano state sostituite tutte le guarnizioni (cioè che
siano state montate delle guarnizioni nuove) e che i
collegamenti di ingresso e di uscita dell’acqua siano
stati eseguiti in modo corretto ed applicando sul corpo
della valvola una pasta sigillante appropriata.
• Durante il riempimento occorre sfogare l’aria dalla
batteria.
28
Page 29

ATTENZIONE: Per evitare danneggiamenti è consigliabile serrare con cautela i collegamenti tra le batterie ed il
corpo della valvola (una coppia di 15 N·m è già sufficiente).
NOTA: In cantiere è possibile scambiare il lato attacchi
scambiando la posizione nelle guide dell’assieme batteria
- bacinella di raccolta condensa. Nel caso della grandezza
3 per ottenere le prestazioni dichiarate occorre invertire
l’ingresso con l’uscita dell’acqua.
4.2.2 - Posizioni di ingresso e di uscita dell’acqua dalla batteria
Attacchi di ingresso/uscita acqua, grandezze 0.5, 1 e 2: Fig. 18.
Attacchi di ingresso/uscita acqua, grandezza 3: Fig. 19.
ATTENZIONE: Osservare scrupolosamente la direzione
indicata dalla freccia apposta sulle valvole a seconda del
lato attacchi e del tipo di valvola.
NOTA: Installando le unità Atmosphera in un controsoffitto è indispensabile accertarsi che nessuna barra di sospensione possa ostruire lo spazio necessario per l’ispezione
e lo smontaggio del filtro dell’aria.
4.5 - Regolatore del flusso d’aria esterna
4.5.1 - Regolatore a portata costante del flusso d’aria esterna
Le Unità 42EM Atmosphera possono venire equipaggiate
con un regolatore a portata costante che consente l’immissione in ambiente di un flusso di aria esterna con la portata
necessaria per garantire la ventilazione.
I regolatori a portata costante per le unità 42EM sono disponibili nella seguente gamma:
Opzione a: 8,3 l/s (30 m3/h) (-10%, +20%)
Opzione b: 16,6 l/s (60 m3/h) (-10%, +20%)
4.3 - Collari di collegamento del canale
Questi collari, che sono inseriti nell’interno dell’unità, sono
realizzati con plastica ad elevata densità avente una classificazione di resistenza agli incendi in classe VO che è più o
meno equivalente alla classe M1 secondo la normativa
francese. I canali possono venire fissati a questi collari usando
fascette circolari piuttosto che adesive. E’ bene evitare di
fissare i canali tramite viti o rivetti.
ATTENZIONE: Per poter garantire un’adeguata tenuta
all’aria è indispensabile sovrapporre ogni canale su tutto
il rispettivo collare di collegamento.
Accertarsi che la temperatura dell’aria di mandata non
possa mai superare i 60°C.
I collari di collegamento non devono mai essere utilizzati
per sollevare e/o per reggere l’unità, né tanto meno venire
sottoposti a delle sollecitazioni meccaniche in quanto in
caso contrario potrebbero subire dei danni.
4.4 - Filtro (optional) e suo accesso
4.4.1 - Descrizione
Le unità Carrier 42EM Atmosphera sono dotate di filtri con
efficienza gravimetrica dell’85% (in classe G3) secondo lo
Standard EN 779. La resistenza al fuoco di tali filtri, che
sono racchiusi in un telaio metallico, è in classe M1.
Per soddisfare al meglio le esigenze di ogni applicazione
sono offerte due possibilità di accesso ai filtri:
• Unità con ripresa non canalizzata: Accesso dal lato
posteriore dell’unità.
• Unità con ripresa canalizzata: Accesso dal lato
inferiore dell’unità.
4.4.2 - Sostituzione del filtro
Tutti i filtri devono venire sostituiti a scadenze regolari. La
frequenza di tali sostituzioni dipende tuttavia dal grado di
pulizia ambientale del luogo in cui funzionano le unità e
quindi dalla velocità con la quale il filtro tende ad intasarsi.
Se il filtro non viene sostituito quando è intasato, la sua
perdita di carico aumenta eccessivamente, la portata d’aria
si riduce, la sporcizia trattenuta potrebbe sfuggire entrando
nel flusso d’aria e quindi in ultima analisi tutte le prestazioni
dell’unità Atmosphera ne soffrirebbero.
Opzioni a e b: Il diametro del collare di alloggiamento del
regolatore di portata è di 125 mm.
Il regolatore del flusso d’aria esterna da 16,6 l/s (60 m3/h) può
venire modificato in cantiere riposizionando o eliminando
due restrittori in plastica fino a portare a 44,4 l/s (160 m3/h)
la massima portata d’aria controllabile. Un’etichetta apposta
sull’unità 42EM indica come realizzare tale modifica (Fig. 11).
Procedura di modifica
• Scollegare il canale di adduzione dell’aria esterna dal
canotto che si trova sull’unità Atmosphera.
• Spostare o eliminare secondo necessità i due restrittori
in plastica, a seconda del tipo del regolatore della
portata di aria esterna.
• Ricollegare il canale di adduzione dell’aria esterna al
canotto.
IMPORTANTE: Se l’unità Atmosphera è dotata di un
sensore della temperatura dell’aria di ripresa la portata
dell’aria esterna non deve essere superiore al 50% della
portata dell’unità stessa in funzionamento a bassa velocità.
NOTA: Per poter funzionare correttamente il regolatore da
8,3 l/s (30 m3/h) ha bisogno di una pressione differenziale
compresa tra 50 e 200 Pa, mentre il regolatore da 16,6 l/s
(60 m3/h) ha bisogno di una pressione differenziale compresa tra 70 e 200 Pa.
4.5.2 - Regolatore a portata variabile del flusso d’aria esterna
Le Unità 42EM Atmosphera possono venire equipaggiate
con un regolatore a portata variabile optional che consente
di controllare l’immissione in ambiente del flusso di aria
esterna tra 0 e 55 l/s (tra 0 e 200 m3/h).
Tale regolatore, che è pilotato dal regolatore numerico
Carrier, può controllare in due modi la portata d’aria esterna
e cioè:
• gestendola su un valore costante impostato dall’installatore e comunque reimpostabile in qualsiasi momento,
• gestendola in funzione del tasso di CO2 in ambiente;
in questo caso occorre collegare un sensore di CO2 al
regolatore numerico (il sensore di CO2 si trova sul
lato opposto a quello di ingresso dell’ aria esterna).
NOTA: In caso d’uso del regolatore a portata variabile del
flusso d’aria esterna la prevalenza nel canale di adduzione
a monte deve essere di 180 Pa.
29
Page 30

4.6 - Valvole di controllo della portata d’acqua (optional)
Tali valvole possono essere di tipo a due vie o di tipo a
quattro vie che in entrambe le versioni hanno il corpo
realizzato in modo da potere reggere una pressione di funzionamento di 16 bar.
4.6.1 - Servomotore on/off elettrotermico
Il servomotore è di tipo on/off e funziona con c.a. a 230 V.
Per permettere che l’impianto possa venire debitamente
riempito d’acqua è indispensabile equalizzare i circuiti
idraulici e sfiatare l’aria dell’unità, mentre i servomotori
devono essere alimentati in modo da provocare l’apertura
delle valvole da essi azionate tramite segnali fatti loro
prevenire tramite i termostati a parete o dal sistema BMS.
4.6.2 - Sostituzione dei servomotori
In caso di guasto dei servomotori delle valvole dell’acqua
refrigerata o dell’acqua calda occorre sostituirli senza
indugio comportandosi come di seguito precisato.
• Interrompere il collegamento della linea elettrica d’alimentazione dell’unità Atmosphera prima di intraprendere qualsiasi lavoro sull’unità stessa.
• Scollegare il cavo d’alimentazione del servomotore
- In caso di servomotori on/off 230 V in c.a. pilotati
da regolatori numerico Carrier: Scollegare dal servomotore il cavo di alimentazione con connettore
rapido.
- In caso di servomotori on/off 230 V in c.a. pilotati
da termostato elettronico: Smontare il coperchio di
protezione in plastica che è tenuto in posizione da
due viti a testa esagonale. Scollegare dal servomotore il cavo di alimentazione con connettore rapido.
Tale opzione può essere eseguita usando un cacciavite per premere verso il basso la linguetta a molla
di ogni terminale ed estrarre il rispettivo cavo.
• Smontare dal corpo della valvola il servomotore guasto.
Montare il servomotore di ricambio seguendo una procedura inversa a quella sopra precisata.
ATTENZIONE: Il servomotore deve essere avvitato saldamente al corpo della valvola (la massima coppia di
serraggio consentita corrisponde a 15 N·m).
4.6.3 - Sostituzione del corpo della valvola
• Interrompere il collegamento della linea elettrica d’alimentazione dell’unità prima di intraprendere qualsiasi
lavoro sull’unità stessa.
• Chiudere le valvole di intercettazione degli attacchi
idraulici dei collettori.
• Svitare i dadi di accoppiamento e scollegare i flessibili
di collegamento al circuito idronico.
• Smontare i servomotori delle valvole avendo cura di
identificare la valvola collegata al circuito di raffreddamento e quella collegata al circuito di riscaldamento.
• Scollegare il flessibile di drenaggio della condensa che
è tenuto in sede da un collare (tale collare non è di
fornitura Carrier).
• Smontare i corpi delle valvole a due o a quattro vie che
controllano il flusso d’acqua. A seconda della modalità
di configurazione delle unità Atmosphera il giunto di
accoppiamento della valvola a tre vie può essere dotato
o non dotato del termostato di commutazione tra
raffreddamento e riscaldamento che se presente deve
comunque essere rimosso.
• Togliere le quattro viti torx (T20) ed estrarre l’assieme
della batteria e della bacinella di raccolta condensa.
• Installare il nuovo corpo della valvola sulla batteria
(non dimenticando i giunti).
• Rimontare l’assieme della batteria e della bacinella di
raccolta condensa.
• Ricollegare il flessibile di drenaggio della condensa che
deve essere tenuto in sede da un collare (tale collare
non è di fornitura Carrier).
• Rimontare il servomotore accertandosi che sia ben
avvitato al corpo della valvola.
• Ricollegare i flessibili di collegamento ai circuiti idronici
dopo avere sostituito le guarnizioni di tenuta ed averle
poste adeguatamente nelle rispettive sedi (i collegamenti devono venire serrati con una coppia di chiusura
massima di 15 N·m).
• Riaprire le valvole di intercettazione degli attacchi dei
collettori e sfogare l’aria dall’impianto.
• Controllare che non vi siano perdite e poi rimettere in
funzione l’unità Atmosphera.
ATTENZIONE: Durante la sostituzione di una valvola
occorre accertarsi sempre che la direzione del flusso attraverso la nuova valvola sia quella indicata dalle frecce
apposte sul suo corpo. Se la direzione del flusso fosse
errata la valvola si deteriorerebbe rapidamente.
4.7 - Tubi flessibili optional
Raggio minimo di curvatura:
• tubi senza isolamento 72 mm
• tubi con isolamento 106 mm.
4.8 - Batteria elettrica di riscaldamento (optional)
ATTENZIONE: Prima di intraprendere qualsiasi operazione sulla batteria elettrica è vitale interrompere il collegamento della linea elettrica d’alimentazione dell’unità.
La batteria elettrica deve essere sostituita non appena si
manifesti un inconveniente; per eseguire tale sostituzione
occorre smontare l’assieme motoventilante: Fig. 17 (17a =
viti).
ATTENZIONE: Non toccare mai gli elementi riscaldanti
mentre la batteria elettrica è sotto tensione.
Sostituzione della batteria elettrica:
• Smontare il filtro.
• Smontare il pannello d’accesso al motore del ventilatore.
• Identificare ed annotare le velocità del ventilatore che
sono collegate alla morsettiera dell’autotrasformatore.
Scollegare il cavo d’alimentazione.
• Smontare l’assieme motoventilante.
NOTA: Durante il processo di smontaggio occorre
prestare attenzione ad evitare di toccare le pale del
ventilatore in quanto in caso contrario si rischierebbe
di compromettere la bilanciatura dei ventilatori.
• Scollegare i cavi che alimentano la batteria elettrica e
sfilarli attraverso la canalina.
• Svitare la batteria elettrica di riscaldamento.
• Rimontare la batteria di ricambio e l’assieme motoventilante seguendo la procedura inversa a quella sopra
precisata.
30
Page 31

5 - CODIFICA
W
Codifica (ultimo digit)
o opzione 600
Cavo rosso
Cavo grigio
Collegamento delle velocità del motore
Impostazione
del ventilatore
Rep. cavo L
Identificazione del morsetto (collegamento elettrico standard), opzione 600 non selezionata
NOTA: Morsetto 1 = velocità più alta, Morsetto 6 = velocità più bassa
Tipo dell’unità Grandezza
Codice di
modifica
Tipo della
batteria
Plenum di man-
data e ripresa
Valvola
Motore della
valvola
Controllo
Sensori
Filtro e suo
accesso
Aria esterna
Riferimento del prodotto 4 2 E M N N C A A A A A A A A A
Cavo nero
Carattere
0 5
1 0
2 1
2 2
2 3
3 1
3 2
3 3
B Unità modulare con 2 collari per collegamento ai canali mandata
C Unità modulare con 3 collari per collegamento ai canali mandata
G Unità modulare con 1 collare all’estremità per collegamento ai canali mandata
H Unità modulare con 1 collare all’estremità per collegamento ai canali mandata (opposto
J Unità modular con 4 collari per il collegamento dei canali di mandata
K Unità modular con 5 collari per il collegamento dei canali di mandata
M Plenum di ripresa con 1 collare ed unità modulare con 1 collare per il collegamento del
N Plenum di ripresa con 1 collare ed unità modulare con 1 collare per il collegamento del
P Plenum di ripresa con 2 collari ed unità modulare con 2 collari per collegamento ai canali
Q Plenum di ripresa con 3 collari ed unità modulare con 2 collari per collegamento ai canali
R Plenum di ripresa con 4 collari ed unità modulare con 2 collari per collegamento ai canali
S Plenum di ripresa con 5 collari ed unità modulare con 2 collari per collegamento ai canali
T Unità compatta con 1 collare per il collegamento dei canali di ripresa ed 1 collare per il
U Unità compatta con 2 collari per il collegamento dei canali di ripresa e 2 collari per il
V Unità compatta con 3 collari per il collegamento dei canali di ripresa e 3 collari per il
A A 2 tubi, con attacchi a destra
B A 2 tubi, con attacchi a sinistra
C A 4 tubi, con attacchi a destra
D A 4 tubi, con attacchi a sinistra
E A 2 tubi/2 cavi, con attacchi a
destra, a bassa pressione
F A 2 tubi/2 cavi, con attacchi a
sinistra, a bassa pressione
G A 2 tubi/2 cavi, con attacchi a
destra, ad alta pressione
H A 2 tubi/2 cavi, con attacchi a
sinistra, ad alta pressione
(configurazione in linea)
alla batteria)
canale di mandata (configurazione in linea)
canale di mandata (configurazione ad U)
mandata
mandata
mandata
mandata
collegamento dei canali di mandata
collegamento dei canali di mandata
collegamento dei canali di mandata
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16
{
A G3 accesso dal lato
posteriore
B G3 accesso dal lato
inferiore
- Nessuna
C Valvola a due vie
D Valvola a quattro vie
J Valvola a due vie + tubi
flessibili
K Valvola a quattro vie + tubi
flessibili
0 Nessuna
A 230 V on/off
- Nessuna
A NTC
B HDB
D NTC + scheda IAQ
E Morsettiera con coperchio in plastica
F E + relay
G E + relay + portafusibile
K NTC + portafusibile
L NTC + scheda IAQ + portafusibile
M HDB + portafusibile
R E + portafusibile
- Nessuna
A Sensore sulla ripresa
B Sensore sulla
mandata
C Sensore di
commutazione
D A + B
E A + B + C
F A + C
G B + C
- Nessuna
A Solo collare per canale aria
B 8,3 l/s (30 m3/h)
C 16,6-44,4 l/s (21/28/36) 60-160 m3/h
E Adattatore per valvola dell’aria
J Solo collare per canale aria
K 8,3 l/s (30 m3/h)
L 16,6-44,4 l/s (21/28/36) 60-160 m3/h
N Adattatore per valvola dell’aria
Motore LEC a
velocità variabile
Avvolgimenti del
motore
esterna, con ø 125 mm
(75/100/130)
esterna, con ø 125 mm
esterna, con ø 125 mm
(75/100/130)
esterna, con ø 125 mm
Sei velocità
collegate
A DESTRA
A SINISTRA
31
Page 32

1 - PRECAUCIONES
1.2 - Espacio necesario para el mantenimiento
1.1 - Límites de funcionamiento
1.1.1 - Funcionamiento del refrigeración
Temperatura del aire de impulsión mínima 12°C, cuando la
unidad se instala en un ambiente a 27°C de temperatura
seca y 65% de humedad relativa.
1.1.2 - Funcionamiento de calefacción
La temperatura del aire suministrado no debe superar 60°C
ya que si no, se pueden producir daños en las conexiones
de las bocas de suministro de aire. Para evitar cualquier
riesgo de estratificación, Carrier recomienda mantener la
temperatura del aire de descarga por debajo de 35°C.
1.1.3 - Entorno de trabajo
El 42EM está diseñado para su aplicación interior en condiciones “urbanas”, en entornos no corrosivos, sin polvo y no
marinos.
Las concentraciones de los siguientes agentes químicos no
deben superar en ningún caso los valores que se indican a
continuación:
• SO2 < 0,02 ppm
• H2S < 0,02 ppm
• NO, NO2 < 1 ppm
• NH3 < 6 ppm
• N2O < 0,25 ppm
Sin plenum de aire de retorno: Fig. 1
Con plenum de aire de retorno: Fig. 2
1.3 - Recepción de un envío - métodos de instalación
Al recibir un envío, comprobar el estado de las unidades y
comunicar a la compañía de transporte cualquier daño
observado. No desembalar las unidades hasta el momento
en que se vayan a instalar y situarlas lo más cerca posible
del punto de instalación cuando se vayan a desembalar. No
colocar ninguna clase de objetos pesados sobre ellas.
1.4 - Tensión de alimentación 230 V ± 10% - 50 Hz
Compruebe que la tensión de alimentación y la frecuencia
corresponden a los valores de la unidad que va a instalarse.
ADVERTENCIA: Si no respetan las advertencias anteriores o si se realiza cualquier modificación no autorizada
de las conexiones eléctricas, la garantía sobre el producto
quedará cancelada automáticamente.
2 - CONSIDERACIONES DE SEGURIDAD
ADVERTENCIA: Desconectar la alimentación eléctrica
de la unidad y los accesorios (en su caso) antes de realizar
cualquier trabajo en la unidad.
No instalar la unidad en un lugar donde pueda haber presentes gases o productos inflamables o de carácter alcalino
o ácido. Las baterías de cobre/aluminio o los componentes
del interior de la unidad pueden sufrir daños irreparables
en presencia de estos productos.
1.1.4 - Calidad recomendada del agua en el serpentín
A la entrega de la instalación y, después, con una periodicidad anual, es aconsejable analizar la presencia de bacterias
en el agua (detección de ferrobacterias y bacterias productoras de H2S y reductoras de sulfatos) y de productos químicos (para evitar problemas de corrosión y descascarillados).
El circuito de agua debe incluir todos los elementos necesarios para el tratamiento del agua: filtros, aditivos, intercambiadores intermedios, purgas, drenajes, válvulas de aislamiento, etc., de acuerdo con los resultados de los análisis.
Los resultados deben estar conformes con los valores que
se indican a continuación:
• Dureza total en mmol/l: 1 < mmol/l < 1,5
• Cloruros [CL-] < 10 mg/litro
• Sulfatos [SO
• Nitratos [NO
2-
] < 30 mg/litro
4
-
] = 0 mg/litro
3
• Hierro disuelto: < 0,5 mg/litro
• Oxígeno disuelto: 4 < [O2] < 9 mg/litro
• Dióxido de carbono [CO2] < 30 mg/litro
• Resistividad: 20 Ohm·m < Resistividad
< 50 Ohm·m
• pH: 6,9 < pH < 8
2.1 - Generalidades
La instalación, puesta en servicio y mantenimiento de los
distintos componentes que constituyen los distintos circuitos
de control pueden ser peligrosos a menos que se tengan en
cuenta ciertos aspectos en la instalación, como la presencia
de electricidad de red y el agua caliente o enfriada en el
equipo de aire acondicionado. Solamente los técnicos e
instaladores especialmente capacitados y cualificados que
hayan sido completamente formados para el producto en
cuestión están autorizados para instalar, poner en servicio
y mantener este equipo.
Durante las operaciones de mantenimiento es esencial
aplicar todas las recomendaciones e instrucciones que se
facilitan en los folletos de mantenimiento, en las etiquetas y
en las instrucciones que se entregan con el equipo, y cumplir
todas las demás instrucciones pertinentes.
Definición de los pictogramas utilizados:
• Peligro de descarga eléctrica - Fig. 3
• Precaución: peligro para las manos - Fig. 4
• Peligro general - Fig. 5
Cumplir todas las reglas y disposiciones de seguridad
vigentes. Utilizar protectores para los ojos y guantes de
trabajo. Tener cuidado al desplazar o situar el equipo.
32
Page 33

2.2 - Precauciones contra la electrocución
Solamente los electricistas capacitados hasta el nivel recomendado por la IEC (Comisión Electrotécnica Internacional) en su norma IEC 364, correspondiente a la HD 384
europea, la NFC 15 100 francesa y las disposiciones de
cableado IEE del Reino Unido, pueden tener acceso a los
componentes eléctricos. En particular, es obligatorio desconectar todas las fuentes de energía eléctrica que alimentan a la unidad y sus accesorios antes de realizar cualquier
trabajo. Desconectar la fuente de energía principal con un
elemento aislante (no suministrado por Carrier).
IMPORTANTE: Los componentes que constituyen los distintos circuitos de control que se describen en este manual
incluyen elementos electrónicos. Como tales, pueden generar interferencias electromagnéticas o verse afectados por
las mismas a menos que se instalen y utilicen de acuerdo
con estas instrucciones. Los componentes que constituyen
estos sistemas de control cumplen los requisitos de compatibilidad electromagnética en zonas residenciales, comerciales
e industriales ligeras. También cumplen la directiva sobre
baja tensión.
2.3 - Recomendaciones generales para la instalación
IMPORTANTE: El controlador numérico, el módulo de
potencia y los circuitos de control con los controladores de
velocidad o en unidades generales provistas de circuitos de
control deben tener un dispositivo aislante curso arriba
(por ejemplo un disyuntor bipolar). Si es necesario, un
dispositivo de paro de emergencia (como un interruptor de
seta) debe desconectar toda la energía que va al equipo.
Estos dispositivos de seguridad deben tener un tamaño y ser
instalados de acuerdo con la Recomendación de IEC 364,
correspondiente a la HD 384 europea, la NFC 15 100
francesa y las disposiciones de cableado IEE del Reino
Unido. Estos elementos no son suministrados por Carrier.
• El cable de alimentación debe tener doble aislamiento
y ha de fijarse utilizando una abrazadera de cable
adecuada o la que se suministra con el controlador
numérico. El cable debe fijarse al aislamiento exterior.
• Los componentes de los circuitos de control deben
instalarse en un entorno que cumpla su índice de
protección (IP).
• El nivel máximo de contaminación es normalmente
contaminante (nivel 2) y la categoría de instalación es
la II.
• El cableado de baja tensión (barra colectora de comunicación) debe mantenerse físicamente separado del
cableado de potencia.
• Para evitar interferencias con los enlaces de comunicación:
- Mantener el cableado de baja tensión separado
de los cables de potencia y evitar el empleo de la
misma trayectoria del cable (un máximo de 300 mm
en común con el cable de 230 V c.a., 30 A).
- No pasar cables de baja tensión a través de circui-
tos de los cables de potencia.
- No conectar cargas inductivas elevadas a la misma
fuente de alimentación (disyuntor) utilizada por
los controladores, módulos de potencia o controladores de velocidad.
- Utilizar el tipo de cable apantallado recomendado
por Carrier y asegurarse de que todos los cables
estén conectados a los controladores y módulos
de potencia.
2.4 - Precaución con el control de la 42EM
IMPORTANTE: No se pueden conectar varias unidades
Atmosphera al mismo dispositivo de control (termostato
mural, controlador NTC electrónico, controlador HDB,
etc.).
2.5 - Conformidad
En términos generales, deben aplicarse las reglas siguientes:
Protección contra sobretensión curso arriba
Unidad sin calentador eléctrico T2A
Estandard tamaños 42EM 0.5/1.0/2.1/3.1 con calentador eléctrico T10A
Estandard tamaños 42EM 2.2/2.3/3.2/3.3 con calentador eléctrico T16A
• Las unidades deben ir provistas de protección contra
una sobretensión curso arriba (no suministrada por
Carrier).
• Las unidades deben protegerse con un dispositivo
contra corrientes de fuga de tierra del tipo diferencial
(no suministrado por Carrier).
• El dispositivo de desconexión de la energía debe estar
claramente etiquetado para identificar los elementos
del equipo que están conectados al mismo.
• El cableado de los componentes que constituyen los
distintos sistemas de control y las barras colectoras de
comunicación debe efectuarse de acuerdo con las
reglas y disposiciones más recientes por instaladores
profesionales.
Este equipo ha sido declarado conforme con los requisitos
principales de las normas siguientes:
• Compatibilidad electromagnética: 2004/108/EEC,
• Directiva sobre baja tensión: 2006/95/EEC.
3 - INSTAlACIóN DE lA 42EM
3.1 - Instalación de la unidad en falso techo
La posición de la unidad no debe constituir un obstáculo
que pueda provocar una distribución o caudal de retorno
desigual. El techo debe estar lo suficientemente nivelado
como para permitir una instalación sencilla sin que la unidad
suponga peligro alguno. La estructura de sustentación debe
poder soportar el peso de la unidad y evitar deformaciones,
roturas o vibraciones durante el funcionamiento.
PRECAUCIONES DE SEGURIDAD: Durante el proceso
de instalación, retirar todos los residuos de los conductos
para no quede nada en ellos que pueda dañar la unidad.
33
Page 34

3.2 - Procedimiento de instalación
• Coloque la 42EM cerca del lugar de instalación en el
hueco del techo. Para la instalación en un falso techo,
utilice un elevador hidráulico y una escalera plegable
para facilitar el proceso (Fig. 6).
• Compruebe que el espacio libre en torno a la unidad
es suficiente para poder realizar el mantenimiento con
facilidad. Consulte el esquema que indica el espacio
libre para el servicio.
• Marque la posición de los soportes de suspensión
roscados en el techo (si hay que instalar varias
unidades, puede ser conveniente producir una
plantilla de taladro). El método para fijar los soportes
roscados (no suministrados por Carrier) depende del
tipo de techo (diámetro máximo del soporte roscado:
10 mm). Una vez colocados los soportes roscados en
el techo, apriete las primeras tuercas.
ADVERTENCIA: Para mover una unidad, no utilizar
las conexiones de los tubos de agua ni los manguitos de
drenaje de condensado, válvulas o tubos flexibles como
puntos para agarrar.
Eleve la unidad y alinéela con los soportes roscados, inserte
las segundas tuercas y apriételas ligeramente.
Cuando la instalación esté terminada, es decir, cuando la unidad 42EM se encuentre fijada al techo, se hayan completado
las conducciones de aire, los colectores de agua se hallen en
su sitio con las válvulas de cierre listas en los terminales de
conexión y la instalación eléctrica esté preparada, conecte
los tubos de agua (Carrier recomienda el uso de tubos de
agua flexibles que se pueden suministrar como accesorio).
Cada tubo flexible tiene un conector de rosca de gas de
1/2”, dependiendo del modelo. Asegúrese de que hay una
junta (no suministrada por Carrier) entre el conector de
rosca y la válvula de cierre.
Cuando estén instaladas todas las unidades, abra la válvulas
de cierre de los colectores, purgue y, luego, presurice los
circuitos. Para purgar las baterías, afloje ligeramente los
tornillos de purga. Ahora ya puede poner en marcha la
instalación.
NOTA: No encienda el sistema hasta realizar y poner a
tierra todas las conexiones.
3.3 - Procedimiento de desmontaje
Apague la alimentación de la unidad en el seccionador
proporcionado a esos efectos durante la instalación
(Carrier no lo suministra).
NOTA: En este punto, no apriete las tuercas al máximo y
no fije la unidad al techo (deje espacio entre el techo y la
unidad). Las tuercas se ajustarán al final, una vez que se
haya conectado la unidad a la tubería y se hayan nivelado
los conductos.
Nivelación de la unidad (Fig. 7).
Ajuste las tuercas de los soportes de suspensión de forma
que la unidad se incline 0,5% hacia la bandeja de drenaje
de condensado. En la otra dirección (dirección del caudal de
aire), la unidad debe estar perfectamente nivelada (Fig. 8).
Tubo de drenaje de condensado (Fig. 9): utilice un conducto
flexible con un diámetro interior de 16 mm y establezca
una caída constante de 20 mm/m (9a) a todo lo largo del
recorrido horizontal. Instale un sifón de 50 mm (mínimo)
(9b) para evitar gases y olores en el hueco del techo.
Si hay conectadas varias unidades a un colector común, es
preciso instalar un dispositivo (Fig. 10).
Antes de poner en marcha la unidad, asegúrese de que entra
agua en la bandeja interna de drenaje de condensado vertiendo agua en ella. Si se detecta algún problema, compruebe
la pendiente del tubo de drenaje y busque posibles obstrucciones.
En cualquier caso, los conductos de conexión de salida de la
unidad deben aislarse para evitar la formación de condensado en las paredes.
NOTA: Las pérdidas de presión de estos conductos deben
ser compatibles con las prestaciones de la unidad. El
conducto debe ser lo más regular posible. Evite dobleces
excesivas. Verifique que no hay fugas ni deformaciones, ni
tampoco suciedad ni residuos de la instalación dentro de
los conductos. Los residuos en el interior de los conductos
pueden dañar la rueda del ventilador y el regulador de
los difusores de aire.
• Desconecte la alimentación y los cables de conexión.
• Cierre las válvulas de aislamiento de los colectores.
• Desconecte los tubos flexibles de agua desatornillando los conectores de gas.
AVISO: Como los tubos flexibles de agua no tienen
válvulas de drenaje, es necesario un receptor para
permitir el drenaje de la batería de refrigeración.
• Desconecte los conductos de suministro de aire.
• Desconecte el tubo flexible de drenaje de condensado.
Vacíe el contenido del sifón en un recipiente adecuado.
• Sostenga ligeramente la unidad y suéltela desatornilando las cuatro tuercas de los soportes de suspensión
roscados. Baje la unidad con cuidado.
4 - COMPONENTES
4.1 - Conjunto motor/ventilador
4.1.1 - Desmontaje del conjunto del ventilador
ADVERTENCIA: Desconectar la alimentación eléctrica
al Atmosphera antes de realizar cualquier trabajo en la
unidad.
Identificar y observar las velocidades del ventilador conectadas. Si el ventilador se avería, será necesario desmontar
y sustituir el conjunto completo (Fig. 12).
• Retirar el filtro.
• Desmontar el panel de acceso al ventilador (12a).
• Desconectar los cables de alimentación del conjunto
del ventilador (conexiones de alimentación y control
del motor de velocidad variable).
• En caso necesario, retirar el controlador (fijado con
tornillos) para acceder a los tornillos de mantenimiento
del panel que sujeta el ventilador.
34
Page 35

• El conjunto del ventilador y su panel se mantienen
mediante cuatro tornillos torx (T20) (12b). Quitar
estos tornillos, empujar las dos lengüetas en cada lado
por debajo del panel que sujeta el conjunto y deslizar
el conjunto hacia abajo (12c).
• Retirar el conjunto del motor del ventilador.
NOTA: No tocar las palas durante el desmontaje
para no desequilibrar los ventiladores.
• En unidades con la opción de calentador eléctrico,
desconectar el cable de alimentación de éste. Retirar
el cable a través del pasacables.
• Desatornillar los calentadores eléctricos.
• El conjunto del motor del ventilador se monta como
acaba de describirse, pero a la inversa.
ADVERTENCIA: Deben realizarse las conexiones eléctricas de acuerdo con las etiquetas del bloque de conectores.
Separe cuidadosamente el cableado de alimentación del
motor de velocidad variable del cableado de control tanto
como sea posible.
4.1.2 - Sustitución del condensador (Fig. 13)
• Desconectar la alimentación eléctrica del Atmosphera
antes de realizar cualquier trabajo en la unidad.
• Retirar el filtro.
• Desmontar el panel de acceso al ventilador.
• Retire el condensador conectado al conjunto del
chasis del motor.
• Desconectar el condensador quitando los terminales
planos de la parte posterior del condensador.
• Invirtiendo el procedimiento anterior, sustituir, fijar y
conectar el nuevo condensador.
4.1.3 - Conexión del ventilador
Cableado de 42EM 0.5/1.0 (motor de varias velocidades)
El motor-ventilador tiene 6 velocidades, proporcionadas por
un autotransformador, que ofrecen al instalador un control
de caudal más flexible. Se deben seleccionar tres velocidades
para permitir la conexión del motor-ventilador, de acuerdo
con la reglamentación electromecánica o electrónica aplicable (velocidad mínima: terminal 6, velocidad máxima:
terminal 1).
4.2 - BATERÍA DE AGUA
4.2.1 - Desmontaje de la batería de agua
ADVERTENCIA: Desconectar la alimentación eléctrica
al Atmosphera antes de realizar cualquier trabajo en la
unidad.
• Cerrar las válvulas de aislamiento en los colectores.
• Desenroscar las tuercas de unión para desconectar los
tubos flexibles de agua.
• Retirar los actuadores de las válvulas asegurándose de
identificar bien las válvulas de refrigeración y calefacción.
• Desconectar la tubería flexible de drenaje de condensado que se sujeta con un collarín (Carrier no suministra
el collarín).
• Desmontar los cuerpos de las válvulas de control de
caudal de agua de 2 o 4 vías. Dependiendo de la configuración del Atmosphera, el acoplamiento de una
válvula de 3 vías puede tener un conmutador de
calefacción/refrigeración. Si es así, no desmontarlo.
• Retirar los 4 tornillos torx (T20) y sacar, deslizándolo,
el conjunto de la batería y la bandeja de drenaje.
• La colocación se realiza siguiendo el procedimiento
anterior a la inversa. Asegurarse de cambiar todas las
juntas (colocar nuevas) y de que las conexiones de
entrada y salida de la batería se han realizando correctamente aplicando una pasta de sellado apropiada
al cuerpo de la válvula.
• Purgar todo el aire de la batería después de llenarla.
ATENCIÓN: Se aconseja fijar el cuerpo de la válvula a
las baterías con cuidado (es suficiente 15 N·m) para asegurarse de que no se dañan.
NOTA: Es posible cambiar la conexión de la batería a pie
de obra cambiando el conjunto de la bandeja de condensado y la batería en las guías.
Con el tamaño 3, deben invertirse la entrada y la salida
de agua para conseguir el rendimiento indicado.
4.2.2 - Posiciones de entrada/salida de la batería
Entradas/salidas del agua, tamaños 0.5, 1 y 2: Fig. 18.
Entradas/salidas del agua, tamaño 3: Fig. 19.
• Unidades 42EM equipadas con controlador Carrier
instalado en fábrica: Fig. 14.
• Unidades sin control electrónico - acceso a seis velocidades del ventilador seleccionables desde el exterior
en el bloque de terminales opcional: Fig. 15 (15a =
conexión del cliente, 15b = motor).
Cableado de 42EM 2.1/2.2/2.3 y 42EM 3.1/3.2/3.3: Fig. 16
42EM 2.1 42EM 2.2 42EM 2.3
42EM 3.1 42EM 3.2 42EM 3.3
Neutro (com)
Fase conectada
No conectada
No conectada
Leyendas del cableado:
Velocidad mínima = terminal 6 Velocidad media = cable gris (14b)
Velocidad máxima = terminal 1 Velocidad alta = cable negro (14c)
Velocidad baja = cable rojo (14a) L = Activo
Blanco Blanco Blanco
1
Rojo Azul Negro
2
Azul Rojo Rojo
3
Negro Negro Azul
4
ATENCIÓN: Fijarse en la dirección indicada por la flecha
en las válvulas, que depende del lado de la conexión y del
tipo de válvula.
4.3 - Tomas de conexión de conductos
Son de plástico de alta densidad con una resistencia contra
incendios VO, más o menos equivalente a la clase M1 (norma
francesa). Están dentro de la unidad. Los conductos deben
fijarse a estas tomas con adhesivos o collarines circulares.
No deben utilizarse ni tornillos ni remaches.
ADVERTENCIA: Para garantizar un buen hermetismo,
el conducto debe recubrir toda la toma.
Asegurarse de que la temperatura máxima del aire suministrado no supera los 60°C.
No levantar ni sostener la unidad por las tomas ni colocar
carga en éstas ni dañarlas durante la instalación o el
funcionamiento.
35
Page 36

4.4 - Filtro (opción) y acceso al filtro
4.4.1 - Descripción
La 42EM Atmosphera de Carrier está equipada con un
filtro gravimétrico de 85% (G3), según la norma EN 779.
Clase de resistencia contra incendio media M1, de rejilla
metálica.
Para adaptarse a distintas necesidades del lugar de instalación, son varias las opciones de acceso al filtro:
• Unidad sin conductos de aire de retorno: El acceso es
desde la parte posterior de la unidad.
• Unidad con conductos de aire de retorno: El acceso es
por la parte inferior.
4.4.2 - Sustitución del filtro de aire
Los filtros de aire deben cambiarse periódicamente. La
frecuencia necesaria depende de la limpieza del entorno
de trabajo y de la velocidad a la cual se obstruye el filtro.
Si no se cambian los filtros obstruidos, aumenta la pérdida
de carga, se desprenden partículas atrapadas que son
arrastradas por el aire de alimentación y el rendimiento
global del Atmosphera puede disminuir al reducirse el
caudal de aire.
NOTA: Al instalar una unidad Atmosphera en un falso
techo, comprobar que ninguna barra en T obstaculiza el
acceso al filtro o el desmontaje de éste.
4.5 - Aire de renovación
4.5.1 - Controlador de aire de renovación costante
Se puede equipar la 42EM Atmosphera con un controlador
de caudal de aire de renovación constante que permite
controlar la introducción del aire de renovación y la tasa de
renovación.
Se dispone de los controladores de aire de renovación que
se indican a continuación:
Opción a: 8,3 l/s (30 m3/h) (-10 %; +20 %)
Opción b: 16,6 l/s (60 m3/h) (-10 %; +20 %)
Opciones a y b: el diámetro de la boca en la que se aloja el
controlador de aire de renovación es de 125 mm.
El controlador de aire de renovación de 16,6 l/s (60 m3/h)
puede modificarse “in situ” cambiando de emplazamiento o
retirando dos reductores de plástico para aumentar la capacidad máxima del caudal de aire de renovación a 44,4 l/s
(160 m3/h). En la 42EM hay una etiqueta que indica como
ajustar los reductores de plástico (Fig. 11).
Procedimiento de modificación
• Desconectar el conducto de aire de renovación del
manguito de plástico del Atmosphera.
• Mover o cambiar la posición las dos restricciones de
plástico, tras el controlador de aire de renovación.
• Conectar el conducto de aire de renovación al
manguito.
NOTA: Para funcionar correctamente, el controlador de
caudal de aire de renovación constante de 8,3 l/s ó 30 m3/s
requiere una presión diferencial comprendida entre 50 Pa
y 200 Pa. El controlador de caudal de aire de renovación
constante de 16,6 l/s ó 60 m3/h requiere una presión diferencial comprendida entre 70 Pa y 200 Pa.
4.5.2 - Controlador de aire de renovación variable
Se puede equipar la 42EM Atmosphera con un controlador
de aire de renovación de caudal variable opcional entre 0 y
55 l/s (0 a 200 m3/h).
Se conecta al controlador numérico Carrier y puede
regular la entrada de aire de renovación de dos formas:
• mediante una proporción fija, determinada por el
instalador, que puede variarse cuando haga falta,
• o bien según el nivel de CO2; en este caso se conecta a
un sensor de CO2 a través del controlador numérico
Carrier (el sensor de CO2 se encuentra situado enfrente
de la entrada de aire de renovación).
NOTA: Con el controlador de caudal de aire de renovación
variable, la presión aguas arriba en el conducto correspondiente debe ser de 180 Pa.
4.6 - Válvulas de control del caudal de agua (opción)
Estas válvulas son del tipo de dos o cuatro vías, con un
cuerpo diseñado para soportar una presión de trabajo de
16 bar.
4.6.1 - Accionador electrotérmico (todo/nada)
El actuador de 230 V CA es del tipo marcha/parada.
Para poder llenar la instalación con agua, igualar los circuitos de agua y purgar las unidades; los actuadores deben
conectarse a la fuente de alimentación para abrir las válvulas mediante un comando desde los termostatos de pared
o el sistema de vigilancia de edificios.
4.6.2 - Sustitución de los accionadores
Los accionadores de las válvulas de agua fría y caliente
pueden sustituirse en caso de avería.
• Desconectar la alimentación eléctrica de la unidad
antes de realizar cualquier trabajo en la misma.
• Desconectar el cable de alimentación del accionador.
- Accionador del tipo todo/nada utilizado con un
controlador numérico Carrier: Desconectar el cable
de alimentación de conexión rápida del accionador.
- Accionador del tipo todo/nada 230 V c.a. utilizado
con un termostato montado en la pared: Quitar la
cubierta protectora de plástico (sujeta con dos tornillos de cabeza hexagonal). Desconectar el cable
de alimentación de conexión rápida del accionador.
Esto puede hacerse presionando hacia abajo con
un destornillador la lengüeta elástica y extrayendo
el conductor del terminal correspondiente.
• Desacoplar el accionador defectuoso. Invertir el procedimiento de desmontaje descrito para la instalación
de un motor de sustitución.
IMPORTANTE: Si se monta en el Atmosphera un sensor
de temperatura del aire de retorno, el caudal de aire de
renovación constante no debe superar el 50% del caudal
de aire suministrado por la unidad a la velocidad mínima.
36
ADVERTENCIA: Verificar que el accionador está perfectamente roscado en el cuerpo de válvula (par máximo
15 N·m).
Page 37

4.6.3 - Sustitución de un cuerpo de válvula
• Desconectar la alimentación eléctrica de la unidad
antes de realizar cualquier trabajo en la misma.
• Cerrar las válvulas de aislamiento en los colectores.
• Desatornillar las tuercas de unión para desconectar
los tubos de agua flexibles.
• Retirar los actuadores de las válvulas asegurándose de
identificar bien las de refrigeración y calefacción.
• Desconectar la tubería flexible de drenaje de condensado que se sujeta con un collarín (Carrier no suministra el collarín).
• Retirar los cuerpos de las válvulas de control del caudal
de agua de dos o cuatro vías. Dependiendo de la configuración de la Atmosphera, la unión de la válvula de
tres vías puede ir equipada con un conmutador de
calefacción/refrigeración: en ese caso, no retirar.
• Retirar los 4 tornillos torx (T20) y sacar, deslizándolo,
el conjunto de la batería y la bandeja de drenaje.
• Instalar un nuevo cuerpo de válvula en la batería (sin
olvidar la colocación de la junta).
• Colocar de nuevo el conjunto de condensado y la
batería.
• Volver a conectar el tubo flexible de drenaje de condensado que se sujeta en su sitio con un collarín (Carrier
no suministra el collarín).
• Instalar el accionador y verificar que está perfectamente
apretado en el cuerpo de válvula.
• Volver a conectar los tubos de agua flexibles apretando
las tuercas de unión. Ajustar de nuevo todas las conexiones de agua y asegurarse de que se han cambiado y
colocado correctamente todas las juntas (par máximo:
15 N·m).
• Abrir las válvulas de aislamiento en los colectores y
purgar todo el aire del sistema.
• Verificar que no hay fugas y poner en marcha el
Atmosphera.
4.7 - Opción de tubo flexible
Radio de curvatura mínimo:
• tuberías sin aislamiento 72 mm
• tuberías aisladas 106 mm.
4.8 - Calentador eléctrico (opción)
PRECAUCIÓN: Es vital desconectar el Atmosphera de la
alimentación eléctrica general antes re realizar cualquier
trabajo en el calentador eléctrico.
Si el calentador eléctrico se avería, será necesario desmontar
y sustituir el conjunto, lo cual requiere el desmontaje de la
unidad del ventilador: Fig. 17 (17a = tornillos).
ADVERTENCIA: No tocar los elementos del calentador
estando éste encendido.
Sustitución del calentador eléctrico:
• Retirar el filtro.
• Desmontar el panel de acceso al motor del ventilador.
• Identificar y observar las velocidades del ventilador
conectadas al bloque de terminales del autotransformador. Desconectar el cable de alimentación.
• Desmontar el conjunto motor/ventilador.
NOTA: No tocar las palas durante el desmontaje
para no desequilibrar los ventiladores.
• Desconectar los cables de alimentación del calentador
eléctrico y sacarlos por el conducto para cables.
• Desatornillar el calentador averiado y sustituirlo.
• Invertir el procedimiento anterior para instalar el nuevo
calentador y montar el conjunto motor/ventilador.
ADVERTENCIA: Al sustituir una válvula, verificar
siempre que el sentido del flujo a través de ella coincide con
la flecha grabada en el cuerpo de válvula. Si el sentido del
flujo es incorrecto, la válvula se deteriorará rápidamente.
37
Page 38

W
5 - CODIFICACIóN
Ventilador
Conexiones para velocidad del motor-ventilador
Codificación (último
dígito) u opción 600
Cable rojo
Cable gris
Cable negro
Rep. cable L
Marcado de terminal (cableado de serie), opción 600 no seleccionada
NOTA: Terminal 1 = velocidad máxima, Terminal 6 = velocidad mínima.
Tipo de unidad Tamaño
Código de
modificación
Tipo de batéria
Plenum de sumi-
nistro/retorno
Válvula
Motores de
Codificación
Digitos
0 5
1 0
2 1
2 2
2 3
3 1
3 2
3 3
A 2 tubos derecha
B 2 tubos izquierda
C 4 tubos derecha
D 4 tubos izquierda
E 2 tubos/2 cavi, derecha, baja presión
F 2 tubos/2 cavi, izquierda, baja presión
G 2 tubos/2 cavi, izquierda,alta presión
H 2 tubos/2 cavi, izquierda, baja presión
B Unidad modular con 2 bocas de descarga
C Unidad modular con 3 bocas de descarga
G Unidad modular con 1 boca de descarga en el extremo (configuración en línea)
H Unidad modular con 1 boca de descarga en el lateral (batería opuesta)
J Unidad modular con 4 bocas de descarga
K Unidad modular con 5 bocas de descarga
M Plenum de retorno 1 boca y unidad modular 1 boca de descarga (configuración en línea)
N Plenum de retorno 1 boca y unidad modular 1 boca de descarga (configuración en forma
de U)
P Plenum de retorno 2 bocas y unidad modular 2 bocas de descarga
Q Plenum de retorno 3 bocas y unidad modular 3 bocas de descarga
R Plenum de retorno 4 bocas y unidad modular 4 bocas de descarga
S Plenum de retorno 5 bocas y unidad modular 5 bocas de descarga
T Unidad compacta con 1 boca de retorno y 1 boca de descarga
U Unidad compacta con 2 bocas de retorno y 2 bocas de descarga
V Unidad compacta con 3 bocas de retorno y 3 bocas de descarga
4 2 E M N N C A A A A A A A A A
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16
{
- Ninguna
C Válvula de 2 vías
D Válvula de 4 vías
J Válvula de 2 vías + tubos
flexibles
K Válvula de 4 vías + tubos
flexibles
0 Ningun
A 230 V todo/nada
- Ninguna
A NTC
B HDB
D NTC + placa IAQ
E Bloque de terminales con
cubierta de plástico
F E + relé
G E + relé + portafusible
K NTC + portafusible
L NTC + placa IAQ + portafusible
M HDB + portafusible
R E + portafusible
válvulas
Sistema de
control
Sensores
A G3 acceso posterior
B G3 acceso por la parte
inferior
- Ninguno
A Sensor de aire de
retorno
B Sensor de aire de
suministro
C Sensor de cambio
D A + B
E A + B + C
F A + C
G B + C
Filtro y acceso al
filtro
Aire de
renovación
Cableado del
motor
- Ninguna
A Sólo toma de aire de renovación de
125 mm ø
B 8,3 l/s (30 m3/h)
C 16,6-44,4 l/s (21/28/36) 60-160 m3/h
(75/100/130)
E Adaptador de válvula motorizada de
aire de renovación 125 mm ø
J Sólo toma de aire de renovación de
125 mm ø
K 8,3 l/s (30 m3/h)
L 16,6-44,4 l/s (21/28/36) 60-160 m3/h
(75/100/130)
N Adaptador de válvula motorizada de
aire de renovación 125 mm ø
Seis
velocidades
conectadas
Motor LEC de
velocidad variable
DERECHO
IZQIERDO
38
Page 39

1 - VOORZORGSMAATREGElEN
1.3 - Ontvangen van een zending - montagemethoden
1.1 - Bedrijfslimieten
1.1.1 - Koelbedrijf
Minimum toevoerluchttemperatuur 12°C, wanneer de
omgevingstemperatuur van de unit 27°C droge bol is bij
70% relatieve vochtigheid.
1.1.2 - Verwarmingsbedrijf
Maximum luchtuittredetemperatuur 60°C om schade aan
de luchtuittrede-openingen te voorkomen. Om stratificatie
en het daaruit voortvloeiende ongemak te vermijden, raden
wij u aan om de uittredetemperatuur beneden 35°C te
houden.
1.1.3 - Bedrijfsomgeving
De 42EM is ontworpen voor binnenopstelling in niet
corro-sieve, stofvrije omgeving (niet op schepen).
Concentraties van de volgende gassen mogen niet worden
overschreden:
• SO2 < 0,02 ppm
• H2S < 0,02 ppm
• NO, NO2 < 1,0 ppm
• NH3 < 6,0 ppm
• N2O < 0,25 ppm
Monteer de units niet op plaatsen waar brandbare gassen
en producten van zure of alkalische aard aanwezig zijn. De
koper/aluminium batterij of de kunststof componenten van
de unit kunnen hierdoor onherstelbaar worden beschadigd.
1.1.4 - Aanbevolen waterkwaliteit
Het wordt aanbevolen om bij de inbedrijfstelling, en daarna
ieder jaar, het water te onderzoeken op bacteriën (aanwezigheid van ferro-bacteriën, H2S producerende en sulfaat
verminderende bacteriën) en chemicaliën (om problemen
door corrosie en kalkafzetting te voorkomen).
Bij het ontvangen van een zending moet de toestand van de
goederen worden gecontroleerd. Eventuele beschadigingen
tijdens het transport moeten aan het expeditiebedrijf
worden gemeld. Pak de units pas uit vlak voordat met de
installatie wordt begonnen. Zorg dat de units tijdens het
uitpakken zich zo dicht mogelijk bij de installatielocatie
bevinden. Plaats geen zware voorwerpen op de units.
1.4 - Voedingsspanning 230 V ± 10% - 50 Hz
Controleer of de voedingsspanning en de frequentie overeenkomen met de waarden van de unit die wordt geïnstalleerd.
WAARSCHUWING: Als deze aanwijzingen niet worden
opgevolgd en in geval van elektrische modificaties zonder
toestemming van Carrier acht Carrier zich niet aansprakelijk voor eventuele schade en vervalt de garantie.
2 - VEIlIGHEID
OPMERKING: Schakel altijd de hoofdstroom af voordat
met werkzaamheden aan de unit wordt begonnen!
2.1 - Algemeen
Montage, inbedrijfstelling en onderhoud van deze units
kunnen door de aanwezigheid van diverse componenten
risico’s met zich meebrengen, tenzij rekening wordt gehouden met bepaalde aspecten van het systeem, zoals de aanwezigheid van hoofdstroom en warm of koud water in de
airconditioning apparatuur. Daarom mogen deze werkzaamheden alleen worden uitgevoerd door gekwalificeerd personeel.
Neem bij werkzaamheden de waarschuwingen in de documentatie, op de stickers in de unit en andere van toepassing
zijnde voorzorgsmaatregelen in acht.
Het watercircuit moet alle nodige elementen bevatten voor
waterbehandeling: filters, toevoegingen, tussenwisselaars,
ontluchting, waterafvoer, isoleerafsluiters, etc., volgens de
analyseresultaten.
De resultaten moeten conform de onderstaande waarden
zijn:
• Totale hardheid in mmol/l: 1 < mmol/l < 1,5
• Chloride [CL-] < 10 mg/l
• Sulfaat [SO
• Nitraat [NO
2-
] < 30 mg/l
4
-
] = 0 mg/l
3
• Opgelost ijzer < 0,5 mg/l
• Ontbonden zuurstof 4 < [O2] < 9 mg/l
• Koolstofdioxide [CO2] < 30 mg/l
• Weerstand 20 Ohm·m < weerstand
< 50 Ohm·m
• pH 6,9 < pH < 8
1.2 - Benodigde vrije ruimte
Zonder retourluchtplenum: Fig. 1
Met retourluchtplenum: Fig. 2
Verklaring van de gebruikte symbolen:
• Gevaar voor elektrische schokken - Fig. 3
• Gevaar door bewegende delen - Fig. 4
• Algemeen gevaar - Fig. 5
Volg alle lokale veiligheidsvoorschriften. Draag een veiligheidsbril en werkhandschoenen. Wees voorzichtig bij het
transporteren en plaatsen van apparatuur.
2.2 - Voorkomen van elektrische schokken
Alleen personeel dat gekwalificeerd is volgens de richtlijnen
van het IEC (IEC = International Electrotechnical Commission) en de NEN 3140 mag toegang krijgen tot de elektrische componenten. Ook bij uitgeschakelde scheidingsc.q. hoofdschakelaar kunnen bepaalde machinedelen onder
spanning staan, omdat ze op een afzonderlijke voeding zijn
aangesloten zijn. Schakel ALTIJD de hoofdstroom af voordat met werkzaamheden aan de unit wordt begonnen!
39
Page 40

BELANGRIJK: Deze apparatuur werkt met elektromagnetische signalen en geeft deze ook af. Wanneer bij de
montage de instructies niet worden gevolgd, kan radiointerferentie ontstaan. Deze apparatuur voldoet aan alle
van toepassing zijnde voorschriften op het gebied van
elektromagnetische compatibiliteit in woonwijken en
zakelijke- en licht industriële gebieden. Ook voldoet de
apparatuur aan de laagspanningsrichtlijn.
2.4 - Waarschuwing voor de regeling van de 42EM
BELANGRIJK: Het is NIET toegestaan om meerdere
42EM units aan te sluiten op dezelfde regelaar (wandthermostaat, elektronische NTC regelaar, HDB regelaar,
etc.). Neem voor meer informatie contact op met Carrier.
2.5 - Conformiteit
2.3 - Algemene aanbevelingen voor de montage
BELANGRIJK: De stroom van de regelaar, schakelmodule,
etc. moet kunnen worden afgeschakeld (bijv. door een tweepolige werkschakelaar). Zo nodig moet met een gemakkelijk te bedienen noodstop voorziening (zoals een drukschakelaar) de stroom naar alle apparatuur kunnen worden
uitgeschakeld. Deze beveiligingen moeten worden gedimensioneerd en geïnstalleerd in overeenstemming met de NEN
1010. Deze beveiligingen worden niet door Carrier
meegeleverd.
Algemeen gesproken moeten de volgende regels worden
toegepast:
Overbelastingsbeveiliging stroomopwaarts
Unit zonder elektrische verwarming T2A
Standaard unit 42EM 0.5/1.0/2.1/3.1 met elektrische verwarming T10A
Standaard unit 42EM 2.2/2.3/3.2/3.3 met elektrische verwarming T16A
• De units moeten stroomopwaarts worden voorzien
van een overbelastingsbeveiliging (levering derden).
• De hoofdstroomschakelaar moet duidelijk gemerkt
zijn om aan te geven welke componenten van de
apparatuur erop zijn aangesloten.
• De bedrading van de componenten van de verschillende
regelsystemen en de communicatiebussen moet worden
uitgevoerd volgens de geldende plaatselijke voorschriften (NEN 1010) door een vakkundig installateur.
• De voedingskabel moet dubbel geïsoleerd zijn en vastgezet worden met een kabelklem. Voor dit doel is een
opening aangebracht in het plastic huis van de regelaar
van Carrier. De kabel mag niet geklemd worden op de
buitenste isolatie.
• De componenten van regelsystemen moeten worden
geïnstalleerd in een omgeving die voldoet aan hun
beschermingsindex (IP).
• Het maximum vervuilingsniveau is gewoonlijk vervuilingsniveau 2 en installatie categorie II.
• De laagspanningsbedrading (communicatiebus) moet
gescheiden worden gehouden van de hoofdstroomkabels.
• Om interferentie met de communicatie verbindingen
te voorkomen:
- Houd laagspannings bedrading gescheiden van
hoofdstroomkabels en vermijd dezelfde kabelroute
te gebruiken (maximaal 300 mm gezamenlijk met
de 230 VAC, 30 A kabel).
- Voer laagspanningsbedrading niet door lussen in
de hoofdstroomkabels.
- Sluit geen hoge inductieve belastingen aan op de
elektrische voeding die wordt gebruikt als voeding
voor regelaars.
- Gebruik de door Carrier aanbevolen afgeschermde
kabel voor de regeling. Houd alle kabels aangesloten op hun respectievelijke regelaars.
Deze apparatuur voldoet aan de belangrijkste eisen van de
richtlijnen:
• Elektromagnetische compatibiliteit: 2004/108/EEC,
• Laagspannings Richtlijn: 2006/95/EEC.
3 - MONTAGE VAN DE 42EM UNIT
3.1 - Montage van de unit boven het verlaagd plafond
De unit mag niet zodanig worden opgesteld dat dit een
ongelijkmatige verdeling en/of terugstroming van de lucht
tot gevolg heeft. Het plafond moet voldoende glad zijn om
eenvoudige installatie van de unit mogelijk te maken, zonder dat dit gevaren met zich meebrengt. De draagconstructie
moet het gewicht van de unit kunnen dragen om vervorming, breuken of trilling tijdens het bedrijf voorkomen.
VOORZORGSMAATREGELEN: Verwijder tijdens de
installatie eventueel vuil en bouwafval uit de kanalen om
schade aan de unit te voorkomen.
3.2 - Montageprocedure
• Plaats de 42EM unit zo dicht mogelijk bij de plaats
waar hij moet worden gemonteerd. De montage in
een verlaagd plafond zal makkelijker verlopen
wanneer gebruik gemaakt wordt van een heflift en
een ladder (Fig. 6).
• Controleer of er voldoende vrije ruimte is voor onderhoudswerkzaamheden. Raadpleeg het schema met
vrije ruimtes voor onderhoudswerkzaamheden.
• Markeer de positie van de schroefdraadhangers aan
het plafond (als meerdere units worden geïnstalleerd
wordt aanbevolen om een boorsjabloon te gebruiken).
De bevestigingsmethode voor de schroefdraadhangers
(niet geleverd door Carrier) hang af van het type plafond
(maximum diameter van de schroefdraadhangers is
10 mm). Draai de eerste moeren vast nadat de schroefdraadhangers aan het plafond zijn bevestigd.
WAARSCHUWING: Til de unit niet op aan de condensaatafvoerbak of de wateraansluitingen, afsluiters, flexibele
leidingen of elektrische bedrading.
Til de unit op en plaats hem in lijn met de draadstangen.
Draai de moeren niet helemaal vast.
OPMERKING: De moeren mogen nu nog niet vast worden
aangedraaid en de unit mag niet strak tegen het plafond
worden geplaatst. Dit mag pas gebeuren nadat alle aansluitingen zijn gemaakt en de unit op afschot is geplaatst.
40
Page 41

Op afschot plaatsen van de unit (Fig. 7).
Plaats de unit dusdanig dat de condensaatafvoerbak ongeveer 0,5% lager ligt dan de andere kant van de unit. In de
andere richting (luchtstroomrichting) moet de unit zuiver
horizontaal zijn (Fig. 8).
• Neem de toevoerluchtkanalen los.
• Neem de flexibele condensaatafvoerleiding los. Ledig
de sifon in een geschikt reservoir.
• Ondersteun de unit en draai de vier moeren op de
draadstangen los. Laat de unit voorzichtig zakken.
Condensaatafvoerleiding (Fig. 9): Gebruik als condensaatafvoerleiding een flexibele slang (ø16 mm inwendig). De
condensaatafvoer moet worden gelegd met een afschot van
tenminste 20 mm/m (9a) over het horizontale leidingdeel.
Ook moet een sifon van minstens 50 mm (9b) worden aangebracht om te voorkomen dat rioollucht in de ruimte komt.
Indien meer units op één afvoer zijn geplaatst, moet een
inrichting worden aangebracht (Fig. 10).
Controleer, voordat de unit in bedrijf wordt gesteld, of het
water in de interne condensaatafvoerbak stroomt, door er
wat water in te gieten. Als u een probleem constateert, moet
de gradiënt van de afvoerpijp worden gecontroleerd en
gezocht worden naar mogelijke obstructies.
In alle gevallen moeten de verbindingskanalen bij de uitlaat
van de unit worden geïsoleerd, om te voorkomen dat zich
condensaat vormt op de wanden.
OPMERKING: De drukverliezen in het kanaal moeten in
overeenstemming zijn met de capaciteit van de units. De
binnenwanden van de kanalen moeten zo glad mogelijk
zijn. Vermijd scherpe bochten. Controleer op lekkage en
aanwezigheid van vuil en afval in de kanalen. Dit kan
namelijk schade veroorzaken aan de ventilator en de klep
van het uitblaasornament.
Wanneer de installatie is voltooid - d.w.z. de 42EM is aan het
plafond bevestigd, de luchtkanalen zijn voltooid, de waterverdeelstukken zijn aangebracht met de afsluitkleppen
gereed op de aansluitstompen en de elektrische installatie
is voltooid - kunnen de waterleidingen worden aangesloten
(Carrier adviseert buigzame waterleidingen, die als accessoire
kunnen worden geleverd). Elke buigzame leiding heeft een
1/2” gasaansluiting met schroefdraad, afhankelijk van het
model. Breng een pakking (niet door Carrier geleverd) aan
tussen de schroefaansluiting en de afsluitklep.
Nadat alle units zijn geïnstalleerd, open de afsluitkleppen
op de verdeelstukken, ontlucht de kringen en zet ze onder
druk. Ontlucht de batterijen door de ontluchtingsschroeven iets los te draaien. Daarna kan de unit in bedrijf
worden gesteld.
4 - COMPONENTEN
4.1 - Ventilatormotor
4.1.1 - Demontage van de ventilator
WAARSCHUWING: Schakel de hoofdstroom uit alvorens
werkzaamheden aan de unit uit te voeren.
Noteer de kabels voor de aangesloten ventilatorsnelheden.
Wanneer een ventilator of motor defect is moet het gehele
samenstel worden gedemonteerd en vervangen (Fig. 12).
• Verwijder het filter.
• Verwijder het toegangspaneel van de ventilator (12a).
• Neem de voedingskabels van de ventilator/motor los
(hoofd- en stuurstroombedrading voor motor met
variabel toerental).
• Demonteer de regelaar, indien toegepast (bevestigd
met schroeven), om toegang te krijgen tot de schroeven
van het paneel waarop de ventilator rust.
• De ventilator en het paneel worden op hun plaats
gehouden door vier torx borgschroeven (T20) (12b).
Verwijder deze schroeven, druk dan op de twee nokjes
aan weerszijden aan de onderkant van het paneel
waarop de ventilator rust en schuif de ventilator
omlaag (12c).
• Verwijder de ventilatormotor en ventilator.
OPMERKING: Raak tijdens de demontage de
schoepen niet aan om beschadiging en onbalans te
voorkomen.
• Voor units met elektrische verwarming (optie) moet de
voedingskabel naar het verwarmingselement worden
losgenomen. Trek de kabel uit de doorvoer.
• Verwijder de bevestigingsschroeven van de verwarmingselementen.
• Volg nadat de ventilatormotor is vervangen de bovenstaande procedure in omgekeerde volgorde.
WAARSCHUWING: De elektrische aansluitingen op de
ventilatormotor moeten worden gemaakt overeenkomstig
de labels op het klemmenblok.
NOOT: Schakel de stroomvoorziening pas in nadat alle
aansluitingen gemaakt en geaard zijn.
3.3 - Demontage
Schakel de hoofdstroom af d.m.v. de op het werk gemonteerde werkschakelaar (levering derden).
• Neem de voedingskabels en de verbindingskabels los.
• Sluit de afsluiters bij de verdeelstukken.
• Neem de flexibele waterslangen los door de gasaansluitingen los te draaien.
WAARSCHUWING: Omdat de flexibele waterslangen
niet zijn voorzien van afsluiters, moet een reservoir
worden geplaatst om de batterij af te tappen.
Motor met variabel toerental: scheid voorzichtig de hoofden stuurstroomkabels en trek ze zo ver mogelijk uit elkaar.
4.1.2 - Vervangen van de condensator (Fig. 13)
• Schakel de hoofdstroom uit alvorens werkzaamheden
aan de unit uit te voeren.
• Verwijder het filter.
• Verwijder het toegangspaneel van de ventilator.
• Verwijder de condensator die op het motorchassis is
bevestigd.
• Neem de platte connectors aan de achterzijde van de
condensator los.
• Vervang de condensator en volg daarna bovenstaande
procedure in omgekeerde volgorde.
41
Page 42

4.1.3 - Bedrading van de ventilator
Bedrading 42EM 0.5/1.0 (motor met meerdere toerentallen)
Een transformator voorziet de ventilatormotor van 6 toerentallen, waarmee de installateur een grote flexibiliteit heeft
bij het instellen van de luchthoeveelheden. Er kunnen 3
van de 6 beschikbare toerentallen worden geselecteerd,
waarbij rekening moet worden gehouden met de plaatselijke
elektromechanische en elektronische voorschriften (minimum toerental: klem 6, maximum toerental: klem 1).
• 42EM units voorzien van in de fabriek ingebouwde
Carrier regelaar: Fig. 14.
• Units zonder elektronische regeling: toegang tot 6
mogelijke ventilatorsnelheden van buitenaf op de
klemmenstrook (optie): Fig. 15 (15a = externe aansluiting, 15b = motor).
4.2.2 - Plaats van de batterij intrede/uitrede
Water intrede/uittrede, typen 0.5, 1 en 2: Fig. 18.
Water intrede/uittrede, type 3: Fig. 19.
LET OP: Houd rekening met de richting die de pijl aangeeft
op de kleppen, gebaseerd op de aansluitzijde en het type
klep.
4.3 - Kanaalaansluitingen
Deze zijn vervaardigd van kunststof, brandklasse VO, ongeveer gelijk aan M1 (Franse standaard). Ze zijn bevestigd
via de binnenzijde van de unit. De kanalen moeten op de
aansluitingen worden bevestigd met ronde slangklemmen of
tape. Schroeven of klinknagels mogen niet worden gebruikt.
Bedrading voor 42EM 2.1/2.2/2.3 en 42EM 3.1/3.2/3.3: Fig. 16
42EM type 2.1 42EM type 2.2 42EM type 2.3
42EM type 3.1 42EM type 3.2 42EM type 3.3
Nul (gezamenlijk)
Fase aangesloten
Niet aangesloten
Niet aangesloten
Bedrading informatie:
Min. toerental = klem 6 Middelste toerental = grijze kabel (14b)
Max. toerental = klem 1 Hoog toerental = zwarte kabel (14c)
Laag toerental = rode kabel (14a) L = Fase
Wit Wit Wit
1
Rood Blauw Zwart
2
Blauw Rood Rood
3
Zwart Zwart Blauw
4
4.2 - Waterbatterij
4.2.1 - Verwijderen van de batterij
WAARSCHUWING: Schakel de hoofdstroom uit alvorens
werkzaamheden aan de unit uit te voeren.
• Sluit de afsluiters op de waterslangen.
• Draai de aansluiting los om de flexibele waterslangen
te demonteren.
• Verwijder de servomotoren en noteer wat de koel- en
verwarmingskleppen zijn.
• Verwijder de flexibele condensaatafvoerleiding die
door een slangklem (levering derden) op zijn plaats
wordt gehouden.
• Verwijder de 2-weg of 4-weg waterregelkleppen.
Afhankelijk van de configuratie kan de koppeling van
de 4-weg klep zijn voorzien van een omschakelthermostaat koeling/verwarming. Is dit het geval dan mag deze
niet worden verwijderd.
• Verwijder de 4 torx schroeven (T20) en schuif de
batterij met condensaatafvoerbak naar buiten.
• Volg nadat de batterij is vervangen bovenstaande procedure in omgekeerde volgorde. Zorg dat alle pakkingen
worden vervangen en dat de intrede en uittrede aansluitingen naar de batterij op correcte wijze worden
gemaakt.
• Tijdens het vullen moet de batterij worden ontlucht.
WAARSCHUWING: Het klephuis moet voorzichtig op
de batterijen worden vastgedraaid (15 N·m is voldoende)
om beschadiging te voorkomen.
OPMERKING: De batterij-aansluiting kan op het werk
worden gewijzigd door de batterij met condensaatafvoerbak vanaf de andere kant in de unit te schuiven. Verwijder
hiervoor het paneel. Voor type 3 moeten de waterintrede
en uittrede worden omgedraaid om de gepubliceerde
capaciteit te behalen.
WAARSCHUWING: Om een goede lekdichtheid te garanderen moet het kanaal helemaal over de aansluiting vallen.
Controleer dat de maximale toevoerluchttemperatuur niet
hoger is dan 60°C.
Til de unit niet op aan de kanaalaansluitingen en zorg dat
ze niet beschadigd worden tijdens transport en montage.
4.4 - Optioneel filter en toegang tot het filter
4.4.1 - Beschrijving
De Carrier Atmosphera is voorzien van een 85% ASHRAE
gravimetrisch filter (G3) volgens EN 779. Media brandklasse M1, stalen frame.
Er zijn verschillende mogelijkheden voor toegang tot het
filter, afhankelijk van de plaats van opstelling:
• Unit zonder retourluchtplenum: Filter te verwijderen
vanaf de achterzijde van de unit.
• Unit met retourluchtplenum: Het filter kan worden
verwijderd vanaf de onderzijde.
4.4.2 - Vervangen van het filter
Luchtfilters moeten regelmatig worden vervangen. De
levensduur van het filter is afhankelijk van de mate van vervuiling, die weer afhankelijk is van de plaats van opstelling.
Als vervuilde filters niet worden vervangen kan de drukval
oplopen, waardoor stofdeeltjes los laten en in de toevoerlucht terechtkomen. Bovendien zal de capaciteit van de
Atmosphera verminderen door de lagere luchthoeveelheid.
OPMERKING: Let er bij montage boven een verlaagd
plafond op dat de toegang tot en verwijderen van het filter
niet wordt belemmerd door T-liggers.
4.5 - Verselucht
4.5.1 - Constant volume regelaar (optie)
De Atmosphera kan worden voorzien van een regelaar voor
constante verseluchthoeveelheid waarmee verselucht wordt
toegevoerd en de mate van luchtverversing kan worden
geregeld.
De volgende constant volume regelaars zijn beschikbaar:
Optie a: 8,3 l/s of 30 m3/h (-10%, +20%)
Optie b: 16,6 l/s of 60 m3/h (-10%, +20%)
42
Page 43

Opties a en b: De diameter van de behuizing van de constant
volume regelaar is 125 mm.
De 16,6 l/s (60 m3/h) constant volume regelaar kan op het
werk worden gemodificeerd door het verplaatsen of verwijderen van twee kunststof schuifjes om de maximum constante verseluchthoeveelheid te verhogen tot max. 44,4 l/s
(160 m3/h). Een label op de 42EM toont hoe de twee kunststof schuifjes moeten worden bijgesteld (Fig. 11).
Modificatieprocedure
• Neem het verseluchttoevoerkanaal los van de kunststof
aansluiting op de Atmosphera.
• Verwijder of verplaats de twee kunstsof schuifjes.
• Sluit het kanaal weer aan.
BELANGRIJK: Als de Atmosphera is voorzien van een
retourlucht temperatuuropnemer, mag de constante hoeveelheid verselucht niet hoger zijn dan 50% van de unit toevoerluchthoeveelheid bij minimum snelheid (de laagste
van de 6 beschikbare toerentallen).
OPMERKING: Voor een goede werking moet de verschildruk voor de 8,3 l/s (30 m3/h) constant volume regelaar
liggen tussen 50 Pa en 200 Pa en voor de 16,6 l/s (60 m3/h)
regelaar tussen 70 en 200 Pa.
4.5.2 - Variabel volume regelaar (optie)
De Atmosphera kan worden voorzien van een regelaar
voor variabele verseluchthoeveelheid van 0 tot 55 l/s (0 tot
200 m3/h).
Deze wordt aangesloten op de Carrier numerieke regeling
en kan de toevoer van verselucht op twee manieren regelen:
• een vaste, door de installateur ingestelde hoeveelheid
die naar wens kan worden aangepast,
• op basis van het CO2 niveau; in dit geval wordt de
regelaar aangesloten op een CO2 opnemer via de
Carrier numerieke regeling regeling (de CO2 sensor
bevindt zich tegenover de verselucht toevoer).
OPMERKING: Bij toepassing van de regelaar voor variabele verseluchthoeveelheid moet de druk stroomopwaarts
in het verseluchtkanaal 180 Pa zijn.
4.6 - Waterregelkleppen (optie)
Deze zijn van het type 2-weg of 4-weg en geschikt voor 16
bar bedrijfsdruk.
4.6.2 - Vervangen van de servomotor
De servomotoren op de gekoeld- en warmwaterkleppen
kunnen, zo nodig, worden vervangen.
• Schakel de hoofdstroom uit alvorens werkzaamheden
aan de unit uit te voeren.
• Neem de voedingskabel van de servomotor los.
- 230 V open/dicht servomotor toegepast met Carrier
numerieke regelaar. Neem de voedingskabel van de
servomotor los die met een connector is aangesloten.
- 230 V open/dicht servomotor toegepast met Carrier
elektronische ruimtethermostaat. Verwijder de
kunststof afdekkap, bevestigd met schroeven. Neem
de op de connectors aangesloten voedingskabel los.
Dit kan gebeuren door met een schroevendraaier
op het lipje te drukken en de kabel uit de betreffende klem te trekken.
c) Ontkoppel de defecte servomotor. Volg nadat de servo-
motor is vervangen de bovenstaande procedure in
omgekeerde volgorde.
WAARSCHUWING: Controleer dat de servomotor goed op
het klephuis is bevestigd (max. aandraaimoment 15 N·m).
4.6.3 - Vervangen van het klephuis
• Schakel de hoofdstroom uit alvorens werkzaamheden
aan de unit uit te voeren.
• Sluit de afsluiters op de waterslangen.
• Neem de flexibele waterslangen los door de aansluitingen los te draaien.
• Verwijder de servomotoren en noteer wat de koel- en
verwarmingskleppen zijn.
• Bevestig het nieuwe klephuis op de batterij. Gebruik
nieuwe pakkingringen.
• Verwijder de 2-weg of 4-weg waterregelkleppen.
Afhankelijk van de configuratie kan de koppeling van
de 4-weg klep zijn voorzien van een omschakelthermostaat koeling/verwarming. Is dit het geval dan mag
deze niet worden verwijderd.
• Monteer de servomotoren en controleer de goede aansluitingen op het klephuis.
• Bevestig de flexibele waterslangen door de aansluitingen vast te draaien. Gebruik nieuwe pakkingringen en
controleer dat deze goed zijn bevestigd (maximum
aandraaimoment 15 N·m).
• Open de afsluiters op de waterslangen en ontlucht het
systeem.
• Controleer op lekkage en schakel de hoofdstroom
weer aan.
4.6.1 - Elektrothermische servomotor (open/dicht)
De servomotor is van het type open/dicht, 230 V a.c.
Om de installatie met water te kunnen vullen, de watercircuits te egaliseren en de units te ontluchten moeten de
servomotoren worden aangesloten op de elektrische
voeding om de afsluiters te openen door een commando
van de ruimtethermostaat of het GBS.
WAARSCHUWING: Let er bij het vervangen van een klep
altijd op dat de stroomrichting door de klep hetzelfde is
als die op de afsluiter is gegraveerd. Als de stroomrichting
niet goed is zal het klephuis snel slijtage vertonen.
43
Page 44

W
4.7 - Flexibele waterslangen (optie)
Minimale buigradius:
• slangen niet geïsoleerd 72 mm
• slangen geïsoleerd 106 mm.
4.8 - Elektrisch verwarmingselement (optie)
Vervangen van het elektrisch verwarmingselement:
• Verwijder het filter.
• Verwijder het toegangspaneel van de ventilator.
• Noteer de kabels voor de ventilatorsnelheden die zijn
aangesloten op het klemmenblok van de transformator.
Neem de voedingskabel los.
• Verwijder de ventilatormotor en de ventilatoren.
WAARSCHUWING: Schakel de hoofdstroom uit alvorens
werkzaamheden aan de unit uit te voeren.
OPMERKING: Raak tijdens de demontage de
schoepen niet aan om beschadiging en onbalans te
voorkomen.
Als het elektrisch verwarmingselement defect is, moet het
worden vervangen; hiervoor moeten de ventilatormotor en
de ventilatoren worden gedemonteerd: Fig. 17 (17a =
schroeven).
• Neem de voedingskabel van het verwarmingselement
los en trek de kabel uit de doorvoer.
• Neem de bevestigingsschroeven van het verwarmingselement los.
WAARSCHUWING: Raak de metalen delen van het verwarmingselement niet aan zo lang het op de elektrische
• Volg nadat het verwarmingselement is vervangen
bovenstaande procedure in omgekeerde volgorde.
voeding is aangesloten.
5 - CODERING
Bedrading ventilatorsnelheid
Codering (laatste
cijfer) of optie 600
Rode kabel
Grijze kabel
instelling
Ventilator
Zwarte kabel
L kabel
Klemaanduiding (standaard bedrading), optie 600 niet geselecteerd
OPMERKING: Klem 1 = hoogste toerental, Klem 6 = laagste toerental.
Zes bedrade
toerentallen
LEC motor met
variabel toerental
Unit type Model
Modificatie-code
Batterijen
Productreferentie
Karakters
0 5
1 0
A 2-pijps rechts
2 1
B 2-pijps links
2 2
C 4-pijps rechts
2 3
D 4-pijps links
3 1
E 2-pijps/+ E-verw., rechts, lage capaciteit
3 2
F 2-pijps/+E-verw., links, lage capaciteit
3 3
G 2-pijps/+ E-verw., rechts, hoge capaciteit
H 2-pijps/+ E-verw., links, hoge capaciteit
B Modulaire uitvoering met 2 toevoerluchtaansluitingen
C Modulaire uitvoering met 3 toevoerluchtaansluitingen
G Modulaire uitvoering met 1 toevoerluchtaansluiting aan de kopse kant (in-line configuratie)
H Modulaire uitvoering met 1 toevoerluchtaansluiting aan de zijkant (U-configuratie)
J Modulaire uitvoering met 4 toevoerluchtaansluitingen
K Modulaire uitvoering met 5 toevoerluchtaansluitingen
M Retourluchtplenum 1 kanaalaansluiting en modulaire uitvoering 1 toevoerluchtaansluiting
(in-line configuratie)
N Retourluchtplenum 1 kanaalaansluiting en modulaire uitvoering 1 toevoerluchtaansluiting
(U-configuratie)
P Retourluchtplenum 2 kanaalaansluitingen en modulaire uitvoering 2 toevoerluchtaansluitingen
Q Retourluchtplenum 3 kanaalaansluitingen en modulaire uitvoering 3 toevoerluchtaansluitingen
R Retourluchtplenum 4 kanaalaansluitingen en modulaire uitvoering 4 toevoerluchtaansluitingen
S Retourluchtplenum 5 kanaalaansluitingen en modulaire uitvoering 5 toevoerluchtaansluitingen
T Compacte uitvoering met 1 retourluchtaansluitingen en 1 toevoerluchtaansluiting
U Compacte uitvoering met 2 retourluchtaansluitingen en 2 toevoerluchtaansluitingen
V Compacte uitvoering met 3 retourluchtaansluitingen en 3 toevoerluchtaansluitingen
4 2 E M N N C A A A A A A A A A
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16
{
- Geen kleppen
C Tweewegklep
D Vierwegklep
J Tweewegklep + flexible waterslangen
K Vierwegklep + flexible waterslangen
0 Geen klepmotoren
A 230 V open/dicht
Toevoer/ retour-
luchtplenum
Kleppen
Klepmotoren
Regeling
Opnemers
A G3 toegang vanaf de achterzijde
B G3 toegang vanaf de onderzijde
- Geen
A Retourluchtsensor
B Toevoerluchtsensor
C Omschakelopnemer
D A + B
E A + B + C
F A + C
G B + C
- Geen regeling of klemmenstrook
A NTC
B HDB
D NTC + IAQ print
E Klemmenstrook met kunststof afdekpaneel
F E + relais
G E + relais + zekeringhouder
K NTC + zekeringhouder
L NTC + IAQ print + zekeringhouder
M HDB + zekeringhouder
R E + zekeringhouder
Filter en toegang
tot het filter
Verse lucht
Motorbedrading
- Geen verselucht
A Verselucht aansluiting Ø 125 mm
B CV regelaar 8,3 l/s (30 m3/h)
C CV regelaar 16,6-44,4 l/s (21/28/36)
60-160 m3/h (75/100/130)
E Adapter gemotoriseerde adapter
verselucht toevoerklep ø 125 mm
J Verselucht aansluiting ø 125 mm
K CV regelaar 8,3 l/s (30 m3/h)
L CV regelaar 16,6-44,4 l/s (21/28/36)
60-160 m3/h (75/100/130)
N Adapter gemotoriseerde adapter
verselucht toevoerklep ø 125 mm
RECHTERZIJDE
LINKERZIJDE
44
Page 45

Page 46

Page 47

Page 48

Carrier is participating in the Eurovent Certification Programme. Products are as listed in the Eurovent Directory of Certified Products.
EN
Carrier participe au programme de certification Eurovent. Les produits figurent dans l’annuaire Eurovent des produits certifiés.
FR
Carrier ist am Zertifikationsprogramm Eurovent beteiligt. Die entsprechend gekennzeichneten Produkte sind im EUROVENT-Jahrbuch
DE
aufgeführt.
Questa azienda è membro del Programma di Certificazione EUROVENT. I prodotti sono elencati nel Directory Eurovent dei prodotti
IT
certificati.
La Compañia participa en el Programa de Certificación EUROVENT. Los productos se corresponden con los relacionados en el
ES
Directorio EUROVENT de productos certificados.
Carrier neemt deel aan het Eurovent Certificatie Programma. Producten voldoen aan de omschrijving in de Eurovent lijst van
NL
gecertificeerde producten.
Order No.: M4226, 01.2009 - Supersedes order No.: 14226, 12.2007
EN
The manufacturer reserves the right to change any product specifications without notice.
N° M4226, 01.2009 - Remplace N° 24226, 12.2007
FR
Le fabricant se réserve le droit de modifier sans préavis les spécifications du produit.
Bestellnr.: M4226, 01.2009 - Ersetzt Bestellnr.: 34226, 12.2007
DE
Nachdruck verboten. Änderungen vorgenommen.
No. ordine: M4226, 01.2009 - Rimpiazza no. ordine: 44226, 12.2007
IT
Il costruttore si reserva il diritto di cambiare senza preavviso i dati pubblicati.
No. de pedido: M4226, 01.2009 - Reemplaza no. de pedido: 84226, 12.2007
ES
El fabricante se reserva el derecho de hace cualquier modificación sin previo aviso.
Ordernr.: M4226, 01.2009 - Vervangt ordernr.: 94226, 12.2007
NL
Wijzingen voorbehouden.
Manufacturer: Carrier SCS Montluel, France
Printed in the Netherlands
Fabricant: Carrier SCS Montluel, France
Imprimé en Hollande
Hersteller: Carrier SCS Montluel, Frankreich
Printed in the Netherlands
Fabbricato per: Carrier SCS Montluel, Francia
Stampato in Olanda
Fabricado por: Carrier SCS Montluel, Francia
Impreso en Holanda
Geproduceerd door: Carrier SCS Montluel, Frankrijk
Gedrukt in Nederland
 Loading...
Loading...