Page 1

IVMD 1.0
Intelligent Video Motion Detection
en Configuration Instructions
Page 2

Copyright
This manual is copyright protected by
Bosch Security Systems. All rights reserved. No part of this
document may be reproduced or transmitted for any
purpose, by whatever method and by whatever means,
electronically or mechanically, without the express written
permission of Bosch Security Systems.
Issue: April 2006 (Software version 1.0)
© Copyright 2006 Bosch Security Systems
Note
This manual has been prepared with all due care and all
information contained in it has been thoroughly checked. The
description was complete and correct at the time of going to
press. Our products are constantly developed and upgraded;
as such, the content of the manual is subject to change
without notice. Bosch Security Systems accepts no liability
for losses that arise directly or indirectly as a result of errors,
incompleteness or discrepancies between the manual and
the product described.
Trade marks
All of the hardware and software names used in this manual
are highly likely to be registered trade marks and must be
treated as such.
Page 3

IVMD | Configuration instructions Table of Contents | en 1
Table of Contents
1 Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3
2 Requirements . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
2.1 License . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
2.1.1 Requesting the Activation Key . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
2.2 Limitations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
3 Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
3.1 VCA tab (Video content analysis) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
4 Area settings. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
4.1 The basics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
4.2 The Area settings window . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
4.2.1 Detector field . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
4.2.2 Detector field context menu . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
4.2.3 Area settings context menu . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
4.3 Calibration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
4.3.1 Adjusting the calibration plane. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
4.3.2 Viewing and editing calibration settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
4.4 Properties of a detector field . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
4.5 Sensitive area. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 33
4.6 Statistics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 36
5 Display of Measurements . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 38
6 Contact and Service . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
Index. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 41
BOSCH Security Systems 1.0 | 2006.04
Page 4

2 en | Table of Contents IVMD | Configuration instructions
1.0 | 2006.04 BOSCH Security Systems
Page 5

IVMD | Configuration instructions Introduction | en 3
1 Introduction
IVMD (Intelligent Video Motion Detection) is a software
algorithm that detects movements of objects within an environment monitored by a video camera and generates alarm events
that can be processed further in a CCTV system.
IVMD makes it possible to capture and evaluate directional
movement of objects, thereby largely preventing false alarms.
IVMD adapts automatically to changing environmental conditions and is therefore non-sensitive to perturbing influences
such as rain and tree movement.
BOSCH Security Systems 1.0 | 2006.04
Page 6

4 en | Introduction IVMD | Configuration instructions
1.0 | 2006.04 BOSCH Security Systems
Page 7

IVMD | Configuration instructions Requirements | en 5
2 Requirements
You will need the Configuration Manager software to configure
IVMD. This must be installed on a Windows PC that can communicate with the respective device over a network.
2.1 License
When you purchase IVMD you are given an Authorization Number.
Together with the Installation code, which you can find in the
Web browser view, you generate the Activation Key on our
Internet platform.
This key is then entered in the Web browser view. Thereafter
you can use IVMD.
1. Open the Web browser view of the device.
2. Select SETTINGS > Service settings > Licenses:
You will find the Installation code here.
BOSCH Security Systems 1.0 | 2006.04
Page 8

6 en | Requirements IVMD | Configuration instructions
2.1.1 Requesting the Activation Key
3. Connect to the Internet on a PC and open this page in a
Web browser:
– https://activation.boschsecurity.com/
(this page always appears in English)
You will see the BOSCH Security Systems License Man-
ager.
4. If you already have an account, log in.
You can create a new account if you wish. One of the benefits of an account is that you can list all of your previous
license activations.
You can also continue the process without logging in.
5. Once you have logged in, the welcome dialog will appear.
6. Next, you will see the License Activation screen. Enter
your Authorization Number then click the check mark next
to the input window.
7. The next step is to enter your Installation Code.
Entering an installation site and comments is optional.
This information will assist you later in assigning the Acti-
vation Key to the device.
8. Click Submit. The Activation Key is displayed.
You can copy the key to the clipboard.
You can have the key e-mailed to you.
You can print the page.
1.0 | 2006.04 BOSCH Security Systems
Page 9

IVMD | Configuration instructions Requirements | en 7
9. If you have clicked the Email Activation Key link, you will
see a dialog in which you can enter two e-mail addresses
for recipients.
10. Open the Web browser view of the device again.
11. Select SETTINGS > Service settings > Licenses again.
12. Enter the Activation key – copy&paste is supported.
13. Click Set to save the Activation key. A window tells you
that installation was successful.
14. Close the window. IVMD is now activated.
The Activation key can no longer be seen.
2.2 Limitations
Please note the following considerations:
IVMD is suitable for monitoring boundaries, fences and enclosures and for the protection of pipelines, overland lines etc.
However, in certain environments the use of this type of motion
detection system may not always be advisable; this is because
movements may not always be detected or too many movements may be detected owing to reflections.
Movements may be falsely detected if there is:
– a reflective metal background
– glass (glazed building frontages)
– water as a background
Large areas of reflected light can also cause spurious motion
detection. However, light reflections caused by falling raindrops, for example, are small enough to be ignored for statistical purposes and owing to the uniform nature of their motion.
Objects that always move uniformly (such as clouds) do not
impair the detection of other objects and do not trigger false
alarms.
A constant background is necessary in order to detect motion
reliably and to assign that motion to a certain object. The more
the background moves, the harder it is to distinguish moving
objects from it. For instance, a person walking in front of a
hedge that is moving in the wind will very probably not be
detected.
BOSCH Security Systems 1.0 | 2006.04
Page 10

8 en | Requirements IVMD | Configuration instructions
If the image consists to a certain extent of nothing but moving
objects – in other words if objects cannot be distinguished
from each other or from the background – the motion of an individual object cannot be detected (e.g. individuals in a large
crowd).
If a very large number of objects are detected, a lot of computing power will be required – this will reduce the power that is
available for the transmission of live video data. If necessary,
change the settings so that only relevant objects are detected.
IVMD and the associated configuration menus offer a number of
simple ways to overcome these limitations and eliminate problem areas.
This means that you will be able to use IVMD reliably in a wide
range of applications.
1.0 | 2006.04 BOSCH Security Systems
Page 11
IVMD | Configuration instructions Configuration | en 9
3 Configuration
IVMD can only be configured with the Configuration Manager.
The Configuration Manager can be installed on any
Windows PC.
NOTE!
The system requirements and operation of the Configuration
Manager are described in the Installation and Operating Manual
i
for the Configuration Manager. You can access online help for
the software by selecting Help > Index when you are in the
Configuration Manager.
1. Start the Configuration Manager.
2. On the Network main tab, select the device for which you
wish to configure IVMD.
3. In the display area, click the VCA tab to switch to Video
content analysis.
BOSCH Security Systems 1.0 | 2006.04
Page 12
10 en | Configuration IVMD | Configuration instructions
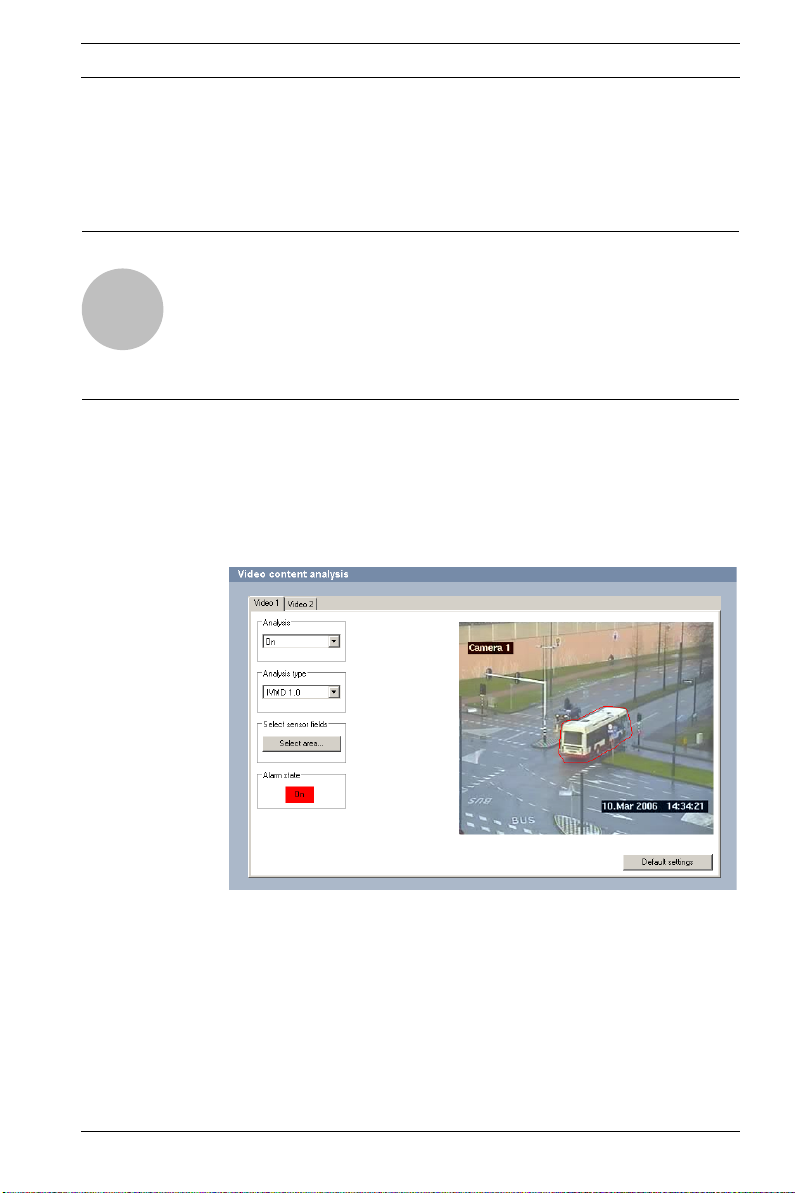
3.1 VCA tab (Video content analysis)
The camera image appears on the right. You see an individual
image that is refreshed at regular intervals. As soon as the analysis is activated, meta data is generated and depending on the
configuration the additional information is overlaid on top of
the image – an object bounding box for example.
1. Move the camera to the required position.
NOTE!
All of the settings you make relate to the selected camera posi-
i
tion. This means that you must reconfigure IVMD for this camera whenever you change the camera's direction or position.
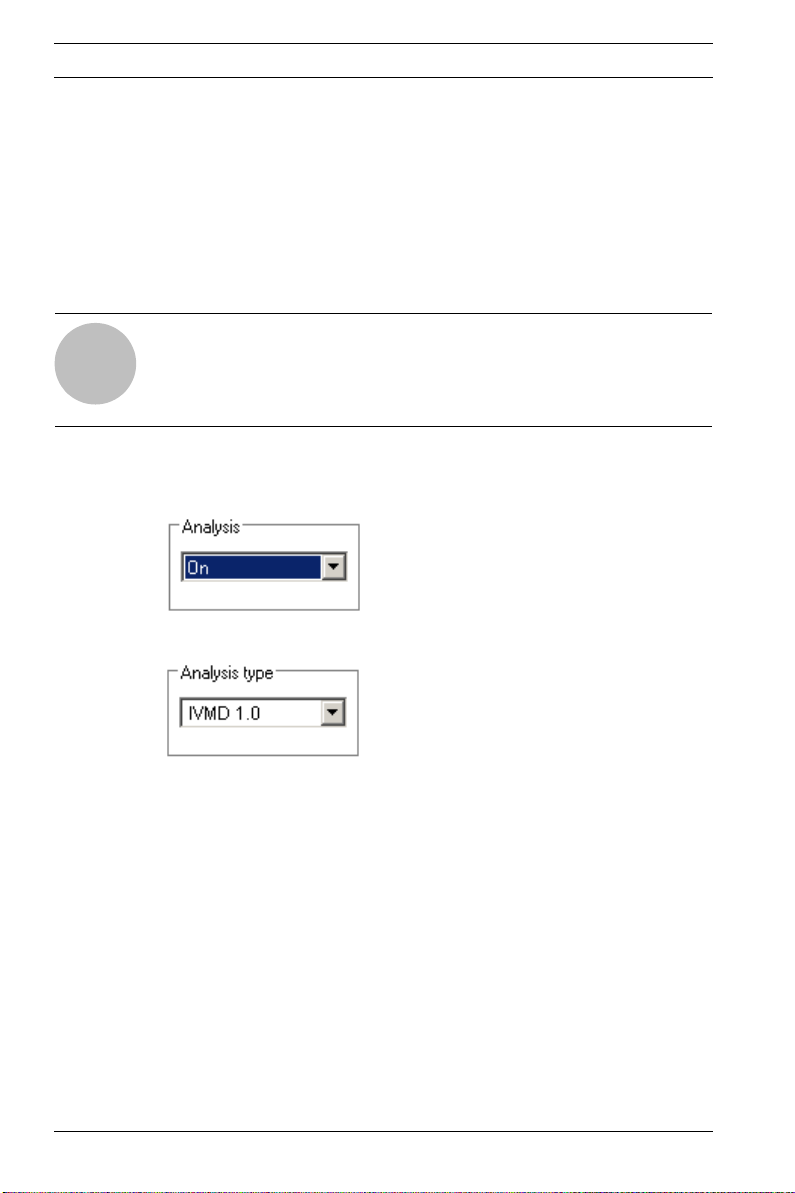
2. Activate the analysis. Otherwise alarm events are not output for further processing.
3. Select IVMD 1.0 under Analysis type.
4. If you are configuring IVMD for a camera for the first time,
select suitable initial settings for all parameters by clicking
Default settings. You should also do this if you have
changed the camera's position or direction.
5. Click Select area...
The Area settings window opens. IVMD is configured using
this window.
You will find full details in the next section.
1.0 | 2006.04 BOSCH Security Systems
Page 13

IVMD | Configuration instructions Configuration | en11
Alarm state
This field shows whether IVMD has generated an alarm event
with the current settings.
Object markings
Objects that generate an alarm event under the current settings
appear on the camera image inside a red outline.
Objects that are detected as moving but do not generate an
alarm event under the current settings appear inside a yellow
outline.
Object (yellow)
(No alarm event generated)
Object (red)
(Alarm event generated)
NOTE!
These object outlines are displayed in real time and are always
i
BOSCH Security Systems 1.0 | 2006.04
synchronized exactly with the moving object. However, because
the camera image is not live video feed, the outline does not
always exactly surround the object.
Page 14

12 en | Configuration IVMD | Configuration instructions
1.0 | 2006.04 BOSCH Security Systems
Page 15

IVMD | Configuration instructions Area settings | en 13
4 Area settings
4.1 The basics
The camera 'sees' a selected area that is displayed as a single,
constantly refreshed image.
Objects
Objects are typically people or vehicles moving within the area
seen by the camera. Objects can be filtered according to certain properties (size, direction of movement, speed, location).
An alarm event can be generated if objects match certain
parameters. Objects that do not match the criteria you define
are filtered out and do not generate an alarm event.
It is always the center of an object that is relevant for generating an alarm event.
Detector fields
Detector fields are polygons that cover a certain area, for example an entrance or the open space in front of a barrier. These
detector fields are defined by you. Moving objects that are outside the detector fields will be detected as such but will not
generate an alarm event. Objects that move inside detector
fields or across detector field boundaries (depending on your
settings) will generate an alarm event.
Sensitive area
The scene that is captured by a camera often includes areas
that are irrelevant for alarm event generation (such as sky).
You can reduce the size of the area that is actually analyzed for
motion. This will make motion detection for the remaining –
sensitive – area all the faster and more effective.
BOSCH Security Systems 1.0 | 2006.04
Page 16

14 en | Area settings IVMD | Configuration instructions
Calibration
If you wish to filter out objects according to their size or speed,
for each camera position a link must be made between the size
of the real-life situation and the dimensions as they appear on
the camera image. For example, you must tell the software that
an object that appears on the camera image with a height of
50 pixels is around 2 m high in reality. The camera angle is used
to compute object speeds. The calibration mode is available for
this operation.
NOTE!
Display of measurements can be adjusted, so that when using
i
the English software interface imperial measurements are
shown. You will find additional information in Section 5 Display
of Measurements, page 38.
Filter hierarchy
Below is an overview of the filter methods. You will find a
description of the filters in the following sections.
Sensitive area Objects outside the sensitive area are
ignored.
Global settings Objects that are smaller than the min-
imum size setting or larger than the
maximum size setting are ignored.
Detector field Only objects with their center (center
of gravity) inside the detector field
are detected.
Properties
of the detector field
1.0 | 2006.04 BOSCH Security Systems
Objects are filtered out based on
their properties. Different properties
can be defined separately for each
detector field.
Page 17

IVMD | Configuration instructions Area settings | en 15
4.2 The Area settings window
If you have previously reset all the settings to their defaults, the
Area settings window will display a square detector field that
covers almost the entire image:
NOTE!
All configuration commands can be found in context menus.
A context menu provides different commands depending on, for
i
example, whether you right click inside or outside a detector
field.
The Area settings window can be enlarged by dragging the bottom right hand corner of the window with the mouse.
NOTE!
i
BOSCH Security Systems 1.0 | 2006.04
Changes to settings are immediately active but are only permanently saved when you click OK.
Page 18

16 en | Area settings IVMD | Configuration instructions
4.2.1 Detector field
Detector fields are displayed as framed areas with a grid pattern. The particular status of a detector field is indicated by the
different colors:
Green field Detector field in which no object that gener-
ates an alarm event was detected.
Light green Detector field is clicked and activated for edit-
ing.
Green Mouse cursor is over the detector field; right
click to see the context menu for the detector
field.
Dark green Mouse cursor is not over this detector field;
right click to see the general context menu for
setting an area (or the context menu of another
detector field).
Red field Detector field in which an object that gener-
ates an alarm event was detected.
Light red Detector field is clicked and activated for edit-
ing.
Red Mouse cursor is over the detector field; right
click to see the context menu for the detector
field.
Dark red Mouse cursor is not over this detector field;
right click to see the general context menu for
setting an area (or the context menu of another
detector field).
When you click a detector field, its 'nodes' (corners) are highlighted by circles and you can edit the detector field.
Nodes can be inserted or deleted. The sides and nodes of a
detector field can be repositioned as desired. However, the
sides of a detector field must not cross over, and distorted
fields are not accepted.
Detector fields can be copied and inserted.
1.0 | 2006.04 BOSCH Security Systems
Page 19

IVMD | Configuration instructions Area settings | en 17
Moving the mouse cursor over a node highlights it more
brightly:
– You can reposition the node using drag&drop.
– You can delete the node using the context menu.
Moving the mouse cursor over a side highlights it more brightly:
– You can reposition the side using drag&drop.
– You can insert a node using the context menu.
Up to 16 detector fields each with up to 16 nodes can be created for each camera image.
For each detector field you can specify that only objects with
certain properties will trigger an alarm event. These configurable properties include:
– the speed at which the object is moving
– the motion of the object relative to the detector field
(inside, leaving, entering)
– the direction in which the object is moving
– the size of the object (the area covered)
For example, you can configure the monitoring of an entrance
and exit so that only large, fast-moving vehicles leaving the
detector field trigger an alarm. Small, slow-moving people will
not trigger an alarm.
BOSCH Security Systems 1.0 | 2006.04
Page 20

18 en | Area settings IVMD | Configuration instructions
4.2.2 Detector field context menu
Overview of commands:
Cut Deletes the detector field – the field is
copied to the clipboard and can be
inserted again if required.
Copy Copies the field to the clipboard.
Insert Node Inserts a node on the side over which the
mouse cursor is positioned.
Delete Node The node on which the mouse cursor is
positioned is deleted.
Statistics Shows the statistics for the detector field
(Section 4.6 Statistics, page 36).
Properties Shows the properties for the detector
field (Section 4.4 Properties of a detector
field, page 28).
1.0 | 2006.04 BOSCH Security Systems
Page 21

IVMD | Configuration instructions Area settings | en 19
4.2.3 Area settings context menu
This context menu appears in the Area settings window when
you right click outside a detector field in the camera image.
Overview of commands:
Paste Inserts the detector field copied to the clip-
board.
Create Detector
Field
Calibrate
View
Edit Sensitive
Area
Show Show or hide:
Creates a new detector field.
Switches to calibration mode
(see Section 4.3 Calibration, page 21).
Switches to the mode for editing the sensitive
area (see Section 4.5 Sensitive area, page 33).
– Sensitive area
– Object outline
– Object bounding box
– Detector fields
– Direction filter
The checked options are shown in the Configuration Manager and on the Video content
analysis configuration page in the Web
browser view for the device. If you wish to
view the options on the Web browser livepage as well, you must check the Show VCA
metadata option on the Livepage configuration page of the Web browser view.
BOSCH Security Systems 1.0 | 2006.04
Page 22

20 en | Area settings IVMD | Configuration instructions
Global Settings Here you can specify a minimum and maxi-
mum size for all objects that will generate an
alarm event. Objects that are smaller or larger
than the specified sizes will be ignored and
this will save computing power as a result.
Make sure that the range between the minimum and maximum size is not too small, or
relevant objects may be unintentionally eliminated from alarm generation.
Preview: Shows the calibration plane
(see page 23). You will also see two nested
cubes that symbolize the selected sizes
according to the calibration. You can use the
mouse to change the size of the cubes and
hence the settings for the minimum and maximum size.
1.0 | 2006.04 BOSCH Security Systems
Page 23

IVMD | Configuration instructions Area settings | en 21
4.3 Calibration
Calibration is only necessary if you want the speed and size of
detected objects to be interpreted correctly. You do not need
to perform this step if you do not want objects to be filtered on
the basis of these two properties.
In the calibration mode, a virtual horizontal plane is overlaid on
top of the camera image:
The virtual plane appears as a blue grille and can be tilted,
rotated and scaled. Position the virtual plane on the camera
image so that it matches the angle and perspective of one of
the actual horizontal areas.
NOTE!
Display of measurements can be adjusted, so that when using
i
BOSCH Security Systems 1.0 | 2006.04
the English software interface imperial measurements are
shown. You will find additional information in Section 5 Display
of Measurements, page 38.
Two red cubes are shown at opposite corners of the plane.
In the default setting, the side length of one of these cubes is
equivalent to 2 meters, so the cube is about the same height as
a person. The cubes are shown in the perspective of the blue
plane.
You can adjust the position and size of the cubes – so that a
cube corresponds to a car, for example.
A section of a street is a suitable reference area, especially if
the sides of the street are marked.
Page 24

22 en | Area settings IVMD | Configuration instructions
Position one of the red cubes over an object that you wish to
trigger an alarm event. Adjust the cube to the size of this object.
The second cube changes its size to suit the selected perspective. You can place the second cube over another object of the
same type, for example a second person who is further back in
the image.
The more care you take over calibration, the more accurately
the size, direction and speed of moving objects can be estimated.
You can of course alter your settings at any time.
NOTE!
i
The system must be recalibrated each time the camera position
is changed.
1.0 | 2006.04 BOSCH Security Systems
Page 25

IVMD | Configuration instructions Area settings | en 23
4.3.1 Adjusting the calibration plane
This section provides an overview of the ways in which the calibration plane can be adjusted. Move the mouse cursor over an
anchor point or a line and then perform the required action
while holding down the left mouse button.
Start position At the beginning, the calibration plane
is shown upright.
Anchor point
Center of a side line of
the plane
Anchor point
Center of the plane
One of the lines of the
plane that is horizontal
in the start position
One of the lines of the
plane that is vertical in
the start position
Anchor point
Corner of the plane
The calibration plane is scaled.
The entire calibration plane is moved.
The calibration plane is tilted horizontally; the tilt angle is changed. Refer to
the description of the settings on
page 26.
The calibration plane is tilted vertically;
the roll angle is changed. Refer to the
description of the settings on page 26.
The calibration plane is rotated.
BOSCH Security Systems 1.0 | 2006.04
Page 26

24 en | Area settings IVMD | Configuration instructions
Anchor point
Corner of a cube
The size of both cubes changes – both
cubes always represent the same size.
Line of a cube The cube can be positioned as desired.
The calibration mode also provides a context menu with the following commands:
Save and Exit
Calibration
The settings are saved. You leave the calibration mode.
Cancel Calibration You leave the calibration mode without
saving the settings.
Reset You stay in calibration mode; all settings
are reset to their original status.
Center Cubes Both cubes are positioned centrally on
the calibration plane.
Settings Shows the calibration settings.
You can change the settings by entering
values. This is described in the next section.
1.0 | 2006.04 BOSCH Security Systems
Page 27

IVMD | Configuration instructions Area settings | en 25
4.3.2 Viewing and editing calibration settings
The context menu for the calibration mode allows you to view
the current calibration settings.
In the Calibration Settings dialog box you can change the settings of each parameter simply by entering the required values.
Tilt angle:
The angle between the horizontal and the camera.
BOSCH Security Systems 1.0 | 2006.04
Page 28

26 en | Area settings IVMD | Configuration instructions
Roll angle:
The angle by which the calibration plane is tilted.
The setting can deviate from the horizontal by up to 10 degrees.
Elevation:
The vertical distance from the camera to the ground plane of
the captured image – typically the height of the mounted camera above the ground (in meters).
Camera constant:
The camera constant determines the basic settings for calibration. The default value of 1000 is preset and should only be
adjusted if the actual camera constant significantly deviates
from this preset. The camera constant is used to compensate
spherical distortions from the combination of image sensor and
lens.
The camera constant is a function of the focal length of the
camera's lens and the pixel pitch of the image sensor. It is calculated with the following formula:
Camera constant = focal length [mm]/(pixel pitch [mm] x 4)
1.0 | 2006.04 BOSCH Security Systems
Page 29

IVMD | Configuration instructions Area settings | en 27
The pixel pitch is obtained by dividing the image sensor size by
the number of pixels. For sensors with 596 pixels, for example,
this gives:
1/2 inch: 5.95 mm/596 = 0.0100 mm
1/3 inch: 4.96 mm/596 = 0.0083 mm
1/4 inch: 3.69 mm/596 = 0.0062 mm
For such a 1/4 inch image sensor with a 28 mm lens:
camera constant = 28 mm/(0.0062 mm x 4) = 1129
For a 1/3 inch sensor with a 12 mm lens:
camera constant = 12 mm/(0.0083 mm x 4) = 361
NOTE!
i
If you change the camera constant, you must also change the
size of the cubes to suit the actual relative sizes in the image.
Cube size:
Side length of the cubes (in meters).
A side length of 2 m (6 ft) corresponds approximately to the
height of a person.
BOSCH Security Systems 1.0 | 2006.04
Page 30

28 en | Area settings IVMD | Configuration instructions
4.4 Properties of a detector field
The Properties of Detector Field dialog is opened from the
context menu of the Area settings window (refer to page 19).
In the dialog you can specify the properties of objects for which
this detector field will generate an alarm event. Objects that do
not match the selections made here will not trigger an alarm. In
other words: Objects are filtered according to their properties.
Only objects that match all filter criteria can trigger an alarm
event (filter criteria are logically linked with AND).
Meaningful settings will help to prevent false alarms. If you are
concerned that objects will not generate an alarm event even
though this would be desirable for those objects, refer to the
descriptions given in Section 4.6 Statistics, page 36.
1.0 | 2006.04 BOSCH Security Systems
Page 31

IVMD | Configuration instructions Area settings | en 29
Objects cannot be detected according to their properties
unless the system has been calibrated for the current camera
position (Section 4.3 Calibration, page 21).
Object size filter
Only objects whose size (captured area) is between the
entered limits can lead to the generation of an alarm event.
A person corresponds to around 0.5 m²; a car to
around 4 m².
Objects are not filtered by size.
Object motion filter
Only objects moving at a speed between the entered limits
can lead to the generation of an alarm event.
The speed of a movement crossways to the camera can be
determined much more accurately than the speed of a
movement directly toward or away from the camera.
Objects are not filtered by speed.
Object moves crossways to camera:
speed is detected more accurately
Object moves in camera’s line of sight:
speed is detected less accurately
NOTE!
i
BOSCH Security Systems 1.0 | 2006.04
Select generous filter settings for object size and speed so that
all relevant movements lead to an alarm being generated.
Page 32

30 en | Area settings IVMD | Configuration instructions
Trigger
Mode: An alarm event is generated when...
Entering ...the center of the object moves across the
boundary of the detector field and into the
field.
Debounce time: If a value other than 0
(zero) is selected, the alarm event will not
be generated until the center of the object
has fully crossed the boundary of the
detector field after this time. This prevents
objects triggering a large number of alarm
events when they are moving around on
the edge of the detector field.
Leaving ...the center of the object moves across the
boundary of the detector field and out of
the field.
Debounce time: as for entering objects,
see above.
Inside ...the center of the object moves inside the
detector field.
Delay [s]: If a value other than 0 (zero) is
selected, the alarm event will not be generated until the object has moved or been
inside the detector field for at least the
selected delay time.
NOTE!
If the boundary of the detector field lies across a static object
i
1.0 | 2006.04 BOSCH Security Systems
that can conceal a moving object (e.g. advertising hoarding),
entering or leaving may not be detected.
Page 33

IVMD | Configuration instructions Area settings | en 31
Object direction filter
Off Objects are not filtered according to
their direction of movement
On Objects will only generate an alarm
event when they move in the selected
direction.
A tolerance angle is entered for the
direction.
Dual Objects will only generate an alarm
event when they move in one of the
selected directions.
A tolerance angle is entered for each
direction.
NOTE!
Only use the speed and direction filters for detecting truly sig-
i
nificant movements; select your settings to ensure the most
robust results possible.
BOSCH Security Systems 1.0 | 2006.04
Page 34

32 en | Area settings IVMD | Configuration instructions
If you have activated Direction under Show in the context menu
of the Area settings window (see page 19), the direction filter
and the motion filter will be graphically displayed for each
detector field:
90°
Tolerance angle
180°
Direction: here 0°
is counted counterclockwise starting from
East.
270°
The direction field can also be repositioned with the mouse in
the graphic display.
You can change the tolerance angle with the mouse by moving
the cursor directly onto the side of the direction indicator and
then moving it with drag&drop.
1.0 | 2006.04 BOSCH Security Systems
Page 35

IVMD | Configuration instructions Area settings | en 33
An object motion filter (if set) is shown by additional moving
white (maximum limit) and yellow (minimum limit) squares
being displayed inside the direction indicator.
NOTE!
Grapic display is adjusted to the size of the detector. For better
i
visibility, either create a detector large enough or resize the
whole window.
4.5 Sensitive area
The sensitive area is that part of the image seen by the camera
that is analyzed. Objects moving outside the sensitive area cannot generate an alarm event even if they are caught by the camera.
Only objects moving inside the sensitive area are detected as
such and generate an alarm event.
The larger the sensitive area, the more computing power is
required, and data will be processed more slowly.
A smaller sensitive area means that data processing is faster.
The sensitive area is shown in yellow hatching.
In the default setting, the whole of the image captured by the
camera is defined as the sensitive area. Any areas that consist
of small squares can be defined as non-sensitive (or again as
sensitive). There are four editing tools you can use for this purpose. You can also repeat this operation as often as you like to
achieve a very precise definition of the sensitive area.
BOSCH Security Systems 1.0 | 2006.04
Page 36

34 en | Area settings IVMD | Configuration instructions
You will find all of the commands in the context menu.
Sensitive area
Examples of areas that could be defined as non-sensitive:
– Railroad: Passing trains can trigger unwanted motion
alarms.
– Public streets: Passers-by moving across a public space
should not be detected – in order to save computing
power and prevent unwanted false alarms.
– Neighboring properties.
– Areas in which moving objects are not anticipated.
– Sky: Birds or planes can trigger false alarms.
– Trees or bushes that move in the wind.
1.0 | 2006.04 BOSCH Security Systems
Page 37

IVMD | Configuration instructions Area settings | en 35
The following commands are available:
i
Save and
Exit Editor
Undo The last action you carried out is undone.
Set All The whole of the captured area is defined as
Clear All The whole of the captured area is defined as
Tool Selects an editing tool:
NOTE!
While you are drawing, hold down the SHIFT key to create nonsensitive areas.
Drawing by itself without the SHIFT key marks out sensitive
areas.
The settings are saved. You exit the Editor for
the sensitive area.
the sensitive area.
non-sensitive.
Rubber Band:
You can use the mouse to draw any size of
square.
Small Square, Medium Square, Large Square
You can edit the sensitive area as with a drawing tool.
BOSCH Security Systems 1.0 | 2006.04
Page 38

36 en | Area settings IVMD | Configuration instructions
4.6 Statistics
The statistics for a detector field help you to refine the filter criteria for objects. For example, you may see an accumulation of
objects that have not triggered an alarm under the current filter
criteria even though this might have been desirable.
You can view the Statistics dialog separately for each detector
field. To create the displayed statistics, start by opening the
dialog. The longer the dialog is left open, the more data will be
entered in the statistics.
Green:
Set of objects
with no alarm
Red:
Set of objects
with alarm
Black:
Filter area that
allows alarm
Gray:
Filtered-out area;
no alarm
The statistics show three histograms:
– Area: accumulation of objects with a certain surface area.
– Speed: accumulation of objects moving at a certain speed.
– Direction: accumulation of objects moving in a certain
direction.
The black area in each histogram is the area that was defined in
the Properties of Detector Field dialog for the particular filter
1.0 | 2006.04 BOSCH Security Systems
Page 39

IVMD | Configuration instructions Area settings | en 37
(see page 28). Areas that are outside the defined limits are
grayed.
The lines indicate the number of objects for which the respective value was detected. The higher the line, the more objects
matched the particular criterion. The histograms distinguish
between objects that trigger an alarm (red line) and those that
do not (green line).
NOTE!
Click Reset to begin building statistics again.
i
BOSCH Security Systems 1.0 | 2006.04
Page 40

38 en | Display of Measurements IVMD | Configuration instructions
5 Display of Measurements
When you are working with the English software interface, measurements can be displayed according to the imperial system.
1. Close the Configuration Manager.
2. Click Start > My Computer.
3. Right-click the window and select Properties from the
popup menu.
The window System Properties opens.
4. Click the Advanced tab.
5. Click Environment Variables.
The respective window opens.
6. Under User Variables click New.
The respective dialog opens.
7. Enter:
Name of the variable: LANG
Value of the variable: us
8. Close all windows by clicking OK.
9. Start the Configuration Manager.
Measurements will be shown according to the imperial
system.
NOTE!
Delete this user variable to return to the default display.
i
1.0 | 2006.04 BOSCH Security Systems
This user variable is only valid for the current Windows login.
You can create various Windows accounts, so that the display is
pre-determined by the Windows-login.
Page 41

IVMD | Configuration instructions Contact and Service | en 39
6 Contact and Service
Contact address
Bosch Sicherheitssysteme GmbH
Robert-Koch-Straße 100
85521 Ottobrunn
Germany
E-mail: de.securitysystems@bosch.com
Internet: www.bosch-sicherheitssysteme.de
BOSCH Security Systems 1.0 | 2006.04
Page 42

40 en | Contact and Service IVMD | Configuration instructions
Service and support
If you have any questions about the programs from the VIDOS
Pro Suite, you can find further information on the Internet at:
www.vidos.net
Technical support is available from:
Americas
Bosch Security Systems
130 Perinton Parkway
Fairport, New York, 14450, USA
Phone: +1 585 223 4060
Fax: +1 585 223 9180
E-mail: security.sales@us.bosch.com
Internet: www.boschsecurity.us
Europe, Middle East, Africa
Bosch Security SystemsB.V.
P.O. Box 8000
25600 JB Eindhoven, The Netherlands
Phone: +31 (0)40 27 83955
Fax. +31 (0)40 27 86668
E-mail: emea.securitysystems@bosch.com
Internet: www.boschsecurity.com
Asia-Pacific
Bosch Security Systems Pte Ltd
38C Jalan Pemimpin
Singapore 577180
Phone: +65 6319 3450
Fax: +65 6319 3499
E-mail: apr.securitysystems@bosch.com
Internet: www.boschsecurity.com
1.0 | 2006.04 BOSCH Security Systems
Page 43

IVMD | Configuration instructions | en 41
Index
A
Analysis type 10
Anchor point
calibration
23
C
Calibration plane 23
Contact address 39
Cube
calibration
Cube size 27
24
D
Default settings 10
Detector fields
displaying
Direction
displaying
19
19
F
Filters 29
H
Height of camera position 26
Object motion filter 29
Object outlines
displaying
19
R
Roll angle 26
S
Sensitive area
displaying
Settings, Global 20
19
T
Tilt angle 25
Tolerance angle 31
Trigger 30
V
VCA 9
M
Meta data 10, 19
N
Node
detector field
18
O
Object bounding box
displaying
Object direction filter 31
Object filter 29
Object markings 11
BOSCH Security Systems 1.0 | 2006.04
19
Page 44

Bosch Sicherheitssysteme GmbH
Robert-Koch-Straße 100
85521 Ottobrunn
Germany
Telephone +49 (0) 89 6290-0
Fax +49 (0) 89 6290-1020
www.bosch-securitysystems.com
© Bosch Sicherheitssysteme GmbH, 2006
 Loading...
Loading...