Brother RJ-4230B, RJ-4250WB, TD-4410D, TD-4420DN, TD-4510D Software Developer's Manual ESC/P Command Reference Version 2.00
...Page 1

Software Developer's Manual
ESC/P Command Reference
RJ-4230B/4250WB
TD-4410D/4420DN/4510D/4520DN/4550DNWB
Version 2.00
Page 2

The Brother logo is a registered trademark of Brother Industries, Ltd.
Brother is a registered trademark of Brother Industries, Ltd.
© 2019 Brother Industries, Ltd. All rights reserved.
BarStar Pro Encode Library (PDF417, Micro PDF417, DataMatrix, MaxiCode, AztecCode,
GS1 Composite, GS1 Databar, Code93, MSI/Plessey, POSTNET, Intelligent Mail Barcode)
Copyright (c) 2007 AINIX Corporation. All rights reserved.
QR Code is registered trademark of DENSO WAVE INCORPORATED.
QR Code Generating Program Copyright © 2008 DENSO WAVE INCORPORATED
Epson ESC/P is a registered trademark of Seiko Epson Corporation.
Portions of this software are copyright © 2014 The FreeType Project (www.freetype.org). All rights reserved.
Each owner whose software title is mentioned in this document has a Software License Agreement specific to
its proprietary programs.
Any trade names and product names of companies appearing on Brother products, related documents and
any other materials are all trademarks or registered trademarks of those respective companies.
Page 3
IMPORTANT - PLEASE READ CAREFULLY
Note
This documentation (“Documentation”) provides information that will assist you in controlling your Printer
(Please refer to “Appendix A: Supported Printers”).
You may use the Documentation only if you first agree to the following conditions.
If you do not agree to the following conditions, you may not use the Documentation.
Condition of Use
You may use and reproduce the Documentation to the extent necessary for your own use of your Printer
Model (“Purpose”). Unless expressly permitted in the Documentation, you may not;
(i) copy or reproduce the Documentation for any purpose other than the Purpose,
(ii) modify, translate or adapt the Documentation, and/or redistribute it to any third party,
(iii) rent or lease the Documentation to any third party, or,
(iv) remove or alter any copyright notices or proprietary rights legends included within the Documentation.
No Warranty
a. Any updates, upgrades or alteration of the Documentation or Printer Model will be performed at the sole
discretion of Brother. Brother may not respond to any request or inquiry about the Documentation.
b. THIS DOCUMENTATION IS PROVIDED TO YOU "AS IS" W ITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND,
WHETHER EXPRESS OR IMPLIED, INCLUDING, BUT NOT LIMITED TO, THE IMPLIED WARRANTY
OF FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. BROTHER DOES NOT REPRESENT OR WARRANT
THAT THIS DOCUMENTATION IS FREE FROM ERRORS OR DEFECTS.
c. IN NO EVENT SHALL BROTHER BE LIABLE FOR ANY DIRECT, INDIRECT, PUNITIVE, INCIDENTAL,
SPECIAL OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES OR ANY DAMAGES WHATSOEVER, ARISING OUT OF
THE USE, INABILITY TO USE, OR THE RESULTS OF USE OF THE DOCUMENTATION OR ANY
SOF TW ARE PROGRAM OR APPLICATION YOU DEVELOPED IN ACCORDANCE WITH THE
DOCUMENTATION.
Page 4

ESC/P Command Reference
Contents
Introduction ····························································································1
What is ESC/P? ·······················································································2
1. Using ESC/P Commands ······································································3
2. Examples of Using ESC/P Commands ···················································5
3. ESC/P Command Limitations ······························································ 11
3.1 Print area .................................................................................................................. 11
3.2 Characters ................................................................................................................ 13
3.2.1 Character sizes ............................................................................................. 13
3.2.2 Character pitches .......................................................................................... 14
3.3 Print position ............................................................................................................. 15
3.3.1 Characters ..................................................................................................... 15
3.3.2 Bitmaps, barcodes and downloaded images .............................................. 15
3.4 Line feed amount ...................................................................................................... 16
4. Control Code List··············································································· 17
5. Control Command Details ·································································· 21
5.1 Character/style selection commands ...................................................................... 21
ESC R Select international character set ..................................................... 21
ESC q Select character style ........................................................................ 22
ESC k Select font .......................................................................................... 23
ESC t Select character code set ................................................................. 24
5.2 Text printing commands ........................................................................................... 25
ESC 4 Apply italic style ................................................................................. 25
ESC 5 Cancel italic style ............................................................................... 25
ESC E Apply bold s tyle ................................................................................. 26
ESC F Cancel bold style ............................................................................... 26
ESC G Apply double-strike printing............................................................... 27
ESC H Cancel double-strike printing ............................................................ 27
ESC P Apply pica pitch (10 cpi) .................................................................... 28
ESC M Apply elite pitch (12 cpi) .................................................................... 30
ESC g Apply micron pitch (15 cpi)................................................................ 31
ESC p Specify proportional characters ........................................................ 32
ESC W Specify double-width characters....................................................... 32
SO Specify auto-canceling stretched characters ................................... 33
ESC SO Specify auto-canceling stretched characters ................................... 33
SI Specify compressed characters ....................................................... 34
ESC SI Specify compressed characters ....................................................... 34
DC2 Cancel compressed characters ........................................................ 35
DC4 Cancel auto-canceling double-width characters .............................. 35
ESC – Apply/cancel underlining ................................................................... 36
ESC ! Global formatting ............................................................................... 37
ESC SP Specify character spacing ................................................................. 38
ESC X Specify character size ....................................................................... 39
5.3 Line feed commands ................................................................................................ 40
ESC 0 Specify line feed of 1/8 inch .............................................................. 40
ESC 2 Specify line feed of 1/6 inch .............................................................. 40
ESC 3 Specify minimum line feed ................................................................ 41
ESC A Specify line feed of n/60 inch ............................................................ 41
5.4 Horizontal movement commands ............................................................................ 42
ESC l Specify left margin ............................................................................. 42
ESC Q Specify right margin........................................................................... 44
- i Introduction
Page 5

ESC/P Command Reference
CR Carriage return................................................................................... 45
ESC D Specify horizontal tab position .......................................................... 46
HT Perform horizontal tab ....................................................................... 47
ESC $ Specify absolute horizontal position ................................................. 48
ESC \ Specify relative horizontal position ................................................... 48
ESC a Specify alignment .............................................................................. 49
5.5 Vertical movement commands ................................................................................ 50
LF Line feed ............................................................................................ 50
FF Page feed........................................................................................... 50
ESC J Forward paper feed ........................................................................... 51
ESC B Specify vertical tab position .............................................................. 52
VT Perform vertical tab ........................................................................... 53
ESC (V Specify absolute vertical position ..................................................... 54
ESC (v Specify relative vertical position ....................................................... 55
5.6 Paper formatting commands.................................................................................... 56
ESC (c Specify page format .......................................................................... 56
ESC (C Specify page length ........................................................................... 57
5.7 Printer control commands ........................................................................................ 59
ESC @ Initialize .............................................................................................. 59
5.8 Graphics commands ................................................................................................ 60
ESC * Select bit image <for 203dpi printers> ............................................. 60
ESC * Select bit image <for 300dpi printers> ............................................. 64
ESC K 8-dot single-density bit image ........................................................... 70
ESC L 8-dot double-density bit image.......................................................... 71
ESC Y 8-dot double-speed double-density bit i mage .................................. 72
ESC Z 8-dot quadruple-density bit image .................................................... 72
5.9 Advanced commands ............................................................................................... 73
ESC i B Barcode .............................................................................................. 73
ESC i Q 2D barcode (QR Code) ..................................................................... 78
ESC i P QR Code version ............................................................................... 81
ESC i V 2D barcode (PDF417) ....................................................................... 82
ESC i D 2D barcode (DataMatrix) ................................................................... 85
ESC i M 2D barcode (MaxiCode) .................................................................... 88
ESC i J 2D barcode (Aztec) ........................................................................... 90
ESC i G Specify font ........................................................................................ 92
ESC i F P Print downloaded data ...................................................................... 93
ESC i a Switch command mode ..................................................................... 97
ESC i S Status information request ................................................................ 98
ESC i L Specify landscape orientation .........................................................101
ESC i C Specify cutting .................................................................................102
ESC i H Specify recovery setting ..................................................................103
5.10 Advanced static commands .................................................................................104
ESC iXQ2 Select default character style..........................................................104
ESC iXQ1 Retrieve default character style ......................................................105
ESC iXk2 Select default font ............................................................................106
ESC iXk1 Retrieve default font ........................................................................107
ESC iXX2 Specify default character size .........................................................108
ESC iXX1 Retrieve default character size .......................................................109
ESC iX32 Specify default line feed ..................................................................109
ESC iX31 Retrieve default line feed ................................................................ 110
ESC iXA2 Select default alignment .................................................................. 110
ESC iXA1 Retrieve default alignment .............................................................. 111
ESC iX(2 Specify default page length............................................................. 11 2
ESC iX(1 Retrieve default page length ........................................................... 112
ESC iXL2 Select default landscape orientation .............................................. 113
- ii Introduction
Page 6

ESC/P Command Reference
ESC iXL1 Retrieve default landscape orientation ........................................... 11 3
ESC iXj2 Select default international character set ....................................... 114
ESC iXj1 Retrieve default international character set ................................... 115
ESC iXm2 Select default character code set ................................................... 116
ESC iXm1 Retrieve default character code set................................................ 11 7
ESC iXd2 Specify recovery setting .................................................................. 118
ESC iXd1 Retrieve recovery setting ................................................................ 118
ESC iXE2 Specify barcode margin setting ...................................................... 119
ESC iXE1 Retrieve barcode margin setting..................................................... 11 9
ESC iX_2 (00h) Specify line print setting .......................................................120
ESC iX_1 (00h) Retrieve line print setting .....................................................120
ESC iX_2 (01h) Specify line print timeout setting .........................................121
ESC iX_1 (01h) Retrieve line print timeout setting ........................................121
Appendix A: Supported Printers ··························································· 122
Appendix B: Specifications ·································································· 123
Appendix C: Character Code Tables ····················································· 125
Character code tables ..................................................................................................125
International character set table ..................................................................................129
Appendix D: Introducing the Brother Developer Center ························· 130
- iii Introduction
Page 7

ESC/P Command Reference
Introduction
This material provides the necessary information for directly controlling your printer.
This information is provided assuming that the user has full understanding of the operating system being used
and basic mastery of communication interfaces in a developer's environment.
Read the model names that appear in the screens in this manual as the name of your printer.
We accept no responsibility for any problems caused by programs that you develop using the information
provided in this material, affecting software, data or hardware, including the printer, and any problems
resulting directly or indirectly from them. Use this material only if you accept these terms.
This material shall not be reproduced, in part or in full, without prior approval. In addition, this material shall
not be used as evidence in a lawsuit or dispute in a way that is unfavorable towards our company.
These ESC/P commands have been adapted specifically for this company.
- 1 Introduction
Page 8

ESC/P Command Reference
What is ESC/P?
ESC/P is one type of control codes used for printers. With the codes introduced in this document, various
labels can be created and printed. In this document, ESC/P codes are provided as both ASCII and binary
codes.
When sending codes to the printer, make sure that the binary codes are used, otherwise the printer cannot
parse the codes.
- 2 -
What is ESC/P?
Page 9
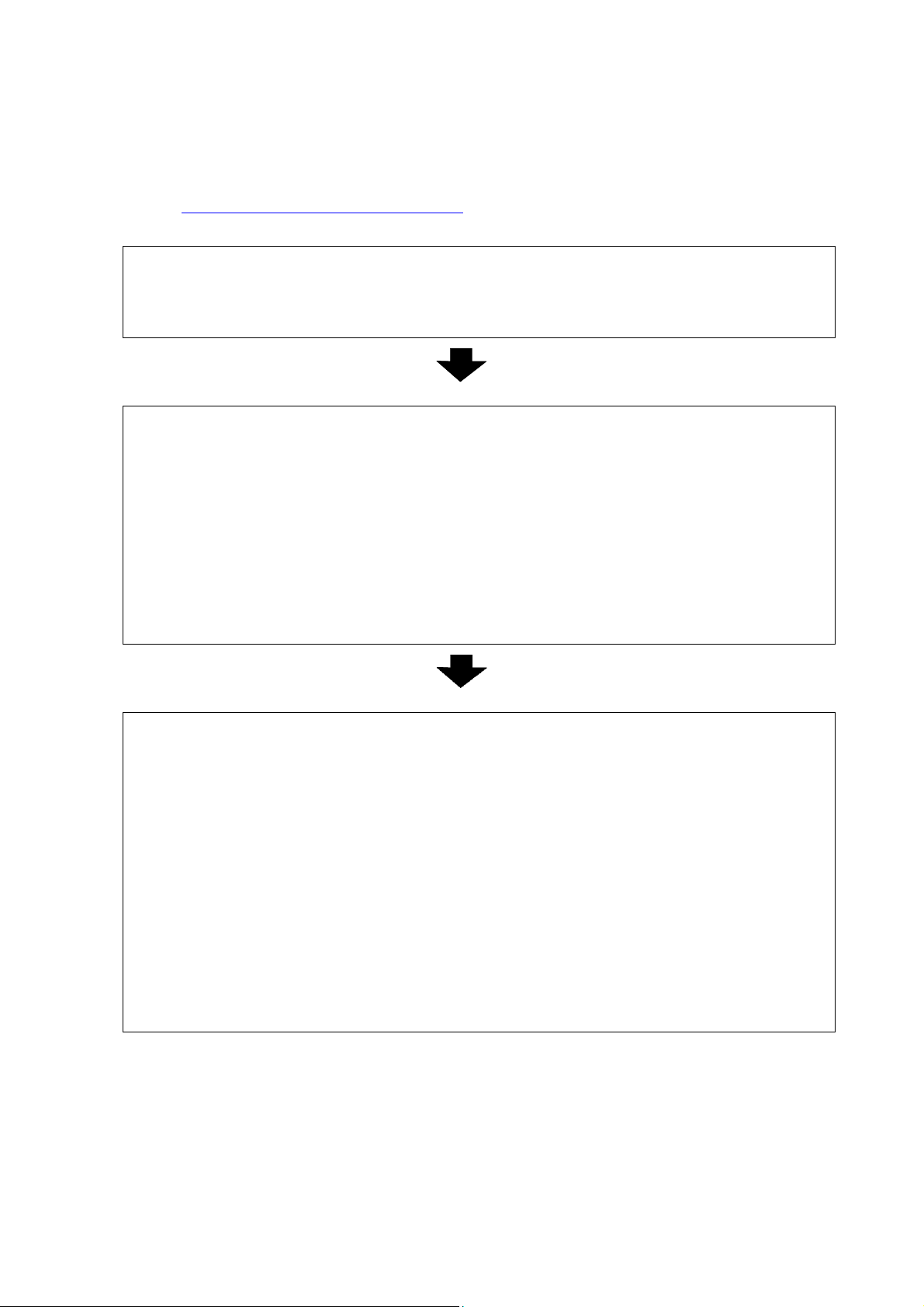
(1) Start ESC/P
1. Switch the command mode.
2. Initialize
- Switch command mode (ESC i a 0) Note: ESC/P mode
- Initialize (ESC @)
(2) Format settings
1. Select the orientation.
- Specify landscape orientation (ESC i L)
2. Specify the page size.
- Specify page length (ESC ( C)
3. Specify print area.
- Specify page format (ESC ( c)
- Specify left/right margins (ESC I, ESC Q)
4. Specify the line feed amount.
- Specify line feed amount (ESC 0, ESC 2, ESC 3, ESC A)
5. Specify tab positions.
- Specify horizontal tab position (ESC D)
- Specify vertical tab position (ESC B)
(3) Print operations
1. Specify the print position.
- Specify the vertical position (ESC ( v, ESC ( V, VT, ESC J)
- Specify the horizontal position (ESC $, ESC \, HT, ESC a)
2. Transfer the print data
(one line).
- Transfer necessary text operation codes (see (4)), bit images,
barcodes, and downloaded data (see (5))
3. End of the line.
- Feed the paper (CR, LF)
4. Repeat 1–3 above.
5. End of the page.
- Specify cutting (ESC i C)
- Feed the page (FF)
6. Repeat 1–5 above.
7. End of the document.
1. Using ESC/P Commands
Below is a description of the flow for creating documents.
Also refer to “2. Exam ples of Using ESC/P Commands”.
ESC/P Command Reference
- 3 -
1. Using ESC/P Commands
Page 10

ESC/P Command Reference
(4) Text operations
1. Specify the character set.
- Select font (ESC k)
- Specify the character spacing (ESC P, ESC M, ESC SP)
2. Specify the character style.
- Specify character style
ESC SO, SI, ESC SI, DC2, DC4, ESC -, ESC !)
3. Specify character codes.
Repeat 1–3 above as necessary.
(5) Bit images, barcodes, and
image data
1. Specify bit images.
- (ESC *, ESC K, ESC L, ESC Y, ESC Z)
2. Specify barcodes.
- (ESC i B)
3. Specify 2D barcodes.
- (ESC i Q, ESC i V, ESC i D, ESC i M, ESC i J)
4. Print the downloaded data
- (ESC i F P)
first.
- Select character code (ESC t)
- Select international character set (ESC R)
- Specify character size (ESC X)
(ESC 4, ESC 5, ESC E, ESC F, ESC G, ESC H, ESC W, SO,
An image data has to be transferred and registered to the printer
- 4 -
1. Using ESC/P Commands
Page 11
Register a media with the Custom Label tool.
Note: The media size to be used is also able to be
output and saved as a command file with the Custom
Label Tool .
Entered Command
ESC i a 00h
2. Examples of Using ESC/P Commands
Set Basic setup first.
Basic setup
1) Register a media to be used.
2) Specify ESC/P command mode.
Basic set up 1: Register a media to be used
ESC/P Command Reference
Basic set up 2: Specify ESC/P command mode
- 5 -
2. Examples of Using ESC/P Commands
Page 12
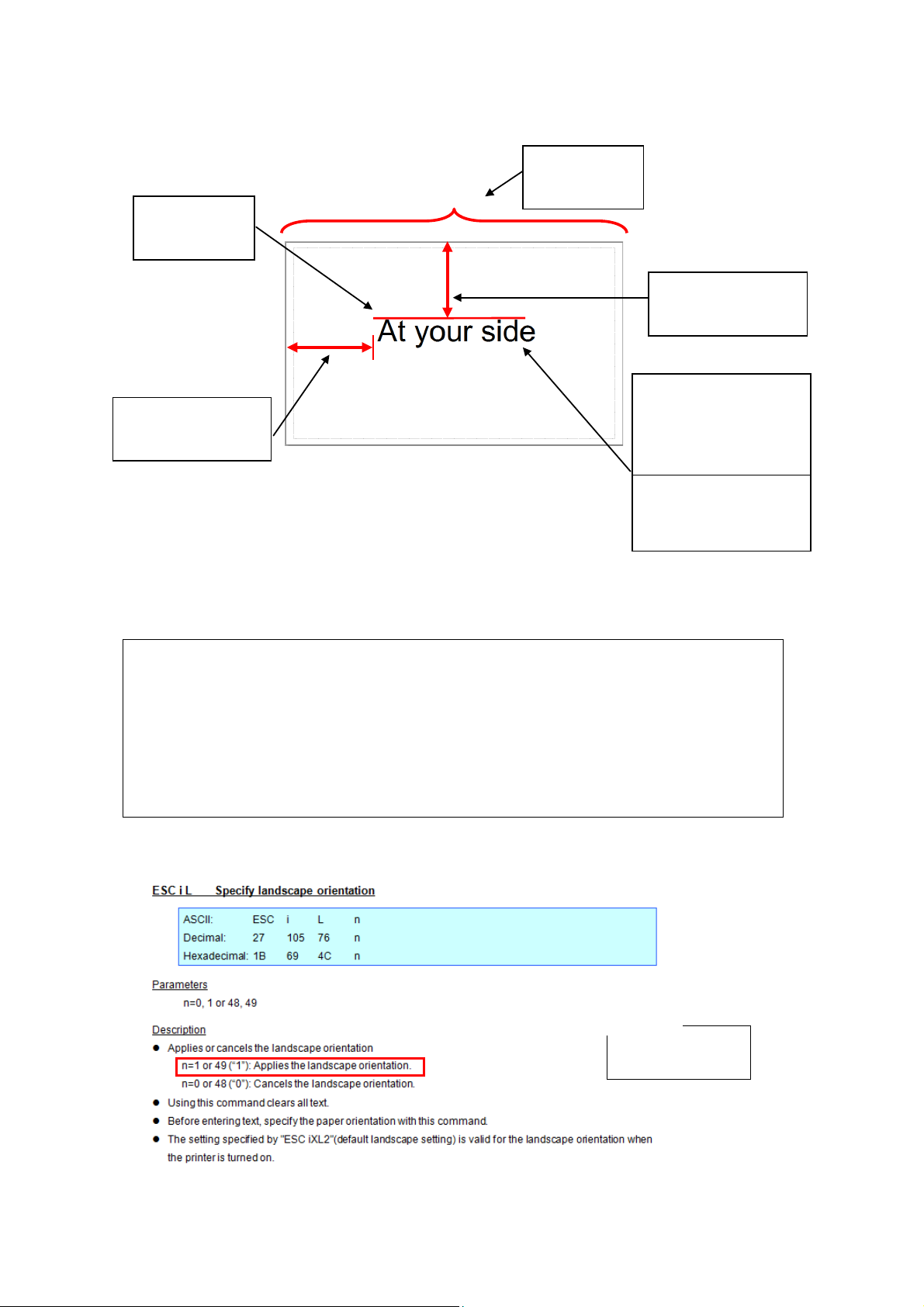
5 inches
1 inch
1 inch
Step 1:
Landscape
Step 2:
Page length
Step 3:
Horizontal position
Step 4:
Vertical position
Step 5:
Font type: Helsinki
(proportional pitch
)
Step 6:
Character size: 100 dots
Entered command
ESC i L 01h
This is the label that will be made.
ESC/P Command Reference
In order to make this label, the following six steps are required.
Step
1. Select the landscape orientation
2. Specify the page length
3. Specify the horizontal position
4. Specify the vertical position
5. Select the font type
6. Specify the character size
Step 1: Select the landscape orientation.
- 6 -
2. Examples of Using ESC/P Commands
Page 13

ESC (C Specify page length
ASCII: ESC
( C nL nH mL mH
Decimal
: 27 40 67 nL nH mL mH
Hexadecimal: 1B 28 43 nL nH mL mH
Parameters
nL=2, nH=0
0≤(mL+mH*256)<8192(for 203dpi printers)
0≤(mL+mH*256)<12000(for 300dpi printers)
Description
Specifies the page length.
* A page length 0 indicates the Auto setting.
The unit is 1 dot.
Page length=mL+
mH*256
The current paper position is the TOF.
The top and bottom m
argins are canceled with ESC ( c.
All previously entered text
is cleared.
A standard unit is not used.
This command is available only with continuous length
tape.
5inches
*The page length does not include the margins.
For the margins, subtract 6 mm (48 dots) from the page length.
nL
nH
mL
mH
ESC ( C 02h 00h C7h 03h
Entered
command
5 inches=101
5 dots
1015 dots–48 dots=967 dots
Page length=mL+mH*256=967
3
03h
199
C7h
Example: A case 203dpi printer is used
1 inch
1 inch=203 dots
Horizontal position=n1+n2*256=203
ESC $ CBh 00h
n1
n2
Entered command
= =
203
CBh
0
00h
= =
Example: A case 203dpi printer is used
Step 2: Specify the page length.
ESC/P Command Reference
Step 3: Specify the horizontal position.
- 7 -
2. Examples of Using ESC/P Commands
Page 14
1 inch
1 inch=203 dots
Vertical position=mL+mH
*256=
203
109
CB
h
0
00h
ESC ( V 02h 00h CB
h
00h
nL
nH
mL
mH
Entered command
Example: A case 203dpi printer is used
Entered command
ESC k 0Bh
n
n=11=0Bh
Font type: Helsinki
(proportional pitch)
Step 4: Specify the vertical position.
ESC/P Command Reference
Step 5: Select the font type.
- 8 -
2. Examples of Using ESC/P Commands
Page 15
Character size=nL+nH
*256=100 dots
ESC X 00h 64h
00h
m
nL
nH
Entered command
100
64h
0
00h
Character size
: 100 dots
Example: A case
203dpi
printer is used
Step 6: Specify the character size.
ESC/P Command Reference
- 9 -
2. Examples of Using ESC/P Commands
Page 16
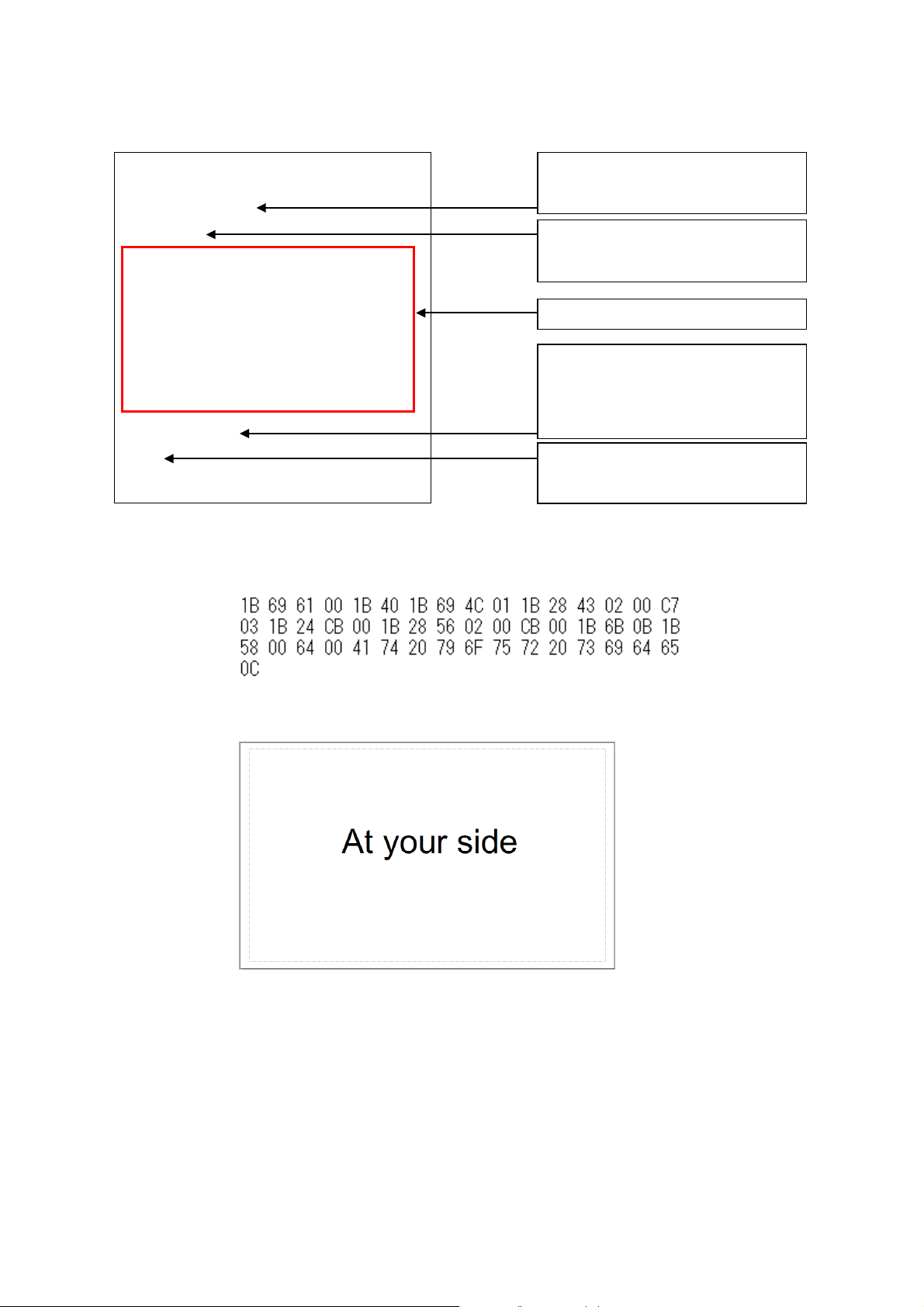
ESC i a
00h
ESC @
ESC i L 01h
ESC ( C 02h 00h C7h 03h
ESC $
CBh 00h
ESC ( V 02h 00h CBh 00h
ESC k 0Bh
ESC X 00h 64h 00h
At your side
FF
Select
ESC/P mode
Binary command: 1B 69 61 00
Initialize ESC/P mode
Binary command: 1B 40
6 steps explained above
Print start command
Binary command: 0C
Text to be print
Binary command: 41 74 20 79 6F 75
72 20 73 69 64 65
All commands together will make the example label shown below.
ESC/P Command Reference
However, these commands should be converted to binary data before sent to the printer, as shown below.
Here is the captured converted binary data.
When the printer receives above binary commands, the label shown below is printed.
- 10 -
2. Examples of Using ESC/P Commands
Page 17
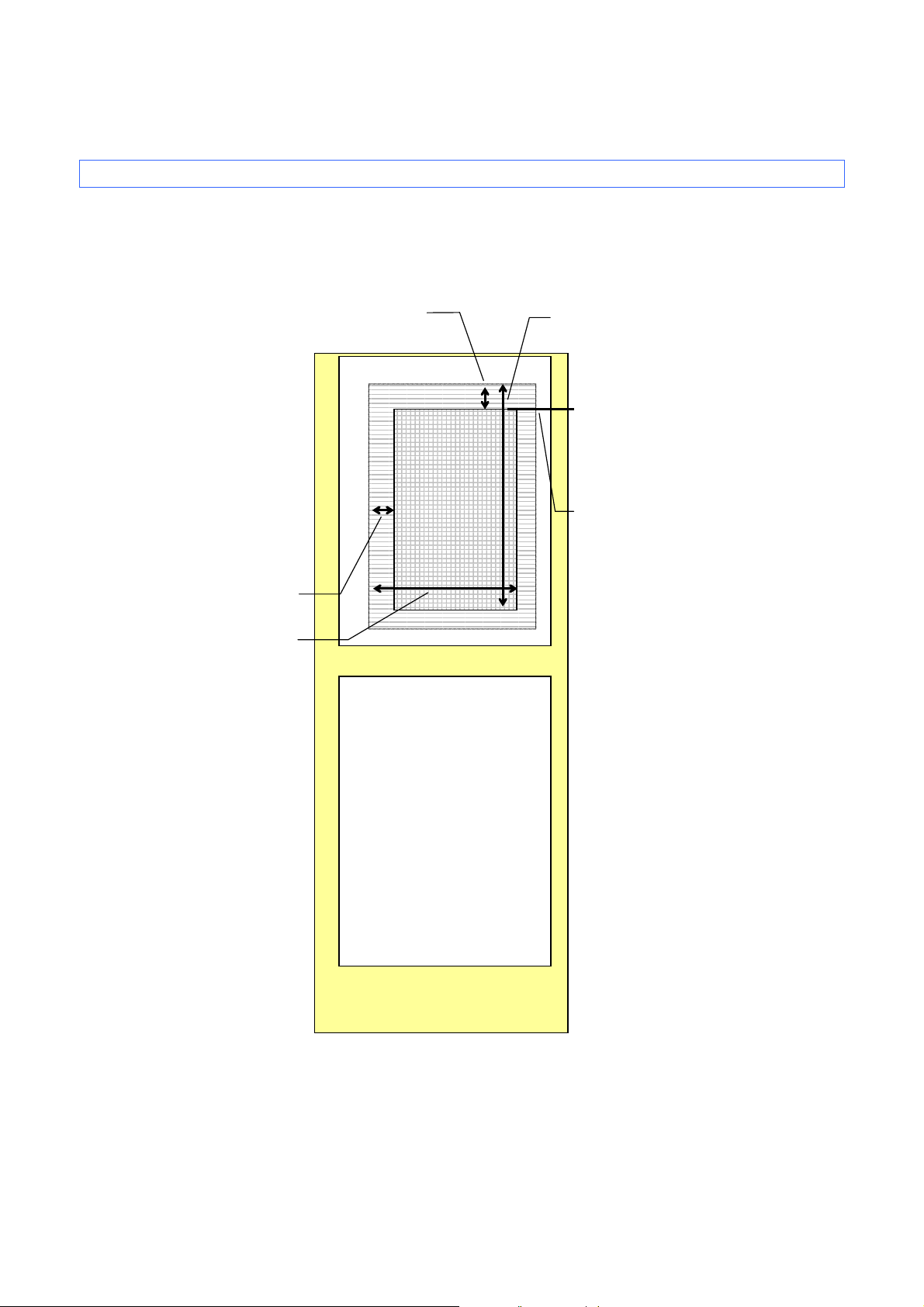
ESC/P Command Reference
Unprintable area
Left margin
Right margin
Top margin
Top margin position
(TOF position)
Bottom margin
Unprinted area
Print area
Unprintable area
3. ESC/P Command Limitations
3.1 Print area
The printing media are die-cut labels and continuous length tape.
The area that can physically be printed on depends on the size and type of the print media.
Die-cut labels
- 11 -
3. ESC/P Command Limitations
Page 18
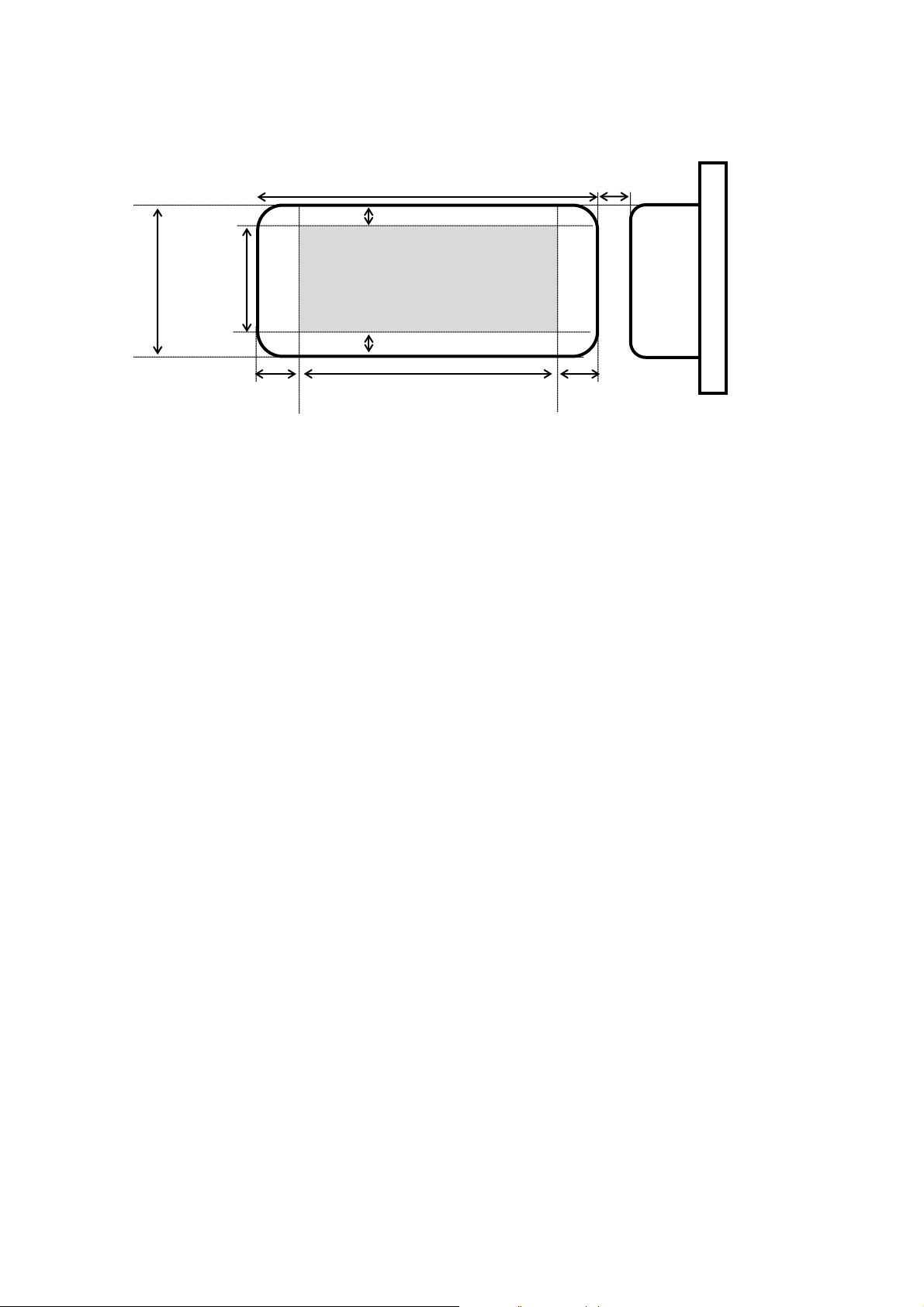
Printable area
Left margin
Right margin
Length of printable area
Bottom margin
Top margin
Label length
Label width
Height of
printable area
Label
spacing
Thermal head
Print area
* To specify media settings, use the Custom Label Tool.
Note: The maximum length of printable area is 3m when a continuous label is used.
ESC/P Command Reference
- 12 -
3. ESC/P Command Limitations
Page 19
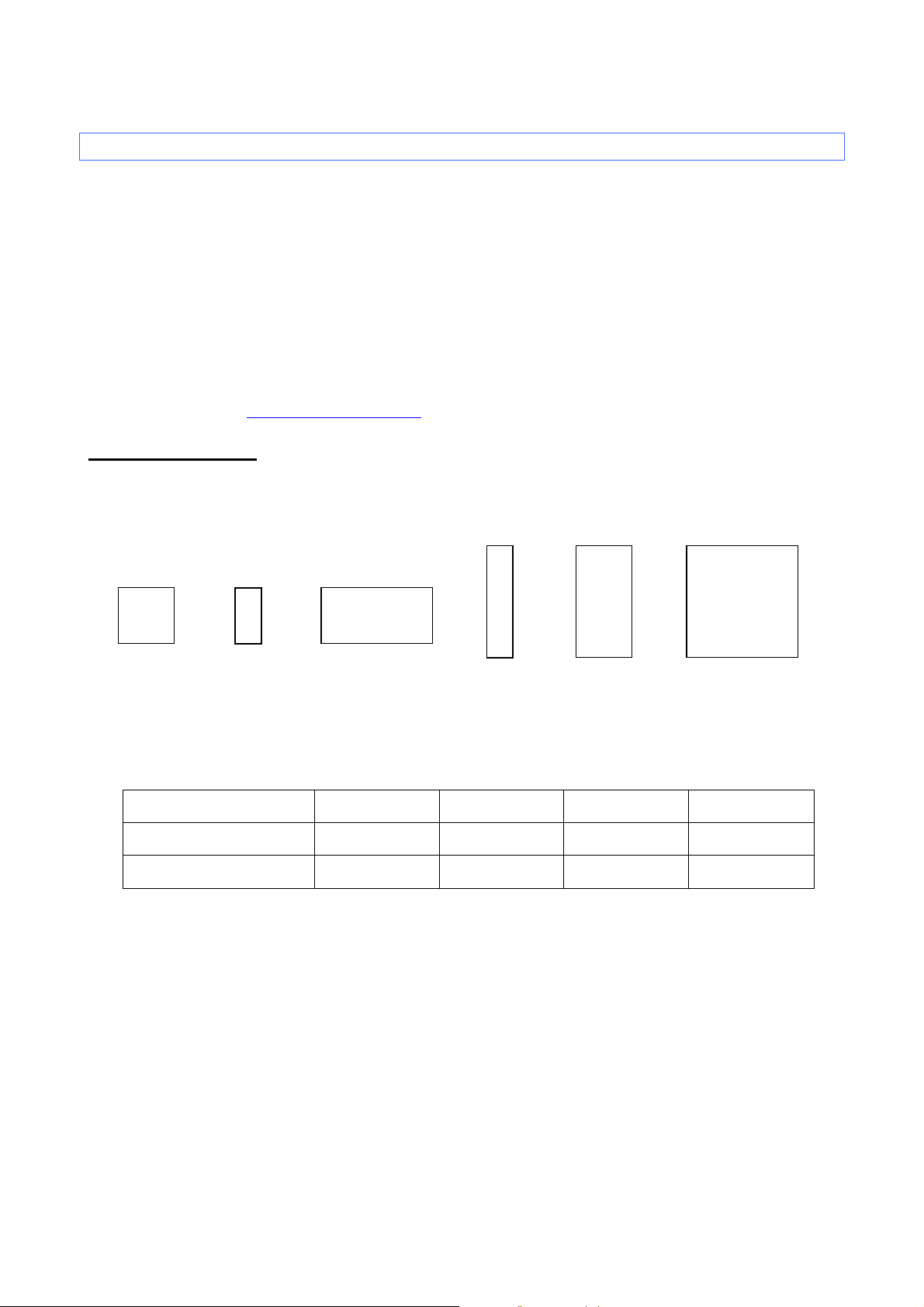
ESC/P Command Reference
Full size
Double width
Double height
Quadruple size
Half width
Double height
and half width
Nominal (dots)
16
24
32
48
Height (dots)
15
21
28
44
Width (dots)
8
10
14
44
3.2 Characters
This system uses single-byte character codes and is installed with 6 bitmap fonts (Letter Gothic Bold, Helsinki,
Gothic, Brussels, San Diego and Brougham) and 4 outline fonts (Letter Gothic, Brussels, Helsinki and
Gothic).
Fixed pitch or proportional pitch can be specified for any of the fonts.
However, there are fonts that are better with a fixed pitch and fonts that are better with a proportional pitch.
The fonts that are better with a fixed pitch are: Letter Gothic and Letter Gothic Bold Brougham.
The font that is better with a proportional pitch are: Brussels, Helsinki and Gothic San Diego.
Each bitmap font has three sizes or four sizes: 16 dots, 24 dots, 32 dots and 48 dots.
Please refer to section AppendixB:Specifications.
3.2.1 Character sizes
Each font is available in full size, compressed size (half width), double width, double height and half width,
double height, and quadruple size.
The actual character size is slightly smaller than the nominal size (the parameter value received with the size
command). This varies depending on the font.
The above example is for Letter Gothic Bold (full size, no character styles applied).
The line-drawing characters (┘└ ┤─ ├ │ ┼ ┬ ┐┌ , etc.) and shaded characters have their own pitch
regardless of the specified font and pitch (proportional or fixed) settings.
- 13 -
3. ESC/P Command Limitations
Page 20
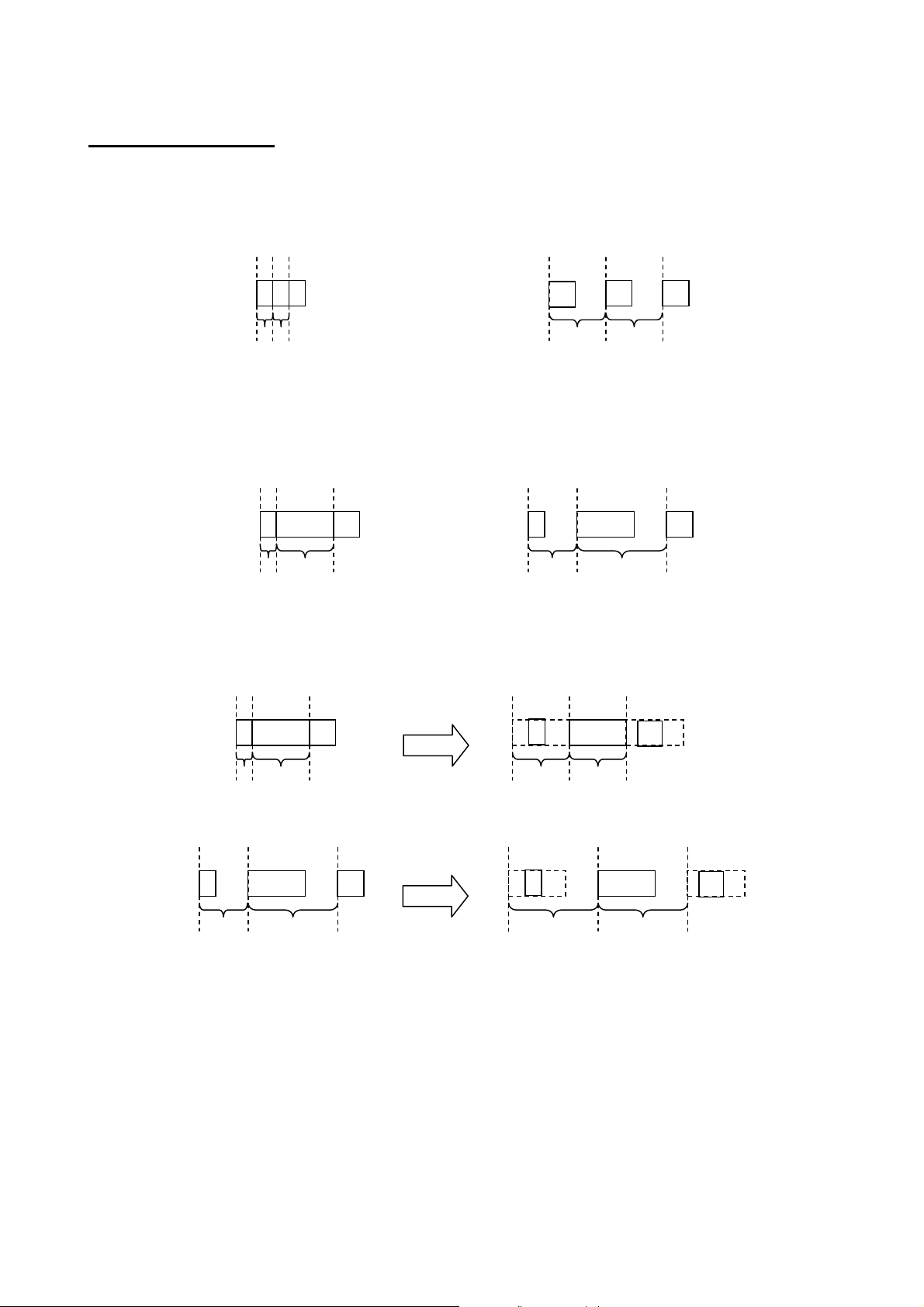
ESC/P Command Reference
Fixed spacing
c
a
b
c
b
a
Fixed
spacing
W
Variable spacing
C
I
W
Variable spacing
C
I
W
Variable spacing
C
I
W
Fixed spacing
C
I
Variable spacing
W
Fixed spacing
C
I
W
C
I
3.2.2 Character pitches
Pitch refers to the spacing between neighboring characters.
When characters are arranged with a fixed pitch, they will be evenly spaced.
If characters extend over several lines, they will align in straight rows.
When characters are arranged with a proportional pitch, the spacing will vary depending on the character.
(For example, “W” is wide but “I” is narrow.)
As a result, the excess space between characters is eliminated and the text appears more compact.
If a fixed pitch is applied to a font that is better with a proportional pitch, all characters are given the same
width as the widest character in the font.
This makes it possible to evenly space the characters of a proportional-pitch font without having to change the
font.
If a proportional pitch is applied to a font that is better with a fixed pitch, all characters are given the same
width, appearing the same as with a fixed pitch.
- 14 -
3. ESC/P Command Limitations
Page 21
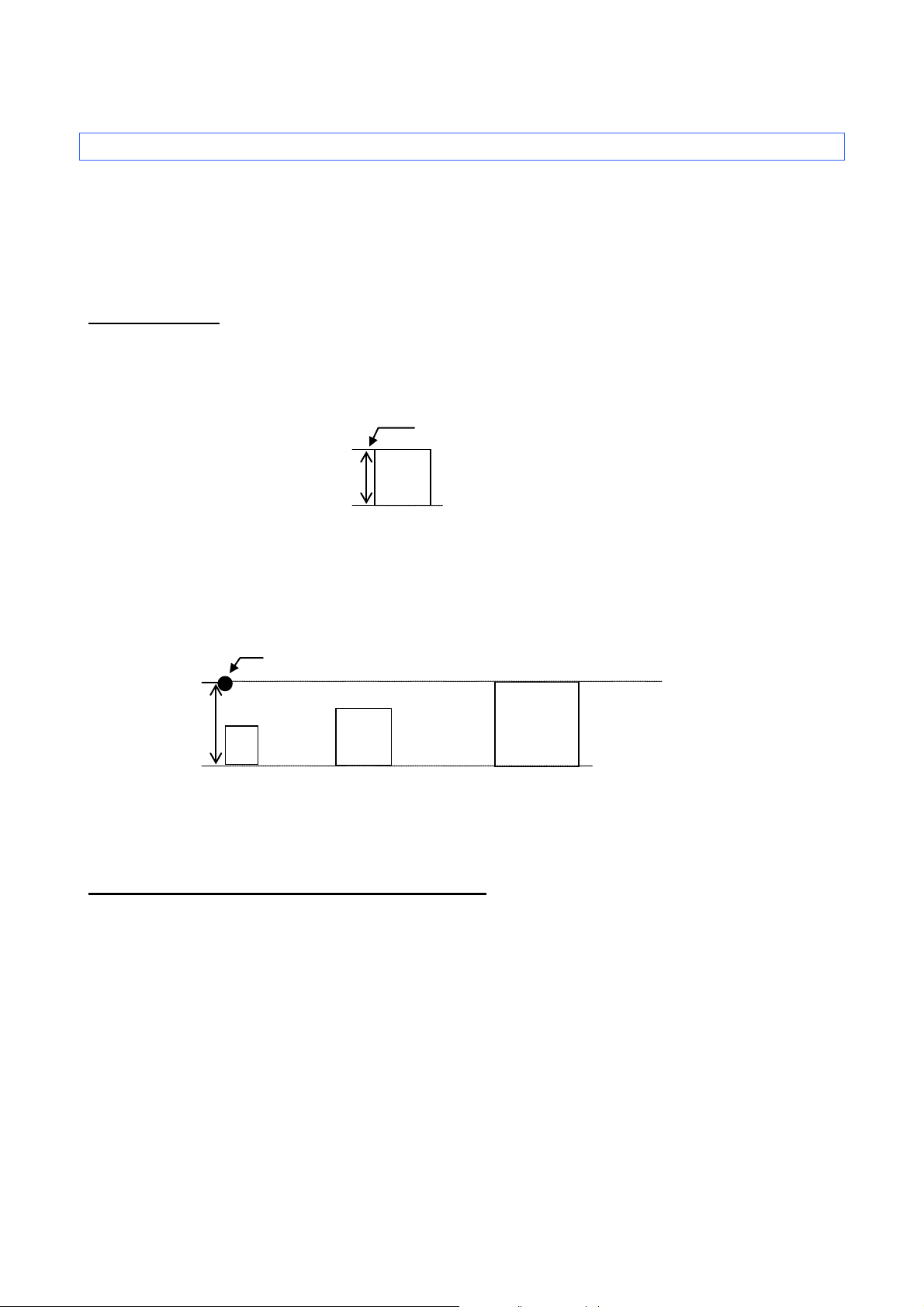
ESC/P Command Reference
A
Print position
Baseline position
A
Print position
A
A
Baseline position
3.3 Print position
The print position is the standard position for printing characters, bitmaps, and barcodes.
There is a horizontal print position and vertical print position, which are the reference points for vertical
position movement and horizontal position movement.
3.3.1 Characters
Characters are arranged with their top edges aligned with the print position.
The baseline of each character is the bottom edge of the character, regardless of size, font, etc.
All characters on a single line are printed with a baseline positions that is the same for each character.
If a single line consists of characters with different heights, the characters are aligned with the baseline of
the tallest character on the line.
Underlines are drawn 4 dots below the baseline position.
3.3.2 Bitmaps, barcodes and downloaded images
These types of image data are treated in the same way as characters and are printed with the bottom
edge of the image aligned with the baseline.
- 15 -
3. ESC/P Command Limitations
Page 22

ESC/P Command Reference
Line feed amount
HHHHHHHHHHHHH
HHHHHHHHHHHHH
HHHHHHHHHHHHH
3.4 Line feed amount
The amount of line feed is the amount of vertical movement from the print position of one line to the print
position of the next line.
The line feed amount is specified with ESC 0, ESC 2, ESC A, and ESC 3.
Within a single line of text, the tallest character is determined, and the baseline is moved so that the top
edge of that character is at the vertical print position.
The tallest character within a line becomes the line height.
If characters are underlined, 4 dots are added to the line height.
If the line height is greater than the specified line feed amount, the line height is used as the actual line
feed amount.
In this way, even if the specified line feed amount is small, the upper and lower lines will not overlap.
(For printer-resident fonts.)
- 16 -
3. ESC/P Command Limitations
Page 23
ESC/P Command Reference
canceling stretched
characters
Specify auto-canceling stretched
characters
Cancel auto-canceling
double-width characters
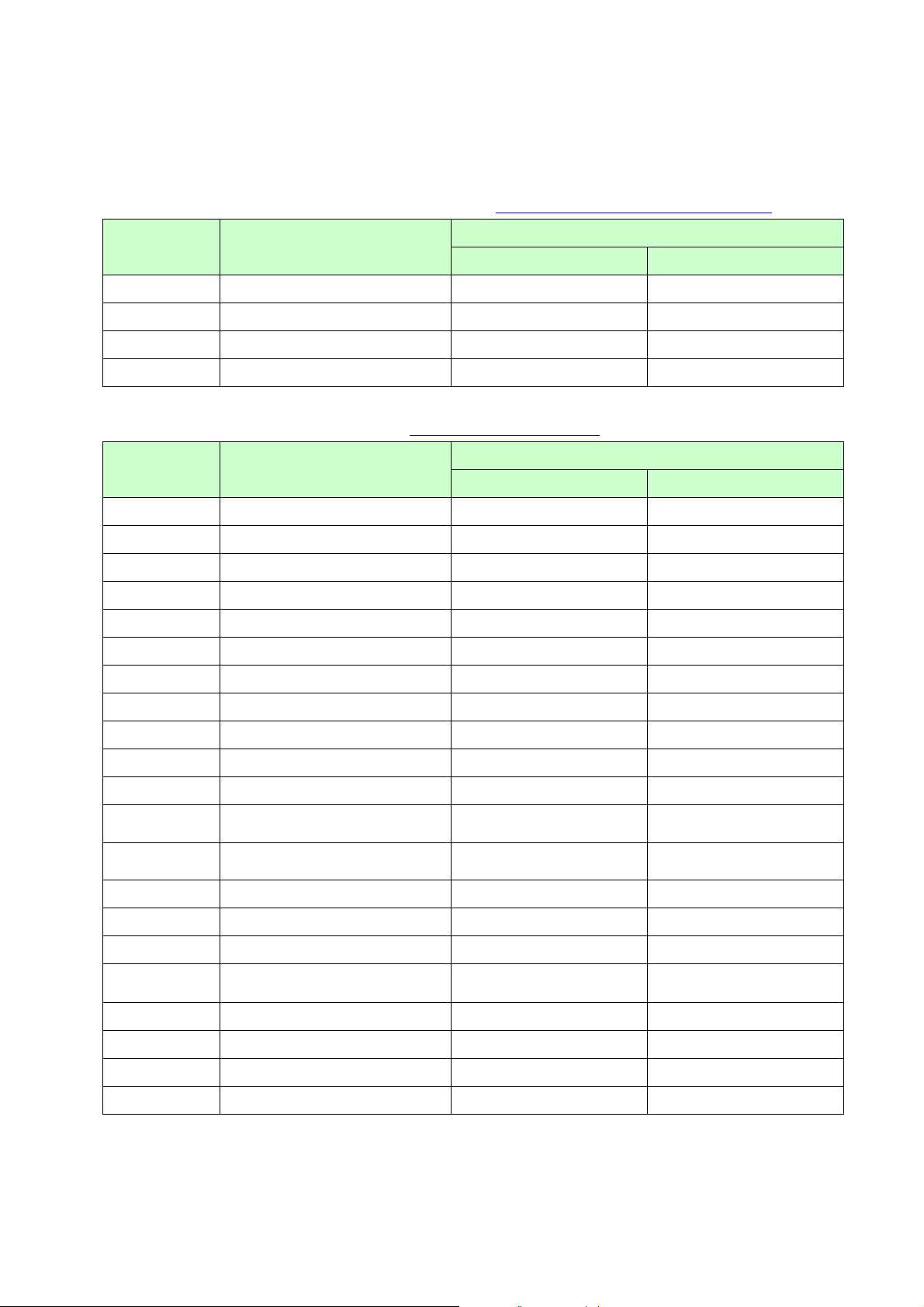
4. Control Code List
Character/style selection commands (Refer to section 5.1 Character/style selection commands.)
Commands Description
RJ-4XXX TD-4XXX
ESC R
ESC q
ESC k
ESC t
Select international character set
Select character style
Select font
Select character code set
○ ○
○ ○
○ ○
○ ○
Text printing commands (Refer to section 5.2 Text printing commands.)
Commands Description
RJ-4XXX TD-4XXX
ESC 4
ESC 5
ESC E
ESC F
ESC G
ESC H
ESC P
Apply italic style
Cancel italic style
Apply bo ld style
Cancel bold style
Apply double-strike printing
Cancel double-strike printing
Apply pica pitch (10 cpi)
○ ○
○ ○
○ ○
○ ○
○ ○
○ ○
○ ○
Series
Series
ESC M
ESC q
ESC p
ESC W
SO
ESC SO
SI
ESC SI
DC2
DC4
ESC -
ESC !
ESC SP
ESC X
Apply elite pitch (12 cpi)
Apply micron pitch (15 cpi)
Specify proportional characters
Specify double-width characters
Specify auto-
○ ○
○ ○
○ ○
○ ○
○ ○
○ ○
Specify compressed characters
Specify compressed characters
Cancel compressed characters
○ ○
○ ○
○ ○
○ ○
Apply/cancel underlining
Global formatting
Specify character spacing
○ ○
○ ○
○ ○
Specify character size ○ ○
- 17 -
4. Control Code List
Page 24
Specify absolute
horizontal position
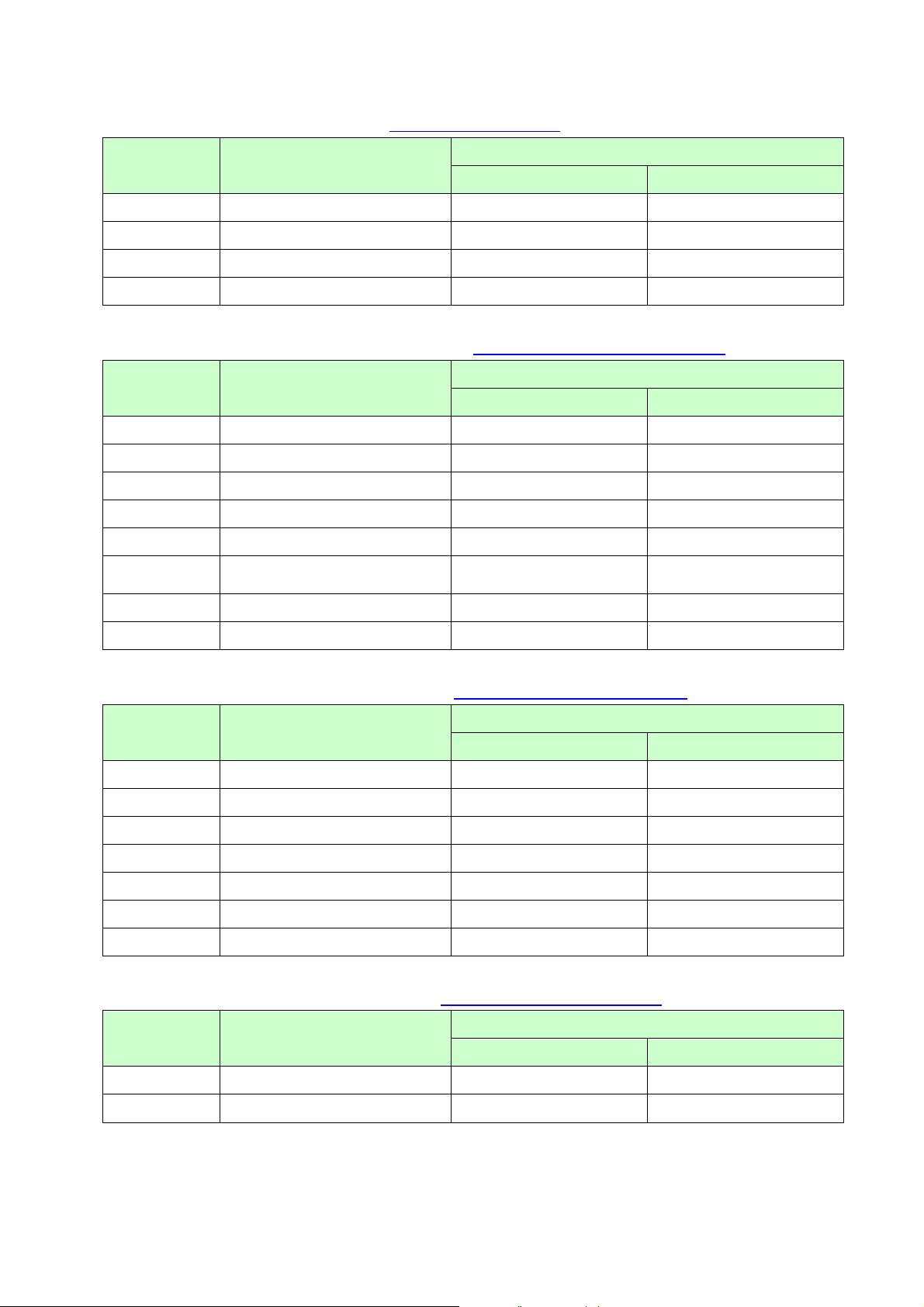
Line feed commands (Refer to section 5.3 Line feed commands.)
ESC/P Command Reference
Commands Description
Series
RJ-4XXX TD-4XXX
ESC 0
ESC 2
ESC 3
ESC A
Specify line feed of 1/8 inch
Specify line feed of 1/6 inch
Specify minimum line feed
Specify line feed of n/60 inch
○ ○
○ ○
○ ○
○ ○
Horizontal movement commands (Refer to section 5.4 Horizontal movement commands.)
Series
Commands Description
RJ-4XXX TD-4XXX
ESC l
ESC Q
CR
ESC D
HT
ESC $
Specify left margin
Specify right margin
Carriage return
Specify horizontal tab position
Perform horizontal tab
○ ○
○ ○
○ ○
○ ○
○ ○
○ ○
ESC \
ESC a
Specify relative horizontal position
Specify alignment
○ ○
○ ○
Vertical movement commands (Refer to section 5.5 Vertical movement commands.)
Series
Commands Description
RJ-4XXX TD-4XXX
LF
FF
ESC J
ESC B
VT
ESC ( V
ESC ( v
Line feed
Page feed
Forward paper feed
Specify vertical tab position
Perform vertical tab
Specify absolute vertical position
Specify relative vertical position
○ ○
○ ○
○ ○
○ ○
○ ○
○ ○
○ ○
Paper formatting commands (Refer to section 5.6 Paper formatting commands.)
Series
Commands Description
RJ-4XXX TD-4XXX
ESC ( c Specify page format ○ ○
ESC ( C Specify page length ○ ○
- 18 -
4. Control Code List
Page 25
8-dot double-speed
double-density bit image
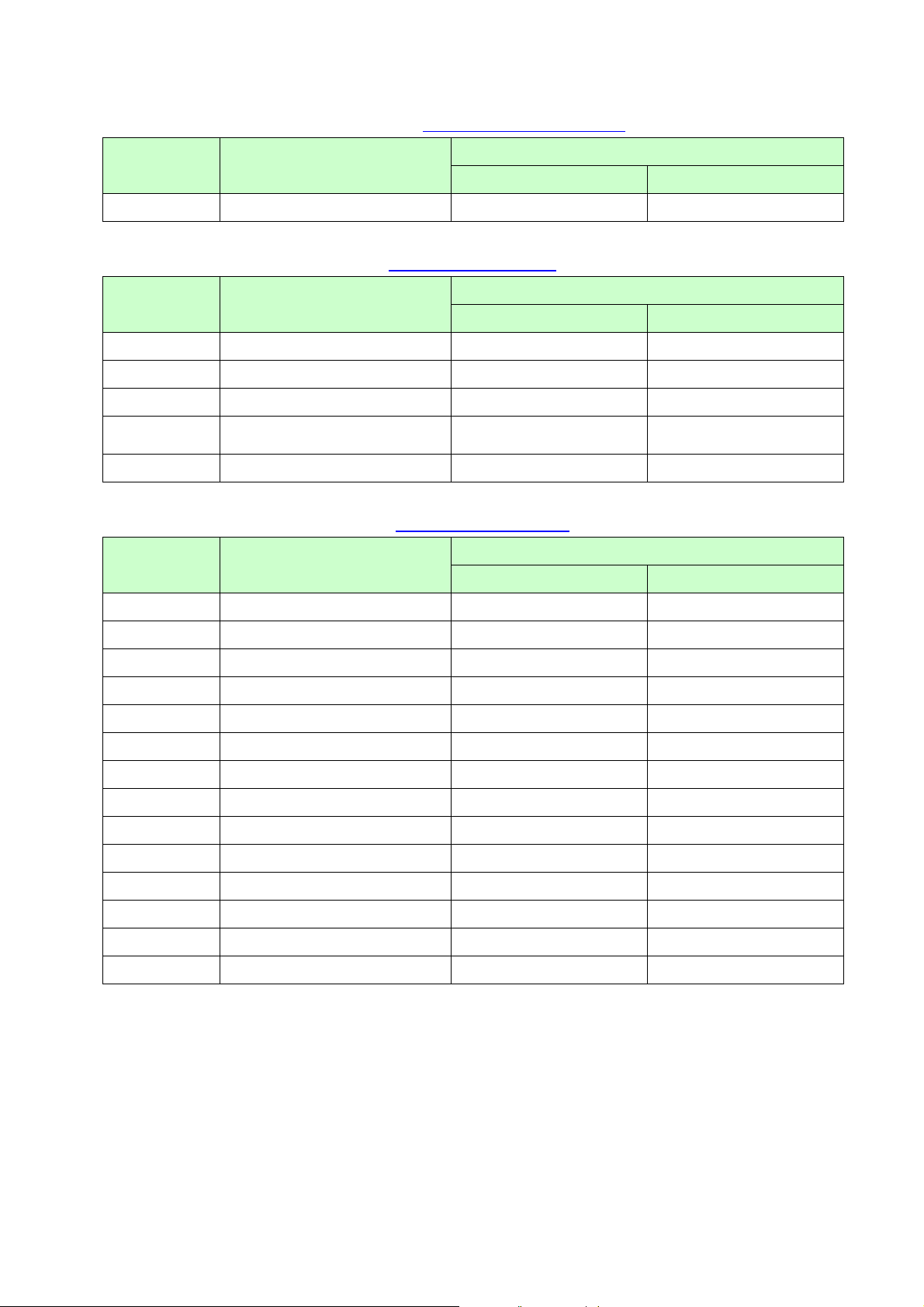
Printer control comm ands (Refer to section 5.7 Printer control commands.)
ESC/P Command Reference
Commands Description
RJ-4XXX TD-4XXX
ESC @
Initialize (defaults)
○ ○
Graphics commands (Refer to section 5.8 Graphics commands.)
Commands Description
RJ-4XXX TD-4XXX
ESC *
ESC K
ESC L
ESC Y
ESC Z
Select bit image.
8-dot single-density bit image
8-dot double-density bit image
8-dot quadruple-density bit image
○ ○
○ ○
○ ○
○ ○
○ ○
Advanced commands (Refer to section 5.9 Advanced commands.)
Commands Description
RJ-4XXX TD-4XXX
Series
Series
Series
ESC i B
ESC i Q
ESC i P
ESC i V
ESC i D
ESC i M
ESC i J
ESC i G
ESC i F P
ESC i a
ESC i S
ESC i L
ESC i C
ESC i H
Barcode
2D barcode (QR Code)
Specify QR Code version
2D barcode (PDF417)
2D barcode (DataMatrix)
2D barcode (MaxiCode)
2D barcode (Aztec)
Specify font setting
Print downloaded data
Switch command mode
Status information request
Specify landscape orientation
Specify cutting
Specify recovery setting
○ ○
○ ○
○ ○
○ ○
○ ○
○ ○
○ ○
○ ○
○ ○
○ ○
○ ○
○ ○
- ○
○ ○
- 19 -
4. Control Code List
Page 26
orientation
Retrieve default landscape
orientation
Select default international
character set
Retrieve default international
character set
set
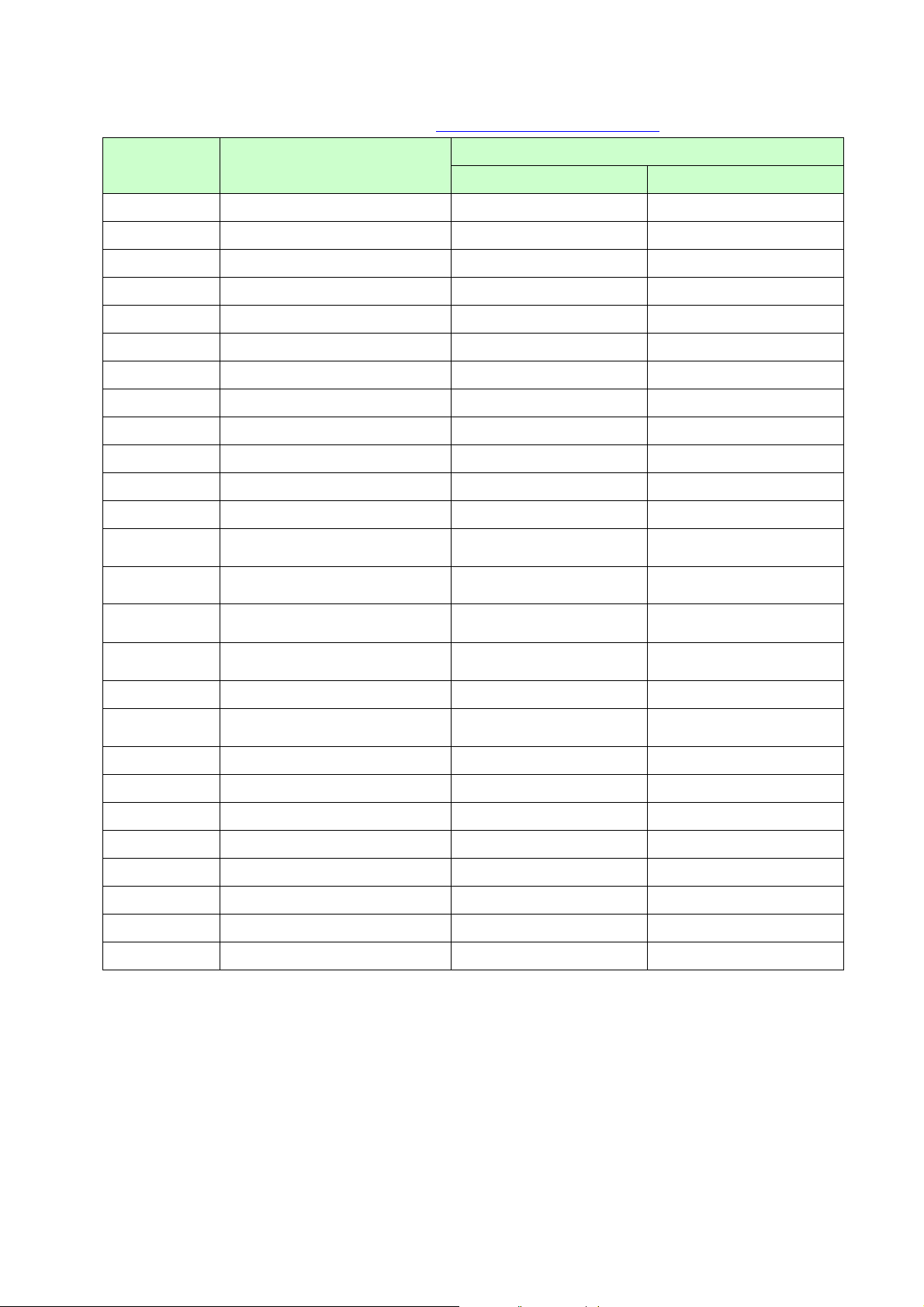
Advanced static commands (Refer to section 5.10 Advanced static commands.)
ESC/P Command Reference
Commands Description
ESC iXQ2
ESC iXQ1
ESC iXk2
ESC iXk1
ESC iXX2
ESC iXX1
ESC iX32
ESC iX31
ESC iXA2
ESC iXA1
ESC iX(2
ESC iX(1
ESC iXL2
ESC iXL1
Select default character style
Retrieve default character style
Select default font
Retrieve default font
Specify default character size
Retrieve default character size
Specify default line feed
Retrieve default line feed
Select default alignment
Retrieve default alignment
Specify default page length
Retrieve default page length
Select default landscape
Series
RJ-4XXX TD-4XXX
○ ○
○ ○
○ ○
○ ○
○ ○
○ ○
○ ○
○ ○
○ ○
○ ○
○ ○
○ ○
○ ○
○ ○
ESC iXj2
ESC iXj1
ESC iXm2
ESC iXm1
ESC iXd2
ESC iXd1
ESC iXE2
ESC iXE1
ESC iX_2 (00h)
ESC iX_1(00h)
ESC iX_2 (01h)
ESC iX_1 (01h)
Select default character code set
Retrieve default character code
Specify recovery setting
Retrieve recovery setting
Specify barcode margin setting
Retrieve barcode margin setting
Specify line-print mode
Retrieve line-print mode
Specify line-print timeout
Retrieve line-print timeout
○ ○
○ ○
○ ○
○ ○
○ ○
○ ○
○ ○
○ ○
○ ○
○ ○
○ ○
○ ○
- 20 -
4. Control Code List
Page 27
ESC/P Command Reference
n=0:
U.S.A.
n=1:
France
n=2:
Germany
n=3:
U.K.
n=4:
Denmark I
n=5:
Sweden
n=6:
Italy
n=7:
Spain I
n=8:
Japan
n=9:
Norway
n=10:
Denmark II
n=11:
Spain II
n=12:
Latin America
n=13:
South Korea
n=64:
Legal
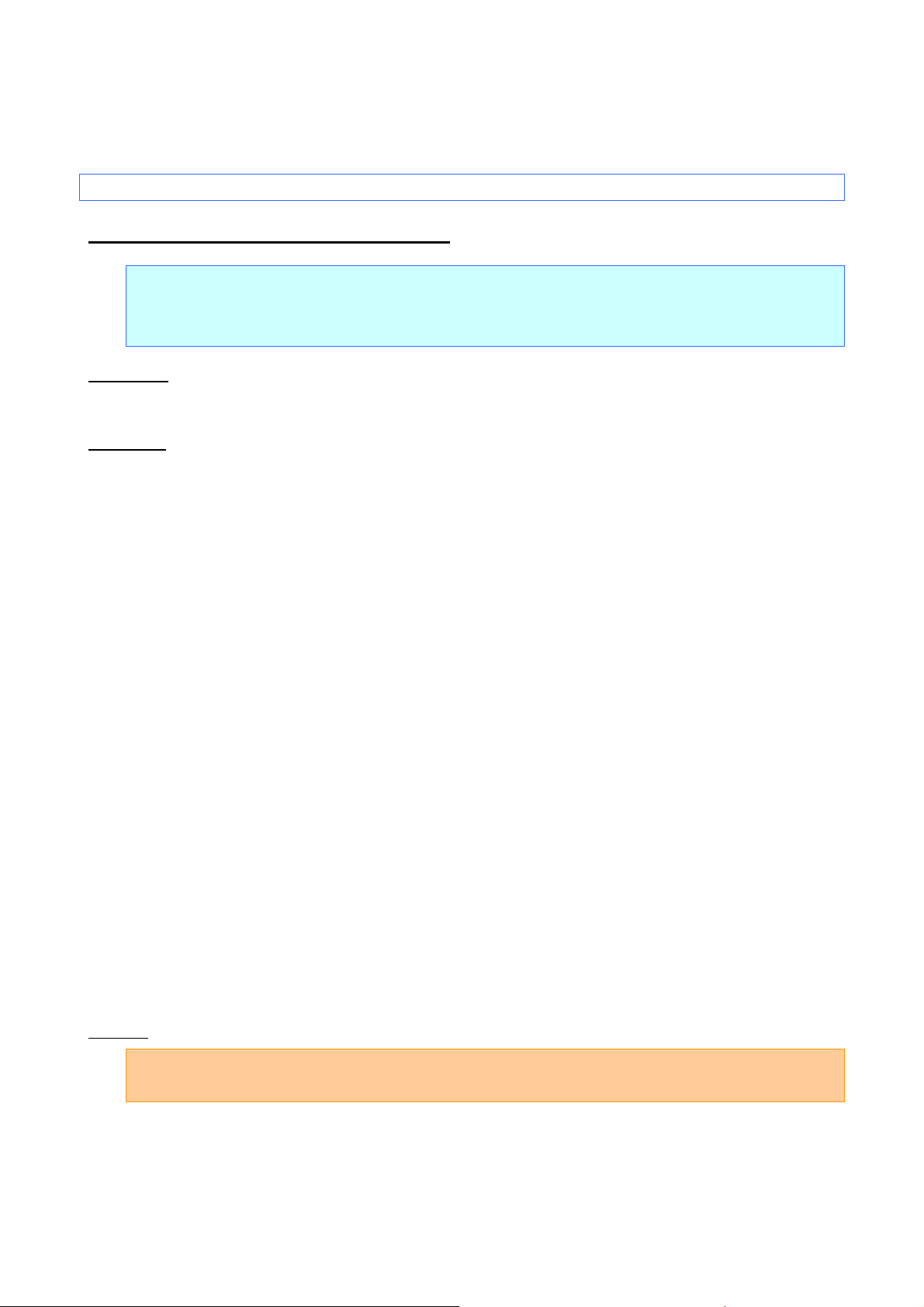
5. Control Command Details
5.1 Character/style selection commands
ESC R Select international character set
ASCII: ESC R n
Decimal: 27 82 n
Hexadecimal: 1B 52 n
Parameters
0≤n≤13, 64
Description
Selects the character set, and switches some of the character codes in the code table according to the
value of n.
The following 12 codes are switched.
The default setting is n=0 (U.S.A.)
Example
23h, 24h, 40h, 5Bh, 5Ch, 5Dh, 5Eh, 60h, 7Bh, 7Ch, 7Dh, 7Eh
Code: 5Ch ESC R 08h 5Ch FF
Print result: \ ¥
- 21 -
5. Control Command Details
Page 28
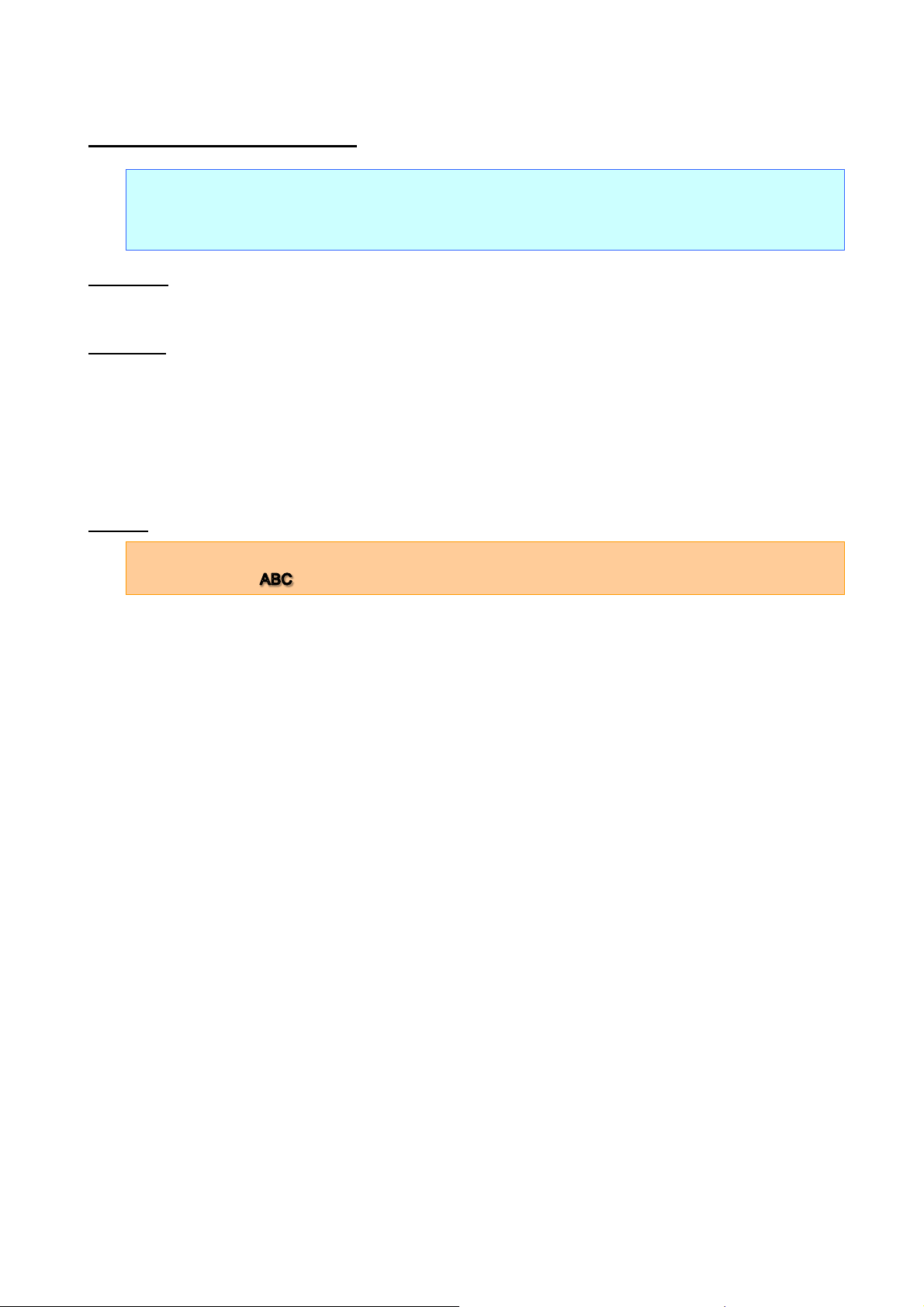
n=0:
None (normal characters)
n=1:
Outline
n=2:
Shadow
n=3:
Shadow and outline
ESC q Select character style
ASCII: ESC q n
Decimal: 27 113 n
Hexadecimal: 1B 71 n
Parameters
0≤n≤3
Description
Selects the character style.
ESC/P Command Reference
Example
Code: ABC ESC q 02h ABC ESC q 00h ABC FF
Print result: ABC ABC
- 22 -
5. Control Command Details
Page 29
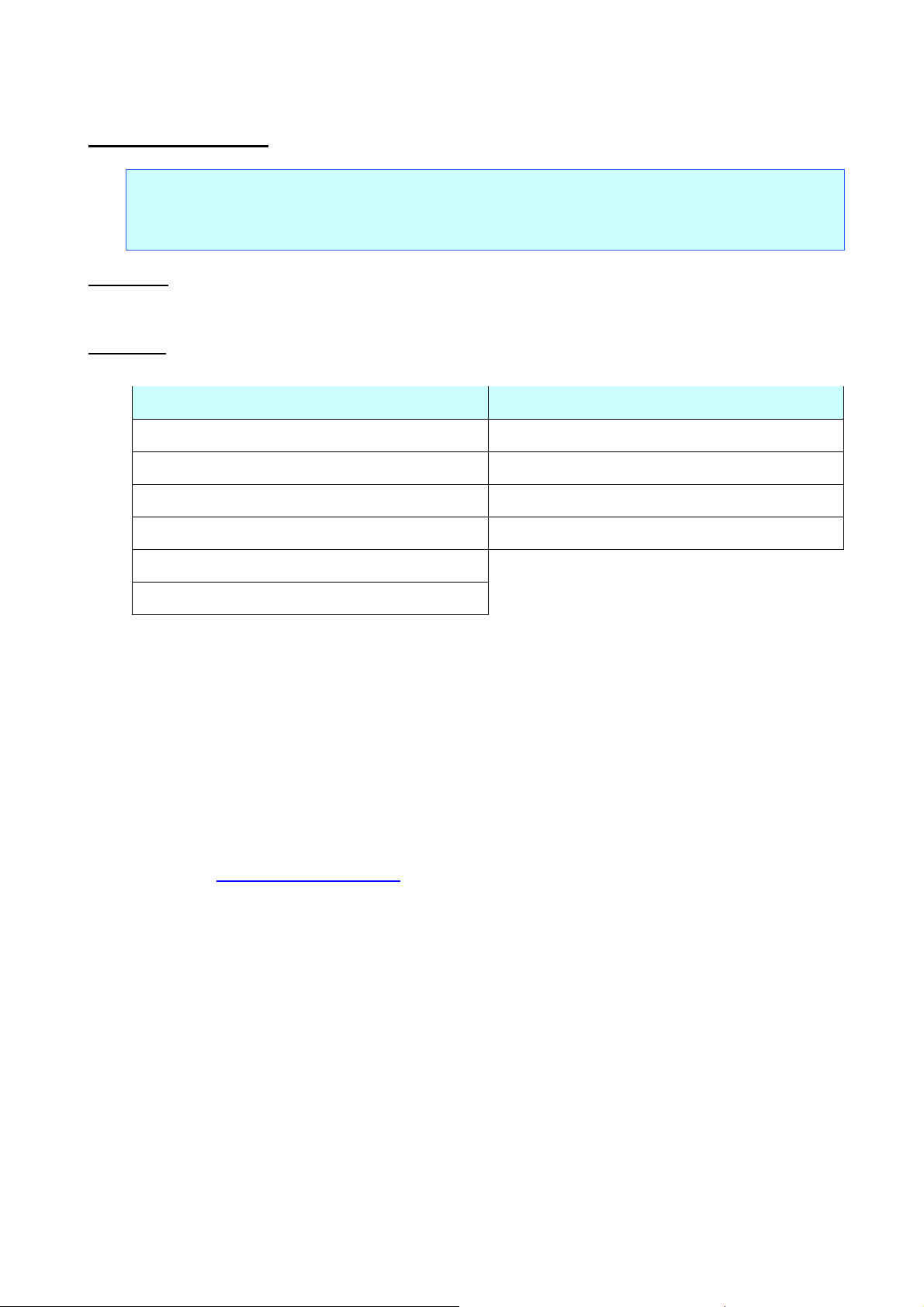
Bitmap Fonts
Outline Fonts
n=0 Gothic (proportional pitch)
n=8 Gothic (proportional pitch)
n=1 Letter Gothic Bold (fixed pitch)
n=9 Letter Gothic (fixed pitch)
n=2 Brussels (proportional pitch)
n=10 Brussels (proportional pitch)
n=3 Helsinki (proportional pitch)
n=11 Helsinki (proportional pitch)
n=4 San Diego (proportional pitch)
n=5 Brougham (fixed pitch)
ESC k Select font
ASCII: ESC k n
Decimal: 27 107 n
Hexadecimal: 1B 6B n
Parameters
0≤n≤5, 8≤n≤11
Description
Selects the font.
ESC/P Command Reference
If the font is changed from a bitmap font to outline font, the character size is changed to the default setting
(28 dots).
If the font is changed from an outline font to bitmap font, the character size is changed to default setting
(24 dots).
If the selected font is not supported current size setting, character size is changed to the default setting (24
dots).
Proportional pitched Gothic is forced to be selected when a character assigned from 0x80 to 0xFF in the
Japanese character code table is used. If the character size is set to 48dot, it is not printed.
The state at power-on is according to the setting of ESC iXk 2 (default type setting).
Please refer to Appendix B: Specifications.
- 23 -
5. Control Command Details
Page 30

n=0:
Standard character code set
n=1:
Eastern European character code set
n=2:
Western European character code set
n=3:
Reserved
n=4:
Japanese character code set
ESC t Select character code set
ASCII: ESC t n
Decimal: 27 116 n
Hexadecimal: 1B 74 n
Parameters
0≤n≤4
Description
From the four built-in character code sets, selects the character code set used.
ESC/P Command Reference
The default setting is n=0.
Invalid if n is a value outside of the allowable range.
- 24 -
5. Control Command Details
Page 31

5.2 Text printing commands
ESC 4 Apply italic style
ASCII: ESC 4
Decimal: 27 52
Hexadecimal: 1B 34
Parameters
None
Description
Prints the subsequent text in italics.
This command is valid anywhere in a text line.
ESC/P Command Reference
ESC 5 Cancel italic style
ASCII: ESC 5
Decimal: 27 53
Hexadecimal: 1B 35
Parameters
None
Description
Cancels the italic character style.
This command is valid anywhere in a text line.
Example
Code: ABC ESC 4 DEF ESC 5 GHI FF
Print result: ABCDEFGHI
- 25 -
5. Control Command Details
Page 32

ESC E Apply bold style
ASCII: ESC E
Decimal: 27 69
Hexadecimal: 1B 45
Parameters
None
Description
Prints the subsequent text in bold.
This command is valid anywhere in a text line.
ESC F Cancel bold style
ESC/P Command Reference
ASCII: ESC F
Decimal: 27 70
Hexadecimal: 1B 46
Parameters
None
Description
Cancels the bold style.
This command is valid anywhere in a text line.
Example
Code: ABC ESC E DEF ESC F GHI FF
Print result: ABCDEFGHI
- 26 -
5. Control Command Details
Page 33

ESC G Apply double-strike printing
ASCII: ESC G
Decimal: 27 71
Hexadecimal: 1B 47
Parameters
None
Description
Prints the subsequent text in bold.
This command is valid anywhere in a text line.
ESC H Cancel double-strike printing
ESC/P Command Reference
ASCII: ESC H
Decimal: 27 72
Hexadecimal: 1B 48
Parameters
None
Description
Cancels the bold style.
This command is valid anywhere in a text line.
Example
Code: ABC ESC G DEF ESC H GHI FF
Print result: ABCDEFGHI
- 27 -
5. Control Command Details
Page 34

ESC/P Command Reference
Full Width
Double Width
Half Width
16
24
32
48
16
24
32
48
16
24
32
48
Letter
Bold
ESC P Apply pica pitch (10 cpi)
ASCII: ESC P
Decimal: 27 80
Hexadecimal: 1B 50
Parameters
None
Description
Prints the subsequent text with the pica pitch (10 characters/inch).
The character spacing is 20 dots (30 dots for 300dpi printers).
If the character width is 20(or 30) dots or less, the character spacing is specified as 20(or 30) minus the
character width.
If the character width exceeds 20(or 30) dots, the character spacing is specified as the character width.
(The spacing between characters is 0 dot.)
In this case, the pitch does not exactly equal the pica pitch.
With double-width characters, the character spacing is doubled (40(or 60) dots).
With half-width characters, the character spacing is halved (10(or 15) dots).
When the character spacing is changed with ESC SP, the setting is updated.
This command is invalid when proportional pitch is selected.
In outline fonts, the spacing between characters is 0 dot.
Please refer to Appendix B: Specifications.
Setting
(dots)
Gothic 16 24 32 - 32 48 64 - 8 12 16 -
Gothic
8 10 14 22 16 20 28 44 4 5 7 11
Width (dots)
Brussels - 25 35 56 - 50 70 112 - 13 18 26
The above table refers to characters with a fixed pitch. (Applying styles may increase the size.)
Helsinki 16 21 28 44 30 42 56 88 8 11 14 22
San Diego - 24 35 57 - 48 70 114 - 12 18 29
Brougham - 11 16 26 - 22 32 52 - 6 8 13
- 28 -
5. Control Command Details
Page 35

A
B
5 dots
15 dots
A
B
30
dots
10 dots
Full width
Double width
Example
For a 15-dot font at full width:
ESC/P Command Reference
- 29 -
5. Control Command Details
Page 36

ESC/P Command Reference
A
B
1 dot
15 dots
A
B
30 dots
2 dots
Full width
Double width
ESC M Apply elite pitch (12 cpi)
ASCII: ESC M
Decimal: 27 77
Hexadecimal: 1B 4D
Parameters
None
Description
Prints the subsequent text with the elite pitch (12 characters/inch).
The character spacing is 16 dots (25 dots for 300dpi printers).
If the character width is 16(or 25) dots or less, the character spacing is specified as 16(or 25) m inus the
character width.
If the character width exceeds 16(or 25) dots, the character spacing is specified as the character width.
(The spacing between characters is 0 dot.)
In this case, the pitch does not exactly equal the elite pitch.
With double-width characters, the character spacing is doubled (32(or 50) dots).
With half-width characters, the character spacing is halved (8(or 13) dots).
When the character spacing is changed with ESC SP, the setting is updated.
This command is invalid when proportional pitch is selected.
In outline fonts, the spacing between characters is 0 dot.
Example
For a 15-dot font at full width:
- 30 -
5. Control Command Details
Page 37

ESC/P Command Reference
A
B
9 dot
11 dots
A
B
22 dots
18 dots
Full width
Double width
ESC g Apply micron pitch (15 cpi)
ASCII: ESC g
Decimal: 27 103
Hexadecimal: 1B 67
Parameters
None
Description
Prints the subsequent text with the micron pitch (15 characters/inch).
This command is not applied to 203dpi printers.
The character spacing is 20 dots.
If the character width is 20 dots or less, the character spacing is specified as 20 minus the character width.
If the character width exceeds 20 dots, the character spacing is specified as the character width.
(The spacing between characters is 0 dot.)
In this case, the pitch does not exactly equal the micron pitch.
With double-width characters, the character spacing is doubled (40 dots).
With half-width characters, the character spacing is halved (10 dots).
When the character spacing is changed with ESC SP, the setting is updated.
This command is invalid when proportional pitch is selected.
In outline fonts, the spacing between characters is 0 dot.
Example
For a 11-dot font at full width:
- 31 -
5. Control Command Details
Page 38

ESC/P Command Reference
n=1 or 49 (“1”): Specifies proportional characters.
n=0 or 48 (“0”): Cancels proportional characters.
n=1 or 49 (“1”): Specifies double-width characters.
n=0 or 48 (“0”): Cancels double-width characters.
ESC p Specify proportional characters
ASCII: ESC p n
Decimal: 27 112 n
Hexadecimal: 1B 70 n
Parameters
n=0, 1, 48 (“0”), 49 (“1”)
Description
Specifies proportional characters.
If proportional characters are specified, the character spacing specified with ESC SP is maintained as is.
ESC W Specify double-width characters
ASCII: ESC W n
Decimal: 27 87 n
Hexadecimal: 1B 57 n
Parameters
n=0, 1 or 48 (“0”), 49 (“1”)
Description
Specifies double-width characters.
Double-width characters specified with this command are not canceled with the DC4 or a line feed.
Canceling double-width characters also cancels compressed (half-width) characters.
Example
Code: ABC ESC W 1 ABC ESC W 0 ABC FF
Print result: ABC
ABC
ABC
- 32 -
5. Control Command Details
Page 39

ESC/P Command Reference
SO Specify auto-canceling stretched characters
ASCII: SO
Decimal: 14
Hexadecimal: 0E
Parameters
None
Description
Prints the subsequent text at double width.
This command is canceled with DC4, CR, LF, VT, FF, ESC J, or an automatic line feed.
This command is canceled with ESC $, ESC \, ESC ( V or ESC ( v.
This command can also be canceled with ESC W0.
ESC SO Specify auto-canceling stretched characters
ASCII: ESC SO
Decimal: 27 14
Hexadecimal: 1B 0E
Parameters
None
Description
Same as SO
Example
Code: ABC ESC SO ABCDEFGHIJK…XYZ FF
Print result: ABC
XYZ
ABCDEFGHIJK…
(Automatic line feed)
- 33 -
5. Control Command Details
Page 40

SI Specify compressed characters
ASCII: SI
Decimal: 15
Hexadecimal: 0F
Parameters
None
Description
Prints the subsequent text at half width.
ESC SI Specify compressed characters
ESC/P Command Reference
ASCII: ESC SI
Decimal: 27 15
Hexadecimal: 1B 0F
Parameters
None
Description
Same as SI
- 34 -
5. Control Command Details
Page 41
DC2 Cancel compressed characters
ASCII: DC2
Decimal: 18
Hexadecimal: 12
Parameters
None
Description
Cancels compressed characters specified with SI.
DC4 Cancel auto-canceling double-width characters
ESC/P Command Reference
ASCII: DC4
Decimal: 20
Hexadecimal: 14
Parameters
None
Description
Cancels double-width characters specified with ESC SO or SO.
Does not cancel the ESC W command.
Example
Code: ABC ESC SO ABCDEF DC4 GHIJK FF
Print result: ABC
ABCDEF
GHIJK
- 35 -
5. Control Command Details
Page 42

n=4 or 52 (“4”): Applies underlining with a width of 4 dots.
n=3 or 51 (“3”): Applies underlining with a width of 3 dots.
n=2 or 50 (“2”): Applies underlining with a width of 2 dots.
n=1 or 49 (“1”): Applies underlining with a width of 1 dot.
n=0 or 48 (“0”): Cancels underlining.
Underline
Underline Position
1 dot wide
2 dots below the characters
2 dots wide
Between 2 dots and 3 dots below the characters
3 dots wide
Between 1 dot and 3 dots below the characters
4 dots wide
Between 1 dot and 4 dots below the characters
ABCDE ABCDE ABCDE
(1-dot width) (3-dot width)
ESC – Apply/cancel underlining
ASCII: ESC - n
Decimal: 27 45 n
Hexadecimal: 1B 2D n
Parameters
n=0, 1, 2, 3, 4 or 48 (“0”), 49 (“1”), 50 (“2”), 51 (“3”), 52 (“4”)
Description
Applies or cancels underlining.
ESC/P Command Reference
This command is valid anywhere in a text line.
The underlining specified with this command is a continuous line.
Spaces between characters and words are also underlined.
Areas with the “specify absolute horizontal position” (ESC $) and “specify relative horizontal position”
(ESC \) commands are not underlined.
4 dots is added to the line feed amount for lines that include underlined characters.
The underline is positioned as follows:
Example
Code: ABC ESC - 1 ABC ESC - 0 ABC FF
Print result: ABCABCABC
- 36 -
5. Control Command Details
Page 43

ESC/P Command Reference
Bit 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
width
heig ht
0
Cancel
Cancel
Cancel
Cancel
Cancel
Cancel
Cancel
10 cpi
ESC ! Global formatting
ASCII: ESC ! n
Decimal: 27 33 n
Hexadecimal: 1B 21 n
Parameters
0≤n≤255
Description
Specifies a combination of print modes.
Specifies modes depending on the bit value of n.
When the ESC ! code is used, a combination of multiple print modes can be specified at one time.
The priority order is from Bit 5 to Bit 2.
Bit 0 is available only if Bit 1 is 0.
Selected character styles are canceled, and the characters return to the normal style.
Canceling double-width characters also cancels compressed (half-width) characters.
1 Underline Italics
Double
Double
Bold Compressed Proportional 12 cpi
Example
To apply underlining and specify double-width characters at the same time:
Code: ABC ESC ! A2h ABC ESC ! 00h ABC FF
Print result: ABC
ABC
A B C
- 37 -
5. Control Command Details
Page 44

ESC/P Command Reference
ESC SP Specify character spacing
ASCII: ESC SP n
Decimal: 27 32 n
Hexadecimal: 1B 20 n
Parameters
0≤n≤127
Description
Specifies the character spacing.
n indicates the number of dots.
The default setting is 0 dot.
With double-width characters, the character spacing is doubled; with half-width characters, it is halved.
- 38 -
5. Control Command Details
Page 45

Character width:
The value of m is irrelevant.
Character size:
<Bitmap fonts>
nH=0
<Outline fonts>
nH=1
ESC X Specify character size
ASCII: ESC X m nL nH
Decimal: 27 88 m nL nH
Hexadecimal: 1B 58 m nL nH
Parameters
ESC/P Command Reference
Valid only with:
nL=16, 24, 32, 48 dots
The maximum is:
nL=144
Description
This command is used only to change the size.
Outline must not be specified.
The character width cannot be specified.
The character size is specified as n=nL+nH*256 dots.
With bitmap font Gothic, only n=16, 24 and 32 are valid.
With bitmap font Letter Gothic Bold and Helsinki, only n=16, 24, 32 and 48 are valid.
With bitmap font Brussels, San Diego and Brougham, only n=24, 32 and 48 are valid.
With outline fonts, n=400 is the maxim um .
The commands for specifying stretched characters, compressed characters and the character spacing
(SO, ESC W, SI, ESC !, ESC SP) remain available.
Please refer to Appendix B: Specifications.
Example
For “ABC” at a 24-dot size and “DEF” at a 48-dot size:
Code: ESC k 01h
ESC X 00h 18h 00h ABC
ESC k 09h
ESC X 00h 30h 00h DEF FF
Print result: ABCDEF
- 39 -
5. Control Command Details
Page 46

5.3 Line feed commands
ESC 0 Specify line feed of 1/8 inch
ASCII: ESC 0
Decimal: 27 48
Hexadecimal: 1B 30
Parameters
None
Description
Specifies a line feed of 1/8 inch (about 0.32 cm).
ESC/P Command Reference
ESC 2 Specify line feed of 1/6 inch
ASCII: ESC 2
Decimal: 27 50
Hexadecimal: 1B 32
Parameters
None
Description
Specifies a line feed of 1/6 inch (about 0.42 cm).
- 40 -
5. Control Command Details
Page 47

ESC 3 Specify minimum line feed
ASCII: ESC 3 n
Decimal: 27 51 n
Hexadecimal: 1B 33 n
Parameters
0≤n≤255
Description
Specifies a line feed of n dots per line.
ESC A Specify line feed of n/60 inch
ESC/P Command Reference
ASCII: ESC A n
Decimal: 27 65 n
Hexadecimal: 1B 41 n
Parameters
0≤n≤255
Description
Specifies a line feed of n/60 inch.
- 41 -
5. Control Command Details
Page 48

ESC/P Command Reference
1 2
3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16
Print area
Unprinted
area
Unprinted
area
Left margin setting
Right margin setting
Left edge
Left margin position
Right margin position
Printable area
Example: Left margin=Column 5; right margin=Column 14
Columns
・
・
5.4 Horizontal movement commands
ESC l Specify left margin
ASCII: ESC l n
Decimal: 27 108 n
Hexadecimal: 1B 6C n
Parameters
0≤n≤255
0≤left margin<right margin
Description
The left margin and the right margin use the left edge of the physically printable area as the reference.
The area between the left edge of the physically printable area and the specified number of columns is
specified as an unprinted area. The left margin position is the right edge of the specified column.
(Character width*n)
The setting is in the range 0≤ (character width*n) ≤x. Settings outside that range are ignored. However, x is
a value dependent on the media.
The area between the left edge (first column) to the nth column is specified as an unprinted area.
The position of the left margin is the character width (when this command was specified)*n from the left
edge.
The character width when the margin specified includes the settings for the character spacing, full-width
character spacing or half-width character spacing. In addition, when a pitch of 10 cpi , 12 cpi or 15 cpi,
compressed characters or double-width characters are specified, that character width is considered as the
unit.
However, character styles that increase the character width are not applied.
- 42 -
5. Control Command Details
Page 49

ESC/P Command Reference
The horizontal print position is moved to the left margin position.
If the left margin setting is not at the beginning of the line, the left margin is specified after a line feed.
The beginning of the line indicates the left margin position for left alignment; for right and center alignment,
it means that no image or character is entered on the line.
Even if the character width is changed after the left margin has been specified, the left margin position
does not change.
A left margin setting that puts the left margin position to the right of the right margin position is ignored.
The left margin should be specified at least one column less than the right margin.
If the difference between the right margin position and the left margin position is less than one character,
that character is ignored.
When proportional pitch is specified with the ESC p command, a character width of 10 cpi is applied.
If the print media is continuous length tape, the printing orientation is landscape and the page length is not
specified, commands specifying the left margin are ignored.
Example
To specify the left margin at Column 3:
Code: ABC CR ESC l 03h EFGHIJ FF
Print result: ABC
EFGHIJ
- 43 -
5. Control Command Details
Page 50

ESC/P Command Reference
ESC Q Specify right margin
ASCII: ESC Q n
Decimal: 27 81 n
Hexadecimal: 1B 51 n
Parameters
1≤n≤255
Left margin<character width (when the command was specified)*n≤printable area
Description
The left margin and the right margin use the left edge of the physically printable area as the reference.
The right margin position is the right edge of the specified column. (Character width*n)
The setting is in the range 1≤(character width*n)≤x. Settings outside that range are ignored. However, x is
a value dependent on the media.
Left margin≤print area<right margin
The position of the right margin is the character width (when the command was specified)*n from the left
edge.
The character width when the margin is specified includes the settings for the character spacing, full-width
character spacing or half-width character spacing. In addition, when a pitch of 10 cpi ,12 cpi or 15cpi,
compressed characters or double-width characters are specified, that character width is considered as the
unit.
However, character styles that increase the character width are not applied.
The horizontal print position is moved to the left margin position.
If the right margin setting is not at the beginning of the line, the right margin is specified after a line feed.
The beginning of the line indicates the left margin position for left alignment; for right and center alignment,
it means that no image or character is entered on the line.
Even if the character width is changed after the right margin has been specified, the right margin position
does not change.
A right margin setting that puts the right margin position to the left of the left margin position is ignored.
The right margin should be specified at least one column greater than the left margin.
If the difference between the right margin position and the left margin position is less than one character,
that character is ignored.
When proportional pitch is specified with the ESC p command, a character width of 10 cpi is applied.
If the print media is continuous length tape, the printing orientation is landscape and the page length is not
specified, commands specifying the right margin are ignored.
- 44 -
5. Control Command Details
Page 51

CR Carriage return
ASCII: CR
Decimal: 13
Hexadecimal: 0D
Parameters
None
Description
Ends input of a line, and waits for input of the next line.
The next print position becomes the beginning of the next line.
A line feed command immediately after the carriage return is ignored.
Auto-canceling double-width characters specified with SO or ESC SO are canceled.
Same process as LF
ESC/P Command Reference
- 45 -
5. Control Command Details
Page 52

ESC/P Command Reference
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16
Unprinted area
HT code
Left edge
Left margin position
Right margin position
Printable area
Example:
After the left margin is specified as Column 3 and the right margin as Column 15,
horizontal tabs were specified at Column 5 and Column 10, and HT were performed.
Column
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
10
11
12 13 14
Tab position
Tab position
HT code
Unprinted area
・
・
・
ESC D Specify horizontal tab position
ASCII: ESC D [n]k NUL
Decimal: 27 68 [n]k 0
Hexadecimal: 1B 44 [n]k 00h
Parameters
1≤n≤255, 0≤k≤32
Description
The horizontal tab position is the character width (when the command was specified)*n from the left
margin.
Enter n values in ascending order and end the settings with NUL.
If an n value is smaller than a previous one, tab setting is ended.
Even if the character width is changed after the horizontal tab positions have been specified, the horizontal
tab position settings do not change.
ESC D NUL cancels all horizontal tab positions.
If the left margin is moved, the horizontal tab positions are also moved by the same amount.
Up to 32 horizontal tab positions can be specified. However, horizontal tab positions beyond the right
margin are invalid and only become valid when a change in the right margin setting or left margin setting
moves the print area to include those tab positions.
The character width when the horizontal tabs are specified includes the settings for the character spacing,
full-width character spacing or half-width character spacing. In addition, when a pitch of 10 cpi, 12 cpi, or
15 cpi, compressed characters or double-width characters are specified, that character width is
considered as the unit.
When proportional pitch is specified with ESC p, horizontal tab positions are specified at 10 cpi.
When the printer is turned on, a horizontal tab position is specified every 8 columns at 10 cpi.
Even if the character width is changed before the horizontal tab positions has been specified, the
horizontal tab positions do not change.
- 46 -
5. Control Command Details
Page 53

ESC/P Command Reference
HT Perform horizontal tab
ASCII: HT
Decimal: 9
Hexadecimal: 09
Parameters
None
Description
Moves the horizontal print position to the nearest horizontal tab position to the right of the input position.
If there is no horizontal tab position to the right of the input position, or if the next horizontal tab position is
beyond the right margin, the HT command is ignored.
If underlining is specified, the space between the current position and the next horizontal tab position is not
underlined.
When the printer is turned on, a horizontal tab position is specified every 8 columns at 10 cpi.
Even if the character width is changed before the horizontal tab positions have been specified, the
horizontal tab positions do not change.
This command is available only with left alignment.
Example
To specify horizontal tabs at Column 4, Column 8, and Column 12, and perform horizontal tabs:
Code: ESC D 04h 08h 0Ch 00h
123456789012 CR A HT B HT C HT D FF
Print result: 123456789012
A B C D
- 47 -
5. Control Command Details
Page 54

ESC/P Command Reference
ESC $ Specify absolute horizontal position
ASCII: ESC $ n1 n2
Decimal: 27 36 n1 n2
Hexadecimal: 1B 24 n1 n2
Parameters
0≤n1≤255, 0≤n2≤255
Description
Specifies the absolute print position (in dots) for the next data.
An absolute print position specifies the next print position as a number of dots from the left margin.
n1 and n2 indicate the number of dots from the left margin.
(Number of dots=n1+n2*256)
The maximum number of dots that can be specified with n1 and n2 depends on the media.
This command is available only with left alignment.
ESC \ Specify relative horizontal position
ASCII: ESC \ n1 n2
Decimal: 27 92 n1 n2
Hexadecimal: 1B 5C n1 n2
Parameters
0≤n1≤255, 0≤n2≤255
Description
Specifies the horizontal print position (in dots) as a relative position from the current position.
A relative position specifies the next print position as a number of dots from the current position.
n1 and n2 indicate the number of dots from the current position. (Number of dots=n1+n2*256)
Left margin position≤horizontal position after moving<right margin position
Horizontal position after moving=n1+n2*256
The specified value for moving to the left is expressed as a two's complement. It is determined by the
following equation.
n1+n2*256=65536-distance actually moved
This command is available only with left alignment.
- 48 -
5. Control Command Details
Page 55

ESC/P Command Reference
n=0 or 48 (“0”): Applies left alignment.
n=1 or 49 (“1”): Applies center alignment.
n=2 or 50 (“2”): Applies right alignment.
n=3 or 51 (“3”): Applies nothing.
ESC a Specify alignment
ASCII: ESC a n
Decimal: 27 97 n
Hexadecimal: 1B 61 n
Parameters
0≤n≤3 or “0”≤n≤“3”
Description
Prints the subsequent text with the alignment described below, according to the value of n.
The default setting is n=0.
Data is aligned between the left and right margins by entering a CR, LF, and FF code or by buffer printing.
If the alignment setting is not at the beginning of the line, the alignment is specified after a line feed.
The beginning of the line indicates the left margin position for left alignment;
for right and center alignment, it means that no image or character is entered on the line.
HT, ESC \ and ESC $ are ignored when n=1 or n=2.
If the print media is continuous length tape, the printing orientation is landscape and the page length is not
specified, commands specifying alignment are ignored.
- 49 -
5. Control Command Details
Page 56
ESC/P Command Reference
5.5 Vertical movement commands
LF Line feed
ASCII: LF
Decimal: 10
Hexadecimal: 0A
Parameters
None
Description
Feeds the paper by the amount specified by a line feed command (ESC 0, ESC 2, ESC 3, ESC A).
The print position becom es the beginning of the next line.
The default value is a line feed of 32 dots.
A carriage return immediately after a line feed is ignored.
Auto-canceling double-width characters specified with SO or ESC SO are canceled.
Same process as CR
FF Page feed
ASCII: FF
Decimal: 12
Hexadecimal: 0C
Parameters
None
Description
Starts the printing.
The previously entered data string of characters and commands is cleared after being printed.
At this time, auto-canceling double-width characters specified with SO or ESC SO are canceled.
- 50 -
5. Control Command Details
Page 57

ESC/P Command Reference
Abcdefg
ABC
SDFASG
Left alignment
Abcdefg
ABC
SD FA S G
Center alignment
Abcdefg
ABC
SD FA S G
Right alignment
Example: Performing a forward paper feed after the second line
ESC J Forward paper feed
ASCII: ESC J n
Decimal: 27 74 n
Hexadecimal: 1B 4A n
Parameters
0≤n≤255
Description
Ends input for the current line and moves the vertical print position forward by n dot.
If the bottom margin setting is exceeded, printing starts.
With left alignment, the print position for the next line becom es the end position of the current line.
(The horizontal position does not move to the left margin.)
With right alignment and center alignment, the horizontal position moves to the beginning of the line.
Auto-canceling double-width characters specified with SO or ESC SO are canceled.
- 51 -
5. Control Command Details
Page 58

ESC/P Command Reference
ESC B Specify vertical tab position
ASCII: ESC B [n]k NUL
Decimal: 27 66 [n]k 0
Hexadecimal: 1B 42 [n]k 00h
Parameters
1≤n≤255
0≤k≤16
Description
The vertical tab position is the line feed amount (when this command was specified)*n from the top
margin.
Enter n values in ascending order and end the settings with NUL.
If an n value is smaller than a previous one, tab setting is ended.
Up to 16 vertical tabs can be specified.
ESC B NUL cancels all vertical tab positions.
Vertical tab positions can be specified regardless of the setting of the bottom margin position. However,
vertical tab positions outside the print area (beyond the bottom margin position) are invalid and only
become valid when a change in the top margin setting or bottom margin setting moves the print area to
include those tab positions.
Use VT to move to the vertical tab position.
When changing vertical tab positions, specify all positions again.
If the top margin is moved, the vertical tab positions are also moved by the same amount.
Even if the line feed amount is changed after the vertical tab positions have been specified, the vertical tab
position settings do not change.
Performing a VT when no vertical tabs have been specified is equal to performing a CR.
- 52 -
5. Control Command Details
Page 59

ESC/P Command Reference
1
2
3
4 5 6 7 8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
VT code
Tab position
Tab position
Tab position
17
18
ABCD
EfghijkL
Abcdefg
ABCDEFG
aiueo
VT code
VT code
Line feed
amount
Example: Vertical tabs are specified at Lines 6, 11, and 15, and
data is entered while VT are performed.
• • •
VT Perform vertical tab
ASCII: VT
Decimal: 11
Hexadecimal: 0B
Parameters
None
Description
Moves the print position to the nearest vertical tab position down from the input position.
The next horizontal print position becomes the beginning of the line.
If the next vertical tab position extends beyond the bottom margin, or if there is no vertical tab position
specified below the current position, VT is performed as if it is (moves to the TOF position of the next
page).
When all vertical tab positions have been canceled by an initialization or with ESC B NUL, performing VT
is equal to performing CR.
Auto-canceling double-width characters specified with SO or ESC SO are canceled.
- 53 -
5. Control Command Details
Page 60

ESC/P Command Reference
ESC (V Specify absolute vertical position
ASCII: ESC ( V nL nH mL mH
Decimal: 27 40 86 nL nH mL mH
Hexadecimal: 1B 28 56 nL nH mL mH
Parameters
nL=2
nH=0
0≤mL≤255
0≤mH≤127
Description
Specifies the vertical print position as an absolute position from the top margin position.
Vertical position=mL+mH*256+top margin
The absolute vertical position is measured from the top margin position when this command was specified.
If a position extending beyond the bottom margin is specified, printing starts.
There is no restriction on the amount of movement back (upward) from the current position.
With left alignment, the print position for the next line becom es the end position of the current line.
(The horizontal position does not move to the left margin.)
With right alignment and center alignment, the horizontal position moves to the beginning of the line.
Auto-canceling double-width characters specified with SO or ESC SO are canceled.
- 54 -
5. Control Command Details
Page 61

Abcdefg
ABC
SDFASG
Abcdefg
ABC
SD FA S G
Abcdefg
ABC
SD FA S G
Example:
Moving to a vertical position specified after the second line
Left alignment
Center alignment
Right alignment
ESC (v Specify relative vertical position
ASCII: ESC ( v nL nH mL mH
Decimal: 27 40 118 nL nH mL mH
Hexadecimal: 1B 28 76 nL nH mL mH
Parameters
nL=2
nH=0
0≤mL≤255
0≤mH≤63, 192≤mH≤255
-16384≤(mL+mH*256)≤16383
Description
Specifies the vertical print position as a relative position from the current position.
ESC/P Command Reference
Vertical position after movement=mL+mH*256+current position
When moving upwards, the specified value is expressed as a two's complement.
It is determined by the following equation.
mL+mH*256=65536–distance actually moved
Settings moving the print position above the top margin are ignored.
If a position extending beyond the bottom margin is specified, printing starts.
With left alignment, the print position for the next line becom es the end position of the current line.
(The horizontal position does not move to the left margin.)
With right alignment and center alignment, the horizontal position moves to the beginning of the line.
Auto-canceling double-width characters specified with SO or ESC SO are canceled.
- 55 -
5. Control Command Details
Page 62

5.6 Paper formatting commands
ESC (c Specify page format
ASCII: ESC ( c nL nH tL tH BL BH
Decimal: 27 40 99 nL nH tL tH BL BH
Hexadecimal: 1B 28 63 nL nH tL tH BL BH
Parameters
nL=4, nH=0
(tL+tH*256)<(BL+BH*256)
Top margin<bottom margin
Description
Specifies settings for the top and bottom margins.
The physically printable area depends on the media.
ESC/P Command Reference
The top margin and the bottom margin are specified in units of 1 dot using the top edge of the physically
printable area as the reference.
(The left margin and the right margin use the left edge of the physically printable area as the reference.)
Top margin=tL+tH*256
Bottom margin= BL+BH*256
The top margin position is the TOF in the vertical direction.
All previously entered text is cleared.
When this command is used previously specified top and bottom margins are canceled.
A standard unit is not used.
If the print media is continuous length tape, the printing orientation is landscape and the page length is not
specified, commands specifying the page format are ignored.
- 56 -
5. Control Command Details
Page 63

Number of dots
(203dpi)
Number of dots
(300dpi)
0
0.0
0
0
1
25.4
203
300
2
50.8
406
600
3
76.2
609
900
4
101.6
812
1200
5
127.0
1015
1500
6
152.4
1218
1800
7
177.8
1421
2100
8
203.2
1624
2400
9
228.6
1827
2700
10
254.0
2030
3000
11
279.4
2233
3300
12
304.8
2436
3600
13
330.2
2639
3900
14
355.6
2842
4200
15
381.0
3045
4500
16
406.4
3248
4800
17
431.8
3451
5100
18
457.2
3654
5400
19
482.6
3857
5700
ESC (C Specify page length
ASCII: ESC ( C nL nH mL mH
Decimal: 27 40 67 nL nH mL mH
Hexadecimal: 1B 28 43 nL nH mL mH
Parameters
nL=2, nH=0
0≤(mL+mH*256)<27575(for 203dpi printers)
0≤(mL+mH*256)<35999(for 300dpi printers)
Description
Specifies the page length.
* A page length 0 indicates the Auto setting.
The unit is 1 dot.
ESC/P Command Reference
Page length=mL+mH*256
The current paper position is the TOF.
The top and bottom margins are canceled with ESC ( c.
All previously entered text is cleared.
A standard unit is not used.
This command is available only with continuous length tape.
Inch, mm, and dot conversion table
inch mm
- 57 -
5. Control Command Details
Page 64

ESC/P Command Reference
Number of dots
(203dpi)
Number of dots
(300dpi)
20
508.0
4060
6000
inch mm
- 58 -
5. Control Command Details
Page 65

Item
Default
Input buffer
Saved
Te xt buffer
Cleared
Print buffer
Cleared
Top margin
0 dot
Bottom margin
Depends on media
Left margin
0 dot
Right margin
Depends on media
Line feed amount
32 dots
Horizontal tab every 8 characters
(based on a character width of 10 cpi)
Vertical tab positions
None
Character size
21 dots
Character spacing
0 dot
International character set
USA
Character style
Canceled
Compressed
Canceled
Horizontal print position
Top margin position (TOF position)
Vertical print position
Left margin position
Landscape setting
Canceled
Page length setting
Canceled
Font
Letter Gothic Bold
5.7 Printer control commands
ESC @ Initialize
ASCII: ESC @
Decimal: 27 64
Hexadecimal: 1B 40
Parameters
None
Description
Returns all commands to their default settings. (See below.)
ESC/P Command Reference
Horizontal tab positions
- 59 -
5. Control Command Details
Page 66

n1:
The remainder from dividing the number of dot positions by 256
n2:
The quotient from dividing the number of dot positions by 256
Horizontal Dot
Density
Vertical Dot
Density
Horizontal Dot
Resolution
Vertical Dot
Resolution
0
60 dpi
60 dpi
4/203 inch
4/203 inch
1
120 dpi
60 dpi
2/203 inch
4/203 inch
2
120 dpi
60 dpi
2/203 inch
4/203 inch
3
240 dpi
60 dpi
1/203 inch
4/203 inch
4
80 dpi
60 dpi
3/203 inch
4/203 inch
6
90 dpi
60 dpi
3/203 inch
4/203 inch
32
60 dpi
180 dpi
4/203 inch
1/203 inch
33
120 dpi
180 dpi
2/203 inch
1/203 inch
38
90 dpi
180 dpi
3/203 inch
1/203 inch
39
180 dpi
180 dpi
1/203 inch
1/203 inch
5.8 Graphics commands
ESC * Select bit image <for 203dpi printers>
ASCII: ESC * m n1 n2 Data
Decimal: 27 42 m n1 n2 Data
Hexadecimal: 1B 2A m n1 n2 Data
Parameters
m=0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 32, 33, 38, 39
The image data is as follows:
- n1+n2*256 bytes when m=0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 6
- (n1+n2*256)*3 bytes when m=32, 33, 38, 39
Description
ESC/P Command Reference
Refer to “ESC * Select bit image <for 300dpi printers>” for 300dpi printers.
Selects and outputs a bit image according to the value of m.
n1 and n2 indicate the number of dot positions.
m
Horizontally neighboring dots are not omitted.
Limitations:
A maximum of 63 can be used with this command.
The total size of the image data contained in one page must be 207,360 bytes or less.
- 60 -
5. Control Command Details
Page 67

n1:
The remainder from dividing the number of dot positions by 256
n2:
The quotient from dividing the number of dot positions by 256
B7
B6
B5
B4
B3
B2
B1
B0
1byte
1byte
1byte
1byte … 1byte
1byte
n1+n2*256 bytes
MSB
LSB
m=0
m=1
m=2
m=3
m=4
m=6
When m=0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 6
n1 and n2 indicate the number of dot positions.
Relationship between the image data and the dots
First, the data is lined up in one row as follows:
ESC/P Command Reference
One dot of the image data is enlarged as follows, according to the value of m.
As a result, the image is sized depending on the value of m, as follows:
m=0 32 dots vertically×(n1+n2*256)*4 dots horizontally
m=1 32 dots vertically×(n1+n2*256)*2 dots horizontally
m=2 32 dots vertically×(n1+n2*256)*2 dots horizontally
m=3 32 dots vertically×(n1+n2*256)*1 dots horizontally
m=4 32 dots vertically×(n1+n2*256)*3 dots horizontally
m=6 32 dots vertically×(n1+n2*256)*3 dots horizontally
- 61 -
5. Control Command Details
Page 68

n1:
The remainder from dividing the number of dot positions by 256
n2:
The quotient from dividing the number of dot positions by 256
1
st
byte 2nd byte 3rd byte
B
7
B
6
B5 B4 B3 B2 B1 B
0
B
7
B
6
B
5
B
4
B3 B
2
B
1
B0 B7 B6 B
5
B4 B3 B2 B1 B
0
. . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . .
1byte
1byte
1byte 1byte
1byte
1byte
1byte
1byte
1byte
1byte
1byte
1byte
1byte
1byte
1byte
1byte
1byte 1byte
…
(n1+n2*256)*3 bytes
MSB
LSB
…
MSB
LSB
…
MSB
LSB
When m=32, 33, 38, 39
n1 and n2 indicate the number of dot positions.
ESC/P Command Reference
Relationship between the image data and the dots
First, the data is lined up in three rows as follows:
- 62 -
5. Control Command Details
Page 69

m=32
m=33
m=38
m=39
One dot of the image data is enlarged as follows, according to the value of m.
As a result, the image is sized depending on the value of m, as follows:
m=32 24 dots vertically×(n1+n2*256)*4 dots horizontally
m=33 24 dots vertically×(n1+n2*256)*2 dots horizontally
m=38 24 dots vertically×(n1+n2*256)*3 dots horizontally
m=39 24 dots vertically×(n1+n2*256)*1 dots horizontally
ESC/P Command Reference
- 63 -
5. Control Command Details
Page 70

n1:
The remainder from dividing the number of dot positions by 256
n2:
The quotient from dividing the number of dot positions by 256
Horizontal Dot
Density
Vertical Dot
Density
Horizontal Dot
Resolution
Vertical Dot
Resolution
0
60 dpi
60 dpi
6/300 inch
6/300 inch
1
120 dpi
60 dpi
3/300 inch
6/300 inch
2
120 dpi
60 dpi
3/300 inch
6/300 inch
3
240 dpi
60 dpi
2/300 inch
6/300 inch
4
80 dpi
60 dpi
4/300 inch
6/300 inch
6
90 dpi
60 dpi
4/300 inch
6/300 inch
32
60 dpi
180 dpi
6/300 inch
2/300 inch
33
120 dpi
180 dpi
3/300 inch
2/300 inch
38
90 dpi
180 dpi
4/300 inch
2/300 inch
39
180 dpi
180 dpi
2/300 inch
2/300 inch
40
300 dpi
180 dpi
1/300 inch
2/300 inch
71
180 dpi
360 dpi
2/300 inch
1/300 inch
72
360 dpi
360 dpi
1/300 inch
1/300 inch
73
360 dpi
360 dpi
1/300 inch
1/300 inch
ESC * Select bit image <for 300dpi printers>
ASCII: ESC * m n1 n2 Data
Decimal: 27 42 m n1 n2 Data
Hexadecimal: 1B 2A m n1 n2 Data
Parameters
m=0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 32, 33, 38, 39, 40, 71, 72, 73
The image data is as follows:
- n1+n2*256 bytes when m=0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 6
- (n1+n2*256)*3 bytes when m=32, 33, 38, 39, 40
- (n1+n2*256)*6 bytes when m=71, 72, 73
Description
Refer to “ESC * Select bit image <for 203dpi printers>” for 203dpi printers.
ESC/P Command Reference
Selects and outputs a bit image according to the value of m.
n1 and n2 indicate the number of dot positions.
m
Horizontally neighboring dots are not omitted.
Limitations:
A maximum of 63 can be used with this command.
The total size of the image data contained in one page must be 207,360 bytes or less.
- 64 -
5. Control Command Details
Page 71

n1:
The remainder from dividing the number of dot positions by 256
n2:
The quotient from dividing the number of dot positions by 256
B7
B6
B5
B4
B3
B2
B1
B0
1byte
1byte
1byte
1byte … 1byte
1byte
n1+n2*256 bytes
MSB
LSB
m=0
m =1
m =
2
m =3
m =4
m =6
When m=0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 6
n1 and n2 indicate the number of dot positions.
Relationship between the image data and the dots
First, the data is lined up in one row as follows:
ESC/P Command Reference
One dot of the image data is enlarged as follows, according to the value of m.
As a result, the image is sized depending on the value of m, as follows:
m=0 48 dots vertically×(n1+n2*256)*6 dots horizontally
m=1 48 dots vertically×(n1+n2*256)*3 dots horizontally
m=2 48 dots vertically×(n1+n2*256)*3 dots horizontally
m=3 48 dots vertically×(n1+n2*256)*2 dots horizontally
m=4 48 dots vertically×(n1+n2*256)*4 dots horizontally
m=6 48 dots vertically×(n1+n2*256)*4 dots horizontally
- 65 -
5. Control Command Details
Page 72

n1:
The remainder from dividing the number of dot positions by 256
n2:
The quotient from dividing the number of dot positions by 256
1
st
byte
2
nd
byte 3rd byte
B
7
B
6
B5 B4 B
3 B2 B1 B0
B
7
B
6
B
5
B
4
B3 B
2
B
1
B0 B
7 B6 B5
B
4 B3 B2 B1 B0
. . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . .
1byte
1byte
1byte 1byte
1byte
1byte
1byte
1byte
1byte
1byte
1byte
1byte
1byte
1byte
1byte
1byte
1byte 1byte
…
(n1+n2*256)*3 bytes
MSB
LSB
…
MSB
LSB
…
MSB
LSB
When m=32, 33, 38, 39, 40
n1 and n2 indicate the number of dot positions.
ESC/P Command Reference
Relationship between the image data and the dots
First, the data is lined up in three rows as follows:
- 66 -
5. Control Command Details
Page 73

m=32
m=33
m=38
m=39
m=40
One dot of the image data is enlarged as follows, according to the value of m.
As a result, the image is sized depending on the value of m, as follows:
m=32 48 dots vertically×(n1+n2*256)*6 dots horizontally
m=33 48 dots vertically×(n1+n2*256)*3 dots horizontally
m=38 48 dots vertically×(n1+n2*256)*4 dots horizontally
m=39 48 dots vertically×(n1+n2*256)*2 dots horizontally
m=40 48 dots vertically×(n1+n2*256)*1 dot horizontally
ESC/P Command Reference
- 67 -
5. Control Command Details
Page 74

n1:
The remainder from dividing the number of dot positions by 256
n2:
The quotient from dividing the number of dot positions by 256
1
st
byte 2
nd
- 5th byte 6th byte
B
7
B
6
B5 B4 B3 B2 B1 B
0
B
7
B
6
B
5
B
4
B3 B
2
B
1
B0 B7 B6 B
5
B4 B3 B2 B1 B
0
. . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . .
When m=71, 72, 73
n1 and n2 indicate the number of dot positions.
ESC/P Command Reference
Relationship between the image data and the dots
- 68 -
5. Control Command Details
Page 75

1byte
1byte
1byte
1byte
1byte
1byte
1byte
1byte
1byte
1byte
1byte
1byte
1byte
1byte
1byte
1byte
1byte
1byte
…
(n1+n2*256)*6 bytes
MSB
LSB
…
MSB
LSB
…
MSB
LSB
1byte
1byte
1byte
1byte
1byte
1byte
1byte
1byte
1byte
1byte
1byte
1byte
1byte
1byte
1byte
1byte
1byte
1byte
…
MSB
LSB
…
MSB
LSB
…
MSB
LSB
m=71
m=72
m=73
First, the data is lined up in six rows as follows:
ESC/P Command Reference
One dot of the image data is enlarged as follows, according to the value of m.
As a result, the image is sized depending on the value of m, as follows:
m=71 48 dots vertically×(n1+n2*256)*2 dots horizontally
m=72 48 dots vertically×(n1+n2*256)*1 dot horizontally
m=73 48 dots vertically×(n1+n2*256)*1 dot horizontally
- 69 -
5. Control Command Details
Page 76

ESC/P Command Reference
ESC K 8-dot single-density bit image
ASCII: ESC K n1 n2 Data
Decimal: 27 75 n1 n2 Data
Hexadecimal: 1B 4B n1 n2 Data
Parameters
0≤n1≤255, 0≤n2≤3
The data contains n1+n2*256 bytes of image data.
Description
Specifies that an 8-dot single-density bit image is printed with the number of dot positions indicated by n1 and
n2.
Same behavior as m=0 specified in ESC *.
- 70 -
5. Control Command Details
Page 77

ESC/P Command Reference
ESC L 8-dot double-density bit image
ASCII: ESC L n1 n2 Data
Decimal: 27 76 n1 n2 Data
Hexadecimal: 1B 4C n1 n2 Data
Parameters
0≤n1≤255, 0≤n2≤3
The data contains n1+n2*256 bytes of image data.
Description
Specifies that an 8-dot double-density bit image is printed with the number of dot positions indicated by n1
and n2.
Same behavior as m=1 specified in ESC *.
- 71 -
5. Control Command Details
Page 78

ESC/P Command Reference
ESC Y 8-dot double-speed double-density bit image
ASCII: ESC Y n1 n2 Data
Decimal: 27 89 n1 n2 Data
Hexadecimal: 1B 59 n1 n2 Data
Parameters
0≤n1≤255, 0≤n2≤3
The data contains n1+n2*256 bytes of image data.
Description
Same as for an 8-dot double-density bit image. Horizontally neighboring dots are not omitted.
ESC Z 8-dot quadruple-density bit image
ASCII: ESC Z n1 n2 Data
Decimal: 27 90 n1 n2 Data
Hexadecimal: 1B 5A n1 n2 Data
Parameters
0≤n1≤255, 0≤n2≤7
The data contains n1+n2*256 bytes of image data.
Description
Specifies that an 8-dot quadruple-density bit image is printed with the number of dot positions indicated by n1
and n2.
Same behavior as m=3 specified in ESC *.
Horizontally neighboring dots are not omitted.
- 72 -
5. Control Command Details
Page 79

T or t (type)
t0: CODE39
th: Intelligent Mail Barcode
s (style)
Ignored
p (number of passes)
Ignored
R or r
(characters below barcode)
r0: OFF
r1: ON
u (units of measurement)
Ignored
x (horizontal position)
Ignored
y (vertical offset)
Ignored
5.9 Advanced commands
ESC i B Barcode
ASCII: ESC i [Parameters] B or b [Barcode data] Backslash
Decimal: 27 105 [Parameters] 66 or 98 [Barcode data] 92
Hexadecimal: 1B 69 [Parameters] 42 or 62 [Barcode data] 5C
Format: ESC i [Parameters] B or b [Barcode data] [Backslash]
(1) (2) (3) (4)
Parameters
(1) [Parameters]: Barcode parameters
t1: ITF (I-2/5)
t5: EAN-8, EAN-13, UPC-A
t6: UPC-E
t9: CODABAR
ta: CODE128
tb: GS1-128 (UCC/EAN-128)
tc: GS1 Databar(RSS)
td: CODE93
te: POSTNET
tf: UPC/EAN EXTENSION
tg: MSI/Plessey
ESC/P Command Reference
- 73 -
5. Control Command Details
Page 80

ESC/P Command Reference
h (height)
h n1 n2
If height>480, height=480.
However, the height is as shown below with tc.
However, the height is as shown below with te.
300dpi : If height<48, height = 37.
However, the height is as shown below with th.
300dpi : If height<48, height = 43.
w
w0: extra small
w3: large
E or e
(parentheses deletion)
e0: ON
e1: OFF
o
o0: GS1 Databar Standard
o6: GS1 Databar Expanded Stacked
c
Expanded Stacked)
c: o. of horizontal characters
z
thin bars)
z0: (3:1)
z2: (2:1)
f
(equalize bar lengths)
f0: OFF
f1: ON
Height=n1+n2*256 (dots)
48≤height≤480
If height<48, height=48.
131≤height≤Max im um width (GS1 Databar Standard)
71≤height≤Maximum width (GS1 Databar Truncated)
71≤height≤Maximum width (GS1 Databar Stacked)
239≤height≤Maxim um wi dth (GS1 Databar Stacked Omni)
62≤height≤Maximum width (GS1 Databar Limited)
134≤height≤Maxim um wi dth (GS1 Databar Expanded)
If height<min., height=min.
If height>max., height=max.
Maximum width depends on each models. Please refer to “Appendix B:
(width)
(GS1 Databar symbols
model)
Specifications”.
203dpi : If height<48, height = 25.
203dpi : If height<48, height = 29.
w1: small
w2: medium
o1: GS1 Databar Truncated
o2: GS1 Databar Stacked
o3: GS1 Databar Stacked Omnidirectional
o4: GS1 Databar Lim ited
o5: GS1 Databar Expanded Standard
(number of horizontal
characters for GS1 Databar
(ratio between thick and
This must be an even value where 2≤no. of horizontal characters≤20.
z1: (2.5:1)
- 74 -
5. Control Command Details
Page 81

ESC/P Command Reference
(A barcode with a large number of stacked rows may be considered out of specifications and
unreadable by the reader.)
- 75 -
5. Control Command Details
Page 82

ESC/P Command Reference
t0:
1–50 characters (“*” is not included)
t1:
1–64 characters
t5:
7 characters (for EAN-8)
11 characters (for UPC-A)
t6:
6 characters
t9:
3–64 characters (Must begin and end with A, B, C, or D.)
ta:
1–64 characters
tb:
1–64 characters
tc:
3–15 characters (begins with “01”) (except with GS1 Databar Expanded)
(numbers, letters, spaces, !, ”, %, &, ’, (, ), *, +, ,, -, ., /, :, ;, <, =, >, ? and _)
td:
1–64 characters
te:
5 characters, 9 characters, 11 characters
tf:
2 characters, 5 characters
tg:
1–14 characters
th:
20 characters, 25 characters, 29 characters, 31 characters (Second digit is “0”-“4”)
Note
* For parameter numerals 0–9, both 00h–09h and 30h–39h are recognized.
* For parameter type, both ‘a’-‘h’ and ‘A’-‘H’ are recognized.
* The parameter “parentheses deletion” is available only when GS1-128 (UCC/EAN-128) is selected.
* The parameter “ratio between thick and thin bars” is available only when t0, t1 or t9 is selected.
* The parameter “equalize bar lengths” is available only when t5 or t6 is selected.
* If any other type is selected, these parameters are ignored.
* When there is no type command or an invalid type command has been specified, CODE39 is
specified.
* The number of characters that can be entered for each barcode type is as follows:
12 characters (for EAN-13)
Third digit is “0” or “1”. (for GS1 Databar Limited)
1–64 numbers or 1–40 letters* (for GS1 Databar Expanded)
* ISO646 characters can be printed.
(2) B or b: Beginning of barcode data
(3) [Barcode data]: Barcode data
? (Generate check digit):
Generates a check digit when “?” is in the barcode data.
The position of “?” is irrelevant as long as it is within the barcode data.
With POSTNET, CODE93, UPC/EAN EXTENSION, CODE128, GS1-128(UCC/EAN-128) and
Intelligent Mail Barcode, no check digit is generated.
If “?” is inserted, it is treated as barcode data.
- 76 -
5. Control Command Details
Page 83

Barcode Type
Co mmand
POSTNET, UPC/EAN EXTENTION, CODE39,
Intelligent Mail Barcode
CODE93, CODE128,
GS1-128 (UCC/EAN-128)
(4) [Backslash]: End of barcode
ESC/P Command Reference
ITF( I-2/5), EAN-8, EAN-13, UPC-A, UPC-E,
CODABAR, GS1 Databar , MSI/Plessey,
ESC i [Parameter] B or b [Barcode data] \
ESC i [Parameter] B or b [Barcode data] \\\
Description
Specifies a barcode image.
Any data extending beyond the right margin is ignored.
Since the check digit is generated automatically from the barcode data, the check digit is not sent as
barcode data. Since the length of the barcode data is also checked, the data would not be correctly
recognized if the check digit data was present.
With CODE39, ITF (I-2/5), CODABAR, CODE128, GS1-128 (UCC/EAN-128) or GS1 Databar Expanded,
the buffer length for the barcode image is about 22 cm. A barcode longer than 22 cm will not be printed.
The characters that can be printed with CODE128 and GS1-128 (UCC/EAN-128) are the 128 ASCII
characters and the special codes FNC1, FNC2, FNC3 and FNC4.
Codes assigned to the special codes:
FNC1: 86h
FNC2: 81h
FNC3: 80h
FNC4: 84h
The control codes and special codes appear as spaces when characters are printed below CODE128 and
GS1-128 (UCC/EAN-128) barcodes.
Special code FNC1 can also be printed with GS1 Databar Expanded.
This special code also appears as a space when characters are printed below the barcode.
Code assigned to the special code:
FNC1: 86h
With only UPC/EAN EXTENSION, the data is printed above the barcode.
Example
For barcode type CODE39, with no characters printed below the barcode, a size of large (width) × 480 dots
(height), without parentheses, a ratio between thick and thin bars of 3:1, and bar lengths not equalized, the
command will be as shown below.
ESC i t0 r0 w3 h E0h 01h e0 z0 f1 B 123456789 \
- 77 -
5. Control Command Details
Page 84

ESC/P Command Reference
1. Cell size
[1-byte decimal] 1–32
Specifies the dot size per cell side.
( The default value is 3.)
2. Symbol
[1-byte decimal] 1
[1-byte decimal] 3
Model 1
Micro QR
3. Structured
setting
[1-byte decimal] 0
Not partitioned. (default value)
4. Code
[1-byte decimal] 1–16
Indicates the number of the symbol in a partitioned QR
5. Number of
[1-byte decimal] 2–16
Indicates the total number of symbols in a partitioned QR
6. Parity data
[1-byte hexadecimal]
Value (in bytes) of exclusively OR’ing all the print data
7. Error
[1-byte decimal] 1
[1-byte decimal] 4
High-density level: L 7%
Ultra-high-reliability level: H 30% (*2)
8. Data input
[1-byte decimal] 0
Auto input (default value)
entered.
ESC i Q 2D barcode (QR Code)
ASCII: ESC i Q or q Data
Decimal: 27 105 81 or 113 Data
Hexadecimal: 1B 69 51 or 71 Data
Format: ESC i Q or q [Parameters] [Barcode data] \\\
(1) (2) (3)
Parameters
(1) [Parameters]
Unlike with 1D barcodes, all parameters must be specified in order, starting from the top.
If a value other than those listed is entered for a parameter, that parameter is specified with its default
value.
type
Append
number
partitions
correction
level
method
[1-byte decimal] 2
[1-byte decimal] 1
00-FF
[1-byte decimal] 2
[1-byte decimal] 3
[1-byte decimal] 1
Model 2 (default value)
Partitioned (*1)
Code.
Code.
(print data before partition)
Standard level: M 15% (default value)
High-reliability level: Q 25%
Manual input
Selects whether numbers, English alphanumeric
characters, kanji characters or binary characters are
- 78 -
5. Control Command Details
Page 85

ESC/P Command Reference
ESC i Q or q [1st parameter] [1st set of barcode data] \\\
ESC i Q or q [3rd parameter] [3rd set of barcode data] \\\
3. Structured append
This determines whether or not the barcode data is partitioned. If the data is
value for these parameters.
4. Code number:
This indicates which number the ESC/P command for that QR Code is.
this is 4.
5. Number of partitions:
This is the number of partitions.
6. Parity data:
This is the value (in bytes) of exclusively OR’ing all the print data (print data
ESC/P command indicates that these codes are linked.
Character
OR’ed (XOR’ed) in bytes
Results
XOR of 31h and 32h
0011 0001 ^= 0011 0010
0000 0011 (03h)
XOR of 03h and 33h
0000 0011 ^= 0011 0011
0011 0000 (30h)
0000 0100 (04h)
Therefore, the parity is 04h.
(*1) With Micro QR, the Structured Append setting is invalid, and the default setting is used.
(*2) With Micro QR, error correction level 4 is invalid, and the default setting is used.
(*3) Some barcode readers cannot recognize a barcode with the cell size specified as 1 dot or 2 dots.
What is the QR Code Structured Append setting?
QR Codes have Structured Append settings.
A long character string can be partitioned into 2 to 16 partitions and printed.
With ESC/P commands, it is necessary to enter only the number of partitions.
For example, if the print data is partitioned into 3 partitions, the barcode data is as follows:
ESC i Q or q [2nd parameter] [2nd set of barcode data] \\\
Refer to the following for specifying settings for 3 through 6 in [Parameters].
setting:
not partitioned, enter 0.
When not partitioning, the values of 4 (code number), 5 (number of
partitions), and 6 (parity data) are ignored; therefore, enter 0 as a dummy
For example, if it is for the second of four partitions, this is 2; for the fourth
before partition). Entering the same value as for the partitioned QR Code
What is exclusive OR’ing in bytes?
The data is exclusively OR’ed (XOR’ed) in bytes and in order.
For example, putting a character string into hexadecimal gives 31h, 32h, 33h, 34h.
XOR of 30h and 34h 0011 0000 ^= 0011 0100
Note
If this parity value is incorrect, the correct QR Code is not generated.
- 79 -
5. Control Command Details
Page 86

ESC/P Command Reference
Without Structured
Append
ESC i Q 04h 02h 00h 00h 00h 00h 02h 00h “123456789” \\\
With Structured
ESC i Q 04h 02h 01h 01h 03h 31h 02h 00h “123” \\\
(The parity for the character string “123456789” is 31h.)
Barcode
Type
Preceded
Character
Number input
N or n
-
Alphanumeric
character input
Kanji character
input
ESC i Q [other parameters] 1 B0005##### \\\
B 0012 (30h, 30h, 31h, 32h)
Model 1
707 English alphanumeric characters, 1167 numbers, 486 binary bytes, 299
kanji characters
Model 2
4296 English alphanumeric characters, 7089 numbers, 2953 binary bytes, 1817
kanji characters
Micro QR
21 English alphanumeric characters, 35 numbers, 15 binary bytes, 9 kanji
characters
Summar y
Printing the character string “123456789” with a cell size of 4 dots, Model 2, standard error correction level,
and automatic data input
Append
[Three partitions]
ESC i Q 04h 02h 01h 02h 03h 31h 02h 00h “456” \\\
ESC i Q 04h 02h 01h 03h 03h 31h 02h 00h “789” \\\
(2) [Barcode data]: Barcode data
When manual input is selected in 8 (data input method), the barcode data must be preceded with one of
the following single-byte alphanumeric characters.
Example
A or a ESC i Q [other parameters] 1 A012345678aBcDe \\\
K or k ESC i Q [other parameters] 1 K kanji character input \\\
Binary character
input
B or b+4-digit
number
With the “4-digit number”, specify the number of binary
characters to actually be entered. For example, if 12 binary
characters are to be entered, specify:
The number of barcode data characters that can be entered depends on the model type and the input
method.
Note
The numbers listed above are for an error correction level at a high-density level (L 7%).
If the standard level or higher is set, the number of characters that can be entered may decrease.
In addition, even if the characters are entered with the high-density level (L) specified, the number
of characters that can be entered may decrease due to compression.
- 80 -
5. Control Command Details
Page 87

(3) \\\: End of barcode
There must be three backslashes to end 2D barcode.
Example
Refer to the section “Summary”.
ESC i P QR Code version
ASCII: ESC i P n
Decimal: 27 105 80 n
Hexadecimal: 1B 69 50 n
Parameters
0≤n≤40
ESC/P Command Reference
Description
The barcode size can be fixed.
The default value is 0.
The available versions differ depending on the symbol type used.
If a setting other than those listed is specified, the setting returns to its default.
The following settings are available for each symbol type.
Model1 (0–14), Model2 (0–40), MicroQR (0–4)
- 81 -
5. Control Command Details
Page 88

ESC/P Command Reference
1. Cell size
[1-byte decimal] 10
Specifies the dot size per cell side.
Prints 10 dots per cell side.
2. Symbol type
[1-byte decimal] 0
[1-byte decimal] 3
Standard (default value)
MicroPDF417 Code128 emulation
3. Data input
[1-byte decimal] 0
Auto input (default value)
4. Error
capacity-type
[1-byte decimal] 0
Level input setting (default value)
5. Error correction capacity-value
- Level input
[2-byte decimal] 0–8
Specifies the level.
(The default value is 0.)
- Percentage
input
[2-byte decimal] 0–400
Specifies the percentage.
(The default value is 10.)
6. Symbol size
[1-byte decimal] 0
*0 and 1–4 with MicroPDF4 17
Auto setting (default value)
7. Symbol size
[1-byte decimal] 0
*0 and 4–44 with MicroPDF417
Auto setting (default value)
ESC i V 2D barcode (PDF417)
ASCII: ESC i V or v Data
Decimal: 27 105 86 or 118 Data
Hexadecimal: 1B 69 56 or 76 Data
Format: ESC i V or v [Parameters] [Barcode data] \\\
(1) (2) (3)
Parameters
(1) [Parameters]
Unlike with 1D barcodes, all parameters must be specified in order, starting from the top.
If a value other than those listed is entered for a parameter, that parameter is specified with its default
value.
method
correction
[1-byte decimal] 1
[1-byte decimal] 2
[1-byte decimal] 3
[1-byte decimal] 4
[1-byte decimal] 5
[1-byte decimal] 6
[1-byte decimal] 8
[1-byte decimal] 1
[1-byte decimal] 2
[1-byte decimal] 1
[1-byte decimal] 1
Prints 1 dot per cell side.
Prints 2 dots per cell side.
Prints 3 dots per cell side. (default value)
Prints 4 dots per cell side.
Prints 5 dots per cell side.
Prints 6 dots per cell side.
Prints 8 dots per cell side.
Truncate
MicroPDF417 standard
Binary input
Percentage input setting
(X direction)
(Y direction)
[1-byte decimal] 1–30
[1-byte decimal] 3–90
Manual settings
Manual settings
- 82 -
5. Control Command Details
Page 89

ESC/P Command Reference
8. Aspect
[2-byte decimal] 1–1000
Specifies the aspect value.
The default value is 50. (The actual value is 0.5.)
Symbol Size
(X Direction)
Symbol Size
(Y Direction)
Auto
Auto
1 Auto
11
14
17
20
24
28
2 Auto
8
11
14
17
20
23
26 3 Auto
6 8 10
12
15
20
26
32
38
44
4 Auto
4 6 8
10
12
15
20
26
32
38
44
value
Actually, this is 0.01–10.0, but since the decimal
point cannot be entered, a value multiplied by 100 is
entered.
Note
* Some barcode readers cannot recognize a barcode with the cell size specified as 1 dot or 2 dots.
* If a setting for the symbol size (X direction) or symbol size (Y direction) has been specified
manually, the aspect value setting is ignored.
* If a setting for the symbol size (X direction) or the symbol size (Y direction) has been entered
manually, the bar code may not be printed or an unreadable bar code may be printed.
* If both a large cell size and a high level error correction capacity have been specified, printing
may not be possible due to a full print buffer.
[With symbol type MicroPDF417]
* Since the error correction capacity is automatically determined from the symbol size (X direction)
setting, the settings for “error correction capacity and type” and “error correction capacity-value” are
ignored.
* The aspect value setting is ignored.
* The following table shows the values available for the symbol size (Y direction) according to the
symbol size (X direction) setting. If an invalid setting is specified for the symbol size (Y direction), the
default setting is specified.
(2) Barcode data
The numbers of barcode data characters that can be entered are as follows.
1850 alphanumeric characters, 2710 numbers, 1108 binary bytes
Note
The numbers listed above are for an error correction level at a high-density level (L 7%). If the
standard level or higher is set, the number of characters that can be entered may decrease. In
addition, even if the characters are entered with the high-density level (L) specified, the number of
characters that can be entered may decrease due to compression.
- 83 -
5. Control Command Details
Page 90

ESC/P Command Reference
Maximum Amount of Information Allowed
Alphanumeric
Characters
Nu mbers
Binary
1
11 6 8
3
1
14
12
17
7
1
17
18
26
10
1
20
22
32
13
1
24
30
44
18
1
28
38
55
22
2 8 14
20
8
2
11
24
35
14
2
14
36
52
21
2
17
46
67
27
2
20
56
82
33
2
23
64
93
38
2
26
72
105
43
3 6 10
14
6
3 8 18
26
10
3
10
26
38
15
3
12
34
49
20
3
15
46
67
27
3
20
66
96
39
3
26
90
132
54
3
32
114
167
68
3
38
138
202
82
3
44
162
237
97
4 4 14
20
8
4 6 22
32
13
4 8 34
49
20
4
10
46
67
27
4
12
58
85
34
4
15
76
111
45
4
20
106
155
63
4
26
142
208
85
4
32
178
261
106
4
38
214
313
128
4
44
250
366
150
[With symbol type MicroPDF417]
Maximum of 250 alphanumeric characters, maximum of 366 numbers, maximum of 150 bytes of binary
data
However, the following table shows the maximum amount of information allowed according to the
settings for symbol size (X direction) and symbol size (Y direction).
X Y
(3) \\\: End of barcode
There must be three backslashes to end 2D barcodes.
- 84 -
5. Control Command Details
Page 91

ESC/P Command Reference
1. Cell size
[1-byte decimal] 10
Specifies the dot size per cell side.
Prints 10 dots per cell side.
2. Symbol
type
[1-byte decimal] 0
[1-byte decimal] 1
ECC200 square (default value)
ECC200 rectangular
3. Vertical
(continued to the next page)
[ECC200 square]
ESC i D 2D barcode (DataMatrix)
ASCII: ESC i D or d data
Decimal: 27 105 68 or 100 data
Hexadecimal: 1B 69 44 or 64 data
Format: ESC i D or d [Parameters] [Barcode data] \\\
(1) (2) (3)
Parameters
(1) [Parameters]
Unlike with 1D barcodes, all parameters must be specified in order, starting from the top.
If a value other than those listed is entered for a parameter, that parameter is specified with its default
value.
size
[1-byte decimal] 1
[1-byte decimal] 2
[1-byte decimal] 3
[1-byte decimal] 4
[1-byte decimal] 5
[1-byte decimal] 6
[1-byte decimal] 8
[1-byte decimal] 0
[1-byte decimal] 10
[1-byte decimal] 12
[1-byte decimal] 14
[1-byte decimal] 16
[1-byte decimal] 18
[1-byte decimal] 20
[1-byte decimal] 22
[1-byte decimal] 24
[1-byte decimal] 26
[1-byte decimal] 32
[1-byte decimal] 36
[1-byte decimal] 40
[1-byte decimal] 44
[1-byte decimal] 48
[1-byte decimal] 52
[1-byte decimal] 64
[1-byte decimal] 72
[1-byte decimal] 80
[1-byte decimal] 88
[1-byte decimal] 96
Prints 1 dot per cell side.
Prints 2 dots per cell side.
Prints 3 dots per cell side. (default value)
Prints 4 dots per cell side.
Prints 5 dots per cell side.
Prints 6 dots per cell side.
Prints 8 dots per cell side.
Vertical no. of cells: AUTO (default value)
Vertical no. of cells: 10 cells
Vertical no. of cells: 12 cells
Vertical no. of cells: 14 cells
Vertical no. of cells: 16 cells
Vertical no. of cells: 18 cells
Vertical no. of cells: 20 cells
Vertical no. of cells: 22 cells
Vertical no. of cells: 24 cells
Vertical no. of cells: 26 cells
Vertical no. of cells: 32 cells
Vertical no. of cells: 36 cells
Vertical no. of cells: 40 cells
Vertical no. of cells: 44 cells
Vertical no. of cells: 48 cells
Vertical no. of cells: 52 cells
Vertical no. of cells: 64 cells
Vertical no. of cells: 72 cells
Vertical no. of cells: 80 cells
Vertical no. of cells: 88 cells
Vertical no. of cells: 96 cells
- 85 -
5. Control Command Details
Page 92

3. Vertical
(continued from the previous page)
[1-byte decimal] 104
[1-byte decimal] 144
Vertical no. of cells: 104 cells
Vertical no. of cells: 144 cells
[1-byte decimal] 16
[ECC200 rectangular]
Vertical no. of cells: 16 cells
4. Horizontal
[1-byte decimal] x
[ECC200 square]
Horizontal no. of cells: Same value as vertical size (x)
[1-byte decimal] 0
[ECC200 rectangular]
Horizontal no. of cells: AUTO (default value)
[1-byte decimal] 32
(2) When the vertical size is 8 cells
Horizontal no. of cells: 32 cells
[1-byte decimal] 36
(3) When the vertical size is 12 cells
Horizontal no. of cells: 36 cells
[1-byte decimal] 48
(4) When the vertical size is 16 cells
Horizontal no. of cells: 48 cells
5. Reserved
[1-byte decimal]×5 0
5 bytes of dummy data (0) is sent.
size
(continued)
[1-byte decimal] 120
[1-byte decimal] 132
ESC/P Command Reference
Vertical no. of cells: 120 cells
Vertical no. of cells: 132 cells
[1-byte decimal] 0
[1-byte decimal] 8
[1-byte decimal] 12
Vertical no. of cells: AUTO (default value)
Vertical no. of cells: 8 cells
Vertical no. of cells: 12 cells
size
[1-byte decimal] 18
[1-byte decimal] 26
[1-byte decimal] 36
(1) When the vertical size is AUTO
Horizontal no. of cells: 18 cells
Horizontal no. of cells: 26 cells
Horizontal no. of cells: 36 cells
Note
Some barcode readers cannot recognize a barcode with the cell size specified as 1 dot or 2 dots.
If the vertical size is specified as a value other than those listed for ECC200 square, the AUTO
setting is selected. If the horizontal size is specified as a value different from the vertical size, the
setting is changed to the same value as the horizontal size.
If the vertical or horizontal size for ECC200 rectangular is specified as a v alue other than those
listed, the AUTO setting is selected.
(2) [Barcode data]: Barcode data
The maximum number of barcode data characters that can be entered is listed below.
2335 alphanumeric characters, 3116 numbers, 1556 bytes of binary data
Note
The numbers of characters that can be entered (as listed above) are for the maximum vertical ×
horizontal cell settings (144 cells × 144 cells). The number of characters that can be entered may
decrease, depending on the specified settings.
- 86 -
5. Control Command Details
Page 93

ESC/P Command Reference
(3) \\\: End of barcode
There must be three backslashes to end 2D barcodes.
Example
For data “12345” with symbol type ECC square at 40 × 40 with a 3-dot cell size, the command will be as
shown below.
ESC i D 03h 00h 28h(40d) 28h 00h 00h 00h 00h 00h “12345” \\\
- 87 -
5. Control Command Details
Page 94

ESC/P Command Reference
1. Symbol
[1-byte decimal] 2
Structured carrier message
2.
setting
[1-byte decimal] 0
With Structured Append (default value)
Maximum Amount of Information Allowed
Alphanumeric Characters
Nu mbers
Standard
93
138
Full EEC
77
113
Structured carrier message
84
126
ESC i M 2D barcode (MaxiCode)
ASCII: ESC i M or m data
Decimal: 27 105 77 or 109 data
Hexadecimal: 1B 69 4D or 6D data
Format: ESC i M or m [Parameters] \ [Barcode data] \\\
(1) (2) (3) (4)
Parameters
(1) [Parameters]
If a value other than those listed is entered for a parameter, that parameter is specified with its default
value.
type
Structured
[1-byte decimal] 0
[1-byte decimal] 1
[1-byte decimal] 1
Standard (default value)
Full EEC
Without Structured Append
Append
(2) \ (backslash)
Separator between parameters and barcode data
(3) [Barcode data]: Barcode data
The number of barcode data characters that can be entered is listed below.
Symbol Type
Note
The numbers of characters that can be entered (as listed above) are for when using only the
common character set (code set A in the MaxiCode specifications). The number of characters that
can be entered may decrease, depending on the characters that are used.
- 88 -
5. Control Command Details
Page 95

ESC/P Command Reference
<data1>\,<data2>\
,<normal_barcode_data>
Service class=default value
Country code
Postal code
Postal code
9 or less numbers, or
6 or less alphanumeric characters
Ignored when not structured carrier message.
Default value: 000000000
Country code
3 or less numbers
Ignored when not structured carrier message.
Default value: 000
Service class
3 or less numbers
Ignored when not structured carrier message.
Default value: 000
When the symbol type is the structured carrier message, the service class, country code and postal
code can be specified separately from the normal data. Specify each value, separated by a backslash
and comma (\,), immediately before the normal data.
<postal_code>\,<country_code>\,<service_class>\,<normal_barcode_data>
When “\,” is not used three times, the data is written as shown in the following example.
If a value other than those listed is entered for a parameter, that parameter is specified with its default
value.
Note
If the postal code is specified as alphanumeric characters, characters other than those listed
below are invalid.
A to Z “ # $ % & ‘ ( ) * + , - . / 0 to 9 :
However, lowercase letters (a to z) are converted to the valid uppercase letters (A to Z).
(4) \\\: End of barcode
There must be three backslashes to end 2D barcodes.
- 89 -
5. Control Command Details
Page 96

ESC/P Command Reference
1. Cell size
[1-byte decimal] 10
Specifies the dot size per cell side.
Prints 10 dots per cell side.
2. Symbol
[1-byte decimal] 0
[1-byte decimal] 2
Full range (default value)
Auto setting
3. Error
capacity
4. Symbol
[Full range]
[1-byte decimal] 4–32
Manual settings
[Compact]
[1-byte decimal] 1–4
Manual settings
Note: Symbol size is fixed as AUTO when Symbol type is specified as AUTO.
5. Structured
setting
[1-byte decimal] 0
[1-byte decimal] 2
Not partitioned. (default value)
Partitioned Specify the number of blocks
6. Number of
blocks
[1-byte decimal] 2–26
Partitioned Only valid when the number of blocks is
specified (Default it 2)
7. Message
ID
Character string(Terminal
val ue is 00h)
Invalid when append setting 0.
ESC i J 2D barcode (Aztec)
ASCII: ESC i J or j data
Decimal: 27 105 74 or 106 data
Hexadecimal: 1B 69 4A or 6A data
Format: ESC i J or j [Parameters] [Barcode data] \\\
(1) (2) (3)
Parameters
(1) [Parameters]
If a value other than those listed is entered for a parameter, that parameter is specified with its default
value.
type
correction
size
[1-byte decimal] 1
[1-byte decimal] 2
[1-byte decimal] 3
[1-byte decimal] 4
[1-byte decimal] 5
[1-byte decimal] 6
[1-byte decimal] 8
[1-byte decimal] 1
[1-byte decimal] 1–99
[1-byte decimal] 0
[1-byte decimal] 0
Prints 1 dot per cell side.
Prints 2 dots per cell side.
Prints 3 dots per cell side. (default value)
Prints 4 dots per cell side.
Prints 5 dots per cell side.
Prints 6 dots per cell side.
Prints 8 dots per cell side.
Compact
Percentage (default value is 23)
Auto setting (default value)
Auto setting (default value)
Append
[1-byte decimal] 1
Partitioned
- 90 -
5. Control Command Details
Page 97

ESC/P Command Reference
(2) [Barcode data]: Barcode data
The maximum number of barcode data characters that can be entered is listed below.
3067 alphanumeric characters, 3832 numbers, 1914 bytes of binary data
Note
The number of characters shown above is only for the Full-Range mode and varies depending on
setting.
(3) \\\: End of barcode
There must be three backslashes to end 2D barcodes.
- 91 -
5. Control Command Details
Page 98

n2:
Specify the length of character string of specified font name.
Data:
Character string of font name.
ESC i G Specify font
ASCII: ESC i G n1 n2 data
Decimal: 27 105 71 n1 n2 data
Hexadecimal: 1B 69 47 n1 n2 data
Parameters
n=0 (Fixed)
1≤n2≤16
Description
Specify font
ESC/P Command Reference
Example
For specifying “HelOb.FNT”.
ESC i G 00h 09h HelOb.FNT
- 92 -
5. Control Command Details
Page 99

This printer
PC
Must be
downloaded
beforehand
Image file
(.bmp)
Abcdefg
ABCDEFG
HIJK
Use P-touch Transfer Manager.
ESC i F P Print downloaded data
ASCII: ESC i F P n
Decimal: 27 105 70 80 n
Hexadecimal: 1B 69 46 50 n
Parameters
n: Minus 1 from the key number assigned when transport the data.
0≤n≤254
Description
Print a transferred image on a current print position.
If there is no image data, this command is ignored.
ESC/P Command Reference
Example: Combination of text and downloaded image
- 93 -
5. Control Command Details
Page 100

ESC/P Command Reference
1. The text is entered.
Abcdefg
1. The text is entered.
Abcdefg
Abcdefg
2. The downloaded image
is entered.
3. Since the image does
not fit, it is pasted in
after an automatic line
feed.
Example: Normal size
Abc
Abc
Abc
3. Since the image does not fit,
it is pasted in after an
automatic line feed and
trimmed to fit between the
left and right margins.
Example: Image larger than the distance between left and right margins
2. The downloaded image
is entered.
As with text, if the image data does not all fit on the current line, an automatic line feed is performed, and
the data is placed at the beginning of the next line. At that time, the any data that does not fit in the print
area is deleted.
- 94 -
5. Control Command Details
 Loading...
Loading...