Page 1
INSTRUCTION MANUAL
FOR
SYNC-CHECK RELAY
BE1-25
Publication: 9170200990
Revision: U 07/13
Page 2

Page 3

INTRODUCTION
This instruction manual provides information about the operation and installation of the BE1-25 SyncCheck relay. To accomplish this, the following information is provided:
• General Information and Specifications
• Controls and Indicators
• Functional Description
• Installation
• Testing
WARNING!
To avoid personal injury or equipment damage, only qualified personnel should
perform the procedures in this manual.
NOTE
Be sure that the BE1-25 is hard-wired to earth ground with no smaller than 12
AWG copper wire attached to the ground terminal on the rear of the unit case.
When the BE1-25 is configured in a system with other devices, it is
recommended to use a separate lead to the ground bus from each unit.
9170200990 Rev U BE1-25 Introduction i
Page 4

First Printing: 1985
Printed in USA
© 2013 Basler Electric, Highland Illinois 62249 USA
All Rights Reserved
July 2013
CONFIDENTIAL INFORMATION
of Basler Electric, Highland Illinois, USA. It is loaned for confidential use, subject
to return on request, and with the mutual understanding that it will not be used in
any manner detrimental to the interest of Basler Electric.
It is not the intention of this manual to cover all details and variations in equipment, nor does this manual
provide data for every possible contingency regarding installation or operation. The availability and design
of all features and options are subject to modification without notice. Should further information be
required, contact Basler Electric.
BASLER ELECTRIC
12570 STATE ROUTE 143
HIGHLAND IL 62249-1074 USA
http://www.basler.com, info@basler.com
PHONE +1 618.654.2341 FAX +1 618.654.2351
ii BE1-25 Introduction 9170200990 Rev U
Page 5
Revision and Date
Change
REVISION HISTORY
The following information provides a historical summary of the changes made to the BE1-25 instruction
manual (9170200990). Revisions are listed in reverse chronological order.
Manual
U, 07/13
T, 10/12
S, 03/11
R, 09/07
P, 11/06
N, 08/02
M, 02/01
L, 08/98
K, 12/97
• Added Caution for contact sensing in Specifications.
• Minor text and formatting edits.
• Standardized case and cover drawings in Section 4.
• Updated power supply burden data in Section 1.
• Updated GOST-R statement in Section 1.
• Updated Storage Statement in Section 4.
• Moved content of Section 6, Maintenance to Section 4.
• Added manual part number and revision to all footers.
• Updated power supply burden data in Section 1.
• Updated Target Indicator description in Section 3.
• Updated Output Specs in Section 1.
• Added footnote to Figures 1-2 and 1-3.
• Updated drawings of case cover in Section 4, Installation.
• Updated front panel drawing in Section 2, Controls and Indicators.
• Moved manual Revision History to the front of manual.
• Updated drawing on front cover.
• Updated drawings in the manual to label terminal 15 (COM) as Vctrl.
• Corrected various minor errors throughout the manual.
• Changed the Specifications, illustrations, and the descriptions
throughout the manual for the minimum voltage required to operate
the sync-check function.
• Corrected Figure 1-6, Style Chart.
• Added contact-sensing burden and enhanced Surge Withstand
Capability description.
• Added new covers information.
• Changed Section 5, Testing, to reflect the minimum voltage
requirements for sync-check function.
• Added Power Supply information to Section 3 and added new wide
range power supply information to Section 1.
• Corrected Style Chart by changing Power Supply Type T from 230
Vac to 240 Vac.
• Moved Testing information from Section 4 to new Section 5, Testing.
• Added new outline dimensions to include all options (S1 Case,
Double-Ended, Semi-Flush, and Projection Mounting).
• Corrected ground symbol in Figure 4-7, Internal Diagram.
• Updated front cover and Manual Change information.
• Deleted the reference to Service Manual 9170200620 on page 1-1.
• Corrected an error found on page 1-11 in Minimum Voltage
Requirement from “45 ±2 Vac” to “80 Vac”.
• Updated front cover and Manual Change information.
9170200990 Rev U BE1-25 Introduction iii
Page 6
Manual
Revision and Date
J, 10/97
H, 01/96
G, 01/95
F, 03/92
E, 05/90
D, 07/88
C, 06/87
B, 12/86
A, 11/85
Change
• Added three new types (A, B, & C) to Option 2. This included new
paragraphs describing Average Detectors.
• Corrected power supply type P, voltage input, and range from Vdc to
Vac.
• Minor page layout changes developed from using a word processor
application upgrade.
• Reformatted instruction manual as Windows Help file for electronic
documentation.
• Added new Figure 4-7, Internal Diagram and incorporated new
instruction manual format.
• Edited General Information section and Controls and Indicators
section for clarification.
• Revised Figure 4-12 and edited Operational Test Procedure.
• Added test plug/adapter information.
• Added TB2 terminal strip to connection diagrams.
• Revised manual to reflect introduction of power supply status option.
• Added note to Style Chart.
• Added footnote to power supply table and deleted the words make
and from inductive contact specification.
• Corrected and clarified phase angle specifications.
• Corrected typographical errors on Slip Frequency graph.
• Added information to Figures 4-4, 4-9, and 4-10.
• Added storage recommendation paragraph.
iv BE1-25 Introduction 9170200990 Rev U
Page 7

CONTENTS
SECTION 1 • GENERAL INFORMATION ................................................................................................ 1-1
SECTION 2 • CONTROLS AND INDICATORS ........................................................................................ 2-1
SECTION 3 • FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION ........................................................................................... 3-1
SECTION 4 • INSTALLATION .................................................................................................................. 4-1
SECTION 5 • TESTING ............................................................................................................................ 5-1
9170200990 Rev U BE1-25 Introduction v
Page 8

This page intentionally left blank.
vi BE1-25 Introduction 9170200990 Rev U
Page 9

SECTION 1 • GENERAL INFORMATION
TABLE OF CONTENTS
SECTION 1 • GENERAL INFORMATION ................................................................................................ 1-1
INTRODUCTION ................................................................................................................................... 1-1
DESCRIPTION ...................................................................................................................................... 1-1
APPLICATION ....................................................................................................................................... 1-1
SYNC-CHECK FUNCTION .................................................................................................................... 1-2
CONTACT SENSING ............................................................................................................................ 1-2
VOLTAGE MONITOR OPTIONS ........................................................................................................... 1-2
Mode Switches ................................................................................................................................... 1-2
Condition Switches ............................................................................................................................. 1-3
Voltage Difference .............................................................................................................................. 1-3
Option 2-R, 2-T, or 2-U (Phasor Voltage Difference) ......................................................................... 1-4
Option 2-A, 2-B, or 2-C (Average Voltage Difference) ....................................................................... 1-5
Output Relay ...................................................................................................................................... 1-6
OTHER OPTIONS ................................................................................................................................. 1-6
Expandable Window ........................................................................................................................... 1-6
External Condition Switches .............................................................................................................. 1-6
Push-to-Energize Output Pushbuttons ............................................................................................... 1-7
MODEL AND STYLE NUMBER............................................................................................................. 1-7
Style Number Example ....................................................................................................................... 1-7
SPECIFICATIONS ................................................................................................................................. 1-9
Figures
Figure 1-1. Voltage Monitor Acceptance Zones ........................................................................................ 1-3
Figure 1-2. Closing Zone (Phasor Sensing) .............................................................................................. 1-4
Figure 1-3. Closing Zone (Average Sensing) ............................................................................................ 1-4
Figure 1-4. Closing Zone Calculation Diagram (Phasor Sensing) ............................................................ 1-5
Figure 1-5. Closing Zone Diagram (Average Sensing) ............................................................................. 1-6
Figure 1-6. Style Number Identification Chart ........................................................................................... 1-8
Tables
Table 1-1. Power Supply ........................................................................................................................... 1-9
9170200990 Rev U BE1-25 General Information i
Page 10

This page intentionally left blank.
ii BE1-25 General Information 9170200990 Rev U
Page 11
SECTION 1 • GENERAL INFORMATION
INTRODUCTION
These instructions provide information concerning the operation and installation of BE1-25 Sync-Check
Relays. To accomplish this, the following is provided:
• Specifications
• Functional characteristics
• Mounting information
• Setting procedures and examples
Relays with a Type T power supply require a Contact Sensing Module, which comes supplied with its own
instructions, publication 9170206990.
WARNING!
To avoid personal injury or equipment damage, only qualified personnel should
perform the procedures presented in these instructions.
These instructions may be used in place of all earlier editions. For change information, see Revision
History in the manual Introduction.
It is not the intention of these instructions to cover all details and variations in equipment, nor does this
manual provide data for every possible contingency regarding installation or operation. The availability
and design of all features and options are subject to modification without notice. Should further
information be required, contact Customer Service, Basler Electric Company, Highland, IL.
DESCRIPTION
The BE1-25 is a solid-state synchronism check relay designed to permit breaker closure when the desired
maximum phase angle conditions have held for a specified minimum time. The maximum allowable phase
angle and time delay requirements can be set on front panel thumbwheel switches. Five voltage
measuring options are available that identify significant line and bus voltage conditions, and this
information is used to influence the relay output.
APPLICATION
BE1-25 Sync-Check Relays are recommended for situations that require verification of synchronism prior
to closing a circuit breaker. Typical applications are:
• Paralleling a generator to a system.
• Reestablishing a connection between two parts of a power system.
• Supervising fast transfer schemes, where fast pickup and dropout of the phase measuring circuit
are required.
If optional voltage measuring circuits are incorporated, the BE1-25 can determine whether an input is live,
dead, or in an overvoltage state.
NOTE
Voltage sensing circuits are guaranteed to operate at a minimum voltage of 60
volts. They are guaranteed not to operate at voltages less than 20 volts. Some
units may operate at voltages in between these two levels because of the
individual characteristics of specific components. Minimum voltage detection is
usually in the range of 45 to 55 volts
9170200990 Rev U BE1-25 General Information 1-1
Page 12

SYNC-CHECK FUNCTION
BE1-25 Sync-Check function measures the phase angle between single-phase voltages of line and bus.
Then sync-check verifies that this angle is less than the front panel PHASE ANGLE selector setting. If the
measured angle has met these criteria for the time period defined by the front panel TIME DELAY setting,
the SYNC output contact closes.
The allowable phase angle is adjustable over the range of 1 to 99 degrees. The time delay is adjustable
over either of two ranges: 1 to 99 cycles, 50/60 hertz (using the bus frequency as the reference), or 0.1
to 99 seconds (using the internal crystal controlled oscillator as the reference).
An optional target may be specified to indicate operation of the Sync-Check function.
CONTACT SENSING
To control operation of the relay, an input from the breaker auxiliary 52b contact is required to signal the
breaker status. If the breaker is open, the relay is enabled to perform its function. When the breaker
closes, the 52b input changes state and causes the relay to terminate its close signal.
Two configurations of the 52b contact sensing input are available to provide additional flexibility for the
protection circuit designer:
• Isolated contact sensing monitors a current supplied by the relay through an isolated contact.
• Non-isolated contact sensing monitors the presence of voltage at its input due to the closure of a
contact.
See Figure 4-11 for typical control circuit connections for each configuration. Also, see Figure 4-12 if a
Type T power supply has been selected.
VOLTAGE MONITOR OPTIONS
Mode Switches
Two Mode switches are located on the Voltage Monitor card. Mode Switch No. 1 serves the bus Voltage
Monitor function. Mode Switch No. 2 serves the line Voltage Monitor function. Mode switch positions are
as follows:
NORMAL Mode (Up) - allows measuring elements to establish live and dead reference levels for
the input level.
NOT-OV Mode (Down) - allows measuring elements to establish live and Not-Overvoltage
reference levels for the input level.
When a Mode Switch is in the NORMAL Mode position (Up), a dead level is defined as a monitored
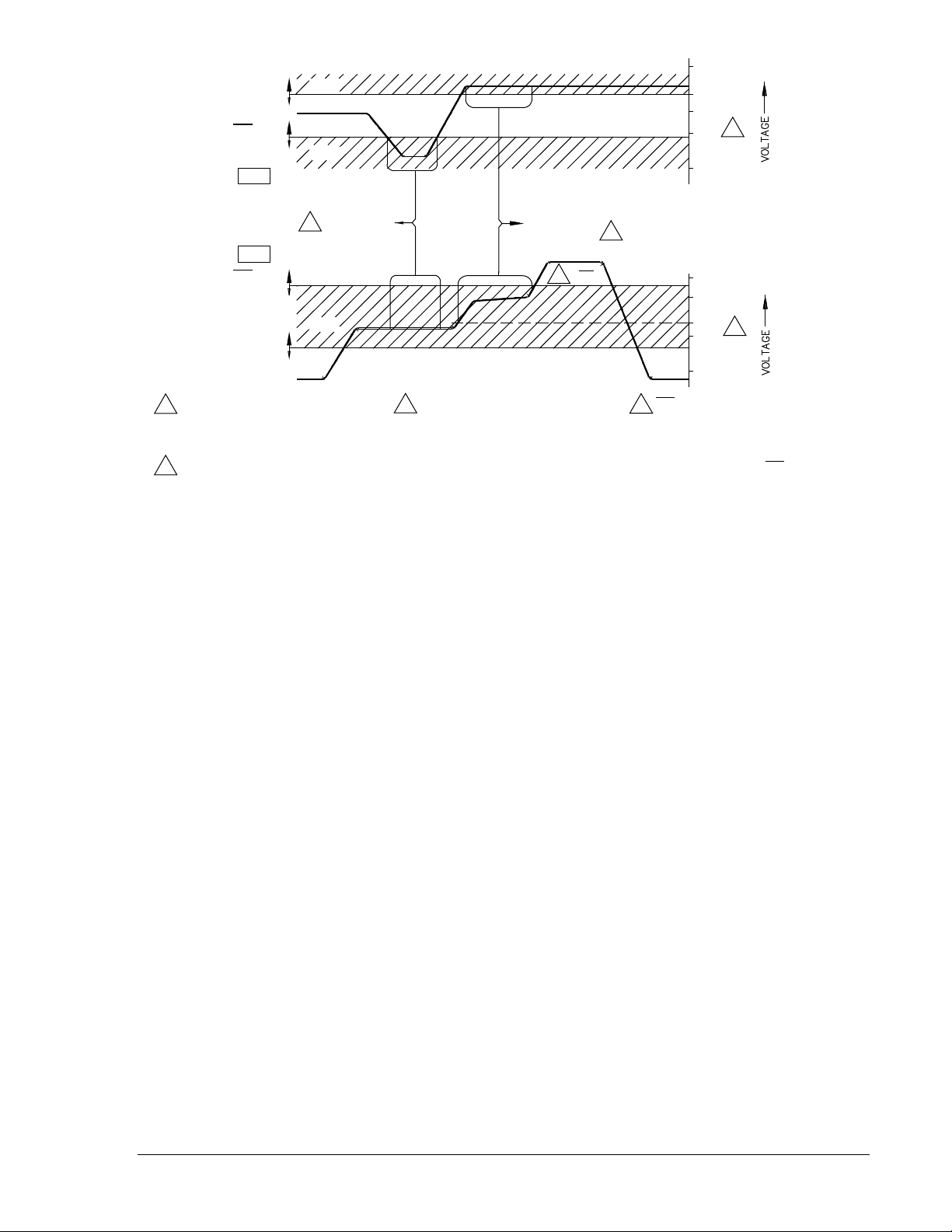
voltage level below the DEAD reference setting. See Figure 1-1 for voltage monitor acceptance zones. A
live level is defined as a monitored voltage above the LIVE reference setting.
When a Mode Switch is in the NOT-OV Mode position (Down), a dead level is defined as a monitored
voltage less than the LIVE reference setting, and a live level is defined as a monitored voltage greater
than the LIVE reference setting, but less than the NOT-OV setting. (An input is considered over-voltage
when it exceeds the NOT-OV reference setting.)
It is permissible to operate the line input in either the same mode or a different mode than the bus input.
This flexibility allows the BE1-25 to be used, for example, to close a generator breaker onto a dead bus,
or to prevent closure if the generator and/or bus voltage is too high.
See Table 2-1, callout R, for a complete description and precautions on setting the Mode Switches. The
location of the switches is shown in Figure 2-2. Also, see Condition and Mode Switches in Section 5.
1-2 BE1-25 General Information 9170200990 Rev U
Page 13
Condition Switches
LL ADJ
=100V
DL / OV ADJ
=40V
LINE
DEAD
LINE VOLTAGE
LIVE
135V (MAX)
100V
50V
10V (MIN)
2
LIVE LINE/
LIVE BUS
CONDITION
4
OV
135V (MAX)
100V
50V
10V (MIN)
P0004-36
BUS
1
DEAD LINE/
LIVE BUS
CONDITION
LIVE
DB / OV ADJ
=120V
LB ADJ
=35V
BUS VOLTAGE
60V FIXED MINIMUM VOLTAGE
LIMIT (LIVE LINE/LIVE BUS
CONDITION SYNC-CHECK
3
NOTES:
SYNC RELAY CONTACTS
CLOSED BY VOLTAGE MONITOR
SYNC-CHECK LOGIC ENABLED
2
1
LOGIC
4 OV EXCEEDED, SYNC-CHECK
TO ON PERMITS
LOGIC NOT ENABLED (SETTING
MODE SWITCH NO. 1 TO ON
AND CONDITION SWITCH NO. 1
FUNCTION ONLY)
OV)
3
3
Five Condition Switches are located on the Voltage Monitor Card, each with two positions to select ON
(Down) and OFF (Up). When ON, Condition Switch No. 1 programs the relay to require recognition that
the line and bus are not in an overvoltage condition (NOT OV) before the SYNC output is allowed.
Condition Switches No. 2 through No. 5 modify the voltage monitor response according to a programmed
set of external conditions. The possible external conditions for each of these four switches are:
Switch 2. Live Line/Live Bus (LL-LB)
Switch 3. Dead Line/Live Bus (DL-LB)
Switch 4. Live Line/Dead Bus (LL-DB)
Switch 5. Dead Line/Dead Bus (DL-DB)
When a selected condition has been recognized, the voltage monitor circuit may be instructed to
immediately energize the Sync-Check output relay, or (if provided) the Voltage Monitor output relay. (See
Figure 1-1, Note 1.)
See Table 2-1, callout S, for a complete description and precautions on setting the Conditions Switches.
The location of the switches is shown in Figure 2-2.
Voltage Difference
A voltage monitor is available that checks the phasor or average voltage difference between the two
inputs. This can be used to prevent the closure of a generator breaker if the voltage difference is too great
(even if the phase angle and voltage level monitoring circuits indicate that proper closing conditions are
otherwise present).
The voltage difference option (included with option 2-A, 2-B, 2-C, 2-R, 2-T or 2-U) is typically used to
reduce the amount of possible system shock or transients when closing a breaker. This option compares
the voltage between line and bus against a selected limit, and initiates either an enable or an inhibit signal
for the sync-check logic, thereby narrowing the voltage across the breaker contacts (as compared to a
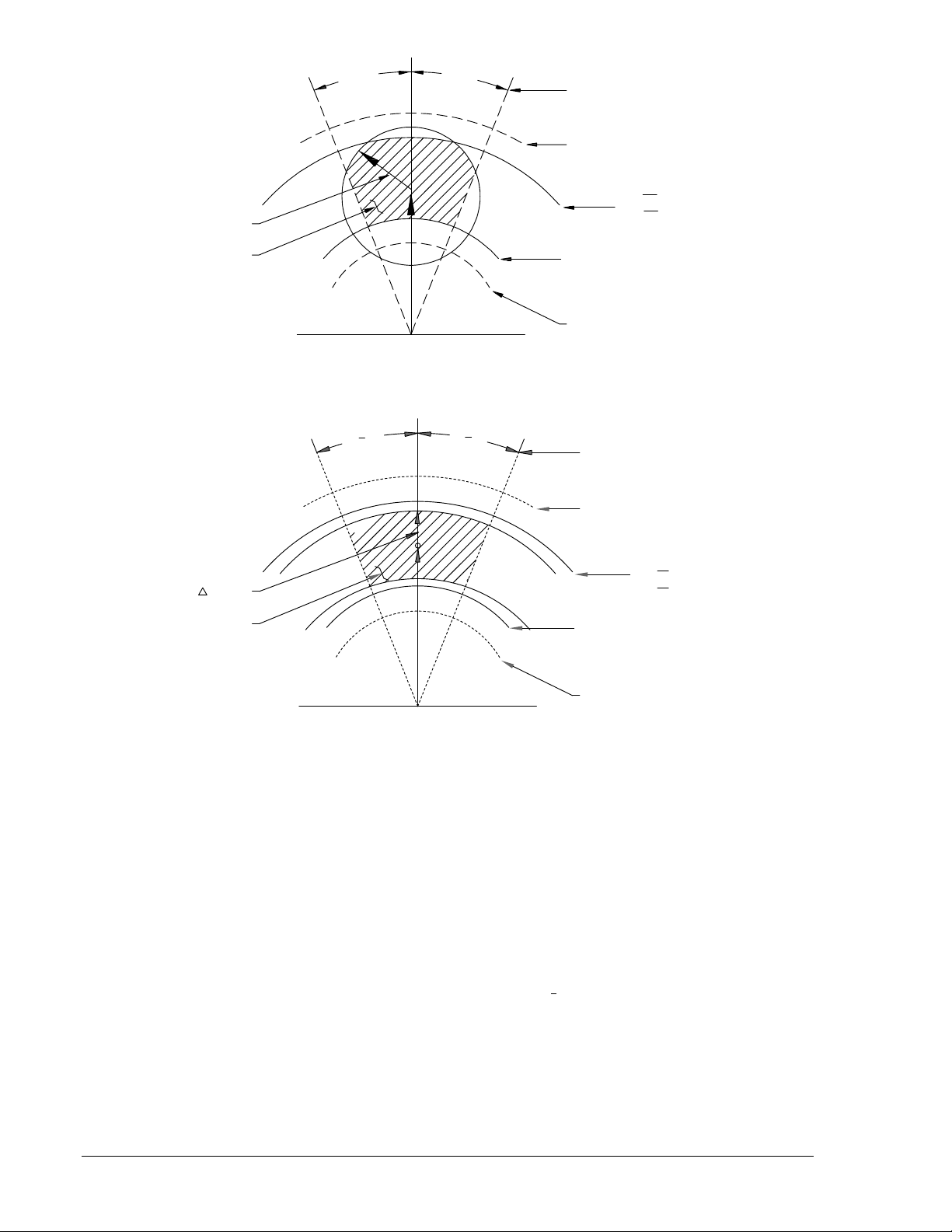
simple sync-check acting alone). Figure 1-2 shows closing zones obtained by combining phasor voltage
difference, phase angle limit, and line and bus live/dead voltage limits. Figure 1-3 shows closing zones
obtained by combining average voltage difference, phase angle limit, and line and bus live/dead voltage
limits.
9170200990 Rev U BE1-25 General Information 1-3
Figure 1-1. Voltage Monitor Acceptance Zones
Page 14
V
B
V
L
∆V V V V V
L B L B
=
+ − ⋅ ⋅ ⋅( cos )
2 2
2
1
2
θ
V
L
V
L
θ
V ADJ∆
ALLOWABLE
CLOSING ZONE
PHASE ANGLE ADJ
135V (MAX)
DL /OV ADJ (LINE) ٭
DB /OV ADJ (BUS) ٭
LL ADJ (LINE)
LB ADJ (BUS)
60V (APPROX.) FIXED
MINIMUM VOLTAGE
P004-35
θ
PHASE ANGLE ADJ
135
V (
MAX
)
DL/
OV ADJ
(LINE)
٭
DB
/
OV ADJ (
BUS
)
٭
LL ADJ (LINE)
LB ADJ (BUS)
60V (APPROX.) FIXED
MINIMUM VOLTAGE
0
0
V ADJ
ALLOWABLE
CLOSING ZONE
P004-38
Figure 1-2. Closing Zone (Phasor Sensing)
Figure 1-3. Closing Zone (Average Sensing)
∗ Lines apply only if using the NOT-OV mode setting. When operating in NORMAL mode, the 135V
(MAX) line applies as an upper limit.
Option 2-R, 2-T, or 2-U (Phasor Voltage Difference)
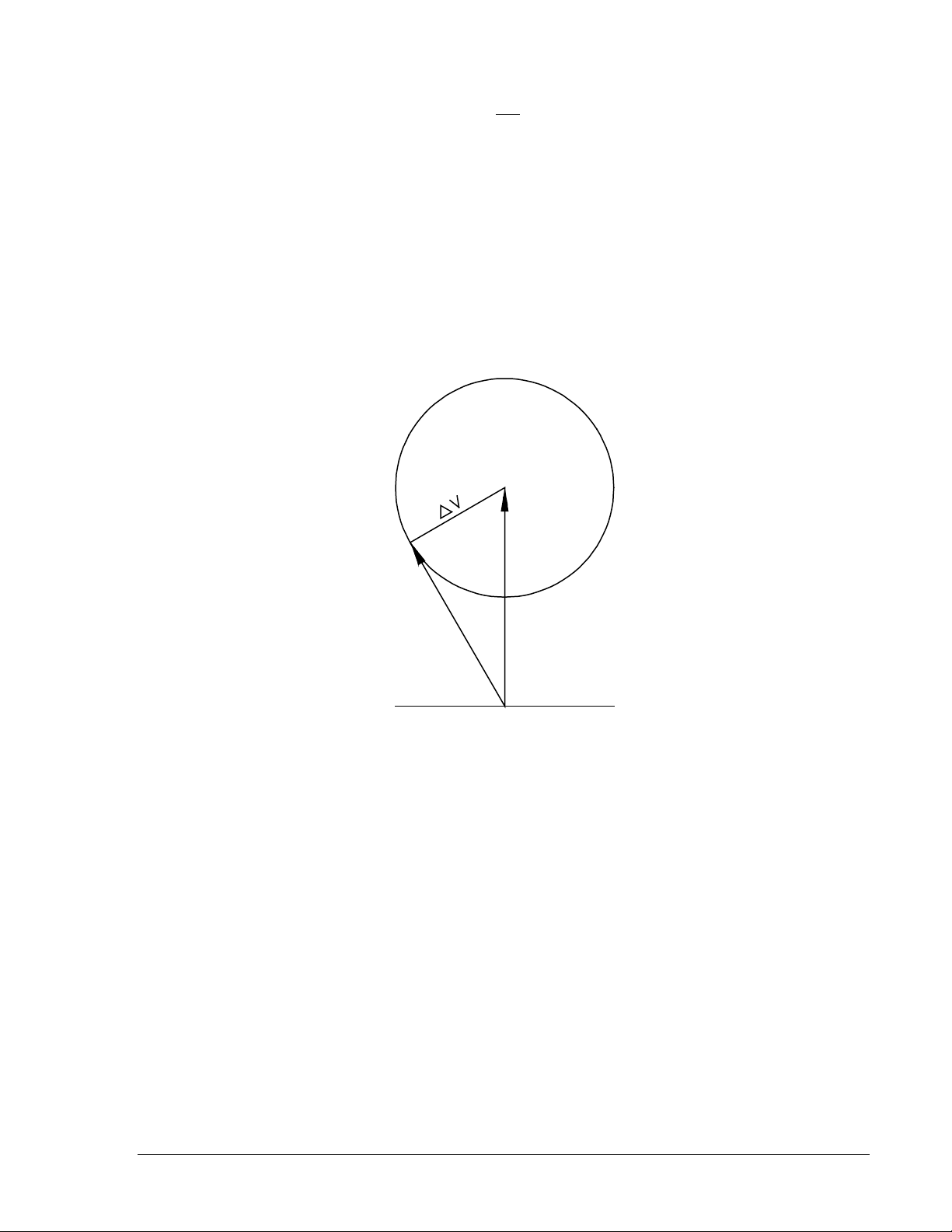
Figure 1-4 may be used as an aid in formulating the voltage difference control settings. Note that the
center reference phasor (
represents the monitored line voltage. The voltage difference control (∆V) forms an area of acceptance
limit when rotated through 360 degrees. This allows either the voltage difference or the phase angle to be
selected, and the remaining value to be calculated.
Calculate the voltage difference (∆V) using the law of cosines. The equation is:
When
is tangent to the voltage difference circle, the ∆V phasor is perpendicular to
angle limit. Accordingly, the voltage difference or the phase angle can be calculated by equations 2 and
3, respectively.
1-4 BE1-25 General Information 9170200990 Rev U
) represents the monitored bus voltage, while the adjacent phasor (
)
(1)
at the phase
Page 15
∆V V sin
B
= θ
θ
∆
=
−
sin
V
V
1
B
V
L
V
B
V
L
V
B
V
L
V
L
V
B
P0004-37
θ
(2)
where:
∆V = Voltage Difference
= Line Voltage
= Bus Voltage
(3)
θ = Phase Angle
Note that the point where
condition of
valid: If the magnitude of the line voltage decreases, the phase angle must also decrease to allow syncacceptance. Therefore, the minimum line voltage possible for sync-acceptance occurs at zero phase
angle.
θ for a closure. Assuming that a constant voltage difference exists, the following condition is
is tangent to the voltage difference circle represents the most extreme
Figure 1-4. Closing Zone Calculation Diagram (Phasor Sensing)
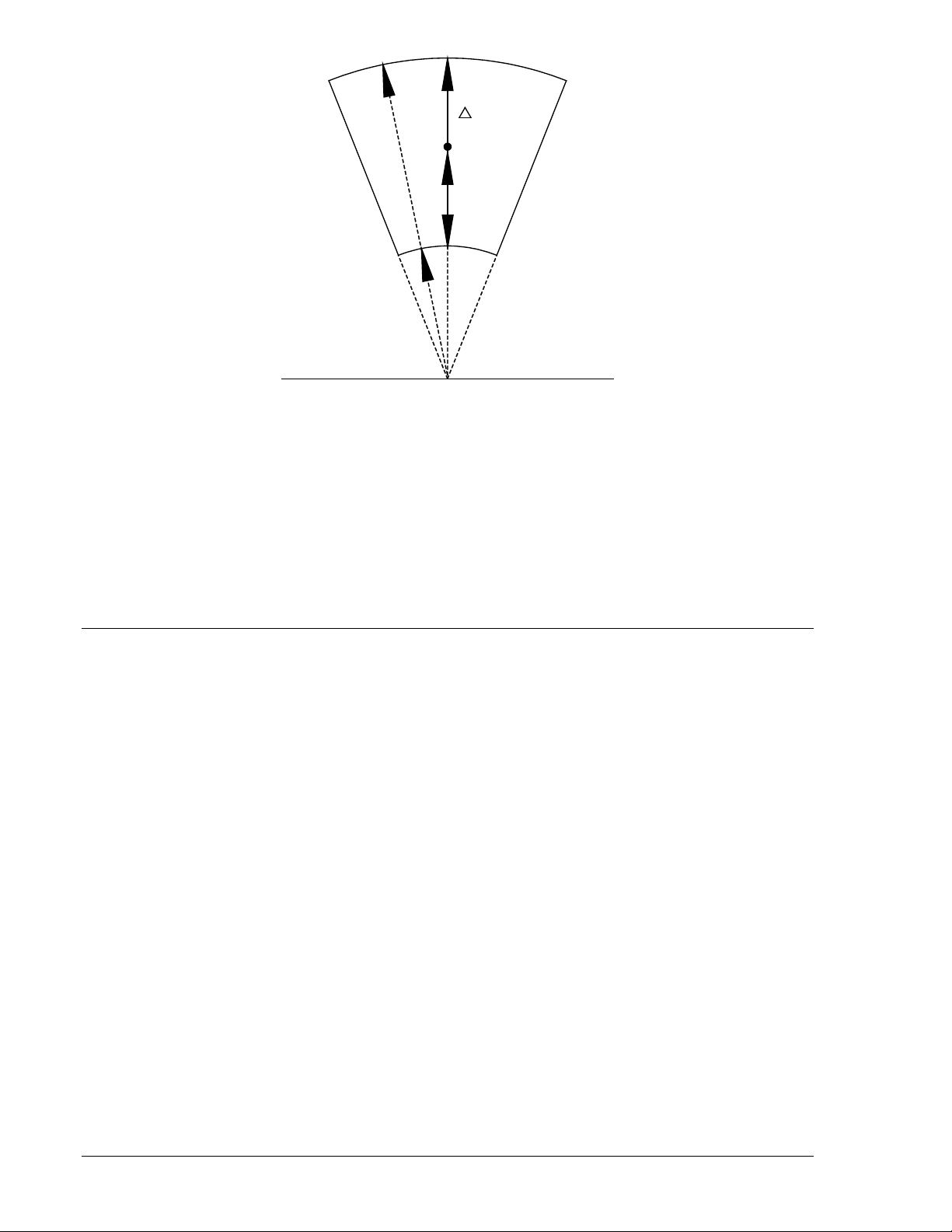
Option 2-A, 2-B, or 2-C (Average Voltage Difference)
This option is similar to option 2-T, 2-R, or 2-U except for the sensing method. This option provides
average voltage sensing instead of phasor voltage sensing. This provides a constant ∆V setting
independent of the phase relationship between the line and bus voltages.
Figure 1-5 may be used as an aid in formulating the voltage difference control settings. Note that the
center reference phasor (
represents the monitored line voltage. The voltage difference control (∆V) forms an area of acceptance
limit.
9170200990 Rev U BE1-25 General Information 1-5
) represents the monitored bus voltage, while the adjacent phasor (
)
Page 16
V
P0004-39
V
B
L
V
Figure 1-5. Closing Zone Diagram (Average Sensing)
Output Relay
The Voltage Monitor output relay option G or H provides additional supervision of the breaker closing
circuit, or provides an indication of the existing voltage conditions for the supervisory control system.
When a Voltage Monitor output relay is installed, the SYNC relay is no longer directly operable by voltage
monitor logic. However, the live line/live bus condition may be utilized to enable the Sync-Check function.
Detailed instructions and precautions for setting the Mode switches and Condition switches are provided
in Table 2-1, callouts R and S. The location of the switches is shown in Figure 2-2.
Voltage sensing connections are shown in Figure 4-9.
OTHER OPTIONS
Expandable Window
An expandable window (option 9 in the second position of the Style Number) is available to enable a local
operator (through a switch) or a remote dispatcher (through the supervisory control system) to expand the
preset phase angle window by a programmed ratio.
Under normal conditions, the phase angle setting is determined by the maximum angular difference that
has been calculated as suitable to meet the expected load flow of the total system. However, under
emergency conditions, the load flow throughout the system may result in excessive phase angle
separation across the opened breaker.
In order to reestablish load on a previously faulted line quickly, it may be necessary to expand the
allowable phase window. With this option, closing a contact input to the relay expands the preset phase
setting by a programmed multiple of 2 or 3 (according to the position of a jumper on the circuit card).
This option is not suggested for use in generator applications for the following reason: The phase angle
setting for a generator breaker is determined by the maximum phase difference that can be tolerated by
the generator when connected to the system. An excessive angle can result in excessive mechanical
forces in the generator and associated mountings.
Internal connections for the expandable window are shown in Figure 4-8; control circuit connections are in
Figures 4-11 and 4-12.
External Condition Switches
If a line and bus Voltage Monitor output is incorporated in the relay, the internal Condition Switches may
be functionally operated by remotely located external contacts. This capability is provided by Voltage
Monitor option 2-C, 2-U, or 2-V, but requires a voltage dropping Resistor Module to be mounted on the
relay back panel (see Figure 4-10).
1-6 BE1-25 General Information 9170200990 Rev U
Page 17

Push-to-Energize Output Pushbuttons
Two PUSH-TO-ENERGIZE OUTPUT switches are available to provide a means of verifying external
output wiring without the inconvenience of having to test the entire relay. These optional switches are
provided for each isolated output function (Sync-Check, Auxiliary Sync-Check and Voltage Monitor), and
may be actuated by inserting a thin, non-conducting rod through access holes in the front panel. See
Figure 2-1 for location.
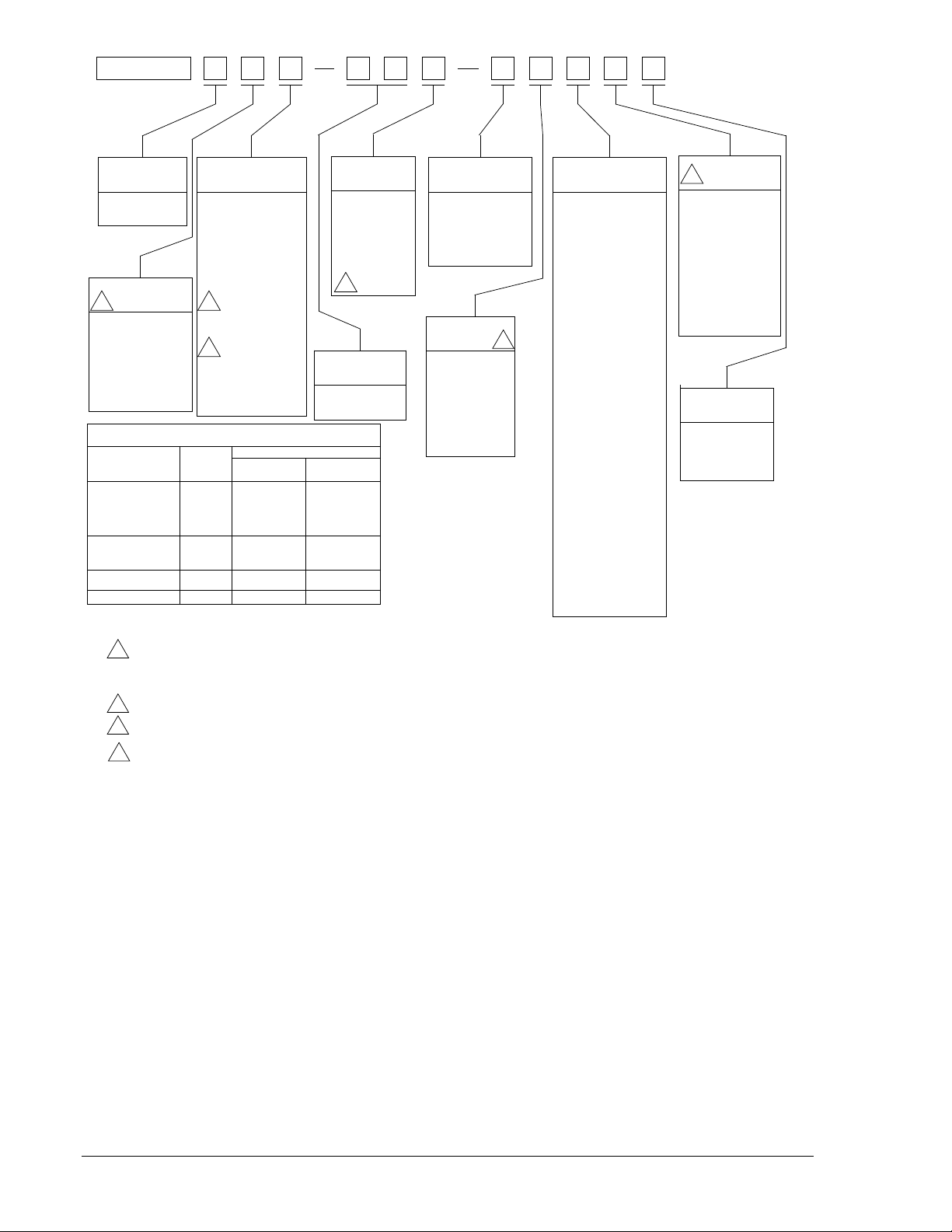
MODEL AND STYLE NUMBER
The electrical characteristics and operational features of the BE1-25 Sync-Check Relays are defined by a
combination of letters and numbers that make up its Style Number. The model number, together with the
Style Number, describes the options included in a specific device, and appears on the front panel,
drawout cradle, and inside the case assembly.
Upon receipt of a relay, be sure to check the Style Number against the requisition and the packing list to
ensure that they agree.
Style Number Example
The Style Number identification chart (Figure 1-6) defines the electrical characteristics and operational
features included in BE1-25 relays. For example, if the Style Number were M9H-A6P-N4R0F, the device
would have the following:
BE1-25 Model Number (designates the relay as a Basler Electric, Class 100, Sync-Check Relay)
M Single-phase sensing
9 Expandable phase angle window
H Voltage Monitor relay and Push-to-Energize outputs
A6 0.1 to 99 seconds timing range
P Operating power derived from 125 Vdc or 120 Vac
N No target
4 Non-isolated contact sensing input
R Line and Bus Voltage Monitor; also a Voltage Difference Monitor with Condition Switches
internal to the relay.
0 No auxiliary output
F Semi-flush mounting
9170200990 Rev U BE1-25 General Information 1-7
Page 18
OPTION 3
OPTION 4
OPTION 2
OPTION 1
SUPPLY
RANGE
SENSING INPUT
M
POWER
BE1-25
MODEL NO.
SENSING INPUT
TYPE
M) Single Phase
Voltage
OUTPUT
TIMING
TARGET
N) None
A) One Internally
Operated
B) One Current
Operated
F) Semi-Flush
Mounting
P) Projection
Mounting
1) 120 Vac, 1-99°
Phase Angle
Setting
9) 120 Vac, 1-99°
Phase Angle
Setting With
Expandable
Window
1
E) Sync-Check
NO Relay
F) Sync-Check
NO Relay with
Push-to Energize
Output
G) Sync-Check
NO Relay and
Voltage Monitor
SPDT Relay
H) Sync-Check
NO Relay and
Voltage Monitor
SPDT Relay
with Push-to Energize
Output (for
both relays)
4
4
A6) 0.1-99 Sec.
A7) 1-99 Cycles
O) 48 Vdc
P) 125 Vdc or
100/120
Vac
R) 24 Vdc
T) 250 Vdc or
240 Vac
3
4) Non-Isolated
Contact
Sensing
Input
5) Isolated
Contact
Sensing
Input
N) None
R) Line and Bus
Voltage Monitor
and Voltage
Difference with
PC Bd Mounted
Switches
S) Line and Bus
Voltage Monitor
with PC Bd
Mounted Switches
T) Voltage Difference
Voltage Monitor
and Voltage
Difference with
External Contact
Inputs
V) Line and Bus
Voltage Monitor
with External
Contact Inputs
0) None
1) Sync-Check
Auxiliary Output
NO Relay
2) Sync-Check
Auxiliary Output
NC Relay
3) Sync-Check
Auxiliary Output
SPDT Relay
6) Power Supply
Status Output
1
CONTACT SENSING MODULES
(Required when Type T Power Supply is specified)
Module Ordering Number
9 1702 06 106
Non-Isolated
Contact Sensing
Isolated
Contact Sensing
Number of
Contacts
Sensed
Relay Options
Voltage Monitor
with External
Contact Inputs
plus Expandable
Phase Window
Voltage Monitor
with External
Contact Inputs
Expandable Phase
Window
None of the above
9 1702 06 100
9 1702 06 101 9 1702 06 107
9 1702 06 104 9 1702 06 110
9 1702 06 105 9 1702 06 111
6
5
2
1
NOTES:
When Sensing Input Range 9 is Selected from the
Style Chart, Option 3 must be 0.
All relays are supplied in an S1 size case.
Requires Contact Sensing Module. See Table in this chart.
Not available if Option 2 is B, N, or T.
1
3
4
2.
D434-006.vsd
01-30-01
A) Average
Voltage Monitor
and Voltage
Difference with
PC Bd Mounted
Switches
U) Line and Bus
C) Average
B) Average Voltage
Difference
Voltage Monitor
and Voltage
Difference with
External Contact
Inputs
For more information on contact sensing see Specifications.
5
5
1-8 BE1-25 General Information 9170200990 Rev U
Figure 1-6. Style Number Identification Chart
Page 19
SPECIFICATIONS
Maximum continuous voltage rating is 160% of nominal.
relay power supply input.
For Power Supply Option O ...... 2.4 VA
For Power Supply Option T…….12.5 VA
selected to provide internal relay operating power.
Voltage and Phase Sensing
Contact Sensing
If contact sensing is isolated (style number Mxxxxxx5xxx), external voltage
should not be applied to the contact sensing inputs. Applying voltage to the
contact sensing inputs will result in damage to the relay.
Contact Sensing Burden
Nominally rated at 60 hertz with a range of 45 to 65 hertz at a
maximum burden of 1 VA per phase to 125% of nominal voltage.
User-supplied contacts with a minimum rating of 0.05 ampere at
250 Vdc are required at all contact sensing inputs. (Specifically the
52b input, the optional expandable phase angle window, and the
optional external voltage condition switches.)
Sensing circuit current is supplied by the relay when isolated
sensing is selected. Non-isolated sensing requires an externally
applied dc sensing voltage equal to the nominal voltage of the
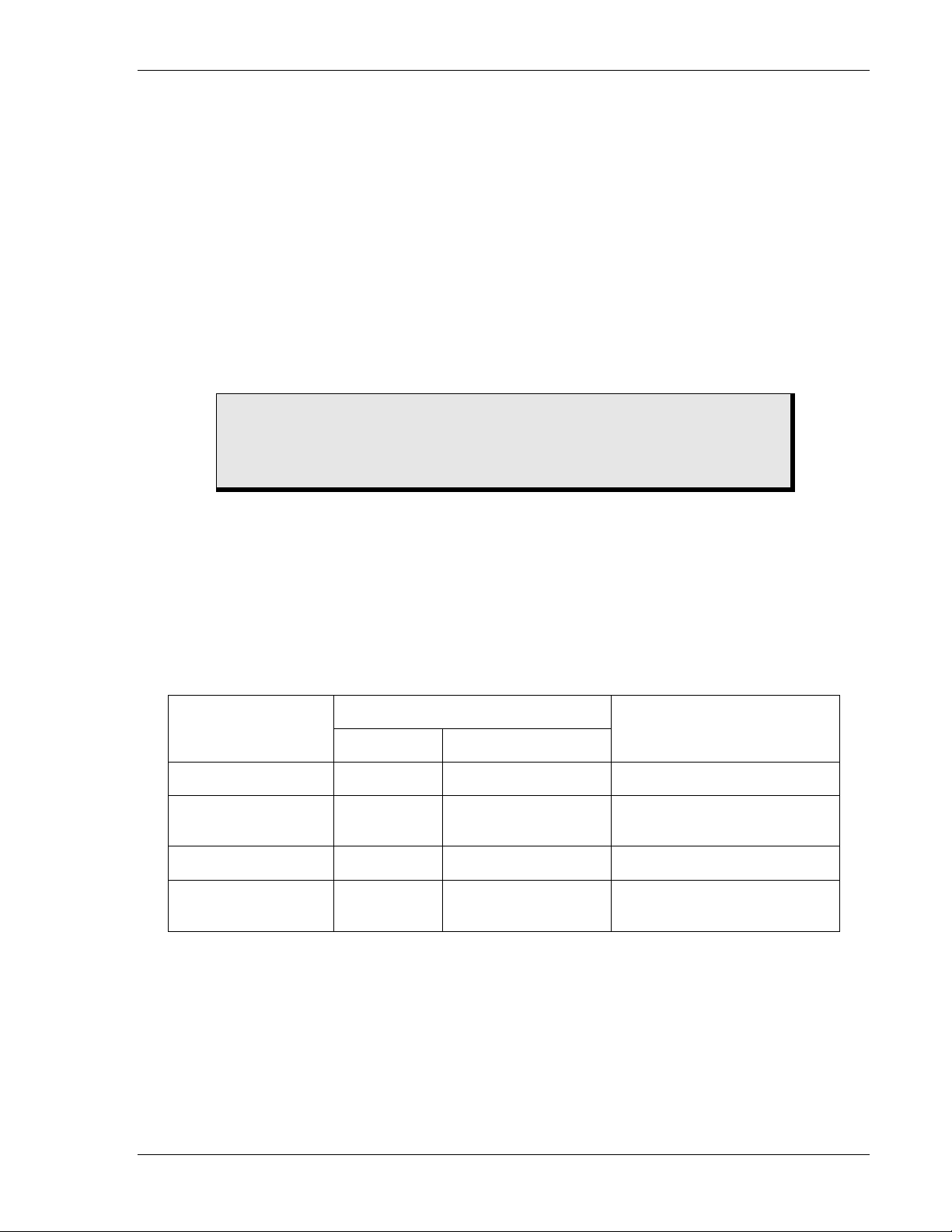
CAUTION
For Power Supply Option P ....... 6.25 VA
For Power Supply Option R ....... 1.2 VA
Power Supply
Type
O (mid range) 48 Vdc 24 to 150 Vdc 1.5 W
P (mid range)
R (low range) 24 Vdc
T (high range)
∗ Type R power supply may require 14 Vdc to begin operation. Once operating, the voltage may be
reduced to 12 Vdc.
One of the four types of power supplies listed in Table 1-1
Table 1-1. Power Supply
Input Voltage
Burden at Nominal
Nominal Range
125 Vdc
120 Vac
250 Vdc
240 Vac
24 to 150 Vdc
90 to 132 Vac
12 to 32 Vdc ∗
68 to 280 Vdc
90 to 270 Vac
1.8 W
10.5 VA
1.6 W
2.1 W
17.4 VA
may be
9170200990 Rev U BE1-25 General Information 1-9
Page 20

Output Contacts
Output contacts are rated as follows:
Resistive
120 Vac
Make, break, and carry 7 Aac continuously.
250 Vdc
Make and carry 30 Adc for 0.2 seconds, carry 7 Adc continuously,
break 0.3 Adc.
500 Vdc
Make and carry 15Adc for 0.2 s, carry 7 Adc continuously, break
0.3 Adc
Inductive
120 Vac, 125 Vdc,
250 Vdc
Break 0.3 A, (L/R = 0.04).
continuously.
Phase Angle
input range of 80 to 135 volts, and at 25°C.
operating range of temperature and input voltages.
hertz at 25°C.
(Overall)
25°C, over the full temperature, voltage, and frequency ranges.
is usually in the range of 45 to 55 volts.
Voltage Difference Option
Range
Continuously adjustable over the range of 1 to 135 Vac.
of +15 to +40°C.
Target Indicator
Selection Accuracy
Setpoint Accuracy
Timing Accuracy at 25°C
TIME Delay Accuracy
Minimum Voltage
Requirement
The target indicator may be either internally operated or current
operated (operated by a minimum of 0.2 A through the output trip
circuit). When the target is current operated, the sync output circuit
must be limited to 30 A for 1 second, 7 A for 2 minutes, and 3 A
± 0.5° or ± 5.0% of the front panel setting for degrees, whichever is
greater, for a nominal input frequency of 50/60 hertz, a sensing
±0.5° or ±5%, whichever is greater, from a reference measurement
at 25°C, at nominal input frequency and levels, over the specified
Maximum of 25 milliseconds or 5% of the front panel setting for
time whichever is greater, for a nominal input frequency of 50/60
±10 milliseconds or ±2%, whichever is greater, of the time delay at
Minimum voltage detection circuitry enables the sync-check
circuitry when both line and bus are within operating range of the
relay. Voltage sensing circuits are guaranteed to operate at a
minimum voltage of 60 volts. They are guaranteed not to operate
at voltages less than 20 volts. Some units may operate at voltages
in between these two levels because of the individual
characteristics of specific components. Minimum voltage detection
Accuracy Voltage difference setpoint does not vary more than 0.5 V or 5%,
whichever is greater, from a reference measurement at 25°C, with
nominal input frequency, and variation of temperature or voltage
inputs over their specified operating range. This setpoint does not
vary more than 3% from a reading at 25°C over the limited range
1-10 BE1-25 General Information 9170200990 Rev U
Page 21

Line and Bus Voltage
Monitor Option
Range
Continuously adjustable over the range of 10 to 135 Vac.
over the limited temperature range of +15 to +40°C.
(SWC) Tests for Protective Relays and Relay Systems.
Interference from Transceivers.
250 V.
performance.
structural damage or degradation of performance.
Operating Temperature
–40°C (–40°F) to 70°C (158°F).
Storage Temperature
–65°C (–85°F) to 100°C (212°F).
Weight
13.7 (6.2 kg) pounds maximum.
Accuracy The line and bus voltage setpoints do not vary more than 3% from
a reference measurement at 25°C, with nominal input frequency,
and with temperature and voltage inputs within specified operating
range. Setpoints do not vary more than 1% from a reading at 25°C
Isolation
Surge Withstand Capability
Oscillatory
Fast Transient
Radio Frequency
Interference (RFI)
UL Recognition
Shock
In accordance with IEC 255-5 and IEEE C37.90, one minute dielectric
(high potential) tests as follows:
All circuits to ground: 2,121 Vdc
Input to output circuits: 1,500 Vac or 2,121 Vdc
Qualified to IEEE C37.90.1-1989 Standard Surge Withstand Capability
(SWC) Tests for Protective Relays and Relay Systems.
Qualified to IEEE C37.90.1-1989 Standard Surge Withstand Capability
Maintains proper operation when tested for interference in
accordance with IEEE C37.90.2-1987, Standard Withstand
Capability of Relay Systems to Radiated Electromagnetic
UL recognized per Standard 508, UL File No. E97033. Note:
Output contacts are not UL recognized for voltages greater than
In standard tests, the relay has withstood 15 G in each of three
perpendicular planes without structural damage or degradation of
Vibration
GOST-R Certification
Case Size
9170200990 Rev U BE1-25 General Information 1-11
In standard tests, the relay has withstood 2 G in each of three
mutually perpendicular axes swept over the range of 10 to 500
hertz for a total of six sweeps, 15 minutes each sweep, without
GOST-R certified per the relevant standards of Gosstandart of Russia.
S1 (Refer to Section 4 for case dimensions.)
Page 22

This page intentionally left blank.
1-12 BE1-25 General Information 9170200990 Rev U
Page 23

SECTION 2 • CONTROLS AND INDICATORS
TABLE OF CONTENTS
SECTION 2 • CONTROLS AND INDICATORS ........................................................................................ 2-1
INTRODUCTION.................................................................................................................................... 2-1
Figures
Figure 2-1. Location of Controls and Indicators (Front Panel View) ......................................................... 2-1
Figure 2-2. Location of Controls and Indicators (Interior View) ................................................................. 2-2
Tables
Table 2-1. Location of Controls and Indicators .......................................................................................... 2-2
9170200990 Rev U BE1-25 Controls and Indicators i
Page 24

This page intentionally left blank.
ii BE1-25 Controls and Indicators 9170200990 Rev U
Page 25

SECTION 2 • CONTROLS AND INDICATORS
INTRODUCTION
BE1-25 controls and indicators are located on the front panel and the right side interior. The controls and
indicators are shown in Figures 2-1 and 2-2. Table 2-1 describes the controls and indicators. Reference
the callouts A through P to Figure 2-1 and Q through S to Figure 2-2.
Figure 2-1. Location of Controls and Indicators (Front Panel View)
9170200990 Rev U BE1-25 Controls and Indicators 2-1
Page 26

Figure 2-2. Location of Controls and Indicators (Interior View)
or the in-sync condition ceases.
sync condition and closing the
over a
9.9 seconds with the multiplier switch in the X 0.1
P0046-05
Table 2-1. Location of Controls and Indicators
Callout Control or Indicator Function
A SYNC Indicator
Red LED lights when an in-sync condition has been of
sufficient duration to match the TIME DELAY setting.
Lighting of the LED coincides with closure of the Sync
Output contacts. The LED extinguishes when 52b opens
B TIME DELAY Selector
Thumbwheel switches establish the time delay between
sensing the desired inSync Output contact. Time delay is in units of seconds or
of cycles, according to the option selected.
Option A6: Adjustable in 1-second increments
range of 01 to 99 seconds when multiplier switch (callout
D) is in the X 1.0 position. Alternatively, the range is 0.1 to
position.
Option A7: Adjustable in 1-cycle increments from 1 to 99
cycles. The multiplier switch (callout D) is omitted.
NOTE
A setting of 00 will inhibit closing of the SYNC
output.
2-2 BE1-25 Controls and Indicators 9170200990 Rev U
Page 27

Callout Control or Indicator Function
LED lights to indicate that the relay power supply is
Switch
∆
∆
panel. CW rotation increases the voltage difference
setting.
Red LED lights when the line voltage exceeds the
panel. CW rotation increases the voltage setting.
that defines an overvoltage condition.
setting.
H
Target Reset Switch
Allows manual reset of the target.
Output contacts and (if specified) the Auxiliary Sync
Monitor Output contacts.
Sync Output relay is or was energized.
C POWER Indicator
functioning properly.
D TIME DELAY Multiplier
E
F LL Indicator
G DL/NOT OV Indicator
V Indicator
V Adjustment
LL Adjustment
Explained above; see callout B.
Red LED lights when the difference between the bus and
line voltage is less than the ∆V setting.
Continuously adjustable from 1 to 135 Vac. Adjustment is
by small screwdriver through an access hole in the front
reference voltage established by the LL setting.
Continuously adjustable from 10 to 135 Vac. Adjustment
is by small screwdriver through an access hole in the front
When in the NORMAL Mode:
Red LED lights when the line voltage is less than the
reference voltage established by the DL/NOT OV setting
that defines a dead line.
When in the NOT OV Mode:
DL/NOT OV Adjustment
I and J PUSH-TO-ENERGIZE
OUTPUT Switches
K Target Indicator (Optional)
Red LED lights when the line voltage does not exceed the
reference voltage established by the DL/NOT OV setting
Continuously adjustable over the range of 10 to 135 Vac.
Adjustment is by small screwdriver through an access
hole in the front panel. CW rotation increases voltage
Momentary pushbuttons are accessible by inserting a 1/8
inch diameter non-conducting rod through access holes in
the front panel. Switch I, when actuated, closes the Sync
Output contacts; Switch J closes the (optional) Voltage
Electronically latching red indicator illuminates when the
9170200990 Rev U BE1-25 Controls and Indicators 2-3
Page 28

Callout Control or Indicator Function
setting.
Output relay is energized.
that defines an overvoltage condition.
setting.
set the acceptable maximum
over a range of 01° to 99°.
established by the adjacent PHASE ANGLE Selector.
expanded phase angle window as a multiple of the
PHASE ANGLE setting. The two positions are X2 and X3.
L LB Indicator
LB Adjustment
M V Indicator
N DB/NOT OV Indicator
DB/NOT OV Adjustment
Red LED lights when bus voltage exceeds the reference
voltage established by the LB setting that defines a live
bus condition.
Continuously adjustable over a range of 10 to 135 Vac.
Adjustment is by small screwdriver through an access
hole in the front panel. CW rotation increases voltage
Red LED lights whenever the (optional) Voltage Monitor
When in the NORMAL Mode:
Red LED lights when the bus voltage is less than the
reference voltage established by the DB/NOT OV setting
that defines a dead bus condition.
When in the NOT OV Mode:
Red LED lights when the bus voltage does not exceed the
reference voltage established by the DB/NOT OV setting
Continuously adjustable over the range of 10 to 135 Vac.
Adjustment is by small screwdriver through an access
hole in the front panel. CW rotation increases the voltage
O PHASE ANGLE Selector
P PHASE ANGLE Indicator
Q Switchable jumper for
EXPAND option
NOTE
A PHASE ANGLE setting of 00 inhibits
operation of the relay.
Thumbwheel switches
phase difference between the line and bus voltages. This
phase difference window is adjustable in 1° increments
Red LED lights when the phase angle is within the limits
Position of jumper in Figure 2-2 controls the width of the
2-4 BE1-25 Controls and Indicators 9170200990 Rev U
Page 29

Callout Control or Indicator Function
either LL or LB and the corresponding NOT OV.
overvoltage region. (This switch does not affect the
Voltage Monitor Output relay.)
R MODE Switch No. 1 (Bus)
MODE Switch No. 2 (Line)
For Both Mode Switches:
Up = NORMAL Mode;
Down = NOT OV Mode.
When in the NORMAL Mode:
(1) A high voltage threshold is established by front panel
controls, above which the bus (or line, as the case may
be) is considered live;
(2) A low voltage threshold is established by front panel
controls, below which the bus (or line) is considered dead.
When in the NOT OV Mode:
(1) A voltage above the high voltage setpoint setting is
considered overvoltage.
(2) A voltage below the low voltage setpoint setting is
defined as dead.
(3) A voltage between the two setpoints is defined as live.
This condition is indicated by the illumination of two LEDs:
S CONDITION Switches
No. 1 (Not-Overvoltage
Enable to the sync logic
circuitry)
Up = OFF: Disables the NOT OV Mode of operation
during a live line/live bus condition.
Down = ON: Allows the NOT OV Mode of operation to
add a further constraint to the live line/live bus condition
(assuming that the NOT OV Mode has been previously
selected on Mode Switch No. 1 or No. 2). The additional
constraint is that the line and/or bus must not be in the
9170200990 Rev U BE1-25 Controls and Indicators 2-5
Page 30

Callout Control or Indicator Function
Bus)
is detected with the breaker open.
S
(Cont’d)
No. 2 (Live Line/Live Bus)
Up = OFF
Down = ON
When ON (Down), the Voltage Monitor Output relay is
actuated when a live line/live bus condition is recognized.
CAUTION
If relay has Output Option E or F:
Condition Switch No. 2 (LL-LB) must be Up
(OFF) when output option E or F is selected.
Otherwise, sync outputs will occur under live
line/live bus conditions without benefit of the
Sync-Check function. No switch or contact
should be connected to the LL-LB input
terminal in this case.
CAUTION
If relay has Output Option G or H:
Condition Switch No. 2 (LL-LB) may be Down
(ON) only when output option G or H has been
selected and the Voltage Monitor Output
contacts do not by-pass the Sync-Check
contact. Use of the external LL-LB switch (if
installed) is similarly limited.
No. 3 (Dead Line/Live
If relay has Output Option E or F:
Up = OFF
The ON (Down) position causes immediate closure of the
Sync Output contact, if a dead line/live bus condition is
detected with the breaker open.
If relay has Output Option G or H:
The ON (Down) position causes immediate actuation of
the Voltage Monitor relay, if a dead line/live bus condition
2-6 BE1-25 Controls and Indicators 9170200990 Rev U
Page 31

Callout Control or Indicator Function
(Cont’d)
Bus)
is detected with the breaker open.
Bus)
is detected with the breaker open.
S
If relay has Output Option E or F:
No. 4 (Live Line/Dead
No. 5 (Dead Line/Dead
If relay has Output Option E or F:
Up = OFF
The ON (Down) position causes immediate closure of the
Sync Output contact, if a live line/dead bus condition is
detected with the breaker open.
If relay has Output Option G or H:
The ON (Down) position causes immediate actuation of
the Voltage Monitor relay, if a live line/dead bus condition
Up = OFF
The ON (Down) position causes immediate closure of the
Sync Output contact if a dead line/dead bus condition is
detected with the breaker open.
If relay has Output Option G or H:
The ON (Down) position causes immediate actuation of
the Voltage Monitor relay if a dead line/dead bus condition
9170200990 Rev U BE1-25 Controls and Indicators 2-7
Page 32

This page intentionally left blank.
2-8 BE1-25 Controls and Indicators 9170200990 Rev U
Page 33

SECTION 3 • FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION
TABLE OF CONTENTS
SECTION 3 • FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION ........................................................................................... 3-1
GENERAL .............................................................................................................................................. 3-1
FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION .............................................................................................................. 3-1
Step-Down Transformers ................................................................................................................... 3-1
Zero-Cross and Phase Difference Measurement ............................................................................... 3-1
Comparator......................................................................................................................................... 3-1
Timer .................................................................................................................................................. 3-1
Minimum Voltage Detection ............................................................................................................... 3-2
Contact Sensing Options .................................................................................................................... 3-2
Power Supply ..................................................................................................................................... 3-2
Power Supply Status Output Option .................................................................................................. 3-2
Voltage Monitor Options ..................................................................................................................... 3-3
Target Indicator .................................................................................................................................. 3-3
Figures
Figure 3-1. Functional Block Diagram ....................................................................................................... 3-2
9170200990 Rev U BE1-25 Functional Description i
Page 34

This page intentionally left blank.
ii BE1-25 Functional Description 9170200990 Rev U
Page 35

SECTION 3 • FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION
GENERAL
BE1-25 Sync-Check Relays are static devices that use digital circuitry to provide a breaker closure signal
when the phase and voltage difference between two voltage inputs, typically line and bus, are within
preset limits. The functional block diagram in Figure 3-1 illustrates the overall operation of the BE1-25
Sync-Check Relay.
FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION
Figure 3-1 is a block diagram that illustrates the BE1-25 Sync-Check Relay circuit functions described in
the following paragraphs.
Step-Down Transformers
Standard system transformers with a 120-volt secondary provide line and bus voltages to the sensing
transformer of the BE1-25 Sync-Check Relay. Internal sensing transformers isolate the relay from the
system and step down the voltage to internal circuit levels.
Zero-Cross and Phase Difference Measurement
Zero-cross detection circuits digitize the output voltages from the sensing transformers. Time delays
between the zero crosses are measured in the phase difference measurement circuitry to provide a
binary output.
Comparator
The binary number representing phase difference is compared with the setting of the PHASE ANGLE
thumbwheel switches. If the detected phase difference is less than the setting of the switches, the time
delay is started and the PHASE ANGLE LED is illuminated.
Timer
The time delay timer clock is controlled by the TIME DELAY multiplier switch on the front panel.
The timer is enabled when:
1. Phase angle is less than the set limit.
2. Minimum line and bus voltages are present.
3. 52b contact is closed.
4. Voltage difference (∆V) is within set limits (if option is selected).
5. A live-line and live-bus condition is present (if the Voltage Monitor option is selected).
When the time delay reaches the count entered by the TIME DELAY select switches, the SYNC output is
energized, the SYNC LED is turned ON, and the target (if selected) turns red. The SYNC LED is turned
OFF as soon as any of the five above listed enables are removed. Generally, this occurs when the circuit
breaker closes.
9170200990 Rev U BE1-25 Functional Description 3-1
Page 36

01-30-01
D1058-04.vsd
OPERATING
POWER
BUS
LINE
EXPAND
PHASE
ANGLE
OPTION
OPTIONAL
EXTERNAL
CONTACTS
LB
DB OR BOV
LL
DL OR LOV
52b
POWER
SUPPLY
CROSS
ZERO
ZERO
CROSS
PHASE
DIFFERENCE
MEASUREMENT
POWER
-2 OR -3
JUMPER
ON PCB
TO INTERNAL
CIRCUITRY
AND
AND
OR
POWER
SUPPLY
SENSOR
PHASE
ANGLE
SELECTOR
COMPARATOR
AND
AND
TIMER
TIME DELAY
SWITCHES
PHASE
SYNC.
OUTPUT
SYNC.
OUTPUT
AUX.
OUTPUT
P.S. STATUS
ISOLATION
MINIMUM
VOLTAGE
DETECTION
ISOLATION
FILTER
ISOLATION
FILTER
FRONT PANEL SETTINGS
PEAK OR AVG
DETECTOR
V
LL LB IF MODE 1:
(LL OV)(LB OV) IF MODE 2
LB
DB OR BOV
LL
DL OR LOV
VOLTAGE
MONITOR
SELECTION
LOGIC
MODE
SWITCHES
CONDITION
SWITCHES
MONITOR
ACCEPT
PATHS
ALTERNATE
MONITOR
VOLTAGE
OUTPUT
OPTION
DEPENDING
VOLT.
SYNC-CHECK CIRCUITRY
VOLTAGE MONITOR OPTIONS
.
.
.
ON OUTPUT
PEAK OR AVG
DETECTOR
PEAK OR AVG
DETECTOR
PEAK OR AVG
DETECTOR
PEAK OR AVG
DETECTOR
Figure 3-1. Functional Block Diagram
Minimum Voltage Detection
Minimum voltage detection circuitry enables the TIME DELAY timer when both line and bus are within
operating range of the relay. Voltage sensing circuits are guaranteed to operate at a minimum voltage of
60 volts. They are guaranteed not to operate at voltages less than 20 volts. Some units may operate at
voltages in between these two levels because of the individual characteristics of specific components.
Minimum voltage detection is usually in the range of 45 to 55 volts.
Contact Sensing Options
Before any relay output can occur, there must be an initiating signal from external contacts. Contact
sensing circuitry allows the relay to monitor circuit breaker status (52b) and various conditions selected by
the user. (Contact requirements are provided in the Specifications.)
In any sync-check relay, all of the contact sensing inputs supplied must use one of two methods.
1. Isolated sensing (Option 1-5), uses current supplied by the relay to monitor the isolated contacts.
2. Non-isolated sensing (Option 1-4), monitors an external dc source whose nominal voltage is
equal to the input to the BE1-25 power supply.
Power Supply
Operating power for the relay circuitry is supplied by a wide range, electrically isolated, low-burden power
supply. Power supply operating power is not polarity sensitive. The front panel power LED and power
supply status output indicate when the power supply is operating. Power supply specifications are listed in
Table 1-1.
Power Supply Status Output Option
The power supply status output relay (Option 3-6) has normally closed (NC) output contacts. The relay is
energized upon power-up, thus opening its contacts. The contacts will remain open as long as normal
relay operating voltage is maintained. However, if the power supply voltage falls below the requirements
for proper operation, the power supply status output relay de-energizes, thus closing the NC output
contacts.
3-2 BE1-25 Functional Description 9170200990 Rev U
Page 37

Voltage Monitor Options
Voltage monitor options are shown in the lower portion of Figure 3-1, and described in the following
paragraphs.
Filters
Input voltages from bus and line are filtered and applied to the peak detectors or average detector
circuitry.
Peak Detectors (Option 2-R, 2-T, or 2-U)
Voltage difference (∆V) peak detectors measure the phasor voltage difference between line and bus, and
compare this difference against the setting of the front panel ∆V control. If the detected difference is less
than the limit, the sync-check timer is enabled, and the front panel ∆V LED is lighted.
Four additional peak detectors compare the sensed line and bus voltages with reference voltages
established by the front panel control settings. To illustrate operation, let us first consider the two upper
peak detectors, noting that they monitor the bus, and that one of them has its output inverted.
When the live bus (LB) peak detector determines the sensed bus voltage is above the threshold voltage,
it outputs a logic-high signal to the selection logic. But the DB/Not Overvoltage peak detector, because of
inversion, only provides a logic-high signal when sensed voltage is below the threshold, thereby
identifying either a dead bus (i.e., Mode Switch No. 1 is Up to select the NORMAL Mode), or a Not
Overvoltage condition (Mode Switch No. 1 is Down to select the NOT OV Mode).
The lower pair of peak detectors works in similar fashion to define line conditions, as determined by the
position of Mode Switch No. 2.
Average Detectors (Option 2-A, 2-B, or 2-C)
Voltage difference average detectors provide the same functionality as the peak detector inputs except
they measure the average voltage difference instead of phasor voltage difference.
Selection Logic
Voltage monitor selection logic is controlled by Mode and Condition switches or External Condition
Switches to produce the Voltage Monitor output.
Another output from the voltage monitor selection logic serves as an additional qualifier for the timer in the
sync output circuit. The specific conditions being monitored depend upon whether NORMAL or NOT OV
operation is used. Live line and live bus is monitored if NORMAL Mode is selected. Live line, live bus, and
Not Overvoltage is monitored if NOT OV Mode is selected.
Detailed instructions and precautions for programming the Mode and Condition switches are provided in
Table 2-1, callouts R and S. The location of the switches is shown in Figure 2-2.
Target Indicator
A target indicator is an optional component selected when a relay is ordered. The electronically latched
and reset target consists of a red LED indicator located on the relay front panel. A latched target is reset
by operating the target reset switch on the front panel. If relay operating power is lost, an illuminated
(latched) target is extinguished. When relay operating power is restored, the previously latched target is
restored to its latched state.
A relay can be equipped with either an internally operated target or a current operated target.
Internally Operated Target
The relay SYNC output is directly applied to drive the target indicator. The indicator is illuminated
regardless of the amount of current flowing through the output contact.
Current Operated Target
A current operated target is triggered when at least 200 milliamperes of current flows through the SYNC
output contact.
NOTE
Prior to September 2007, BE1-25 the target indicator consisted of a magnetically
latched, disc indicator. This mechanically latched target indicator has been
replaced by the electronically latched LED target in use today.
9170200990 Rev U BE1-25 Functional Description 3-3
Page 38

This page intentionally left blank.
3-4 BE1-25 Functional Description 9170200990 Rev U
Page 39

SECTION 4 • INSTALLATION
TABLE OF CONTENTS
SECTION 4 • INSTALLATION .................................................................................................................. 4-1
INTRODUCTION.................................................................................................................................... 4-1
RELAY OPERATING GUIDELINES AND PRECAUTIONS .................................................................. 4-1
MOUNTING ............................................................................................................................................ 4-1
Relay .................................................................................................................................................. 4-1
Resistor Module ................................................................................................................................. 4-1
Contact Sensing Module .................................................................................................................... 4-2
CONNECTIONS..................................................................................................................................... 4-9
MAINTENANCE ................................................................................................................................... 4-13
STORAGE ............................................................................................................................................ 4-13
Figures
Figure 4-1. Panel Cutting/Drilling, Semi-Flush, S1 Case .......................................................................... 4-2
Figure 4-2. S1 Case Dimensions, Rear View, Double Ended, Semi-Flush Mount ................................... 4-3
Figure 4-3. S1 Case Dimensions, Side View, Double Ended, Semi-Flush Mount .................................... 4-4
Figure 4-4. Panel Cutting/Drilling, Double Ended, Projection Mount, S1 Case ........................................ 4-5
Figure 4-5. S1 Case Dimensions, Rear View, Double Ended, Projection Mount ...................................... 4-6
Figure 4-6. S1 Case Dimensions, Side View, Double Ended, Projection Mount ...................................... 4-7
Figure 4-7. S1 Case Cover Dimensions, Front View ................................................................................. 4-8
Figure 4-8. Internal Diagram ...................................................................................................................... 4-9
Figure 4-9. Voltage Sensing Connections ............................................................................................... 4-10
Figure 4-10. Resistor Module Connections ............................................................................................. 4-11
Figure 4-11. Control Circuit Connections (Typical) ................................................................................. 4-12
Figure 4-12. Contact Sensing and Resistor Modules for Type T Power Supply Only ............................ 4-13
9170200990 Rev U BE1-25 Installation i
Page 40

This page intentionally left blank.
ii BE1-25 Installation 9170200990 Rev U
Page 41

SECTION 4 • INSTALLATION
INTRODUCTION
BE1-25 relays are shipped in sturdy cartons to prevent damage during transit. Upon receipt of a relay,
check the model and style number against the requisition and packing list to see that they agree. Inspect
the relay for shipping damage. If there is evidence of damage, file a claim with the carrier, and notify your
sales representative or Basler Electric.
If the relay will not be installed immediately, store it in its original shipping carton in a moisture- and dustfree environment. Before placing the relay in service, it is recommended that the test procedures of
Section 5, Testing be performed.
RELAY OPERATING GUIDELINES AND PRECAUTIONS
Before installing or operating the relay, not the following guidelines and precautions.
• For proper current operated target operation, a minimum current of 200 milliamperes must flow
through the output trip circuit.
• If a wiring insulation test is required, remove the connection plugs and withdraw the relay from its
case.
CAUTION
When the connection plugs are removed, the relay is disconnected from the
operating circuit and will not provide system protection. Always be sure that
external operating (monitored) conditions are stable before removing a relay for
inspection, test, or service.
NOTE
Be sure that the relay is hard-wired to earth ground with no smaller than 12 AWG
copper wire attached to the ground terminal on the rear of the case. When the
relay is configured in a system with other devices, it is recommended to use a
separate lead to the ground bus from each device.
MOUNTING
Relay
Because the relay is of solid-state design, it does not have to be mounted vertically. Any convenient
mounting angle may be chosen. Relay outline dimensions and panel drilling diagrams are illustrated in
Figures 4-1 through 4-7.
Resistor Module
When the condition and mode switching of the Voltage Monitor option is controlled by external contacts
(option 2-C, 2-U, or 2-V), a voltage dropping Resistor Module is bolted to the rear of the relay
Figure 4-10). If the relay is to be projection mounted (Figure 4-6), it will be necessary to first remove the
module when mounting the relay, then reattach it so that the mounting panel lies between the relay and
module.
In planning the installation, reserve a clear space directly behind the relay or behind the mounting panel if
projection mounted, since the Resistor Module will give off some heat during use.
9170200990 Rev U BE1-25 Installation 4-1
Page 42

Contact Sensing Module
If a type T power supply (250 Vdc or 240 Vac) is used, an external Contact Sensing Module is required.
(See Figure 4-12.) If external control of condition and mode switching is also specified, the Resistor
Module must also be used in addition to the Contact Sensing Module.
The ideal mounting position for the contact-sensing module is with the fins vertical (to facilitate upward air
movement). This module is best mounted as close to the relay as is conveniently possible in order to take
full advantage of transient suppressors within the module.
Further installation information for the contact-sensing module is contained in Publication 9170206990,
which is packed with the module.
Figure 4-1. Panel Cutting/Drilling, Semi-Flush, S1 Case
4-2 BE1-25 Installation 9170200990 Rev U
Page 43

Figure 4-2. S1 Case Dimensions, Rear View, Double Ended, Semi-Flush Mount
9170200990 Rev U BE1-25 Installation 4-3
Page 44

.75
(19
.
1)
(
157
.2
)
6.19
(49
.
53)
1
.95
10
-32
SCREWS
(7
.
9)
.31
10-32
SCREWS
(
102.
4)
4.03
4.03
(102.
4)
(
7.9
)
.31
MOUNTING PANEL
(55.
75)
2
.195
P0066-64
Figure 4-3. S1 Case Dimensions, Side View, Double Ended, Semi-Flush Mount
4-4 BE1-25 Installation 9170200990 Rev U
Page 45

Figure 4-4. Panel Cutting/Drilling, Double Ended, Projection Mount, S1 Case
9170200990 Rev U BE1-25 Installation 4-5
Page 46

Figure 4-5. S1 Case Dimensions, Rear View, Double Ended, Projection Mount
4-6 BE1-25 Installation 9170200990 Rev U
Page 47

.75
(19.1)
(157.2)
6.19
(49.53)
1.95
10-32 SCREWS
(7.9)
.31
10-32 SCREWS
(102.4)
4.03
4.03
(102.4)
(7.9)
.31
(55.75)
2.195
P0066-67
TERMINAL EXTENSION (TYP.)
FOR DETAILED INSTRUCTIONS,
SEE THE TERMINAL PROJECTION
MOUNTING KIT SUPPLIED.
.25
(6.4)
5/16-18 STUD
2 PLACES
MOUNTING PANEL
Figure 4-6. S1 Case Dimensions, Side View, Double Ended, Projection Mount
9170200990 Rev U BE1-25 Installation 4-7
Page 48

P
0066-
68
Figure 4-7. S1 Case Cover Dimensions, Front View
4-8 BE1-25 Installation 9170200990 Rev U
Page 49

PADDLE
OPERATED
SHORTING
BARS
TERMINAL
19
WILL VARY
DEPENDING
ON OPTIONS
SYNC
OUT
OR
P
.S.S.
NON
-
ISOL
.
CONT.
SENS.
AUX.
EXPAND
LINE BUS
OPTO-
ISOLATOR
INTERNAL
CIRCUITRY
OPTO
-
ISOLATOR
OPTO-
ISOLATOR
OPTO-
ISOLATOR
OPTO
-
ISOLATOR
OPTO-
ISOLATOR
ISOL.
CONT.
SENS.
COM. TO
OPTO-ISOL
.
Vctrl
J1
LL
-DB
DL-LB
52b
Vctrl
DL-DB
LL
-
LB
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
EXTERNAL
CASE GROUND
TERMINAL
COM
10
9
EXTERNAL CONTACT
INPUTS FROM
RESISTOR MODULE
TARGET
VOLTAGE
MONITOR
OUT
SYNC
OUT
POWER
SUPPLY
D2819-03
08-29-02
LINE
COM
BUS
8
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
CONNECTIONS
Be sure to check the model and style number of a relay before connecting and energizing the relay.
Incorrect wiring may result in damage to the relay. Except where noted, connections should be made with
wire no smaller than 14 AWG.
Typical internal connections are shown in Figure 4-8. Typical external connections are shown in Figures
4-9 through 4-12.
Figure 4-8. Internal Diagram
9170200990 Rev U BE1-25 Installation 4-9
Page 50

Figure 4-9. Voltage Sensing Connections
4-10 BE1-25 Installation 9170200990 Rev U
Page 51

NOTE
The Resistor Module shown in Figure 4-10 is required for BE1-25 Sync-Check relays,
Voltage Monitor option 2-C, 2-U, or 2-V.
When the relay is to be projection mounted (see Figure 4-6), the Resistor Module must
be removed prior to installation. Once the relay is installed, the Module is then attached
to the rear of the mounting panel. The external contact inputs are then wired to the
Resistor Module at TB2.
Figure 4-10. Resistor Module Connections
9170200990 Rev U BE1-25 Installation 4-11
Page 52

Figure 4-11. Control Circuit Connections (Typical)
4-12 BE1-25 Installation 9170200990 Rev U
Page 53

Figure 4-12. Contact Sensing and Resistor Modules for Type T Power Supply Only
MAINTENANCE
BE1-25 relays require no preventative maintenance other than a periodic operational check. If the relay
fails to function properly, contact Technical Sales Support at Basler Electric to coordinate repairs.
STORAGE
This device contains long-life aluminum electrolytic capacitors. For devices that are not in service (spares
in storage), the life of these capacitors can be maximized by energizing the device for 30 minutes once
per year.
9170200990 Rev U BE1-25 Installation 4-13
Page 54

This page intentionally left blank.
4-14 BE1-25 Installation 9170200990 Rev U
Page 55

SECTION 5 • TESTING
TABLE OF CONTENTS
SECTION 5 • TESTING ............................................................................................................................ 5-1
GENERAL .............................................................................................................................................. 5-1
RELAY OPERATING PRECAUTIONS .................................................................................................. 5-1
SWITCH SETTINGS .............................................................................................................................. 5-1
Setting Time Delay or Phase Angle ................................................................................................... 5-1
Condition and Mode Switches ............................................................................................................ 5-2
OPERATIONAL TEST PROCEDURE ................................................................................................... 5-3
Preliminary Settings ........................................................................................................................... 5-3
Test Procedure ................................................................................................................................... 5-4
NORMAL Mode Testing ..................................................................................................................... 5-5
NOT OV Testing ................................................................................................................................. 5-7
Figures
Figure 5-1. Maximum Slip Frequency versus Time Delay and Phase Angle Settings .............................. 5-2
Figure 5-2. Test Setup (Typical) ................................................................................................................ 5-3
Tables
Table 5-1. NORMAL Mode Testing ........................................................................................................... 5-5
Table 5-2. NOT OVERVOLTAGE Mode Testing ....................................................................................... 5-7
9170200990 Rev U BE1-25 Testing i
Page 56

This page intentionally left blank.
ii BE1-25 Testing 9170200990 Rev U
Page 57

SECTION 5 • TESTING
GENERAL
In the event the relay is not to be installed immediately, store the relay in its original shipping carton.
When the relay is to be placed into service, it is recommended that the operational test procedure in this
section be performed prior to installation.
RELAY OPERATING PRECAUTIONS
Before installation or operation of the relay, note the following precautions:
1. A minimum of 0.2 ampere in the output circuit is required to ensure operation of current operated
targets.
2. The relay is a solid-state device. If a wiring insulation test is required, remove the connection
plugs and withdraw the cradle from its case.
3. When the connection plugs are removed the relay is disconnected from the operating circuit and
will not provide system protection. Always be sure that external operating (monitored) conditions
are stable before removing a relay for inspection, test, or service.
4. Be sure the relay case is hard wired to earth ground using the ground terminal on the rear of the
unit. It is recommended to use a separate ground lead to the ground bus for each relay.
SWITCH SETTINGS
Setting Time Delay or Phase Angle
Figure 5-1 graphically relates time delay settings to phase angle settings in terms of slip frequency.
9170200990 Rev U BE1-25 Testing 5-1
Page 58

Figure 5-1. Maximum Slip Frequency versus Time Delay and Phase Angle Settings
Condition and Mode Switches
Detailed instructions and precautions for programming the Mode switches and Condition switches are
provided in Table 2-1, callouts R and S. The location of the switches is shown in Figure 2-2.
When output contacts of both Sync and Voltage Monitor functions are wired in parallel, the live line/live
bus Condition Switch No. 2 must be in OFF position. Otherwise, the Sync function will be overruled. If the
condition switches are external (option 2-C, 2-U, or 2-V), the external LL-LB switch should be omitted
when Sync and Voltage Monitor contacts are in parallel.
5-2 BE1-25 Testing 9170200990 Rev U
Page 59

OPERATIONAL TEST PROCEDURE
The following procedure verifies operation of the relay. The test setup of Figure 5-2 is intended primarily
as an illustration of the principles involved. Other test setups known to be capable of testing within the
stated and implied tolerances (including equipment specifically designed for testing relays) may be used.
Preliminary Settings
(a) All contact-sensing inputs are open circuited.
(b) All Condition Switches and Mode Switches are UP.
(c) Some styles of relay are equipped with multiturn pots accessible through holes in the front panel.
All such controls should be turned fully CCW (to their minimum settings) except the ∆V control,
which is turned fully CW.
(d) Adjust bus and line sensing input voltages to 95 Vac with zero phase difference.
(e) Apply power to the relay.
(f) If equipped with power supply status output (option 3-6), verify that the power supply status
output contacts are open.
(g) Remove input power and verify that the status contacts close.
(h) Apply power to the relay.
Figure 5-2. Test Setup (Typical)
9170200990 Rev U BE1-25 Testing 5-3
Page 60

Test Procedure
NOTE
A 00 setting of either control must inhibit the Sync-Check function.
If target option B (current operated target) is present, check that targets operate
at closure of the sync contacts. (Requires a minimum of 0.2 A in the output
circuit.)
Step 1. Confirm proper sync-check operation at selected PHASE ANGLE settings with TIME DELAY set
at minimum (for convenience). Check that go/no-go operation is within specs.
NOTE
When making this test, observe that the PHASE ANGLE LED is turned ON
during the delay period, and that the SYNC LED flashes when the output
contacts close. (Both LEDs go out as soon as the 52b input is open.)
If auxiliary contacts are supplied, check for proper switching action as relay cycles.
Step 2. With line and bus inputs in phase, check for proper operation of timer, using a time delay of 9.9
seconds, and again at 99 seconds (multiplier switch at 0.1 and at 1.0 respectively). (Close and
open the 52b input to begin and terminate the timing cycle.) Check that accuracy of timing cycle
is within specs.
Step 3. Check that operation of the sync function is inhibited during low voltage conditions of line or bus.
(a) Lower line and bus sensing input to 60 Vac and repeat Step 1. SYNC output should not be
inhibited.
(b) Lower the line sensing inputs to 20 Vac. Attempt Step 1. SYNC function is inhibited and
PHASE ANGLE LED should not turn ON.
(c) Return the line input to 60 Vac and lower the bus input to 20 Vac. Attempt Step 1. Sync
function is inhibited and PHASE ANGLE LED should not turn ON.
It is not necessary to determine the exact voltage threshold at which inhibition occurs in order to confirm
proper operation of this circuit.
NOTE
Steps 4 through 8 check for proper operation of line and bus Voltage Monitor
(options 2-A, 2-C, 2-R, 2-S, 2-U, or 2-V). If these options are not present,
proceed to step 7.
Step 4. Verify that the voltage monitor controls operate over the specified range as follows.
(a) Rotate the LL and LB controls (front panel) fully CW; rotate the DL/NOT overvoltage and
DB/NOT overvoltage controls fully CCW.
(b) Adjust line and bus sensing inputs to 135 Vac.
(c) Slowly rotate the LL and LB controls CCW until LEDs turn ON. This should occur only a few
turns from the maximum (fully CW) position.
(d) Adjust line and bus sensing inputs to 10 Vac.
(e) Rotate the LL and LB controls CCW until their indicators LEDs turn ON. This should occur
only a few turns from the minimum (fully CCW) position.
(f) With input voltages remaining at 10 Vac, rotate the DL/NOT overvoltage and DB/NOT
overvoltage controls CW until their LEDs just light. Both adjustments should require only a
few turns from the minimum (fully CCW) position.
(g) Return line and bus sensing inputs to 135 Vac. (Both LEDs of step (f) must now be OFF.)
5-4 BE1-25 Testing 9170200990 Rev U
Page 61

(h) Again rotate the DL/NOT overvoltage and DB/NOT overvoltage controls CW until the LEDs
just light. Both adjustments should be near their maximum (fully CW) limits.
NORMAL Mode Testing
Step 5. Test NORMAL Mode operation of the line and bus voltage monitor as follows. (Proceed to step 6
if the NORMAL Mode is not used.)
(a) Adjust the following front panel controls by applying the voltages listed below, adjusting each
control to the threshold where its LED just lights. (Reference callouts L, N, F, and G of Figure
2-1.)
LB: Adjust to 80 Vac.
DB/NOT OV: Adjust to 30 Vac.
LL: Adjust to 80 Vac.
DL/NOT OV: Adjust to 30 Vac.
(b) If the relay is not equipped with a separate relay for Voltage Monitor (output options G and
H), set TIME DELAY to 99 seconds. This allows the convenience of using in-phase voltages
for testing non-synchronous functions (without unwanted SYNC contact closures).
(c) Apply simulated line and bus voltages, adjusted to check the bus and line voltage criteria
given in Table 5-1. To be valid, an output must occur immediately after line and bus voltages
are applied.
NOTE
In some units, both the internal Condition Switches and the external condition
sensing inputs are present and in parallel. Take care that only one input method
is utilized when testing the relay, and (most importantly) after the relay is
installed.
Table 5-1. NORMAL Mode Testing
No output∗ throughout voltage range.
Condition Switch
1 Up
2 Up
3 Up
4 Up
5 Up
Mode Switch
1 Up
2 Up
Output* only when bus input voltage is greater than 80 volts and line is less than 30 volts.
Condition Switch
1 Up
2 Up
3 Down
4 Up
5 Up
Mode Switch
1 Up
2 Up
Output∗ only when bus input voltage is less than 30 volts and line is greater than 80 volts.
9170200990 Rev U BE1-25 Testing 5-5
Page 62

Condition Switch
1 Up
2 Up
3 Up
4 Down
5 Up
Mode Switch
1 Up
2 Up
Output∗ only when bus and line input voltages are less than 30 volts.
Condition Switch
1 Up
2 Up
3 Up
4 Up
5 Down
Mode Switch
1 Up
2 Up
Output∗ only when bus and line input voltages are greater than 80 volts.
Condition Switch
1 Up
2 Down†
3 Up
4 Up
5 Up
Mode Switch
1 Up
2 Up
∗ Contact is SYNC output for output option E or F. Voltage Monitor output for output option G or H.
† The only valid use for the LB-LL Condition Switch No. 2 Down is when there is an independent output
relay for the Voltage Monitor output options G and H.
If the delta voltage option is present, it is factory set to 20 volts. (The timed SYNC output is inhibited if the
voltage difference between the line and the bus is greater than 20 volts.)
CAUTION
Condition Switch No. 2, shown in Figure 2-2, must be OFF (Up) when output
option E or F is selected. Otherwise, SYNC outputs will occur under live line/live
bus conditions without benefit of the Sync-Check function.
5-6 BE1-25 Testing 9170200990 Rev U
Page 63

NOT OV Testing
Step 6. Test the NOT OV Mode of the Voltage Monitor as follows. (Proceed to step 7 if this mode is not
used.)
(a) Adjust the following front panel controls by applying the voltages stated below, adjusting each
control to the threshold where its LED indicator just turns ON. (Reference callouts L, N, F,
and G of Figure 2-1).
LB: Adjust to 80 Vac.
DB/NOT OV: Adjust to 120 Vac.
LL: Adjust to 80 Vac.
DL/NOT OV: Adjust to 120 Vac.
(b) Set TIME DELAY to 99 seconds. This allows the convenience of using in-phase voltages for
testing non-synchronous functions (without unwanted SYNC outputs).
(c) Apply simulated line and bus voltages adjusted to check the bus and line voltage criteria
given in Table 5-2. To be valid, an output must occur immediately after line and bus voltages
are applied.
Step 7. If the voltage difference option is furnished, check for proper enabling of the Sync-Check output
contacts when the voltage differential between line and bus is within selected ∆V settings.
Step 8. If the expand phase angle option is furnished, check that the phase window widens by a factor of
2 or 3 (according to the position of the jumper on the Sync-Check PC board) when the expand
phase input terminal is closed.
Table 5-2. NOT OVERVOLTAGE Mode Testing
No output∗ throughout voltage range. (Normal SYNC output function still operates. SYNC output occurs
after 99 seconds time delay if the line and bus voltages are greater than 60 Vac. This 60 Vac corresponds
to the minimum voltage requirement for the sync-check function, not the LL and LB settings.) For the
following tests, if your unit has a minimum voltage requirement of less than 60 Vac, use a voltage that is
appropriate for your unit.
Condition Switch
1 Up
2 Up
3 Up
4 Up
5 Up
Mode Switch†
1 Down
2 Down
Output∗ only when bus input voltage is greater than 60 volts but less than 120 volts, and line is less than
60 volts.
Condition Switch
1 Up
2 Up
3 Down
4 Up
5 Up
Mode Switch†
1 Down
2 Down
Output∗ only when bus input voltage is less than 60 volts and line is greater than 60 volts but less than
120 volts.
9170200990 Rev U BE1-25 Testing 5-7
Page 64

Condition Switch
1 Up
2 Up
3 Up
4 Down
5 Up
Mode Switch†
1 Down
2 Down
Output∗ only when bus and line input voltages are less than 60 volts.
Condition Switch
1 Up
2 Up
3 Up
4 Up
5 Down
Mode Switch†
1 Down
2 Down
Output∗ only when bus and line input voltages are greater than 60 volts but less than 120 volts.
Condition Switch
1 Up
2 Down‡
3 Up
4 Up
5 Up
Mode Switch†
1 Down
2 Down
No output throughout voltage range. (Normal SYNC function still operates with the additional NOT
overvoltage constraint. Output occurs after 99 seconds time delay if the line and bus voltages are greater
than 60 Vac and less than the NOT overvoltage setting of 120 Vac.)
Condition Switch
1 Down
2 Up
3 Up
4 Up
5 Up
Mode Switch†
1 Down
2 Down
Notes for Table 5-2:
∗ Contact is SYNC output for output option E or F. Voltage Monitor output for output option G or H.
† Placing both bus and line NOT OV Mode Switches Down, does NOT imply that line and bus must
operate in the same mode. Any combination is permissible.
‡ The only valid use for the LB-LL Condition Switch No. 2 Down is when there is an independent output
relay for the Voltage Monitor output options G and H.
If the delta voltage option is present, it is factory set to 20 volts. (The timed SYNC output is inhibited if the
voltage difference between the line and the bus is greater than 20 volts.)
5-8 BE1-25 Testing 9170200990 Rev U
Page 65

Page 66

12570 State Route 143
Highland IL 62249-1074 USA
Tel: +1 618.654.2341
Fax: +1 618.654.2351
email: info@basler.com
P.A.E. Les Pins
67319 Wasselonne Cedex
FRANCE
Tel: +33 3.88.87.1010
Fax: +33 3.88.87.0808
email: franceinfo@basler.com
No. 59 Heshun Road Loufeng District (N)
Suzhou Industrial Park
215122 Suzhou
P.R. CHINA
Tel: +86 512.8227.2880
Fax: +86 512.8227.2887
email: chinainfo@basler.com
111 North Bridge Road
15-06 Peninsula Plaza
Singapore 179098
Tel: +65 68.44.6445
Fax: +65 68.44.8902
email: singaporeinfo@basler.com
 Loading...
Loading...