Canon iR5570, iR6570 universal send kit-d1 Service Manual

Service Manual
Canon BW
Universal Send Kit-D1
Feb 22 2005


Application
This manual has been issued by Canon Inc. for qualified persons to learn technical theory, installation, maintenance, and
repair of products. This manual covers all localities where the products are sold. For this reason, there may be
information in this manual that does not apply to your locality.
Corrections
This manual may contain technical inaccuracies or typographical errors due to improvements or changes in products.
When changes occur in applicable products or in the contents of this manual, Canon will release technical information
as the need arises. In the event of major changes in the contents of this manual over a long or short period, Canon will
issue a new edition of this manual.
The following paragraph does not apply to any countries where such provisions are inconsistent with local law.
Trademarks
The product names and company names used in this manual are the registered trademarks of the individual companies.
Copyright
This manual is copyrighted with all rights reserved. Under the copyright laws, this manual may not be copied,
reproduced or translated into another language, in whole or in part, without the written consent of Canon Inc.
COPYRIGHT © 2001 CANON INC.
Printed in Japan
Caution
Use of this manual should be strictly supervised to avoid disclosure of confidential information.

Symbols Used
This documentation uses the following symbols to indicate special information:
Symbol Description
Indicates an item of a non-specific nature, possibly classified as Note, Caution, or Warning.
Indicates an item requiring care to avoid electric shocks.
Indicates an item requiring care to avoid combustion (fire).
Indicates an item prohibiting disassembly to avoid electric shocks or problems.
Introduction
Memo
REF.
Indicates an item requiring disconnection of the power plug from the electric outlet.
Indicates an item intended to provide notes assisting the understanding of the topic in question.
Indicates an item of reference assisting the understanding of the topic in question.
Provides a description of a service mode.
Provides a description of the nature of an error indication.

Introduction
The following rules apply throughout this Service Manual:
1. Each chapter contains sections explaining the purpose of specific functions and the relationship between electrical
and mechanical systems with reference to the timing of operation.
In the diagrams, represents the path of mechanical drive; where a signal name accompanies the symbol ,
the arrow indicates the direction of the electric signal.
The expression "turn on the power" means flipping on the power switch, closing the front door, and closing the
delivery unit door, which results in supplying the machine with power.
2. In the digital circuits, '1'is used to indicate that the voltage level of a given signal is "High", while '0' is used to
indicate "Low".(The voltage value, however, differs from circuit to circuit.) In addition, the asterisk (*) as in
"DRMD*" indicates that the DRMD signal goes on when '0'.
In practically all cases, the internal mechanisms of a microprocessor cannot be checked in the field. Therefore, the
operations of the microprocessors used in the machines are not discussed: they are explained in terms of from
sensors to the input of the DC controller PCB and from the output of the DC controller PCB to the loads.
The descriptions in this Service Manual are subject to change without notice for product improvement or other
purposes, and major changes will be communicated in the form of Service Information bulletins.
All service persons are expected to have a good understanding of the contents of this Service Manual and all relevant
Service Information bulletins and be able to identify and isolate faults in the machine."


Contents
Contents
Chapter 1 Specifications
1.1 Product composition.......................................................................................................................................... 1- 1
1.1.1Product configuration .................................................................................................................................. 1- 1
1.2 Specifications .................................................................................................................................................... 1- 3
1.2.1Specifications .............................................................................................................................................. 1- 3
Chapter 2 Functions
2.1 New Function .................................................................................................................................................... 2- 1
2.1.1Authentication at TX ................................................................................................................................... 2- 1
2.1.2Encrypted transmission ............................................................................................................................... 2- 5
2.1.3Authentication at RX................................................................................................................................... 2- 6
2.1.4Encrypted reception..................................................................................................................................... 2- 9
2.1.5MAC Address Block Function .................................................................................................................. 2- 11
2.1.6URL Send .................................................................................................................................................. 2- 11
2.1.7Setting for communicate SSL.................................................................................................................... 2- 12
2.1.8Initialization of all data and settings.......................................................................................................... 2- 12
2.1.9Backup of Mail Box .................................................................................................................................. 2- 15
Chapter 3 Installation
3.1 Installation procedure ........................................................................................................................................ 3- 1
3.1.1Overview of the Installation Procedure....................................................................................................... 3- 1
Chapter 4 Maintenance
4.1 Notes when service............................................................................................................................................ 4- 1
4.1.1Points to Note ............................................................................................................................................. 4- 1
4.2 Troubleshooting................................................................................................................................................. 4- 2
4.2.1Troubleshooting........................................................................................................................................... 4- 2
4.3 Related Error code............................................................................................................................................. 4- 6
4.3.1E-mail Transmission errors ......................................................................................................................... 4- 6
4.3.2I-Fax Transmission errors ......................................................................................................................... 4- 10
4.3.3I-Fax Reception errors............................................................................................................................... 4- 15
4.3.4SMB Transmission errors.......................................................................................................................... 4- 19
4.3.5FTP Transmission errors ........................................................................................................................... 4- 22
4.3.6NCP Transmission errors .......................................................................................................................... 4- 24
4.3.7Box Transmission errors ........................................................................................................................... 4- 26
4.4 Related Service Mode ..................................................................................................................................... 4- 28
4.4.1Related Service Modes List....................................................................................................................... 4- 28
4.4.2Invalidating the License for Transfer to a Different Device (Level 2)......................................................4- 29


Chapter 1 Specifications


Contents
Contents
1.1 Product composition........................................................................................................................................... 1-1
1.1.1 Product configuration .................................................................................................................................. 1-1
1.2 Specifications ..................................................................................................................................................... 1-3
1.2.1 Specifications .............................................................................................................................................. 1-3


1.1 Product composition
Chapter 1
1.1.1 Product configuration
This kit consists of:
- License access number certificate sheet
- Sending and Facsimile Guide
- License Key notice
Using this kit, you can get a license key from the License Management System (LMS) and register it in an iR/
imageRUNNER to activate the specific feature included in the System Software.
Note:What's LMS?
A license server system to activate software options of iRs/imageRUNNERs, provided by Canon Inc. Collectively
manages options in the form of licenses and protects copy rights of optional products. The options are activated with
license keys being different from conventional activation measures that use dongles and PCs. Whereas the details
of its management differ among countries and regions, it is designed assuming the users access it and activate
licenses by themselves respectively. Per optional product, the license access number certificate sheet is supplied.
Per license access number, a user can get a license key and activate the feature on an iR/imageRUNNER. To get a
license key, a user accesses the Web server of the LMS.
URL for LMS:
http://www.canon.com/lms/ir/
0008-4667
When a user enters the license access number and the serial number for an iR/imageRUNNER in the LMS, 24-digit
figure of a license key is generated. The license key includes the information of serial number for the iR/
imageRUNNER so that the key cannot be used for iRs/imageRUNNERs. Once the option is activated, the option
information is saved as the backup in the iR/imageRUNNER. Parts replacement will not deactivate the feature.
The staff in each regional headquarters can access the administrator's pages of the LMS. They can view the license
number issued for each iR/imageRUNNER and can reissue the license. The procedures are the same as the license
management system for MEAP except for the point the license key is used instead of the license file.
Transfer of a License
An optional function that has been enabled by the LMS may be used on a different device by transferring its license,
as when the original iR device needs to be replaced, say at the end of its lease arrangement. Specifically, individual
licenses registered for optional functions must first be invalidated in Addtional Functions before transfer may take
place. Doing so will invalidate the optional functions on the source iR device and, at the same time, proof of
invalidation will be generated within the device in the form of an invalidation license key. The user may then
communicate the indicated invalidation license key, the serial number of the original iR device, and the serial number
1-1

of the new iR device to the Sales Company, which in turn may issue a new license key for the new iR device. The
user now may register the new license key to the new iR device in Addtional Functions, thereby enabling the optional
function on the new iR device. For details of transferring a license in service mode, see the descriptions of service
mode that come later.

1.2 Specifications
Chapter 1
1.2.1 Specifications
<SEND function basic specifications>
E-mail transmission
- Transmission protocol: SMTP, POP3
- Transmission authentication: SMTP AUTH, POP before SMTP
- Reception authentication: POP3, APOP, POP AUTH
- Encoded transmission: Corresponds to SSL communication in each protocol when SMTP transmission and SMTP
and POP reception. (The server side needs to correspond.)
- Key and certificate: Server certificate that the device has is used when SSL communication.
- Supported formats: TIFF (monochrome), PDF (monochrome), PDF (OCR) = Searchable PDF
However, encrypted PDF and searchable PDF are the options.
- PDF files can be split and sent page by page.
- Resolution: 100 X 100, 150 X 150, 200 X 100, 200 X 200, 200 X 400, 300 X 300, 400 X 400, 600 X 600 (dpi)
- Document size: A3 to A5
A3, B4, A4 (I-Fax Tx/Rx, A3/B4 transmission possible by setting other party's reception conditions)
- Addresses available from LDAP server (e-mail address and FAX telephone number)
Max. number of searching: 2000; The number of broadcasting selection after searching: 64
- No E-mail reception function. Error mails can be printed out.
When broadcasting transmission, display/write all the addresses in the To: field and separate every 100 addresses to
send.
0008-4670
I-Fax Tx/ Rx function
- Transmission protocol: SMTP (Tx/ Rx), POP3 (Rx), I-Fax (Simple mode, Full mode)
- Transmission authentication: SMTP AUTH, POP before SMTP
- Reception authentication: POP3, APOP, POP AUTH
- Encoded transmission: Corresponds to SSL communication in each protocol when SMTP transmission and SMTP
and POP reception. (The server side needs to correspond. When the server-less transmission, the encoded
transmission is not executed. )
- Key and certificate: Server certificate that the device has is used when SSL communication.
- Supported formats: TIFF (monochrome: MH, MR MMR) , Not supported when sending/receiving the color data.
- Resolution: 100 X 100, 150 X 150, 200 X 100, 200 X 200, 200 X 400, 300 X 300, 400 X 400, 600 X 600 (dpi)
- Document size: A3 to A5
- Reception sizes: A3, B4, A4
- Server-less transmission supported
- Addresses available from LDAP server (e-mail address and FAX telephone number)
Max. number of searching: 2000; The number of broadcasting selection after searching: 64
- When broadcasting transmission, display/write all the addresses in the To: field.
File transmission function
1-3

- Transmission protocol: SMB (NetBios over TCP/IP), FTP(TCP/IP), NCP(IPX)
- Supported formats: TIFF (monochrome), PDF (monochrome), PDF (OCR)
However, encrypted PDF and searchable PDF are the options.
- PDF files can be split and sent page by page.
- Resolution: 100 X 100, 150 X 150, 200 X 100, 200 X 200, 200 X 400, 300 X 300, 400 X 400, 600 X 600 (dpi)
- Document sizes: A3, B4, A4
- CanonFTP automatically distinguishes responses from the server and switches operation accordingly.
E-mail/I-fax operation confirmed server applications
SMTP server
Sendmail 8.93 or later
Exchange Server 5.5+SP1 or later
Exchange 2000
Domino R4.6 or later
SMTP AUTH-enabled SMTP server
Sendmail 8.12.5 or later + Cyrus SASL API 1.5.28 combination
Exchange Server 5.5+SP1 or later
Exchange 2000
POP server
Qpopper 2.53 or later
Exchange Server 5.5+SP1 or later
Domino R4.6 or later
Exchange 2000
Qpop v4.0.5
POP before SMTP
Sendmail 8.12.5 or later +DRAC 1.11 or later +Qpopper 2.53 or later combinations
POP authentication function-enabled server
Exchange 2000Server: NTLM authentication when the integration authentication operation:
Qpop v4.0.5: STLS, APOP. However, OpenSSL and Popauth need to be installed.
POP authentication function of main PC mail clients
Outlook 2000:NTLM
Outlook Express 6:NTLM
Becky 2.05:APOP
WinBiff 2.42:APOP
Eudora 5.1:STLS, APOP, Kerberos
File transmission operation confirmed operating environments
SMB

Windows 98/ME
Windows NT 4.0 Workstation/Server SP6a
Windows 2000 Professional/Server SP1
Windows XP Home/Professional
Windows Server 2003
Sun Solaris (SPARC) 2.6 or later
RedHat Linux7.2
MacOS 10.2.x
MacOS 10.3.x
FTP
Windows NT 4.0 Server + IIS4.0
Windows 2000 Professional/Server + IIS5.0
Windows XP Professional + IIS5.1
Windows Server 2003
Sun Solaris (SPARC) 2.6 or later
RedHat Linux7.2
Mac OS 10.x.x
NCP
NetWare 3.20
NetWare 4.1, 4.11, 4.2
NetWare 5 +SP1a
NetWare 5.1


Chapter 2 Functions


Contents
Contents
2.1 New Function ..................................................................................................................................................... 2-1
2.1.1 Authentication at TX ................................................................................................................................... 2-1
2.1.2 Encrypted transmission ............................................................................................................................... 2-5
2.1.3 Authentication at RX................................................................................................................................... 2-6
2.1.4 Encrypted reception..................................................................................................................................... 2-9
2.1.5 MAC Address Block Function .................................................................................................................. 2-11
2.1.6 URL Send .................................................................................................................................................. 2-11
2.1.7 Setting for communicate SSL.................................................................................................................... 2-12
2.1.8 Initialization of all data and settings.......................................................................................................... 2-12
2.1.9 Backup of Mail Box .................................................................................................................................. 2-15


2.1 New Function
Chapter 2
2.1.1 Authentication at TX
When the mail server is set on the internet, you need to prevent from Third Party Mail Relay that the third party uses
the false name. Third Party Mail Relay means that the third party sends large amount of spam mails using the mail
server which other people are operating. If you do not take any measures for this, resources like server and network
lines are exhausted and at the same time, you will get the claim from the user who received the spam mail. As a
measure, the authentication operation when SMTP transmission is prepared.
In case of the inner network (LAN), you can prevent from Third Party Mail Relay by restricting the IP address and
the domain name. In order to send from the outside domain using the mail address or securely use the mail server set
on the internet which the provider prepares, the authentication is indispensable at the transmission. This machine uses
two authentication methods, POP Before SMTP and SMTP AUTH and they enable to send i-FAX and e-mail to
SMTP server which requests the sender's authentication.
POP before SMTP
With this method, before SMTP transmission is performed, the POP server is logged into. SMTP transmission can
only be continued once the POP server has confirmed the IP address of the connected client as authorized within a
specific period of time. After user authentication is carried out at the POP server, the authenticated client IP address
is relayed to the SMTP server, where it is processed. The process requires a certain amount of time. Taking this
processing time into consideration, there is an idle period of 300msec, from POP authentication to the start of SMTP
transmission. If a POP before SMTP transmission is generated during POP reception, POP authentication is made
to wait until the reception is finished and then POP authentication and SMTP transmission are performed. Errors
occurring while the POP server is connected are treated as transmission errors.
0008-4675
With regard to the actual programming, all that is necessary is for System Settings > Network Settings > E-Mail/
I-Fax > Authent./ Encryption > POP Authentication bofore Sending to be set to ON.
Related new user error codes are #810 and #813. For details, refer to Troubleshooting.
SMTP AUTH
In SMTP AUTH, user authentication is performed when the SMTP server is connected, so that mail can only be
received from registered users. This method was standardized in March, 1999, as RFC2554. SMTP AUTH uses
ESMTP protocol, which is an extension of SMTP, and uses the SASL (Simple Authentication and Security Layer)
authentication mechanism, standardized as RFC2222, to authenticate the user by sending the user name and
password information in response to the server challenge data.
<Authentication mechanisms>
The SMTP server can have multiple authentication mechanisms and the most suitable authentication mechanism is
programmed in accordance with the security policy decided by the SMTP server administrator. The client E-Mail
client application selects the authentication algorithm from among the available authentication mechanisms and
performs authentication upon transmission.
This model supports the following five types of authentication mechanism.
2-1

CRAM-MD5
Challenge-Response Authentication Mechanism, computed by using the key-protected MD5 algorithm by HMAC-
MD5 (RFC2104)
NTLM
Windows NT authentication method
User name must be set in the form 'username@NTdomainname'
E.g.:
Windows2000 or earlier: username\\CANON (domain name may be omitted, depending on the environment)
Windows2000: username@canon.co.jp (domain name may be omitted, depending on the environment)
GSSAPI
Authentication system using Kerberos Version 5 (RFC1510)
User name must be set in the form 'username@realmname'.
username@CANON.CO.JP
(In Exchange2000, realm name = domain name)
PLAIN
Assumes that user name and password are sent as plain text (BASE64 encoded) and the communication packet is
encoded. (RFC2595) Allows secure authentication when used in combination with the encoded transmission
described later.
LOGIN
Sends the user name and password as plain text (BASE64 encoded). Actual transaction is the same as with PLAIN.
Similarly, allows secure authentication when used in combination with encoded transmission.
<SMTP AUTH transmission operation>
Even if the unit is programmed for transmission with SMTP AUTH, if the mail server does not support SMTP AUTH
and the encoding system supported by the server does not match that supported by this model, SMTP AUTH
transmission will not be possible. In that case, even if SMTP AUTH is programmed, transmission will be by normal
SMTP and there will be no transmission error generated. If an unauthenticated mail transmission is attempted to a
server that will not allow such transmission, subsequent SMTP protocols will generate an error in the mail server.
Unauthenticated mail can be transmitted to a server that will accept such transmission. These security policies are
determined by the server so, even if SMTP AUTH is not programmed, it is impossible to tell whether transmission
is possible without checking with the customer's server administrator.
<Authentication protocol>
Examples of transmission protocol using SMTP AUTH are given below.
The EHLO response from the client tells whether SMTP AUTH is supported by the server and the authentication
algorithm being used at that time is described. In the event that there are multiple authentication algorithms, multiple
algorithm names are described. The client selects one of the relayed authentication algorithms and then relays it on
to the server. Server challenge data come from the server and coded data made up from the server challenge data,
user name and password are returned in response for authentication. In general, the authentication algorithm to be

Chapter 2
used can be selected on the server side and PLAIN and LOGIN authentication and others which are undesirable from
the perspective of security can be blocked by the server setting. (Security policy is determined by the server.)
Server:220 smtp.example.com ESMTP server ready
Client(iR):EHLO ifax.example.com
S: 250-smtp.example.com
S: 250-DSN
S: 250-EXPN
S: 250 AUTH CRAM-MD5 DIGEST-MD5 : <- server declares authentication algorithm
C: AUTH CRAM-MD5 : <- client selects CRAM-MD5
S: 334 : <- server response (subsequently, authentication begins with CRAM-MD5.)
S: PENCeUxFREJoU0NnbmhNWitOMjNGNndAZWx3b29kLmlubm9zb2Z0LmNvbT4=
C: ZnJlZCA5ZTk1YWVlMDljNDBhZjJiODRhMGMyYjNiYmFlNzg2ZQ==
S: 235 Authentication successful.
<Authorisation algorithm selection>
Where the SMTP has multiple authentication mechanisms, selection is made in the order of the priority list given
below.
1) CRAM-MD5
2) NTLM
3) GSSAPI
4) STARTTLS operation PLAIN
5) STARTTLS operation LOGIN
6) STARTTLS non-operation LOGIN
7) STARTTLS non-operation PLAIN
Authentication methods can be disabled in service mode. When the service mode value is set to '1', the encoding
system can be disabled. (The default setting is all enabled.)
Ordinarily, the default setting is used, but if the server administrator wants to disable a particular encoding system,
the settings need to be changed by the service mode settings.
<SMTP AUTH related user modes>
For the actual SMTP AUTH settings, system administrator settings > network settings > E-Mail/ I-Fax > Authent./
Encryption > SMTP Authentication (SMTP AUTH) should be set ON and the required user names and passwords
for SMTP AUTH need to be entered. If SSL permission, which is the encoded transmission setting, described later,
is ON, with PLAIN and LOGIN authentication, the authentication encoded by the STARTTLS command can be
used.
<Outlook Express example>
For reference, this section describes what happens to the Outlook Express settings when using an SMTP server that
supports SMTP AUTH. Outlook Express PLAIN authentication only.
1) From the Outlook Express tools menu, select Accounts. In the example, pop3.canon.com is selected.
2-3
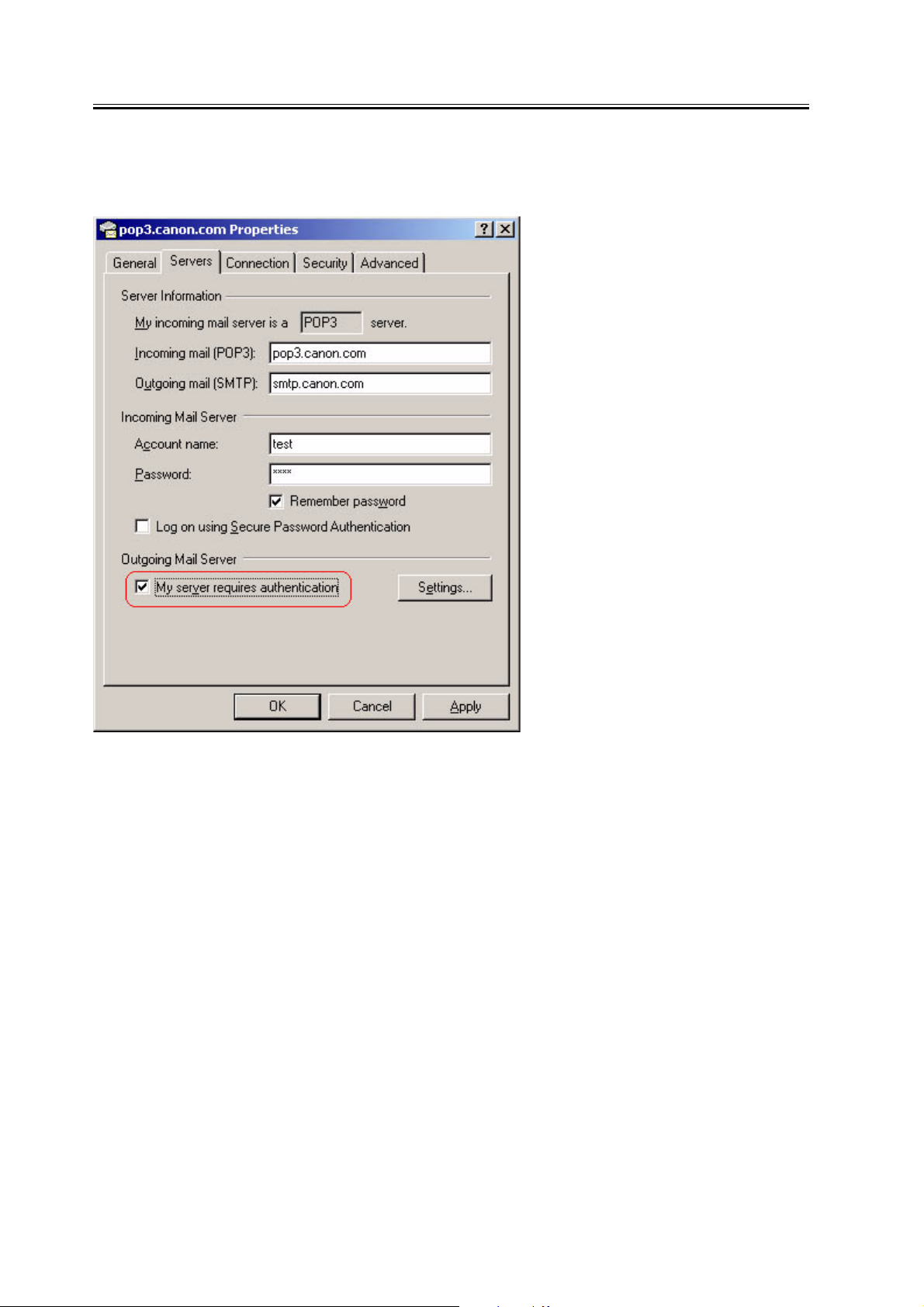
Chapter 2
2) From Internet Accounts, select the desired account and click on Properties. In the example, the pop3.canon.com
server tab has been selected from the Properties window.
3) Put a check in the 'My server requires authentication' box against the OutGoing mail server.
F-2-1
4) Press the settings button that has been made active.
5) Programme the transmission mail server window's logon information. In the default, 'use same settings as my
incoming server' is selected. This setting uses the POP3 authentication account name and password entered against
the reception mail server in the previous window and performs SMTP AUTH operation.
2-4
 Loading...
Loading...