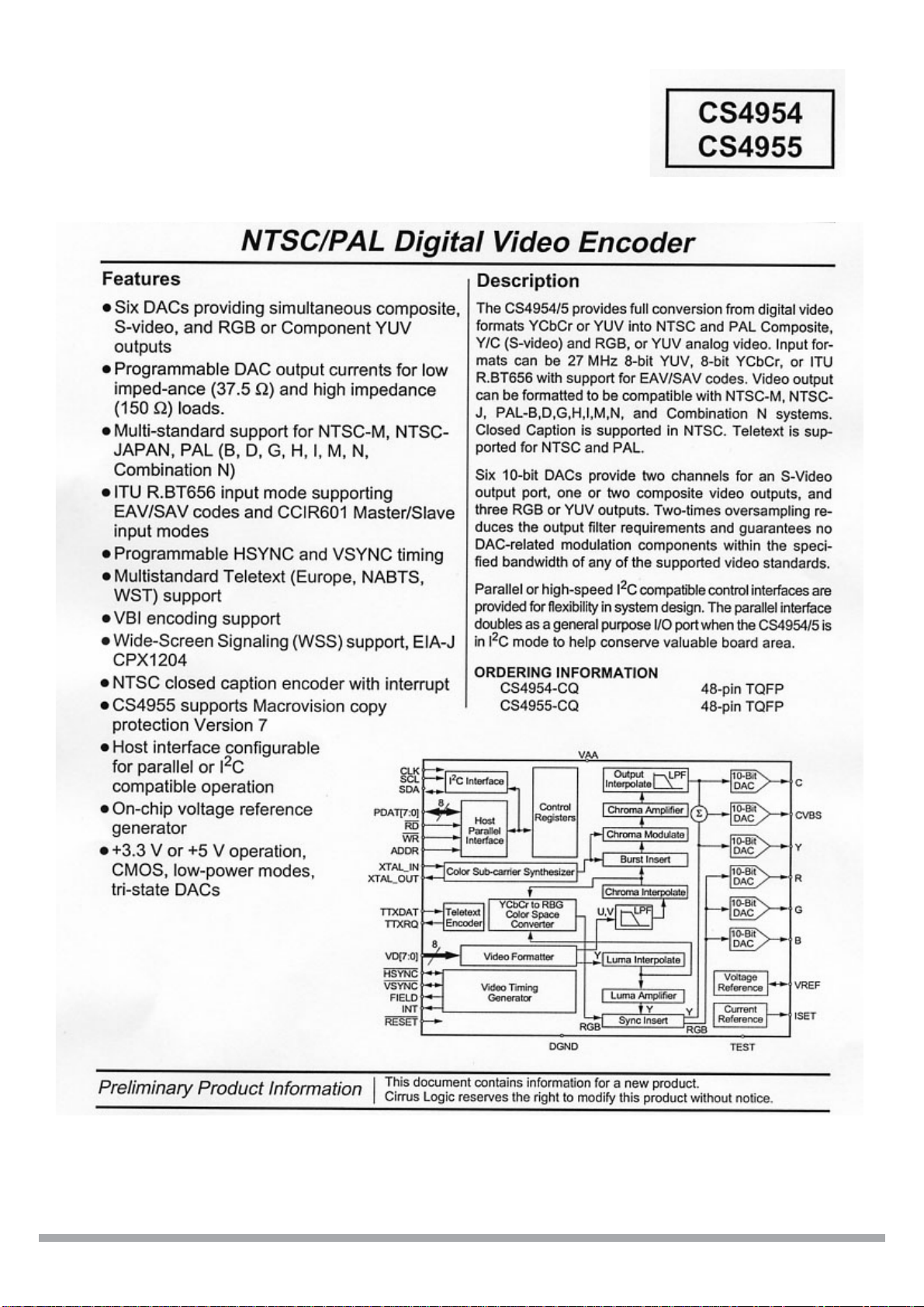
Page 1

Page 2

INDEX
INDEX
1. PRAFACE
1.1 PRAFACE.....................................................................................................................1
1.2 FRANT PENEL& REAR PENEL.....................................................................................2
1.3 REMOTE CONTROL............................................................................. .......................3
2. BLOCK DIAGRAM
2.1 BLOCK DIAGRAM........................................................................................................4.
2.2 SCHEMATIC DIAGRAM.................................................................................................5
3. EXPLODED VIEW......................................................................6
4. PARTS SPECIFICATIONS
4.1 2A265.....................................................................................................................7-10
4.2 CS9800.................................................................................................................11-18
4.3 DRAM 2M*32(EM638165).......................................................................................19-22
4.4 CS4955.................................................................................................................23-25
4.5 CS4360.................................................................................................................26-30
4.6 CS92288...............................................................................................................31-45
4.7 DRAM 1M*16(VT3617161)......................................................................................46-49
4.8 SAA7114H.............................................................................................................50-57
4.9 CS533...................................................................................................................58-59
4.10 PCF8563.............................................................................................................60-62
4.11 TUNER................................................................................................................... .63
4.12 VFD DRIVER PT6312.................................................................... ......................64-65
4.13 SERVO............................................................................................. .......................66
4.14 HDD INFORMATION.............................................................................................67-68
INDEX
5. SCHEMATIC DIAGRAM
5.1 POWER SCHEMATIC..................................................................... .......................69-70
5.2 MAIN SCHEMATIC......................................................................... .......................71-79
5.3 AV INPUT /OUTPUT SCHEMATIC.................................................... ...................... 80-87
5.4 VFD DRIVER........................................................................................................ 88-89
6. PARTS LIST
6.1 MAIN BOARD........................................................................................................90-92
6.2 VFD DRIVER BOARD.......................................................................... .......................93
6.3 POWER BOARD....................................................................................................94-95
6.4 AV BOARD.................................................................................................................96
Page 3

1
Page 4
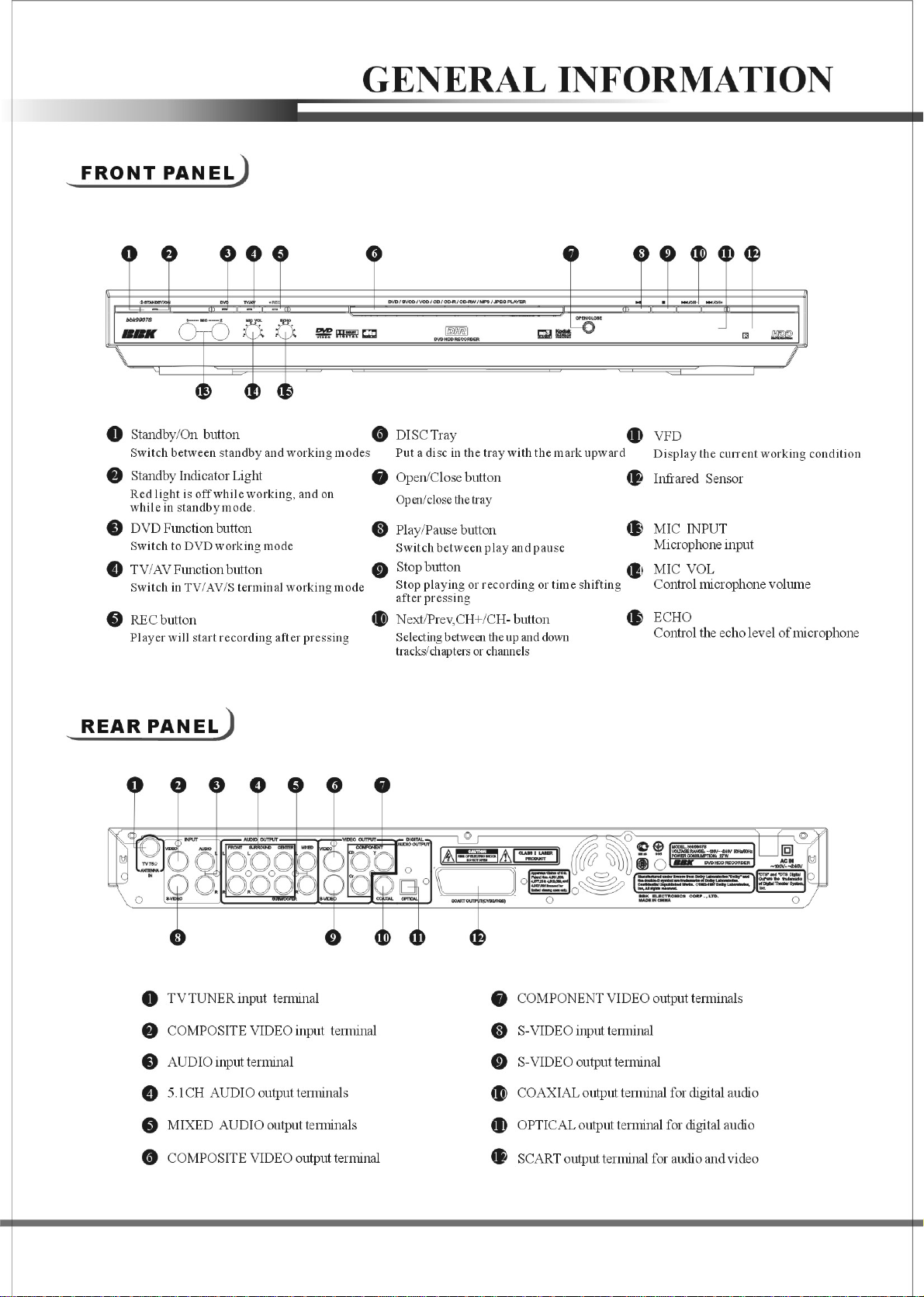
2
Page 5
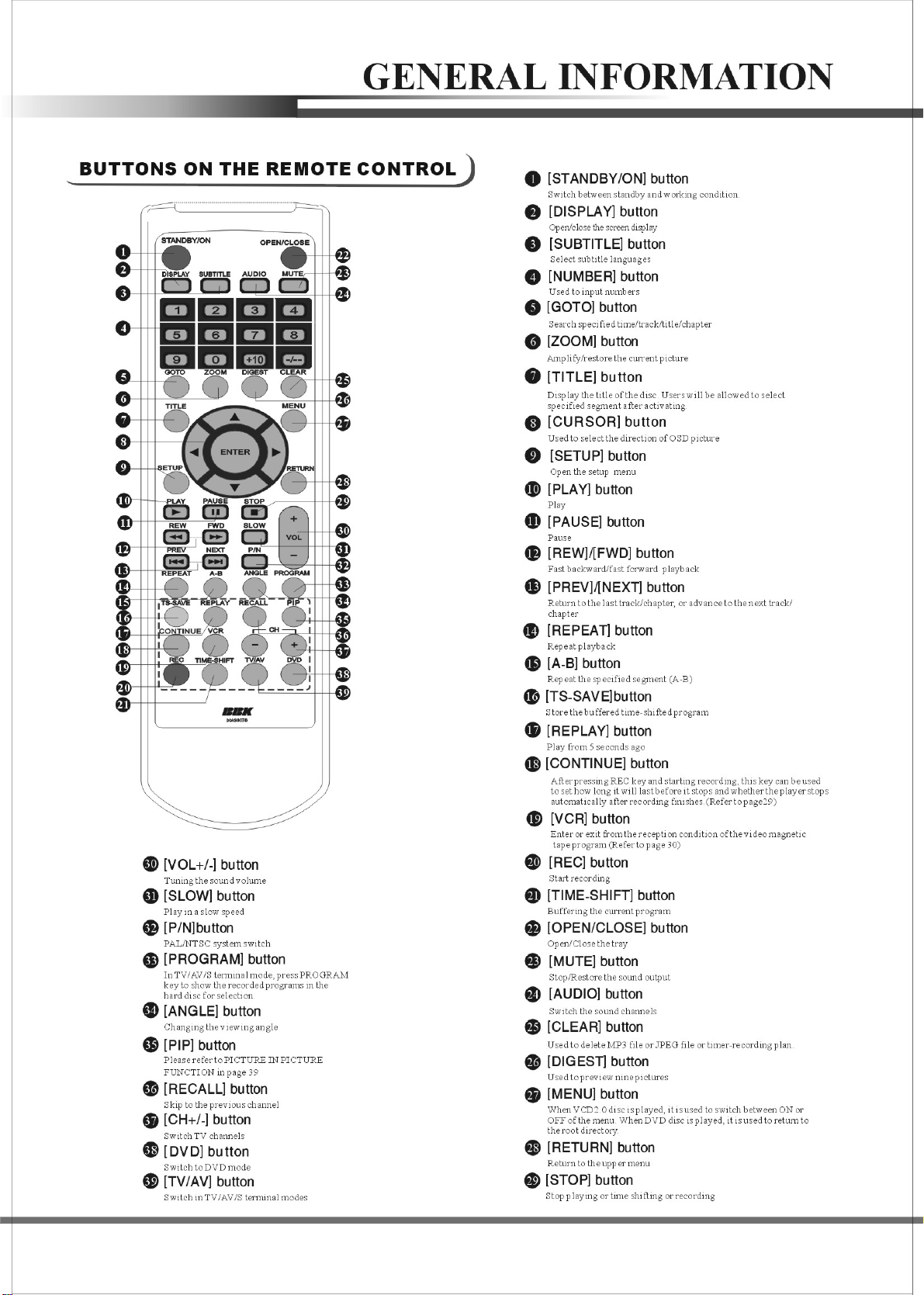
3
Page 6
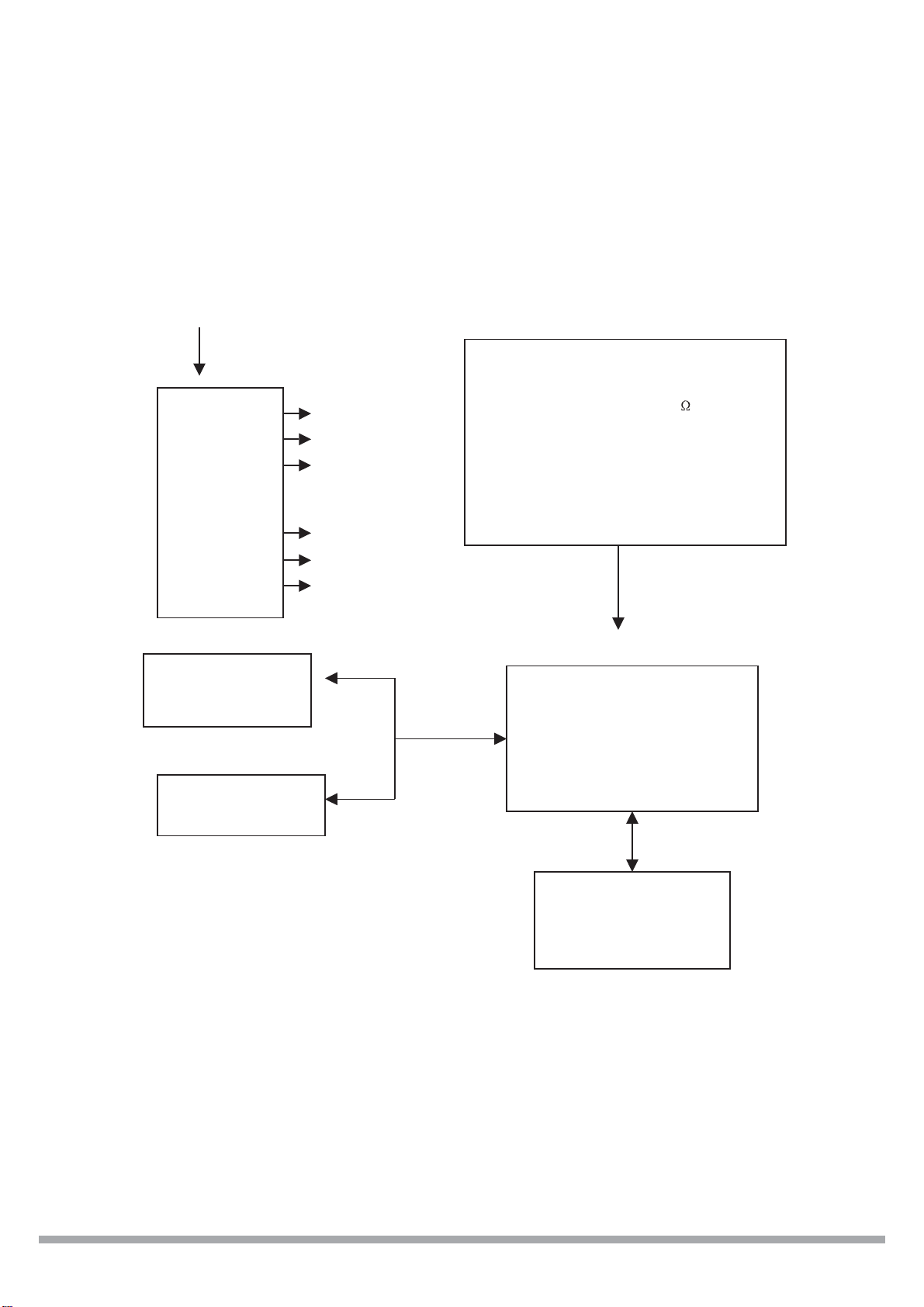
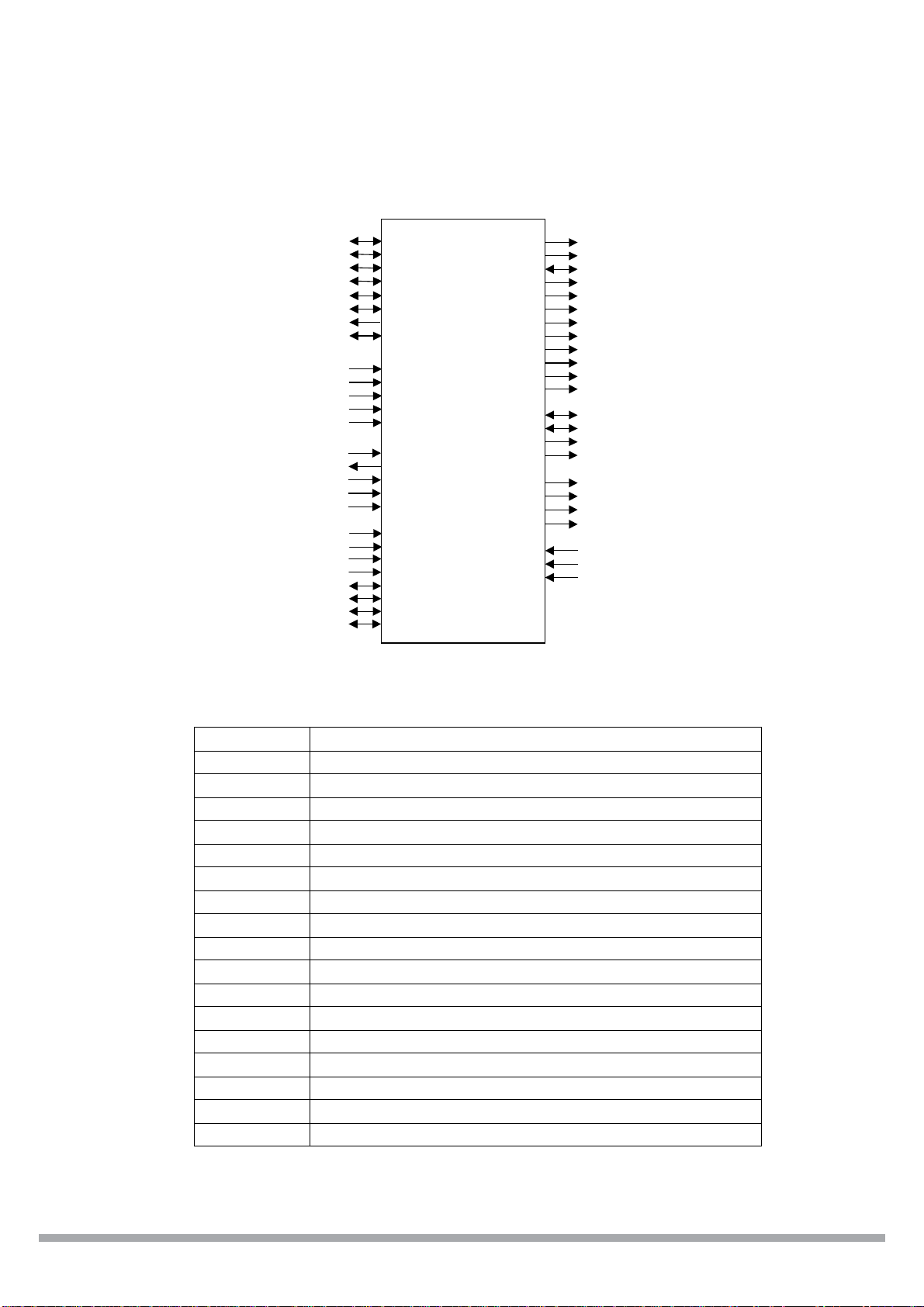
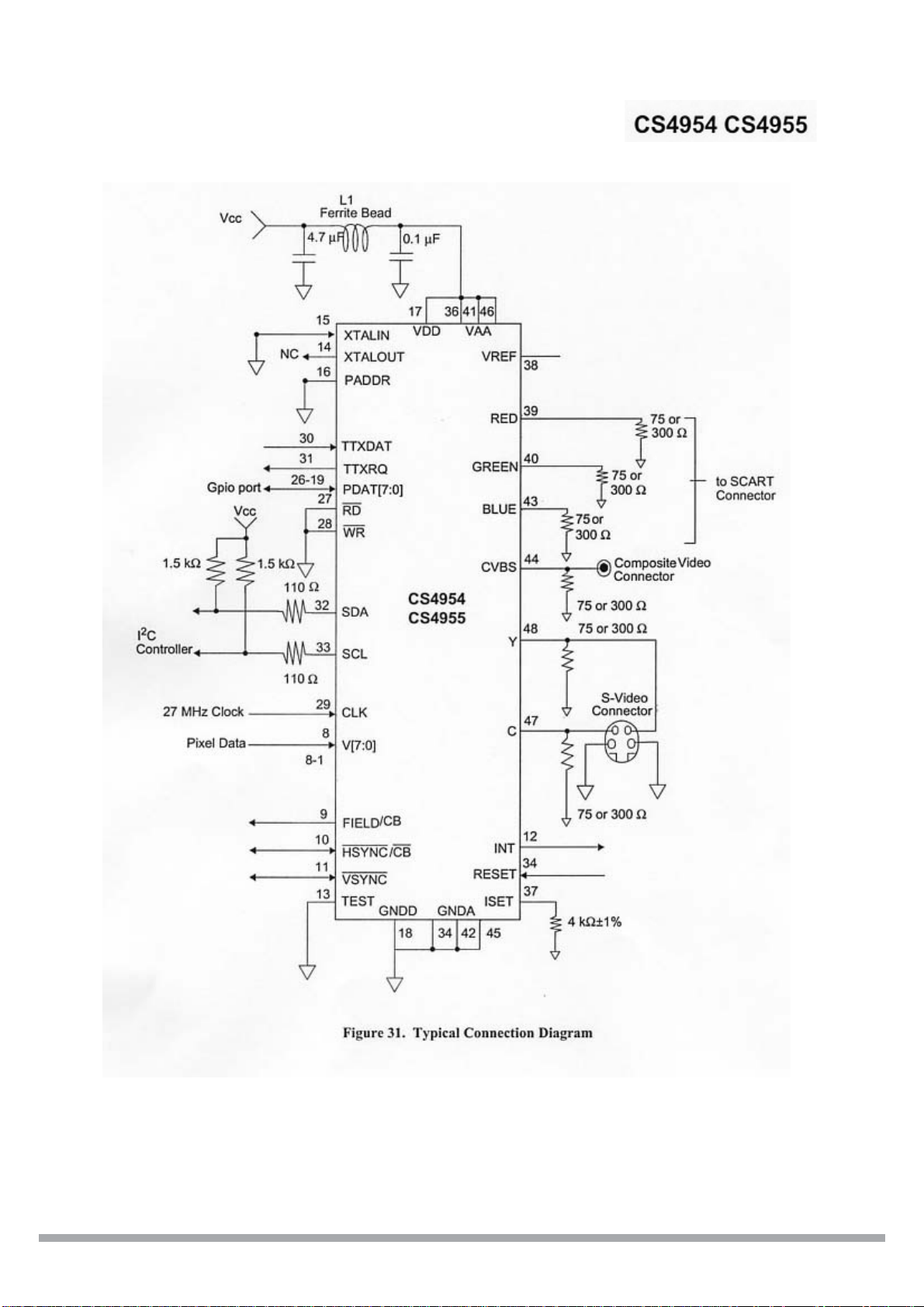
~110~240V
POWER
BOARD
BLOCK DIAGRAM
VIDEO OUT VIDIO IN PUT
AUDIO OUT AUDIO IN PUT
+12V
+5V
-12V
+3.3V
+2.5V
+1.8V
S-VIDEO OUT
CB.CR.YOUT
COAXIAL OUT
OPTICAL OUT
TUNER75
IN PUT
AV BOARD
DVD LOADER
DRIVE
40GB HDD
40GB HDD DRIVE
MAIN BOARD
MPEG VIDEO DECODER&
MPEG-2
AUDIO/ VIDEO CODER
PT16312
KEY SCANNING &
VFD DISPLAY
4
Page 7
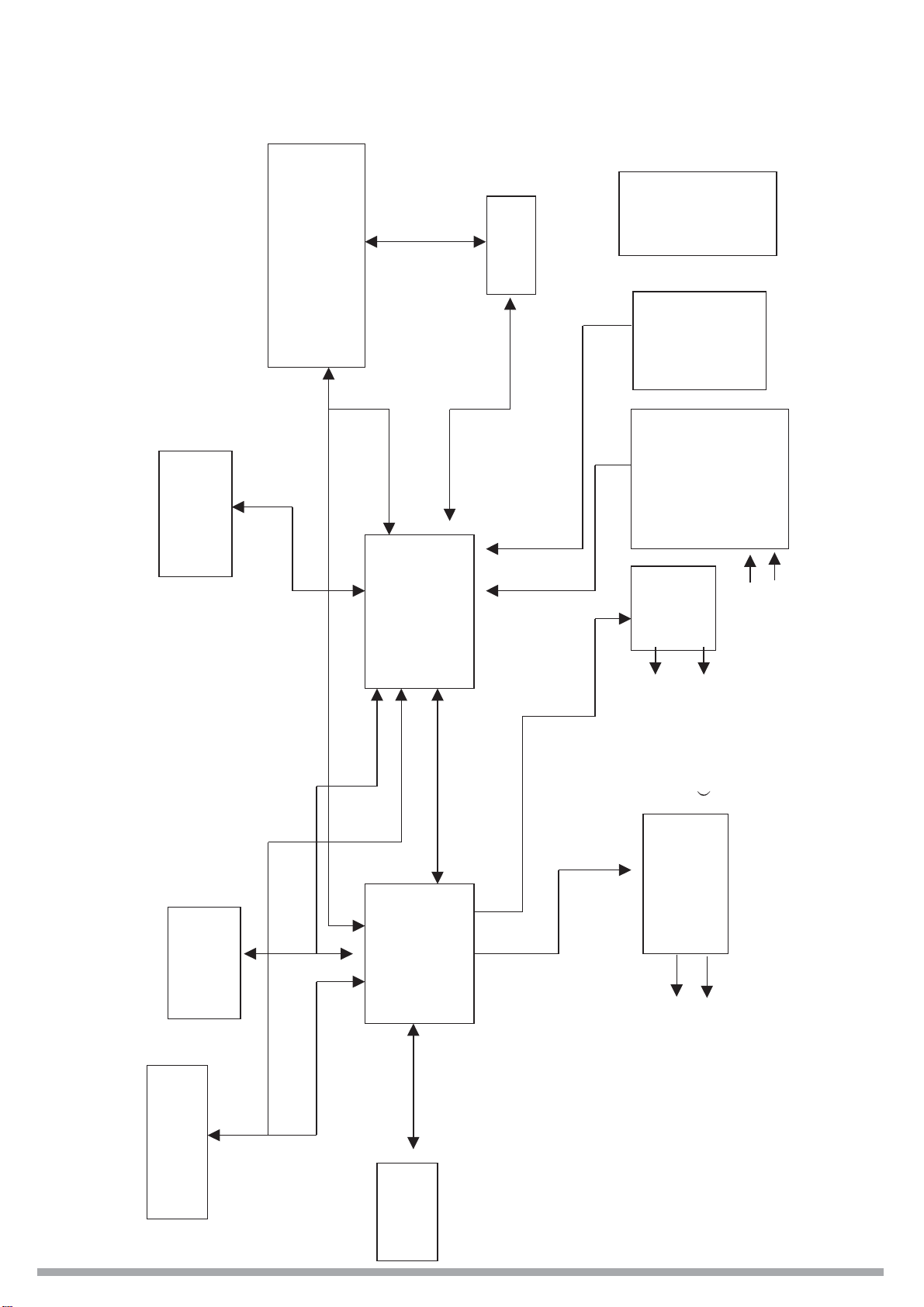
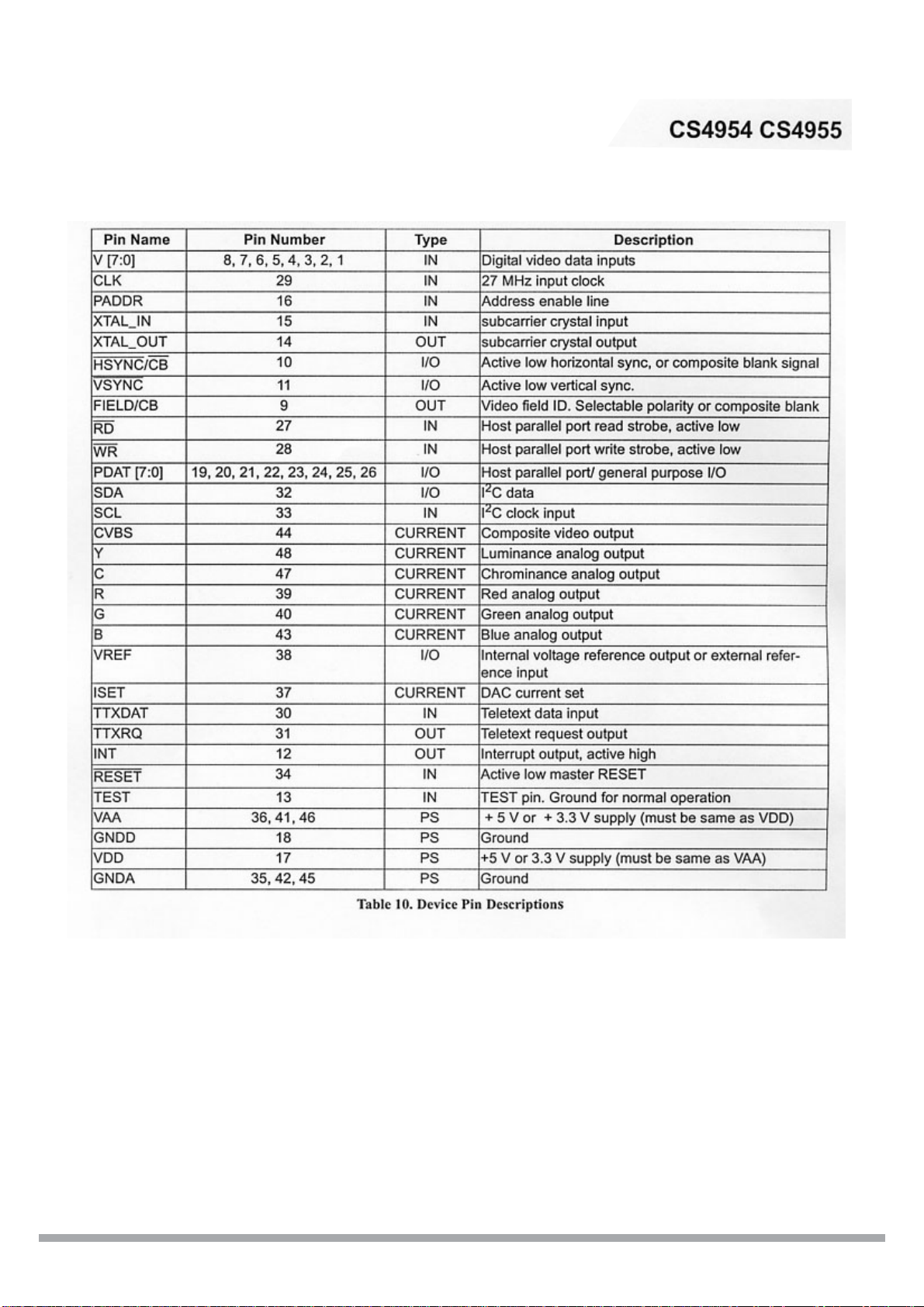
SCHEMATIC DIAGRAM
ATAPI
TO DVD LOADER DRIVE
HDD ATAPI I/O CHAN
CPLD
Host interface
3.3V
L.R CH
2.5V
VCC
AUDIO
TO-TUNER
5VSTB
1.8V
AUDIO
ADC
DECOD
S-VIDEO
P-CT L
CS5331
SAA7114
VIDEO
1M*16 4PCS
DRAM
16M
FLASH
CS92288
MPEG-2
A/V CODEC
To front panel
SS9800
MPEG
DECODER
CS4360
AUDIO
DACS
AUDIO R(3CH)
AUDIO L3CH
ENCODER
VIDEO
—— D/A
ER
TO TUNER
CS4955
TO S-VIDEO
TO VFD BOARD
CN104
To front panel
2M*32
DRAM
5
COMPOSITE VIDEO
S-VIDEO
Page 8
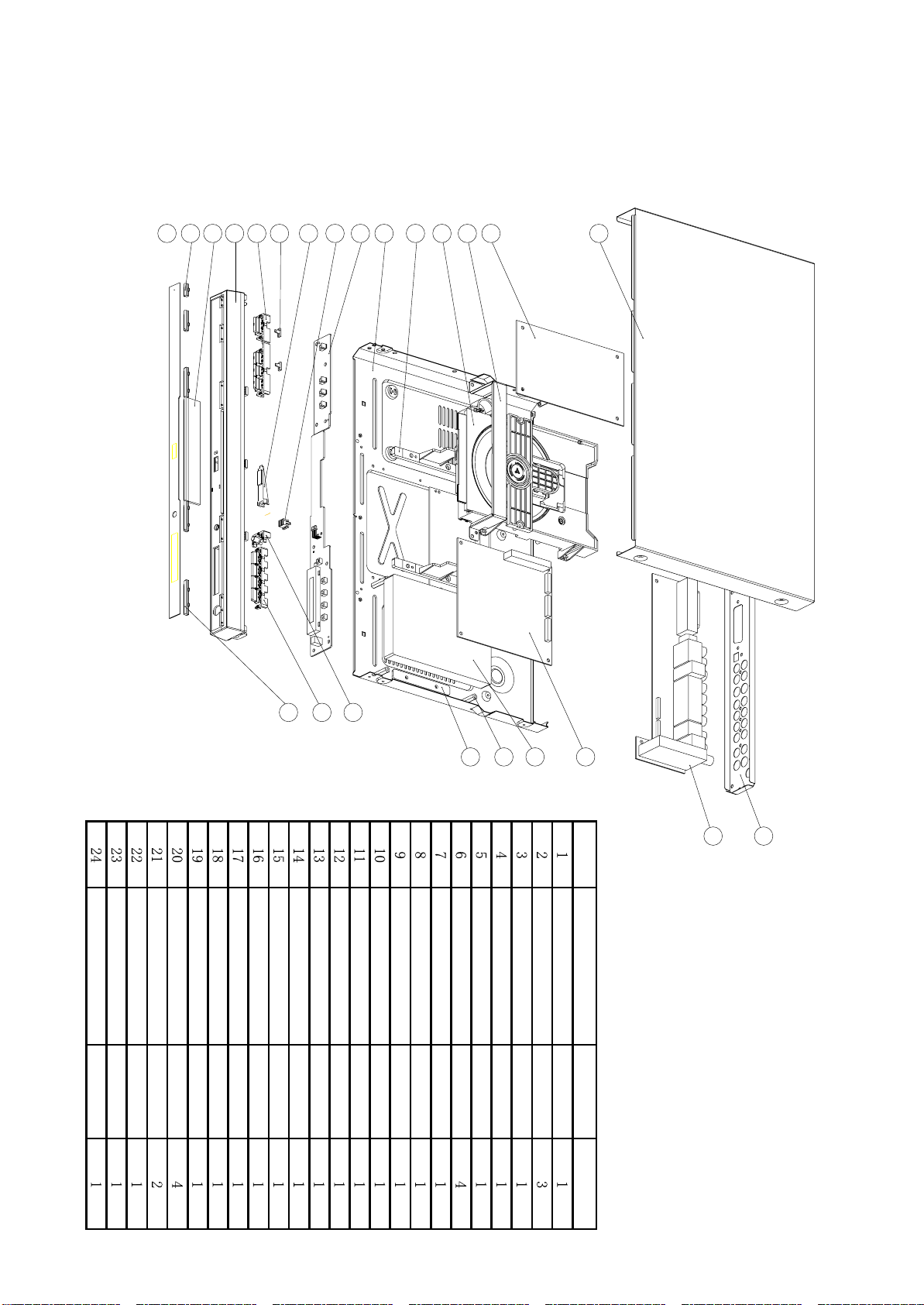
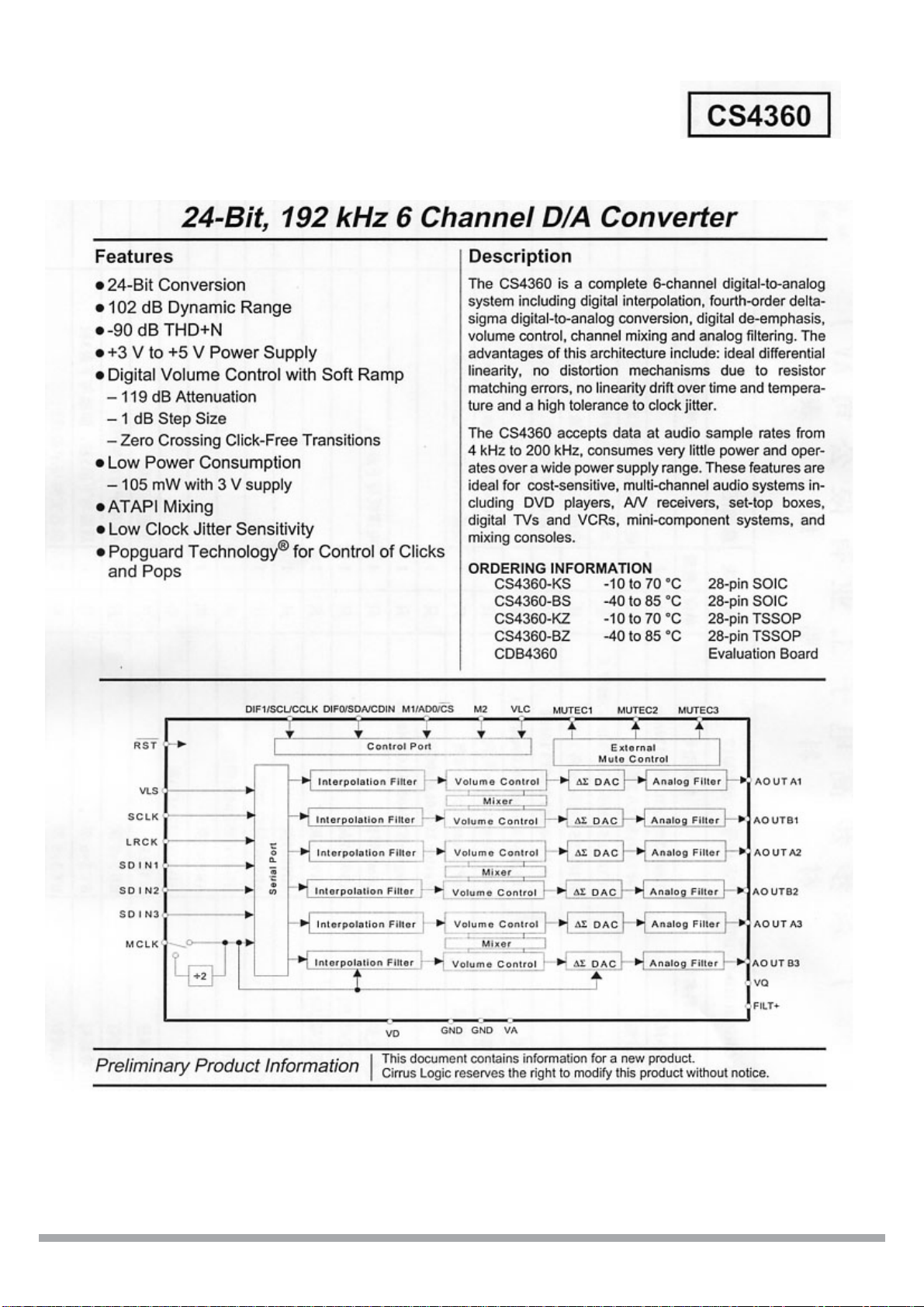
NO. ITEM NAME MATERIAL QUANTITY
Mirror bar pc
Left decorative bar ABS
Tray door ABS
Front panel ABS
Left four-key button ABS
Small light conductor PMMA
Big light conductor PMMA
LED stander PS
VFD driver board
Chasis SECC
Loader mechanism PS
DVD loader
Iron stand SECC
Power board
Top cover SECC
Rear panel SECC
AV board
Main board
Hard disc
Copper column
Rubber pad RUBBER
Open/close button ABS
Right four-key button ABS
Right decorative bar ABS
EXPLODED VIEW
14
10
4
5
3
2
1
6
7
8
9
11
13
12
15
24
23
22
21
19
20
18
17
16
6
Page 9
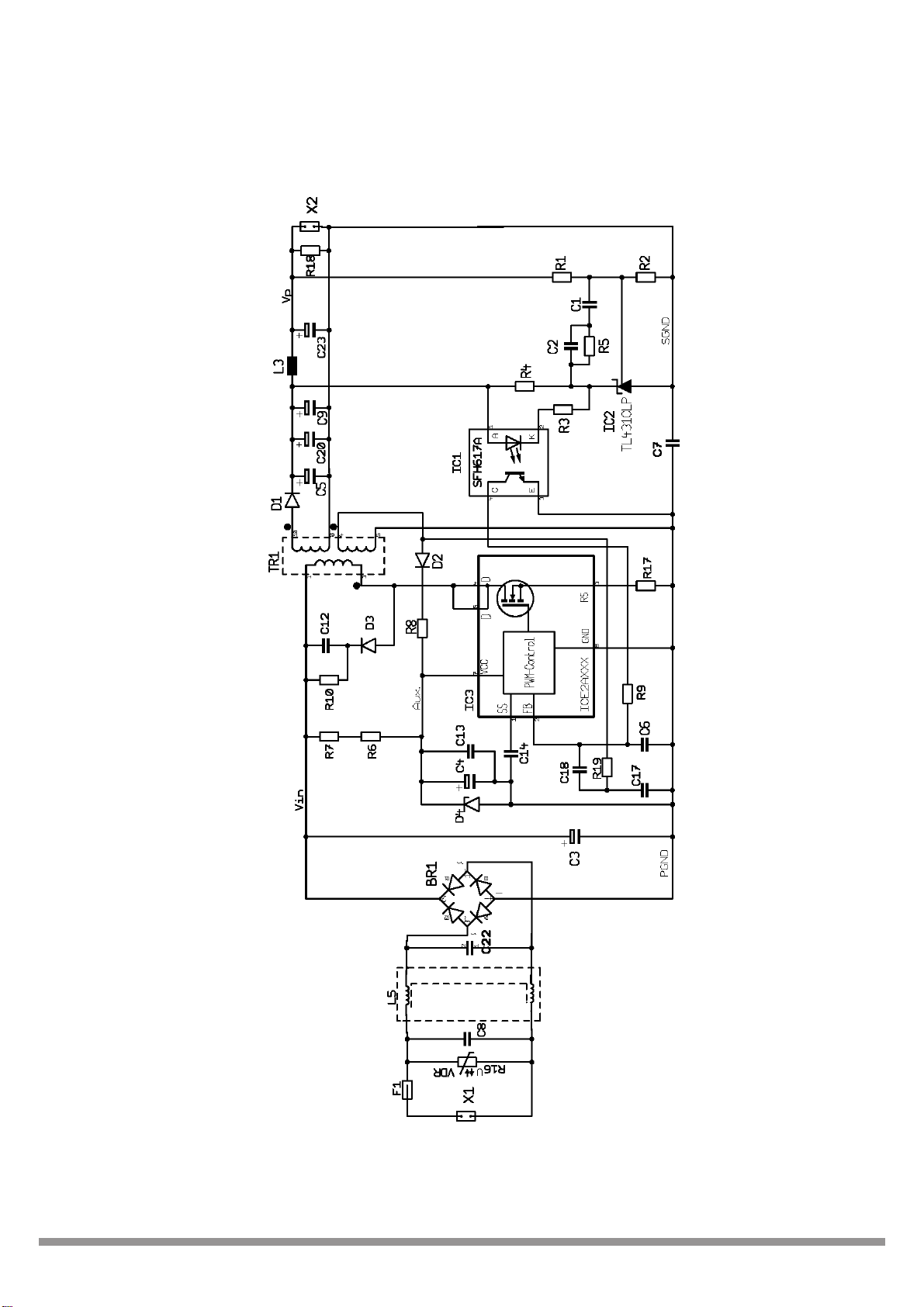
Circuit Diagram: ICE2AXXX for OFF ¨C Line Switch Mode Power Supplies
7
Page 10
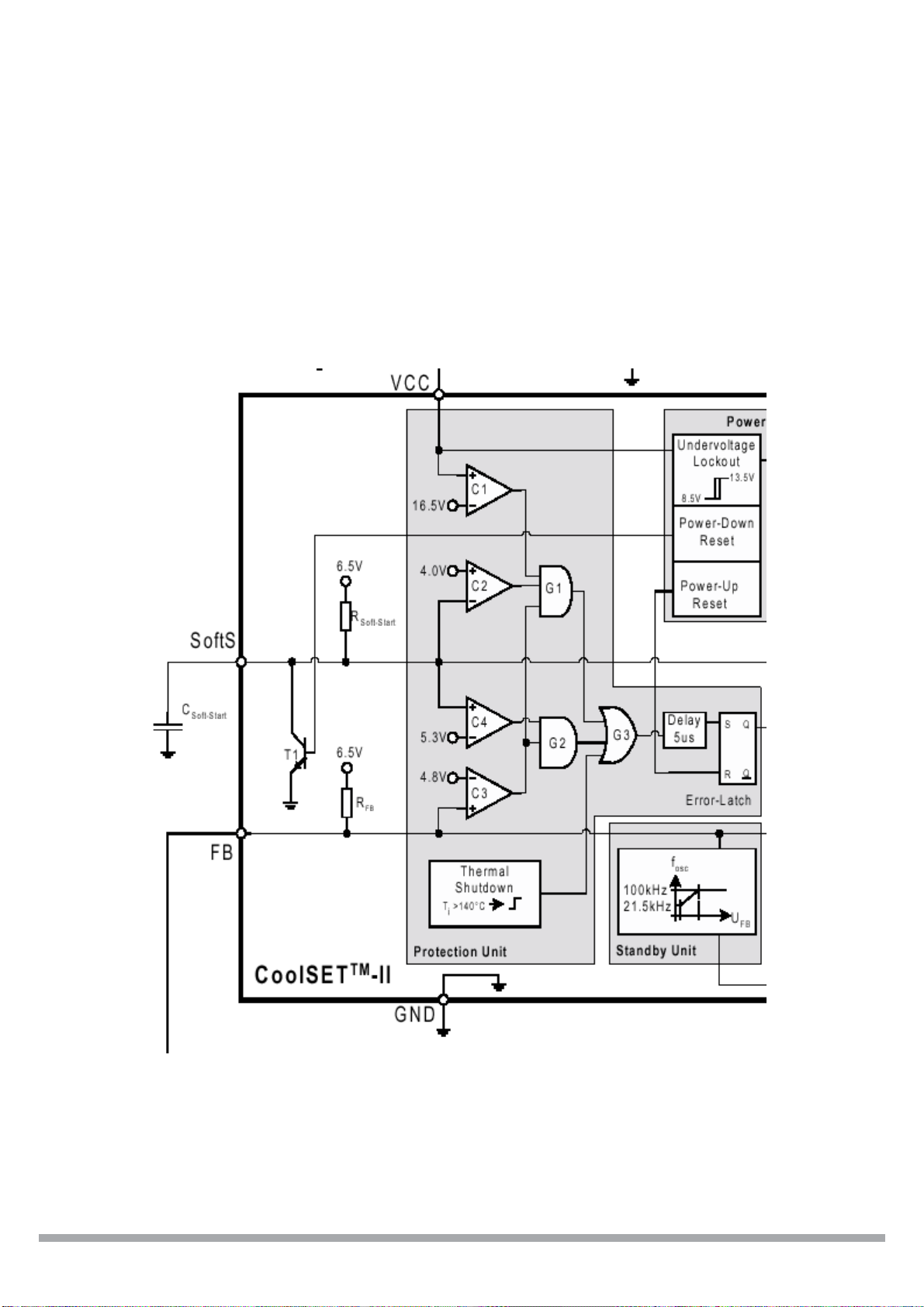
ICE2AXXX for OFF – Line Switch Mode Power Supplies
Protection Functions
The block diagram displayed in Fig. 4 shows the interal functions of the protection unit. The
comparators C1, C2, C3 and C4 compare the soft-start and feedback-pin voltages. Logic gates
connected to the comparator outputs ensure the combination of the signals and enables the setting of
the “Error-Latch”.
8
Page 11
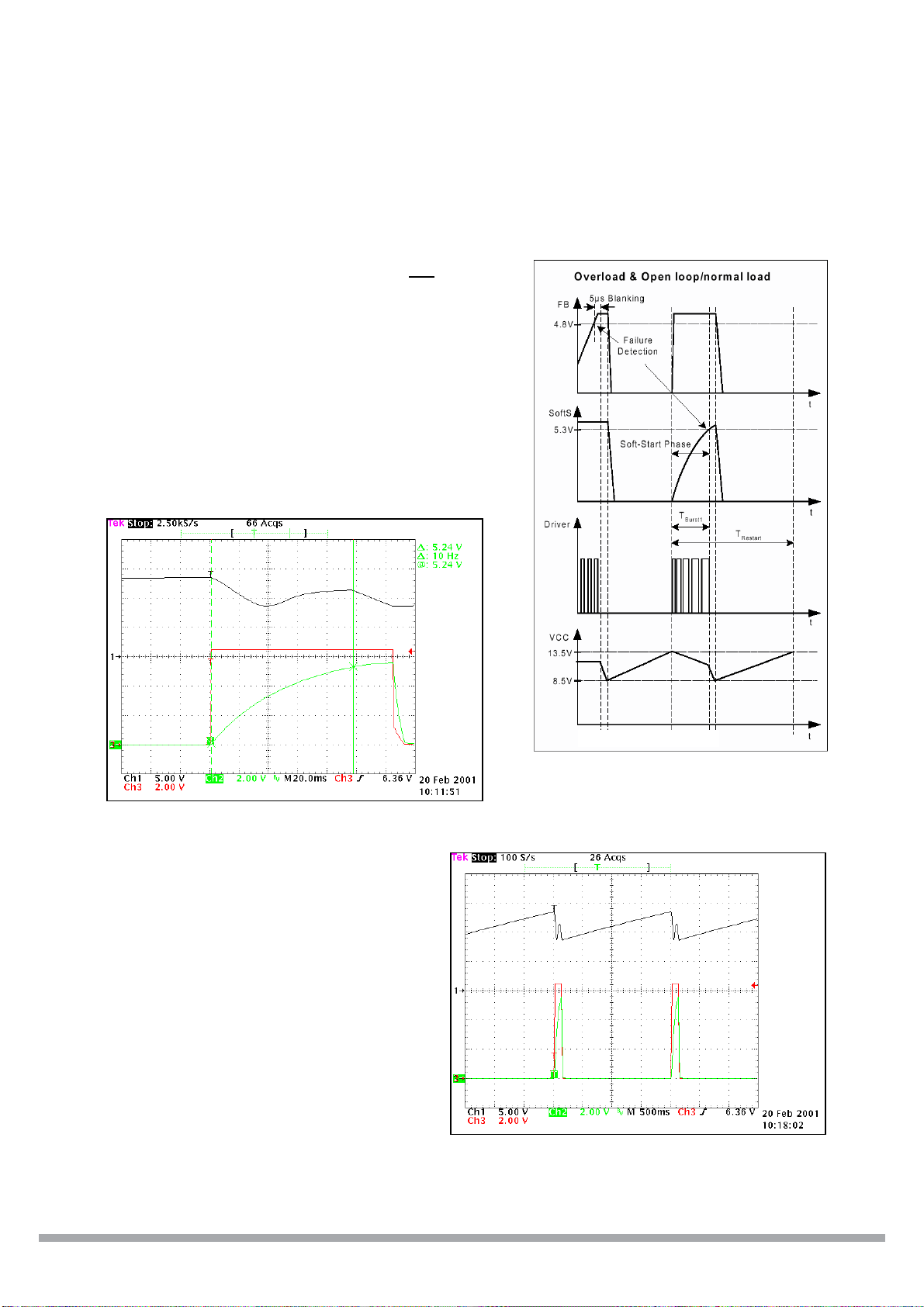
ICE2AXXX for OFF – Line Switch Mode Power Supplies
V
V
Overload and Open-Loop Protection
• Feedback voltage (VFB) exceeds 4.8V and soft start
voltage (VSS) is above 5.3V (soft start is completed) (t1)
• After a 5µs delay the CoolMOS is switched off (t2)
• Voltage at Vcc – Pin (VCC) decreases to 8.5V (t2)
• Control logic is switched off (t3)
• Start-up resistor charges Vcc capacitor (t3)
• Operation starts again with soft start after Vcc voltage
has exceeded 13.5V (t4)
t1, t2
CC
VFB
VSS
Fig. 6
Fig. 7
t1, t2
t3
t4
CC
VFB
VSS
9
Page 12

ICE2AXXX for OFF – Line Switch Mode Power Supplies
References
[1] Keith Billings,
Switch Mode Power Supply Handbook
[2] Ralph E. Tarter,
Solid-State Power Conversion Handbook
[3] R. D. Middlebrook and Slobodan Cuk,
Advances in Switched-Mode Power Conversion
[4] Herfurth Michael,
Ansteuerschaltungen für getaktete Stromversorgungen mit Erstellung eines linearisierten
Signalflußplans zur Dimensionierung der Regelung
[5] Herfurth Michael,
Topologie, Übertragungsverhalten und Dimensionierung häufig eingesetzter
Regelverstärker
[6] Infineon Technologies, Datasheet,
CoolSET-II
Off – Line SMPS Current Mode Controller with 650V/800V CoolMOSääää on Board,
[7] Robert W. Erickson,
Fundamentals of Power Electronics
10
Page 13
Internet DVD (iDVD) Chip Solution
CS98000
Features
l
Powerful Dual 32-bit RISCs >160MIPS
l
Software based on popular RTOS, C/C++
l
MPEG video decoder supports DVD, VCD,
VCD 3.0, SVCD standards
l
Video input with picture-in-picture & zoom
l
8-bit multi-region OSD w/vertical flicker filter
l
Universal subpictur e unit for DVD and SVCD
l
PAL<->NTSC Scaling ~ Transcoding
l
Supports SDRAM and FLASH memories
l
Powerful 32-bit Audio DSP >80 MIPS
l
Decodes: 5.1 channel AC-3, MPEG Stereo
l
Plays MP-3 CDs (a MP-3 CD =12 albums)
l
Karaoke echo mix and pitch shift
l
Optional 3-D Virtual, bass & treble control
l
8-channel dual-zone PCM output
l
IEC-60958/61937 Out: AC-3, DTS, MPEG
l
Multi-Mode Serial Audio I/O: I2S & AC-Link
l
AV Bus or ATAPI interface or DVD/CD/HD
l
GPIO support for all common sub-circuits
Description
Overall the CS98000 Crystal DVD Processor is targeted
as a market s pecific c onsum er ent ert ainment proces sor
empowering new product classes with the inclusion of a
DVD player as a fundamental feature. This integrated
circuit when used with al l the other Crystal mixed signal
data converters, DSPs and high quality factory firmware
enables the conception and rapid design of market leading internet age products like:
• DVD A/V Mini-System
• Home Media Controller
• Combination DVD Player
• Car/SUV Entertainment Unit
Future Fir m w are Enhancem ent s :
• Web I/O vi a AC-Li n k In put & Built-in Soft Modem
• DVD Audio Navigation
• MLP Decoder, DTS Dec oder, AAC Decoder
• MP-3 Encoder, Ripping Controller
ORDERING INFORMATION
CS98000-CQ 0° to 70° C 208-pin
CS98010-CQ 0° to 70° C 128-pin
RISC-1
I-Cache D-Cache
MMU
Video Input
Filter
MPEG Decoder
VLC Parser
RAM MoCo
Video Processor
On-Screen Display
Picture-in-Picture
Video/Graphics Display
MAC
Scaler
IDCT
Preliminary Product Information
RISC-2
I-Cache D-Cache
MMU
Clock Manager
Dataflow Engine
External I/Os
This document contains information for a new product.
Cirrus Logic reserves the right to modify this product without notice.
MAC
DMA / BitBlit
SRAM Buffer
Remote Input
GPIOs
Memory Controller
SDRAM Control
FLASH Control
Subpicture Decode
Scaler
System Controls
STC
Interrupts
Registers
SDRAM
32- Bit DSP
I-Cache
X,Y Data
Memory
CPU / MAC
Audio I/O
PCM Out
PCM In
XMT958
A/V Bus
ATAPI-IDE
Local Bus
11
Page 14
6. PIN DESCRIPTION
CS98000
Host/Loader
(30)
Video In
(12)
CODEC IF
(5)
MISC.
(41)
GPIO_[15-10, 8-7, 4-2, 0]
H_D_[15:0]
H_CS_[3:0]
H_A_[4:0]
H_ALE
H_RD
H_WR
H_CKO
H_RDY
VIN_D[7:0]
VIN_HSNC
VIN_VSNC
VIN_CLK
VIN_FLD
CDC_DI
CDC_DO
CDC_RST
CDC_CK
CDC_SY
XTLCLOCK
RST_N
IR_IN
MFG_TST
GPIO_D[20-0]
GPIO_H[16-14]
GPIO_V10
CS98000
M_A_[11:0]
M_BS_L
M_D_[31:0]
M_DQM_[3:0 ]
M_RAS_L
M_CAS_L
M_WE_L
M_AP
M_CKE
M_CKO
NVR_OE_L
NVR_WR_L
HSYNC
VSYNC
CLK27_O
VDAT_[7:0]
AUD_BCK
AUD_LRCK
AUD_DO_[3:0]
SPDIF_O
AIN_BCK
AIN_LRCK
AIN_DATA
Memory IF
(57)
Video out
(11)
DAC Out
(7)
ADC In
(3)
Table 5 lists the conventions used to identify the pin type and direction in the table that follows.
I Input
IS Input, with schmitt trigger
ID Input, with pull down resistor
IU Input, with pull up resistor
O Output
O4 Output – 4mA drive
O8 Output – 8mA drive
T4 Tri-State-able Output – 4mA drive
B Bi-direction
B4 Bi-direction – 4mA drive
B4U Bi-direction – 4mA drive, with pull-up
B8U Bi-direction – 8mA drive, with pull-up
B4S Bi-direction – 4mA drive, with schmitt trigger
B4SU Bi-direction – 4mA drive, with pull-up and schmitt trigger
Pwr +2.5V or +3.3V power supply voltage
Gnd Power supply ground
Name_N Low active
Name_L Low active
Table 5. Pin Type legend
12
Page 15
CS98000
6.1 Pin Assignments
Table 6 lists the pin number, pin name and pin type
for the 208 pin CS98000 package. The primary
function and pin direction is shown for all signal
Pin Name Type Primary Function Dir Seco ndary Function Dir Note
1 V DD_P LL Pwr PLL Power 2.5V
2 M_A_11 O8 SDRAM Address[11] O ROM/NVRAM Address[11] O
3 M_A_10 O8 SDRAM Address[10] O ROM/NVR AM Ad dress[10] O
4 GPIO_D18 B4U GenioDVD[18] B System Clock PLL Bypass I
5 M_A_9 O8 SDRAM Address[9] O ROM/NVRAM Address[9] O
6 M_A _8 O8 SDRAM Address[8] O ROM/NVRAM Address8] O
7 M_A_7 O8 SDRAM Address[7] O ROM/NVRAM Address[7] O
8 GPIO_D16 B4SU GenioDVD[16] B
9 M_A_6 O8 SDRAM Address[6] O ROM/NVRAM Address[6] O
10 M_A_5 O8 SDRAM Address[5] O ROM/NVRAM Address[5] O
11 M_A_4 O8 SDRAM Addre ss[4] O ROM/NVRAM Address[4] O
12 GPIO_D17 B4U GenioDVD[17] B
13 M_A_3 O8 SDRAM Address[3] O ROM/NVRAM Address[3] O
14 M_A_2 O8 SDRAM Address[2] O ROM/NVRAM Address[2] O
15 M_A_1 O8 SDRAM Address[1] O ROM/NVRAM Address[1] O
16 M_A_0 O8 SDRAM Address[0] O ROM/NVRAM Address[0] O
17 GPIO_D19 B4U GenioDVD[19] B Memory Clock PLL Bypass I
18 VSS_IO G nd I/O Ground
19 M_CKO O8 SDRAM Clock O
20 VDD_IO Pwr I/O Power 3.3V
21 M_BS_L O8 SDRAM Bank Select O
22 M_CKE B8 SDRAM Clock Enable O GenioMis(7) B
23 M_ AP O8 SDRAM Auto Pre-charge O
24 M_RAS _L O8 SDRAM Row Strobe O
25 M_CAS _L O8 SDRAM Column Strobe O
26 GPIO_D20 B4U G enioDVD[20] B
27 M_WE_L O8 SDRA M Write Enable O
28 M_DQM_0 O8 SDRAM DQM[0] O
29 M_DQM_1 O8 SDRAM DQM[1] O
30 GPIO_D0 B4U GenioDVD[0] B
31 M_DQM_2 O8 SDRAM DQM[2] O
32 M_DQM_3 O8 SDRAM DQM[3] O
33 M_D_8 B8U SDRAM Data[8] B ROM/NVRAM Data[8] B
34 GPIO_D1 B4U GenioDVD[1] B
35 VSS_IO G nd I/O Ground
pins. For some signal pins, a secondary function
and direction are also shown. For pins having more
than one function, the primary function is chosen
when the chip is reset.
Table 6. Pin assignments
13
Page 16
CS98000
36 VSS_CORE Gnd Core Ground
37 M_D_7 B8U SDRAM Data[7] B ROM/NVRAM Data[7] B
38 VDD_IO Pwr I/O Power 3.3V
39 GPIO_D2 B4U GenioDVD[2] B
40 M_D_9 B8U SDRAM Data[9] B ROM/NVRAM Data[9] B
41 VDD_CORE Pwr Core Power 2.5V
42 M_D_6 B8U SDRAM Data[6] B ROM/NVRAM Data[6] B
43 GPIO_D3 B4U GenioDVD[3] B
44 M_D_10 B8U SDRAM Data[10] B ROM/NVRAM Data[10] B
45 M_D_5 B8U SDRAM Data[5] B ROM/NVRAM Data[5] B
46 M _D_11 B8U S DRAM Data[11] B ROM/NVRAM Data[11] B
47 GPIO_D4 B4U GenioDVD[4] B
48 M_D_4 B8U SDRAM Data[4] B ROM/NVRAM Data[4] B
49 M_D_12 B8U SDRAM Data[12] B ROM/NVRAM Data[12] B
50 GPIO_D5 B4U GenioDVD[5] B
51 M_D_3 B8U SDRAM Data[3] B ROM/NVRAM Data[3] B
52 UNUSED may leave unconnected
53 UNUSED may leave unconnected
54 M_D_13 B8U SDRAM Data[13] B ROM/NVRAM Data[13] B
55 M_D_2 B8U SDRAM Data[2] B ROM/NVRAM Data[2] B
56 M_D_14 B8U SDRAM Data[14] B ROM/NVRAM Data[14] B
57 GPIO_D6 B4U GenioDVD[6] B
58 VSS_IO G nd I/O Ground
59 M_D_1 B8U SDRAM Data[1] B ROM/NVRAM Data[1] B
60 M_D_15 B8U SDRAM Data[15] B ROM/NVRAM Data[15] B
61 GPIO_D7 B4U GenioDVD[7] I B
62 M_D_0 B8U SDRAM Data[0] B ROM/NVRAM Data[0] B
63 VSS_CORE Gnd Core Ground
64 M_D_24 B8U SDRAM Data[24] B ROM/NVRAM Address[20] O
65 GPIO_D11 B4U GenioDVD[11] B
66 VDD_CORE Pwr Core Power 2.5V
67 M_D_23 B8U SDRAM Data[23] B ROM/NVRAM Address[19] O
68 M_D_25 B8U SDRAM Data[23] B ROM/NVRAM Address[21] O
69 GPIO_D10 B4U GenioDVD[10] B
70 M_D_22 B8U SDRAM Data[22] B ROM/NVRAM Address[18] O
71 M_D_26 B8U SDRAM Data[26] B ROM/NVRAM Address[22] O
72 M_D_21 B8U SDRAM Data[21] B ROM/NVRAM Address[17] O
73 GPIO_D9 B4U GenioDVD[9] B
74 M_D_27 B8U SDRAM Data[27] B ROM/NVRAM Address[23] O
75 M_D_20 B8U SDRAM Data[20] B ROM/NVRAM Address[16] O
76 M_D_28 B8U SDRAM Data[28] B
Table 6. Pin assignments (Continued)
14
Page 17
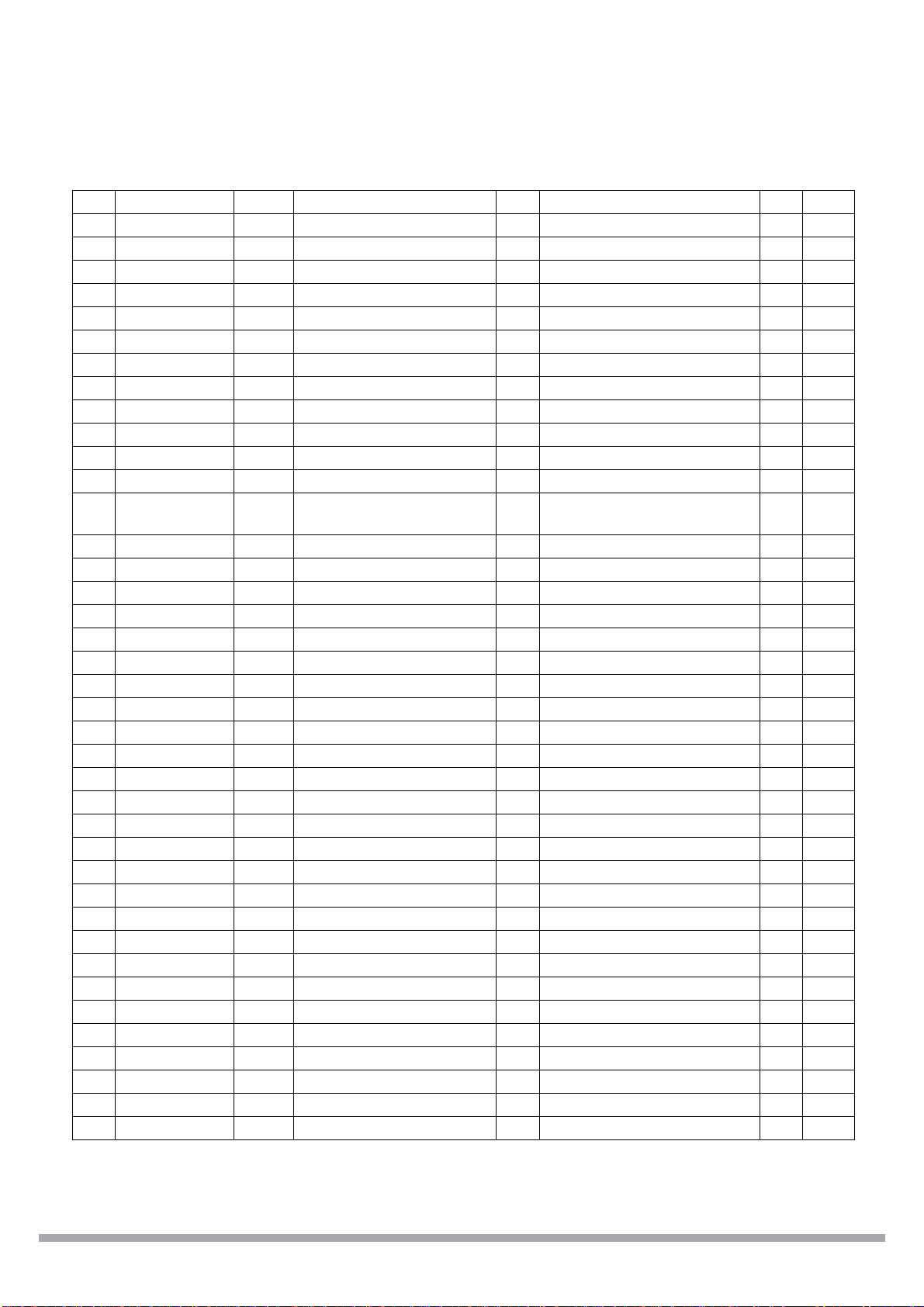
CS98000
77 GPIO_D8 B4U GenioDVD[8] B
78 M_D_19 B8U SDRAM Data[19] B ROM/NVRAM Address[15] O
79 M_D_29 B8U SDRAM Data[29] B
80 M_D_18 B8U SDRAM Data[18] B ROM/NVRAM Address[14] O
81 NV_WE_L B4U NV RA M Write Enable O GenioMis[8] B
82 VSS_CORE Gnd Core Ground
83 M_D_30 B8U SDRA M Data[30] B ROM/NVRAM Decode Low O
84 VDD_CORE Pwr Core Power 2.5V
85 H_ALE B4U Host Address Latch O GenioHst[13] B
86 M_D_17 B8U SDRAM Data[18] B ROM/NVRAM Address[13] O
87 M_D_31 B8U SDRAM Data[31] B ROM/NVRAM Decode High O
88 M_D_16 B8U SDRAM Data[16] B ROM/NVRAM Address[12] O
89 GPIO_H14 B4U GenioHst[14] B
90 NV_OE_L O4 ROM/NVRAM Output
Enable
91 VDD_IO Pwr I/O Power 3.3V
92 H_RD B4S Host Read Strobe O DVD Data Strobe I 1
93 H_WR B4 Host Write Strobe O DVD Data Enable I 1
94 GPIO_H15 B4U GenioHst[15] B
95 H_RDY B4 Host Ready I DVD Data Ready O 1
96 VSS_IO G nd I/O Ground
97 H_A_2 B4 Host Address[2] O GenioHst[10] B 1
98 GPIO_H16 B4U GenioHst[16] B
99 H_A_1 B4 Host Address[1] O GenioHst[9] B 1
100 H_A_0 B4 Host Address[0] O GenioHst[8] B 1
101 H_CS_1 B4 Host Chip Select [1] O DVD Error I 1
102 H_A_4 B4 Host Address[4] O GenioHst[12] B 1
103 VSS_CORE Gnd Core Ground
104 VSS_PLL Gnd PLL Ground
105 VDD_PLL Pwr PLL Power 2.5V
106 H_CS_0 B4 Ho st Chip Select[0] O DVD Start Sector I 1
107 H_A_3 B 4 Host Address[3] O G enioH st[11] B 1
108 VDD_CORE Pwr Core Power 2.5V
109 H_D_15 B4 Host Data[15] B CD Data I 1, 2
1 10 H_D_14 B4 Host Data[14] B CD Left Right Clock I 1, 2
111 H_CS_3 B4 Host Chip Select[3] O Gen ioHst[18] B 1
112 H_D_13 B4S Host Data[13] B CD Clock I 1, 2
113 H_D_12 B4 Host Data[12] B CD Error I 1, 2
1 14 H_D_11 B4 Host Data[11] B DVD Control Data In I 1, 2
115 H_CS_2 B4 Host Chip Select[2] O GenioHst[17] B 1
1 16 H_D_10 B4 Host Data[10] B DVD Control Data Out O 1, 2
O
Table 6. Pin assignments (Continued)
15
Page 18
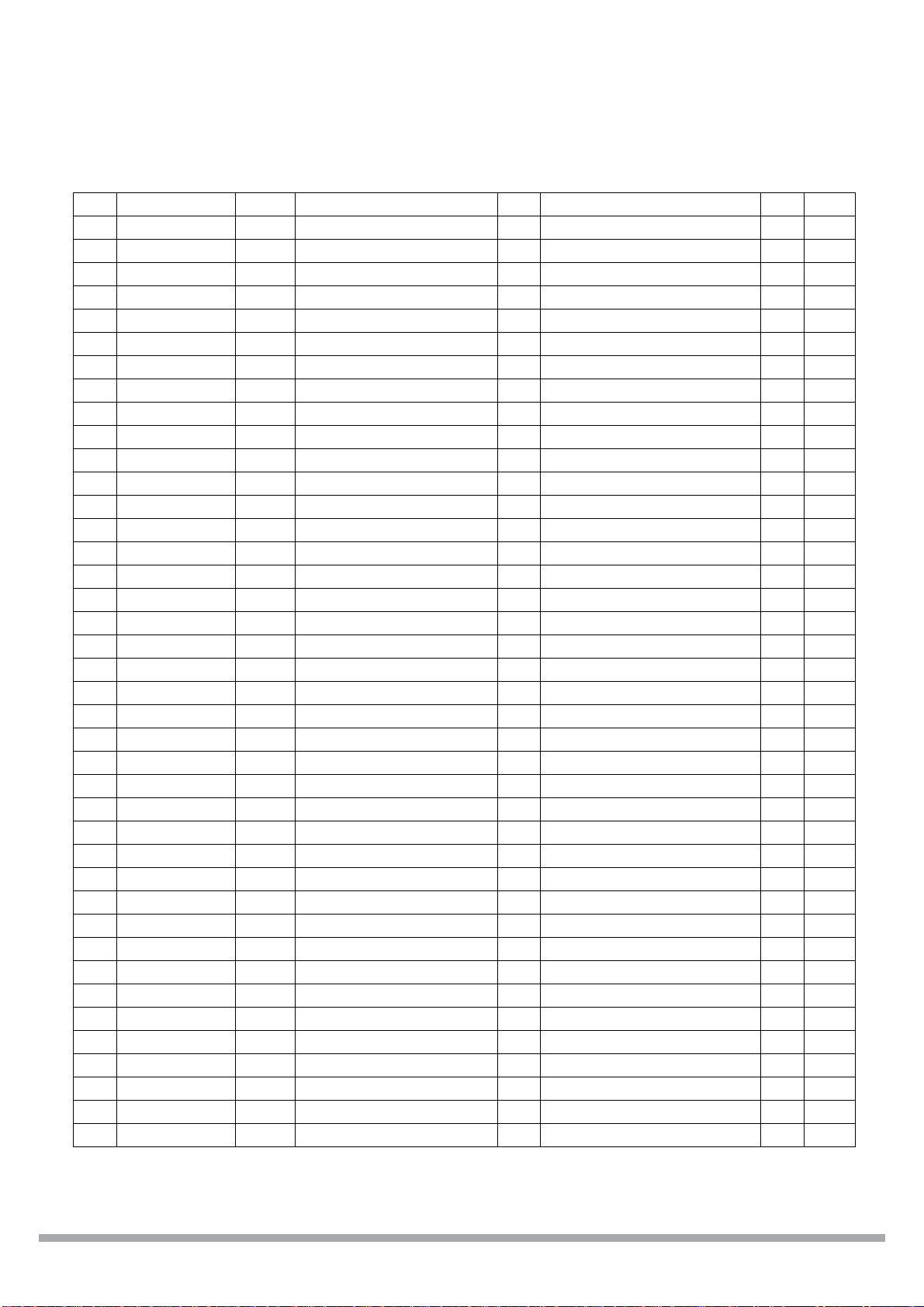
CS98000
117 H_D_9 B4 Host Data[9] B DVD Control Ready I 1, 2
1 1 8 H_D_8 B4 Host Data[8] B DVD Control Clock O 1, 2
119 VSS_IO Gnd I/O Ground
120 H_CKO B4 Host Clock O GenioHst[19] B 1
121 H_D_7 B4 Host Data[7] B DVD Data[7] I 1
122 H_D_6 B4 Host Data[6] B DVD Data[6] I 1
123 H_D_5 B4 Host Data[5] B DVD Data[5] I 1
124 AUD_BCK B4 Audio Out Bit Clock O GenioMis[3] B
125 H_D_4 B4 Host Data[4] B DVD Data[4] I 1
126 VSS_CORE Gnd Core Ground
127 H_D_3 B4 Host Data[3] B DVD Data[3] I 1
128 AUD_LRCK O4 A udio Out LR Clock O
129 VDD_CORE Pwr Core Power 2.5V
130 H_D_2 B4 Host Data[2] B DVD Data[2] I 1
131 VDD_IO Pwr I/O Pow er 3.3V
132 H_D_1 B4 Host Data[1] B DVD Data[1] I 1
133 AUD_DO_2 B4 Audio Out Data[2] O GenioMis[2] B
134 H_D_0 B4 Host Data[0] B DVD Data[0] I 1
135 AUD_DO_0 O4 Audio Out Data[0] O
136 AUD_DO_1 B4 Audio Out Data[1] O GenioMis[1] B
137 AIN_BC K IU Audio In Bit Clock I
138 VSS_CORE Gnd Core Ground
139 AIN_LRCK IU A udio In LR Clock I
140 AIN_DATA B4U Audio In Data I GenioMis[0] B
141 VDD_CORE Pwr Core Power 2.5V
142 CDC_DI IU S erial CODEC Data In I
143 VSS_IO Gnd I/O Ground
144 CDC_DO T4 Serial CODEC Data Out O
145 VIN_CLK IU Video Input Clock I
146 CDC_RST T4 Serial CODEC Reset O
147 CDC_CK IU Seri al CODEC Bit Clock I
148 CDC_SY B4U Serial CODEC Sync B
149 GPIO_V10 B4U GenioMis[26] B
150 GPIO_D15 B4U GenioDvd[15]
151 GPIO_D14 B4U GenioDvd[14]
152 GPIO_D13 B4SU GenioDvd[13]
153 VIN_VSNC B4U Video Input Vsync I GenioMis[25] B
154 CLK 27_O B4U Video Output Clock O GenioMis[6] B
155 GPIO_D12 B4U GenioDvd[12]
156 VDD_PLL Pwr PLL Power 2.5V
157 VSS_PLL Gnd PLL Ground
Table 6. Pin assignments (Continued)
16
Page 19
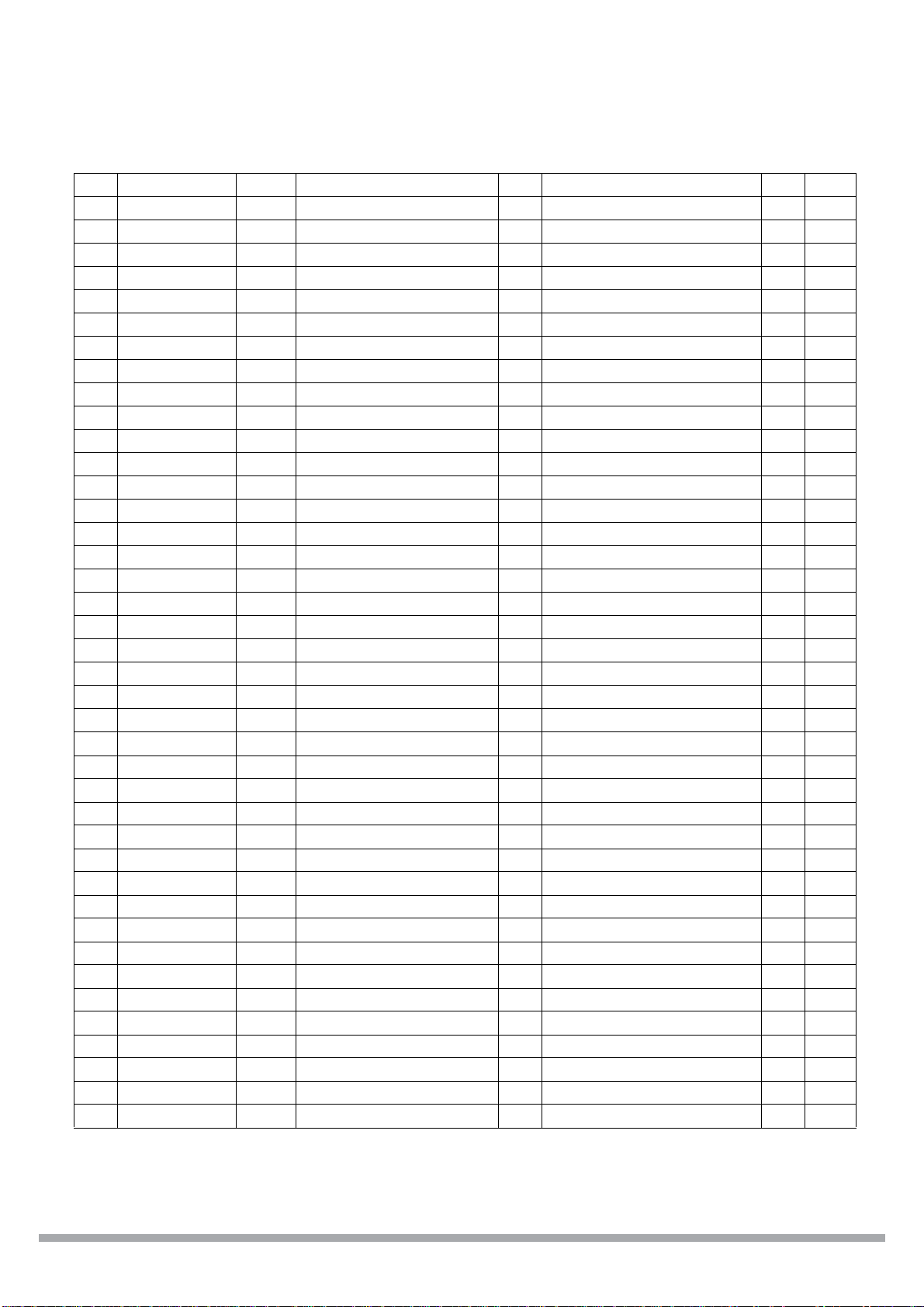
CS98000
158 VSS_CORE Gnd Core Ground
159 HSYNC B4U Video Output Hsync O GenioMis[4] B
160 VIN_HSYNC B4U Video Input Hsync I GenioMis[24] B
161 VDD_CORE Pwr Core Power 2.5V
162 VSYNC B4U Video Output Vsync O GenioMis[ 5] B
163 VDAT_0 O4 Video Output Data[0] O
164 VIN_D0 B4U Video Input Data[ 0] I GenioMis[16] B
165 VDAT_1 O4 Video Output Data[1] O
166 VDAT_2 O4 Video Output Data[2] O
167 VDAT_3 O4 Video Output Data[3] O
168 VIN_D1 B4U Video Input Data[ 1] I GenioMis[17] B
169 VDAT_4 O4 Video Output Data[4] O
170 VDAT_5 O4 Video Output Data[5] O
171 UNUSED may leave unconnected
172 VDAT_6 O4 Video Output Data[6] O
173 VDAT_7 O4 Video Output Data[7] O
174 GPIO_0 B4U General Purpose IO[0] B Audio PLL Input Bypass I
175 VIN_D2 B4U Video Input Data[ 2] I GenioMis[18] B
176 VSS_CORE Gnd Core Ground
177 AUD_DO_3 B4U Audio Out Data[3] O General Purpos e IO[1] B
178 VDD_CORE Pwr Core Power 2.5V
179 VIN_D3 B4U Video Input Data[ 3] I GenioMis[19] B
180 VDD_IO Pwr I/O Pow er 3.3V
181 GPIO_2 B4U G eneral Purpose IO [2] B
182 VSS_IO Gnd I/O Ground
183 GPIO_3 B4U G eneral Purpose IO [3] B
184 VIN_D4 B4U Video Input Data[ 4] I GenioMis[20] B
185 GPIO_4 B4U G eneral Purpose IO [4] B
2
186 SCL B4U I
187 SDA B4U I
188 GPIO_7 B4U G eneral Purpose IO [7] B
189 VIN_D5 B4U Video Input Data[ 5] I GenioMis[21] B
190 GPIO_8 B4U G eneral Purpose IO [8] B
191 AUD_XCLK B4U Audio 256x/384x Clock B General Purpose IO[9] B
192 GPIO_10 B4U General Purpose IO[10] B
193 VIN_D6 B4U Video Input Data[ 6] I GenioMis[22] B
194 GPIO_11 B4U General Purpos e IO[11] B
195 GPIO_12 B4U General Purpose IO[12] B
196 GPIO_13 B4U General Purpose IO[13] B
197 GPIO_14 B4U General Purpose IO[14] B
198 VIN_D7 B4U Video Input Data[ 7] I GenioMis[23] B
C Clock B General Purpose IO[5] B
2
C Data B General Purpose IO[6] B
Table 6. Pin assignments (Continued)
17
Page 20
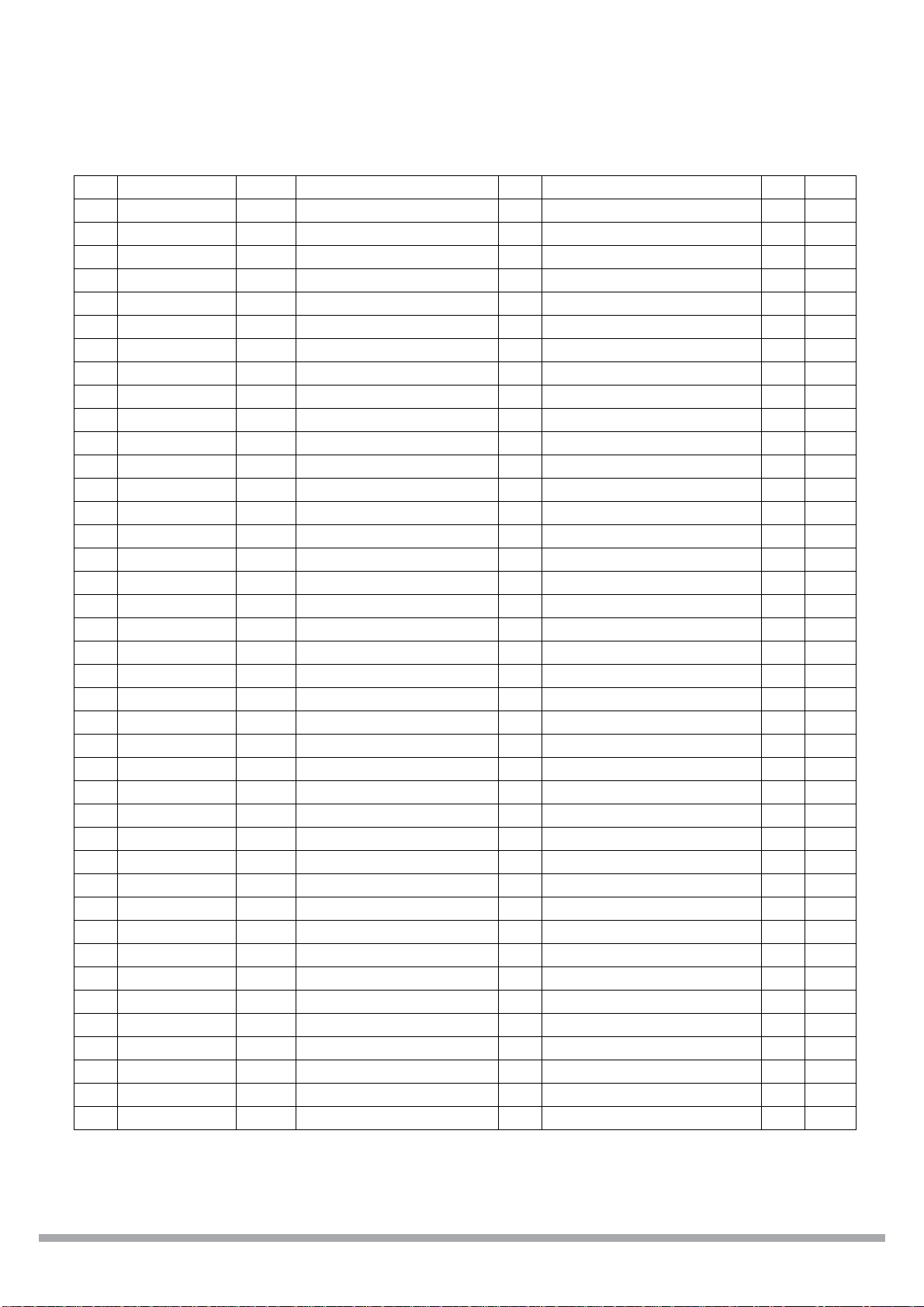
CS98000
158 VSS_CORE Gnd Core Ground
159 HSYNC B4U Video Output Hsync O GenioMis[4] B
160 VIN_HSYNC B4U Video Input Hsync I GenioMis[24] B
161 VDD_CORE Pwr Core Power 2.5V
162 VSYNC B4U Video Output Vsync O GenioMis[ 5] B
163 VDAT_0 O4 Video Output Data[0] O
164 VIN_D0 B4U Video Input Data[ 0] I GenioMis[16] B
165 VDAT_1 O4 Video Output Data[1] O
166 VDAT_2 O4 Video Output Data[2] O
167 VDAT_3 O4 Video Output Data[3] O
168 VIN_D1 B4U Video Input Data[ 1] I GenioMis[17] B
169 VDAT_4 O4 Video Output Data[4] O
170 VDAT_5 O4 Video Output Data[5] O
171 UNUSED may leave unconnected
172 VDAT_6 O4 Video Output Data[6] O
173 VDAT_7 O4 Video Output Data[7] O
174 GPIO_0 B4U General Purpose IO[0] B Audio PLL Input Bypass I
175 VIN_D2 B4U Video Input Data[ 2] I GenioMis[18] B
176 VSS_CORE Gnd Core Ground
177 AUD_DO_3 B4U Audio Out Data[3] O General Purpos e IO[1] B
178 VDD_CORE Pwr Core Power 2.5V
179 VIN_D3 B4U Video Input Data[ 3] I GenioMis[19] B
180 VDD_IO Pwr I/O Pow er 3.3V
181 GPIO_2 B4U G eneral Purpose IO [2] B
182 VSS_IO Gnd I/O Ground
183 GPIO_3 B4U G eneral Purpose IO [3] B
184 VIN_D4 B4U Video Input Data[ 4] I GenioMis[20] B
185 GPIO_4 B4U G eneral Purpose IO [4] B
2
186 SCL B4U I
187 SDA B4U I
188 GPIO_7 B4U G eneral Purpose IO [7] B
189 VIN_D5 B4U Video Input Data[ 5] I GenioMis[21] B
190 GPIO_8 B4U G eneral Purpose IO [8] B
191 AUD_XCLK B4U Audio 256x/384x Clock B General Purpose IO[9] B
192 GPIO_10 B4U General Purpose IO[10] B
193 VIN_D6 B4U Video Input Data[ 6] I GenioMis[22] B
194 GPIO_11 B4U General Purpos e IO[11] B
195 GPIO_12 B4U General Purpose IO[12] B
196 GPIO_13 B4U General Purpose IO[13] B
197 GPIO_14 B4U General Purpose IO[14] B
198 VIN_D7 B4U Video Input Data[ 7] I GenioMis[23] B
C Clock B General Purpose IO[5] B
2
C Data B General Purpose IO[6] B
Table 6. Pin assignments (Continued)
18
Page 21
CLK is driven by the system clock. All SDRAM input signals are
nal burst
CKE activates(HIGH) and deactivates(LOW) the CLK signal. If
up and hold time same as other
the next clock cycle and the state
of output and burst address is frozen as long as the CKE remains low. When all
banks are in the idle state, deactivating the clock controls the entry to the Power
ter the device
enters Power Down and Self Refresh modes, where CKE becomes
asynchronous until exiting the same mode. The input buffers, including CLK,
are disabled during Power Down and Self Refresh modes, providing low
A11 are sampled during the BankActivate command (row
A7 with A10
defining Auto Precharge) to select one location out of the 2M available in the
respective bank. During a Precharge command, A10 is sampled to determine if
dress inputs also provide
CS# enables (sampled LOW) and disables (sampled HIGH) the
command decoder. All commands are masked when CS# is sampled HIGH.
lection on systems with multiple banks. It is
The RAS# signal defines the operation commands in
conjunction with the CAS# and WE# signals and is latched at the positive edges
RAS# and CS# are asserted "LOW" and CAS# is asserted
"HIGH," either the BankActivate command or the Precharge command is
selected by the WE# signal. When the WE# is asserted "HIGH," the
ned on
to the active state. When the WE# is asserted "LOW," the Precharge command
is selected and the bank designated by BS is switched to the idle state after the
n commands in
conjunction with the RAS# and WE# signals and is latched at the positive edges
of CLK. When RAS# is held "HIGH" and CS# is asserted "LOW," the column
access is started by asserting CAS# "LOW." Then, the Read or Write command
EM638165
Pin Descriptions
Symbol Type Description
CLK Input
CKE Input
BA0,BA1 Input
Table 1. Pin Details of EM638165
Clock:
sampled on the positive edge of CLK. CLK also increments the inter
counter and controls the output registers.
Clock Enable:
CKE goes low synchronously with clock(setinputs), the internal clock is suspended from
Down and Self Refresh modes. CKE is synchronous except af
standby power.
Bank Select:
BA0,BA1 input select the bank for operation.
BA1 BA0 Select Bank
0 0 BANK #A
0 1 BANK #B
1 0 BANK #C
1 1 BANK #D
A0-A11 Input
CS# Input
RAS# Input
CAS# Input
Address Inputs:
address A0-A11) and Read/Write command (column address A0-
all banks are to be precharged (A10 = HIGH). The ad
the op-code during a Mode Register Set command.
Chip Select:
CS# provides for external bank se
considered part of the command code.
Row Address Strobe:
of CLK. When
BankActivate command is selected and the bank designated by BS is tur
precharge operation.
Column Address Strobe:
is selected by asserting WE# "LOW" or "HIGH."
A0-
The CAS# signal defines the operatio
19
Page 22
CLK is driven by the system clock. All SDRAM input signals are
nal burst
CKE activates(HIGH) and deactivates(LOW) the CLK signal. If
up and hold time same as other
the next clock cycle and the state
of output and burst address is frozen as long as the CKE remains low. When all
banks are in the idle state, deactivating the clock controls the entry to the Power
ter the device
enters Power Down and Self Refresh modes, where CKE becomes
asynchronous until exiting the same mode. The input buffers, including CLK,
are disabled during Power Down and Self Refresh modes, providing low
A11 are sampled during the BankActivate command (row
A7 with A10
defining Auto Precharge) to select one location out of the 2M available in the
respective bank. During a Precharge command, A10 is sampled to determine if
dress inputs also provide
CS# enables (sampled LOW) and disables (sampled HIGH) the
command decoder. All commands are masked when CS# is sampled HIGH.
lection on systems with multiple banks. It is
The RAS# signal defines the operation commands in
conjunction with the CAS# and WE# signals and is latched at the positive edges
RAS# and CS# are asserted "LOW" and CAS# is asserted
"HIGH," either the BankActivate command or the Precharge command is
selected by the WE# signal. When the WE# is asserted "HIGH," the
ned on
to the active state. When the WE# is asserted "LOW," the Precharge command
is selected and the bank designated by BS is switched to the idle state after the
n commands in
conjunction with the RAS# and WE# signals and is latched at the positive edges
of CLK. When RAS# is held "HIGH" and CS# is asserted "LOW," the column
access is started by asserting CAS# "LOW." Then, the Read or Write command
EM638165
Pin Descriptions
Symbol Type Description
CLK Input
CKE Input
BA0,BA1 Input
Table 1. Pin Details of EM638165
Clock:
sampled on the positive edge of CLK. CLK also increments the inter
counter and controls the output registers.
Clock Enable:
CKE goes low synchronously with clock(setinputs), the internal clock is suspended from
Down and Self Refresh modes. CKE is synchronous except af
standby power.
Bank Select:
BA0,BA1 input select the bank for operation.
BA1 BA0 Select Bank
0 0 BANK #A
0 1 BANK #B
1 0 BANK #C
1 1 BANK #D
A0-A11 Input
CS# Input
RAS# Input
CAS# Input
Address Inputs:
address A0-A11) and Read/Write command (column address A0-
all banks are to be precharged (A10 = HIGH). The ad
the op-code during a Mode Register Set command.
Chip Select:
CS# provides for external bank se
considered part of the command code.
Row Address Strobe:
of CLK. When
BankActivate command is selected and the bank designated by BS is tur
precharge operation.
Column Address Strobe:
is selected by asserting WE# "LOW" or "HIGH."
A0-
The CAS# signal defines the operatio
20
Page 23
EM638165
Operation Mode
Fully synchronous operations are performed to latch the commands at the positive edges of CLK.
Table 2 shows the truth table for the operation commands.
Table 2. Truth Table (Note (1), (2) )
BankActivate
BankPrecharge
PrechargeAll
Write
Write and AutoPrecharge
Read
Read and Autoprecharge
Mode Register Set
No-Operation
Burst Stop
Device Deselect
AutoRefresh
SelfRefresh Entry
SelfRefresh Exit
Clock Suspend Mode Entry
Power Down Mode Entry
Clock Suspend Mode Exit
Power Down Mode Exit
Data Write/Output Enable
Data Mask/Output Disable
Command State CKE
(3)
Idle
H X X V Row address L L H H
Any H X X V L X L L H L
Any H X X X H
(3)
Active
Active
Active
Active
H X X V L L H L L
(3)
H X X V H
(3)
H X X V L L H L H
(3)
H X X V H
Idle H X X OP code L L L L
Any H X X X X
(4)
Active
H X X X X
Any H X X X X
Idle H H X X X
Idle H L X X X
Idle L H X X X
(SelfRefresh)
Active
(5)
Any
H L X X X
H L X X X
Active
L H X X X
Any L H X X X
(PowerDown)
Active
Active
H X L X X
H X H X X
n-1
CKE
DQM BA
n
0,1
A
A
10
0-9,11
X L L H L
Column
address
(A0 ~ A7)
Column
address
(A0 ~ A7)
X L H H H
X L H H L
X H
X L L L H
X L L L H
X H
X X
X H
X X
X H
X X
X X
CS# RAS# CAS# WE#
L H L L
L H L H
X X X
X X X
L H H H
X X X
X X X
L H H H
X X X
X X X
L H H H
X X X
X X X
Note:
1. V=Valid X=Don't Care L=Low level H=High level
2. CKEn signal is input level when commands are provided.
CKE
signal is input level one clock cycle before the commands are provided.
n-1
3. These are states of bank designated by BS signal.
4. Device state is 1, 2, 4, 8, and full page burst operation.
5. Power Down Mode can not enter in the burst operation.
When this command is asserted in the burst cycle, device state is clock suspend mode.
21
Page 24
EM638165
Commands
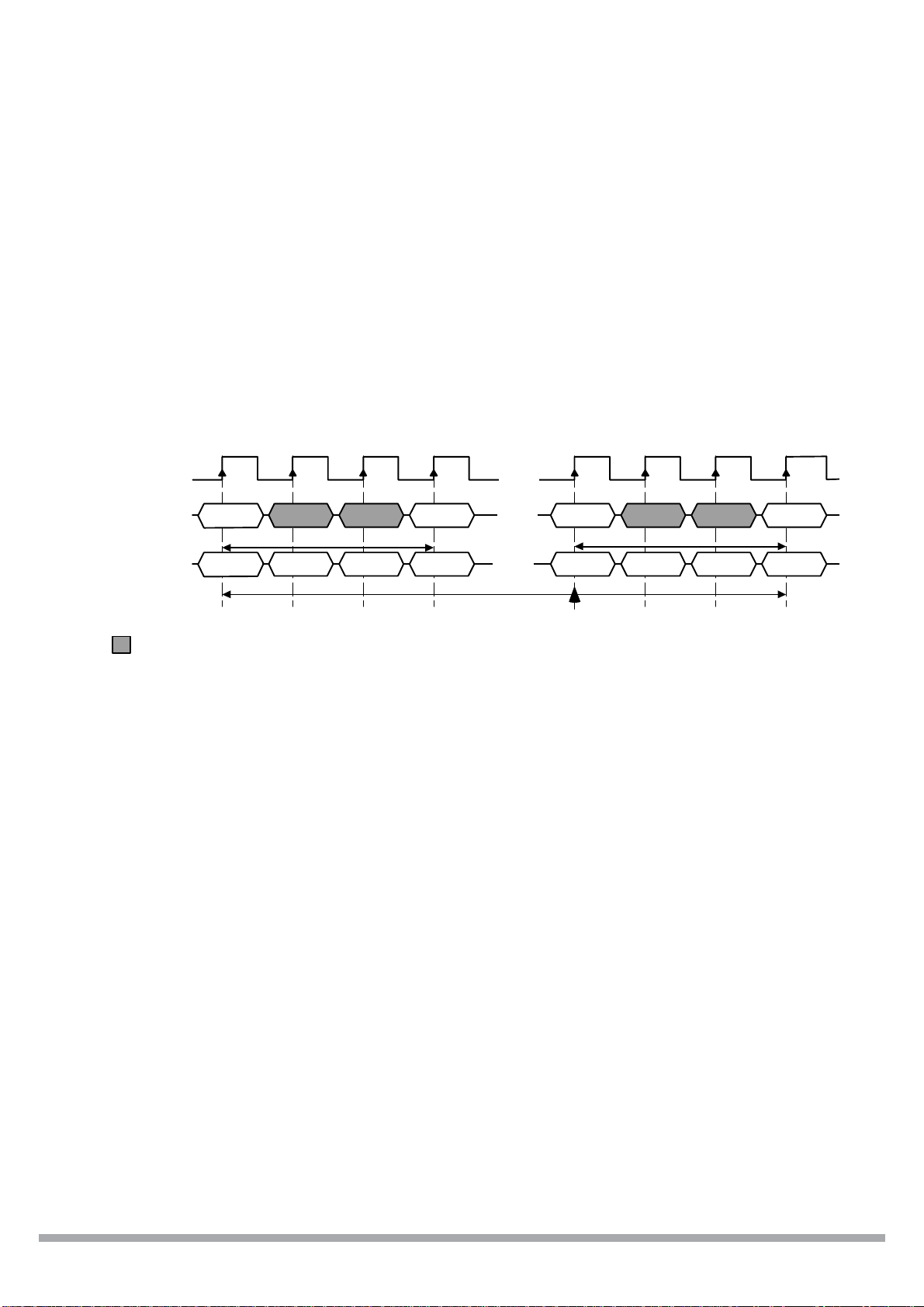
1 BankActivate
(RAS# = "L", CAS# = "H", WE# = "H", BAs = Bank, A0-A11 = Row Address)
The BankActivate command activates the idle bank designated by the BA0,1 signals. By
latching the row address on A0 to A11 at the time of this command, the selected row access is
initiated. The read or write operation in the same bank can occur after a time delay of t
from the time of bank activation. A subsequent BankActivate command to a different row in the
same bank can only be issued after the previous active row has been precharged (refer to the
following figure). The minimum time interval between successive BankActivate commands to the
same bank is defined by tRC(min.). The SDRAM has four internal banks on the same chip and
shares part of the internal circuitry to reduce chip area; therefore it restricts the back-to-back
activation of the four banks. t
different banks. After this command is used, the Write command and the Block Write command
perform the no mask write operation.
(min.) specifies the minimum time required between activating
RRD
T0 T 1 T2 T3 Tn+3 Tn+4 Tn+5 T n+6
RCD
(min.)
CLK
ADDRESS
COMM A ND
Bank A
Row Addr.
Bank A
Activate
RAS# - CAS# delay (tRCD)
: "H" or "L"
BankActivate Command Cycle
2 BankPrecharge command
(RAS# = "L", CAS# = "H", WE# = "L", BAs = Bank, A10 = "L", A0-A9 and A11 = Don't care)
The BankPrecharge command precharges the bank disignated by BA signal. The precharged
bank is switched from the active state to the idle state. This command can be asserted anytime after
t
(min.) is satisfied from the BankActivate command in the desired bank. The maximum time any
RAS
bank can be active is specified by t
in any active bank within t
state and is ready to be activated again.
3 PrechargeAll command
(RAS# = "L", CAS# = "H", WE# = "L", BAs = Don’t care, A10 = "H", A0 -A9 and A11 = Don't care)
The PrechargeAll command precharges all banks simultaneously and can be issued even if all
banks are not in the active state. All banks are then switched to the idle state.
NOP
..............
NOP
Bank A
Col Addr.
R/W A with
AutoPrecharge
RAS# Cycle time (tRC)
..............
..............
(Burst Length = n, CAS# Latency = 3)
(max.). Therefore, the precharge function must be performed
RAS
(max.). At the end of precharge, the precharged bank is still in the idle
RAS
Bank B
Row Addr.
Bank B
Activate
AutoPrecharge
Begin
RAS# - RAS# delay time (tRRD)
NOP
NOP
Bank A
Row Addr.
Bank A
Activate
4 Read command
(RAS# = "H", CAS# = "L", WE# = "H", BAs = Bank, A10 = "L", A0-A7 = Column Address)
The Read command is used to read a burst of data on consecutive clock cycles from an active
row in an active bank. The bank must be active for at least t
issued. During read bursts, the valid data-out element from the starting column address will be
available following the CAS# latency after the issue of the Read command. Each subsequent dataout element will be valid by the next positive clock edge (refer to the following figure). The DQs go
into high-impedance at the end of the burst unless other command is initiated. The burst length,
burst sequence, and CAS# latency are determined by the mode register, which is already
programmed. A full-page burst will continue until terminated (at the end of the page it will wrap to
column 0 and continue).
222324252627282930
(min.) before the Read command is
RCD
Page 25
Page 26
Page 27
Page 28
Page 29
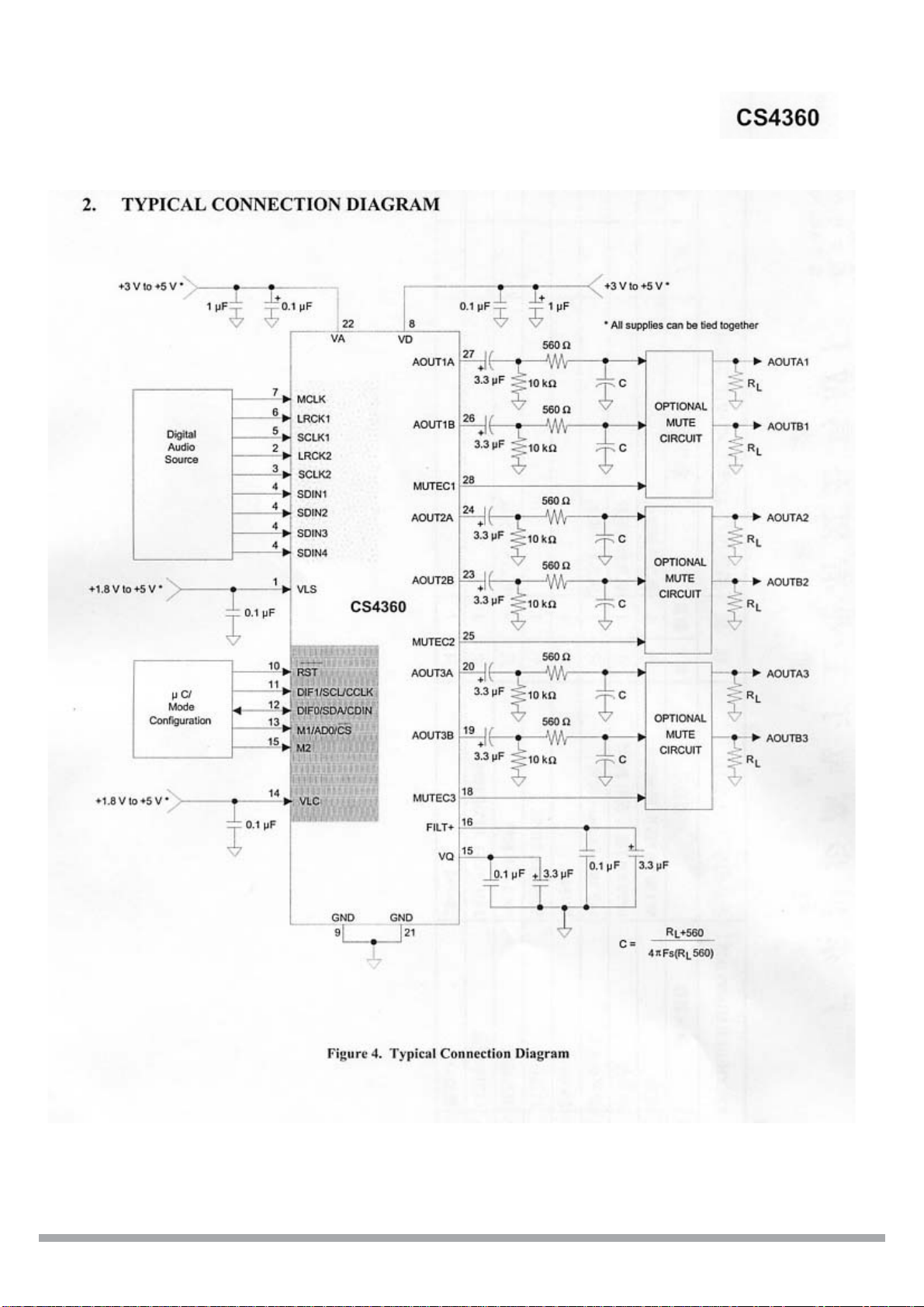
Page 30

Page 31

Page 32

Page 33

CS92288 MPEG-2 AUDIO/VIDEO CODEC DATA BOOK
IMPORTANT NOTICE
"Preliminary" product information describes products that are in production, but for which full characterization data is not yet
available. "Advance" product information describes products that are in development and subject to development changes.
Cirrus Logic, Inc. and its subsidiaries ("Cirrus") believe that the information contained in this document is accurate and reliable. However, the information is subject to change without notice and is provided "AS IS" without warranty of any kind
(express or implied). Customers are advised to obtain the latest version of relevant information to verify, before placing
orders, that information being relied on is current and complete. All products are sold subject to the terms and conditions of
sale supplied at the time of order acknowledgment, including those pertaining to warranty, patent infringement, and limitation
of liability. No responsibility is assumed by Cirrus for the use of this information, including use of this information as the
basis for manufacture or sale of any items, or for infringement of patents or other rights of third parties. This document is the
property of Cirrus and by furnishing this information, Cirrus grants no license, express or implied under any patents, mask
work rights, copyrights, trademarks, trade secrets or other intellectual property rights. Cirrus owns the copyrights of the information contained herein and gives consent for copies to be made of the information only for use within your organization with
respect to Cirrus integrated circuits or other parts of Cirrus. This consent does not extend to other copying such as copying for
general distribution, advertising or promotional purposes, or for creating any work for resale.
An export permit needs to be obtained from the competent authorities of the Japanese Government if any of the products or
technologies described in this material and controlled under the "Foreign Exchange and Foreign Trade Law" is to be exported
or taken out of Japan. An export license and/or quota needs to be obtained from the competent authorities of the Chinese Government if any of the products or technologies described in this material is subject to the PRC Foreign Trade Law and is to be
exported or taken out of the PRC.
CERTAIN APPLICATIONS USING SEMICONDUCTOR PRODUCTS MAY INVOLVE POTENTIAL RISKS OF DEATH,
PERSONAL INJURY, OR SEVERE PROPERTY OR ENVIRONMENTAL DAMAGE ("CRITICAL APPLICATIONS").
CIRRUS PRODUCTS ARE NOT DESIGNED, AUTHORIZED, OR WARRANTED TO BE SUITABLE FOR USE IN LIFESUPPORT DEVICES OR SYSTEMS OR OTHER CRITICAL APPLICATIONS. INCLUSION OF CIRRUS PRODUCTS IN
SUCH APPLICATIONS IS UNDERSTOOD TO BE FULLY AT THE CUSTOMER'S RISK.
Cirrus Logic, Cirrus, and the Cirrus Logic logo designs are trademarks of Cirrus Logic, Inc. All other brand and product
names in this document may be trademarks or service marks of their respective owners.
Preliminary Information - Confidential
Use of this product in any manner that complies with the MPEG-2 video standard as defined in ISO documents IS 13818-1
(including annexes C, D, F, J, and K), IS 13818-2 (including annexes A, B, C, and D, but excluding scalable extensions), and
IS 13818-4 (only as it is needed to clarify IS 13818-2) is expressly prohibited without a license under applicable patents in the
MPEG-2 patent portfolio, which license is available from MPEG LA, L.L.C. 250 Steele Street, Suite 300, Denver, Colorado
80296.
31
Page 34

CS92288 MPEG-2 AUDIO/VIDEO CODEC DATA BOOK
Overview
The CS92288 is a real time MPEG-2 audio/video encoder and decoder (CODEC), with system multiplexor/demultiplexor and
on-screen display (OSD). For video coding, the CS92288 fully complies with the ISO/IEC 13818 Main Level @ Main Profile
(ML@MP) or with the ISO/IEC 11172 (MPEG-1) formats. For audio encoding, the CS92288 supports a variety of audio formats, including MPEG-1 or MPEG-2 audio (all Layers) and Dolby Digital (AC-3).
In encode mode, the CS92288 accepts digital video in ITU-R
digital audio in LPCM format. The input video is filtered and then encoded to produce a compressed bitstream in either
MPEG-1 or MPEG-2 ML@MP syntax. The audio is compressed in either MPEG or Dolby Digital formats. The compressed
video and audio streams are multiplexed to produce an MPEG-compliant program bit stream.
In decode mode, the CS92288 accepts an MPEG program bit stream or audio and video elementary streams and produces ITUR BT.601 or BT.656 video and LPCM audio outputs.
The CS92288 is designed to provide a high degree of integration and ease of system design. It makes an ideal solution for a
variety of MPEG-based audio/visual applications, such as PC-based content creation, VCD and DVD-RAM players/recorders,
set-top boxes, and time-shift recording. For example, a single CS92288 is adequate for a complete Super VCD (SVCD) player/
recorder.
For the evaluation of the CS92288, Cirrus Logic provides a PC-based Evaluation Board, window drivers, and application software. In addition, Cirrus Logic offers a complete reference design for a stand-alone MPEG-based video recorder/player. This
design allows designers and manufacturers a quick entry to the digital recording markets.
BT.601 (CCIR-601) or ITU-R BT.656 (CCIR-656) formats, and
Features
• Single Chip Real Time MPEG-2 Audio/Video CODEC with system Mux/Demux and On-screen Display (OSD)
• Supports MPEG-1 audio/video encoding and decoding
• Supports Dolby Digital audio encoding and decoding
• Programmable system mux/demux supports DVD, VCD, and SVCD encoding and decoding
• 8-bit OSD support (2-b text, 2-b to 8-b graphics)
• Support for Constant Bit Rate (CBR) and one-pass Variable Bit Rate (VBR)
– IPB-pictures, CBR (average), VBR (max) up to 15Mbps.
– I-pictures only to 30Mbps
• Proprietary High Performance Motion Estimation
• Low external SDRAM memory:
– 8 Mbytes for D1, 2B picture format
• Supports Multiple Resolutions & Scan Rates
– NTSC: (720, 704, 640, 544, 480, 352) x 480 or 352 x 240 (CIF), and 176x112 (QCIF) at 30 or 29.97 Hz
– PAL: (720, 704, 640, 544, 480, 352) x 576 or 352 x 288 (CIF), and 176x144 (QCIF) at 25 Hz
• Integrated video pre and post processor
• 108 MHz operating frequency with separate 27 MHz input video clock
• Video Preprocessor
– Accepts ITU-R BT.601 4:2:2 and D1 input formats
– 4:2:2 to 4:2:0 Conversion
– Built-in, programmable, pre-processing filters
– Half Horizontal Resolution (HHR), SIF decimation filtering, or Two-Thirds Horizontal resolution filtering
– Temporal filtering
– Automatic inverse telecine
– Sync Extraction
• Video Encoder
– Real Time Encoding of MPEG-2 Main Level/Main Profile digital video
• ISO/IEC 13818-2 compliant
• SP@ML, MP@LL, MP@ML
• Video Streams up to 13.5Mpels/s (16-bit) and 27Mpel/s (8-bit)
– Real Time Encoding of MPEG-1
– Support for Full D1, 2/3 D1, 1/2 D1, CIF, and QCIF
Preliminary Information - Confidential
32
Page 35

– Constant Bit Rate Support: up to 15Mbps (IPB frames) and 30Mbps (I frame only)
– Variable Bit Rate Support:
• Real-time one-pass rate control
• User-selectable average bitrate
– Proprietary High Performance Motion Estimation Engine
• Half-pel accuracy
• Horizontal Search Ranges: ±63.5, ±31.5, ±15.5, ±7.5 Pel/Frame
• Vertical Search Range: ±31.5, ±15.5, ±7.5 Pel/Frame
– Guaranteed to operate at 30 frames/second
– Field-based or Frame-based DCT
– Field, 16x8, and frame-mode prediction
– Programmable encoding parameters
• I and P-picture interval
• quantization matrices
• Encoding time
• Average bitrate, upper and lower bitrate bounds
• Active Picture Area Selection
•
Video Decode
– Decodes ML@MP MPEG-2 video and MPEG-1 video
– Support Full D1, 2/3 D1, 1/2 D1, CIF, and QCIF
– Variable Length Decoder
• Video stream syntax parsing and decoding
• Error detection and handling
– Motion Prediction
• Supports frame, field, 16 x 8 and dual prime motion compensation modes
• Performs half-pel interpolation and bi-directional interpolation
– Error detection, handling and mitigation
•
Video Postprocessor
– Filters for interpolation to ITU-R BT.601 and BT.656 format
– Display Management
– Automatic repetition of dropped field for 3:2 Pulldown (Telecine)
– Horizontal and vertical scaling
– Master mode D1/VMI output
– Slave mode CCIR output
– Letter-box, NTSC to PAL format conversion
– OSD/OGD; 2-bit text, 2-,4-, or 8-bit graphics
Preliminary Information - Confidential
• Audio Processor
– Programmable, 24-bit, digital signal processor
– Input/Output sampling rates: 32, 44.1, 48, or 96 kHz
– Data resolution up to 24 bits/sample
– Two channel audio encoding or decoding in either MPEG (all Layers) or Dolby Digital (AC-3)
– 5.1 channels audio decoding (downmixed to two channels)
– Additional audio encoding/decoding algorithms can be supported via firmware upgrades
•
System Processo
– System Multiplexor/Demultiplexor
– Based on powerful embedded ARC core
– Programmable, supports DVD, VCD, SVCD, encoding and decoding
– Supports Transport, Program, and Elementary streams
– Trick Play; fast and slow play forward, fast play backward
• System Interfaces
– 16-bit bus that supports Intel and Motorola interfaces
– 8-bit interface supports the Philips Trimedia TM1300 and other 8-bit microcontrollers with either separate or multiplexed
address and data buses.
– Gluless interface to Philips 7146 PCI bridge
– Direct interface to NTSC/PAL industry standard NTSC/PAL video encoders/decoders (Philips, Harris)
CS92288 MPEG-2 AUDIO/VIDEO CODEC DATA BOOK
r
r
33
Page 36

CS92288 MPEG-2 AUDIO/VIDEO CODEC DATA BOOK
– Glueless interface to industry standard SDRAM(s)
– Glueless interface to Data Flash and EPROM memories
– 8051 Protocol interface
2
–I
S
– General Purposed I/O
– Glueless interface to USB controllers
– Programmable clock output for audio A/D and D/A converters.
• Technology
– 0.18um CMOS technology
– 272-pin PBGA package
– 3.3 and 1.8 Volts power supplies
– 5V I/O tolerance
– Internal pull-ups for SDRAM and HIU data buses
– 1 W typical average power consumption at 108 MHz
Ordering Information
Part Number Package Operating Temp Range
o
o
CS92288 272L-BGA 0
~ +70
Preliminary Information - Confidential
Application Information
Figure 1shows a digital audio/video deck using the CS92288, a host microcontroller, a CD-R/W drive, and supporting commodity devices. A drive interface is supported by the controller CPU to transfer data between the CS92288 and the CD-R/W
drive. The functionality of the CS92288 can be controlled either from the host microcontroller or from an optional Firmware
EPROM. The OSD EPROM is also optional
Encoding
Analog video is demodulated and passed to the CS92288. The setup and control for the NTSC/PAL video decoder are handled
by an external I
PAL video encoder for video output loopback.
Analog audio is digitized by the A/D converter, and LPCM data is transfered to the CS92288 via the I
back is provided by a separate I
the input audio and video, producing an MPEG-compliant output to the Host CPU. The Host CPU directs the writing of the
data to the media.
Decoding
The compressed audio and video data is read off the media device. The CS92288 demultiplexes and decompresses the audio
and video data and transfers digital video to the NTSC/PAL video encoder and digital LPCM audio to the audio D/A converter.
Furthermore, the output video data can be mixed with OSD or OGT (On-screen Graphics and Text) data before the final output. The NTSC/PAL video encoder is configured by an external I
using the I
2
C interface master. Input video can be overlayed with on-screen graphics and be passed back to the NTSC/
2
2
S interface to the output audio D/A of the system. The CS92288 utilizes the SDRAM to process
2
S bus and associated interface circuitry.
2
C master. The audio D/A interfaces with the CS92288
S interface. Audio loop-
34
Page 37

CS92288 MPEG-2 AUDIO/VIDEO CODEC DATA BOOK
Video Out
Figure 1:
I2C
Video In
YC/CV
YC/CV
Audio In
Audio Out
System diagram of an CS92288-based digital A/V Recorder/Player
NTSC/PAL
Decoder
I2C
NTSC/PAL
Encoder
A/D
D/A
Front
Panel
Video In
Video Out
Audio I/O
2
I
S
Optional Firmware
EPROM or Flash
CS92288
MPEG-2 A/V
CODEC
Host Interface
Host CPU
SDRAM
Controller
Interface
Drive
64-bit
8MB
SDRAM
CD-R/W
Functional Descriptions
The CS92288 is organized as a process pipeline that implements the MPEG-2 audio and video encoding and decoding algorithms.
The CS92288 provides application program control over a large number of encoding parameters. For example, for video
encoding one can control such parameters as I, P, B-picture cadence, GOP structure, bit rates, and decoder buffer sizes. For
audio encoding, one can select coding format and average bit rate.
The algorithmic and architectural innovations of the CS92288 allow a unique degree of integration for the MPEG audio/video
CODEC function. The CS92288 is also designed to provide a high degree of system integration and ease of system design.
These combined benefits make it an ideal platform for a variety of MPEG-2-based digital audio/video applications
For communication applications, the CS92288 can match the output bit rate to the channel rate. This feature allows the host
controller to make bit rate changes as needed to demonstrate better bandwidth utilization across multiple channels.
Preliminary Information - Confidential
Internal rate control provides a high degree of flexibility in relation to the output bit rate, including the ability to generate variable bit rate compressed video stream in one pass. This makes it suitable for storage sensitive applications such as digital camcorders and digital versatile discs (DVDs).
The CS92288 also has features geared toward MPEG-2 publishing and authoring systems. These include the ability to specify
the initial decoder buffer fullness.
Architecture
Figure 2 shows the major functional units of the CS92288.These units include:
• The RISC microcontroller (an ARC RISC core)
• The Video Interface Unit (VIO)
• The Audio Interface Unit (AIU)
• The Video Engine Unit (VEU)
• The Audio Engine (DSP)
• The Host Interface Unit (HIU), and
• The SDRAM Control Unit (DCU)
35
Page 38

CS92288 MPEG-2 AUDIO/VIDEO CODEC DATA BOOK
All blocks inter-communicate with two major data buses: a 64-bit wide data bus (D-Bus) and a 16-bit wide register bus (RBus). The PLL block is used to multiply (4X) the SYSCLK frequency to provide for all internal blocks and external memory
clocking. A separate PLL is used to provide an output clock to external audio A/D and D/A converters.
+1.8V +3.3V SYSCLK
CLK27_DEM
CLK27_MOD
Video In
Video Out
(27 MHz)
Video
Interface
Unit (VIO)
Video Engine
Unit (VEU)
RISC micro-
controller (ARC)
PLL
R-BUS
D-BUS
SDRAM Control
Unit (DCU)
SDRAM
Memory
(108 MHz)
Preliminary Information - Confidential
Audio In
Audio Out
Figure 2: CS92288 Chip Architecture
Audio
Interface
Unit (AIU)
Audio
PLL
AM_SCLK
Audio
Engine Unit
(DSP)
Bitstream/Command
Host
Interface
Unit (HIU)
Host Interface
The Video Interface Unit (VIO)
Figure 3 shows a block diagram of the VIO. It includes the Video Input Unit (VIU), the Video Output Unit (VOU), the Video
Processing Unit (VPU), and the OSD Unit.
The VIU selects the input video active area and performs chroma conversion, inverse telecine, spatial and/or temporal prefilter-
Digital Video In
601/656
Digital Video Out
601/656
Video Input
Unit (VIU)
Video Output
Unit (VOU)
OSD
D-Bus
Video Processing
Unit (VPU)
Figure 3:
Interface Unit
Block diagram of the Video
ing, and data arrangement to facilitate the subsequent encoding processes. It preprocesses the input data so that encoding can
36
Page 39

CS92288 MPEG-2 AUDIO/VIDEO CODEC DATA BOOK
be done in the most efficient way.
The VOU can perform a variety of postprocessing operations, including horizontal and vertical scaling, telecine, and video format
conversion.
The OSD block mixes text and/or graphics from the OSD buffer (in SDRAM) with the output of the VOU and generates a correctly sequenced ITU-R BT.601 or 656 4:2:2 output video stream. The flexible architecture of the VIO unit allows it to operate in
a number of different configurations.
Video Encoding - Normal Mode
Figure 4 shows the operation of the VIO unit under the normal encoding mode. Input video is captured by the VIU and is
transferred to SDRAM. The buffered input is passed first to the VOU and then to the OSD unit, where it is mixed with text or
graphics from the OSD buffers. The output of the OSD unit provides digital loopback of the input video, overlaid with onscreen text or graphics.
Video Encoding - Intermediate Mode
Digital Video In
VIU
VOU
Input/Encoding
Video Buffers
OSD Buffers
SDRAM
Dig. Video Out
Figure 4:
OSD
Text/
Graphics
Video Encoding - Normal Mode
Figure 5 shows the flow of operations in the VIO unit under the intermediate encoding mode. As in the normal mode, this
mode allows for digital video loopback of the input video with overlaid text or graphics. However, this mode also allows for
additional preprocessing of the input video by the video processing unit (VPU). Among its functions, the VPU can initialize
the video frame buffer with specific YCbCr values (e.g., blue screen generation), copy data from one video buffer to another,
or scale data from one frame-buffer region to another frame-buffer region.
Preliminary Information - Confidential
VPU
Video In
VIU
VOU
Video Out
OSD
Text/
Graphics
Encoding Video
Buffers
Input Video
Buffers
OSD Buffers
SDRAM
Figure 5:
Mode
Video Encoding - Intermediate
Video Encoding - Advanced Mode
Figure 6 shows the flow of operations when the VIO is used in advanced encoding mode. In this mode, input video is captured
37
Page 40

CS92288 MPEG-2 AUDIO/VIDEO CODEC DATA BOOK
directly by the OSD unit, where it can be mixed with OSD data. The output of the OSD unit is passed back to the VIU and then
to SDRAM for video encoding. As in the previous mode, additional preprocessing of the video data by the VPU may also be
enabled.
Encoding Video
Buffers
Input Video
Buffers
OSD Buffers
SDRAM
Video Out
Video In
Figure 6:
VPU
VIU
VOU
OSD
Text/
Graphics
Video Encoding - Advanced Mode
Video Decoding
Figure 7 shows the flow of data in the VIO unit during video decoding. At minimum, decoded video data are transferred from
the SDRAM to the VOU for chroma upconversion and other postprocessing. The output of the VOU is passed to the OSD unit
where it can be mixed with text or graphics before it is transferred to the video output. Optionally, the VPU may also be
enabled to process the decoded data before they are being transferred to the VOU.
.
VPU
VIU
Decoded Video
Buffers
Display Video
Buffers
Preliminary Information - Confidential
VOU
Video Out
Figure 7:
OSD
Text/
Graphics
Video Decoding
OSD Buffers
SDRAM
The Audio Interface Unit (AIU)
The audio interface unit provides the interface between the CS92288 and external audio devices. Audio samples are transferred in and out of the CS92288 using I
audio A/D and D/As.
2
S signaling. The CS92288 also provides a user-configurable output clock for external
38
Page 41

CS92288 MPEG-2 AUDIO/VIDEO CODEC DATA BOOK
The RISC Microcontroller
This is an embedded, programmable,32-bit ARC RISC processor. It performs multiplexing and demultiplexing of MPEG program streams and acts as a central sequencer. Its microcode can be downloaded either from an external host, from external data
Flash, or from an external EEPROM, through the Host Interface Unit.
The Video Engine Unit (VEU)
This is the core video processor for the CS92288. During encoding, it operates on the video data and generates an MPEG-compliant video elementary stream. It includes several dedicated processing units, such as the motion estimation and refinement
units. Among its many functions, it performs motion estimation and compensation, DCT, quantization, rate control, and variable length coding. During decoding, it operates on a video elementary stream and generates decompressed video frames. It
performs, variable length decoding, IDCT, and motion compensation. The IDCT output is fully compliant with the IEEE-1800
accuracy requirements.
The Audio Engine
The Audio Engine provides the core processing power for all audio-related functions. It consists of an embedded, 24-bit, general purpose, and programmable digital signal processor (DSP). The DSP operates from its own embedded program and data
memories for the most efficient processing of audio data.
The Host Interface Unit
The CS92288 host interface is used for communication with the host controller and external EPROMS or flash memory. It is
designed to support a variety of communication protocols. The host interface has a glue-less interface to USB controllers and
it may also be used in PC-based host systems using a PCI bridge interface, such as the Philips 7146.
The SDRAM Control Unit (DCU)
The SDRAM control unit (DCU) provides a 64-bit interface from all functional units to the off-chip memory (SDRAM) storage.
It is designed to sustain real-time audio and video encoding and decoding at 30 frames per second.
Related Documentation
Additional information about the CS92288 can be found in:
• The “CS92288 Programming Guide”
• “CS92288 JTAG Operation and Programming Guide”
Preliminary Information - Confidential
• “CS92288 - Data Book Addendum”
available from Cirrus Logic.
39
Page 42

CS92288 MPEG-2 AUDIO/VIDEO CODEC DATA BOOK
Signal Descriptions
This section groups the signals according to the bus interface type. The convention for active-low signals is to apply an overscore to the signal name, e.g., active-low SIGNAL and active-high SIGNAL. Pin Types are defined as: I/O = Input and output; I =
Input only; O = Output only; Ts = Tri-State.
Table 1: Host Interface
Pin Name Type Pin Number Description
HAD[15:0] I/O, Ts J1,J3,H2,H1,H3,G2,G1,G3,
F2,F1,F3,E2,E1,D2,E3,D3
HA[7:0] I L3,M1,L2,L1,K3,K1,K2,J2 8-bit Address Bus
INTX16 I R3 Bus Width Select. 0 = 8-bit bus; 1 = 16-bit bus
INTL_MOT I T2 Interface Select. 0 = Motorola interface; 1 = Intel interface
AS_ALE
DMA_REQ O N1 DMA Request. Active-low or active-high is configurable. Default =
DMA_ACK
DTACK
HSEL
RWN_SBHE
LDS_RDN I P3 Lower Data Strobe (Motorola); Read not (Intel). Both are low
UDS_WRN
HIU_INT
SYS_RDY O T1 System Ready signal, high assertive
GPIO[5:0] I/O Y3,W3,Y2,Y1,V1,T3 6-bit General purpose I/O. Function is configurable by software.
FLASH_SEL I U1 Flash memory indicator. If FLASH_SEL=1, then Flash memory is
ROM_SEL I U2 EPROM indicator. If ROM_SEL=1, read firmware from bootram
ROMDATA_EN
SER_OUT O V2 If FLASH_SEL=1, serial output to data.
SCL I/O B9 Serial clock, normally configured as input
SDA I/O C9 Serial data bus, normally configured as input
_RDY O N3 Data Transfer Acknowledge - Low assertive(Motorola); Data
I M2 Address Strobe (Motorola); Address Latch Enable (Intel) (Pull-up
I N2 DMA Acknowledge, low assertive. Pull-up resistor is provided.
I P1 Host Select, low assertive (Internal Resistor Pull-ups)
I P2 Read Write not (Motorola); System Byte High Enable (Intel). Both
I R1 Upper Data Strobe (Motorola); Write not (Intel). Both are low
O R2 Host Interrupt, low assertive. Level triggered
O W1 If ROM_SEL=1, then chip enable for EPROM; active low.
16-bit Host Multiplexed Address/data (Pull-up Resistor Provided)
Resistor Provided). Both are low assertive
active-high
Ready - High assertvie (Intel).
are low assertive
assertive
assertive
GPIO[0] is shared with the AM_WS signal of the audio interface
present.
EPROM
Preliminary Information - Confidential
Table 2: Video Interface
Pin Name Type Pin Number Description
YIN[7:0] I B15,C15,A15,A16,B16,A17,
C16,B17
YOUT[7:0] O, Ts B12,A12,C13,B13,A13,A14,
C14,B14
CLK27_DEM I C12 2x Input NTSC/PAL Decoder (Demodulator) Pixel-Clock (27MHz)
CLK27_MOD I B4 2x Input NTSC/PAL Encoder (Modulator) Pixel-Clock (27MHz)
HREF_DEM I A11 Horizontal Input Reference for ITU-R BT.601. High assertive
8-bit Input video data
8-bit Output video data. Can be set into tristate mode by microcode
40
Page 43

CS92288 MPEG-2 AUDIO/VIDEO CODEC DATA BOOK
Table 2: Video Interface
HREF_MOD I/O B11 Horizontal Output Reference for ITU-R BT.601. Input in Slave
mode; output in Master mode. High assertive
VSYNC_DEM I A10 Vertical Input Sync for ITU-R BT.601. Low assertive
VSYNC_MOD
DREADY_DEM I B10 Data Ready signal, high assertive. Input in encode mode with field
DREADY_MOD O A9 Data Ready signal, high assertive. Output in decode mode with
_DEC O C10 Mode Select. 0 = Encode; 1 = Decode
ENC
I/O C11 Vertical Output Sync for ITU-R BT.601. Input in Slave mode; output
in Master mode. Low assertive
sync. Pull high with external resistor.
vertical sync; Pull high with external resistor.
Table 3: Audio Interface
Pin Name Type Pin Number Description
WS_IN_ENC I C8 Input word select; value may be controlled by firmware. Defaults:
WS_IN_ENC=0: Channel 1 (left), WS_IN_ENC=1: Channel 2 (right)
SD_IN_ENC I A7 Serial input audio data; used for audio encoding only
BCK_IN_ENC I B8 Serial data input bit clock for audio encoding
BCK_IN_DEC I A8 DAC input bit clock for audio data; used only for audio decoding in slave
mode
BCK_OUT O B7 Serial data output bit clock; for decoding or loop-back during encoding
SD_OUT O A6 Serial output audio data; for decoding or loop-back during encoding
WS_OUT O C7 Output word select; value may be controlled by firmware. Defaults:
WS_OUT=0: Channel 1 (left), WS_OUT=1: Channel 2 (right); for decoding
or loop-back during encoding
AM_BCK O B3 Output Master bit clock from internal PLL for external audio A/D and D/A
converters
AM_WS O T3 Output Master word select for slaves ADCs. This pin is shared with GPIO[0]
AM_SCLK O A3 Output Master system audio clock from internal PLL for external audio A/D
and D/A converters.
Table 4: Memory Interface
Preliminary Information - Confidential
Pin Name Type Pin Number Function
MD[63:0] I/O V4,W4,V5,Y4,W5,Y5,W6,Y6,V7,W7,Y7,V8,W8,Y8,V9,W9,
Y9,V10,W10,Y10,V11,W11,Y11,W12,Y12,W13,Y13,V13,
W14,Y14,V14,W15,P19,P20,N19,M19,N20,M20,L19,L20,
K19,K20,J18,J19,J20,H19,H20,H18,G19,G20,G18,F19,
F18,C19,D18,B20,W17,V17,Y18,W18,Y19,Y20,V19,T18
MA[11:0] O U18,W20,U19,V20,R18,T19,U20,P18,T20,N18,R19,R20 12-bit SDRAM Address bus
DQMU O Y15 SDRAM Upper Byte I/O Mask
DQML O V15 SDRAM Lower Byte I/O Mask
WE
CS
RAS
CAS
CLKOUT[1:0] O A19,C17 SDRAM output Clocks (108MHz)
O V16 SDRAM Write Enable, low assertive
O Y16 SDRAM Chip Select, low assertive
O W16 SDRAM RAS, low assertive
O Y17 SDRAM CAS, low assertive
64-bit SDRAM Data bus (Pull-up
Resistor Provided)
41
Page 44

CS92288 MPEG-2 AUDIO/VIDEO CODEC DATA BOOK
Table 5: Global Interface
Pin Name Type Pin Number Function
SYSCLK I C4 System Clock (27 MHz)
HARD_RESET
PLL_RESET I E19 PLL Reset, low assertive. Pull high for normal
APLL_RESET
CS_IN
VDD +1.8V D9,D10,D13,G4,G17,H17,K4,L4,N17,U6,U10,
VDDD +3.3V D6,D7,D11,D14,F4,J4,J17,K17,M4,M17,P4,P17,
VSS GND D4,D17,J9-J12,K9-K12,L9-L12,M9-M12,U4,U17 VDD ground
VSSD GND B2,B19,C3,C18,D5,D8,D12,D15,D16,E4,E17,
PLL_VDD +1.8V F20 1.8V Video PLL power supply
PLL_VDDA +1.8V D20 1.8V Analog video PLL power supply
PLL_VSSA GND C20 Analog video PLL ground
PLL_VSS GND E20 Video PLL ground
APLL_VDD +1.8V D1 1.8V Audio PLL power supply
APLL_VDDA +1.8V B1 1.8V Analog Audio PLL power supply
APLL_VSSA GND A2 Analog Audio PLL ground
APLL_VSS GND C2 Audio PLL ground
TCK I B6 JTAG Input Clock
TDI I C6 JTAG Input Data
TMS I B5 JTAG Control Input
TDO O A5 JTAG Output Data
TEST_MODE I A20 For chip test only; ground for normal operation
GLOBAL_PD I E18 For chip test only; ground for normal operation
SE I A18 For chip test only; ground for normal operation
PLL_BP I A1 For chip test only; ground for normal operation
BIDI_IN I D19 Forces all bidirectional drivers to input-only
MBIST_EN I B18 For chip test only; ground for normal operation
ND_TREE O A4 For board test only; floating for normal operation
I U3 Chip Reset, low assertive (Pull-up Resistor
Provided)
operation.
I C1 Audio PLL Reset, low assertive. Pull high for
normal operation.
I C5 Chip Select Input, low assertive. When set to
high, it tristates all output and bidirectional
drivers. Set to low for normal operation
1.8V core power supply
U11,V6
3.3V I/O power supply
R4,R17,U7,U8,U12,U14,U15,V12
VDDD ground
F17,H4,K18,L17,L18,M3,M18,N4,T4,T17,U5,
U9,U13,U16,V3,V18,W2,W19
mode. For chip test only; ground for normal
operation
Preliminary Information - Confidential
42
Page 45

System Interfaces
CS92288 MPEG-2 AUDIO/VIDEO CODEC DATA BOOK
The system interfaces consists of Host, Video, Audio, Memory, and Global interfaces; their definitions are detailed as follows
Host Interface
The Host Interface Unit (HIU) port of the CS92288 provides an interface between the CS92288 on-chip CPU and components
of an off-chip host system, such as boot ROM, Flash memory, or a host microcontroller. One of the main functions of the HIU
module is to provide a communication link between a host and the CS92288 core modules so that encoding and decoding
parameters can be properly set. Specifically, the HIU relays requests from the CS92288 on-chip CPU to the off-chip host system, and vice versa. Such requests include starting, loading of control parameters, stopping, loading of microcode, user status
query and so forth.
The other function of the HIU is to serve as an interface for compressed bitstreams. During encoding, compressed audio/video bitstreams (Program Stream or Elementary Audio and Video Streams) output from the HIU to an application- specific host system.
During decoding, compressed bit streams input from a host system to the CS92288 SDRAM via HIU.
CS92288 External Pins and Interfaces
Figures 8-10 shows typical connections of the CS92288 with external hosts.
Host Interface Signal Descriptions
HAD[15:0]
pull-up resistors are provided. In 8-bit demultiplexed mode, the higher 8 bits are used as data and the lower 8 bits are used as
address (see Figure 10).
HA[7:0]
are bidirectional multiplexed address/data pins. 8-bit or 16-bit operation is selectable by signal INTX16. Internal
is an 8-bit input address bus. It is used in demultiplexed or 8-bit mode.
:
INTX16
INTL_MOT
AS_ALE
For Motorola mode (when INTL_MOT
phase is presented. An internal pull-up resistor is provided.
DMA_REQ
transfer. This pin can be configured as active-high (default upon power up) or active-low.
is an input pin defining the data bus width, 16-bit (set HIGH) and 8-bit (set LOW).
is an input pin which can be selected in either Intel/ISA mode (set HIGH) or Motorola-68K mode (set LOW).
is a dual-purpose input pin. For Intel mode (when INTL_MOT
=0), it is an active-low Address Strobe. This signal toggles only when a new address
is an active-high output signal which can be asserted by CS92288 to an external processor to request an operand
=1), it is an active-low Address Latch Enable signal.
Preliminary Information - Confidential
DMA_ACK
response to a previous transfer request. An internal pull-up resistor is provided.
DTACK
Motorola mode (when INTL_MOT
HSEL
RWN_SBHE
signal. For Motorola mode (when INTL_MOT
LDS_RDN
mode (when INTL_MOT
UDS_WRN
mode (when INTL_MOT
, an active-low input signal, is asserted by an external processor to indicate an operand being transferred in
is a dual-purpose output pin. For Intel mode (when INTL_MOT
_RDY
=0), it is an active-low Data Transfer Acknowledge.
is an active-low Chip-Select input pin, set LOW for normal operation. An internal pull-up resistor is provided.
is a dual-purpose input pin. For Intel mode (when INTL_MOT=1), it is an active-low System Byte High Enable
=0), it is an active-low Read/Write-not signal.
is a dual-purpose input pin. For Intel mode (when INTL_MOT=1), it is an active-low Read signal. For Motorola
=0), it is an active-low Lower Data Strobe.
is a dual-purpose input pin; for Intel mode (when INTL_MOT=1), it is an active-low Write signal. For Motorola
=0), it is an active-low Upper Data Strobe.
=1), it is an active-high Ready signal. For
HIU_INT
interrupt. This pin is nonmaskable.
is an active-low level-triggered output pin which can be asserted by CS92288 to an external processor to request an
43
Page 46

CS92288 MPEG-2 AUDIO/VIDEO CODEC DATA BOOK
SYS_RDY
is an active-high output System Ready signal to indicate HIU power-up properly and is ready for software down-
load.
GPIO[5:0]
is an 6-bit bidirectional bus for general purpose I/O. After reset, these pins are configured as input only. After-
wards, their function is programmable by microcode.
FLASH_SEL
ROM_SEL
is an input pin which when set to high (FLASH_SEL=1) indicates the presense of Flash memory.
is an input pin which when set to high (ROM_SEL=1) indicates the presence of an EPROM for downloading firm-
ware.
ROMDATA_EN
SER_OUT
is a bidirectional clock pin. When active, a clock is outputted from this pin. When inactive, it is configured as an input
SCL
is an active-low output pin. When ROM_SEL=1, this pin is being used as a chip select for the boot EPROM.
is an output serial signal bus for Flash memory (used when FLASH_SEL=1).
pin to allow other activities on this pin. This pin is used for the EPROM and Data Flash interface.
is a bidirectional serial data pin. This pin outputs for write mode and inputs for read mode. When inactive, it is configured
SDA
as an input pin to allow other activities on this pin. This pin is used for the EPROM and Data Flash interface.
.
HIU Interface Signals for Intel Mode
(with no Flash or EPROM present)
CS92288 Host I/F Intel-like Processor
HAD[15:0]
HA[7:0]
AD[15:0]
HIU Interface Signals for Motorola Mode
(with no Flash or EPROM present)
CS92288 Host I/F
HAD[15:0]
HA[7:0]
Motorola-like Processor
AD[15:0]
Preliminary Information - Confidential
AS_ALE
DMA_ACK
DMA_REQ
DTACK
_RDY
HIU_INT
HSEL
LDS_RDN
RWN_SBHE
UDS_WRN
HARD_RESET
GPIO[5:0]
INTX16
INTL_MOT
SYS_RDY
SER_OUT
ROMDATA_EN
FLASH_SEL
ROM_SEL
ALE
DACK
DREQ
RDY
IRQ
CS
RD
SBHE
WR
RESET
NC
+3.3V/5V +3.3V/5V
+3.3V/5V
NC
NC
NC
Figure 8:
HIU Interface signals for 16-bit host processors
AS_ALE
DMA_ACK
DMA_REQ
_RDY
DTACK
HIU_INT
HSEL
LDS_RDN
RWN_SBHE
UDS_WRN
HARD_RESET
GPIO[5:0]
INTX16
INTL_MOT
SYS_RDY
SER_OUT
ROMDATA_EN
FLASH_SEL
ROM_SEL
NC
NC
NC
NC
AS
DACK
DREQ
DTACK
IRQ
CS
LDS
R/W
UDS
RESET
44
Page 47

CS92288 MPEG-2 AUDIO/VIDEO CODEC DATA BOOK
CS92288 Host I/F
HAD[15:8]
HAD[7:0]
HA[7:0]
AS_ALE
DMA_ACK
DMA_REQ
DTACK
_RDY
HIU_INT
HSEL
LDS_RDN
RWN_SBHE
UDS_WRN
HARD_RESET
GPIO[5:0]
INTX16
INTL_MOT
SYS_RDY
SER_OUT
ROMDATA_EN
FLASH_SEL
ROM_SEL
Figure 9:
Intel MCS51-like Processor
A/D[7:0]
A[15:8]
ALE
DACK
DREQ
NC
INT
CS
RD
NC
WR
RST
NC
+3.3V/5V
NC
NC
NC
CS92288 Host I/F Other 8-bit Processor
HAD[15:8]
HAD[7:0]
HA[7:0]
AS_ALE
DMA_ACK
DMA_REQ
DTACK_RDY
HIU_INT
HSEL
LDS_RDN
RWN_SBHE
UDS_WRN
HARD_RESET
GPIO[5:0]
INTX16
INTL_MOT
SYS_RDY
SER_OUT
ROMDATA_EN
FLASH_SEL
ROM_SEL
NC
NC
NC
NC
NC
NC
A/D[7:0]
A[15:8]
ALE
DACK
DREQ
IRQ
CS
RD
WR
RST
HIU Interface Signals for 8-bit Hosts with multiplexed address and data buses
Preliminary Information - Confidential
Figure 10:
CS92288 Host I/F
HAD[15:8]
HAD[7:0]
HA[7:0]
AS_ALE
DMA_ACK
DMA_REQ
DTACK_RDY
HIU_INT
HSEL
LDS_RDN
RWN_SBHE
UDS_WRN
HARD_RESET
GPIO[5:0]
INTX16
INTL_MOT
NC
NC
NC
8-bit Host
DATA[7:0]
ADDR[7:0]
ADDR[15:8]
ALE
DACK
DREQ
IRQ
CS
RD
WR
RST
HIU Interface Signals for 8-bit Hosts with separate address and data buses
45
Page 48

KRETON VT3617161 Jan., 1999
Description
The VT3617161 is CMOS Synchronous Dynamic RAM organized as 524,288-word X 16-bit X 2-bank. It
is fabricated with an advanced submicron CMOS technology and designed to operate from a single 3.3V
power supply. This SDRAM is delicately designed with perfor m ance concern for current high-speed application. Programmable CAS Latency and Burst Length make it possible to be used in widely various domains. It
is packaged by using JEDEC standard pinouts and standard plastic 50-pin TSOP II.
Features
• Single 3.3V +/- 0.3V power supply
• Clock Frequency: 166MHz, 143MHz, 125MHz, 100MHz
• Fully synchronous with all signals referenced to a positive clock edge
• Programmable CAS
• Programmable burst length (1,2,4,8,& Full page)
• Programmable wrap sequence (Sequential/Interleave)
• Automatic precharge and controlled precharge
• Auto refresh and self refresh modes
• Dual internal banks controlled by A11(Bank select)
• Simultaneous and independent two bank operation
• I/O level : LVTTL interface
• Random column access in every cycle
• X16 organization
• Byte control by LDQM and UDQM
• 2048 refresh cycles/32ms
• Burst termination by burst stop and precharge command
Iatency (2,3)
46
Page 49

KRETON VT3617161 Jan., 1999
Pin Configuration
50-Pin Plastic TSOP(II)(400 mil)
V
V
V
V
LDQM
(BS)A
V
DQ0
DQ1
SSQ
DQ2
DQ3
DDQ
DQ4
DQ5
SSQ
DQ6
DQ7
DDQ
WE
CAS
RAS
CS
A
V
DD
11
A
A
A
DD
V
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
10
0
A
1
2
3
20
21
22
23
24
25
VT3617161
50
49
48
47
46
45
44
43
42
41
40
39
38
37
36
35
34
33
32
31
30
29
28
27
26
SS
DQ15
DQ14
V
SSQ
DQ13
DQ12
V
DDQ
DQ11
DQ10
V
SSQ
DQ9
DQ8
V
DDQ
NC
UDQM
CLK
CKE
NC
A9
A8
A7
A6
A5
A4
V
SS
Pin Description
(VT3617161)
Pin Name Function Pin Name Function
A0-A11 Address inputs
- Row address A0-A10
LDQM,
UDQM
Lower DQ mask enable and
Upper DQ mark enable
- Column address A0-A8
A11: Bank select
DQ0~DQ15 Data-in/data-out CLK Clock input
RAS
CAS
WE
V
SS
V
DD
Row address strobe CKE Clock enable
Column address strobe CS Chip select
Write enable V
Ground V
DDQ
SSQ
Supply voltage for DQ
Ground for DQ
Power
47
Page 50

KRETON VT3617161 Jan., 1999
Block Diagram
CLK
CKE
Address
CS
RAS
CAS
WE
Clock
Gene rator
Command Decoder
Mode
Register
Control Logic
Row
Address
Buffer
&
Refresh
Counter
Column
Address
Buffer
&
Bu rst
Counter
Bank B
Bank A
Row D ecoder
Sense Am plifier
Column Decoder &
Latch Circuit
Data Control Circuit DQ
Latch Circuit
DQM
Buffer
Input & Output
48
Page 51

KRETON VT3617161 Jan., 1999
Absolute Maximum Ratings
Parameter Symbol Value Unit
Voltage on any pin relative to Vss V
Supply voltage relative to Vss V
Short circuit output current I
Power dissipation P
Operating temperature T
Storage temperature T
Recommended DC Operating Conditions
Parameter Symbol Min Typ Max U nit Note
Supply Voltage V
Input High Voltage, all inputs V
Input Low Voltage, all inputs V
Note 1.Overshoot limit : V
2.Undershoot lim it : V
IH(MAX.)=VDDQ
IL=VSSQ
-2.0V with a pulse < 3ns and -1.5V with a pulse < 5ns
DD
IH
IL
+2.0V with a pulse width < 3ns
3.0 3.3 3.6 V
2.0
-0.3
IN,VOUT
DD,VDDQ
OUT
D
OPT
STG
-1.0 to +4.6 V
-1.0 to +4.6 V
50 mA
1.0 W
0 to + 70
-55 to + 125
VDD+0.3 V 1
0.8 V 2
Capacitance
(Ta=25°C,f=1MHZ)
Parameter Symbol Typ Max Unit
Input capacitance(CLK) C
Input capacitance(all input pins except data
pins)
Data input/output capacitance C
11
C
12
I/O
2.5 4 pF
2.5 5 pF
4.0 6.5 pF
49
Page 52

Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
PAL/NTSC/SECAM video decoder with adaptive PAL/NTSC
comb filter, VBI-data slicer and high performance scaler
CONTENTS
1 FEATURES
1.1 Video decoder
1.2 Video scaler
1.3 Vertical Blanking Interval (VBI) data decoder
and slicer
1.4 Audio clock generation
1.5 Digital I/O interfaces
1.6 Miscellaneous
2 APPLICATIONS
3 GENERAL DESCRIPTION
4 QUICK REFERENCE DATA
5 ORDERING INFORMATION
6 BLOCK DIAGRAM
7 PINNING
8 FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION
8.1 Decoder
8.2 Decoder output formatter
8.3 Scaler
8.4 VBI-data decoder and capture
(subaddresses 40H to 7FH)
8.5 Image port output formatter
(subaddresses 84H to 87H)
8.6 Audio clock generation
(subaddresses 30H to 3FH)
9 INPUT/OUTPUT INTERFACES AND PORTS
9.1 Analog terminals
9.2 Audio clock signals
9.3 Clock and real-time synchronization signals
9.4 Video expansion port (X-port)
9.5 Image port (I-port)
9.6 Host port for 16-bit extension of video data I/O
(H-port)
9.7 Basic input and output timing diagrams I-port
and X-port
10 BOUNDARY SCAN TEST
10.1 Initialization of boundary scan circuit
10.2 Device identification codes
11 LIMITING VALUES
12 THERMAL CHARACTERISTICS
13 CHARACTERISTICS
14 APPLICATION INFORMATION
15 I2C-BUS DESCRIPTION
15.1 I2C-bus format
15.2 I2C-bus details
15.3 Programming register audio clock generation
15.4 Programming register VBI-data slicer
15.5 Programming register interfaces and scaler
part
16 PROGRAMMING START SET-UP
16.1 Decoder part
16.2 Audio clock generation part
16.3 Data slicer and data type control part
16.4 Scaler and interfaces
17 PACKAGE OUTLINE
18 SOLDERING
18.1 Introduction to soldering surface mount
packages
18.2 Reflow soldering
18.3 Wave soldering
18.4 Manual soldering
18.5 Suitability of surface mount IC packages for
wave and reflow soldering methods
19 DEFINITIONS
20 LIFE SUPPORT APPLICATIONS
21 PURCHASE OF PHILIPS I2C COMPONENTS
SAA7114H
50
Page 53

Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
PAL/NTSC/SECAM video decoder with adaptive PAL/NTSC
comb filter, VBI-data slicer and high performance scaler
1 FEATURES
1.1 Video decoder
• Six analog inputs, internal analog source selectors, e.g.
6 × CVBS or (2 × Y/C and 2 × CVBS) or (1 × Y/C and
4 × CVBS)
• Two analog preprocessing channels in differential
CMOS style inclusive built-in analog anti-alias filters
• Fully programmable static gain or Automatic Gain
Control (AGC) for the selected CVBS or Y/C channel
• Automatic Clamp Control (ACC) for CVBS, Y and C
• Switchable white peak control
• Two 9-bit video CMOS Analog-to-Digital Converters
(ADCs), digitized CVBS or Y/C signals are available on
the expansion port
• On-chip line-locked clock generation according
“ITU 601”
• Digital PLL for synchronization and clock generation
from all standards and non-standard video sources e.g.
consumer grade VTR
• Requires only one crystal (32.11 or 24.576 MHz) for all
standards
• Horizontal and vertical sync detection
• Automatic detection of 50 and 60 Hz field frequency,
and automatic switching between PAL and NTSC
standards
• Luminance and chrominance signal processing for
PAL BGDHIN, combination PAL N, PAL M, NTSC M,
NTSC-Japan, NTSC 4.43 and SECAM
• Adaptive 2/4-line comb filter for two dimensional
chrominance/luminance separation
– Increasedluminanceand chrominance bandwidthfor
all PAL and NTSC standards
– Reduced cross colour and cross luminance artefacts
• PAL delay line for correcting PAL phase errors
• Independent Brightness Contrast Saturation (BCS)
adjustment for decoder part
• User programmable sharpness control
• Independent gain and offset adjustment for raw data
path.
1.2 Video scaler
• Horizontal and vertical down-scaling and up-scaling to
randomly sized windows
• Horizontal and vertical scaling range: variable zoom to
1
⁄64(icon); it should be noted that the H and V zoom are
restricted by the transfer data rates
• Anti-alias and accumulating filter for horizontal scaling
• Vertical scaling with linear phase interpolation and
accumulating filter for anti-aliasing (6-bit phase
accuracy)
• Horizontal phase correct up and down scaling for
improved signal quality of scaled data, especially for
compression and video phone applications, with 6-bit
phase accuracy (1.2 ns step width)
• Two independent programming sets for scaler part, to
define two ‘ranges’ per field or sequences over frames
• Fieldwise switching between decoder part and
expansion port (X-port) input
• Brightness, contrast and saturation controls for scaled
outputs.
1.3 Vertical Blanking Interval (VBI) data decoder
and slicer
• Versatile VBI-data decoder, slicer, clock regeneration
and byte synchronization e.g. for World Standard
Teletext (WST), North-American Broadcast Text
System(NABTS), closecaption,Wide ScreenSignalling
(WSS) etc.
1.4 Audio clock generation
• Generation of a field locked audio master clock to
support a constant number of audio clocks per video
field
• Generation of an audio serial and left/right (channel)
clock signal.
SAA7114H
51
Page 54

Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
PAL/NTSC/SECAM video decoder with adaptive PAL/NTSC
comb filter, VBI-data slicer and high performance scaler
1.5 Digital I/O interfaces
• Real-time signal port (R port), inclusive continuous
line-locked reference clock and real-time status
information supporting RTC level 3.1 (refer to external
document
• Bi-directional expansion port (X-port) with half duplex
functionality (D1), 8-bit YUV
– Output from decoder part, real-time and unscaled
– Input to scaler part, e.g. video from MPEG decoder
(extension to 16-bit possible)
• Video image port (I-port) configurable for 8-bit data
(extension to 16-bit possible) in master mode (own
clock), or slave mode (external clock), with auxiliary
timing and hand shake signals
• Discontinuous data streams supported
• 32-word × 4-byte FIFO register for video output data
• 28-word × 4-byte FIFO register for decoded VBI output
data
• Scaled 4:2:2, 4:1:1, 4:2:0, 4:1:0 YUV output
• Scaled 8-bit luminance only and raw CVBS data output
• Sliced, decoded VBI-data output.
1.6 Miscellaneous
“RTC Functional Specification”
for details)
3 GENERAL DESCRIPTION
The SAA7114H is a video capture device for applications
at the image port of VGA controllers.
The SAA7114H is a combination of a two-channel analog
preprocessing circuit including source selection,
anti-aliasing filter and ADC, an automatic clamp and gain
control, a Clock Generation Circuit (CGC), a digital
multi-standard decoder containing two-dimensional
chrominance/luminance separation by an adaptive comb
filter and a high performance scaler, including variable
horizontal and vertical up and down scaling and a
brightness, contrast and saturation control circuit.
It is a highly integrated circuit for desktop video
applications. The decoder is based on the principle of
line-lockedclockdecoding andisable todecodethe colour
of PAL, SECAM and NTSC signals into ITU 601
compatible colour component values. The SAA7114H
accepts as analog inputs CVBS or S-video (Y/C) from
TV or VCR sources, including weak and distorted signals.
An expansion port (X-port) for digital video (bi-directional
halfduplex,D1compatible) is also supportedtoconnectto
MPEG or video phone codec. At the so called image port
(I-port) the SAA7114H supports 8 or 16-bit wide output
data with auxiliary reference data for interfacing to VGA
controllers.
SAA7114H
• Power-on control
• 5 V tolerant digital inputs and I/O ports
• Software controlled power saving standby modes
supported
• Programming via serial I2C-bus, full read-back ability by
an external controller, bit rate up to 400 kbits/s
• Boundary scan test circuit complies with the
1149.b1 - 1994”
2 APPLICATIONS
• Desktop video
• Multimedia
• Digital television
• Image processing
• Video phone applications.
.
“IEEE Std.
The target application for SAA7114H is to capture and
scale video images, to be provided as digital video stream
through the image port of a VGA controller, for display via
VGA’s frame buffer, or for capture to system memory.
In parallel SAA7114H incorporates also provisions for
capturing the serially coded data in the vertical blanking
interval (VBI-data). Two principal functions are available:
1. To capture raw video samples, after interpolation to
the required output data rate, via the scaler
2. A versatile data slicer (data recovery) unit.
SAA7114H incorporates also a field locked audio clock
generation. This function ensures that there is always the
same number of audio samples associated with a field, or
a set of fields. This prevents the loss of synchronization
between video and audio, during capture or playback.
The circuit is I2C-bus controlled (full write/read capability
for all programming registers, bit rate up to 400 kbits/s).
52
Page 55

53.
Page 56

Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
PAL/NTSC/SECAM video decoder with adaptive PAL/NTSC
SAA7114H
comb filter, VBI-data slicer and high performance scaler
7 PINNING
SYMBOL PIN TYPE DESCRIPTION
V
DDD(EP1)
TDO 2 O test data output for boundary scan test; note 1
TDI 3 I test data input for boundary scan test; note 1
XTOUT 4 O crystal oscillator output signal; auxiliary signal
V
SS(XTAL)
XTALO 6 O 24.576 MHz (32.11 MHz) crystal oscillator output; not connected if TTL clock
XTALI 7 I input terminal for 24.576 MHz (32.11 MHz) crystal oscillator or connection of
V
DD(XTAL)
V
SSA2
AI24 10 I analog input 24
V
DDA2
AI23 12 I analog input 23
AI2D 13 I differential input for ADC channel 2 (pins AI24, AI23, AI22 and AI21)
AI22 14 I analog input 22
V
SSA1
AI21 16 I analog input 21
V
DDA1
AI12 18 I analog input 12
AI1D 19 I differential input for ADC channel 1 (pins AI12 and AI11)
AI11 20 I analog input 11
AGND 21 P analog ground connection
AOUT 22 O do not connect; analog test output
V
DDA0
V
SSA0
V
DDD(EP2)
V
SSD(EP1)
CE 27 I chip enable or reset input (with internal pull-up)
LLC 28 O line-locked system clock output (27 MHz nominal)
LLC2 29 O line-locked
RES 30 O reset output (active LOW)
SCL 31 I(/O) serial clock input (I
SDA 32 I/O serial data input/output (I
V
DDD(ICO1)
RTS0 34 O real-time status or sync information, controlled by subaddresses 11H and 12H;
RTS1 35 O
1 P external digital pad supply voltage 1 (+3.3 V)
5 P ground for crystal oscillator
input of XTALI is used
external oscillator with TTL compatible square wave clock signal
8 P supply voltage for crystal oscillator
9 P ground for analog inputs AI2n
11 P analog supply voltage for analog inputs AI2n (+3.3 V)
15 P ground for analog inputs AI1n
17 P analog supply voltage for analog inputs AI1n (+3.3 V)
23 P analog supply voltage (+3.3 V) for internal Clock Generation Circuit (CGC)
24 P ground for internal clock generation circuit
25 P external digital pad supply voltage 2 (+3.3 V)
26 P external digital pad supply ground 1
1
⁄2clock output (13.5 MHz nominal)
2
C-bus) with inactive output path
2
C-bus)
33 P internal digital core supply voltage 1 (+3.3 V)
see Section 15.2.18, 15.2.19 and 15.2.20
54
Page 57

Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
PAL/NTSC/SECAM video decoder with adaptive PAL/NTSC
SAA7114H
comb filter, VBI-data slicer and high performance scaler
SYMBOL PIN TYPE DESCRIPTION
RTCO 36 (I/)O real-time control output; contains information about actual system clock
frequency, field rate, odd/even sequence, decoder status, subcarrier frequency
and phase and PAL sequence (see external document
Description”
, available on request); the RTCO pin is enabled via I2C-bus
bit RTCE; see notes 2, 3 and Table 34
AMCLK 37 O audio master clock output, up to 50% of crystal clock
V
SSD(ICO1)
38 P internal digital core supply ground 1
ASCLK 39 O audio serial clock output
ALRCLK 40 (I/)O audio left/right clock output; can be strapped to supply via a 3.3 kΩ resistor to
indicate that the default 24.576 MHz crystal (ALRCLK = 0; internal pull-down)
has been replaced by a 32.110 MHz crystal (ALRCLK = 1); see notes 2 and 4
AMXCLK 41 I audio master external clock input
ITRDY 42 I target ready input, image port (with internal pull-up)
V
DDD(ICO2)
43 P internal digital core supply voltage 2 (+3.3 V)
TEST0 44 O do not connect; reserved for future extensions and for testing: scan output
ICLK 45 I/O clock output signal for image port, or optional asynchronous back-end clock
input
IDQ 46 O output data qualifier for image port (optional: gated clock output)
ITRI 47 I(/O) image port output control signal, effects all input port pins inclusive ICLK, enable
and active polarity is under software control (bits IPE in subaddress 87H); output
path used for testing: scan output
IGP0 48 O general purpose output signal 0; image port (controlled by subaddresses
84H and 85H)
IGP1 49 O general purpose output signal 1; image port (controlled by subaddresses
84H and 85H)
V
SSD(EP2)
V
DDD(EP3)
50 P external digital pad supply ground 2
51 P external digital pad supply voltage 3 (+3.3 V)
IGPV 52 O multi purpose vertical reference output signal; image port (controlled by
subaddresses 84H and 85H)
IGPH 53 O multi purpose horizontal reference output signal; image port (controlled by
subaddresses 84H and 85H)
IPD7 to IPD4 54 to 57 O image port data outputs
V
DDD(ICO3)
58 P internal digital core supply voltage 3 (+3.3 V)
IPD3 to IPD0 59 to 62 O image port data output
V
SSD(ICO2)
63 P internal digital core supply ground 2
HPD7 to HPD4 64 to 67 I/O host port data I/O, carries UV chrominance information in 16-bit video I/O modes
V
DDD(ICO4)
68 P internal digital core supply voltage 4 (+3.3 V)
HPD3 to HPD0 69 to 72 I/O host port data I/O, carries UV chrominance information in 16-bit video I/O modes
TEST1 73 I do not connect; reserved for future extensions and for testing: scan input
TEST2 74 I do not connect; reserved for future extensions and for testing: scan input
V
DDD(EP4)
V
SSD(EP3)
75 P external digital pad supply voltage 4 (+3.3 V)
76 P external digital pad supply ground 3
TEST3 77 I do not connect; reserved for future extensions and for testing: scan input
“RTC Functional
55
Page 58

Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
PAL/NTSC/SECAM video decoder with adaptive PAL/NTSC
SAA7114H
comb filter, VBI-data slicer and high performance scaler
SYMBOL PIN TYPE DESCRIPTION
TEST4 78 O do not connect; reserved for future extensions and for testing: scan output
TEST5 79 I do not connect; reserved for future extensions and for testing: scan input
XTRI 80 I X-port output control signal, affects all X-port pins (XPD7 to XPD0, XRH, XRV,
XDQ and XCLK), enable and active polarity is under software control (bits XPE
in subaddress 83H)
XPD7 81 I/O expansion port data
XPD6 82 I/O expansion port data
V
DDD(ICO5)
XPD5 to XPD2 84 to 87 I/O expansion port data
V
SSD(ICO3)
XPD1 89 I/O expansion port data
XPD0 90 I/O expansion port data
XRV 91 I/O vertical reference I/O expansion port
XRH 92 I/O horizontal reference I/O expansion port
V
DDD(ICO6)
XCLK 94 I/O clock I/O expansion port
XDQ 95 I/O data qualifier I/O expansion port
XRDY 96 O task flag or ready signal from scaler, controlled by XRQT
TRST 97 I test reset input (active LOW), for boundary scan test (with internal pull-up);
TCK 98 I test clock for boundary scan test; note 1
TMS 99 I test mode select input for boundary scan test or scan test; note 1
V
SSD(EP4)
Notes
1. In accordance with the
pull-up transistor and TDO is a 3-state output pad.
2. Pin strapping is done by connecting the pin to supply via a 3.3 kΩ resistor. During the power-up reset sequence the
corresponding pins are switched to input mode to read the strapping level. For the default setting no strapping
resistor is necessary (internal pull-down).
3. Pin RTCO: operates as I2C-bus slave address pin; RTCO = 0 slave address 42H/43H (default); RTCO = 1 slave
address 40H/41H.
4. Pin ALRCLK: 0 = 24.576 MHz crystal (default); 1 = 32.110 MHz crystal.
5. For board design without boundary scan implementation connect the TRST pin to ground.
6. This pin provides easy initialization of the Boundary Scan Test (BST) circuit. TRST can be used to force the Test
Access Port (TAP) controller to the TEST_LOGIC_RESET state (normal operation) at once.
83 P internal digital core supply voltage 5 (+3.3 V)
88 P internal digital core supply ground 3
93 P internal digital core supply voltage 6 (+3.3 V)
notes 5 and 6
100 P external digital pad supply ground 4
“IEEE1149.1”
standard the pads TDI, TMS, TCK and TRST are input pads with an internal
56
Page 59

Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
PAL/NTSC/SECAM video decoder with adaptive PAL/NTSC
comb filter, VBI-data slicer and high performance scaler
handbook, full pagewidth
V
DDD(EP1)
XTOUT
V
SS(XTAL)
XTALO
XTALI
V
DD(XTAL)
V
V
V
V
AGND
AOUT
V
V
V
DDD(EP2)
TDO
TDI
SSA2
AI24
DDA2
AI23
AI2D
AI22
SSA1
AI21
DDA1
AI12
AI1D
AI11
DDA0
SSA0
SSD(EP4)
V
100
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
TRST
TMS
TCK
XRDY
99989796959493929190898887868584838281
XDQ
DDD(ICO6)
XCLK
V
XRH
XRV
XPD0
SAA7114H
XPD1
V
SSD(ICO3)
XPD2
XPD3
XPD4
DDD(ICO5)
XPD5
V
XPD6
XPD7
XTRI
80
TEST5
TEST4
78
79
SAA7114H
SSD(EP3)
TEST3
V
76
77
75
74
73
72
71
70
69
68
67
66
65
64
63
62
61
60
59
58
57
56
55
54
53
52
51
V
DDD(EP4)
TEST2
TEST1
HPD0
HPD1
HPD2
HPD3
V
DDD(ICO4)
HPD4
HPD5
HPD6
HPD7
V
SSD(ICO2)
IPD0
IPD1
IPD2
IPD3
V
DDD(ICO3)
IPD4
IPD5
IPD6
IPD7
IGPH
IGPV
V
DDD(EP3)
26
27
CE
SSD(EP1)
V
28
LLC
31323334353637383940414243444546474849
29
30
SCL
RES
LLC2
SDA
DDD(ICO1)
V
RTS0
RTS1
RTCO
AMCLK
SSD(ICO1)
V
ASCLK
ALRCLK
ITRDY
AMXCLK
TEST0
DDD(ICO2)
V
Fig.2 Pin configuration.
57
ICLK
IDQ
ITRI
IGP0
IGP1
50
SSD(EP2)
V
MHB529
Page 60

58
Page 61

59
Page 62

1. General description
The PCF8563 is a CMOS real time clock/calendar optimized for low power
consumption. A programmable clock output, interrupt output and voltage-low detector
are also provided. All address and data are transferred serially via a two-line
bidirectional I2C-bus. Maximum bus speed is 400 kbit/s. The built-in word address
register is incremented automatically after each written or read data byte.
2. Features
■ Provides year, month, day, weekday, hours, minutes and seconds based on
32.768 kHz quartz crystal
■ Century flag
■ Clock operating voltage: 1.8 to 5.5 V
■ Low backup current; typical 0.25 µA at VDD= 3.0 V and T
■ 400 kHz two-wire I2C-bus interface (at VDD= 1.8 to 5.5 V)
■ Programmable clock output for peripheral devices (32.768 kHz, 1024 Hz,
32 Hz and 1 Hz)
■ Alarm and timer functions
■ Integrated oscillator capacitor
■ Internal power-on reset
■ I2C-bus slave address: read A3H and write A2H
■ Open-drain interrupt pin.
PCF8563
Real time clock/calendar
=25°C
amb
3. Applications
■ Mobile telephones
■ Portable instruments
■ Fax machines
■ Battery powered products.
60
Page 63

Philips Semiconductors
Block diagram
PCF8563
Real time clock/calendar
CLKOUT
OSCI
OSCO
INT
V
SS
V
DD
SCL
SDA
Fig 1. Block diagram.
Pinning information
1
2
3
4
8
6
5
OSCILLATOR
32.768 kHz
VOLTAGE
DETECTOR
OSCILLATOR
MONITOR
I2C-BUS
INTERFACE
POR
PCF8563
DIVIDER
CONTROL
LOGIC
ADDRESS
REGISTER
7
CONTROL/STATUS 1
1 Hz
CONTROL/STATUS 2
SECONDS/VL
MINUTES
HOURS
DAYS
WEEKDAYS
MONTHS/CENTURY
YEARS
MINUTE ALARM
HOUR ALARM
DAY ALARM
WEEKDAY ALARM
CLKOUT CONTROL
TIMER CONTROL
TIMER
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
A
B
C
D
E
F
MGM662
Pinning
OSCI
INT
V
SS
1
2
PCF8563P
3
4
MCE403
V
8
DD
CLKOUTOSCO
7
SCL
6
SDA
5
OSCI
INT
V
SS
1
2
3
4
PCF8563T
MCE198
V
8
DD
CLKOUTOSCO
7
SCL
6
SDA
5
OSCI
INT
V
SS
1
2
PCF8563TS
3
4
MCE199
Fig 2. Pin configuration DIP8. Fig 3. Pin configuration SO8. Fig 4. Pin configuration TSSOP8.
V
8
DD
CLKOUTOSCO
7
SCL
6
SDA
5
61
Page 64

Philips Semiconductors
handbook, halfpage
OSCI
PCF8563
Real time clock/calendar
1
8
V
DD
Fig 5. Device diode protection diagram.
Pin description
Table 3: Pin description
Symbol Pin Description
OSCI 1 oscillator input
OSCO 2 oscillator output
INT 3 interrupt output (open-drain; active LOW)
V
SS
SDA 5 serial data input and output
SCL 6 serial clock input
CLKOUT 7 clock output, open-drain
V
DD
V
INT
SS
2
3
4
PCF8563
MGR886
OSCO
4 ground
8 positive supply voltage
7
6
5
CLKOUT
SCL
SDA
Functional description
The PCF8563 contains sixteen 8-bit registers with an auto-incrementing address
register, an on-chip 32.768 kHz oscillator with one integrated capacitor, a frequency
divider which provides the source clock for the Real Time Clock/calender (RTC), a
programmable clock output, a timer, an alarm, a voltage-low detector and a 400 kHz
I2C-bus interface.
All 16 registers are designed as addressable 8-bit parallel registers although not all
bits are implemented. The first two registers (memory address 00H and 01H) are
used as control and/or status registers. The memory addresses 02H through 08H are
used as counters for the clock function (seconds up to years counters). Address
locations 09H through 0CH contain alarm registers which define the conditions for an
alarm. Address 0DH controls the CLKOUT output frequency. 0EH and 0FH are the
timer control and timer registers, respectively.
The seconds, minutes, hours, days, weekdays, months, years as well as the minute
alarm, hour alarm, day alarm and weekday alarm registers are all coded in BCD
format.
When one of the RTC registers is read the contents of all counters are frozen.
Therefore, faulty reading of the clock/calendar during a carry condition is prevented.
62
Page 65

62
Page 66

64
Page 67

65
Page 68

1
C231
104
D3.3V
C232
104
C233
104
C234
104
C235
104
C236
104
47u/6.3V
EC212
D5V
+
C247
104
C248
104
C249
104
C251
104
CSTCW3386MX01-T
X201
1
BREAK
URST
BDO
DGND
D7
D3
D2
D4
D5
2526272829
O2
O3
O4
A2A3A4
171615141332311124
A4A8A1
A5
A3
D0
A15
33
353637
UAD0
UP2_7/UCS2
CS1FX
HA2
124
122
121
1 2
3 4
5 6
RA206
82X4
D1
O0
O1
A0
A1
D1
UAD2
UAD1
PDIAG
HA0
125
O7
A7
A8
A9
A10
A9
A11
A10D0A14
A9D4A8
UP2_4
UP2_3
UP2_2
DVCVDD
NC
NC
118
117
116
R215
4.7
A5V
C209
C210
R232
D6
O5
O6
A5
A6
A7
A6
A13
A12
3839404142
UP2_6/UCS1
UP2_5
CS3FX
DASP
120
119
7 8
D5V
24
8
U204
A290011UV-70
GND
VCC
WE
A15
CE
6
UA0
RD3
RD13
I/O14
GND
GND
GND
RA7
A0
UA1
RD12
106
RD3
RD14
I/O15
A9
RA8
A16
OE
10
73230
A3D7A2
A4
A1
495051
UA5
UA4
UA3
UA2
RD14
RD13
RD2
RD1
107
108
110
109
RD13
RD12
RD1
RD2
RD15
39
40
35
21
IC41C16256-35T
U202
15
RA9
A17
D5V
A[0..15]
47u/6.3V
EC202
R231
220
+
C207
104
53
DMVDD
54
UA16
55
UPSEN
56
UWR
57
URD
58
URST
59
RXD
TXD
UINT
1 3
A B
2
G
RA3
RA4
RA2
RA5
RA1
RA6
RA0
RA7
RA8
RA9
R212 15k
R213 22
7 8
D5V
1 2
3 4
5 6
RA207
33X4
RA[0..9]
R211
100K
RD[0..15]
I/O0
20
VCC
6
VCC
1
VCC
LCAS
DQM
BA1
BA0
CKE
CLK
RD7
RD8
RD6
RD9
RD5
RD10
RD4
RD11
220u/6.3V
EC203
C208
104
RD1
RD0
RD2
234
I/O1
I/O2
UCAS
WE
282713
29
I/O3
RAS
UP3_0
60
UP3_1
61
UP3_2
62
UINT
63
UP3_4
64
UP3_5
66
XTALI
67
XTALO
69
DQM
70
BA1
71
BA0
72
CKE
73
CLK
74
RA11
75
RA10
77
RA3
78
RA4
79
RA2
80
RA5
81
RA1
82
RA6
83
RA0
85
RA7
86
RA8
88
RA9
90
ROE
89
RAS
91
RWE
92
CASH/RWEH
93
CAS
95
RD7
96
RD8
97
RD6
98
RD9
99
RD5
100
RD10
102
RD4
103
RD11
104
IPLLVDD
+
R214
220
A5V
RD6
RD3
5
I/O4
OE
14
RD8
RD5
RD7
RD4
10
31323334363738
789
I/O5
I/O6
I/O7
I/O8
I/O9
A0A1A2A3A4A5A6A7A8
161718192223242526
RA0
RA2
RA1
RD9
I/O10
RA3
RD10
RD11
I/O11
RA5
RA4
RD12
I/O12
RA6
I/O13
A14
5
11
A15
A6
A5
45
464748
UA6
RD0
112
111
RD14
RD0
A13
A13D6A14
A7
44
UA7
RD15
113
RD15
D5V
A12
NC
A11
A11
A12
UP2_0
114
104
10K
10K
A10
UP2_1
NC
C215
20P
20P
R233
VREF
C239
561
D[0..7]
D5
UAD5
262728
UAD7
UAD6
561
472
472
153
472
D5V
25
UALE
C240
C253
C237
C241
C242
212223
201918
A0
UAD3
D3A2D2
303132
UAD4
MT1388E
DMACK
IOCS16
IORDY
INTRQ
129
130
R216 22
131
DIOR
132
R217 22
7 8
133
5 6
126
HA1
20P
127
C211
FG
TRCLOSE
R226 39K
23
TRCLOSE
IO9/CS
U201
DIOW
82X4
3 4
FG
22
FG
DMARQ
HD15
136
135
R218 22
RA205
1 2
20
137
10K
LOAD
19
TROPENPWM
HD0
138
R229 10K
D5V
R228
FMSO
DMSO
R210 10K
DMO
FMO
HD14
139
TILT
R235 10K
R209 10K
TRO
FOO
15
172418
PWMOUT2
HD13
HD1
142
141
33X4
3 4
5 6
7 8
PWMOUT1
TRSO
FOSO
R207 20K
R208 10K
R206 1M
R234 10K
PLLVDD
FOO
TRO
PWMOUT1
HD12
HD3
HD2
145
144
143
5 6
7 8
RA204
1 2
JITFO
151
R205 3M
11
JITFN
HD11
33X4
3 4
15K
C206
109121314
JITFO
HD4
148
147
RA203
1 2
7 8
R204
8
IREF
PDO
HD10
HD5
149
5 6
103
5.1K
LPFN
150
33X4
3 4
C204
47P
C203
R202
LPFO
HD9
152
7 8
RA202
1 2
5.1K
LPIN
HD6
153
5 6
47u/6.3V
+
R203
C202 10P
34567
LPIO
HD7
HD8
154
3 4
EC201
C205
105
C201
473
47K
1
VBDPLL
RFDTSLV
RFRPSLV
RFRP_AC
RFRP_DC
PWMVREF
PWM2VREF
PDMVDD
TRAYOUT
155
RA201
33X4 1 2
391
R201
220u/6.3V
RFIN
RFIP
SCO
ADCVDD
HRFZC
RFLEVEL
FEI
TEI
TEZI
TEZISLV
ADIN/IN0
BDO
SLCK
SDEN
SDATA
IO0
IO1
IO2
IO3
IO4
IO5
IO6
IO7
IO8
FLAGA
FLAGB
FLAGC
FLAGD
ENDM
LED
PLY/PAU
EJ/STOP
LIMIT
TRAYIN
TEST
VPVSS
VCOCIN
VPVDD
PRST
HRST
104
100u/6.3V
EC210
104
C212
HTRC
EQP
EQN
LPIO
LPFO
EC209
+
C214
+
2
C213
+
220u/6.3V
EC211
208
207
206
205
204
203
202
201
200
199
198
197
196
195
194
190
191
189
188
187
186
185
184
183
182
181
180
179
178
177
176
174
173
172
171
169
168
167
166
165
164
163
162
161
160
159
158
157
VSS
D3.3V
1
OUT
VDD
3
RFIN
C230 102
ADIN
PLAY
STOP
LIMIT
TEST
C218 104
HH-1M2012-600JT
RFL
HTRC
RFRP
RFIP
R225 10K
C228 102
C229 102
100K
RFRPC
IO0
IO1
IO2
IO3
IO4
IO6
JUMPER
IO8
FLA
FLB
FLC
FLD
47K
1 2
1SS355TE
D201
2
D33V
BA201
AIC1722 33CX
100u/25V
EC207
220u/6.3V
EC208
D5V
D5V
L204
R220
JP1
R230
TEO
CSO
FEO
DPDMUTE
VSS
C217
104
+
104
+
104
SDATA
SDEN
SLCK
BDO
104
47u/6.3V
+EC204
C219
104
3
U203
KIA7442F
OUT
VIN
1
A5V
C216
C250
HH-1M2012-600JT
L203
R227
15
R224
15
47u/6.3V
C227
104
47u/6.3V
TR_IN
1u/50V
D5V
EC206
+
C226
104
C225
101
R223 12K
47P
R222 12K
151
SCO
R221
103
RFRPSL
18K
104
BDO6
C220
+
EC205
VREF2
TR_OUT
A5V
R219
220
D5V
+
EC213
A12V
R5V
A12V
R5V
A5V
HH-1M2012-600JT
HH-1M2012-600JT
L201
L202
A5V
VREF
C224
C223
C222
C221
VREF2
1
40
GND
/HCS1
/DASP
HA2
/HCS0
HA0
HA1
/PDIAG
GND
HINTRQ
/IOCS16
66
IOCHRDY
CSEL
DMACK
GND
252627282930313233343536373839
GND
/HIOR
GND
/HIOW
222324
NC
DMAREQ
192021
GND
HD0
HD15
HD14
HD1
HD2
HD13
HD3
HD12
101112131415161718
HD4
HD11
HD5
HD10
HD9
HD6
HD8
HD7
GND
123456789
/HRST
414243
44
IDE CONN
CN201
12V
GND
GND
5V
STBY
Page 69

&*,0,1#%3$(&$#%
!"
Two drives may be accessed via a c ommon interface c able, us ing the same range of
I/O addresses. The drives have a jumper configuration as device 0 or 1 (Master/
Slave), and are selected by the drive select bit in the Device/Head register of the
task file.
All Task File registers are written in parallel to both drives. The interface processor
on each drive decides whether a command written to it should be executed; this
depends on the type of command and which drive is selected. Only the drive
selected executes the command and activates the data bus in response to host I/O
reads; the drive not selected remains inactive.
A master/slave relationship exists between the two drives: device 0 is t he master and
device 1 the slave. When the Master is closed (factory default, f igure 2-1), the drive
assumes the role of master; when open, the drive acts as a slave. In single drive
configurations, the Master jumper must be closed.
!!
CSEL (cable select) is an optional feature per ANSI ATA specification. Dr ives
configured in a multiple drive system are identified by CSEL’s value:
Product Description
– If CSEL is grounded, then the drive address is 0.
– If CSEL is open, then the drive address is 1.
PCBA Jumper Location and Configuration
67
Page 70

Product Specifications
68
Page 71

C3
C14
2 2
F1
250V/T2AL
RV1
*910K/1/2W
104/~275
C13
LF1
40mHX2
221 AC400V
BCN1
2P7.92
1
2
221 AC400V
1
2
J12
7.5mm
221 AC400V
BCN2
*2P7.92
C6
470
R15
C11
104
C10
473
R12
0.47 1W
C9
*104
C5
*101 1KV
t
RT1
GND
VCC
DRAIN
6
NC
10/4A(104MS)
8
7
6
5
33 1/4W
5
CE11
22u/25
+
D7
HER105
R5
3
L4
FB
HER107
D4
1N4007
R6
470K 1/2W
D12
D9
1N4007
100uF/400V
CE5
+
R1
470K 1/2W
R2
68K 2W
D11
1N4007
103/1KV
C4
D10
1N4007
*221 AC400V
C1
1
BCK-28-0300
T1
ICE2A365/ICE2A365
IC1
1
SOFT
2
FB
3
ISENCE
4
DRAIN
R13
22 1/4W
43
IC2
PC817
12
10K
STBY
1K
R10
R20
+
104
+12V
Q4
2N5401
C15
CE13
47u/50
-25V
R11
10K 1%
GND
+5V
-25V
GZ2200u/10
104
+
CE14
100u/25
D16
12.5mm
+
CE18
*1000u/10
HER105
D6
+
CE9
+
R8
+
CE15
220u/16
C16
5VSTB
10
C12
Q3
2N5551
+12V
123
798
5.1V 1/2W
CN4
4P3.96
HER105
CE12
D13
10u/25
CE7
10K
D8
+
100u/25
330 1/4W
+
R3
R14
1.2K
IC3
TL431
C7
104
104
R17
4.7K
R9
47K
R7
10K 1/4W
C21
102
F+
F-
CN5
5P2.0
12345
104
TO HDD
4
C8
+5V
D5
BYW29E-200
R18
10K 1%
L5
10uH
GZ1000u/10
CE10
Q2
1PP15N03L
+5V
+2.5V/G
GND
+2.5V/5
10
101
*1N5401
GND
GND
11
C17
R16
*10K 1%
GZ1000u/10
150 1/6W
104
D15
+5V
+3.3V
12
GZ2200u/10
CE6
+
CE8
+
R21
C20
+
D14
*1N5401
5VSTB
+3.3V
P_CTL
123456789
13
SR1060
L3
10uH
Q1
1PP15N03L
CE17
220u/16
+3.3V
CN3
9P2.5
14
C18 *101/500V
D3
+
CE3
470u/25
470u/25
CE4
+
3
GND
Vc
R4
1K
+5V
D2
HER303
L2
FB
+
GND
+12V
1 2
Vin Vo
100u/25
+12V
GND
-12V
12345
15
C19
*101/500V
IC4
PQ12RD21
CE16
CN2
5P2.5
STBY
D1
HER105
+
CE1
100u/25
L1
FB
R19
10K
+12V
1
2
TO fan
104
2P2.5
+
CE2
100u/25
C2
CN1
Q5
2N5551
-12V
69
1
3
4
Page 72

70
Page 73

9P2.5
CN101
D101
*3.3V
+
104
LED
CE106
10u/16
C110
5V_STB
R121
2.2 1/4W
3V3_STB
R122 4.7K
DIG1_2V5
104
104
CE102
330u/16
C106
104
R119
4.7K
VCC
C104
+
CE101
330u/16
C105
+
330u/16
+
L106 FB
CE103
L104 *FB
4.7K
4.7K
L103 FB
R107
R123
123456789
L102 FB
L101 *FB
L105 FB
VCCDIG1_3V3 DIG1_1V8
P_CTL
5V_STB
POWER PORT
101
101
101
CE104
4.7u/50
+
+
CE105
10u/16
C112 101
C111 101
C101
C102
C103
VFD_DIO6
VFD_CLK6
VFD_STB6
IR_IN6
VCC 5V_STB
R116 100
R117 100
R118 100
VFD FRONT PANEL
R103
*0
R104
*0
R110
*0
R102 *0
SCART1
SCART2
POWER
5V_STB
LED
IR_IN
VFD_STB
GND
VFD_DIO
VFD_CLK
AAGND
*3.3K
Q101
*3904
*1K
R112
R114
R125
1K
R124
15K
5V_STB
R113
*10K
Q102
*3906
R115
1K
P_CTL
19
202122
23
24
25
26
R120
0
13
14
15
161718
RTC_INT
CPUMUTE
4 5
GP4
GP3 GP2
GP1
678
STBY
POFF
GPIO12 4,6
101112
GP5
GP0
0
PSW
123
VDD
GND
R106
IR_IN
R111
4.7K
PSW
U101
68HC908QT1
0
IR ADDRESS:07F8
KEY VALUE:01FE
R101
10K
123456789
RTC_INT
R109
CN103
26P1.0
3V3_STB
AAGND
R108
*0
STBY
GPIO4 4,6
SCART1
24
SCART2
GPIO12 4,6
20
212223
CN104
8P2.0(12P)
12
GPIO12 POWER_OFF/16316 RDY
V2_IN EXT_CVBS1
V3_IN EXT_CVBS2/SCART_CVBS
V1_IN TUNER_CVBS
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
171819
1234567891011
GPIO3 AUDIO CLK CONTROL
GPIO4 MICDETCT
GPIO7 AUDIO_SEL1
GPIO8 AUDIO_SEL2
24P1.0
123456789
CN102
A_R_IN
A_R_IN 2
A_L_IN
A_L_IN 2
V1_IN
V1_IN 3
V2_IN
V2_IN 3
V3_IN
V3_IN 3
S_Y_IN
S_Y_IN 3
S_C_IN
S_C_IN 3
B_U_OUT
B_U_OUT 8
G_Y_OUT 8
R_V_OUT
G_Y_OUT
R_V_OUT 8
CPUMUTE
SCART1
SCART2
S_C_OUT 8
V_OUT 8
S_Y_OUT 8
5V_STB
IIC_SCL 2,3,6,8
IIC_SDA 2,3,6,8
GPIO4 6
GPIO7 6
GPIO8 6
A_L_OUT 2
REAR_R 2
A_R_OUT 2
REAR_L 2
SPDIF_OUT 6
MUTE 2
CENTER 2
SUBWOOFER 2
OPTICAL 6
71
Page 74

PCMD1_O6
PCMD2_O6
AAGND
22K
NC
U203
CS4360
9
21
R213
R214
+
CE208
3.3u/50
C207
104
+
CE209
3.3u/50
C208
104
IIC_SDA1,3,6,8
12
13
SDA
AD0
GND
AGND
FILT+
M2
151617
IIC_SCL1,3,6,8
11
SCL
VQ
GPIO116
10
7
MCLK
/RST
MUTEC2
MUTEC1
MUTEC3
18
28
LRCK
XCLK
BCK
SDATA3
SCLK
LRCK
AOUTB2
AOUTB3
AOUTA3
19
20
CE213 10u/16
+
R220 5.6K
SDATA1
SDATA2
VLS
VLC
AOUTA2
AOUTB1
23
242526
CE212 10u/16
+
R219 5.6K
DATA
23456
VD
VA
AOUTA1
27
CE211 10u/16
+
R218 5.6K
8
1
14
22
AAGND
CE210 10u/16
+
R217 5.6K
CE207 10u/16
+
R216 5.6K
104
1u/50
104
CE206 10u/16
+
R215 5.6K
C202
104
C204
104
+
CE204
1u/50
C205
+
CE205
C206
B601
L202
DIG1_3V3
AAGND
VCC
FB
R206 0
R212 0
A_R_IN1
A_L_IN1
R201
22K
CE202
10u/16
R202
22K
+
5
R_IN
LRCK
L201
R209 *0
R210 *0
R211 0
LRCK_OUT 6
BCK_OUT 6
CLK_7114 3
ADC_LRCK 4,6
150
3
R204
BCK
R207 0
ADC_BCK 4,6
L_IN
SDOUT
XCLK
ADC_D 4,6
CE201
10u/16
+
150
8
VCCAGND
142
R205 0
R203
CS5331
U202
76
104
AAGND
C201
R234
*47K
+
CE203
1u/50
R238 *0
R237 *0
VCC
R239 *0
AAGND
122
122
122
122
122
122
C209
C210
C211
C212
C213
C214
LRCK_7114 3
BCK_7114 3
PCM_XCLK6
LRCK_OUT6
BCK_OUT6
PCMD0_O6
R223 *0
R221 *0
R224 *0
R222 *0
A_R_OUT 1
MUTE 1
CENTER 1
SUBWOOFER 1
REAR_R 1
A_L_OUT 1
REAR_L 1
XCLK
LRCK
BCK
DATA
GPIO31,6
PCMD0_O6
LRCK_OUT6
BCK_OUT6
PCM_XCLK6
R225
33
15
10
13
1
SEL
EN
104
4B
C203
2B
3B
R232 0
R231 0
R230 0
R233 0R208 *0
11
14
2
5
3
6
1A
2A
3A
4A
1B
1Y
2Y
3Y
4Y
479
12
R229 33
R226 33
R228 33
R227 33
VCC
DATA
BCK
XCLK
LRCK
U201
74HC157
R235
0
5 6
74HCT14
R236
0
U604C
ADC_BCK1 4,6
ADC_LRCK1 4,6
ADC_D1 4,6
72
Page 75

27PF
27PF
C310
C311
S_Y_IN1
S_C_IN1
V_IN8
V1_IN1
V2_IN1
V3_IN1
DIG1_3V3 DIG1_3V3
+
CE302
220u/16
R304
56
R305
56
R306
56
R307
56
R308
56
C304
104
R309
56
473
Y301
24.576
473
C309
C308
104
104
C307
104
C324
104
C306
104
C323
C305
WRITE ADDRESS = 42
IIC_SDA1,2,6,8
IIC_SCL1,2,6,8
GPIO136
104
104
READ ADDRESS = 43
104
C301
C302
C303
FB
+
CE301
47u/16
功率磁珠
L301
98
99
14
20
12
16
AI22-C(MD7)
AI21
AI11-CVBS(MD0)
XPD3
XPD2
XPD4
85
868789
R320 22
R318 22
R319 22
VDEC_D2
VDEC_D3
VDEC_D1
18
2
AI12-Y(MD7)
TDO
VIDEO DECODER
SAA7114
XPD7
XPD6
XPD5
818284
R314 22
R315 22
R316 22
R317 22
VDEC_D4
VDEC_D6
VDEC_D7
VDEC_D5
TDI
ITRDY
65
7170697267
66
64
HPD6
HPD4
HPD5
HPD7
9
VSSA2
15
VSSA1
24
VSSA0
21
VSSA
VXSS
26
VSSE1
L303
FB
50
76
100
38
63
88
VSSE2
VSSE3
VSSE4
VSSI1
VSSI2
VSSI3
AMXCLK
ALRCLK
ASCLK
414039537
R302 33
CLK_7114 2
LRCK_7114 2
BCK_7114 2
AMCLK
R301 33
IGPH
53
IGPV
HPD3
IGP1
HPD2
IGP0
HPD1
ITRI
4746484952
HPD0
IDQ
3 4
GND Y
R324 *33
6
XTO
ICLK
45
2
A
XTI
TEST5
LLC2(13.5MHZ)
LLC(27MHZ)
IPD1
IPD0
29
28
62
1
U302
*NC7SZ125
OE
VCC
5
TEST3
TEST4
IPD3
IPD2
DIG1_3V3
777879
74
TEST2
TEST1
IPD5
IPD4
73
IPD6
GPIO3 1,6
AI2D
IPD7
R303 *33
19713
AI24-CVBS(MD5)
AI1D
AI23
XPD1
XPD0
90
54555657596061
R321 22
VDEC_D0
10
3
TMS
RESO
VDEC_D[7..0] 4,6
TCK
97
TRSTN
XTOUT
43042
27
RESET/CE
XCLK
94
R313 0
VDEC_VCLK 4,6
XDQ
XRDY
95
80
32
31
XTRI
SDA
SCL
VDDA2
VDDA1
VDDA0
VDDE1
VDDE2
VDDE3
VDDE4
TESTO
RTCO
RTSO
RTS1
XRH
XRV
91
92
96
343536
44
R311 22
R310 22
104
104
VDEC_HSYNC_ 4,6
VDEC_VSYNC_ 4,6
104
104
VXDD
VDDI1
VDDI2
VDDI3
VDDI4
VDDI5
VDDI6
AOUT
C325
C326
C327
C328
U301
11
17
23
1
25
L302 FB
51
75
8
33
43
58
68
83
93
22
功率磁珠
SAA3V3
R323 4.7K
VDEC_DVALID 4,6
C329
C312
*104
PCM_XCLK
104
+
CE303
100u/16
73
Page 76

GPIO121,6
GPIO156
R412 4.7K C456
R413 4.7K
TMSTMS
B5
A5
TDI
TMS
TDO
ADBCK_OUT
DABCK_OUT
DABCK_IN
SD_IN
A8
B7
ADC_D 2,6
R411 4.7K
TCKTCK
TDI
TCK
ADBCK_IN
ADWS_IN
B8C8A7B3A6
ADC_BCK 2,6
ADC_LRCK 2,6
R416 *0
SM3.3V
E19
C1
C5B6C6
PLL_RESET_
APLL_RESET_
CS_IN_
R415
0
SYSCLK_27MHZ5,6
GPIO146
SYSCLK_27MHZ
C4
U3
SYSCLK
HARD_RESET_
SDA
CLKOUT1
CLKOUT0
RAS_
CAS_
Y17
A19
C17
CAS_
R407 22
R408 22
C9
B9
SCL
CS_
Y16
W16
RAS_
VDEC_DVALID3,6
ENC_DEC_
DREADY_MOD
C10
B10
A9
DREADY_DEM
DREADY_MOD
ENC_DEC_
DQMU
DQML
WE_
Y15
V15
V16
MCS_
MWE_
DQML
VDEC_HSYNC_3,6
VDEC_VSYNC_3,6
HREF_MOD
VSYNC_MOD_
C11
B11
A10
HREF_DEM
HREF_MOD
VSYNC_DEM_
VSYNC_MOD_
MA02
MA01
MA00
R19
R20
DQMU
MA0
MA1
VDEC_VCLK3,6
C12
A11
B4
CLK27_DEM
CLK27_MOD
MA05
MA04
MA03
P18
T20
N18
MA2
MA3
MA4
R401
4.7K
R402
10K
SM3.3V
R403
R406 1K
P1P2P3
DMA_ACK_
DTACK_RDY_
HSEL_
HDMA_REQ5
HALE_5
M2
N1N2N3
AS_ALE_
INTL_MOT_
DMA_REQ
T2
INTLMOT_
INTX16
R3
INTX16
10K
HMS_D13
HMS_D14
HMS_D15
J3J1J2
HAD13
HAD14
HMS_D12
HAD11
HAD12
HMS_D10
HMS_D11
H3H1H2
HAD9
HAD10
HMS_D8
HMS_D9
G3G1G2
HAD8
HAD7
HMS_D[15..0]5,6
HD[7..0]5
HD0
HD1
HD2
HD3
HD4
HD5
HD6
HD7
D3E3D2
E1
E2
F3F1F2
HAD0
HAD1
HAD2
HAD3
HAD4
HAD5
HAD6
U401
R404
10K
R405
10K
HA7
HA5
HA4
HA3
HA6
HA2
HA1
HA0
K2K1K3
L1
L2M1L3
HAD15
HA0
HA1
HA2
HA3
HA4
HA5
HA6
HA7
B14
YOUT0
C14
YOUT1
YOUT2
A14
A13
YOUT3
YOUT4
B13
YOUT5
C13
A12
YOUT6
YOUT7
VDEC_D[7..0]3,6
HRD_5
HWR_5
T7
VDEC_D1
VDEC_D2
VDEC_D7
VDEC_D5
VDEC_D0
VDEC_D6
VDEC_D3
VDEC_D4
C15
C16
B15
A15
A16
B16
A17
B17
B12
YIN7
YIN6
YIN5
YIN4
YIN3
YIN2
YIN1
YIN0
ROM_SEL
W1
U2
V2
FLASH_SEL
ROM_SEL
ROMDATA_EN_
SER_OUT
FLASH_SEL
U1
GPIO5
GPIO4
1
Y2W3Y3
GPIO3
V1
Y1
T3
GPIO0/ADWS_OUT
GPIO1
GPIO2
HIRQ_
HSYSRDY
R2
T1
HIU_INT_
SYS_RDY
RWNSBHE
R1
RWN_SBHE_
LDS_RDN_
UDS_WRN_
CS92288
D9
VDD
D10
VDD
D13
VDD
G4
VDD
G17
VDD
H17
VDD
K4
VDD
L4
VDD
N17
VDD
U6
VDD
U10
VDD
U11
VDD
V6
VDD
F20
MD52
MD52
MD53
MD53
MD54
MD54
MD55
MD55
MD56
MD57
MD56
MD57
MD58
MD58
PLL_VDD
PLL_VDDA
APLL_VDD
APLL_VDDA
MD61
MD60
MD59
MD59
MD60
MD61
MD62
VDDD
VDDD
VDDD
VDDD
VDDD
VDDD
VDDD
VDDD
VDDD
VDDD
VDDD
VDDD
VDDD
VDDD
VDDD
VDDD
VDDD
VDDD
VDDD
VDDD
MD62
MD63
D20
D1
B1
D6
D7
D11
D14
F4
J4
J17
K17
M4
M17
P4
P17
R4
R17
U7
U8
U12
U14
U15
V12
V4W4V5Y4W5Y5W6Y6V7W7Y7V8W8Y8V9W9Y9
MD63
MA[11..0]
MD[63..0]
CS92288
MD51
MD50
MD49
MD48
MD47
MD46
MD45
MD44
MD43
MD42
MD41
MD40
MD39
MD38
MD37
MD36
MD35
MD34
MD33
MD32
MD31
MD30
MD29
MD28
MD27
MD26
MD25
MD24
MD23
MD22
MD21
MD20
MD19
MD18
MD17
MD16
MD15
MD14
MD13
MD12
MD11
MD10
MD09
MD08
MD07
MD06
MD05
MD04
MD03
MD02
MD01
MD00
MA11
MA10
MA09
MA08
MA07
MA06
V10
W10
Y10
V11
W11
Y11
W12
Y12
W13
Y13
V13
W14
Y14
V14
W15
P19
P20
N19
M19
N20
M20
L19
L20
K19
K20
J18
J19
J20
H19
H20
H18
G19
G20
G18
F19
F18
C19
D18
B20
W17
V17
Y18
W18
Y19
Y20
V19
T18
U18
W20
U19
V20
R18
T19
U20
MD10
MA8
MA9
MA10
MA7
MA5
MA6
MA11
MD7
MD6
MD3
MD11
MD12
MD4
MD2
MD8
MD5
MD0
MD1
MD9
MD13
MD14
MD15
MD16
MD17
MD18
MD19
MD20
MD21
MD22
MD23
MD24
MD25
MD26
MD27
MD28
MD29
MD30
MD31
MD32
MD33
MD34
MD35
MD36
MD37
MD38
MD39
MD40
MD41
MD42
MD43
MD44
MD45
MD46
MD47
MD48
MD49
MD50
MD51
104
104
104
104
104
104
104
104
104
104
+
CE401
220u/16
104
104
104
104
104
104
104
104
104
104
104
+
CE407
47u/16
PLL_VDD
PLL_VDDA
C424
C425
C426
C427
C428
C429
C430
C431
C432
C433
C401
C402
C403
C404
C407
C408
C409
C410
C411
C412
C413
APLL_VDD
APLL_VDDA
DIG1_1V8
104
104
104
104
104
104
104
104
104
104
+
CE402
47u/16
+
CE408
220u/16
C414
C415
C416
C417
C418
C419
C420
C421
C422
SM3.3V
C423
L401
FB
DIG1_3V3
T3
1
T4
1
T5
1
T6
1
VSYNC_MOD_
DREADY_MOD
HREF_MOD
ENC_DEC_
L403
B601
+
CE404
10u/16
APLL_VDD
C435
104
L405
B601
L409
B601
PLL_VSSAPLL_VSS
10u/16
104
B601
+
CE406
L404
B601
L408
L407
B601
PLL_VDD
C437
HSYSRDY
HIRQ_
APLL_VSSA
+
10u/16
104
+
10u/16
104
PLL_VSSA
B601
CE403
B601
CE405
C436
L402
C434
L406
T1
1
T2
1
APLL_VDDA
PLL_VDDA
PLL_VSSA
PLL_VSS
APLL_VSSA
APLL_VSS
DIG1_1V8DIG1_1V8
D4
D17
J9
J10
J11
J12
K9
K10
K11
K12
L9
L10
L11
L12
M9
M10
M11
M12
U4
U17
B2
B19
C3
C18
D5
D8
D12
D15
D16
E4
E17
F17
H4
K18
L17
L18
M3
M18
N4
T4
T17
U5
U9
U13
U16
V3
V18
W2
W19
C20
E20
A2
C2
B18
A4
MBIST_EN
ND_TREE
VSS
VSS
VSS
VSS
VSS
VSS
VSS
VSS
VSS
VSS
VSS
VSS
VSS
VSS
VSS
VSS
VSS
VSS
VSS
VSS
VSSD
VSSD
VSSD
VSSD
VSSD
VSSD
VSSD
VSSD
VSSD
VSSD
VSSD
VSSD
VSSD
VSSD
VSSD
VSSD
VSSD
VSSD
VSSD
VSSD
VSSD
VSSD
VSSD
VSSD
VSSD
VSSD
VSSD
VSSD
VSSD
PLL_VSSA
PLL_VSS
APLL_VSSA
APLL_VSS
D19
BIDI_IN
A1
PLL_BP
SE
A20
E18
A18
TEST_MODE
GLOBAL_PD
DAWS_OUT
SD_OUT
AUDCLK
C7
A3
0
CE411
330u/16
104
MEMCLK1
MEMCLK0
10
33
37
4
KM416S1020
TSOP-50
GND1
GND2
NC1
NC2
GND3
GND4
GND5
TSOP-50
GND6
2641384447
50
10
33
37
4
KM416S1020
GND1
GND2
NC1
NC2
GND3
GND4
GND5
GND6
2641384447
50
+
CE409
220u/16
+
CE410
47u/16
104
C454
U406
LT1117-1.8
DIG1_1V8DIG1_3V3
104
104
C455
104
104
104
C457
104
104
104
C458
104
104
C459
104
C460
104
3
R417
VIN
1
ADJ
VOUT
R414
*1K
2
+
C461
CE412
47u/16
+
C448
C442
104
C449
C443
104
C450
C444
104
C445
104
C451
C452
C446
104
C453
C447
104
SM3.3V
DQMU
DQMU
VCC6
104
DQMU
DQMU
VCC6
104
DQML
VCC5
DQML
VCC5
CAS_
MEMCLK0
DQML
RAS_
MCS_
MWE_
MA11
MA10
MA9
19
35
17161518341436
RAS
A11/BA
CLK
CASWECS
CKE
VCC1
VCC2
VCC3
VCC4
25
C440
DQML
VCC4
25
C441
CKE
VCC3
CLK
VCC2
D10
D11
D12
D13
D14
D15
D9
MD29 MD61
MD31
MD30
MD27
MD25
MD28
MD26
MCS_
RAS_
MEMCLK1
CAS_
MWE_
MA9
MA10
MA11
19
35
17161518341436
RAS
A11/BA
CASWECS
VCC1
D10
D11
D12
D13
D14
D15
D9
MD62
MD63
MD57
MD59
MD58
MD60
MA8
MD24
MA8
MD56
MA7
MD23
MA7
MD55
MA6
MD22
MA6
MD54
MA5
MD21
MA5
MD53
MA4
MD20
MA4
MD52
MA3
MD19
MA3
MD51
MA2
MD18
MA2
MD50
MA1
MD17
MA1
MD49
MA0
2122232427282930313220
TSOP-50
U403
A0A1A2A3A4A5A6A7A8A9A10
D0D1D2D3D4D5D6D7D8
235689111239404243454648491713
MD16
MA0
2122232427282930313220
TSOP-50
U405
A0A1A2A3A4A5A6A7A8A9A10
D0D1D2D3D4D5D6D7D8
235689111239404243454648491713
MD48
DQML
MEMCLK0
MWE_
CAS_ CAS_
DQMU
MCS_
RAS_
MA11
MA10
MA5
MA6
MA3
MA4
MA9
MA8
MA7
MA0
MA1
MA2
MD9
MD41
2122232427282930313220
U402
A0A1A2A3A4A5A6A7A8A9A10
MEMCLK0
D0D1D2D3D4D5D6D7D8
235689111239404243454648491713
MD8
MD4
MD6
MD3
MD1
MD2
MD5
MD0
MD7
MA1
MA2
MA6
MA4
MA8
MA7
MA3
MA0
MA5
MA9
2122232427282930313220
U404
A0A1A2A3A4A5A6A7A8A9A10
D0D1D2D3D4D5D6D7D8
235689111239404243454648491713
MD39
MD37
MD40
MD36
MD32
MD33
MD35
MD34
MD38
MEMCLK1
R409
62
R410
62
C405
47PF
C406
47PF
GND1
GND5
GND1
GND5
35
33
37
4
NC1
NC2
GND3
GND4
264138
47
33
37
4
NC1
NC2
GND3
GND4
264138
47
DQMU
VCC6
44
DQMU
VCC6
44
DQML
VCC5
104
DQMU
DQML
VCC5
104
17161518341436
RAS
A11/BA
CLK
CASWECS
CKE
VCC1
VCC2
VCC3
VCC4
25
C438
DQML
CKE
VCC3
VCC4
25
SM3.3V
D10
D11
D12
D13
D14
D15
D9
MD13
MD12
MD15
MD14
MD11
MD10
SM3.3V
MCS_
RAS_
MEMCLK1
MWE_
MA10
MA11
19
35
17161518341436
RAS
A11/BA
CLK
CASWECS
VCC1
VCC2
D10
D11
D12
D13
D14
D15
D9
MD47
MD44
MD46
MD45
MD42
MD43
C439
10
KM416S1020
GND2
GND6
50
10
KM416S1020
GND2
GND6
50
19
74
Page 77

VCC
10K
R521
HD[7..0]4
R533
10K
IDE_RD
IDE_WR
HD1
HD2
R517 22
IDE_DRQ
17
19
18
20
R532 22
HD0
R516 22
R513 22
R514 22
R515 22
11
13
15
12
14
16
R529 22
R528 22
R530 22
R531 22
R518 22
29
31
33
30
32
34
PDIAG_L
IDE0_CS1
R519 22
IDE0_DACK
IDE_IRQ
23
25
27
24
26
28
CSEL_H
21
22
HMS_CS06
HMS_A06
HMS_A16
35
37
39
36
38
40
R523 22
HD3
R512 22
R527 22
HD4
R511 22
R526 22
HD5
R510 22
R525 22
13579
246810
HD6
HD7
HD7
XS501
RESET_L6,7
HDD AND DVD_LOADER INTERFACE
CONNECTOR
+
CE501
100u/16
C501
104
C502
104
C503
104
5.6K
R524
R502 0
35
VCC
VCCINT
GND
GND
42
HMS_A2 6
DIG1_3V3
23
VCCINT
VCC
GND
GND
30
22
R501 *0
3
10
R522 10K
VCC
SYSCLK_27MHZ4,6
VCC
CLK
cdc/ALE
cdc/WR
cdc/RD
41
43
cdcDRQ
39
38
HMS_CS16
HMS_CS06
32
34
1
hostA2
host/CS1
host/CS0
ide0/DACK
ide1/CS1
ide/CS1
37
17
36
HMS_D14
HMS_D15
HMS_A[2..0]6
HMS_A2
31
33
hostA1
host/WR
hostA0
ide/DACK
ide/WR
ide/RD
27
IDE0_CS1
HMS_D11
HMS_D12
HMS_D13
HMS_WR_L6
HMS_RD_L6
HMS_A1
HMS_A0
44
2
host/RD
hostD7 ideD7
ideDRQ
ideIRQ
281926
25
29
IDE_WR
IDE_RD
HMS_D10
HMS_D9
HMS_D8
HMS_D[15..0] 4,6
HMS_D7
11
12 13
9
hostD5
hostD6
hostD4
ideD4
ideD6
ideD5
14
16
HD7
HMS_D5
HMS_D6
7406
8
hostD3
hostD2
ideD3
ideD2
18
2015215
HD5
HD6
HMS_D4
HMS_D2
HMS_D3
4
hostD0
ideD0
ideD1hostD1
24
HD2
HD3
HD4
HMS_D1
HMS_D0
U501
ASIC
HD0
HD1
HDMA_REQ 4
HRD_ 4
HWR_ 4
HALE_ 4
R507 22
R508 5.6K
R509 10K
R505 22
R506 22
IDE_DRQ
IDE0_DACK
IDE_IRQ
75
Page 78

SPDIF_OUT1
OPTICAL1
35
58
18
96
119
143
182
36
63
82
103
126
138
158
176
200
208
52
104
157
77
73
69
65
155
152
151
150
HMS_D1
HMS_D0
134
132
HD0
HD1
HD2
VSS_IO
VSS_IO
VSS_IO
VSS_IO
VSS_IO
VSS_IO
VSS_IO
VSS_C
VSS_C
VSS_C
VSS_C
VSS_C
VSS_C
VSS_C
VSS_C
VSS_C
VSS_PLL_0
VSS_PLL_1
VSS_PLL_2
VSS_PLL_3
DVDL_CK
DVDL_RDY
DVDL_DO
DVDL_DI
CD_C2PO
CD_BCK
CD_LRCK
CD_DATA
GPIO13
GPIO14
GPIO15
197
199
GPIO15
GPIO14
GPIO15 4
GPIO13 3
GPIO14 4
HMS_D4
HMS_D3
HMS_D2
130
127
125
123
HD3
HD4
HD5
GPIO10
GPIO11
GPIO12
192
194
195
196
GPIO12
GPIO13
GPIO11
GPIO11 2
GPIO10 8
GPIO12 1,4
(PCM_XCLK=16.9M)
HMS_D7
HMS_D6
HMS_D5
122
121
HD6
HD7
GPIO8
GPIO9
190
191
GPIO9
GPIO10
R620 22
GPIO8 1
PCM_XCLK 2
HMS_D8
118
HD8
HD9
GPIO6
GPIO7
188
GPIO8
GPIO7
IIC_SDA 1,2,3,8
GPIO7 1
HMS_D10
HMS_D9
117
116
HD10
HD11
GPIO4
GPIO5
186
187
GPIO6
GPIO5
GPIO4 1
IIC_SCL 1,2,3,8
HMS_D12
HMS_D11
114
113
112
HD12
HD13
GPIO2
GPIO3
181
183
185
GPIO3
GPIO4
VFD_STB 1
GPIO3 1,3
HMS_D14
HMS_D15
HMS_D13
110
109
HD14
HD15
GPIO0
GPIO1
174
177
GPIO1
GPIO2
GPIO0
VFD_CLK 1
VFD_DIO 1
HMS_D[15..0]4,5
HMS_A0
100
99
HA0
HA1
XTLCLK
RST_N
202
205
HMS_A1
HMS_A2
102
97
HA2
HA3
MFG_TST1
IR_IN
201
207
IR_IN 1
HMS_A[2..0]5
111
107
H_CS_2
H_CS_3
HA4
NVM_OE_L
MFG_TST0
206
NVR_OE_L 7
RESET_L 5,7
R639 22
HMS_RDY
HMS_CS15
HMS_CS05
106
101
115
H_CS_0
H_CS_1
H-RDY
NVM_WE_L
M_DQM_3
NVR_WE_L 7
M_DQM[0..3] 7
HMS_RDY
HMS_RD_L5
HMS_WR_L5
929395
H-RD
H-WR
M_DQM_1
M_DQM_2
M_DQM2
M_DQM3
M_DQM1
VCC
85
89
98
H_ALE
H_BH16
H_DACK
M_DQM_0
M_CAS_L
M_WE_L
R619 22
M_DQM0
M_CAS_L 7
M_WE_L 7
22
120
94
H_CKO
H_DREQ
M_RAS_L
M_AP
R617 22
R618 22
M_RAS_L 7
M_AP 7
R615
M_BS_L
M_CKE
M_BS_L 7
M_CKE 7
VDO_CLK8
VDO_HSYNC8
VDO_VSYNC8
154
159
CLK27_O
HSYNC
VSYNC
M_CKO
MA0
19212223242527282931328190
R616 22
M_CKO 7
R602
91
VCC
+
CE609
47u/16
74HCT14
C623
104
VDO_D5
VDO_D6
VDO_D3
VDO_D1
VDO_D2
VDO_D4
VDO_D7
162
VDAT7
173
172
VDAT5
VDAT6
170
169
VDAT3
VDAT4
167
VDAT2
166
VDAT1
165
VDAT0
CS98000
MA1
MA2
MA3
MA4
MA5
MA6
MA7
MA8
MA9
16151413111097653
MADDR4
MADDR1
MADDR2
MADDR8
MADDR7
MADDR5
MADDR6
MADDR3
MADDR0
R601
330
L601
0
U604B
C619
104
U604E
1110
PCMD0_O2
LRCK_OUT2
BCK_OUT2
VDO_D[0..7]8
R614 22
R613 22
VDO_D0
163
124
128
135
AUD_BCK
AUD_LRCK
AUD_DO_0
MA10
MA11
MD0
MD1
62595551484542373340444649545660888680787572706764687174767983
2
MADDR11
MDATA0
MADDR10
MADDR9
MADDR[0..11] 7
PCMD1_O2
PCMD2_O2
R638 22
R612 22
R637 22
136
133
AUD_DO_1
AUD_DO_2
AUD_DO_3
MD2
MD3
MD4
MDATA3
MDATA2
MDATA1
1312
204
MD5
MDATA4
74HCT14
ADC_LRCK12,4
ADC_BCK12,4
137
AIN_BCK
AIN_LRCK
MD6
MD7
MDATA6
MDATA5
U604F
ADC_D12,4
139
AIN_DATA
MD8
MDATA7
74HCT14
34
U604A
74HCT14
12
VDEC_HSYNC_3,4
VDEC_VSYNC_3,4
VDEC_DVALID3,4
VDEC_VCLK3,4
145
149
153
140
142
144
148
146
CDC_DI
CDC_DO
CDC_SY
CDC_RST
CDC_CK
MD10
MD11
MD12
MD13
MD14
MD15
MD9
MDATA12
MDATA14
MDATA10
MDATA11
MDATA13
MDATA8
MDATA9
147
MD16
MDATA15
MD17
MDATA16
MDATA17
220u/16
47u/16
AUX_STB
AUX_ENA
AUX_SOS
MD18
MD19
MD20
MDATA18
MDATA19
+
CE605
+
CE607
160
AUX_ERR
MD21
MDATA20
171
AUX_RDY
MD22
MD23
MDATA23
MDATA22
MDATA21
IIC_SDA
IIC_SCL
678
SCLWPVDD
VSSSDA
45
VDEC_D7
VDEC_D6
193
198
AUX_D6
AUX_D7
MD24
MD25
MDATA24
MDATA25
A0A1A2
123
VDEC_D4
VDEC_D5
184
189
AUX_D4
AUX_D5
MD26
MD27
MDATA27
MDATA26
104
C622
U605
24C08
VDEC_D2
VDEC_D1
VDEC_D3
168
175
179
AUX_D0
AUX_D1
AUX_D2
AUX_D3
VDD_IO
VDD_IO
VDD_IO
VDD_IO
VDD_IO
VDD_C
VDD_C
VDD_C
VDD_C
VDD_C
VDD_C
VDD_C
VDD_C
VDD_C
VDD_PLL_3
VDD_PLL_2
VDD_PLL_1
VDD_PLL_0
DVD_RDY
DVD_STB
DVD_ENA
DVD_SOS
DVD_ERR
DVD_D7
DVD_D6
DVD_D5
DVD_D4
DVD_D3
DVD_D2
DVD_D1
DVD_D0
MD28
MD29
MD30
MD31
MDATA29
MDATA28
MDATA30
DIG1_3V3
VDEC_D0
164
87
MDATA31
MDATA[0..31] 7
VCC
VDEC_D[7..0]3,4
220u/16
U601
CS98000
38
91
131
180
20
41
66
84
108
129
141
161
178
203
156
105
53
1
4
8
12
17
26
61
57
50
47
43
39
34
30
CE602
C601
104
+
C605 104
C608 104
C611 104
DIG1_3V3
C602 104
C604 104
C603 104
C606 104
C607 104
CE601
220u/16
+
DIG1_2V5
C610 104
C609 104
CE603
47u/16
+
DIG1_2V5
C612
104
C613
104
C614
104
C624
104
GPIO8
R632 10K
GPIO6
GPIO7
R631 10K
R630 2.2K
GPIO5
R629 2.2K
GPIO4
GPIO3
R628 10K
R627 10K
GPIO2
R625 1K
GPIO0
GPIO1
R624 1K
R623 1K
VCC
C616
L603
Y601
27MHZ
330
R604
U603B
74HC04
102
1 2
R603
3K
147
U603A
74HC04
3
147
4
+
CE610
47u/16
B601
L602
VCC
1N4148
1 2
33K
104
D601
R621
C615
98
10u/16
+
U604D
74HCT14
CE608
VCC
C617
104
1
U602
PQ070XZ
VIN
2
VC
5
GND
VOUT
4
ADJ
3
DIG1_2V5
R635
1K
R636
1K
CE606
330u/16
+
C618
104
C625
102
C620
20PF
C621
20PF
SYSCLK_27MHZ 4,5
R622
100
B601
76
Page 79

MDATA[0..31]6
MADDR[0..11]6
M_DQM[0..3]6
M_DQM0
71
DQM1
DQ4
8910
MDATA3
M_DQM1
DQM2
DQ5
MDATA4
M_DQM2
28
MDATA5
M_DQM3
59
DQM3
DQ6
DQ7
111213
MDATA6
MDATA7
M_WE_L6
WE
DQ8
M_RAS_L6
171819
RAS
DQ9
747576
MDATA8
M_CAS_L6
CAS
DQ11
DQ10
777879
MDATA9
MDATA10
MADDR0
252627
A0A1A2
DQ12
DQ13
DQ14
808182
MDATA12
MDATA11
MDATA13
MADDR2
MADDR3
MADDR4
MADDR1
60616263646566
A3A4A5A6A7A8A9
DQ17
DQ18
DQ15
DQ16
313233
343536
838485
MDATA17
MDATA14
MDATA15
MDATA16
M_CKE6
M_CKO6
16
67
68
DQM0
CKE
CLK
20
CS
72
Vss
VssQ
VssQ
VssQ
VssQ
44
Vss
VssQ
VssQ
58
Vss
VssQ
VssQ
86
Vss
DQ0
DQ1
DQ2
DQ3
234
567
MDATA0
MDATA2
MDATA1
MADDR7
MADDR6
MADDR5
DQ19
DQ20
DQ21
373839
MDATA19
MDATA18
MDATA20
M_AP6
MADDR10
MADDR8
MADDR9
BS1
A10/AP
DQ22
DQ23
DQ24
404142
MDATA23
MDATA21
MDATA22
M_BS_L6
222324
BS0
DQ25
DQ26
454647
484950
MDATA26
MDATA24
MDATA25
30
57
NC
NC
NC
DQ27
DQ28
DQ29
515253
MDATA27
MDATA28
70
73
NC
NC
DQ30
DQ31
545556
MDATA29
MDATA30
14
21
69
NC
NC
VCC
VccQ
VccQ
VccQ
Vcc
Vcc
VccQ
Vcc
VccQ
VccQ
VccQ
VccQ
MDATA31 MADDR7
+
CE701
100u/16
104
104
104
104
U701 W986432
1
15
29
43
C701
C702
C703
C704
DIG1_3V3
46
GND1
RESET_L5,6
14
RESETWEBYTECEOE
VPP
WP
1M X 16 GENERIC
TSOP-48W
NVR_OE_L6
NVR_WE_L6
R717
*0
1N4148
D702
MADDR4
MADDR2
MADDR0
MADDR3
MADDR6
MADDR9
MADDR5
A04
DQ00
29
DQ_0
R716 33
A05
DQ01
DQ_1
R715 33
A06
DQ02
DQ_2
R714 33
18192021222324
A07
DQ03
DQ_3
R713 33
MADDR8
8
A09
A08
DQ05
DQ04
DQ_4
R712 33
A10
DQ06
DQ_5
R711 33
MADDR1
25121147262813
A03
A02
A01
A00
RY_BY
15
Note:Resistors should be 300ohm when
FLASH TYPE is +5V and 33ohm when
FLASH TYPE is +3.3V.
MDATA16
MADDR11
MADDR10
A13
A12
A11
DQ09
DQ08
DQ07
DQ_8
DQ_6
DQ_7
R708 33
R710 33
R709 33
MDATA19
MDATA18
MDATA17
1234567
A16
A15
A14
DQ12
DQ11
DQ10
DQ_9
DQ_10
DQ_11
R707 33
R706 33
R705 33
1N4148
D701
MDATA20
MDATA21
MDATA22
161748
A19
A18
A17
VCCGND0
DQ15
DQ14
DQ13
DQ_14
DQ_13
DQ_12
R704 33
R703 33
R702 33
10K
10K
MDATA23
9
454341393634323044424038353331
DQ_15
R701 33
R719
R718
U703
FLASHROM
3727
104
104
R721 *0
C707
C708
VCC DIG1_3V3
R720 0
MDATA0
77
C709
104
C710
104
MDATA3
MDATA2
MDATA4
MDATA5
MDATA1
MDATA11
MDATA6
MDATA12
MDATA7
MDATA9
MDATA8
MDATA10
MDATA15
MDATA13
MDATA14
+
CE702
47u/16
Page 80

10K
R803
VDO_HSYNC6
VDO_VSYNC6
VDO_CLK6
IIC_SDA1,2,3,6
100
R802
IIC_SCL1,2,3,6
100
R801
VDO_D1
VDO_D0
VDO_D2
VDO_D4
VDO_D3
GPIO106
VDO_D6
VDO_D7
VDO_D5
VDO_D[0..7]6
C801
104
*220
18
R809
R810
6.8K
34
RST
GNDD
GNDA0
GNDA1
GNDA2
XTALI
15
R807
0
13
TST
CVBS
+
30
31
TTXDATI
TTXDATO
CE802
220u/16
33
SCL
32
SDA
RD
27
WR
16
28
HPD1/GPIO1
HPD0/GPIO0
PADDR
XTALO
VCC
L808
B601
2217236243525526
HPD5/GPIO5
HPD4/GPIO4
HPD3/GPIO3
HPD2/GPIO2
INT
14
12
4.7K
20
21
HPD7/GPIO7
HPD6/GPIO6
VSYNC
FLD_CB
ISET
37
9
R804
R819
*220
C819
*331
L806
1.8uH
29
10
11
VDAT0
CLK27
HSYNC/CB
VREF
B/Y-U
38
G_Y
*22PF
VDAT1
G/Y
40
43
G_Y
B_U
C817
4423412451
VDAT3
VDAT2
R/Y-V
39
R_V
VDAT5
VDAT4
CVBS
44
CVBS1YC
*220
*331
8
7
VDAT7
VDAT6
VDD
VAA0
VAA1
VAA2
C
Y
481947
R817
C813
L804
1.8uH
36
46
CVBS1
U801
CS4955
C811
*22PF
C804 104
FB
L801
C803 104
*220
*331
DIG1_3V3
R815
C807
L802
1.8uH
C802 104
Y
100u/16
+
C805
*22PF
CE801
470
470
R811
R813
6.8K
R814
C808
C820
101
Q801
9014
V_OUT 1 V_IN 3
R806
3.9K
R812
0
Q802
9014
*220
*331
101
R805
C821
L807
1.8uH
C822
G_Y_OUT 1 B_U_OUT 1
B_U
*22PF
C818
101
*220
*331
101
C814
R818
C815
L805
1.8uH
C816
CVBS
R_V
R_V_OUT 1
C812
*22PF
101
*220
*331
101
R816
C809
L803
1.8uH
C810
S_Y_OUT 1
C
C806
*22PF
S_C_OUT 1
78
Page 81

79
Page 82

*4.7K
R125
*4.7K
R127
*4.7K
SCART2
SCART1
*4.7K
Q2
3904
R124
R28
4.7K
12345
R126
1K
+5V
104
R26
CN3
*5P2.0
C22
1N4148
+5V
R24
4.7K
S3
*SCART
123456789
R_OUT 3,6
L_OUT 3,6
R17
*3.9K
C16
*4.7u/50
+
+5V
SCART_AUDIO_IN_L
*10K
R15
CVBS/S_VIDEO IN
R11
*56
R13
*3.9K
R12
*56
0
C14
*4.7u/50
+
1N4148
SCART_AUDIO_IN_R
18
C11
D8
R10
342
S_C_IN
342
R9 18
D7
1N4148
S
C10
0
D6
1N4148
+5V
1
S_Y_IN
1
*56
D5
1N4148
R7
C8
0
D4
1N4148
+5V
R6 0
V2_IN
S2 CS-09
D2
1N4148
10K
10K
3
3
3.9K
R4
R5
4.7u/50
+5V
1
2
1
2
R2
3.9K
R3
C6
4.7u/50
+
+
EXT_AUDIO_IN_L
EXT_AUDIO_IN_R
S1 AV2-8.4-6G
AUDIO IN
C3
R_Cr 3
R22
C21
*104
D10
*1N4148
G_Y 3
*18
V3_IN
1011121314151617181920
R21
*1N4148
B_Cb 3
R19
*10K
D9
21
CVBS 3
*56
D11
Q1
3906
R23
22
10K
10K
R29
R30
R27
3.9K
4.7u/50
R_OUT 3,6
C24
IN_R
TUN1
JS-6A/L1615BG
L_OUT 3,6
3.9K
+
+
IN_L
R25
C23
4.7u/50
V3_IN EXT_CVBS2
V2_IN EXT_CVBS1
V1_IN TUNER_CVBS
+12V
3.9K
R20
10K
C20
102
C17
4.7u/50
CVBS
AFO
Vif
12
13
14
R18
+
TUNER_AUDIO_IN
V1_IN
+
C18
220u/10
+5V
C19
103
1011121314151617181920212223242526
AFC OUT
IF OUT
2nd
11
R16 18
C15
0
AGC
9
10
817
R14
*56
SDA
SCL
BM
R117
3
BT
2
+5V
3904
R120
3.3K
GPIO8
104
Q20
NC
C65
A
B
7
R122 3.3K
5V_STBR132 0
10K
R121 3.3K
R118
VEE
C9
104
+
C7
47u/16
R8 220
D3
6.2V
+6V
-12V
101112131415161718192021222324
NC
AS
4
5
6
IIC_SCL
IIC_SDA
C13
103
C12
100u/16V
+
10K
Q19
3904
R119
3.3K
GPIO7
CN2
26P1.0
123456789
IN_R
IN_L
121415
11
15246109
X3
Y0Y1Y2Y3INH
123456789
Y
3
+
4.7u/50
A_R_IN
CN1
24P1.0
VDDVSS
X0X1X2
X
C5
4052
13
+
C4
4.7u/50
A_L_IN
U1
168
C2
104
+
C1
47u/16
+6V
R1 220
D1
6.2V
+12V
GPIO7 AUDIO_SEL1
GPIO8 AUDIO_SEL2
GPIO12 POWER_OFF/16316 RDY
GPIO4 MICDETCT
A_R_IN
A_L_IN
V1_IN
V2_IN
V3_IN
S_Y_IN
S_C_IN
B_U_OUT 6
G_Y_OUT
B_U_OUT
G_Y_OUT 6
R_V_OUT
V_OUT 2
R_V_OUT 6
GPIO7
SCART1
SCART2
GPIO8
S_Y_OUT 2
S_C_OUT 2
RTC_INT 2
IIC_SCL 2
IIC_SDA 2
5V_STB
A_L_OUT 3
GPIO4 3
A_R_OUT 3
SCART1 3
CPUMUTE 3
SCART2 3
MUTE 3
REAR_R 4
CENTER 5
REAR_L 4
OPTICAL 6
SPDIF_OUT 6
SUBWOOFER 5
80
Page 83

S_C_OUT 1
S_Y_OUT 1
V_OUT 1
+5V
R43
220
R42
6.8K
R44
470
1N4148
BT1
3V
D13
C26
220u/10
+
R41
0
Q4
3904
D12
1N4148
6.8K
5V_STB
R39
2.2
R38
220
470
R36
6.8K
R37
2.2
R35
R34
C25
220u/10
+
R33
0
Q3
3904
6.8K
R32
+5V
2.2
R31
C28
20PF
C29
*20PF
32.766KHZ/20pF
X1
IIC_SCL 1
IIC_SDA 1
GND SDA
4 5
INT
SCL
678
X1
X2
SQW
VCC
123
PCF8563
U2
104
C27
RTC_INT1
342
342
4.7K
R40
5V_STB
S4
CS-09
CVBS
1
CVBS/S-VIDEO
1
S
CVBS 1
81
Page 84

+5V
GND
+12V
AGND
12345
-12V
47u/16
CN5
5P2.5
C42
+
SCART1 1
MICDET
+5V
R129
*2.2K
R128
*2.2K
-12V +5V
+
C64
10u/16
+12V
R71
10
R130
*2.2K
3906
Q9
*3904
Q21
R65
*2.2K
*1K
R64
102
C37
4.7K
R58
A_L_OUT 1
4.7K
R57
102
C32
4.7K
4.7K
A_R_OUT 1
R46
R47
103
C43
MICDET
MICON
GPIO4 1
MICIN
A+12V
CPUMUTE 1
2.2K
1234567
*7P2.0
R72
3904
CN4
-12V+12V +5V
SCART1
R70
*2.2K
R131
2.2K
Q11
10K
47u/16
MUTE 1
2.2K
R69
C40
103
R68
30K
+
C41
R67
R50
R51
*33K
3
8 4
+
U3A
4558
1
A+12V
R49
47K
C33
102
8050D
Q5
R_OUT 1,6
2
-
+
10u/16
330
R48
R_OUT
C31
151
R45 20K
C30
A-12V
MICIN
R61
*33K
C35
151
5
6
8 4
+
-
A-12V
R66
10
-12V
5V_STB
C38
102
Q8
8050D
47K
U3B
4558
A+12V
R62
7
+
L_OUT
L_OUT 1,6
C36
10u/16
R59 330
1K
A-12V
R56
20K
R53
1K
C34
103
3906
Q10
100
R123
AMUTE 4,5
220
C39
100u/16V
+
R63
Q73906
82
R6022K
100K
Q6*3906
*0
0
A-12V
R52
R54
+5V
R55
5V_STB
Page 85

REAR_L 1
4.7K
C50
102
R82
4.7K
5
6
8 4
+
-
U4B
4558
7
A+12V
R81
151
C48
A-12V
20K
R78
REAR_R 1
R74
4.7K
C46
102
R75
4.7K
3
2
8 4
+
-
U4A
4558
1
A+12V
151
R73 20K
C44
A-12V
C51
102
Q13
8050D
47K
R84
+
C49
10u/16
R83 330
LT_OUT
1K
REAR_L_OUT
REAR_L_OUT 6
R80
AMUTE 3,5
+
C45
10u/16
R77
47K
330
R76
C47
102
R79
1K
Q12
8050D
REAR_R_OUT
REAR_R_OUT 6
83
Page 86

SUBWOOFER 1
4.7K
C58
102
R94
4.7K
5
6
8 4
+
-
U5B
4558
7
A+12V
R93
151
C56
A-12V
20K
R90
CENTER 1
R86
4.7K
C54
102
R87
4.7K
3
2
8 4
+
-
U5A
4558
1
A+12V
151
R85 20K
C52
A-12V
C59
102
Q15
8050D
47K
R96
+
C57
10u/16
R95 330
R92
1K
SUBWOOFER_OUT
SUBWOOFER_OUT 6
AMUTE 3,4
+
C53
10u/16
R89
47K
330
R88
C55
102
R91
1K
8050D
Q14
CENTER_OUT
CENTER_OUT 6
84
Page 87

G_Y_OUT1
B_U_OUT1
R_V_OUT1
220
470
R115
R114
6.8K
R116
C63
220u/10
+
R113
0
Q18
3904
AV2X2 TOPVIEW
+5V
R110
220
470
R109
6.8K
R111
0
R112
6.8K
5623
+
R108
3904
Q17
C61
220u/10
6.8K
R106
+5V
R103
220
R102
6.8K
R104
470
R98 2.2
G_Y3
R_Cr3
B_Cb3
R101 2.2
0
R100 2.2
+
R99
3904
220u/10
Q16
C60
6.8K
R97
+5V
1346791012
AV4X2 TOPVIEW
14
SUBWOOFER_OUT5
R_OUT1,3
L_OUT1,3
R_OUT1,3
CENTER_OUT5
REAR_L_OUT4
REAR_R_OUT4
L_OUT1,3
R105 2.2
10
11
12
123456789
S5
AV4X2
SPDIF_OUT1
R107 2.2
S6
AV2X2
6
12345
104
C62
OPTICAL1
123
+5V
OP1
GP1F32T
11852
858687
Page 88

Page 89

Page 90

10uF/16V
C7
+
C8
104
123
REM1
HS0038B3V
GND
R13 10
VCC
IR
C10
101
POWER
VCC
+
C3
47u/16
C4
C5
C6
G5
G6
S9
VCC
33
32
31
30
29
28
-24V
27
26
25
24
23
U1
UPD16312
104
VCC
C1
22u/50
+
C2
G5
G6
P16
P15
P14
P13
P12
P11
P10
P9
Q1
9015
P_CTL
1K
VCC
R5
R3
RED
D1
5V_STB
D9
BLUE
R19
330
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
BLUE
330
51K
SW1
SW2
SW3
SW4
DO
DIN
VSS
CLK
STB
KEY1
KEY2
CN2
10P2.0
10
SCART1
SCART2
P_CTL
POWER
IR
R9
10K
R10
10K
R11
10K
R12
10K
IR
VFD_STB
123456789
VFD_DATA
VFD_CLK
R6
2.2K
2.2K
2.2K
2.2K
2.2K
5V_STB
R7
R8
R1
R4
2.2K
D8
R18
R2
D7
R/REC
R17
330
VCC
44
VSS
OSC
KEY4
KEY3
12
VCC
43
13
42
LED1
VDD
14
D6
G/TV/AV
R16
330
SCART2
SCART1
40
41
LED4
LED3
LED2
S3
S2
S1
16
15
P1
D5
G/DVD
R15
330
38
39
VDD
S4
18
17
P4P3P6
G1G3G2
36
37
G2
G1
S6
S5
20
19
P5P2P7
G3
S7
35
21
G4
34
G4
S16/G7
S15/G8
S14/G9
S8
22
P8
104
104
104
S13
VEE
S12
S11
S10
-24V
12345
R14 2.2 1/4W
F+
F-
P[1:16]
CN1
CON5
G[1:6]
101
C9
D2
1N4148
K9
K8 RECORD
K9 STANDBY/ON
K5 DVD
K6 TV/AV
K7 OPEN/CLOSE
K5
K7
K6
K8
K2 CH+/NEXT
K3 STOP
K4 PLAY/PAUSE
K3
K1
1N4148
K4
K2
1N4148
K1 CH-/PREV
F+
34
35
6G
F2
F2
VCC
P1
D3
P2
D4
P8
P5
NX
P3P2P4
16
17
18
19
20
P5
P4
P3
P2
P1
G4G2G3
G6
G5
G1
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
31
32
30
NX
NX
NX
NX
NX
NX
1G
2G
3G
5G
4G
P9P1P10
P13
P15
P14
P12
P13
P14
P15
45678
P16
P16
F-
1
2
F1
F1
VFD1
HNVC05SS41
P6
15
14
13
P6
P7
P11
P7
10
11
12
9
P12
P11
P10
P9
P8
88
Page 91

89
Page 92

r
PARTS LISTPARTS LIST
main board
ITEM
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
Carbon film Resisto
RESISTOR
RESISTOR
RESISTOR
RESISTOR
RESISTOR
RESISTOR
RESISTOR
RESISTOR
RESISTOR
RESISTOR
RESISTOR
RESISTOR
RESISTOR
DESCRIPTION
1/4W2.2Ω±5% 1 R121
1/16W 0Ω ±5% 25
1/16W 22Ω ±5% 46
1/16W 33Ω ±5% 23 R225~R229,R301,R302,R701~R716
1/16W 56Ω ±5% 6 R304~R309
1/16W 220Ω ±5% 1 R809
1/16W 330Ω ±5% 1 R601
1/16W 470Ω ±5% 2 R811,R814
1/16W 1K ±5% 8 R115,R125,R406,R623,R624,R625,R635,R636
1/16W 2.2K ±5% 2 R629,R630
1/16W 4.7K ±5% 11
1/16W 6.8K ±5% 2 R810,R813
1/16W 10K ±5% 15
1/16W 15K ±5% 1 R124
QTY LOCATION
R104,R106,R109,R110,R120,R205~R207,R211,R
212,R230~R233,R235,236,R313,R415,R417,R50
2,L601,R720,R807,R812,R604
R310,R311,R314~R321,R407,R408,R505,R506,R
507,R510~R519,R523,R525~R532,R612~R620,R6
37,R638,R639
R107,R111,R119,R122,R123,R323,R401,R411,R
412,R413,R804
R101,R402~R405,R509,R521,R522,R533,R627,R
631,R632,R718,R719,R803
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
RESISTOR
RESISTOR
RESISTOR
RESISTOR
RESISTOR
RESISTOR
RESISTOR
RESISTOR
RESISTOR
ELEC.CAP
ELEC.CAP
ELEC.CAP
ELEC.CAP
ELEC.CAP
1/16W 22K ±5% 3 R201,R202,R213
1/16W 33K ±5% 1 R621
1/16W 100Ω ±5% 6 R116,R117,R118,R622,R801,R802
1/16W 100K ±5% 1 R603
1/16W 3.9K ±5% 1 R806
1/16W 5.6K ±5% 8 R508,R524,R215~R220
1/16W 150Ω ±5% 2 R203,R204
1/16W 91Ω ±5% 1 R602
1/16W62Ω±5% 2 R409,R410
CD11 16V10U±20%5×11 2 15
CD11 16V47U±20%5×11 2 10
CD11 16V100U±20%6×12 2.5 4 CE303,CE501,CE701,CE801
CD11 16V220U±20%6×12 2.5 8
CD11 50V1U+20%-10%5×11 2 3 CE203,CE204,CE205
CE105,CE106,CE201,CE202,CE206,CE207,CE210
~CE213,CE403,CE404,CE405,CE406,CE608
CE301,CE402,CE407,CE410,CE412,CE603,CE607
,CE609,CE610,CE702
CE302,CE401,CE408,CE409,CE601,CE602,CE605
,CE802
90
Page 93

PARTS LIST
main board
ITEM
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
ELEC.CAP
ELEC.CAP
ELEC.CAP
CER.CAP
CER.CAP
CER.CAP
CER.CAP
CER.CAP
CER.CAP
CER.CAP
FERRITE BEAD
FERRITE BEAD
INDUCTOR IRON
DESCRIPTION
CD11 50V4.7U±20%5×11 2 1 CE104
CD11 50V3.3U±20%5×11 2 2 CE208,CE209
CD11 16V330U±20%8×12 3.5 5 CE101,CE102,CE103,CE411, CE606
50V 47P ±5% NPO 0603 2 C405,C406
50V 101 ±5% NPO 0603 11
50V 122 ±10% 0603 6 C209~C214
50V 102 ±10% 0603 2 C616,C625
50V 27P ±5% NPO 0603 4 C310,C311,C620,C621
50V 473 ±10% 0603 2 C308,C309
50V104 ±20% 0603 121
FCM1608-601T02 12 L202,L602,L603,L808,L402~L409
FB 10
1.8UH ±10% 1608 6 L802~L807
QTY LOCATION
C101,C102,C103,C111,C112,C808,C810,C814,C
816,C820,C822
C104,C105,C106,C110,C201~C208,C301~C307,C
323~C329,C401~C404,C407~C461,C501,C502,C5
03,C601~C615,C617,C618,C619,C622,C623,C62
4,C701~C704,C707~C710,C801~C804
L102,L103,L105,L106,L201,L301,L302,L303,L
401,L801
DIODE
42
TRANSISTOR
43
44 IC 74HCU04D SOP 1 U603
45 IC MM74HCU04M SOP 1 U603
46 IC HCU04 SOP 1 U603
47 IC LVU04 SOP 1 U603
48 IC VHCU04 SOP 1 U603
49 IC MM74HCT14M SOP 1 U604
50 IC HCT14 SOP 1 U604
51 IC CS4360 SSOP 1 U203
52 IC CS4955-CQ TQFP 1 U801
53 IC LM1117MP-1.8 SOT-223 1 U406
54 IC W981616BH-7 SOP 4 U402~U405
55 IC PQ070XZ01ZP SC-63 1 U602
56 IC W986432DH-7 TSOP 1 U701
57 IC SAA7114 QFP 1 U301
1N4148 3 D601,D701,D702
9014C 2 Q801,Q802
58 IC CS92288 BGA 1 U401
59 IC CS98000 QFP 1 U601
91
Page 94

PARTS LIST
main board
ITEM
60 IC CS5331A-KS SOP 1 U202
61 IC 24C08 SOP 1 U605
62 IC HC157 SOP 1 U201
63 IC MM74HC157M SOP 1 U201
CRYSTAL
64
CRYSTAL
65
CRYSTAL
66
67 PCB 2AB9905-1 1
WAFER
68
WAFER
69
WAFER
70
WAFER
71
WAFER
72
DESCRIPTION
27.00MHz 49-S 1 Y601
24.576MHz 49-S 1 Y301
24.576MHz 49-U 1 Y301
10P 2.0mm 1 CN104
9P 2.5mm 1 CN101
20P 2.5mm 1 XS501
13P 1.0mm 1 CN103
12P1.0mm 1 CN102
QTY LOCATION
92
Page 95

Y
PARTS LIST
key board
ITEM QT
1 ELEC.CAP CD11C 50V22U±20%6×7 2.5 1 C1
2 ELEC.CAP CD11C 16V10U±20%4×7 1.5 1 C7
3 ELEC.CAP CD11C 16V47U±20%5×7 2 1 C3
4 CER.CAP 50V 104 ±20% 5mm 5 C2,C4,C5,C6,C8
5 CER.CAP 50V 100P ±10% 5mm 2 C9,C10
6 LED 2R 53HD RED 2 D1,D7
7 DIODE 1N4148 3 D2~D4
8 LED 2G 53HD 2×5×7 2 D5,D6
9 LED 3B4ST 2 D8,D9
10 Tact Switch 6×6×1 9 K1~K9
11 Transistor 9015C 1 Q1
12 REMOTE RECEIVING HS0038B3V 1 REM1
13 Carbon film Resistor 1/6W2.2K±5% 4 R5~R8
14 Carbon film Resistor 1/6W51K±5% 1 R2
15 Carbon film Resistor 1/6W10K±5% 2 R11,R12
16 Carbon film Resistor 1/6W10Ω±5% 1 R13
17 Carbon film Resistor 1/6W2.2Ω±5% 1 R14
18 Carbon film Resistor 1/6W330Ω±5% 2 R1,R4
19 Carbon film Resistor 1/6W1K±5% 2 R3,R17
20 Carbon film Resistor 1/6W220Ω±5% 2 R15,R16
DESCRIPTION
LOCATION
21 Carbon film Resistor 1/4W10K±5% 2 R9,R10
22 IC PT6312LQ QFP 1 U1
23 LED Displays HNVC06SC020 1 VFD1
24 PCB 4AB9907-0 1
93
Page 96

PARTS LIST power board
ITEM QTY LOCATION
1 RESISTOR 1/4W22Ω±5% 10 1 R13
2 RESISTOR 1/4W33Ω±5% 10 1 R5
3 RESISTOR 1/4W330Ω±5% 10 1 R8
4 RESISTOR 1/4W470Ω±5% 10 1 R15
5 RESISTOR 1/4W1K±5% 10 2 R4,R20
6 RESISTOR 1/4W4.7K±5% 10 1 R17
7 RESISTOR 1/4W10K±5% 10 4 R3,R7,R19,R10
8 RESISTOR 1/4W47K±5% 10 1 R9
9 RESISTOR 1/4W1.2K±5% 10 1 R14
10 RESISTOR 1W0.47Ω±5% 12.5 1 R12
11 METAL FILM RESISTOR 1/4W10K±1% 10 2 R11,R18
12 METAL OXIDE FILM RESISTOR 2W68K±5% 15 1 R2
13 METAL OXIDE FILM RESISTOR 1/2W470K±5% 12.5 2 R1,R6
14 CER.CAP 50V 104 +80%-20% 5mm 7 C2,C7,C8,C11,C12,C15,C16
15 CER.CAP 1000V 103 +80%-20% 7.5mm 1 C4
DESCRIPTION
16 CER.CAP 500V 101 ±10% 5mm 1 C17
17 CAP CT81 400V221±10% 10mm 2 C3,C14
18 CAP 400VAC 222 ±20% 10mm 1 C6
19 CAP 275V 104 ±20% 15mm 1 C13
20 CER.CAP 50V 473 ±20% 2.5mm 1 C10
21 ELEC.CAP ELEC.CAP11 25V100U±20%6×12 2.5 5 CE1,CE2,CE12,CE14,CE16
22 ELEC.CAP ELEC.CAP11 25V10U±10%5×11 2 1 CE7
23 ELEC.CAP ELEC.CAP110 25V470U±20%10×16 5 2 CE3,CE4
24 ELEC.CAP ELEC.CAP110 25V22U±20%5×11 2 1 CE11
25 ELEC.CAP ELEC.CAP110 50V47U±20%6×12 2.5 1 CE13
26 ELEC.CAP LS 400V100U±20%22×30 10 1 CE5
27 ELEC.CAP ELEC.CAP110 16V220U±20%6×12 2.5 2 CE15,CE17
28 ELEC.CAP GZ 10V2200U±20%10×20 5 2 CE6,CE9
29 ELEC.CAP GZ 10V1000U±20%8×16 3.5 2 CE8,CE10
30 FERRITE BEAD FB 3 L1,L2,L4
31 INDUCTOR IRON 10UH 3A 5mm 2 L3,L5
32 TRANSFOMER BCK-28-0300 1 T1
33 DIODE 1N4007 4 D9,D10,D11,D12
34 DIODE HER105 4 D1,D6,D7,D8
35 DIODE HER107 1 D4
36 DIODE HER303 1 D2
37 ZENER 5.1V 1/2W 1 D13
94
Page 97

PARTS LIST power board
ITEM QTY LOCATION
38 DIODE MBR1060 TO-220 1 D3
39 DIODE BYW29E-200 TO-220 1 D5
40 TRANSISTOR 2N5401 1 Q4
41 TRANSISTOR 2N5551 2 Q3,Q5
42 MOSFET AP40N03P TO-220 2 Q1,Q2
43 IC LM431ACZ TO-92 1 IC3
44 IC PQ12RD21 TO-220 1 IC4
45 IC ICE 2A265 DIP 1 IC1
46 INDUCTOR IRON UT-20 40mH ±20% 10×13 1 LF1
47 THERM RESISTOR NTC SCK-104MS±20% 1 RT1
48 OPTOTRANSISTOR NEC2561 1 IC2
49 PCB 5AB9915-0 1
50 WAFER 5P 2.5mm 1 CN2
51 WAFER 5P 2.0mm 1 CN5
52 WAFER 2P 2.5mm 1 CN1
DESCRIPTION
53 WAFER 9P 2.5mm 1 CN3 1~9PIN
54 WAFER 4P 3.96mm 1 CN4
55 WAFER 2P 8.0mm 2# 1 BCN1
60 FUSE T2AL 250V 1 F1
62 RADIATOR 11×15×31 LFDR9905 2
64 RESISTOR 1/2W910K±5% 12.5×7 1 RV1
95
Page 98

PARTS LIST AVV board
ITEM QTY LOCATION
1 RESISTOR 1/16W 0Ω ±5% 7 R18,R33,R41,R55,R99,R108,R113
2 RESISTOR 1/16W 10Ω ±5% 2 R71,R66
3 RESISTOR 1/16W 22Ω ±5% 1 R23
4 RESISTOR 1/16W 220Ω ±5% 8 R1,R8,R36,R43,R63,R103,R110,R115
5 RESISTOR 1/16W 330Ω ±5% 6 R48,R59,R76,R83,R88,R95
6 RESISTOR 1/16W 470Ω ±5% 5 R37,R44,R104,R111,R116
7 RESISTOR 1/16W 1K ±5% 7 R26,R53,R56,R79,R80,R91,R92
8 RESISTOR 1/16W 2.2K ±5% 3 R68,R72,R131
9 RESISTOR 1/16W 3.3K ±5% 4 R119~R122
10 RESISTOR 1/16W 4.7K ±5% 15
11 RESISTOR 1/16W 6.8K ±5% 10
12 RESISTOR 1/16W 10K ±5% 7 R4,R5,R29,R30,R69,R117,R118
13 RESISTOR 1/16W 20K ±5% 6 R45,R51,R73,R78,R85,R90
14 RESISTOR 1/16W 22K ±5% 1 R60
16 RESISTOR 1/16W 47K ±5% 6 R49,R62,R77,R84,R89,R96
17 RESISTOR 1/16W 100K ±5% 1 R52
18 RESISTOR 1/16W 100Ω ±5% 1 R123
19 RESISTOR 1/16W 30K ±5% 1 R67
20 RESISTOR 1/16W 3.9K ±5% 4 R2,R3,R25,R27
21 RESISTOR 1/16W 18Ω ±5% 4 R6,R9,R10,R16
22 ELEC.CAP ELEC.CAP11 10V220U±20%6×12 2.5 6 C18,C25,C26,C60,C61,C63
23 ELEC.CAP ELEC.CAP11 16V10U±20%5×11 2 6 C31,C36,C45,C49,C53,C57
24 ELEC.CAP ELEC.CAP11 16V47U±20%5×11 2 4 C1,C7,C40,C42
25 ELEC.CAP ELEC.CAP11 16V100U±20%6×12 2.5 2 C12,C39
26 ELEC.CAP ELEC.CAP11 16V4.7U±20%5×11 2 7 C3~C6,C17,C23,C24
27 CER.CAP 50V 102 ±10% 0603 13
28 CER.CAP 50V 103 ±10% 0603 5 C13,C19,C34,C41,C43,
29 CER.CAP 50V 20P ±5% 0603 1 C28
30 CER.CAP 50V104 ±20% 0603 6 C2,C9,C22,C27,C62,C65
31 CER.CAP 50V 151 ±5% NPO 0603 6 C30,C35,C44,C48,C52,C56
32 FERRITE BEAD FCM1608K-221T05 12
33 ZENER 6.2V 1/2W 2 D1,D3
34 DIODE 1N4148 9 D2,D4~D8,D11,D12,D13
35 TRANSISTOR 3904 9 Q2,Q3,Q4,Q11,Q16~Q20
36 TRANSISTOR 3906 3 Q1,Q7,Q10
37 TRANSISTOR 8050D 6 Q5,Q8,Q12~Q15
38 IC ELEC.CAP4052BCN DIP 1 U1
39 IC PCF8563T SO8 1 U2
40 IC RC4558D SOP 3 U3,U4,U5
41 CRYSTAL 32.768KHz 3×9 1 X1
42 TUNER JS-6B2/L121 1 TUN1
DESCRIPTION
R24,R40,R46,R47,R57,R58,R74,R75,R81,R
82,R86,R87,R93,R94,R126
R32,R35,R39,R42,R97,R102,R106,R109,R1
12,R114
C20,C32,C33,C37,C38,C46,C47,C50,C51,C
54,C55,C58,C59
R31,R34,R38,R98,R100,R101,R105,R107,C
8,C10,C11,C15
43 OPTICAL OUTPUT TP01A 1 OP1
44 BATTERY CR2032 1 BT1
45 PCB 7AB9905K-2 1
96
 Loading...
Loading...