Page 1

Page 2

1-
-
~
ATSaT
t
308-380
Issue 1
AT&T
3270
lEmWlUa1.tCrf
ESCORTTM
User's Guide
-D-.-.-.-.-.-.-.-.-.-.-.-.-.-.-.-.-.-.-.-.-.-.-.-.-.-.-.-.-.-.-.-.-.-
L-o
•••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••
r!:.
~.
...............................................................
•
r·
-"
•••••••••••••••••••••••••••••
• I
•••••••••••••••••••••••••••••
• I
••••••••••••••••••••••••••••
•
"'_-'T1I" •••••••••••••••••••••••••••••
•
•••••••••••••••••••••••••••••
· ............................. .
· .............................. .
....
-
.............................................................
• I I
•••••••••••••••••••••••••••••
. , ............................ .
· ................................... .
· .............................. .
· .............................. .
· .............................. .
·
..
~,
............................ .
• I
•••••••••••••••••••••••••••••
• 1
••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••
....
"'
............................ .
· .............................. .
· .............................. .
· ................................
·.·A·.·.·.·.·.·.·.·.·.·.·.·.·.·.·.·.·.·.·.·.·.·.·.·.·.·.·.·.x
:.:1
~.:.:.:.:.:.:.
· .............................. .
· .............................. .
· ............................. .
· . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
• r ~
•••
..
.... ' ..................... .
••
J
~...
•••
• • • • • • I •
·;"!r:·:·:·:·
. ............................ .
•
L._~·
••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••
· .............................. .
·rr~~:.:.:.:.:.:.
. ............................ .
L.
.•
..J
••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••
· ............................... .
· ............................... .
:I~.:.:.:.:.:.:.
•
t..-.....I •••••••••••••••••••••••••••••
· .............................. .
~
.....................................•...•.•.•••
•
If
••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••
. ............................. .
·
~
............................. .
· ................................ .
-!
.. ! ..
!
.. ! ..
!.... •
:.:.:
.:.:.:
.:.:.:.:.:.:.:.:.:.:.:.:.:.:.:.x
[ -
........................
'
••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••
••••••••••••••••••••
.•
:-:
.:.:.:.:.
:.:.:.:.:.:.:.:.:.:.:.:.:.:.:-:.:.:
:.:.:.:.
:.:.:.:.:.:.:.:.:.:.:.:.:.:.:.:.:.:.:
:.:
.:.:.:.:.:.:.:.:.:.:.:.:.:.:.:.:.:.:.:.:.x
....
-!
... ! ... ! ... ! ...
!-~-~-.
-~-!-~-!-!-~-!-~-~-~-~-!-!-~-!-~.J!I-_
•
iii
•
.
..,.
••
..
.
.
...
~
...........
.
•••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••
...
:.:.:.:.:.:.:-:.:.:.:.:.:.:.:.:.:.:.:.:.:.:.:.:.:.:.:.:.:.:.:.:.:.:.:
+
..
1
1
Page 3

©1988
All
Printed
NOTICE
The
assumes
DEC
Corporation.
I
Machines Corporation.
MS-DOS
Tektronix
AT&T
Rights Reserved
in
USA
information
is
a registered trademark
BM
is
a registered trademark
in
no
responsibility for any errors that may appear
is
a registered trademark of Microsoft Corporation.
is
a registered trademark of Tektronix,
this document
and
and
is
subject
VT100
CICS
to
change without notice.
in
this document.
is
a trademark of Digital Equipment
is
a trademark of International Business
Inc.
AT&T
Page 4

Contents
1
2
Getting Started
Overview
What
Is
In
This Guide
Before You Begin
Other
ESCORT Documentation
Using ESCORT
OverView
Using Interactive, Script, and Tutorial Modes
Working in Host and Local Sessions
ESCORT Utility Files
Command Line
Special
Key
Combinations
Glossary
Appendix
Appendix
A:
Key Sequences
B:
Environment
Variables
1-1
1-3
1-7
1-9
2-1
2-3
2-23
2-39
2-41
2-43
A-1
8-1
Appendix
C:
Interpretation of
Attribute Bytes
Index
C-1
Page 5

Page 6

1 Getting Started
Overview 1
-1
What Is In This Guide 1 -3
Organization
Conventions
of
This Guide 1 -3
1
-4
Before You Begin 1 -7
Other ESCORT Documentation 1 -9
Page 7

Page 8

Overview
This user's guide contains the information you need to know to
use
ESCORT™.
This guide assumes
o operate
terminal
o use
host (for
VM/CMS, CICS
o use
based
Before you begin using
an
an
application running
an
application running
AT&T
that
IBM®
exampleiMan
3278 or
,or
3B
processor.
ESCORT, you should understand
a user knows how to
DEC®
on
IBM
host system under IMS, TSO,
VTAM)
on a UNIX®
VT100™ (or similar)
a synchronous or asynchronous
operating system
o the modes of operation featured in ESCORT
o
the
special features of the software
o the concept of accessing multiple sess'ions.
..
Overview
1-1
Page 9

Page 10

What Is
In
This Guide
Organization of This Guide
This guide
Getting Started
contains information about this user's guide. Read this chapter
to learn how
used throughout
Using ESCORT
discusses
multiple sessions. Special features,
files available,
presented
Appendices
is
divided into five parts:
the
guide
is
organized, and what conventions are
the
guide.
the
procedures for using ESCORT and accessing
the
types of ESCORT utility
~nd
ESCORT special key combinations are also
in
this chapter.
A:
Appendix
consists of tables
and/or key sequences for specific terminal types.
Appendix
provides informatton
Appendix
contains information
Key Sequences
that
present functions and
B:
Environment Variables
on
setting environment variables.
C:
Interpretation of
on
reading attribute bytes.
the
associated
Attrib~te
Bytes
keys
Glossary
contains definitions for terms and acronyms used in this guide.
Index
lists page references for locating specific items
What
in
this guide.
Is
In
This
Guide
1-3
Page 11

Conventions
Documentation Conventions
The
conventions listed below are used throughout this guide:
o Special function keys
in a rectangle with rounded comers; for example,
o Standard alphabetic and numeric
keyboard are printed in bold; for example,
o Two or more
should press each key sequentially; for example,
keys
o Two keys separated by a hyphen indicate
hold down
second key; for example, ( CTRL) - d.
the
first key while simultaneously pressing
on
your terminal keyboard are enclosed
keys
on
your terminal
f.
separated by spaces indicate
that
you should
tfat
ESC
@.
YjU
f
the
1.
o Commands, functions, and keyword operands are printed in
bold capital letters. Functions always start with a dollar sign
($). For example,
$SCAN
is
a function.
o ESCORT specific key functions and other key functions are
printed in capital letters; for example, CLEAR.
o
The
following type
at
the
o
The
following type
system displays
terminal:
escort scrlpt-IJame
auto script generation started
is
used to indicate data
is
used to indicate information
on
the
screen:
that
the
user types
that
the
o
The
following type
CONNECT
o Multi
o Brackets [ ] indicate optional operands.
..
word operands are separated by
example,
str_expr represents
is
used to indicate program text:
(HI)
an
the
words, string expression.
o Braces { } indicate a choice of operands.
o
The
UNIX file
character
operating system and
versions of
1-4 Getting Started
path
names are shown with
(I). Scripts are portable between
the
MS
..
DOS®
ESCORT and you may, therefore, substitute
operating system
underscore. For
the
standard slash
the
UNIX
the
Page 12

standard UNIX operating system slash character with
MS
..
DOS
operating system back
character. .
..
slash (\) file name separation
the
Note
Throughout this guide, default key combinations are shown for
ESCORT
Interrupt/Resume (I/R) key combination
sequence
amended by the
environment.
specific functions, for example,
~
f
2.
These default key combinations may be
System Administrator for your particular
If
the
ESCORT
amended you
key combinations for
combinations shown
the
example scripts and
in
this user's guide.
default key combinations are
must
substitute
the
default
in
the
the
the
ESCORT
is
shown
the
document text,
sample programs
as
amended
the
key
Data Entry Conventions
o
ESCORT
lowercase characters
to this
is
case
insensitive, which means
is
string constants.
the
same
as
uppercase.
that
it treats
The
exception
o
The
UNIX shell
lowercase characters differently from uppercase. Thus, when
you invoke
command line,
exactly
the
is
case
sensitive, which means
ESCORT with parameters from
the
same
parameters, such
as
those
in
the
as
file names, must be
file system.
that
the
UNIX shell
Definitions
The
following term
Host
is
used throughout this user's guide.
A host session refers to either a synchronous
or
an
session
otherwise specifically noted.
asynchronous session, unless
What
Is
In
This
Guide 1-5
it
treats
Page 13

Page 14

Before You Begin
Before you begin using ESCORT, you should review your specific
operating procedures with your System Administrator and
the
familiarize yourself with
key sequences used in ESCORT:
o Your System Administrator will install
on
the
3B computer and will arrange for
ESCORT to suit your particular location and operating
environment.
Administrator
operating
you of any specific restrictions or requirements.
o You should familiarize yourself with the key sequences
applicable to your terminal. Refer to Appendix A
Quick Reference Card for
your specific ASCII terminal.
of
Some
asynchronous environment. Refer to
the
for
sequences applicable in
o
The
keys, performs special tasks in
combinations are defined
your Quick Reference Card. Familiarize yourself with these
ESCORT specific key combinations.
o Part of
includes
different types
Review with your System Administrator any additional
combinations
environment. Your System Administrator will also advise
any changes to
VT100 terminal, in Appendix
Escape key,
the
When
the
ESCORT, your System Administrator will advise
the
key sequences listed may
System Administrator's installation procedure
the
customization
of
that
you review with your System
environment in which you will be
the
appropriate key sequences for
an
asynchronous environment.
~,
terminals
the
used with certain other terminal
ESCORT. These special key
in
this section and are also listed
of
the
that
will be used
have been defined for your operating
ESCORT specific key combinations.
the
ESCORT
the
customization of
not
be applicable in
the
key sequence table
A,
for
the
key
key sequences for
in
your system.
or
the
software
your
an
in
key
of
You can list these customized key sequences
on
provided
your Key Sequence Card.
Before You Begin 1-7
in
the
space
Page 15

Refer to Appendix B for information
ESCORT environment variables.
Once
you become familiar with
the
proceed to
next section, which describes the procedures for
the
entering the three different modes of
on
setting
the
various
keyboard layout, you can
ESCORT.
1-8 Getting Started
Page 16

Other ESCORT
Documentation
This User's Guide
ESCORT documentation.
includes the following:
o
AT&T
Programmer's Guides
AT&T
This binder contains the following three documents:
o
ESCORT
AT&T
publication number 308
ESCORT Overview
ESCORT User's Guide
ESCORT Programmer's Guide
publication number 308
is
part of the
3270
Emulator+
Quick Reference Card and
AT&T
The
entire documentation package
ESCORT
..
..
389.
3270 Emulator+
User's
402.
Key
and
Sequence Card,
Other
ESCORT
Documentation 1-9
Page 17

Page 18

Page 19

2 Using ESCORT
Overview
Using
Interactive, Script,
and Tutorial Modes
Interactive Mode
Script Mode
Tutorial Mode
Interactive Mode Special Features
Working
in
Host and
Local Sessions
Session Identification
Active and Displayed Sessions
in Script Mode
Active and Displayed Sessions
in Interactive Mode
Status Line Information
Modes of Operation Summary
ESCORT Utility Files
2-1
2-3
2-4
2-7
2-12
2-15
2-23
2-23
2-24
2-27
2-34
2-35
2-39
Command Line
Special Key Combinations
2-41
2-43
Page 20

Page 21

Overview
The
first section of this chapter describe
modes of
description of the multiple sessions abilities of the software.
Read these sections to understand how to access different host
and local sessions either interactively or via script control.
The
utility files and command line structure, and the final section
describes the operation of
combinations.
chapter will allow you to make optimal use of
ESCORT.
next two sections of this chapter contain information
The
An
understanding
next
section provides a detailed
the
ESCORT specific key
of
the
three operating
the
information in this
ESCORT.
on
Overview
2-1
Page 22

Page 23

Using Interactive, Script,
and Tutorial Modes
There are three modes of operation in ESCORT: Interactive
Mode, Script Mode, and Tutorial Mode.
o Interactive (or Terminal Emulation) Mode. This mode
provides simultaneous access to multiple host applications.
Special
o Script Mode. This mode allows you to simulate a user on
one of
ESCORT accepts data from a script instead of from the
keyboard.
instructions contained in the script.
ESCORT features are available in this mode.
the
multiple sessions. While in Script mode,
ESCORT can simulate a user by executing the
o Tutorial Mode. This mode
however, it can be used to verify data entered by the operator
before sending data to the host.
This section contains
the
is
similar to Interactive mode,
procedures for using these three modes.
Using Interactive, Script, and Tutorial Modes 2-3
Page 24

Interactive Mode
In
Interactive mode, you can work
you were entering data
DEC
VT100 asynchronous terminal connected to a host
on
an
computer.
To
enter Interactive mode:
1 Enter one of the following commands at the shell prompt,
depending
on
the session type.
on
your application just
as
IBM 3278 synchronous terminal or
if
D For a synchronous host, type escort and press (
D For
You
an
asynchronous host, type escort async.p t
( RETURN).
will see
the
ESCORT banner screen briefly before you
get to your initial application screen.
2
Log
in to your application and continue to use the terminal
as
you usually do.
3
To
leave Interactive mode and return to the UNIX shell, you
can use a special key combination, QUIT.
Interactive mode, press
~
f 1.
To
RETURN)
and
QUIT
•
press
t
The
async.p
ESCORT script
parameters to a specific asynchronous host.
SERINIT
operating environment.
2-4
Using
command contained in the script must be amended to suit your
ESCORT
is
used to initialize the communication port
The
default operands to the
Page 25
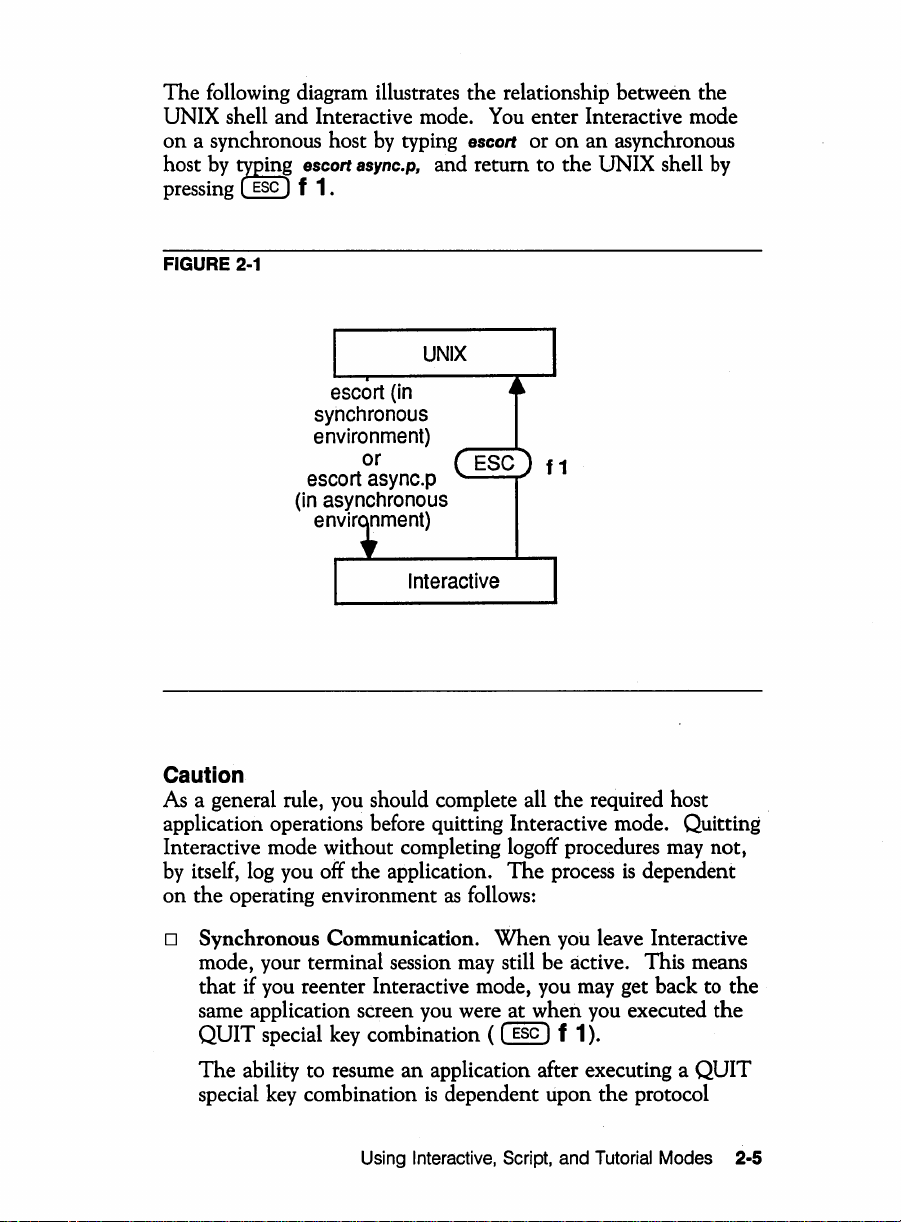
The following diagram illustrates the relationship between the
UNIX shell and Interactive mode.
on
a synchronous host
by
host
pressing
(,piny escort Bsync.p, and return to the UNIX shell
ESC
f
1.
by
typing escort or
You
enter Interactive mode
on
an asynchronous
by
FIGURE
2-1
escort
synchronous
environment)
or
escort
async.p
(in
asynchronous
envir
nment)
UNIX
(in
f1
Interactive
Caution
As a general rule, you should complete all the required host
application operations before quitting Interactive mode. Quitting
may
Interactive mode without completing logoff procedures
by
itself, log you off the application.
on
the operating environment
as
The
follows:
process
is
dependent
not,
o Synchronous Communication.
mode, your terminal session
that
if you reenter Interactive mode, you
same application screen you were at
QUIT
The
special
key
combination ( ( ESC) f 1).
ability to resume an application after executing a
special key combination
Using Interactive, Script, and Tutorial Modes 2-5
may
is
dependent upon the protocol
When
you leave Interactive
still be active. This means
may
get back
to
when you executed the
QUIT
the
Page 26

being used (bisynchronous communication,
Synchronous Data Link Control in
parameter defined in
and
the
application itself. Refer to
documentation to determine whether you will be able to
an
resume
environment.
In
addition,
environment may affect your ability to resume
after executing a
the
AT&T
Guides
application
the
3270 Emulator+ User's and System Administrator's
for further information.
the
host system front
in
your particular operating
controller configuration file in
QUIT
special key combination. Refer
an
the
bsc,
or
sna environment);
..
end,
VT
AM
appropriate
the
sna
an
application
the
..
GEN;
to
o Asynchronous Communication. Executing a
in
an
key combination
same result
disconnecting
If
the
using
Interactive mode will
application. However, unlike
you will
QUIT
the
While
features
in
of
as
,breaking the host connection by, for example,
the
Interactive asynchronous host operation
the
UNIX operating system nohup command, quitting
not
be
able to resume
special key combination.
Interactive mode, you can choose any
ESCORT:
asynchronous session produces
modem.
not
affect
the
operation of
the
synchronous environment,
the
application after executing
o Automatic Script Generation (ASG)
o Automatic Screen Logging (ASL)
o Display Screen Attributes (A TTRIB) ,
(synchronous communication only)
o Local Screen Printing
o Escape to
the
UNIX shell
o Activate, open and close host sessions
o Display active sessions (SHOW)
QUIT
was
of
the
special
the
executed
the
following
These features are described
2-6
Using
ESCORT
in
more detail later
in
this section.
Page 27

Script Mode
Script mode
mode, you can simulate a user
mode,
keyboard. A script
To
activate Script mode, type
escort script-IJame
and press ( RETURN).
The
script-IJame
The
ESCORT
performs syntax checking and parsing. ESCORT
the
appropriate host application screen and starts to execute
commands from
data entered
application may be displayed
is
the
most powerful feature
at
a terminal. While
of
ESCORT.
ESCORT accepts data from a script instead
is
a set
of
commands contained in a file.
is
the
name
of
the
script you want to execute.
banner screen appears briefly while ESCORT
then
the
parsed list. During execution of
on
the
screen and responses received from
on
the
monitor.
of
In
in
this
your
displays
the
script,
the
Script
the
host
When
statement), ESCORT
the
last statement
in
the
program
is
terminated and control
is
reached (the
is
returned to
ENDP
the
UNIX operating system. You can also terminate script execution
the
prematurely (before
ENDP
quitting script mode (pressing
statement
@)
f 1).
is
encountered)
by
Using Interactive, Script,
and
Tutorial
Modes 2-7
Page 28
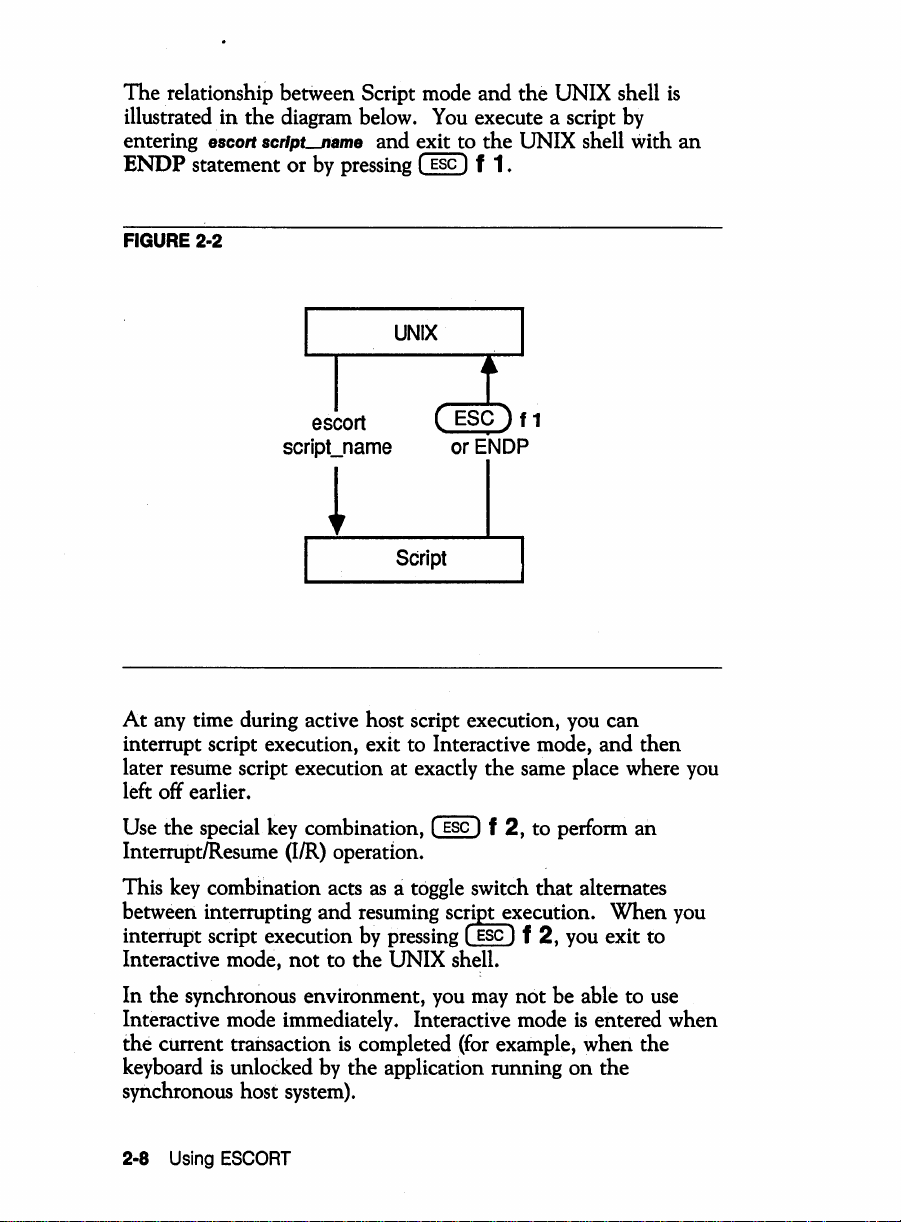
The relationship betWeen Script mode and the UNIX shell
illustrated in
entering escort scrlpLname and exit to the UNIX shell with
ENDP
the
diagram below .
statement or
by
pressing
You
execute a script
@§)
f
1.
by
is
an
FIGURE
2·2
escort
script_name
or
ENDP
~
Script
At
any time during active host script execution, you can
interrupt script execution, exit to Interactive mode, and then
later resume script execution at exactly the same place where you
left off earlier.
Use the special key combination,
InterruptlResume
This
key
combination acts
between interrupting and resuming
interrupt script execution
Interactive mode,
In the synchronous environment, you may
Interactive mode immediately. Interactive mode
the current transaction
keyboard
synchronous host system).
2·8
Using
is
ESCORT
(IIR)
not
unlocked
operation.
as
by
to the UNIX shell.
is
completed
by
the application running
@§)
f
2,
a toggle switch
SC(ipt
ejecution.
pressing
ESC
(for
example, when the
to perform an
that
f
2,
not
be able to
alternates
When
you exit to
use
is
entered when
on
the
you
Page 29

Interactive mode
asynchronous host script execution. However,
transaction may continue to execute.
is
entered immediately when you interrupt
the
current
Another
mode
command can be coded anywhere in your program. ESCORT
commands are discussed in detail
is
to use
way
to enter Interactive mode from active host Script
an
EXIT
command in a script.
in
the ESCORT
The
Programmer's
EXIT
Guide.
Once
you are in Interactive mode (either due to a manual
interrupt by pressing
script), you can press
combination) to
The
following diagram illustrates the relationship of host Script
mode to Interactive mode and
you want to quit script execution and return to
Use @ f 2 if you want to interrupt script execution and enter
Interactive mode.
@ f 2 or due to
an
EXIT
command in a
@ f 2 (the Interrupt/Resume (I/R) key
go
back to Script mode.
the
UNIX shell. Use @ f 1 if
the
UNIX shell.
Using Interactive, Script, and Tutorial Modes 2-9
Page 30
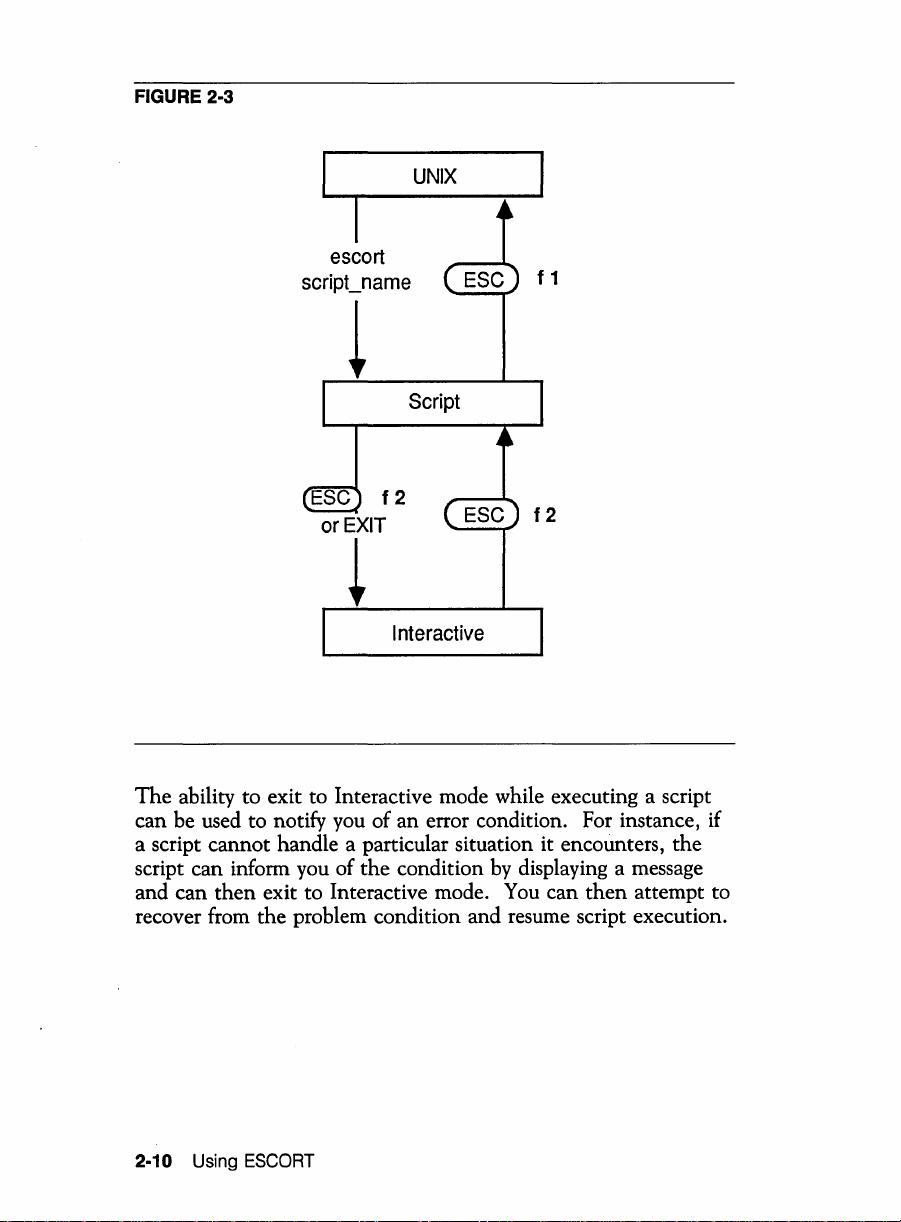
FIGURE 2-3
escort
script_name
~
UNIX
f 1
Script
or
f2
EXIT
f2
~
Interactive
The
ability to exit to Interactive mode while executing a script
can be used to notify you of an error condition. For instance, if
a script cannot handle a particular situation it encounters,
script can inform you of
and can
recover from the problem condition and resume script execution.
then
exit to Interactive mode.
the
condition by displaying a message
You
can
then
the
attempt to
2-10
Using
ESCORT
Page 31

You
will automatically be put back into Interactive mode
ESCORT if two error conditions occur. Both
conditions cause
print file and displayed in the operator information area, before
exiting to Interactive mode.
an
error message to be printed in
The
two conditions are:
of
these error
an
by
ESCORT
o A response has
user
..
specified time
60 minutes.
not
arrived from the host system before a
..
out occurs.
The
default time
..
out period
o A script attempts to enter data in a protected field
screen. This situation occurs if you have a bug
if
an
unexpected screen
which case
application screen.
the
script gets out of synchronization with the
is
received from
the
in
host system, in
is
on
a
a script or
Using Interactive, Script, and Tutorial Modes 2-11
Page 32

Tutorial Mode
Tutorial mode provides you with
checks and validate data entry before sending data to
is
execution. This mode
your application.
Tutorial mode can be entered from a script by executing one of
EXIT
two
connected. Host and local connections are described
detail later
commands, depending upon which session
in
this section.
also useful
the
ability to perform edit
as
an
on
..
line tutorial for
the
host for
is
currently
in
more
If connected to a host session, Tutorial mode
executing
EXIT
(TUTORIAL)
If connected
executing
to
a local session, Tutorial mode
EXIT
The
following diagram summarizes
to
Script mode
shell.
Tutorial mode, Interactive mode, and
the
means of getting from
is
entered
is
entered
the
by
by
UNIX
2-12
Using
ESCORT
Page 33

FIGURE 2-4
EXIT
(T~TORIAL)
in
host
session
or
I
EXIT
in
local
session
escort
script_name
t
t
AID
key
UNIX
Script
or
EXIT
f 1
f2
f2
Tutorial
Entering Tutorial mode
from a script since you enter Tutorial mode
command. However, unlike Interactive mode, when you press
Attention
screen), script execution
data
The
o in
CLEAR,
Identifier (AID) key (after entering data
is
not
sent to the host system.
AID
keys
are
the
synchronous environment, ENTER,
PAl
is
similar to entering Interactive mode
is
resumed automatically but the entered
to PA3,
Using Interactive, Script, and Tutorial Modes 2-13
ATTN,
and
Interactive
by
using
on
PFl
SYS~EQ
an
EXIT
the
to PF24,
an
Page 34

o in
In
to send data to
script perfonn edit checks
pressed.
the
data and send a message to you to correct and reenter it.
The
discussed under
Programmer's Guide.
the
asynchronous environment, ENTER, PFI to PF8
(corresponding to soft function keys @ to @ ) and
CLEAR.
Tutorial mode it
The
data
as
an
way
ESCORT
is
up to
the
script to decide whether or
the
host. This provides
on
entered data and
script may
input parameter later
the
then
send
handles AID commands and AID
CONNECT command in
the
in
the
data to
the
ability to have a
on
the
AID key
the
host and use
script, or reject
keys
the
ESCORT
not
the
is
2-14 Using ESCORT
Page 35

Interactive Mode Special Features
This section describes
you can use from Interactive mode. They are Automatic Script
Generation (ASG), Automatic Screen Logging (ASL) , Displaying
Screen Attributes, Local Screen Print, and Escape to the UNIX
shell.
the
additional features of ESCORT
that
Using Interactive, Script, and Tutorial Modes 2-15
Page 36

Automatic Script Generation (ASG)
ESCORT has a feature
the
simulate
To
generate a script automatically, you must
actions you perform
mode. From Interactive mode, press
auto script generation started
that
automatically generates a script to
at
a terminal.
be
@ f
3.
in
Interactive
The
message
appears
tasks you wish oil
work, you again press
message
Each time you automatically generate a script, it
file, in the directory defined by
variable, named
To
1 Exit Interactive mode. Press @ f
2 Execute
When
same tasks
at
the
bottom
is
displayed:
auto script generation stopped
of
you~ication.
~
escort.ky{proc,id}.
execute
the
the
you run
that
automatically generated script:
script by typing escort escort.ky{proc-Id}.
the
script, ESCORT automatically performs
you just did
the
screen. Continue to perform
After you complete your
f 3 to turn off
ASG.
is
the
ESCDIR environment
1.
at
your terminal.
the
The
following
written to a
the
Try using this feature to generate a script to perform your login
procedures for you. This
a good
way
to see how
ESCORT
is
works for yourself, and you can use this script whenever you need
to
log in to your application. Sample login and logoff scripts for
IMS and
TSO
are provided
on
your ESCORT installation
diskette.
Note
The
generated script may require editing prior to execution so
that
both
variable responses and multiple responses from
the
host
may be anticipated.
Refer to the section, "Synchronizing Data Transmissions"
Chapter 2
in
the
ESCORT
Programmer's
Guide
for further
information.
2-16 Using
ESCORT
in
Page 37

Automatic Screen Logging (ASL)
The
automatic screen logging feature saves
application screen and any data entered
an
Interactive mode in
k(y
special
pressing
cjmbination
ESC
f
6.
auto screen logging started
active host session, you
for Automatic Screen Logging by
The
message
the
on
image of a specific
it. While in
can
select the
appears
the
work, you again press
message
Screen images are captured when
o In
o In
at
the
bottom
tasks you wish
of
on
your application. After you complete your
@ f 6 to
is
displayed:
auto screen logging stopped
the
synchronous environment, press ENTER, PFn, PAn,
CLEAR,
ATTN
the
asynchronous environment, press ENTER, PFI to PF8
or
your screen. Continue to perform all
tum
off ASL.
an
AID key
is
SYS.-REQ.
(corresponding to soft function keys @ to ® ) or
CLEAR.
The
screen image
the
ESCDIR environment variable,
escort.lg{proc~id}
.
is
logged
in
the directory defined by
in
the
file named
The
following
pressed.
Using Interactive, Script, and Tutorial Modes 2-17
Page 38

Displaying Screen Attributes
The
Displaying Screen Attributes feature shows you attributes
a specific synchronous host application screen, such
an
and unprotected fields. While you are using
in
screen
screen by pressing
to
Appendix C for information
displayed
The
Interactive mode, you can see
the
special key combination @ f
on
at
the
attribute positions
Displaying Screen Attributes feature has
the
translating
on
the
asynchronous environment.
application
attributes
the
screen.
no
characters
effect
as
protected
on
the
5.
in
of
Refer
the
2-18
Using
ESCORT
Page 39

Local Screen Print
The
Local Screen Print feature saves
in
While
can save
sequence for
specific key combination for
terminal.
The
accordance with
Interactive mode in either a host or local session you
the
current screen image
the
PRINT
function. Refer to Appendix A
information contained in
the
following:
the
the
PRINT
the
current screen image.
by
pressing
function for your
screen image
the
appropriate key
is
saved in
for
the
Synchronous session Local Screen
D
If
the
3270 Emulator+ variable PRNT
Screen Print images are saved
D If
the
3270 Emulator+ variable PRNT
Screen Print images are saved
Print
in
in
is
specified, Local
the
specified file.
is
not
the
directory defined
set, Local
ESCDIR environment variable, in a file named
escort.pr{proc-id} .
D Local Screen Print output can be directed using
function.
Asynchronous session Local Screen
D
If
the
variable PRNT
images are saved
D If
the
variable PRNT
Print images are saved in
in
is
set in your profile, Local Screen Print
the
specified file.
is
not
the
Print
set
in
your profile, Local Screen
directory defined by
ESCDIR environment variable, in a file named
escort.pr{proc-id} .
D Local Screen Print output can be directed using
function.
Directing Local Screen Print Using IDENT
While
direct Local Screen Print output by pressing
sequence for
in
Interactive mode in a host or local session, you can
the
appropriate key
the
IDENT function. You
can
select
screen print modes:
the
the
one
IDENT
the
IDENT
of
four
by
the
D Press 0 to disable Local Screen Print.
The
PRINT
function key
is
disabled and any attempt to use
Local Screen Print causes the following message
in
the
displayed
operator information area:
Using Interactive, Script, and Tutorial Modes 2-19
to
be
Page 40

Screen Print Disabled
o Press 1 to direct Local Screen Print output to a file.
ESCORT
permission for the specified pathname, a message
and you must reenter
prompts for a pathname; if you do
the
required mode number.
not
have write
is
displayed
o Press 2 to pipe Local Screen Print output to a UNIX
operating system command.
ESCORT
specifies
PRINT
directed
o Press 9 to retain
prompts for a valid command line; for example,
lusrlblnllp
the
printer spooler
lp.
Subsequent use
of
the
function causes Local Screen Print output to be
to
the
system default printer.
the
present screen print mode.
2-20
Using
ESCORT
Page 41

Escape to the UNIX Shell
While in Interactive mode in either a host or local session, you
can escape to
ESCORT
the
SHELL function, to escape from Interactive mode to the
UNIX shell. Refer to Appendix A for the specific
combination for the SHELL function for your terminal. Once in
the
UNIX shell you will be able to perform any of the Restricted
Shell mode functions.
prompt
to return to ESCORT Interactive mode.
the
UNIX shell
is
executing. Press the appropriate key sequence for
Press (
exit
on
the
machine
CTRL)
- d or type at
on
which
key
the
shell
This feature
ability to check the contents of a
is
useful, for example, in providing you with the
UNIX file to ensure
that
download of data from a host system has been completed
successfully.
a
Using Interactive, Script, and Tutorial Modes 2-21
Page 42

Page 43

Working
in
Host and
Local Sessions
ESCORT
sessions. This section describes
and contains
sessions.
scripts are able to access various host and local
the
concept of multiple sessions
the
procedures for accessing and displaying these
Session Identification
ESCORT
of
10 concurrent sessions from a single script. Sessions are either
host or local. Each session
identification:
D
provides
Host
Sessions. Host sessions may utilize either synchronous
or asynchronous communications.
eight host applications, of which four may be synchronous
and four may be asynchronous.
ESCORT allows for automatic or interactive switching
between sessions and for
applications.
The
synchronous host session identifications are
H3, and H4.
The
asynchronous host session identifications are
A2, A3, and A4.
the
user with
the
ability to access a maximum
in
ESCORT has a session
ESCORT can access
the
exchange of data between
HI,
AI,
up
H2,
to
D Local Sessions.
an
from
end
-
Each session has its own presentation space; presentation space
and session are synonymous. Sessions can be considered
virtual terminals, while
screen buffers for those terminals.
ESCORT script. Local sessions can provide a front,
user interface, for data entry or display.'
The
local session identifications are
Up
to two local sessions can be connected
Ll
and L2.
the
presentation spaces are
Working in Host and Local Sessions 2·23
the
as
associated
Page 44

Active and Displayed Sessions
in
Script Mode
Active Sessions
Only one session can be active at any given time;
session
ESCORT script. All other sessions are dormant. You can
change a dormant session into
is
any host or local session
that
is
an
active session
connected to
CONNECT command.
The
communication ports used
initialized by using the
SERINIT command.
in
asynchronous host sessions are
by
an
using
active
the
the
All terminal keyboard
active session. However, in relation to all dormant sessions,
keyboard
combinations,
These special
in this section.
When
session
session's relevant application screen
default can be changed by specifying a session identification
parameter in the
discussed in detail in
The
exchange data easily and quickly between sessions. Data can be
manipulated by using reading, writing and searching commands
in the active session's presentation space.
A session
a script.
data from one active session to another.
moved from local session LI to synchronous host session
1 Use
is
disabled, with the exception of two
QUIT
key
ESCORT
HI
is
connected and
flexible multiple session features of ESCORT allow you to
is
made active by use
The
following procedure illustrates how you can move
the
CONNECT command to make
active, for exampie,
CONNECT
(ll)
keys
are available for you to use with
reci)l
(
~
f
1)
and
SHOW
combinations are described in more detail later
is
started in Script mode, the synchronous host
is
the
active session by default. This
is
also displayed. This
(
ESC
an
the
key
f 9).
as
PROG statement. ESCORT commands are
the
ESCORT
Programmer's
of
the CONNECT command in
In
Guide.
this example, data
HI:
the
source session
a
is
2 Capture
2-24
Using
the
desired data.
ESCORT
Page 45

3 Use
the
CONNECT command to make
active, for example,
CONNECT
(HI)
the
target session
4 Write
Each active or dormant host session in
the
the
host session.
previously captured data from
an
the
local session to
ESCORT
script utilizes
a host system connection. Host system connections are a limited
that
resource. You can release host system connections,
that
you
no
associated with host applications
access in your script, by using the
DISCON command.
longer need to
are
Working
in
Host and Local Sessions 2-25
Page 46

Displayed Sessions
The
presentation space of
terminal can be changed
presentation space
using
the
SHOW
The
SHOW
which session
is
command.
and
CONNECT
is
displayed and which session
displayed and active sessions need
to display
(SHOW) one session while another session
and possibly executing (through
the
background.
the
active session displayed
so
that
displayed. You can change the display by
commands in the script determine
the
any dormant session's
is
active. Since
not
be the same, it
CONNECT
command) in
on
the
is
possible
is
active
the
When
display
the
SHOW
the displayed and active sessions are
on
the
terminal monitor
active session executing in
command to refresh
is
the
the
terminal monitor display.
ESCORT will automatically refresh
with
the
active session presentation space when you enter
Interactive mode.
not
the same,
not
updated, or refreshed, by
the
background. You can use
the
terminal monitor display
the
2-26 Using
ESCORT
Page 47

Active and Displayed Sessions
in
Interactive Mode
Active Sessions
ESCORT provides you with the ability to connect or disconnect
host sessions in Interactive mode, through the use of six
functions.
functions are
The
Interactive mode host session connection
o connect to
next
host session, NEXTS
o connect to previous host session, PREYS
o open a new synchronous host session, OPENS
o open a new asynchronous host session, OPENA
o close a host session, EXIT
o close all host sessions,
NEXTS, PREYS and EXIT are
A for the specific key combinations for these functions for your
terminal.
OPENS,
"Special
specific key combinations for these functions. .
The
function in Interactive mode.
The
followed by asynchronous connections.
connections,
host sessions, and
asynchronous host sessions.
OPENA
Key
following describes the operation of each host connection
cycling order
and
Combinations" at
of
HI
is
the
Al
QUIT.
key
QUIT
host sessions
the
are ESCORT key functions; refer to
lowest and
lowest and
functions; refer to Appendix
the
end of this chapter for the
is
synchronous connections,
In
the
hierarchy of these
H4
the highest synchronous
A4
the
highest
NEXTS
Connects to
If
you press the NEXTS key combination,
ESCORT connects to and makes active
previously opened, next higher host session.
For example, your
host sessions
host session
next
host session.
the
ESCORT script has opened
HI,
H3,
AI,
and A2. Synchronous
HI
is
the
active (connected) and
Working in Host and Local Sessions 2-27
Page 48

displayed session when you enter Interactive
Al
and
A2
mode, sessions H3,
the
If you now press
synchronous host session H3
displayed. Repeated use of
combination, in this example, connects and
the
displays
then
the
asynchronous sessions
synchronous session
NEXTS key combination,
remain dormant.
is
connected and
the
NEXTS key
AI,
A2,
HI,
and so on.
and
PREVS
If only one session
Interactive mode, use of
combination displays
operator information area:
No other host session active
Connects to previous
The
PREYS key combination works in a similar
manner to
sessions are connected and displayed in
descending order.
Using
the
PREYS key combination in Interactive mode
when connected to synchronous host session
connects and displays
the
the
example detailed
is
connected when you
the
NEXTS key
the
following message
host
session.
NEXTS function, however, host
in
NEXTS, pressing
the
asynchronous session
A2.
Similarly, if only one session
you enter Interactive mode, pressing
key combination displays
in
the
operator information area:
No other host session active
is
connected
the
the
following message
when
PREYS
enter
in
the
HI
OPENS
2-28 Using
Opens new synchronous
Pressing
next
For example, if synchronous host session
the
mode, synchronous host session H3 being
dormant, and you press
combination,
ESCORT
the
OPENS key combination opens
available higher synchronous host session.
active session when you enter Interactive
ESCORT
host
session.
the
OPENS key
opens synchronous host
HI
the
is
Page 49

session H2. This session
session. If
the
OPENS key combination
then
becomes
the
is
active
pressed again, in this example, ESCORT opens
the
nex,t available higher synchronous host
session, H4.
ESCORT displays the following message in the
operator information area
when
you press the
OPENS key combination:
OPENA
Connecting
to
new synchronous session
If all four synchronous host sessions are
connected, and you attempt to open a further
synchronous host session by pressing the
key combination, the following message
OPENS
is
displayed:
Max. number
active
If
no
host system logical unit connections are
of
synchronous sessions already
available when you attempt to open a
synchronous host session using
logical unit open failed,
the
OPENS, or the
following message
displayed:
Unable
to
open new synchronous session
Opens new asynchronous
Pressing the
next
available higher asynchronous host session.
OPENA key combination opens
You are prompted for
host
the
asynchronous
session.
cOlnmunication port initialization parameters,
defaults for which are
established either interactively or via a
the
last parameters
SERINIT
command in a script.
is
the
the
To
abort
the
asynchronous host connection after
the
communication port initialization parameters
have been entered but before
established, press
the
EXIT key combination.
the
connection
For example, if asynchronous host session
the
active session when you enter Interactive
Working
in
Host and Local
Sessions
Al
is
is
2-29
Page 50

mode and asynchronous host session A 4 (being
the
last session established)
the
press
OPENA key combination, ESCORT
opens asynchronous host session
is
dormant, and you
A2
. You are
prompted for the asynchronous communication
port initialization parameters (speed, parity,
stopbits, length, duplex, telephone
TIY
number/machine name,
control).
default,
the
By
for asynchronous host session
port, and flow
initialization parameters
A4
are displayed;
these defaults can be amended. Asynchronous
then
host session A2
becomes
the
active session.
Repeated use
this example, opens and makes active
of
the
OPENA
key combination, in
the
asynchronous session A3.
ESCORT displays
the
following message in
the
operator information area when you press the
OPENA
If
all four asynchronous host sessions are
key combination:
Connecting to new asynchronous session
connected, and you attempt to open a further
asynchronous host session
OPENA
is
displayed:
If
ESCORT
key combination,
Max. number of asynchronous sessions already
active
is
unable to establish a connection
when you attempt to open
session using
OPENA,
the
pressing
the
following message
an
asynchronous host
following message
the
by
displayed:
Unable to open new asynchronous session
ESCORT writes specific error messages to the
escort,pr{proc,id} file, created in
c1pfinprl
--------
hu
- J _
t-hp
'P~rnT1~
...... ---
~n";rf"\n1'Y'l~nf-
-_
...
_ .. _
...
&"
the
directory
.A.A."""............................. • ................
'Hl')r1l')hlo
....,
...
is
"".
2-30
Using
Some asynchronous applications request terminal
type information. You should specify your
as
terminal
ESCORT
a VT100
on
these remote
Page 51

asynchronous hosts, regardless of
terminal type being used.
the
actual
EXIT
host
Closes a
The
EXIT key combination closes the active host
session and automatically activates
host session, if any, within
environment.
the
same environment, the lowest available
in
host session
If
synchronous host sessions H2 and H3, and
asynchronous host sessions
for example, and you press
combination
synchronous host session H3
is
terminated, the following message
session.
the
If
no
other host session
is
activated.
Al
the
in
Interactive mode when
is
the
lowest
same
is
available
and
A2
are open,
EXIT key
active, this session
is
displayed
briefly:
TERMINAL SESSION TERMINATED
and synchronous host session H2 becomes the
active session.
the
Repeated use of
EXIT key combination, in
this example, closes the synchronous host session
the
H2 and makes active
AI,
and
session
If
the
EXIT function
session
is
so
connected,
asynchronous host
on.
is
used when only
the
ESCORT process
one
host
is
terminated.
QUIT
host
Close all
The
QUIT
sessions.
key combination terminates all
connected host sessions, quits
the
returns to
message
TERMINAL SESSION TERMINATED
UNIX
is
displayed briefly:
Working
shell.
in
Host and
ESCORT and
The
following
Local
Sessions
2-31
Page 52

Caution
You should ensure
sessions are open but dormant and which session
resuming a script from Interactive mode, duplicates
the
point when script execution
Interactive mode. Script execution may be affected and results
may be unpredictable if
available and
way.
the
that
status
the
status
of
host sessions (that
is
was
interrupted by entering
the
script anticipates host sessions to
of
the
sessions has been altered
is,
active)
the
status
in
which
on
any
at
be
2-32
Using
ESCORT
Page 53

Displayed Sessions
While
a host or local session, you
presentation space by using
To
in
Interactive mode
SHOW
the
next
presentation space press
in
a host session, or Tutorial mode
can
display another session's
the
SHOW
special key combination.
~
f
9.
in
Each time the
presentation space
example, if the synchronous host session
currently displayed and you press
(
~
f 9)
is
displayed.
Repeated use
SHOW
the
of
the
key combination
is
displayed
in
a circular manner. For
the
is
pressed
HI
SHOW
the
next
presentation space
key combination
synchronous host session H2 presentation space
SHOW
key combination displays
other
synchronous and asynchronous host, and local sessions, if any,
and eventually redisplays
presentation space for
the
HI
the
synchronous host session.
The
SHOW
not
does
the
displayed session
the
and
session and
Information
function only displays
change
the
active session.
is
shown
session identification
the
active session are
II
in
this section for more information.
the
appropriate session and
The
in
the
operator information area
is
highlighted if
the
same. See II Status Line
session identification
the
displayed
is
of
Working in Host and Local Sessions 2-33
Page 54

Status Line Information
The
session identification
the
you use
combination
information area
highlighted if
same.
SHOW
(@
the
on
displayed session and
of
the
command
f 9),
is
displayed
the
terminal.
session
in
a script or
The
that
you display when
the
SHOW
in
the
operator
session identification
the
active session are
key
is
the
If your terminal has a 24
area, or status line, must first be toggled
key sequence for
the
specific key combination for
terminal.
displayed
The
information area
I for Interactive mode,
mode.
The
on
mode
the
operator information area
terminals with
of
operation
on
..
line screen,
STAT
the
function. Refer to Appendix A for
25
..
is
also displayed in
terminal by use
S for Script mode and T for Tutorial
the
the
STAT
line screens.
operator information
on
using
the
appropriate
function for your
is
automatically
the
operator
of
the
following codes:
2·34
Using
ESCORT
Page 55

Modes of Operation Summary
The
following diagrams illustrate the relationship between Script,
Interactive and Tutorial modes, and summarize the Interactive
mode special features and the methods of changing active
sessions and displays.
Working in Host and Local Sessions 2-35
Page 56

Changing Modes
FIGURE 2-5
or
/,Orl
Interactive
Mode
Bsync.
~
,
ENDPor
p
escort
script. name
"
'"
f 2 (Interrupt)
7UTOR'AL)
---I
---1.~
r----~
Script
Mode
'-_--,_.....,...
EXIT
or
......
2-36 Using
__
ESCORT
--f---r-u-to-ri-a-I
MOde.
--.1
...
----
AID
key
----
.......
Page 57

Interactive Mode Special Features
FIGURE
2·6
SHELL
function
Interactive
Mode
PRINT/IDENT
function
Working
in
Host and Local Sessions
2·37
Page 58

Active and Displayed
Local sessions
L1
CONNECT
command
Synchronous
sessions,
H1
to
H4
Interactive Mode
OPENA
function
Asynchronous
Sesslo
and
L2
sessions,
A1
to
· ns
A4
OPENS
function
2-38
NEXTS
function
I
/
sing
U
~
ESCORT
SynChrOnous
sessions,
H1
to
H4
I
EXIT
function
;
QUIT
function
/
~C)
ES
f9(SHOW)
~
o
Page 59

ESCORT Utility Files
This section describes five utility files
that
ESCORT
automatically creates in the directory defined
environment variable. Refer to the section,
II
Environment Variable
the
directory environment variable.
The
five utility file names have the following format
escort.
{type}
{proc~id}
The
five {type}s produced are
cp
Data saved
command in a script
dp
A
produces
ky
In
generated script
file type. See
in Appendix B for information
as
a result
DUMP command
an
ESCORT
of
a CAPTURE
is
written to this file type.
in
a script or a fatal error
dump to this file type.
Automatic Script Generation (ASG) mode
is
automatically written to this
II Automatic Script Generation
this section for more information.
In
19
Automatic Screen Logging (ASL) mode screen
images are automatically written to this file type.
II Automatic Screen Logging
See
for more information.
by
the ESCDIR
II Directory
II
in this section
on
ON
setting
the
II
in
pr
Data specified by a
LOG command in a script
written to this file type.
Data specified
is
written to this file type.
If
an
error occurs during syntax checking or script
execution,
message information to a
by
a
PRINT
command in a script
ESCORT will write certain error
pr
type utility file.
ESCORT
Utility
Files
is
2-39
Page 60

The
identifier,
identification number
{proc,id},
that
refers to the unique process
the UNIX operating system
automatically assigns to each process.
For example the file named
escort.ky23658
contains a script automatically generated by ESCORT through
the Automatic Script Generation feature;
system assigned
to
the
process.
the
unique process identification number 23658
the
UNIX operating
When
an
ESCORT session
identification number
Process Id
Use
the
process identification number to access
files created by
of
your
ESCORT during the session.
is
displayed
ESCORT
is
terminated, the process
on
the
terminal, for example
session was: 23658
the
various utility
2-40 Using
ESCORT
Page 61

Command Line
The
ESCORT
D operate interactively
D run a script
command line allows you to
D perform syntax checking
an
create
The
where
The
full
path
The
syntax of
the
script-.name
p1,p2 .•..
executable run
the
command line
escort [script-.name [p1,p2, ..•.
items enclosed in brackets are optional.
is
the
for
the
script; for instance,
lusrlescortlsliblupload
,p9
are parameters passed to
command line. You may pass up to nine parameters
command line. You must
..
name
not
on
a script without execution, and
time script.
is
,p9]
[NORUN] [NOLOGO]]
of
a script file. You can specify
the
script from
on
insert any blanks between
the
the
the
parameters. Parameters may be passed when you run (parse and
interpret) a
Passing
ll
in Chapter 2
time script. See
in
the
ESCORT
the
section II Parameter
Programmer's Guide for
non
..
run
..
further information.
The
NORUN keyword parameter
..
time version
run
lowercase letters.
parameter,
the
of
a script. You may specify
When
script
is
checked) and, provided
created with
the
file extension,
you execute a script with
parsed only (that is, the syntax
no
is
used to create
an
executable
the
parameter in
the
NORUN
is
syntax errors occur, a new script
x,
in
the
form script_name.x.
is
This new script
is
a binary file and
eliminated when this script
the
interpreting
script immediately, saves time.
the
parsing phase
is
executed. Eliminating parsing, and
Command Line 2-41
is
Page 62

No
parameters may be passed to
line when executing a run
the
script from
..
time script. Use one
the
command
of
the
following
options if you need to pass parameters when executing a run
script:
D
Set
UNIX environment variables to
the
value
of
the
parameters and read these environment variables from within
the
your script using
$GETENV
function.
..
time
D Store
The
the
required parameters
of
the
file using
NOLOGO keyword parameter
the
READ
in
a file and read
command.
is
used to eliminate
screen. This keyword may be specified
Examples
escort
escort
escort script-.l1ame NORUN
escort script-.l1ame.x
escort script-.l1ame p1,p2,p3
escort
escort script-.l1ame p1,p2,p3 NOLOGO
of
using
the
command line follow:
script-.l1ame
script-.l1ame p1,p2,p3
NOR
UN
the
contents
the
banner
in
lowercase letters.
Enter Interactive mode
Parse and interpret (execute) a
script
..
Parse script and create run
time
script
..
Interpret (execute) run
time
script
Parse and interpret a script and
pass 3 parameters
Parse script, pass 3 parameters
..
and create run
Parse and interpret script,
time script
pass
3 parameters and eliminate
banner
escort script-.l1ame 2 > /usr/errors
script-.l1ame 1 > /dev/null &
escort
2-42
Using
ESCORT
Parse and interpret script,
redirect standard error to
specified file
Parse and interpret script
background, and redirect
standard output
in
Page 63

Special Key Combinations
Use of the default special key combinations, (
letter
f and numeric keys, or (
simulate function
To
access these functions press the following sequentially:
o
o
o
The
@,
@,
@,
the letter f
the letter 0 key and the letter S key,
the letter 0 key and the letter a key.
list of special
keys
with special meaning in ESCORT.
key
key
combinations
ESC)
and letters
and the appropriate numeric key,
is
also contained in your
ESC)
0,
(Escape),
a and s
and
keys,
Quick Reference Card.
The
use
of the special
Most of the
key
key
combinations
is
summarized below.
combinations have been explained in greater
detail earlier in this chapter.
If the
ESCORT default key combinations have been amended
your System Administrator,
you
must substitute the amended key
by
combinations for the default combinations shown in this section.
[Esc)f1
Quit
(QUIT)
Terminates ESCORT execution and
returns to the UNIX shell with a default
exit code
example, the
O.
All open files are closed. For
files
escort.lg{proc,id}
and
escort.ky{proc,id} are automatically closed.
(
ESC)
f 1 may be used from either
Interactive mode when connected to a
host session, or Script mode when
connected to a host or local session.
Special
Key
Combinations 2-43
Page 64

@£)f2
InterruptlResume (l!R)
@£)f3
@£)f4
Interrupts active host script execution
enters Interactive mode. You may also use
this key combination to resume script
execution.
Automatic Script Generation (AS G)
Activates or deactivates automatic script
@£)
generation (ASG).
only from Interactive mode
host session. After you press
ESCORT
keyboard entries after
pressed. You may deactivate automatic
script generation
The
the
in
Cursor
Displays
operator information area. Both
absolute position and row and column
position appear.
from Interactive mode in a synchronous
host session or from Tutorial mode
local session.
generates a script containing all
by
automatically generated script appears
escort.ky{proc,id} file.
Position
the
(CURSIL-POS)
current cursor position
(ESC)
f 3 may be used
in
an
@£)
the
@£)
pressing
@£) f 3.
f 4 may be used
active
f 3
the
in
f 3
was
in
and
the
a
@£)f5
2-44 Using
ESCORT
@£)
f 4 has
session
Display
Fispltys all field attributes
mode
from Tutorial mode
@£)
session
is
ESC
f 5 may be used from Interactive
in
f 5 has
is
no
effect when
an
asynchronous session.
Attributes
a synchronous host session
an
asynchronous session.
(A
in
no
effect when
TTRIB)
a local session.
on
the
the
the
active
screen.
or
active
Page 65

[EscJf6
Automatic Screen Logging (ASL)
~f7
[EscJf8
~f9
Activates
logging.
contains
be used from Interactive mode
session
session.
or
deactivates automatic screen
The
escort.lg{proc.i1
the
screen images.
or
from Tutorial mode
1
ESC
in
Key Status (KEY_STATUS).
Displays
Automatic
Screen Logging,
~
mode
No
This
ESCORT.
the
status
of
the
Script Generation, Automatic
and
AID
f 7 may
in
an
be
active
used only
host
effect.
key combination has
special keys for
Substitution.
in
session.
no
effect in
Show Session (SHOW).
Displays
in
does
f 9 may
in
in
the
next
session
circular manner. Use
not
change
be
an
active host session
an
active host
used
the
active session.
in
either
or
local session.
on
the
of
this function
Interactive mode
or
Tutorial mode
fill
f 6 may
in
a host
a local
Interactive
terminal
(ESC
J
~fO
AID Substitution
Activates
substitution while
Generation. [
while you are
Generation
active synchronous
time
automatically generated script,
generates a subroutine call
named
or
an
AID
aid_resp.
in
(AID_SUB).
deactivates
ESC
J f 0 may
in
Automatic
Interactive mode
key
is
Special
AID
in
Automatic
host
session. Each
encountered
Key
Combinations
be
Script
to
subroutine
Script
used only
in
an
in
the
ESCORT
a script
2-45
Page 66

This feature
is
required for synchronous
host applications
mode transactions.
that
have no
..
response
@£)os
@£)oa
For further information
subroutines, see
ResponselNo
the
..
Response Mode
Transactions" in
on
AID key
section "Synchronous
Chapter 2, and the
appendix, "AID Subroutines Library" in
the
ESCORT
@£)
f 0 has
session
Open Synchronous
Programmer's
no
effect when the active
is
an
asynchronous session.
Host
Guide.
Session
(OPENS).
Opens
synchronous host session.
the
next
available
fighjr
ESC
0 S may
be used in Interactive mode while
connected to either a synchronous host
an
asynchronous host session.
The
or
synchronous host session opened when you
press
@£)
0 S becomes the connected
session.
Open
Asynchronous
Host
Session
(OPENA).
Opens
asynchronous host session.
be used
connected to either a synchronous host
an asynchronous host session.
the
next
available htgher)
in
Interactive mode while
ESC
0 a may
or
The
asynchronous host session opened when
you press
@£)
0 a becomes the
connected session.
2·46
Using
ESCORT
Page 67

Page 68

Appendices
A
B
c
Key Sequences
Key
Sequences for
Standard
Key
Sequences for
and Teletype 5410 Terminals
Key
Sequences for
and Teletype 5418 Terminals
Key
Sequences for
and Teletype 5425 Terminals
Key
Sequences for
Business Communications Terminal A -10
Key
Sequences for
and 630 Business Communications Terminals A -12
Key
Sequences for
DEC
ASCII Terminals A -2
AT&T
AT&T
AT&T
AT&T
AT&T
VT100 Terminal
4410
4418
4425
605
610, 615, 620,
Environment Variables
Setting 3270 Emulator+
ESCORT Environment Variables
Interpretation of Attribute Bytes
A-1
A-4
A-6
A-8
A-14
8-1
8-2
C-1
Page 69

Page 70

Key Sequences
This appendix lists the
functions for the following terminals:
Synchronous Terminals
o Standard ASCII terminals
o
AT&T
o
AT&T
o
AT&T
o
AT&T
o
AT&T
Terminals (BCTs).
Asynchronous Terminals
4410 and Teletype® 5410 terminals
4418 and Teletype 5418 terminals
4425 and Teletype 5425 terminals
605
Business Communications Terminal (BCT)
610,615,620,
key
sequences that emulate
and 630 Business Communications
o DEC VT100 terminal.
Note that certain
the terminal does
are
not supported
key
functions are ignored if either ESCORT or
not
support them. The following
by
ESCORT:
ALLCAP COLR
ALT_CR
BLINK
BOT
CAN
CLICK TOP
CTRL
CURSR-SEL
NULLEND
NU~OV
IBM
key
3278
key
functions
The synchronous keyboard
used
by
the
AT&T
3270 Emulator+ software.
files
are the same
as
the keyboard
Key
Sequences
files
A-1
Page 71

Key Sequences for
Standard
The
AT&T
these
key
ASCII Terminals
4415,5420 and
sequences.
the
Tektronix™ 4105 terminals
use
3278 Key Standard
Function
ATTN
BAKTAB
BS
CENT
CLEAR
DEL
DEV_CNCL
DOWN~
DUP
EJOF
E_INPUT
ENTER
ENTER 1
EXIT
FM
HOME
IDENT
INS
LDUB
LEFT~
NEWL
NEXTS
Key Sequence
@ a (
(
CTRL)
e
(
CTRL)
A
@z
h
(@
@d
[
CTRL)
V
[CTRL)d
@ef
@ei
(
RETURN
[
RETURN
@xx
(CTRL)k
(
CTRL)
0
@i
(CTRL)U
(
CTRL)
r
(CTRL)f
(
CTRL
) j
@+
NOT
~
@
@@p
(
CTRL)
@r
(
CTRL)
(
CTRL)
a
key
Y
a
9
PAl
to PA3
PF1
to PF24
PREYS
PRINT
RDUB
REDRAW
RESET
RIGHT~
ASCII
RETURN)
)
)
key
number (
number
Terminal
RETURN
(
RETURN
)
)
A-2
Key
Sequences
Page 72

Key Sequences for
Standard
3278
ASCII Terminals (continued)
Key Standard ASCII Terminal
Function
Kev
Sequence
SHELL
SOLID
STAT
SYS~EQ
TAB
TEST
~EQ
only)
UP~
(SNA only)
(BSe
~s
~I
~q
(
CTRL
) i
~q
(
CTRL
) t
Key
Sequences
A-3
Page 73

Key Sequences for AT&T 4410
and Teletype 5410 Terminals
3278
Key
Function Kev Sequence
AT&T
4410
and Teletype
5410
ATIN
BAKTAB
BS
CENT
CLEAR
DEL
DEV_CNCL
DOWN~
DUP
EJOF
E_INPUT
ENTER
ENTERl
EXIT
FM
HOME
IDENT
INS
LDUB
LEFT~
NEWL
NEXTS
NOT
PAl
to
PA3
to
PFl
PF9
PFlO
PFll
PFl2
PFl3
PFl4
PFl5
@ a ( RETURN)
0
(
CTRL
)"
h
"
@z
[@
@d
IT)
( CTRL) d
( ESC) e f
@ei
(
RETURN
(
RETURN
)
)
@xx
(
CTRL
) k
G
@i
( CTRL) U
( CTRL) r
B
(
CTRL
) j
@>
~
a key number (
@ key number
@O
@@=
@
(SHIFT)
@
(SHIFT)
( ESC) ( SHIFT) 3
1
2
RETURN
)
A-4
Key
Sequences
Page 74

Key Sequences for AT&T 4410
and Teletype 5410 Terminals (continued)
3278
Key
Function
PF16
PF17
PF18
PF19
PF20
PF21
PF22
PF23
PF24
PREYS
PRINT
RDUB
REDRAW
RESET
RIGHT-A
SHELL
AT&T
Sequence
Kev
~
~
~
~
~
~
~
~
~
~<
~p
(
CTRL
) Y
~r
(
CTRL
) a
B
~s
4410
(SHIFT]
(SHIFT]
(SHIFT]
(SHIFT]
(SHIFT]
(SHIFT]
(SHIFT)
(SHIFT)
(SHIFT)
and Teletype
4
5
6
7
8
9
0
-
=
SOLID
STAT
SYS~EQ
TAB
TEST
~EQ
(SNA
(Bse
only)
~I
~q
(
CTRL
) i
~q
only)
UP-A
OJ
5410
Key
Sequences A-5
Page 75

Key Sequences for AT&T 4418
. and Teletype 5418 Terminals
Note that
(CTRLJ.
To
emulate
For (
3278
Function Kev Sequence
CTRL
Key
on
these terminals there
~
, press (
)
use
the
key
immediately to the left of the space bar.
ALT
AT&T
) and
is
I.
4418
no
key
and Teletype
marked
~
or
5418
ATTN
BAKTAB
BS
CENT
CLEAR
DEL
DEV_CNCL
DOWN~
DUP
EJOF
E_INPUT
ENTER
ENTERl
EXIT
FM
HOME
IDENT
INS
LDUB
LEFT~
NEWL
NEXTS
NOT
(ATIN)
(
BACK
TAB
(
BACK
SPACE
1\
(
CLEAR
@)
(
DEV
CNCL
rn
~
(
ERASE
EOF)
(
ERASE
INPUT
(
ENTER
(
ENTER
~xx
(
FIELD
MARK
( HOME)
(
IDENT
)
Q@
~
B
(
NEW
LINE
~+
]
)
)
)
)
)
) (lower right side)
) (upper left side)
)
)
A-6
Key
Sequences
Page 76

Key Sequences for AT&T 4418
Teletype 5418 Terminals (continued)
and
3278
Key
Function
AT&T
KeyS~uence
4418
and Teletype
5418
PAl
PA2
PA3
PFl to PF24
PREYS
PRINT
RDUB
REDRAW
RESET
RIGHT-A
SHELL
SOLID
STAT
SYS~EQ
TAB
TEST
~EQ
only)
UP-A
(SNA only)
(BSC
@D
@D
(SHIFT]
@D
~-
(
PRINT
@
to
LCL
(PF24]
]
G2J
~r
[RESET]
(lower left side)
G
( SHIFT] ( RESET] (upper left side)
~
RESET)
(
SYS
(
CURSOR
(
SYS
(upper left side)
REO
]
TAB
]
REO
]
CD
Key
Sequences A-7
Page 77

Key Sequences for AT&T 4425
and
Teletype 5425 Terminals
3278
Key
Function . Key Sequence
AT&T
4425
and Teletype
5425
ATIN
BAKTAB
BS
CENT
CLEAR
DEL
DEV_CNCL
DOWN~
DUP
EJOF
E_INPUT
ENTER
ENTERl
EXIT
FM
HOME
IDENT
INS
LDUB
LEFT~
NEWL
NEXTS
NOT
PAl to
PFl to
PA3
PF4
PF5
PF6
PF7
PF8
PF9
PFlO
( ESC) a (
( SHIFT) (
(
BACK
"
(
CLEAR
TAB)
SPACE
)
RETURN
)
~
@£)d
IT)
( CTRL) d
(
CLEAR
LINE
)
(
DELETE
LINE
)
(
RETURN
(
ENTER
)
) (on keypad)
@£)xx
( CTRL) k
(
HOME)
@£)
i
(
INSERT
CHAR
( CTRL) r
B
( CTRL) j
@£)
~
@to
7 (on keypad)
8 (on keypad)
9 (on keypad)
4 (on keypad)
5 (on keypad)
+
a
f:Y
PF4
- (on keypad)
)
T
)
-
mber
( RElURN 1
A-a
Key
Sequences
Page 78

Key Sequences for AT&T 4425
Teletype 5425 Terminals (continued)
and
3278
Key
Function
AT&T
Ke
Se
4425 and Teletype 5425
uence
PFll
PF12
to
PF13
PF24
PREYS
PRINT
RDUB
REDRAW
RESET
RIGHT-A
SHELL
SOLID
STAT
SYS--REQ (SNA only)
TAB
TEST
--REQ
only)
UP-A
(BSe
CD
Key
Sequences
A·9
Page 79

Key Sequences for AT&T 605
Business Communications Terminal
The
l02
AT&T
..
key
605
keyboard.
Business Communications Terminal
(BeT)
has a
3278 Key
Function
ATTN
BAKTAB
BS
CENT
CLEAR
DEL
DEV_CNCL
DOWN~
DUP
E-EOF
E_INPUT
ENTER
ENTERl
EXIT
FM
HOME
IDENT
INS
LDUB
LEFT~
NEWL
NEXTS
NOT
PAl
to PA3
PFl
to PF24
PREYS
PRINT
RDUB
REDRAW
RESET
RIGHT~
AT&T
605
BeT
Key Sequence
@ a ( RETURN)
( SHIFT) (
(
BACK
TAB)
SPACE
)
"
( SHIFT) (
(
CTRL
@d
) (
CLEAR
DELETE
)
)
CD
( CTRL) d
@ef
( SHIFT) (
(
RETURN
(
RETURN
DEL
)
)
LN
)
@xx
( CTRL) k
(
CLEAR
HOME
)
@i
(
INS
LN
)
( CTRL) r
B
(
CTRL
) j
@+
~
a
key
number
@
key
number
(ESC)
-
@p
( CTRL) Y
@r
@C
G
(
RETURN
(
RETURN
)
)
A-10
Key
Sequences
Page 80

Key Sequences for AT&T 605
Business Communications Terminal (continued)
3278
Key
Function
AT&T
Key Sequence
605
BeT
SHELL
SOLID
STAT
SYS~Q
TAB
TEST~Q(BSC
only)
UP~
(SNA only)
@s
~I
@q
( TAB)
(ESC) q
OJ
Key
Sequences A·11
Page 81

Key Sequences for AT&T
610,615,
and 630 Business Communications
Terminals
The
AT&T
Terminals (BCTs) have 98
3278
Function
ATTN
BAKTAB
BS
CENT
CLEAR
DEL
DEV_CNCL
DOWN~
DUP
EJOF
E_INPUT
ENTER
ENTER 1
EXIT
FM
HOME
IDENT
INS
LDUB
LEFT~
NEWL
NEXTS
NOT
PAl
PF1
PREYS
PRINT
RDUB
REDRAW
RESET
RIGHT~
610,615,620,
Key
to PA3
to PF24
and 630 Business Communications
..
key
keyboards.
AT&T
BeTs
@)
( SHIFT) (
(
BACK
1\
(
CLEAR
(
DELETE
610, 615, 620, and 630
Kev Sequence
a (
RETURN
)
TAB
J
SPACE
J
J
J
@)d
OJ
(
CTRL
J d
@)ef
@)ei
(
RETURN
(
RETURN
J
J
@)xx
(CTRLJk
( HOME)
@)i
(CTRLJU
(
CTRL
J r
B
(
CTRL
J j
@)+
~
a key number (
@)
key number (
RETURN
RETURN
J
@)-
@)p
(CTRL)Y
@)r
@)C
G
620,
J
A-12 Key Sequences
Page 82

Key Sequences for AT&T 610, 615, 620,
and 630 Business Communications Terminals
(continued)
3278 Key
Function
SHELL
SOLID
STAT
SYS~EQ
TAB
TEST
~EQ
only)
UP~
(SNA only)
(BSC
AT&T
BeTs
610, 615, 620, and 630
Kev
Se~uence
@£)s
~I
@£)q
( TAB)
@£)q
rn
Key
Sequences A-13
Page 83

Key Sequences for
DEC
VT100 Terminal
DEC
VT100
Function
BAKTAB.
BS
CLEAR
DEL
DOWN~
ENTER
ENTERl
EXIT
HOME
IDENT
LEFT~
NEWL
NEXTS
PFl to PF8
PREYS
PRINT
REDRAW
RIGHT~
SHELL
STAT
TAB
UP~
Key
ESCORT
Equivalent
Key Sequence
(
CTRL
) e
( CTRL) h
@£)z
@
( CTRL) V
(
RETURN
(
RETURN
)
)
@£)xx
(CTRL)
@£)
(
(
@£)
@£)
@£)
CTRL
CTRL
0
i
) f
) j
+
key
-
number (
@£)p
@£)r
(CTRL)g
@£)S
@£)
I
( CTRL) i
(
CTRL
) t
RETURN
)
Note
This
key
sequence table should be used in asynchronous,only
environments. If you communicate with both synchronous and
key
asynchronous hosts, use the appropriate
sequence table for
your specific synchronous terminal for all synchronous and .
asynchronous applications.
A-14 Key Sequences
Page 84

Environment
Variables
This appendix provides information on setting environment
variables applicable to your operating environment.
Environment
Variables
8-1
Page 85

Setting 3270 Emulator +
ESCORT Environment Variables
Once
the ESCORT software has been installed, certain
prerequisite variables should be set in your
invoking ESCORT, ensure
manager process
is
running.
that
the
3270 Emulator+ terminal
Terminal Environment Variable
ESCORT
terminal information in
management.
variable set for an
uses
the environment variable,
The
TERM=4410
export TERM
the
system file
following example shows
AT&T
4410 terminal type.
3270 Emulator + Environment Variables
ESCORT runs in conjunction with
software. Your
profile
file should be edited to include
the
following command:
• /usr/bscadm/runtime/bscenvset
or
• /usr/snaadm/runtime/snaenvset
profile
TERM,
terminfo
the
AT&T
for screen
environment
3270 Emulator+
file.
When
to access
the
Set
the
appropriate environment variable
so
that
3270
Emulator+ and ESCORT will execute properly.
03274 Environment Variable
The
default value for the D3 274 environment variable provided
by
the
snaenvset
unit connections.
command allows access to all available logical
Setting the D3274 environment variable
provides controlled access to certain host applications. You can
assign ranges of logical unit ports to particular users.
following example, a user
is
given access to eight logical unit
In
the
ports.
D3274 = 1-5,13,14,15
export D3274
B-2 Environment Variables
Page 86

Host/Local Session Environment Variable
The
UNIX operating system environment variable, ESCHOST,
determines whether a synchronous connection
established.
to a value
environment variable
of
1 (the default value if this variable
can
The
ESCORT script will be able to connect to a synchronous host
session.
is
to be
be set to 0 or
is
not
set)
1;
the
if set
Setting
the
ESCHOST
in
limiting access to prototyping local screen formats
if
ISC or SOLI cards have
environment variable to 0
not
been installed in
processor
the
user accesses only asynchronous host applications.
if
In
the
following example, a user's ESCORT connections will
default to a local session.
ESCHOST=O
export
ESCHOST
Directory Environment Variable
The
UNIX operating system environment variable,
determines
the
ESCDIR
files are created
example, a user's
directory named
the
path
for
environment variable
in
your
ESCORT
sys_l,
ESCDIR =
export
/usr/john/sys_1
ESCDIR
the
five types of
$HOME
directory.
is
not
ESCORT
set,
ESCORT
In
the
utility files will be created
a subdirectory of lusrljohn.
Terminal Information Environment Variable
To
use
the
terminfo terminal information files installed by
ESCORT, set the terminfo variable
as
follows:
is
useful
the
3B
ESCDIR,
utility files.
utility
following
in
a
If
TERMINFO
export
=/usr/escortltermlnfo
TERMINFO
Setting this environment variable
supplied files contain errors
and ESCORT does
not
or
have been modified
function correctly.
is
only necessary if
Environment
the
in
some
Variables
system
way
..
8-3
Page 87

Page 88

Interpretation of
Attribute Bytes
When
host session,
of
represents
shows you how to interpret
The
displayed
you press
each attribute byte
~
f 5 while connected to a synchronous
ESCORT displays
on
the
Primary Attributes for each field; this appendix
the
an
alpha character
screen.
the
displayed characters.
following table shows you how to convert
on
the
terminal screen into attribute bytes.
ASCII
Character to Attribute Byte Conversion
Char
@
A 11000001
B 11000010
C
D 11000100
E 11000101
F 11000110
G 11000111
H 1100 1000
I
J
K 1100
L 1100 1100
M 1100
N 1100 1110
0 1100
Attr
11000000
Char
Q
11000011
W
1100
1001
1100 1010 Z
1011
1101
1111
-
Attr
1101
P
1101
1101
R
1101
S
T
1101
11010101
U
V 11010110 f
1101
1101
X
Y
1101
1101
[
1101
1101
\
1101 1101
1
A
1101
1101 1111
Char
0000
0001
0010
0011
0100 d 11100100
0111
1000
1001
1010
1011
1100 1 1110 1100
1110 n 1110 1110
.
a
b
c 11100011 s
e
g
h
i 1110
j
k 1110
m 1110
0
in
the position
The
character displayed
the
character
Attr
11100000 p 11110000
11100001 q 11110001
11100010
11100101
11100110
11100111
1110 1000 x
1110 1010 z
11101111
1001
1011
1101
Char
11110010
r
11110011
11110100
t
11110101
u
11110110
v
11110111
w
1111
11111001
y
11111010
11111011
1111
f
} 11111101
11111110
-
11111111
<
Attr
1000
1100
Interpretation of Attribute Bytes
C-1
Page 89

The
following diagram shows you how to read
attribute byte. Note
together.
BITS
Detectable
in
an
that
bits 3 and 2 are coupled and are read
refers to detectable
ATTRIBUTE
BYTE
'--
____
the
bits in
by
a light pen.
o not modified
1 modified
0 always
00
normal & nondetectable
10
highlit & detectable
01
normal & nondetectable
11
dark & nondetectable
o alphanumeric
1 numeric
o unprotected
1 protected
an
100--------------1
'-----------------
C-2
Interpretation
of
Attribute
Bytes
always
1 always (most significant
bit)
Page 90

For example, if the alphabetic character X
Display Attribute key sequence ( (
corresponding attribute byte
attribute byte shows
that
the field has
ESC)
f
is
1101 1000. Interpretation of the
the
characteristics:
L...-
________
is
displayed when the
5)
is
pressed,
the
following
not
modified
highlit & detectable
numeric
unprotected
Interpretation of Attribute Bytes . C-3
Page 91

Page 92

Glossary
This glossary contains definitions for tenus and acronyms
throughout this guide. These tenus are defined according to
their meaning in
in other programming languages.
Active session
Administrative
command
AID key
Arithmetic operator A character (such
Array
ESCORT and
Any host or local session connected
script or connected interactively, to which
all
ESCORT commands are directed.
A command that shows where a program,
subroutine, or comment begins or ends.
PROG
Attention
commands simulate the action of one
the attention
example of an AID key.
mathematical operation.
A collection of values of the same type
referred to
an array
may
not
have the same meaning
is
an administrative command.
..
identifier key. AID
..
identifier
by
a single name. Each entry in
is
called an element.
as
+)
keys.
that
used
key
ENTER
represents a
to
of
is
a
an
Automatic screen
logging
A feature of
of a specific application screen and
data entered on it. Also called ASL.
ESCORT
that
saves the image
Glossary-1
any
Page 93

Automatic script
generation
A feature of
ESCORT that automatically
creates a script from a user's tenninal
session. Also called ASG.
Concatenation
The operation that joins two strings
together.
Constant
A fixed value or data item. A constant
may
be a string or a numeric constant.
Debugging command A programming aid used to check for
errors or to detect failures in program
execution.
DUMP
is
a debugging
command.
Declaration
A statement that defines the type and
amount of data associated with a symbolic
label. Declaration commands include
and
CHAR.
Default
Destination
The value or option that
none
is
given. For example, if you use the
command
number of back
BT
AB and do
..
tabs to be executed,
ESCORT assumes the value
The
variable to the left of the equal sign
is
assumed when
not
specify the
is
1.
in an assignment statement.
INT
Emulator
Expression
Glossary-2
The
ESCORT component
that
allows an
ASCII tenninal to perform the functions of
IBM
an
environment, or a DEC
3278 terminal in the synchronous
VT100 tenninal in
the asynchronous environment.
A single operand or multiple operands
separated
by
operators.
Page 94

Extended Field
Attributes
Three arguments used in a
statement
characteristics similar to those found
IBM synchronous host screen formats.
Also called EFA.
that
define advanced screen
FIELD
in
Field variable
File management
command
Format
Function
Global variable
Host
session
An
area of the screen buffer defined
user and assigned a symbolic name. Also
called screen field variable.
A command used to open or close a file
to control the input and output
from a file.
command.
A symbolic name for a group of fields
constitute a screen.
An
algorithm
string value. Function names in ESCORT
are preceded
A variable
program.
The
connection
through
or
an
providing you with access to a host
computer application.
READ
that
the
3 B processor to a synchronous
asynchronous host computer,
is
a file management
that
returns
by
a
$.
is
accessible throughout a
of
your ASCII terminal
an
integer
of
by
data
or
the
or
that
ISC
card
Intelligent Serial Controller card. A card
installed in the 3B2 processor
communications ability to synchronous
host computers.
that
provides
Glossary-3
Page 95

Interactive mode
An
ESCORT feature
use your ASCII terminal
IBM
3278
terminal, or
DEC
VT100 terminal.
that
an
allows you to
as
a synchronous
asynchronous
Interpreter
Keyword
Label
Local screen format Templates used to provide
Local session
Local variable
The
ESCORT component
script.
An
operand predefined by ESCORT, such
as
SCREEN.
A word or symbol used
a program statement to branch from a
GOTO
between you and host computer
applications.
The
the 3 B processor, allowing access to user
defined screen layouts
format)
the user and host applications, and allows
the user to exchange data between
applications.
A variable
particular script or subprogram.
statement.
connection of your ASCII terminal
that
provide
that
is
at
(see
an
interface between
defined only for a
that
executes a
the beginning of
an
interface
to
Local
screen
Loop
Glossary-4
A series
repeatedly until a given condition
of
instructions
that
is
executed
is
met.
Page 96

Null
string
A string of zero length (with no
characters).
double quotation marks
It
is
represented
by
("").
two
Offset
The
number of bytes from a starting point
to some other point.
that
is
Operand
A constant or variable
an operator.
argument
Operand
that
follows a command or
also refers to any
acted on by
function.
that
Operator
A character
(or logical) operation.
represents a mathematical
ESCORT
uses
arithmetic, relational, and string
concatenation operators.
Operator information
area which messages to
An
area
on
the
by
ESCORT.
On
screens, this area
from column
21
terminal display screen, in
the
operator are written
terminals with 25,line
is
on
line 25, extending
to column 80.
On
terminals with 24,line screens, this area
on
line 24, extending from column
column
80. Also called
Status
21
Line.
Operator notification A command used to communicate with
command operator of a terminal.
WTO
is
an
operator notification command.
is
to
the
Overflow
Parameter
An
error
that
returned by
develops when
an
operation
the
is
too large
given register or location.
An
argument passed to a subroutine on a
CALL
statement.
value
for
a
Glossary-S
Page 97

Parser
The
ESCORT component
program and checks syntax.
that
decodes a
Preprocessor
command
Presentation space
Primary Attributes
Program control
command
Relational operator
Reserved word
A command
program execution.
that
requests
COpy
an
action before
is
a
preprocessor command.
See
Screen
buffers.
Four arguments used in a FIELD statement
that
define basic screen characteristics
similar to those found in IBM synchronous
host screen formats.
A command
program execution.
that
changes
BREAK
the
path of
is
a program
control command.
A character (such
as
=)
that
represents a
comparison of two values.
A word used in
purpose, such
name. Reserved words cannot be used
ESCORT for a special
as
a command or function
as
names for variables, labels, programs, or
scripts.
SDLI
card
Glossary-6
Synchronous Data Link Interface card. A
card installed
that
provides synchronous communications
in
the
3B5 or 3B15 processor
ability between host computers and
terminals.
Page 98

Screen buffers
Buffers
maintained
by
ESCORT which
contain the last refreshed screen image for
The
each host and local session.
active
session screen buffer can be accessed with
the system global variable named
Also called
Presentation
space.
SCREEN.
Screen field variable See
Script
A program written in ESCORT.
also means a subroutine labeled with a
script name.
Script
Simulator
mode
This mode executes an
The
a parser and
checks for correct syntax and executes
parsed code.
Statement
An
some sequence of operations. A statement
consists of a command or function and its
operands.
Status line
String
See Operator information
A sequence of characters or words.
ESCORT
variables, and string array variables. String
constants are enclosed in double quotation
marks. String variables are declared in a
CHAR
name.
Field
variable.
Script
ESCORT script.
ESCORT component that consists of
an
interpreter. The simulator
the
instruction to the computer to perform
area.
uses
string constants, string
statement, such
as
CHAR
(20)
Glossary-7
Page 99

String concatenation A symbol
operator operands.
string concatenation operator in
that
links a series of string
The
plus sign
(+)
is
used
ESCORT.
as
a
Terminal keyboard
command
Tutorial
mode
Variable
Window
A command
that
simulates the action
of
a
given keyboard function. For example,
CLEAR
This
to perform edit checks
before sending data to
allows you to set up
is
a terminal keyboard command.
ESCORT feature provides the ability
on
data entered
the
host. It also
on
..
line training
sessions.
A symbol used to represent a value. There
are five types of variables in
ESCORT:
integer, integer array, string, string array,
and field.
A display area
defined in
on
a screen. Windows are
ESCORT
by a WINDOW
statement.
Glossary-8
Page 100

 Loading...
Loading...