Page 1

IMPORTANT: IMPORTANT : IMPORTANTE:
Read Before Using Lire avant usage Leer antes de usar
Operating/Safety Instructions
Consignes de fonctionnement/sécurité
Instrucciones de funcionamiento y seguridad
4405
Call Toll Free for
Consumer Information
& Service Locations
Pour obtenir des informations et
les adresses de nos centres de
service après-vente,
appelez ce numéro gratuit
Llame gratis para
obtener información
para el consumidor y
ubicaciones de servicio
1-877-BOSCH99 (1-877-267-2499) www.boschtools.com
For English Version Version française Versión en español
See page 2 Voir page 78 Ver la página 42
Page 2
Safety
!
WARNING
“READ ALL INSTRUCTIONS” — Failur
BULLET (l) symbol listed BELOW and other safety precautions, may result in serious personal injury.
General Safety Rules
For Bench Top Tools
Work Area
l Keep work area clean and well lit. Cluttered
benches and dark areas invite accidents.
l Do not operate power tools in explosive
atmospheres, such as in the presence of
flammable liquids, gases or dust. Power
tools create sparks which may ignite the dust
or fumes.
l Keep bystanders, children and visitors away
while operating a power tool. Distractions
can cause you to lose control.
l Store idle tools out of reach of children and
other untrained persons. Tools are dangerous in the hands of untrained users.
l Do not leave tool running unattended, turn
power off. Do not leave tool until it comes to a
complete stop.
l MAKE WORKSHOP CHILDPROOF with pad
lock, master switches, or by removing starter
keys.
Electrical Safety
l Before plugging in the tool, be certain the
outlet voltage supplied is compatible with
the voltage marked on the nameplate within
10%. An outlet voltage incompatible with that
specified on the nameplate can result in serious
ds and damage to the tool.
hazar
l Double insulated tools are equipped with a
polarized plug (one blade is wider than the
other). This plug will fit in a polarized outlet
only one way. If the plug does not fit fully in
the outlet, reverse the plug. If it still does
not fit, contact a qualified electrician to
install a polarized outlet. Do not change the
plug in any way.
the need for the thr
powercord and grounded power supply.
l Avoid body contact with gr
such as pipes, radiators, ranges and refrigerators.
shock if your body is grounded.
There is an increased risk of electric
Double insulation eliminates
ee wire grounded
ounded surfaces
e to follow the SAFETY RULES identified by
l Do not expose power tools to rain or wet
conditions.
increase the risk of electric shock.
l Do not abuse the cord. Never use the cord
to carry the tools or pull the plug from an
outlet. Keep cord away from heat, oil, sharp
edges or moving parts. Replace damaged
cords immediately.
the risk of electric shock.
l When operating a power tool outside, use an
outdoor extension cord marked “W-A” or
“W”. These cords are rated for outdoor use and
reduce the risk of electric shock.
Water entering a power tool will
Damaged cords increase
Personal Safety
l Stay alert, watch what you are doing and use
common sense when operating a power
tool. A moment of inattention or use of drugs,
alcohol or medication while operating power
tools can be dangerous.
l Dress properly. Do not wear loose clothing
or jewelry. Contain long hair. Keep your
hair, clothing and gloves away from moving
parts. Loose clothes, jewelry or long hair can
be caught in moving parts. Roll long sleeves
above elbows. Rubber gloves and non-skid
footwear are recommended when
working outdoors.
l Avoid accidental starting. Be sure switch is
“OFF” before plugging in. Carrying tools with
your finger on the switch or plugging in tools
that have the switch “ON” invites accidents.
l Remove adjusting keys or wr
ning the tool “ON”.
tur
is left attached to a r
be thrown.
l Do not overreach, keep proper footing and
balance at all times. Proper footing and balance enables better control of the tool in unexpected situations.
l Do not stand on tool or its stand. Serious
injury may occur if the tool is tipped or if the
cutting tool is accidentally contacted. Do not
store materials on or near the tool such that it is
necessary to stand on the tool or its stand to
reach them.
otating part of the tool will
enches before
ench or a key that
A wr
“SAVE THESE INSTRUCTIONS”
2.
Page 3
Safety
!
WARNING
l Use safety equipment. Always wear safety
goggles. Dust mask, safety shoes, hard hat or
hearing protection must be used for
appropriate conditions. Everyday eyeglasses
only have impact resistant lenses, they are NOT
safety glasses.
“READ ALL INSTRUCTIONS” — Failur
BULLET (l) symbol listed BELOW and other safety precautions, may result in serious personal injury.
Tool Use and Care
l Use clamps or other practical way to secure
and support the workpiece to a stable platform. Holding the work by hand or against
your body is unstable. It allows for work to
shift, causes binding of the tool and loss
of control.
l Do not force tool. Use the correct tool for
your application.
job better and safer at the rate for which it is
designed. Do not use the tool for purpose not
intended - for example; do not use the miter
saw for slicing meats.
l Do not use tool if switch does not turn it
“ON” or “OFF”. Any tool that cannot be controlled with the switch is dangerous.
l Disconnect the plug from the power source
before making any adjustments or changing
accessories. Such preventive safety mea-
sures reduce the risk of starting the tool accidentally.
l Keep cutting tools sharp and clean. Properly
maintained tools, with sharp cutting edges, are
less likely to bind and easier to control. When
mounting saw blades be certain that the arrow
on the blade matches the direction of the arrow
marked on the tool and that the teeth are also
pointing in the same direction.
l Inspect guards before using a tool. Keep
ds in place. Check moving parts for
guar
binding or any other condition that may
affect the normal operation or safety features of the tool. If damaged, have tool serviced befor
are caused by poorly maintained tools.
l Do not alter or misuse tool. Any alteration or
modification is a misuse and may result in serious personal injury
l The use of any other accessories not speci-
fied in this manual may create a hazard.
Accessories that may be suitable for one type
of tool, may become hazardous when used on
an inappropriate tool.
e using the tool.
The correct tool will do the
Many accidents
.
e to follow the SAFETY RULES identified by
Service
l Tool service must be performed only by
qualified repair personnel. Service or maintenance performed by unqualified personnel may
result in misplacing internal wires and components which could cause serious hazard.
l When servicing a tool, use only identical
replacement parts. Follow instructions in
the Maintenance section of this manual. Use
of unauthorized parts or failure to follow
Maintenance Instructions may create a hazard.
Safety Rules
For Miter Saws
l Use clamps to support workpiece whenever
possible. If supporting the workpiece by
hand, you must always keep hand outside of
“No Hand” area as marked with a symbol on
the base. Do not use this saw to cut pieces
that are too small to be securely clamped.
Your hand if placed inside the “No Hands”
region can easily slip or be pulled into
the blade.
l Do not reach in back of the saw blade
behind the fence with either hand to hold
down or support the workpiece, remove
wood scraps, or for any other reason. The
proximity of the spinning saw blade to your
hand may not be obvious and you may be
seriously injured.
l Never cross your hand over intended line of
cutting. Supporting the workpiece “cross
handed” i.e. holding the left side of the
workpiece with your right hand is
very danger
l Always disconnect the power cord from the
power sour
ments or attaching any accessories. Y
may unintentionally start the saw, leading to
serious personal injury.
l Miter saws are intended to cut wood or
woodlike products, they cannot be used
with abrasive cutoff wheels for cutting
ous material such as bars, r
ferr
etc. However
aluminum or other non-ferr
only saw blades specifically r
for non-ferr
materials causes excessive sparking and will
damage the lower guar
motor
does not offer 10” metal cutting blades.)
ous.
ce before making any adjust-
, if cutting materials like
ous metals, use
ous metal cutting.
d and will overload the
. (NOTE: Bosch Power T
ou
ods, studs,
ecommended
Cutting ferr
ool Company
ous
“SAVE THESE INSTRUCTIONS”
3.
Page 4
Safety
!
WARNING
l Inspect your workpiece before cutting. If
“READ ALL INSTRUCTIONS” — Failur
BULLET (l) symbol listed BELOW and other safety precautions, may result in serious personal injury.
workpiece is bowed or warped, clamp it with
the outside bowed face towar
d the fence.
Always make certain that there is no gap between the workpiece, fence and table along
the line of the cut. Bent or warped workpieces
can twist or rock and may cause binding on the
spinning saw blade while cutting. Also, make
sure there are no nails or foreign objects in the
workpiece.
l Do not use the saw until the table is clear of
all tools, wood scraps, etc., except the
workpiece. Small debris or loose pieces of
wood or other objects that contact the revolv
ing blade can be thrown with high speed at
the operator.
l Do not feed workpiece into the blade or cut
“freehand” in any way. Workpiece must be
stationary and clamped or braced by your
hand.
Saw must be fed through the workpiece
smoothly and at a rate which will not overload
the saw’s motor.
l Cut only one workpiece at a time. Multiple
workpieces cannot be adequately clamped or
braced and may bind on the blade or shift during cutting.
l Be certain the miter saw is mounted or
placed on a level, firm work surface before
using. A level and firm work surface reduces
the risk of the miter saw becoming unstable.
l Plan your work. Provide adequate support
accessories such as tables, saw horses,
table extension, etc. for workpieces wider or
longer than the table top (see page 20).
Workpieces longer or wider than the miter saw
table can tip if not secur
ely supported. If the
cutoff piece or workpiece tips it can lift the
lower guar
l Do not use another person as a substitute
d or be thr
own by the spinning blade.
for a table extension or as additional support. Unstable support for the workpiece can
cause the blade to bind or the workpiece to
shift during the cutting operation pulling you
and the helper into the spinning blade.
l The cutoff piece must not be jammed
ed by any other means
against or pr
against the spinning saw blade.
essur
If confined,
i.e. using length stops, it could get wedged
against the blade and thrown violently.
l Always use a clamp or a fixture designed to
properly support r
dowel rods, or tubing.
ound material such as
Rods have a tendency
to roll while being cut, causing the blade to
“bite” and pull the work with your hand into
the blade.
e to follow the SAFETY RULES identified by
l When cutting irregularly shaped work-
pieces, plan your work so it will not slip and
pinch the blade and be tor
n from your hand.
A piece of molding, for example, must lie flat or
be held by a fixture or jig that will not let it twist,
rock or slip while being cut.
l Let the blade reach full speed before con-
tacting the workpiece.
This will help avoid
thrown workpieces.
l If the workpiece or blade becomes jammed
or bogged down, turn miter saw “OFF” by
releasing switch. Wait for all moving parts
to stop and unplug the miter saw, then work
to free the jammed material. Continued saw-
ing with jammed workpiece could cause loss of
control or damage to compound miter saw.
l Braking action of the saw causes the saw
head to jerk downward. Be ready for this
reaction when making an incomplete cut or
when releasing the switch before the head is
completely in the down position.
l After finishing the cut, release the switch,
hold the saw arm down and wait for blade to
stop before removing work or cutoff piece.
If blade does not stop within five (5) seconds, unplug the saw and follow the instructions in the Troubleshooting section.
REACHING WITH YOUR HAND UNDER A
COASTING BLADE IS DANGEROUS!
l There are additional safety instructions
for particular operations of the saw in the
operating section. Read the rest of the manual for safe operation.
l For slide action cutting, first PULL saw head
assembly away from the fence, until blade
clears the workpiece or to its maximum
extension if blade cannot clear the workpiece. Make certain the clamp does not
interfer
e with the guar
d and head assembly
.
Second, turn saw “ON” and lower the saw to
the table. Then PUSH saw thr
ough the workpiece. Release the switch and wait for the
blade to completely stop befor
e raising the
head assembly and removing the workpiece.
Never “pullcut” since the blade may climb the
workpiece causing KICKBACK.
l For chop action cutting, slide the head
assembly to the rear as far as it will go and
tighten slide lock knob. Then tur
n the saw
“ON” and lower the head assembly to make
the cut. Release the switch and wait for the
blade to completely stop before raising the
head assembly and removing the workpiece.
Failure to tighten the slide lock knob can cause
the blade to suddenly climb up on the top of the
workpiece and force itself toward you.
“SAVE THESE INSTRUCTIONS”
4.
Page 5

Safety
!
WARNING
l Do not allow familiarity gained from frequent
use of your miter saw to become commonplace.
tion of a second is suf
injury
l THINK SAFETY! SAFETY IS A COMBINATION
OF OPERATOR’S COMMON SENSE, KNOWLEDGE OF THE SAFETY AND OPERATING
INSTRUCTIONS AND ALERTNESS AT ALL
TIMES WHEN THE MITER SAW IS BEING
USED.
!
WARNING
YOUR TOOL. THESE WARNINGS ARE ONLY A
CONDENSED FORM OF THE MORE DETAILED
SAFETY RULES AND PRECAUTIONS THAT
APPEAR IN YOUR OWNER'S MANUAL. THEY
SERVE AS A REMINDER OF ALL SAFETY RULES
NEEDED FOR SAFE OPERATION OF THIS MITER
SAW.
“READ ALL INSTRUCTIONS” — Failure to follow the SAFETY RULES identified by
BULLET (l) symbol listed BELOW and other safety precautions, may result in serious personal injury.
Always remember that a careless frac-
ficient to inflict severe
.
THE WARNINGS SHOWN
BELOW CAN BE FOUND ON
!
WARNING
drilling, and other construction activities contains
chemicals known
other r
these chemicals are:
• Lead from lead-based paints,
• Crystalline silica from bricks and cement and other
• Arsenic and chromium from chemically treated
Your risk from these exposures varies, depending on
how often you do this type of work. T
exposure to these chemicals: work in a well ventilated
area, and work with approved safety equipment,
such as those dust masks that are specially
designed to filter out microscopic particles.
eproductive harm. Some examples of
masonry products, and
lumber.
Some dust created by power
sanding, sawing, grinding,
to cause cancer, birth defects or
o reduce your
DESIGNATED
DANGER ZONE.
AVOID POSITIONING
HANDS, FINGERS OR
ARMS IN THE AREA
DESIGNATED BY
THIS SYMBOL.
“SAVE THESE INSTRUCTIONS”
5.
Page 6
Safety
!
WARNING
“READ ALL INSTRUCTIONS” — Failur
BULLET (l) symbol listed BELOW and other safety precautions, may result in serious personal injury.
Double Insulated Tools
Double insulation is a design concept used in
electric power tools which eliminates the need for the
three wire grounded power cord and grounded power
supply system. It is a recognized and approved system by Underwriter’s Laboratories, CSA and Federal
OSHA authorities.
l Servicing of a tool with double insulation
requires care and knowledge of the system
and should be performed only by a qualified
service technician.
l WHEN SERVICING, USE ONLY IDENTICAL
REPLACEMENT PARTS.
l POLARIZED PLUGS. Your tool is equipped with
a polarized plug (one blade is wider than the
other), this plug will fit in a polarized outlet only
one way. If the plug does not fit fully in the outlet, reverse the plug. If it still does not fit, contact
a qualified electrician to install the proper outlet.
To reduce the risk of electrical shock, do not
change the plug in any way.
e to follow the SAFETY RULES identified by
Extension Cords
l Replace damaged cords immediately. Use of
damaged cords can shock, burn or electrocute.
l If an extension cord is necessary, a cord with
adequate size conductors should be used
to prevent excessive voltage drop, loss of power
or overheating. The table shows the correct size
to use, depending on cord length and name
plate amperage rating of tool. If in doubt, use
the next heavier gauge. Always use U.L. and
CSA listed extension cords.
RECOMMENDED SIZES OF EXTENSION CORDS
Tools 120 Volt A.C. Tools
Ampere Cord Length in Feet
Rating Cord Size in A.W.G.
25 50 100 150
3-6 18 16 16 14
6-8 18 16 14 12
8-10 18 16 14 12
10-12 16 16 14 12
12-16 14 12 N/A N/A
“SAVE THESE INSTRUCTIONS”
Table of Contents
Safety . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
General Safety Rules For Bench Top Tools . . . . . . . . 2
Safety Rules For Miter Saws . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-6
Table of Contents. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
Electrical Requirements . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
Getting To Know Your Miter Saw . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8-9
Assembly. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Tools Needed For Assembly And Alignment . . . . . . 10
Unpacking and Checking Contents . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
Attaching Miter Lock Knob
Assembling Dust Elbow and Dust Bag . . . . . . . . . . . 11
Installation and Removal of the Blade . . . . . . . . . . . 12
Adjustments . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13-16
Blade Square To Table (90°) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
Blade 45° To The Table . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
Blade 33.9º T
Blade Square To Fence. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
Miter Scale Indicator Adjustment . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
Installation. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Mounting Applications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
Portable Mounting Using Clamps
Stability Bar Adjustment . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
o The T
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
able
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
2-6
10-12
11
15
17-18
18
NOTE: The smaller the gauge number, the heavier
the cord.
Basic Saw Operations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Body and Hand Position . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
Workpiece Support . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
Auxilliary Fence . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
Switch Activation. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
Detent Override . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
Sliding Base/Fence Extension
Saw Operations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24-31
Chop Cut . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
Slide Cut
Miter Cut . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
Bevel Cut . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25-26
Compound Cuts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
Cutting Grooves (Dado Cut) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27
Cutting Base Molding . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
Cutting Cr
Special Cuts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
Maintenance and Lubrication. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32
roubleshooting
T
Slide Action Adjustment . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 35
Adjusting Bevel Lock Lever T
Accessories . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 36
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
own Molding
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . 35
ension
19-22
22-23
24
28-30
33-35
6.
Page 7
Electrical Requirements
Connect this saw to a 120V, 15-amp branch cir-
1.
cuit with a 15-amp time delay fuse or cir
breaker. Using the wrong size fuse can damage
the motor.
Fuses may “blow” or circuit breakers may trip
2.
equently if motor is overloaded. Overloading
fr
can occur if you feed the blade into the workpiece too rapidly, start and stop too often in a
short time, or use the wrong blade for
the application.
3. Most motor troubles may be traced to loose or
incorrect connections, overload, low voltage
(such as small size wire in the supply circuit or
overly long supply circuit wire). Always check the
connections, the load and the supply circuit
whenever motor does not work well.
Electric Brake
Your saw is equipped with an automatic electric
brake which is designed to stop the blade from spinning in about five (5) seconds after you release the
trigger switch. It is useful when making certain cuts
in wood where a coasting blade would result in a
wide, imprecise cut.
cuit
!
WARNING
motor will gradually slow down and the braking
action is initiated ONLY by the release of the
trigger switch.
The electric blade brake of your miter saw has been
designed for highest degree of reliability, but unexpected circumstances such as contamination on the
commutator and brushes or failure of motor’s components can cause the brake not to activate. If this
condition occurs, turn the saw “ON” and “OFF” four
to five times without contacting the workpiece. If the
tool operates but the brake does not consistently
stop the blade in about five (5) seconds, DO NOT use
saw and have it serviced immediately.
!
WARNING
Remember to let the saw blade come to a complete
stop before raising the blade from the workpiece. As
always the guard system is your best protection
against unintentional contact with a spinning saw
blade. NEVER wedge open or defeat the closing
action of the lower guard.
When electrical power is lost due to
blown fuse or other causes, the
The brake action of this saw is not
intended as a safety feature.
7.
Page 8
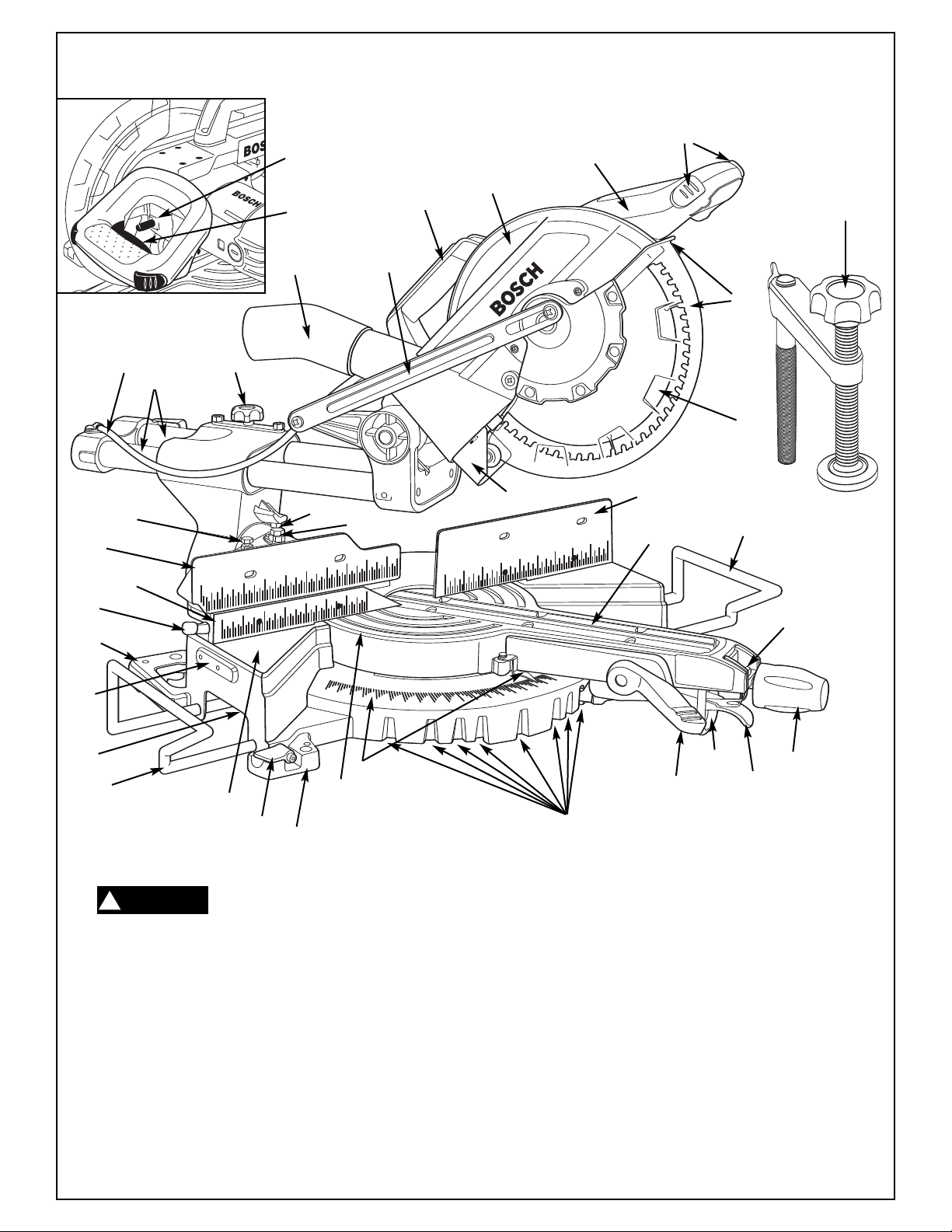
Getting To Know Your Miter Saw
1
4
30
2
40
3
28
20
16
41
19
32
25
22
29
5
26
27
6
23
21
24
7
8
18
7
9
40
12
18
14
15
17
16
o avoid injury fr
!
WARNING
source outlet before making any adjustments.
1. Switch “Lock-OFF” Button
This button must be pressed to activate the power switch.
2. Power Switch
The power switch (used with the “Lock-OFF” button) ener
gizes the unit.
3. Switch Handle
This handle contains the switch. The blade is lowered into
the workpiece by pushing/pulling down on the handle.
Never pick up tool by switch handle.
4. Arbor Lock
Allows the user to keep the blade fr
ening or loosening arbor scr
or removal.
T
starting, remove plug from power
ew during blade replacement
om accidental
otating while tight-
om r
43
34
11
13
5. Lower Blade Guar
The lower blade guard helps protect your hands from the
spinning blade. It r
Lip can be used to raise the lower guard manually, only as
recommended in this manual.
6. Blade
Use only 10" blades between 1.4 and 3.0mm thick, with
5/8" arbor hole.
-
7. Stationary Fence
Supports the workpiece. The fence has a cast in scale to
make repetitive cuts easy. The fence also has holes which
e used to secur
ar
8. Kerf Inserts
9. Miter Detent Override
Allows detent action to be locked out allowing for fine
adjustments to any miter angle.
d/Lower Guar
etracts as the blade is lower
e an auxiliary fence if desir
d Lip
8.
10
ed. Guard
ed.
Page 9
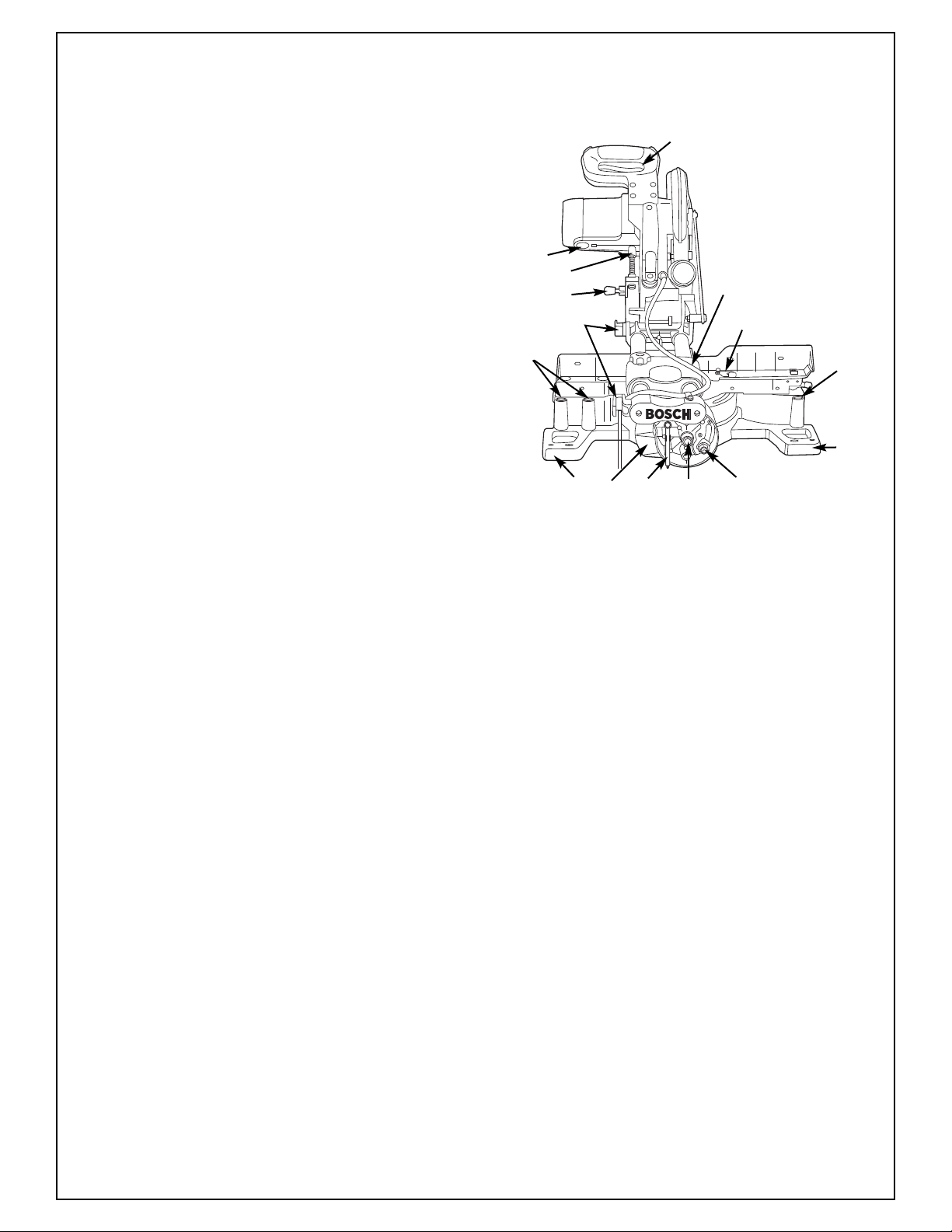
Getting To Know Your Miter Saw
10. Miter Lock Knob
The miter lock knob locks the miter saw table at any
desired miter angle.
11. Miter Detent Trigger
The trigger releases the table from the detent.
12. Miter Scale/Miter Angle Indicator
Scale is cast in on the base of the saw. Indicator is fastened to the table.
13. Miter Detents
e are ten (10) miter detents for fast and accurate miter
Ther
cuts of common miter angles.
14. Table
Sits in base, provides workpiece support, rotates for desired
miter cuts and rotates the head assembly. The front extended part of the table is called the miter arm.
15. Base
Provides working surface to support workpiece.
16. Tool Mounting Pads
17. Base Extension Clamping Levers
Locks Base Extensions into place. One for each extension.
18. Extension Rods
Add support for long workpieces.
19. Sliding Fence
This provides extra support and clamping area for compound miter cuts.
20. Sliding Fence Clamping Lever
Locks the Sliding Fence in place.
21. Chip Deflector with Dust Flap
This protects against large chips from entering the upper
guard.
22. Dust Chute Elbow
The dust chute elbow rotates 360° and can accommodate
the dust bag or a vacuum hose hookup.
23. 0° Bevel Stop
Adjustable stop for a quick and accurate 0° bevel index.
24. 33.9º Bevel Stop
Adjustable stop for a quick and accurate 33.9° bevel index.
25. 45° Bevel Stop
Adjustable stop for a quick and accurate 45
26. Slide Rail Lock Knob
The slide rail lock knob locks the slide rails when you are
not making slide cuts and when you are transporting the
.
saw
27. Slide Rails
Guide the head assembly when making slide cuts.
28. Workpiece Clamp
Provides fast clamping of workpiece.
29. Lower Guard Actuation Link
Allows for smooth movement of the lower guard.
30. Upper Blade Guard
Covers upper portion of the blade.
31. Blade Wrench
Used for tightening/loosening blade and adjusting fence
and glide blocks. Blade wrench is stored in rear of saw.
32. Power Cord
Supplies power to motor. Has molded cord retainer for storage.
° bevel index.
2
38
37
36
42
33
32
39
33
16
35
31
16
33. Workpiece Clamp Positions
There are three (3) positions behind the fence for the workpiece clamp.
34. Bevel Lock Lever
The bevel lock handle locks the head assembly at a desired
bevel angle.
35. Bevel Scale
Indicator used to set bevel angles.
36. Head Assembly Lock Pin
Saw is equipped with a lock pin used to lock the head
assembly in the lower position. Should be locked in the
lower position during transportation.
37. Depth Stop
Allows you to adjust the depth of the blade for cutting
grooves in the workpiece.
38. Brush Caps
These caps keep the motor brushes in position and provide
easy access for inspecting and replacing brushes.
39. Sliding Fence Cover Plate
Rotate cover plate to remove fence.
40. Carry Handles
own Stop Bosses
41. Cr
Allow use of Bosch crown stops.
42. Cord Wrap
ovides location to stor
Pr
43. Stability Bar
Provides support for the end of the table.
44. Pivot Bolt
Tighten/Loosen to adjust bevel tension.
45. Bevel Lock Nut
Adjusts bevel lock clamp force.
44 45
e power cor
d.
9.
Page 10
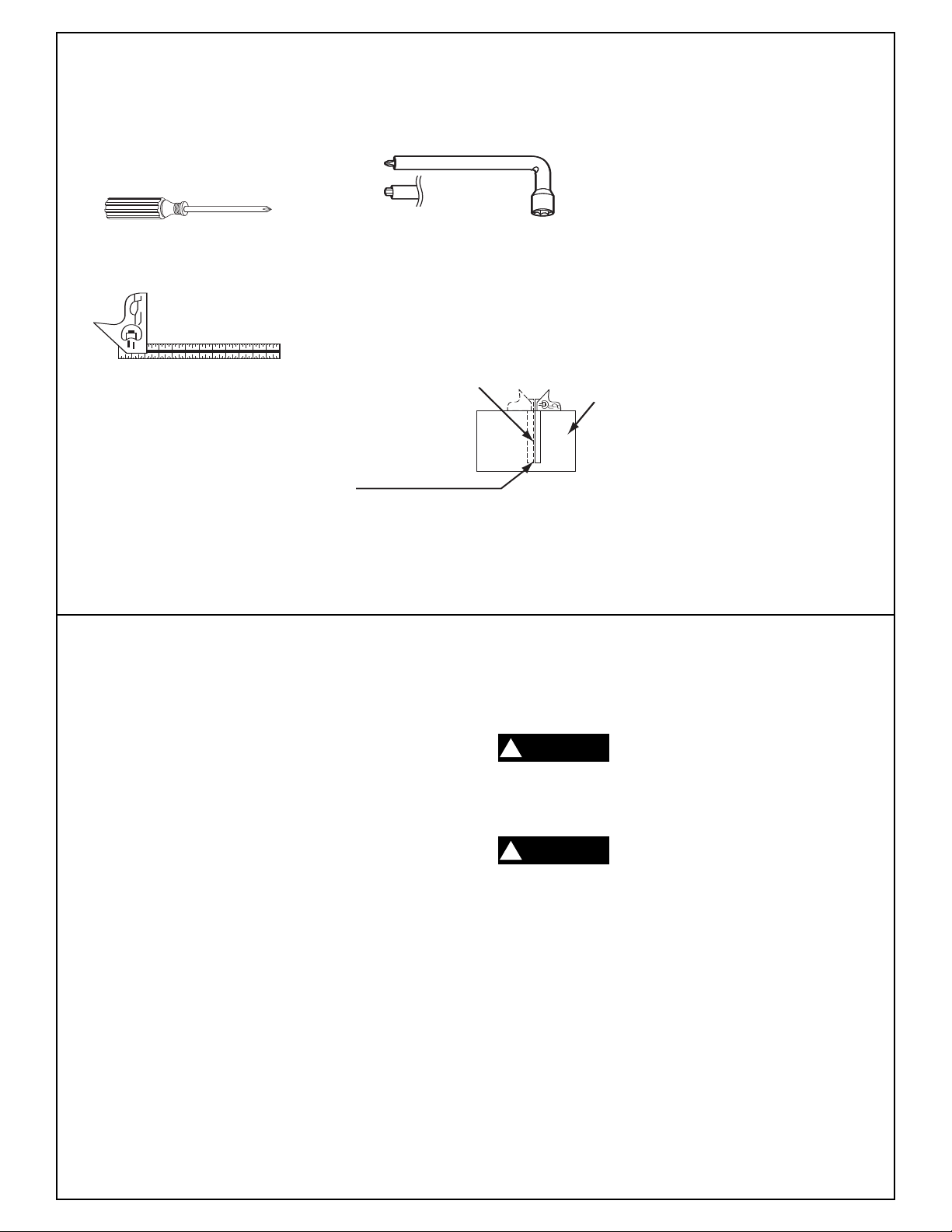
Assembly
Tools Needed For Assembly And Alignment
Phillips Screwdriver
Combination Square
Should be no Gap or Overlap
when Square is Flipped Over in
Dotted Position
Disconnect plug from power source before performing any assembly, adjustment or repair to avoid possible
injury.
Blade Wrench (supplied), hex on
other side of phillips.
Combination Square Must be True
Draw Light
Line on Board
Along this Edge
Straight Edge of
Board 3/4" Thick
This Edge Must be
Perfectly Straight
Unpacking And Checking Contents
Model 4405 Slide Compound Miter Saw is shipped
complete in one box.
1. Separate all parts from packing materials and
check each one with the “Table of Loose Parts” to
make sure all items are accounted for before discarding any packing material.
2. Table of Loose Parts: (See pages 8 and 9)
ew Clamp
Scr
Dust Elbow/Dust Bag
Miter Lock Knob
Call 1-877-BOSCH99; if you need assistance.
!
WARNING
switch on until the missing parts are obtained and
are installed correctly. Call 1-877-BOSCH99 to
obtain missing parts.
!
WARNING
Lock bevel lock handle. Pull the head assembly
completely toward you and tighten the slide rail lock
knob. Lock head assembly in the down position.
Never carry the tool by the slide rails, this may
cause blade misalignment.
Never carry the tool by the cord or head assembly
power switch handle. Damage to insulation could
cause an electric shock. Damage to wire connections could cause a fire.
If any parts are missing, do not
plug in power cord or turn the
Before moving the saw: Lock the
miter lock knob in 45° position.
10.
Page 11
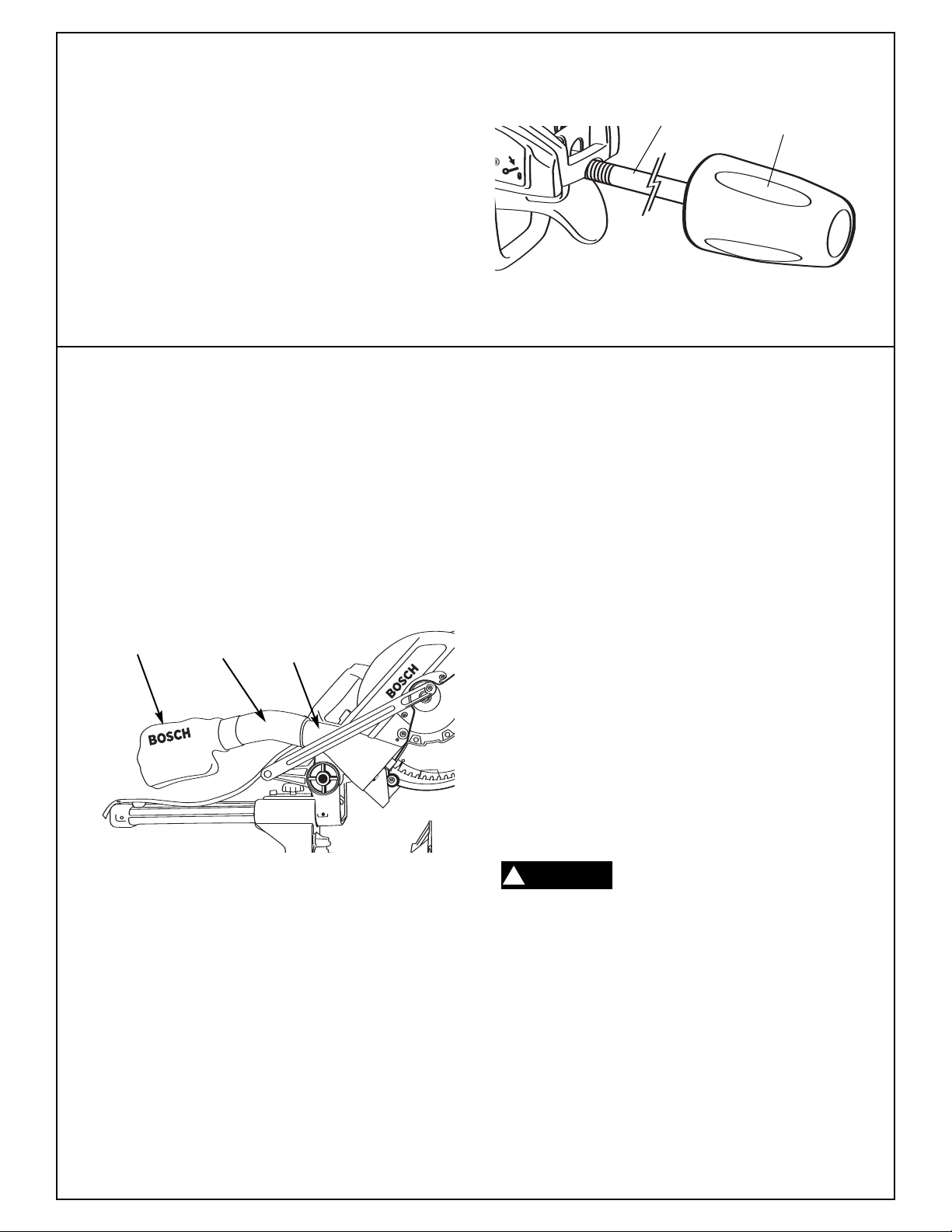
Assembly
Attaching Miter Lock Knob
Locate the miter lock knob fr
parts and thread shaft into miter detent assembly as
shown in Figur
e 4.
om among the loose
Assembling Dust Elbow And Dust Bag
1. Push the dust elbow onto the dust nozzle.
Rotate elbow to the desired position. (Figure 5).
Dust
Bag
Dust
Elbow
Dust
Nozzle
Shaft
Figure 4: Miter Lock Knob
2. The dust bag attaches to the dust chute elbow
and is used to collect sawdust. The dust elbow
can also be attached to a standard 2" vacuum tube for dust collection.
3. Position dust elbow/bag so that it does not
interfere with the tool during the cutting operation
for all miter/bevel settings. Make sure dust bag
does not interfere with the slide rails during slide
cutting.
4. The dust bag requires emptying when full of
sawdust. Empty it frequently and after completion of sawing. Carefully remove dust bag from
dust elbow. Empty dust bag in proper trash bin
by unzipping the bag. Be extr
disposed dust, materials in fine particle form may
be explosive. Do not throw sawdust on an open
fire. Over time, spontaneous combustion can
result from mixing oil or water with dust
particles.
Miter Gauge
Lock Knob
emely careful of
Figure 5. Dust Bag and Elbow
!
WARNING
lead based, or any other materials that may contain
carcinogens, use special precautions. A suitable respirator must be wor
work ar
sheeting and persons not protected should be kept
out until work areas are thoroughly cleaned.
ea. W
When sawing chemically pressure
treated lumber, paint that may be
n by all personnel entering the
eas should be sealed by plastic
ork ar
11.
Page 12
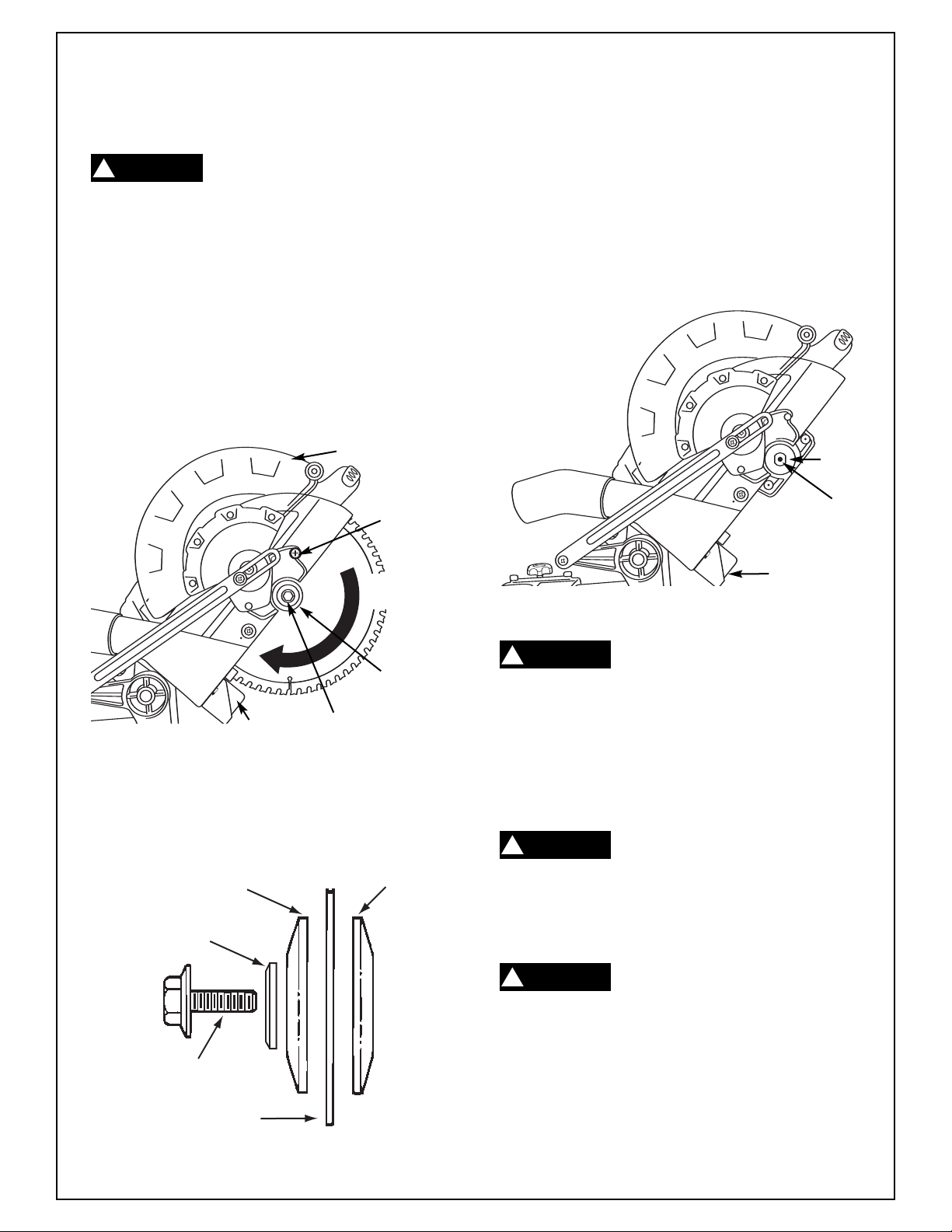
Assembly
Installation And Removal Of The Blade
!
WARNING
adjustment or repair to avoid possible injury.
1. Loosen rear cover plate screw one full turn. Do
not completely remove screw.
Loosen front cover plate screw (approximately three full
2.
turns) until it clears the tab on the cover plate; but do
not completely remove screw. Rotate coverplate
counter-clockwise, exposing arbor bolt blade area.
3. Rotate the guard by hand to clear the blade. Let go of
guard. Plastic will be held out of way by front screw.
4. Press and hold the arbor lock. The blade may
need to be rotated for the arbor lock to catch.
Use the blade wrench to remove the blade bolt
by turning wrench clockwise. NOTE: The blade
bolt has a left hand thread.
Disconnect plug from power source
before performing any assembly,
To install the 10" blade, fit blade between the
6.
chip deflectors and onto arbor shaft (Figure 3).
NOTE: Make sure the rotation arrow on the
blade matches the clockwise rotation arrow on
the lower guard.
Lower Guar
Turn Bolt This
Way to Loosen
Chip
Deflector
Figure 1. Blade Removal
5. Remove the blade bolt, arbor washer, outer
washer and the blade. Inner washer does not
need to be r
Arbor Washer
Blade Bolt
(Left Hand Thread)
emoved (Figur
Outer Washer Inner Washer
Sawblade
Blade Bolt
(Hex Cap)
e 2).
d
Front Cover
Plate Screw
Outer
Washer
Inner
Washer
Arbor Shaft
Chip
Deflector
Figure 3. Blade Installation
!
WARNING
and 5/8" arbor.
7. Replace the outer washer, arbor washer, and
tighten blade bolt finger tight counter-clockwise
(see Figure 2). Press the arbor lock and tighten
blade bolt securely using blade wrench, but do
not overtighten.
8. Rotate cover plate clockwise to original position
and tighten cover plate scr
!
WARNING
interfere with and hang-up lower blade guard.
Never use saw without cover plate secur
place. Lower guard will not function properly.
Be sur
9.
turns freely.
!
WARNING
with the table insert at the 0
tions. Lower the blade into the table slot and check
for any contact with the base or turn table structure. If
blade contacts base or table, seek authorized service
1-877-BOSCH99
at
Replace blade wr
10.
To avoid injury, do not use a blade
larger or smaller than 10" diameter
ews.
Tighten the cover plate screws.
Loose cover plate screw may
ely in
e the arbor lock is released so the blade
After installing a new blade, make
sure the blade does not interfere
° and 45° bevel posi-
.
ench in storage ar
ea on saw
.
e 2. Blade Har
Figur
dwar
e
12.
12.
Page 13
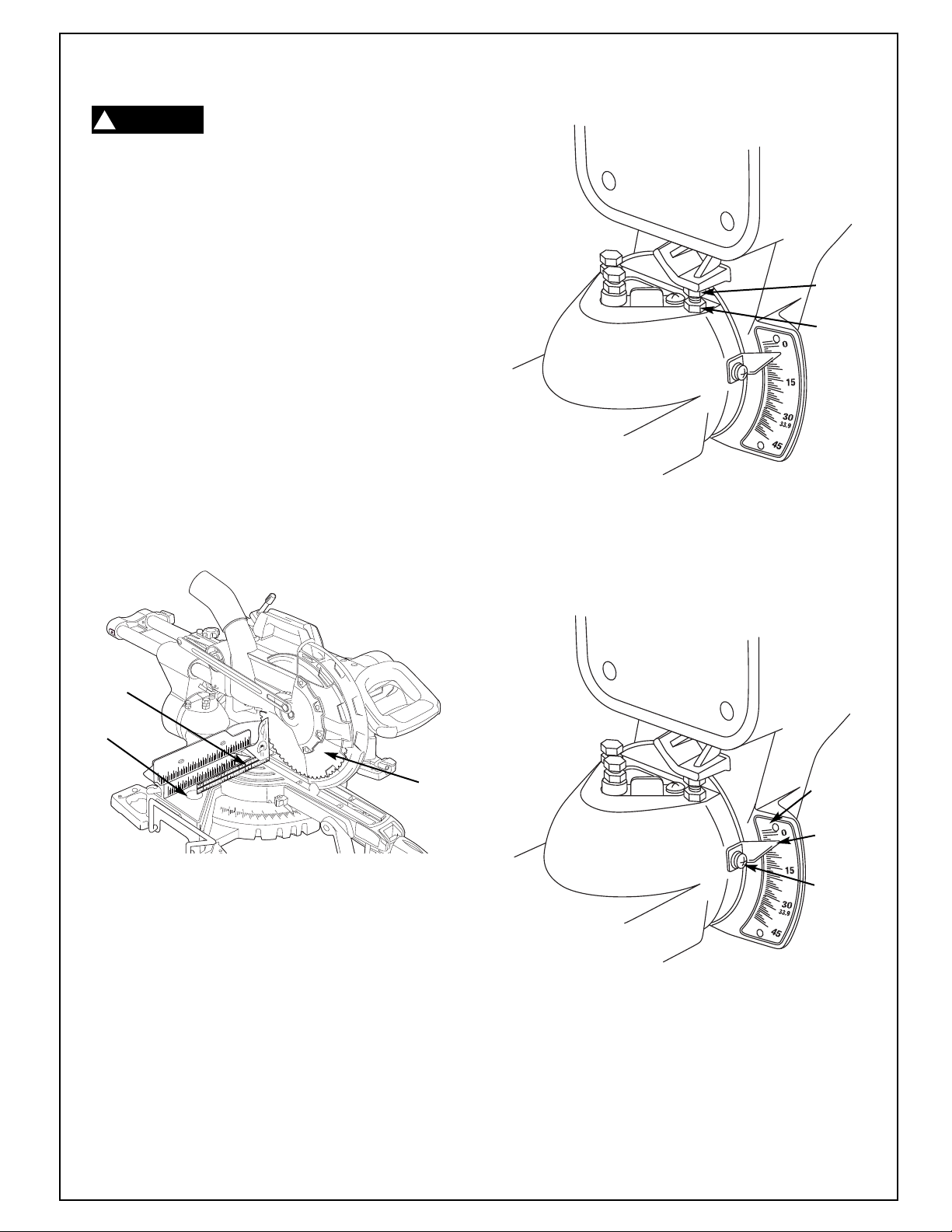
Adjustments
!
WARNING
adjustment or repair to avoid possible injury.
NOTE: Your slide compound miter saw was completely adjusted at the factory. However, during shipment, slight misalignment may have occurr
the following settings and adjust if necessary prior to
using this compound miter saw.
Disconnect plug fr
before performing any assembly,
om power source
ed. Check
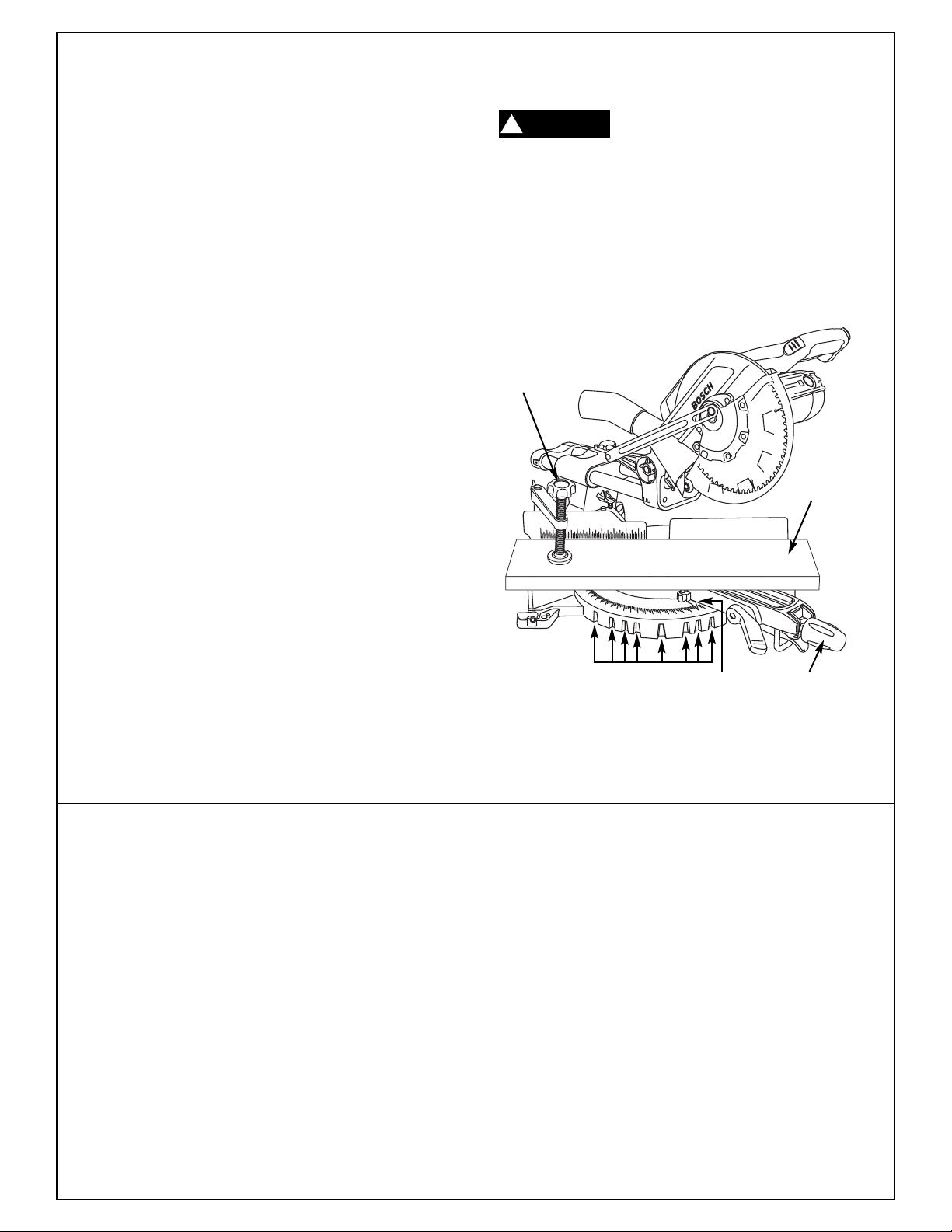
Blade Square (90°)
To Table
90° Blade Alignment Check
1. Rotate table to 0° position and lock in place.
Make sure head assembly is pushed back fully
2.
against stop and slide rail lock knob is tightened.
3. Lower head assembly. Lock in place.
4. Use a combination square to check blade squareness to table. Place the combination square on
the table and press it against the blade. If the
blade does not contact the full length of the
square, (Figure 6) follow the alignment procedure.
0º Stop
Screw
Jam
Nut
Figure 7. Bevel 0° Stop Screw and Jam Nut
7. Adjust bevel indicator. Loosen screw and
align indicator to the 0° mark. Tighten screw
(Figure 8).
Combination
Square
Table
90° Blade Alignment Adjustment
1. Loosen bevel lock handle.
2. Move the head off of the 0º stop.
3. Lower 0° stop screw and jam nut with 12mm
4. Move the saw back to 0º stop.
5. Push square against blade (fig. 6).
6. Adjust 0° bevel stop screw with 12mm or
Blade
Figure 6. Blade Square to Table
or adjustable wr
adjustable wr
contact with the full length of the square.
Tighten jam nut (Figure 7).
ench.
ench until the blade makes
Figure 8. Bevel Indicator
Adjust
to 0º
Bevel
Indicator
ew
Scr
13.
Page 14

Adjustments
Blade 45° To Table
45° Blade Alignment Check
1. Rotate table to 0° position and lock in place.
2. Make sure head assembly is pushed back
fully against stop and slide rail lock knob
is tightened.
3. Lower head assembly. Lock in place.
4. Make sure the 33.9º bevel stop screw jam
nut is in the passive position, out of line with
the 90º and 45º bevel stop screw jam nuts.
5. Loosen bevel lock handle and tilt the head
assembly to 45° bevel. Check the 45° bevel
stop. The bevel indicator should be on the
45° mark, the 45° bevel stop should be in full
contact with the 45° bevel stop screw. Place
the combination square on the table and
press it against the blade. The blade should
contact the full length of the combination
square (Figure 9).
6. If the blade is not 45° to the table, adjust
45°bevel stop.
45° Blade Alignment Adjustment
1. Lower the 45° bevel stop screw jam nut using
12mm or adjustable wrench (Figure 10).
Combination
Square
Figure 9. Blade 45° To The Table
45º/33.9º
Stop
45º Stop
Screw
Blade
Table
2. Loosen bevel lock handle.
Lower the saw onto the 45º stop.
3.
4. Push combination square against the blade.
5. Adjust the 45º bevel stop until the blade
makes contact with the full length of the
square. Tighten 45° jam nut (Figure 10).
6. Check that bevel indicator is pointing to the
45° mark on the bevel scale (see Figure 10).
If bevel indicator is not aligned with the 45°
mark, first recheck the blade squareness to
the table and 0° bevel indicator alignment.
Then, repeat the 45° blade alignment and
make appropriate adjustments.
14.
Jam
Nut
e 10. Bevel 45° Stop Screw and Jam Nut
Figur
Page 15
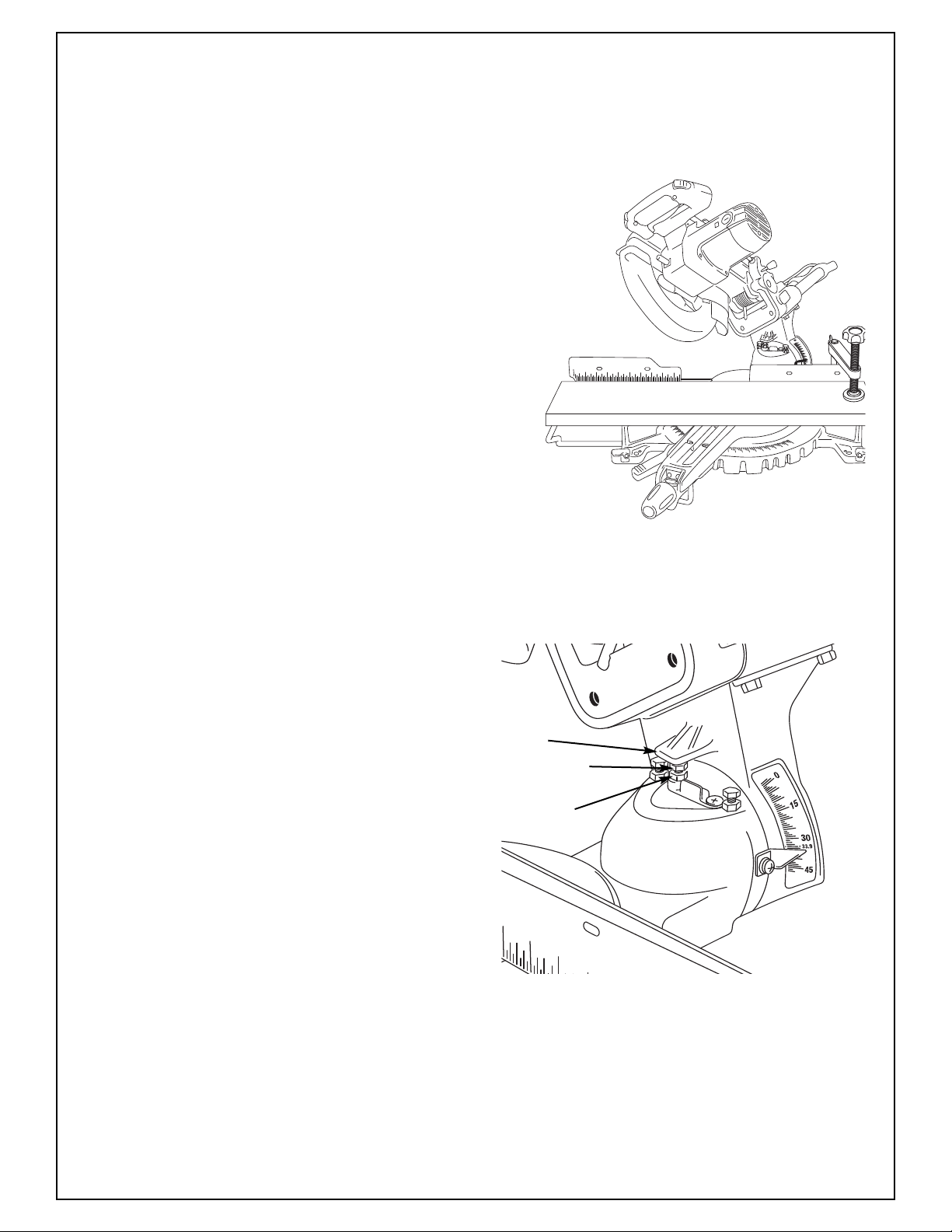
Adjustments
Blade 33.9° To Table
33.9° Blade Alignment Check
NOTE: You must check and align 45º and 90º settings first before doing 33.9º (See pages 13 and 14).
1. Rotate table to 0° position and lock in place.
2. Make sure head assembly is pushed back
fully against stop and slide rail lock knob
is tightened.
3. Lower head assembly. Lock in place.
4. Make sure the 33.9º bevel stop screw jam
nut is in the active position, in-line with the
90º and 45º bevel stop screw jam nuts.
5. Loosen bevel lock handle and tilt the head
assembly to 33.9° bevel. Check the 33.9°
bevel stop. The bevel indicator should be on
the 33.9° mark.
Figure 11. Blade 33.9° To The Table
6. If the blade is not 33.9° with the table, adjust
33.9°bevel stop.
33.9° Blade Alignment Adjustment
1. Lower the 33.9° bevel stop screw jam nut
using 12mm or adjustable wrench (Figure 12).
2. Loosen bevel lock handle.
3. Lower the saw onto the 33.9º stop.
4. Adjust the 33.9º bevel stop until bevel indicator is pointing to the 33.9° mark on the bevel
scale (see Figure 12). Tighten 33.9° jam nut.
45º/33.9º
Stop
33.9º Stop
Screw
Jam Nut
Figure 12. Bevel 33.9° Stop Screw and Jam Nut
15.
Page 16
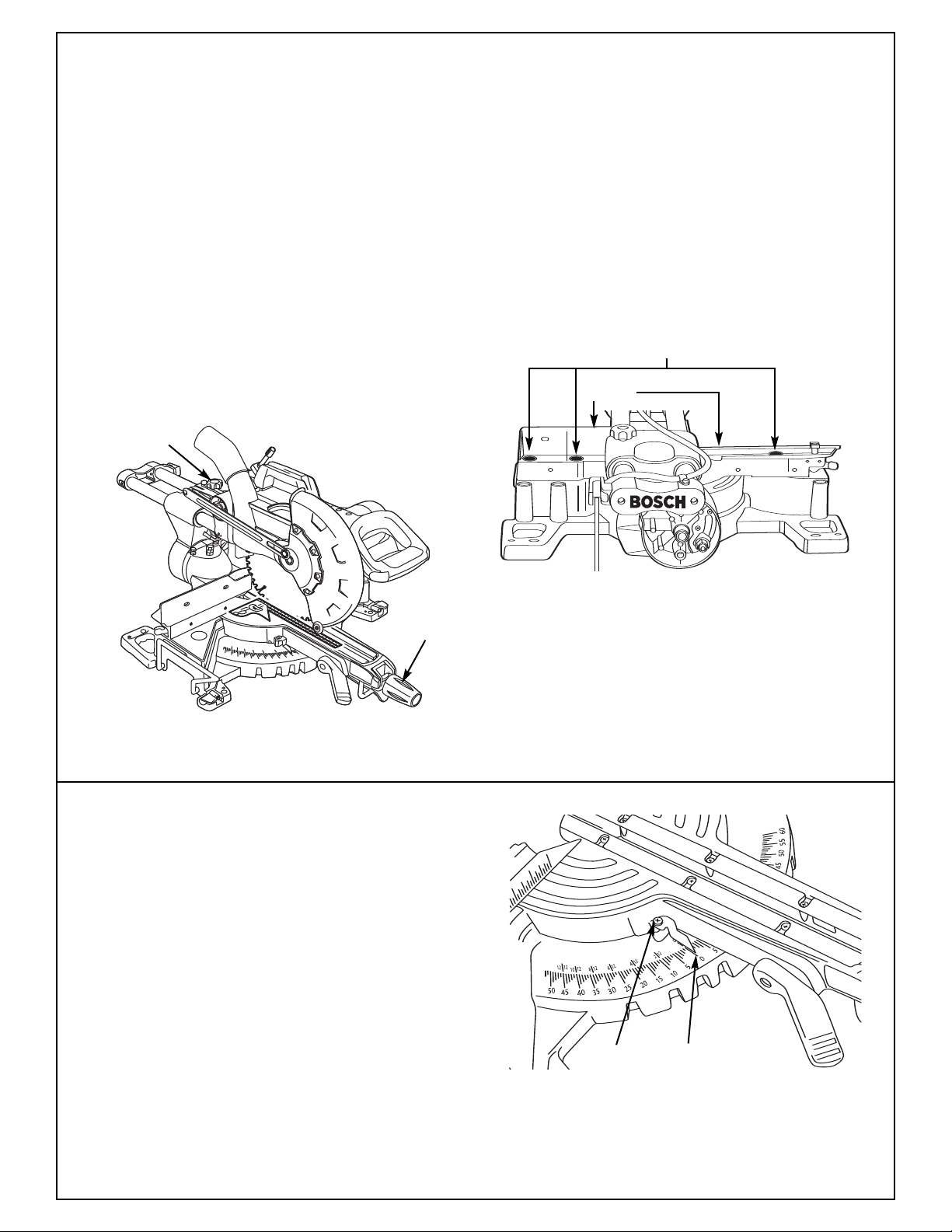
Adjustments
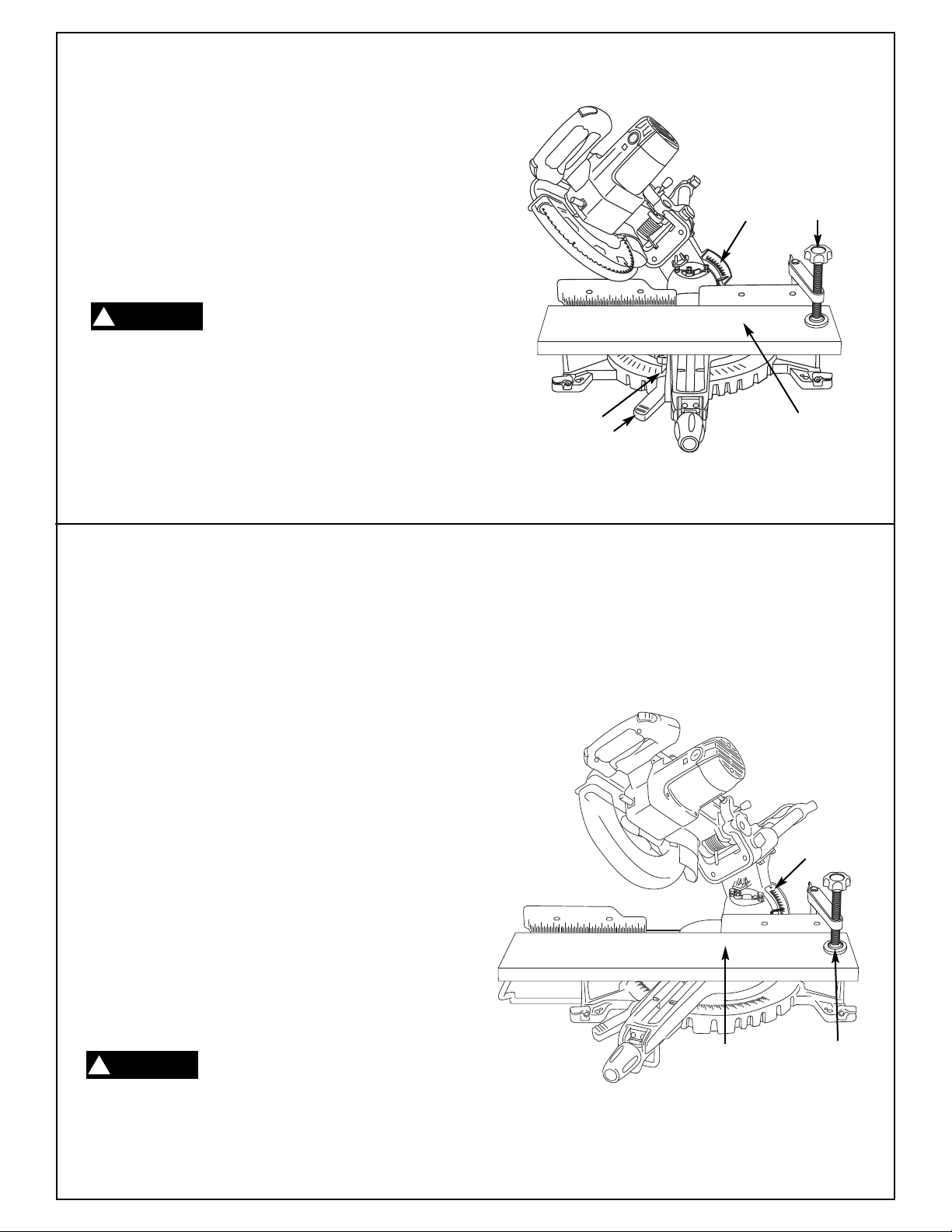
Blade Square to Fence
Fence Alignment Check
Make sure head assembly is pulled forward near
1.
the center of the table and slide rail lock knob is
tightened (Figure 13).
2. Lower the head assembly, and lock in the
lower position.
3. Make sure table is in 0° detent and tighten miter
lock knob.
4. Place a combination square against the fence
and next to the blade as illustrated. Locate the
square properly so it does not contact the tooth
of saw blade. The saw blade should contact the
full length of the square (Figure 13).
5. If blade does not contact the square, follow the
fence alignment procedure.
Slide Rail
Lock Knob
Fence Alignment Adjustment
The head assembly should remain in lowered
1.
position.
Extend sliding fence. Use blade wrench (sup-
2.
plied) and loosen three (3) bolts behind fence
(Figure 14).
3. Adjust fence until blade and the fence has full
contact with the square.
4. Tighten hex cap screws.
Hex Cap Screws
Fence
Miter Lock
Knob
Figure 13. Blade Square to Fence
Miter Scale
Indicator Adjustment
1. Rotate table to 0° position and lock in place.
2. Raise the head assembly to the full-up position.
3.
Loosen the Phillips screw that holds the indicator in place (Figure 15).
Slide Rail Unit
Figure 14. Fence Adjustment
(Back view of table/base area)
4. Position the indicator to align with the 0° miter
mark. Tighten the screw.
16.
Indicator
Screw
0º Mark
Figure 15.
Page 17
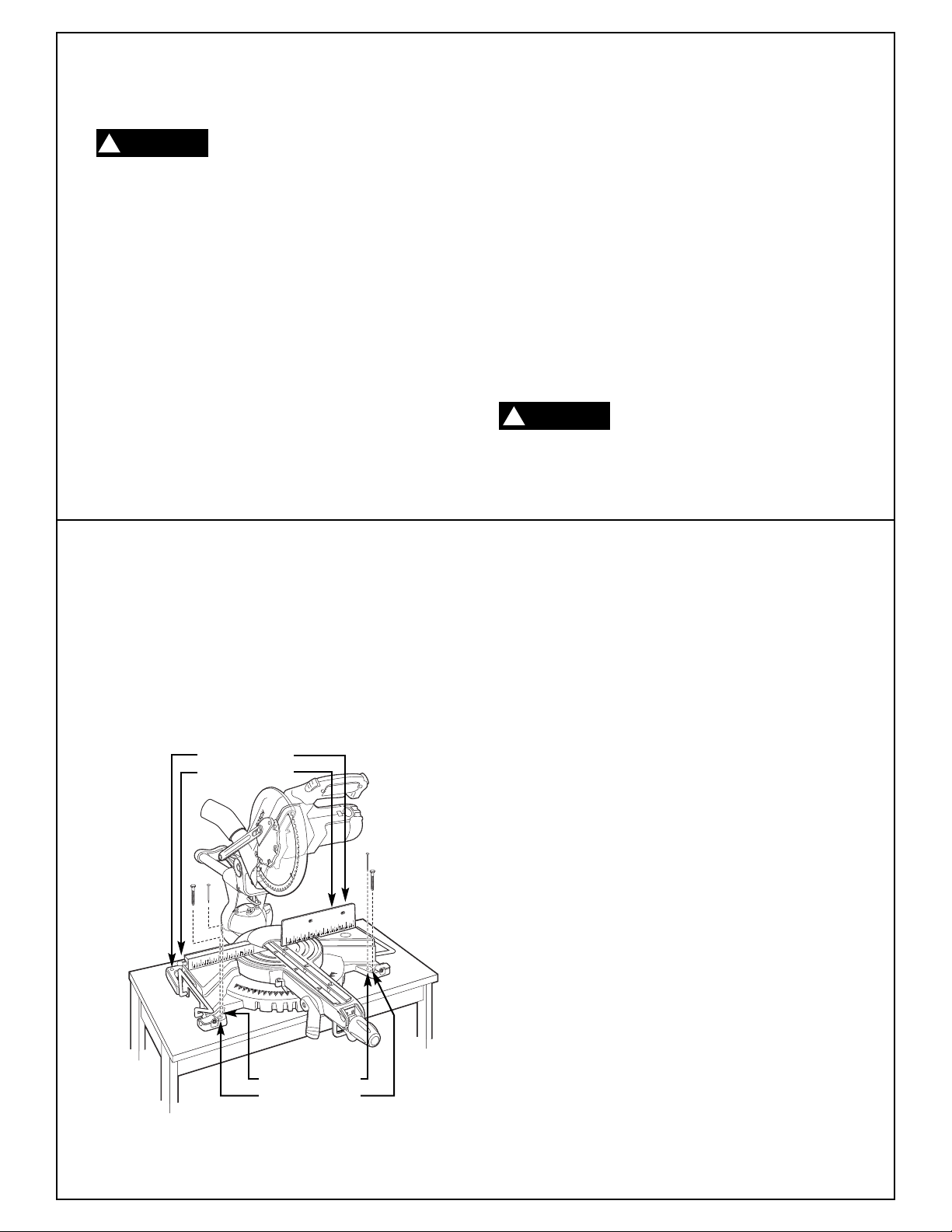
Installation
o avoid injury always observe
!
WARNING
l Unplug electric cor
saw, rotate head assembly to 45° right miter,
lock into detent, pull the head assembly com
pletely forward toward you, tighten the slide
rail lock knob and lock the head assembly in
the lowered position.
l To avoid back injury, hold the tool close to your
body when lifting. Bend your knees so you can
lift with your legs, not your back. Lift by using
the cast-in carry handles at each side of the bottom of the base or the carry handle.
l Never carry the tool by the slide rails, this
may cause blade misalignment.
T
the following:
d. Before transporting the
Mounting Applications
l Never carry the miter saw by the power cord or
the operational handle. Attempting to lift or
carry the tool by the power cord will damage
the insulation and the wir
-
ing in electric shock or fir
l Observe the position of the saw. People
standing behind it could be injured by thrown
debris.
l Place the saw on a firm, level surface where
there is plenty of room for handling and properly supporting the workpiece.
l Bolt, screw, nail or clamp the saw to its
support surface.
!
CAUTION
attaching to support surface. This could crack foot
or damage base.
Be careful not to over drive nail
or over torque the bolt when
e connections result-
e.
Workbench
Mount the saw using either the four bolt holes (7/16") or
the four screw holes (1/4”) to the workbench (Figure
16). Check for clearance to the left and right of the saw.
Bolt Holes
ew Holes
Scr
Screw Holes
Bolt Holes
1. Each of the four mounting holes should be bolted securely using 3/8" bolts, lock washers, and
hex nuts (not included).
2. Locate and mark where the saw is to be mounted.
3. Drill four (4) 3/8" diameter holes through workbench.
Place the slide compound miter saw on the
4.
workbench aligning holes in base with holes
drilled in workbench. Install bolts, lock washers and hex nuts.
Supporting surface where saw is to be mounted
should be examined carefully after mounting to
ensure that no movement can occur during use. If
any tipping or walking of the saw is noted, check your
mounting to the workbench or stand, and make necessary adjustments before operating the slide compound miter saw (see Stability Bar Adjustment on
page 18).
Figure 16. Workbench Mounting
17.
Page 18
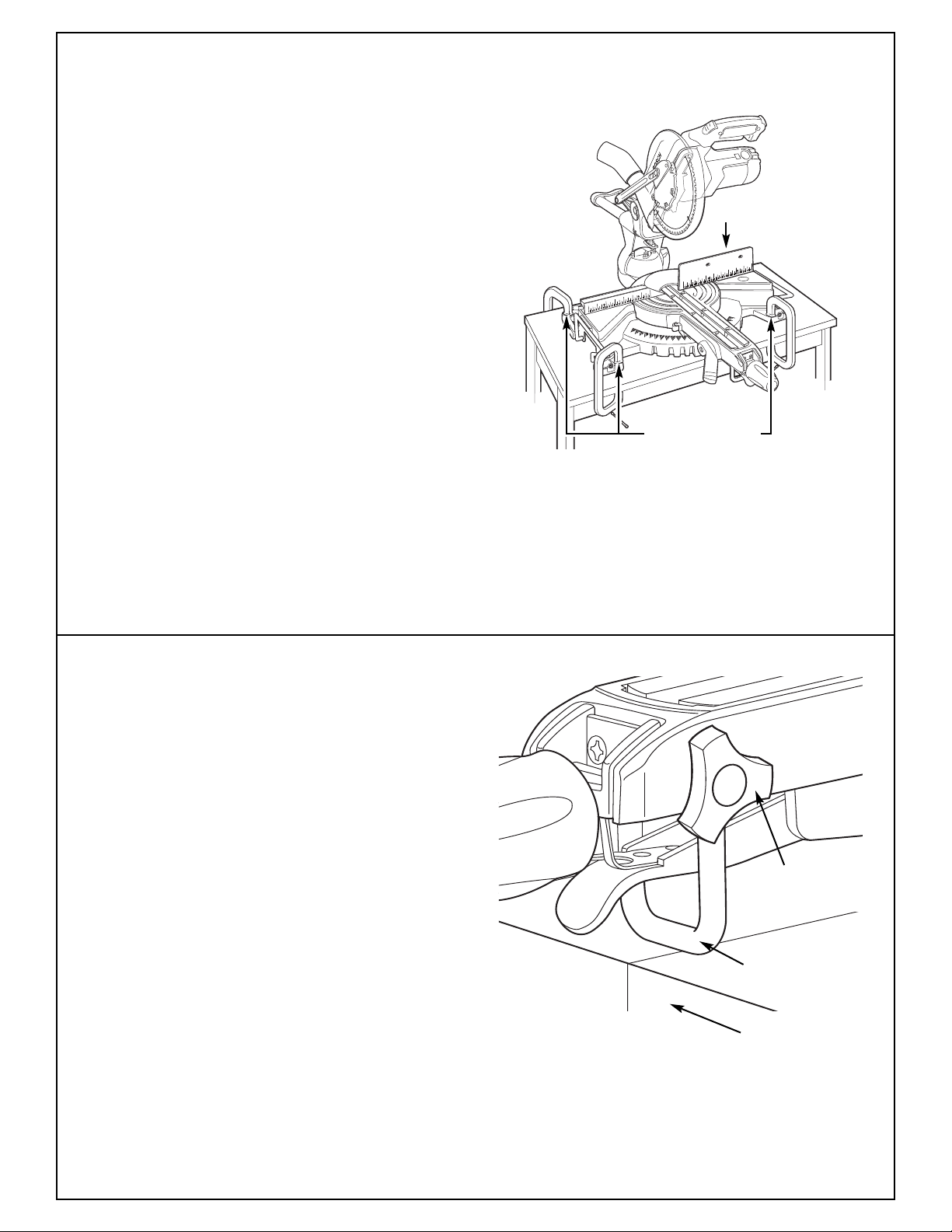
Installation
Portable Mounting Using Clamps
• If using bolts or screws is not possible, clamp the
slide compound miter saw to a workbench or
table top using clamps.
• Place a “C” clamp on each of the clamping areas
and secure (Figure 17).
Note: Use of clamps will limit use of extreme
miter angles.
Clamping Area
Clamping Area
Figure 17. Portable Mounting Using Clamps
Stability Bar Adjustment
For added support of the table during cutting, the
stability bar should be adjusted before use.
1. Loosen the knob for the stability bar.
2. Slide the stability bar up or down until it contacts the workbench.
Note: If the workbench surface is not flat, the
stability bar may require readjustment at different
miter angles.
3. Tighten the knob.
Stability Bar
Adjustment Knob
Stability Bar
Workbench
18.
Page 19
0
5
10
15
20
25
30
35
40
45
50
50
45
40
35
30
BOSCH
0
5
10
15
20
25
30
35
40
45
50
50
45
40
35
30
BOSCH
0
5
10
15
20
25
30
35
40
45
50
50
45
40
35
30
BOSCH
0
5
10
15
20
25
30
35
40
45
50
50
45
40
35
30
BOSCH
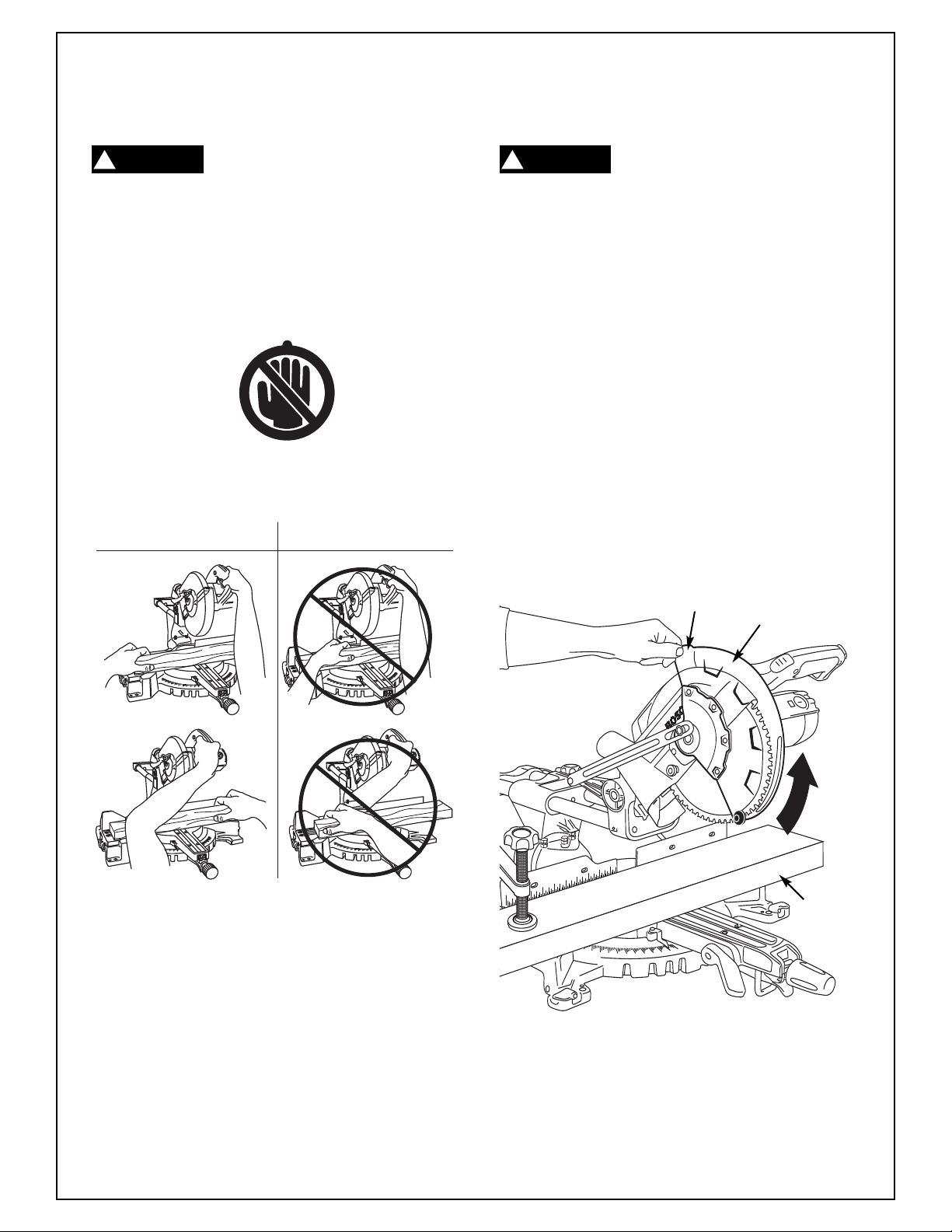
Basic Saw Operations
Body and Hand Position
!
WARNING
Position your body and hands prop-
erly to make cutting easier and
safer. Observe the following instructions (Figure 18).
l Never place hands near cutting area. Keep
hands outside the “No Hands” zone.
l The “No Hands Zone” is defined as the entire
Table and fixed portions of the base and portions of the fence within this boundary. This
zone is labeled by “No Hands” symbols placed
on the Base.
l Hold workpiece (outside of the “No Hands”
zone) firmly to the fence to prevent movement
(Fig 18).
Correct Incorrect Use
!
WARNING
The lower guard may not automatically open under certain cutting
conditions.
l Typically this may occur when trying to cut work-
pieces that are near the maximum cutting height
capacity (3.5”), or when making extreme bevel
cuts at maximum cutting height capacity. Under
these conditions, the workpiece can stop the
lower guard movement before the downward
motion of the arm could pre-open the lower
guard. If this occurs:
1. Workpiece must be securely clamped. This
frees a hand to raise the guard by the lip just
enough to clear the workpiece (Figure 19).
Start the saw and begin your cut.
2.
3. Once you have cleared the position where the
lower guard may bind, release the guard and
it will continue to operate automatically as
you cut.
Lip
Lower Guard
e 18. Hand Positions
Figur
l Keep hands in position until trigger has been
released and blade has stopped completely.
l Never place hands on slide rails.
l Keep feet firmly on the floor and maintain prop-
er balance.
l Follow the miter arm when mitering left or right.
Stand slightly to the side of the saw blade.
l Before making any cut, with the power off, lower
the blade to preview the blade path.
Open
Workpiece
Figure 19. Raising Lower Guard
19.
Page 20
Basic Saw Operations
Workpiece Support
!
WARNING
and properly supported from underneath.
Long workpieces have a tendency
to tip over unless clamped down
Clamps
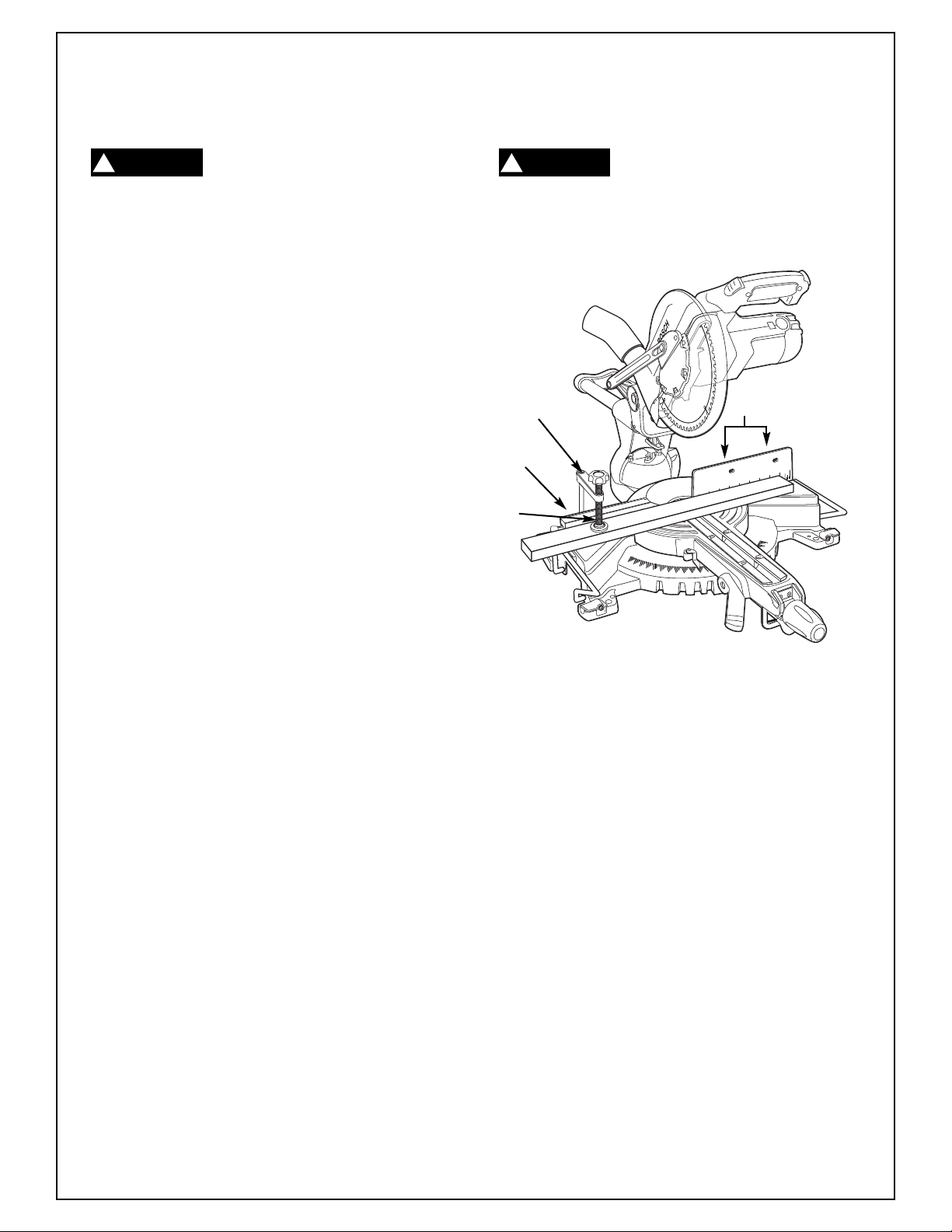
Workpiece Clamp - This clamp easily secures a
workpiece in any of three (3) clamp holes behind the
fence (Figure 20).
• Insert clamp post into clamp hole.
• Loosen wing nut and adjust arm to proper height,
and securely tighten wing nut.
• Rotate screw knob of the clamp clockwise to
tighten, counter
• Move the head assembly to check clearance
with clamp.
-clockwise to loosen.
!
WARNING
Support workpiece with hand outside No Hands
Zone.
Do not try to cut short pieces that cannot be
clamped and cause your hand to be in the No Hands
Zone.
Workpiece
Clamp
Clamp
Hole
Screw
Rod
There may be extreme compound
cuts where clamp cannot be used.
Clamp
Holes
Figure 20. Workpiece Clamp
Conventional Clamps and other hold down devices
can be used to hold the workpiece firmly against the
table and the fence.
20.
Page 21
Basic Saw Operations
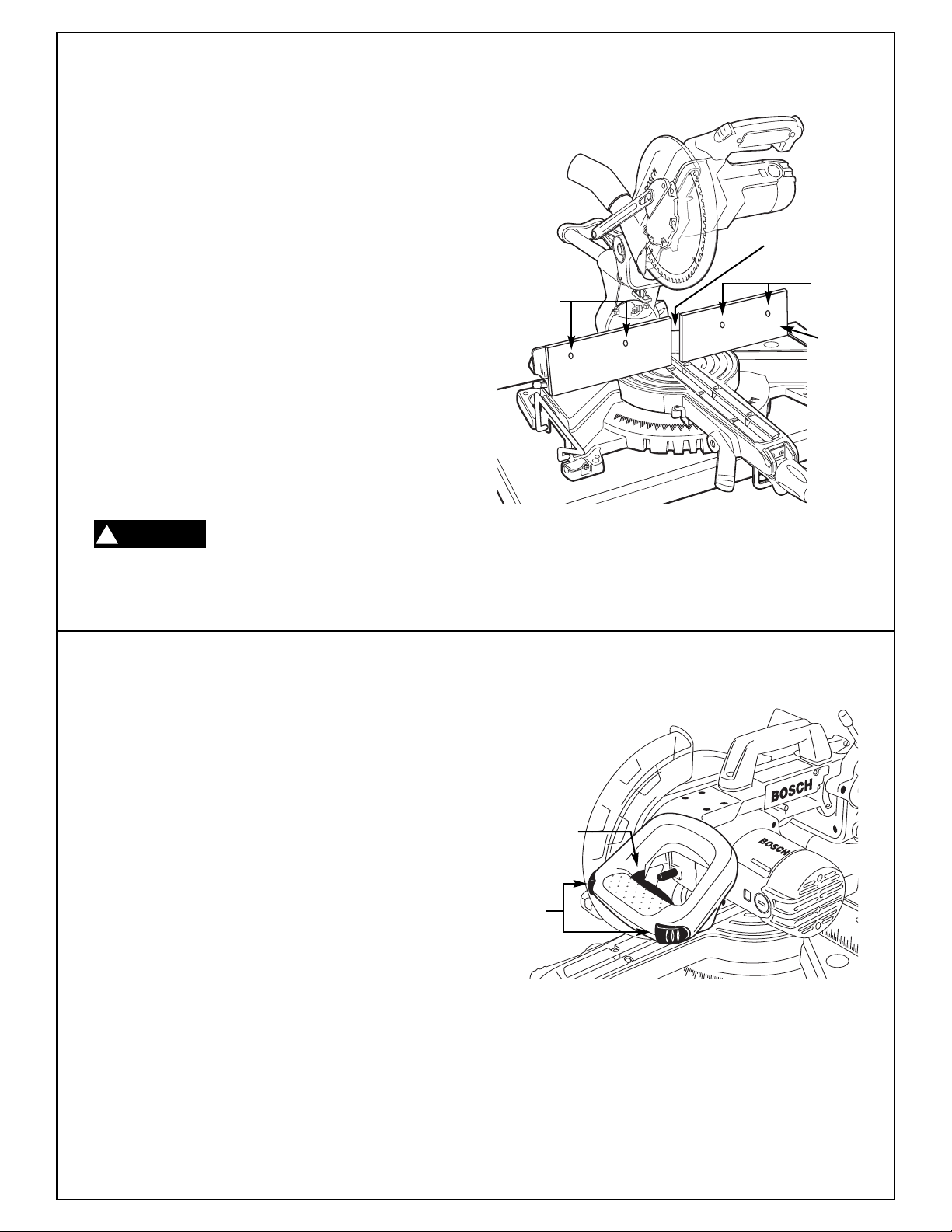
Auxiliary Fence - Certain types of molding need a
fence face extension because of the size and position of the workpiece. Dado cuts also require an auxiliary fence. Holes are provided in the fence to attach
an auxiliary fence. The auxiliary fence is used with
the saw in the 0
° bevel position only.
1. Place a piece of wood against the miter saw
fence (Figure 21). (Wood can have a maximum
height of 3-1/2". Check that head assembly
does not interfere with auxiliary fence.)
2. Mark the locations of the support holes on the
wood from the back side of the fence.
3. Drill and countersink the holes on the front of the
support board.
4. Attach the auxiliary fence using two at least (2)
1/4" flat head machine screws per side. Make a
full depth cut to create the blade slot. Check for
interference between the auxiliary fence and the
lower blade guard. Make adjustments as necessary.
!
WARNING
Check for interference from any
components.
Flat Head
Machine
Screws
Blade Slot
Flat Head
Machine
Screws
Auxiliary
Fence
Figure 21. Auxiliary Fence
Switch Activation
For safety, the switch lever is designed to prevent
accidental starts. To operate safety switch, press the
switch “Lock-OFF” button with either thumb to disengage the lock, then pull the power switch lever
and release the switch “Lock-OFF” release button.
When the power switch lever is released, the switch
“Lock-OFF” button will engage the safety switch
automatically
until either “Lock-Of
NOTE: Switch lever can accommodate a padlock
with a long shackle of up to 1/4" in diameter (not
supplied) to prevent unauthorized use.
, and the lever will no longer operate
f” button is pr
essed again.
Power
Switch Lever
Switch
“Lock-Off”
Release
Buttons
Figure 22. Switch Activation
21.
Page 22
Basic Saw Operations
1
Detent Override
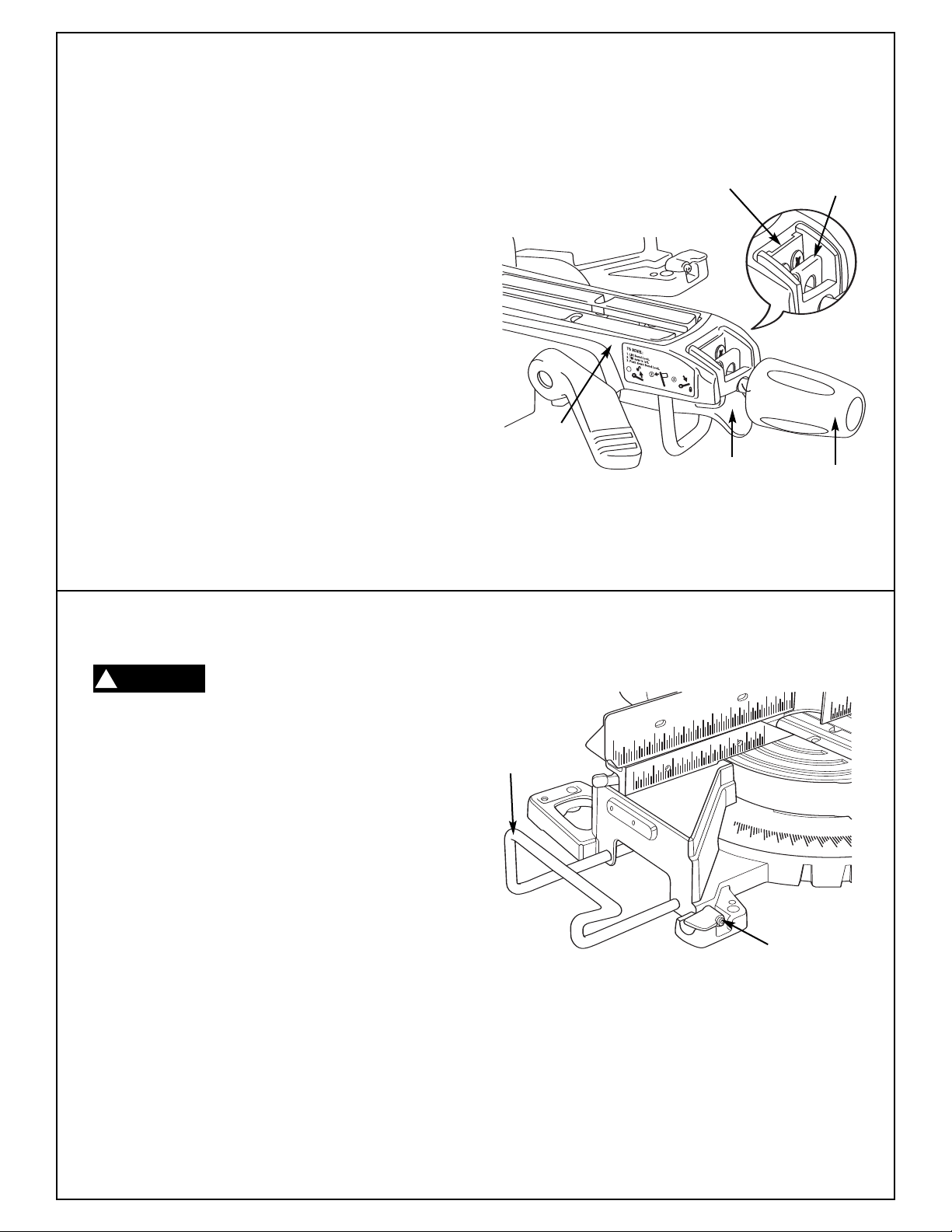
To Engage:
1. Lift the miter detent trigger.
Push the detent override clip forward and latch
2.
in place over edge. Release miter detent trigger
(Figure 23).
3. Move miter arm to any position on the miter
scale.
4. Lock the miter lock knob to retain miter position.
To Disengage:
5. Loosen miter lock knob and lift the miter detent
trigger to release the detent override clip. The
clip should automatically disengage and the
table should lock into any desired miter detent.
Table
Clip Edge
Detent
Override Clip
Base Extensions
!
WARNING
saw blade, extend the sliding fences and base
extensions when making extreme bevel, miter or
compound cuts.
The base extensions can also be used to provide
extra support for long workpieces.
Adjusting the Extensions:
1. Loosen the base extension clamping levers.
2. Extend sliding base extensions to the desired
position.
3. Press the levers down to clamp the extensions
into place.
If the clamping force of the Base Extension Clamping
Levers needs to be adjusted, simply pull the r
outwar
Let the red tab spring back into a new groove. When
the red tabs ar
will grip the rods with gr
d and r
So as to provide sufficient (mini-
mum 6”) spacing from hand to
ed tab
otate it towar
e rotated down to clamp the rods, they
d the center of the saw
eater for
ce.
.
Base
Extension
Miter Detent
Trigger
Figure 23. Detent Override
Figure 24: Base Extensions
Miter Lock
Knob
Base Extension
Clamping lever
22.
Page 23
Basic Saw Operations
Sliding Fence
Sliding Fence
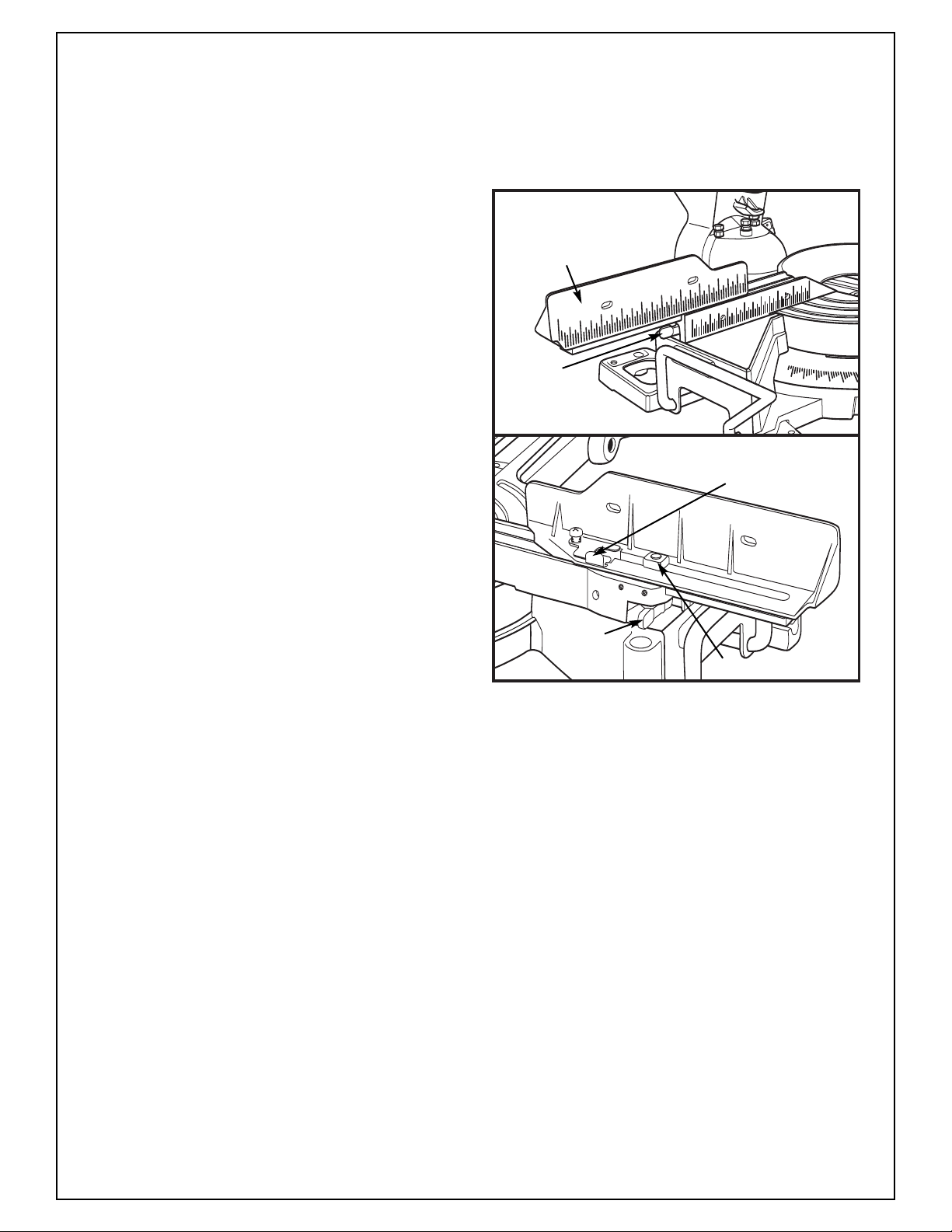
Operating Sliding Fence
1. Turn the fence lever counter clockwise.
2. Slide the fence to the desired position.
3. Turn the fence lever clockwise
to tighten.
Removing the Sliding Fence
1. Lift up on the cover plate tab and
rotate clockwise.
2. Turn the fence lever counter clockwise.
3. Slide the fence as far as it will go to the left.
4. Lift up on the sliding fence to remove.
Adjusting the Sliding Fence
Lock - Make lock tighter
1. Remove the sliding fence.
2. Push down on the locking block to expose the
screw head.
3. Turn the screw counter clockwise to move it to
the next hex setting.
4. Replace the sliding fence
5. Check the clamping force in several positions.
Be sure the lever does not block the
clamp hole.
FRONT VIEW
Sliding Fence
Fence
Lever
REAR VIEW
Cover Plate Tab
Fence
Lever
Locking Block
Figure 25: Sliding Fence
Adjusting the Sliding Fence
Lock - Make lock looser
1. Remove the sliding fence.
2. Push down on the locking block to expose the
screw head.
3. Turn the screw clockwise to move it to the next
hex setting.
Replace the sliding fence
4.
5. Check the clamping force in several positions.
Be sure the lever does not block the clamp hole.
23.
Page 24
Saw Operations
Chop Cut
During a chop cut, the slide rail lock knob is
•
tightened and the head assembly is lowered to
cut through the workpiece.
This type of cut is used mainly for narr
•
Follow these instructions for making your chop cut:
1. Slide the head assembly to the rear as far as it
will go (Figure 26).
2. Tighten the slide rail lock knob (Figure 26).
3. Properly position workpiece. Make sure workpiece is clamped firmly against the table and the
fence.
ow pieces.
Wait until blade comes to a complete stop
5.
before returning head assembly to the raised
position and/or removing workpiece.
Slide Lock
Knob Tightened
!
WARNING
switching on, lower head assembly to make sure
clamp clears guard and head assembly.
4. Activate the switch. Lower the head assembly
and make your cut.
Use clamping position that does not
interfere with operation. Before
Slide Cut
During a slide cut, the slide rail lock knob is loose,
•
the head assembly is pulled towards the operator,
the head assembly is lowered to the workpiece
and then pushed to the rear of the saw to make
the cut.
This type of cut is used mainly for wide pieces.
•
A positive blade hook of 10 degrees or more is
•
recommended for best performance when making aggressive cuts or cutting thicker materials.
See page 36 for accessory blade listing.
!
WARNING
up on top of the workpiece and force itself toward you.
Follow these instructions for making your
slide cut:
operly position workpiece. Make sur
Pr
1.
piece is clamped firmly against the table and
the fence.
!
WARNING
switching on, lower head assembly to make sure clamp
clears guar
NEVER pull the saw toward you during
a cut. The blade can suddenly climb
Use clamping position that does not
interfere with operation. Before
d and head assembly
.
e work-
Slide Completely
Against Rest
Figure 26. Chop Cut
4. Activate the switch. Lower the assembly all the
way down and cut through the edge of the workpiece.
5. Push (but do not force) the head assembly
towards the fence to the full rear position to
complete the cut.
6. Wait until blade comes to a complete stop before
returning head assembly to the raised position
and/or removing workpiece.
First:
Pull
Forward
Slide Rail
Lock Knob
Second:
Turn Saw
On, Lower
Head
Assembly
d:
Thir
Push
Blade Into
Workpiece
2. Loosen the slide rail lock knob (figure 27).
3. Grasp the switch handle and pull the head
assembly away fr
clears the workpiece or to its maximum extension if blade cannot clear the workpiece
(Figure 27).
om the fence, until the blade
24.
e 27. Slide Cut
Figur
Page 25
Saw Operations
Miter Cut
• A miter cut is made at 0° bevel and any miter
angle in the range from 50° left to 60° right.
• The miter scale is cast-in on the table for easy
reading.
• Positive detents have been provided for fast and
accurate mitering at 0°, 15°, 22.5°, and 45° left
and right and 60° right.
• There are crown molding detents (left and right)
at 31.6° (see Cutting Crown Molding for more
information page 28).
• For off detent settings, use the detent override to
lock out the detent.
• A miter cut can be made as either a chop cut or
a slide cut depending on the width of the workpiece.
Follow these instructions for making your
miter cut:
1. Loosen miter lock knob. Lift miter detent trigger
and move the saw to the desired angle, using
either the detents or the miter scale. Tighten
miter lock knob (Figure 28).
!
WARNING
switching on, lower head assembly to make sur
clamp clears guard and head assembly.
3. Follow procedures for either chop cut or slide
cut (see page 24).
4. Wait until blade comes to a complete stop before
returning head assembly to the raised position
and/or removing workpiece.
Workpiece
Clamp
Use clamping position that does
not interfere with operation. Before
e
Workpiece
2. Properly position workpiece. Make sure work
piece is clamped firmly against the table and the
fence.
Bevel Cut
• A bevel cut is made at 0° miter and any bevel
angle in the range of 0° to 45°.
• There are factory set bevel stops at 0° and 45°. (See
ed.)
equir
Adjustment section if adjustments ar
• The bevel scale faces the operator for easy r
e r
eading.
Miter ScaleDetents
Figure 28. Miter Cut
• Ther
• A bevel cut can be made as either a chop cut or
• Use sliding fence and work supports as appropri-
e is a positive crown molding bevel stop at
33.9°. Disengage this stop unless using. (See
Cutting Crown Molding for details.)
a slide cut depending on the width of the workpiece.
ate. (See Sliding Base/Fence Extension page 23.)
Miter Lock
Knob
25.
Page 26
Saw Operations
Bevel Cut (Continued from page 25)
Follow these instructions for making your
bevel cut:
1. To loosen, lift the bevel lock lever. Tilt the head
assembly to desired bevel angle. Tighten the
bevel lock lever (Figure 29).
2. Properly position workpiece. Make sure workpiece
is clamped firmly against the table and the fence.
!
WARNING
switching on, lower the head assembly to make sure
the clamp clears the guard and head assembly.
3. Follow the procedures for either a chop cut or
slide cut (see page 24).
Wait until blade comes to a complete stop before
4.
eturning head assembly to the raised position
r
and/or removing workpiece.
Use clamping positions that do not
interfere with operation. Before
Compound Cuts
• A compound cut is a cut requiring both a miter
setting and a bevel setting.
• A compound cut can be made as either a chop
cut or a slide cut depending on the width of the
workpiece.
Bevel
Angle
0º Miter
Bevel Lock Lever
Figure 29. Bevel Cut
3. Follow the procedures for either chop cut or slide
cut (see page 24).
4. Wait until blade comes to a complete stop before
returning head assembly to the raised position
and/or removing workpiece.
Workpiece
Clamp
orkpiece
W
• Because it may take several tries to obtain the
ed compound angle, perform test cuts on
desir
scrap material before making your cut.
Follow these instructions for making your
compound cut:
1. Extend the sliding fence and work supports when
making compound cuts that ar
left (see Sliding Base/Fence Extension on pages
22-23). Select the desir
(Figure 30). (See Miter Cut and Bevel Cut on page
25.)
operly position the workpiece. Make sur
Pr
2.
workpiece is clamped firmly against the table and
the fence.
!
WARNING
switching on, lower head assembly to make sur
clamp clears guard and head assembly.
Use clamping positions that do not
interfere with operation. Before
ed miter and bevel angles
e mitered to the
e the
e
26.
e 30. Compound Cut
Figur
orkpiece
W
Bevel
Angle
Workpiece
Clamp
Page 27
Saw Operations
Cutting Grooves
(Dado Cut)
The depth stop adjustment is a featur
•
when cutting grooves (dados) in the workpiece.
The depth adjustment is used to limit blade
•
depth to cut grooves.
A groove can be cut as a slide cut.
•
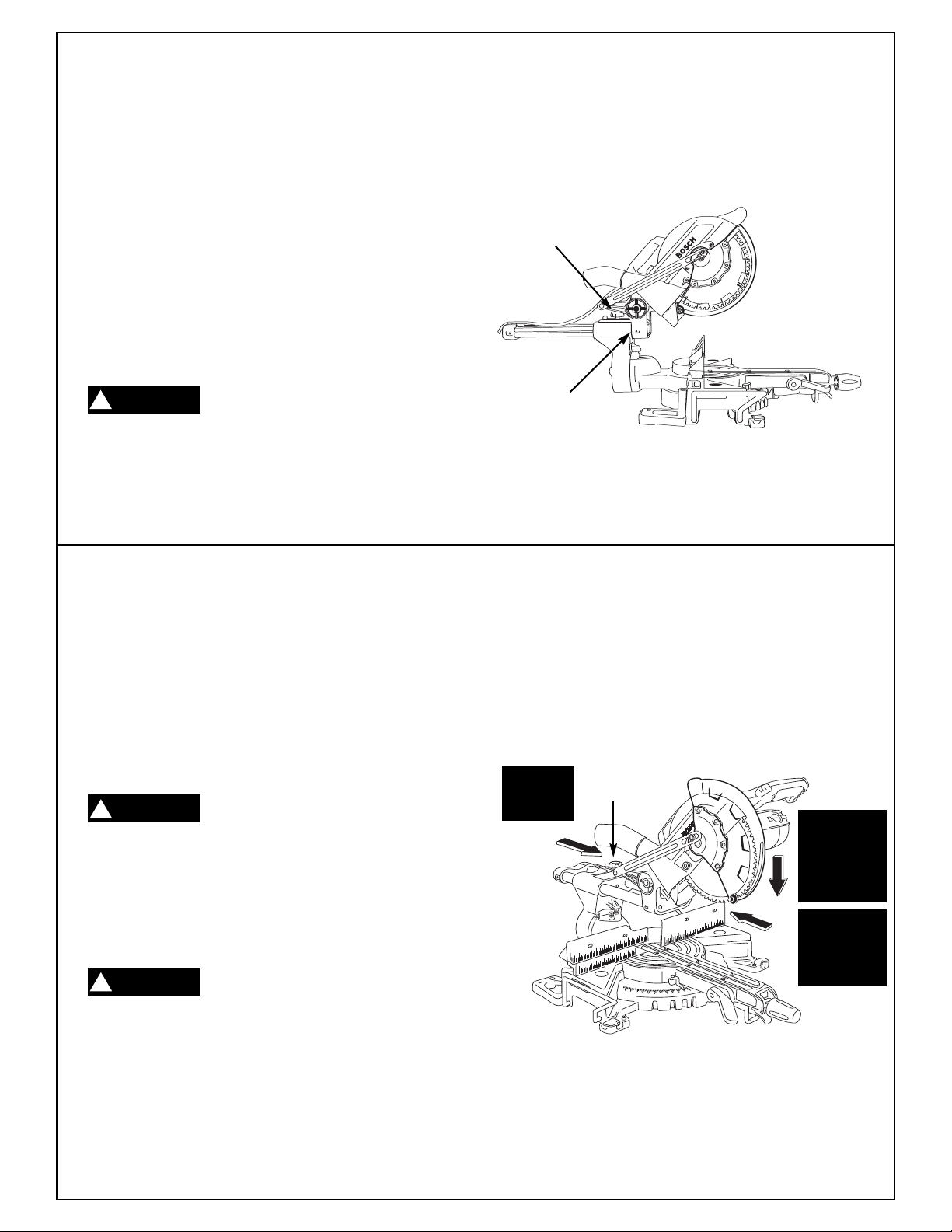
1. Set the depth of cut by loosening the jam nuts on
the depth adjustment bolt (Figure 31). Do not
change the position of the two (2) jam nuts on the
end of the bolt.
2. Turn the depth stop bolt to the correct setting.
e used
Knurled Grip
Depth Stop Bolt
Jam Nuts
Depth Stop Base
Jam Nuts
Depth Stop
3. Tighten the jam nuts against the depth stop tab.
4. Cut the two outside grooves.
5. Use a wood chisel or make multiple passes by
sliding the wood over to one side to r
material between the outside grooves (Figure 32).
Grooves
Chisel Cut
Workpiece
Figure 32. Rough Cut Groove
emove the
e 31. Cutting Gr
Figur
ooves
Note: Auxillary fence is needed to get a con-
stant depth. The thickness of the fence
depends on the depth of the dado.
Depth Stop Tab
27.
Page 28
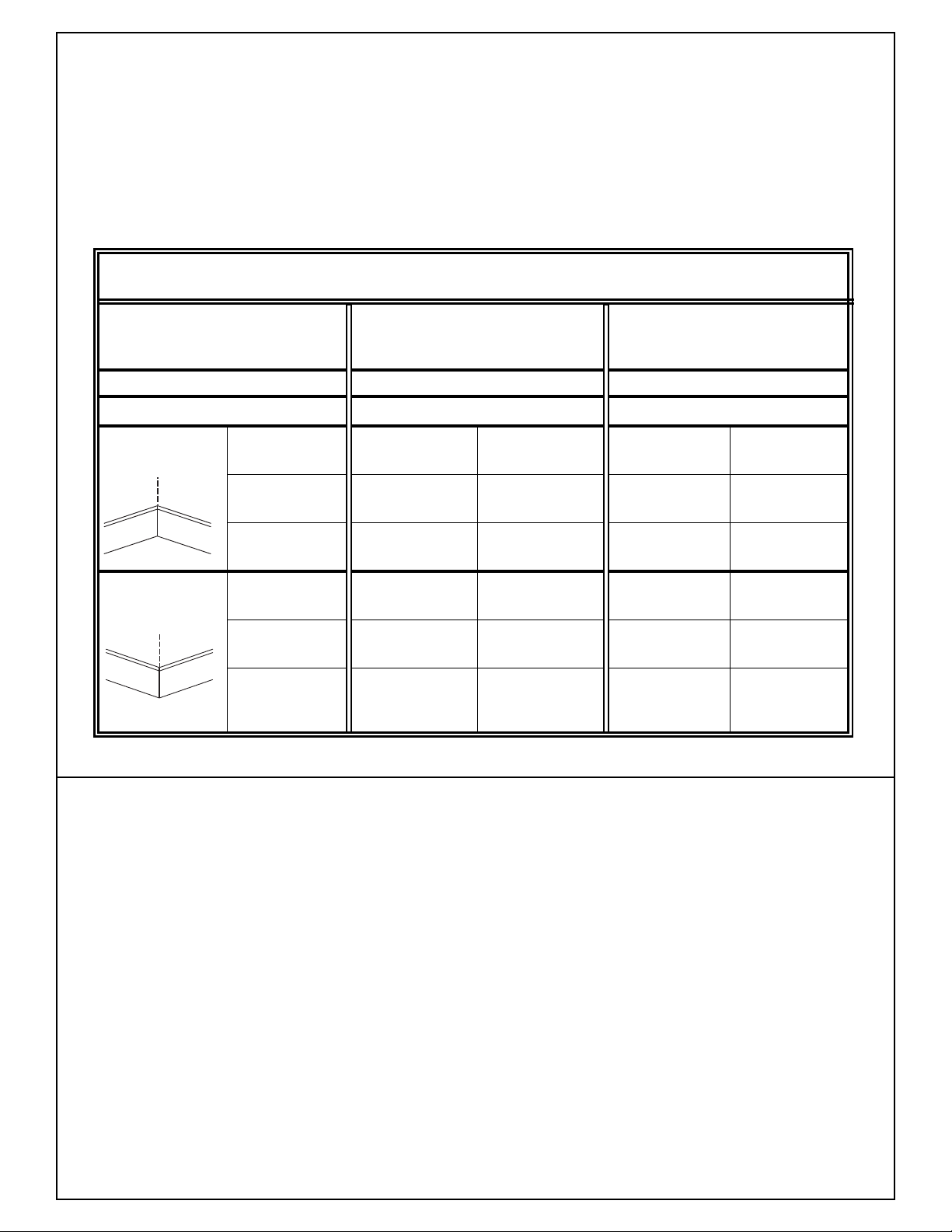
Saw Operations
Cutting Base Molding
• 3 1/2” or smaller base molding can be cut vertical
against fence. All base molding can be cut flat on
the table, up to a maximum width of 12”.
• Follow the table for helpful hints on cutting
base molding.
• Cutting base molding can be done either as a
chop cut or a slide cut depending on the width of
the workpiece.
BASE MOLDING CUTTING INSTRUCTIONS
SETTINGS Vertical Position Horizontal Position
/ Back of molding is Back of molding is flat
INSTRUCTIONS against the fence on the table
Bevel Angle 0° 45°
Molding position Left Side
Inside Miter Angle Left at 45° Right at 45° 0° 0°
corner of wall
Molding Bottom Bottom Top against Bottom
position against table against table fence against fence
Right
Left
Outside Miter Angle Right at 45° Left at 45° 0° 0°
corner of wall
Finished Keep left Keep right Keep left Keep left
side side of cut side of cut side of cut side of cut
Right Side Left Side Right Side
Molding Bottom Bottom Bottom against Top against
position against table against table fence fence
Left
Right
Finished Keep left Keep right Keep right Keep right
side side of cut side of cut side of cut side of cut
Cutting Crown Molding
• Crown molding mustbe cut exactly to fit properly.
• There are two ways to cut crown molding:
flat on table or angled to table and fence.
our miter saw has special miter detents of
• Y
31.6° left and right and a bevel detent of 33.9°
for cutting cr
• These special detents angles have been
designed into your compound miter saw for the
standard cr
States with the following angles:
own molding flat on the table.
own molding used in the United
52° between the back of the molding and the
top flat surface that fits against the wall.
38° between the back of the molding and the
bottom flat surface that fits against the wall.
crown
NOTE:
molding.
• Even though these angles are standards, most
• Cutting cr
These detents cannot be used with 45
rooms do not have angles of exactly 90°, therefore, you will need to fine tune your settings
using the detent override.
own molding flat on the table can be
done either as a chop cut or a slide cut depending on the width of the workpiece.
°
28.
Page 29
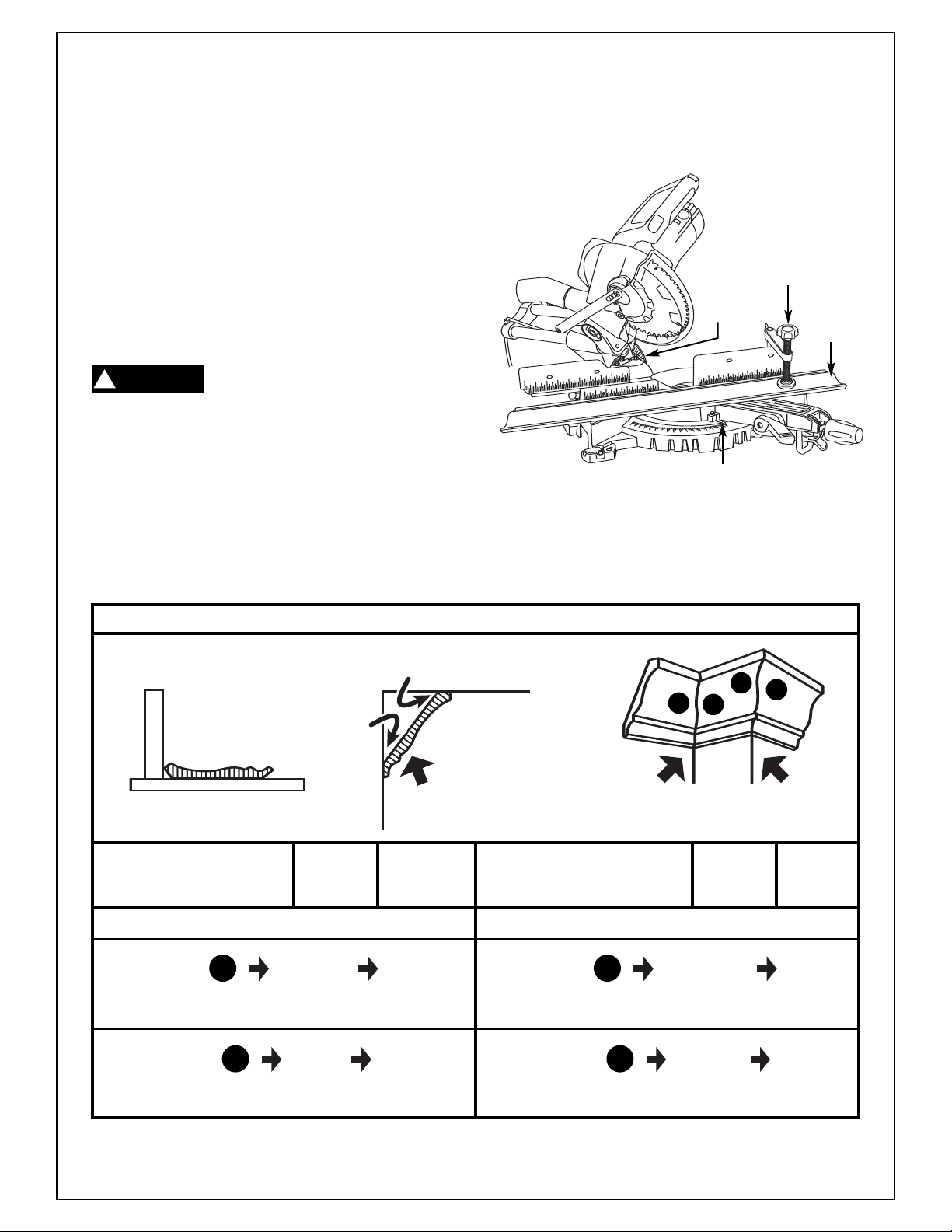
Saw Operations
Crown Molding Laying Flat on Table
Follow these instructions for cutting crown
molding:
1. Set the bevel and miter angles using Chart 1
below. Tighten the miter lock knob and the
bevel lock handle (Figur
e 33).
2. Position molding on saw table. Use the chart
below for correct position. Clamp workpiece in
place using the quick clamp.
NOTE: ALWAYS TAKE A TEST CUT USING
SCRAP TO CONFIRM CORRECT ANGLES.
!
WARNING
switching on, lower head assembly to make sure
clamp clears guard and head assembly.
3. Follow procedures for either chop cut or slide cut
(see page 24).
4. Wait until blade comes to a complete stop
before returning head assembly to the raised
position and/or removing workpiece.
Use clamping position that does not
interfere with operation. Before
Figure 33. Crown Molding Laying Flat
CROWN MOLDING CUTS - CUTTING METHOD #1 - FLAT ON TABLE
MAX. SIZE: 10-1/4"
F
E
N
C
E
ABLE
T
38º
W
A
L
L
52º CEILING
ANGLES OF U.S.
STANDARD MOLDING
INSIDE
CORNER
A
Workpiece
Clamp
33.9º
Bevel
31.6º Miter
C
B
OUTSIDE
CORNER
Crown
Molding
D
TYPE
OF (TABLE) (TILT) OF (TABLE) (TILT)
CUT
MITER
SETTNING
INSIDE CORNER
RIGHT
LEFT SIDE 31.6º 33.9º LEFT SIDE 31.6º 33.9º
PLACE TOP EDGE OF PLACE BOTTOM EDGE OF
MOLDING AGAINST FENCE - SA
VE LEFT END OF CUT
LEFT LEFT
RIGHT SIDE 31.6º 33.9º RIGHT SIDE 31.6º 33.9º
PLACE BOTTOM EDGE OF
MOLDING AGAINST FENCE - SAVE LEFT END OF CUT MOLDING AGAINST FENCE - SAVE RIGHT END OF CUT
BEVEL TYPE MITER BEVEL
SETTING
CUT
SETTNING
SETTING
OUTSIDE CORNER
RIGHT
CA
MOLDING AGAINST FENCE - SA
DB
PLACE TOP EDGE OF
VE RIGHT END OF CUT
29.
Page 30
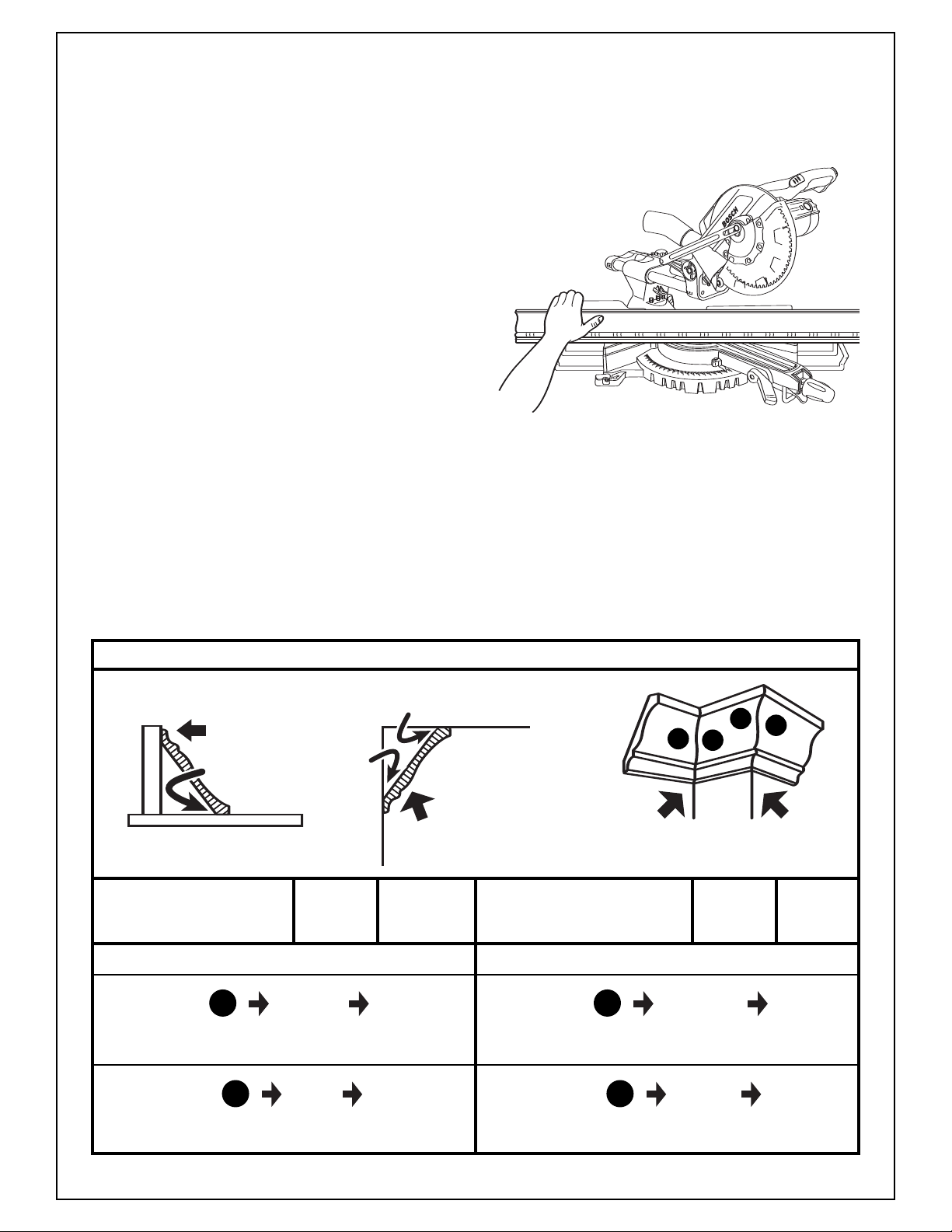
Saw Operations
Crown Molding Angled to
Table and Fence
• The advantage to cutting in this position is that
no bevel setting is required. Cutting is done with
45° miter angle.
• The maximum crown molding width that can be
cut and angled to table and fence is 4-1/4". The
preferred method for cutting crown molding with
this saw is with the molding laying flat on the
table at a maximum width of 10”. Crown stops
can be purchased as an accessory.
Follow these instructions for cutting crown
molding angled to table and fence.
1. Position the molding so the bottom (part which
is installed against the wall) is against the fence.
2. Set the miter angle using Chart 2. Tighten the
miter lock knob (Figure 34).
3. Support crown molding against the fence (see
“Body and Hand Position” on page 19.)
4. Follow the procedures for chop or slide cut (see
page 24).
5. Wait until blade comes to a complete stop
NOTE: ALWAYS TAKE A TEST CUT USING
SCRAP TO CONFIRM CORRECT ANGLES.
Figure 34. Crown Molding Angled to
Table and Fence
before returning head assembly to the raised
position and/or removing workpiece.
CROWN MOLDING CUTS - CUTTING METHOD #2 - ANGLED TO TABLE AND FENCE
MAX. SIZE: 4-
F
E
N
C
E
1
/4"
BOTTOM EDGE
52º
ABLE
T
38º
W
A
L
L
52º CEILING
ANGLES OF U.S.
ANDARD MOLDING
ST
A
INSIDE
CORNER
B
C
D
OUTSIDE
CORNER
TYPE MITER BEVEL TYPE MITER BEVEL
OF (TABLE) (TILT) OF (TABLE) (TILT)
CUT SETTNING SETTING CUT SETTNING SETTING
INSIDE CORNER
RIGHT
LEFT SIDE 45º 0º LEFT SIDE 45º 0º
SAVE RIGHT END OF CUT SAVE RIGHT END OF CUT
LEFT
RIGHT SIDE 45º 0º RIGHT SIDE 45º 0º
SAVE LEFT END OF CUT
OUTSIDE CORNER
CA
DB
VE LEFT END OF CUT
SA
RIGHT
LEFT
30.
Page 31

Saw Operations
Cutting Bowed Material
Special Cuts
!
WARNING
face toward the fence. Always make certain that there
is no gap between the workpiece, fence and table
along the line of cut. Bent or warped workpieces can
twist or rock and may cause binding on the spinning
saw blade while cutting (Figure 35).
If workpiece is bowed or warped,
clamp it with the outside bowed
Workpiece
Clamp
No Gap at
This Point
Bowed
Material
Figure 35. Bowed Material
Cutting Round or Irregularly
Shaped Material
!
WARNING
or a fixtur
against the fence and table. Rods have a tendency to
roll while being cut, causing the blade to “bite” and
pull the work with your hand into the blade (Figure 36).
e designed to clamp the workpiece firmly
For round material such as dowel
rods or tubing, always use a clamp
Workpiece
Clamp
Fence
Round
Material
Figure 36. Round Material
31.
Page 32

Maintenance and Lubrication
Service
!
WARNING
result in misplacing of internal wires and components
which could cause serious hazard. We recommend
that all tool service be performed by a Bosch Factory
Service Center or Authorized Bosch Service Station.
Call 1-877-BOSCH99 to locate a service center.
Preventive maintenance performed
by unauthorized personnel may
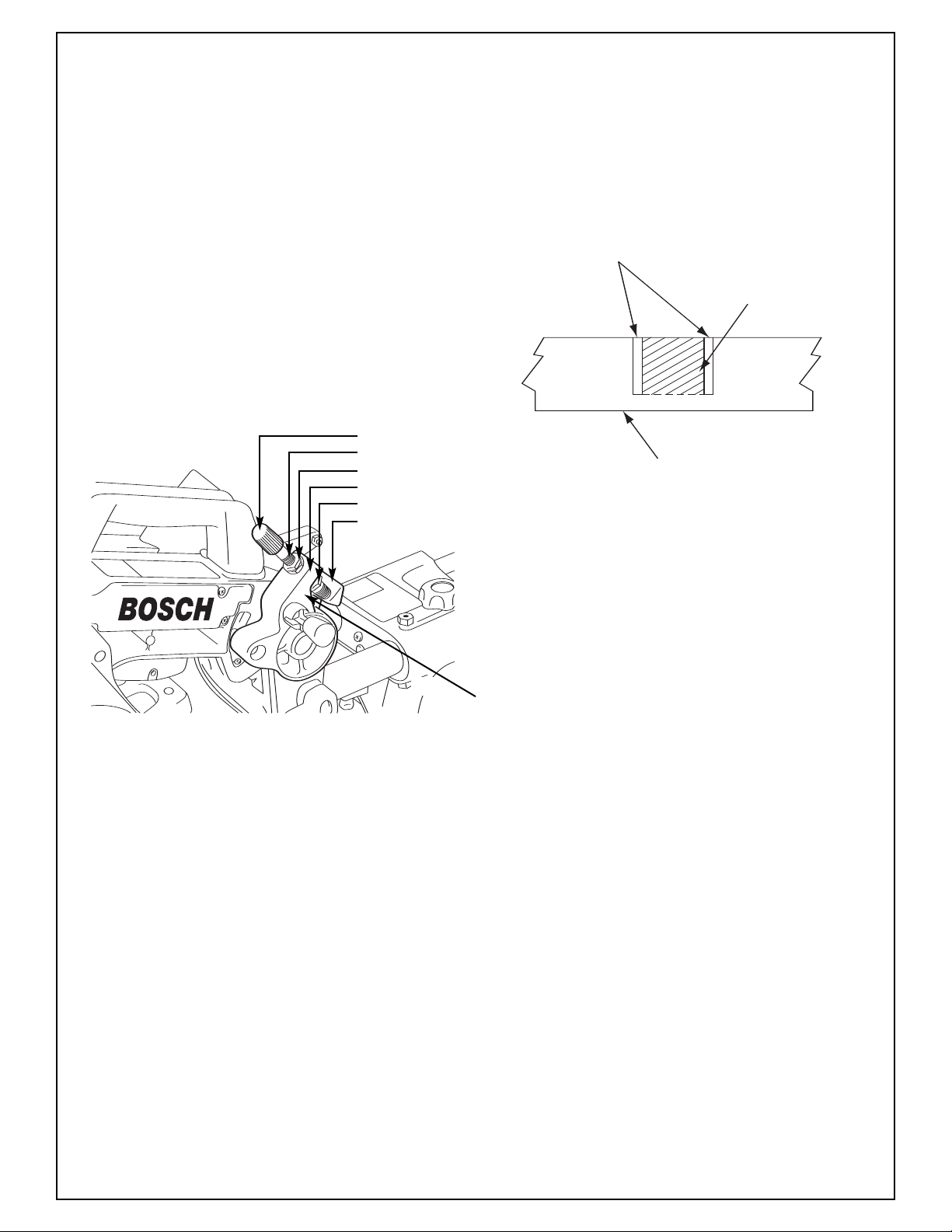
Carbon Brushes
The brushes and commutator in your tool have been
engineered for many hours of dependable service. To
maintain peak efficiency of the motor, we recommend every two to six months the brushes be examined. Only genuine Bosch replacement brushes specially designed for your tool should be used.
Motor Brush Replacement
To Inspect or Replace Brushes:
NOTE: If installing the existing brush or brushes,
make sure the brush goes in the same way it came
out. Otherwise a break-in period will occur that will
reduce motor performance and increase brush wear.
1. Unplug the saw.
!
WARNING
2. Remove the brush cap on the motor using a
wide flat blade screwdriver.
3. Pull out the brush (Figure 37). Repeat for the
opposite side.
4. Inspect brushes for wear. On the wide flat side
of brush is a wear limit line. If the brush contact
face is at or beyond (no line visible) the limit
replace brushes as a set.
Install new brush. The two (2) tabs on the brush
5.
terminal go in the same hole the carbon part fits into.
Tighten the brush cap but do not overtighten.
6.
The brush cap is spring loaded by
the brush assembly.
Terminal
BrushBrush
ear Line
W
Cleaning
!
WARNING
before cleaning or performing any maintenance. The
tool may be cleaned most effectively with compressed air. Always wear safety goggles when cleaning tools with compressed air.
Ventilation openings and switch levers must be kept
clean and free of foreign matter. Do not attempt to
clean by inserting pointed objects through openings.
Check regularly to make sure the lower guard and all
moving parts are working properly.
Remove accumulated sawdust from working parts by
blowing with compr
!
WARNING
of these are: gasoline, carbon tetrachloride, chlorinated cleaning solvents, ammonia and household
detergents that contain ammonia. Ammonia should
never be used on aluminum.
To avoid accidents, always disconnect the tool from the power supply
essed air or wiping with a damp cloth.
Certain cleaning agents and solvents damage plastic parts. Some
Care of Blades
Blades become dull even from cutting regular lumber.
If you find yourself forcing the saw forward to cut
instead of just guiding it through the cut, chances are
the blade is dull or coated with wood pitch.
When cleaning gum and wood pitch from blade,
unplug the saw and remove the blade. Remember,
blades are designed to cut, so handle carefully. Wipe
the blade with kerosene or similar solvent to remove
the gum and pitch. Unless you are experienced in
sharpening blades, we recommend you do not try.
Tool Lubrication
our Bosch tool has been pr
Y
eady to use. It is r
r
be regreased with a special gear lubricant at every
brush change. W
performed by
Authorized Bosch Service Station. Call 1-877BOSCH99 to locate a service center.
Periodically lubricate moving parts with a silicone, or
light oil spray. Do not use grease because it tends to
attract and hold sawdust.
ecommended that tools with gears
ecommend that this service be
e r
a Bosch Factory Service Center or
operly lubricated and is
Figure 37. Motor Brush
Bearings
All bearings in this tool are lubricated with a sufficient
amount of high grade lubricant for the life of the unit
under normal operating conditions. No further lubrication is required.
32.
Page 33

Troubleshooting
Troubleshooting Guide - Electrical
PROBLEM
Brake does not stop blade in
about 5 seconds
Motor does not start.
CAUSE
1. Brushes not seated or lightly
sticking or worn.
2. Motor overheated from use
of dull blade/too heavy of a
blade, not recommended
accessory or rapid on/off
cycling.
3. Blade bolt loose.
4. Other
1. Check that unit is plugged in.
2. Power source fuse or
time delay fuse.
3. Brushes worn.
CORRECTIVE ACTION
• Inspect/clean or replace
brushes (see Maintenance
Section).
• Use sharp blade.
• Use a recommended blade.
• Let saw cool down.
• Tighten blade bolt.
• Authorized service
• Plug unit in. Use different
outlet.
• 15-Amp time delay fuse or
circuit breaker.
• See Brush Replacement in
the Maintenance and Lubrication section.
Flash of light from motor endcap when switch is released.
Note: To find an authorized service center,
4. Other.
1. Normal - brake
working properly.
• Authorized service.
• None required.
call 1-877-BOSCH99 (1-877-267-2499)
or visit www.boschtools.com.
33.
Page 34

Troubleshooting
Troubleshooting Guide - General
PROBLEM
Blade hits table.
Angle of cut not accurate.
Cannot move miter adjustment.
Head assembly will not fully rise
or blade guard will not fully close.
Blade binds, jams, burns wood.
Rough cuts.
CAUSE
Misalignment
Misalignment
1. Lock knob tightened/detent
engaged.
2. Sawdust under table.
3. Blade interferes with fence.
1. Sawdust accumulation.
2. Cover plate not tightened
after replacing blade.
3. Lubrication needed
4. Part failure.
5. Pivot spring or guard spring
not replaced properly.
1. Improper operation.
2. Dull blade.
3. Improper blade.
4. Bent blade.
CORRECTIVE ACTION
• Check proper installation of
blade onto saw.
• Authorized service.
• See Adjustments section.
• Loosen lock knob/move out
of detent.
• Vacuum or blow out dust.
Wear eye protection.
• Extend sliding fence.
• Clean head assembly.
• See Blade Installation
page 12.
• Lubricate head pivot pin with
light oil spray or silicone lube.
• Authorized service.
• Authorized service.
• See Basic Saw
Operation section.
• Replace or sharpen blade.
• Replace with 10” diameter
blade designed for the
material being cut.
• Replace blade.
Tool vibrates or shakes.
Head assembly does not move
to 45º bevel position.
Blade does not completely cut
workpiece.
Head assembly does not slide
eely when attempting a slide cut.
fr
Head assembly slides forwar
and back when making a chop cut.
Slide fence loose
d
1. Saw blade loose.
2. Saw blade not balanced.
3. Saw blade damaged.
4. Other.
33.9º Bevel detent engaged.
Depth stop screw adjusted for
groove cutting.
Slide rail lock knob tightened.
Slide rail lock knob
not tightened.
Adjustment needed to lever
34.
• Check proper installation of
blade onto saw. See page 12
or replace blade.
• Replace blade.
• Tighten arbor screw.
• Authorized service.
Rotate detent to non-use
•
position (see page 15).
• See Depth Stop Adjustment
in the Adjustment section.
Loosen slide rail lock knob.
•
Glide pods need adjustment.
•
Push head assembly com-
•
pletely against stop. Tighten
slide rail lock knob.
• Tighten fence lever.
Adjust lower tension
•
Page 35

Troubleshooting
Slide Action Adjustment
!
WARNING
adjustment or repair to avoid possible injury.
If the slide action on the miter saw is not easy to
actuate you will need to make needed adjustments to
correct. Use these instructions to adjust your
slide action.
1. Locate the 4 Set Screws (A, B, C, & D) on the
Rail Guide Housing.
2. Loosen the Nuts on all four set screws with an
adjustable wrench. Loosen all Set Screws.
3. Slowly tighten Set Screw (B) with the 4mm end
on the blade wrench. Stop when you feel the
screw touch the rail.
4. Tighten Set Screw (B) about 1/16 of a turn more.
5. Hold Set Screw (B) in place and tighten the nut.
Don’t let the Set Screw move.
6. Slowly tighten Set Screw (D). Stop when you feel
the screw touch the rail.
7. Hold Set Screw (D) in place and tighten the nut.
Don’t let the Set Screw move.
8. Slowly tighten Set Screw (A). Stop when you feel
the screw touch the rail.
9. Loosen Set Screw (A) less than 1/16 of a turn.
10. Hold Set Screw (A) in place and tighten the nut.
Don’t let the Set Screw move.
11. Repeat Steps 8-10 for Set Screw (C).
Disconnect plug from power source
e performing any assembly,
befor
C
A
B
D
Figure 38. Set Screws
Figure 39. Adjust and Tighten Set Screw
Adjusting Bevel Lock
Lever Tension
Lift bevel lock lever to r
1.
2.Place 17mm socket wrench on bolt head “E”
(Figure 40).
n nut “E” clockwise 1/8 tur
ur
T
3.
lock tension or turn counter-clockwise to 1/8 turn
to loosen bevel lock tension.
4.Push down bevel lock lever until you feel the lever
snap into the locked position.
Verify that bevel lock tension holds the bevel posi-
5.
tion secure and also allows bevel lock lever to lock
down to the point that a solid stop is felt.
6.If necessary, repeat steps 1–5 to adjust the tension.
elease bevel lock.
n to tighten bevel
35.
e 40. Bevel Lock Lever T
Figur
E
ension Adjustment
Page 36

Accessories
Various Blades
A range of blades of various materials, tooth configurations and rakes are offered to provide the correct
blade for various applications.
10" 40 Tooth Carbide Tipped ATB Thin Kerf 0° Hook
5/8" Arbor (BB1040M)
10" 40 Tooth Carbide Tipped ATB Thin Kerf 13°
Hook 5/8" Arbor (BB1040M)
10" 60 Tooth Carbide Tipped ATB Thin Kerf 0° Hook
5/8" Arbor (BB1060M)
Crown Stops (MS1233) Miter Finder (DWM40LK)
Quick action Clamp (BA160)
Provides fast clamping of workpiece.
Note: To find an authorized service center,
call 1-877-BOSCH99 (1-877-267-2499)
or visit www.boschtools.com.
36.
Page 37

Notes
37.
Page 38

Seguridad
!
ADVERTENCIA
puede dar lugar a lesiones personales graves.
“LEA TODAS LAS INSTRUCCIONES”. El incumplimiento de las NORMAS DE SEGURIDAD identificadas por
el símbolo del PUNTO NEGRO (
Normas generales de seguri-
dad para herramientas para
tablero de banco
Area de trabajo
l Mantenga limpia y bien iluminada el área de trabajo. Los
bancos desordenados y las áreas oscuras invitan a que se produzcan accidentes.
l No utilice herramientas mecánicas en atmósferas explosivas,
tales como las existentes en presencia de líquidos, gases o
polvos inflamables.
pas y éstas pueden dar lugar a la ignición del polvo o los vapores.
l Mantenga alejadas a las personas que se encuentren pre-
sentes, a los niños y a los visitantes mientras esté utilizando
una herramienta mecánica.
perder el control.
l Guarde las herramientas que no esté usando fuera del
alcance de los niños y otras personas no capacitadas.
herramientas son peligrosas en las manos de los usuarios no
capacitados.
l No deje desatendida la herramienta en marcha. Apáguela.
No deje la herramienta hasta que se haya detenido por completo.
l HAGA EL TALLER A PRUEBA DE NIÑOS con candados, inter-
ruptores maestros o quitando las llaves de arranque.
Las herramientas mecánicas generan chis-
Las distracciones pueden hacerle
Las
l) que se indican A CONTINUACION y otras precauciones de seguridad
l No exponga las herramientas mecánicas a la lluvia ni a
situaciones húmedas.
mienta mecánica aumentará el riesgo de que se produzcan
sacudidas eléctricas.
l No abuse del cordón. Nunca use el cordón para llevar las
herramientas ni tire de él para desconectarlo del tomacorriente. Mantenga el cordón alejado del calor
los bordes afilados o las piezas móviles. Cambie los cordones dañados inmediatamente.
mentan el riesgo de que se produzcan sacudidas eléctricas.
l Cuando utilice una herramienta mecánica a la intemperie,
use un cordón de extensión para intemperie marcado “W-A”
o “W”.
Estos cordones tienen capacidad nominal para uso a la
intemperie y reducen el riesgo de que se produzcan sacudidas
eléctricas.
La entrada de agua en una herra
, el aceite,
Los cordones dañados au-
Seguridad personal
l Manténgase alerta, fíjese en lo que está haciendo y use el
sentido común al utilizar una herramienta mecánica.
momento de descuido o el consumo de drogas, alcohol o
medicamentos mientras se utilizan herramientas mecánicas
puede ser peligroso.
l Vístase adecuadamente. No se ponga ropa holgada ni joyas.
Sujétese el pelo largo. Mantenga el pelo, la ropa y los
guantes alejados de las piezas móviles.
joyas o el pelo largo pueden quedar atrapados en las piezas
móviles. Súbase las mangas largas por encima de los codos.
Se recomiendan guantes de caucho y calzado antideslizante
cuando se trabaja a la intemperie.
La ropa holgada, las
Un
-
Seguridad eléctrica
l Antes de enchufar la herramienta, asegúrese de que la ten-
sión del tomacorriente es compatible con la tensión especificada en la placa del fabricante dentro de un margen del
Una tensión del tomacorriente incompatible con la que
10%.
se especifica en la placa del fabricante puede dar como resul
tado peligros graves y daños a la herramienta.
l Las herramientas con aislamiento doble están equipadas
con un enchufe polarizado (un terminal es más ancho que
el otro). Este enchufe entrará en un tomacorriente pola
rizado solamente de una manera. Si el enchufe no entra por
completo en el tomacorriente, déle la vuelta. Si sigue sin
entrar, póngase en contacto con un electricista competente
para instalar un tomacorriente polarizado. No haga ningún
tipo de cambio en el enchufe.
necesidad de un cordón de energía de tres cables conectado
a tierra y de una fuente de energía conectada a tierra.
l Evite el contacto del cuerpo con las superficies conectadas
a tierra, tales como tuberías, radiadores, estufas de cocina
y refrigeradores.
sacudidas eléctricas si su cuerpo está conectado a tierra.
Hay mayor riesgo de que se produzcan
El aislamiento doble elimina la
“CONSERVE ESTAS INSTRUCCIONES”
l Evite el arranque accidental. Asegúrese de que el interrup-
tor esté en la posición “OFF” (apagado) antes de enchufar
la herramienta.
interruptor o el enchufar las herramientas que tienen el inter
ruptor en la posición “ON” (encendido) invita a que se pro-
-
-
duzcan accidentes.
l Quite las llaves de ajuste o las llaves de tuerca antes de
ENCENDER
que se deje puesta en una pieza giratoria de la herramienta
saldrá despedida.
l No intente alcanzar demasiado lejos. Mantenga un apoyo
de los pies y un equilibrio adecuados en todo momento.
apoyo de los pies y el equilibrio adecuados permiten un mejor
control de la herramienta en situaciones inesperadas.
l No se suba en la herramienta ni en su base. Se pueden pro-
ducir lesiones graves si la herramienta vuelca o si se hace
contacto con la herramienta de corte accidentalmente. No
guarde materiales sobre ni cerca de la herramienta de tal
modo que sea necesario subirse a la herramienta o a su base
para alcanzarlos.
El llevar las herramientas con el dedo en el
la herramienta.
Una llave de tuer
38.
-
ca o de ajuste
El
Page 39

Seguridad
!
ADVERTENCIA
puede dar lugar a lesiones personales graves.
l Utilice equipo de seguridad. Use siempre gafas de segu-
Se debe utilizar una máscara antipolvo, calzado de
ridad.
seguridad, casco o protección en los oídos según lo requieran las condiciones. Los lentes de uso diario sólo tienen
lentes resistentes a los golpes. NO son gafas de seguridad.
“LEA TODAS LAS INSTRUCCIONES”. El incumplimiento de las NORMAS DE SEGURIDAD identificadas por
el símbolo del PUNTO NEGRO (
Utilización y cuidado de las herramientas
l Utilice abrazaderas u otro modo práctico de fijar y soportar
la pieza de trabajo en una plataforma estable.
de la pieza de trabajo con la mano o contra el cuerpo resulta
inestable. Permite que la pieza de trabajo se desplace y cause
atasco de la herramienta y pérdida de control.
l No fuerce la herramienta. Use la herramienta correcta para
la aplicación que desea.
bajo mejor y con más seguridad a la capacidad nominal para
la que está diseñada. No utilice la herramienta para propósitos para los que no está diseñada. Por ejemplo, no use la sierra para cortar ingletes para trocear metales.
l No utilice la herramienta si el interruptor no la ENCIENDE o
APAGA.
el interruptor es peligrosa.
l Desconecte el enchufe de la fuente de energía antes de
hacer cualquier ajuste o de cambiar accesorios.
medidas de seguridad preventivas reducen el riesgo de arrancar la herramienta accidentalmente.
l Mantenga las herramientas de corte afiladas y limpias. Es
menos probable que las herramientas mantenidas adecuadamente, con bordes de corte afilados, se atasquen, y son más
fáciles de controlar. Al montar hojas de sierra, asegúrese de
que la flecha de la hoja coincida con el sentido de la flecha
marcada en la herramienta y de que los dientes también estén
orientados en el mismo sentido.
l Inspeccione los protectores antes de usar una herramienta.
Mantenga los protectores en su sitio. Compruebe si las
piezas móviles se atascan o si existe cualquier otra situación que pueda afectar el funcionamiento normal o los dispositivos de seguridad de la herramienta. Si la herramienta
se daña, haga que realicen servicio de ajustes y reparaciones antes de usarla.
por herramientas mal mantenidas.
l No altere ni haga uso incorrecto de la herramienta. Cual
quier alteración o modificación constituye un uso incorrecto y
puede dar lugar a lesiones personales graves.
l La utilización de cualquier otro accesorio no especificado
en este manual puede constituir un peligro.
que pueden ser adecuados para un tipo de herramienta pue
den resultar peligrosos cuando se utilizan en una herramienta
inadecuada.
Cualquier herramienta que no se pueda controlar con
La herramienta correcta hará el tra-
Muchos accidentes son causados
La sujeción
Estas
Los accesorios
l) que se indican A CONTINUACION y otras precauciones de seguridad
Servicio
l El servicio de ajustes y reparaciones de una herramienta
debe ser realizado únicamente por personal de repara
vicio o mantenimiento realizado
ciones competente.
por personal no competente puede tener como resultado una
colocación incorrecta de los cables y componentes internos
que podría causar un peligro grave.
l Al realizar ser
mienta, utilice únicamente piezas de repuesto idénticas.
Siga las instrucciones que figuran en la sección Mantenimiento de este manual.
incumplimiento de las instrucciones de Mantenimiento puede
constituir un peligro.
El ser
vicio de ajustes y reparaciones de una herra-
El uso de piezas no autorizadas o el
Normas de seguridad para
sierras para cortar ingletes
l Use abrazaderas para soportar la pieza de trabajo siempre
que sea posible. Si soporta la pieza de trabajo con la mano,
siempre debe mantener la mano fuera del área de “No tocar
con la mano” según se marca con un símbolo en la base. No
use esta sierra para cortar piezas que sean demasiado
pequeñas para fijarlas firmemente con abrazaderas.
ca la mano dentro de la región de “No tocar con la mano”, ésta
puede resbalar o experimentar tracción hacia la hoja.
l No ponga ninguna mano detrás de la hoja de sierra tras el
tope-guía para sujetar o soportar la pieza de trabajo, quitar
desechos de madera ni por cualquier otra razón.
la proximidad de la mano a la hoja de sierra que gira no sea obvia, y sin embargo usted puede resultar lesionado gravemente.
l Nunca atraviese la mano sobre la línea de corte prevista. Es
muy peligroso soportar la pieza de trabajo “con las manos
cruzadas”, es decir, sujetando el lado izquierdo de la pieza de
trabajo con la mano derecha.
l Desconecte siempre el cordón de energía de la fuente de
energía antes de hacer cualquier ajuste o colocar cualquier
accesorio.
teniendo como resultado lesiones personales graves.
l Las sierras para cortar ingletes están diseñadas principalmen
-
-
te para cortar madera o productos parecidos a la madera y no
se pueden usar con ruedas de corte abrasivas para cortar
material ferroso tal como barras, varillas, espigas, etc. Sin
embargo, si corta materiales como aluminio u otros materia
les no ferrosos, utilice únicamente hojas de sierra recomen
dadas específicamente para el corte de metales no ferrosos.
El corte de materiales ferrosos genera un exceso de chispas, dañará el protector inferior y sobrecargará el motor. (NOTA: Bosch
Power T
l Inspeccione la pieza de trabajo antes de cortar. Si la pieza
Usted podría arrancar la sierra involuntariamente,
ool Company no ofrece hojas de 10" para cortar metales.)
Si colo-
Puede que
-
-
-
-
“CONSERVE ESTAS INSTRUCCIONES”
39.
Page 40

Seguridad
!
ADVERTENCIA
“LEA TODAS LAS INSTRUCCIONES”. El incumplimiento de las NORMAS DE SEGURIDAD identificadas por
el símbolo del PUNTO NEGRO (
puede dar lugar a lesiones personales graves.
de trabajo está arqueada o combada, fíjela con el lado arqueado exterior orientado hacia el tope-guía. Asegúrese
siempre de que no haya espacio libre entre la pieza de
trabajo, el tope-guía y la mesa a lo largo de la línea de
Las piezas de trabajo arqueadas o combadas pueden
corte.
torcerse u oscilar y pueden causar atasco en la hoja de sierra
que gira durante el corte. Además, asegúrese de que no haya
clavos ni objetos extraños en la pieza de trabajo.
l No use la sierra hasta que se hayan retirado de la mesa todas
las herramientas, desechos de madera, etc., excepto la
pieza de trabajo.
Los desperdicios pequeños o las piezas
sueltas de madera u otros objetos que hagan contacto con la
hoja que gira pueden salir despedidos a alta velocidad hacia el
operador.
l No haga avanzar la pieza de trabajo hacia la hoja ni corte a
pulso de ningún modo. La pieza de trabajo debe estar estacionaria y fijada con abrazaderas o sujetada con la mano.
Se debe hacer avanzar la sierra a través de la pieza de trabajo
de modo suave y a una velocidad que no sobrecargue el
motor de la sierra.
l Corte únicamente una pieza de trabajo por vez. No se pue-
den fijar con abrazaderas ni sujetar de modo adecuado múltiples piezas de trabajo y éstas pueden atascarse en la hoja o
desplazarse durante el corte.
l Asegúrese de que la sierra para cortar ingletes esté montada
o colocada sobre una superficie de trabajo nivelada y firme
antes de utilizarla.
Una superficie de trabajo nivelada y firme
reduce el riesgo de que la sierra para cortar ingletes se vuelva
inestable.
l Planifique el trabajo que va a hacer. Proporcione acceso-
rios de soporte adecuados, tales como mesas, caballetes
de aserrar, extensiones de mesa, etc., para piezas de trabajo más anchas o más largas que el tablero de la mesa
(vea la página 54).
Las piezas de trabajo más largas o más
anchas que la mesa de la sierra para cortar ingletes se pueden
inclinar si no se soportan adecuadamente. Si la pieza cortada
o la pieza de trabajo se inclina, puede hacer subir el protector
inferior o salir despedida por acción de la hoja que gira.
l No use a otra persona como sustituto de una extensión de
mesa o como soporte adicional.
Un soporte inestable de la
pieza de trabajo puede hacer que la hoja se atasque o que la
pieza de trabajo se desplace durante la operación de corte,
tirando de usted y del ayudante hacia la hoja que gira.
l La pieza cortada no debe estar bloqueada contra ningún
otro medio ni presionada por ningún otro medio contra la
hoja de sierra que gira.
Si se confina, es decir, si se usan
topes de longitud, podría quedar acuñada contra la hoja y salir
despedida violentamente.
l Use siempre una abrazadera o un dispositivo de sujeción
diseñado para soportar adecuadamente material redondo
tal como varillas con espiga o tubos.
Las varillas tienen tendencia a rodar mientras son cortadas, haciendo que la hoja
“muerda” la pieza de trabajo y tire de ésta, junto con la mano
del operador, hacia la hoja.
“CONSERVE ESTAS INSTRUCCIONES”
l) que se indican A CONTINUACION y otras precauciones de seguridad
l Al cortar piezas de trabajo que tienen forma irregular,
planifique su trabajo de modo que la pieza de trabajo no
resbale y pellizque la hoja y le sea arrancada de la mano.
Por ejemplo, una pieza de moldura debe estar colocada en
posición horizontal o estar sujeta por un dispositivo de sujeción o un posicionador que no permita que la pieza se tuerza,
oscile o resbale mientras esté siendo cortada.
l Deje que la hoja alcance toda su velocidad antes de hacer
contacto con la pieza de trabajo.
Esto ayudará a evitar que
las piezas de trabajo salgan despedidas.
l Si la pieza de trabajo o la hoja se atasca o engancha, APA-
GUE la sierra para cortar ingletes soltando el interruptor.
Espere a que todas las piezas móviles se detengan y desenchufe la sierra para cortar ingletes. Luego, suelte el material atascado. El aserrado continuo de una pieza de trabajo
atascada podría causar pérdida de control o daños a la sierra
para cortar ingletes compuestos.
l La acción de frenado de la sierra hace que el cabezal de la
sierra dé sacudidas hacia abajo. Este preparado para esta
reacción
al hacer un corte incompleto o al soltar el interruptor antes de que el cabezal esté en la posición completamente
hacia abajo.
l Después de terminar el corte, suelte el interruptor, sujete el
brazo de la sierra hacia abajo y espere a que la hoja se detenga antes de retirar la pieza de trabajo o la pieza cortada.
Si la hoja no se detiene al cabo de cinco (5) segundos, desenchufe la sierra y siga las instrucciones que figuran en la
sección Localización y reparación de averías.
¡ES PELIGROSO PONER LA MANO BAJO UNA HOJA QUE AUN GIRA
POR INERCIA!
l Hay instrucciones de seguridad adicionales para operacio-
nes específicas de la sierra en la sección de operaciones.
Lea el resto del manual para informarse sobre la utilización
con seguridad.
l Para el corte con acción deslizante, TIRE primero del ensam-
blaje del cabezal de la sierra alejándolo del tope-guía hasta
que la hoja no toque la pieza de trabajo o hasta su extensión
máxima si la hoja no puede dejar de tocar la pieza de trabajo. Asegúrese de que la abrazadera no interfiera ni con el
protector ni con el ensamblaje del cabezal. Segundo,
ENCIENDA la sierra y bájela hasta la mesa. Luego, EMPUJE
la sierra a través de la pieza de trabajo. Suelte el interruptor
y espere a que la hoja se detenga por completo antes de
subir el ensamblaje del cabezal y retirar la pieza de trabajo.
Nunca “corte tirando de la sierra”, ya que la hoja puede subir a
ficie de la pieza de trabajo y causar RETROCESO.
la super
l Para el corte con acción de troceado, deslice el ensamblaje
del cabezal hacia la parte posterior tanto como se pueda y
apriete el pomo de fijación del carro. Luego, ENCIENDA la
sierra y baje el ensamblaje del cabezal para hacer el corte.
Suelte el interruptor y espere a que la hoja se detenga por
completo antes de subir el ensamblaje del cabezal y retirar
la pieza de trabajo.
El no apretar el pomo de fijación del carro
puede hacer que la hoja suba repentinamente a la superficie de
la pieza de trabajo y llegue hasta usted.
40.
Page 41

Seguridad
!
ADVERTENCIA
puede dar lugar a lesiones personales graves.
l No permita que la familiarización obtenida por el uso fre-
cuente de la sierra para cortar ingletes se vuelva algo
habitual.
de segundo es suficiente para causar una lesión grave.
l ¡PIENSE EN LA SEGURIDAD! LA SEGURIDAD ES UNA COM-
BINACION DE SENTIDO COMUN Y CONOCIMIENTO DE LAS
INSTRUCCIONES DE SEGURIDAD Y DE FUNCIONAMIENTO
POR PARTE DEL OPERADOR Y DE QUE ESTE PERMANEZCA
ALERTA EN TODO MOMENTO MIENTRAS SE ESTA UTILIZANDO LA SIERRA PARA CORTAR INGLETES.
!
SE PUEDEN ENCONTRAR EN LA HERRAMIENTA. ESTAS ADVERTENCIAS SON SOLAMENTE UNA FORMA CONDENSADA DE LAS
NORMAS Y PRECAUCIONES DE SEGURIDAD MAS DETALLADAS
QUE APARECEN EN EL MANUAL DEL USUARIO. SIRVEN COMO
RECORDATORIO DE TODAS LAS NORMAS DE SEGURIDAD
NECESARIAS PARA LA UTILIZACION CON SEGURIDAD DE ESTA
SIERRA PARA CORTAR INGLETES.
Recuerde siempre que un descuido de una fracción
ADVERTENCIA
“LEA TODAS LAS INSTRUCCIONES”. El incumplimiento de las NORMAS DE SEGURIDAD identificadas por
el símbolo del PUNTO NEGRO (
LAS ADVERTENCIAS QUE SE
MUESTRAN A CONTINUACION
l) que se indican A CONTINUACION y otras precauciones de seguridad
!
ADVERTENCIA
do mecánicos, y por otras actividades de construcción, contiene
agentes químicos que se sabe que causan cáncer
nacimiento u otros daños sobre la reproducción. Algunos ejemplos de estos agentes químicos son:
• Plomo de pinturas a base de plomo,
• Sílice cristalina de ladrillos y cemento y otros productos de mampostería, y
• Arsénico y cromo de madera tratada químicamente.
Su riesgo por causa de estas exposiciones varía, dependiendo de
con cuánta frecuencia realice este tipo de trabajo. Para reducir su
exposición a estos agentes químicos: trabaje en un área bien venti
lada y trabaje con equipo de seguridad aprobado, como por ejemplo
máscaras antipolvo que estén diseñadas especialmente para impedir
mediante filtración el paso de partículas microscópicas.
Cierto polvo generado por el lijado, aserrado, amolado y taladra-
, defectos de
-
ZONA DESIGNADA DE
PELIGRO. EVITE SITUAR
LAS MANOS, LOS
DEDOS O LOS BRAZOS
EN EL AREA DESIGNADA
POR ESTE SIMBOLO.
“CONSERVE ESTAS INSTRUCCIONES”
41.
Page 42

Seguridad
!
ADVERTENCIA
puede dar lugar a lesiones personales graves.
“LEA TODAS LAS INSTRUCCIONES”. El incumplimiento de las NORMAS DE SEGURIDAD identificadas por
el símbolo del PUNTO NEGRO (
Herramientas con aislamiento doble
El aislamiento doble
herramientas mecánicas eléctricas que elimina la necesidad de un
cordón de energía de tres cables conectado a tierra y de un sistema
de fuente de energía conectado a tierra. Es un sistema reconocido
y aprobado por Under
dades federales de la OSHA.
l El servicio de ajustes y reparaciones de una herramienta con
aislamiento doble requiere cuidado y conocimiento del sistema
y deberá ser realizado únicamente por un técnico de servicio
competente.
l DURANTE EL SERVICIO DE AJUSTES Y REPARACIONES,
UTILICE UNICAMENTE PIEZAS DE REPUESTO IDENTICAS.
l ENCHUFES POLARIZADOS. Si su herramienta está equipada
con un enchufe polarizado (un terminal es más ancho que el
otro), este enchufe entrará en un tomacorriente polarizado
solamente de una manera. Si el enchufe no entra por completo
en el tomacorriente, déle la vuelta. Si sigue sin entrar, póngase
en contacto con un electricista competente para instalar el
tomacorriente adecuado. No haga ningún tipo de cambio en el
enchufe.
es un concepto de diseño utilizado en las
writer’s Laboratories, la CSA y las autori-
l) que se indican A CONTINUACION y otras precauciones de seguridad
Cordones de extensión
l Sustituya los cordones dañados inmediatamente. La utilización
de cordones dañados puede causar sacudidas, quemar o electrocutar.
l Si se necesita un cordón de extensión, se debe utilizar un cor
dón con conductores de tamaño adecuado para prevenir caídas
de tensión excesivas, pérdidas de potencia o sobrecalentamiento. La tabla muestra el tamaño correcto a utilizar, según
la longitud del cordón y la capacidad nominal en amperios indicada en la placa del fabricante de la herramienta. En caso de
duda, utilice la medida más gruesa siguiente. Utilice siempre
cordones de extensión catalogados por U.L. y la CSA.
TAMAÑOS RECOMENDADOS DE CORDONES DE EXTENSION
Capacidad nomi-
nal en amperios
de la herramienta
3-6
6-8
8-10
10-12
12-16
HERRAMIENTAS DE 120 VOLT A.C.
Longitud del cordón en pies
Tamaño del cordón en calibres A.W.G.
25 50 100 150
18 16 16 14
18 16 14 12
18 16 14 12
16 16 14 12
14 12 N/A N/A
-
“CONSERVE ESTAS INSTRUCCIONES”
Indice
Seguridad . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Normas generales de seguridad para herramientas
para tablero de banco . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .38
Normas de seguridad para sierras para cortar ingletes .39-42
Indice . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Requisitos eléctricos . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Familiarización con la sierra para cortar ingletes . . . . . .44-45
Ensamblaje . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .46-48
Herramientas necesarias para el ensamblaje y
la alineación
Desempaquetado y comprobación del contenido
Instalación del pomo de fijación de inglete . . . . . . . . . . . . .47
Ensamblaje del codo para polvo y la bolsa para polvo . . . .47
Instalación y remoción de la hoja . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .48
Ajustes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .49-52
Hoja en ángulo recto con la mesa (90°) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .49
Hoja a 45
Hoja a 33.9º respecto a la mesa
Hoja en ángulo recto con el tope-guía
Ajuste del indicador de la escala de ingletes . . . . . . . . . . . .52
Instalación . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Aplicaciones de montaje . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .53
Montaje portátil usando abrazaderas . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .54
Ajuste de la barra de estabilidad . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .54
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
respecto a la mesa
°
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .52
38-42
. . . . . . . .
53-54
42
43
46
46
50
51
Cuanto más pequeño es el número de calibre, más grueso es el
NOTA:
cordón.
Operaciones básicas de la sierra . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Posición del cuerpo y de las manos . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .55
Soporte de la pieza de trabajo . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .56
Tope-guía auxiliar . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .57
Activación del interruptor . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .57
Sobrecontrol del retén
Extensión de la base/tope-guía deslizante
Operaciones de la sierra . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Corte de troceado . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .60
Corte deslizante . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .60
Corte a inglete . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .61
Corte en bisel . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .61-62
Cortes compuestos
Corte de ranuras (corte de mortajas) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .63
Corte de moldura de base . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .64
Corte de moldura de techo
Cortes especiales
Mantenimiento y lubricación . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .68
Localización y reparación de averías . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .69-71
Ajuste de la acción de deslizamiento . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .71
Ajuste la de la tensión de la palanca de fijación de bisel . . .71
Accesorios . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .72
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . .58-59
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
55-59
60-67
64-66
58
62
67
42.
Page 43

Electrical Requirements
1. Conecte esta sierra a un circuito derivado de 120 V y 15 A con
cuito o un fusible de 15 amperios de acción retardada.
cortacir
La utilización de un fusible de tamaño incorrecto puede dañar
el motor.
Los fusibles pueden fundirse o los cortacircuitos pueden dis-
2.
pararse frecuentemente si se sobrecarga el motor
producir sobrecarga si se hace avanzar la hoja por la pieza de
trabajo demasiado rápidamente, si se arranca y se detiene
demasiado a menudo en un período de tiempo corto o si se
utiliza una hoja incorrecta para la aplicación.
3. La mayoría de los problemas del motor se pueden atribuir a
conexiones flojas o incorrectas, sobrecarga, tensión baja
(debida por ejemplo a un cable de tamaño pequeño en el circuito de alimentación o un cable del circuito de alimentación
demasiado largo). Compruebe siempre las conexiones, la
carga y el circuito de alimentación suministro cuando el
motor no funcione bien.
. Se puede
Freno eléctrico
La sierra está equipada con un freno eléctrico automático que está
diseñado para hacer que la hoja deje de girar en unos cinco (5)
segundos después que usted suelte el interruptor gatillo. Es útil al
hacer ciertos cortes en madera donde una hoja que aún gire por
inercia podría producir un corte ancho e impreciso.
!
ADVERTENCIA
un fusible o a otras causas, la velocidad del motor se reducirá gra
dualmente y la acción de frenado se iniciará UNICAMENTE al soltar
el interruptor gatillo.
El freno eléctrico de la hoja de la sierra ha sido diseñado para proporcionar el más alto grado de confiabilidad, pero circunstancias
inesperadas, tales como presencia de contaminación en el conmutador y en las escobillas o avería de los componentes del motor,
pueden hacer que el freno no se active. Si se produce esta
situación, encienda (posición “ON”) y apague (posición “OFF”) la
sierra cuatro o cinco veces sin entrar en contacto con la pieza de
trabajo. Si la herramienta funciona pero el freno no detiene la hoja
cada vez en unos 5 segundos, NO utilice la sierra y haga que se
realice servicio de ajustes y reparaciones inmediatamente.
!
ADVERTENCIA
positivo de seguridad. Recuerde dejar que la hoja de la sierra se
detenga por completo antes de retirarla de la pieza de trabajo.
Como siempre, el sistema de protectores constituye la mejor protección para usted contra el contacto no intencional con la hoja de
sierra que gira. NUNCA ponga cuñas para mantener abierto el protector inferior ni anule la acción de cierre de dicho protector.
Cuando se pierda la energía eléctrica debido a que se haya fundido
La acción de frenado de esta sierra no está proyectada como dis-
-
43.
Page 44

Familiarización con la sierra para cortar ingletes
1
4
30
2
40
3
28
20
16
41
19
32
25
22
29
5
26
27
6
23
21
24
7
8
18
7
9
40
12
18
14
15
17
16
!
ADVERTENCIA
enchufe del tomacorriente de la fuente de energía antes de hacer
cualquier ajuste.
1. Botón de “Fijación en OFF” (apagado) del interruptor
Este botón debe estar oprimido para activar el interruptor de
encendido.
2. Interruptor de encendido
El interruptor de encendido (utilizado con el botón de “Fijación en
OFF”) enciende la unidad.
3. Mango con interruptor
Este mango contiene el interruptor
de trabajo empujando/tirando hacia abajo sobre el mango.
No levante nunca la herramienta por el mango con interruptor.
Para evitar lesiones debidas a un
arranque accidental, saque el
. La hoja se baja hacia la pieza
43
34
11
13
4. Cierre del eje portaherramienta
Permite al usuario evitar que la hoja gire mientras aprieta o afloja
el tornillo del eje portaherramienta al cambiar o quitar la hoja.
5. Protector inferior de la hoja/reborde del protector inferior
El protector inferior de la hoja ayuda a proteger las manos del operador contra la hoja que gira. Se retrae al bajar la hoja.
del protector se puede usar para subir manualmente el protector
inferior, solamente según se recomienda en este manual.
6. Hoja
Utilice únicamente hojas de 10" de entre 1.4 y 3.0 mm de grosor
con un agujero para eje portaherramienta de 5/8".
7. Tope-guía estacionario
Soporta la pieza de trabajo. El tope-guía tiene una escala fundida para
hacer cortes repetitivos fácilmente. El tope-guía también tiene agujeros que se usan para fijar un tope-guía auxiliar si así se desea.
44.
10
El reborde
,
Page 45

Familiarización con la sierra para cortar ingletes
8. Accesorios de inserción para la separación de corte
9. Sobrecontrol del retén de inglete
Permite anular la acción del retén, lo cual permite realizar ajustes
finos a cualquier ángulo de inglete.
10. Pomo de fijación de inglete
El pomo de fijación de inglete fija la mesa de la sierra para cortar
ingletes en cualquier ángulo de inglete que se desee.
11. Gatillo del retén de inglete
El gatillo suelta la mesa del retén.
12. Indicador de la escala de ingletes/del ángulo de inglete
La escala está fundida en la base de la sierra.
to a la mesa.
13. Retenes de inglete
Hay diez (10) retenes de inglete para cortes de inglete de ángulos
de inglete comunes con rapidez y precisión.
14. Mesa
Está asentada sobre la base, proporciona soporte a la pieza de trabajo, gira
para realizar los cortes de inglete deseados y gira el ensamblaje del cabezal.
La parte delantera extendida de la mesa se llama brazo de inglete.
15. Base
Proporciona una superficie de trabajo para soportar la pieza de trabajo.
16. Plataformas de montaje de la herramienta
17. Palancas de fijación de las extensiones de la base
Fijan las extensiones de la base en su sitio. Una para cada extensión.
18. Varillas de extensión
Añaden soporte para piezas de trabajo largas.
19. Tope-guía deslizante
Esto proporciona soporte adicional y un área para fijar con abrazadera
a fin de hacer cortes de ingletes compuestos.
20. Palanca de fijación del tope-guía deslizante
Fija el tope-guía deslizante en su sitio.
21. Deflector de virutas con aleta para polvo
Este deflector evita que las virutas grandes entren en el protector
superior.
22. Deflector de virutas
El codo de conducto para polvo gira 360° y puede acomodar la bolsa
para polvo o una conexión de manguera de aspiración.
23. Tope de bisel de 0°
Tope ajustable para un índice de bisel de 0° rápido y preciso.
24. Tope de bisel de 33.9°
ope ajustable para un índice de bisel de 33.9
T
Tope de bisel de 45°
25.
Tope ajustable para un índice de bisel de 45° rápido y preciso.
26. Pomo de fijación de los rieles de deslizamiento
El pomo de fijación de los rieles de deslizamiento fija los rieles de
deslizamiento cuando no se están haciendo cortes deslizantes y
cuando se está transportando la sierra.
27. Rieles de deslizamiento
Guían el ensamblaje del cabezal al hacer cortes deslizantes.
Abrazadera para la pieza de trabajo
28.
Proporciona fijación rápida de la pieza de trabajo.
29. Eslabón de accionamiento del protector inferior
Permite un movimiento suave del protector inferior.
30. Protector superior de la hoja
Cubre la porción superior de la hoja
31. Llave de tuerca para la hoja
Se utiliza para apretar y aflojar la hoja y ajustar el tope-guía y los
bloques de deslizamiento. La llave de tuerca para la hoja se almacena en la parte trasera de la sierra.
El indicador está suje-
rápido y preciso.
°
38
37
36
42
33
35
16
32. Cordón de energía
Suministra energía al motor. Tiene un retenedor moldeado de cordón para almacenamiento.
33. Posiciones de la abrazadera para la pieza de trabajo
Hay tres (3) posiciones detrás del tope-guía para la abrazadera para
la pieza de trabajo.
34. Palanca de fijación de bisel
El mango de fijación de bisel fija el ensamblaje del cabezal a un ángulo
de bisel deseado.
35. Escala de biseles
Indicador utilizado para ajustar los ángulos de bisel.
36. Pasador de fijación del ensamblaje del cabezal
La sierra está equipada con un pasador de fijación que se utiliza
para bloquear el ensamblaje del cabezal en la posición inferior. Se
debe fijar en la posición inferior durante el transporte.
37. Tope de profundidad
Le permite ajustar la profundidad de la hoja para cortar ranuras en
la pieza de trabajo.
38. Tapas de las escobillas
Estas tapas mantienen las escobillas del motor en su sitio y facilitan el
acceso para inspeccionar y cambiar las escobillas.
39. Placa de cubierta del tope-guía deslizante
Rote la placa de cubierta para retirar el tope-guía.
Mangos de transporte
40.
Salientes de tope de moldura de techo
41.
Permiten utilizar los topes de moldura de techo Bosch.
42. Enrollador del cordón
Proporciona una ubicación para almacenar el cordón de energía.
Barra de estabilidad
43.
Proporciona soporte para el extremo de la mesa.
44. Perno de pivote
Apriételo o aflójelo para ajustar la tensión de bisel.
45. Tuerca de fijación de bisel
Ajusta la fuerza de sujeción del cierre de bisel.
31
2
32
39
44 45
33
16
45.
Page 46

Ensamblaje
Herramientas necesarias para el ensamblaje y la alineación
Destornillador Phillips
Escuadra de combinación
!
ADVERTENCIA
Desempaquetado y comprobación del contenido
Llave de tuerca para la hoja (suministra
da), hexagonal al otro lado de la cabeza
Phillips.
La escuadra de combinación debe estar alineada
Trace una línea ligera
sobre la tabla a lo largo
de este borde
No debe haber espacio libre ni superposición cuando se dé la vuelta a la
escuadra sobre la posición marcada
con una línea de puntos
Desconecte el enchufe de la fuente de energía antes de realizar cualquier ensamblaje, ajuste o reparación
para evitar posibles lesiones.
-
Borde recto de la tabla de 3/4" de
grosor. Este borde debe ser perfectamente recto
La sierra de carro para cortar ingletes compuestos modelo 4405
se envía completa en una caja.
1. Separe todas las piezas de los materiales de empaquetamiento y compruebe cada una usando la “Tabla de piezas
sueltas” para asegurarse de que no falte ningún artículo antes
de tirar cualquier material de empaquetamiento.
2. Piezas sueltas: (Consulte las páginas 44 y 45)
Abrazadera de tornillo
Codo para polvo/bolsa para polvo
Pomo de fijación de inglete
Llame al 1-877-BOSCH99 si necesita asistencia.
!
ADVERTENCIA
interruptor hasta que las piezas que faltan se obtengan e instalen
correctamente. Llame al 1-877-BOSCH99 para obtener las piezas
que falten.
!
ADVERTENCIA
. Fije el mango de fijación de bisel. T
posición de 45
blaje del cabezal completamente hacia usted y apriete el pomo de
fijación de los rieles de deslizamiento. Fije el ensamblaje del
cabezal en la posición hacia abajo.
Nunca lleve la herramienta por los rieles de deslizamiento, ya
que esto puede causar desalineación de la hoja.
No lleve nunca la herramienta por el cordón o por el mango con
interruptor de encendido del ensamblaje del cabezal. Los daños al
aislamiento podrían causar una descarga eléctrica. Los daños a
las conexiones de los cables podrían causar un incendio.
°
Si falta alguna pieza, no enchufe el
cordón de energía ni encienda el
Antes de mover la sierra: Fije el
pomo de fijación de inglete en la
46.
ire el ensam
-
Page 47

Ensamblaje
Instalación del pomo de
fijación de inglete
Localice el pomo de fijación de inglete entre las piezas
sueltas y enrosque el eje en el ensamblaje del retén de
inglete, de la manera que se muestra en la Figura 4.
Ensamblaje del codo para polvo y la bolsa para polvo
1. Empuje el codo para polvo sobre la boquilla para polvo.
Gire el codo hasta la posición deseada (Figura 5).
Bolsa para
polvo
Codo para
polvo
Boquilla
para polvo
Eje
Figura 4: Pomo de fijación de inglete
2. La bolsa para polvo se conecta al codo de conducto para polvo
y se usa para recoger serrín. El codo para polvo también se
puede conectar a un tubo de aspiración estándar de 2" para
recoger polvo.
3. Posicione el codo/la bolsa para polvo de modo que no interfiera con la herramienta durante la operación de corte para
todas las posiciones de inglete/bisel. Asegúrese de que la
bolsa para polvo no interfiera con los rieles de deslizamiento
durante el corte deslizante.
4. Hay que vaciar la bolsa para polvo cuando esté llena de serrín.
Vacíela frecuentemente y después de terminar de aserrar.
Quite cuidadosamente la bolsa para polvo del codo para polvo.
Vacíe la bolsa para polvo en un cubo de basura adecuado
abriendo la cremallera de la bolsa. Tenga sumo cuidado con el
polvo desechado, ya que los materiales en forma de partículas
finas pueden ser explosivos. No tire el serrín a un fuego abierto. Con el transcurso del tiempo, se puede producir una combustión espontánea como resultado de mezclar aceite o agua
con partículas de polvo.
Pomo de fijación del
calibre de ingletes
Figura 5. Bolsa y codo para polvo
!
ADVERTENCIA
pueda estar basada en plomo o cualquier otro material que pueda
contener car
sonal que entre en el área de trabajo debe usar un aparato de respiración adecuado. Las áreas de trabajo se deben sellar con
cubiertas colgantes de plástico y se debe mantener fuera a las
personas no protegidas hasta que las áreas de trabajo se hayan
limpiado completamente.
cinógenos, tome precauciones especiales. Todo el per-
Al aserrar madera tratada químicamente a presión, pintura que
47.
Page 48

Ensamblaje
Instalación y remoción de la hoja
!
ADVERTENCIA
ensamblaje, ajuste o reparación para evitar posibles lesiones.
Afloje el tornillo de la placa de cubierta trasera una vuelta completa. No
1.
quite completamente el tornillo.
2. Afloje el tornillo de la placa de cubierta delantera (aproximadamente
tres vueltas completas) hasta que rebase la lengüeta ubicada en la
placa de cubierta, pero no retire completamente el tornillo. Gire la placa
de cubierta en sentido contrario al de las agujas del reloj, para dejar al
descubierto el área de la hoja correspondiente al perno del eje portaherramienta.
3. Gire el protector a mano para rebasar la hoja sin tocarla. Suelte el protector. El plástico quedará sujeto fuera del paso por el tornillo delantero.
4. Oprima y mantenga fijo el cierre del eje portaherramienta. Es posible
que sea necesario girar la hoja para que el cierre del eje portaherramienta se acople. Use la llave de tuerca para la hoja para quitar el
tornillo de la hoja girando la llave de tuerca en el sentido de las agujas
del reloj. NOTA: El tornillo de la hoja es de rosca a izquierdas.
Desconecte el enchufe de la fuente de
energía antes de realizar cualquier
Protector inferior
Tornillo de la
placa de cubierta
delantera
6. Para instalar la hoja de 10", ajuste la hoja entre los deflectores de
virutas y en el eje portaherramienta (Figura 3). NOTA: Asegúrese
de que la flecha de rotación que está en la hoja coincida con la
flecha de rotación en el sentido de las agujas del reloj que está
en el protector inferior
.
Arandela
interior
Eje porta-
herramienta
Deflector de
virutas
Figura 3. Instalación de la hoja
Gire el perno en
este sentido para
aflojarlo
Arandela
exterior
Deflector de
virutas
Figura 1. Remoción de la hoja
Quite el perno de la hoja, la arandela del eje portaherramienta, la
5.
arandela exterior y la hoja. No es necesario quitar la arandela
interior (Figura 2).
Arandela exterior Arandela interior
Arandela del eje
portaherramienta
Perno de la hoja
(de rosca a izquierdas)
Hoja de sierra
Perno de la hoja
(de casquete
hexagonal)
!
ADVERTENCIA
a 10", ni que sea para un eje portaherramienta superior ni inferior a 5/8".
7. Coloque de nuevo la arandela exterior y la arandela del eje portaherramienta, y apriete el perno de la hoja con los dedos en sentido contrario al de las agujas del reloj (Figura 2). Oprima el cierre del eje
portaherramienta y apriete el perno de la hoja firmemente usando
la llave de tuerca para la hoja, pero no lo apriete demasiado.
Gire la placa de cubierta en el sentido de las agujas del reloj hasta
8.
la posición original y apriete los tornillos de la placa de cubierta.
!
ADVERTENCIA
placa de cubierta está flojo, podrá interferir con el protector inferior de la hoja y atascarlo.
cubierta firmemente en su sitio.
funcionará adecuadamente.
Asegúrese de que el cierre del eje portaherramienta esté suelto
9.
para que la hoja gire libremente.
!
ADVERTENCIA
no interfiera con el accesorio de inserción de la mesa en las
posiciones de inglete de 0° y 45°.
de la ranura de la mesa y compruebe si hay contacto con la base
o la estructura de la mesa giratoria.
con la base o la mesa, obtenga ser
877-BOSCH99.
Coloque de nuevo la llave de tuer
10.
almacenamiento ubicada en la sierra.
Para evitar lesiones, no use una hoja
cuyo diámetro sea superior ni inferior
Apriete los tornillos de la placa
de cubierta.
Nunca use la sierra sin la placa de
Después de instalar una hoja
nueva, asegúrese de que la hoja
Baje la hoja hasta el interior
Si la hoja entra en contacto
vicio autorizado llamando al 1-
Si el tornillo de la
El protector inferior no
ca para la hoja en el área de
Figura 2. Herrajes de la hoja
48.
48.
Page 49

Ajustes
!
ADVERTENCIA
cualquier ensamblaje, ajuste o reparación para evitar posibles
lesiones.
A: La sierra de carro para cortar ingletes compuestos se ajustó
NOT
completamente en la fábrica. Sin embargo, durante el transporte se
puede haber producido una ligera desalineación. Compruebe las
posiciones siguientes y haga ajustes si es necesario antes de usar
esta sierra para cortar ingletes compuestos.
Desconecte el enchufe de la fuente
de energía antes de realizar
Hoja en ángulo recto con
la mesa (90°)
Comprobación de la alineación de la hoja a 90°
1. Gire la mesa hasta la posición de 0° y fíjela en su sitio.
2. Asegúrese de que el ensamblaje del cabezal esté empujado
hacia atrás completamente contra el tope y de que el pomo
de fijación de los rieles de deslizamiento esté apretado.
3. Baje el ensamblaje del cabezal. Fíjelo en esa posición.
4. Use una escuadra de combinación para comprobar si la hoja
está en ángulo recto con la mesa. Coloque la escuadra de combinación sobre la mesa y presiónela contra la hoja. Si la hoja
no hace contacto con toda la longitud de la escuadra (Figura
6), siga el procedimiento de alineación.
Tornillo de
tope de 0°
Contratuerca
Figura 7. Tornillo de tope de bisel de 0° y contratuerca
7. Ajuste el indicador de bisel. Afloje el tornillo y alinee el
indicador con la marca de 0°. Apriete el tornillo (Figura 8).
Escuadra de
combinación
Mesa
Figura 6. Hoja en ángulo recto con la mesa
Ajuste de la alineación de la hoja a 90°
1. Afloje el mango de fijación de bisel.
2. Mueva el cabezal hasta separarlo del tope de 0º.
Baje el tornillo de tope de 0° y la contratuerca con una llave de
3.
tuerca de 12 mm o ajustable.
4. Mueva la sierra de vuelta al tope de 0º.
5. Empuje la escuadra contra la mesa. (fig. 6).
6. Ajuste el tornillo de tope de bisel de 0
de 12 mm o ajustable hasta que la hoja haga contacto con toda
la longitud de la escuadra. Apriete la contratuerca (Figura 7).
Hoja
con una llave de tuerca
°
Ajuste
a 0°
Indicador
de bisel
Tornillo
Figura 8. Indicador de bisel
49.
Page 50

Ajustes
Hoja a 45° respecto a la mesa
Compruebe la alineación de la hoja a 45°
1. Gire la mesa hasta la posición de 0° y fíjela en su sitio.
2. Asegúrese de que el ensamblaje del cabezal esté empujado hacia
atrás completamente contra el tope y de que el pomo de fijación
de los rieles de deslizamiento esté apretado.
3. Baje el ensamblaje del cabezal. Fíjelo en su sitio.
4. Asegúrese de que la contratuerca del tornillo de tope de bisel de
33.9º esté en la posición pasiva, fuera de línea con las contratuercas de los tornillos de tope de bisel de 90º y 45º.
5. Afloje el mango de fijación de bisel e incline el ensamblaje del
cabezal hasta un bisel de 45°. Compruebe el tope de bisel de
45°. El indicador de bisel debe estar en la marca de 45° y el tope
de bisel de 45° debe estar en contacto completo con el tornillo
de tope de bisel de 45°. Coloque la escuadra de combinación
sobre la mesa y presiónela contra la hoja. La hoja debe hacer
contacto con toda la longitud de la escuadra de combinación.
(Figura 9).
6. Si la hoja no está a 45° respecto a la mesa, ajuste el tope de bisel
de 45°
Ajuste de la alineación de la hoja a 45°
1. Baje la contratuerca del tornillo de tope de bisel de 45° utilizan-
do una llave de tuerca de 12 mm o ajustable (Figura 10).
2. Afloje el mango de fijación de bisel.
3. Baje la sierra sobre el tope de 45º.
Escuadra de
combinación
Figura 9. Hoja a 45° respecto a la mesa
Tope de
45°/33.9º
Tornillo de
tope de 45°
Hoja
Mesa
Empuje la escuadra de combinación contra la hoja.
4.
5. Ajuste el tope de bisel de 45º hasta que la hoja haga contacto con
toda la longitud de la escuadra. Apriete la contratuer
(Figura 10).
6. Compruebe que el indicador de bisel señale hacia la marca de 45°
en la escala de biseles (vea la Figura 10). Si el indicador de bisel
no está alineado con la marca de 45°, primero vuelva a comprobar la perpendicularidad de la hoja respecto a la mesa y la alineación del indicador de bisel de 0°. Luego, repita la operación
para la alineación de la hoja a 45° y haga los ajustes adecuados.
ca de 45
.
°
Contratuerca
50.
Figura 10. Tornillo de tope de bisel de 45
° y contratuerca
Page 51

Ajustes
Hoja a 33.9° respecto a la mesa
Compruebe la alineación de la hoja a 33.9°
NOTA: Usted debe comprobar y alinear primero los ajustes de 45º
y 90º antes de hacer los de 33.9º (Consulte las páginas 49 y 50).
Gire la mesa hasta la posición de 0° y fíjela en esa posición.
1.
2. Asegúrese de que el ensamblaje del cabezal esté empujado
completamente hacia atrás contra el tope y que el pomo de
fijación de los rieles de deslizamiento esté apretado.
3. Baje el ensamblaje del cabezal. Fíjelo en esa posición.
4. Asegúrese de que la contratuerca del tornillo de tope de
bisel de 33.9º esté en la posición activa, en línea con las
contratuercas de los tornillos de tope de bisel de 90º y 45º.
5. Afloje el mango de fijación de bisel e incline el ensamblaje del cabezal hasta un bisel de 33.9°. Compruebe el
tope de bisel de 33.9°. El indicador de bisel debería estar
sobre la marca de 33.9°.
6. Si la hoja no está a 33.9° respecto a la mesa, ajuste el
tope de bisel de 33.9°.
Ajuste de la alineación de la hoja a 33.9°
1. Baje la contratuerca del tornillo de tope de bisel de 33.9°
utilizando una llave de tuerca de 12 mm o ajustable
(Figura 12).
2. Afloje el mango de fijación de bisel.
3. Baje la sierra sobre el tope de 33.9º.
4. Ajuste el tope de bisel de 33.9º hasta que el indicador de
de la escala
bisel esté señalando hacia la mar
de bisel (Figura 12). Apriete la contratuerca de 33.9°.
ca de 33.9
°
Figura 11. Hoja a 33.9° respecto a la mesa
Tope de
45°/ 33.9º
Tornillo de
tope de 33.9
Contratuerca
Figura 12. Tornillo de tope de bisel de 33.9° y contratuerca
°
51.
Page 52

Ajustes
Hoja en ángulo recto con el
tope-guía
Comprobación de la alineación del tope-guía
1. Asegúrese de que se haya tirado del ensamblaje del cabezal
hacia adelante para que esté cerca del centro de la mesa y de
que el pomo de fijación de los rieles de deslizamiento esté apre
(Figura 13).
tado
2. Baje el ensamblaje del cabezal y fíjelo en la posición inferior.
3. Asegúrese de que la mesa esté en el retén de 0° y apriete el
pomo de fijación de inglete.
4. Coloque una escuadra de combinación contra el tope-guía y
junto a la hoja tal como se ilustra. Sitúe la escuadra adecuadamente para que no haga contacto con el diente de la hoja de
sierra. La hoja de sierra debe hacer contacto con toda la longitud de la escuadra (Figura 13).
5. Si la hoja no hace contacto con la escuadra, siga el procedimiento de alineación del tope-guía.
Pomo de fijación de
los rieles de
deslizamiento
-
Ajuste de la alineación del tope-guía
1. El ensamblaje del cabezal debe permanecer en la posición bajada.
Extienda el tope-guía deslizante. Use la llave de tuerca
2.
para la hoja (suministrada) y afloje los tres (3) pernos
ubicados detrás del tope-guía (Figura 14).
3. Ajuste el tope-guía hasta que la hoja y el tope-guía hagan
contacto completo con la escuadra.
4. Apriete los tornillos de casquete hexagonales.
Tornillos de casquete hexagonales
Tope-guía
Pomo de fijación
del calibre de
ingletes
13. Hoja en ángulo recto con el tope-guía
Figura
Ajuste del indicador
de la escala de ingletes
y fíjela en esa posición.
Gire la mesa hasta la posición de 0
1.
2. Suba el ensamblaje del cabezal hasta la posición completamente hacia arriba.
Afloje el tornillo Phillips que sujeta el indicador en su sitio
3.
(Figura 15).
4. Posicione el indicador para alinearlo con la marca de inglete de
0°. Apriete el tornillo.
°
Unidad de rieles de deslizamiento
Figura 14. Ajuste del tope-guía
(Vista trasera del área de la mesa/base)
Tornillo del
indicador
Marca de 0°
52.
Figura 15.
Page 53

Instalación
!
ADVERTENCIA
l Desenchufe el cordón eléctrico. Antes de transportar la sierra,
gire el ensamblaje del cabezal hasta el inglete derecho de 45°,
fíjelo en el retén, tire del ensamblaje del cabezal completamente
hacia adelante, hacia usted, apriete el pomo de fijación de los
rieles de deslizamiento y fije el ensamblaje del cabezal en la
posición bajada.
l Para evitar lesiones en la espalda, sujete la herramienta cerca
del cuerpo cuando la levante. Doble las rodillas para poder
levantar la herramienta haciendo fuerza con las piernas, no
con la espalda. Levante la herramienta usando los mangos de
transporte fundidos que se encuentran a los lados de la parte
inferior de la base.
l Nunca lleve la herramienta por los rieles de deslizamiento,
ya que esto puede causar desalineación de la hoja.
l Nunca lleve la sierra para cortar ingletes por el cordón de
Para evitar lesiones, siga siempre las instrucciones siguientes:
Aplicaciones de montaje
energía ni por el mango operativo. El intentar levantar o llevar
la herramienta por el cordón de energía dañará el aislamiento
y las conexiones de los cables, dando como resultado sacudidas eléctricas o incendio.
l Fíjese en la posición de la sierra. Las personas que se encuen
tren detrás de ella podrían resultar lesionadas por residuos
que salgan despedidos.
l Coloque la sierra sobre una super
haya suficiente espacio para manejar y soportar adecua
damente la pieza de trabajo.
l Emperne, atornille, clave o sujete con abrazaderas la sierra a
su superficie de soporte.
!
PRECAUCION
perno cuando sujete la sierra a la superficie de soporte.
podría agrietar el pie o dañar la base.
Tenga cuidado de no clavar demasiado el clavo o girar demasiado el
ficie firme y nivelada, donde
Esto
-
-
Banco de trabajo
Monte la sierra en el banco de trabajo usando los cuatro agujeros para
pernos (de 7/16") o los cuatro agujeros para tornillos (de 1/4") (Figura 16).
Compruebe el espacio libre a la izquierda y a la derecha de la sierra.
Agujeros para pernos
Agujeros para tornillos
Agujeros
para tornillos
Agujeros para pernos
1. Cada uno de los cuatro agujeros de montaje debe empernarse
firmemente usando pernos de 3/8", arandelas de seguridad y
tuercas hexagonales (no se incluyen).
2. Localice y marque donde se va a montar la sierra.
3. Haga cuatro (4) agujeros de 3/8" de diámetro a través del
banco de trabajo.
4. Coloque la sierra para cortar ingletes compuestos sobre el
banco de trabajo alineando los agujeros de la base con los agu
jeros hechos en el banco de trabajo. Instale los pernos, las
arandelas de seguridad y las tuercas hexagonales.
La superficie de soporte donde se va a montar la sierra se debe
examinar cuidadosamente después de montarla para asegurarse de
que no se pueda producir ningún movimiento durante la utilización.
Si se observa alguna inclinación o desplazamiento de la sierra,
compruebe el montaje en el banco de trabajo o la base de soporte
y haga los ajustes necesarios antes de utilizar la sierra de carro para
cortar ingletes compuestos (consulte Ajuste de la barra de estabilidad en la página 54).
-
Figura
Montaje en un banco de trabajo
16.
53.
Page 54

Instalación
Montaje portátil usando abrazaderas
• Si no es posible utilizar pernos o tornillos, sujete la sierra de
carro para cortar ingletes compuestos a un banco de trabajo
o un tablero de mesa utilizando abrazaderas.
• Coloque una abrazadera en “C” en cada una de las áreas de
sujeción y fije firmemente cada abrazadera (Figura 17).
Nota: La utilización de abrazaderas limitará el uso de los
ángulos de inglete extremos.
Area de fijación
con abrazaderas
Area de fijación
con abrazaderas
Figura 17. Montaje portátil usando abrazaderas
Ajuste de la barra de estabilidad
Para disponer de soporte adicional de la mesa durante el corte, la
barra de estabilidad se debe ajustar antes del uso.
1. Afloje el pomo de la barra de estabilidad.
2. Deslice la barra de estabilidad hacia arriba o hacia abajo
hasta que entre en contacto con el banco de trabajo.
Nota: Si la superficie del banco de trabajo no es plana, es
posible que sea necesario reajustar la barra de estabilidad a
diferentes ángulos de inglete.
3. Apriete el pomo.
Pomo de ajuste de la
barra de estabilidad
Barra de estabilidad
Banco de trabajo
54.
Page 55

0
5
10
15
20
25
30
35
40
45
50
50
45
40
35
30
BOSCH
0
5
10
15
20
25
30
35
40
45
50
50
45
40
35
30
BOSCH
0
5
10
15
20
25
30
35
40
45
50
50
45
40
35
30
BOSCH
0
5
10
15
20
25
30
35
40
45
50
50
45
40
35
30
BOSCH
Operaciones básicas de la sierra
Posición del cuerpo y de las manos
!
ADVERTENCIA
Posicione el cuerpo y las manos
de modo adecuado para hacer que
las operaciones de corte sean más fáciles y seguras. Siga las
instrucciones siguientes (Figura 18).
l Nunca ponga las manos cerca del área de corte. Mantenga
las manos fuera de la “Zona de no tocar con la mano”.
l La “Zona de no tocar con la mano” se define como toda la
mesa, las partes fijas de la base y las partes del tope-guía ubi
cadas dentro de este límite. Esta zona esta marcada con símbolos de “No tocar con la mano” ubicados en la base.
l Sujete la pieza de trabajo (fuera de la zona de “No tocar con la
mano”) firmemente contra el tope-guía para impedir que se
mueva (Fig. 18).
Uso correcto Uso incorrecto
!
ADVERTENCIA
Puede que el protector inferior no
se abra automáticamente en cier-
tas condiciones de corte. Si esto sucede:
• Típicamente, esto pude ocurrir cuando se intente cortar
piezas de trabajo que estén cerca de la capacidad de altura de
corte máxima (3.5”) o cuando se realicen cortes en bisel
-
extremos a la capacidad de altura de corte máxima. En estas
condiciones la pieza de trabajo puede detener el movimiento
del protector inferior antes de que el movimiento hacia abajo
del brazo pueda preabrir el protector inferior.
1. La pieza de trabajo debe sujetarse firmemente con
abrazaderas. Esto deja libre una mano para subir el protector por el reborde justo lo suficiente para que no toque
la pieza de trabajo (Figura 19).
2. Arranque la sierra y comience el corte.
3. Una vez que haya despejado la posición donde el protec-
tor inferior podría atascarse, suelte el protector y éste
continuará subiendo automáticamente a medida que
usted corte.
Reborde
Protector inferior
Figura 18. Posiciones de las manos
l Mantenga las manos en su sitio hasta que se haya soltado
el gatillo y la hoja se haya detenido completamente.
l Nunca ponga las manos en los rieles de deslizamiento.
l Mantenga los pies firmemente en el piso y mantenga un
equilibrio adecuado.
l Siga el brazo de inglete al ingletear a la izquierda o a la
derecha. Sitúese ligeramente a un lado de la hoja de sierra.
l Antes de hacer cualquier corte, con la herramienta apagada,
baje la hoja para ver con antelación la trayectoria de la misma.
Abrir
Pieza de
trabajo
Figura 19. Subida del protector inferior
55.
Page 56

Operaciones básicas de la sierra
Soporte de la pieza de trabajo
!
ADVERTENCIA
que estén sujetas con abrazaderas y soportadas adecuadamente
desde debajo.
Las piezas de trabajo largas tienen
tendencia a inclinarse a menos
Abrazaderas
Abrazadera para la pieza de trabajo: Esta abrazadera fija fácilmente una pieza de trabajo en cualquiera de los tres (3) agujeros
para abrazadera ubicados detrás del tope-guía (Figura 20).
• Introduzca el poste de la abrazadera en el agujero
para abrazadera.
• Afloje la tuerca de mariposa, ajuste el brazo a la altura adecuada
y apriete firmemente la tuerca de mariposa.
• Gire el pomo roscado de la abrazadera en el sentido de las agu-
jas del reloj para apretar y en sentido contrario al de las agujas
del reloj para aflojar.
• Mueva el ensamblaje del cabezal para comprobar el espacio libre
con la abrazadera.
!
ADVERTENCIA
pueda usar una abrazadera. Sujete la pieza de trabajo con la mano
fuera de la “Zona de no tocar con la mano”.
piezas cortas
puedan hacer que la mano quede dentro de la “Zona de no tocar
con la mano”.
Abrazadera
para la pieza
de trabajo
Agujeros
para
abrazadera
Varilla
roscada
que no se puedan fijar con una abrazadera y que
Es posible que haya cortes com
puestos extremos en que no se
No intente cortar
Agujeros
para abrazadera
-
Figura 20. Abrazadera para la pieza de trabajo
Las abrazaderas convencionales
se pueden usar para sujetar las piezas de trabajo firmemente con
tra la mesa y el tope-guía.
y otros dispositivos de sujeción
-
56.
Page 57

Operaciones básicas de la sierra
ope-guía auxiliar:
T
sión de la cara del tope-guía debido al tamaño y la posición de la
pieza de trabajo. Los cortes de mortajas también requieren un
tope-guía auxiliar. El tope-guía cuenta con agujeros para sujetar un
tope-guía auxiliar. El tope-guía auxiliar se usa con la sierra en la
posición de bisel de 0
Coloque un pedazo de madera contra el tope-guía de la
1.
sierra para cortar ingletes (Figura 21). (La madera puede
tener una altura máxima de 3-1/2”. Compruebe que el ensamblaje del cabezal no interfiera con el tope-guía auxiliar.)
2. Marque las ubicaciones de los agujeros de soporte en la
madera desde el lado posterior del tope-guía.
3. Taladre y avellane los agujeros en la parte delantera de la
tabla de soporte.
4. Instale el tope-guía auxiliar utilizando al menos (2) tornillos para metales de cabeza plana de 1/4" por lado. Haga
un corte de profundidad completa para crear la ranura para
la hoja. Compruebe si hay interferencia entre el tope-guía
auxiliar y el protector inferior de la hoja. Haga ajustes según
sea necesario.
!
ADVERTENCIA
Ciertos tipos de moldura necesitan una exten
° solamente.
Compruebe si alguno de los componentes interfiere.
-
Tornillos de
cabeza plana
para metales
Ranura para la hoja
Tornillos de
cabeza plana
para metales
Tope-guía
auxiliar
Figura 21. Tope-guía auxiliar
Activación del interruptor
Por motivos de seguridad, la palanca del interruptor está diseñada para evitar los arranques accidentales. Para operar el interruptor de seguridad, oprima el botón de “Fijación en OFF” (apagado)
del interruptor con cualquiera de los pulgares para desacoplar el
cierre y luego tire de la palanca del interruptor de encendido y
suelte el botón de liberación de “Fijación en OFF” del interruptor
Al soltar la palanca del interruptor de encendido, el botón de
“Fijación en OFF” acoplará automáticamente el interruptor de
seguridad y la palanca ya no operará hasta que se oprima de
nuevo cualquiera de los dos botones de “Fijación en OFF”.
NOTA: La palanca del interruptor puede acomodar un candado con
una barra larga de hasta 1/4" de diámetro (no suministrado) para
evitar el uso no autorizado.
.
Palanca del
interruptor de
encendido
Botones de
liberación
de “Fijación
en OFF”
(apagado)
del
interruptor
Figura 22. Activación del interruptor
57.
Page 58

Operaciones básicas de la sierra
1
Sobrecontrol del retén
Para acoplarlo:
1. Suba el gatillo del retén de inglete.
Empuje el clip de sobrecontrol del retén hacia adelante y acó-
2.
plelo en su sitio sobre el borde. Suelte el gatillo del retén de
inglete (Figura 23).
Mueva el brazo de inglete hasta cualquier posición en la escala
3.
de ingletes.
4. Fije el pomo de fijación de inglete para retener la posición de
inglete.
Para desacoplarlo:
Borde del clip
Clip de
sobrecontrol
del retén
5. Afloje el pomo de fijación de inglete y suba el gatillo del retén
de inglete para soltar el clip de sobrecontrol del retén. El clip
debe desacoplarse automáticamente y la mesa se debe fijar en
cualquier retén de inglete deseado.
Extensiones de la base
!
ADVERTENCIA
desde la mano hasta la hoja de sierra, extienda los topes-guía
deslizantes y las extensiones de la base cuando realice cortes en
bisel extremos, de inglete extremos o compuestos extremos.
Las extensiones de la base también se pueden utilizar para brindar
soporte adicional para piezas de trabajo largas.
Ajuste de las extensiones:
1. Afloje las palancas de fijación de las extensiones de la base.
2. Extienda las extensiones de la base deslizantes hasta la posición
deseada.
3. Presione las palancas hacia abajo para sujetar las extensiones
en esa posición.
Si es necesario ajustar la fuer
sujeción de las extensiones de la base, simplemente tire hacia
fuera de la lengüeta roja y gírela hacia el centro de la sierra. Deje
que la lengüeta roja salte hacia atrás por acción de resorte hasta
una nueva ranura. Al girar los lengüetas rojas hacia abajo para
sujetar las varillas, agarrarán las varillas con mayor fuer
Para proporcionar una separación
suficiente (6” como mínimo)
za de sujeción de las palancas de
za.
Mesa
Extension de
la base
Gatillo del
retén de
inglete
Figura 23. Sobrecontrol del retén
Figura 24: Extensiones de la base
Pomo de
fijación
de inglete
Palanca de
fijación de la
extension de
la base
58.
Page 59

Operaciones básicas de la sierra
Topes-guía deslizante
Tope-guía deslizante
Utilización del tope-guía deslizante
1. Gire la palanca del tope-guía en sentido contrario al de
las agujas del reloj.
2. Deslice el tope-guía hasta la posición deseada.
3. Gire la palanca del tope-guía en el sentido de las agu-
jas del reloj para apretar el tope-guía.
Remoción del tope-guía deslizante
1. Levante la lengüeta de la placa de cubierta y gírela en
el sentido de las agujas del reloj.
2. Gire la palanca del tope-guía en sentido contrario al de
las agujas del reloj.
3. Deslice el tope-guía tanto como se pueda hacia la
izquierda.
4. Levante el tope-guía deslizante para retirarlo.
Ajuste del cierre del tope-guía deslizante:
Apriete el cierre
1. Retire el tope-guía deslizante.
2. Empuje hacia abajo sobre el bloque de fijación para
dejar al descubierto la cabeza del tornillo.
3. Gire el tornillo en sentido contrario al de las agujas del
reloj para moverlo hasta el próximo ajuste hexagonal.
Coloque de nuevo el tope-guía deslizante.
4.
Compruebe la fuerza de sujeción en varias posiciones.
5.
Asegúrese de que la palanca no bloquee el agujero
para abrazadera.
VISTA DELANTERA
Tope-guía
deslizante
Palanca
del topeguía
VISTA TRASERA
Lengüeta de la placa
de cubierta
Palanca
del topeguía
Bloque de fijación
Figura 25: Tope-guía deslizante
Ajuste del cierre del tope-guía deslizante:
Afloje el cierre
1. Retire el tope-guía deslizante.
2. Empuje hacia abajo sobre el bloque de fijación para
dejar al descubierto la cabeza del tornillo.
3. Gire el tornillo en el sentido de las agujas del reloj
para moverlo hasta el próximo ajuste hexagonal.
4. Coloque de nuevo el tope-guía deslizante
5. Compruebe la fuer
Asegúrese de que la palanca no bloquee el agujero
para abrazadera.
za de sujeción en varias posiciones.
59.
Page 60

Operaciones de la sierra
Corte de troceado
Durante un corte de troceado, se aprieta el pomo de fijación de
•
los rieles de deslizamiento y se baja el ensamblaje del cabezal
para cortar a través de la pieza de trabajo.
Este tipo de corte se usa principalmente para piezas estrechas.
•
Siga estas instrucciones para hacer un corte de troceado:
1. Deslice el ensamblaje del cabezal hasta la parte trasera tanto
como se pueda (Figura 26).
2. Apriete el pomo de fijación de los rieles de deslizamiento
(Figura 26).
3. Posicione adecuadamente la pieza de trabajo. Asegúrese de que
la pieza de trabajo esté fijada con abrazadera firmemente contra la mesa y el tope-guía.
Espere hasta que la hoja se detenga por completo antes de
5.
regresar el ensamblaje del cabezal a la posición subida y/o retirar la pieza de trabajo.
Pomo de fijación del
carro apretado
!
ADVERTENCIA
operación. Antes de encender la sierra, baje el ensamblaje del
cabezal para asegurarse de que la abrazadera no toque ni el protector ni el ensamblaje del cabezal.
4. Active el interruptor. Baje el ensamblaje del cabezal y haga el corte.
Use una posición de fijación con
abrazadera que no interfiera con la
Corte deslizante
Durante un corte deslizante, se afloja el pomo de fijación de los
•
rieles de deslizamiento, se tira del ensamblaje del cabezal hacia el
operador, se baja el ensamblaje del cabezal hasta la pieza de trabajo y luego se empuja hacia la parte de atrás de la sierra para
realizar el corte.
Este tipo de corte se usa principalmente para piezas anchas.
•
Se recomienda un enganche de hoja positivo de 10 grados o más
para lograr el mejor rendimiento al hacer cortes agresivos o cortar
materiales más gruesos. Consulte la lista de hojas accesorio en la
página 72.
!
ADVERTENCIA
repentinamente a la super
Siga estas instrucciones para hacer un corte deslizante:
1. Posicione adecuadamente la pieza de trabajo. Asegúrese de
que la pieza de trabajo esté fijada con abrazadera firmemente
contra la mesa y el tope-guía.
!
ADVERTENCIA
operación. Antes de encender la sierra, baje el ensamblaje del
cabezal para asegurarse de que la abrazadera no toque ni el protector ni el ensamblaje del cabezal.
2. Afloje el pomo de fijación de los rieles de deslizamiento (Figura 27).
3. Agarre el mango con interruptor y tire del ensamblaje del
cabezal alejándolo del tope-guía hasta que la hoja no toque la
pieza de trabajo o hasta su extensión máxima si la hoja no
puede dejar de tocar la pieza de trabajo (Figura 27).
NUNCA tire de la sierra hacia usted
durante un corte. La hoja puede subir
ficie de la pieza de trabajo y llegar hasta usted.
Use una posición de fijación con
abrazadera que no inter
fiera con la
Deslice completamente
contra el apoyo
Figura 26. Corte de troceado
4. Active el interruptor. Baje el ensamblaje completamente hasta
abajo y corte a través del borde de la pieza de trabajo.
5. Empuje (pero no fuerce) el ensamblaje del cabezal hacia el
tope-guía hasta la posición completamente hacia atrás para
completar el corte.
6. Espere hasta que la hoja se detenga por completo antes de
regresar el ensamblaje del cabezal a la posición subida y/o retirar la pieza de trabajo.
Pomo de fijación
Primero:
ire hacia
T
adelante
de los rieles de
deslizamiento
Segundo:
Encienda
la sierra
Baje el
ensamblaje
del cabezal
Tercero:
Empuje
la hoja hasta
la pieza
de trabajo
Figura 27. Corte deslizante
60.
Page 61

Operaciones de la sierra
Corte a inglete
• Un corte a inglete se hace a un bisel de 0
de inglete en el intervalo de 50° a la izquierda a 60° a la
derecha.
• La escala de ingletes está fundida sobre la mesa para poder
leerla fácilmente.
• Se han provisto unos retenes positivos para ingleteado rápido
y preciso a 0
a 60° a la derecha.
°, 15°, 22.5° y 45° a la izquierda y a la derecha y
• Hay retenes para moldura de techo (izquierda y derecha) a
31.6° (vea Corte de moldura de techo para obtener más información en las páginas 64-66).
• Para realizar ajustes fuera del retén, utilice el sobrecontrol del retén para anular el retén.
• Un corte a inglete se puede hacer como un corte de troceado
o como un corte deslizante según la anchura de la pieza de
trabajo.
Siga estas instrucciones para hacer un corte a inglete:
1. Afloje el pomo de fijación de inglete. Suba el gatillo del retén
de inglete y mueva la sierra hasta el ángulo deseado usando
los retenes o la escala de ingletes. Apriete el pomo de fijación
de inglete (Figura 28).
° y cualquier ángulo
!
ADVERTENCIA
operación. Antes de encender la sierra, baje el ensamblaje del
cabezal para asegurarse de que la abrazadera no toque ni el protector ni el ensamblaje del cabezal.
3. Siga los procedimientos para corte de troceado o corte
deslizante (vea la página 60).
4. Espere hasta que la hoja se detenga por completo antes de
volver a colocar el ensamblaje del cabezal en la posición subi
da y/o retirar la pieza de trabajo.
Abrazadera para la
pieza de trabajo
Use una posición de fijación con
abrazadera que no inter
fiera con la
Pieza de trabajo
-
2. Posicione la pieza de trabajo adecuadamente. Asegúrese de
que la pieza de trabajo esté fijada con abrazadera firmemente
contra la mesa y el tope-guía.
Corte en bisel
• Un corte en bisel se hace a un inglete de 0° y cualquier ángu-
lo de bisel en el intervalo de 0° a 45°.
• Hay topes de bisel ajustados en fábrica a 0° y 45°. (Vea la
sección Ajustes si hay que hacer ajustes.)
• La escala de bisel está orientada hacia el operador para facilitar
su lectura.
Escala de ingletesRetenes
Figura 28. Corte a inglete
Pomo de
fijación de
inglete
• Hay un tope de bisel positivo para moldura de techo a 33.9
Desenganche este tope a menos que lo esté usando. (Vea
Corte de moldura de techo para obtener detalles.)
• Un corte en bisel se puede hacer como un corte de troceado
o como un corte deslizante según la anchura de la pieza de
trabajo.
• Utilice el tope-guía deslizante y soportes para la pieza de tra
bajo según sea apropiado (Consulte Extensión de la base/topeguía deslizante en las páginas 58-59).
°.
-
61.
Page 62

Operaciones de la sierra
Corte en bisel (Viene de la página 61)
Siga estas instrucciones para hacer un corte en bisel:
1. Para aflojar, suba la palanca de fijación de bisel. Incline el
ensamblaje del cabezal hasta el ángulo de bisel deseado.
Apriete la palanca de fijación de bisel (Figura 29).
2. Posicione adecuadamente la pieza de trabajo. Asegúrese de
que la pieza de trabajo esté fijada con abrazadera firmemente
contra la mesa y el tope-guía.
Angulo
de bisel
Abrazadera
para la pieza
de trabajo
!
ADVERTENCIA
operación. Antes de encender la sierra, baje el ensamblaje del cabezal
para asegurarse de que la abrazadera no toque ni el protector ni el
ensamblaje del cabezal.
3. Siga los procedimientos para un corte de troceado o un corte
deslizante (vea la página 60).
4. Espere hasta que la hoja se detenga por completo antes de
volver a colocar el ensamblaje del cabezal en la posición subida y/o retirar la pieza de trabajo.
Use una posición de fijación con
abrazadera que no interfiera con la
Cortes compuestos
• Un corte compuesto es un corte que requiere tanto una posi-
ción de inglete como una de bisel.
• Un corte compuesto se puede hacer como un corte de trocea-
do o como un corte deslizante según la anchura de la pieza de
trabajo.
Inglete de 0°
Palanca de fijación de bisel
Figura 29. Corte en bisel
4. Espere hasta que la hoja se detenga por completo antes de
volver a colocar el ensamblaje del cabezal en la posición subida y/o retirar la pieza de trabajo.
Pieza de
trabajo
• Como puede que se necesiten varios intentos para lograr el
ángulo compuesto deseado, realice cortes de prueba en material de desecho antes de hacer el corte.
Siga estas instrucciones para hacer un corte compuesto:
1. Extienda el tope-guía deslizante y los soportes de la pieza
de trabajo cuando realice cortes compuestos que estén
ingleteados hacia la izquierda.
base/tope-guía deslizante en las páginas 58-59). Seleccione los
ángulos de inglete y de bisel deseados (Figura 30). (Vea Corte a
inglete y Corte en bisel en la página 61.)
(vea la sección Extensión de la
2. Posicione la pieza de trabajo adecuadamente. Asegúrese de
que la pieza de trabajo esté fijada con abrazadera firmemente
contra la mesa y el tope-guía.
!
ADVERTENCIA
operación. Antes de encender la sierra, baje el ensamblaje del cabezal
para asegurarse de que la abrazadera no toque ni el protector ni el
ensamblaje del cabezal.
Use una posición de fijación con
abrazadera que no interfiera con la
3. Siga los procedimientos para un corte de troceado o un corte
deslizante (vea la página 60).
62.
Pieza de
trabajo
Figura 30. Corte compuesto
Ángulo de
bisel
Abrazadera
para la pieza
de trabajo
Page 63

Operaciones de la sierra
Corte de ranuras
(corte de mortajas)
Apriete las contratuercas contra la lengüeta del tope de
3.
profundidad.
4. Corte las dos ranuras exteriores.
El ajuste del tope de profundidad es un dispositivo que se usa
•
al cortar ranuras (mortajas) en la pieza de trabajo.
El ajuste de profundidad se usa para limitar la profundidad de
•
la hoja para cortar ranuras.
Una ranura se puede cortar como un corte deslizante.
•
1. Ajuste la profundidad de corte aflojando las contratuercas ubi-
cadas en el perno de ajuste de profundidad (Figura 31). No
cambie la posición de las dos (2) contratuercas que están en
el extremo del perno.
2. Gire el perno del tope de profundidad hasta la posición correcta.
Agarre estriado
Perno del tope de profundidad
Contratuercas
Base del tope de profundidad
Contratuercas
Tope de profundidad
5. Use un cincel para madera o haga múltiples pasadas deslizando la madera hacia un lado para quitar el material que
está entre las ranuras exteriores (Figura 32).
Ranuras
Corte de cincel
Pieza de trabajo
Figura 32. Ranura cortada de modo basto
Figura 31. Corte de ranuras
Nota: Se necesita el tope-guía auxiliar para obtener una profundidad constante. El grosor del topeguía depende de la profundidad de la mortaja.
Lengüeta del tope
de profundidad
63.
Page 64

Operaciones de la sierra
Corte de moldura de base
• La moldura de base de 3 1/2” o más pequeña se puede
cortar vertical contra el tope-guía. Toda la moldura de
base se puede cortar plana sobre la mesa, hasta una
anchura máxima de 12”.
• Siga el cuadro para obtener consejos útiles sobre el corte de
moldura de base.
• El corte de moldura de base se puede hacer como un corte de
troceado o como un corte deslizante según la anchura de la
pieza de trabajo.
INSTRUCCIONES PARA EL CORTE DE MOLDURA DE BASE
POSICIONES Posición vertical Posición horizontal
/ La parte posterior de la moldura La parte posterior de la moldura
INSTRUCCIONES está contra el tope-guía está horizontal sobre la mesa
Angulo de bisel 0° 45°
Posición de la moldura Lado izquierdo Lado derecho Lado izquierdo Lado derecho
Esquina interior Angulo de inglete Izquierda a 45° Derecha a 45° 0° 0°
de la pared
Posición de Parte inferior Parte inferior Parte superior Parte inferior
la moldura contra la mesa contra la mesa contra el tope-guía contra el tope-guía
Izquierda
Esquina exterior Angulo de inglete Derecha a 45° Izquierda a 45° 0° 0°
Derecha
de la pared
Lado Conservar el lado Conservar el lado Conservar el lado Conservar el lado
acabado izquierdo del corte derecho del corte izquierdo del corte izquierdo del corte
Posición de Parte inferior Parte inferior Parte inferior Parte superior
la moldura contra la mesa contra la mesa contra el tope-guía contra el tope-guía
Izquierda
Derecha
Lado Conservar el lado Conservar el lado Conservar el lado Conservar el lado
acabado izquierdo del corte derecho del corte derecho del corte derecho del corte
Corte de moldura de techo
• La moldura de techo se debe cortar con precisión para que
encaje adecuadamente.
• Hay dos maneras de cortar moldura de techo: horizontal
sobre la mesa o en ángulo respecto a la mesa y al tope-guía.
• La sierra para cortar ingletes tiene retenes de inglete especiales
de 31.6° a la izquierda y a la derecha y un retén de bisel de
33.9° para cortar moldura de techo en posición horizontal
sobre la mesa.
• Estos ángulos de retén especiales han sido diseñados en la
sierra para cortar ingletes compuestos para la moldura de
techo estándar que se usa en los Estados Unidos con los
siguientes ángulos:
entre la parte posterior de la moldura y la super
°
52
superior plana que encaja contra la pared.
entre la parte posterior de la moldura y la super
°
38
inferior plana que encaja contra la pared.
A: Estos retenes no se pueden usar con moldura de techo
NOT
de 45°.
• Aunque estos ángulos son estándar
y cuartos no tienen ángulos de exactamente 90°. Por lo
tanto, usted tendrá que ajustar con precisión las posiciones
usando el sobrecontrol del retén.
, la mayoría de las salas
ficie
ficie
• El corte de una moldura de techo en posición horizontal sobre
la mesa se puede hacer como un corte de troceado o como
un corte deslizante según la anchura de la pieza de trabajo.
64.
Page 65

Operaciones de la sierra
Moldura de techo colocada horizontalmente
sobre la mesa
Siga estas instrucciones para cortar moldura de techo:
1. Ajuste los ángulos de bisel y de inglete usando el Cuadro 1 que
aparece más abajo. Apriete el pomo de fijación de inglete y el
mango de fijación de bisel (Figura 33).
2. Posicione la moldura sobre la mesa de la sierra. Use el cuadro que
aparece más abajo para obtener la posición correcta. Fije la pieza
de trabajo en su sitio usando la abrazadera de acción rápida.
NOTA: HAGA SIEMPRE UN CORTE DE PRUEBA USANDO MADERA DE
DESECHO PARA CONFIRMAR QUE LOS ANGULOS SON CORRECTOS.
Bisel de
°
33.9
Abrazadera
para la pieza
de trabajo
Moldura de
techo
!
ADVERTENCIA
operación. Antes de encender la sierra, baje el ensamblaje del
cabezal para asegurarse de que la abrazadera no toque ni el protector ni el ensamblaje del cabezal.
3. Siga los procedimientos para corte de troceado o para corte
deslizante (vea la página 60).
4. Espere hasta que la hoja se detenga por completo antes de
volver a colocar el ensamblaje del cabezal en la posición subida y/o retirar la pieza de trabajo.
Use una posición de fijación con
abrazadera que no interfiera con la
Inglete de 31.6°
Figura 33. Moldura de techo colocada horizontalmente
CORTES DE MOLDURA DE TECHO - METODO DE CORTE NO. 1: HORIZONTAL SOBRE LA MESA
1
MESA
/4"
38º
P
A
R
E
D
52° TECHO
ANGULOS DE MOLDURA
. EE.UU.
EST
ESQUINA
INTERIOR
C
A
B
D
ESQUINA
EXTERIOR
TAMAÑO MAX: 10
T
O
P
E
G
U
I
A
TIPO POSICION POSICION TIPO POSICION POSICION
DE DE INGLETE DE BISEL DE DE INGLETE DE BISEL
TE
COR
ESQUINA INTERIOR
(MESA)
(INCLINACION)
ESQUINA EXTERIOR
COR
TE
DERECHA
Lado Izquierda 31.6º 33.9º Lado Izquierda 31.6º 33.9º
COLOQUE LA PARTE SUPERIOR DE LA MOLDURA CONTRA EL TOPE-GUIA – COLOQUE LA PARTE INFERIOR DE LA MOLDURA CONTRA EL TOPE-GUIA –
CONSERVE EL EXTREMO IZQUIERDO DEL CORTE CONSERVE EL EXTREMO IZQUIERDO DEL CORTE
IZQUIERDO IZQUIERDO
Lado Derecho 31.6º 33.9º Lado Derecho 31.6º 33.9º
COLOQUE LA PARTE INFERIOR DE LA MOLDURA CONTRA EL TOPE-GUIA – COLOQUE LA PARTE SUPERIOR DE LA MOLDURA CONTRA EL TOPE-GUIA –
CONSERVE EL EXTREMO IZQUIERDO DEL CORTE CONSERVE EL EXTREMO IZQUIERDO DEL CORTE
CA
DB
(MESA) (INCLINACION)
DERECHA
65.
Page 66

Operaciones de la sierra
Moldura de techo en ángulo respecto
a la mesa y al tope-guía
• La ventaja de cortar en esta posición es que no se requiere
ajuste de bisel. El corte se hace con el ángulo de inglete de 45°.
• La anchura máxima de moldura de techo que se puede cortar
y poner en ángulo con el tope-guía y la mesa es de 4-1/4". El
método preferido para cortar moldura de techo con esta sierra es con la moldura ubicada en posición plana sobre la mesa
con una anchura máxima de 10”. Los topes de moldura de
techo se pueden comprar como un accesorio.
Siga estas instrucciones para cortar moldura de techo en ángulo respecto a la mesa y al tope-guía.
1. Posicione la moldura de modo que la parte inferior (la parte que
se instala contra la pared) esté contra el tope-guía.
2. Ajuste el ángulo de inglete usando el cuadro 2. Apriete el pomo
de fijación de inglete (Figura 34).
3. Soporte la moldura de techo contra el tope-guía (vea “Posición
del cuerpo y de las manos” en la página 55).
4. Siga los procedimientos para corte de troceado o corte
deslizante (vea la página 60).
Figura 34. Moldura de techo en ángulo respecto a
la mesa y al tope-guía
5. Espere hasta que la hoja se detenga por completo antes de
volver a colocar el ensamblaje del cabezal en la posición subida
y/o retirar la pieza de trabajo.
NOTA: HAGA SIEMPRE UN CORTE DE PRUEBA USANDO MADERA DE
DESECHO PARA CONFIRMAR QUE LOS ANGULOS SON CORRECTOS.
CORTES DE MOLDURA DE TECHO - METODO DE CORTE NO. 2: EN ANGULO CON LA MESA Y EL TOPE-GUIA
TAMAÑO MAX: 101/4"
T
O
P
E
G
U
I
A
BORDE INFERIOR
52º
MESA
38º
P
A
R
E
D
52° TECHO
ANGULOS DE MOLDURA
EST. EE.UU.
ESQUINA
INTERIOR
C
A
B
D
ESQUINA
EXTERIOR
TIPO POSICION POSICION TIPO POSICION POSICION
DE DE INGLETE DE BISEL DE DE INGLETE DE BISEL
CORTE (MESA) (INCLINACION) CORTE (MESA) (INCLINACION)
ESQUINA INTERIOR
DERECHA
Lado Izquierda 45º 0º Lado Izquierda 45º 0º
CONSERVE EL EXTREMO DERECHO DEL CORTE CONSERVE EL EXTREMO DERECHO DEL CORTE
IZQUIERDO
Lado Derecho 45º 0º Lado Derecho 45º 0º
CONSERVE EL EXTREMO IZQUIERDO DEL CORTE CONSERVE EL EXTREMO IZQUIERDO DEL CORTE
ESQUINA EXTERIOR
DERECHA
CA
IZQUIERDO
DB
66.
Page 67

Operaciones de la sierra
Corte de material arqueado
Cortes especiales
!
ADVERTENCIA
con la cara exterior arqueada orientada hacia el tope-guía. Asegúrese
siempre de que no haya espacio libre entre la pieza de trabajo, el
tope-guía y la mesa a lo largo de la línea de corte. Las piezas de trabajo dobladas o combadas pueden torcerse u oscilar y pueden causar atasco en la hoja de sierra que gira durante el corte (Figura 35).
Si la pieza de trabajo está arqueada
o combada, fíjela con abrazadera
Abrazadera
para la pieza
de trabajo
No debe haber
espacio libre
en este punto
Material
arqueado
Figura 35. Material arqueado
Corte de material redondo o
que tenga forma irregular
!
ADVERTENCIA
siempre una abrazadera o un dispositivo de sujeción diseñado para
fijar la pieza de trabajo firmemente contra el tope-guía y la mesa.
Las varillas tienen tendencia a rodar mientras son cortadas, haciendo que la hoja “muerda” y tire de la pieza de trabajo con la mano del
operador hacia la hoja (Figura 36).
Para material redondo, tal como
varillas con espiga o tubos, use
Abrazadera
para la pieza
de trabajo
Tope-guía
Material
redondo
Figura 36. Material redondo
67.
Page 68

Mantenimiento y lubricación
Servicio
!
ADVERTENCIA
pude dar lugar a la colocación incorrecta de cables y componentes
internos que podría constituir un peligro serio. Recomendamos que
todo el servicio de las herramientas sea realizado por un Centro de
servicio de fábrica Bosch o por una Estación de servicio Bosch autorizada. Llame al 1-877-BOSCH99 para localizar un centro de servicio.
El mantenimiento preventivo realizado por personal no autorizado
Escobillas de carbón
Las escobillas y el conmutador de la herramienta han sido diseñados
para muchas horas de servicio confiable. Para mantener un rendimiento óptimo del motor, recomendamos que cada dos a seis meses se
examinen las escobillas. Sólo se deben usar escobillas de repuesto
Bosch genuinas diseñadas específicamente para su herramienta.
Cambio de las escobillas del motor
Para inspeccionar o cambiar las escobillas:
NOTA: Si instala la escobilla o escobillas existentes, asegúrese de
que la escobilla entre del mismo modo en que salió. De lo contrario, se producirá un período de rodaje que reducirá el rendimiento
del motor y aumentará el desgaste de las escobillas.
1. Desenchufe la sierra
!
PRECAUCION
blaje de las escobillas.
2. Quite la tapa de las escobillas que está en el motor usando un
destornillador de hoja plana ancha.
3. Tire de la escobilla para sacarla (Figura 37). Repita la operación
para el lado contrario.
4. Inspeccione las escobillas para comprobar si están desgastadas. En el lado ancho y plano de la escobilla hay una línea de
límite de desgaste. Si la cara de contacto de la escobilla está
en el limite o más allá de éste (no se ve la línea), cambie el
juego de escobillas.
5. Instale la escobilla nueva. Las dos (2) lengüetas del terminal de la escobilla van en el mismo agujero en que se acopla la pieza de carbón.
6. Apriete la tapa de las escobillas pero no la apriete demasiado.
La tapa de las escobillas está
accionada por resorte por el ensam-
erminal
de la escobilla
EscobillaT
Línea de
desgaste
Limpieza
!
ADVERTENCIA
de energía antes de la limpieza o de la realización de cualquier mantenimiento. La herramienta se puede limpiar más eficazmente con
aire comprimido seco. Use gafas de seguridad siempre que limpie
herramientas con aire comprimido.
Las aberturas de ventilación y las palancas de interruptor deben
mantenerse limpias y libres de materias extrañas. No intente limpiar introduciendo objetos puntiagudos a través de las aberturas.
Revise periódicamente para asegurarse de que el protector inferior y
todas las piezas móviles estén funcionando en forma adecuada.
Saque el serrín acumulado en las piezas que están trabajando, soplando con aire a presión o limpiando con un paño húmedo.
!
ADVERTENCIA
plástico. Algunos de estos son: gasolina, tetracloruro de carbono,
disolventes de limpieza clorados, amoníaco y detergentes domésticos que contienen amoníaco. No se debe usar nunca amoníaco en
aluminio.
Para evitar accidentes desconecte
siempre la herramienta de la fuente
Ciertos agentes de limpieza y
disolventes dañan las piezas de
Cuidado de las hojas
Las hojas se desafilan incluso al cortar madera normal. Si usted
tiene que forzar la sierra hacia adelante para que corte, en vez de
simplemente guiarla a través del corte, lo más probable es que la
hoja esté desafilada o cubierta de resina de madera.
Cuando limpie la hoja para quitarle la goma y la resina de madera,
desenchufe la sierra y quite la hoja. Recuerde, las hojas están diseñadas para cortar, así que manipúlelas cuidadosamente. Limpie la
hoja con queroseno o con un disolvente similar para eliminar la
goma y la resina. A menos que usted tenga experiencia en afilar
hojas, le recomendamos que no lo intente.
Lubricación de las herramientas
Su herramienta Bosch ha sido lubricada adecuadamente y está lista
para la utilización. Se recomienda que las herramientas con engranajes se vuelvan a engrasar con un lubricante especial para
engranajes en cada cambio de escobillas. Recomendamos que este
vicio sea realizado por un Centro de Ser
ser
o una Estación de Servicio Bosch autorizada. Llame al 1-877BOSCH99 para localizar un centro de servicio.
Lubrique periódicamente las piezas en movimiento con silicona, o un
rocío de aceite liviano. No utilice grasa porque tiende a atraer y retener el serrín.
vicio de Fábrica Bosch
Figura 37. Escobilla del motor
Cojinetes
odos los cojinetes de esta herramienta están lubricados con una
T
cantidad suficiente de lubricante de alto grado para la vida de la
unidad en circunstancias normales de funcionamiento. No se requiere lubricación adicional.
68.
Page 69

Localización y reparación de averías
Guía de localización y reparación de averías eléctricas
PROBLEMA
El freno no detiene la hoja al cabo de
5 segundos.
El motor no arranca.
CAUSA
1. Escobillas no asentadas o que se pegan
ligeramente o gastadas.
Motor recalentado debido al uso de una
2.
hoja desafilada o al uso demasiado pesado
de una hoja, al uso de un accesorio no
recomendado o a la realización de ciclos
rápidos de encendido y apagado.
3. Perno de la hoja flojo.
4. Otra.
1. Compruebe que la unidad esté enchufada.
2. Fusible de fuente de energía o de acción
retardada.
3. Escobillas desgastadas.
MEDIDA DE CORRECCION
• Inspeccione/limpie o cambie las escobillas (vea la sección Mantenimiento).
Use una hoja afilada.
•
• Use una hoja recomendada.
• Deje que la sierra se enfríe.
• Apriete el perno de la hoja.
• Servicio autorizado.
• Enchufe la unidad. Use otro
tomacorriente.
• Fusible de acción retardada o
cortacircuito de 15 A.
• Vea Cambio de las escobillas en la sección Mantenimiento y lubricación.
Se produce un destello de luz proveniente de
la tapa del extremo del motor cuando se
suelta el interruptor.
Nota: Para localizar un centro de servicio autorizado,
llame al 1-877-BOSCH99 (1-877-267-2499)
4. Otra.
1. Normal. El freno automático funciona
adecuadamente.
o visite www.boschtools.com.
• Servicio autorizado.
• No se requiere ninguna.
69.
Page 70

Localización y reparación de averías
Guía de localización y reparación de averías generales
PROBLEMA
La hoja golpea la mesa.
El ángulo de corte no es preciso.
No se puede mover el ajuste de ingletes.
El ensamblaje del cabezal no sube completamente o el protector de la hoja no se
cierra completamente.
La hoja se engancha, se atasca, quema la
madera. Cortes bastos.
CAUSA
1. Desalineación.
Desalineación.
1.
1. Pomo de fijación apretado/retén acoplado
2. Serrín debajo de la mesa.
3. La hoja interfiere con el tope-guía.
1. Acumulación de serrín.
2. No se apretó la placa de cubierta después
de cambiar la hoja.
3. Se necesita lubricación
4. Fallo de pieza.
5. Resorte del pivote o resorte del protector
no reinstalado apropiadamente.
1. Funcionamiento inadecuado.
2. Hoja desafilada.
MEDIDA DE CORRECCION
• Compruebe la instalación apropiada de la
• Servicio autorizado.
•
•
• Limpie el polvo por aspiración o con chorro de
• Extienda el tope-guía deslizante.
• Limpie el ensamblaje del cabezal.
• Vea Instalación de la hoja en la página 48.
• Lubrique el pasador de pivote del cabezal
• Servicio autorizado.
• Servicio autorizado.
• Vea la sección Operaciones básicas de la sierra.
• Cambie o afile la hoja.
hoja en la sierra
Vea la sección Ajustes.
Afloje el pomo de fijación/muévalo hacia
afuera del retén.
aire. Use protección para los ojos.
con un rocío de aceite ligero o usando
lubricante de silicona.
La herramienta vibra o tiembla.
El ensamblaje del cabezal no se mueve hasta
la posición de bisel de 45º.
La hoja no corta completamente
la pieza de trabajo.
El ensamblaje del cabezal no se desliza libremente al intentar un corte deslizante.
El ensamblaje del cabezal se desliza hacia
adelante y hacia atrás al hacer un corte de
troceado.
Tope-guía deslizante flojo
3. Hoja inadecuada.
4. Hoja doblada.
1. Hoja de sierra floja.
2. Hoja de sierra no equilibrada.
3. Hoja de sierra dañada.
4. Otra.
Retén de bisel de 33.9º desacoplado.
1. El tornillo del tope de profundidad está
ajustado para el corte de ranuras.
1. El pomo de fijación de los rieles de
deslizamiento está apretado.
1. El pomo de fijación de los rieles de
deslizamiento no está apretado.
Es necesario ajustar la palanca
• Cámbiela por una hoja de 10" de diámetro
diseñada para el material que se esté cortando.
• Cambie la hoja.
• Compruebe la instalación apropiada de la
hoja en la sierra (Consulte la página 48) o
reemplace la hoja.
• Cambie la hoja.
• Apriete el tornillo del eje portaherramienta.
• Servicio autorizado.
Gire el retén hasta una posición que no sea
•
de utilización (consulte la página 51).
• Vea Ajuste del tope de profundidad en la
sección Ajustes.
• Afloje el pomo de fijación de los rieles de
deslizamiento.
• Los alojamientos de deslizamiento
necesitan ajuste.
• Empuje el ensamblaje del cabezal completamente contra el tope. Apriete el pomo
de fijación de los rieles de deslizamiento.
• Apriete la palanca del tope-guía.
• Ajuste la tensión inferior
70.
Page 71

Localización y reparación de averías
Ajuste de la acción
de deslizamiento
!
ADVERTENCIA
cualquier ensamblaje, ajuste o reparación, para evitar posibles
lesiones.
Si la acción deslizante de la sierra para cortar ingletes no funciona
con facilidad, usted tendrá que hacer los ajustes necesarios para
corregirla. Utilice estas instrucciones para ajustar la acción
deslizante.
1. Localice los 4 tornillos de ajuste (A, B, C y D) ubicados en la
carcasa de la guía de los rieles.
2. Afloje las tuercas de los cuatro tornillos de ajuste con una
llave de tuerca ajustable. Afloje todos los tornillos de ajuste.
3. Apriete lentamente el tornillo de ajuste (B) con el extremo de
4 mm de la llave de tuerca para la hoja. Deténgase cuando
note que el tornillo toca el riel.
4. Apriete el tornillo de ajuste (B) aproximadamente 1/16 de
vuelta más.
5. Sujete el tornillo de ajuste (B) en esa posición y apriete la
tuerca. No deje que el tornillo de ajuste se mueva.
6. Apriete lentamente el tornillo de ajuste (D). Deténgase cuando note que el tornillo toca el riel.
7. Sujete el tornillo de ajuste (D) en esa posición y apriete la
tuerca. No deje que el tornillo de ajuste se mueva.
8. Apriete lentamente el tornillo de ajuste (A). Deténgase cuando note que el tornillo toca el riel.
9. Afloje el tornillo de ajuste (A) menos de 1/16 de vuelta.
10. Sujete el tornillo de ajuste (A) en esa posición y apriete la
tuerca. No deje que el tornillo de ajuste se mueva.
11. Repita los pasos 8-10 para el tornillo de ajuste (C).
Desconecte el enchufe de la fuente
de energía antes de realizar
C
A
B
D
Figura 38. Tornillos de ajuste
Figura 39. Ajuste y apriete el tornillo de ajuste
Ajuste de la tensión de la
palanca de fijación de bisel
1. Suba la palanca de fijación de bisel para soltar el cierre de
bisel.
2. Coloque una llave de tubo de 17 mm en la cabeza del perno
“E” (Figura 40).
Gire la tuer
3.
vuelta para aumentar la tensión del cierre de bisel o gírela en
sentido contrario al de las agujas del reloj 1/8 de vuelta para
reducir la tensión del cierre de bisel.
4. Empuje hacia abajo la palanca de fijación de bisel hasta que note
que la palanca se acopla a presión en la posición bloqueada.
5. Verifique que la tensión del cierre de bisel mantenga firme la
posición de bisel y también permita que la palanca de fijación
de bisel se bloquee hacia abajo hasta el punto en que se sienta un tope sólido.
6. Si es necesario, repita los pasos 1–5 para ajustar la tensión.
ca “E” en el sentido de las agujas del reloj 1/8 de
E
Figura 40. Ajuste de la tensión de
la palanca de fijación de bisel
71.
Page 72

Accesorios
Hojas diversas
Se ofrece una amplia gama de hojas de diversos materiales, configuraciones e inclinaciones de dientes para propor
correcta para diversas aplicaciones.
Hoja de 10" de 40 dientes con punta de carburo con enganche de
0° para separación de corte estrecha de BSA para eje portaherramienta de 5/8" (BB1040M)
Hoja de 10" de 40 dientes con punta de carburo con enganche de
13° para sección de corte estrecha de BSA para eje portaherramienta de 5/8" (BB1040M)
Hoja de 10" de 60 dientes con punta de carburo con enganche de
0° para sección de corte estrecha de BSA para eje portaherramieta de 5/8" (BB1060M)
Topes de moldura de techo (MS1233) Localizador de ingletes (DWM40LK)
cionar la hoja
Abrazadera de acción rápida (BA160)
Proporciona sujeción rápida de la pieza de trabajo.
Nota: Para localizar un centro de servicio autorizado,
llame al 1-877-BOSCH99 (1-877-267-2499)
o visite www.boschtools.com.
72.
Page 73

Notas
73.
Page 74

Sécurité
!
AVERTISSEMENT
querait de subir de graves blessures.
« LISEZ TOUTES LES INSTRUCTIONS » — L’utilisateur qui négligerait de suivre les CONSIGNES DE
SÉCURITÉ précédées d’un POINT NOIR (
Consignes générales de sécu-
rité pour les outils d’établi
Zone de travail
l Gardez la zone de travail propre et bien éclairée. Les étab
lis encombrés et les endroits sombres invitent les accidents.
l N’utilisez pas les outils électriques en atmosphères explo-
sives, comme en présence de poussière, de gaz ou de liquides inflammables.
celles qui peuvent enflammer la poussière ou les vapeurs.
l Gardez les spectateurs, les enfants et les visiteurs à l’écart
lorsque vous utilisez un outil électrique.
peuvent vous faire perdre le contrôle.
l Rangez les outils inutilisés hors de portée des enfants et
autres personnes sans formation à cet égard.
dangereux entre les mains d’utilisateurs non formés.
l Ne laissez pas l’outil en marche, sans surveillance, mettez
hors tension.
complet.
l RENDEZ L'ATELIER À L'ÉPREUVE DES ENFANTS à l'aide de
cadenas ou d'interrupteurs principaux, ou en retirant les clés
du démarreur.
l Avant de brancher l’outil à une prise de courant, assurez-
vous que la tension fournie correspond, à 10 % près, à celle
spécifiée sur la plaque signalétique.
incompatible avec celle spécifiée sur la plaque signalétique
risque de blesser sérieusement l’utilisateur sans mentionner
l’endommagement de l’outil.
Les outils électriques créent des étin-
Les distractions
Les outils sont
Ne laissez pas l’outil avant qu’il soit à l’arrêt
Sécurité électrique
Une tension de sortie
l) CI-DESSOUS et de prendre d’autres précautions élémentaires ris-
l N’exposez pas les outils électriques à la pluie ou à l’humi
’eau pénétrant dans un outil électrique augmentera le
dité.
L
risque de secousses électriques.
l N’abusez pas du cordon. N’utilisez jamais le cordon pour
transporter les outils et ne tirez pas la fiche d’une prise.
-
Tenez le cordon à l’écart de la chaleur, de l’huile, des
arêtes vives ou des pièces mobiles. Remplacez les cordons
abîmés immédiatement.
risque de secousses électriques.
l Lorsque vous utilisez un outil électrique à l’extérieur, utili-
sez un cordon de rallonge pour service extérieur marqué
« W-A » ou « W ».
extérieur et réduisent le risque de secousses électriques.
Les cordons abîmés augmentent le
Ces cordons sont prévus pour usage
Sécurité personnelle
l Demeurez vigilant, surveillez ce que vous faites et faites
preuve de discernement en utilisant un outil électrique.
moment d’inattention ou la prise de drogues, d’alcool ou de
médicaments peut s’avérer dangereux durant l’utilisation d’un
outil électrique.
l Portez des vêtements convenables. Ne portez pas de vête-
ments amples ni de bijoux. Pour les cheveux longs, nous
conseillons le port d’un serre-tête. Tenez les cheveux, les
vêtements et les gants à l’écart des pièces mobiles.
vêtements amples, les bijoux ou les cheveux longs risquent de
s’accrocher dans les pièces mobiles. Roulez les manches
longues au-dessus du coude. Le port de gants en caoutchouc
et de chaussures à semelle antidérapante est recommandé si
vous travaillez à l’extérieur.
l Évitez la mise en marche accidentelle. Assurez-vous que
avant de brancher
l’interrupteur est à l’
de l’outil avec le doigt sur l’interrupteur ou le branchement
d’outils dont l’interrupteur est à la position de MARCHE invite
les accidents.
ARRÊT
.
-
Un
Les
Le transport
l Les outils à double isolation sont pourvus d’une fiche pola-
risée (une lame est plus large que l’autre). Cette fiche ne
peut être insérée dans une prise polarisée que d’une seule
façon. Si la fiche ne s’insère pas à fond dans la prise, inver
sez la fiche. Si elle ne rentre toujours pas, contactez un
électricien qualifié pour faire poser une prise polarisée. Ne
modifiez la fiche d’aucune façon.
la nécessité d’un cordon mis à la terre à trois fils et d’une ali
mentation mise à la terre.
l Évitez tout contact corporel avec les surfaces mises à la
terre telles que tuyaux, radiateurs, cuisinières et réfrigérateurs.
électriques si votre corps est mis à la terre.
faces posent un risque accru de secousses
Ces sur
La double isolation élimine
« CONSERVEZ CES INSTRUCTIONS »
l Enlevez les clés de réglage et autres clés avant de mettre
l’outil en
-
-
rotative de l’outil sera projetée.
l Travaillez avec aplomb et équilibre à tout moment, ce qui
aide à mieux contrôler l’outil dans les cas imprévus.
l Ne montez pas sur l’outil ni sur son support. Des blessures
graves peuvent être causées en cas de basculement de l’outil
ou de contact accidentel avec l’outil de coupe. Ne conservez
pas de matériaux sur ou à proximité de l’outil de sorte qu’il soit
nécessaire de monter sur l’outil ou son support pour les atteindre.
MARCHE.
Une clé qui est laissée fixée à une pièce
74.
Page 75

Sécurité
!
AVERTISSEMENT
querait de subir de graves blessures.
l Utilisez l’équipement de sécurité. Portez toujours des lu-
nettes à coques latérales.
chaussures de sécurité, un casque dur ou des protège-oreilles
doivent être utilisés si la situation l’exige.
les jours comportent uniquement des verres résistant aux
chocs. Ce NE SONT PAS des lunettes de sécurité.
« LISEZ TOUTES LES INSTRUCTIONS » — L’utilisateur qui négligerait de suivre les CONSIGNES DE
SÉCURITÉ précédées d’un POINT NOIR (
Un masque anti-poussière, des
Les lunettes de tous
Utilisation et entretien de l’outil
l Utilisez des pinces ou autre façon pratique d’assujettir et de
supporter l’ouvrage à une plate-forme stable.
à la main ou contre son corps n’assure pas la stabilité voulue.
L’ouvrage peut ainsi se déplacer, faire gripper l’outil et vous
faire perdre le contrôle de l’outil.
l Ne forcez pas l’outil. Utilisez l’outil convenant à votre appli-
cation.
cement et plus sûrement à la vitesse à laquelle il est conçu.
N’utilisez pas l’outil à une fin autre que celle à laquelle il est
prévu — ainsi, n’utilisez pas la scie à onglet pour trancher les
viandes.
l N’utilisez pas l’outil si l’interrupteur ne le met pas en MARCHE
et à l’ARRÊT.
l’interrupteur est dangereux.
l Débranchez la fiche de la prise de courant avant d’effectuer
tout réglage ou de changer les accessoires.
préventives réduisent le risque d’une mise en marche accidentelle.
l Gardez les outils de coupe affilés et propres. Des outils bien
entretenus, avec tranchants affilés, sont moins susceptibles
de gripper et plus faciles à contrôler. Lorsque vous montez
des lames de scie, assurez-vous que la flèche de la lame correspond au sens de la flèche marquée sur l’outil et que les
dents pointent également dans le même sens.
l Inspectez les protecteurs avant d’utiliser un outil. Gardez les
protecteurs en place. V
ou tout autre état pouvant influer sur le fonctionnement normal ou les fonctions de sécurité de l’outil. Si l’outil est abîmé, faites-le réparer avant de l’utiliser.
sont causés par des outils mal entretenus.
l Ne modifiez pas l’outil et n’en faites pas un usage inap
proprié.
inapproprié et peut causer des blessures graves.
l L’utilisation de tout autre accessoire non précisé dans ce
manuel peut créer un danger.
être adéquats pour un type d’outil peuvent devenir dangereux
lorsqu’ils sont utilisés sur un outil inapproprié.
L’outil convenable exécutera le travail plus effica-
Tout outil qui ne peut être commandé par
érifiez si les pièces mobiles grippent
Toute altération ou modification constitue un usage
Les accessoires qui peuvent
Tenir l’ouvrage
Ces mesures
Beaucoup d’accidents
l) CI-DESSOUS et de prendre d’autres précautions élémentaires ris-
Réparation
’outil ne doit être réparé que par des techniciens de répa-
l L
ration qualifiés.
des personnes non qualifiées peuvent résulter en un positionnement erroné de composants et de fils internes, ce qui
peut provoquer des dangers sérieux.
l N’utilisez que des pièces de rechange identiques pour
réparer un outil. Suivez les consignes contenues dans la
section Entretien de ce manuel.
autorisées ou le non-respect des consignes d’entretien peut
être dangereux.
Les réparations ou l’entretien effectués par
L’utilisation de pièces non
Consignes de sécurité
pour les scies à onglet
l Utilisez des pinces pour supporter l’ouvrage chaque fois que
possible. Si vous supportez l’ouvrage à la main, vous devez
toujours garder la main à l’extérieur de la zone interdite aux
mains, identifiée par un symbole sur la base. N’utilisez pas
cette scie pour couper des pièces qui sont trop petites pour
être bien assujetties.
interdite aux mains, votre main peut glisser facilement ou être
tirée dans la lame.
l N’insérez pas la main à l’arrière de la lame de scie, derrière
le guide, pour tenir ou supporter l’ouvrage, enlever des
débris de bois ou toute autre raison.
de scie en rotation à votre main peut ne pas être évidente, et
vous pourriez être grièvement blessé.
l Ne passez jamais la main à travers la ligne de coupe
prévue.
croisée, à savoir, en tenant le côté gauche de l’ouvrage avec
votre main droite.
l Débranchez toujours le cordon de la prise de courant avant
d’effectuer quelque réglage que ce soit ou de poser des
accessoires.
garde, et être blessé grièvement.
l Les scies à onglet sont destinées principalement à couper le
-
bois ou des produits similaires ; on ne peut les utiliser avec
des meules à tronçonner pour couper des matériaux ferreux
tels que barres, tiges, poteaux, etc. Cependant, pour couper
des matériaux tels que l’aluminium ou autres métaux non
ferreux, utilisez uniquement des lames de scie recomman
dées spécifiquement pour la coupe de métaux non ferreux.
La coupe de matériaux ferreux forme une quantité excessive
d’étincelles et abîmera le protecteur inférieur en plus de créer
une sur
Company n’offre pas de lames de 10 po pour couper les
métaux.)
Il est très dangereux de supporter l’ouvrage à main
Vous pouvez mettre la scie en marche par mé-
charge sur le moteur
Si elle est placée à l’intérieur de la zone
La proximité de la lame
. (REMARQUE
: Bosch Power T
-
ool
« CONSERVEZ CES INSTRUCTIONS »
75.
Page 76

Sécurité
!
AVERTISSEMENT
« LISEZ TOUTES LES INSTRUCTIONS » — L’utilisateur qui négligerait de suivre les CONSIGNES DE
SÉCURITÉ précédées d’un POINT NOIR (
querait de subir de graves blessures.
l Inspectez votre ouvrage avant de couper. Si l’ouvrage est
cintré ou gondolé, pincez-le avec la face cintrée extérieure
dirigée vers le guide. Assurez-vous toujours qu’il n’y a pas
d’écartement entre l’ouvrage, le guide et la table le long de
la ligne de coupe.
Les ouvrages pliés ou gondolés peuvent se
tordre ou culbuter, et peuvent faire gripper la lame de scie en
rotation durant la coupe. Assurez-vous également de l’absence
de clous ou de corps étrangers dans l’ouvrage.
l N’utilisez pas la scie tant que la table n’est pas libérée de
tous outils, débris de bois, etc, sauf l’ouvrage.
Les petits
débris ou pièces détachées de bois ou autres objets venant en
contact avec la lame en rotation peuvent être projetés à haute
vitesse en direction de l’opérateur.
l N’introduisez pas l’ouvrage dans la lame et ne coupez d’au-
cune manière à « main libre ». L’ouvrage doit être fixe et
cramponné ou serré par votre main.
La scie doit être insérée
à travers l’ouvrage doucement et à une vitesse qui ne surchargera pas le moteur de la scie.
l Coupez un seul ouvrage à la fois. Les ouvrages multiples ne
peuvent être cramponnés ou serrés adéquatement, et ils peuvent gripper sur la lame ou se déplacer durant la coupe.
l Assurez-vous que la scie à onglet est montée ou placée sur
une surface de travail ferme et à niveau avant de l’utiliser.
Une surface de travail ferme et à niveau réduit le risque d’instabilité de la scie à onglet.
l Planifiez votre travail. Obtenez des accessoires de support
adéquats tels que tables, chevalets de scieur, rallonge de
table, etc. pour les ouvrages plus larges ou plus longs que
le dessus de la table (voir page 88).
Les ouvrages plus longs
ou plus larges que la table de la scie à onglet peuvent basculer
s’ils ne sont pas supportés adéquatement. Si la pièce tronçonnée ou l’ouvrage bascule, il peut lever le protecteur inférieur
ou être projeté par la lame en rotation.
l N’utilisez pas une autre personne en remplacement d’une
rallonge de table ou comme support supplémentaire.
Un
support instable de l’ouvrage peut faire gripper la lame ou
déplacer l’ouvrage durant la coupe, tirant ainsi votre assistant
et vous-même dans la lame en rotation.
l La pièce tronçonnée ne doit pas être bloquée contre la lame
de scie en rotation ni être pressée par aucun autre moyen
contre celle-ci.
Si elle est captive, en utilisant des butées de
longueur, par exemple, elle pourrait être coincée contre la lame
et être projetée violemment.
l Utilisez toujours un serre-joints ou un dispositif conçu de
manière à supporter adéquatement les matériaux ronds tels
que les goujons ou les tubes.
Les goujons ont tendance à
rouler pendant qu’on les coupe, ce qui amène la lame à « mordre » et tire l’ouvrage et votre main dans la lame.
l En coupant des ouvrages de forme irrégulière, planifiez
votre travail de manière à ce que l’ouvrage ne glisse pas et
ne vienne pas pincer la lame, pour être ensuite tiré de votre
l) CI-DESSOUS et de prendre d’autres précautions élémentaires ris-
main.
Une pièce de moulure doit ainsi être posée à plat et être
tenue par un dispositif ou une monture qui l’empêchera de tordre, basculer ou glisser pendant la coupe.
l Laissez la lame atteindre une vitesse maximum avant de la
mettre en contact avec l’ouvrage.
Ceci aidera à éviter la pro
jection d’ouvrages.
l Si l’ouvrage ou la lame se bloque ou se coince, mettez la
scie à onglet à l’ARRÊT en relâchant l’interrupteur. Attendez
que toutes les pièces mobiles s’arrêtent et débranchez la
scie à onglet avant de libérer les matériaux coincés.
Le fait
de continuer à scier avec l’ouvrage coincé pourrait entraîner
une perte de contrôle ou des dommages à la scie à onglet
composée.
l La tête de scie est secouée vers le bas sous l’effet de l’ac-
tion de freinage de la scie. Soyez prêt à cette réaction
en
pratiquant une coupe incomplète ou en relâchant l’interrupteur
avant que la tête ne soit complètement descendue.
l Après avoir terminé la coupe, relâchez l’interrupteur, tenez
le bras de la scie en bas et attendez que la lame s’arrête
avant de retirer l’ouvrage ou la pièce tronçonnée. Si la lame
ne s’arrête pas dans un délai de cinq (5) secondes, débranchez la scie et suivez les consignes apparaissant dans la
section Dépannage.
IL EST DANGEREUX D’INSÉRER LA
MAIN SOUS UNE LAME EN TRAIN DE S’IMMOBILISER.
l Il existe des consignes de sécurité supplémentaires pour
les opérations particulières de la scie dans la section relative au fonctionnement. Lisez le reste du manuel pour une
utilisation sûre de la scie.
l Pour une coupe à action coulissante, TIREZ d’abord
l’ensemble de tête de scie à l’écart du guide, jusqu’à ce
que la lame dégage l’ouvrage ou jusqu’à son prolongement
maximum si la lame ne peut dégager l’ouvrage. Assurezvous que le serre-joint ne gêne pas l’ensemble de protecteur et tête. Mettez ensuite la scie en MARCHE et abaissez la scie jusqu’à la table. POUSSEZ alors la scie à travers
l’ouvrage. Relâchez l’interrupteur et attendez que la lame
s’arrête complètement avant de relever l’ensemble de tête
et de retirer l’ouvrage. Ne jamais « coupez en tirant » car la
lame peut grimper sur l’ouvrage causant ainsi un REBOND.
l Pour une coupe à action de fente, faites glisser l’ensemble
de tête vers l’arrière aussi loin que possible et serrez le
bouton de blocage de glissière. Mettez ensuite la scie en
MARCHE
et abaissez l’ensemble de tête pour pratiquer la
coupe. Relâchez l’interrupteur et attendez que la lame s’arrête complètement avant de relever l’ensemble de tête et
de retirer l’ouvrage.
Si le bouton de blocage de glissière n’est
pas serré, la lame peut soudainement grimper sur le dessus
de l’ouvrage et for
cer son chemin vers vous.
-
« CONSERVEZ CES INSTRUCTIONS »
76.
Page 77

Sécurité
!
AVERTISSEMENT
querait de subir de graves blessures.
l Ne laissez pas la familiarité tirée d’une utilisation
fréquente de votre scie à onglet atténuer votre vigilance.
N’oubliez jamais qu’une fraction de seconde d’insouciance
suffit à causer des blessures graves.
l PENSEZ EN TERMES DE SÉCURITÉ. LA SÉCURITÉ EST UNE
COMBINAISON DE BON SENS, DE CONNAISSANCE DES
CONSIGNES DE SÉCURITÉ ET DE FONCTIONNEMENT, ET DE
VILIGANCE CONSTANTE DE LA PART DE L’OPÉRATEUR LORS
DE L’UTILISATION DE LA SCIE À ONGLET.
!
AVERTISSEMENT
CES AVERTISSEMENTS NE SONT QU’UNE FORME CONDENSÉE
DES RÈGLES ET PRÉCAUTIONS DE SÉCURITÉ PLUS DÉTAILLÉES
QUI APPARAISSENT DANS VOTRE MANUEL. ELLES SERVENT À
VOUS RAPPELER TOUTES LES RÈGLES DE SÉCURITÉ
NÉCESSAIRES À UNE UTILISATION SÛRE DE CETTE SCIE À
ONGLET.
« LISEZ TOUTES LES INSTRUCTIONS » — L’utilisateur qui négligerait de suivre les CONSIGNES DE
SÉCURITÉ précédées d’un
LES AVERTISSEMENTS CI-APRÈS
SE TROUVENT SUR VOTRE OUTIL.
POINT NOIR (
CI-DESSOUS et de prendre d’autres précautions élémentaires ris-
l)
!
AVERTISSEMENT
et autres travaux du bâtiment peuvent créer des poussières con
tenant des produits chimiques qui sont des causes reconnues de
cancer, de malformation congénitale ou d’autres problèmes
reproductifs. Ces produits chimiques sont, par exemple :
• Le plomb provenant des peintures à base de plomb,
• Les cristaux de silices provenant des briques et du ciment et
d’autres produits de maçonnerie, et
• L’arsenic et le chrome provenant des bois traités chimiquement
Le niveau de risque dû à cette exposition varie avec la fréquence de
ces types de travaux. Pour réduire l’exposition à ces produits chimiques, il faut travailler dans un lieu bien ventilé et porter un
équipement de sécurité approprié tel que certains masques à poussière conçus spécialement pour filtrer les particules microscopiques.
Les travaux à la machine tel que
ponçage, sciage, meulage, perçage
-
ZONE DÉSIGNÉE DE
DANGER. ÉVITER DE
PLACER LES MAINS, LES
DOIGTS OU LES BRAS
DANS LA ZONE DÉSIGNÉE
PAR CE SYMBOLE.
« CONSERVEZ CES INSTRUCTIONS »
77.
Page 78

Sécurité
!
AVERTISSEMENT
subir de graves blessures.
« LISEZ TOUTES LES INSTRUCTIONS » — L’utilisateur qui négligerait de suivre les CONSIGNES DE SÉCURITÉ
précédées d’un POINT NOIR (
l) CI-DESSOUS et de prendre d’autres précautions élémentaires risquerait de
Double isolation
La double isolation est utilisée dans les outils électriques pour
éliminer le besoin de cordon d’alimentation avec prise de terre et de
dispositif d’alimentation à prise de terre. Elle est homologuée par
l’Underwriter’s Laboratories, l’ACNOR et l’OSHA.
l L’entretien d’un outil à double isolation exige la connaisance du
système et la compétence d’un technicien qualifié.
l EN CAS D’ENTRETIEN, N’UTILISEZ QUE DES PIÈCES DE
RECHANGE IDENTIQUES.
l FICHES POLARISÉES. Si votre outil est équipé d’une fiche
polarisée (une lame plus large que l’autre) elle ne s’enfiche que
d’une manière dans une prise polarisée. Si la fiche n’entre pas à
fond dans la prise, tournez-la d’un demi-tour. Si elle refuse
encore d’entrer, demandez à un électricien qualifié d’installer
une prise appropriée. Ne modifiez la fiche d’aucune façon.
Rallonges
l Remplacez immédiatement toute rallonge endommagée.
L’utilisation de rallonges endommagées risque de provoquer
un choc électrique, des brûlures ou l’électrocution.
l En cas de besoin d’une rallonge, utilisez un cordon de calibre
satisfaisant pour éviter toute chute de tension, perte de courant
chauffe. Le tableau ci-contre indique le calibre des ral-
ou sur
longes recommandées en fonction de leur longueur et de l’in
tensité indiquée sur la plaque du constructeur de l’outil. En cas
de doute, optez pour le prochain calibre inférieur. Utilisez toujours des rallonges homologuées par l’U.L. et l’ACNOR.
DIMENSIONS DE RALLONGES RECOMMANDÉES
Intensité
nominale
de l’outil
3-6
6-8
8-10
10-12
12-16
OUTILS 120 VOLTS C.A.
Longueur en pieds
Calibre A.W.G.
25 50 100 150
18 16 16 14
18 16 14 12
18 16 14 12
16 16 14 12
14 12 S/O S/O
-
« CONSERVEZ CES INSTRUCTIONS »
Table des matières
Sécurité . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Consignes générales de sécurité pour les
outils d’établi . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .74
Consignes de sécurité pour les scies à onglet . . . . . . . . . .75-78
able des matières
T
Spécifications électriques . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .79
Familiarisez-vous avec votre scie à onglet . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Assemblage . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .82-84
Outils nécessaires à l’assemblage et à l’alignement . . . . . . . . .82
Déballage et vérification du contenu . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .82
Fixation du bouton de blocage d'onglet
Assemblage du coude de poussière et du sac à poussière . . . .83
Pose et dépose de la lame . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .84
Réglages . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Lame d’équerre par rapport à la table (90
Lame à 45° par rapport à la table . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .86
Lame à 33.9° par rapport à la table . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .87
Lame d’équerre par rapport au guide . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .88
Réglage de l’indicateur d’échelle d’onglet . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .88
Installation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .89-90
Applications de montage
Montage portatif à l’aide de serre-joints
Réglage de la barre de stabilisation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .90
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .83
°) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .85
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .90
74-78
78
80-81
85-88
89
REMARQUE : Plus le calibre est petit, plus le fil est gros.
Opérations de base de la scie . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Position du corps et des mains . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .91
Support de l’ouvrage . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .92
Guide auxiliaire . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .93
Actionnement de l’interrupteur . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .93
Court-circuitage du cran d’arrêt . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .94
Rallonge de base/guide à glissière
Opérations de la scie . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .96-103
Coupe de fente
Coupe par glissement
Coupe à l’onglet . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .97
Coupe en biseau . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .97-98
Coupes composées . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .98
Coupe de rainures . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .99
Coupe de moulures de base
Coupe de moulures en couronne . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .100-102
Coupes spéciales . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .103
Maintenance et lubrification . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Dépannage . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .105-107
Réglage de l'action coulissante . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .107
Réglage de la tension du levier de blocage de biseau . . . . .107
Accessoires . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .94-95
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .100
91-95
96
96
104
108
78.
Page 79

Spécifications électriques
1. Branchez cette scie sur un circuit de dérivation de 120 V, 15 A
avec disjoncteur ou fusible à action différée de 15 A. L
sation du mauvais type de fusible peut abîmer le moteur
2. Les fusibles peuvent sauter ou les disjoncteurs peuvent se
déclencher souvent si le moteur est surchargé. Une surcharge
est possible si vous faites pénétrer la lame trop rapidement
dans l'ouvrage, si vous commencez et arrêtez le travail trop
souvent en très peu de temps ou si vous utilisez une lame
inappropriée pour votre application.
La plupart des problèmes affectant le moteur sont imputables
3.
à des connexions lâches ou incorrectes, à une sur
une tension basse (en conséquence de fils de petit calibre
dans le circuit d'alimentation ou de fils trop longs dans le circuit d'alimentation). Vérifiez toujours les connexions, la
charge et le circuit d'alimentation lorsque le moteur ne fonctionne pas bien.
’utili.
charge, à
Frein électrique
Votre scie est équipée d’un frein électrique automatique qui est
conçu de manière à empêcher la lame de tourner environ cinq (5)
secondes après que vous ayez relâché la gâchette de commande.
Cette particularité est utile pour pratiquer certaines coupes dans le
bois alors qu’une lame qui se déplace par inertie entraînerait une
coupe large et imprécise.
!
AVERTISSEMENT
causes, le moteur ralentit progressivement et l’action de freinage
est amorcée UNIQUEMENT par le relâchement de la gâchette de
commande.
Le frein électrique de lame de votre scie a été conçu en vue du plus
haut niveau de fiabilité, mais il se peut que le frein ne soit pas actionné sous l’effet de circonstances imprévues telles que la contamination sur le commutateur et les balais ou la défaillance des composants du moteur. Dans ce cas, mettez la scie en MARCHE et à
l’ARRÊT quatre ou cinq fois en évitant tout contact entre la scie et le
matériau. Si l’outil fonctionne mais le frein n’arrête pas uniformément la lame en environ cinq (5) secondes, N’utilisez P
et faites-la réparer immédiatement.
!
AVERTISSEMENT
de sécurité. N’oubliez pas de laisser la lame de scie s’arrêter complètement avant de la retirer du matériau. Comme toujours, le système de protecteurs constitue la meilleure façon d’éviter le contact
accidentel avec une lame de scie qui tourne. Vous ne devez JAMAIS
ouvrir en forçant ni empêcher l’action de fermeture du protecteur
inférieur.
Lorsqu’il y a panne de courant en
raison d’un fusible grillé ou d’autres
AS la scie
L’action de freinage de cette scie
n’est pas destinée à servir de mesure
79.
Page 80

Familiarisez-vous avec votre scie à onglet
1
4
30
2
40
3
28
20
16
41
19
32
25
22
29
5
26
27
6
23
21
24
7
8
18
7
9
40
12
18
14
15
17
16
!
AVERTISSEMENT
débranchez la fiche de la prise de courant avant d’effectuer quelque
réglage que ce soit.
1. Bouton de blocage à l’arrêt « Lock-OFF »
On doit appuyer sur ce bouton pour actionner l’interrupteur.
Interrupteur
2.
’interrupteur utilisé avec le bouton de blocage à l’arrêt « Lock-OFF »
L
met la scie sous tension.
3. Poignée-interrupteur
Cette poignée contient l’interrupteur. La lame est abaissée dans l’ouvrage en poussant/tirant la poignée vers le bas. Ne saisissez jamais
l'outil par la poignée contenant l'interrupteur.
Pour éviter les blessures résultant
d’une mise en mar
che accidentelle,
43
34
11
13
4. Blocage d’arbre
Permet à l’utilisateur d’empêcher la lame de tourner tout en serrant
ou desserrant la vis de l’arbre durant le remplacement ou la dépose
de la lame
Protecteur inférieur de lame/rebord de protecteur inférieur
5.
Le protecteur inférieur de lame aide à protéger vos mains contre la
lame en rotation. Il se rétracte au fur et à mesure que la lame est
abaissée. Le rebord du dispositif de protection peut être utilisé
pour élever à la main le dispositif de protection inférieur, seulement conformément aux recommandations de ce manuel.
6. Lame
Utilisez uniquement des lames de 10 po d'une épaisseur comprise
entre 1,4 et 3,0 mm, avec un trou d'arbre de 5/8 po.
80.
10
Page 81

Familiarisez-vous avec votre scie à onglet
7. Guide fixe
Supporte l’ouvrage. Le guide possède une échelle graduée incorporée
pour faciliter les coupes à répétition. Le guide comporte également
des trous qui servent à fixer un guide auxiliaire, si désiré.
Inserts d’encoche
8.
9. Court-circuitage du cran d’arrêt d’onglet
Permet d'inhiber le cran d'arrêt et d'effectuer ainsi des réglages fins
à tout angle d'onglet.
10. Bouton de blocage d’onglet
Le bouton de blocage d’onglet bloque la table de la scie à onglet à
tout angle d’onglet désiré.
Gâchette de cran d’arrêt d’onglet
11.
La gâchette libère la table du cran d’arrêt.
12. Indicateur d’angle d’onglet/échelle d’onglet
L'échelle est moulée dans la base de la scie. L’indicateur est fixé à
la table.
13. Crans d’arrêt d’onglet
Il existe dix (10) crans d’arrêt d’onglet en vue de coupes rapides et
exactes d’angles courants d’onglet.
14. Table
Repose dans la base, supporte l’ouvrage, tourne pour coupes à
onglet désirées et tourne la tête. La partie avant prolongée de la
table est appelée le bras d’onglet.
15. Base
Assure une surface de travail pour supporter l’ouvrage.
16. Coussinets de montage de l’outil
17. Leviers de cramponnage des rallonges de la base
Verrouille les rallonges de la base en place. Un pour chaque extension.
18. Tiges de rallonge
Ajoute du support pour les ouvrages longs.
19. Guide coulissant
Offre une surface plus grande de support et de cramponnage pour
les scies à onglet composées.
20. Levier de cramponnage du guide coulissant
Verrouille le guide coulissant en place
21. Déflecteur de copeaux avec pan de retenue
Ce déflecteur empêche les gros copeaux de pénétrer dans le protecteur supérieur.
22. Coude de chute de poussière
Le coude de chute de poussière tourne sur 360° et peut recevoir le
sac à poussière ou un raccord de flexible d'aspiration.
23. Butée de biseau de 0°
Butée réglable pour un repère rapide et exact de biseau de 0
24. Butée de biseau de 33.9°
Butée réglable pour un repère rapide et exact de biseau de 33.9°.
25. Butée de biseau de 45°
Butée réglable pour un repère rapide et exact de biseau de 45°.
Bouton de blocage de rail coulissant
26.
Le bouton de blocage de rail coulissant bloque les rails coulissants
lorsque vous ne pratiquez pas de coupes par glissement et lorsque
vous transportez la scie.
Rails coulissants
27.
Guident l’ensemble de tête lorsque vous pratiquez des coupes par glissement.
Serre-joint d'ouvrage
28.
Permet un cramponnage rapide de l’ouvrage.
29. Raccord d’actionnement du protecteur inférieur
Permet un mouvement en douceur du protecteur inférieur
30. Protecteur supérieur de lame
Couvre la partie supérieure de la lame.
31. Clé à lame
Utilisé pour serrer/desserrer la lame et pour régler le guide et les
blocs de glissement. La clé à lame est rangée à l'arrière de la scie.
.
°
.
2
38
37
36
42
33
32
39
33
16
35
31
16
32. Cordon d’alimentation
Fournit le courant au moteur. Possède un dispositif moulé de
retenue de cordon pour le rangement.
33. Positions du Serre-joint d'ouvrage
Il existe trois (3) positions possibles derrière le guide pour le serrejoint de l'ouvrage.
34. Levier de blocage de biseau
La poignée de blocage de biseau bloque la tête à l’angle de biseau
désiré. Cliquets de poignée pour usage dans les espaces restreints.
35. Échelle graduée de biseau
Indicateur utilisé pour régler les angles de biseau
36. Cheville de blocage de tête
La scie est pourvue d'une cheville de blocage servant à bloquer la
tête en position abaissée. Cette cheville doit être verrouillée en position abaissée pendant le transport.
Butée de profondeur
37.
ous permet de régler la profondeur de la lame pour pratiquer des
V
rainures dans l’ouvrage.
38. Capuchons de balai
Ces capuchons gardent les balais de moteur en place et facilitent
l’accès pour inspection et remplacement des balais.
39. Plaque de recouvrement du guide coulissant
Faites tourner la plaque de recouvrement pour retirer le guide.
40. Poignées de transport
41. Bossages de butées pour moulures en couronnes
Permettent l'utilisation des butées pour moulures de couronnes de
Bosch.
42. Rembobineur de cordon
Fournit un endroit où ranger le cordon d'alimentation.
43. Barre de stabilisation
Fournit un soutien pour le bout de la table.
44. Boulon de pivotement
Serrez/desserrez pour régler la tension de biseau.
45. Écrou de blocage de biseau
Règle la force de cramponnage du blocage de biseau.
44 45
81.
Page 82

Assemblage
Outils nécessaires à l’assemblage et à l’alignement
Tournevis à empreinte cruciforme
Équerre à combinaison
Il ne doit y avoir aucun écartement
ou chevauchement lorsque l’équerre
est renversée à la position en tirets.
!
AVERTISSEMENT
Débranchez la fiche de la prise de courant avant d’effectuer tout assemblage, réglage ou réparation pour éviter
d’éventuelles blessures.
Déballage et vérification du contenu
Clé à lame (fournie), clé hexagonale
de l'autre côté du tournevis à
empreinte cruciforme
L’équerre à combinaison doit être vraie.
Tracez une ligne délicate sur la planche le
long de ce bord.
Bord droit de la planche
3/4 po d’épaisseur
Ce bord doit être parfaitement droit.
La scie à onglet composée, à glissière, modèle 4405 est expédiée
complète dans une boîte.
1. Séparez toutes les pièces des matériaux d’emballage et vérifiez chacune à l’aide de la « Liste des pièces détachées » pour
vous assurer de la présence de toutes les pièces avant de jeter
tout matériel d’emballage.
2. Pièces détachées : (Voir pages 80 et 81)
Ferrure de fixation
Sac à poussière/coude de poussière
Bouton de blocage d'onglet
Téléphonez au 1-877-BOSCH99 si vous avez besoin d'assistance.
!
AVERTISSEMENT
pas l’interrupteur à la position de marche avant d’avoir obtenu les
pièces manquantes et de les avoir posées correctement.
éléphonez au 1-877-BOSCH99 pour obtenir les pièces man
T
quantes.
!
AVERTISSEMENT
position 45°. Bloquez la poignée de blocage de biseau. Tirez la tête
entièrement vers l’avant vers vous et serrez le bouton de blocage
des rails coulissants. Bloquez la tête à la position abaissée.
Ne transportez jamais l’outil par les rails coulissants, ce qui
pourrait causer un défaut d’alignement de lame.
Ne transportez jamais l'outil par le cordon ou par la poignée contenant l'interrupteur de la tête. L'endommagement de l'isolation
risquerait de provoquer des chocs électriques. L'endommagement
des connexions de fils risquerait de provoquer un incendie.
Si des pièces manquent, ne
branchez pas le cordon et ne mettez
vant de déplacer la scie : bloquez
A
le bouton de blocage de l’onglet à la
82.
-
Page 83

Assemblage
Fixation du bouton de
blocage d'onglet
Localisez le bouton de blocage d'onglet parmi les pièces détachées
et enfilez l'arbre dans l'ensemble de cran d'arrêt d'onglet comme
illustré à la Figure 4.
Assemblage du coude de poussière et du sac à poussière
1. Poussez le coude de poussière sur la buse à poussière.
Tournez le coude à la position désirée. (Figure 4)
Arbre
Figure 4: Bouton de blocage du guide d'onglet
2. Le sac à poussière se fixe sur le coude de chute à poussière et
sert à recueillir le bran de scie. Le coude à poussière peut également être fixé à un tube d’aspiration standard de 2 po pour collecte de la poussière.
3. Positionnez le coude/sac à poussière de manière à ce qu’il ne
gêne pas l’outil durant la coupe pour tous les réglages d’onglet
et de biseau. Assurez-vous que le sac à poussière ne gêne pas
les rails coulissants durant la coupe par glissement.
Bouton de blocage
du guide d'onglet
Sac à
poussière
Coude de
poussière
Figure 5. Coude et sac à poussière
Buse à
poussière
4. Le sac doit être vidé lorsqu’il est plein de bran de scie. Videz-le
souvent et après avoir fini de scier. Retirez soigneusement le
sac à poussière du coude à poussière. Videz le sac à poussière
dans une poubelle appropriée en ouvrant la fermeture à glissière du sac. Faites particulièrement attention à la poussière
mise au rebut, car les fines particules de matières peuvent être
explosives. Ne jetez pas de bran de scie dans un feu ouvert. Au
bout d'un certain temps, une combustion spontanée peut être
causée par le mélange d'huile ou d'eau avec des particules de
poussière.
!
AVERTISSEMENT
sion, de la peinture pouvant être à base de plomb ou tout autre
matériau pouvant contenir des agents cancérigènes. Un respirateur
adéquat doit être porté par tous les personnes pénétrant dans l’aire
de travail. Les zones de travail doivent être enveloppées par des
feuilles de plastique et les personnes qui ne sont pas protégées
doivent être empêchées d'entrer dans les zones de travail tant que
celles-ci n'auront pas été complètement nettoyées.
Redoublez de prudence en sciant du
bois traité chimiquement sous pres-
83.
Page 84

Assemblage
Pose et dépose de la lame
!
AVERTISSEMENT
ou réparation pour éviter d’éventuelles blessures.
1. Desserrez la vis arrière de la plaque de recouvrement d'un tour complet.
Ne retirez pas complètement la vis.
2. Desserrez la vis de la plaque de recouvrement avant (d'environ trois
tours complets) jusqu'à ce qu'elle dépasse de la languette de la plaque
de recouvrement ; mais ne retirez pas complètement la vis. Faites tourn
er la plaque de recouvrement dans le sens contraire des aiguilles d'une
montre afin d'exposer la région de la lame et du boulon de l'arbre.
3. Faites tourner le dispositif de protection à la main pour libérer la lame.
Laissez le dispositif de protection de côté. Le plastique sera maintenu à
un endroit non gênant par la vis avant.
Appuyez sur le blocage de l’arbre et tenez celui-ci. Il peut être nécessaire
4.
de faire tourner la lame pour permettre l'enclenchement du dispositif de
blocage de l'arbre. Utilisez la clé à lame pour déposer le boulon de lame
en tournant la clé en sens horaire. REMARQUE : Le boulon de lame
présente un filet gauche.
Figure 1. Dépose de la lame
Retirez le boulon de lame, la rondelle de l’arbre, la rondelle
5.
extérieure et la lame. Il n’est pas nécessaire de retirer la rondelle
intérieure (Figure 2).
Boulon de lame
(filet gauche)
Rondelle extérieure Rondelle intérieure
Rondelle de l’arbre
Lame de scie
Débranchez la fiche de la prise de courant
avant d’effectuer tout assemblage, réglage
Protecteur inférieur
Vis avant
de la plaque
de recouvrement
Tournez le boulon
dans ce sens pour
desserrer
Rondelle
extérieure
Déflecteur
de copeaux
Boulon de retenue
de la lame (à tête
hexagonale)
6. Pour poser la lame de 10 po, insérez la lame entre les déflecteurs
de copeaux et sur la tige de l’arbre (Figure 3). REMARQUE
Assurez-vous que la flèche de rotation de la lame correspond à la
flèche de rotation en sens horaire sur le protecteur inférieur.
-
Figure 3. Pose de lame
!
AVERTISSEMENT
moins que 10 po de diamètre et arbre de 5/8 po.
7. Remplacez la rondelle extérieure et la rondelle de l'arbre, et serrez le boulon de retenue de la lame à fond à la main dans le sens
contraire des aiguilles d'une montre. (Figure 2). Appuyez sur le
blocage de l’arbre et serrez le boulon de lame fermement, à
l’aide d’une clé à lame, sans serrer excessivement.
Faites tourner la plaque de recouvrement dans le sens des aigu
8.
illes d'une montre jusqu'à ce qu'elle soit dans sa position
d'origine, et serrez les vis de la plaque de recouvrement.
!
AVERTISSEMENT
plaque de recouvrement peut gêner le protecteur inférieur de lame et
suspendre ce dernier.
recouvrement solidement en place.
tionnera pas adéquatement.
9. Assurez-vous que le blocage de l’arbre est relâché de manière
à ce que la lame tourne librement.
!
AVERTISSEMENT
pas l’insert de table aux positions de biseau de 0 et de 45 degrés.
Abaissez la lame dans la fente de la table et vérifiez s’il y a quelque
contact que ce soit avec la base ou la structure de la table tournante.
Si la lame entre en contact avec la base ou la table, téléphonez au 1877-BOSCH99 pour parler à un technicien agréé.
10. Remettez la clé à lame dans la zone de rangement
prévue à cet effet sur la scie.
Pour éviter d’éventuelles blessures,
n’utilisez pas de lame de plus ou de
Serrez les vis de la plaque de
recouvrement.
N’utilisez jamais la scie sans la plaque de
Le protecteur inférieur ne fonc-
Après avoir posé une nouvelle lame,
assurez-vous que la lame ne gêne
Une vis lâche de
:
Rondelle
intérieure
Tige de l’arbre
Déflecteur de
copeaux
-
Figure 2. Ferrures de lame
84.
84.
Page 85

Réglages
!
AVERTISSEMENT
blage, réglage ou réparation pour éviter d’éventuelles blessures.
REMARQUE : Votre scie à onglet composée, à glissière, a été entièrement réglée à l’usine. Cependant, un léger désalignement peut
s’être produit en cours d’expédition. Vérifiez les réglages suivants
et ajustez, au besoin, avant d’utiliser cette scie à onglet composée.
Débranchez la fiche de la prise de
courant avant d’effectuer tout assem-
Lame d’équerre par rapport
à la table (90°)
Vérification de l'alignement de la lame à 90°
Tournez la table à la position 0° et bloquez en place.
1.
2. Assurez-vous que la tête est repoussée vers l’arrière à fond
contre la butée et que le bouton de blocage des rails coulissants est serré.
3. Abaissez la tête. Verrouillez en place.
4. Utilisez une équerre à combinaison pour vérifier si la lame est
d’équerre par rapport à la table. Placez l'équerre à combinaison
sur la table et appuyez-la contre la lame. Si la lame ne vient pas
en contact avec toute la longueur de l’équerre (Figure 6),
suivez la procédure d’alignement décrite ci-après.
Vis d’arrêt
°
0
Contre-
écrou
Figure 7. Vis d’arrêt 0° de biseau et contre-écrou
7. Ajustez l’indicateur de biseau. Desserrez la vis et alignez
l’indicateur sur la marque 0°. Serrez la vis (Figure 8).
Équerre à
combinaison
Table
Réglage de l'alignement de la lame à 90°
1. Desserrez la poignée de blocage de biseau.
2. Déplacez la tête pour qu'elle ne soit plus contre la butée
3. Abaissez la vis d'arrêt de biseau 0° et le contre-écrou
4.
5. Poussez l'équerre contre la lame. (Figure 6).
6. Ajustez la vis d'arrêt de biseau 0° avec la clé de 12 mm
Lame
Figure 6. Lame d’équerre par rapport à la table
°.
0
avec une clé de 12 mm ou une clé à ouverture variable.
Remettez la scie contre la butée de 0
ou la clé à ouverture variable jusqu'à ce que la lame entre
en contact avec toute la longueur de l'équerre. Serrez le
contre-écrou (Figure 7).
°.
Ajustez à
0°
Indicateur
de biseau
Vis
Figure 8. Indicateur de biseau
85.
Page 86

Réglages
Lame à 45° par rapport à la table
Vérification de l'alignement de la lame à 45°
1. Tournez la table à la position 0° et bloquez en place.
2. Assurez-vous que la tête est repoussée vers l’arrière à fond
contre la butée et que le bouton de blocage des rails coulis
sants est serré.
-
3. Abaissez la tête. Bloquez en place.
4. Assurez-vous que le contre-écrou de la vis d'arrêt de biseau
33,9° est en position passive, hors de l'axe des contre-écrous
des vis d'arrêt de biseau à 90° et à 45°.
5. Desserrez la poignée de blocage de biseau et inclinez la tête au
biseau de 45°. Vérifiez la butée de biseau de 45°. L'indicateur
de biseau doit être sur la marque 45°, et la butée de biseau de
45° doit être entièrement en contact avec la vis d'arrêt de
biseau de 45°. Placez l'équerre à combinaison sur la table et
appuyez-la contre la lame. La lame doit être en contact avec
toute la longueur de l'équerre à combinaison (Figure 9).
6. Si la lame n’est pas à 45° par rapport à la table, ajustez la butée
de biseau 45°.
Réglage de l'alignement de la lame à 45°
1. Abaissez la vis d'arrêt de biseau 45° et le contre-écrou
avec une clé de 12 mm ou une clé à ouverture variable.
(Figure 10).
2. Desserrez la poignée de blocage de biseau.
3. Abaissez la scie sur la butée de 45°.
4. Poussez l'équerre à combinaison contre la lame.
Équerre à
combinaison
Figure 9. Lame à 45° par rapport à la table
Butée 45°/33,9º
Vis d’arrêt 45°
Contreécrou
Lame
Table
5. Ajustez la vis d'arrêt de biseau 45° jusqu'à ce que la lame
entre en contact avec toute la longueur de l'équerre.
Serrez le contre-écrou de la vis d'arrêt de biseau 45°
(Figure 10).
6. Assurez-vous que l’indicateur de biseau pointe vers la
marque 45° sur l’échelle graduée de biseau (voir Figure 7).
Si l’indicateur de biseau n’est pas aligné sur la marque
45°, revérifiez d’abord si la lame est d’équerre par rapport
à la table et revérifiez l’alignement de l’indicateur de biseau
0°. Répétez ensuite l’alignement de lame 45° et faites les
réglages appropriés.
Figure 10. Vis d’arrêt 45° de biseau et contre-écrou
86.
Page 87

Réglages
Lame à 33,9° par rapport à la table
Vérification de l'alignement de la lame à 33,9°
REMARQUE : vous devrez vérifier et aligner les réglages à 45° et 90° en
premier avant de faire de même à 33,9° (voir pages 85 et 86).
Faites tourner la table jusqu'à la position 0° et verrouillez-la
1.
en place.
2. Assurez-vous que la tête est poussée complètement vers
l'avant contre la butée et que le bouton de blocage des rails
coulissants est serré.
3. Abaissez la tête. Verrouillez-la en place.
4. Assurez-vous que le contre-écrou de la vis d'arrêt de biseau
33,9° est en position active, aligné avec les contre-écrous des
vis d'arrêt de biseau de 90° et 45°.
5. Desserrez la poignée de blocage de biseau et inclinez la tête au
biseau 33,9°. Vérifiez la butée du biseau 33,9°. L'indicateur de
biseau doit être sur la marque 33,9°.
6. Si la lame n'est pas à 33,9° par rapport à la table, réglez la
butée de biseau 33,9°.
Réglage de l'alignement de la lame à 33,9°
1. Abaissez le contre-écrou de la vis d'arrêt de biseau de
33,9° en utilisant une clé de 12 mm ou une clé à ouverture variable.
2. Desserrez la poignée de blocage de biseau.
3. Abaissez la scie à la butée de 33,9°.
4. Réglez la butée de biseau de 33,9° jusqu'à ce que l'indicateur soit sur la marque 33,9° sur l'échelle graduée de
biseau (see Figure 12). Serrez le contre-écrou de 33,9
°
Figure 11. Lame à 33,9° par rapport à la table
Butée
45°/33,9º
Vis d’arrêt 45°
Contre-écrou
.
Figure 12. Vis d’arrêt 33,9° de biseau et contre-écrou
87.
Page 88

Réglages
Lame d’équerre par
rapport au guide
Vérification de l'alignement du guide
1. Assurez-vous que la tête est tirée vers l’avant près du centre de
la table et que le bouton de blocage des rails coulissants est
serré (Figure 13).
2. Abaissez la tête et verrouillez-la dans la position inférieure.
3. Assurez-vous que la table est au cran d'arrêt 0° et serrez le bouton de blocage d'onglet.
Placez l’équerre adéquatement de manière à ce qu’elle ne vienne
4.
pas en contact avec les dents de la lame de scie. La lame de scie
doit venir en contact avec toute la longueur de l’équerre (Figure 13).
5. Si la lame ne vient pas en contact avec l’équerre, suivez la
procédure d’alignement du guide.
Bouton de
blocage de rail
coulissant
Réglage de l'alignement du guide
La tête doit demeurer abaissée.
1.
2. Allongez le guide coulissant. Utilisez la clé à lame
(fournie) et desserrez trois (3) boulons derrière le guide
(Figure 14).
3. Ajustez le guide jusqu’à ce que lame et le guide soient
entièrement en contact avec l’équerre.
4. Serrez les vis à tête hexagonale.
Vis à tête hexagonale
Guide
Bouton de
blocage du
guide d'onglet
Figure 13. Lame d’équerre par rapport au guide
Réglage de l’indicateur de
l’échelle graduée d’onglet
1. Tournez la table à la position 0° et bloquez en place.
2. Levez la tête jusqu’à sa position entièrement levée.
3. Desserrez la vis à empreinte cruciforme qui tient l’indicateur en
place (Figure 15).
4. Positionnez l’indicateur de manière à ce qu’il s’aligne sur la
marque d’onglet 0°. Serrez la vis.
Unité de rails coulissants
Figure 11. Réglage du guide
(Vue arrière de la zone de la base/table)
88.
Vis de réglage
de l’indicateur
Figure 15.
Marque 0°
Page 89

Installation
!
AVERTISSEMENT
l Débranchez le cordon électrique. Avant de transporter la scie,
tournez la tête à l’onglet droit 45°, bloquez dans le cran d’arrêt, tirez la tête entièrement vers l’avant vers vous, serrez le
bouton de blocage des rails coulissants et bloquez la tête en
position abaissée.
l Pour éviter des lésions au dos, tenez l’outil à proximité de
votre corps lorsque vous le soulevez. Pliez vos genoux de
manière à pouvoir le lever avec les jambes, et non avec le dos.
Soulevez en utilisant les poignées moulées sur chaque côté au
bas de la base.
l Ne transportez jamais l’outil par les rails coulissants, ce
qui pourrait causer un défaut d’alignement de lame.
l Ne transportez jamais la scie à onglet par le cordon électrique
ou par la poignée d’opération. Toute tentative de soulever ou
de transporter l’outil par le cordon électrique abîmera l’isola-
Pour éviter des blessures, observez
toujours les mesures suivantes :
Applications de montage
tion et les connexions de fils, provoquant ainsi une secousse
électrique ou un incendie.
l Notez la position de la scie. Les personnes se tenant derrière
la scie pourraient être blessées par la projection de débris.
l Placez la scie sur une surface ferme et à niveau comportant
amplement d’espace pour manier et supporter adéquatement
l’ouvrage.
l Boulonnez, vissez, clouez ou cramponnez la scie à sa
surface d'appui.
!
MISE EN GARDE
de ne pas trop serrer le boulon lorsque vous attachez la scie à
la surface d'appui.
Ceci pourrait craquer le pied ou abîmer la base.
Faites attention de ne pas enfoncer le clou trop profondément ou
Établi
Montez la scie sur l'établi en utilisant les quatre trous de
boulon de 7/16 po ou les quatre trous de boulon de 1/4 po.
(Figure 16). Assurez-vous d’un dégagement suffisant à gauche et
à droite de la scie.
Trous de boulon
Trous pour vis
1. Chacun des quatre trous de montage doit être boulonné solidement à l’aide de boulons de 3/8 po, de rondelles d’arrêt et
d’écrous hexagonaux (non fournis).
2. Repérez et marquez l’emplacement du montage de la scie.
3. Percez quatre (4) trous de 3/8 po de diamètre à travers l’établi.
4. Placez la scie à onglet composée sur l’établi en alignant les
trous de la base sur ceux percés dans l’établi. Posez des
boulons, des rondelles d’arrêt et des écrous hexagonaux.
La surface d’appui où la scie doit être montée doit être examinée
soigneusement après le montage pour s’assurer qu’il ne pourra y
avoir aucun mouvement durant l’usage. Si vous constatez un basculement ou une avance de la scie, vérifiez votre montage sur
l'établi ou la surface d'appui, et procédez aux réglages nécessaires
avant d'utiliser la scie à onglet composée coulissante (voir Réglage
de la barre de stabilisation à la page 90).
Trous pour vis
Trous de boulon
Figure 16. Montage à l’établi
89.
Page 90

Installation
Montage portatif à l’aide de serre-joints
• S'il n'est pas possible d'utiliser des boulons ou de vis,
cramponnez la scie à onglet composée coulissante à un
établi ou à un dessus de table au moyen de crampons.
• Placez un crampon en « C » sur chacune des zones de
cramponnage et assujettissez la scie (Figure 17).
Remarque : l'utilisation de crampons limitera l'emploi
d'angles d'onglet extrêmes.
Surface de cramponnage
Surface de
cramponnage
Figure 17. Montage portatif à l’aide de serre-joints
Réglage de la barre de stabilisation
Pour mieux supporter la table pendant la coupe, ajustez la barre
de stabilisation avant l'emploi.
1. Desserrez le bouton pour ajuster la barre de stabilisation.
2. Faites glisser la barre de stabilisation vers le haut ou vers le
bas jusqu'à ce qu'elle entre en contact avec l'établi.
Remarque : si la surface de l'établi n'est pas plate, la barre de
stabilisation nécessitera peut-être un nouveau réglage en
fonction des angles d'onglet.
3. Serrez le bouton.
Réglage de barre de
stabilisation
Barre de stabilisation
Établi
90.
Page 91

0
5
10
15
20
25
30
35
40
45
50
50
45
40
35
30
BOSCH
0
5
10
15
20
25
30
35
40
45
50
50
45
40
35
30
BOSCH
0
5
10
15
20
25
30
35
40
45
50
50
45
40
35
30
BOSCH
0
5
10
15
20
25
30
35
40
45
50
50
45
40
35
30
BOSCH
Opérations de base de la scie
Position du corps et des mains
!
AVERTISSEMENT
Positionnez votre corps et vos mains
adéquatement pour rendre la coupe
plus facile et plus sûre. Observez les instructions suivantes (Figure 18).
l Ne placez jamais les mains à proximité de l’aire de coupe.
Gardez les mains à l’extérieur de la zone interdite aux
mains.
l La « zone interdite aux mains » est définie comme la totalité
de la table ainsi que des parties fixes de la base et des parties
du guide à l'intérieur de ces limites. Cette zone est identifiée
par des symboles d'interdiction aux mains placés sur la base.
enez fermement l'ouvrage (en dehors de la zone interdite
l T
aux mains) contre le guide pour empêcher tout mouvement
(Fig. 18).
Utilisation correcte Utilisation incorrecte
!
AVERTISSEMENT
Il se peut que le protecteur inférieur
ne s’ouvre pas automatiquement
dans certaines conditions de coupe. Dans ce cas :
l Ceci peut se produire généralement en tentant de couper des
ouvrages qui se rapprochent de la capacité maximum de hauteur de coupe (3,5 po), ou en faisant des coupes en biseau
extrêmes à la capacité maximum de hauteur de coupe. Dans
ces conditions, l’ouvrage peut arrêter le mouvement du protecteur inférieur avant que le mouvement vers le bas du bras
ne puisse préouvrir le protecteur inférieur. Dans ce cas :
1. L’ouvrage doit être cramponné solidement. Ceci libère
une main pour soulever le protecteur par le rebord suffisamment pour passer à côté de l’ouvrage (Figure 19).
2. Mettez la scie en marche et commencez votre coupe.
3. Lorsque vous êtes passé à côté de la position où le
protecteur inférieur peut gripper, relâchez le protecteur et
il continuera à lever automatiquement au fur et à mesure
que vous coupez.
Rebord
Protecteur inférieur
Figure 18. Positions des mains
l Gardez les mains en place jusqu’à ce que la gâchette ait été
relâchée et que la lame se soit complètement arrêtée.
l Ne placez jamais les mains sur les rails coulissants.
l Gardez les pieds fermement sur le plancher et maintenez un
bon équilibre.
l Suivez le bras d’onglet en coupant à gauche ou à droite. Tenez-
vous légèrement sur le côté de la lame de scie.
l Avant de pratiquer quelque coupe que ce soit et l’outil étant
hors tension, abaissez la lame pour visualiser préalablement le
parcours de la lame.
Ouvrir
Ouvrage
Figure 19. Levée du protecteur inférieur
91.
Page 92

Opérations de base de la scie
Support de l’ouvrage
!
AVERTISSEMENT
cramponnés et ne soient dûment supportés par en-dessous.
Les ouvrages longs ont tendance à
basculer à moins qu’ils ne soient
Serre-joints
Serre-joint d'ouvrage - Ce crampon assujettit facilement un
ouvrage dans l'un quelconque des trois (3) trous de crampon derrière le guide (Figure 20).
• Insérez le montant de serre-joint dans le trou de serre-joint.
• Desserrez l'écrou à oreilles et ajustez le bras à la hauteur
appropriée, puis serrez l'écrou à oreilles à fond.
• Tournez le bouton à vis du serre-joint en sens horaire pour
serrer, en sens anti-horaire pour desserrer.
• Déplacez la tête afin de vérifier l’écartement avec le serre-joint.
!
AVERTISSEMENT
joint ne peut pas être utilisé. Supportez l’ouvrage avec la main à
l’extérieur de la zone interdite aux mains.
des pièces courtes
geraient à mettre la main dans la zone interdite aux mains.
Serre-joint
d'ouvrage
Trous de
serre-joint
Tige
filetée
qui ne peuvent être cramponnées et vous obli-
Il peut y avoir des coupes composées extrêmes lorsque le serre-
N’essayez pas de couper
Trous de
serre-joint
Figure 20. Serre-joint d'ouvrage
On peut utiliser les serre-joints conventionnels et autres dispositifs
de retenue pour tenir l’ouvrage fermement contre la table et le guide.
92.
Page 93

Opérations de base de la scie
Guide auxiliaire — Certains types de moulure nécessitent une ral
longe de face de guide en raison de la dimension et de la position
de l’ouvrage. Les coupes de rainures nécessitent aussi un guide
auxiliaire. Des trous sont pratiqués dans le guide pour fixer un
guide auxiliaire. Le guide auxiliaire est utilisé avec la scie en position biseau 0
Placez une pièce de bois contre le guide de la scie à onglet (Figure
1.
21). (Le bois peut avoir une hauteur maximum de
3 1/2 po.). Assurez-vous que la tête ne gêne pas le guide auxiliaire.
2. Marquez les emplacements des trous de support sur le bois
depuis l’arrière du guide.
3. Percez et fraisez les trous à l’avant de la planche de support.
4. Attachez le guide auxiliaire en utilisant deux (2) vis mécaniques
à tête plate d'au moins 1/4 po de chaque côté. Pratiquez une
coupe de profondeur normale pour créer la fente à lame.
Vérifiez s’il y a interférence entre le guide auxiliaire et le protecteur inférieur de lame. Faites des ajustements au besoin.
!
° seulement.
AVERTISSEMENT
Vérifiez s’il y a interférence causée
par un composant quelconque.
-
Vis à tôle
à tête plate
Fente à lame
Vis à tôle
à tête plate
Guide auxiliaire
Figure 21. Guide auxiliaire
Actionnement de l’interrupteur
Pour des raisons de sécurité, le levier de l'interrupteur a été conçu
de façon à empêcher des démarrages accidentels. Pour utiliser
l'interrupteur de sécurité, appuyez sur le bouton « Lock-OFF »
(blocage à l'arrêt) de l'interrupteur avec l'un de vos pouces afin de
relâcher le verrouillage, puis tirez sur le levier de l'interrupteur et
relâchez le bouton de blocage de l'interrupteur à l'arrêt (« LockOFF »). Lorsque l'interrupteur est relâché, le bouton de blocage de
l'interrupteur à l'arrêt « Lock-OFF » engage automatiquement l'interrupteur de sécurité et le levier de l'interrupteur ne fonctionnera
plus jusqu'à ce que le bouton de blocage de l'interrupteur à l'arrêt
(« Lock-OFF ») soit enfoncé à nouveau.
REMARQUE : le levier de l'interrupteur peut recevoir un cadenas
avec une tige longue d'un diamètre pouvant atteindre 1/4 po (non
fourni) afin d'empêcher toute utilisation non autorisée.
Levier de
l'interrupteur
Boutons de
-
relâche
ment/blocage
à l'arrêt «
Lock-OFF »
de l'interrup
teur
-
Figure 22. Actionnement de l’interrupteur
93.
Page 94

Opérations de base de la scie
1
Court-circuitage du cran d’arrêt
Pour engager :
1. Soulevez la gâchette du cran d’arrêt d’onglet.
Poussez la pince de court-circuitage du cran d’arrêt vers l’avant
2.
et verrouillez en place par-dessus le bord. Relâchez la gâchette
du cran d’arrêt d’onglet (Figure 23).
Déplacez le bras d’onglet à toute position sur l’échelle graduée
3.
d’onglet.
4. Bloquez le bouton de blocage d’onglet pour fixer la position de
l’onglet.
Pour relâcher :
Bord de la pince
Pince de court-
circuitage du
cran d’arrêt
5. Desserrez le bouton de blocage d’onglet et soulevez la gâchette
du cran d’arrêt d’onglet pour relâcher la pince de court-circuitage du cran d’arrêt. La pince doit se dégager automatiquement et la table doit se bloquer à tout cran d’arrêt d’onglet
désiré.
Rallonges de base
!
AVERTISSEMENT
main et la lame de la scie, rallongez les guides et les bases à
glissière lorsque vous effectuez des coupes extrêmes au biseau
ou à l'onglet, ou des coupes composées.
Les rallonges de la base peuvent également être utilisées pour
fournir un appui additionnel en cas de travail sur des ouvrages
très longs.
Réglage des rallonges :
1. Desserrez les leviers de cramponnage des rallonges de la base.
2.
Faites sortir les rallonges de la base à glissière et tirez-les
jusqu'à la position désirée.
3. Appuyez sur les leviers pour cramponner les rallonges en place.
Si la force de cramponnage des leviers de cramponnage des rallonges de la base doit être ajustée, tirez simplement sur la
languette rouge (vers l'extérieur) et faites-la tourner vers le centre
de la scie. Laissez la languette rouge rebondir dans une nouvelle
rainure. Une fois que les languettes rouges auront été tournées
pour assujettir les tiges, elles les saisiront avec plus de for
Pour assurer un écartement suffisant (au minimum 6 po) entre la
ce.
Table
Tiges de
rallonge
Gâchette du
cran d’arrêt
d’onglet
Figure 23. Court-circuitage du cran d’arrêt
Leviers de cramponnage des rallonges
de la base
Figure 24: Rallonges de base
Bouton de
blocage
d’onglet
94.
Page 95

Opérations de base de la scie
Guide à glissière
Guide à glissière
Utilisation du guide à glissière
1. Faites tourner le levier du guide dans le sens contraire
des aiguilles d'une montre.
2. Faites glisser le guide jusqu'à la position désirée.
3. Tournez le levier du guide dans le sens des aiguilles
d'une montre pour serrer.
Retrait du guide à glissière
1. Soulevez la languette de la plaque de recouvrement et
faites-la tourner dans le sens des aiguilles d'une montre.
2. Faites tourner le levier du guide dans le sens contraire
des aiguilles d'une montre.
3. Faites glisser le guide aussi loin que possible vers la gauche.
4. Tirez sur le guide à glissière afin de le soulever et de le retirer.
Réglage du verrouillage du guide à glissière –
Serrez le mécanisme de verrouillage
1. Retirez le guide à glissière
2. Appuyez sur le bloc de verrouillage pour exposer la tête
de la vis.
3. Tournez la vis dans le sens contraire des aiguilles d'une
montre afin de la mettre dans le réglage hexagonal suivant.
4. Remise en place du guide à glissière.
5. Vérifiez la force de cramponnage dans plusieurs positions.
Assurez-vous que le levier ne bloque pas le trou à crampon.
VUE AVANT
Guide à glissière
Levier
du guide
VUE ARRIÈRE
Languette de la plaque
de recouvrement
Levier
du guide
Bloc de verrouillage
Figure 25: Guide à glissière
Réglage du verrouillage du guide à glissière –
desserrez le mécanisme de verrouillage
1. Retirez le guide à glissière
2. Appuyez sur le bloc de verrouillage pour exposer la tête
de la vis.
3. Tournez la vis dans le sens des aiguilles d'une montre
afin de la mettre dans le réglage hexagonal suivant.
4. Remise en place du guide à glissière.
5. Vérifiez la force de cramponnage dans plusieurs positions.
Assurez-vous que le levier ne bloque pas le trou à crampon.
95.
Page 96

Opérations de la scie
Coupe de fente
Pendant une coupe de fente, le bouton de blocage des rails
•
coulissants est serré et la tête est abaissée pour permettre de
couper à travers l'ouvrage.
Ce type de coupe est utilisé principalement pour
•
les pièces étroites.
Suivez ces instructions pour pratiquer votre coupe de fente :
1. Faites glisser la tête vers l’arrière aussi loin que possible
(Figure 26).
2. Serrez le bouton de blocage des rails coulissants (Figure 26).
3. Positionnez l’ouvrage correctement. Assurez-vous que l’ouvrage est cramponné fermement contre la table et le guide.
Attendez que la lame s’arrête complètement avant de relever la
5.
tête et/ou de retirer l’ouvrage.
Bouton de blocage des
rails coulissants serré
!
AVERTISSEMENT
Avant de mettre en marche, abaissez la tête pour vous assurer que
le serre-joint dégage le protecteur et la tête.
4. Actionnez l’interrupteur. Abaissez la tête et pratiquez votre
coupe.
Utilisez une position de cramponnage
qui ne gêne pas le fonctionnement.
Coupe par glissement
Pendant une coupe par glissement, le bouton de blocage des rails
•
coulissants est desserré, et la tête est tirée dans la direction de
l'opérateur, abaissée jusqu'à l'ouvrage et ensuite poussée vers
l'arrière de la scie pour permettre de faire la coupe.
Ce type de coupe est utilisé principalement pour les pièces
•
larges.
Un crochet de lame positif de 10 degrés ou plus est recom-
•
mandé pour une meilleure performance en pratiquant des
coupes agressives ou en coupant des matériaux plus épais.
Reportez-vous à la page 108 pour la liste des lames offertes en
accessoire.
!
AVERTISSEMENT
dainement grimper sur le dessus de l’ouvrage et for
vers vous.
Suivez ces instructions pour pratiquer votre coupe par glissement :
1. Positionnez l’ouvrage correctement. Assurez-vous que l’ouvrage est cramponné fermement contre la table et le guide.
!
AVERTISSEMENT
vant de mettre en marche, abaissez la tête pour vous assurer que le
A
serre-joint dégage le protecteur et la tête.
Desserrez le bouton de blocage des rails coulissants.
2.
3. Saisissez la poignée de l’interrupteur et tirez la tête en sens
opposé au guide, jusqu’à ce que la lame dégage l’ouvrage ou
jusqu’à son prolongement maximum si la lame ne peut dégager
l’ouvrage (Figure 27).
Ne tirez JAMAIS la scie vers vous
durant une coupe. La lame peut sou
cer son chemin
Utilisez une position de cramponnage
qui ne gêne pas le fonctionnement.
Faites glisser entièrement contre la butée
Figure 26. Coupe de fente
4. Actionnez l’interrupteur. Abaissez la tête jusqu’en bas et coupez
à travers le bord de l’ouvrage.
5. Poussez (sans forcer) la tête vers le guide jusqu’à la position
arrière maximum pour terminer la coupe.
6. Attendez que la lame s’arrête complètement avant de relever la
tête et/ou de retirer l’ouvrage.
Bouton de
blocage
En premier
lieu :
Tirez vers
-
l’avant
des rails
coulissants
Figure 27. Coupe par glissement
En deuxième
lieu :
Mettez la scie
en marche
Abaissez
la tête
En troisième
lieu :
Poussez la
lame dans
l’ouvrage
96.
Page 97

Opérations de la scie
Coupe à l’onglet
• Une coupe à l’onglet est pratiquée au biseau 0° et à tout angle
d’onglet variant entre 50° à gauche et 60° à droite.
’échelle graduée d’onglet est coulée dans la table pour
• L
faciliter la lecture.
• Des crans d’arrêt positifs ont été créés à 0°, 15°, 22,5° et 45°
à gauche et à droite, et à 60° à droite.
• Il existe des crans d’arrêt moulures en couronne (à gauche et
à droite) à 31,6° (voir Coupe de moulures en couronne pour
de plus amples informations, à la page 100).
• Pour effectuer des réglages sans utiliser le cran d'arrêt,
utilisez le mécanisme de court-circuitage du cran d'arrêt pour
inhiber le cran d'arrêt.
• Une coupe à l’onglet peut être pratiquée comme coupe de
fente ou comme coupe par glissement, suivant la largeur de
l’ouvrage.
Suivez ces instructions pour pratiquer votre coupe à l’onglet :
1. Desserrez le bouton de blocage d’onglet. Soulevez la gâchette
du cran d’arrêt d’onglet et déplacez la scie à l’angle désiré, en
utilisant soit les crans d’arrêt soit l’échelle graduée d’onglet.
Serrez le bouton de blocage d’onglet (Figure 28).
!
AVERTISSEMENT
nement. Avant de mettre en marche, abaissez la tête pour vous
assurer d’un écartement suffisant entre le serre-joint, d’une part, et
le protecteur et la tête, d’autre part.
Suivez les instructions pour la coupe de fente ou la coupe par
3.
glissement (voir page 96).
4. Attendez que la lame s’immobilise complètement avant de
remettre la tête à la position levée et/ou de retirer l’ouvrage.
Serre-joint
d'ouvrage
Utilisez une position de cramponnage qui ne gêne pas le fonction
Ouvrage
-
2. Positionnez l’ouvrage adéquatement. Assurez-vous que l’ouvrage est cramponné fermement contre la table et le guide.
Coupe en biseau
et à tout
• Une coupe en biseau est pratiquée à onglet de 0
angle de biseau variant entre 0º et 45°.
• Il existe bon nombre de butées de biseau réglées en usine à
oir section Réglage si des ajustements sont
. (V
°
et 45
°
0
nécessaires.)
• L'échelle graduée de biseau est orientée face à l'opérateur pour
faciliter la lecture.
°
Crans d’arrêt
Figure 28. Coupe à l’onglet
• Il existe une butée positive de biseau de moulures en
couronne à 33,9°. Relâchez cette butée à moins que vous ne
l’utilisiez. (V
amples informations.)
• Une coupe en biseau peut être pratiquée comme coupe de
fente ou comme coupe par glissement, suivant la largeur de
l’ouvrage.
• Utilisez le guide à glissière et les appuis pour l'ouvrage suivant
les besoins. (Voir Guides à glissière et rallonges de base page
94-95).
oir Coupe de moulures en couronne pour de plus
Échelle graduée
d’onglet
Bouton de
blocage d’onglet
97.
Page 98

Opérations de la scie
Coupe en biseau (Suite de la page 97)
Suivez ces instructions pour pratiquer votre coupe en biseau :
1. Pour desserrer, soulevez le levier de blocage de biseau. Inclinez
la tête à l’angle de biseau désiré. Serrez le levier de blocage de
biseau (Figure 29).
2. Positionnez l’ouvrage adéquatement. Assurez-vous que l’ouvrage est cramponné fermement contre la table et le guide.
Angle de
biseau
Serre-joint
d'ouvrage
!
AVERTISSEMENT
Avant de mettre en marche, abaissez la tête pour vous assurer d’un
écartement suffisant entre le serre-joint, d’une part, et le protecteur
et la tête, d’autre part.
3. Suivez les instructions pour la coupe de fente ou la coupe par
glissement (voir page 91).
4. Attendez que la lame s’immobilise complètement avant de
remettre la tête à la position levée et/ou de retirer l’ouvrage.
Utilisez une position de cramponnage
qui ne gêne pas le fonctionnement.
Coupes composées
• Une coupe composée est une coupe nécessitant un réglage
d’onglet aussi bien qu’un réglage de biseau.
• Une coupe composée peut être pratiquée comme coupe de
fente ou comme coupe par glissement, suivant la largeur de
l’ouvrage.
Onglet 0°
Levier de blocage de biseau
Figure 29. Coupe en biseau
4. Attendez que la lame s’immobilise complètement avant de
remettre la tête à la position levée et/ou de retirer l’ouvrage.
Ouvrage
• Étant donné qu’il faudra peut-être plusieurs essais pour
obtenir l’angle composé désiré, effectuez des coupes d’essai
sur des matériaux de rebut avant de pratiquer votre coupe.
Suivez ces instructions pour pratiquer votre coupe composée
Faites sortir le guide à glissière et les appuis pour l'ouvrage
1.
lorsque vous effectuez des coupes d'onglet composées vers la
gauche. (voir Rallonge de base/guide à glissière à la page 94-
95). Sélectionnez les angles désirés d’onglet et de biseau (Figure
30). (Voir Coupe à l’onglet et Coupe en biseau à la page 97.)
2. Positionnez l’ouvrage adéquatement. Assurez-vous que l’ouvrage est cramponné fermement contre la table et le guide.
!
AVERTISSEMENT
vant de mettre en mar
A
écartement suffisant entre le serre-joint, d’une part, et le protecteur
et la tête, d’autre part.
3. Suivez les instructions pour la coupe de fente ou la coupe par
glissement (voir page 96).
Utilisez une position de cramponnage
qui ne gêne pas le fonctionnement.
che, abaissez la tête pour vous assurer d’un
:
98.
Ouvrage
Figure 30. Coupe composée
Angle de
biseau
Serre-joint
d'ouvrage
Page 99

Opérations de la scie
Coupe de rainures
Le réglage de la butée de profondeur est utilisé lors de la
•
coupe de rainures dans l’ouvrage.
Serrez les contre-écrous contre a butée de profondeur.
3.
4. Coupez les deux rainures extérieures.
Le réglage de la profondeur est utilisé pour limiter la pro-
•
fondeur de la lame afin de pratiquer des rainures.
Une rainure peut être pratiquée comme coupe par glissement.
•
1. Réglez la profondeur de coupe en desserrant les contre-
écrous sur le boulon de réglage de la profondeur (Figure 31).
Ne modifiez pas la position des deux (2) contre-écrous à l’extrémité du boulon.
2. Tournez le boulon de butée de profondeur à la position voulue.
Bord moleté
Boulon de butée de profondeur
Contre-écrous
Base de butée de profondeur
Contre-écrous
Butée de profondeur
5. Utilisez un burin à bois ou effectuez des passes multiples
faisant glisser le bois pour enlever le matériau entre les rainures extérieures (Figure 32).
Rainures
Coupe au burin
Ouvrage
Figure 32. Rainure coupée grossièrement
Figure 31. Coupe de rainures
Remarque : un guide auxiliaire est nécessaire pour assurer l'uni-
formité de la profondeur. L'épaisseur du guide dépend de l'épaisseur de la rainure.
Butée de
profondeur
99.
Page 100

Opérations de la scie
Coupe de moulures de base
• Une moulure de base de 3 1/2 po ou moins peut être coupée
à la verticale contre le guide. Toutes les moulures de base peuvent être coupées à plat sur la table, jusqu'à une largeur max
imum de 12 po.
• Reportez-vous au tableau contenant des conseils utiles sur la
coupe de moulures de base.
-
• La coupe de moulures de base peut être pratiquée comme
coupe de fente ou comme coupe par glissement, suivant la
largeur de l’ouvrage.
INSTRUCTIONS DE COUPE DE MOULURES DE BASE
RÉGLAGES Position verticale Position horizontale
/ L’arrière de la moulure repose L’arrière de la moulure repose
INSTRUCTIONS contre le guide à plat sur la table
Angle de biseau 0° 45°
Position de moulure Côté gauche Côté droit Côté gauche Côté droit
Coin intérieur Angle d’onglet Gauche à 45° Droit à 45° 0° 0°
du mur
Position de Fond contre Fond contre Dessus contre Fond contre
moulure la table la table le guide le guide
Gauche
Coin extérieur Angle d’onglet Droit à 45° Gauche à 45° 0° 0°
Droit
du mur
Côté Gardez le côté Gardez le côté Gardez le côté Gardez le côté
fini gauche de la coupe droit de la coupe gauche de la coupe gauche de la coupe
Position de Fond contre Fond contre Fond contre Dessus contre
moulure la table la table le guide le guide
Gauche
Droit
Côté Gardez le côté Gardez le côté Gardez le côté Gardez le côté
fini gauche de la coupe droit de la coupe droit de la coupe droit de la coupe
Coupe de moulures en couronne
• Les moulures en couronne doivent être coupées exactement
pour se raccorder adéquatement.
• Il existe deux façons de couper les moulures en couronne :
à plat sur la table ou
à angle par rapport à la table et au guide.
• Votre scie à onglet possède des crans d’arrêt d’onglet spéci-
aux de 31,6° à gauche et à droite, et un cran d’arrêt de biseau
° pour couper les moulures en couronne à plat sur la
de 33,9
table.
• Ces angles de crans d’arrêt spéciaux ont été incorporés dans
votre scie à onglet composée pour les moulures en couronne
standard utilisées aux États-Unis avec les angles suivants :
entre l’arrière de la moulure et la sur
°
52
périeure qui repose contre le mur.
° entre l’arrière de la moulure et la surface plate inférieure
38
qui repose contre le mur.
REMARQUE : Ces crans d’arrêt ne peuvent pas être utilisés avec les
moulures en couronne de 45°.
face plate su
• Bien que ces angles soient standard, la plupart des pièces n’ont
pas d’angles d’exactement 90° ; vous devrez donc ajuster vos
réglages à l’aide du court-circuitage de cran d’arrêt.
• La coupe de moulures de base à plat sur la table peut être
pratiquée comme coupe de fente ou comme coupe par
glissement, suivant la largeur de l’ouvrage.
-
100.
 Loading...
Loading...