Page 1

Principle and Maintenance of ABS530T(RU)
Table of Contents
Chapter I Overview of ABS530T (RU)
1. Description of Functions
2. Block Diagram of Player
3. Composition of IC for Player
Chapter II Operating Principle of Servo Circuit
1. Processing Procedure of Digital Signal
2. Processing Procedure of Control Signal
Chapter III Operating Principle of Decoding Circuit
1. Control Circuit of System
2. Audio and Video Output Circuit
Chapter IV Operating Principle of Power Board
1. Block Diagram
2. Operating Principle of Circuits
Chapter V Operating Principle of Panel
1. Operating Principle
Chapter VI Troubleshooting
Appendix: Functions of IC Pins
Operating Principle Analysis of ABS530T(RU)
Page 2

Chapter I Overview of ABS530T(RU)
I. Description of Functions
ABS530T(RU)is a mini-type music center integrating with video disc and power
amplifier, with the following major features:
1. The layer adopts “Sanyo deck+MT1389” solution;
2. The power amplifier adopts the analogue power amplification circuit, with the
power IC of TDA7265;
3. The audio DAC adopts CS4340 192KHz/24bit sampling, with high integration and
high performance and price ratio;
4. It has the function of radio reception, and the tuner adopts Sanzhenxing DTS -44K
(CE)module;
5. The power supply adopts the linear power, with stable performance and lower cost;
6. Equipped with SCART(CVBS/RGB)port;
7. “RSD” function;
8. Timed ON/OFF functions.
9. Compact and with beautiful appearance.
Page 3
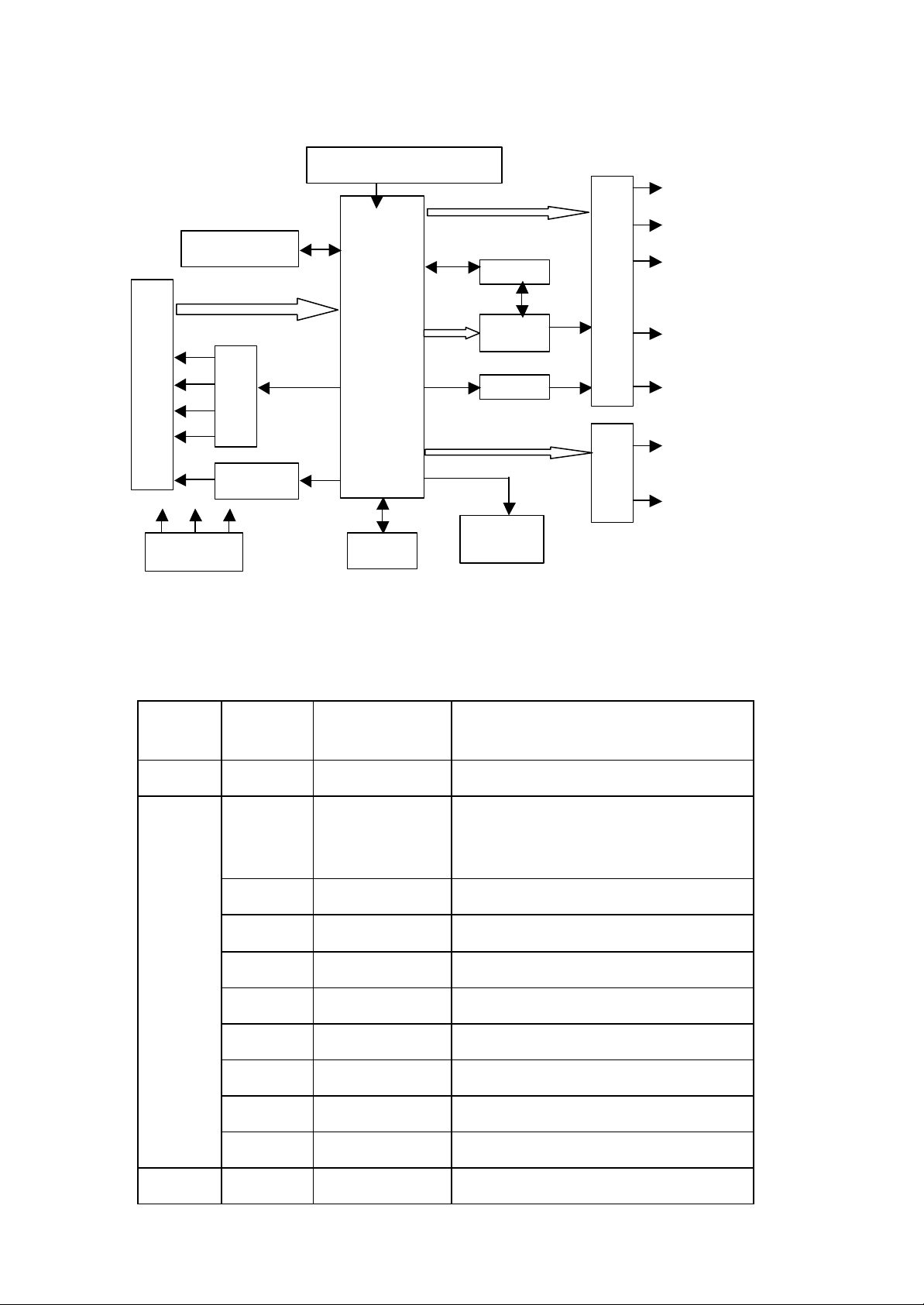
II. Block Diagram of ABS530T Complete Player and IC Function Table:
track
power
servo drive
channel output
VGA
Sanyo
deck
focus
29LV160BE
16M ROM
BA5954
feed
main
load
Load drive
Power circuit
Radio reception head
AT24C02
MT1389
digital signal
digital servo
SDRAM
MPEG decoder
4340,7265
HCU04
status
Audio D/A,
Refor
Panel circuit
AV output circuit
Progressive
Composite video
S-video
Y/Cb/Cr
2-
Optical, coaxial
Y/Pb/Pr
Figure 1
III. Function Table of ICs for ABS530T
Circuit
Board
Deck
Number Name Function
Sanyo Pick-up of disc signal
U201 MT1389
U202 AT24C02 Series EEPROM, status memory
U205 HCU04 Hexaphase
Mother
U207 CS4340 AF digital/analog converter circuit
Board
U209 LM1117MP-1.8 1.8v voltage -regulated power supply
U211 AE45164016 64Mbit SDRAM
U214 29LV160BE 16Mbit FLASH ROM
RF signal processing, digital signal
processing, servo processing, MPEG
decoding, line scan, system control
U219-221
4580 Dual operational amplifier
U302 D5954 4-channel servo driver circuit
Panel U401 IC 0791 Panel control, VFD display drive
Page 4
U402 HS0038A2 IR sensor
+12V 3-terminal voltage-regulated
power supply
-12V 3-terminal voltage -regulated
power supply
5V 3-terminal voltage -regulated
power supply
+3.3V 3-terminal voltage -regulated
power supply
Power
Board
N100 LM7812
N102 LM7912
N101 LM1085
N104 IC BA033
N103 TDA 7265 Power amplification IC
Chapter II Operating Principle of Servo Circuit
I. Processing Procedure of Digital Signal
ABS530T(RU) adopts Sanyo double super error correction mechanism and MTK
decoding solution, and its servo circuit mainly consists of preposition signal
processing, digital servo processing, digital signal processing IC MT1389 and driver
circuit BA5954. MT1389 is also a main part of the decoding circuit.
The A, B, C, D, E, F, SA, SB and RFO signal transmitted from the mechanism are
mainly inputted through the 2-13 pins of MT1389, and after amplifying treatment of
built-in amplifier of MT 1389, the signals are treated in two parts within MT1389:
After being processed by the internal digital servo signal circuit of MT1389, part of
the signal forms into corresponding servo control signal, and output focus (FOSO),
tracking (TRSO), main shaft (DMSO) and feed (FMSO) servo control signal from the
P42, P41, P37 and P38 of MT1389 and send them to the driver circuit BA5954 to
amplify the drive. After drive amplification, the signals will drive the focus coil,
tracking coil, main shaft motor and feed motor. The focus and tracking servo s will be
used to adjust the object lens and enable laser beam to identify signal from compact
disc correctly; the feed servo will be used to drive the laser head to move
longitudinally, and scan the compact disc; the main shaft servo is used to control the
main shaft motor to read the signals in constant linear speed and drive the disc to
rotate.
After being processed by the internal VGA voltage -controlled amplifier of MT1389 in
amplification and balance frequency compensation; another part of the signals is
converted into digital signal by the internal A/D converter. When the mechanism
reads the CD/VCD signals, these signals will be EFM demodulated in MT1389, and
after accomplishing CIRC error regulation in internal MT1389, output to the next
grade to carry out audio and video decoding; when the deck reads the DVD signals,
these signals will be ESM demodulated in MT1389, and after accomplishing RSPC
error regulation in internal MT1389, output to the next grade to carry out audio and
Page 5
video decoding.
II. Processing Procedure of Control Signal
1. Automatic control of laser power, with the circuit shown as the Figure II:
MT1389 is integrated with APC (automatic light power control) circuit. Its Pin 20 is
the pin for inputting VCD laser power rate detection signal, the Pin 21 is the pin for
inputting DVD laser power rate detection signal, and the Pin 23 is the pin for
outputting VCD laser power rate drive control. When the Pin 23 finds that the laser
output power rate is too strong, the output voltage on Pin 23 will increase after the
processing of internal circuit of MT1389, and then the conduction degree of V302
(2SB1132) and the voltage on its integration polar will decrease, which consequently
lead to the decrease of voltage supplied to the laser tube, the weakening of laser head
lighting, and thus achieve the automatic adjustment on laser output power. The Pin 22
is the pin for outputting DVD laser power drive control, with the specific control
procedure similar to that of VCD.
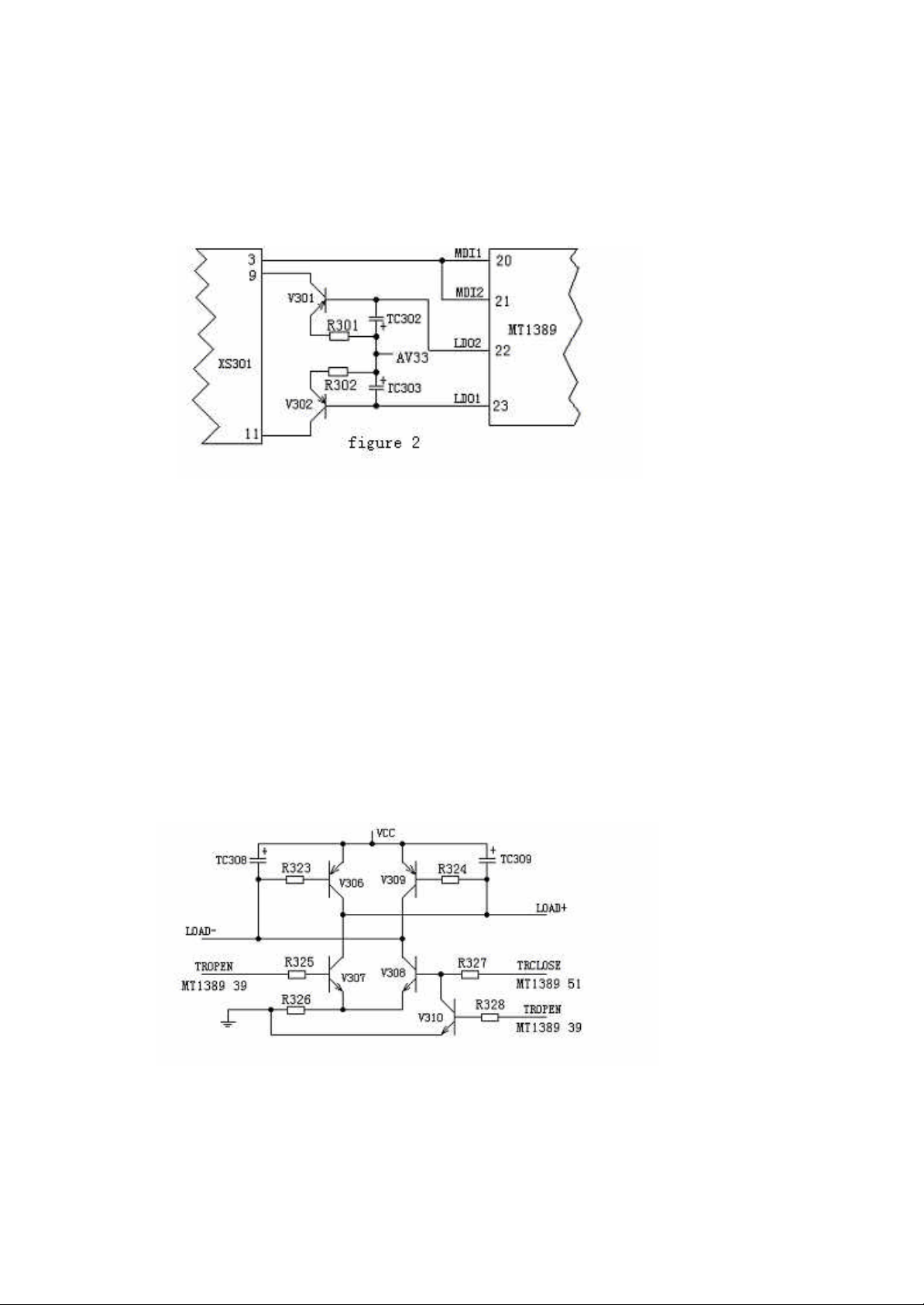
2. The tray open/close control circuit is shown as the Figure III:
Figure 3
Different from the circuit in former MTK solution, the MT1389 is integrated with
preposition signal processing circuit, so the tray open/close control signals are
accomplished by MT1389, that is to say, the close control signal is accomplished by
the Pin 51 of MT1389, while the open control signal by Pin 39 of MT1389.
Page 6
When we press the open button, the Pin 51 of MT1389 is in high power level, while
the Pin 39 is in low power level, and then the triode V308 will be on-state. Through
resistor R323, the base of V306 will be made to be in low power le vel, and V306 will
be on-state, with the current direction as the following figure:
Power voltage VCC ? V306E-C junction ? motor negative
terminal LOAD- ? motor positive Load +? V308 C-E
junction ? grounding
So the motor will rotate clockwise to accomplish the action of tray closing.
When we press the open button, the Pin 51 of MT1389 is in low power level, while
the Pin 39 is in high power level, and then the triode V307 will be conducted.
Through resistor R324, the base of V309 will be made to be in low power level, and
V309 will be conducted, with the current direction as the following figure:
Power voltage VCC ? V309E-C junction ? motor negative
terminal LOAD- ? motor positive Load +? V307 C-E
junction? grounding
So the motor will rotate anti-clockwise to accomplish the action of tray opening.
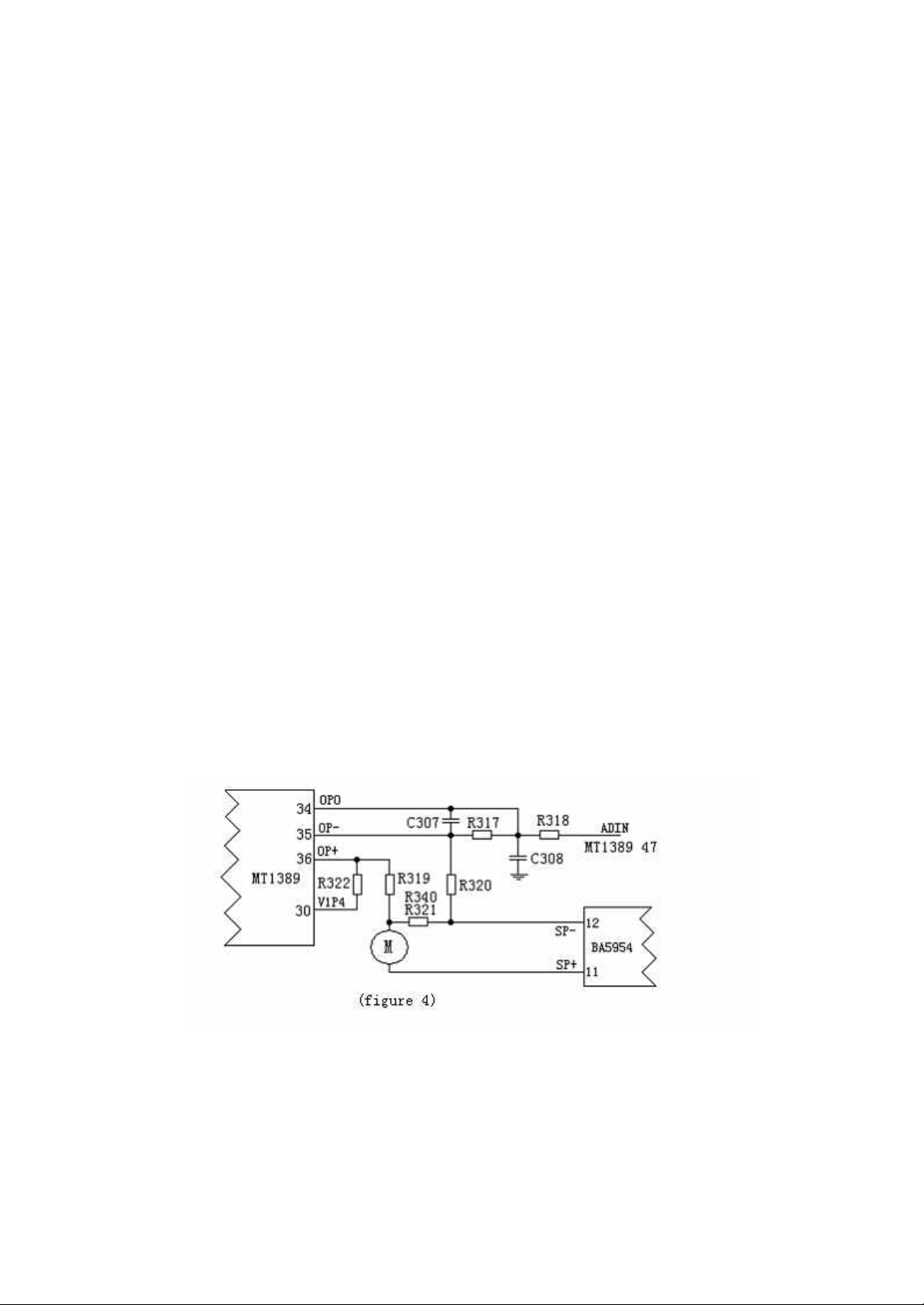
3. The main shaft motor braking circuit is as the Figure IV:
To prolong the lifespan of motor and reduce the influence of start-up impact
current, with the installation of disc, our R&D personnel design the main shaft motor
to be in the state of constant operation, so that even if the STOP button is pressed, the
disc will not be stopped. Therefore, when we press the OPEN button, a braking signal
is required to stop the rotation of main shaft motor immediately to accomplish the
opening action in a short time.
During playing, if we press the OPEN button, the main shaft drive signal will
disappear, and because of inertia, the main shaft motor is still in operation. As the
electromotive force generated in the operation of motor receives the induction voltage
on sampling resistors R321 and R340, which, through the resistor R319 and R320, is
added to the Pin 36 and Pin 35 of MT1389, and outputted from the Pin 34 after
internal processing for amplification in MT1389, and delivered to Pin 47 of MT1389
through R318. After the internal A/D conversion and corresponding processing, an
Page 7
instant motor reversal braking signal will be outputted from the Pin 37 of MT1389 to
stop the rotation of main shaft motor immediately, so as to ensure the standstill of the
disc when opening the player.
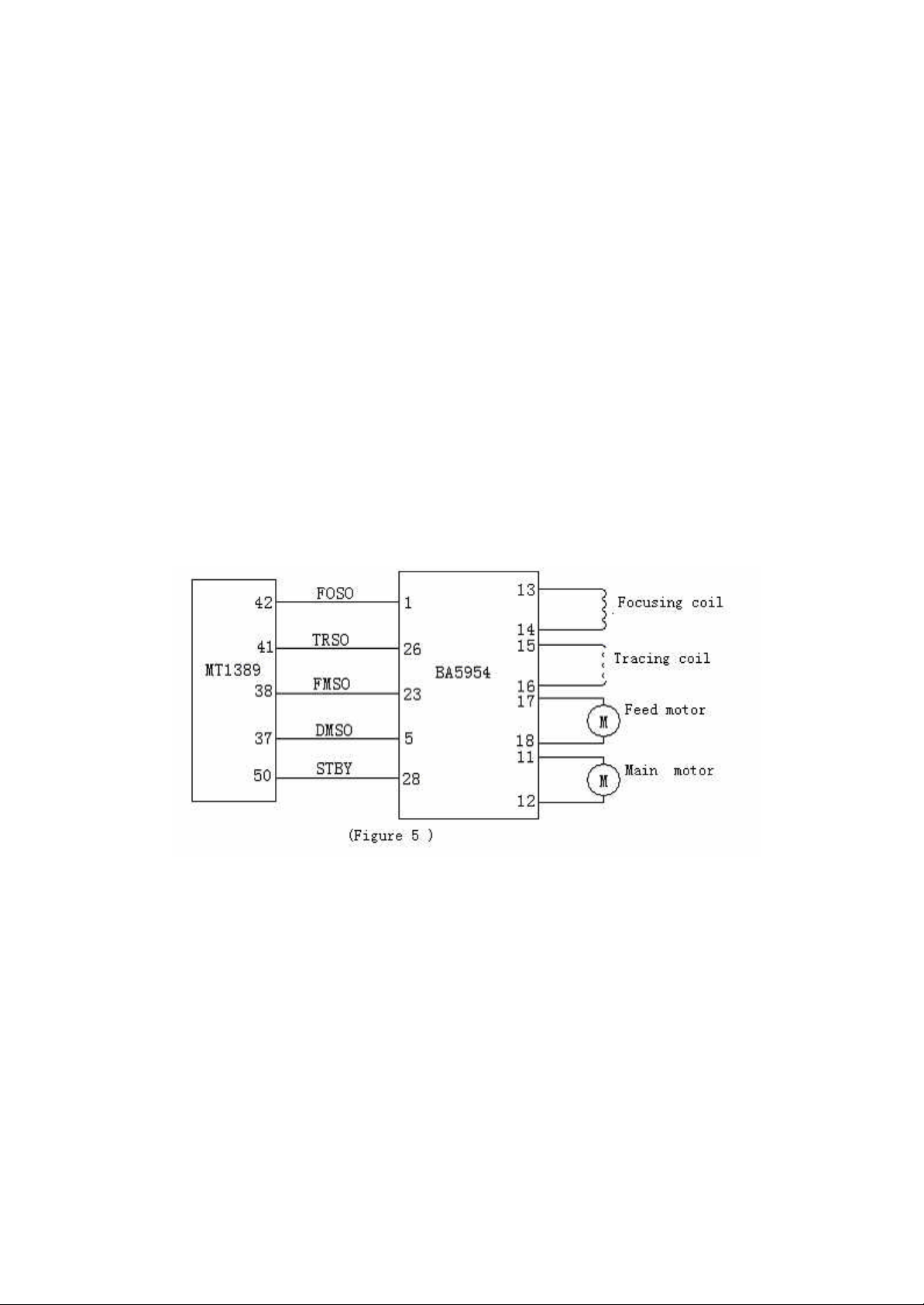
III. Servo drive circuit
The servo drive of the player is accomplished through a piece of 4-channel dedicated
drive circuit BA5954, with the circuit as Figure V:
The 4 servo control signals generated in digital servo circuit processing of MT1389,
i.e. focusing control FOSO, tracking control TRSO, feed control FMSO and main
shaft control DMSO signals, are added to the pins 1, 26, 23 and 5 of BA5954
respectively, and after drive amplification of BA5954, the focusing and tracking drive
signals will be outputted from the pins 13 and 14 and pins 15 and 16 of BA5954
respectively, and added to the focusing and tracking coils to drive the light head to
accomplish the actions of focusing and tracking.
The feed and main shaft drive signals will be outputted from the pins 17 and 18
and pins 11 and 12 of BA5954 respectively, and added to the feed motor and main
shaft motor to drive the light head to move longitudinally and enable the disc to rotate
in constant linear speed.
The STBY on Pin 28 of BA5954 is an output -enabling signal, and only when the pin
is in high power level, there will be output of drive voltage on the output terminal.
Chapter III Operating Principle of Decoding Circuit
The decoding circuit of the player mainly consists of decoding chips (including
MT1389, SDRAM AE45164016 and FLASH ROM 29LV160BE) and audio DAC
CS4360.
I. Control Circuit of System
1. Reset circuit is as the Figure VI:
Page 8
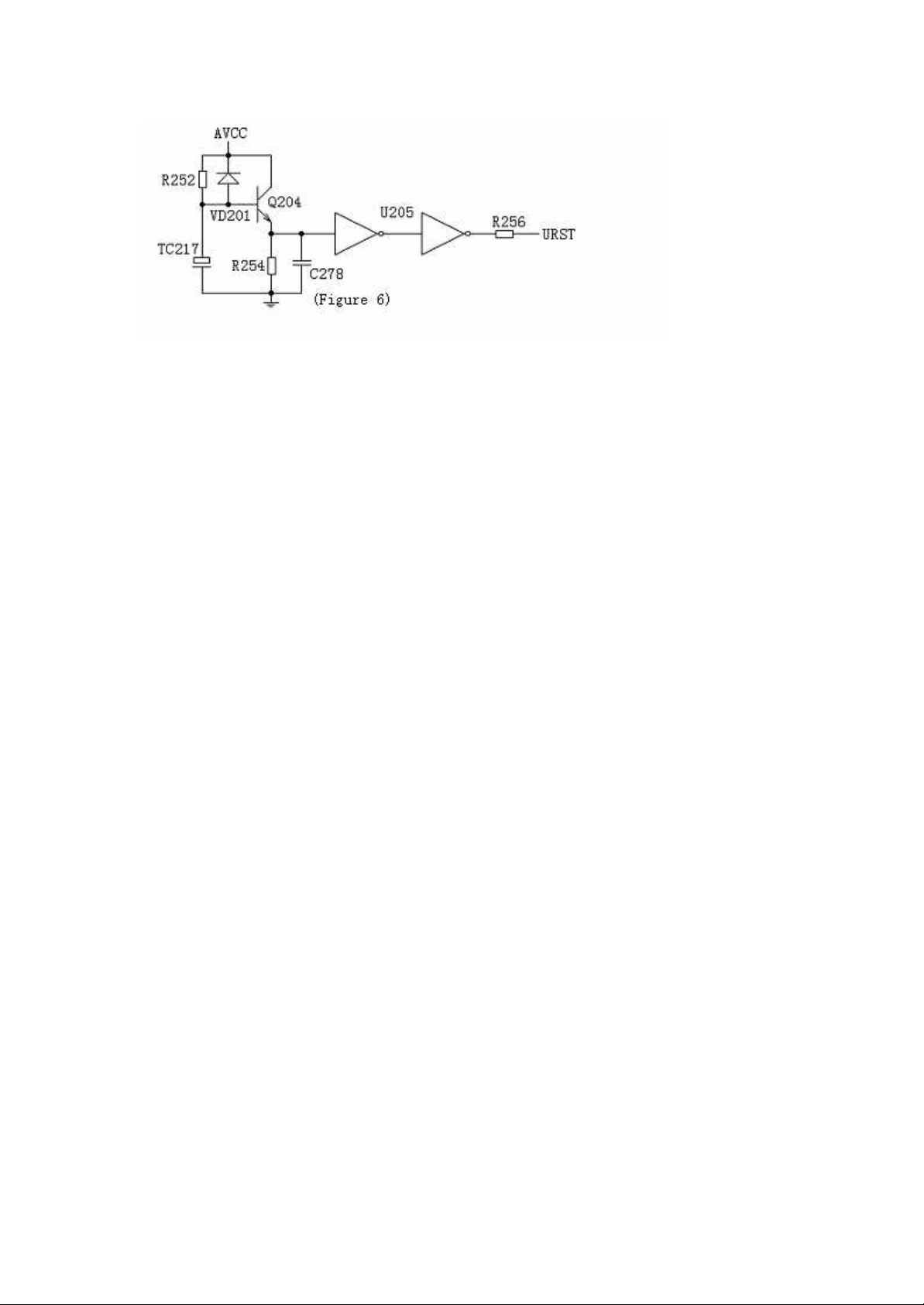
The reset circuit of the player consists of triode Q204 9014, reset capacitor TC217
100uF/16V and phase inverter U205 HCU04. In starting up, as the terminal voltage of
capacitor cannot be changed suddenly, the basic of Q204 is in low power level. After
the cut-off of Q204, its emission polar is in low power level, after secondary phase
inversion by U205 and regulation, the low power level reset signal is outputted to the
Pin 110 of MT1389 to reset MT 1389.
When the recharging of TC217 is finished, the base of Q204 will be in high power
level, Q204 will be conducted, and the emission polar is in high power level. After the
secondary phase inversion and regulation by U205, a high power level is outputted
and added to the Pin 110 of MT1389 to maintain high power level during its normal
operation.
2. Clock circuit
The crystal oscillator of X201 27MHz, C275/27PF, C276/27PF and phase inverter
HCU04 form into clock oscillation circuit, and the clock signals generated are added
to the pins 229 and 228 of MT1389 through R244 and 4248 to provide operating
clock for MT1389.
3. Data communication circuit
The data communication circuit of the player consists of decoding chip MT1389,
SDRAM, AE45164016 and FLASH ROM 29LV160BE, as the Figure VII:
MT1389 is a piece of super large integrated circuit, with the operation voltage of
+3.3V and +1.8V. Its functions include: RF small signal preposition processing,
digital servo, digital signal processing and accomplishing MPEG decoding and video
coding. The built-in MCU of MT1389 is also the system control circuit of the whole
player .
AE45164016 is a piece of 4M*16bit large capacity SDRAM, with the operation
voltage of +3.3 V. In DV971, the 6ns module is adopted, with high speed and the
maximum operation frequency up to 166MHz. Its main function is for operation
buffer storage of decoding chip MT1389 to store the audio and video data stream in
decoding.
29LV160BE is a piece of 16Mbit FLASH ROM, with the operation voltage of +3.3V,
mainly for storing the user’s information including OSD character information,
operational microcode and LOGO in start-up.
Page 9
39 38 37 18 17 19 16 20 21
77
26 28 11 15 47 79 66 VD
RY/BY
29LV160BE
BYTE
GND
A0—A21
AD0—AD7
DCE
DRD
DWR
MT1389
DMA0—DMA11
DQ0—DQ15
113
137
156
157
140
139
142
138
145
143
AE45164016
DQML
15
DQMH
CLK
CKE
RAS
CAS
CS
WE
BA1
BA0
Figure 7
II. Audio and Video Output Circuit
1. Video output circuit
ABS530T(RU) can not only output three types of interlacing video signal (including
CVBS composite video, S terminal Y-C signal and Y/Cb/Cr color difference signal),
but also output two types of progressive video signal (including Y/Pb/Pr progressive
color difference signal and VGA progressive signal).
The decoding chip MT1389 has built-in video encoding circuit for direct output of
analogue comp osite video signal CVBS, S terminal, color difference signal and VGA
signal.
The CVBS composite video signal is outputted from the Pin 198 of MT1389, the S
terminal signal Y-C is outputted from the pins 194 and 196 of MT1389, the color
difference signal and the R-B-G signal of VGA port is outputted from the pins 203,
202 and 200 of MT1389, the row and field synchronization signals of VGA port are
outputted from the pins 207 and 205 of MT1389 respectively.
To mention specifically, the interlacing color difference signal, the progressive color
difference signal and progressive R-B-G signal are outputted from the same pin,
therefore the signal output shall be selected according to the ports of TV, otherwise
there will be only sound but without picture display.
2. Audio DAC circuit, as the Figure VIII:
Page 10
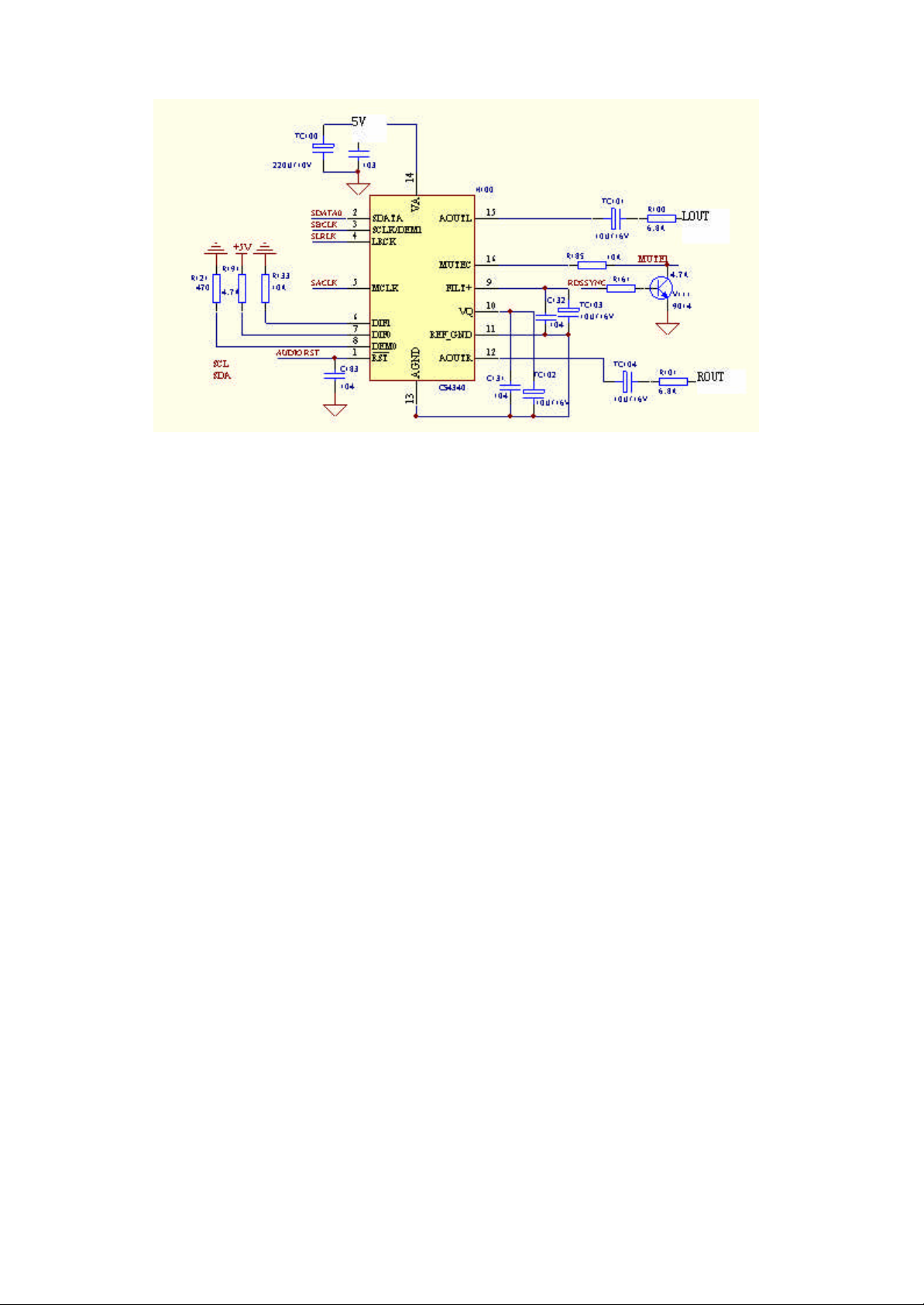
The main function of audio DAC c ircuit is to convert the digital audio signal decoded
from MT1389 into analogue audio signal through D/A converting circuit, and output
the audio signal after buffing and amplification to the next amplifying devices to
restore it to voice.
The digital audio signals ASDATA0 decoded from MT1389 are outputted from the
Pin 217 of MT1389, and delivered to the Pin 2 of audio DAC circuit CS4360. In the
mean time, the left and right sound channel clock signal ALRCK, bit clock signal
ABCK and the external audio clock signal ACLK required in D/A conversion are
outputted from the pins 213, 214 and 215 of MT1389, and added to the pins 5, 3 and 4
of CS4360 respectively.
CS4340 will carry out D/A conversion on the digital audio signals from the channels
of SDATA0 under the control of I2C(SDA, SCL) delivered by MT1389, and output
the 2-way analogue audio signals from the pins 12 and 15 of CS4340 for the
amplification in the next step. The related functions of various signals are as follows:
ASDATA0---- Digital audio signal, including the signals of left and right
channels
ALRCK-----Left and right bit clock signals, for separating left and right
channels
ABCK-----Bit clock signal, for ensuring the accuracy of signal transmission
ACLK-----External clock signal, as the operation clock of CS4340
3. Audio output amplification circuit
The audio digital signals outputted from the decoding board are delivered to the
power amplification part for processing after D/A conversion by IC CS4340.
Power amplification parts:
This model carries 2-channel power amplification, and adopts IC TDA7265 to
amplify the sound channels. In rated power and the load resistance of 8 ohms, the
output power of each sound channel can reach 6W. With the combination of active
The amplifying circuit adopts solely power IC amplification; therefore it has high
Page 11
integration degree, simple circuit and easy control. The analogue signal outputted
from IC4340 will be amplified by IC 4558, and delivered to N103 IC PT2315 for
electronic sound volume regulating processing after the left and right sound channels
are gated by N102 IC 4052, and then to IC TDA7265 for power amplification, and
output.
IC TDA7265 is a double-channel power amplification IC, with standby and muting
mode, without switching impact, but with the function of overcurrent and overload
protection to prevent the IC from being damaged in abnormalities effectively. The IC
can provide the maximum 30W power output for each channel in normal output mode,
and when adopting BTL output, the power can reach 50W. Besides, the IC has strong
anti-ripple function, and is featured with low power consumption in standby state.
The functions of the pins of IC TDA9843J are as follows:
Mark Pin Function of Pins
-VS 1 Negative supply
OUTPUT1 2 Output of first channel
+VS 3 Positive supply
OUTPUT2 4 Input of second channel
MUTE 5 Mute control line
-VS 6 Negative supply
IN+(2) 7 Channel 2 positive phase
input
IN-(2) 8 Channel 2 antiphase input
GND 9 Grounding pin
IN-(1) 10 Channel 1 antiphase input
IN+(1) 11 Channel 1 positive input
Additionally, ABS530T(RU) also has optical and coaxial digital audio output. The
digital audio signals after the decompressing of MT1389 are outputted from the Pin
225 of MT1389 in the format of IEC958, and added to the corresponding optical and
coaxial terminal output after the regulation by phase inverter HCU04 of U205.
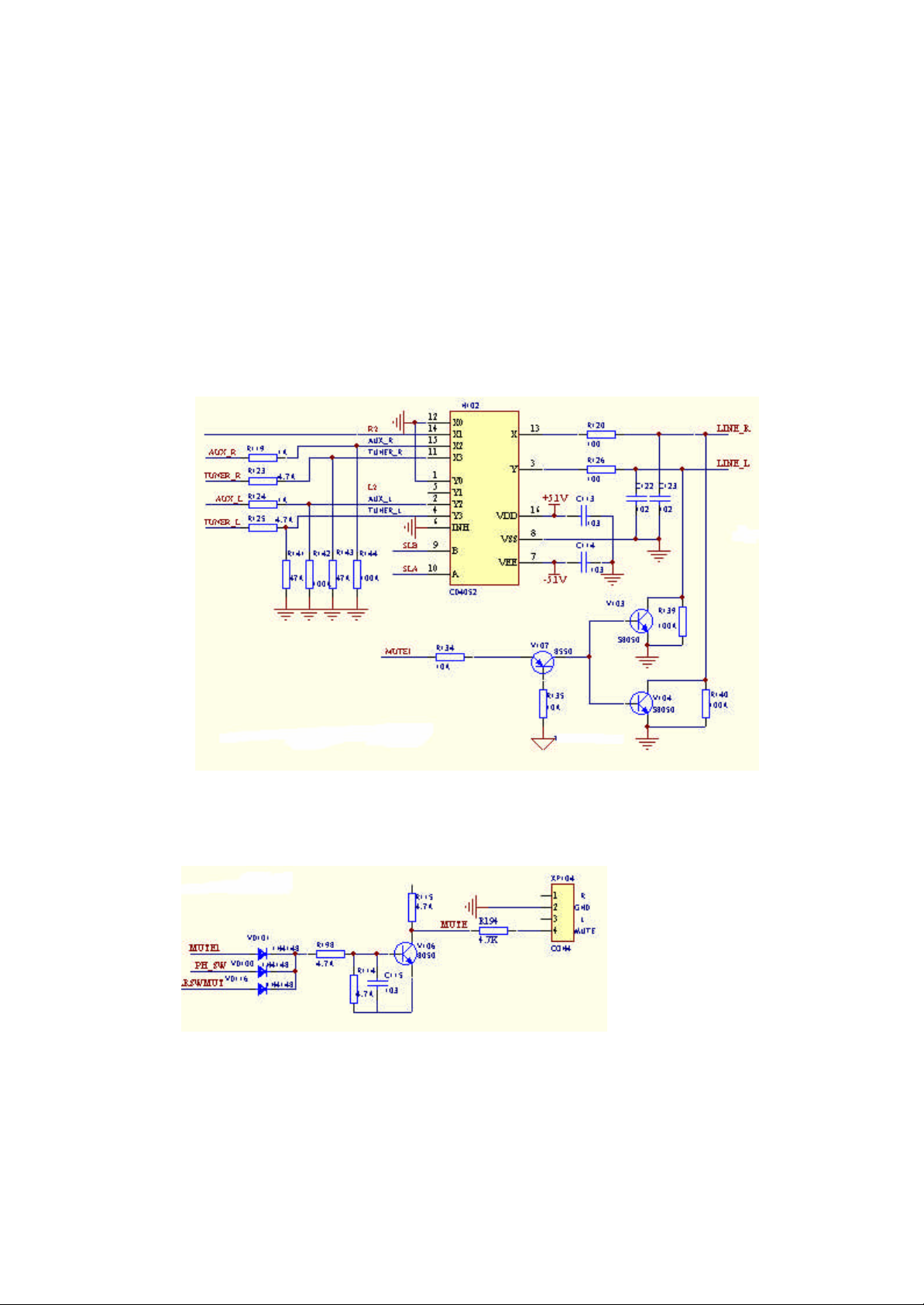
4. Muting and power-off quieting
The muting part of the player is controlled by the SCMUT and LRSWMUT outputted
by MT1389. During starting up till reading out the disc, the two controlling lines will
output high power level to mute the sound channels. After the disc reads out the
signals, MT1389 will alternate the two controlling lines into lower power level to
carry out normal signal output. When the remote control muting is pressed, the two
controlling lines will be alternated into high power level to realize muting. For this
model has just the amplification output of left/right channel, the central mute control
line is applied to control the mute of the Karaoke.
Page 12
5. Automatic Power-on Function
This model is equipped with the IC M41T81, so that it has the function of a clo ck; just
like a clock, when you power it off, it is supplied with the power from one group of
battery inside it; when the external power is cut off, the internal power supply is
switched on. Therefore, the clock can still work in case of the power cut.
The most distinctive feature of this player is its automatic turnon function. Whenever
you want to turn it on, you just preset the turnon time and then set it to a standby
status. As a result, when the clock runs to the preset turnon time, the player will give a
high level trigger to the STANBY at P50 of 1389, and the player will be turned on.
The preset time is stored in the IC 24C02 while the clock is controlled by the 1389
and IC M41T81.
When the MUTE1 is at the high level, the triode V107 is turned on, so that the triode
V103 and V104 are turned on, and the left/right channel signal is connected with the
grounding, so that the mute is realized therefore.
This mute circuit includes three diodes in parallel connection; among the three control
lines, when there is any one at high level, the MUTE signal outputs at low level, so
that the power amplifier tube TDA7265 works normally; only when the three control
lines are at low level synchronously, the triode V106 cuts off, so that the MUTE
Page 13

outputs high level and the zener diode on the power board turns on at the reversed
direction while the triode V100 turns on and pulls down the voltage at P5 of
TDA7265, and finally the complete mut ing is realized.
In addition, there is a C128 1U/50V capacitor on the peripheral circuit of IC
TDA7265 and the mute control line. The start-up mute is realized, for the voltage at
both ends of the capacitor can not change abruptly at the very moment when the
player is turned on, so as to make the level at the P5 to be low at the very moment of
turning on the player. When the player is turned off, this capacitor discharges quickly
via the resistor R114 so as to make the level at P5 to become low rapidly, so that the
function of turnoff mut ing is realized.
5. Function of Tuning
ABS530T(RU)has the function of tuning, and can receive RDS signal. The signals of
radio reception, the auxiliary channel input signal and the left and right sound signal
outputted from CS 4360 are gated through N111IC CD4052, and the controlling A and
B are controlled by the low and high power level of AUIN SL0 and AUIN SL1
emitted from MT1389.
The radio head control lines CE, DI, CL and DO are controlled by the array lines
connected to MT1389 for the direct control by 1389. When any one of the controlling
lines is in abnormality, the radio reception will be in malfunction. The RDS signal
received by radio head will be delivered to the dedicated IC SAA6588 for processing.
Page 14
y and
Chapter IV Operating Principle of Power Circuit
I. Block Diagram
Transf
ormer
output
Service voltage of amplifier
II. Analysis of Operating Principle
The player adopts linear power for power supply, and is featured with high power,
stable power supply and low cost.
After the input voltage is switched via the insulating transformer, the two groups of
AC outputs are rectified via the bridge rectifier composed of the VD100, VD101,
VD102, VD103 and filtered via the C100, C101, C112 and C113, and then a group of
±20V DC supplies the power to the amplifier IC — such voltage outputs the stable ±
12V via the IC 7812 and IC 7912. For the current is purified by two groups of filter
capacitor, and the stabilizing IC is for the voltage stabilizing output, therefore the
output voltage is relatively stable, with low ripple factor. After the rectifying and
filtering, the other group of 8.4V AC voltage outputs +5V CD via the stabilization of
IC 1805, then after the filtering and the stabilization via the stabilizing IC BA033, it
outputs +3.3V to supply the power to the decoding IC. For this model adopts the
linear power supply, and the voltage part and signal amplification part are on the same
board, it’s better to process at the power purifying part in order to keep the effect upon
the signals from the power supply surge. In doing so, the player can be ensured to
have relatively low fluctuation in its service voltage in case of any change to the
public power supply, so that the reliability of the player is ensured. The transformer
has another group of voltage output, with an AC connecting directly to the panel so as
to supply the filament voltage to the display; another group of voltage outputs a group
of +27V DC after the rectifying and filtering, so as to supply the grid voltage to the
display.
Rectif
filtre
Stabilizing
Additionally, this player has the timed power-on function. To ensure some circuits of
this player to work normally without the external voltage so as to realize the purpose
of timed start function, this player is added with a group of lithium battery supplying
3V voltage, so that the clock can still work normally when the player is turned off.
When the power on the player is turned on, the VCC voltage effects on the diode
VD118 and the diode cuts off, so the battery can not supply the power to the entire
player. When the power on the player is turned off, the VCC is at zero without the
external voltage, and the diode is positive ly conducted, so that the battery supplies the
necessary voltage to the working part of the clock on the player to ensure its normal
work.
Page 15
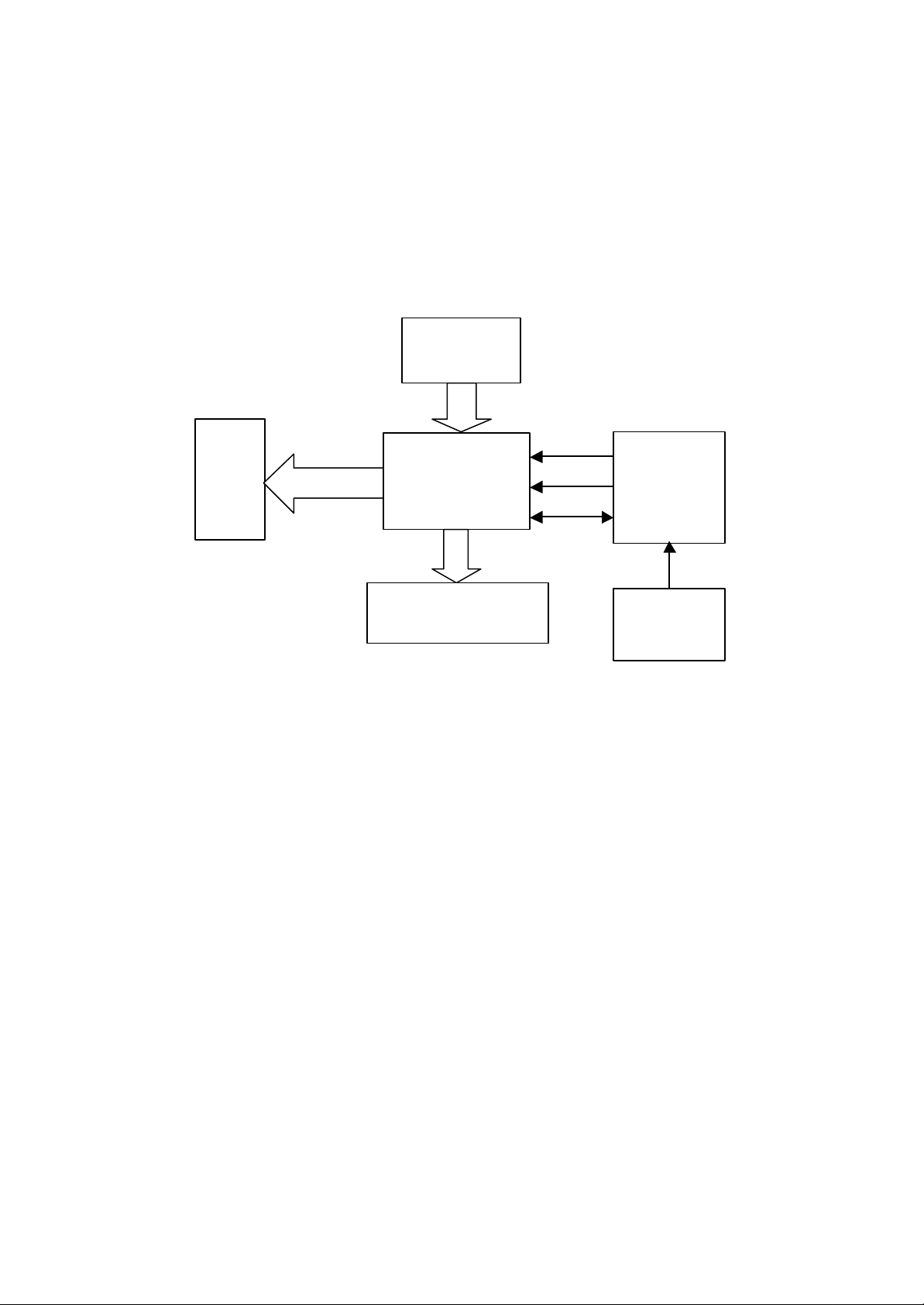
Chapter 5: Panel control and VFD display circuit
IC6311
The panel mainly consists of VFD screen, driver IC6311, IR sensor HS0038A2
and button and indicator display circuit, mainly for accomplishing man-player
dialogue and display of operation status.
The structural drawing is as follows:
Keystoke
VFD
display
control
U401
VFDST
VFDCK
VFDAT
U201
MT1389
MT1389 will control the U401 IC 6311 to display the operation status of the player
through the VFDST status, VFDCK clock and VFDAT data, under the control of
CPU built in MT1389, receive the user control commands sent by IC 6311, and
control the controlled circuit of the player to limit the player to operate in specified
status.
When the user operates the panel buttons, the control command is sent to the IC 6311
through keyboard-scanning circuit, and through internal decoding drive, the IC 6311
outputs the control data from the pins 5 and 6 (VFDAT) to the built-in CPU of
MT1389, which will realize the control on the controlled circuit, and control the VFD
through IC 6311.
VFD401 is a vacuum fluorescence screen, and its biggest feature is its high brightness.
Its operation principle is similar to the kinescope of TV. The pins 1, 2, 34 and 35 are
for filament power supply; the pins 27-32 are GRID poles, each GRID has 16
different characters of display; the pins 4-19 are SEG poles, and the CPU control the
SEG poles through its control on UPD6311, and display the characters of
corresponding operation status on the screen.
Panel indicator control
Figure 11
Remote
receiving
The remote reception circuit mainly consists of remote receptors HS0038A2, of which
Page 16

the pin 1 is for grounding, the pin 2 for power supply, the pin 3 for output of reception
signal, and they are all connected directly to the CPU in MT1389 to control the
corresponding circuit.
Moreover, there are two digital potential device knobs on the panel, one is for track
control, and the other is for volume control. Through array lines, they are connected
to the pin 168,169,181 and 184 of MT1389 directly.
Page 17

T roubleshooting
I. Voltage on key points of ABS530T(RU)
Power circuit:
1. PVCC: Around 20V;
Decoding circuit:
Reset:
1. U205 (HCU04): 8 pins, around 3.3V;
2. MT1389: 110 pins, around 3.3V;
3. FLAHS ROM: 12 pins, around 3.3V
Clock:
27MHZ crystal oscillator two ends: Around 0.77V.
I2C bus SDA: 3.3V
I2C bus SCL 3.3V
Servo circuit:
LD01: 3.3V;LD02:3.3V
V301 and V302 electron collector LD voltage: 2.3V
BA5954 pin 4 base voltage: 1.4V
BA5954 pins 15 and 16 tracking drive output: Around 2.5V
BA5954 pins 17 and 18 feed drive output: Around 2.5V
BA5954 pins 13 and 14 focus drive signal output: Around 2.5V
BA5954 pins 11 and 12 main shaft drive output: Around 2.5V
BA5954 pin 1 focus control signal input: 1.4V
BA5954 pin 5 main shaft control signal input: 1.4V
BA5954 pin 26 tracking control signal input: 1.4V
BA5954 pin 23 feed control signal input: 1.4V
Page 18

No
display
Check if power supply of MT1389
Check the voltage of power board,
is
, C275,
is
Check if the reset circuit which is
Q204 etc.
SDA, SCL 3.3V
short
R260
If SDRAM CLK, CS, RAS, CAS, WE
If FLASH ROM, URST, DCE, DRD,
Check if the connection between
FLASH
II. Troubleshooting of main troubles
picture, no sound, no VFD
3.3V, 1.8V is right?
YES
If the clock signal output XO
and XI is right?
YES
Check if reset signal URST#
NO
in 5V high level?
YES
If I2C bus,
voltage is right?
NO
NO
NO
and check if the decoding board
short circuit to the grounding.
Check if clock oscillating circuit
27M crystal oscillator
C276, R224, R248 are damaged?
comprised by HCU04 and
is in working order?
Check if the AT24C16, CS4360,
MT1389 SDA and SCL are
circuit to grounding, if R259 and
are in working order?
YES
communication signals are right?
YES
YES
Do not read disc
MT1389, FLASH, SDRAM is right?
If the MT1389, SDRAM and
are damaged?
DWR signals are right?
Page 19

laser
feed control
23 is
17,18
Check if BA5854 and the power
Check if laser head
control
voltage output of
13 and 14 are
coil and its
Check if BA5854 and 5V power
NO
Check if the
head has feed action.
Check if the
input of BA5954 Pin
1.4V?
YES
Check if the
connection from
BA5954 to MT1389
is open circuit?
YES
YES
has focus action?
YES
YES
Check if BA5954 pin
have 2.5V voltage output?
NO
supply 5V are in working order?
NO
Check if BA5954 pin 1
has focus
voltage input of 1.4V.
Check if the
BA5954 pin
2.5V?
Check feed motor
and its connection.
Check if the
connection from
BA5954 to MT1389
is open circuit?
Check focus
connection.
YES NO
supply are in working order?
Page 20

89 and its
Check if V301 and V302
electron collector voltage is
Check if the laser head
and its array line are
5
Check if the connection from
BA5954 to MT1389 is open
main shaft
11
Check if MT1389
its peripheral
k if BA5854 and 5V power
Check if there is
NO
laser coming out
from laser head?
Check if the signal
voltage of LD01, LD02
is 3.2V?
YES
Check MT13
connection.
YES YES
Check if the
NO
main shaft
rotates?
YES
YES
YES
2.3V?
Check if the control
voltage of BA5954 pin
main shaft is 1.4V?
Check if BA5954 pin
and 12 output is 2.5V?
right?
circuit?
Check if BA5954 or
motor is damaged?
NO
and
circuit is right?
Chec
supply are in working order?
Page 21

Check if there is sound when disc
assistant channel
Check if there is output on the
control line is
Check main channel
Check radio head control line, if
there are no abnormity, then
Check these two control lines
is open circuit
Radio has no sound
YES
playing or with
NO
YES
radio head.
NO
YES
Check if N111
NO
in working order.
YES
output line.
change the head.
to MT1389
or not?
Confirm if MT1389 is ok?
Page 22

Attachment :Functions of IC Pins
I. MT1389
MT1389 adopts the LQFP 256 pin packaging and 3.3V/1.8V double voltage operation
mode. It is a piece of large -scale CD-ROM and DVD-ROM preposition processing
CMOS integrated circuit with excellent performance, and a single chip dedicated to
CD/VCD/DVD player. It contains focusing servo error amplification; tracking servo
error amplification and RF level output servo control, including the following main
functions:
RF small signal preposition processing, mainly for carrying our corresponding
processing and amplification on the RF signals transmitted from the light head part,
adjusting the laser output power automatically, and identifying the VCD disc and
DVD disc.
Digital servo processing can generate focusing, tracking, feed and main shaft servo
control signals; digital signal processing, accomplishing the EFM/EFM +
demodulating of RF signals.
MPEG-1/MPEG-2/MPEG4/JPEG Video decoding chip, which can not only realize
the decoding of VCD and DVD, but also realize MPEG 4 network video decoding,
being compatible to “network movie” disc, and decipher JPED pictures to realize the
function of digital photo album play.
On audio aspect, it can not only realize AC-3/DTS double decoding, decipher
MP3, and is also compatible to DVD-Audio decoding to achieve high-resolution
sound restoration in 1000 times higher than CD.
By utilizing the 8032 microprocessor with built-in chip, MT1369E can also
realize the system control function of player, which simplifies the circuit design
substantially.
The pin functions of MT1389 is as the following table:
Pin Name Function
1 AGND Analogue grounding
2 DVDA
3 DVDB
DVD-RF high-frequency AC coupling
signal A
DVD-RF high-frequency AC coupling
signal B
4 DVDC
5 DVDD
DVD-RF high-frequency AC coupling
signal C
DVD-RF high-frequency AC coupling
signal D
Page 23

6 DVDRFIP
DVD-RF high-frequency AC coupling
signal RFIP input
7 DVDRFIN
8 MA
9 MB
10 MC
11 MD
12 SA
13 SB
14 SC
DVD-RF high-frequency AC coupling
signal RFIN input
DVD-RAM main light beam RF DC
signal input A
DVD-RAM main light beam RF DC
signal input B
DVD-RAM main light beam RF DC
signal input C
DVD-RAM main light beam RF DC
signal input D
DVD-RAM auxiliary light beam RF DC
signal input A
DVD-RAM auxiliary light beam RF DC
signal input B
DVD-RAM auxiliary light beam RF DC
signal input C
15 SD
16 CDFON CD focusing error phase inversion input
17 CDFOP CD focusing error phase input
18 TNI
19 TPI
20 MDI1 Laser power monitoring input 1
21 MDI2 Laser power monitoring input 2
22 LDO2 Laser power monitoring output 2
23 LDO1 Laser power monitoring output 1
24 SVDD3 Servo 3.3V power supply
25 CSO/RFOP
DVD-RAM auxiliary light beam RF DC
signal input D
3 light beam auxiliary PD signal phase
inversion input
4 light beam auxiliary PD signal phase
input
Main servo signal output/RF phase
output
26 RFLVL/RFON
RF level output/RF phase inversion
output
Page 24

27 SGND Servo grounding
28 V2REFO Reference voltage 2.8V
29 V20 Reference voltage 2.0V
30 VREFO Reference voltage 1.4V
31 FEO Focusing error signal output
32 TEO Tracking error signal output
33 TEZISLV Tracking zero crossover error input
34 OP_OUT Sensing signal amplification output
35 OP_INN Sensing signal phase inversion input
36 OP_INP Sensing signal noninverting input
37 DMO Main shaft control signal output
38 FMO Feed control signal output
39 TROPEN PWM Tray Open signal output
40 PWMOUT1/ADIN9
41 TRO Tracking control signal output
42 FOO Focusing control signal output
43 USB_VSS USB grounding
44 USBP USB data
45 USBM USB data
46 USB_VDD3 USB 3.3V power supply
47 FG/ADIN8
48 TDI/ADIN4
49 TMS/ADIN5
First-route pulse width demodulating
signal output/AD universal input
Motor sensing signal input/AD universal
input
Open position detecting signal input/AD
universal input
Close position detecting signal input/AD
universal input
50 TCK/ADIN6
51 TDO/ADIN7
52、97、122、
152、173、221
DVDD18 Digital 1.8V power supply
BA5954 enabling signal output/AD
universal output
Tray close signal output/AD universal
input
Page 25

53-58 IOA2-7 Micro-controller address bit 2-7
59 HIGHA0 Micro-controller address bit 0
60、61 IOA18-19 Micro-controller address 18-19
62、85、94、116、
119、134、144、
148、161、163、
175、216、223
DVSS Digital grounding
63 APLLCAP
64 APLLVSS Analogue phase lock loop grounding
65 APLLVDD3 Analogue phase lock 3.3V power supply
66 IOWR FLASH read control signal
67-72 HIGHA3-7 Micro-controller address bit 3-7
73、80、108、
127、141、155、
167、182、204、
212
74、75 HIGHA1-2 Micro-controller address bit 1-2
76 IOA20 Micro-controller address bit 20
77 IOCS FLASH chip selection
78 IOA1 Micro-controller address bit 1
DVDD3 Digital 3.3V power supply
Analogue phase lock loop external
capacitor
79 IOOE FLASH output enabling
81-84 AD0-3 Micro-controller address/data bit 0-3
86-88 AD4-6 Micro-controller address/data bit 4-6
89 IOA21/ADIN0
90 ALE Micro-controller address enabling
91 AD7 Micro-controller address/data bit 7
92 A17 FLASH address bit 17
93 IOA0 Micro-controller address bit 0
95 UWR Micro-processor reading operation
96 URD Micro-processor reading operation
98 UP1_2-1_7 Micro-processor port
Micro-controller address bit 21/AD
universal input
Page 26

104 UP3_0 Micro-processor port
105 UP3_1 Micro-processor port
106 UP3_4 Micro-processor port
107 UP3_5 Micro-processor port
109 ICE
110 PRST Reset input
111 IR Remote control signal input
112 INT0 Micro-processor interruption 0
113 DQM0 DRAM input output shielding signal
114 DQS0 DRAM input output shielding signal
115 RD7 DRAM data
117-118 RD5-6 DRAM data
120-121 RD3-4 DRAM data
123-125 RD0-2 DRAM data
126 RD15 DRAM data
128-133 RD9-14 DRAM data
Micro-processor correction mode
enabling
135 RD8 DRAM data
136 DQS1 DRAM input output shielding signal
137 DQM1 DRAM input output shielding signal
138 RWE DRAM writing enabling
139 CAS DRAM column address selection
140 RAS DRAM row address selection
142 RCS DRAM chip selection
143 BA0 DRAM section address 0
145 BA1 DRAM section address 1
146 RA10 DRAM address
147 RA0 DRAM address
149 RA1-3 DRAM address
153 RVREF/ADIN3 Reference voltage/AD universa l input
154 RCLKB DRAM clock
Page 27

156 RCLK DRAM clock
157 CKE DRAM clock enabling
158 RA11 DRAM address
159-160 RA8-9 DRAM address
162 RA7 DRAM address
164 RA4-6 DRAM address
168 RD13/ASDATA5 DRAM data/audio series data
169 RD27-30 DRAM data
174 RD26 DRAM data
176-177 RD24-25 DRAM data
178-179 DQM2-3 DRAM I/O shielding signal
180-181 RD22-23 DRAM data
183-188 RD16-21 DRAM data
189 DACVDDC D/A conversion 3.3V power supply
190 VREF Reference voltage
191 FS
192 YUV0/CIN
193 DACVSSC D/A conversion grounding
194 YUV1/Y
195 DACVDDB D/A conversion 3.3V power supply
196 YUV2/C
197 DACVSSB D/A conversion grounding
198 YUV3/CVBS
199 DACVDDA D/A conversion 3.3V power supply
Video signal YUV1 output/Y signal
output
Video signal YUV2 output/C signal
output
Video signal YUV3 output/CVBS signal
output
200 YUV4/G
201 DACVSSA D/A conversion grounding
202 TUV5/B
Video signal YUV4 output/G signal
output
Video signal YUV5 output/B signal
output
Page 28

203 YUV6/R
Video signal YUV6 output/R signal
output
205 VSYNC/ADIN1
206 YUV7/ASDATA5
207 HSYNC/ADIN2
208 SPMCLK
209 SPDATA
210 SPLRCK
211 SPBCK/ASDATA5
213 ALRCK Audio left and right sound channel clock
214 ABCK Audio bit clock
215 ACLK Audio DAC external clock
217-220 ASDATA0-3 Audio series data
Field synchronization signal output/AD
universal input
Video signal YUV7 output/audio series
data
Row synchronization output/AD
universal input
222 ASDATA4 Audio series data
224 MC_DATA Microphone digital audio input
225 SPDIF Digital audio signal output
226 RFGND18 RF signal grounding
227 RFVDD18 RF signal 1.8V power supply
228 XTALO Clock output
229 XTALI Clock input
230 JITFO RF small signal output
231 JITFN
232 PLLVSS Phase lock loop grounding
233 IDACEXLP
234 PLLVDD3 Phase lock loop 3.3V power supply
RF small signal phase inversion and
amplification input
235 LPFON Amplifier loop wave filtration output
236 LPFIP Amplifier loop wave filtration input
237 LPFIN Amplifier loop wave filtration input
Page 29

238 LPFOP Amplifier loop wave filtration output
239 ADCVDD3 A/D conversion 3.3V power supply
240 S_VCM
241 ADCVSS A/D conversion grounding
242 S_VREFP
243 S_VREFN
244 RFVDD3 RF 3.3V power supply
245 RFRPDC DC RF error signal input
246 RFRPAC AC RF error signal input
247 HRFZC
248 CRTPLP
249 RFGND RF grounding
250 CEQP
251 CEQN
252 OSP
253 OSN
254 RFGC
255 IREF Reference current
256 AVDD3 Analogue 3.3V power supply
Ⅱ.BA5954
High-frequency RF signal zero
crossover checking
BA5954 is a piece of servo drive single-piece integrated circuit, with built-in
4-channel BTL drive circuit. It can receive directly the PWM control signal outputted
by digital servo IC, and with internal wave filter and drive amplifier, it pushes the
execution part in the servo mechanism to accomplish the focus ing, tracking, feed and
main shaft drives. BA5954 adopts the packaging of 28 pins.
Note: The 28 pins of BA5954 are for outputting effective control signal, which is
provided by the 50 pins of MT1389. When the signal is in high power level, BA5954
output is in validity, while the signal is in low power level, BA5954 will not be
activated, and its output ports are in the state of cutoff.
The functions of pins of BA5954 are as the following table:
Page 30

Pin Name Function
1 VINFC Focusing control signal input
2 CF1 External feedback loop
3 CF2 External feedback loop
4 VINSL+ Forward control input, connected to the reference voltage
5 VINSL- Main shaft control signal input
6 VOSL External feedback resistance
7 VINFFC Focusing feedback signal input
8 VCC 5V power supply
9 PVCC1 5V power supply
10 PGND Grounding
11 VOSL- Main shaft drive inverse voltage output
12 VO2+ Main shaft forward voltage output
13 VOFC- Focusing drive inverse voltage output
14 VOSC+ Focusing drive forward voltage output
15 VOTK+ Tracking drive forward voltage output
16 VOTK- Tracking drive inverse voltage output
17 VOLD+ Feed drive forward voltage output
18 VOLD- Feed drive inverse voltage output
19 PGND Grounding
20 VINFTK Tracking feedback signal input
21 PVCC2 5V voltage
22 PREGND Grounding
23 VINLD Feed control signal input
24 CTK2 External feedback loop
25 CTK1 External feedback loop
26 VINTK Tracking control signal input
27 BIAS 1.4 reference voltage input
28 STBY Enabling control signal
Page 31

III. 29LV160BE
29LV160BE is a type of 16Mbit FLASH memory manufactured via 0.23um
technology, with 16 byte width DQ0-DQ15, memory capacity of 16M bit, operation
voltage of 3.3V, and packaging method of 48 pins TSOP. The specific operation mode
is as the following table:
DQ8~DQ15
Operation
status
Read L L H H Ain Dout Dout High resistance
Write L H L H Ain Din Din High resistance
CE OE WE RESET A0~A19 DQ0~QD7
BYTE:high
level
BYTE: Low
level
Waiting H × × H ×
Output
forbidden
Reset × × × L ×
L H H H ×
high
resistance
High
resistance
High
resistance
high resistance high resistance
High resistance High resistance
High resistance High resistance
The functions of pins of 29LV160BE are as the following table:
Pin Name Function
15 RY/BY Ready/system is busy
1~9、16~25 、48 A0~A19 20-byte address bus
26 CE Chip enabling
27、46 VSS Grounding
28 OE Output enabling
29~36、38~44 DQ0~DQ14 15-byte data bus
37 VCC 5V power supply
45 DQ15/A-1
47 BYTE
11 WE Write enabling
12 RESET Reset, valid in low level
10、13、14 NC Neutral pin
Character extension mode as the data line; byte expansion
mode as the address line
Adopting 8-byte (in low level) or 16-byte output mode (in
high level)
Page 32

IV. AE45164016
AE45164016 is a type of 64Mb (4Banks×1M×16bit) CMOS synchronization DRAM,
featured with large memory and high speed. Its operation power voltage is 3.0V~3.6V,
and it is packaged in 54-pin TSOP.
The functions of pins of AE45164016 are as the following table:
Pin Name Function
1、14、27 VDD +3.3V power supply
2、4、5、7、8、10、11、
13、42、44、45、47、48、
50、51、53
3、9、43、49 VDDQ +3.3V power supply
6、12、46、52 VSSQ Grounding
28、41、54 VSS Grounding
DQ[0~15]
16-byte data bus
15 LDQM Data I/O shielding signal
16 WE Write control signal
17 CAS Column address gate signal
18 RAS Row address gate signal
19 CS Chip selection signal
20 SD-BS0 Section address 0 gate signal
21 SD-BS1 Section address 1 gate signal
22~26、29~35 MA[0~11]
36、40 NC Neutral pin
37 CKE Clock enabling signal
38 CLK System clock input
39 UDQM Data I/O shielding signal
12-byte address bus
V. CS4360
CS4360 is a type of 6- channel audio D/A conversion circuit manufactured by
CIRRUS LOGIC Company. It can achieve digital sound volume regulation through
software, with 1dB regulation coefficient per level, 119dB attenuating scope and
+3.3V or +5V voltage power supply. It adopts 28-pin packaging, and has the
following characteristics:
Page 33

① 24-byte sampling precision
Series audio power supply, +3.3V
Control port power supply, +3.3V
② Maximum 192KHZ sampling frequency
③ Dynamic range: 102dB
④ Signal/noise ratio: -90dB
⑤ Low power consumption (105mW under +3.3V operation voltage)
The functions of pins of CS4360 are as the following table:
Pin Name
1 VLS
2 SDIN1
3 SDIN2
4 SDIN3
5 SCLK
6 LRCK
7 MCLK
8 VD Digital power supply 22 VA Analogue power supply, +5V
9 GND
10 RST Reset input 24 AOUTA2
11 SCL Series control clock 25 MUTEC2
12 SDA
Series audio data 1 input 16 FILT+ In -phase feedback voltage output
Series audio data 2 input 17 VQ Static operation voltage external wave filter
Series audio data 3 input 18 MUTEC3
Function Pin
15 M2 Mode 2
Bit clock 19 AOUTB3
Left and right clock 20 AOUTA3
Main clock input 21 GND Grounding
Grounding 23 AOUTB2
Series control data 26 AOUTB1
Name Function
3 muting control output
Analogue audio 3 output
Analogue audio 3 output
Analogue audio 2 output
Analogue audio 2 output
Output 2 muting control
Analogue audio 1 output
13 CS/M1
14 VLC
ATTACHMENT:
I: CIRCUIT DIAGRAM
Chip selection/mode 1 27 AOUTA1
1) DECODER BOARD:
28 MUTEC1
Analogue audio 1 output
Output 1 muting control
Page 34

ADC_DAT
ASPDIF
R268
224
225
SPDIF
RFGND18
MC_DATA
V18
URST#
R269
0R
AUDIO_RST
V18
AMUTE
R220
(DNS)
33R
222
221
220
223
DVSS
DVDD18
ASDATA4
100
101
VFDCK
VFDAT
VFDST
ASDAT1
ASDAT2
219
218
ASDATA3
ASDATA2
ASDATA1
UP1_5
UP1_6
UP1_7
102
103
SCL
SDA
5
ACLK
ASDAT0
217
215
216
DVSS
ACLK
ASDATA0
UP3_0
UP3_1
UP3_4
104
105
106
RXD
DAVNIN
LRSWMUTE
ALRCK
ABCK
213
214
ABCK
UP3_5
107
108
TXD
ALRCK
DVDD3
R219
R218
R217
R216
R215
SPBCK
89V33
SPDATA
SPLRCK
SPBCK
211
210
209
212
DVDD3
SPLRCK
SPDATA
SPBCK/ASDATA5
ICE
PRST
INT0
109
110IR111
112
IR
URST#IRDQM0
(DNS)
(DNS)
(DNS)
(DNS)
1K
208
207
206
205
SPMCLK
YUV7/ASDATA5
HSYNC/V_ADIN2
VSYNC/V_ADIN1
DVSS
DQM0
DQS0
RD7
116
113
114
115
DQS0
DQ7
204
DVDD3
RD6
117
DQ6
Y5
Y6
203
202
YUV6/R
RD5
118
119
DQ5
Y4
201
200
YUV5/B
DACVSSA
RD4
DVSS
120
121
DQ4
DQ3
Y3
199
198
YUV4/G
DACVDDA
DVDD18
RD3
122
123
DQ2
Y2
197
196
195
YUV2/C
DACVSSB
DACVDDB
YUV3/CVBS
RVREF/V_ADIN3
RD2
RD1
RD0
RD15
124
125
126
DQ1
DQ0
DQ15
Y1
HSYNC#
ADC_DAT
VSYNC#
SPMCK
194
193
YUV1/Y
DACVSSC
YUV0/CIN
VREF
DACVDDC
RD16
RD17
RD18
RD19
RD20
RD21
DVDD3
RD22
RD23
DQM2
DQM3
RD24
RD25
DVSS
RD26
DVDD18
RD27
RD28
RD29
RD30
RD31/ASDATA5
DVDD3
RA4
RA5
RA6
DVSS
RA7
DVSS
RA8
RA9
RA11
CKE
RCLK
DVDD3
RCLKB
DVDD18
RA3
RA2
RA1
DVSS
RA0
RA10
BA1
DVSS
BA0
RCS
DVDD3
RAS
CAS
RWE
DQM1
DQS1
RD8
DVSS
RD9
RD10
RD11
DR12
RD13
RD14
DVDD3
128
127
DQ14
6
C233 100pF
R227 750K
DACVDD3 DV33
192
191
FS
190
189
188
187
186
185
184
183
182
181
180
179
178
177
176
175
174
173
172
171
170
169
168
167
166
165
164
163
162
161
160
159
158
157
156
155
154
153
152
151
150
149
148
147
146
145
144
143
142
141
140
139
138
137
136
135
134
133
132
131
130
129
R213
1K
JITFNJITFO
L203
FB
C217
104
89V33 V18
R214
FS
C216
DTS_DO
DTS_CL
DTS_DI
DTS_CE
R261
TUNER_ON
CLK
RDS_DATA
VDATA3
POWER_ON_RST
RDSSYNC
SCMUTE
RDSID
RDSCE
AUIN_SL0
AUIN_SL1
J3
J4
R2164
10K
TC201
10uF/16V
510R
33R
SCMUTE
DMA4
DMA5
DMA6
DMA7
DMA8
DMA9
DMA11
DCKE
DCLK
DMA3
DMA2
DMA1
DMA0
DMA10
BA1
BA0
CS#
RAS#
CAS#
WE#
DQM1
LIMIT
DQ8
DQ9
DQ10
DQ11
DQ12
DQ13
DV33
A
B
VOICE_DET
C
D
E
F
1
AVCC
V305
3904-S
V304
FBSMT
10uH
FBSMT
FBSMT
10uH
FBSMT
FBSMT
FBSMT
FBSMT
FBSMT
FBSMT
FBSMT
FBSMT
FBSMT
FBSMT
FBSMT
FBSMT
FBSMT
FBSMT
FBSMT
R309
10K
R311
10K
R310
100K
AVCC
C301
104
IOA
MDI1
E
V20
F
B
A
RFO
IOA
D
C
DV33
L238
FB
TC301
220uF/16V
R301
10R
R302
10R
MO_VCC
V301
2SB1132-S
R331
V302
2SB1132-S
R308
100K
A
V303
24
23
22
21
20
19
18
17
16
15
14
13
12
11
10
9
8
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
C311
104
2SK3018-S
L301
L303
L304
L305
L306
L307
L308
L310
L311
R303 0R
L312
L314
L316
L317
L318
L319
L320
L321
L322
L323
L324
C312
104
XS301
24P0.5mm
B
2SK3018-S
C
30
VOTK+
VOTKVOLD+
VOLDPGND
VNFTK
PVCC2
PREGND
VINLD
CTK2
CTK1
VINTK
BIAS
STBY
U302
BA5954
R318
R322
680K
VCC
0R
V309
8550
V308
8050
V310
9014-S
29
GND
VOFC+
GND
VOFC-
VO2+
VOSL-
PGND
PVCC1
VINFFC
VOSL
VINSL-
VINSL+
VINFC
OPO
ADIN
OPOP+
C310
2200pF
V1P4
SP-
R324
1.5K
R327
470R
VCC
CF2
CF1
14
13
12
11
10
9
8
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
XS303
XS06
TC309
47uF/16V
R339
10K
V1P4
FOSO
1
2
3
4
5
6
LOAD+
TRCLOSE
(TRCLOSE1)
TROPEN
R305
R304
1R
1R
SL+
SL-
MO_VCC
GND
FMSO
D
C305
104
R319
150K
E
F
C302
104
C303
R313
10K
1R
1R
R326
2.2R\1/4W
104TC304
TRSO
V1P4
STBY
C307 2200pF
R317
R320
150K
R323
1.5K
R325
470R
47uF/16V
R312 20K
C304 151
R321
R340
TC308
47uF/16V
LOAD-
(TRCLOSE1) (TROPEN1)
TROPEN
680K
C308
DNS
V306
8550
V307
8050
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
2 3 4
LDO-AV33
0R
LDO-AV33
L302
FB
R314 10K
R316 20K
SL+
SLLIMIT
SP+
RFV33
TC211
220uF/16V
L309
FB
TC302
47uF/16V
LDO2
DQS0
LDO1
TC303
47uF/16V
VCC
R3061RR307
SPSP+
DMSO
R315
20K
C306
151
XS302
XS05
DV33
1R
C231
104
C241
104
C242
104
C243
104
V1P4
ADIN
1
2
3
4
5
L235
FB
L236
47uF/16V
L205
FB
DV33
DV33
R328
10K
C343
FB
TC248
L206
4.7R
L207
FB
L208
FB
L250
FB
L234
V18 RFV18
FB
C230
104
TC206
47uF/16V
TC205
47uF/16V
TC204
47uF/16V
C208
C209
R207
R206
TRSO
FOSO
C210
153pF
V1P4
89V33
R329
10K
C309
C344
104
89V33
C2167
104
104
C244
104
DV33A
104
C345
V18
LOADLOAD+
TROUT
TRIN
104
C277
R205
104
C245
104
AVDD3
C251
104
C254
104
104
DMSO
FMSO
C211
104
L201
FB
C234
C346
PLLVDD3
TC203
104
47uF/16V
ADCVDD3
C235
104
RFVDD3
C236
104
RFSVDD3
C237
104
C
B
A
D
RFO
120p
R201 0R
C
R202 0R
B
R203 0R
A
R204 0R
D
E
F
LDO2
LDO1
RFSVDD3
R2165 0R
V2P8
V20
V1P4
R2166 0R
C207 104
R208
R209
R210
R211
C213
330pF
C212
330pF
C214
104
R212
0R
C246
C247
C252
104
C2174
104
104
C248
104
C253
104
C256
104
104
VREFN VREFP
C238
C240
104
1uF
C229
104
C201 1uF
C202 1uF
C203 1uF
C204 1uF
C205 DNSC206
R228 0R
10K
15K
18K
20K
C215
1500pF
RFOP
RFON
FEO
TEO
TEZISLV
OPO
OPOP+
DMO
FMO
TROPEN
TRO
FOO
USBVDD
ADIN
TROUT
TRIN
STBY
TRCLOSE
V18
A2
A3
A4
A5
A6
A7
A8
A18
A19
C249
104
C257
104
MDI1
MDI2
TDI
TMS
TCK
TDO
C250
104
C258
104
L202
FB
C239
104
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
TC247
47uF/16V
PWR#
PCE#
PRD#
R223
15K
AVDD3
AGND
DVDA
DVDB
DVDC
DVDD
DVDRFIP
DVDRFIN
MA
MB
MC
MD
SA
SB
SC
SD
CDFON
CDFOP
TNI
TPI
MDI1
MDI2
LDO2
LDO1
SVDD3
CSO/RFOP
RFLVL/RFON
SGND
V2REFO
V20
VREFO
FEO
TEO
TEZISLV
OP_OUT
OP_INN
OP_INP
DMO
FMO
TROPENPWM
PWMOUT1/V_ADIN9
TRO
FOO
USB_VSS
USBP
USBM
USB_VDD3
FG/V_ADIN8
TDI/V_ADIN4
TMS/V_ADIN5
TCK/V_ADIN6
TDO/V_ADIN7
DVDD18
IOA2
IOA3
IOA4
IOA5
IOA6
IOA7
HIGHA0
IOA18
IOA19
DVSS
APLLCAP
APLLVSS
C2175
104
R297 0R
R298 0R
R299 0R
104
C228
256
AVDD3
APLLVDD3
65
104
C227
255
254
IREF
IOWR
67
66
PWR#
A16
C226
253
RFGC
A16
68
A15
104
C225
252
251
OSP
OSN
HIGHA6
HIGHA7
70
69
A14
A13
DWR#
DCE#
DRD#
C224
0.033uF
250
249
CEQP
CEQN
HIGHA4
HIGHA5
72
71
A12
A11
R224
104
248
247
RFGND
CRTPLP
HIGHA3
DVDD3
74
73
A10A9A20
V1P4
1000pF
100K
245
246
HRFZC
RFRPAC
HIGHA1
HIGHA2
75
C222
20pFC223
RFVDD3
VREFN
VREFP
244
243
242
RFVDD3
RFRPDC
S_VREFN
IOA2076IOA1
IOCS
78
79
77
PCE#A1PRD#
C221 1uF
241
240
S_VCM
ADCVSS
S_VREFP
DVDD3
IOOE
81
80
AD0
C220
0.047uF
ADCVDD3
238
237
239
LPFIN
LPFOP
ADCVDD3
AD384AD283AD182AD0
AD1
AD2
AD3
TC202
10uF/16V
C219
0.047uF
PLLVDD3
236
234
235
LPFIP
LPFON
DVSS
86
85
AD4
AD5
C218 0.47uF
XIXOJITFO
JITFN
231
230
232
233
229
JITFN
JITFO
PLLVSS
PLLVDD3
IDACEXLP
U201
MT1389
AD7
AD587AD4
ALE
AD688IOA21/V_ADIN0
91
92
90
89
AD6
A21
AD7
A17
RFV18
226
228
227
XTALI
XTALO
RFVDD18
IOA0
A17
DVSS94UWR95URD96DVDD1897UP1_298UP1_399UP1_4
93
A0
1 2 3 4 5 6
Page 35

1 2 3 4
U211
23
DMA0
DMA1
DMA2
DMA3
DMA4
DMA5
DMA11
DMA6
DMA7
R232
DMA8
33R
DMA9
DMA10
MA11
BA0
#BA1
33R
SDCLK
33R
SDCKE
DCS#
DRAS#
DCAS#
DWE#
DQM0
DQM1
VD
AD3
AD2
AD0
VD DV33
TC237
47uF/16V
5 6
C278
U205C
102
HCU04
TC208
220uF/16V
C282
C2168
104
L230
L231
L232
L233
47pF
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
TC210
47uF/16V
VOICE_DET
DV33
C271
104
220uF/16V
FB
L240
N107
VL
MCLK
SCLK
SDATA
VA
GND
LRCK
DIV
CS5333
CLK
J4
J3
C265
47pF
TC207
DV33
R_GND
BT
FBSMT
FBSMT
FBSMT
FBSMT
L227
FB
/RST
VQ
LIN
RIN
FIL+
TST
DIF
C2170
104
C266
47pF
C191
104
VCC
C186
20P
VFDAT
VFDST
VFDCK
IR
R230
4.7K
16
15
14
13
12
11
10
9
R195
4.7K
DV33
C272
104
AUDIO_RST
C189 104
C190 104
G101
32.768K
C2171
104
DV33A
C187
20P
+
C286
1UF
C2173
104
1
2
3
4
TC213
220uF/16V
+
1
X1
2
X2
3
INT
4
GND
M41T81
AT24C16X4050
DC/NC
RST_/NC
WP/RST_
VSS
C287
1UF
N106
U202
SCMUTE
VCC
SQW
SCL
SDA
VCC
RST/WP
SCL
SDA
R238 4.7K
VD
R241
4.7K(DNS)
VCC
8
7
6
5
R240 4.7K
R239 4.7K
R2140 4.7K
+12V
-12V
SCMUTE
4.7K
R100
AVCC
VD119 1N4148
8
R193 4.7K
7
6
5
SCL
SDA
C260
102(DNS)
A20
R257 0R
R258 0R A21
XS104
SCL
SDA
1
2
3
4
5
CON5
R259
10K
A19
A18
A7
A6
+12V
GND
-12V
OK_A
OK_T
VCC
A16
A15
A14
A13
A12
A11
A10
A9
AA20
AA21
DWR#
URST#
VP
A4
A3
A2
R260
10K
C261
102(DNS)
A19
A18
A8
A7
A6
A5
C259
104
U214 8M_FLASH(TSOP)
1
A15
2
A14
3
A13
4
A12
5
A11
6
A10
7
A9
8
A8
9
A19
10
NC
11
WE
12
RESET
13
NC
14
NC
15
RY/BY
16
A18
17
A17
18
A7
19
A6
20
A5
21
A4
22
A3
23
A2
24
A1
DV33
R252
10K
R253
0R(DNS)
A16
BYTE
Vss
DQ15/A-1
DQ7
DQ14
DQ6
DQ13
DQ5
DQ12
DQ4
Vcc
DQ11
DQ3
DQ10
DQ2
DQ9
DQ1
DQ8
DQ0
OE
Vss
CE
A0
VD201
1N4148
Q204
9016
TC217
100uF/16V
DCLK
DCKE
R264
R265 33R
CS#
R266 33R
RAS#
R267 33R
CAS#
R2162 33R
WE#
48
47
46
45
44
43
42
41
40
39
38
37
36
35
34
33
32
31
30
29
28
27
26
25
BA1
R263
R254
1K
R231
33R
A17
GND
A0
AD7
AD6
AD5
AD4
VD
AD3
AD2
AD1
AD0
DRD#
GND
DCE#
A1
C279
104
AVCC
L241
FB
SD33
C281
104
C285
10U/16V
R190
C2162
104
XS103
CON10
ADC_DAT
10
9
8
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
C283
0.1u
SACLK
SBCLK
SLRLK
47K
C2163
104
C263
47pF C264
VCC
C270
104
47UF/16V
DV33
L226
FB
A
XS202
1
2
3
4
XS04(DNS)
DV33
RXD
TXD
GND
C267
104
B
C
D
L222 FB
VCC
L223 FB
DV33
L209 FB
AVCC
U208
BA033FP(DNS)
IN1GND2OUT
VCC DV33
3
C284
0.1u
E
R244
0R
C2158
27pF(DNS)
R291 220
R292 220
R293 220
R294 220
R295 220
R296 220
100K
R246
X201
C275
27pF
27MHz
R248
0R
C276
27pF
SDATA1
SDATA2
XO
ACLK SACLK
ABCK SBCLK
ALRCK SLRCK
ASDAT0 SDATA0
ASDAT1
ASDAT2
XI
L249
F
2.7uH(DNS)
24
25
26
29
30
31
32
33
34
22
35
20
21
38
37
19
18
17
16
15
39
36
40
54
41
28
R255
0R
L204
FB(DNS)
A0
A1
A2
A3
A4
A5
A6
A7
A8
A9
A10/AP
A11
BA0/A13
BA1/A12
CLK
CKE
/CS
/RAS
/CAS
/WE
DQML
DQMH
NC
NC
VSS
VSS
VSS
SDRAM 64M
VCC
DQ0
DQ1
DQ2
DQ3
DQ4
DQ5
DQ6
DQ7
DQ8
DQ9
DQ10
DQ11
DQ12
DQ13
DQ14
DQ15
VCC
VCC
VCC
VCCQ
VCCQ
VCCQ
VCCQ
VSSQ
VSSQ
VSSQ
VSSQ
5
R256
33R
URST#
2
DQ0
4
DQ1
5
DQ2
7
DQ3
8
DQ4
10
DQ5
11
DQ6
13
DQ7
42
DQ8
44
DQ9
45
DQ10
47
DQ11
48
DQ12
50
DQ13
51
DQ14
53
DQ15
SD33
1
14
27
SD33
3
9
43
49
6
12
46
52
V18
R251
0R
L228
FB
C2160
104
10 11
C273
104
POWER_ON_RST
ADC_DAT
U205E
HCU04
TC209
220uF/16V
VCC
VCC
R225
R226
R250
0R(DNS)
12 13
U205F
HCU04
VD202
1N4004(DNS)
LM1117MP-1.8
R242
3.3K
R243
1.2K
R235
U209
GND1OUT
4.7K
R249
4.7K
IEC958
DV33 C274
VD203
1N4004(DNS)
2
Y1
Y2
Y3
Y4
Y5
Y6
HSYNC#
VSYNC#
VDATA3
147
IN
3
104
0
0
R233
75R
6
AUDIO_RST
SDATA0
SDATA1
SDATA2
GND
SACLK
GND
SBCLK
SLRCK
AUIN_SL0
AUIN_SL1
SCL
SDA
LRSWMUTE
DTS_DO
DTS_CL
DTS_DI
DTS_CE
TUNER_ON
DAVNIN
GND
RDSID
DV33
VGND
R2159
0R
SPDIF
AUDIO_RST
SDATA0
SDATA1
SDATA2
GND
SACLK
GND
SBCLK
SLRCK
AUIN_SL0
AUIN_SL1
SCL
SDA
LRSWMUTE
DTS_DO
DTS_CL
DTS_DI
DTS_CE
TURN_ON
DVDNIN
GND
RDSID
Y1
Y2
Y3
Y4
Y5
Y6
HSYNC#
VSYNC#
VDATD3
VGND
SPDIF
ASPDIFIEC958
A
B
C
D
E
F
1 4
5
6
Page 36

654321
+5V
33K
C119
102
C120
102
TO POWER BOARD
SPDIF
L110
1.8uH
L111
1.8uH
L114
1.8uH
R116
C128
2
3
R117
6
5
R109
R110 4.7K
+5.1V
XP104
1
2
GND
3
4
MUTE
CON4
82P
+12v
8 4
-12V
33K
C129
82P
TC150 16V/10U
4.7K
TC149
L116
4.7
R
L
R167
C134 104
R177
0
C164
47P
R178
0
C165
47P
R181
0
C171
47P
N101A
IC4558
N101B
IC4558
PH5V
VCC
VCC
VCC
1
7
16V/10U
R147
47K
R148
47K
68
1N4148
VD102
VD103
1N4148
1N4148
VD104
VD105
1N4148
1N4148
VD110
VD111
1N4148
R118
470
R122
470
TC151
16V/100U
10U/16V
VCC
TC110
R168
220
L104
L105
L108
N102
12
R137
100K
R138
100K
122
C118
C121
102
AUX_R
TUNER_R
AUX_L
TUNER_L
R119
R123
R124
R125
1K
4.7K
1K
4.7K
R141
47K
R142
100K
R143
47K
R2
AUX_R
TUNER_R
L2
AUX_L
TUNER_L
R144
100K
MUTE1
SLB
SLA
X0
14
X1
X2
X3
Y0
Y1
Y2
Y3
INH
B
A
X
Y
VDD
VSS
VEE
15
11
1
5
2
4
6
9
10
CD4052
R134
V107
13
3
+5.1V
16
8
7
-5.1V
8550
C113
C114
R120
100
R126
100
103
103
V103
S8050
C122
102
C123
102
R139
100K
10K
R135
R111
4.7K
TC153 16V/100U
N104
PT2308
1
Out1
IN1-
IN1+
VDD
Vout2
2
3
Vss4IN2+
IN2-
PH5V
8
7
6
5
TC152
16V/100U
TC109
100U/16V
R149
47K
R150
47K
PH_R
R112
4.7K
PH_L
PH_SW
10K
AUX_R
AUX_L
TO PANEL BOARD
XS102
PH_R
1
2
GND
3
PH_L
4
PH_SW
CON4
C124
C125
102
C135
104
R169
100K
L
C177
20P
1
2
3
3
2
1
R?
GND
VCC
INPUT
TORX178A
R
XC100A
L
AV4
R152
47K
L101
L
L102
L
LINE_R
LINE_L
R128
R127
R151
47K
470
470
VCC
Y3 CVBS
Y3
R17375C166
L112
1.8uH
47P
C168
47P
R179
0
VD106
1N4148
VD107
1N4148
102
L100
L
L103
L
L106
L
FR
FL
C126
102
V104
S8050
C127
102
6
5
4
3
2
1
C178
20P
VCC
L
C176
20P
6
XC101B
R
VD108
1N4148
VD109
1N4148
L107
L
C167
47P
L113
1.8uH
Y2 SV_Y
Y2
R174
75
C169
47P
R180
0
C179
20P
5
4
L
L
C180
20P
AV4
Y1 SV_C
Y1
R176
75
C172
47P
L115
1.8uH
C173
47P
R182
0
VCC
VD112
1N4148
VD113
1N4148
L109
L
C181
20P
220U/10V
R133
10K
AUDIO RST
47U/16V
C157
473
R166
470K
R160
C161
220
C138
104
TC156
220U/16V
C139
TC100
1K
G100
AVCC
VCC
DGND
-12V
GND
+12V
DV33
BT
R162
SDATA0
SBCLK
SLRLK
SACLK
C185
103
C143
C144
VCC
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
1
C183
104
TC184
100U/16V
1
2
3
4
562
5
562
6
7
8
9
10
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
XP102
CON7
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
C111
103
SDATA
SCLK/DEM1
LRCK
MCLK
DIF1
DIF0
DEM0
RST
VD117
9.1V
N103PT2315
REF
VDD
AGND
TREBL
TREBR
RIN
LOUD_R
NC
LOUD_L
NC
N105
MRO
MPTH
TCON
OSCO
OSC1
VSSD
VDDD
DAVN
SDA
SCL
SAA6588
VDATA3
HSYNC#
R186
220
14
VA
REF_GND
AGND
13
C112
103
DGND
BOUT_R
BIN_R
BOUT_L
BIN_L
LRSWMUT
R187
2.2K
AOUTL
MUTEC
AOUTR
CS4340
+12V
CLK
DATA
LOUT
ROUT
LIN
MUTE1
SCONT
VDDA
PSWN
VCC
FILT+
VQ
PH_SW
LVIN
CIN
Vref
MPX
VSSA
AFIN
MAD
R170
4.7K
N100
15
16
9
10
11
R185
RDSSYNC
C132
104
12
TC102
C131
104
10U/16V
TC130
47uF/16V
20
SCL
19
SDA
18
TC107
10U/16V
17
16
15
C145 683
C146
14
C147
13
12
C148
683
683
683
R156
5.6K
R157
5.6K
11
VD101
VD100 1N4148
VD116
20
19
18
TC174
17
16
C175
15
R198
1N4148 V106
4.7K
1N4148
C158
223 RDSCE
C159
150P
2.2U/16V
330P
14
13
12
11
R163
C136
104
RDSID
220
A+12V
R153
1K
V108
8050
R188
2.2K
R155
33R
V109
8050
R154
330
TC101
10U/16V
TC103
10U/16V
TC108
RDS
VCC
+12V
10K
R161
TC104
10U/16V
10U/16V
R114
4.7K
TC14047U/16V
R100
6.8K
MUTE1
R101
6.8K
R158 1K
R159
VCC
R115
4.7K
C115
103
Y5
Y6
R102
4.7K
C116
122
4.7K
V111
9014
R106
4.7K
C117
122
L
1K
R145
47K
MUTE
R146
47K
R194
R
4.7K
8050
SPDIF
Y4 G/Y
Y4
R17175C162
47P
Y5 B/U
R172
C163
75
47P
Y6 R/V
R175
C170
75
47P
F
AUDIO_RST
SDATA0
SDATA1
SDATA2
GND
SACLK
GND
SBCLK
SLRCK
AUIN_SL0
E
AUIN_SL1
SCL
SDA
SCMUTE
LRSWMUTE
DTS_DO
DTS_CL
DTS_DI
DTS_CE
TURN_ON
DVDNIN
GND
RDSID
D
XS105
10
AUDIO RST
SDATA0
SDATA1
SDATA2
DGND
SACLK
DGND
SBCLK
SLRLK
AUIN SL0
AUIN SL1
SL
R129
SD
R130 10
DTS DO
DTS CL
DTS DI
DTS CE
TUNER ON
DAVNIN
DGND
RDSID
GND
DTS CE
9
DTS DI
8
DTS CL
7
DTS DO
6
RDS
5
T+12V
4
TROUT
3
AGND
2
TLOUT
1
R131
10K
R183 0
R184
75K
R121
470
10
SCMUT
LRSWMUT
R132
10K
VCC
LINE_R
LINE_L
R191
4.7K
SCL
SDA
R105
4.7K
TC105
10U/16V
TC106
10U/16V
+5V
CON8
V102
TC133
8550+12V
C
104
TC154
220U/16V
TUNER ON
R136
10K
R113
4.7K
V105
C9014
82P
T+12V
C160
4.332MHz
R1970
B
R1990
TC141
47U/16V
-5.1V
+5.1V
A
VD114
5.1V
TC142
47U/16V
R165 220
R164
VD115
5.1V
47P
DAVNIN
SDA
SCL
C137
104
220
TC155
220U/16V
SLA
LINE_R
LINE_L
R140
100K
R
L
AV4
R
L
AV4
C9014
SLB
XC100B
XC101A
VCC
R103
4.7K
VCC
R107
4.7K
VSYNC#
V100
V101
C9014
CVBS
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
R104
4.7K
R108
4.7K
A+12V
X103
DASW-02
FR
FL
B/U
G/Y
R/V
AUIN SL0
AUIN SL1
XS101
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
CON10
VCC
R189
75R
V110
8050
C188
104
F
E
D
C
B
A
1 2 3 4 5 6
Page 37

2)POWER BOARD
654321
C100
4700U/25V
C101
4700U/25V
C117
6800U/16V
PVCC+VD102
C102
473
C111
CAP
R100
0
R101
68/1W
C112
330U/25V
C113
330U/25V
N101 1085
2
OUT
FL103 T4AL 250V
R105
560K
C107
473
3
IN
GND
1
XS103
2
1
CON2
~14V/2A
F
FL100
T1AL 250V
~0
VD100
1N5404
1N5404
VD103
1N5404
XS105
~14V/2A
1
~0
2
~14V/2A
3
~8.4V/2A
4
E
~01
5
~14V/2A
~8.4V/2A
FL101
T1AL 250V
FL102
T2AL 250V
CON5
C116
224
VD101
1N5404
VD104 RL254
RL254
VD105
VD114 RL254
RL254
VD115
VD116 RL254
VD106
RL254
VD117 RL254
D
~01
VD107 RL254
-27V
XS103
4
3
2
1
DGND
F1
F2
~VS
CON4
C
VD110
5.1V
R103
1/0.25W
R102
4.7K/0.25W
VD111
1N4004
150/0.5W
R104
C120
100U/35V
C121
47U/35V
473
-27V
R110
100/0.5W
VD112
24V/1WC110
C136 47p
R108
20K
C126
C129
C130
16V/4.7u
16V/4.7u
10U/16V
R112
820
R113
820
10U/16V
C127
R
R106
XS104
B
GND
MUTE
L103 100u
4
R
3
L102 100u
2
L
1
CON3
1K
L
R107
1K
R119
68K
R120
68K
C138
221
C139
221
N103
7
IN+(2)
8
IN-(2)
9
GND
10
IN-(1)
11
IN+(1)
TDA7265
R109 20K
-Vs
MUTE
OUT(2)
+Vs
OUT(1)
-Vs
6
5
4
100U/25V
3
C131
C132
100U/25V
C133
103
C134
103
2
1
C137 47p
A
DVcc
XS105
CON2
R-OUT
PVCC+
PVCC-
L-OUT
C103
473
C104
473
2
N100 7812
1
Vin
2
Vin
N1027912
L100
L
C108
473
C122
472
1
F1
F2
-27V
DGND
DVCC
GND
2
1
GND
1
C118
220U/16V
XS101
CON5
C128
1U/50V
L101
L
1
2
3
4
5
PVCC+
R114
200K
Vout
Vout
Vin
AVCC
BA033
R111
47K
R115
20K
3
3
2
C123
104
V100
9014
N104
GND
Vout
220U/16V
VD113
3.3V
R116
27K
C114
100U/16V
C115
100U/16V
3
C119
+12V
C105
473
C106
473
-12VPVCC-
DV33
C109
473
XS104
1
2
CON2
C135
10U/16V
R-OUT
L-OUT
AVCC
DVcc
DGND
-12V
AGND
+12V
DV33
VD118
IN6263
R117
4.7/05W
C124
104
R118
4.7/05W
C125
104
XS101
8
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
CON7
BT1
BATTERY
XL100A
1
2
WP4
XL100B
3
4
WP4
F
E
D
C
B
A
1 2 3 4 5 6
Page 38

3)FRONT PANEL BOARD
F
E
D
C
B
A
1 2 3 4 5 6
39
F+
FIL+
38
F+
1G
2G
3G
4G
5G
6G
7G
8G
9G
10G
NC
NC
NC
NC
NC
P16
P15
P14
P13
P12
P11
P10
P9
P8
P7
P6
P5
P4
P3
P2
P1
FF-
VFD1
HNVC10SM25
JK1
PHONE
K1
K2
K3
K4
KEY1
KEY2
KEY3
KEY4
GRID1
35
GRID2
34
GRID3
33
GRID4
32
GRID5
31
GRID6
30
GRID7
29
GRID8
28
GRID9
27
26
GRID10
25
24
23
22
21
SEG1
20
SEG2
19
SEG3
18
SEG4
17
SEG5
16
SEG6
15
SEG7
14
SEG8
13
SEG9
12
SEG10
11
SEG11
10
SEG12
9
SEG13
8
SEG14
7
SEG15
6
SEG16
5
2
FIL-
1
C15
104
SEG1
D2
1N4148D31N4148
K5
K6
1
2
3
4
5
AGND
C14
104
47uF/50V
SEG2
PHONE_SW
27
SEG13
SEG14
SEG15
AGND
SEG3
AGND
C17
104
D4
1N4148
SEG16
GRID10
GRID9
C2
GRID8
GRID7
104
GRID6
K11
K12
K13
XS3
1
2
3
4
4P2.0
CPU+5V
C1
104
C16
K7
K8
K9
K10
PHONE_L
PHONE_R
R35
10K
CPU+5V
SEG4
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
D5
1N4148
CPU+5V
LED3
SEG13
SEG14
SEG15
SEG16
SEG17
SEG18
VDD
VEE
SEG19
SEG20
G8
G7
G6
1 2
SEG6
SEG7
SEG8
SEG9
SEG10
SEG11
SEG12
23
26
SEG1024SEG1125SEG12
40
GRID5
GRID4
GRID3
GRID2
GRID1
R36
R37
330
330
LED10
LED9
LED
LED
red red blue blue
1 2
R24
3.3K
R10
SEG5
LED4
330R
SEG4
LED3
DVCC
SEG3
LED2
1 2
CPU+5V
SEG2
LED1
LED11
LED
12
SEG1
R9
330R
V1
8550
R16
330 7.5MM
LED1
LED
VDD14SEG115SEG216SEG317SEG418SEG519SEG620SEG721SEG822SEG9
OSV52VSS51LED150LED249LED348LED447LED546VDD45G144G243G342G441G5
CPU+5V
16311
KEY4
KEY3
KEY2
KEY1
STB
CLK
DO
SW4
SW3
SW2
SW1
R11
51K
XS2
U1
VOL1-
VOL1+
FB1
FIL-
FB2
FIL+-27V
100
R26
220
R32
220
R33
220
R34
CPU+5V
V2
8550
R29
330 7.5MM
12
LED5
LED
R1
R2 33K
R3 33K
R4
CPU+5V
C4
100uF/16V
VR1
RVP
R25
330 7.5MM
12
LED3
LED
33K
33K
R5
33KR633KR733KR833K
R13
10K
R14 10K
R15 10K
1
A
2
B
3
C
R27
330 7.5MM
LED4
LED
13
12
11
10
9
8
7
IC
6
DI
5
4
3
2
1
C3
104
LED12
LED
1 2
R19
330 7.5MM
12
12
LED2
LED
KEY4
KEY3
KEY2
KEY1
C6
C7
openC5 open
open
CPU+5V
R18
R17
10K
10K
C8
C9
104
104
R23
LED4
3.3K
CPU+5V
5P2.0
1
C10
104
12
R20
10K
R31
330 7.5MM
LED7
LED
10P2.0
2
3
4
5
XS1
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
CPU+5V
12
CPU+5V
R28
330 7.5MM
LED8
LED
R21
10K
VR2
RVP
1
A
2
B
3
C
C11
104
U2
IR
IR
R22
10R
+
C12
47u
3
IR
2
VDD
1
GND
C13
104
-27V
FB
FB
IR
VSTB
VSCK
VSDA
J11
J12
J21
J22
VOL2-
VOL2+
R30
330 7.5MM
12
LED6
LED
1 2 3 4 5 6
F
E
D
C
B
A
Page 39

Page 40

II PA RT DATASHEET
1) POWER AMPLIFIER IC TDA7265
Page 41

Page 42

2) DIGITAL VOLUME CONTROL
Page 43

3) HEADPHONE DRIVER
Page 44

4)DAC –CS4340
Page 45

5)RDS DECODER –SAA6588
Page 46

6) VFD DRIVER
Page 47

 Loading...
Loading...