Page 1

Model: 2190E
100 MHz Digital Storage
Oscilloscope
USER MANUAL
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com
Page 2

Safety Summary
The following safety precautions apply to both operating and maintenance
personnel and must be followed during all phases of operation, service,
and repair of this instrument.
Before applying power to this instrument:
Read and understand the safety and operational information in
this manual.
Apply all the listed safety precautions.
Verify that the voltage selector at the line power cord input is set
to the correct line voltage. Operating the instrument at an
incorrect line voltage will void the warranty.
Make all connections to the instrument before applying power.
Do not operate the instrument in ways not specified by this
manual or by B&K Precision.
Failure to comply with these precautions or with warnings elsewhere in
this manual violates the safety standards of design, manufacture, and
intended use of the instrument. B&K Precision assumes no liability for a
customer’s failure to comply with these requirements.
Category rating
The IEC 61010 standard defines safety category ratings that specify the
amount of electrical energy available and the voltage impulses that may
occur on electrical conductors associated with these category ratings. The
category rating is a Roman numeral of I, II, III, or IV. This rating is also
accompanied by a maximum voltage of the circuit to be tested, which
defines the voltage impulses expected and required insulation clearances.
These categories are:
Category I (CAT I): Measurement instruments whose measurement inputs
are not intended to be connected to the mains supply. The voltages in the
environment are typically derived from a limited-energy transformer or a
i
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com
Page 3

battery.
Category II (CAT II): Measurement instruments whose measurement inputs
are meant to be connected to the mains supply at a standard wall outlet or
similar sources. Example measurement environments are portable tools
and household appliances.
Category III (CAT III): Measurement instruments whose measurement
inputs are meant to be connected to the mains installation of a building.
Examples are measurements inside a building's circuit breaker panel or the
wiring of permanently-installed motors.
Category IV (CAT IV): Measurement instruments whose measurement
inputs are meant to be connected to the primary power entering a
building or other outdoor wiring.
Do not use this instrument in an electrical environment with a higher
category rating than what is specified in this manual for this instrument.
You must ensure that each accessory you use with this instrument has a
category rating equal to or higher than the instrument's category rating to
maintain the instrument's category rating. Failure to do so will lower the
category rating of the measuring system.
Electrical Power
This instrument is intended to be powered from a CATEGORY II mains
power environment. The mains power should be 120 V RMS or 240 V RMS.
Use only the power cord supplied with the instrument and ensure it is
appropriate for your country of use.
Ground the Instrument
ii
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com
Page 4

To minimize shock hazard, the instrument chassis and cabinet must be
connected to an electrical safety ground. This instrument is grounded
through the ground conductor of the supplied, three-conductor AC line
power cable. The power cable must be plugged into an approved threeconductor electrical outlet. The power jack and mating plug of the power
cable meet IEC safety standards.
Do not alter or defeat the ground connection. Without the safety ground
connection, all accessible conductive parts (including control knobs) may
provide an electric shock. Failure to use a properly-grounded approved
outlet and the recommended three-conductor AC line power cable may
result in injury or death.
Unless otherwise stated, a ground connection on the instrument's front or
rear panel is for a reference of potential only and is not to be used as a
safety ground.
Do not operate in an explosive or flammable atmosphere
Do not operate the instrument in the presence of flammable gases or
vapors, fumes, or finely-divided particulates.
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com
iii
Page 5

The instrument is designed to be used in office-type indoor environments.
Do not operate the instrument
In the presence of noxious, corrosive, or flammable fumes, gases,
vapors, chemicals, or finely-divided particulates.
In relative humidity conditions outside the instrument's
specifications.
In environments where there is a danger of any liquid being
spilled on the instrument or where any liquid can condense on
the instrument.
In air temperatures exceeding the specified operating
temperatures.
In atmospheric pressures outside the specified altitude limits or
where the surrounding gas is not air.
In environments with restricted cooling air flow, even if the air
temperatures are within specifications.
In direct sunlight.
This instrument is intended to be used in an indoor pollution degree 2
environment. The operating temperature range is 0 °C to 40 °C and the
operating humidity is ≤ 85 % relative humidity at 40 °C, with no
condensation allowed. Measurements made by this instrument may be
outside specifications if the instrument is used in non-office-type
environments. Such environments may include rapid temperature or
humidity changes, sunlight, vibration and/or mechanical shocks, acoustic
noise, electrical noise, strong electric fields, or strong magnetic fields.
Do not operate instrument if damaged
If the instrument is damaged, appears to be damaged, or if any liquid,
chemical, or other material gets on or inside the instrument, remove the
instrument's power cord, remove the instrument from service, label it as
not to be operated, and return the instrument to B&K Precision for repair.
iv
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com
Page 6

Notify B&K Precision of the nature of any contamination of the instrument.
Clean the instrument only as instructed
Do not clean the instrument, its switches, or its terminals with contact
cleaners, abrasives, lubricants, solvents, acids/bases, or other such
chemicals. Clean the instrument only with a clean dry lint-free cloth or as
instructed in this manual.
Not for critical applications
This instrument is not authorized for use in contact with the human body
or for use as a component in a life-support device or system.
Do not touch live circuits
Instrument covers must not be removed by operating personnel.
Component replacement and internal adjustments must be made by
qualified service-trained maintenance personnel who are aware of the
hazards involved when the instrument's covers and shields are removed.
Under certain conditions, even with the power cord removed, dangerous
voltages may exist when the covers are removed. To avoid injuries, always
disconnect the power cord from the instrument, disconnect all other
connections (for example, test leads, computer interface cables, etc.),
discharge all circuits, and verify there are no hazardous voltages present
on any conductors by measurements with a properly-operating voltagesensing device before touching any internal parts. Verify the voltagesensing device is working properly before and after making the
measurements by testing with known-operating voltage sources and test
v
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com
Page 7

for both DC and AC voltages. Do not attempt any service or adjustment
unless another person capable of rendering first aid and resuscitation is
present.
Do not insert any object into an instrument's ventilation openings or other
openings.
Hazardous voltages may be present in unexpected locations in circuitry
being tested when a fault condition in the circuit exists.
Servicing
Do not substitute parts that are not approved by B&K Precision or modify
this instrument. Return the instrument to B&K Precision for service and
repair to ensure that safety and performance features are maintained.
Cooling fans
This instrument contains one or more cooling fans. For continued safe
operation of the instrument, the air inlet and exhaust openings for these
fans must not be blocked nor must accumulated dust or other debris be
allowed to reduce air flow. Maintain at least 25 mm clearance around the
sides of the instrument that contain air inlet and exhaust ports. If mounted
in a rack, position power devices in the rack above the instrument to
minimize instrument heating while rack mounted. Do not continue to
operate the instrument if you cannot verify the fan is operating (note some
fans may have intermittent duty cycles). Do not insert any object into the
fan's inlet or outlet.
vi
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com
Page 8

For continued safe use of the instrument
Do not place heavy objects on the instrument.
Do not obstruct cooling air flow to the instrument.
Do not place a hot soldering iron on the instrument.
Do not pull the instrument with the power cord, connected
probe, or connected test lead.
Do not move the instrument when a probe is connected to a
circuit being tested.
vii
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com
Page 9

Compliance Statements
This product is subject to Directive
2002/96/EC of the European
Parliament and the Council of the
European Union on waste electrical
and electronic equipment (WEEE),
and in jurisdictions adopting that
Directive, is marked as being put on
the market after August 13, 2005,
and should not be disposed of as
unsorted municipal waste. Please
utilize your local WEEE collection
facilities in the disposition of this
product and otherwise observe all
applicable requirements.
Disposal of Old Electrical & Electronic Equipment (Applicable in the
European Union and other European countries with separate collection
systems)
viii
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com
Page 10

CE Declaration of Conformity
This instrument meets the requirements of 2006/95/EC Low Voltage
Directive and 2004/108/EC Electromagnetic Compatibility Directive with
the following standards.
Low Voltage Directive
- EN61010-1: 2001
- EN61010-031: 2002+A1: 2008
EMC Directive
- EN 61326-1:2006
- EN 61000-3-2: 2006+A2: 2009
- EN 61000-3-3: 2008
ix
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com
Page 11

Safety Symbols
Refer to the user manual for warning information to
avoid hazard or personal injury and prevent damage
to instrument.
Electric Shock hazard
Alternating current (AC)
Chassis (earth ground) symbol.
Ground terminal
On (Power). This is the In position of the power
switch when instrument is ON.
Off (Power). This is the Out position of the power
switch when instrument is OFF.
Off (Supply). This is the AC mains
connect/disconnect switch on top of the
instrument.
CAUTION indicates a hazardous situation which, if
not avoided, will result in minor or moderate injury
WARNING indicates a hazardous situation which, if
not avoided, could result in death or serious injury
DANGER indicates a hazardous situation which, if
not avoided, will result in death or serious injury.
x
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com
Page 12

Table of Contents
Safety Summary ........................................................................................i
Compliance Statements ........................................................................ viii
Safety Symbols ......................................................................................... x
1 General Information .........................................................................1
1.1 Product Overview ......................................................................... 1
1.2 Package Contents ......................................................................... 1
1.3 Front Panel ................................................................................... 2
Front Panel Description ........................................................................ 2
1.4 Back Panel .................................................................................... 3
Back Panel Description ......................................................................... 4
1.5 Display Information ...................................................................... 4
User Interface Description ................................................................... 5
2 Getting Started .................................................................................6
2.1 Input Power Requirements .......................................................... 6
Input Power .......................................................................................... 6
2.2 Preliminary Check ......................................................................... 6
Verify AC Input Voltage ........................................................................ 7
Connect Power ..................................................................................... 7
Self-Test ................................................................................................ 7
Self Cal .................................................................................................. 7
Check Model and Firmware Version .................................................... 8
Function Check ..................................................................................... 8
Probe Safety ....................................................................................... 10
Probe Attenuation .............................................................................. 11
Probe Compensation .......................................................................... 11
3 Functions and Operating Descriptions ............................................ 13
3.1 Menu and Control Button .......................................................... 14
3.2 Connectors ................................................................................. 16
3.3 Auto Setup .................................................................................. 17
xi
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com
Page 13

3.4 Default Setup .............................................................................. 19
3.5 Universal Knob............................................................................ 23
3.6 Vertical System ........................................................................... 23
Using Vertical Position Knob and Volts/div Knob ............................... 24
3.7 Channel Function Menu ............................................................. 25
Setting up Channels ............................................................................ 28
3.8 Math Functions ........................................................................... 34
FFT Spectrum Analyzer ....................................................................... 36
3.9 Using REF .................................................................................... 43
3.10 Horizontal System....................................................................... 45
Horizontal Control Knob ..................................................................... 45
Window Zone ..................................................................................... 46
3.11 Trigger System ............................................................................ 47
Signal Source ...................................................................................... 48
Trigger Type ........................................................................................ 49
Coupling .............................................................................................. 67
Position ............................................................................................... 67
Slope and Level ................................................................................... 68
Trigger Holdoff ................................................................................... 69
3.12 Signal Acquisition System ........................................................... 70
3.13 Display System ............................................................................ 75
X-Y Format .......................................................................................... 79
3.14 Measure System ......................................................................... 80
Scale Measurement ............................................................................ 80
Cursor Measurement ......................................................................... 80
3.15 Storage System ........................................................................... 94
Recalling Files ..................................................................................... 96
Creating Folders and Files .................................................................. 96
Save/Recall Setup ............................................................................... 97
Save/Recall Waveform ..................................................................... 102
3.16 Utility System............................................................................ 109
System Status ................................................................................... 113
Language .......................................................................................... 114
Self Calibration ................................................................................. 115
Self Test ............................................................................................ 116
Update Firmware.............................................................................. 119
xii
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com
Page 14

Pass/Fail ............................................................................................ 120
Waveform Record ............................................................................ 125
Recorder (Scan Mode Only) ............................................................. 129
Help Menu ........................................................................................ 134
Education Mode ............................................................................... 134
4 Application Examples ................................................................... 135
4.1 Taking Simple Measurements .................................................. 135
4.2 Taking Cursor Measurements................................................... 136
4.3 Capturing a Single-Shot Signal .................................................. 138
4.4 Analyzing Signal Details ............................................................ 139
4.5 Triggering on a Video Signal ..................................................... 140
4.6 Application of X-Y Function ...................................................... 141
4.7 Analyzing a Differential Communication Signal........................ 143
5 Remote Control ............................................................................ 144
6 Message Prompts and Troubleshooting ........................................ 146
6.1 Message Prompts ..................................................................... 146
6.2 Troubleshooting ....................................................................... 147
7 Specifications ............................................................................... 149
8 Calibration .................................................................................... 153
SERVICE INFORMATION ....................................................................... 154
LIMITED ONE-YEAR WARRANTY ........................................................... 155
xiii
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com
Page 15

1 General Information
1.1 Product Overview
The B&K Precision 2190E digital storage oscilloscope (DSO) is a portable
benchtop instrument used for making measurements of signals and
waveforms. The oscilloscope’s bandwidth is capable of capturing up to 100
MHz signals with a real time sampling rate of up to 1 GSa/s. With up to 40k
points of deep memory, more details of a signal can be captured and
displayed on a large color LCD display for analysis.
Features:
2 channels with bandwidth up to 100 MHz
Single channel real-time sampling rate of up to 1 GSa/s
Up to 40k points of memory depth
7” Color TFT LCD display
Trigger types: Edge, Pulse, Video, Slope, and Alternative
Digital filter and waveform recorder functions
Automatic measurement of 32 parameters (Voltage and Time)
Standard USB host, USBTMC device, and LAN ports
1.2 Package Contents
Please inspect the instrument mechanically and electrically upon receiving
it. Unpack all items from the shipping carton, and check for any obvious
signs of physical damage that may have occurred during transportation.
Report any damage to the shipping agent immediately. Save the original
packing carton for possible future reshipment. Every instrument is shipped
with the following contents:
1 x Quick Start guide (printed)
1 x AC power cord
1 x USB type A to Type B cable
2 x 1:1/10:1 Passive Oscilloscope Probes
1
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com
Page 16

Front USB (Type A) Connector
Menu Function Keys, Menu On/Off, Print Key
Input Channels (1 MΩ BNC)
Probe Compensator (1 kHz and Ground)
1 2 3 4 5
10
1
2
3
4
Verify that all items above are included in the shipping container. If
anything is missing, please contact B&K Precision.
1.3 Front Panel
It is important for you to familiarize yourself with the DSO’s front panel
before operating the instrument. Below is a brief introduction of the front
panel function operation.
Figure 1.1 – Front Panel
Front Panel Description
2
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com
Page 17

Horizontal Controls (Time Base)
Trigger Controls
Auto Setup Button
Menu and Measurement Buttons
Universal Knob
Vertical Controls
1 2 3
5
6
4
6
10
9 5 7
8
1.4 Back Panel
The following images show back and side panel connection locations.
Figure 1.2 – Back Panel
3
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com
Page 18

Back Panel Description
Security Lock Receptacle
LAN Interface
Pass/Fail Output
Rear USB (Type B) Device Connector
Power Input Connector
AC Power Switch
1
2
3 4 5
6
1.5 Display Information
Figure 1.3 – Display Screen
4
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com
Page 19

User Interface Description
Trigger Status
USB Host Port Connection Indicator
Waveform Display Preview
Horizontal Trigger Position Marker
LAN Port Connection Indicator
Menu
Trigger Source, Type, and Level Indicator
Frequency Counter
Horizontal Delay Position
Horizontal Time Base Setting
Channel Source, Coupling Type, Volts/Division, BW Limit
Indicator
Vertical Display Markers (Ground Reference)
Trigger Level Display Marker
13
1
2
3 4 5 6 7
8
9
10
11
12
5
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com
Page 20

2 Getting Started
The included AC power cord is safety certified for this
instrument operating in rated range. To change a cable or add
an extension cable, be sure that it can meet the required
power ratings for this instrument. Any misuse with wrong or
unsafe cables will void the warranty.
Before connecting and powering up the instrument, please review and go
through the instructions in this chapter.
2.1 Input Power Requirements
Input Power
The supply has a universal AC input that accepts line voltage and
frequency input within:
100 – 240 V (+/- 10%), 50/60 Hz (+/- 5%)
100 – 127 V, 45 – 440 Hz
Before connecting to an AC outlet or external power source, be sure that
the power switch is in the OFF position and verify that the AC power cord,
including the extension line, is compatible with the rated voltage/current
and that there is sufficient circuit capacity for the power supply. Once
verified, connect the cable firmly.
2.2 Preliminary Check
Complete the following steps to verify that the oscilloscope is ready for
use.
6
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com
Page 21

Verify AC Input Voltage
Verify and check to make sure proper AC voltages are available to
power the instrument. The AC voltage range must meet the
acceptable specification as explained in section 2.1.
Connect Power
Connect AC power cord to the AC receptacle in the rear panel and
press the power switch to the ON position to turn ON the
instrument. The instrument will have a boot screen while
loading, after which the main screen will be displayed.
Self-Test
The instrument has 3 self-test options to test the screen, keys,
and the LED back lights of the function, menu, and channel keys
as shown below.
Figure 2.1 – Self Test Menu
To perform the self-test, please refer to the Self Test section for
further instructions.
Self-Cal
This option runs an internal self-calibration procedure that will
check and adjust the instrument. To perform the self-calibration,
please refer to the Self Calibration section for further
instructions.
7
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com
Page 22

Check Model and Firmware Version
The model and firmware version can be verified from within the menu
system.
Press Utility and select System Status option. The software/firmware
version, hardware version, model, and serial number will be displayed.
Press the Single key to exit.
Function Check
Follow the steps below to do a quick check of the oscilloscope’s
functionality.
1. Power on the oscilloscope. Press “DEFAULT SETUP” to show the
result of the self-check. The probe default attenuation is 1X.
Figure 2.2 – Scope Layout
2. Set the switch to 1X on the probe and connect the probe to
channel 1 on the oscilloscope. To do this, align the slot in the
probe connector with the key on the CH 1 BNC, push to connect,
and twist to the right to lock the probe in place. Connect the
probe tip and reference lead to the PROBE COMP connectors.
8
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com
Page 23

Figure 2.3 – Probe Compensation
PROBE
COMP
CH1
3. Press “AUTO” to show the 1 kHz frequency and about 3V peak-
peak square wave in couple seconds.
Figure 2.4 – 3 Vpp Square Wave
4. Press “CH1” two times to turn off channel 1, Press“CH2” to
change screen into channel 2, reset the channel 2 as step 2 and
step 3.
9
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com
Page 24

Probe Safety
SHOCK HAZARD
To avoid electric shock when using the probe, keep fingers
behind the guard on the probe body.
To avoid electric shock while using the probe, do not touch
metallic portions of the probe head while it is connected to a
voltage source. Connect the probe to the oscilloscope and
connect the ground terminal to ground before you take any
measurements.
A guard around the probe body provides a finger barrier for protection
from electric shock.
Figure 2.5 – Oscilloscope Probe
Connect the probe to the oscilloscope and connect the ground terminal to
ground before you take any measurements.
10
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com
Page 25

Probe Attenuation
NOTE: The default setting for the Probe option is 1X.
NOTE: When the attenuation switch is set to 1X, the probe limits
the bandwidth of the oscilloscope to 6 MHz (according to Probe
spec). To use the full bandwidth of the oscilloscope, be sure to set
the switch to 10X
Probes are available with various attenuation factors which affect the
vertical scale of the signal. The Probe Check function verifies that the
Probe attenuation option matches the attenuation of the probe.
You can push a vertical menu button (such as the CH 1 MENU button), and
select the Probe option that matches the attenuation factor of your probe.
Be sure that the attenuation switch on the probe matches the Probe
option in the oscilloscope. Switch settings are 1X and 10X.
Probe Compensation
As an alternative method to Probe Check, you can manually perform this
adjustment to match your probe to the input channel.
11
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com
Page 26

Figure 2.6 – Probe Compensation Setup
AUTO
BUTTON
PROBE
COMP
CH1
Undercompensated
Correctly Compensated
Overcompensated
1. Set the Probe option attenuation in the channel menu to 10X. Do
so by pressing CH1 button and selecting “Probe” from menu.
Select 10X. Set the switch to 10X on the probe and connect the
probe to channel 1 on the oscilloscope. If you use the probe
hook-tip, ensure a proper connection by firmly inserting the tip
onto the probe.
2. Attach the probe tip to the PROBE COMP 3V connector and the
reference lead to the PROBE COMP Ground connector. Display
the channel and then push the “AUTO” button.
3. Check the shape of the displayed waveform.
Figure 2.7 – Compensation Illustration
4. If necessary, adjust your probe’s compensation trimmer pot.
Repeat as necessary.
12
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com
Page 27

3 Functions and Operating
Descriptions
To use your oscilloscope effectively, you need to learn about the following
oscilloscope functions:
• Menu and control button
• Connector
• Auto Setup
• Default Setup
• Universal knob
• Vertical System
• Channel Function Menu
• Math Functions
• Using REF
• Horizontal System
• Trigger System
• Acquiring signals System
• Display System
• Measuring waveforms System
• Utility System
• Storage System
• Online Help function
13
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com
Page 28

3.1 Menu and Control Button
Figure 3.1 – Control Buttons
Channel buttons (CH1, CH2): Press a channel button to turn
that channel ON or OFF and open the channel menu for that
channel. You can use the channel menu to set up a channel.
When the channel is on, the channel button is lit.
MATH: Press to display the Math menu. You can use the
MATH menu to use the oscilloscope’s Math functions.
REF: Press to display the Ref Wave menu. You can use this
menu to save and recall four or two reference waveforms to
and from internal memory.
14
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com
Page 29

HORI MENU: Press to display the Horizontal menu. You can
use the Horizontal menu to display the waveform and zoom
in a segment of a waveform.
TRIG MENU: Press to display the Trigger menu. You can use
the Trigger menu to set the trigger type (Edge. Pulse, Video,
Slope, Alternative) and trigger settings.
SET TO 50%: Press to stabilize a waveform quickly. The
oscilloscope can set the trigger level to be halfway between
the minimum and maximum voltage level automatically. This
is useful when you connect a signal to the EXT TRIG
connector and set the trigger source to Ext or Ext/5.
FORCE: Use the FORCE button to complete the current
waveform acquisition whether the oscilloscope detects a
trigger or not. This is useful for Single acquisitions and
Normal trigger mode.
SAVE/RECALL: Press to display the Save/Recall menu. You
can use the Save/Recall menu to save and recall up to 20
oscilloscope setups and 10 waveforms to/from internal
memory or a USB memory device (limited by memory
capacity of the USB flash drive). You can also use it to recall
the default factory settings, to save waveform data as a
comma-delimited file (.CSV), and to save the displayed
waveform image.
ACQUIRE: Press to display Acquire menu. You can use the
Acquire menu to set the acquisition Sampling Mode
(Sampling, Peak Detect, and Average).
MEASURE: Press to display a menu of measurement
parameters.
CURSORS: Display the Cursor Menu. Vertical Position
controls adjust cursor position while displaying the Cursor
Menu and the cursors are activated. Cursors remain
displayed (unless the “Type” option is set to “Off”) after
leaving the Cursor Menu but are not adjustable.
DISPLAY: Press to open the Display menu. You can use the
Display menu to set grid and waveform display styles, and
persistence.
UTILITY: Press to open the Utility menu. You can use the
Utility menu to configure oscilloscope features, such as
15
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com
Page 30

sound, language, counter, etc. You can also view system
status and update software.
DEFAULT SETUP: Press to reset the oscilloscope’s settings to
the default factory configuration.
HELP: Enter the online help system.
AUTO: Automatically sets the oscilloscope controls to
produce a usable display of the input signals.
RUN/STOP: Continuously acquires waveforms or stops the
acquisition.
Note: If waveform acquisition is stopped (using the
RUN/STOP or SINGLE button), the TIME/DIV control expands
or compresses the waveform.
SINGLE: Acquire a single waveform and then stops waveform
acquisition.
3.2 Connectors
Figure 3.2 – Connectors
Channel Connector (CH1, CH2): Input connectors for waveform
display.
EXT TRIG: Input connector for an external trigger source. Use the
Trigger Menu to select the “Ext” or “Ext/5” trigger source.
Probe Compensation: 1 kHz voltage probe compensation output
and ground. Use to electrically match the probe to the
oscilloscope input circuit.
16
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com
Page 31

3.3 Auto Setup
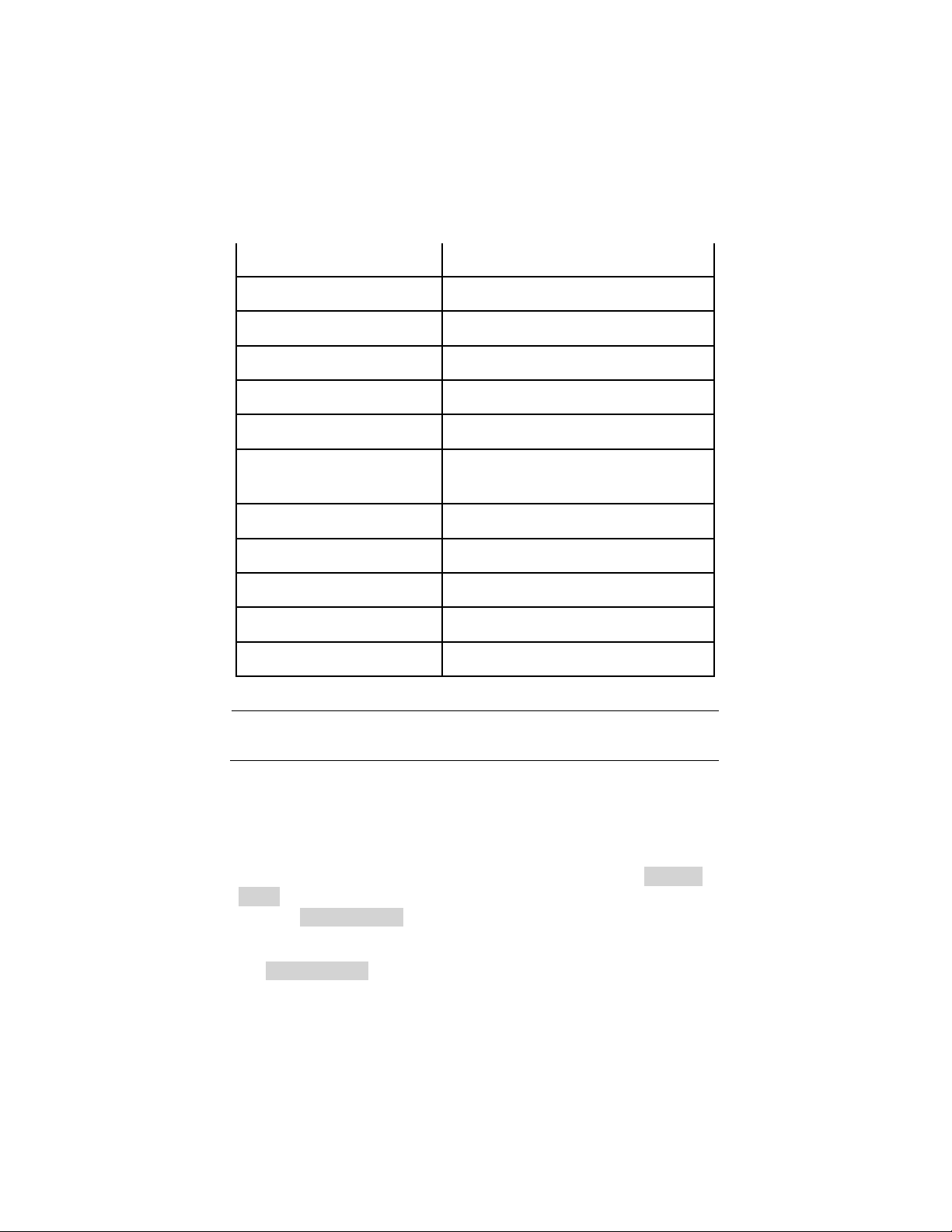
Option
Description
(Multi-cycle sine)
Auto set the screen and display
several cycles signal.
(Single-cycle sine)
Set the screen and auto display
single cycle signal.
The 2190E Digital Storage Oscilloscope has an Auto Setup function that
identifies the waveform types and automatically adjusts controls to
produce a usable display of the input signal.
Press the AUTO front panel button, and then press the menu option
button adjacent to the desired waveform as follows:
Figure 3.3 – Auto Setup
Table 3.1 – Autoset Menu
17
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com
Page 32

(Rising edge)
Auto set and show the rising time.
(Falling edge)
Auto set and show the falling time.
(Undo Setup)
Causes the oscilloscope to recall the
previous setup.
Function
Setting
Acquire Mode
Adjusted to Sampling
Display Format
Y-T
Display Type
Set to Dots for a video signal, set to
Vectors for an FFT spectrum; otherwise,
unchanged
Vertical Coupling
Adjusted to DC or AC according to the
input signal
Bandwidth Limit
Off(full)
Auto Set determines the trigger source based on the following conditions:
• If multiple channels have signals, channel with the lowest
frequency signal.
• No signals found, the lowest-numbered channel displayed when
Auto set was invoked.
• No signals found and no channels displayed, oscilloscope displays
and uses channel 1.
Table 3.2 – Auto Set Function Menu Items
18
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com
Page 33
V/div
Adjusted
VOLTS/DIV adjustability
Coarse
Signal inverted
Off
Horizontal position
Center
Time/div
Adjusted
Trigger type
Edge
Trigger source
Auto detect the channel which has the
input signal
Trigger slope
Rising
Trigger mode
Auto
Trigger coupling
DC
Trigger holdoff
Minimum
Trigger level
Set to 50%
NOTE: The AUTO button can be disabled. Please see “Education
Mode” for details.
3.4 Default Setup
The oscilloscope is set up for normal operation when it is shipped from the
factory. This is the default setup. To recall this setup, press the DEFAULT
SETUP button. For the default options, buttons and controls when you
press the DEFAULT SETUP button, refer to “Table 3.3 – Default Setup
Table” below.
The DEFAULT SETUP button does not reset the following settings:
19
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com
Page 34

• Language option
Menu or system
Options, knobs
or buttons
Default setup
CH1,CH2
Coupling
DC
BW limit
Off
Volts/div
Coarse
Probe
1X
Invert
Off
Filter
Off
Volts/div
1.00V
MATH
Operation
CH1+CH2
CH1 Invert
Off
CH2 Invert
Off
FFT operation:
Source
CH1
Window
Hanning
FFT Zoom
1X
Scale
dBVrms
Display
Split
HORIZONTAL
Window
Main
Position
0.00μs
Sec/div
500μs
Window Zone
50.0μs
Trigger knob
level
CURSOR
Type
Off
• Saved reference waveform files
• Saved setup files
• Display contrast
• Calibration data
Table 3.3 – Default Setup Table
20
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com
Page 35

21
Source
CH1
Horizontal (voltage)
+/-3.2divs
Vertical (time)
+/-5divs
ACQUIRE
three mode options
Sampling
Averages
16
Sampling mode
Real Time
DISPLAY
Type
Vectors
Persist
off
Gird
Intensity
60%
Brightness
40%
Format
YT
Menu Display
infinite
SAVE/RECALL
Type
Setups
Save To
Device
Setup
No.1
REF
REFA/REFB
REFA
Source
CH1
REFA
off
REFB
off
UTILITY
Sound
on
Counter
On
Back USB
USBTMC
Pass/Fail
off
Record
off
TRIGGER (edge)
Type
edge
Source
CH1
Slope
Rising
Mode
Auto
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com
Page 36

Coupling
DC
LEVEL
0.00V
TRIGGER (pulse)
Type
pulse
Source
CH1
When
=
Set Pulse Width
1.00ms
Mode
Auto
Coupling
DC
TRIGGER (Video)
Type
Video
Source
CH1
Polarity
Normal
Sync
All Lines
Standard
NTSC
Mode
Auto
TRIGGER
(Slope)
Type
Slope
Source
CH1
Time
1.00ms
Mode
Auto
TRIGGER (Alternative)
Type
Alternative
Source
CH1
Mode
Edge
Coupling
DC
22
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com
Page 37

3.5 Universal Knob
Figure 3.4 – Universal Knob
You can use the Universal knob with many functions, such as adjusting the
hold off time, moving cursors, setting the pulse width, setting the video
line, adjusting the upper and lower frequency limit, adjusting the X and Y
masks when using the pass/fail function, etc. You can also turn the
“Universal” knob to adjust the storage position of setups, waveforms,
pictures when saving/recalling, and to select menu options. With some
functions, the light indicator above the knob will turn on to indicate that
the knob can be used to make changes or adjustments for that function.
The knob can also be pushed to make a selection after
changes/adjustments have been made.
3.6 Vertical System
The vertical control could be used for displaying waveform, rectify scale
and position.
23
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com
Page 38

Figure 3.5 – Vertical System Controls
Using Vertical Position Knob and Volts/div Knob
• Vertical “POSITION” Knob
1. Use the Vertical “POSITION” knobs to move the channel
waveforms up or down on the screen. This button’s
resolution varies as per the vertical scale.
2. When you adjust the vertical position of channels
waveforms, the vertical position information will display
on the bottom left of the screen. For example “Volts
Pos=24.6mV”.
3. Press the vertical “POSITION” knob to set the vertical
position to zero.
• “Volts/div” Knob
1. Use the “Volts/div” knobs to control how the
oscilloscope amplifies or attenuates the source signal of
channel waveforms. When you turn the “volts/div”
knob, the oscilloscope increases or decreases the vertical
size of the waveform on the screen with respect to the
ground level.
2. When you press the “Volt/div” knob, you can switch
“Volts/div” option between “Coarse” and “Fine”. The
24
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com
Page 39

vertical scale is set by a 1-2-5 step sequence in Coarse
Option
Setting
Introduction
Coupling
DC
AC
GND
DC passes both AC and DC
components of the input signal.
AC blocks the DC component of the
input signal and attenuates signals
below 10 Hz.
GND disconnects the input signal.
BW limit
On
Off
Limits the bandwidth to reduce
display noise; filters the signal to
reduce noise and other unwanted
high frequency components.
Volts/Div
Coarse
Fine
Selects the resolution of the
Volts/Div knob
Coarse defines a 1-2-5 sequence.
Fine changes the resolution to small
steps between the coarse settings.
mode. Increase in the clockwise direction and decrease
in the counterclockwise direction. In Fine mode, the
knob changes the Volts/Div scale in small steps between
the coarse settings. Again, increase in the clockwise
direction and decrease in the counterclockwise
direction.
3.7 Channel Function Menu
Table 3.4 – Channel Function Menu
25
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com
Page 40

Probe
1X, 5X
10X, 50X
100X, 500X,
1000X
Set to match the type of probe you
are using to ensure correct vertical
readouts.
Next Page
Page 1/3
Press this button to enter the second
page menu
Option
Setting
Instruction
Invert
on
off
Turn on invert function.
Turn off invert function.
Filter
Press this button to enter the
“Digital Filter menu”.
Next Page
Page 2/3
Press this button to enter the third
page menu.
Option
Setting
Introduction
Unit
V A Set the scale unit to voltage
Set the scale unit to current.
Skew
-100 ns –
100ns
Set the skew time between two
channels.
Next Page
Page 3/3
Press this button to return to the
first page menu.
Table 3.5 – Channel Function Menu 2
Table 3.6 – Channel Function Menu 3
26
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com
Page 41
Table 3.7 – Digital Filter Menu
Option
Setting
Introduction
Digital Filter
On
Off
Turn on the digital filter.
Turn off the digital filter.
Type
Setup as LPF (Low Pass Filter).
Setup as HPF (High Pass Filter).
Setup as BPF (Band Pass Filter).
Setup as BRF (Band Reject Filter).
Upper limit
Turn the “Universal” knob to set
upper limit.
Lower limit
Turn the “Universal” knob to set
lower limit.
Return
Return to the second page menu.
NOTE:
The oscilloscope’s vertical response rolls off slowly above its
specified bandwidth. Therefore, the FFT spectrum can show valid
frequency information higher than the oscilloscope’s bandwidth.
However, the magnitude information near or above the
bandwidth will not be accurate.
• “GND” Coupling: Use GND coupling to display a zero-volt
waveform. Internally, the channel input is connected to a zerovolt reference level.
• Fine Resolution: The vertical scale readout displays the actual
Volts/Div setting while in the fine resolution setting. Changing the
setting to coarse does not change the vertical scale until the
VOLTS/DIV control is adjusted.
27
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com
Page 42

If the channel is set to DC coupling, you can quickly measure the
DC component of the signal by simply noting its distance from the
ground symbol.
If the channel is set to AC coupling, the DC component of the
signal is blocked allowing you to use greater sensitivity to display
the AC component of the signal.
Setting up Channels
Each channel has its own separate Menu. The items are set up separately
according to each channel.
1. Setup Channel Coupling
Take CH1 for example; the tested signal is a sine wave signal with
DC deflection:
• Press “CH1”→“Coupling”→“AC”, Set to AC couple mode.
This will block the DC component of the input signal.
• Press “CH1”→“Coupling”→“DC”, Set to DC couple mode.
Both DC and AC components of the input signal will be
captured.
28
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com
Page 43

• Press “CH1”→“Coupling”→“GND”, Set to GROUND
mode. This disconnects the input signal.
2. Bandwidth Limiting
Take CH1 for example:
• Press “CH1”→“BW Limit”→ “On”, and bandwidth will be
limited to 20 MHz.
• Press “CH1”→“BW Limit”→ “Off”, and bandwidth limit
will be disabled.
Figure 3.6 – DC Coupling
29
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com
Page 44

Figure 3.7 – Bandwidth Limit
3. Volts/Div Settings
Vertical scale adjust have Coarse and Fine modes, Vertical
sensitivity range of 2 mV/div – 10 V/div.
Take CH1 for example:
• Press “CH1”→“Volts/Div”→“Coarse”. It is the default
setting of Volts/Div, and makes the vertical scaling in a 12-5-step sequence from 2 mV/div, 5 mV/div, and 10
mV/div to 10 V/div.
• Press “CH1”→ Volts/Div”→ Fine”. This setting changes
the vertical control to small steps between the coarse
settings. It will be helpful when you need to adjust the
waveform vertical size in smaller steps.
30
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com
Page 45

Figure 3.8 – Coarse/Fine Control
4. Setting Probe Attenuation
In order to set the attenuation coefficient, you need to specify it
in the channel operation Menu. If the attenuation coefficient is
10:1, the input coefficient should be set to 10X, so that the
Volts/div information and measurement testing is correct.
Take CH1 for example, when you use the 100:1 probe:
• Press “CH1”→“Probe” →“100X”
31
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com
Page 46
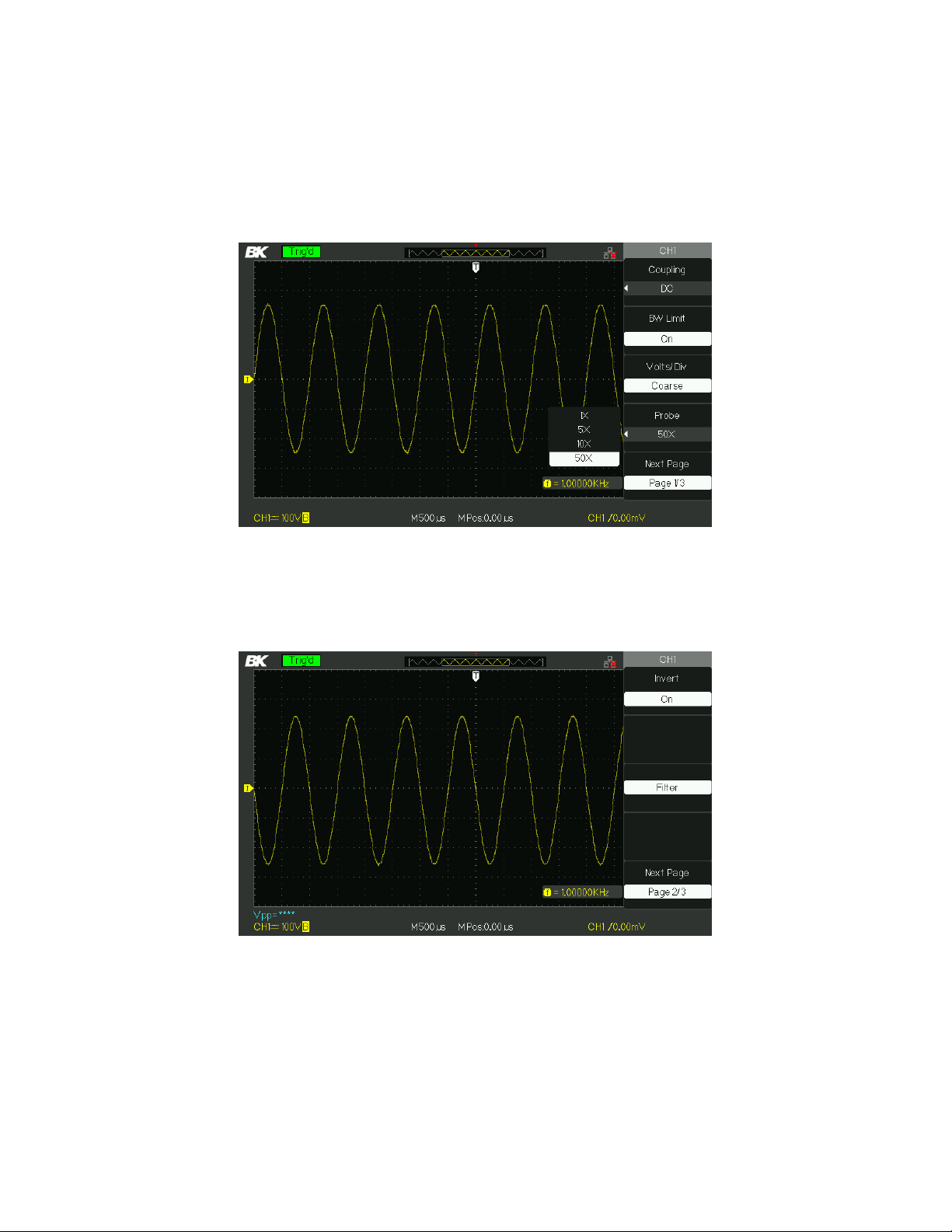
Figure 3.9 – Probe Attenuation Setting
5. Inverting Waveforms
Take CH1 for example:
• Press “CH1”→ Next Page “Page 1/3” →“Invert”→“On”:
Figure 3.10 – Invert Waveform Screen
32
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com
Page 47

6. Using the Digital Filter
• Press “CH1”→ Next Page “Page 1/3”→ “Filter”, display
the digital filter menu. Select “Filter Type”, then select
“Upper Limit” or “Lower Limit” and turn the “Universal”
knob to adjust them.
• Press “CH1”→ Next Page “Page 1/3”→ “Filter” →“Off”.
Turn off the Digital Filter function.
Figure 3.11 – Digital Filter Menu
• Press “CH1”→ “Next Page “Page 1/3”→ “Filter” → “On”.
Turn on the Digital Filter function.
33
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com
Page 48

Figure 3.12 – Digital Filter Adjustment Screen
Function
Setting
Description
Operation
+, -, *, /, FFT
Math operates between signal
source CH1 and CH2.
Source A
CH1 – CH2
Select CH1 or CH2 as Source A.
Source B
CH1 – CH2
Select CH1 or CH2 as Source B.
Invert
on
Invert the MATH waveform.
3.8 Math Functions
Math shows the results after +,-,*, / and FFT operations of the CH1 and
CH2. Press the MATH button to display the waveform math operations.
Press the MATH button again to remove the math waveform display.
Table 3.8 – Math Function Menu
34
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com
Page 49

off
Turn off MATH Invert function.
Next Page
Page 1/2
Enter the second page of MATH
menu.
Function
Setting
Description
Use universal knob to adjust the
vertical position of the MATH
waveform.
Use universal knob to adjust the
vertical scale of the MATH
waveform.
Next Page
Page 2/2
Go back to first page of MATH
menu.
Operation
Setting
Description
+
A+B
Source A waveform adds Source B
waveform.
-
A-B
Source B waveform is subtracted
from Source A waveform.
*
A*B
Source A multiplied by Source B
/
A/B
Source A divided by Source B
FFT
Fast Fourier Transform.
Table 3.9 – Math Function Menu 2
Table 3.10 – Math Function Description
35
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com
Page 50

Figure 3.13 – Math Waveform
FFT Option
Setting
Description
Source
CH1, CH2
Select this channel as the FFT
source.
FFT Spectrum Analyzer
The FFT process mathematically converts a time-domain signal into its
frequency components. You can use the Math FFT mode to view the
following types of signals:
• Analyze the harmonic wave in the Power cable.
• Test the harmonic content and distortion in the system
• Show the Noise in the DC Power supply
• Test the filter and pulse response in the system
• Analyze vibration
Table 3.11 – FFT Function Menu 1
36
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com
Page 51

Window
Hanning
Hamming
Rectangular
Blackman
Select FFT window types.
FFT ZOOM
1X
2X
5X
10X
Changes the horizontal
magnification of the FFT display.
Next Page
Page 1/2
Enter the second page of FFT
menu.
FFT Option
Setting
Description
Scale
Vrms
Set Vrms to be the Vertical Scale
unit.
dBVrms
Set dBVrms to be the vertical
Scale unit.
Display
Split
Full screen
Display FFT waveform on half
screen.
Display FFT waveform on full
screen.
Next Page
Page 2/2
Return to the first page of FFT
menu.
Table 3.12 – FFT Function Menu 2
37
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com
Page 52

To use the Math FFT mode, you need to perform the following steps:
1. Set up the source (time-domain) waveform.
2. Press the AUTO button to display an YT waveform.
3. Turn the vertical “POSITION” knob to move the YT waveform to
the center vertically (zero divisions).
4. Turn the horizontal “POSITION” knob to position the part of the
YT waveform that you want to analyze in the center eight
divisions of the screen. The oscilloscope calculates the FFT
spectrum using the center 1024 points of the time-domain
waveform.
5. Turn the “Volts/div” knob to ensure that the entire waveform
remains on the screen.
6. Turn the “S/div” knob to provide the resolution you want in the
FFT spectrum.
7. If possible, set the oscilloscope to display many signal cycles.
To display FFT correctly, follow these steps:
1. Push the “MATH” button.
2. Set the “Operation” option to FFT.
3. Press the “Source” button to select “CH1” or “CH2” according to
input signal channel.
4. Turn the “Time/div” knob to adjust the sampling rate (this
parameter is displayed behind the time base parameter), making
sure it is at least double the input signal frequency. (to avoid
aliasing according to Nyquist’s theorem)
Displaying the FFT Spectrum
Press the MATH button to display the Math Menu. Use the options to
select the Source channel, Window algorithm, and FFT Zoom factor. You
can display only one FFT spectrum at a time. You can select “Full screen”
or “Split” in “Display” option to display FFT waveform on full screen or
display channel waveform and its FFT waveform on half screen at a time.
38
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com
Page 53

Figure 3.14 – FFT Function
Window
Characteristics
Applications
Rectangular
Best frequency
resolution, worst
magnitude resolution.
This is essentially the
same as no window.
Symmetric transients
or bursts. Equalamplitude sine waves
with fixed frequencies.
Broadband random
noise with a relatively
slowly varying
spectrum.
Select FFT window
Windows reduce spectral leakage in the FFT spectrum. The FFT assumes
that the YT waveform repeats forever. With an integral number of cycles,
the YT waveform starts and ends at the me amplitude and there are no
discontinuities in the signal shape A non-integral number of cycles in the
YT waveform causes the signal start and end points to be at different
amplitudes. The transitions between the start and end points cause
discontinuities in the signal that introduce high-frequency transients.
Table 3.13 – FFT Window Description
39
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com
Page 54

Hanning
Hamming
Better frequency,
poorer magnitude
accuracy than
Rectangular. Hamming
has slightly better
frequency resolution
than Hanning.
Sine, periodic, and
narrow-band random
noise. Asymmetric
transients or bursts.
Blackman
Best magnitude, worst
frequency resolution.
Single frequency
waveforms, to find
higher order
harmonics.
Magnifying the FFT Spectrum
You can magnify and use cursors to take measurements on the FFT
spectrum. The oscilloscope includes an “FFT Zoom” option to magnify
horizontally, press this option button to select “1X”, “2X”, “5X” or “10X”.
Moreover, you also can turn the “Universal” knob to magnify FFT
waveform horizontally in a 1-2-5 step. To magnify vertically, turn the
“Volts/div” knob.
Measuring an FFT Spectrum Using Cursors
You can take two measurements on FFT spectrums: magnitude (in dB) and
frequency (in Hz). Magnitude is referenced to 0 dB, where 0 dB equals 1
VRMS. You can use the cursors to take measurements at any zoom factor.
Use horizontal cursors to measure amplitude and vertical cursors to
measure frequency.
If you input a sine signal into channel 1, follow these steps:
• Measure FFT Amplitude
1. Input a sine signal to channel 1, and press the
“AUTO” button.
2. Press the “MATH” button to enter the “MATH”
menu.
3. Press the “Operation” option button to select “FFT”.
4. Press the “Source” option button to select “CH1”.
5. Press CH1 button to display CH1 menu.
40
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com
Page 55

6. Turn the “Time/div” knob to adjust the sampling
rate (at least double the frequency of input signal).
7. If FFT is displayed on full screen, press CH1 button
again to remove channel waveform display.
8. Press the “CURSOR” button to enter “Cursor” menu.
9. Press the “Cursor Mode” button to select “Manual”.
10. Press the “Type” option button to select “Voltage”.
11. Press the “Source” option button to select “MATH”.
12. Press the “CurA” option button; turn the “Universal”
knob to move Cursor A to the highest point of the
FFT waveform.
13. Press the “CurB” option button, turn the “Universal”
knob to move Cursor B to the lowest point of the
FFT waveform.
14. The amplitude (△T) displays on the top of the left
screen.
Figure 3.15 – Measuring FFT Amplitude
• Measure FFT Frequency
1. Press the CURSOR button.
2. Press the “Cursor Mode” button to select “Manual”.
3. Press the “Type” option button to select “Time”.
41
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com
Page 56

4. Press the “Source” option button to select “MATH”.
NOTE:
The FFT of a waveform that has a DC component or offset can
cause incorrect FFT waveform magnitude values. To minimize the
DC component, choose AC Coupling on the source waveform.
To display FFT waveforms with a large dynamic range, use the
dBVrms scale. The dBVrms scale displays component magnitudes
using a log scale.
The Nyquist frequency is the highest frequency that any real-time
digitizing oscilloscope can acquire without aliasing. This frequency
is half that of the sample rate provided it is within the analog
5. Press the “CurA” option button, turn the “Universal”
button to move Cursor A to the highest position of
the FFT waveform.
6. The value of CurA displaying on the top of the left
screen is FFT frequency. This frequency should be
the same as input signal frequency.
Figure 3.16 – Measuring FFT Frequency
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com
42
Page 57

bandwidth of the oscilloscope. Frequencies above the Nyquist
frequency will be undersampled, which causes aliasing.
Option
Setting
Description
Source
CH1,CH2,
CH1 off
CH2 off
Choose the waveform display to
store.
REFA
REFB
Choose the reference location to
store or recall a waveform.
Save
Stores source waveform to the
chosen reference location.
REFA
REFB
on
off
Recall the reference waveform on
the screen.
Turn off the reference waveform.
3.9 Using REF
The reference control saves waveforms to a nonvolatile waveform
memory. The reference function becomes available after a waveform has
been saved.
Table 3.14 – REF Function Menu
43
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com
Page 58

Press the Ref button to display the “Reference waveform menu”.
NOTE:
X-Y mode waveforms are not stored as reference waveforms.
You cannot adjust the horizontal position and scale of the
reference waveform.
Figure 3.17 – Reference Waveform Menu
Operation step:
1. Press the “REF” menu button to display the “Reference waveform
menu”.
2. Press the “Source” option button to select input signal channel.
3. Turn the vertical “POSITION” knob and “Volts/div” knob to adjust
the vertical position and scale.
4. Press the third option button to select “REFA” or “REFB” as
storage position.
5. Press the “Save” option button.
6. Press the bottom option button to select “REFA On” or “REFB On”
to recall the reference waveform.
44
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com
Page 59

3.10 Horizontal System
Option
Setting
Description
Delayed
On
Off
Turn on this function for main time base
waveform to display on the top half screen
and window time base waveform to display
on the below half screen at the same time.
Turn off this function to only display main
time base waveform on the screen.
Shown below are two knobs and one button in the HORIZONTAL area.
Figure 3.18 – Horizontal Controls
Table 3.15 – Horizontal System Function Menu
Horizontal Control Knob
You can use the horizontal controls to change the horizontal scale and
position of waveforms. The horizontal position readout shows the time
represented by the center of the screen, using the time of the trigger as
45
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com
Page 60

zero. Changing the horizontal scale causes the waveform to expand or
contract around the screen center.
• Horizontal “POSITION” knob
1. Adjust the horizontal position of all channels and
math waveforms (the position of the trigger relative
to the center of the screen). The resolution of this
control varies with the time base setting.
2. When you press the horizontal “POSITION” Knob,
you can set the horizontal position to zero.
• “Time/div” knob
1. Used to change the horizontal time scale to magnify
or compress the waveform. If waveform acquisition
is stopped (using the RUN/STOP or SINGLE button),
turn the Time/div knob to expand or compress the
waveform.
2. Select the horizontal Time/div (scale factor) for the
main or the window time base. When Window Zone
is enabled, it changes the width of the window zone
by changing the window time base.
• Display scan mode
When the Time/div control is set to 100 ms/div or slower and the
trigger mode is set to Auto, the oscilloscope enters the scan
acquisition mode. In this mode, the waveform display updates
from left to right. There is no trigger or horizontal position control
of waveforms during scan mode.
Window Zone
Use the Window Zone option to define a segment of a waveform to see
more detail. This function behaves like zooming into a portion of the
captured waveform. The window time base setting cannot be set slower
than the Main time base setting.
You can turn the Horizontal Position and Time/div controls to enlarge or
minimize waveforms in the Window Zone.
If you want to see a section of the waveform in details, follow these steps:
1. Press the “HORI MENU” button to enter the “Horizontal menu”.
46
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com
Page 61

2. Turn the “Time/div” knob to change the main time base scale.
3. Press the “Delayed” option button to select “On”.
Figure 3.19 – Horizontal Delay Menu
4. Turn the “Horizontal Position” knob (adjust window’s position) to
select the window that your need and expanded window
waveform display on the below half screen at the same time.
3.11 Trigger System
The trigger determines when the oscilloscope starts to acquire data and
display a waveform. When a trigger is set up properly, the oscilloscope
converts unstable displays or blank screens into meaningful waveforms.
Here are three buttons and one knob in the trigger area. See below:
47
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com
Page 62

Figure 3.20 – Trigger Controls
• “TRIG MENU” Button: Press the “TRIG MENU” Button to
display the “Trigger Menu”.
• “LEVEL” Knob: The LEVEL knob is to set the
corresponding signal voltage of trigger point in order to
sample. Press the “LEVEL” knob to set trigger level to
zero.
• “SET TO 50%” Button: Use the “SET TO 50%” button to
stabilize a waveform quickly. The oscilloscope can set
the Trigger Level to be about halfway between the
minimum and maximum voltage levels automatically.
This is useful when you connect a signal to the EXT TRIG
BNC and set the trigger source to Ext or Ext/5.
• “FORCE Button: Use the FORCE button to complete the
current waveform acquisition whether the oscilloscope
detects a trigger or not. This is useful for SINGLE
acquisitions and Normal trigger mode.
Signal Source
You can use the Trigger Source options to select the signal that the
oscilloscope uses as a trigger. The source can be any signal connected to a
channel BNC, to the EXT TRIG BUS, or the AC power line (available only
with Edge Trigger).
48
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com
Page 63

Option
Setting
Description
Type
Edge
With Edge highlighted, the rising or falling edge
of the input signal is used for the trigger.
Source
CH1
CH2
Triggers on a channel whether or not the
waveform is displayed.
EXT
Does not display the trigger signal; the Ext
option uses the signal connected to the EXT TRIG
front-panel BNC and allows a trigger level range
of -1.2V to +1.2V.
EXT/5
Same as Ext option, but attenuates the signal by
a factor of five, and allows a trigger level range
of +6V to -6V.This extends the trigger level
range.
AC Line
This selection uses a signal derived from the
power line as the trigger source; trigger coupling
is set to DC and the trigger level to 0 volts.
Slope
Trigger on Rising edge of the trigger signal.
Trigger on Falling edge of the trigger signal.
Trigger Type
The scopes have five trigger types: Edge, Video, Pulse, Slope, and
Alternate.
Edge Trigger
Use Edge triggering to trigger on the edge of the oscilloscope input signal
at the trigger threshold.
Table 3.16 – Edge Trigger Function Menu
49
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com
Page 64

Trigger on Rising edge and Falling edge of the
trigger signal.
Mode
Auto
Use this mode to let the acquisition free-run in
the absence of a valid trigger; This mode allows
an untriggered, scanning waveform at 100
ms/div or slower time base settings.
Normal
Use this mode when you want to see only valid
triggered waveforms; when you use this mode,
the oscilloscope does not display a waveform
until after the first trigger.
Single
When you want the oscilloscope to acquire a
single waveform, press the “SINGLE” button.
Set up
Enter the “Trigger Setup Menu” (See Table 3.17).
Option
Setting
Explain
Coupling
DC
Passes all components of the signal
AC
Blocks DC components, attenuates
signals below 50 Hz.
HF Reject
Attenuates the high-frequency
components above 150 kHz.
LF Reject
Blocks the DC component, attenuates the
low-frequency components below 7 kHz.
Holdoff
Using the “universal” knob to adjust
holdoff time (sec), the holdoff value is
displayed.
Holdoff
Reset holdoff time to 100ns.
Table 3.17 – Trigger Setup Function Menu
50
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com
Page 65

Reset
Return
Return to the first page of “Trigger main
menu”.
Figure 3.21 – Trigger Menu Screen
Operating Instructions:
1. Setup Type
Press the “TRIG MENU” button to display “Trigger”
menu.
Press the “Type” option button to select “Edge”.
2. Set up Source
According to the input signal, press the “Source” option
button to select “CH1”, “CH2”, “EXT”, “EXT/5” or “AC
Line”.
3. Set up Slope
Press the “Slope” option button to select “ ”, “
” or “ ”.
51
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com
Page 66

4. Set up Trigger mode
Option
Setting
Description
Type
Pulse
Select the pulse to
trigger the pulse match
the trigger condition.
Source
CH1
CH2
EXT
EXT/5
AC Line
Select input signal
source.
Press the “Trigger mode” option button to select “Auto”,
“Normal”, or “Single”.
Auto: The waveform refreshes at a high speed whether
the trigger condition is satisfied or not.
Normal: The waveform refreshes when the trigger
condition is satisfied and waits for next trigger event
occurring when the trigger condition is not satisfied.
Single: The oscilloscope acquires a waveform when the
trigger condition is satisfied and then stops
5. Set up Trigger coupling
Press the “Set Up” button to enter the “Trigger Setup
Menu”.
Press the “Coupling” option button to select “DC”, “AC”,
“HF Reject” or “LF Reject”.
Pulse Trigger
Use Pulse Width triggering to trigger on aberrant pulses.
Table 3.18 – Pulse Trigger Function Menu 1
52
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com
Page 67

When
(Positive pulse width less
than pulse width setting)
(Positive pulse width larger
than pulse width setting)
(Positive pulse width equal
to pulse width setting)
(Negative pulse width less
than pulse width setting)
(Negative pulse width
larger than pulse width setting)
(Negative pulse width
equal to pulse width setting)
Select how to compare
the trigger pulse
relative to the value
selected in the Set
Pulse Width option.
Set Width
20.0ns~10.0s
Selecting this option
can turn the universal
to set up the pulse
width.
Next Page
Page 1/2
Press this button to
enter the second page.
Figure 3.22 – Pulse Trigger Menu 1
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com
53
Page 68
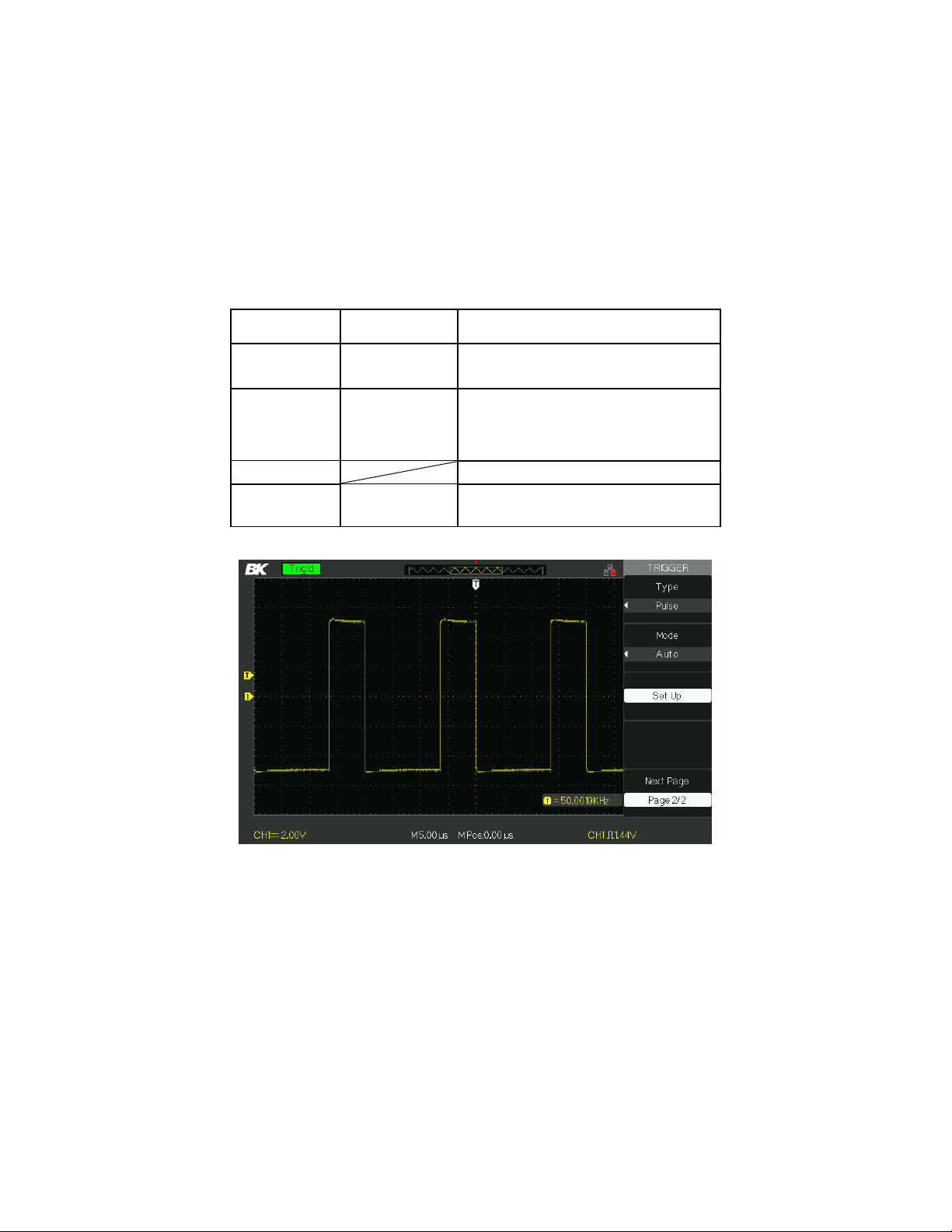
Option
Setting
Description
Type
Pulse
Select the pulse to trigger the pulse
match the trigger condition.
Mode
Auto
Normal
single
Select the type of triggering; Normal
mode is best for most Pulse Width
trigger applications.
Set up
Enter the “Trigger setup menu”.
Next Page
Page 2/2
Press this button to return to the first
page.
Table 3.19 – Pulse Trigger Function Menu 2
Figure 3.23 – Pulse Trigger Menu 2
Operating Instructions:
1. Setup Type
Press the “TRIG MENU” button to display “Trigger”
menu.
54
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com
Page 69

Press the “Type” option button to select “Pulse”.
Option
Setting
Description
Type
Video
When you select the video type,
put the couple set to the AC, then
you could trigger the NTSC, PAL
and SECAM video signal.
Source
CH1
CH2
Select the input source to be the
trigger signal.
EXT
EXT/5
Ext and Ext/5 use the signal
applied to the EXT TRIG
connector as the source.
Polarity
(Normal)
Normal triggers on the negative
edge of the sync pulse.
(Inverted)
Inverted triggers on the positive
edge of the sync pulse.
Sync
Line Num
All lines
Odd field
Even Field
Select appropriate video sync.
Next Page
Page 1/2
Enter the second page of
“Video trigger menu”.
2. Set up condition
Press the “When” option button to select “ ”, “
”, “ ”, “ ”, “ ”or“ ”.
3. Set up pulse width
Turn the “Universal” knob to set up width.
Video Trigger
Trigger on fields or lines of standard video signals.
Table 3.20 – Video Trigger Function Menu 1
55
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com
Page 70
Option
Setting
Description
Type
Video
When you select the video
type, put the couple set to the
AC, then you could trigger the
NTSC, PAL and SECAM video
signal.
Standard
NTSC
Pal/Secam
Select the video standard for
sync and line number count.
Mode
Auto
Use this mode to let the
acquisition free-run in the
absence of a valid trigger; This
mode allows an untriggered,
scanning waveform at 100
ms/div or slower time base
settings.
Normal
Use this mode when you want
to see only valid triggered
waveforms; when you use this
mode, the oscilloscope does
not display a waveform until
after the first trigger.
Single
When you want the
oscilloscope to acquire a single
waveform, press the “SINGLE”
button.
Set up
Enter the “Trigger setup
menu”.
Next Page
Page 2/2
Return to the first page of
“Video Trigger menu”.
Table 3.21 - Video Trigger Function Menu 2
56
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com
Page 71

Operating Instructions:
1. Set up Type
Press the “TRIG MENU” button to display “Trigger”
menu.
Press the “Type” option button to select “Video”.
2. Set up Polarity
Press the “Polarity” option button to select “ ” or “
3. Set up Synchronization
Press the “Sync” option button to select “All Lines”, “Line
Num”, “Odd Field”, and “Even Field”.
If you select “Line Num”, you can turn the “Universal”
knob to set the appointed line number.
4. Set up Standard
Press the “Next Page - Page 2/2” option
Press the “Standard” option button to select
“PAL/SECAM” or “NTSC”.
Figure 3.24 – Video Trigger Menu
”.
57
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com
Page 72

Slope Trigger
Option
Setting
Instruction
Type
Slope
Trigger on positive slope of
negative slope according to setup
time of the oscilloscope.
Source
CH1
CH2
EXT
EXT/5
Select trigger source.
When
Select trigger condition.
Time
<Set time>
Turn the “Universal” knob to set
slope time. Time setup range is
20ns-10s.
Next Page
Page 1/2
Enter the second page of slope
trigger.
Trigger on positive slope or negative slope of waveform, according to
setup time of the oscilloscope.
Table 3.22 – Slope Trigger Function Menu 1
58
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com
Page 73

Figure 3.25 – Slope Trigger Menu 1
Option
Setting
Instruction
Type
Slope
Trigger on positive slope or negative
slope according to setup time of the
oscilloscope.
Vertical
Select the trigger level that can be
adjusted by “LEVEL” knob. You can
adjust “LEVEL A”, “LEVEL B” or adjust
them at the same time.
Mode
Auto
Use this mode to let the acquisition freerun in the absence of a valid trigger; This
mode allows an untriggered, scanning
waveform at 100 ms/div or slower time
base settings.
59
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com
Page 74

Normal
Use this mode when you want to see
only valid triggered waveforms; when
you use this mode, the oscilloscope does
not display a waveform until after the
first trigger.
Single
When you want the oscilloscope to
acquire a single waveform, press the
“SINGLE” button.
Set up
Enter “Trigger setup menu” (See Table
3.17).
Next Page
Page 2/2
Return to the first page of slope trigger.
Figure 3.26 – Slope Trigger Menu 2
Operating Instructions:
Follow the next steps after “Slope Trigger” is selected:
1. Input a signal to CH1 or CH2.
2. Press the “AUTO” button.
3. Press the “TRIG MENU” button to enter “Trigger menu”.
60
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com
Page 75

4. Press the “Type” option button to select “Slope”.
5. Press the “Source” option button to select “CH1” or “CH2”.
6. Press the “When” option button to select “ ”, “ ”,
“ ”, “ ”, “ ” and “ ”.
7. Press the “Time” button, turn the “Universal” knob to adjust
slope time.
8. Press the “Next Page - Page 1/2” option button to enter the
second page of the “Slope trigger menu”.
9. Press the “Vertical” option button to select trigger level that can
be adjusted.
10. Turn the “LEVEL” knob.
Alternate Trigger
The trigger signal comes from two vertical channels when you use
alternate trigger. In this mode, you can observe two irrelative signals at
the same time. You can select different trigger types for two vertical
signals, and selected types cover edge, pulse, video and slope trigger.
Trigger information of two channel signals display on the bottom right of
the screen.
Figure 3.27 – Alternate Trigger Menu
61
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com
Page 76

Option
Setting
Description
Type
Alternate
When using alternate trigger, the triggered
signal comes from two vertical channels. In
this mode, you can observe two irrelative
signals at a time.
Channels
CH1-CH2
Set the trigger channels
Source
CH1
CH2
Set trigger type information for CH1 signal
Set trigger type information for CH2 signal
Mode
Edge
Set trigger type of vertical channel signal to
edge
Next Page
Page 1/2
Go to the second page of the TRIGGER
Menu.
Option
Setting
Description
Slope
Triggering on rising edge.
Triggering on falling edge.
Triggering on rising edge and falling edge.
Set up
Enter “Trigger setup menu” (See Table
3.17).
Next Page
Page 2/2
Go to the back to the first page of the
TRIGGER Menu.
Table 3.23 – Alternate Trigger Edge Mode Function Menu 1
Table 3.24 – Alternate Trigger Edge Mode Function Menu 2
62
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com
Page 77

Table 3.25 – Alternate Trigger Pulse Mode Function Menu 1
Option
Setting
Description
Type
Alternate
The trigger signal comes from two
vertical channels when you use
alternative trigger. In this mode, you
can observe two irrelative signals at the
same time.
Channels
CH1-CH2
Set the trigger channels
Source
CH1
CH2
Set trigger type information for CH1
signal
Set trigger type information for CH2
signal
Mode
Pulse
Set trigger type of the vertical channel
signal to Pulse trigger.
Next Page
Page 1/2
Enter the second page of Alternative
trigger menu.
Option
Setting
Description
When
Select how to compare the trigger
pulse relative to the value selected in
the Set Pulse Width option.
Set Width
20.0ns-10.0s
Selecting this option can turn the
universal to set up the pulse width.
Table 3.26 – Alternate Trigger Pulse Mode Function Menu 2
63
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com
Page 78

Set up
Enter the “Trigger Setup Menu” (See
Table 3.17).
Next Page
Page 2/2
Press this button to return to the first
page.
Option
Setting
Description
Type
Alternative
The trigger signal comes from two
vertical channels when you use
alternative trigger. In this mode, you
can observe two irrelative signals at
the same time.
Channels
CH1-CH2
Set the trigger channels
Source
CH1
CH2
Set trigger type information for CH1
signal
Set trigger type information for CH2
signal
Mode
Video
Set trigger type of the vertical
channel signal to Video trigger.
Next Page
Page 1/2
Enter the second page of Alternative
trigger menu.
Option
Setting
Description
Polarity
(Normal)
(Inverted)
Normal triggers on the negative edge
of the sync pulse.
Inverted triggers on the positive edge
of the sync pulse.
Table 3.27 – Alternate Trigger Video Mode Function Menu 1
Table 3.28 – Alternate Trigger Video Mode Function Menu 2
64
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com
Page 79
Sync
Line Num
All lines
Odd field
Even Field
Select appropriate video sync.
Standard
NTSC
Pal/Secam
Select the video standard for sync and
line number count.
Set up
Enter the “Trigger Setup Menu” (See
Table 3.17).
Next Page
Page 2/2
Press this button to return to the first
page.
Option
Setting
Description
Type
Alternative
The trigger signal comes from two
vertical channels when you use
alternative trigger. In this mode, you
can observe two irrelative signals at the
same time.
Channels
CH1-CH2
Set the trigger channels
Source
CH1
CH2
Set trigger type information for CH1
signal
Set trigger type information for CH2
signal
Mode
Slope
Set trigger type of the vertical channel
signal to slope trigger.
Next Page
Page 1/2
Enter the second page of the
alternative trigger.
Table 3.29 – Alternate Trigger Slope Mode Function Menu 1
65
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com
Page 80

Table 3.30 – Alternate Trigger Slope Mode Function Menu 2
Option
Setting
Description
When
Select slope trigger condition.
Time
<Set time>
Turn the “Universal” knob to set the
slope time. Time setup range is 20ns10s.
Vertical
Select the trigger level that can be
adjusted by “LEVEL” knob. You can
adjust “LEVEL A”, “LEVEL B” or adjust
them at the same time.
Set up
Enter “Trigger setup menu” (See Table
3.17).
Next Page
Page 2/2
Return to the first page of “Alternative
trigger menu”.
Operating Instructions:
To use alternate triggering, follow these steps:
1. Input two irrelative signals to channel 1 and channel 2.
2. Press the AUTO button.
3. Press the TRIG MENU button to enter “trigger menu”.
4. Press the “Type” option button to select “Alternative”.
5. Press the “Channels” option button to select “CH1-CH2”
66
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com
Page 81

6. Press the “Source” option button to select “CH1”.
7. Press the CH1 button and turn the “Time/div” knob to optimize
waveform display.
8. Press “Mode” option button to select “Edge”, “Pulse”, “Slope”
or “Video”.
9. Set the trigger according to trigger edge.
10. Press the “Source” option button to select “CH2”.
11. Press the CH2 button and turn the “Time/div” knob to optimize
waveform display.
12. Repeat steps 8 and 9.
Coupling
Use “Coupling” to make sure the signal passes through the trigger circuit.
It is useful for obtaining a steady waveform.
If you use trigger coupling, you should press the “TRIG MENU” button and
then select “Edge”, “Pulse”, “Video”, or “Slope” trigger. Then select the
“Coupling” option in the “Set Up menu”.
Position
The horizontal position control establishes the time between the trigger
position and the screen center. You can adjust the horizontal “POSITION”
knob control to view waveform data before the trigger, after the trigger,
or some of each. When you change the horizontal position of a waveform,
you are changing the time between the trigger and the center of the
display actually. (This appears to move the waveform to the right or left on
the display.)
67
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com
Page 82

Slope and Level
NOTE: Press the SINGLE button when you want the oscilloscope to
acquire a single waveform.
Trigger coupling affects only the signal passed to the trigger system.
It does not affect the bandwidth or coupling of the signal displayed
on the screen.
Normal Polarity Sync triggers always occur on negative-going
horizontal sync pulses. If the video waveform has positive-going
horizontal sync pulses, use the Inverted Polarity selection.
Falling edge
Rising edge
T
r
i
g
g
e
r
l
e
v
e
l
c
a
n
b
e
a
d
j
u
s
t
e
d
v
e
r
t
i
c
a
l
l
y
The Slope and Level controls help to define the trigger. The Slope option
(Edge trigger type only) determines whether the oscilloscope finds the
trigger point on the rising and/or the falling edge of a signal.
The TRIGGER LEVEL knob controls at what point on the edge the trigger
occurs.
Figure 3.28 – Rising and Falling Edge Illustration
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com
68
Page 83
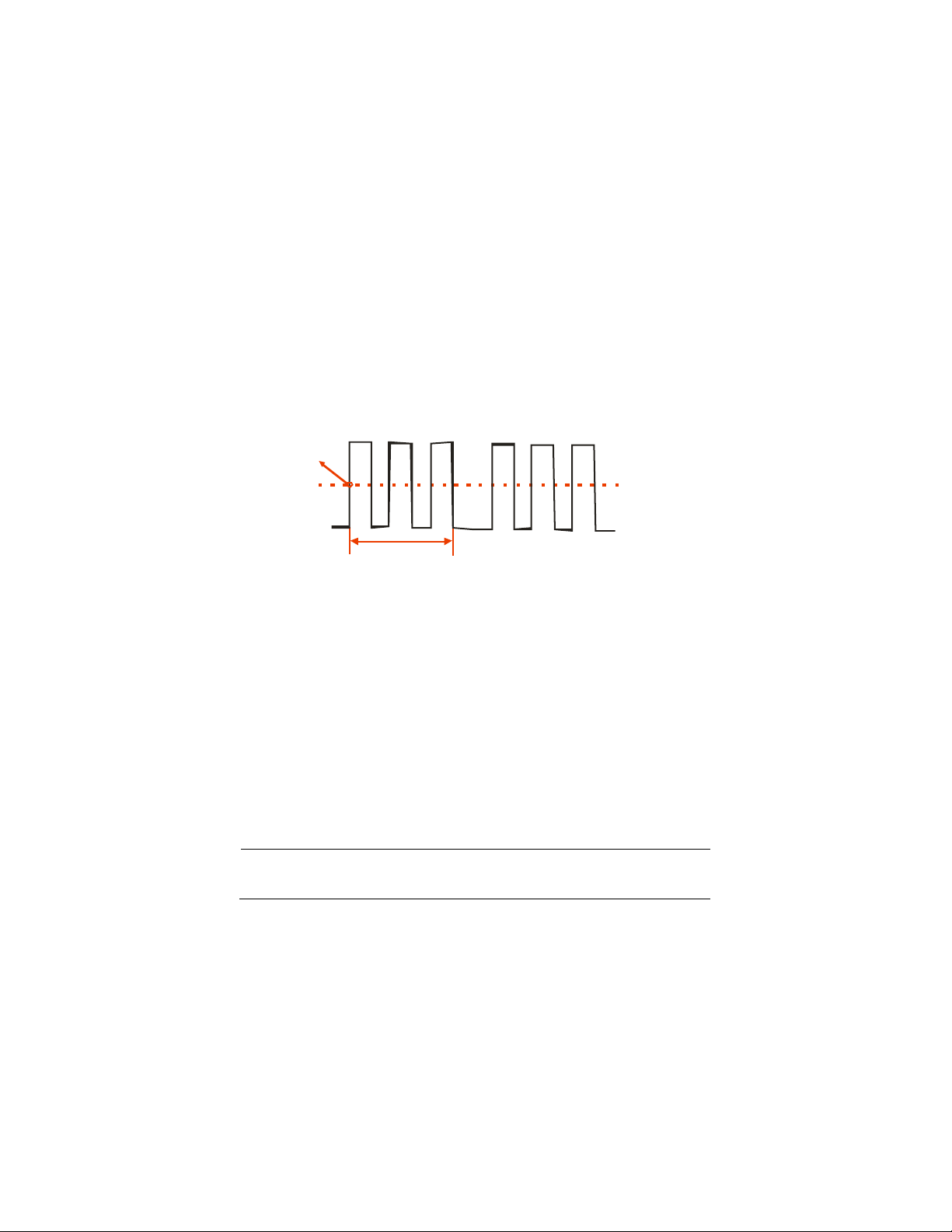
Trigger Holdoff
Holdoff time
Trigger position
Trigger level
NOTE: Use trigger holdoff to help stabilize the display of aperiodic
waveforms.
You can use the Trigger Holdoff function to produce a stable display of
complex waveforms. Holdoff is time between when the oscilloscope
detects one trigger and when it is ready to detect another. The
oscilloscope will not trigger during the holdoff time. For a pulse train, you
can adjust the holdoff time so the oscilloscope triggers only on the first
pulse in the train.
Figure 3.29 – Trigger Holdoff Illustration
If you want to change holdoff time, please follow the steps below:
1. Press the “TRIG MENU” button to show the “TRIG
Menu”.
2. Press the “Type” option button to select trigger type.
3. Press the “Set Up” option button to enter the “Trigger
setup menu”.
4. Press the “Holdoff” option button and turn the
“Universal” knob to change the holdoff time until the
waveform triggers steadily.
69
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com
Page 84

3.12 Signal Acquisition System
Option
Setting
Description
Acquisition
Sampling
Use for sampling and accurately
display most of the waveform.
Peak Detect
Detect the noise and decrease the
possibility of aliasing.
Average
Use to reduce random or
uncorrelated noise in the signal
display.
Averages
(4, 16, 32, 64,
128, 256)
Select number of averages.
Sinx/x
Sinx
x
Use sin interpolation
Use linear interpolation
Mode
Equ time
Real time
Set the Sampling mode to Equivalent
time.
Set the Sampling mode to Real time.
Sa Rate
Displays system sampling rate.
Shown below is the “ACQUIRE” button for entering the menu for
“Acquiring Signals”.
Table 3.31 – Acquire Function Menu
When you acquire a signal, the oscilloscope converts it into digital form
and displays a waveform. The acquisition mode defines how the signal is
digitized and the time base setting affects the time span and level of detail
in the acquisition.
Sampling: In this acquisition mode, the oscilloscope samples
the signal in evenly spaced intervals to construct the waveform.
This mode accurately represents signals most of the time.
Advantage: You can use this mode to reduce random noise.
70
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com
Page 85

Disadvantage: This mode does not acquire rapid variations in the
signal that may occur between samples. This can result in aliasing
may cause narrow pulses to be missed. In these cases, you should
use the Peak Detect mode to acquire data.
Figure 3.30 – Acquire Menu
Peak Detect: Peak Detect mode capture the maximum and
minimum values of a signal Finds highest and lowest record
points over many acquisitions.
Advantage: In this way, the oscilloscope can acquire and display
narrow pulses, which may have otherwise been missed in Sample
mode.
Disadvantage: Noise will appear to be higher in this mode.
71
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com
Page 86

Figure 3.31 – Peak Detect
Average: The oscilloscope acquires several waveforms, averages
them, and displays the resulting waveform.
Advantage: You can use this mode to reduce random noise.
72
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com
Page 87

Figure 3.32 – Average Acquisition
Equivalent Time Sampling: The equivalent time sampling mode
can achieve up to 20 ps of horizontal resolution (equivalent to
50GSa/s). This mode is good for observing repetitive waveforms.
Real Time Sampling: The scope has a maximum Real-time
sampling rate of 1GSa/s.
“RUN/STOP” Button: Press the RUN/STOP button when you want
the oscilloscope to acquire waveforms continuously. Press the
button again to stop the acquisition.
“SINGLE” Button: Press the SINGLE button to acquire a single
waveform. Each time you push the SINGLE button, the
oscilloscope begins to acquire another waveform. After the
oscilloscope detects a trigger it completes the acquisition and
stops.
When you push the RUN/STOP or SINGLE buttons to start an
acquisition, the oscilloscope goes through the following steps:
1. Acquire enough data to fill the portion of the waveform
record to the left of the trigger point. This is also called
the pre-trigger.
73
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com
Page 88

2. Continue to acquire data while waiting for the trigger
Sampled points
Apparent low-frequency
waveform due to aliasing
Actual high-frequency waveform
condition to occur.
3. Detect the trigger condition.
4. Continue to acquire data until the waveform record is
full.
5. Display the newly-acquired waveform.
Time Base: The oscilloscope digitizes waveforms by acquiring the
value of an input signal at discrete points. The time base allows
you to control how often the values are digitized. To adjust the
time base to a horizontal scale that suits your purpose, use the
Time/div knob.
Time Domain Aliasing: Aliasing occurs when the oscilloscope
does not sample the signal fast enough to construct an accurate
waveform record. When this happens, the oscilloscope displays a
waveform with a frequency lower than the actual input
waveform, or triggers and displays an unstable waveform.
Figure 3.33 – Time Domain Aliasing Illustration
Operating Instructions:
Set up Sampling Format
You can press the “Acquisition” option button or turn the “Universal” knob
to select “Sampling” mode, “Peak Detect” mode or “Average” mode.
Set up Averages
When you select “Average” format, you can press the “Averages” option
button to select “4”, “16”, “32”, “64”, “128”or “256”.
74
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com
Page 89

Set up function interpolation
Option
Setting
Description
Type
Vectors
Dots
Vectors fill the space between
adjacent sample points in the
display.
There is no link between
adjacent sample points.
Persist
Off
1 sec
2 sec
5 sec
Infinite
Sets the length of time each
displayed sample point remains
displayed.
Intensity
<Intensity>
Set waveforms’ intensity.
Brightness
<Brightness>
Set grid brightness.
Next Page
Page 1/3
Press this button to enter second
page.
You can select Sinx interpolation or linear interpolation.
Set up Sampling Mode
Press the “Mode” option button to select “Real Time” or “Equ Time”.
Set up Sampling Rate
The sampling rate is based on the time division scaling on the screen.
Adjust the sampling rate by turning the Time/div front panel knob. The
sampling rate is shown under the “Sa Rate” display.
3.13 Display System
The display function can be setup by pressing the “DISPLAY” button.
Table 3.32 – Display System Menu 1
75
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com
Page 90

Option
Setting
Description
Format
YT
XY
YT format displays the vertical
voltage in relation to time
(horizontal scale). XY format
displays a dot each time a sample
is acquired on channel 1 and
channel 2
Screen
Normal
Inverted
Set to normal mode.
Set to invert color display mode.
Grid
Display grids and axes on the
screen.
Turn off the grids.
Turn off the grids and axes.
Menu Display
2sec
5sec
10sec
Set menu display time on screen.
Figure 3.34 – Display Menu 1
Table 3.33 – Display System Menu 2
76
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com
Page 91

20sec
Infinite
Next Page
Page 2/3
Press this button to enter the
second page of “Display menu”.
Option
Setting
Description
Skin
Classical
Modern
Tradition
Succinct
Set up screen style.
Next Page
Page 3/3
Press this button to return to
the first page.
Figure 3.35 – Display Menu 2
Table 3.34 – Display System Menu 3
Operating Instructions:
Set up waveform display type
77
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com
Page 92

1. Press the “DISPLAY” button to enter the “Display” menu.
2. Press the “Type” option button to select “Vectors” or “Dots”.
Set up Persist
Press “Persist” option button to select “Off”, “1 Sec”, “2 Sec”, “5 Sec” or
“Infinite”. You can use this option to observe some special waveforms.
Figure 3.36 – Persist Screen
Set up Intensity
Press the “Intensity” option button and turn the “Universal” knob
to adjust waveforms’ intensity.
Set up Brightness
Press the “Brightness” option button and turn the “Universal” knob
to adjust grid brightness.
Set up display format
1. Press the “Next Page” option button to enter second
display menu.
2. Press the “Format” option button to select “YT” or “XY”.
Set up Screen
Press the “Screen” option button to select “Normal” or “Inverted” to
set the screen display color.
78
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com
Page 93

Set up Grid
NOTE: The oscilloscope can capture a waveform in normal YT mode
at any sampling rate. You can view the same waveform in XY mode.
To do so, stop the acquisition and change the display format to XY.
Press the “Grid” option button to select “ ”, “ ”or“
”to set the screen whether display grid or not.
Set up Menu Display
Press the “Menu Display” option button to select “2 sec”, “5sec”,
“10sec”, “20sec” or “Infinite” to set menu display time on screen.
Set Skin
Press the “skin” option button or turn the “Universal” knob to select
“Classical”, “Modern”, “Traditional” or “Succinct”.
X-Y Format
Use the XY format to analyze phase differences, such as those represented
by Lissajous patterns. The format plots the voltage on channel 1 against
the voltage on channel 2, where channel 1 is the horizontal axis and
channel 2 is the vertical axis. The oscilloscope uses the untriggered Sample
acquisition mode and displays data as dots.
Operation steps:
Channel 1 “Volt/div” and vertical “POSITION” set up the
horizontal scale and position.
Channel 2 “Volt/div” and vertical “POSITION” set up the
horizontal scale and position.
Turn the “Time/div” knob to adjust the sampling rate
The following functions are forbidden in XY display form:
o Benchmark wave form and wave mathematic
o Cursor
o Auto (resets display format to YT)
o Trigger Control
79
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com
Page 94
o Horizontal Position Knob
NOTE: The CURSORS and MEASURE buttons can be disabled. Please
see “Education Mode” for details.
o Vector Display Type
o Scan Display
3.14 Measure System
The oscilloscope displays the voltage in relation to time and tests the
waveform displayed. Different measurement techniques such as scale,
Cursor and auto measure modes are used.
Scale Measurement
This method allows you to make a quick, visual estimate. For example, you
might look at waveform amplitude and determine that it is a little more
than 100 mV. You can take simple measurements by counting the major
and minor graticule divisions involved and multiplying by the scale factor.
For example, if you counted five major vertical graticule divisions between
the minimum and maximum values of a waveform and knew you had a
scale factor of 100 mV/div, then you could easily calculate your peak-topeak voltage as follows:
5 𝑑𝑖𝑣𝑖𝑠𝑖𝑜𝑛𝑠 ×
100 𝑚𝑉
𝑑𝑖𝑣𝑖𝑠𝑖𝑜𝑛
= 500 𝑚𝑉
Cursor Measurement
Press the “CURSORS” button to display the “Cursor” menu.
The cursor measurement has three modes: Manual, Track, and Auto
Measure.
80
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com
Page 95

Manual Mode
Option
Setting
Description
Cursor
Mode
Manual
In this menu, set the manual cursor
measure.
Type
Voltage
Time
Use cursor to measure voltage
parameters.
Use cursor to measure time
parameters.
Source
CH1
CH2
MATH
REFA
REFB
Select input signal channel.
Cur A
Select this option, use “Universal”
knob to adjust cursor A.
Cur B
Select this option, use “Universal”
knob to adjust cursor B.
Table 3.35 – Manual Cursor Menu
In this mode, the screen displays two horizontal parallel cursors or vertical
parallel cursors to measure voltage or time. You can move the cursor by
turning the “Universal” knob. Before using cursors, you should make sure
that you have set the signal source as the channel for measuring.
Voltage Cursor: Voltage cursors appear as horizontal lines on the
display and measure the vertical parameters.
Time Cursor: Time cursors appear as vertical lines on the display
and measure the horizontal parameters.
Cursor Moving: Use the “universal” knob to move cursor 1 and
cursor 2. They could be moved when the corresponding cursor
option are selected, and cursor value will display on the bottom
left and top left of the screen when you move the cursor.
81
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com
Page 96

To do manual cursor measurements, follow these steps:
1. Press CURSOR button to enter the cursor function menu.
2. Press the “Cursor Mode” option button to select “Manual”.
3. Press the “Type” option button to select “Voltage” or “Time”.
4. Press the “Source” option button to select “CH1”, “CH2”,
“MATH”, “REFA”, or “REFB” according to input signal
channel.
5. Select “Cur A”, turn the “Universal” knob to adjust Cursor A.
6. Select “Cur B”, turn the “Universal” knob to adjust Cursor B.
7. The measurement values are displayed on the top of the left
corner.
If the measurement type is set to “Voltage”, the values are as
followed:
The voltage increment between Cursor A and Cursor
B: ΔV
The value of Cur A: CurA
The value of Cur B: Cur B
If the measurement type is set to “Time”, the values are as
followed:
The time increment between Cursor A and Cursor B:
ΔT
The reciprocal of time increment between Cursor A
and Cursor B: 1/ΔT
The value of Cur A: CurA
The value of Cur B: Cur B
82
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com
Page 97

Option
Setting
Description
Cursor Mode
Track
In this mode, set track cursor
measure.
Cursor A
CH1
CH2
NONE
Set the input signal channel that
the Cursor A will measure.
Cursor B
CH1
CH2
NONE
Set the input signal channel that
the Cursor B will measure.
Cur A
Select this option, turn the
“Universal” knob to adjust
horizontal coordinate of Cursor A.
Cur B
Select this option, turn the
“Universal” knob to adjust
horizontal coordinate of Cursor B.
Track Mode
Figure 3.37 – Cursor Menu (Manual)
Table 3.36 – Track Mode Menu
83
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com
Page 98

In this mode, the screen displays two cross cursors. The cross cursor sets
the position on the waveform automatically. You could adjust cursor’s
horizontal position on the waveform by turning the “Universal” knob. The
oscilloscope displays the values on the top left of the screen.
To do track cursor measurement, follow these steps:
1. Press CURSOR button to enter the cursor measure function
menu.
2. Press the “Cursor Mode” option button to select “Track”.
3. Press the “Cursor A” option button to select the input signal
channel.
4. Press the “Cursor B” option button to select the input signal
channel.
5. Select “Cur A”, turn the “Universal” knob to move Cursor A
horizontally.
6. Select “Cur B”, turn the “Universal” knob to move Cursor B
horizontally.
7. The measurement values are displayed on the top left of the
screen:
A→T: The horizontal position of Cursor A (Time cursor
centered around the midpoint of screen).
A→V: The Vertical position of Cursor A (Voltage cursor
centered around channel ground level).
B→T: The horizontal position of Cursor B (Time cursor
centered around the midpoint of screen).
B→V: The Vertical position of Cursor B (Voltage cursor
centered around channel ground level).
ΔT: Horizontal space between Cursor A and Cursor B (Time
value between two cursors).
1/ΔT: The reciprocal of horizontal space between cursor A
and cursor B.
84
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com
Page 99

ΔV: Vertical space between Cursor A and Cursor B (Voltage
value between two cursors).
Figure 3.38 – Cursor Menu (Track)
Auto Mode
This mode will take effect with automatic measurements. The instruments
will display cursors while measuring parameters automatically. These
cursors demonstrate the physical meanings of these measurements.
To do auto cursor measurements, follow these steps:
1. Press the CURSOR button to enter “Cursor measure menu”.
2. Press the “Cursor Mode” option button to select “Auto”.
3. Press the “MEASURE” button to enter “Auto cursor measure
mode menu” to select the parameter that you want to
measure.
85
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com
Page 100

Figure 3.39 – Auto Mode
Option
Description
Voltage
Press this button to enter the Voltage measure menu.
Auto Measurement
When you take automatic measurements, the oscilloscope does all the
calculation for you. The measurements use all the recorded points in the
memory, which are more accurate than measurements made using the
graticule lines or cursor measurements because these measurements are
confined to be made by only using points on the display and not all the
data points recorded by the oscilloscope.
Press the ‘MEASURE’ button for Automatic Test.
There are three auto measurement types: Voltage Measure, Time
Measure, and Delay Measure. There are a total of 32 measurement
parameters.
Table 3.37 – Auto Measurement Menu
86
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com
 Loading...
Loading...