Page 1

Avaya 1600 Series IP Deskphones
Administrator Guide
Release 1.3.5
16-601438
Issue 5
May 2014
Page 2

© 2014 Avaya Inc.
All Rights Reserved.
Notice
While reasonable efforts were made to ensure that the infor mation in this
document was complete and accurate at the time of printing, Avaya Inc. can
assume no liability for any errors. Changes and corrections to the information
in this document may be incorporated in future releases.
For full legal page information, please see the complete document, A vaya
Legal Page for Hardware Documentation, Document number 03-600759.
To locate this document on our Web site, simply go to http://
www.avaya.com/support and search for the document number in the
search box.
Documentation disclaimer
Avaya Inc. is not responsible for any modifications, addition s, or deletions to
the original published version of this documentation unless such modifications,
additions, or deletions were performed by Avaya. Customer and/or End User
agree to indemnify and hold harmless Avaya, Avaya's agents, servants and
employees against all claims, lawsuits, demands and judgments arising out of,
or in connection with, subsequent modifications, additions or deletions to this
documentation to the extent made by the Customer or End User.
Link disclaimer
Avaya Inc. is not responsible for the contents or reliability of any linked Web
sites referenced elsewhere within this documentation, and Avaya does not
necessarily endorse the products, services, or informa tion described or o ff ered
within them. We cannot guarantee that these links will work all of the time and
we have no control over the availability of the linked pages.
Warranty
Avaya Inc. provides a limited warranty on this product. Refer to your sales
agreement to establish the terms of the limited warran ty. In addition, Avaya’s
standard warranty language, as well as information regarding support for this
product, while under warranty, is available through the following Web site:
http://www.avaya.com/support
Copyright
Except where expressly stated otherwise, the Product is protected by copyrigh t
and other laws respecting proprietary rights. Unauthorized reproduction,
transfer, and or use can be a criminal, as well as a civil, offense un der the
applicable law.
Avaya support
Avaya provides a deskphone number for you to use to report problems or to
ask questions about your product. The support deskphone number
is 1-800-242-2121 in the United St ates. For additional support deskphone
numbers, see the Avaya Web site:
http://www.avaya.com/support
Software License
USE OR INSTALLATION OF THE PRODUCT INDICATES THE END USER’S
ACCEPTANCE OF THE TERMS SET FORTH HEREIN AND THE GENERAL
LICENSE TERMS AVAIL ABLE ON T HE AVAYA WEBSITE AT http://
support.avaya.com/LicenseInfo/ (“GENERAL LICENSE TERMS”). IF YOU DO
NOT WISH TO BE BOUND BY THESE TERMS, YOU MUST RETURN THE
PRODUCT(S) TO THE POINT OF PURCHASE WITHIN TEN (10) DAYS OF
DELIVERY FOR A REFUND OR CREDIT.
Avaya grants End User a license within the scope of the license types
described below. The applicable number of licenses and units of capacity for
which the license is granted will be one (1), unless a different number of
licenses or units of capacity is specified in the Documentation or other
materials available to End User. “Designated Processor” means a single
stand-alone computing device. “Server” means a Designated Processor that
hosts a software application to be accessed by multiple users. “Soft w are”
means the computer programs in object code, originally licensed by Avaya and
ultimately utilized by End User, whether as stand-alone Products or
pre-installed on Hardware. “Hardware” means the standard hardware
Products, originally sold by Avaya and ultimately utili zed by End User.
License Type(s):
Designated System(s) License (DS). End User may install and use each copy
of the Software on only one Designated Processor, unless a different number
of Designated Processors is indicated in the Documentation or other mat erials
available to End User. Avaya may require the Designated Processor(s) to be
identified by type, serial number, feature key, location or other specific
designation, or to be provided by End User to Avaya through elect roni c mean s
established by Avaya specifically for this purpose.
Third-party Components
Certain software programs or portions thereof included in the Product may
contain software distributed under third party agreements (“Third Party
Components”), which may contain terms that expand or limit rights to use
certain portions of the Product (“Third Party Terms”). Information identifying
Third Party Components and the Third Party Terms that apply to them is
available on Avaya’s Web site at:
http://support.avaya.com/ThirdPartyLicense/
Interference
Using a cell, mobile, or GSM deskphone, or a two-way radio in close proximity
to an Avaya IP Deskphone might cause interference.
Security
See http://support.avaya.com/security
vulnerabilities in Avaya products. See http://support.avaya.com
latest software patches and upgrades. For information about secure
configuration of equipment and mitigation of toll fraud threats, see the Avaya
Toll Fraud and Security Handbook at http://support.avaya.com
to locate and/or report known
to locate the
.
Page 3

Contents
Chapter 1: Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1
About This Guide . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1
New in this release. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1
Document Organization . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2
Other Documentation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3
Chapter 2: Administration Overview and Requirements . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
1600 Series IP Deskphones . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
Parameter Data Precedence . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
The Administrative Process. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
Administrative Checklist . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
Deskphone Initialization Process. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
Step 1: Deskphone to Network . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
Step 2: DHCP Server to Deskphone . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
Step 3: Deskphone and File Server. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
Step 4: Deskphone and the Call Server . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
Error Conditions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
Chapter 3: Network Requirements . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
Network Assessment . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
Hardware Requirements. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
Server Requirements . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
DHCP Server . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
HTTP/HTTPS Server . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
Required Network Information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
Other Network Considerations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
SNMP . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
Reliability and Performance. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
QoS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
IEEE 802.1P and 802.1Q . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
Network Audio Quality Display on 1600 Series IP Deskphones . . . . . . . . . . . 20
IP Address Lists and Station Number Portability . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
TCP/UDP Port Utilization . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
Security. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
Registration and Authentication . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
Chapter 4: Avaya Aura Communication Manager Administration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
Call Server Requirements. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
Switch Compatibility and Aliasing IP Deskphones . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
Issue 5 May 2014 1
Page 4

Media Server (Switch) Administration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27
IP Interface and Addresses . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27
UDP Port Selection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
RSVP and RTCP . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
QoS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
IEEE 802.1P and 802.1Q . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
NAT . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
DIFFSERV . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
Voice Mail Integration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30
1600 Series IP Deskphones with Avaya Aura Communication Manager 5.2 Native Support
30
1600 Series IP Deskphones Aliased as 4600 Series IP Deskphones. . . . . . . . . 30
Deskphone Administration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
System-Wide Administration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
Feature-Related System Parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
Administering Stations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32
Aliasing 1600 Series IP Deskphones . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 33
Administering Features . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 33
Feature Buttons and Call Appearances . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 34
For the 1603/1603SW/1603-I/1603SW-I and 1608/1608-I IP Deskphones . . . . . . . 34
For the 1616/1616-I IP Deskphones. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 34
Conference Details Screen for Ad-Hoc Conferences . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 35
Shuffling . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 35
Printing Button Labels . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 36
Chapter 5: Server Administration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 37
Software Checklist. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 37
DHCP and File Servers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 37
DHCP Server Administration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 38
DHCP Generic Setup . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 38
Windows NT 4.0 DHCP Server . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 42
Verifying the Installation of the DHCP Server . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 42
Creating a DHCP Scope for the IP Deskphones . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 43
Editing Custom Options. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 44
Adding the DHCP Option . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 44
Activating the Leases . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 45
Verifying Your Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 45
Windows 2000 DHCP Server . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 46
Verifying the Installation of the DHCP Server . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 46
Adding DHCP Options. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 48
2 1600 Series IP Deskphone Administrator Guide Releas e 1.3.5
Page 5

Activating the New Scope. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 49
HTTP Generic Setup. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 49
HTTP Configuration for Backup/Restore. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 50
For IIS Web Servers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 50
Web Configuration Tool . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 52
Chapter 6: Deskphone Software and Application Files. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 55
General Download Process . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 55
Software . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 55
1600 Series IP Deskphone Scripts and Application Files. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 56
Choosing the Right Application File and Upgrade Script File . . . . . . . . . . . . 56
Upgrade Script File . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 56
Settings File . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 57
Contents of the Settings File . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 58
The GROUP System Value . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 59
Call Center Administration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 59
Chapter 7: Administering Deskphone Options . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 65
Administering Options for the 1600 Series IP Deskphones . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 65
VLAN Considerations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 72
VLAN Tagging . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 72
VLAN Default Value and Priority Tagging . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 72
VLAN Separation. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 73
DNS Addressing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 75
IEEE 802.1X . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 75
802.1X Pass-Through and Proxy Logoff . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 76
802.1X Supplicant Operation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 76
Link Layer Discovery Protocol (LLDP) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 78
Local Administrative Options Using the Deskphone Dialpad . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 83
Clear Procedure . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 83
Disabling or enabling the Debug mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 84
Group Identifier . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 85
Reset System Values . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 86
Restart the Deskphone . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 88
Interface Control. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 89
The View Local Procedure . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 91
Static Addressing Installation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 94
Disable/Enable Event Logging . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 97
Logoff. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 98
Issue 5 May 2014 3
Page 6

Self-Test Procedure . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 99
Language Selection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 101
1600 Series Global Deskphones . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 101
1600 Series International Deskphones. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 103
Enhanced Local Dialing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 106
Backup/Restore . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 107
Backup . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 108
Restore . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 109
Chapter 8: Administering Applications and Options . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 111
Customizing 1600 Series IP Deskphone Applications and Options . . . . . . . . . . . 111
The Application Status Flag (APPSTAT) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 114
Appendix A: Glossary of Terms . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 117
Appendix B: Related Documentation. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 119
IETF Documents . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 119
ITU Documents. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 120
ISO/IEC, ANSI/IEEE Documents . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 121
Appendix C: Sample Administration Forms . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 123
Index . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 133
4 1600 Series IP Deskphone Administrator Guide Releas e 1.3.5
Page 7
Chapter 1: Introduction
!
CAUTION:
About This Guide
This guide is for personnel who administer Avaya Aura™ Communication Manager, Avaya Aura
Communication Manager Branch (formerly known as Avaya Distributed Office), DHCP, HTTP/HTTPS
servers for Avaya 1600 Series IP Deskphones, a Local Area Network (LAN), or a Web server.
The 1600 Series IP Deskphones use Internet Protocol (IP) technology with Ethernet line interfaces and
support the H.323 protocol only . The 1600 Series IP Deskphones provide support for DHCP, HTTP, and
HTTPS over IPv4, which enhances the administration and servicing of the deskphones. These
deskphones use DHCP to obtain dynamic IP Addresses, and HTTPS or HTTP to download new
versions of software or customized settings for the deskphones.
CAUTION: Avaya does not support many of the products mentioned in this document. Take care to
ensure that there is adequate technical support available for servers used with any 1600
Series IP Deskphone system. If the servers are not functioning correctly, the 1600 Series
IP Deskphones might not operate correctly.
New in this release
Release 1.3.5 has the following new enhancements:
● Supported on the 1603, 1603-I, 1603SW, 1603SW-I, 1608, 1608-I, 1616, and 1616-I IP
Deskphones only. This package will not load or operate on any other models.
● Avaya recommends that all the customers upgrade both new and installed 1600 Series IP
Deskphones to this version at their earliest convenience.
Issue 5 May 2014 1
Page 8

Introduction
Document Organization
The guide contains the following sections:
Chapter 1:
Chapter 2: Administrat ion
Overview and Requirements
Chapter 3: Network
Requirements
Chapter 4: Avaya Aura
Communication Manager
Administration
Chapter 5: Server
Administration
Chapter 6: Deskphone
Software and Application Files
Chapter 7: Administering
Deskphone Options
Chapter 8: Administering
Applications and Options
Appendix A: Glossary of
Terms
Appendix B: Related
Documentation
Appendix C: Sample
Administration Forms
Introduction Provides an overview of this document.
Provides an overview of the administrative process and
describes general hardware, software, and operational
requirements.
Describes administrative requirements for your Local Area
Network.
Describes how to administer Avaya Aura Communication
Manager to operate with 1600 Series IP Deskphones.
Describes DHCP, HTTP, and HTTPS administration for the
1600 Series IP Deskphones.
Describes deskphone software, covers application software
downloads, and provides information about the configuration
file.
Describes how to use file parameters and options to
administer 1600 Series IP Deskphones. Covers backup and
restoration of deskphone data. Also describes how to use
local procedures to customize a single deskphone from the
dialpad.
Provides a table of customizable application-specific
parameters, to provide administrative control of deskphone
functions and options.
Provides a glossary of terms used in this document or which
can be applicable to 1600 Series IP Deskphones.
Provides references to external documents that relate to
telephony in general, which can provide additional
information about specific aspects of the deskphones.
Provides examples of Avaya Aura Communication Manager
forms related to system-wide and individual deskphone
administration.
2 1600 Series IP Deskphone Administrator Guide Releas e 1.3.5
Page 9

Other Documentation
Other Documentation
See the Avaya support site at http://www.avaya.com/support for 1600 Series IP Deskphone technical
and end user documentation.
The following documents are available for the 1600 Series IP Deskphones:
● Avaya 1600 Series IP Deskphones Installation and Maintenance Guide, Document Number
16-601438.
● Avaya one-X™ Deskphone Value Edition 1600 Series IP Deskphone Pre-Installation Checklist,
Document Number 16-601439.
● Avaya one-X™ Deskphone Value Edition 1600 Series IP Deskphone Safety Instructions,
Document Number 16-601440.
● Avaya one-X™ Deskphone Value Edition 1600 Series IP Deskphones BM32 Button Module
Installation and Safety Instructions, Document Number 16-601441.
● Avaya one-X™ 9600 Series IP Deskphone Application Programmer Interface (API) Guide,
Document Number 16-601442.
● Avaya 1600 Series IP Deskphones Administrator Guide, Document Number 16-601443.
● Avaya 1603/1603SW/1603-I/1603SW-I IP Deskphone User Guide, Document Number
16-601444.
● Avaya 1608/1608-I IP Deskphone User Guide, Document Number 16-601446.
● Avaya 1616/1616-I IP Deskphone User Guide, Document Number 16-601448.
● Avaya one-X™ Deskphone Value Edition 1600 Series IP Deskphones BM32 Button Module User
Guide, Document Number 16-601450
● Avaya one-X™ Deskphone Value Edition 1600 Series IP Deskphone Wall Mount Instructions,
Document Number 16-601453.
● Avaya one-X™ Deskphone Value Edition 1600 Series IP Deskphone Stand Instructions,
Document Number 16-601451.
● Avaya 1603/1603SW/1603-I/1603SW-I IP Deskphone Quick Reference,
Document Number 16-601445.
● Avaya 1608/1608-I IP Deskphone Quick Reference, Document Number 16-601447.
● Avaya 616/1616-I IP Deskphone Quick Reference, Document Number 16-601449.
See Appendix B: Related Documentation
for a list of non-Avaya documents, such as those published
by the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF) and the International Telecommunication Union (ITU).
Issue 5 May 2014 3
Page 10

Introduction
4 1600 Series IP Deskphone Administrator Guide Releas e 1.3.5
Page 11
Chapter 2: Administration Overview and
Requirements
1600 Series IP Deskphones
The 1600 Series IP Deskphones currently support the H.323 signaling protocol.
The H.323 standard provides for real time audio, video, and data communications transmission over a
packet network. An H.323 deskphone protocol stack comprises several protocols:
● H.225 for registration, admission, status (RAS), and call signaling,
● H.245 for control signaling,
● Real Time Transfer Protocol (RTP), and
● Real Time Control Protocol (RTCP)
The parameters under which the 1600 Series IP Deskphones need to operate are summarized as
follows:
● Deskphone and System Administration on the Avaya Media Server, as covered in
Chapter 4: Avaya Aura Communication Manager Administration
.
● IP address management for the deskphone, as covered in DHCP and File Servers on page 37 for
dynamic addressing. For static addressing, see the Avaya 1600 Series IP Deskphones Installatio n
and Maintenance Guide.
● Tagging Control and VLAN administration for the deskphone, if appropriate, as covered in Chapter
7: Administering Deskphone Options.
● Quality of Service (QoS) administration for the deskphone, if appropriate. QoS is covered in
QoS
on page 19 and QoS on page 28.
● Interface administration for the deskphone, as appropriate. Administer the deskphone to LAN
interface using the PHY1 parameter described in Chapter 3: Network Requirements
. Administer
the deskphone to PC interface using the PHY2 parameter described in “Local Procedures” in the
Avaya 1600 Series IP Deskphones Installation and Maintenance Guide.
● Application-specific deskphone administration, if appropriate, as described in Chapter
8: Administering Applications and Options. An example of application-specific data is specifying
the extent to which users can add/edit/delete data for Contacts entries.
● Protocol administration, for example, Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) and Link
Layer Discovery Protocol (LLDP).
Issue 5 May 2014 5
Page 12

Administration Overview and Requirements
Note:
Table 1 indicates that you can administer system parameters in a variety of ways and use a variety of
delivery mechanisms like:
● Maintaining the information on the call server.
● Manually entering the information by means of the deskphone dialpad.
● Administering the DHCP server.
● Editing the configuration file on the applicable HTTP or HTTPS file server.
● User modification of certain parameters, when given administrative permission to do so.
Note: Not all parameters can be administered on all delivery mechanisms.
Table 1: Administration Alternatives and Options for 1600 Series IP
Deskphones
Administrative
Parameter(s)
Mechanisms
For More Information See:
Deskphone
Avaya call server Chapter 4: Avaya Aura Communication Manager
Administration
IP Addresses DHCP
(strongly
recommended)
Configuration file Chapter 6: Deskphone Software and Application
Manual administration
at the deskphone
LLDP Link Layer Discovery Protocol (LLDP) on page 78.
Tagging and
LLDP Link Layer Discovery Protocol (LLDP)
VLAN
DHCP DHCP Server Administration
Configuration file
(strongly
recommended)
Administration, Chapter 5: Server Administration,
and Appendix B: Related Documentation.
DHCP and File Servers on page 37, and especially
DHCP Server Administration
on page 38.
Files and Chapter 7: Administering Deskphone
Options.
“Static Addressing Installation” in the Avaya 1600
Series IP Deskphones Installation and
Maintenance Guide.
on page 78.
on page 38, and
Chapter 7: Administering Deskphone Options
DHCP and File Servers
on page 37 and Chapter
.
7: Administering Deskphone Options.
6 1600 Series IP Deskphone Administrator Guide Releas e 1.3.5
1 of 3
Page 13
Table 1: Administration Alternatives and Options for 1600 Series IP
Deskphones (continued)
Administrative
Parameter(s)
Mechanisms
For More Information See:
1600 Series IP Deskphones
Manual administration
at the deskphone
“Static Addressing Installation” in the Avaya 1600
Series IP Deskphones Installation and
Maintenance Guide.
Avaya call server Use the change ip-network-map command to
configure the VLAN ID.
2 of 3
Issue 5 May 2014 7
Page 14

Administration Overview and Requirements
Table 1: Administration Alternatives and Options for 1600 Series IP
Deskphones (continued)
Administrative
Parameter(s)
Mechanisms
For More Information See:
Quality of
Service
Avaya call server
(strongly
UDP Port Selection on page 28 and
Appendix B: Related Documentation
recommended)
DHCP DHCP and File Servers on page 37, and Chapter
7: Administering Deskphone Options.
Configuration file DHCP and File Servers on page 37, and Chapter
7: Administering Deskphone Options.
Interface DHCP DHCP and File Servers
6: Deskphone Software and Application Files.
Configuration file
(strongly
DHCP and File Servers
6: Deskphone Software and Application Files.
recommended)
Manual administration
at the deskphone
“Ethernet (Hub) Interface Enable/Disable” in the
Avaya 1600 Series IP Deskphones Installation and
Maintenance Guide.
LLDP Link Layer Discovery Protocol (LLDP)
Application specific
parameters
DHCP DHCP and File Servers on page 37, and especially
DHCP Server Administration on page 38.
Also, Chapter 8: Administering Applications and
Options.
.
on page 37, and Chapter
on page 37, and Chapter
on page 78.
Configuration file
(strongly
recommended)
DHCP and File Servers on page 37, and especially
HTTP Generic Setup on page 49. Also,
Chapter 8: Administering Applications and Options
.
3 of 3
General information about administering DHCP servers is covered in DHCP and File Servers on
page 37, and more specifically, DHCP Server Administration
administering HTTP servers is covered in DHCP and File Servers
on page 38. General information about
, and more specifically , HT TP Generic
Setup. Once you are familiar with that material, you can administer deskphone options as described in
Chapter 7: Administering Deskphone Options
8 1600 Series IP Deskphone Administrator Guide Releas e 1.3.5
.
Page 15
Parameter Data Precedence
Note:
Parameter Data Precedence
If a given parameter is administered in multiple places, the last server to provide the parameter has
precedence. The precedence, from lowest to highest, is:
1. LLDP,
2. Manual administration, with the two exceptions described for the system parameter STATIC
page 71,
3. DHCP,
4. HTTP/HTTPS script file,
5. the Avaya Media Server, and finally,
6. Backup files, if administered and if permitted.
Settings the IP deskphone receives from backup files or the media server overwrite any previous
settings, including manual settings. The only exception to this sequence is in the case of VLAN IDs. In
the case of VLAN IDs, LLDP settings of VLAN IDs are the absolute authority. Then the usual sequence
applies through HTTP/HTTPS.
Note: For the L2QVLAN and L2Q system values, LLDP settings of VLAN IDs are the absolute
authority only if the LLDP task receives the VLAN IDs before DHCP and HTTP, and the
DHCP client of the deskphone is activated at all. If the LLDP task receives the VLAN IDs
after DHCP negotiation, several criteria must be successful before the deskphone
accepts VLAN IDs from LLDP. For more information, see Link Layer Discovery Protocol
(LLDP).
on
The Administrative Process
The following list depicts administration for a typical 1600 Series IP Deskphone network. Your own
configuration might differ depending on the servers and system you have in place.
1. LAN and applicable servers administered to accept the deskphones.
2. Deskphone software downloaded from the Avaya support site.
3. 46xxsettings file updated with site-specific information, as applicable.
4. 1600 Series Deskphones installed. For more information, see the Avaya 1600 Series IP
Deskphones Installation and Maintenance Guide.
5. Individual 1600 Series IP Deskphones updated using local procedures, as applicable. For more
information, see “Local Administrative Procedures” in the Avaya 1600 Series IP Deskphones
Installation and Maintenance Guide.
Issue 5 May 2014 9
Page 16

Administration Overview and Requirements
Note:
Administrative Checklist
Use the following checklist as a guide to system and LAN administrator responsibilitie s. This high-le vel
list helps ensure that all deskphone system prerequisites and requirements are met prior to deskphone
installation.
Note: One person might function as both the system administrator and the LAN administrator
in some environments.
Table 2: Administrative Checklist
Task Description For More Information See:
Network Requirements
Assessment
Administer the call
server
DHCP server
installation
Administer DHCP
application
HTTP/HTTPS server
installation
Application file(s), script
file, and settings file
installation on HTTP/
HTTPS server
Determine that network
hardware is in place and can
handle deskphone system
requirements.
Verify that the call server is
licensed and is administered for
Voice over IP (VoIP).
Verify the individual
deskphones are administered
as desired.
Install a DHCP application on at
least one new or existing PC on
the LAN.
Add IP deskphone
administration to DHCP
application.
Install an HTTP/HTTPS
application on at least one new
or existing PC on the LAN.
Download the files from the
Avaya support site.
Chapter 3: Network
Requirements.
Chapter 4: Avaya Aura
Communication Manager
Administration.
Chapter 4: Avaya Aura
Communication Manager
Administration.
Vendor-provided instructions.
DHCP Server Administration in
Chapter 5: Server
Administration.
Vendor-provided instructions.
http://www.avaya.com/support
Chapter 6: Deskphone Software
and Application Files.
Modify settings file as
desired
Edit the settings file as desired,
using your own tools or the
[Avaya] Web configuration tool.
10 1600 Series IP Deskphone Administrator Guide Release 1.3.5
Chapter 6: Deskphone Software
and Application Files and Web
Configuration Tool on page 52.
1 of 2
Page 17

Deskphone Initialization Process
Note:
Table 2: Administrative Checklist (continued)
Task Description For More Information See:
Administer deskphones
locally as applicable
As a Group: The GROUP System Value
page 59 and the Avaya 1600
Series IP Deskphones
Installation and Maintenance
Guide.
Individually: The applicable Local
Procedures in the Avaya 1600
Series IP Deskphones
Installation and Maintenance
Guide.
Installation of
deskphones in the
network
Allow user to modify
Options, if applicable
Avaya 1600 Series IP
Deskphones Installation and
Maintenance Guide.
OPSTAT
on page 68 and the
respective User Guide for the
specific deskphone model.
2 of 2
Note: The 1608/1608-I and 1616/1616-I deskphones support the Top Line Text and Audio
Push types (but not the WML Push type).
on
Deskphone Initialization Process
These steps offer a high-level descrip tion of the information e xchanged when the deskph one initializes
and registers. This description assumes that all equipment is properly administered ahead of time. This
description can help you understand how the 1600 Series IP Deskphones relate to the routers and
servers in your network.
Step 1: Deskphone to Network
The deskphone is appropriately installed and powered. After a short initialization process, the
deskphone identifies the LAN speed and sends a message out into the network, identifying itself and
requesting further information. A router on the network receives and relays this message to the
appropriate DHCP server if the phone IP address is 0.0.0.0.
Issue 5 May 2014 11
Page 18
Administration Overview and Requirements
Step 2: DHCP Server to Deskphone
The DHCP file server provides information to the deskphone, as described in DHCP and File
Servers on page 37. Among other data passed to the deskphone is the IP address of the HTTP or
HTTPS server.
Step 3: Deskphone and File Server
The 1600 Series IP Deskphones can download script files and settings files from either an HTTP or
HTTPS server. These deskphones can also download the application files from the HTTP server. The
deskphone queries the file server, which transmits a script file to the deskphone. This script file, at a
minimum, tells the deskphone which application file the deskphone must use. T he application file is the
software that has the telephony functionality.
The deskphone uses the script file to determine if it has the proper application file. If the deskphone
determines the proper application file is missing, the deskphone requests an application file download
from the HTTP server. The deskphone then downloads the file and conducts some checks to ensure
that the file was downloaded properly. If the deskphone determines it already has the proper file, the
deskphone proceeds as described in the next paragraph without downloading the application file again.
The deskphone checks and loads the application file, then uses the script file to look for a settings file,
if appropriate. The optional settings file can cont ain settings you have administered for any or all of the
1600 Series IP Deskphones in your network. For more information about this download process and
settings file, see Chapter 6: Deskphone Software and Application Files
.
Step 4: Deskphone and the Call Server
The call server referred to in this step is the Avaya Media Server.
In this step, the deskphone might prompt the user for an extension and password. The deskphone uses
that information to exchange a series of messages with the call server. For a new installation and for full
service, the user can enter the deskphone extension and password. For a restart of an existing
installation, this information is already stored on the deskphone, but the user might ha ve to conf irm the
information. The deskphone and the call server exchange more messaging. The expected result is that
the deskphone is appropriately registered and call server data such as featur e button assignme nts are
downloaded.
12 1600 Series IP Deskphone Administrator Guide Release 1.3.5
Page 19
Error Conditions
Note:
The 1600 Series IP Deskphones support a feature called Unnamed Registration. Unnamed
Registration allows a deskphone to register with the Avaya Media Server without an extension,
assuming the Avaya Media Server also supports this feature. To invoke Unnamed Registration, take no
action. Allow the Extension... prompt to display for 60 seconds without making an entry. The
deskphone automatically attempts to register by means of Unnamed Registration. A deskphone
registered with Unnamed Registration has the following characteristics:
● only one call appearance,
● no administrable features,
● can make only outgoing calls, subject to call server Class of Restriction/Class of Service
limitations, and
● can be converted to normal “named” registration by the user entering a valid extension and
password (that is, logging in).
Note: Unnamed Registration requires administration on the Avaya Aura Communication
Manager system.
You can also administer the deskphone to avoid unnamed registration and remain unregistered if no
extension and password are provided. For more information, see UNNAMEDSTAT
in Table 9.
For more information about the installation process, see the Avaya 1600 Series IP Deskphones
Installation and Maintenance Guide.
Error Conditions
Assuming proper administration, most of the problems reported by deskphone users are likely to be
LAN-based. Quality of Service, server administration, and other issues can impact user perception of
IP deskphone performance.
The Avaya 1600 Series IP Deskphones Installation and Maintenance Guide covers possible
operational problems that might be encountered after successful 1600 Series IP Deskphone
installation. The following User Guides also contain guidance for users having problems with specific IP
deskphone applications:
● Avaya 1603/1603SW/1603-I/1603SW-I IP Deskphone User Guide,
Document Number 16-601444.
● Avaya 1608/1608-I IP Deskphone User Guide, Document Number 16-601446.
● Avaya 1616/1616-I IP Deskphone User Guide, Document Number 16-601448.
● Avaya one-X™ Deskphone Value Edition 1600 Series IP Deskphones BM32 Button Module User
Guide, Document Number 16-601450.
Issue 5 May 2014 13
Page 20

Administration Overview and Requirements
14 1600 Series IP Deskphone Administrator Guide Release 1.3.5
Page 21
Chapter 3: Network Requirements
!
Important:
Network Assessment
Perform a network assessment to ensure that the network will have the capacity for the expected data
and voice traffic, and that it can support for all applications:
● H.323,
● DHCP,
● HTTP/HTTPS, and
● Jitter buffers
Also, QoS support is required to run VoIP on your configuration. For more information, see Appendix
B: Related Documentation and UDP Port Selection on page 28.
Hardware Requirements
To operate properly, you need:
● Category 5e cables designed to the IEEE 802.3af-2003 standard, for power over Ethernet,
● For Avaya Aura Communication Manager: TN2602 IP Media Processor circuit pack. Sites with a
TN2302 IP Media Processor circuit pack are strongly encouraged to install a TN2602 circuit pack.
● For Avaya Aura Communication Manager: TN799C or D Control-LAN (CLAN) circuit pack.
Important: IP deskphone firmware Release 1.0 or greater requires TN799C V3 or greater CLAN
circuit pack(s). For more information, see the Avaya Aura Communication Manager
Software and Firmware Compatibility Matrix on the Avaya support Web site
http://www.avaya.com/support
To ensure that the appropriate circuit pack(s) are administered on your media server, see Chapter
4: Avaya Aura Communication Manager Administration. For more information about hardware
requirements in general, see the Avaya 1600 Series IP Deskphones Installation and Maintenance
Guide.
.
Issue 5 May 2014 15
Page 22
Network Requirements
Note:
!
CAUTION:
Server Requirements
Two server types can be configured for the 1600 Series IP Deskphones:
● DHCP
● HTTP or HTTPS
Note: HTTPS does not provide all of the functionality of HTTP. For example, backup/restore is
unavailable via HTTPS, and firmware cannot be downloaded via HTTPS.
While the servers listed provide different functions that relate to the 1600 Series IP Deskphones, they
are not necessarily different boxes. For example, DHCP provides file management whereas HTTP
provides application management, yet both functions can co-exist on one hardware unit. Any
standards-based server is recommended.
For parameters related to Avaya Media Server information, see Chapter 4: Avaya Aura Communication
Manager Administration, and the administration documentation for your call server. For parameters
related to DHCP and file servers, see Chapter 5: Server Administration
.
CAUTION: The deskphones obtain important information from the script files on the file server and
depend on the application file for software upgrades. If the DHCP file server is
unavailable when the deskphones reset, the deskphones register with the media server
and operate. Some features might not be available. To restore them you need to reset
the deskphone(s) when the file server is available.
DHCP Server
Avaya recommends that a DHCP server and application be installed and that static addressing be
avoided. Install the DHCP server and application as described in DHCP and File Servers
on page 37.
HTTP/HTTPS Server
Administer the HTTP or HTTPS file server and application as described in HTTP Generic Setup on
page 49.
16 1600 Series IP Deskphone Administrator Guide Release 1.3.5
Page 23

Required Network Information
Required Network Information
Before you administer DHCP and HTTP, and TLS, as applicable, complete the information in Table 3. If
you have more than one Gateway, HTTP/TLS server, subnetwork mask, and Gatekeeper in your
configuration, complete Table 3
The 1600 Series IP Deskphones support specifying a list of IP addresses for a gateway/router, HTTP/
HTTPS server, and Avaya Media Server Gatekeeper(s). Each list can contain up to 255 total ASCII
characters, with IP addresses separated by commas with no intervening spaces. Depending on the
specific DHCP application, only 127 characters might be supported.
When specifying IP addresses for the file server or media server, use either dotted decimal format
(“xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx”) or DNS names. If you use DNS, the system value DOMAIN is appended to the IP
addresses you specify. If DOMAIN is null, the DNS names must be fully qualified, in accordance with
IETF RFCs 1034 and 1035. For more information about DNS, see DHCP Generic Setup
and DNS Addressing
on page 75.
Table 3: Required Network Information Before Installation - Per DHCP Server
1. Gateway (router) IP address(es)
2. HTTP server IP address(es)
for each DHCP server.
on page 38
3. Subnetwork mask
4. Avaya Media Server Gatekeeper IP
address(es)
5. Avaya Media Server Gatekeeper port Although this can be a value between 0 and
65535, the default value is 1719. Do not change
the default value unless that value conflicts with
an existing port assignment.
6. HTTP server file path
7. Deskphone IP address range
From:
To:
8. DNS server address(es) If applicable.
9. HTTPS server address(es) If applicable.
The file server file path is the “root” directory used for all transfers by the server . All files are uploaded to
or downloaded from this default directory. In configurations where the upgrade script and application
files are in the default directory, do not use item 6 in Table 3
.
As the LAN or System Administrator, you are also responsible for:
● Administering the DHCP server as described in Chapter 5: Server Administration.
● Editing the configuration file on the applicable HTTP or HTTPS file server, as covered in 1600
Series IP Deskphone Scripts and Application Files.
Issue 5 May 2014 17
Page 24

Network Requirements
Note:
Other Network Considerations
SNMP
The 1600 Series IP Deskphones are fully compatible with SNMPv2c a nd with S tructure of Manage ment
Information Version 2 (SMIv2). The deskphones respond correctly to queries from entities that comply
with earlier versions of SNMP, such as SNMPv1. “Fully compatible” means that the deskphones
respond to queries directed either at the MIB-II or the read-only Custom MIB. Read-only means that the
values therein cannot be changed externally by means of network management tools.
You can use the system value SNMPADD to restrict the IP addresses from which the deskphone
accepts SNMP queries. You can also customize your community string with the system value
SNMPSTRING. For more information, see Chapter 5: Server Administration
IP Deskphone Customizable System Parameters.
Note: As of Release 1.0, SNMP is disabled by default. Administrators must initiate SNMP by
setting the SNMPADD and SNMPSTRING system values appropriately.
and Table 9: 1600 Series
For more information about SNMP and MIBs, see the IETF references listed in
Appendix B: Related Documentation
available for download in *.txt format on the Avaya support Web site at
http://www.avaya.com/support
.
. The Avaya Custom MIB for the 1600 Series IP Deskphones is
18 1600 Series IP Deskphone Administrator Guide Release 1.3.5
Page 25

Other Network Considerations
Reliability and Performance
All 1600 Series IP Deskphones respond to a ping or traceroute message sent from the DEFINITY®,
MultiVantage™, Avaya Aura Communication Manager, or Avaya Aura Communication Manager
Branch system (formerly known as Avaya Distributed Office) or any other network source. The
deskphones do not originate a ping or traceroute. The 1600 Series IP Deskphones offer and support
“remote ping” and “remote traceroute.” The switch can instruct the deskphone to originate a ping or a
traceroute to a specified IP address. The deskphone carries out that instruction and sends a message
to the switch indicating the results. For more information, see your switch administration
documentation.
If applicable, the deskphones test whether the network Ethernet switch port supports IEEE 802.1P/Q
tagged frames by ARPing the router with a tagged frame. For more information, see VLAN
Considerations on page 72. If your LAN environment includes Virtual LANs (VLANs), your router must
respond to ARPs for VLAN tagging to work properly.
QoS
For more information about the extent to which your network can support any or all of the QoS
initiatives, see your LAN equipment documentation. See QoS
on page 28 about QoS implications for
the 1600 Series IP Deskphones.
All 1600 Series IP Deskphones provide some detail about network audio quality. For more information
see, Network Audio Quality Display on 1600 Series IP Deskphones
on page 20.
IEEE 802.1P and 802.1Q
For more information about IEEE 802.1P and IEEE 802.1Q and the 1600 Series IP Deskphones, see
IEEE 802.1P and 802.1Q
tag are reserved for identifying packet priority to allow any one of eight priorities to be assigned to a
specific packet.
● 7: Network management traffic
● 6: Voice traffic with less than 10ms latency
● 5: Voice traffic with less than 100ms latency
● 4: “Controlled-load” traffic for critical data applications
● 3: Traffic meriting “extra-effort” by the network for prompt delivery, for example, executive
e-mail
● 2: Reserved for future use
● 0: The default priority for traffic meriting the “best-effort” for prompt delivery of the network.
● 1: Background traffic such as bulk data transfers and backups
on page 28 and VLAN Considerations on page 72. Three bits of the 802.1Q
Issue 5 May 2014 19
Page 26

Network Requirements
Note:
Note: Priority 0 is a higher priority than Priority 1.
Network Audio Quality Display on 1600 Series IP Deskphones
All 1600 Series IP Deskphones give the user an opportunity to monitor network audio performance
while on a call. For more information, see the deskphone user guide.
While on a call, the deskphones display network audio quality parameters in real-time, as shown in
Table 4
:
Table 4: Parameters in Real-Time
Parameter Possible Values
Received Audio Coding G.711, G.711u, G.711a, G.726, G.729A, or G.729B.
Packet Loss "No data" or a percentage. Late and out-of-sequence packets
are counted as lost if they are discarded. Packets are not
counted as lost until a subsequent packet is received and the
loss confirmed by the RTP sequence number.
Packetization Delay "No data" or an integer number of milliseconds. The number
reflects the amount of delay in received audio packets, and
includes any potential delay associated with the codec.
One-way Network Delay "No data" or an integer number of milliseconds. The number is
one-half the value RTCP computes for the round-trip delay.
Network Jitter
Compensation Delay
"No data" or an integer number of milliseconds reporting the
average delay introduced by the jitter buffer of the deskphone.
The implication for LAN administration depends on the values the user reports and the specific nature
of your LAN, like topology, loading, and QoS administration. This information gives the user an idea of
how network conditions affect the audio quality of the current call. Avaya assumes you have more
detailed tools available for LAN troubleshooting.
IP Address Lists and Station Number Portability
The 1600 Series IP Deskphones provide the capability to specify IP address lists. On startup or a
reboot, the deskphone attempts to establish communication with these various network elements in
turn. The deskphone starts with the first address on the respective list. If the communication is denied
or times out, the deskphone proceeds to the next address on the approp riate list and tries that one. The
deskphone does not report failure unless all the addresses on a given list fail, thereby improving the
reliability of IP telephony.
20 1600 Series IP Deskphone Administrator Guide Release 1.3.5
Page 27

Other Network Considerations
This capability also has the advantage of making station number portability easier. Assume a situation
where the company has multiple locations in London and New York, all sharing a corporate IP network.
Users want to take their deskphones from their offices in London and bring them to New York. When
users start up their deskphones in the new location, the local DHCP server usually routes them to the
local call server. With proper administration of the local DHCP server, the deskphone knows to try a
second call server IP address, this one in London. The user can then be automatically registered with
the London call server.
Chapter 5: Server Administration
contains details on administration of DHCP servers for lists of
alternate media servers, router/gateways, and HTTP/HTTPS servers. For more information, see DNS
Addressing on page 75.
TCP/UDP Port Utilization
The 1600 Series IP Deskphones use a variety of protocols, particularly TCP and UDP, to communicate
with other equipment in the network. Part of this communication identifies which TCP or UDP ports
each piece of equipment uses to support each protocol and e ach task within the pro tocol. For additional
TCP/UDP port utilization information as it applies to Avaya Aura Communication Manager, see UDP
Port Selection on page 28.
Depending on your network, you might need to know what ports or ran ges are u sed in the o peration of
1600 Series IP Deskphones. Knowing these ports or ranges helps you administer your networking
infrastructure.
In Figure 1
● The box on the left always represents the 1600 Series IP Deskphone.
● Depending on the diagram, the boxes on the right refer to various pieces of network equipment
● Open-headed arrows (for example, ) represent the direction(s) of socket initialization.
and Figure 2:
with which the deskphone can communicate.
● Closed-headed arrows (for example, ) represent the direction(s)
of data transfer.
● The text the arrows point to identifies the port or ports that the 1600 Series IP Deskphones
support for the specific situation. Brackets identify ranges when more than one port applies. The
text indicates any additional qualifications or clarifications. In many cases, the ports used are the
ones called for by IETF or other standards bodies.
Issue 5 May 2014 21
Page 28
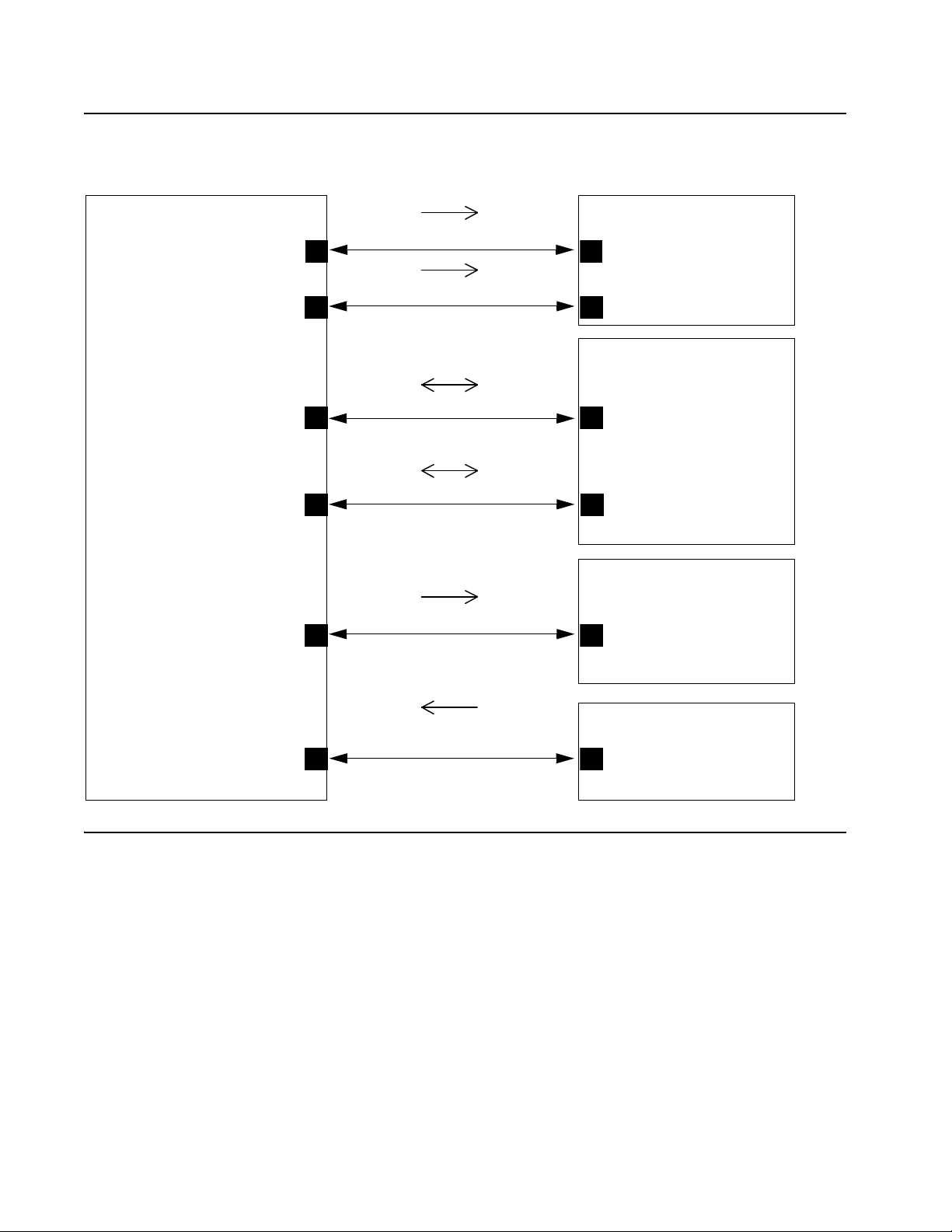
Network Requirements
1600 Series IP
Deskphone
Port: 49300
Port: [1500–6500]
randomly selected
Port: [4000–10000]
randomly selected;
range may be changed via
Gatekeeper administration;
always an even number
Port: audio port + 1
(only active during a call
if RTCP is enabled)
Port: audio port + 2
(only active during a call
if RTCP monitoring
is enabled)
Port:161
Signaling, Audio and Management
H.323 Gatekeeper
Port: 1719
Port: 1720
H.323 RAS (UDP/IP)
H.323 Signaling (TCP/IP)
RTP Audio (UDP/IP)
RTCP (UDP/IP)
SNMP (UDP/IP)
SNMP MIB Viewer
Port depends on
MIB viewer admin
Voice Monitoring
Manager
Port depends on Voice
Monitoring Manager
admin
Media Gateway or
another IP endpoint
Port selected from the
audio port range
administered for the
network region
Port: audio port + 1
RTCP (UDP/IP)
Figure 1: Signaling, Audio and Management Diagram
22 1600 Series IP Deskphone Administrator Guide Release 1.3.5
Page 29
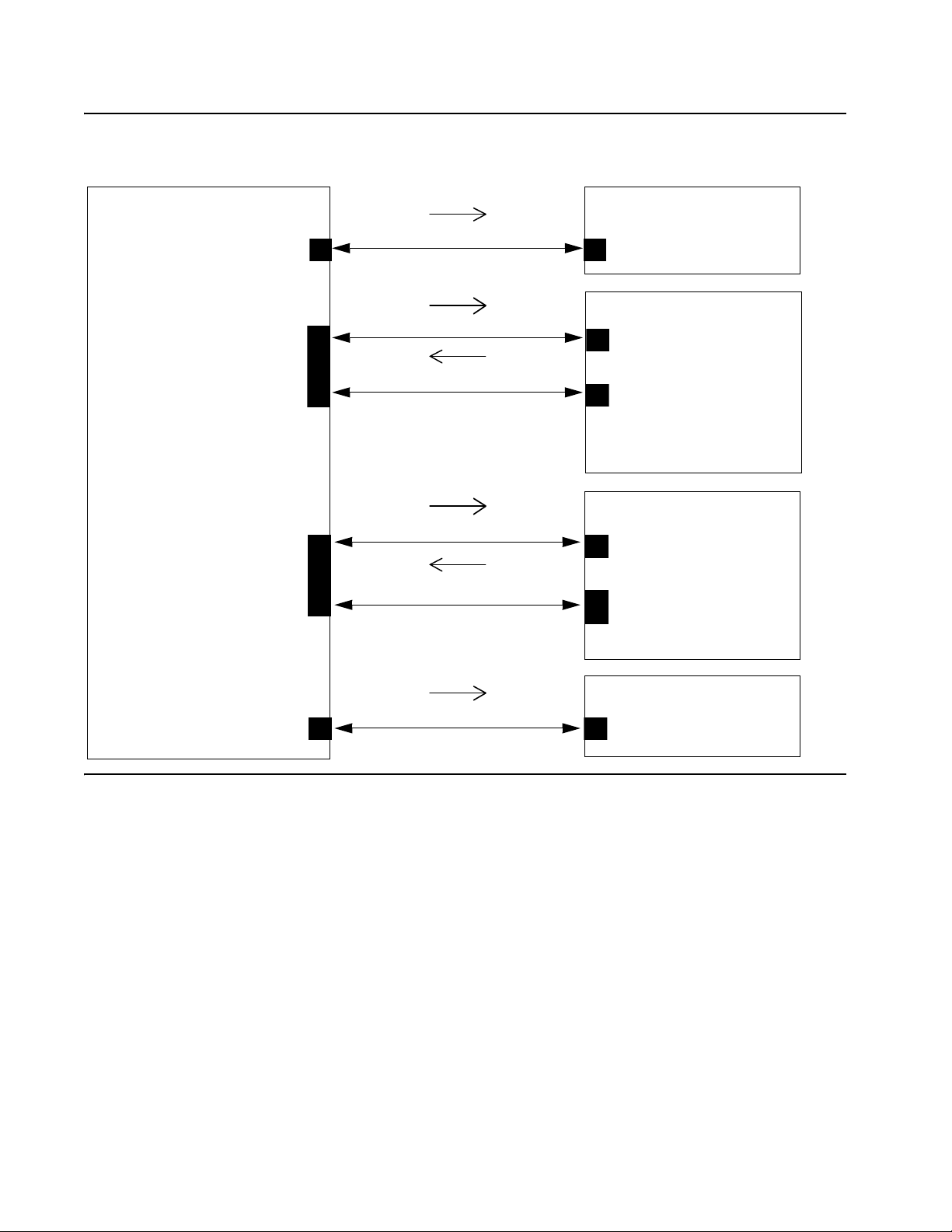
Figure 2: Initialization and Address Resolution Diagram
1600 Series IP
Deskphone
Port: 68
Port: [1024 - 5000]
Operating System
–selected (a new port is
used for each file
requested)
Port: [1024 - 5000]
Operating System –
selected (a new port
is used for each file
requested)
Port: [1024 - 5000]
Operating System
Initialization and Address Resolution
DHCP Server
Port: 67
DHCP (TCP/IP)
HTTP Read Request (TCP/IP)
HTTPS Data, ACKs & Errors (TCP/IP)
DNS(UDP/IP)
HTTP Server
Port: 80
Port: Operating System
– selected (a new port is
used for each file)
HTTPS Server
Port:411
Port: Operating
System – selected (a
new port is used for
each file
HTTPS Read Request (TCP/IP)
HTTPS Data, ACKs & Errors (TCP/IP)
DNS Server
Port: 53
Other Network Considerations
Issue 5 May 2014 23
Page 30

Network Requirements
Note:
Security
For information about toll fraud, see the DEFINITY®, Avaya Aura Communication Manager, or Avaya
Aura Communication Manager Branch documents on the Avaya support Web site. The 1600 Series IP
Deskphones cannot guarantee resistance to all Denial of Service attacks. However, there are checks
and protections to resist such attacks while maintaining appropriate service to legitimate users.
You also have a variety of optional capabilities to restrict or remove how crucial network information is
displayed or used. These capabilities are covered in more detail in
Chapter 5: Server Administration
● Support signaling channel encryption while registering, and when registered, with appropriately
administered Avaya Media Servers.
Note: Signaling and audio are not encrypted when unnamed registration is effective.
● Restricting the response of the 1600 Series IP Deskphones to SNMP queries to only IP addresses
on a list you specify.
● Specifying an SNMP community string for all SNMP messages the deskphone sends.
.
● Restricting dialpad access to Local Administration Procedures, such as specifying IP addresses,
with a password.
● Removing dialpad access to most Local Administration Procedures.
● Restricting the end user’s ability to use a deskphone Options application to view network data.
As of Release 1.1, three existing security-related parameters can be administered on the call server
and downloaded with encrypted signaling, in addition to unencrypted HTTP or encrypted HTTPS.
Those parameters are SNMP community string, SNMP Source IP Addresses, and Craft Access Code
(PROCPSWD).
Registration and Authentication
The Avaya Media Server supports using the extension and p assword to register a nd authenticate 1600
Series IP Deskphones. For more information, see the current version of your call server administratio n
manual.
24 1600 Series IP Deskphone Administrator Guide Release 1.3.5
Page 31

Chapter 4: Avaya Aura Communication Manager
Administration
Call Server Requirements
Before you perform administration tasks, ensure that the proper hardware is in place, and your call
server software is compatible with the 1600 Series IP Deskphones. Av aya recommends the latest PBX
software and the latest IP deskphone firmware.
Switch Compatibility and Aliasing IP Deskphones
As of Release 1.1, 1600 Series IP Deskphones were natively supported by Avaya Aura Communication
Manager Release 5.2. Native support means that if you have Avaya Aura Communication Manager
Release 5.2, you:
● do not have to alias 1600 Series IP Deskphones,
● can add up to two BM32 Button Modules on each 1616 Series IP Deskphone, and
● can administer a call coverage deskphone number on a station-by-station basis.
If you have Avaya Aura Communication Manager Release 5.1 or earlier, you must alias the
deskphones as follows:
1600 Series
Deskphone Model
1603 4610 Avaya Aura Communication
1603-I 4610 Avaya Aura Communication
1603SW 4610 Avaya Aura Communication
1603SW-I 4610 Avaya Aura Communication
1608 4610 Avaya Aura Communication
Aliased as... Earliest Avaya Aura
Communication Manager Release
Manager 3.0
Manager 3.0
Manager 3.0
Manager 3.0
Manager 3.0
Issue 5 May 2014 25
Page 32

Avaya Aura Communication Manager Administration
Note:
1600 Series
Deskphone Model
Aliased as... Earliest Avaya Aura
Communication Manager Release
1608-I 4610 Avaya Aura Communication
Manager 3.0
1616 4620 Avaya Aura Communication
Manager 3.0
1616-I 4620 Avaya Aura Communication
Manager 3.0
BM32 EU24 Avaya Aura Communication
Manager 3.0
The 1603, 1603SW, 1603-I, and 1603SW-I IP Deskphones support three administrable call
appearances or feature buttons. The 1608 and 1608-I IP Deskphones support eight administrable call
appearances or feature buttons. The 1616 and 1616-I IP Deskphones support 16 administrable call
appearances or feature buttons. In addition, the 1616/1616-I IP Deskphones support the BM32 Button
Module. The 1616/1616-I always support a single BM32, and with Avaya Aura Communication
Manager Release 5.2 or later, support up to two BM32 Button Modules per deskphone.
Note: Using one BM32 can be supported by PoE. If you use a second button module, you must
use the Avaya approved external auxiliary 5V power supply for the 1616/1616-I IP
Deskphone. While the auxiliary power supply can support up to three BM32 button
modules, Communication Manager Release 5.2 can only configured to support up to two
BM32.
The BM32 Button Module provides another 32 administrable call appearances and features. When
attached to a 1616/1616-I IP Deskphone that is aliased as a 4620, the first 16 administered call
appearances and features are placed directly on the deskphone, and the next 32 administered call
appearances and features are placed on the button module, for a total of 48 administrable buttons.
For more information about aliasing one deskphone model as another, see “Using an Alias” in the
Administrator Guide for Avaya Aura™ Communication Manager (Document 03-300509).
Avaya Aura Communication Manager Branch systems provide native support for the 1600 Series
Deskphones. See the Avaya Aura Communication Branch Device Manager online help for more
information.
26 1600 Series IP Deskphone Administrator Guide Release 1.3.5
Page 33

Media Server (Switch) Administration
Media Server (Switch) Administration
If you are using the 1600 Series IP Deskphones with Avaya Aura Communication Manager, see the
following documents on the Avaya support Web site for information about specific switch
administration:
● The Administrator Guide for Avaya Aura™ Communication Manager (Document 03-300509)
provides detailed instructions for administering an IP deskphone system on Avaya Aura
Communication Manager. See Chapter 3 “Managing Deskphones,” which describes the process
of adding new deskphones. Also, you can locate pertinent screen illustrations and field
descriptions in Chapter 19 “Screen References” of that guide.
● Administration for Network Connectivity for Avaya Aura™ Communication Manager (Document
Number 555-233-504) provides detailed information about swit ch administration for your network.
If you are using the 1600 Series IP Deskphones with Avaya Aura Communication Manager Branch, see
the Avaya Aura Communication Manager Branch Device Manager online help for information about
specific switch administration.
IP Interface and Addresses
If you are using the 1600 Series IP Deskphones with Avaya Aura Communication Manager, follow
these general guidelines:
● Define the IP interfaces for each CLAN and Media processor circuit pack on the switch that uses
the IP Interfaces screen. For more information, see Administration for Network Connectivity for
Avaya Aura™ Communication Manager (Document 555-233-504).
● On the Customer Options form, verify that the IP Stations field is set to “y” (Yes). If it is not,
contact your Avaya sales representative. The IP Softphone field does not have to be set to “y”
(Yes).
If you are using the 1600 Series IP Deskphones with Avaya Aura Communication Manager Branch, see
the Avaya Aura Communication Manager Branch Device Manager online help for information about
administering these deskphones.
Issue 5 May 2014 27
Page 34

Avaya Aura Communication Manager Administration
!
Important:
UDP Port Selection
The 1600 Series IP Deskphones can be administered from the Avaya Aura Communication Manager
Network Region form to support UDP port selection. Locate specific port assignment diagrams in the
1600 IP Deskphone Installation and Maintenance Guide. For information about Avaya Aura
Communication Manager implementation, see Administration for Network Connectivity for Avaya
Aura™ Communication Manager (Document Number 555-233-504) on the Avaya support Web site.
Administer the switch to use a port within the proper range for the specific LAN, and the IP
deskphone(s) copy that port. If no UDP port range is administered on the switch, the IP deskphone
uses an even-numbered port, randomly selected from the interval 4000 to 10000.
RSVP and RTCP
Avaya IP Deskphones implement the Resource ReSerVation Protocol (RSVP) administered from the
media server and the RTP Control Protocol (RTCP). The Avaya Voice over IP (VoIP) Monitoring
Manager (VMON) software can then provide real-time monitoring and historical data of audio quality f or
VoIP calls.
The only way to change these parameters is by appropriate switch administration. For more
information, see your Avaya Media Server administration documentation and Administration for
Network Connectivity for Avaya Aura™ Communication Manager (Document Number 555-233-504).
QoS
The 1600 Series IP Deskphones support both IEEE 802.1P/Q and DiffServ. Other network-based QoS
initiatives such as UDP port selection do not require support by the deskphones. However, they
contribute to improved QoS for the entire network.
IEEE 802.1P and 802.1Q
The 1600 Series IP Deskphones can simultaneously support receipt of packets using, or not using,
802.1Q parameters. To support IEEE 802.1P/Q, you can administer 1600 Series IP Deskphones from
the network by appropriate administration of the DHCP or HTTP/HTTPS servers, or by using dialpad
input at the deskphone.
Important: Avaya Aura Communication Manager administration always takes precedence over
manual administration of IEEE 802.1P/Q data.
28 1600 Series IP Deskphone Administrator Guide Release 1.3.5
Page 35

Media Server (Switch) Administration
Note:
The four IEEE 802.IP/Q QoS parameters in the deskphones that can be administered on the IP
Network Region form are L2Q, L2QVLAN, L2QAUD, and L2QSIG. To set these parameters at the
switch, see “About Quality of Service (QoS) and voice quality administration” in Administration for
Network Connectivity for Avaya Aura™ Communication Manager (Document Number 555-233-504).
To set these parameters manually see the 1600 IP Deskphone Installation and Maintenance Guide.
You can specify VLAN ID and VLANTEST values with the ADDR Local Administrative Option.
Note: All local administrative procedures are on a phone-by-phone basis. Administration using
Avaya Aura Communication Manager, DHCP, and HTTP applies to the deskphone
system itself or to a range of deskphones.
NAT
Network Address Translation (NAT) usage can lead to problems that affect the consistency of
addressing throughout your network. All H.323 IP Deskphones support NAT interworking. Support for
NAT does not imply support for Network Address Port Translation (NAPT). The deskphones do not
support communication to the PBX through any NAPT device.
NAT requires specific administration on the media server. A direct Avaya IP Deskphone-to-Avaya IP
Deskphone call with NAT requires Avaya Aura Communication Manager Release 3.0 or greater
software. For more information, see Administration for Network Connectivity for Avaya Aura™
Communication Manager (Document Number 555-233-504) on the Avaya support Web site.
DIFFSERV
The DiffServ values change to the values administered on the media server as soon as the deskp hone
registers. For more information, see Chapter 4 “Network Quality Administration” in Administration for
Network Connectivity for Avaya Aura™ Communication Manager (Document Number 555-233-504).
Unless there is a specific need in your enterprise LAN, Avaya recommends that you d o not change the
default values.
Issue 5 May 2014 29
Page 36

Avaya Aura Communication Manager Administration
Voice Mail Integration
1600 Series IP Deskphones with Avaya Aura Communication Manager 5.2 Native Support
Release 1.1 provides native support for 1600 Series IP Deskphones running on Avaya Aura
Communication Manager Release 5.2 or later. When native support applies, pressing the Messages
button causes the deskphone to first determine if the call server has a dedicated number for retrieving
voice mail and when found, to proceed with voice mail retrieval.
1600 Series IP Deskphones Aliased as 4600 Series IP Deskphones
When native support does not apply, 1600 Series IP Deskphones are aliased as 4600 Series IP
Deskphones and run under an Avaya Aura Communication Manager Release earlier than 5.2. In this
case, use the settings file to configure the Messages button by setting the system parameter
MSGNUM
to any dialable string. MSGNUM examples are:
● a standard deskphone number the deskphone should dial to access your voice mail system, such
as AUDIX or Octel.
● a Feature Access Code (FAC) that allows users to transfer an active call directly to voice mail.
FACs are su pported only for QSIG-integrated voice mail systems like AUDIX or Octel. QSIG is an
enhanced signaling system that allows the voice mail system and Avaya Aura Communication
Manager Automated Call Processing (ACP) to exchange information.
When the user presses the Messages button on the deskphone, that number or FAC is automatically
dialed, giving the user one-touch access to voice mail.
The settings file specifies the deskphone number to be dialed automatically when the u ser presses this
button. The command is:
SET MSGNUM 1234
where 1234 is the Voice Mail extension (A vaya Aura Communication Mana ger hunt group or VDN). For
more information, see Table 9
MSGNUM is used both in native support and when the deskphone is aliased using non-n ative support.
Messaging must be configured for native support.
A separate Voice Mail extension can be administered for each station.
.
30 1600 Series IP Deskphone Administrator Guide Release 1.3.5
Page 37

Deskphone Administration
Note:
Deskphone Administration
This section describes how to administer Avaya Aura Communication Manager for 1600 Series IP
Deskphones. For detailed information about administering Avaya Aura Communication Manager, see
the following Avaya documents:
● Administrator Guide for Avaya Aura™ Communication Manager (Document 03-300509).
● Feature Description and Implementation for Avaya Aura™ Communication Manager (Document
555-245-770).
For detailed information about administering Avaya Aura Communication Manager Branch for 1600
Series IP Deskphones, see the Avaya Aura Communication Manager Branch Device Manager online
help.
System-Wide Administration
This section refers to Avaya Aura Communication Manager admin istration on the Switch Administration
Terminal (SAT) or by Av aya Site Administration. The system wide Av aya Aura Communication Manager
form and the particular page that needs to be administered for each feature are provided. These
features, which already exist, are not required but are recommended because they optimize the
deskphone user interface. Avaya Aura Communication Manager Release 3.0 or greater is required.
Note: See Appendix C: Sample Administration Forms for illustrated examples of the pages
used to administer Avaya Aura Communication Manager features.
Feature-Related System Parameters
Release 1.1 supports the functionality introduced on A vaya Aura Communication Man ager Release 5.2
that allows call server administration of three system-wide parameters. By administering these
parameters on Avaya Aura Communication Manager, they can be automatically downloaded to the
deskphone during registration, instead of or in addition to from the settings file or locally per
deskphone. The three system parameters are: SNMP community string, SNMP Source IP addresses,
Issue 5 May 2014 31
Page 38

Avaya Aura Communication Manager Administration
and Craft Access Code (PROCPSWD). Administer these three parameters using Page 3 of the change
system-parameters ip-options form.
Avaya Aura Communication Manager Feature Administration
Feature Administration
On-Hook Dialing Set up Avaya Aura Communication Manager so that the phone
supports on-hook dialing. Use the System Parameters Features
form page 10. Use the command Change
system-parameters features to view the form and make
the change.
Auto Hold Set up Avaya Aura Communication Manager to enable Auto
Hold, so that the phone automatically places an active call on
hold when the user answers or resumes a call on another call
appearance. Use the System Parameters Features form, page 6
Coverage Path Administer a coverage path for both phone demonstration and
normal operations. Use the Coverage Path form and give it a
number, for example, Coverage path 1. If Voice Mail is available,
this is also where you administer the hunt group or VDN,
depending on the type of Voice Mail system being used.
.
Enhanced Conference
Features
Enable enhanced conference display to support the user
experience for conferences. Block Enhanced Conference Display
on the Class of Restriction (COR) form must be set to No. Use
the command Change COR, followed by a number, to view the
form and make the change. a sample of the Class of Restriction
form.
Administering Stations
This section refers to Avaya Aura Communication Manager admin istration on the Switch Administration
Terminal (SAT) or by Avaya Site Administration. Administer the following items on the Station form,
sample screens of which are provided in Figure 1
features covered in this section because they optimize the user interface.
Release 1.1 supports the functionality introduced on A vaya Aura Communication Man ager Release 5.2
that allows call server administration of the GROUP parameter on a station-by-station basis. As
covered in The GROUP System Value
with the 46xxsettings file to allow administration to apply to specific “groups” of deskphones. Before
Release 1.1, the Group Identifier had to be administered locally on each applicable deskphone. As of
Release 1.1, the Group Identifier can be administered centrally, and downloaded to each applicable
deskphone. The GROUP ID parameter is administered on page 3 of the Change Station Form. Once
downloaded, the Group Identifier takes effect starting with the next deskphone boot-up.
For sample Station Forms, see Appendix C: Sample Administration Forms
on page 59, the GROUP Identifier can be used in conjunction
through Figure 4. Avaya recommends setting the
.
32 1600 Series IP Deskphone Administrator Guide Release 1.3.5
Page 39

Administering Stations
Aliasing 1600 Series IP Deskphones
Avaya Aura Communication Manager releases earlier than 5.2 do not provide native support for 1600
Series IP Deskphones. On the Station Form, administer (alias) the deskphones as follows:
Change Alias Station:
● Alias set up type 1603/1603SW/1603-I/1603SW-I to a 4610
● Alias set up type 1608/1608-I to a 4610
● Alias set up type 1616/1616-I to a 4620SW/4621SW
Avaya Aura Communication Manager Release 5.2 (and later) provides native support for the
1603,1603SW, 1603-I, 1603SW-I, 1608, 1608-I, 1616, and 1616-I.
Administering Features
The following are administrable S t ation Features that A vaya recommend s you administer for your 1600
Series IP Deskphones for maximum user experience.
Administrable Station Features
Feature Administration
Enhanced Conference
Features
Administer Conf-dsp (conference display) on the station form as
a feature button. Doing so turns on enhanced conference
features and gives users advanced conference features.
Far End Mute Administer fe-mute (far end mute). When this is enabled the
phone shows a “Silence” softkey on the Conference details
screen. This feature works only for trunk calls.
Send All Calls (SAC) On the Sta tion form, administer SAC (send-calls) as a feature
button. On the Station form to the right of where send all calls is
administered, leave the extension box empty. This feature
requires a coverage path to be administered on the station form.
Coverage Path For normal operation, you must set up a coverage path for each
deskphone. Administer the St ation form to point to the appropriate
system coverage path, for example, coverage path 1.
Auto select any idle
appearance
Restrict Last Call
Set Auto select any idle appearance to N (no) to optimize
answering calls.
Set Restrict Last Call Appearance to Y (yes).
Appearance
Conference/Transfer on
Primary Appearance
Set Conference/Transfer on Primary Appearance to Y (yes) to
ensure that conference/transfer of a bridged appearance works
properly.
Issue 5 May 2014 33
Page 40

Avaya Aura Communication Manager Administration
Feature Buttons and Call Appearances
For the 1603/1603SW/1603-I/1603SW-I and 1608/1608-I IP Deskphones
You can administer Feature/Call Appearance Buttons 1 – 8 on the Avaya Aura Communication
Manager Station form, which the deskphone Feature screen then displays in sequence. The
deskphone does not display any of the Feature Button labels administered on buttons 9 – 24. These
deskphones do not support the BM32 Button Module.
For the 1616/1616-I IP Deskphones
You can administer Feature/Call Appearance Buttons 1 – 16 on the Avaya Aura Communication
Manager St ation fo rm. The feat ures administered on the Station form appear in the same sequence on
the deskphone Feature screen. Features administered on the Expansion Module BM32 Call
Appearance buttons display on the deskphone Features screen following the first 16 administered
feature buttons. All administered BM32 Button Labels (Call Appearances and Feature Buttons) display
on the corresponding BM32 module buttons.
In Table 5
as applicable to the button type.
the term “phone screen” refers to either the call appearance screen or the features screen,
Table 5: Station Form Administration Results
Feature / Call Appearance (CA) /
Bridged Call Appearance (BA)
buttons on the Station form...
1 Phone screen Phone screen Phone screen
2 to 16 CAs/BAs on
17 to 48 N/A N/A First BM32
49 to 80 N/A N/A Second BM32
Is displayed on
the phone as:
1603/1603SW
1603-I/1603SW-I
Phone screen;
must scroll to
see more than 1
1608/1608-I 1616/1616-I
CAs/BAs on
Phone screen;
must scroll to
see more than 1
CAs/BAs on
Phone screen;
must scroll to
see more than 1
34 1600 Series IP Deskphone Administrator Guide Release 1.3.5
Page 41

Shuffling
For additional information about administering the call server for 1600 Series IP Deskphones, see the
following Avaya documents, available on the Avaya Support Web site:
● Administrator Guide for Avaya Aura™ Communication Manager (Document Number 03-300509).
● Feature Description and Implementation for Avaya Aura™ Communication Manager (Document
Number 555-245-770).
Conference Details Screen for Ad-Hoc Conferences
Conference Details allows the user to view parties on a conference call and selectively mute or drop
individual parties for a conference call setup.
If administered on an Expansion Module button, the BM32 Button Module must be connected.
To enable Conference Details capabilities:
1. On the Class of Restriction (COR) form make sure that Block Enhanced Conference/Transfer
Displays is set to No.
2. As described in On-Hook Dialing
, administer the Conference Display Feature Button to a Phone
button on the Phone screen.
Shuffling
Administer shuffling on three forms:
● Feature-Related Parameters form, shown in Figure 5. Set the Direct IP-IP Audio Connections?
field to y (yes).
● IP Network Region form, shown in Figure 9. Set both the Intra-region IP-IP Direct Audio field
and the Inter-region IP-IP Direct Audio field to y (yes).
● Station form, shown in Figure 2. Set the Direct IP-to-IP Audio Connection to y (yes). The S t ation
form setting overrides the network region, which overrides the system setting.
Issue 5 May 2014 35
Page 42

Avaya Aura Communication Manager Administration
Printing Button Labels
You can download software from www.desi.com that enables you to print button labels for the 1600
series deskphones. To download this software, perform the following steps:
1. Using your web browser, go to www.desi.com.
2. Click DESI downloads.
3. Download the appropriate application.
If you are using Avaya Aura Communication Manager Branch, you can export the button settings from
Local Manager and import the settings into the DESI application. For more information, see the Avaya
Aura Communication Manager Branch Device Manager online help.
36 1600 Series IP Deskphone Administrator Guide Release 1.3.5
Page 43

Chapter 5: Server Administration
Note:
!
CAUTION:
Software Checklist
Ensure that you own licenses to use the DHCP, HTTP, and HTTPS server software.
Note: You can install the DHCP and HTTP server software on the same machine.
CAUTION: The firmware in the 1600 Series IP Deskphones reserves IP addresses of the form
192.168.0.24 and 192.168.1.x for internal communications. The deskphone(s)
improperly use addresses you specify if they are of that form.
DHCP and File Servers
Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) minimizes maintenance for a 1600 Series IP Deskphone
network by removing the need to individually assign and maintain IP addresses and other parameters
for each IP deskphone on the network.
The DHCP server provides the following information to the 1600 Series IP Deskphones:
● IP address of the 1600 Series IP Deskphone(s)
● IP address of the Gatekeeper board on the Avaya Media Server
● IP address of the HTTP or HTTPS server
● The subnet mask
● IP address of the router
● DNS Server IP address
Administer the LAN so each IP deskphone can access a DHCP server that contains the IP addresses
and subnet mask.
The IP deskphone cannot function without an IP address. The failure of a DHCP server at boot time
leaves all the affected deskphones unusable. A user can manually assign an IP address to an IP
deskphone. When the DHCP server finally returns, the deskphone never looks for a DHCP server
unless the static IP data is unassigned manually. In addition, manual entry of IP data is an error-prone
process.
Issue 5 May 2014 37
Page 44

Server Administration
!
CAUTION:
Avaya recommends that:
● A minimum of two DHCP servers be available for reliability.
● A DHCP server be available when the IP deskphone reboots.
● A DHCP server be available at remote sites if WAN failures isolate IP deskphones from the central
site DHCP server(s).
The file server provides the 1600 Series IP Deskphone with a script file and, if appropriate, new or
updated application software. See Step 3: Deskphone and File Server
on page 12 under Deskphone
Initialization Process. In addition, you can edit an associated settings file to customize deskphone
parameters for your specific environment. For more information, see Chapter 7: Administering
Deskphone Options.
DHCP Server Administration
This document concentrates on the simplest case of the single LAN segment. Information provided
here can be used for more complex LAN configurations.
CAUTION: Before you start, understand your current network configuration. An improper inst allation
can cause network failures or reduce the reliability and performance of your network.
DHCP Generic Setup
This document is limited to describing a generic administration that works with the 1600 Series IP
Deskphones. Three DHCP software alternatives are common to Windows operating systems:
● Windows NT
● Windows 2000
● Windows 2003
®
4.0 DHCP Server
®
DHCP Server
®
DHCP Server
38 1600 Series IP Deskphone Administrator Guide Release 1.3.5
Page 45

DHCP Server Administration
Any other DHCP application might work. It is the responsibility of the customer to install and configure
the DHCP server correctly.
DHCP server setup involves:
1. Installing the DHCP server software according to vendor instructions.
2. Configuring the DHCP server with:
● IP addresses available for the 1600 Series IP Deskphones.
● The following DHCP options:
- Option 1 - Subnet mask.
As described in Table 3
, item 3.
- Option 3 - Gateway (router) IP address(es).
As described in Table 3
, item 1. If using more than one address, the total list can contain up to
255 total ASCII characters. You must separate IP addresses with commas with no intervening
spaces.
- Option 6 - DNS server(s) address list.
If using more than one address, the total list can contain up to 127 total ASCII characters. You
must separate IP addresses with commas with no intervening sp aces. At least o ne address in
Option 6 must be a valid, non zero, dotted decimal address.
- Option 12 - Host Name.
Value is AVohhhhhh, where: o is “A” if the OID (first three octets) of the MAC address for the
deskphone is 00-04-0D. “E” if the OID is 00-09-6E, “L” if the OID is 00-60-1D, and “X” if the
OID is anything else and where hhhhhh are ASCII characters for the hexadecimal
representation of the last three octets of the MAC address for the deskphone.
- Option 15 - DNS Domain Name.
This string contains the domain name to be used when DNS names in system parameters ar e
resolved into IP addresses. This domain name is appended to the DNS name before the 1600
IP Deskphone attempts to resolve the DNS address. Option 15 is necessary if you want to
use a DNS name for the HTTP server. Otherwise, you can specify a DOMAIN as part of
customizing HTTP as indicated in DNS Addressing
on page 75.
- Option 51 - DHCP lease time.
If this option is not received, the DHCPOFFER is not be accepted. Avaya recommends a
lease time of six weeks or greater. If this option has a value of FFFFFFFF he x, the IP address
lease is assumed to be infinite as per RFC 2131, Section 3.3, so that renewal and rebinding
procedures are not necessary even if Options 58 and 59 are received. Expired leases cause
Avaya IP Deskphones to reboot. Avaya recommends providing enough leases so an IP
address for an IP deskphone does not change if it is briefly taken offline.
Issue 5 May 2014 39
Page 46

Server Administration
Note:
Note: The DHCP standard states that when a DHCP lease expires, the device should
immediately cease using its assigned IP address. If the network has problems and the
only DHCP server is centralized, the server is not accessible to the given deskphone. In
this case the deskphone is not usable until the server can be reached.
Avaya recommends, once assigned an IP address, the deskphone continues using that
address after the DHCP lease expires, until a conflict with another device is detected. As
Table 9: 1600 Series IP Deskphone Customizable System Parameters
indicates, the
system parameter DHCPSTD allows an administrator to specify that the deskphone will
either:
a). Comply with the DHCP standard by setting DHCPSTD to “1”, or
b). Continue to use its IP address after the DHCP lease expires by setting DHCPSTD to
“0.”
The latter case is the default. If the default is invoked, after the DHCP lease expires the
deskphone sends an ARP Request for its own IP address every five seconds.
The request continues either forever, or until the deskphone receives an ARP Reply.
After receiving an ARP Reply, the deskphone displays an error message, sets its IP
address to 0.0.0.0, and attempts to contact the DHCP server again.
- Option 52 - Overload Option, if desired.
If this option is received in a message, the deskphone interprets the sname and file fields in
accordance with IETF RFC 2132,
Section 9.3, listed in Appendix B: Related Documentation
.
- Option 53 - DHCP message type.
Value is 1 (DHCPDISCOVER) or 3 (DHCPREQUEST).
- Option 55 - Parameter Request List.
Acceptable values are:
1 (subnet mask),
3 (router IP address[es])
6 (domain name server IP address[es])
15 (domain name)
NVSSON (site-specific option number)
- Option 57 - Maximum DHCP message size.
- Option 58 - DHCP lease renew time.
If not received or if this value is greater than that for Option 51, the default value of T1
(renewal timer) is used as per IETF RFC 2131, Section 4.5, listed in Related Documentation
- Option 59 - DHCP lease rebind time.
If not received or if this value is greater than that for Option 51, the default value of T2
(rebinding timer) is used as per RFC 2131, Section 4.5
.
40 1600 Series IP Deskphone Administrator Guide Release 1.3.5
Page 47

DHCP Server Administration
The 1600 Series IP Deskphones do not support Regular Expression Matching, and therefore, do not
use wildcards. For more information, see Administering Options for the 1600 Series IP Deskphones
on
page 65.
In configurations where the upgrade script and application files are in the default directory on the HTTP
server, do not use the HTTPDIR=<path>.
You do not have to use Option 242. If you do not use this option, you must ensure that the key
information, especially HTTPSRVR and MCIPADD, is administered appropriately elsewhere.
Avaya recommends that you administer DHCP servers to deliver only the options specified in this
document. Administering additional, unexpected options might have unexpected results, including
causing the IP deskphone to ignore the DHCP server.
The media server name and HTTP server name must each be no more than 32 characters in length.
Examples of good DNS administration include:
- Option 6: “aaa.aaa.aaa.aaa”
- Option 15: “dnsexample.yourco.com,zzz.zzz.zzz.zzz”
- Option 242: “MCIPADD=xxxx.xxx.xxx.xxx”
Depending on the DHCP application you choose, be aware that the application most likely
does not immediately recycle expired DHCP leases. An expired lease might remain reserved
for the original client a day or more. For example, Windows NT
®
DHCP reserves expired
leases for about one day. This reservation period protects a lease for a short time. If the client
and the DHCP server are in two different time zones, the clocks of the computers are not in
sync, or the client is not on the network when the lease expires, there is time to correct the
situation.
The following example shows the implication of having a reservation period: Assume two IP
addresses, therefore two possible DHCP leases. Assume three IP deskphones, two of which
are using the two available IP addresses. When the lease for the first two deskphones
expires, the third deskphone cannot get a lease until the reservation period expires. Even if
the other two deskphones are removed from the network, the third deskphone remains
without a lease until the reservation period expires.
Issue 5 May 2014 41
Page 48

Server Administration
In Table 6, the 1600 Series IP Deskphone sets the system values to the DHCPACK message field
values shown.
Table 6: DHCPACK Setting of System Values
System Value Set to
IPADD The yiaddr field.
NETMASK Option #1 (if received).
GIPADD Option #3 (if received, which might be a list of IP
addresses).
TLSSRVR The siaddr field, if that field is non-zero.
HTTPSRVR The siaddr field, if that field is non-zero.
DNSSRVR Option #6 (if received, which might be a list of IP
addresses).
DOMAIN Option #15 (if received).
DHCP lease time Option #51 (if received).
DHCP lease renew time Option #58 (if received).
DHCP lease rebind time Option #59 (if received).
The system values L2Q, L2QVLAN, and PHY2VLAN are not set from a name=value pair if those
system values were previously set by LLDP. For more information, see Link Layer Discovery Protocol
(LLDP).
Windows NT 4.0 DHCP Server
Verifying the Installation of the DHCP Server
Use the following procedure to verify whether the DHCP server is installed.
1. Select Start-->Settings-->Control Panel.
2. Double-click the Network icon.
3. Verify that Microsoft DHCP Server is listed as one of the Network Services on the
Services tab.
4. If it is listed, continue with the next section. If it is not listed, install the DHCP server.
42 1600 Series IP Deskphone Administrator Guide Release 1.3.5
Page 49

DHCP Server Administration
Note:
Note:
Creating a DHCP Scope for the IP Deskphones
Use the following procedure to create a DHCP scope for the IP deskphones.
1. Select Start-->Programs-->Admin Tools-->DHCP Manager.
2. Expand Local Machine in the DHCP Servers window by double clicking it until the + sign changes
to a - sign.
3. Select Scope-->Create.
4. Using information recorded in Table 3:
Required Network Information Before Installation - Per
DHCP Server:
Define the Deskphone IP Address Range.
Set the Subnet Mask.
To exclude any IP addresses you do not want assigned to IP deskphones within the Start and
End addresses range:
a. In the Exclusion Range Start Address field, enter the first IP Address in the range that you
want to exclude.
b. In the Exclusion Range End Address field, enter the last IP Address in the range that you
want to exclude.
c. Click the Add button.
d. Repeat steps a. through c. for each IP address range to be excluded.
Note: Avaya recommends that you provision the 1600 Series IP Deskphones with sequential
IP addresses. Also do not mix 1600 Series IP Deskphones and PCs in the same scope.
5. Under Lease Duration, select the Limited To option and set the lease duration to the maximum.
6. Enter a sensible name for the Name field, such as “DEFINITY IP Deskphones.”
7. Click OK.
A dialog box prompts you: Activate the new scope now?
8. Click No.
Note: Activate the scope only after setting all options.
Issue 5 May 2014 43
Page 50

Server Administration
Editing Custom Options
Use the following procedure to edit custom options.
1. Highlight the newly created scope.
2. Select DHCP Options-->Defaults in the menu.
3. Click the New button.
4. In the Add Option Type dialog box, enter an appropriate custom option name, for example,
“1600OPTION.”
5. Change the Data Type Byte value to String.
6. Enter 242 in the Identifier field.
7. Click the OK button.
The DHCP Options menu displays.
8. Select the Option Name for 242 and set the value string.
9. Click the OK button.
10. For the Option Name field, select 003 Router from the drop-down list.
11. Click Edit Array.
12. Enter the Gateway IP Address recorded in Table 3:
Installation - Per DHCP Server for the New IP Address field.
13. Select Add and then OK.
Required Network Information Before
Adding the DHCP Option
Use the following procedure to add the DHCP option.
1. Highlight the scope you just created.
2. Select Scope under DHCP Options.
3. Select the 242 option that you created from the Unused Options list.
4. Click the Add button.
5. Select option 003 from the Unused Options list.
6. Click the Add button.
7. Click the OK button.
8. Select the Global parameter under DHCP Options.
9. Select the 242 option that you created from the Unused Options list.
10. Click the Add button.
11. Click the OK button.
44 1600 Series IP Deskphone Administrator Guide Release 1.3.5
Page 51

DHCP Server Administration
Note:
Activating the Leases
Use the following procedure to activate the leases.
● Click Activate under the Scope menu.
The light-bulb icon for the scope lights.
Verifying Your Configuration
This section describes how to verify that the 1600OPTION is correctly config ured for the Windows NT®
4.0 DHCP server.
Note: Although this configuration represents that for 1600 Series IP Deskphones, the file
remains as 46XXOPTIONS. This allows shared use by 4600, 9600, and 1600 Series IP
Deskphones.
Verify the Default Option, 242 1600OPTION
1. Select Start-->Programs-->Admin Tools-->DHCP Manager.
2. Expand Local Machine in the DHCP servers window by double clicking until the + sign changes to
a - sign.
3. In the DHCP servers frame, click the scope for the IP deskphone.
4. Select Defaults from the DHCP_Options menu.
5. In the Option Name pull-down list, select 242 1600OPTION.
6. Verify that the Value String box contains the correct string from DHCP Server Administration
If not, update the string and click the OK button twice.
Verify the Scope Option, 242 1600OPTION
1. Select Scope under DHCP OPTIONS.
2. In the Active Options: scroll list, click 242 1600OPTION.
3. Click the Value button.
4. Verify that the Value String box contains the correct string from DHCP Generic Setup
If not, update the string and click the OK button.
on page 38.
.
Issue 5 May 2014 45
Page 52

Server Administration
Note:
Verify the Global Option, 242 1600OPTION
1. Select Global under DHCP OPTIONS.
2. In the Active Options: scroll list, click 242 1600OPTION.
3. Click the Value button.
4. Verify that the Value String box contains the correct value from DHCP Generic Setup
on page 38.
If not, update the string and click the OK button.
Windows 2000 DHCP Server
Verifying the Installation of the DHCP Server
Use the following procedure to verify whether the DHCP server is installed.
1. Select Start-->Program-->Administrative Tools-->Computer Management.
2. Under Services and Applications in the Computer Management tree, find DHCP.
3. If DHCP is not installed, install the DHCP server. Otherwise, proceed directly to Creating and
Configuring a DHCP Scope for instructions on server configuration.
Creating and Configuring a DHCP Scope
Use the following procedure to create and configure a DHCP scope.
1. Select Start-->Programs-->Administrative Tools-->DHCP.
2. In the console tree, click the DHCP server to which you want to add the DHCP scope for the IP
deskphones. This is usually the name of your DHCP server machine.
3. Select Action-->New Scope from the menu.
Windows displays the New Scope Wizard to guide you through rest of the setup.
4. Click the Next button.
The Scope Name dialog box displays.
5. In the Name field, enter a name for the scope such as “DEFINITY IP Deskphones,” then enter a
brief comment in the Description field.
6. When you finish Steps 1 - 5, click the Next button.
The IP Address Range dialog box displays.
7. Define the range of IP addresses used by the IP deskphones listed in Table 3:
Required Network
Information Before Installation - Per DHCP Server. The Start IP Address is the first IP address
available to the IP deskphones. The End IP Address is the last IP address available to the IP
deskphones.
Note: Avaya recommends not mixing 1600 Series IP Deskphones and PCs in the same scope.
8. Define the subnet mask in one of two ways:
46 1600 Series IP Deskphone Administrator Guide Release 1.3.5
Page 53

DHCP Server Administration
Note:
● The number of bits of an IP address to use for the network/subnet IDs.
● The subnet mask IP address.
Enter only one of these values. When you finish, click the Next button.
The Add Exclusions dialog box displays.
9. Exclude any IP addresses in the range specified in the previous step that you do not want assigned
to an IP deskphone.
a. In the Start Addres s field un der Exclus ion Range, enter the first IP Address in the range you
want to exclude.
b. In the End Address field under Exclusion Range, enter the last IP Address in the range you
want to exclude.
c. Click the Add button.
d. Repeat steps a. through c. for each IP address range that you want to exclude.
Note: You can add additional exclusion ranges later by right clicking the Address Pool under
the newly created scope and selecting the New Exclusion Range option.
Click the Next button after you enter all the exclusions.
The Lease Duration dialog box displays.
10. For all deskphones that obtain their IP addresses from the server, enter 30 days in the Lease
Duration field. This is the duration after which the IP address for the device expires and which the
device needs to renew.
11. Click the Next button.
The Configure DHCP Options dialog box displays.
12. Click the No, I will activate this scope later button.
The Router (Default Gateway) dialog box displays.
13. For each router or default gateway, enter the IP Address and click the Add button.
When you are done, click the Next button.
The Completing the New Scope Wizard dialog box displays.
14. Click the Finish button.
The new scope appears under your server in the DHCP tree. The scope is not yet active and
does not assign IP addresses.
15. Highlight the newly created scope and select Action-->Properties from the menu.
Issue 5 May 2014 47
Page 54

Server Administration
!
CAUTION:
Note:
16. Under Lease duration for DHCP clients, select Unlimited and then click the OK button.
CAUTION: IP address leases are kept active for varying periods of time. To avoid having calls
terminated suddenly, make the lease duration unlimited.
Adding DHCP Options
Use the following procedure to add DHCP options to the scope you created in the previous procedure.
1. On the DHCP window, right-click the Scope Options fold er under the scope you created in the last
procedure.
A drop-down menu displays.
2. In the left pane of the DHCP window, right click the DHCP Server name, then click Set Predefined
Options....
3. Under Predefined Options and Values, click Add.
4. In the Option Type Name field, enter any appropriate name, for example, “Avaya IP
Deskphones.”
5. Change the Data Type to String.
6. In the Code field, enter 242, then click the OK button twice.
The Predefined Options and Values dialog box closes, leaving the DHCP dialog box enabled.
7. Expand the newly created scope to reveal its Scope Options.
8. Click Scope Options and select Action-->Configure Options from the menu.
9. In the General tab page, under the Available Options, check the Option 242 checkbox.
10. In the Data Entry box, enter the DHCP IP deskphone option string as described in
DHCP Generic Setup
Note: You can enter the text string directly on the right side of the Data Entry box under the
on page 38.
ASCII label.
11. From the list in Available Options, check option 003 Router.
12. Enter the gateway (router) IP Address from the IP address field of Table 3:
Required Network
Information Before Installation - Per DHCP Server.
13. Click the Add button.
14. Click the OK button.
48 1600 Series IP Deskphone Administrator Guide Release 1.3.5
Page 55

HTTP Generic Setup
!
CAUTION:
Note:
!
Important:
Activating the New Scope
Use the following procedure to activate the new scope.
1. In the DHCP console tree, click the IP Deskphone Scope you just created.
2. From the Action menu, select Activate.
The small red down arrow over the scope icon disappears, indicating that the scope was
activated.
HTTP Generic Setup
You can store the same application software, script file, and settings file on an HTTP server as you can
on a TFTP server. TFTP is not supported for 1600 Series IP Deskphones. With proper administration,
the deskphone seeks out and uses that material. Some functionality might be lost by a reset if the
HTTP server is unavailable. For more information, see DHCP and File Servers
on page 37.
CAUTION: The files defined by HTTP server configuration must be accessible from all IP
deskphones invoking those files. Ensure that the file names match the names in the
upgrade script, including case, since UNIX systems are case-sensitive.
Note: Use any HTTP application you want. Commonly used HTTP applications include
Apache
Important: You must use the Avaya Web configuration server to obtain HTTPS so information is
®
and Microsoft® IIS™.
authenticated.
The Avaya Web configuration server does not support backup/restore. If you intend to
use HTTP for backup/restore purposes, you must use an HTTP server that is
independent of the Avaya Web configuration server.
To set up an HTTP server:
● Install the HTTP server application.
● Administer the system parameter HTTPSRVR to the address(es) of the HTTP server. Include
these parameters in DHCP Option 242, or the appropriate SSON Option.
Issue 5 May 2014 49
Page 56

Server Administration
Note:
● Download the upgrade script file and application file(s) from the Avaya Web site
http://www.avaya.com/support
Contents of the Settings File
Note: Many LINUX servers distinguish between upper and lower case names. Ensure that you
to the HTTP server. For more information, see
on page 58.
specify the settings file name accurately, as well as the names and values of the data
within the file.
If you choose to enhance the security of your HTTP environment by using Transport Layer Security
(TLS), you also need to:
● Install the TLS server application.
● Administer the system parameter TLSSRVR to the address(es) of the Avaya HTTPS server.
HTTP Configuration for Backup/Restore
For IIS Web Servers
For IIS 4.0 (WinNT4.0), IIS 5.0 (Win2000), IIS 5.1 (WinXP), IIS 6.0 (Win2003):
1. Create a “backup” folder under the root directory of your Web server. All backu p files will be store d
in that directory.
For example, if your backup folder is C:/Inetpub/wwwroot/backup the 46xxsettings.txt file should
have a line similar to:
[SET BRURI http://www.website.com/backup/
If your backup folder is the root directory, the 46xxsettings.txt file should have a line similar to:
[SET BRURI http://www.website.com/
]
2. Use Internet Information Services Manager or Internet Information Services depending on
your OS. Go to Start --> Settings --> Control Panel --> Administrative Tools.
3. Right click on the folder created for backup, or right click on Default Web Site if there is no specific
backup directory.
4. Select Properties.
5. In the Directory tab, make sure the Write box is checked.
]
50 1600 Series IP Deskphone Administrator Guide Release 1.3.5
Page 57

HTTP Configuration for Backup/Restore
Note:
Additional step for IIS 6.0 (Win2003):
1. Use Internet Information Services. Go to Start --> Settings --> Control Panel -->
Administrative Tools.
2. Below Default Web Site select Web Services Extension.
3. Make sure the WebDAV option is set to Allowed.
For Apache Web servers:
1. Create a “backup” folder under the root directory of your Web server, and make the folder
writable by everyone. All backup files will be stored in that directory.
If your backup folder is for instance C:/Program Files/Apache Group/Apache2/htdocs/backup,
the 46xxsettings.txt file should have a line similar to:
[SET BRURI http://www.website.com/backup/
]
If your backup folder is the root directory, the 46xxsettings.txt file should have a line similar to:
[SET BRURI http://www.website.com/
]
2. Edit your Web server configuration file httpd.conf.
3. Uncomment the two LoadModule lines associated with DAV:
LoadModule dav_module modules/mod_dav.so
LoadModule dav_fs_module modules/mod_dav_fs.so
Note: If these modules are not available on your system, typically the case on some Unix/Linux
Apache servers, you have to recompile these two modules (mod_dav & mod_dav_fs)
into the server. Other ways to load these modules might be available. Check your
Apache documentation at http://httpd.apache.org/docs/
for more details.
4. Add the following lines in the httpd.conf file:
#
# WebDAV configuration
#
DavLockDB "C:/Program Files/Apache Group/Apache2/var/DAVLock"
<Location />
Dav On
</Location>
For Unix/Linux Web servers the fourth line might look more like:
DavLockDB/usr/local/apache2/var/DAVLock
5. Create the var directory and make it writable by everyone. Right click
Properties-->Security-->Add-->Everyone-->Full Control.
Issue 5 May 2014 51
Page 58

Server Administration
Note:
Web Configuration Tool
Recent call server versions provide all the Web configuration support the 1600 Series IP Deskphones
require. Also, the media server has an easy to use, PC-based interface for creating script files. Given
these resources, you do not need to manually create the text files discussed in 1600 Series IP
Deskphone Scripts and Application Files. For more information about the media server, see Installation
and Upgrades for Avaya G700 Media Gateway and A vaya S8300 Media Server , available on the A vaya
support Web site.
Table 9: 1600 Series IP Deskphone Customizable System Parameters
lists the parameters you can
administer when manually creating the configuration file. Manual administration is discussed in 1600
Series IP Deskphone Scripts and Application Files. When using the media server, you do not need to
know the specific parameter names, since the media server handles that. For more information, Table 7
lists the parameter names from 1600 Series IP Deskphone Customizable System Parameters
and the
corresponding field name from the media server HTTP server application. Any limits, restrictions, etc.
about the parameters are built into the media server.
Note: The Web Configuration application covers other IP deskphones in addition to the 1600
Series IP Deskphones. This document covers only data applicable to 1600 Series IP
Deskphones.
Table 7: Media Server Field Names & Corresponding Script File Parameter
Names
Media Server Field Name Script File Parameter Name
Handset Audio Gain Control Status AGCHAND
Headset Audio Gain Control Status AGCHEAD
Speaker Audio Gain Control Status AGCSPKR
Application Status APPSTAT
Script File Server Authentication
Note: Applicable only when configuration file
downloaded using HTTPS. Not applicable if file
downloaded using HTTP.
Idle Time Before Backlight Turnoff BAKLIGHTOFF
Backup and Restore URI BRURI
802.1X Supplicant Mode DOT1X
52 1600 Series IP Deskphone Administrator Guide Release 1.3.5
AUTH
DOT1XSTAT
1 of 3
Page 59

Web Configuration Tool
Table 7: Media Server Field Names & Corresponding Script File Parameter
Names (continued)
Media Server Field Name Script File Parameter Name
DHCP Lease Violation Flag DHCPSTD
Domain Name DOMAIN
Domain Name Server DNSSRVR
HTTP Server IP Address HTTPSRVR
HTTP Directory HTTPDIR
Send Destination Unreachable Messages ICMPDU
Process Received Redirect Messages ICMPRED
Layer 2 Frame Tagging L2Q
802.1A VLAN Identifier L2QVLAN
System-Wide Language LANGSYS
English Language Selection Status LANG0STAT
Language File Name LANGxFILE (with x being 1-4)
Font File Name FONTFILE
Event Log Security Level LOGLOCAL
Syslog Server Address LOGSRVR
Management Complex IP Addresses MCIPADD
Voice Mail Deskphone Number MSGNUM
User Options Access OPSTAT
Deskphone Country Code PHNCC
Deskphone Dial Plan Length PHNDPLENGTH
International Access Code PHNIC
Long Distance Access Code PHNLD
National Deskphone # Length PHNLDLENGTH
Outside Line Access Code PHNOL
Ethernet Line Interface Status PHY1STAT
2 of 3
Issue 5 May 2014 53
Page 60

Server Administration
Table 7: Media Server Field Names & Corresponding Script File Parameter
Names (continued)
Media Server Field Name Script File Parameter Name
Secondary Ethernet Interface Layer 2 Priority Value PHY2PRIO
Secondary Ethernet Line Interface Status PHY2STAT
Secondary Ethernet Interface VLAN Identifier PHY2VLAN
Local (dial pad) Procedure Password PROCPSWD
Local Dialpad Procedures Allowed PROCSTAT
Reregistration Timer REREGISTER
RTCP Monitor IP Address RTCPMON
Source IP Addresses for SNMP Queries SNMPADD
SNMP Community String SNMPSTRING
Subscription List SUBSCRIBELIST
Trusted Domains/Paths TPSLIST
Unnamed Registration Status UNNAMEDSTAT
Secondary Ethernet Interface Layer 2 Frame Tagging VLANSEP
Wait Time for DHCP Offer VLANTEST
3 of 3
54 1600 Series IP Deskphone Administrator Guide Release 1.3.5
Page 61

Chapter 6: Deskphone Software and Application
Note:
Files
General Download Process
The 1600 Series IP Deskphones download script files and settings files from either an HTTP or HTTPS
server. These deskphones download the application files from the HTTP server. The HTTPS server
applies only if the server supports Transport Layer Security (TLS) encryption.
Note: The script files, application files, and settings files discussed in this chapter are identical
for HTTP and HTTPS servers. The generic term “file server” refers to both “HTTP server”
and “HTTPS server.”
The file downloading process is the same for both servers, except when you use an HTTPS server, a
TLS server is contacted first. The deskphone queries the file server, which transmits a script file to the
deskphone. The script file tells the deskphone which application file the deskphone must use. The
application file is the software that has the telephony functionality, and is easily updated for future
enhancements. In a newly installed deskphone, the application file might be missing. In a previously
installed deskphone, the application file might not be the proper one. In both cases, the deskphone
requests a download of the proper application file from the HTTP server. The file server downloads the
file and conducts some checks to ensure that the file was downloaded properly. If the deskphone
determines it already has the proper file, the deskphone proceeds to the next step without downloading
the application file again.
After checking and loading the application file, the 1600 Series IP Deskphone, if appropriate, uses the
script file to look for a settings file. The settings file contains options you have administered for any or
all of the 1600 Series IP Deskphones in your network. For more information about the settings file, see
Contents of the Settings File
on page 58.
Software
When shipped from the factory, the1600 Series IP Deskphones might not con tain suf ficient sof tware for
registration and operation. When the deskphone is first plugged in, a sof tware download from an HTTP
server starts to give the phone its proper functionality.
For software upgrade downloads, the call server pr ovides the cap ability for a remote rest art of the 1600
Series IP Deskphone. As a result of restarting, the deskphone automatically start s reboot procedures. If
new software is available on the server , the deskpho ne downloads it as p art of the reboot process. The
Avaya 1600 Series IP Deskphones Installation and Maintenance Guide covers upgrades to a
previously installed deskphone and related information.
Issue 5 May 2014 55
Page 62

Deskphone Software and Application Files
Note:
1600 Series IP Deskphone Scripts and Application Files
Choosing the Right Application File and Upgrade Script File
The software releases containing the files needed to operate the 1600 Series IP Deskphones are
bundled together. You download this self-extracting executable file to your file server from the Avaya
support Web site at: http://www.avaya.com/support
format.
The bundle contains:
● An upgrade script file and a settings file, which allow you to upgrade to new software releases and
new functionality without having to replace IP deskphones.
● Application files for all current 1600 Series IP Deskphones.
● Other useful information such as a ReadMe file and a settings file template to customize
parameters and settings, and the latest binary code.
. The file is available in both zipped and unzipped
● Font files
● Language files
Upgrade Script File
An upgrade script file tells the IP deskphone whether the deskphone needs to upgrade software. The
Avaya IP Deskphones attempt to read this file whenever they reset. The upgrade script file also points
to the settings file.
You download a default upgrade script file, sometimes called the “script file,” from
http://www.avaya.com/support
customer-definable options. This file must reside in the same directory as the upgrade script file, and
must be called 46xxsettings.txt. The settings file contains settings for 16 00, 9600, and 4600 Series IP
Deskphones.
Note: Avaya recommends that the settings file have the extension *.txt. The Avaya IP
Deskphones can operate without this file. You can also change these settings with
DHCP or, in some cases, from the dialpad of the deskphone.
. This file allows the deskphone to use default settings for
56 1600 Series IP Deskphone Administrator Guide Release 1.3.5
Page 63

1600 Series IP Deskphone Scripts and Application Files
Note:
Note:
Settings File
The settings file contains the option settings you need to customize the Avaya IP Deskphones for your
enterprise.
Note: You can use one settings file for all your Avaya IP Deskphones. The settings file includes
the 1600 Series IP Deskphones covered in this document as well as 9600 Series IP
Deskphones and 4600 Series IP Deskphones.
The settings file can include any of five types of statements, one per line:
● Comments, which are statements with a “#” character in the first column.
● Tags, which are comments that have exactly one space character after the initial #, followed by a
text string with no spaces.
● Goto commands, of the form GOTO tag. Goto commands cause the deskphone to continue
interpreting the configuration file at the next line after a # tag statement. If no such statement
exists, the rest of the configuration file is ignored.
● Conditionals, of the form IF $name SEQ string GOTO tag. Conditionals cause the Goto
command to be processed if the value of name is a case-insensitive equivalent to string. If no
such name exists, the entire conditional is ignored. The only system values that can be used in a
conditional statement are: BOOTNAME, GROUP, and SIG.
● SET commands, of the form SET parameter_name value. Invalid values cause the specified
value to be ignored for the associated parameter_name so the default or previously
administered value is retained. All values must be text string s, even if the value it self is n umeric,
a dotted decimal IP address, and so on.
Note: Enclose all data in quotation marks for proper interpretation.
The upgrade script file Avaya provides includes a line that tell the deskpho ne to GET 46xxsettings.txt.
This lines causes the deskphone to use HTTP or HTTPS to attempt to down load the file specified in the
GET command. If the file is obtained, its content s are inter preted as an additional script file. That is how
your settings are changed from the default settings. If the file cannot be obtained, the deskphone
continues processing the upgrade script file.
If the configuration file is successfully obtained but does not include any setting changes the
deskphone stops using HTTP. This happens when you initially download the script file template from
the Avaya support Web site, before you make any changes. When the configuration file contains no
setting changes, the deskphone does not go back to the upgrade script file.
Avaya recommends that you do not alter the upgrade script file. If Avaya changes the upgrade script
file in the future, any changes you have made will be lost. Avaya recommends that you use the
46xxsettings file to customize your settings instead. However, you can change the settings file name,
if desired, as long as you also edit the corresponding GET command in the upgrade script file.
For more information on customizing your settings file, see Contents of the Settings File
.
Issue 5 May 2014 57
Page 64

Deskphone Software and Application Files
Note:
Note:
Contents of the Settings File
After checking the application software, the 1600 Series IP Deskphone looks for a 46xxsettings file.
This optional file is where you identify non-default option settings, application-specific parameters, an d
so on. Yo u can download a template for this file from the Avaya support Web site. An example of what
the file might look like follows.
Note: The following is intended only as a simple example. Your settings will vary from the
settings shown. This sample assumes specification of a DNS Server and turning off
enhanced local dialing for 96xx Series IP Deskphones.
DNSSRVR=”dnsexample.yourco.com”
ENDIALSTAT=0
See Chapter 7: Administering Deskphone Options
for details about specific values. You need
only specify settings that vary from defaults, although specifying defaults is harmless.
VLAN separation controls whether or not traffic received on the secondary Ethernet interface are
forwarded on the voice VLAN and whether network traffic received on the data VLAN are forwarded to
the deskphone. Add commands to the 46xxsettings.txt file to enable VLAN separation. The following
example assumes the voice VLAN ID is “xxx”, the data VLAN ID is “yyy” and the data traffic priority is
“z”:
SET VLANSEP 1
SET L2Q 1 (or 0 for auto)
SET L2QVLAN xxx
SET PHY2VLAN yyy
SET PHY2PRIO z
Note: Also configure the network switch so that 802.1Q tags are not removed from frames
forwarded to the deskphone.
58 1600 Series IP Deskphone Administrator Guide Release 1.3.5
Page 65

The GROUP System Value
The GROUP System Value
Y ou might have different communities o f users, all of which have the same deskphone model, but which
require different administered settings. For examp le, you might want to restrict Call Center agent s from
being able to Logoff, which might be an essential capability for “hot-desking” associates. We provide
examples of the group settings for each of these situations later in this section.
Use the GROUP system value for this purpose:
1. identify which deskphones are associated with which group, and designate a number for each
group. The number can be any integer from 0 to 999, with 0 as the default, meaning your largest
group is assigned as Group 0.
2. At each non-default deskphone, instruct the installer or user to invoke the GROUP Local (dialpad)
Administrative procedure as specified in the Avaya 1600 Series IP Deskphones Installation and
Maintenance Guide and specify which GROUP number to use. The GROUP System value can only
be set on a phone-by-phone basis.
3. Once the GROUP assignments are in place, edit the configuration file to allow each deskphone of
the appropriate group to download its proper settings.
Here is an example of the configuration file for the Call Center agent:
IF $GROUP SEQ 1 goto CALLCENTER
IF $GROUP SEQ 2 goto HOTDESK
{specify settings unique to Group 0}
goto END
# CALLCENTER
{specify settings unique to Group 1}
goto END
# HOTDESK
{specify settings unique to Group 2}
# END
{specify settings common to all Groups}
Call Center Administration
With Release 1.3.3, you can control the operations of the following buttons in a call center environment
by setting the appropriate values in the settings file.
Issue 5 May 2014 59
Page 66

Deskphone Software and Application Files
● HOLD
● CONFERENCE
● DROP
● MUTE
● HEADSET
● SWITCH HOOK
● TRANSFER
60 1600 Series IP Deskphone Administrator Guide Release 1.3.5
Page 67

Table 8: Call Center administration parameters
Call Center Administration
Parameter
name
Default
value
Valid values Usage
CCBTNST AT 1 1 ASCII numeric
digit; 0 and 1
HEADST AT 0 1 ASCII numeric
digit; 0 and 1
HOLDST AT 0 1 ASCII numeric
digit; 0 and 1
HOOKST AT 0 1 ASCII numeric
digit; 0 and 1
Call Center permission flag;
1 = all buttons have normal operation;
0 = Conference, Drop, Headset, Hold,
Mute, and Transfer buttons, and the
switchhook are disabled unless you
individually configure the values as
indicated in the following rows.
Headset button permission flag;
1 = normal operation;
0 = normal operation unless
CCBTNSTAT = 0, in which case the
Headset button is disabled.
Hold button permission flag;
1 = normal operation;
0 = normal operation unless
CCBTNSTAT = 0, in which case the
Hold button is disabled.
Switchhook permission flag;
1 = normal operation;
0 = normal operation unless
CCBTNSTAT = 0, in which case the
switchhook is disabled.
MUTEST AT 0 1 ASCII numeric
digit 0 and 1
XFERST AT 0 1 ASCII numeric
digit 0 and 1
Mute button permission flag;
1 = normal operation;
0 = normal operation unless
CCBTNSTAT = 0, in which case the
Mute button is disabled.
Transfer button permission flag;
1 = normal operation;
0 = normal operation unless
CCBTNSTAT = 0, in which case the
Transfer button is disabled.
Issue 5 May 2014 61
Page 68

Deskphone Software and Application Files
!
Important:
Table 8: Call Center administration parameters
Parameter
name
Default
value
Valid values Usage
CONFST AT 0 1 ASCII numeric
digit; 0 and 1
DROPST AT 0 1 ASCII numeric
digit; 0 and 1
HEADST AT 0 1 ASCII numeric
digit; 0 and 1
HOLDST AT 0 1 ASCII numeric
digit; 0 and 1
Conference button permission flag;
1 = normal operation;
0 = normal operation unless
CCBTNSTAT = 0, in which case the
Conference button is disabled.
Drop button permission flag;
1 = normal operation;
0 = normal operation unless
CCBTNSTAT = 0, in which case the
Drop button is disabled.
Headset button permission flag;
1 = normal operation;
0 = normal operation unless
CCBTNSTAT = 0, in which case the
Headset button is disabled.
Hold button permission flag;
1 = normal operation;
0 = normal operation unless
CCBTNSTAT = 0, in which case the
Hold button is disabled.
HOOKST AT 0 1 ASCII numeric
digit; 0 and 1
Switchhook permission flag;
1 = normal operation;
0 = normal operation unless
CCBTNSTAT = 0, in which case the
switchhook is disabled.
MUTEST AT 0 1 ASCII numeric
digit 0 and 1
Mute button permission flag;
1 = normal operation;
0 = normal operation unless
CCBTNSTAT = 0, in which case the
Mute button is disabled.
XFERST AT 0 1 ASCII numeric
digit 0 and 1
Transfer button permission flag;
1 = normal operation;
0 = normal operation unless
CCBTNSTAT = 0, in which case the
Transfer button is disabled.
Important: You can access the local procedures only if you have enabled the Mute button.
Example
62 1600 Series IP Deskphone Administrator Guide Release 1.3.5
Page 69

Call Center Administration
If you want to disable all the buttons, except the switchhook so that the switchhook functions normally,
set CCBTNSTAT to 0 so that by default, all the applicable buttons are disabled and set HOOKSTAT=1
to enable the switchhook button.
Issue 5 May 2014 63
Page 70

Deskphone Software and Application Files
64 1600 Series IP Deskphone Administrator Guide Release 1.3.5
Page 71

Chapter 7: Administering Deskphone Options
!
CAUTION:
Administering Options for the 1600 Series IP Deskphones
This chapter explains how to change parameters by means of the DHCP or HTTP servers. In all cases,
you are setting a system parameter in the deskphone to a desired value. Table 9
● the parameter names,
● their default values,
● the valid ranges for those values, and
● a description of each one.
For DHCP, the DHCP Option sets these parameters to the desired values as discussed in DHCP and
File Servers on page 37. For HTTP, the parameters in Table 9 are set to desired values in the script file.
For more information, see Contents of the Settings File
Table 7:
Media Server Field Names & Corresponding Script File Parameter Names on page 52 for
on page 58. When using a media server, see
information on parameters set by the media server application.
Avaya recommends that you administer options on the 1600 Series IP Deskphones using script files.
Some DHCP applications have limits on the amount of user-specified information. The administration
required can exceed those limits for the more full-featured deskphone models.
lists:
You might choose to completely disable the capability to enter or change option settings from the
dialpad. You can set the system value, PROCPSWD, as part of standard DHCP/HTTP administration.
Alternately, you can set PROCPSWD on the system-parameters ip-options form, as of Avaya Aura
Communication Manager Release 5.2.
For more information on dialpad options, see the Avaya 1600 Series IP Deskphones Installation and
Maintenance Guide.
CAUTION: PROCPSWD is likely stored on the server in clear text and is sent to the deskphone in
the unencrypted. Therefore, do not consider PROCPSWD as a high-security technique
to inhibit a sophisticated user from obtaining access to local procedures.
Administering this password can limit access to all local procedures, including
V I E W. VIEW is a read-only o ption that allows review of the curren t deskphone settings.
Table 9: 1600 Series IP Deskphone Customizable System Parameters
Parameter Name Default Value Description and Value Range
AGCHAND 1 Automatic Gain Control status for handset
(0=disabled, 1=enabled).
1 of 7
Issue 5 May 2014 65
Page 72

Administering Deskphone Options
Table 9: 1600 Series IP Deskphone Customizable System Parameters (continued)
Parameter Name Default Value Description and Value Range
AGCHEAD 1 Automatic Gain Control status for headset
(0=disabled, 1=enabled).
AGCSPKR 1 Automatic Gain Control status for Speaker
(0=disabled, 1=enabled).
APPNAME " " (Null) Primary application image file name, as provided in the
1600upgrade.txt file.
APPSTAT 1 Controls whether specific applications are enabled,
restricted, or disabled. Values are: 1=all applications
enabled, 2=Speed Dial (Contacts) changes and Call
Log disabled and Redial last number only, 3=Speed
Dial (Contacts) changes disabled, 0=Speed Dial
(Contacts) changes, Call Log, and Redial disabled.
AUTH 0 Script file authentication value (0=HTTP is acceptable,
1=HTTPS is required).
BAKLIGHTOFF 120 Number of minutes without display activity to wait
before turning off the backlight. Values: 0-999, no
spaces and no null value. A value of 0 means the
backlight never turns off.
BRURI " " (Null) URL used for backup and retrieval of user data. S pecify
HTTP server and directory path to backup file. Do not
specify backup file name. Value: 0-255 ASCII
characters. Null is a valid value and spaces are
allowed.
DHCPSTD 0 DHCP Standard lease violation flag. Indicates whether
to keep the IP address if there is no response to lease
renewal. If set to “1” (No) the deskphone strictly follows
the DHCP standard with respect to giving up IP
addresses when the DHCP lease expires. If set to “0”
(Yes) the deskphone continues using the IP address
until it detects reset or a conflict (see DHCP Generic
Setup).
DNSSRVR 0.0.0.0 Text string containing the IP address of zero or more
DNS servers, in dotted-decimal format, separated by
commas with no intervening spaces (0-255 ASCII
characters, including commas).
DOMAIN " " (Null) Text string containing the domain name to be used
when DNS names in system values are resolved into
IP addresses. V alid values are 0-255 ASCII characters.
If Null, no spaces allowed.
DOT1X 0 802.1X Supplicant operation mode. Valid values are:
0=With PAE pass-through, 1=with PAE pass-through
and proxy Logoff, 2=without PAE pass-through or
proxy Logoff. For more information, see
802.1X on page 75.
IEEE
2 of 7
66 1600 Series IP Deskphone Administrator Guide Release 1.3.5
Page 73

Administering Options for the 1600 Series IP Deskphones
Table 9: 1600 Series IP Deskphone Customizable System Parameters (continued)
Parameter Name Default Value Description and Value Range
DOT1XSTAT 0 Determines how the deskphone handles Supplicants.
Valid values are:
0=Supplicant operation is completely disabled.
1=Supplicant operation is enabled, but responds only
to received unicast EAPOL messages.
2=Supplication operation is enabled and responds to
received unicast and multicast EAPOL messages. For
more information, see
IEEE 802.1X on page 75.
ENHDIALSTAT 1 Enhanced Dialing Status. If set to “1” the Enhanced
Local Dialing feature is turned on for all associated
applications. If set to “0” the feature is turned off.
FONTFILE " " (Null) Name of the font file for a language for a 1600 Series
International deskphone.
HTTPDIR " " (Null) HTTP server directory path. The path name prepended
to all file names used in HTTP and HTTPS get
operations during initialization. Value: 0-127 ASCII
characters, no spaces. Null is a valid value. Leading or
trailing slashes are not required.
HTTPSRVR " " (Null) Text list of HTTP server addresses in dotted decimal or
DNS format, separated by commas (0-255 ASCII
characters, including commas).
ICMPDU 0 Controls whether ICMP Destination Unreachable
messages will be processed. Values are: 0=No,
1=Send limited Port Unreachable messages, 2=Send
Protocol and Port Unreachable messages.
ICMPRED 0 Controls whether ICMP Redirect messages will be
processed. Values are: 0=No, 1=Yes.
L2Q 0 Controls whether Layer 2 frames have IEEE 802.1Q
tags (0=auto, 1=enabled, 2=disabled).
L2QVLAN 0 802.1Q VLAN Identifier (0 to 4094). Null (" ") is not a
valid value and the value cannot contain spaces. VLAN
identifier used by IP deskphones. Set this parameter
only when IP deskphones are to use a VLAN that is
separate from the default data VLAN. If the VLAN
identifier is to be configured via H.323 signaling based
on Avaya Aura Communication Manager
administration forms, it should not be set here.
LANG0STAT 1 Controls whether the built-in English language text
strings can be selected by the user. Valid values are:
0 = User cannot select English language text strings
1 = User can select English language text strings/
LANGxFILE " " (Null) Name of the language file in use:
LANG1FILE =
LANG2FILE =
LANG3FILE =
LANG4FILE =
3 of 7
Issue 5 May 2014 67
Page 74

Administering Deskphone Options
Table 9: 1600 Series IP Deskphone Customizable System Parameters (continued)
Parameter Name Default Value Description and Value Range
LANGSYS " " (Null) 0 to 32 ASCII characters. The file name of the system
default language file, if any.
LOGLOCAL 0 Event Log Severity Level (one 0-8 ASCII numeric
digit). Controls the level of events logged in the
endptRecentLog and endptResetLog objects in the
SNMP MIB. Events with the selected level and with a
higher severity level will be logged. Valid values are:
0=Disabled, 1=emergencies, 2=alerts, 3=critical,
4=errors, 5=warnings, 6=notices, 7=information,
8=debug.
LOGSRVR " " (Null) Voice Monitoring Manager (VMM) Server Address.
Zero or one IP address in dotted-decimal format or
DNS Name format (0-15 ASCII characters).
MCIPADD 0.0.0.0 Call Server Address. Zero or more Avaya Aura
Communication Manager server IP addresses. Format
is dotted-decimal or DNS name format, separated by
commas without intervening spaces (0-255 ASCII
characters, including commas). Null is a valid value.
MSGNUM " " (Null) V oice mail deskphone number . S pecifies th e number to
be dialed automatically when the deskphone user
presses the Message button. Value: 0-30 ASCII
dialable characters (0-9, * and #) and no spaces. Null
is a valid value.
OPSTAT 111 Options status flag(s) (1 or 3 ASCII numeric digits)
indicate which options are user-selectable. The default
of 111 grants access to all options and related
applications.
Single digit valid values are:
1=user can access all options, including Logout,
2= user can access only view-oriented applications.
Three-digit valid values are a concatenation of binary
values, in the form abc, where each letter represents a
0 (disabled/off) or 1 (enabled/on), interpreted as:
a = base settings for all user options and related
applications, except as noted in b or c.
b = setting for view-oriented applications (for example,
the Network Information application), as applicable.
c = setting for Logout application, if applicable.
The binary "0" does not allow an end user to see or
invoke options and related applications. The binary "1"
allows full display and access to all options and related
applications.
PHNCC 1 Deskphone country code. The administered
international country code for the location by the
algorithm that dials calls from the incoming Call Log or
from Web pages. Range: 1-3 digits, from “1” to “999.”
68 1600 Series IP Deskphone Administrator Guide Release 1.3.5
4 of 7
Page 75

Administering Options for the 1600 Series IP Deskphones
Table 9: 1600 Series IP Deskphone Customizable System Parameters (continued)
Parameter Name Default Value Description and Value Range
PHNDPLENGTH 5 Internal extension deskphone number length. S pecifies
the number of digits associated with internal extension
numbers by the algorithm that dials calls from the
incoming Call Log or from Web pages. Range: 1 or 2
digits, from “3” to “10.”
PHNIC 011 Deskphone international access code. The maximum
number of digits, if any, dialed to access public network
international trunks by the algorithm that dials calls
from the incoming Call Log or from Web p ages. Range:
0-4 digits.
PHNLD 1 Deskphone long distance access code. The digit, if
any, dialed to access public network long distance
trunks by the algorithm that dials calls from the
incoming Call Log or from Web pages. Range: 1 digit
or " " (Null).
PHNLDLENGTH 10 Length of national deskphone number. The number of
digits in the longest possible national deskphone
number by the algorithm that dials calls from the
incoming Call Log or from Web pages. Range: 1 or 2
digits, from “3” to “10.” Range: 1 or 2 ASCII numeric
characters, from “5” to “15.”
PHNOL 9 Outside line access code. The character(s) dialed,
including # and *, if any, to access public network local
trunks by the algorithm that dials calls from the
incoming Call Log or from Web pages. Range: 0-2
dialable characters, including " " (Null).
PHY1STAT 1 Ethernet line interface setting (1=auto-negotiate,
2=10Mbps half-duplex, 3=10Mbps full-duplex,
4=100Mbps half-duplex, 5=100Mbps full-duplex, and
6=1000Mbps full-duplex if supported by the hardware).
PHY2PRIO 0 Layer 2 priority value for frames received on or
forwarded to the secondary Ethernet interface. Set this
parameter only when VLAN separation is "1"
(enabled). Values are from 0-7 and correspond to the
drop-down menu selection.
PHY2STAT 1 Secondary Ethernet interface setting
(0=Secondary Ethernet interface off/disabled,
1=auto-negotiate, 2=10Mbps half-duplex, 3=10Mbps
full-duplex, 4=100Mbps half-duplex, 5=100Mbps
full-duplex), and 6=1000Mbps full-duplex if supported
by the hardware).
5 of 7
Issue 5 May 2014 69
Page 76

Administering Deskphone Options
Note:
Table 9: 1600 Series IP Deskphone Customizable System Parameters (continued)
Parameter Name Default Value Description and Value Range
PHY2VLAN 0 VLAN identifier used by frames received on or
forwarded to the secondary Ethernet interface. Set this
parameter only when VLAN separation is "1"
(enabled). V alue is 1-4 ASCII numeric d igits from “0” to
“4094.” Null is not a valid value, nor can the value
contain spaces. If this value is set by LLDP using the
Port VLAN ID TLV value, it will not change regardless
of settings from other sources. For more information,
see Parameter Data Precedence
.
PROCPSWD 27238 Text string containing the local dialpad procedure
password. The string can have a value of 4 to 7 ASCII
digits from 0000 to 9999999. If set, you must enter the
password immediately after you press the Mute button
and before you enter the procedure command, for
example, the VIEW command. The password is
Intended to facilitate restricted access to local
procedures even when command sequences are
known. Password is viewable, not hidden.
Note: After you upgrade the deskphone to
Release 1.3.3, a default value of 27238
is assigned to PROCPSWD if you have
not previously changed the value of
PROCPSWD.
PROCSTAT 0 Local (dialpad) Administrative procedures status
(0=Local procedures enabled, 1=all Administrative
Options are disabled).
REREGISTER 20 Registration timer in minutes. Controls an H.323
protocol timer that should only be changed under very
special circumstances by someone who fully
understands the system operation impact. Value is
1-120.
RTCPMON " " (Null) Text string containing the 4-octet IP address of the
RTCP monitor currently in use, in dotted decimal or
DNS Name format (0-15 ASCII characters, no spaces).
SNMPADD " " (Null) Text string containing zero or more allowable source IP
addresses for SNMP queries, in dotted decimal or DNS
format, separated by commas, with up to 255 total
ASCII characters including commas.
SNMPSTRING " " (Null) Text string containing the SNMP community name
string (up to 32 ASCII characters, no spaces).
6 of 7
70 1600 Series IP Deskphone Administrator Guide Release 1.3.5
Page 77

Administering Options for the 1600 Series IP Deskphones
Table 9: 1600 Series IP Deskphone Customizable System Parameters (continued)
Parameter Name Default Value Description and Value Range
STATIC 0 Static programming override flag. If set to “0” static
programming never overrides call server (DHCP) or
call server administered data. If set to “1” static
programming overrides only file server administered
data. If set to “2” static programming overrides only call
server administered data. If set to “3” static
programming overrides both file server- and call
server-administered data. Allows a call server IP
address that has been manually programmed into a
deskphone to override any value received via DHCP or
via this configuration file. A manually programmed IP
address will only be used if it is not 0.0.0.0, so this
parameter may be used to allow only specific
deskphones to use a different value than otherwise
provided by this configuration file. If STATIC is to be
used to select a manual override of file server IP
address(es), STATIC must be set via DHCP, not via
this configuration file.
SUBSCRIBELIST " " (Null) One or more Push application server subscription
URLs, separated by commas without any intervening
spaces (0-255 ASCII characters, including commas).
TPSLIST " " (Null) One or more trusted domain/path strings, separated by
commas without any intervening spaces (0-255 ASCII
characters, including commas). A URL pushed to a
deskphone must contain one of these strings if it is to
be used to obtain content to be rendered by the
deskphone.
UNNAMEDSTAT 1 Unnamed Registration Status. Specifies whether
unnamed registration is initiated if the user fails to e nter
a value at the Extension: prompt or Login screen.
Unnamed registration provides the deskphone with a
TTI-level service, enabling a user, for example, to dial
emergency services like 911. Value 1=Yes, 0=No.
VLANSEP 1 VLAN separation. Controls whether frames to/from the
secondary Ethernet interface receive IEEE 802.1Q
tagging treatment. The tagging treatment enables
frames to be forwarded based on their tags in a
manner separate from deskphone frames. If tags are
not changed, no tag-based forwarding is employed.
Values are: 1=On/Enabled, 0= Off/Disabled. This
parameter is used with several related parameters. For
more information, see VLAN Separation
VLANTEST 60 Number of seconds to wait for a DHCPOFFER when
using a non-zero VLAN ID (1-3 ASCII digits, from “0” to
“999”).
on page 73.
7 of 7
Issue 5 May 2014 71
Page 78

Administering Deskphone Options
Note:
Note: Table 9 applies to all 1600 Series IP Deskphones. Certain 1600 IP Deskphones might
have additional, optional information that you can administer. For more information, see
Chapter 8: Administering Applications and Options
.
VLAN Considerations
If your LAN environment does not include Virtual LANs (VLANs), ignore this section. Otherwise, this
section contains information on how to administer 1600 Series IP Deskphones to minimize registration
time and maximize performance in a VLAN environment.
VLAN Tagging
IEEE 802.1Q tagging (VLAN) is a useful method of managing VoIP traffic in your LAN. Avaya
recommends that you establish a voice LAN, set L2 QVLAN to that VLAN, and provide vo ice traffic with
priority over other traffic. If LLDP was used to set the deskphones’ VLAN, that setting has absolute
authority. Otherwise, you can set VLAN tagging manually, by DHCP, or in the 46xxsettings.txt file.
If VLAN tagging is enabled (L2Q=0 or 1), the 1600 Series IP Deskphones set the VLAN ID to
L2QVLAN, and VLAN priority for packets from the deskphone to L2QAUD for audio packets and
L2QSIG for signalling packets. The default value (6) for these parameters is the recommended value
for voice traffic in IEEE 802.1D.
Regardless of the tagging setting, a 1600 Series IP Deskphone will always transmit packets from the
deskphone at absolute priority over packets from secondary Ethernet. The priority settings are useful
only if the downstream equipment is administered to give the voice LAN priority.
VLAN Default Value and Priority Tagging
The system value L2QVLAN is initially set to “0” and identifies the 802.1Q VLAN Identifier. This default
value indicates “priority tagging” as defined in IEEE 802.IQ Section 9.3.2.3. Priority tagging specifies
that your network closet Ethernet switch automatically insert the switch port default VLAN without
changing the user priority of the frame (cf. IEEE 802.1P and 802.1Q).
If you do not want the default VLAN to be used for voice traffic:
● Ensure that the switch configuration lets frames tagged by the 1600 Series IP Deskphon e through
without overwriting or removing them.
● Set the system value L2QVLAN to the VLAN ID appropriate for your voice LAN.
72 1600 Series IP Deskphone Administrator Guide Release 1.3.5
Page 79

VLAN Considerations
Note:
Another system value you can administer is VLANTEST. VLANTEST defines the number of seconds
the 1600 IP Series Deskphone waits for a DHCPOFFER message when using a non-zero VLAN ID.
The VLANTEST default is “60” seconds. Using VLANTEST ensures that the deskphone returns to the
default VLAN if an invalid VLAN ID is administered or if the phone moves to a port where the L2QVLAN
value is invalid. The default value is long, allowing for the scenario that a major power interruption is
causing the phones to restart. Always allow time for network routers, the DHCP servers, etc. to be
returned to service. If the deskphone restarts for any reason and the VLANTEST time limit expires, the
deskphone assumes the administered VLAN ID is invalid. The deskphone then initiates registration
with the default VLAN ID.
Setting VLANTEST to “0” has the special meaning of telling the phone to use a non-zero VLAN
indefinitely to attempt DHCP. In other words, the deskphone does not return to the default VLAN.
Note: If the deskphone returns to the default VLAN but must be put back on the L2QVLAN
VLAN ID, you must Reset the deskphone. See the Reset procedure in the Avaya 1600
Series IP Deskphones Installation and Maintenance Guide.
VLAN Separation
VLAN separation controls whether or not traffic received on the secondary Ethernet interface can be
forwarded on the voice VLAN. VLAN separation also controls whether network traffic received on the
data VLAN can be forwarded to the deskphone. The following system parameters control VLAN
separation:
● VLANSEP - enables (1) or disables (0) VLAN separation. The default is 1 (on), which allows full
separation. When set to 0 (off), VLAN IDs are not used as a criteria for forwarding frames.
● L2Q - 802.1Q tagging must be set to 1 (on) or 0 (auto).
● L2QVLAN - must be set to the non-zero VLAN ID of the voice VLAN.
● PHY2VLAN - must be set to the non-zero VLAN ID of the data VLAN, which cannot be the same
as the voice VLAN ID.
● PHY2PRIO - the layer 2 priority value to be used for tagged frames received on the secondary
Ethernet interface.
Table 10
provides several VLAN separation guidelines.
Issue 5 May 2014 73
Page 80

Administering Deskphone Options
Table 10: VLAN Separation Rules
If Then
VLANSEP is “0”
(Off/Disabled),
OR the deskphone is
not tagging frames,
Frames received on the secondary Ethernet
interface will not be changed before
forwarding. For example, tagging is not added
OR the deskphone is
tagging frames with a
VLAN ID equal to
PHY2VLAN.
or removed and the VLAN ID and tagged
frames priority are not changed. The Ethernet
switch forwarding logic determines that frames
received on the Ethernet line interface are
forwarded to the secondary Ethernet interface
or to the deskphone without regard to specific
VLAN IDs or the existence of tags.
VLANSEP is “1” (On/Enabled) All tagged frames received on the secondary
Ethernet interface are changed before
forwarding to make the VLAN ID equal to the
PHY2VLAN value and the priority value equal
to the PHY2PRIO value.
Untagged frames received on the secondary
Ethernet interface are not changed before
forwarding.
VLANSEP is “1”
(On/Enabled)
AND the deskphone is
not tagging frames,
The Ethernet switch forwarding logic
determines that frames received on the
Ethernet line interface are forwarded to the
OR if the deskphone is
tagging frames with a
VLAN ID equal to
secondary Ethernet interface or to the
deskphone without regard to specific VLAN
IDs or the existence of tags.
PHY2VLAN,
VLANSEP is “1”
(On/Enabled)
OR if the PHY2VLAN
value is zero.
AND the deskphone is
tagging frames with a
VLAN ID not equal to
PHY2VLAN,
AND the PHY2VLAN
value is not zero.
Tagged frames received on the Ethernet line
interface will only be forwarded to the
secondary Ethernet interface if the VLAN ID
equals PHY2VLAN.
Tagged frames received on the Ethernet line
interface will only be forwarded to the
deskphone if the VLAN ID equals the VLAN ID
used by the deskphone.
Untagged frames will continue to be forwarded
or not forwarded as determined by the
Ethernet switch forwarding logic.
74 1600 Series IP Deskphone Administrator Guide Release 1.3.5
Page 81

DNS Addressing
Note:
DNS Addressing
The 1600 IP Deskphones support DNS addresses and dotted decimal addresses. The deskphone
attempts to resolve a non-ASCII-encoded dotted decimal IP address by checking the content s of DHCP
Option 6. See DHCP Generic Setup
be a valid, non-zero, dotted decimal address, otherwise, DNS fails. The text string for the DOMAIN
system parameter (Option 15, Table 9
deskphone attempts DNS address resolution. If Option 6 contains a list of DNS addresses, those
addresses are queried in the order given if no response is received from previous addresses on the list.
As an alternative to administering DNS by DHCP, you can specify the DNS server and/or Domain name
in the HTTP script file. But first SET the DNSSRVR and DOMAIN values so you can use those names
later in the script.
Note: Administer Options 6 and 15 appropriately with DNS servers and Domain names
respectively.
on page 38 for information. At least one address in Option 6 must
) is appended to the address(es) in Option 6 before the
IEEE 802.1X
Certain 1600 Series IP Deskphones support the IEEE 802.1X standard for pass-through and
Supplicant operation. The system parameter DOT1X
multicast packets and proxy logoff, as follows:
● When DOT1X = 0, the deskphone forwards 802.1X multicast packet s from the Authenticator to the
PC attached to the deskphone and forwards multicast packets from the attached PC to the
Authenticator (multicast pass-through). Proxy Logoff is not supported.
● When DOT1X = 1, the deskphone supports the same multicast pass-through as when DOT1X=0.
Proxy Logoff is supported.
● When DOT1X = 2, the deskphone forwards multicast packets from the Authenticator only to the
deskphone, ignoring multicast packets from the attached PC (no multicast pass-through). Proxy
Logoff is not supported.
● Regardless of the DOT1X setting, the deskphone always properly directs unicast packet s from the
Authenticator to the deskphone or its attached PC, as dictated by the MAC address in the packet.
All 1600 Series deskphones support Supplicant operation and parameter values as specified in IEEE
802.1X, but, as of software Release 1.2, only if the value of the parameter DOT1XSTAT is "1" or "2". If
DOT1XSTAT has any other value, Supplicant operation is not supported.
IP deskphones will respond to unicast EAPOL frames (frames with the deskphone’s MAC address as
the destination MAC address, and a protocol type of 88-8E hex) received on the Ethernet line interface
if the value of DOT1XSTAT is "1" or "2", but will only respond to EAPOL frames that have the PAE
group multicast address as the destination MAC address if the value of DOT1XSTAT is "2". If the value
determines how the deskphones handle 802.1X
Issue 5 May 2014 75
Page 82

Administering Deskphone Options
Note:
of DOT1XSTAT is changed to "0" from any other value after the Supplicant has been authenticated, an
EAPOL-Logoff will be transmitted before the Supplicant is disabled.
As of software Release 1.2, the system parameter DOT1XSTAT determines how the deskphone
handles Supplicants as follows:
● When DOT1XSTAT=0, Supplicant operation is completely disabled. This is the default value.
● When DOT1XSTAT=1, Supplicant operation is enabled, but responds only to received unicast
EAPOL messages.
● When DOT1XSTAT=2, Supplicant operation is enabled and responds to received unicast and
multicast EAPOL messages.
Note: If the Ethernet line interface link fails, the 802.1X Supplicant, if enabled, enters the
Disconnected state. The 802.1X Supplicant variable userLogoff normally has a value of
FALSE. This variable will be set to TRUE before the deskphone drops the link on the
Ethernet line interface (and back to FALSE after the link has been restored). The
userLogoff variable may also be briefly set to TRUE to force the Supplicant into the
LOGOFF state when new credentials are entered.
802.1X Pass-Through and Proxy Logoff
1600 Series IP Deskphones with a secondary Ethernet interface support pass-through of 802.1X
packets to and from an attached PC. This enables an att ached PC running 802.1X supplicant software
to be authenticated by an Ethernet data switch.
The IP Deskphones support two pass-through modes:
● pass-through and
● pass-through with proxy logoff.
The DOT1X parameter setting controls the pass-through mode. In Proxy Logoff mode (DOT1X=1),
when the secondary Ethernet interface loses link integrity, the deskphone sends an 802.1X
EAPOL-Logoff message to the data switch on behalf of the attached PC. The message alerts the
switch that the device is no longer present. For example, a message would be sent when the attached
PC is physically disconnected from the IP deskphone. When DOT1X = 0 or 2, the Proxy Logof f function
is not supported
802.1X Supplicant Operation
1600 IP Deskphones that support Supplicant operation also support Extensible Authentication Protocol
(EAP), but only with the MD5-Challenge authentication method as specified in IETF RFC 3748
[8.5-33a].
76 1600 Series IP Deskphone Administrator Guide Release 1.3.5
Page 83

IEEE 802.1X
A Supplicant identity (ID) and password of no more than 12 numeric characters are stored in
reprogrammable non-volatile memory. The ID and password are not overwritten by deskphone
software downloads. The default ID is the MAC address of the deskphone, converted to ASCII format
without colon separators, and the default pa ssword is null. Both the ID and p assword are set to defaults
at manufacture. EAP-Response/Identity frames use the ID in the Type-Data field. EAP-Response/
MD5-Challenge frames use the password to compute the digest for the Value field, leaving the Name
field blank.
When a deskphone is installed for the first time and 802.1x is in effect, the dynamic address process
prompts the installer to enter the Supplicant identity and p assword. The IP de skphone does no t accept
null value passwords. See “Dynamic Addressing Process” in the Avaya 1600 Series IP Deskphones
Installation and Maintenance Guide. The IP deskphone stores 802.1X credentials when successful
authentication is achieved. Post-installation authentication attempts occur using the stored 802.1X
credentials, without prompting the user for ID and password entry.
An IP deskphone can support several different 802.1X authentication scenarios, depending on the
capabilities of the Ethernet data switch to which it is connected. Some switches may authenticate only
a single device per switch port. This is known as single-supplicant or port-based operation. These
switches typically send multicast 802.1X packets to authenticating devices.
These switches support the following three scenarios:
● Standalone deskphone (Deskphone Only Authenticates) - When the IP deskphone is
configured for Supplicant Mode (DOT1XSTAT=2), the deskphone can support authentication from
the switch.
● Deskphone with attached PC (Deskphone Only Authenticates) - When the IP deskphone is
configured for Supplicant Mode (DOT1X=2 and DOT1XSTAT=2), the deskphone can support
authentication from the switch. The attached PC in this scenario gains access to the network
without being authenticated.
● Deskphone with attached PC (PC Only Authenticate s) - When the IP deskphone is configured
for Pass-Through Mode or Pass-Through Mode with Logof f (DOT1X=0 or 1 and DOT1XSTAT=0),
an attached PC running 802.1X supplicant software can be authenticated by the data switch. The
deskphone in this scenario gains access to the network without being authenticated.
Some switches support authentication of multiple devices connected through a single switch port. This
is known as multi-supplicant or MAC-based operation. These switches typically send unicast 802.1X
packets to authenticating devices. These switches support the following two scenarios:
● Standalone deskphone (Deskphone Only Authenticates) - When the IP deskphone is
configured for Supplicant Mode (DOT1XSTAT=2), the deskphone can support authentication from
the switch. When DOT1X is "0" or "1", the deskphone is unable to authenticate with the switch.
● Deskphone and PC Dual Authentication - Both the IP deskphone and the connected PC can
support 802.1X authentication from the switch. The IP deskphone may be configured for
Pass-Through Mode or Pass-Through Mode with Logoff (DOT1X=0 or 1 and DOT1XSTAT=1 or
2). The attached PC must be running 802.1X supplicant software.
Issue 5 May 2014 77
Page 84

Administering Deskphone Options
Link Layer Discovery Protocol (LLDP)
Release 1.1 1600 Series IP Deskphones support IEEE 802.1AB. Link Layer Discovery Protocol (LLDP)
is an open standards layer 2 protocol IP Deskphones use to ad vertise their identity and cap abilities and
to receive administration from an LLDP server. LAN equipment can use LLDP to manage power,
administer VLANs, and provide some administration.
The transmission and reception of LLDP is specified in IEEE 802.1AB-2005. The 1600 Series IP
Deskphones use Type-Length-Value (TLV) elements specified in IEEE 802.1AB-2005, TIA TR-41
Committee - Media Endpoint Discovery (LLDP-MED, ANSI/TIA-1057), and Proprietary element s. LLDP
Data Units (LLDPDUs) are sent to the LLDP Multicast MAC address (01:80:c2:00:00:0e).
These deskphones:
● do not support LLDP on the secondary Ethernet interface.
● will not forward frames received with the 802.1AB LLDP group multicast address as the
destination MAC address between the Ethernet line interface and the secondary Ethernet
interface.
A 1600 Series IP Deskphone initiates LLDP after receiving an LLDPDU message from an appropriate
system. Once initiated, the deskphones send an LLDPDU every 30 seconds with the following
contents:
Table 11: LLDPDU Transmitted by the 1600 Series IP Deskphones
Category TLV Name (Type) TLV Info String (Value)
Basic Mandatory Chassis ID IPv4 IP Address of deskphone.
Basic Mandatory Port ID MAC address of the deskphone.
Basic Mandatory Time-To-Live 120 seconds.
Basic Optional System Name The Host Name sent to the DHCP server in
DHCP option 12.
Basic Optional System Capabilities Bit 2 (Bridge) will be set in the System
Capabilities if the deskphone has an internal
Ethernet switch. If Bit 2 is set in Enabled
Capabilities then the secondary port is
enabled.
Bit 5 (Deskphone) will be set in the System
Capabilities. If Bit 5 is set in the Enabled
Capabilities than the deskphone is registered.
1 of 3
78 1600 Series IP Deskphone Administrator Guide Release 1.3.5
Page 85

Link Layer Discovery Protocol (LLDP)
Table 11: LLDPDU Transmitted by the 1600 Series IP Deskphones (continued)
Category TLV Name (Type) TLV Info String (Value)
Basic Optional Management Address Mgmt IPv4 IP Address of deskphone.
Interface number subtype = 3 (system port).
Interface number = 1.
OID = SNMP MIB-II sysObjectID of the
deskphone.
IEEE 802.3
Organization
MAC / PHY
Configuration / Status
Reports autonegotiation status and speed of
the uplink port on the deskphone.
Specific
TIA LLDP MED LLDP-MED
Capabilities
TIA LLDP MED Extended
Power-Via-MDI
Media Endpoint Discovery - Class III - IP
Deskphone.
Power Value = 0 if the deskphone is not
currently powered via PoE, else the
maximum power usage of the deskphone
plus
all modules and adjuncts powered by the
deskphone in tenths of a watt.
TIA LLDP MED Network Policy Tagging Yes/ No, VLAN ID for voice, L2 Priority,
DSCP Value.
TIA LLDP MED Inventory – Hardware
MODEL - Full Model Name.
Revision
TIA LLDP MED Inventory – Firmware
BOOTNAME.
Revision
TIA LLDP MED Inventory – Software
APPNAME.
Revision
TIA LLDP MED Inventory – Serial
Deskphone serial number.
Number
TIA LLDP MED Inventory –
Manufacturer Name
TIA LLDP MED Inventory – Model
Name
Avaya Proprietary PoE Conservation
Level Support
Avaya Proprietary Call Server IP
Address
Avaya.
MODEL with the final Dxxx characters
removed.
Provides Power Conservation abilities/settings,
Typical and Maximum Power values.
OUI = 00-40-0D (hex), Subtype = 1.
Call Server IP Address.
Subtype = 3.
2 of 3
Issue 5 May 2014 79
Page 86

Administering Deskphone Options
Table 11: LLDPDU Transmitted by the 1600 Series IP Deskphones (continued)
Category TLV Name (Type) TLV Info String (Value)
Avaya Proprietary IP Phone Addresses Phone IP Address, Phone Address Mask,
Gateway IP Address.
Subtype = 4.
Avaya Proprietary File Server File Server IP Address.
Subtype = 6.
Avaya Proprietary 802.1Q Framing 802.1Q Framing = 1 if tagging or 2 if not.
Subtype = 7.
Basic Mandatory End-of-LLDPDU Not applicable.
3 of 3
On receipt of a LLDPDU message, the Avaya IP Deskphones will act on the TLV elements described in
Table 12
:
80 1600 Series IP Deskphone Administrator Guide Release 1.3.5
Page 87

Link Layer Discovery Protocol (LLDP)
Table 12: Impact of TLVs Received by 1600 Series IP Deskphones on System Parameter
Values
System
Parameter Name
TLV
Name
PHY2VLAN IEEE 802.1 Port
VLAN ID
L2QVLAN and
L2Q
IEEE 802.1 VLAN
Name
Impact
System value changed to the Port VLAN identifier in
the TLV.
The system value is changed to the TLV VLAN
Identifier. L2Q will be set to 1 (ON).
VLAN Name TLV is only effective if:
● The deskphone is not registered with the Call
Server.
● Name begins with VOICE (case does not
matter).
● The VLAN is not zero.
● DHCP Client is activated.
● The deskphone is registered but is not
tagging layer 2 frames with a non-zero VLAN
ID.
If VLAN Name causes the deskphone to change
VLAN and the deskphone already has an IP
Address the deskphone will release the IP Address
and reset.
If the TLV VLAN ID matches the VLAN ID the
deskphone is using, the VLAN ID is marked as set
by LLDP. Otherwise, if already registered, the
deskphone waits until there are no active calls,
releases its IP Address, turns on tagging with the
TL V VLAN ID, sets L2Q to "on," changes the default
L2Q to "on," and resets. If there is no valid IP
Address, the deskphone immediately start s t agg ing
with the new VLAN ID without resetting.
Issue 5 May 2014 81
Page 88

Administering Deskphone Options
Table 12: Impact of TLVs Received by 1600 Series IP Deskphones on System Parameter
Values (continued)
System
Parameter Name
L2Q, L2QVLAN,
L2QAUD,
TLV
Name
MED Network
Policy TLV
L2QSIG,
DSCPAUD,
DSCPSIG
MCIPADD Proprietary Call
Server TLV
TLSSRVR and
HTTPSRVR
Proprietary File
Server TLV
Impact
L2Q - set to “2” (off) If T (the Tagged Flag) is set to
0; set to “1” (on) if T is set to 1.
L2QVLAN - set to the VLAN ID in the TLV.
L2QAUD and L2QSIG - set to the Layer 2 Priority
value in the TLV.
DSCPAUD and DSCPSIG - set to the DSCP value
in the TLV.
A check is made as to whether a reset is necessary
to obtain a new IP address due to a change in the
values of the parameters L2Q or L2QVLAN.
This TLV is ignored if:
● the value of USE_DHCP is “0” and the value
of IPADD is not “0.0.0.0”, or
● the Application Type is not 1 (Voice) and is
not 2 (Voice Signaling), or
● the Unknown Policy Flag (U) is set to 1.
MCIPADD will be set to this value if it has not
already been set.
TLSSRVR and HTTPSRVR will be set to this value
if neither of them have already been set.
L2Q Proprietary 802.1
Q Framing
Proprietary - PoE
Conservation TLV
Extended
Power-Via-MDI
The default L2Q is set to the value of this TLV. No
change is made to the current L2 tagging, but the
new default value is used on the next reboot. If TLV
= 1, L2Q set to "1" (On). If TLV = 2, L2Q set to "2"
(Off). If TLV = 3, L2Q set to "0" (Auto).
This proprietary TLV can initiate a power
conservation mode. The deskphones that support
this will turn on/off the deskphone backlight and the
backlight of an attached Button Module in response
to this TLV.
Power conservation mode will be enabled if the
received binary Power Source value is 10, and
power conservation mode will be disabled if the
received binary Power Source value is not 10.
Power conservation mode is enabled even if the
deskphone is not powered over Ethernet because
the deskphone sends information about the power
source that it is using in a TIA LLDP MED Extended
Power-Via-MDI TLV; it is assumed that the power
management system intends to conserve local
power as well.
82 1600 Series IP Deskphone Administrator Guide Release 1.3.5
Page 89

Local Administrative Options Using the Deskphone Dialpad
!
CAUTION:
Local Administrative Options Using the Deskphone
Dialpad
The local procedures you use most often as an administrator are:
● CLEAR - Remove all administered values, user-specified data, option settings, etc. and return a
deskphone to its initial “out of the box” default values.
● DEBUG - Enable or disable debug mode for the button module serial port.
● GROUP - Set the group identifier on a per-phone basis.
● RESET - Reset all system values and system initialization values except AUTH, NVAUTH,
registration extension, and password to the default values. Also resets the 802.1X identity and
password to the default values.
● VIEW - Review the 1600 IP Deskphone system parameters to verify current values and file
versions.
● Ethernet Interface Enable/Disable - Enable or disable the Ethernet Interface locally.
Clear Procedure
Sometimes, you might want to remove all administered values, user-specified data, a nd option settings.
Essentially, you want to return a deskphone to its initial “clean slate” or out of the box condition. This is
usually done when passing a deskphone to a new, dedicated user when the user’s L O G O F F option
is not sufficient. For example, a new user is assigned the same extension, but requires different
permissions than the previous user.
The C L E A R option erases all administered data—static programming, file server and call server
programming, and user settings including Contact button labels and locally programmed Feature
button labels, and restores all such data to default values. The C L E A R option does not affect the
software load itself. If you have upgraded the deskphone, the deskphone retains the latest software.
Once you have cleared a deskphone, you can administer it normally.
CAUTION: This procedure erases all administered data, without any possibility of recovering the
data.
Issue 5 May 2014 83
Page 90

Administering Deskphone Options
!
Important:
Note:
Note:
Use the following procedure to clear the deskphone of its administrative, user-assigned and options
values.
1. While the deskphone is on-hook and idle, press the following sequence of keys on the faceplate of
the deskphone:
Mute 2 7 2 3 8 2 5 3 2 7 # (Mute C R A F T C L E A R #)
Important: 2 7 2 3 8 is the default password. If you have changed that password by changing the
value of PROCPSWD, replace 27238 with the latest password.
Note: Press the Mute button momentarily. Do not press this button while pressing other keys/
buttons.
The following text displays left-justified at the top of the display:
Clear all values?
*=no #=yes
2. If you do not want to clear all values, press * (no) to terminate the procedure and retain the current
values.
A screen displays the following prompt on the top line:
Are you sure?
*=no #=yes
3. Press the * button to terminate the procedure without clearing the values. Press the # button to
clear all values to their initial default values.
A confirmation tone sounds and the following text displays left-justified at the top of the display:
Clearing values.
The deskphone is cleared to its “out of the box” state.
Disabling or enabling the Debug mode
Note: The Debug mode is available only on the 1616 deskphone.
With Release 1.3.3, the Debug mode is available only if you change the default CRAFT
password. You can change the password to any value between 0000 to 9999999.
84 1600 Series IP Deskphone Administrator Guide Release 1.3.5
Page 91

Local Administrative Options Using the Deskphone Dialpad
!
Important:
Note:
Note:
Use the following procedure to turn the debug mode for the button module serial port to on or off.
1. While the deskphone is on-hook and idle, press the following sequence of keys on the faceplate of
the deskphone:
Mute XXXXX 3 3 2 8 4 # (Mute XXXXX D E B U G #)
where XXXXX is the changed or non-default CRAFT password.
Important: 2 7 2 3 8 is the default password. If you have changed that password by changing the
value of PROCPSWD, replace 27238 with the latest password.
Note: Press the Mute button momentarily. Do not press this button while pressing other keys/
buttons.
2. After entry of the command sequence, the following displays, based on the current value of the
system value NVDEBUG:
If NVDEBUG = 1: Debug mode=on
0=off #=OK
If NVDEBUG = 0: Debug mode=off
1=on #=OK
If a value different from the current NVDEBUG value is entered, the following text displays
left-justified at the top of the display:
Save new value?
*=no #=yes
3. Press the * button to terminate the procedure, or the # button to save the new value. If you press
the # button, the deskphone displays the following text:
New value being saved
The deskphone saves the new value.
Group Identifier
Use the following procedure to set or change the Group Identifier.
Note: Perform this procedure only if the LAN Administrator instructs you to do so.
The GROUP System Value on page 59.
For more information about groups, see
Issue 5 May 2014 85
Page 92

Administering Deskphone Options
!
Important:
Note:
!
CAUTION:
While the deskphone is on-hook and idle, press the following sequence of keys on the faceplate of the
deskphone:
Mute 2 7 2 3 8 4 7 6 8 7 (Mute C R A F T G R O U P)
Important: 2 7 2 3 8 is the default password. If you have changed that password by changing the
value of PROCPSWD, replace 27238 with the latest password.
Note: Press the Mute button momentarily. Do not press this button while pressing other keys/
buttons.
The following text displays left-justified at the top of the display:
Group=ddd
New=_
where ddd is the Group value.
1. Enter a valid Group value (0-999).
If a value different from the current Group value is entered, the following text displays left-justified at
the top of the display:
Save new value?
*=no #=yes
2. Press the * button to terminate the procedure, or the # button to save the new value.
If you press the # button, the following text displays:
New value
being saved
The new value is saved and the user interface is restored to its previous state.
Reset System Values
Use the following procedure to reset all system values and system initialization values except AUTH,
NVAUTH, registration extension, and password to the default values. Also resets the 802.1X identity
and password to the default values.
CAUTION: This procedure erases all static information except the extension number and password,
without any possibility of recovering the data.
86 1600 Series IP Deskphone Administrator Guide Release 1.3.5
Page 93

Local Administrative Options Using the Deskphone Dialpad
!
Important:
Note:
!
CAUTION:
1. While the deskphone is on-hook and idle, press the following sequence of keys on the faceplate of
the deskphone:
Mute 2 7 2 3 8 7 3 7 3 8 # (Mute C R A F T R E S E T #)
Important: 2 7 2 3 8 is the default password. If you have changed that password by changing the
value of PROCPSWD, replace 27238 with the latest password.
Note: Press the Mute button momentarily. Do not press this button while pressing other keys/
buttons.
The IP deskphones display the following text left-justified at the top of the display:
Reset values?
*=no #=yes
CAUTION: As soon as you press the # button, all static information except the extension number
and password will be erased, without any possibility of recovering the data.
2. If you do not want to reset the system values, press * (no) and proceed to Step 4.
The following prompt displays on the top line:
Are you sure?
*=no #=yes
3. Press the * button to continue without resetting the values and proceed to Step 4. Or, press the #
button to reset values to their defaults.
All deskphones display the following text left-justified at the top of the display while the system
values are reset to defaults:
Resetting
values.
The deskphone resets from the beginning of registration, which takes a few minutes.
4. If you do not reset the deskphone, the deskphone displays the following prompt:
Restart phone?
*=no #=yes
5. Press the * key to terminate the procedure without restarting the deskphone. Otherwise, press #
and perform the following Restart procedure.
Issue 5 May 2014 87
Page 94

Administering Deskphone Options
!
Important:
Note:
Restart the Deskphone
Use the following procedure to restart the deskphone.
1. While the deskphone is on-hook and idle, press the following sequence of keys on the faceplate of
the deskphone:
Mute 2 7 2 3 8 7 3 7 3 8 # (Mute C R A F T R E S E T #)
Important: 2 7 2 3 8 is the default password. If you have changed that password by changing the
value of PROCPSWD, replace 27238 with the latest password.
Note: Press the Mute button momentarily. Do not press this button while pressing other keys/
buttons.
The IP deskphone displays the following text left-justified at the top of the display:
Reset values?
*=no #=yes
2. Press the # button to reset values to their defaults, or * to continue a restart without resetting the
values to their defaults.
The deskphones display the following text left-justified at the top of the display while the system
values are reset to defaults:
Resetting
values.
Once the system values are reset, the following prompt displays on all IP deskphones:
Restart phone?
*=no #=yes
3. Press the * key to terminate the procedure without restarting the deskphone.
Press the # key to restart the deskphone.
The remainder of the procedure depends on the status of the boot and application files.
88 1600 Series IP Deskphone Administrator Guide Release 1.3.5
Page 95

Interface Control
!
Important:
Note:
Interface Control
Use the following procedure to set or change the interface control value.
1. While the deskphone is on-hook and idle, press the following sequence of keys on the faceplate of
the deskphone:
Mute 2 7 2 3 8 4 6 8 # (Mute C R A F T I N T #)
Important: 2 7 2 3 8 is the default password. If you have changed that password by changing the
value of PROCPSWD, replace 27238 with the latest password.
Note: Press the Mute button momentarily. Do not press this button while pressing other keys/
buttons.
2. After entry of the command sequence, deskphones with an internal Ethernet switch display the
following text, depending on the current interface control value:
PHY1=status
*=change #=OK
where status is the value of PHY1STAT, defined as:
● Status is auto when PHY1STAT = 1
● Status is 10Mbps HDX when PHY1STAT = 2
● Status is 10Mbps FDX when PHY1STAT = 3
● Status is 100Mbps HDX when PHY1STAT = 4
● Status is 100Mbps FDX when PHY1STAT = 5
3. To change the PHY1 value, press *.
Depending on the current value, the next sequential valid PHY1 value is selected and displayed as
the status. For example, if the current value is 10Mbps HDX (2), pressing * changes the value to 3
(10Mbps FDX).
4. Press the * button to terminate the procedure, or the # button to save the new value. If you press
the # button, the following text displays:
PHY2=status
*=change #=OK
where status is the value of PHY2STAT, defined as:
● Status is disabled when PHY2STAT = 0
● Status is auto when PHY2STAT = 1
Issue 5 May 2014 89
Page 96

Administering Deskphone Options
● Status is 10Mbps HDX when PHY2STAT = 2
● Status is 10Mbps FDX when PHY2STAT = 3
90 1600 Series IP Deskphone Administrator Guide Release 1.3.5
Page 97

Interface Control
● Status is 100Mbps HDX when PHY2STAT = 4
● Status is 100Mbps FDX when PHY2STAT = 5
5. To change the PHY2 value, press *.
Depending on the current value, the next sequential valid PHY2 value is selected and displayed as
the status. For example, if the current value is 10Mbps HDX (2), pressing * changes the value to 3
(10Mbps FDX).
The following text displays left-justified at the top of the display:
Save new value?
*=no #=yes
6. Press the * button to terminate the procedure, or the # button to save the new values.
If you press the # button, the following text displays.
New value
being saved
The new values are saved and a restart occurs automatically. The user interface is restored to its
previous state.
The View Local Procedure
If you are using static addressing and encounter problems, use the following procedure to verify the
current values of system parameters and file versions.
Issue 5 May 2014 91
Page 98
Administering Deskphone Options
!
Important:
Note:
1. While the deskphone is on-hook and idle, press the following sequence of keys on the faceplate of
the deskphone:
Mute 2 7 2 3 8 8 4 3 9 # (Mute C R A F T V I E W #)
Important: 2 7 2 3 8 is the default password. If you have changed that password by changing the
value of PROCPSWD, replace 27238 with the latest password.
Note: Press the Mute button momentarily. Do not press this key while pressing other keys.
The following text displays left-justified at the top of the display:
View settings
*=next #=exit
2. Press the * button at any time during viewing to display the next name and system value pair or
filename from Table 13
. The first pair returns after the last pair displays. Values that cannot display
on one line wrap to the next line.
Press the # button at any time during viewing to terminate the procedure and restore the user
interface to its previous state. The names and values display in the following order:
Table 13: Parameter Values
Name System Value Format
Model 16ccDccc Up to 8 ASCII characters: MODEL
Phone SN cccccccccccccccccc Deskphone Serial Number, up to 18
PWB SN cccccccccccccccccc Printed Wiring Board (circuit board)
PWB comcode nnnnnnnnn 9 ASCII numeric characters. Applies
MAC address hh:hh:hh:hh:hh:hh Each octet of the MAC address displays
value.
ASCII characters.
Serial Number, up to 18 ASCII
characters. Applies only to 16xx IP
Deskphones that have a
software-readable PWB serial number
and comcode.
only to 16xx IP Deskphones that have a
software-readable PWB serial number
and comcode.
as a pair of hexadecimal numbers.
1 of 3
92 1600 Series IP Deskphone Administrator Guide Release 1.3.5
Page 99

Table 13: Parameter Values (continued)
Name System Value Format
L2 tagging ccccccccc Up to 9 ASCII characters:
VLAN ID cccc Up to 4 ASCII characters. Value is
IP address nnn.nnn.nnn.nnn Up to 15 ASCII characters:
Subnet mask nnn.nnn.nnn.nnn Up to 15 ASCII characters:
Router nnn.nnn.nnn.nnn Up to 15 ASCII characters:
Interface Control
“on” if NVL2Q = 1
“off” if NVL2Q = 2
“auto: on” if NVL2Q = 0 and 802.1Q
tagging is on
“auto: off” if NVL2Q = 0 and 802.1Q
tagging is off
L2QVLAN if 802.1Q tagging is on or
“none” of 802.1Q tagging is off.
IPADD value.
NETMASK value.
the IP address of the router in use.
File server nnn.nnn.nnn.nnn.nnnnn Up to 21 ASCII characters: IP address
and port of last file server used
successfully during initialization or
“0.0.0.0” if no file server was used
successfully.
Call server nnn.nnn.nnn.nnn.nnnnn Up to 21 ASCII characters: IP address
and port of the call server currently in
use, otherwise “0.0.0.0.”
802.1X If DOT1X = 0
If DOT1X = 1
If DOT1X = 2
Pass-thru mode.
Pass-thru with Logoff.
Supplicant mode.
Group nnn Up to 3 ASCII numeric characters:
GROUP value.
2 of 3
Issue 5 May 2014 93
Page 100

Administering Deskphone Options
!
CAUTION:
Table 13: Parameter Values (continued)
Name System Value Format
Protocol: cccccccc
Up to 8 ASCII characters, currently only
“H.323.”
filename.ext
4 to 32 ASCII characters. The name of
the primary ("big app") image file
currently stored in the deskphone
(endptAPPINUSE).
cccccccc Ethernet
2 to 7 ASCII characters, either
“100Mbps”, “10Mbps”, or “No”
depending on the current speed of the
Ethernet line interface.
bootcodename
1 to 32 ASCII characters. The name of
the backup ("little app") image file
currently stored in the deskphone
(endptBOOTNAME).
Button Module 1 cccccccccccccc Up to 14 ASCII characters. The version
identifier of the software in the Button
Module, if applicable.
Button Module 2 cccccccccccccc Up to 14 ASCII characters. The version
identifier of the software in the Button
Module, if applicable.
Button Module 3 cccccccccccccc Up to 14 ASCII characters. The version
identifier of the software in the Button
Module, if applicable.
Static Addressing Installation
The usual way to assign IP addresses to IP deskphones is the automatic method. There might be
times, however, when manual assignment of IP addresses is desired.
CAUTION: Static addressing is necessary when a DHCP server is unavailable.
Because of the increased opportunities for text entry errors associated with static
addressing, we very strongly recommend that a DHCP server be installed and static
addressing avoided.
Use the following procedure to invoke manual address information programming.
1. Start manual address programming by performing one of the following steps:
3 of 3
94 1600 Series IP Deskphone Administrator Guide Release 1.3.5
 Loading...
Loading...