Canon iR3250 Owner's Manual

Network Guide
Please read this guide before operating this equipment.
After you finish reading this guide, store it in a safe place for future reference.

Network Guide
iR3250

Preface
Thank you for purchasing the Canon iR3250.
This manual describes the machine, its functions, and its methods of use. It also describes the
various precautions to be observed in order to ensure safe operation. Please read this manual
thoroughly before operating the machine in order to familiarise yourself with its capabilities, and to
make the most of its many functions. After reading this manual, store it in a safe place for future reference.
CAUTION:
In this manual, CAUTION MESSAGES with this symbol indicate that neglecting the
suggested procedure or practice could result in personal injury.
NOTICE:
Considerable effort has been made to make sure that this manual is free of inaccuracies and
omissions. However, as we are constantly improving our products, some of the data contained
herein may not exactly reflect the current model of the particular product with which this manual
has been included. If you have a need for an exact specification, please contact Canon for the
current specification.
Copyright © 2000 Canon Inc. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED.
2

About Trademarks
Microsoft, MS-DOS, Windo ws , and Windows NT are registered trademarks of Microsoft Corporation
(US) in the U.S and other countries.
Apple, AppleTalk, EtherTalk, LocalTalk, Macintosh, and Power Macintosh are trademarks of Apple
Computer, Inc. (US).
Adobe, PostScript and PostScript 3 are trademarks of Adobe Systems Incorporated.
NetWare and Novell are registered trademarks, and IPX/SPX is a trademark of Novell Inc. (US),
©1996 Novell Inc., all rights reserved.
Ethernet is a trademark of Xerox Corporation (US).
UNIX is a registered trademark exclusively licensed to X/Open Company, Ltd. in the US and other
countries.
IBM is a trademark of International Business Machines Corporation (US).
Sun, Sun Microsystems, and SunOS are trademarks of Sun Microsystems (US) in the U.S. and
other countries.
Canon is a registered trademark and NetSpot is a trademark of Canon Inc.
Names of other companies or products appearing in this document are registered trademarks or
trademarks of the respective companies.
About Abbreviations
In this guide:
Microsoft
Microsoft® Windows® 98 is referred to as Windows 98.
Microsoft® Windows NT® is referred to as Windows NT.
Microsoft® Windows® 2000 is referred to as Windows 2000.
®
Windows® 95 is referred to as Windows 95.
About Trademarks
3

About the Manuals for the Machine
Printed Manual
Setup Guide
The
Setup Guide
ods from the computer through producing printed output.
Online Manuals
User's Guide
The
User’s Guide
User's Guide
Reference Guide
The
Reference Guide
the user’s conditions and environment. For example, you can set the amount of time before the
machine goes into the sleep mode when unused, you can turn on and off various automatic features, and you can set up security features.
Maintenance Guide
The
Maintenance Guide
jams, and solve other hardware problems with the machine.
gives a general overview of the machine, and also describes simple setup meth-
describes the principal functions and basic operations of the machine. Turn to this
for general operating instructions.
describes how to set up and change various functions of the machine to suit
describes how to load paper and toner, clean the machine, remove paper
Remote UI User’s Guide
The
Remote UI User’s Guide
variety of settings using the Remote UI.
describes the main features of the Remote UI and how to change a
PostScript/PCL Reference Guide
The
PostScript/PCL Reference Guide
as well as how to handle printing problems that may occur.
describes the basic uses of the machine’s printer functions,
PCL Driver Guide
The
PCL Driver Guide
change the factory print settings.
describes the main features of the printer functions, and tells you how to
Network Guide (This Document)
This
Network Guide
as e-mail/I-fax settings, and settings for sharing files sent from the machine to a network server.
describes settings for connecting the machine to a network for printing, as well
Fax Reference Guide
The
Fax Reference Guide
change the factory settings for the fax functions.
4
About the Manuals for the Machine
describes the main features for sending and receiving faxes, and how to

How This Manual Is Organized
Chapter 1 Before You Start
Describes system and network environments required for using the machine on a network.
Chapter 2 Using a TCP/IP Network
Describes procedures for setting up the machine on a TCP/IP network.
Chapter 3 Using a NetWare Network (Windows)
Describes procedures for setting up the machine on a NetWare network.
Chapter 4 Using an AppleTalk Network
Describes procedures for setting up the machine on an AppleTalk network.
Chapter 5 Using the Network and Printer Settings with NetSpot
Describes how to use NetSpot software for network and printer management.
Chapter 6 Appendix
Describes troubleshooting procedures and methods for checking the machine's network settings,
provides lists of network menus accessed from the control panel, and lists the principal network
specifications of the machine.
How This Manual Is Organized
5

Table of Contents
About Trademarks. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3
About the Manuals for the Machine. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4
How This Manual Is Organized. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
Table of Contents . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
How to Use This Manual . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
Symbols Used in This Manual . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
Chapter 1 Before You Start
System Environment Requirements . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1-2
System Environment Requirements for Printing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1-2
System Environment Requirements for Using E-mail/I-Fax. . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1-3
System Environment Requirements for File Sharing. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1-3
Checking Your Network Environment. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1-4
Sample Windows 95/98/NT/2000 Network (With a NetWare Server) . . . . . . .1-4
Sample Windows 95/98/NT/2000 Network (Without a
NetWare Server) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1-5
Sample Macintosh Network. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1-5
Sample UNIX Network. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1-6
Using a Network With Various Types of Computers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1-6
Chapter 2 Using a TCP/IP Network
TCP/IP Network Setup Operating Procedures . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2-2
Setup Preparations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2-2
E-mail/I-Fax Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2-2
Printing Settings. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2-3
File Sharing Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2-3
Protocol Settings. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2-5
Settings from the Control Panel. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2-5
Setting Up a Computer for Printing (Windows) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2-14
Connecting to a TCP/IP Network. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2-14
Installing the Printer Driver and Specifying the Printer
Destination Setting. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2-14
Print Server Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2-22
Setting Up a Computer for Printing (UNIX) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2-23
File Sharing Settings. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2-25
Using Windows 95/98 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2-25
Using Windows NT 4.0 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2-28
Using Windows 2000. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2-36
Using UNIX . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2-43
6
Table of Contents
Chapter 3 Using a NetWare Network (Windows)
NetWare Network Setup Operating Procedures. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-2
Printing Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .3-2
File Sharing Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .3-3
NetWare Print Service Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .3-4
Types of Print Service . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .3-4
Setup Using NetWare Administrator . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-5
Setup Using PCONSOLE . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .3-6
Protocol Settings. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .3-9
Settings from the Control Panel. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-9
Setting Up a Computer for Printing. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-12
Connecting to a NetWare Network . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .3-12
Installing Printer Drivers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .3-12
Setting the Printer Destination. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .3-12
File Sharing Settings. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .3-13
Chapter 4 Using an AppleTalk Network
AppleTalk Network Setup Operating Procedures . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .4-2
Printing Setup . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .4-2
Macintosh Network Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .4-3
Protocol Settings. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .4-4
Settings from the Control Panel. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-4
Chapter 5 Using the Network and Printer Settings with NetSpot
Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-2
Minimum Requirements. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-2
Related Documentation. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .5-3
Installing and Using NetSpot . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .5-4
Installation (Windows 95/98/NT/2000). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-4
Installation (Macintosh) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-4
Installation (UNIX) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .5-5
Configuration. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-6
Overview of Network Device Management . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .5-6
Chapter 6 Appendix
Troubleshooting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-2
Printing Problems and Solutions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .6-2
File Sharing Problems and Solutions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .6-4
Control Panel Menu List. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .6-7
To Confirm Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-9
Specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-10
Table of Contents
7

Hardware Specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .6-10
Software Specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .6-10
Index . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .6-11
8
Table of Contents
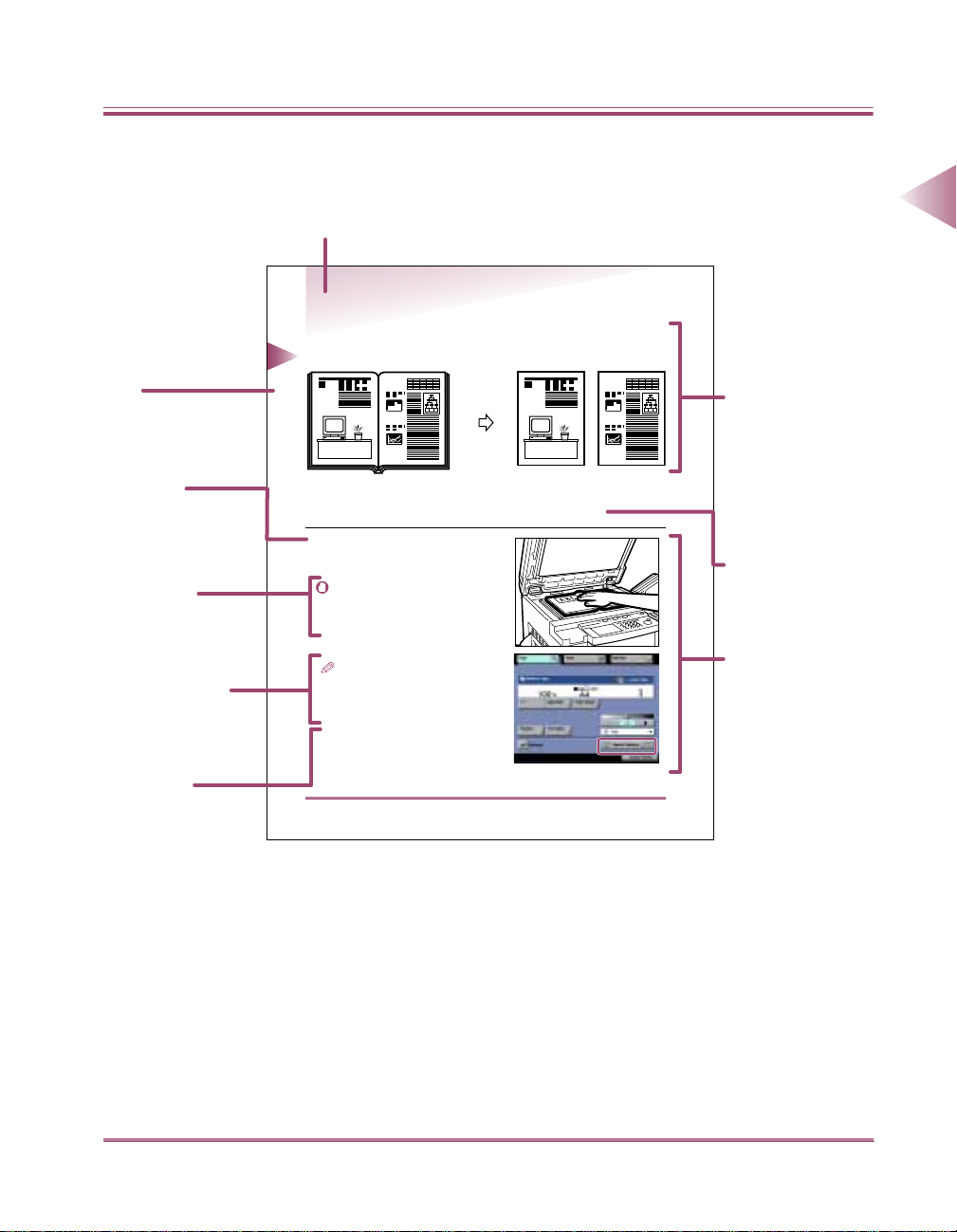
How to Use This Manual
This manual is organized as shown.
Main Heading
Copying Facing Pages onto Separate Pages (2-page Separation)
This feature enables you to copy facing pages in a book or magazine on separate sheets
of copy paper in a single step.
Original Copy
Chapter Heading
Operation
Instructions
Numbered steps
describe how to set and
operate various
functions.
Cautionary
Information
Presents cautionary
information or warnings
related to operation.
Supplementary
Description
Provides supplementary
description of operations
or reference information.
Reference
Page and chapter
numbers containing
related items are
provided.
(Special Features)
Features
Making Copies Using Special
3
Making Copies of Facing Pages in a Book onto Two Separate
Copy Sheets in One Step (Two Page Separation)
Place your original on the platen glass,
1
and press the [Special Features] key.
IMPORTANT
¥ Two Page Separation mode cannot be combined with
the use of the Transparency Interleaving,
Image Combination, Image Separation, Two-sided
Copy, Booklet, and Multi-PG Enlarge modes.
NOTE
¥ If you want to make copies in page order, begin copying
from the first pages and work your way forward.
¥ Place the original face down so that the original’s top
edge is against the back edge of the platen glass.
(See p. 2-20.)
Making Copies of Facing Pages in a Book onto Two Separate Copy Sheets in One Step (Two Page Separation)
3-2
The above page does not actually exist in this manual.
11
Description of
Modes and
Operations
Illustration provides
easy-to-understand
description of the
results of the
operation.
Sub-heading
Illustration
Shows key location,
status of operation, etc.
How to Use This Manual
9

Symbols Used in This Manual
IMPORTANT
NOTE
Key names are shown in this manual as follows:
Control panel keys.................. key
Touch panel display keys..........[OK]
Indicates important items or prohibited actions that should always be
observed when operating the machine. These should always be read to
avoid damage to the machine or improper operation.
Indicates items for reference or supplementary information that should
be noted by users.
Start
10
How to Use This Manual

1
Before You Start
This chapter describes what you need to know before you start using the machine, including the
network environments the machine is compatible with, and how to check the netw ork environment
you are using.
System Environment Requirements. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-2
System Environment Requirements for Printing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-2
System Environment Requirements for Using E-mail/I-Fax. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-3
System Environment Requirements for File Sharing. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-3
Checking Your Network Environment. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-4
Sample Windows 95/98/NT/2000 Network (With a NetWare Server) . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-4
Sample Windows 95/98/NT/2000 Network (Without a NetWare Server). . . . . . . . . . . 1-5
Sample Macintosh Network. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-5
Sample UNIX Network. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-6
Using a Network With Various Types of Computers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-6
CHAPTER
Before You Start
1
1-1

System Environment Requirements
System Environment Requirements for Printing
The following network and system environments are compatible when printing with the machine.
●
Printing using a TCP/IP network:
Compatible OS: Microsoft Windows 95/98
Microsoft Windows NT Server 4.0
Microsoft Windows NT Workstation 4.0
Microsoft Windows 2000 Server
Before You Start
1
Compatible computers: Windows 95/98/NT/2000; IBM PC/compatibles
●
Printing using a NetWare
Compatible servers: Novell NetWare Version 3.2/4.1/4.11/4.2/5
Compatible clients: Microsoft Windows 95/98
Compatible computers: IBM PC/compatibles
Microsoft Windows 2000 Professional
Solaris Version 1.1x (SunOS Version 4.1x) or later
Solaris Version 2.5x (SunOS Version 5.5x) or later
network:
Microsoft Windows NT Server 4.0
Microsoft Windows NT Workstation 4.0
Microsoft Windows 2000 Server
Microsoft Windows 2000 Professional
●
Printing using an AppleTalk network:
Compatible AppleTalk: EtherTalk Phase2
For more information on the OS and computers supported, see the
IMPORTANT
• If you are using Windows NT 4.0, you will need to install Service Pack 5 or later.
• The machine does not support Macintosh LocalTalk networks.
1-2
System Environment Requirements
Setup Guide
.
System Environment Requirements for Using E-mail/I-Fax
●
The following system environment is required for using the e-mail/I-fax functions.
The machine sends e-mail/I-fax messages to mail servers using the SMTP protocol.
The machine can receive incoming e-mail/I-fax messages from a mail server using the POP3 protocol or directly using the machine’s own SMTP receiving function.
If the latter method is used, it is not necessary for the mail server to support the POP3 protocol.
Compatible mail forwarding server software: Sendmail 8.9.3
Microsoft Exchange Server 5.5 + SP2
Lotus Domino R5
Compatible mail receiving server software: qpopper 2.43
Microsoft Exchange Server 5.5 + SP2
Lotus Domino R5
System Environment Requirements for File Sharing
The following network and system environments apply when using the machine both to send documents to a file server and to share files, depending on the type of network used.
●
Using a NetWare network:
Compatible server: Novell NetWare Version 3.2/4.11/4.2/5
Compatible protocol: IPX
IMPORTANT
• When using a NetWare 3.x server, it is necessary to support long file names.
Before You Start
1
●
Using a NetBIOS network (File Sharing for Windows):
Compatible servers: Microsoft Windows 95/98
Microsoft Windows NT Server 4.0
Microsoft Windows NT Workstation 4.0
Microsoft Windows 2000 Server
Microsoft Windows 2000 Professional
Compatible protocol: NetBIOS over TCP/IP (NetBT)
●
Using FTP:
Compatible servers: Microsoft Windows NT Server 4.0 and Internet Information Server 4.0
Microsoft Windows 2000 Server and Internet Information Server 5.0
Solaris Version 2.6 or later
Compatible protocol: TCP/IP
IMPORTANT
• If you are using Windows NT 4.0, you need to install Service Pack 5 or later.
System Environment Requirements
1-3
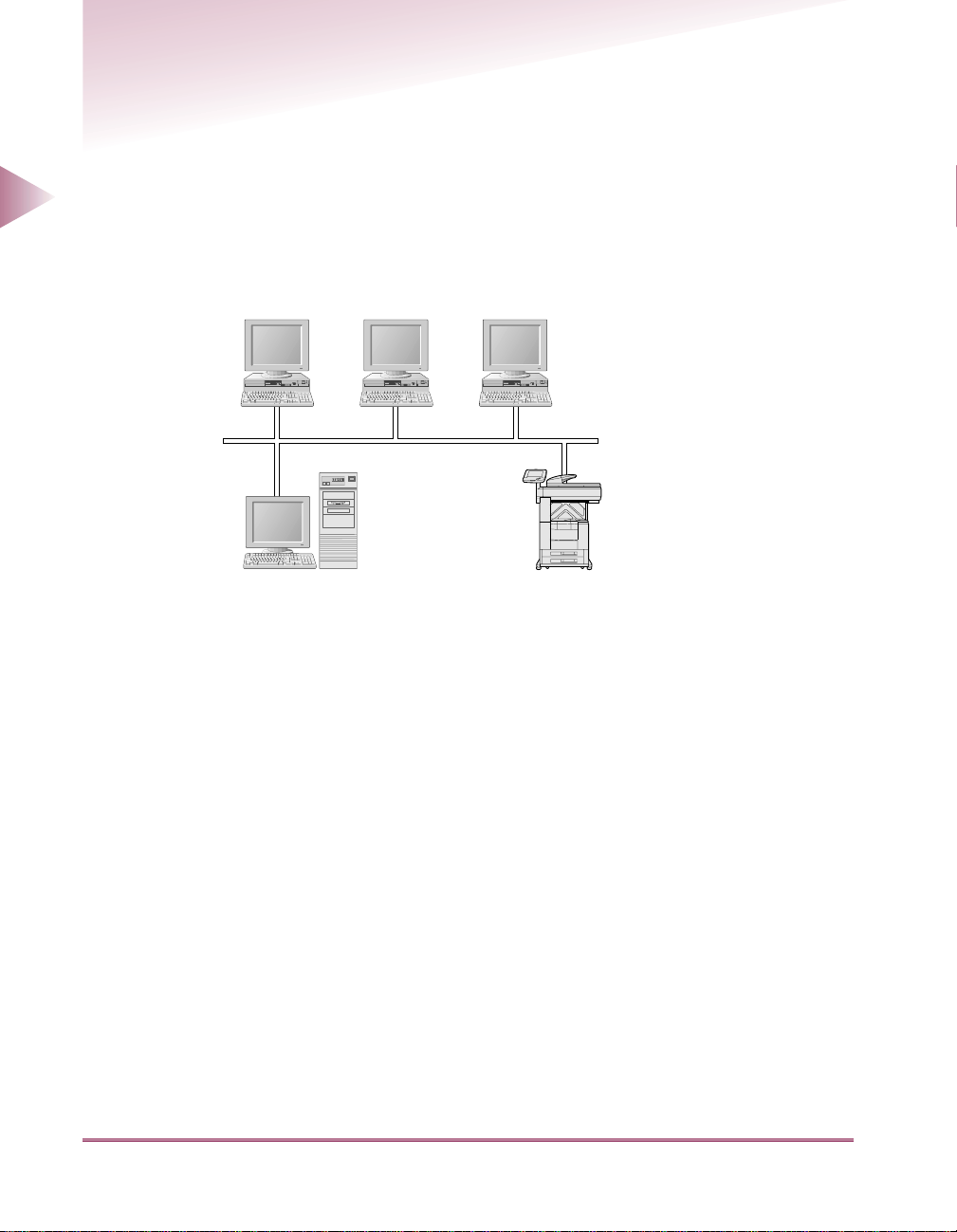
Checking Your Network Environment
Refer to the following diagram example to confirm the network environment that is connected to the
machine, and then perform the necessary operations.
Sample Windows 95/98/NT/2000 Network (With a NetWare
Server)
Windows 95
Before You Start
Windows 98
Windows NT
1
Protocol: NetWare, TCP/IP
NetWare Server
In a network environment like the one above, either NetWare or TCP/IP protocol can be used for
printing or file sharing. Multiple protocols can also be used at the same time.
Depending on the protocol, see either “Using a TCP/IP Network,” on p. 2-1 or “Using a NetWare Net-
work (Windows),” on p. 3-1.
The use of e-mail or I-fax functions require the TCP/IP protocol. (See “Using a TCP/IP Network,” on
p. 2-1.)
iR3250
1-4
Checking Your Network Environment

Sample Windows 95/98/NT/2000 Network (Without a
NetWare Server)
Windows 95 Windows 98
In a network environment like the one above, the TCP/IP protocol can be used. (See “Using a TCP/
IP Network,” on p. 2-1.)
Windows NT
Protocol: TCP/IP
iR3250
Sample Macintosh Network
Macintosh
Protocol: AppleTalk
Before You Start
1
iR3250
In a network environment like the one above, the AppleTalk (EtherTalk) protocol is used for printing.
(See “Using an AppleTalk Network,” on p. 4-1.)
The use of e-mail or I-fax functions requires the TCP/IP protocol. (See “Using a TCP/IP Network,” on
p. 2-1.)
Checking Your Network Environment
1-5
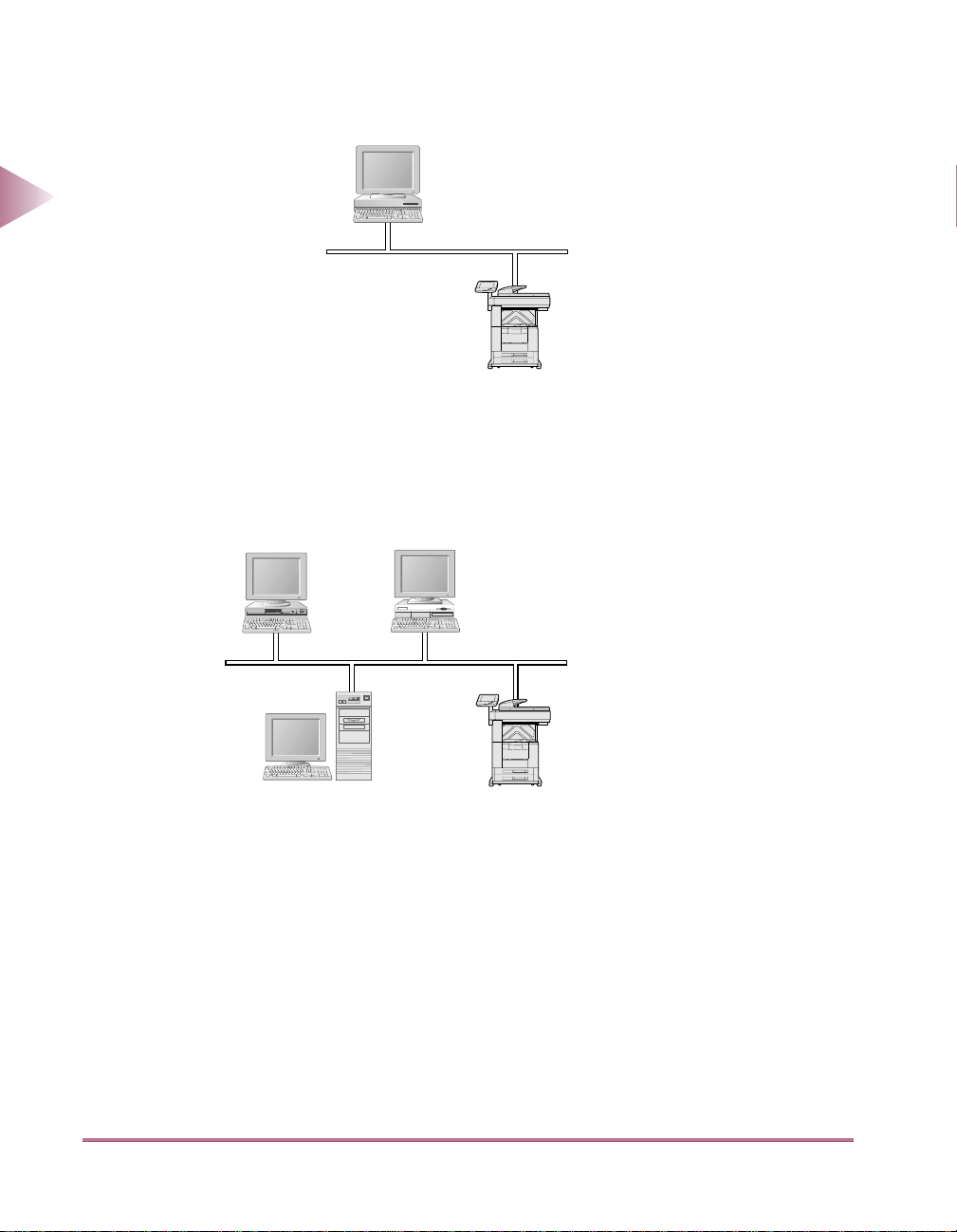
Sample UNIX Network
Solaris (Sun OS)
Protocol: TCP/IP
Before You Start
1
With UNIX computers, the TCP/IP protocol is used. (See “Using a TCP/IP Network,” on p. 2-1.)
iR3250
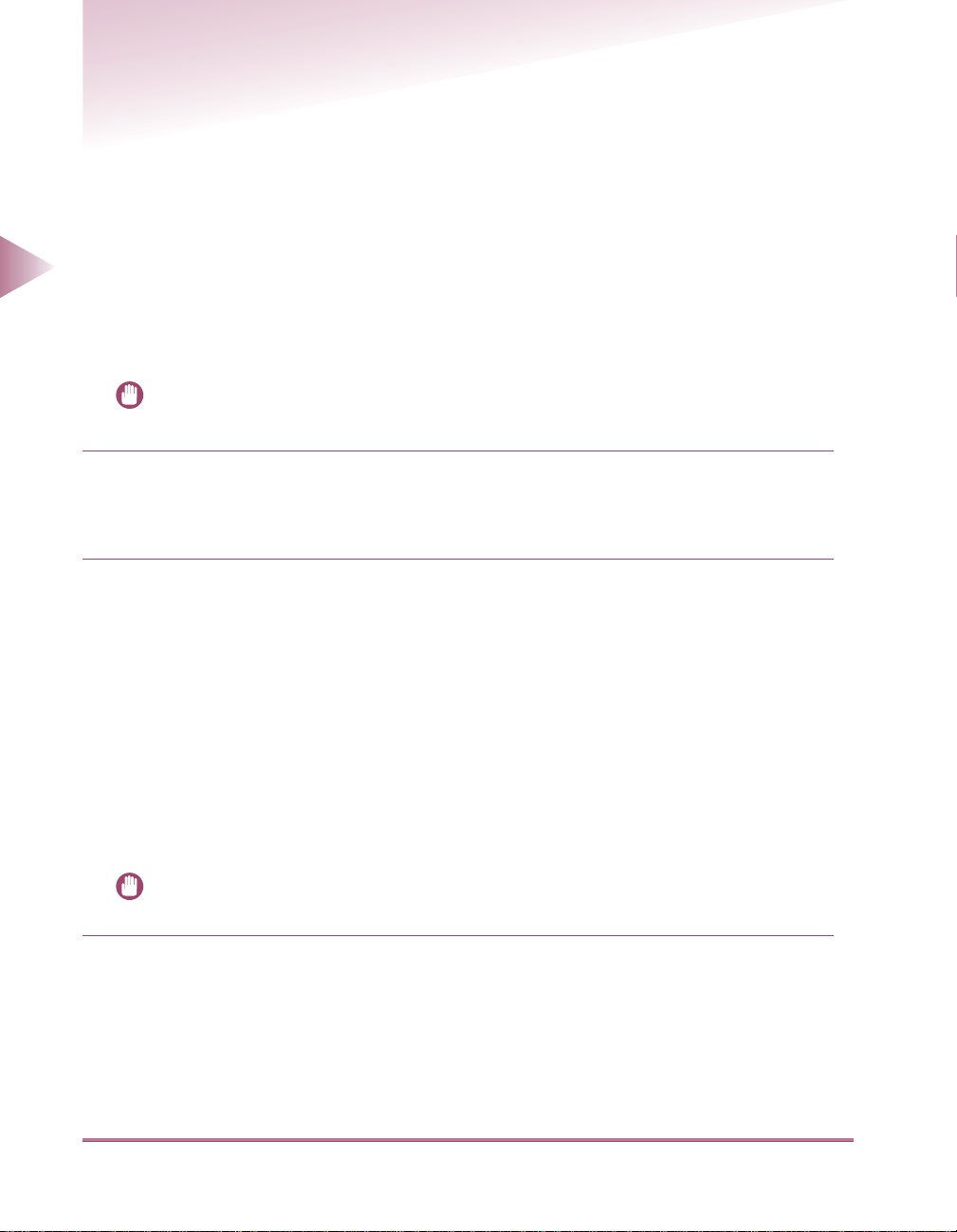
Using a Network With Various Types of Computers
Windows
NetWare Server
When there are various types of computers on the network, network operations depend on the type
of computer being used.
For example, if Windows 98 and Macintosh computers are used, you will need to enter the settings
described in both the “Sample Windows 95/98/NT/2000 Network” and “Sample Macintosh Network”
sections.
The use of e-mail or I-fax functions requires the TCP/IP protocol. (See “Using a TCP/IP Network,” on
p. 2-1.)
Macintosh
Protocol: TCP/IP, NetWare, AppleTalk
iR3250
1-6
Checking Your Network Environment

2
Using a TCP/IP Network
This chapter describes the settings and procedures necessary to connect and use the machine
with a TCP/IP network.
TCP/IP Network Setup Operating Procedures. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-2
Setup Preparations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-2
E-mail/I-Fax Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-2
Printing Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-3
File Sharing Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-3
Protocol Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-5
Settings from the Control Panel. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-5
Setting Up a Computer for Printing (Windows) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-14
Connecting to a TCP/IP Network. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-14
Installing the Printer Driver and Specifying the Printer Destination Setting . . . . . . . 2-14
Print Server Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-22
Setting Up a Computer for Printing (UNIX) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-23
File Sharing Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-25
Using Windows 95/98 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-25
Using Windows NT 4.0 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-28
Using Windows 2000. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-36
Using UNIX . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-43
CHAPTER
Using a TCP/IP Network
2
2-1
TCP/IP Network Setup Operating Procedures
To use a TCP/IP network, it is first necessary to enter the Ethernet driver settings and IP address
settings. You also need to enter e-mail/I-fax settings, as well as settings f or printing and file sharing if
necessary.
Setup Preparations
Ethernet driver and IP address settings.
These settings are entered from the control panel of the machine. You can also use the Remote UI
to change the values of these settings.
IMPORTANT
• It is recommended that a network manager enters Ethernet driver and IP address settings.
1
Using a TCP/IP Network
2
Enter the Ethernet driver settings.
(See “Setting Up the Ethernet Driver,” on p. 2-5.)
Enter the IP address settings.
2
(See “Setting the IP Address,” on p. 2-7.)
E-mail/I-Fax Settings
The following operations are necessary to enter e-mail/I-fax settings.
E-mail/I-fax settings for the machine can be entered from the control panel or the Remote UI. Use
whichever is more convenient. (The Remote UI enables you to enter a variety of settings for the
machine from a computer with a web browser.) For instructions on using the Remote UI, see the
Remote UI User’s Guide
IMPORTANT
• It is recommended that a network manager enters the e-mail/I-fax settings.
E-mail/I-Fax settings.
1
(See “Entering E-mail and I-Fax Settings,” on p. 2-11.)
2-2
TCP/IP Network Setup Operating Procedures
.

Printing Settings
The following operations are necessary to enter printing settings.
1
Computer settings for printing.
Enter settings for each computer you use for printing.
●
Using Windows
(See “Setting Up a Computer for Printing (Windows),” on p. 2-14.)
●
Using UNIX
(See “Setting Up a Computer for Printing (UNIX),” on p. 2-23.)
NOTE
• The machine’s Salutation Print Functional Unit enables you to do the following:
- Manage print jobs sent to the machine from a personal computer. This enables you to view job lists, cancel jobs, etc.
- Notify a personal computer about the status of the machine. This enables the machine to send information about installed optional equipment, low paper levels, etc.
• The use of the Salutation Pr int Functional Unit requires Ethernet driver and IP address settings. (See
“Protocol Settings,” on p. 2-5.) The use of the Salutation Print Functional Unit also requires Salutationcompatible software such as IBM NuOffice. For the necessary Salutation software and computer settings,
see the manuals provided with the respective products. Also, this Print Functional Unit may be affected by
limitations from Salutation-compatible software. (See the related manuals.)
File Sharing Settings
The following settings are necessary to send files to servers, and to share files on servers over a
network.
Using a TCP/IP Network
2
IMPORTANT
• It is recommended that a network manager enters the e-mail/I-fax settings.
1
Computer settings (File Sharing Settings).
●
Using Windows 95/98 (See “Using Windows 95/98,” on p. 2-25.)
●
Using Windows NT (See “Using Windows NT 4.0,” on p. 2-28.)
●
Using Windows 2000 (See “Using Windows 2000,” on p. 2-36.)
●
Using UNIX (See “Using UNIX,” on p. 2-43.)
TCP/IP Network Setup Operating Procedures
2-3

The machine’s Settings (File Recipient Address Settings).
2
Recipient address settings for the machine can be entered from the control panel or the
Remote UI. Use whichever is more convenient. (The Remote UI enables you to enter a
variety of settings for the machine from a computer with a web browser.) For instructions on
using the Remote UI, see the
panel, see the
Using a TCP/IP Network
User’s Guide
Remote UI User’s Guide
.
. F or instructions on using the control
2
2-4
TCP/IP Network Setup Operating Procedures

Protocol Settings
This section describes how to enter Ethernet driver settings, IP address settings, and e-mail/I-fax
settings.
These settings can be entered by either of the following methods:
The machine’s control panel
The Remote UI
NOTE
• The Remote UI enables you to enter a variety of settings for the machine from a computer with a web
browser. For instructions on using the Remote UI, see the
• You can also specify IP address settings using NetSpot. For instructions on entering settings using
NetSpot, see Chapter 5, “Network and Printer Settings Using Netspot.”
Settings from the Control Panel
IMPORTANT
• Settings entered from the control panel become enabled after the machine is restarted (with the power
switches).
• For details about entering characters using the touch panel display, see the
Setting Up the Ethernet Driver
Remote UI User’s Guide
User’s Guide
.
.
Using a TCP/IP Network
2
Additional
Press the key.
1
Press the [System Settings] key.
2
• If the message “Enter the System Man-
Functions
IMPORTANT
ager ID and Password using the numeric
keys” appears in the touch panel display,
enter the System Manager ID and password. F or instructions on entering the System Manager ID and password, see the
User's Guide
.
Protocol Settings
2-5

Press the [Network Settings] key.
3
4
Press the [Ethernet Driver Settings]
key.
Using a TCP/IP Network
2
5
Select Auto Detect [On] or [Off].
●
If [On] is selected
Determines the communication mode
(Half duplex/Full duplex) and Ethernet
type (10 Base-T/100 Base-TX)
automatically. Go to step 8.
●
If [Off] is selected
Enables you to enter the
communication mode (Half duplex/Full
duplex), and Ethernet type (10 Base-T/
100 Base-TX) manually. Go to step 6.
NOTE
• The factory setting is [On]. Use the [Off]
setting to specify a particular Ethernet setting.
2-6
Protocol Settings

Select the Communication Mode.
6
Select the appropriate communication mode for your network environment.
●
When [Half Duplex] is selected
Sending and receiving is alternated.
●
When [Full Duplex] is selected
Sending and receiving is simultaneous.
7
Select the Ethernet Type.
Select the appropriate Ethernet type for your network environment.
●
When [10 Base-T] is selected
The network is compatible with 10 Base-T connections.
●
When [100 Base-TX] is selected
The network is compatible with 100 Base-TX connections.
8
Confirm the settings you entered and press the [OK] key.
The display returns to the Network Settings screen.
Continue to the next section and set the IP address.
Setting the IP Address
NOTE
• When settings are made using DHCP, BOOTP, or RARP, the setting values will appear on the TCP/IP Settings screen after the machine is restarted. (If the IP address, host name, and domain name have been
set previously, these will be overwritten by the settings made using DHCP, BOOTP, or RARP.)
Additional
1
Press the key.
2
Press the [System Settings] key.
• If the message “Enter the System Man-
Functions
IMPORTANT
ager ID and Password using the numeric
keys” appears in the touch panel display,
enter the System Manager ID and password. F or instructions on entering the System Manager ID and password, see the
User's Guide
.
Using a TCP/IP Network
2
Protocol Settings
2-7

Press the [Network Settings] key.
3
4
Press the [TCP/IP Settings] key.
Using a TCP/IP Network
2
2-8
Protocol Settings

Enter the address settings.
5
Enter the address settings using the
keypad on the control panel.
IMPORTANT
• For information on entering characters
using the touch panel display, see the
User's Guide
• Only one of the DHCP, BOOTP, or RARP
settings can be checked at one time.
• Even when using the DHCP, BOOTP, and
RARP settings, you should enter an IP
Address, Subnet Mask, and Gateway
Address. If this information cannot be
obtained from the DHCP, BOOTP, or
RARP server, the settings entered from
the control panel are used.
• When using DHCP, it is recommended
that identical IP address be assigned to
the machine at all times. (If the identical IP
address is not assigned, the machine’s
host name cannot be related to the
machine’s IP address.)
• It takes about two minutes to check
whether the DHCP, BOOTP, or RARP settings can be used. If you do not plan to
use one of these settings, it is recommended that you turn them off.
.
Using a TCP/IP Network
2
●
Using a fixed IP address
Press the [IP Address] key, and enter
the IP address using the keypad.
●
Using DHCP
Press the [Enable DHCP] key. Enter
the IP Address, Subnet Mask, and
Gateway Address. (If this information
cannot be obtained by the DHCP, the
settings entered from the control panel
are used.)
●
Using RARP
Press the [Enable RARP] key. Enter
the IP Address, Subnet Mask, and
Gateway Address. (If this information
cannot be obtained by the RARP, the
settings entered from the control panel
are used.)
Protocol Settings
2-9

Using BOOTP
●
Press the [Enable BOOTP]. Enter the
IP Address, Subnet Mask, and
Gateway Address. (If this information
cannot be obtained by the BOOTP, the
settings entered from the control panel
are used.)
6
Enter the DNS Server.
If you are using a DNS server, press the [DNS Server] key and enter the address of the
DNS server.
7
Enter the Host Name and Domain Name.
For the Host Name, press the [Host Name] key and enter the name of your machine. For
the Domain Name, press the [Domain Name] key and enter the domain name of the
network to which your machine belongs. Each name can be up to 47 characters in length.
●
Example
Using a TCP/IP Network
2
Host name: host_name
Domain name: organization.company.com
8
Confirm the settings you entered, and press the [OK] key.
The display returns to the Network Settings screen.
9
Press the [Done] key.
Repeat until the Additional Functions screen closes.
10
Restart the machine.
Turn the printer unit power switch, the scanner unit power switch, and the control panel
power switch to OFF, and then turn the power to ON after waiting at least 3 seconds.
NOTE
• If you are entering additional e-mail/I-fax settings, you do not need to restart the machine at this
point. Finish entering the e-mail/I-fax settings, and then restart the machine.
The settings are now complete.
2-10
Protocol Settings

Entering E-mail and I-Fax Settings
Additional
1
Press the key.
2
Press the [System Settings] key.
• If the message “Enter the System Man-
Press the [Network Settings] key.
3
Functions
IMPORTANT
ager ID and Password using the numeric
keys” appears in the touch panel display,
enter the System Manager ID and password. F or instructions on entering the System Manager ID and password, see the
User's Guide
.
Using a TCP/IP Network
2
4
Press the [E-mail/I-Fax] key.
Protocol Settings
2-11

Enter the SMTP Server settings.
5
Press the [SMTP Server] key to enter a
SMTP server IP address or name. Up to
48 characters can be entered.
●
Example
IP address: 192.168.1.1
Name:
mail_server.organization.company.com
IMPORTANT
• IP Address segments of less than three
digits should not be filled with leading
zeroes (do not enter as 001, 023, etc.).
Enter the E-mail Address.
6
To send and receive e-mail and I-faxes, it is necessary to enter the address of your
machine. Press the [E-mail Address] key, then enter the address up to 64 characters.
Using a TCP/IP Network
2
Your machine supports both SMTP and POP3 functions. To receive using SMTP, you need
to register the host name of your machine with the DNS server and then enter the host
name after the “@” symbol in the e-mail address.
●
Example
To receive e-mail/I-fax messages using POP3:
account1@pop_server.organization.company.com
(In this example the name of the POP server is “pop_server.organization.company.com”)
To receive e-mail/I-fax messages using SMTP:
account1@host_name.organization.company.com
(In this example the host name of the machine registered with the DNS server is
“host_name.organization.company.com”)
If you are receiving e-mail/I-fax messages by SMTP, go to step 11.
Enter the POP Server for directly receiving e-mail and I-faxes.
7
If you want to use a POP Server to receive e-mail and I-faxes, press the [POP Server] key
and enter a POP Server IP address or name. Up to 48 characters can be entered.
●
Example
IP address: 192.168.1.1
Name: pop_server.organization.company.com
IMPORTANT
• IP Address segments of less than three digits should not be filled with leading zeroes (do not
enter as 001, 023, etc.).
2-12
Protocol Settings

Enter the POP Address.
8
If you want to use a POP Server to receive e-mail and I-f ax es, press the [POP Address] k ey,
and enter the POP address. Up to 32 characters can be entered.
●
Example
account1
9
Enter the POP Password.
If you want to use a POP Server to receive e-mail and I-faxes, press the [POP Password]
key, and enter the password for access to the POP Server. Up to 32 characters can be
entered.
10
Enter the POP interval.
If you want to use a POP Server to receive e-mail and I-faxes, enter the time interval at
which you want the POP Server to check f or incoming mail. Press the [-] and [+] keys to set
the POP interval. If the interval is set to 0, the POP Server is not checked. The interval can
be set from 1 to 99 minutes.
IMPORTANT
• The machine cannot be used to manually check the POP Server for incoming mail. To receive
using the POP server, the interval must be set to a value other than “0.”
Confirm the settings you entered and press the [OK] key.
11
Using a TCP/IP Network
2
Press the [Done] key.
12
Repeat until the Additional Functions screen closes.
Restart the machine.
13
Turn the printer unit power switch, the scanner unit power switch, and the control panel
power switch to OFF, and then turn the power to ON after waiting at least 3 seconds.
The protocol settings are now complete.
Protocol Settings
2-13
 Loading...
Loading...