Page 1

Automated Purification of a GST-Tagged Protein With the
Profinia™Protein Purification System: Comparison to Manual
Protein Purification Using Commercial Kits
fractions allows determination of the effectiveness of
purification. Automated desalting of the purified protein by
size exclusion chromatography is also possible without the
need for user intervention between the affinity and desalting
chromatography steps. When used with Profinia software, the
system displays purification data in real time and allows
generation and printing of publication-quality reports that
include chromatograms, method steps, and data tables
containing pertinent purification information, including yield,
concentration, and sample application and elution volumes
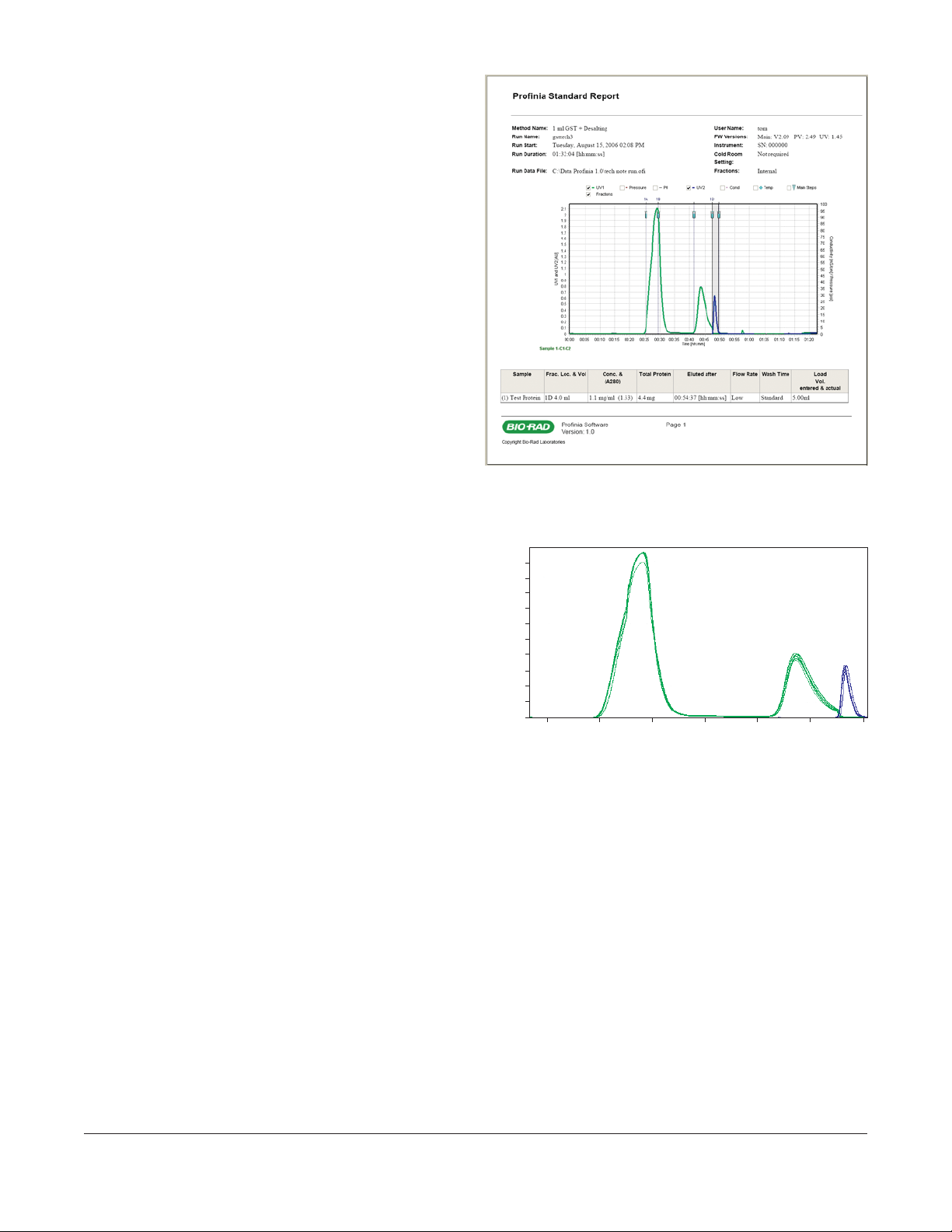
(Figure 1).
This study compares the performance and reproducibility of
the Profinia system to traditional manual gravity-flow column
purification for GST affinity purification and sequential
desalting. The B-PER GST fusion protein purification kit from
Pierce Biotechnology was chosen for comparison, as the
column volume (1 ml) is identical to the column volume used
by kits available for the Profinia protein purification system.
For the comparison, identical application and elution volumes
were used for the columns tested between the two systems,
further allowing a valid comparison. Desalting of the gravityflow column-purified protein requires manual application of
the protein eluted from the affinity column to a second column
for desalting, and this step was performed using Zeba desalt
spin columns from Pierce Biotechnology. These are available
with a column volume identical to the desalting column used
in the Profinia system (10 ml). The two purification methods ––
automated and manual –– were compared with respect to
yield, reproducibility, electrophoretic purity, total time required,
and hands-on time required.
chromatography
tech note 5513
Tom Berkelman and Michael Urban, Bio-Rad Laboratories Inc.,
Hercules, CA 94547 USA
Introduction
Fusion tags are widely used to assist in the purification of
recombinant protein expressed from a gene of interest. Among
the various fusion tags that have been developed, glutathione
S-transferase (GST) is one of the most commonly used (Smith
and Johnson 1988). Protein fused to GST can be purified from
crude bacterial lysates under nondenaturing conditions by
affinity chromatography on an immobilized glutathione column.
The lysate is applied to the column, the GST-tagged protein
binds to the immobilized glutathione, and unbound host
proteins are collected from the column in the flow-through
fraction. The column is then washed with several column
volumes of buffer to ensure complete removal of untagged
proteins. Purified protein is eluted and recovered in buffer
containing reduced glutathione, which displaces the GSTtagged protein from the immobilized glutathione. This widely
performed procedure is often performed under gravity-flow
conditions, in which sample and buffers are applied onto an
open column and fractions are collected manually.
The Profinia protein purification system is an automated liquid
chromatography system designed to perform unattended
affinity purification and desalting of tagged proteins. Optimized
preprogrammed methods for the most common affinity
applications are available and can be used together with
the buffers and prepacked columns available in the Profinia
purification kits. All of the parameters for routine purifications
are preset, and the preplumbed system is easily maintained
through automated self-cleaning protocols. Integrated
collection of the flow-through, column washes, and elution
Page 2
© 2006 Bio-Rad Laboratories, Inc. Bulletin 5513
Results and Discussion
UV absorbance data from the Profinia purifications
demonstrate the performance of the automated GST +
Desalting method (Figure 2). The profiles of the UV traces at
the output of either column were virtually indistinguishable
from one another when compared using Profinia software.
The elution times for both the affinity and desalting peaks
varied by no more than 10 sec.
Fig. 2. Superimposed UV absorbance profiles from replicate GST + Desalting
purifications of the 51 kD protein on the Profinia system. The UV absorbance of
samples at 280 nm (AU) was collected over time for five consecutive purifications,
and the data are shown on the same pair of axes. ( ——), absorbance at the output
of the affinity column; ( ——), absorbance at the output of the desalting column.
Methods
A 51 kD GST-tagged protein expressed in Escherichia coli
was purified using both a Profinia system method and a
manual gravity-flow method for purification and desalting.
Five purification runs were performed, and samples of the
lysate, flow-through, wash, and purified protein fractions
from runs 1, 3, and 5 were then analyzed by SDS-PAGE.
The concentration of the purified 51 kD protein was determined
spectrophotometrically using the absorbance at 280 nm and
the known absorbance of a 1 mg/ml solution of the 51 kD
protein. Purity of the 51 kD protein was evaluated using the
Experion
™
automated electrophoresis system.
Protein Purification With the Profinia System
All purification reagents, columns, and a lyophilized E. coli
lysate containing the 51 kD GST-tagged protein were obtained
from the Profinia GST starter kit (catalog #620-0230). Each vial
of lysate was resuspended as directed in the kit instructions in
10 ml of Profinia lysis buffer. Purifications were performed with
the Profinia method template for “GST + Desalting” and with
the “low” sample flow rate. The 1 ml GST cartridge and 10 ml
desalting cartridge provided in the GST starter kit were used.
For each purification run, 5 ml of sample was loaded, which
required placement of 6 ml of lysate in the sample tube to
ensure complete loading of 5 ml of lysate. From each
purification run, 4 ml of purified and desalted protein was
collected. The five replicate runs were performed consecutively
using the same columns. Profinia software was used for realtime monitoring of the purification runs and collection of the
subsequent run data.
Protein Purification With the Pierce GST Fusion Protein Purification
Kit and Zeba Desalt Spin Columns
Each vial of E. coli lysate containing the 51 kD GST-tagged
protein from the Profinia GST starter kit was dissolved in 10 ml
of the B-PER bacterial protein extraction reagent provided in the
B-PER GST fusion protein purification kit (Pierce Biotechnology).
Purifications were carried out according to the supplied
instructions using an application volume of 5 ml and an elution
volume of 4 ml. Eluted protein from each GST purification was
desalted using 10 ml Zeba desalt spin columns (Pierce
Biotechnology) following the manufacturer’s instructions.
Five purification runs were performed using new columns for
each replicate.
SDS-PAGE and Experion Pro260 Analysis
SDS-PAGE analysis was performed using the Criterion™system
and 8–16% Tris-HCl precast gels. Gels were stained with
Bio-Safe
™
Coomassie stain. The sample, flow-through, and
wash fractions were diluted 10-fold into Laemmli sample buffer
and loaded in a volume of 10 µl. Purified protein was diluted in
Laemmli sample buffer to 0.1 µg/µl and loaded in a volume of
10 µl (1 µg). Experion analysis of the purified protein fractions
was performed using the Experion Pro260 analysis kit
following the protocol described in the instruction manual.
20 25 30 35 40 45 50
Run time, min
AU
2.0
1.8
1.6
1.4
1.2
1.0
0.8
0.6
0.4
0.2
0.0
Fig. 1. Example of a Profinia standard report. Profinia software prepares a report
containing chromatograms, continuous records of various method parameters,
protein yield, sample application and elution volumes, and purification conditions.
51 kD
affinity peak
51 kD
desalted peak
Page 3

Both the automated and manual methods compared in this
study are capable of purifying the 51 kD protein to apparent
homogeneity, as determined by SDS-PAGE and Coomassie
Blue staining (Figure 3). Both the Bio-Scale
™
Mini GST
cartridges used with the Profinia system and the gravity-flow
affinity columns used with the manual method bound most
of the tagged fusion protein applied, as judged by comparing
the profiles of the flow-through fractions to those of the
unfractionated lysate. The protein profile in the flow-through
fraction and the purity of the protein product were consistent
from run to run with both methods tested (Figure 3).
Though both systems delivered 51 kD GST-tagged protein
of comparable purity, the Profinia system yielded slightly more
purified protein with less variability in yield than did the manual
system (Table 1). This increased reproducibility may be due to
the fact that the Profinia system reduces sample handling.
Table 1. Yield and purity of the 51 kD protein. Protein was purified and desalted
either with the Profinia system and GST starter kit, or manually with the B-PER GST
fusion protein purification kit and Zeba desalt spin columns. Average yield of the five
runs performed using each method is shown ± standard deviation.
Purification Method Average Yield (mg) Average Purity (%)
Manual system 4.34 ± 0.24 96.1
Profinia system 4.76 ± 0.14 96.2
Both purification methods required approximately 90 min to
complete. With the manual method, purified and desalted
protein was available in 90 min. However, the purified protein
from the Profinia system was available and ready for use in
downstream applications within 55 min for all five purifications.
The remaining time required for the Profinia system is
accounted for by the automated cycle for column cleaning and
regeneration, a step not carried out using the manual method.
The manual method required continuous user presence in
order to apply buffer and collect fractions, while the Profinia
© 2006 Bio-Rad Laboratories, Inc. Bulletin 5513
Fig. 3. SDS-PAGE analysis of purification fractions. Samples were separated by SDS-PAGE on 8–16% Tris-HCl Criterion precast gels, and gels were stained with Bio-Safe
Coomassie stain. A, samples from the Profinia separations; B, samples from the manual separations. Lane designations are as follows: M, markers (Precision Plus Protein
™
dual color standards); L, lysate (unfractionated); FT, flow-through fraction; W, wash fraction; P, purified protein.
system ran unattended and only required approximately
5 min of hands-on time to initiate and complete the
purification. The Profinia system automatically collected the
sample from the affinity column and applied it to the desalting
column. This must be performed manually in the gravity-flow
method in a step that also requires the use of a centrifuge.
In contrast to the Profinia system, the length of time using
the gravity-based purification varied by as much as 30 min due
to flow rate differences between the columns used in the
manual method.
Conclusions
The Profinia protein purification system has been tested
against a manual gravity-flow purification system for
purification of a GST-tagged protein. The manual system
used in this comparison matched the Profinia system in
application volume, column volumes, and elution volume.
The Profinia system is fully automated and requires no user
handling between application of the sample and conclusion of
both the affinity purification and desalting steps. While reduced
sample handling and hands-on time are the principal benefits
of the Profinia system over manual purification, the Profinia
system appeared superior when compared to the manual
method tested in terms of protein yield and reproducibility, and
equivalent in terms of protein purity.
A key feature of the Profinia system is automated collection
of purification data, an option not available with the manual
system, and this simplifies evaluation of the effectiveness of
purification. In addition, a report is prepared that contains
chromatograms, continuous records of various method
parameters, yield, volumes, and purification conditions
(Figure 1).
B. Manual system
Run 1 Run 3 Run 5
M L FT W P FT W P FT W P
A. Profinia system
Run 1 Run 3 Run 5
M L FT W P FT W P FT W P
MW, kD
250
150
100
75
50
37
25
20
15
10
MW, kD
250
150
100
75
50
37
25
20
15
10
Page 4

Reference
Smith DB and Johnson KS, Single-step purification of polypeptides expressed in
Escherichia coli as fusions with glutathione S-transferase, Gene 67, 31–40 (1988)
B-PER and Zeba are trademarks of Pierce Biotechnology, Inc. Coomassie is a
trademark of BASF Aktiengesellschaft.
LabChip and the LabChip logo are trademarks of Caliper Life
Sciences, Inc. Bio-Rad Laboratories, Inc. is licensed by Caliper Life
Sciences, Inc. to sell products using the LabChip technology for
research use only. These products are licensed under US Patent Nos.
5,863,753, 5,658,751, 5,436,134, and 5,582,977, and pending patent
applications, and related foreign patents, for internal research and development
use only in detecting, quantitating, and sizing macromolecules, in combination
with microfluidics, where internal research and development use expressly
excludes the use of this product for providing medical, diagnostic, or any other
testing, analysis, or screening services, or providing clinical information or
clinical analysis, in any event in return for compensation by an unrelated party.
Information in this tech note was current as of the date of writing (2006) and not
necessarily the date this version (rev A, 2006) was published.
Life Science
Group
Bulletin 5513 US/EG Rev A
Bio-Rad
Laboratories, Inc.
Web site www.bio-rad.com USA 800 4BIORAD Australia 61 02 9914 2800 Austria 01 877 89 01 Belgium 09 385 55 11 Brazil 55 21 3237 9400
Canada 905 712 2771 China 86 21 6426 0808 Czech Republic 420 241 430 532 Denmark 44 52 10 00 Finland 09 804 22 00 France 01 47 95 69 65
Germany 089 318 84 0 Greece 30 210 777 4396 Hong Kong 852 2789 3300 Hungary 36 1 455 8800 India 91 124 4029300 Israel 03 963 6050
Italy 39 02 216091 Japan 03 5811 6270 Korea 82 2 3473 4460 Mexico 52 555 488 7670 The Netherlands 0318 540666 New Zealand 0508 805 500
Norway 23 38 41 30 Poland 48 22 331 99 99 Portugal 351 21 472 7700 Russia 7 495 721 14 04 Singapore 65 6415 3188 South Africa 27 861 246 723
Spain 34 91 590 5200 Sweden 08 555 12700 Switzerland 061 717 95 55 Taiwan 886 2 2578 7189 United Kingdom 020 8328 2000
06-0572 1206 Sig 1206
 Loading...
Loading...