Page 1

Page 2
SpaceLink™ B&W PCI Card
®
WL-230
User’ s Manual
Page 3

Copyright Information
No part of this manual, including the products and software described in it,
may be reproduced, transmitted, transcribed, stored in a retrieval system,
or translated into any language in any form or by any means, except
documentation kept by the purchaser for backup purposes, without the
express written permission of ASUSTeK COMPUTER INC. (“ASUS”).
ASUS PROVIDES THIS MANUAL “AS IS” WITHOUT WARRANTY
OF ANY KIND, EITHER EXPRESS OR IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT
NOT LIMITED TO THE IMPLIED WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS
OF MERCHANTABILITY OR FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR
PURPOSE. IN NO EVENT SHALL ASUS, ITS DIRECT ORS, OFFICERS,
EMPLOYEES OR AGENTS BE LIABLE FOR ANY INDIRECT,
SPECIAL, INCIDENTAL, OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES
(INCLUDING DAMAGES FOR LOSS OF PROFITS, LOSS OF
BUSINESS, LOSS OF USE OR DAT A, INTERRUPTION OF BUSINESS
AND THE LIKE), EVEN IF ASUS HAS BEEN ADVISED OF THE
POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGES ARISING FROM ANY DEFECT
OR ERROR IN THIS MANUAL OR PRODUCT.
Product warranty or service will not be extended if: (1) the product is
repaired, modified or altered, unless such repair, modification of alteration
is authorized in writing by ASUS; or (2) the serial number of the product is
defaced or missing.
Products and corporate names appearing in this manual may or may not be
registered trademarks or copyrights of their respective companies, and are
used only for identification or explanation and to the owners’ benefit, without
intent to infringe.
SPECIFICATIONS AND INFORMATION CONTAINED IN THIS
MANUAL ARE FURNISHED FOR INFORMATIONAL USE ONLY, AND
ARE SUBJECT T O CHANGE AT ANY TIME WITHOUT NOTICE, AND
SHOULD NOT BE CONSTRUED AS A COMMITMENT BY ASUS. ASUS
ASSUMES NO RESPONSIBILITY OR LIABILITY FOR ANY ERRORS
OR INACCURACIES THAT MAY APPEAR IN THIS MANUAL,
INCLUDING THE PRODUCTS AND SOFTWARE DESCRIBED IN IT.
Copyright © 2003 ASUSTeK COMPUTER INC. All Rights Reserved.
Product Name: SpaceLink B&W PCI Card (WL-230)
Manual Revision: 1 E1165
Release Date: March 2003
2 ASUS SpaceLink B&W PCI Card
Page 4

Copyright Information
ASUSTeK COMPUTER INC. (Asia-Pacific)
Address: 150 Li-Te Road, Peitou, Taipei, Taiwan 112
General Tel: +886-2-2894-3447
General Fax: +886-2-2894-3449
General Email: info@asus.com.tw
Technical Support
MB/Others (Tel):+886-2-2890-7121 (English)
Notebook (Tel): +886-2-2890-7122 (English)
Desktop/Server: +886-2-2890-7123 (English)
Support Fax: +886-2-2890-7698
Support Email: tsd@asus.com.tw
Web Site: www.asus.com.tw
ASUS COMPUTER INTERNATIONAL (America)
Address: 44370 Nobel Drive, Fremont, CA 94538, USA
General Fax: +1-510-608-4555
General Email: tmd1@asus.com
Technical Support
Support Fax: +1-510-608-4555
General Support: +1-502-933-8713
Web Site: www.asus.com
Support Email: tsd@asus.com
ASUS COMPUTER GmbH (Germany & Austria)
Address: Harkortstr. 25, 40880 Ratingen, BRD, Germany
General Fax: +49-2102-442066
General Email: sales@asuscom.de (for marketing requests only)
Technical Support
Support Hotline: MB/Others: +49-2102-9599-0
Notebook (Tel): +49-2102-9599-10
Support Fax: +49-2102-9599-11
Support (Email): www.asuscom.de/de/support (for online support)
Web Site: www.asuscom.de
ASUS SpaceLink B&W PCI Card 3
Page 5

Table of Contents
1. Introduction ............................................................................. 7
Overview .............................................................................................. 7
The SpaceLink™ Family ...................................................................... 8
System Requirements ........................................................................ 10
The Product Package......................................................................... 10
ASUS SpaceLink B&W PCI Card Layout ........................................... 11
LED Definitions ............................................................................ 11
ASUS SpaceLink B&W Specifications ......................................... 12
2. Installation ............................................................................. 13
2.1 Installing the ASUS Bluetooth Software ...................................... 14
2.2 Installing the ASUS SpaceLink B&W PCI Card........................... 16
2.3 Installing SpaceLink B&W PCI Card WLAN Drivers.................... 17
2.4 Verifying Drivers .......................................................................... 18
2.5 Installing SpaceLink Wireless Utilities ......................................... 19
3. Wireless LAN Reference....................................................... 20
Chapter Overview............................................................................... 20
Preliminary Information ................................................................ 21
3.1 Control Center (Utility).................................................................. 22
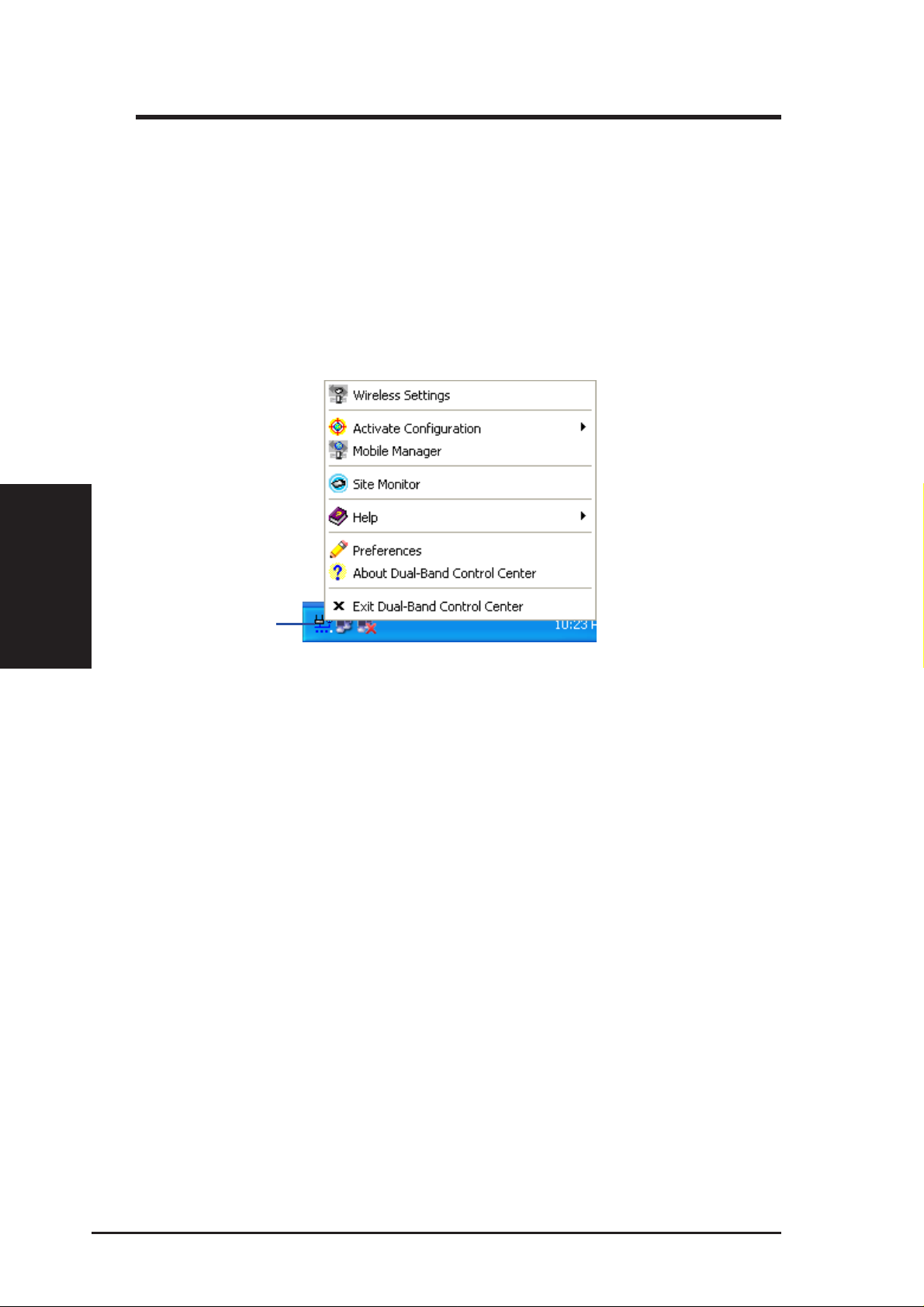
3.1.1 Taskbar Right-Click Menu.................................................. 24
3.1.2 Taskbar Left-Click Menu .................................................... 24
3.2 Wireless Settings (Utility) ............................................................. 25
3.2.1 Status - Status Tab ............................................................ 25
3.2.2 Save as Profile .................................................................. 26
3.2.3 Status - Connection Tab .................................................... 28
3.2.4 Frame Statistics................................................................. 29
3.2.5 Status - IP Config Tab........................................................ 30
3.2.6 Config - Basic Tab ............................................................. 31
3.2.7 Config - Encryption Tab ..................................................... 34
3.2.8 Config - Advanced Tab ...................................................... 37
3.2.9 Survey - Site Survey Tab ................................................... 39
3.2.10About ................................................................................. 40
3.2.11 Link Status ......................................................................... 41
3.2.12Exit Wireless Settings ........................................................ 41
4 ASUS SpaceLink B&W PCI Card
Page 6

Table of Contents
3.3 Activate Configuration .................................................................. 42
3.4 Mobile Manager (Utility) ............................................................... 43
3.4.1 Main Window ..................................................................... 44
3.4.2 View Menu......................................................................... 46
3.4.3 Help Menu ......................................................................... 46
3.4.3 Using New Configuration Wizard....................................... 47
3.4.4 Using Edit Configuration.................................................... 50
3.5 Site Monitor .................................................................................. 59
3.5.1 Starting Site Monitor .......................................................... 59
3.5.2 Main Screen ...................................................................... 59
3.5.3 Monitor............................................................................... 60
3.6 Windows XP Wireless Properties................................................. 61
4. Bluetooth Reference ............................................................. 63
4.1 Introduction to Bluetooth .............................................................. 63
4.2 Using the Bluetooth Software....................................................... 64
4.2.1 Bluetooth Connection Wizard ............................................ 66
4.2.2 Explore .............................................................................. 68
4.2.3 Setup ................................................................................. 69
4.2.4 Security.............................................................................. 69
4.2.5 Configuration ..................................................................... 70
4.2.6 Services............................................................................. 72
4.2.7 Serial Port.......................................................................... 74
4.2.8 Dial-Up Networking............................................................ 76
4.2.9 Fax..................................................................................... 77
4.2.10Inbox .................................................................................. 78
4.2.1 1 Network Access ................................................................. 79
4.2.12 File Transfer ..................................................................... 80
4.3 File Transfer Example (to Public Folder)...................................... 82
4.3.1 Bluetooth Cellular Phone................................................... 83
4.3.2 Dial-Up Networking with Bluetooth Cellular Phone ............ 84
5. Troubleshooting.................................................................... 85
Wireless LAN...................................................................................... 85
Bluetooth ............................................................................................ 87
ASUS SpaceLink B&W PCI Card 5
Page 7

Chapter 1 - Introduction
Chapter 1
6. Glossary................................................................................. 89
7. Safety Information .............................................................. 108
Wireless LAN-Related ........................................................................ 89
Bluetooth-Related............................................................................... 92
IEEE 802.11b (11Mbits/sec) ............................................................. 104
Direct-Sequence Spread Spectrum (for 802.11b) ............................ 105
IEEE 802.11a (54Mbits/sec)............................................................. 106
COFDM (for 802.11a)....................................................................... 107
Federal Communications Commission Statement ........................... 108
Canadian Department of Communications ...................................... 109
Regulatory Information / Disclaimers ............................................... 109
Safety Information ............................................................................ 109
MPE Statement ................................................................................ 110
Caution Statement of the FCC Radio Frequency Exposure............. 110
SAR Exposure.................................................................................. 110
Radio Frequency Interference Requirements .................................. 110
6 ASUS SpaceLink B&W PCI Card
Page 8

1. Introduction
Overview
Chapter 1 - Introduction
Thank you for purchasing the ASUS SpaceLink B&W PCI Card. The ASUS SpaceLink
B&W PCI Card is a PCI compliant “wireless” network interface card (NIC) for any
computer equipped with a PCI slot.
ASUS SpaceLink B&W PCI Card is designed to be fully compliant with both the
IEEE 802.11b and IEEE 802.1 1a wireless local area network (Wireless LAN) standards
as well as Bluetooth for interconnecting personal devices. The ASUS SpaceLink B&W
PCI Card product provides high-speed, standards-based W ireless LAN solutions. The
ASUS SpaceLink B&W PCI Card can auto-switch between 802.11b and 802.11a
networks, while maintaining Bluetooth connectivity.
Bluetooth
Bluetooth can communicate with a wide range of Bluetooth-enabled devices from mobile
phones, headsets, PDAs, printers, and other computers. Bluetooth can create virtual
connections for serial communication, network access, file transfer, and device sharing.
802.11b
The ASUS SpaceLink B&W PCI Card supports data rates up to 1 1 Mbps (or up to 108
Mbps in ASUS turbo mode), with automatic fallback to 5.5, 2, and 1 Mbps in 802.11b
networks. It operates in the unlicensed 2.4 GHz frequencies called the Instrumentation,
Science, and Medical (ISM) band. Unlicensed means free of charge to users.
Chapter 1
802.11a
The ASUS SpaceLink B&W PCI Card also supports data rates up to 54 Mbps in 802.11a
networks using 5 GHz frequencies and Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing
(OFDM) technology .
Wireless LAN Software
The ASUS SpaceLink B&W PCI Card configuration utility is a user-friendly application
that helps you quickly setup multiple roaming nodes. You can even export the
configuration settings to a file and import them to other computers for fast multiple
installations. Wireless LANs are complementary extensions to existing wired LANs,
offering complete mobility while maintaining continuous network connectivity to both
corporate and home Intranets.
Bluetooth Software
Integrated Widcomm software provides easy Bluetooth connections user-friendly
interface and complete with user profiles for quick saving and loading of settings.
ASUS SpaceLink products keep you connected anytime, anywhere!
ASUS SpaceLink B&W PCI Card 7
Page 9
Chapter 1 - Introduction
LNK
AIR
Chapter 1
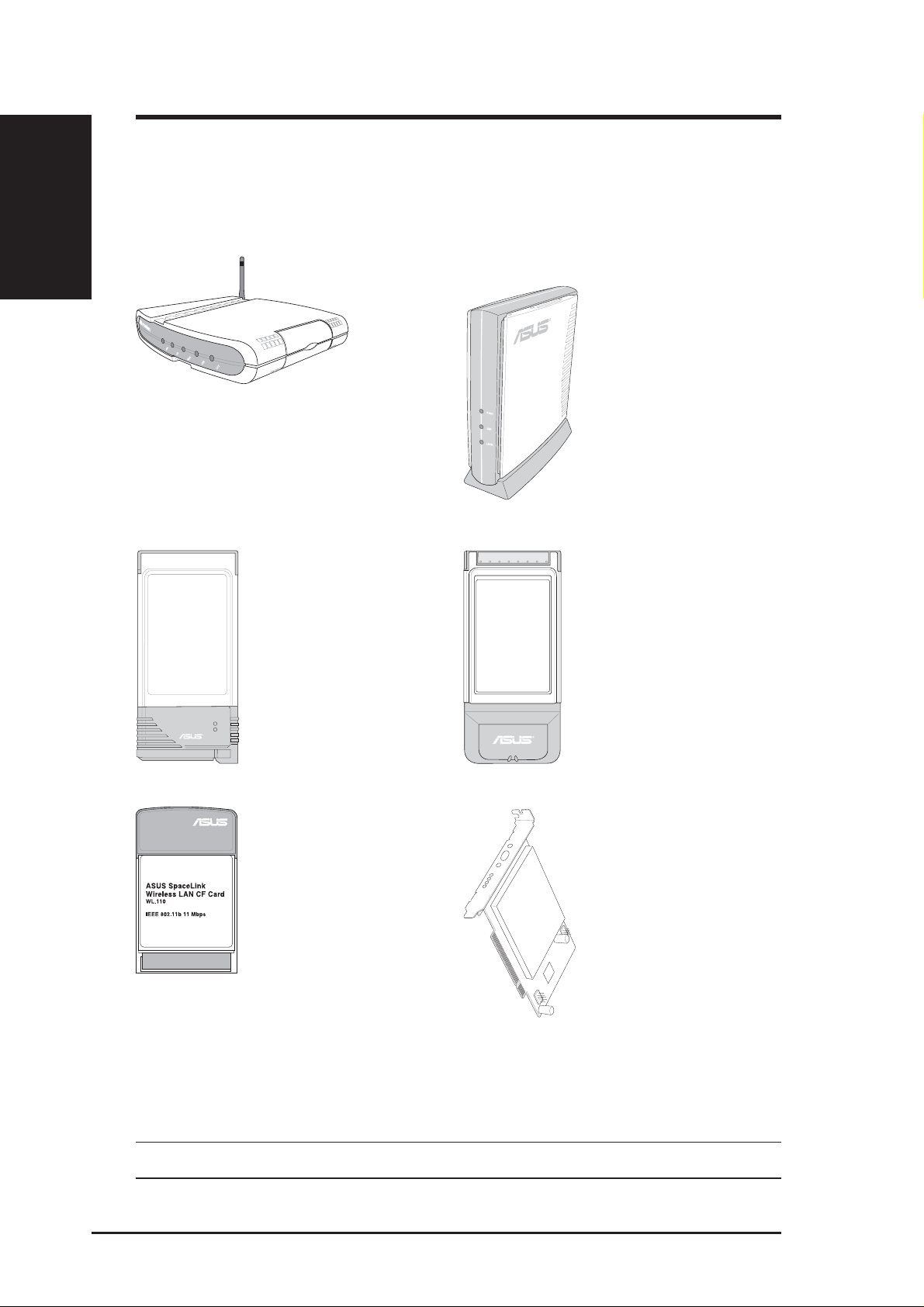
The SpaceLink™ Family
The SpaceLink™ Wireless PCI Card is a member of a product family that
provides a complete wireless networking solution.
The SpaceLink™ Home Gateway
(WL-500) creates a wireless network
using the IEEE 802.11b wireless
standard and allows sharing a single
Internet connection.
The SpaceLink™
PC Card (WL-100)
is a IEEE 802.11b
wireless LAN adapter
that fits into a
PCMCIA T ype II slot
in a Notebook PC.
The SpaceLink™
Access Point (WL-
300) creates a wireless
network using the IEEE
802.11b wireless
standard.
The SpaceLink™
Cardbus Card (WL-
200) is a dual band (IEEE
802.11a/b) wireless LAN
adapter that fits into a
Notebook PC’s PCMCIA
T ype II slot with Cardbus
support.
The SpaceLink™
CF Card (WL-110)
is a IEEE 802.11b
wireless LAN adapter
that fits into a
Compact Flash Type
II slot in a Portable
Digital Assistant
(PDA).
The above illustrations are not to scale.
8 ASUS SpaceLink B&W PCI Card
The SpaceLink™
B&W PCI Card
(WL-230) is a dual
band (IEEE 802.11a/b)
wireless PCI card that
supports IEEE 802.11a,
802.11b, and
Bluetooth.
Page 10

Chapter 1 - Introduction
Chapter 1
The SpaceLink™ Dual-Band Home
Gateway (WL-600) creates a wireless
network using the IEEE 802.11b and
802.11a wireless standards and allows
sharing a single Internet connection.
The USB SpaceLink™ Client
(WL-140) is an IEEE 802.11b
wireless USB LAN adapter that
connects to any computer’s USB
port with the benefit of being able
to place the antenna anywhere in
order to maximize signal strength.
ASUS SpaceLink B&W PCI Card 9
Page 11

Chapter 1 - Introduction
Chapter 1
System Requirements
To begin using the SpaceLink™ Wireless B&W PCI Card, you must have
the following minimum requirements:
• Motherboard with an available PCI slot
• USB 2.0 header (10-1 pins) on motherboard or USB 2.0 PCI card
• Windows XP/2000/ME/98SE
• 32MB system memory or larger
• 300MHz processor or higher
The Product Package
When you receive the Wireless LAN package, it should contain the
following items:
• One SpaceLink™ Wireless B&W PCI Card with Antenna
• One SpaceLink™ Wireless B&W PCI Card User’s Manual
• One Support CD (tools and documentation)
• One short USB 2.0 cable (for card to motherboard use only)
• One 2-port USB bracket with cable (for individual package)
The SpaceLink Wireless B&W PCI Card comes in two packages –
bundled with an ASUS motherboard and individual package for separate sale.
If any of the above items are not included or damaged, contact your
local dealer for instructions.
10 ASUS SpaceLink B&W PCI Card
Page 12
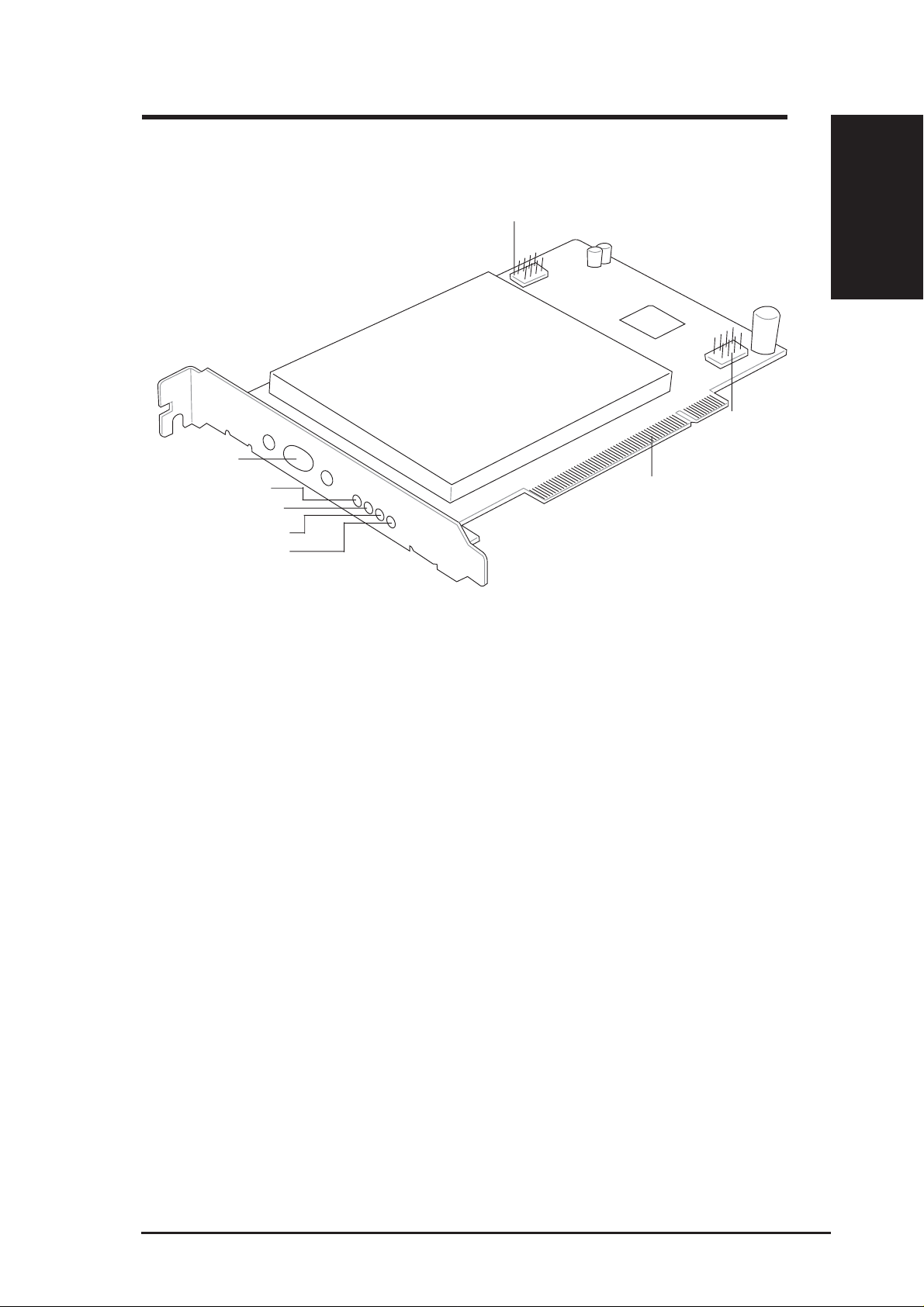
Chapter 1 - Introduction
ASUS SpaceLink B&W PCI Card Layout
USB 2.0 Out (up to 2 ports)
Antenna Port
Chapter 1
USB 2.0 In
Bluetooth Receive
Bluetooth Transmit
Wireless LAN Activity
Wireless LAN Status
LED Definitions
Bluetooth
Bluetooth Receive LED:
Blink - Receiving data packets
OFF - No data packets received
Bluetooth Transmit LED:
Blink - Transmitting data packets
OFF - No data packets transmitted
Standard PCI 2.2
Connector
Wireless LAN (802.11a/b)
Activity LED Status LED Meaning
Fast Blink Fast Blink Associated or joined with network
Slow Blink Slow Blink Associated or joined with network, no activity
Alternating Alternating Searching for network connection
OFF Slow Blink Power save mode (Power-Up or Reset)
OFF OFF No power received
ASUS SpaceLink B&W PCI Card 11
Page 13

Chapter 1 - Introduction
Chapter 1
ASUS SpaceLink B&W Specifications
Industry Standards: Bluetooth, IEEE802.11a, IEEE802.11b
Host Interface: WLAN: PCI 2.2 compliant slot, Bluetooth: USB 2.0
Antenna: Integrated Bluetooth and dual-band wireless LAN
Bluetooth
Operating Freq: 2.4GHz to 2.5GHz
Data Rate: 1 Mbps
Range: Up to 10 meters
Architecture: Piconet, scatter net
IEEE802.11a
Operating Freq: 5.15GHz to 5.35GHz, 5.725GHz to 5.85GHz
Data Rate: 54, 48, 36, 24, 12, 9, 6Mbps, turbo mode up to 108Mbps
Range: Indoor: 12 meters @ 11Mbps, 50 meters @ 6Mbps
Architecture: Infrastructure and Ad-Hoc
IEEE802.11b
(
turbo mode available only when connecting with other ASUS 802.11a devices)
Outdoor: 30 meters @ 54Mbps, 150 meters @ 6Mbps
Operating Freq: 2.4GHz to 2.5GHz
Data Rate: 11, 5.5, 2, 1Mbps
Range: Indoor: 30 meters @ 11Mbps, 90 meters @ 2Mbps
Outdoor: 150 meters @ 11Mbps, 300 meters @ 2Mbps
Architecture: Infrastructure and Ad-Hoc
12 ASUS SpaceLink B&W PCI Card
Page 14

Chapter 2 - Installation
2. Installation
This chapter explains how to install the ASUS SpaceLink B&W PCI Card
hardware, drivers, and utilities. This product is designed to operate in
Windows 98SE, Windows Me, 2000, and XP. Examples in this manual will
be that of Windows XP.
Complete the following steps to install the ASUS SpaceLink B&W PCI
Card.
1. Install the ASUS SpaceLink Bluetooth Software.
2. Install the ASUS SpaceLink B&W PCI Card.
3. Install the ASUS SpaceLink B&W PCI Card WLAN Driver.
4. Install the ASUS SpaceLink B&W PCI Card WLAN Utilities.
Note: Install the ASUS Bluetooth Software first before inserting the
SpaceLink B&W PCI Card.
Chapter 2
ASUS SpaceLink B&W PCI Card 13
Page 15
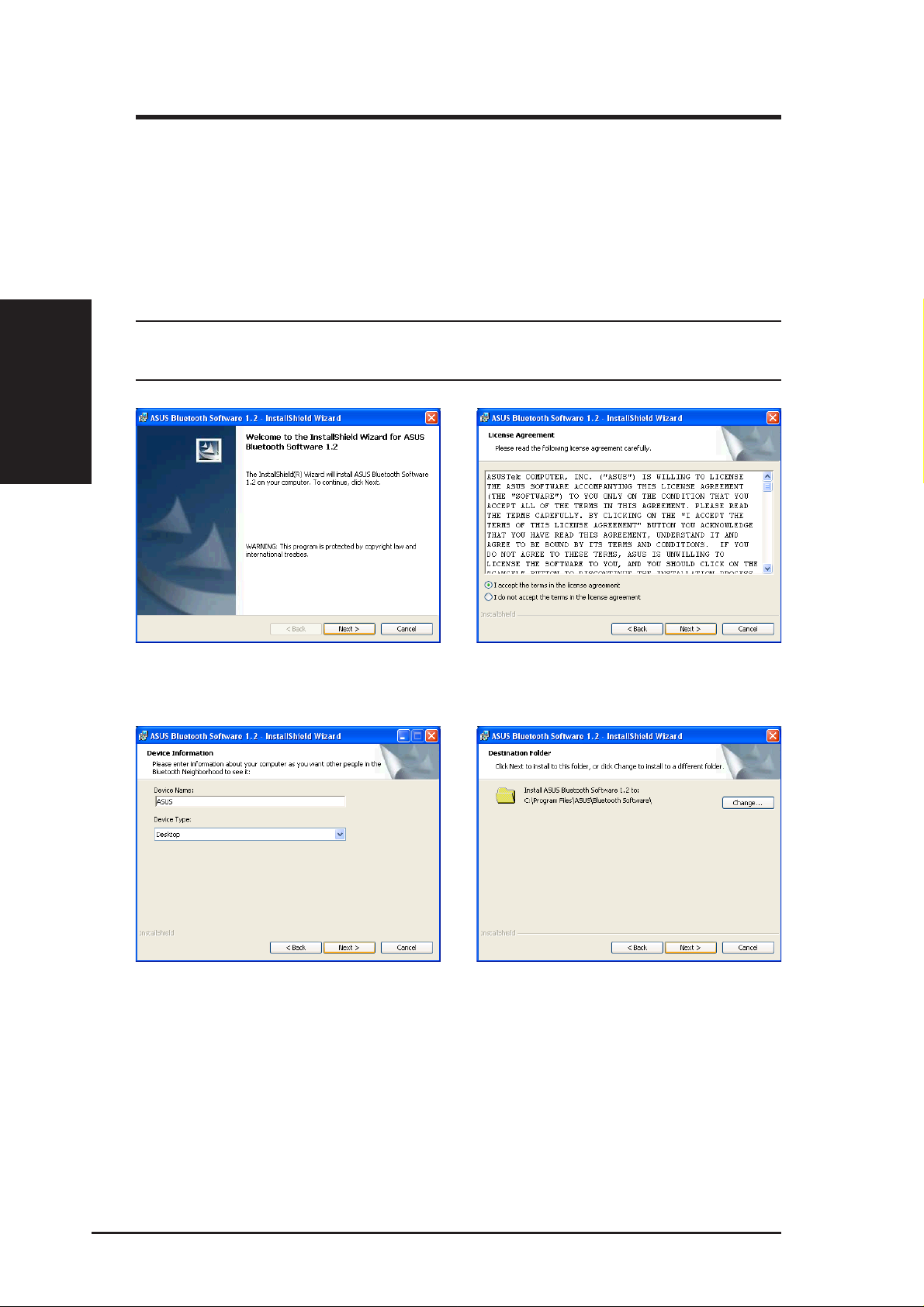
Chapter 2 - Installation
2.1 Installing the ASUS Bluetooth Software
The SpaceLink Bluetooth function requires the installation of the ASUS
Bluetooth Software. Insert the ASUS SpaceLink B&W PCI Card support CD
and the autorun screen should appear. On the autorun menu, click Install
Bluetooth Software. If your autorun is disabled, double-click SETUP.EXE in
the root directory of the support CD.
Chapter 2
Note: Install the ASUS Bluetooth Software first before inserting the
SpaceLink B&W PCI Card.
1. Click Next to begin.
2. Click Next after reading the License
Agreement and selecting “I accept...”.
3. Select your computer type: Desktop
14 ASUS SpaceLink B&W PCI Card
4. Click Next to accept the destination folder
or click “Change” to specify another folder.
Page 16
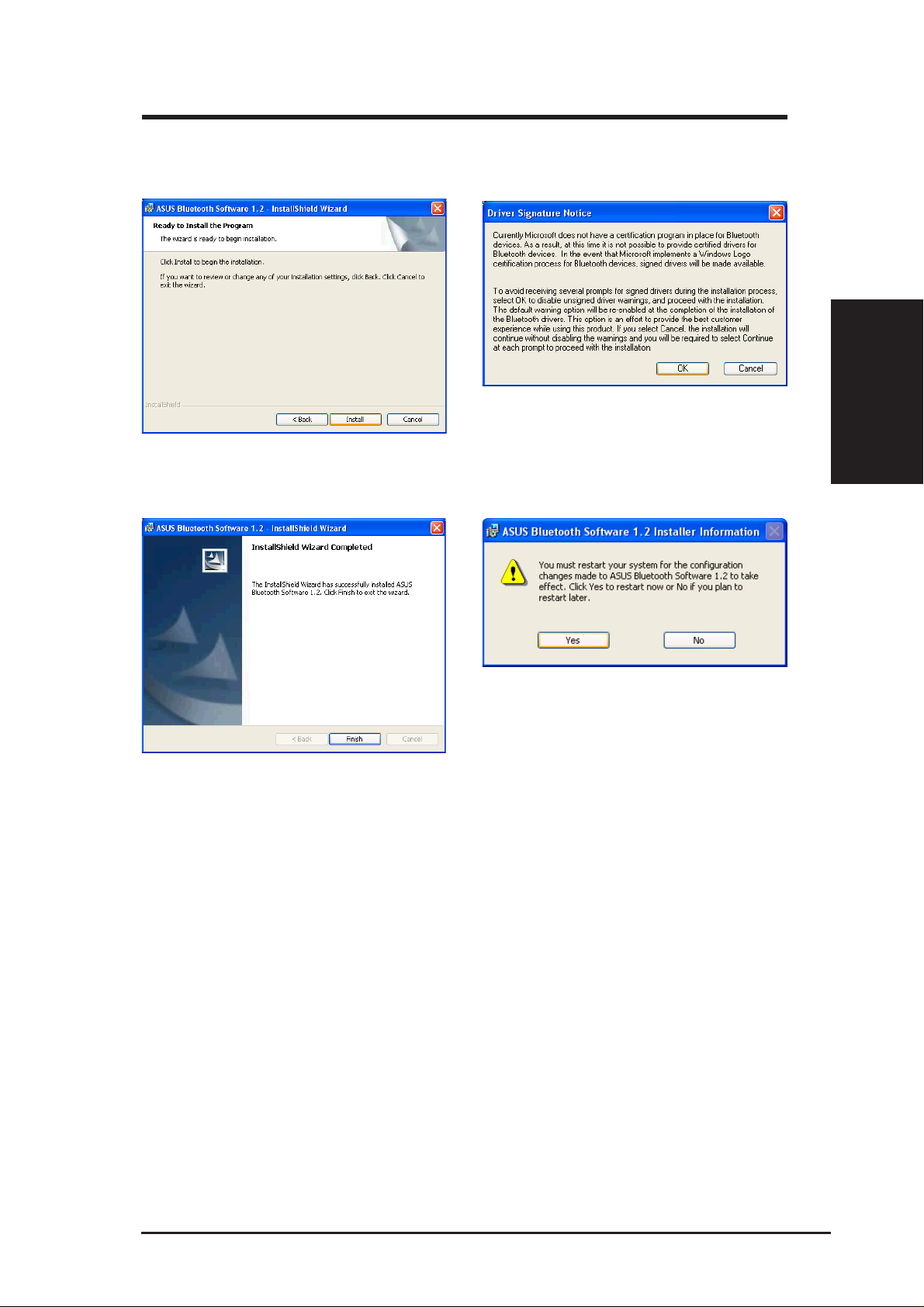
Chapter 2 - Installation
2.1 Installing the ASUS Bluetooth Software (Cont.)
Chapter 2
5. Click Install when ready to install the
software.
7. Click Finish when installation is complete. 8. Click Y es to restart your computer.
6. Click OK after reading the driver notice.
ASUS SpaceLink B&W PCI Card 15
Page 17
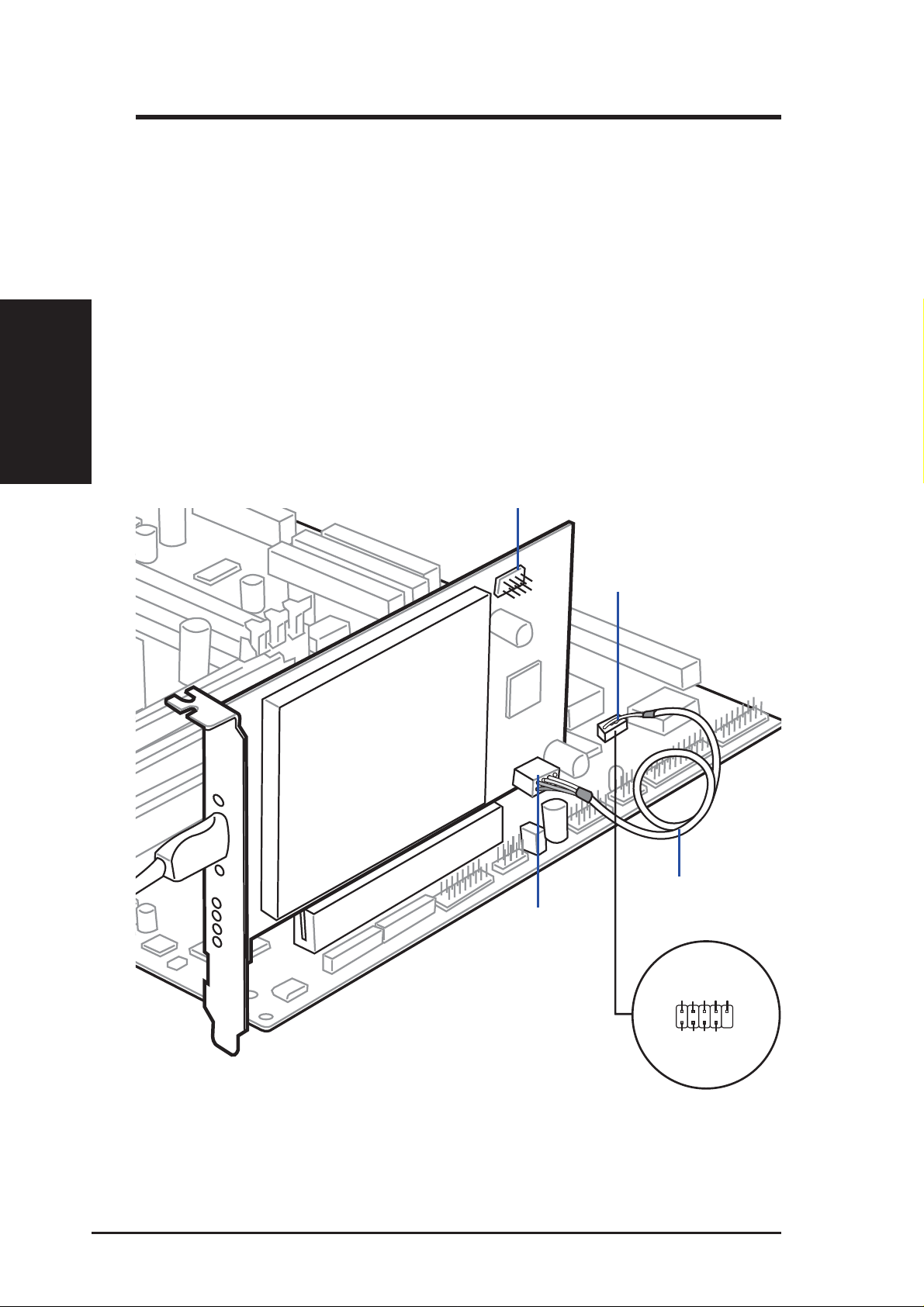
2.2 Installing the ASUS SpaceLink B&W PCI Card
USB P2 +
USB Power
Ground
Over Current
USB Power
USB P1 –
USB P1+
Ground
USB P2 –
1. Turn OFF your computer and open your computer chassis.
2. Insert the ASUS SpaceLink B&W PCI Card into a PCI slot.
3. Connect the provided short USB 2.0 cable from the ASUS SpaceLink
Chapter 2
4. Attach the antenna to the ASUS SpaceLink B&W PCI Card as shown.
Chapter 2 - Installation
B&W PCI Card (USB 2.0 IN) to the USB 2.0 OUT header on the motherboard or USB 2.0 PCI expansion card. You can use the USB 2.0 port
by connecting your motherboard’s USB bracket (not included) to the
USB 2.0 OUT on the ASUS SpaceLink B&W PCI Card.
USB 2.0 Out
(Blue on card)
USB 2.0 Out (Blue
on motherboard)
USB 2.0 In
(Yellow on card)
USB 2.0 Out
Short USB 2.0 Cable
(Color coded plugs)
Color Coded Plugs
USB 2.0 connectors and cable are color coded. Connect the same color plug to
the same color connectors.
16 ASUS SpaceLink B&W PCI Card
Page 18
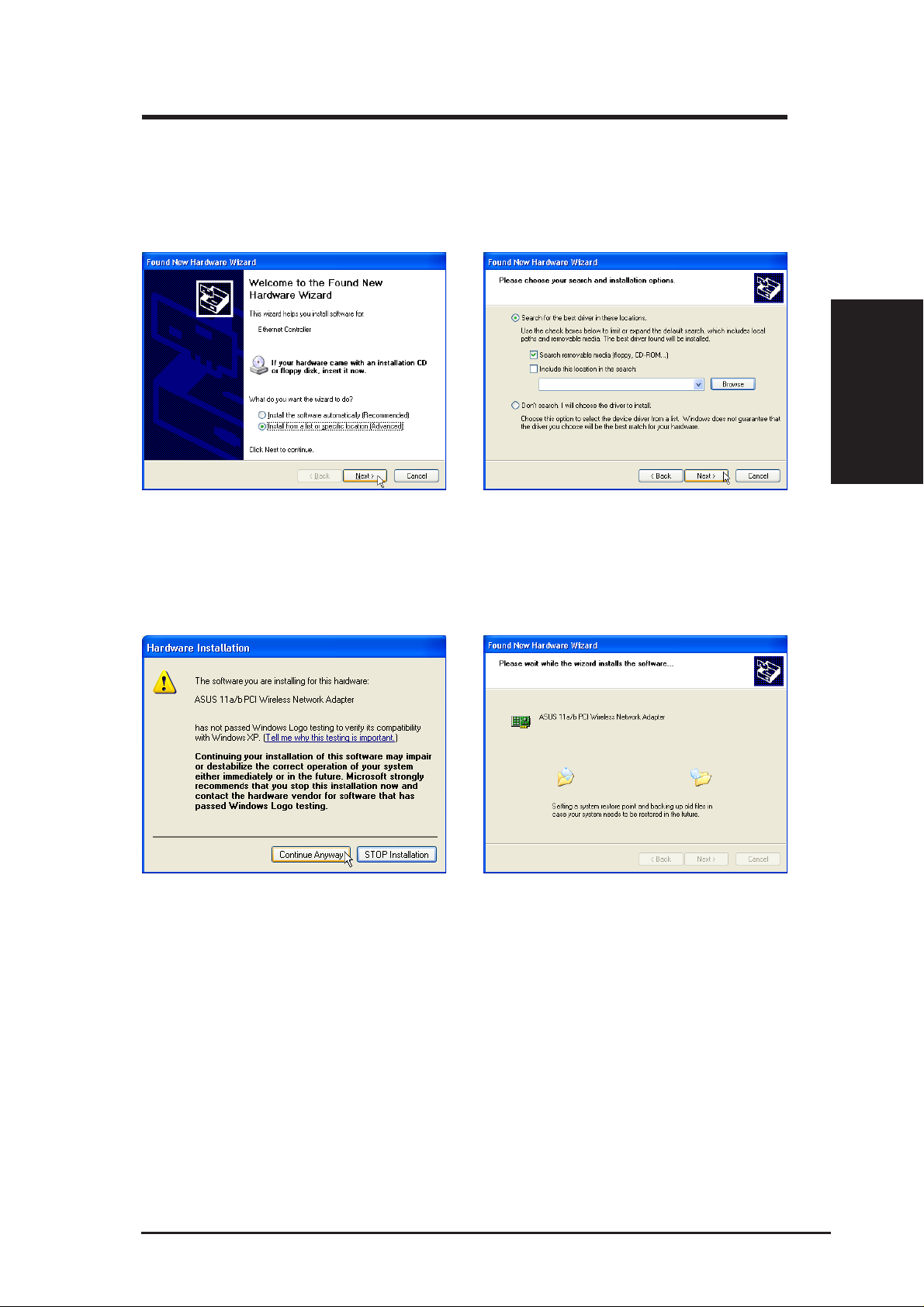
Chapter 2 - Installation
2.3 Installing SpaceLink B&W PCI Card WLAN Drivers
With the SpaceLink B&W PCI Card installed, turn ON your computer and
enter Windows.
Chapter 2
1. Windows will automatically detect the ASUS
SpaceLink B&W PCI Card once you enter
Windows with the card properly installed.
Once the “Add New Hardware Wizard”
dialog appears, click Next.
4. When asked about driver compatibility with
Windows XP. Click Continue Anyway
since ASUS has always tests its drivers
before product shipment.
2. Insert the support CD that came with your
ASUS SpaceLink B&W PCI Card .
3. Select “Search for the best driver in”...
“Search removable media...” Click Next.
5. Wait while Windows XP creates a restore
point for you system files in case you need
to restore your current system.
ASUS SpaceLink B&W PCI Card 17
Page 19
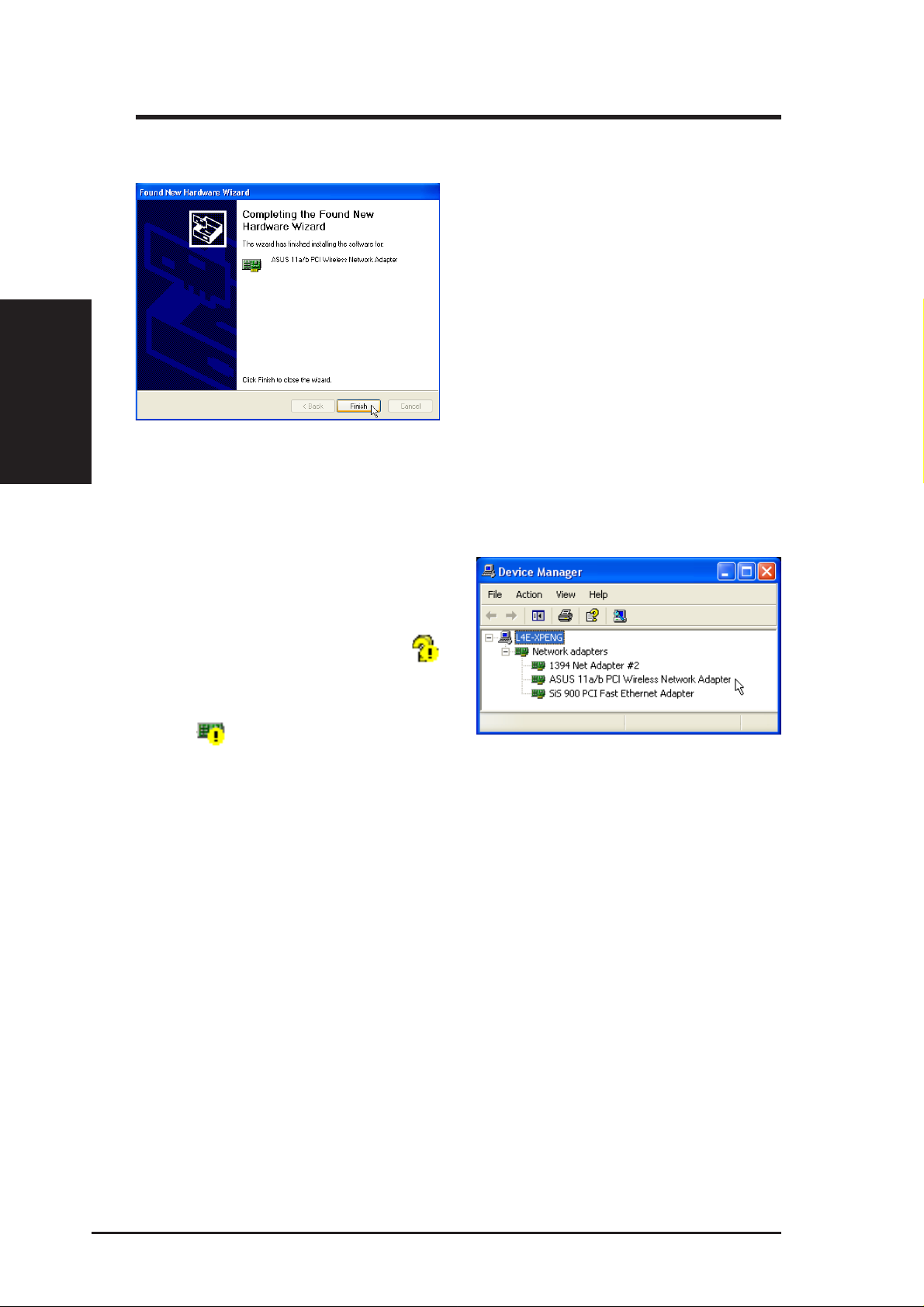
2.3 Installing SpaceLink B&W PCI Card WLAN Drivers (Cont.)
Chapter 2
6. Click Finish when installation has complete.
2.4 Verifying Drivers
Chapter 2 - Installation
Restart your computer if prompted.
You can verify the driver in Device
Manager. (Access Device Manager
from Start | Control Panel | System |
Hardware). A question mark
means that no driver has been
installed. An exclamation mark over
a card
incorrect. Verify that you are using the correct product and driver CD. Try
repeating the installation and contact customer support if necessary.
WLAN
If it is installed successfully , the “ASUS 11a/b PCI W ireless Network Adapter”
will appear under “Network adapaters”.
Bluetooth
If it is installed successfully, “ASUS Bluetooth Device” will appear under
“Universal Serial Bus controllers”.
means that the driver is
18 ASUS SpaceLink B&W PCI Card
Page 20
Chapter 2 - Installation
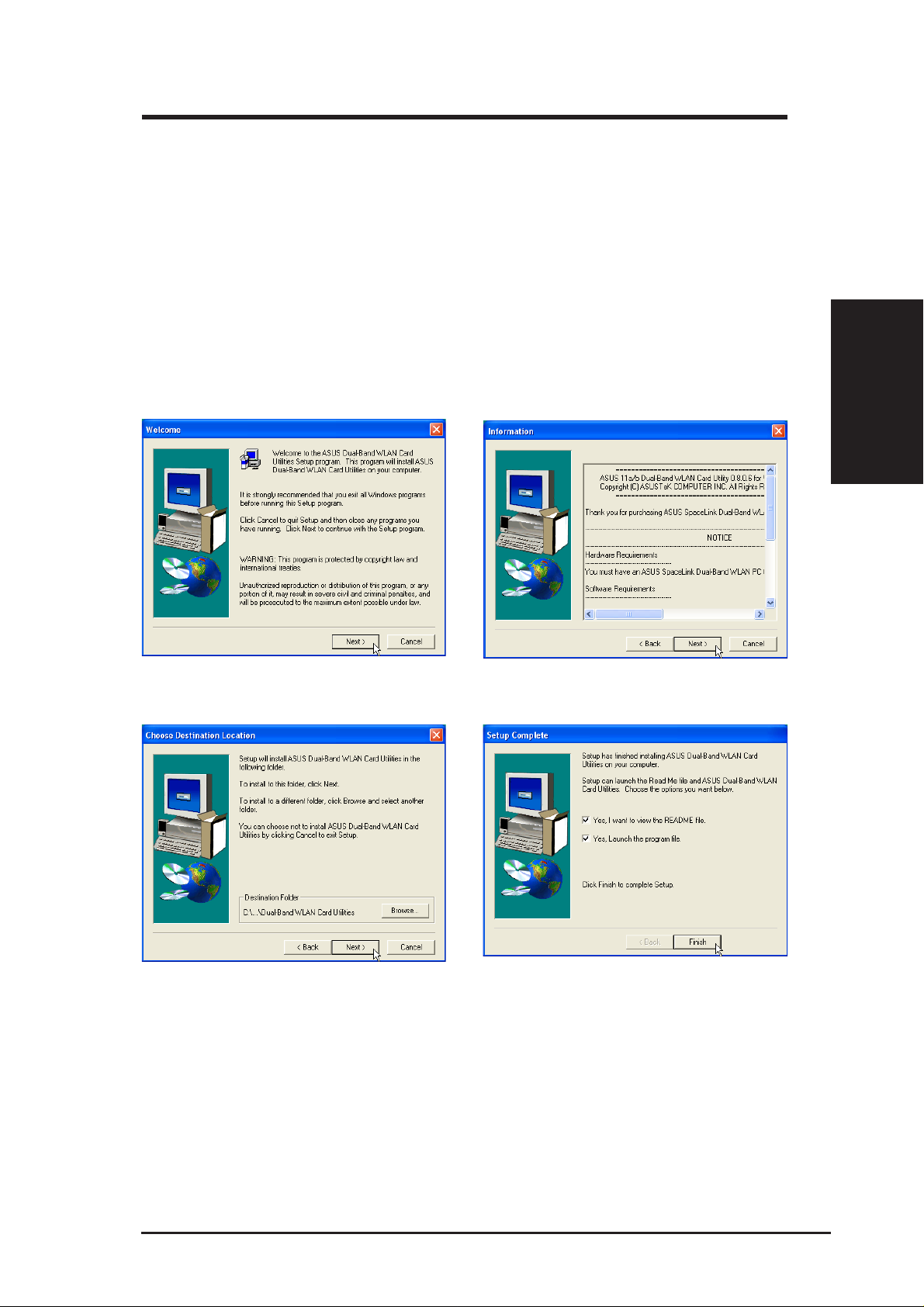
2.5 Installing SpaceLink Wireless Utilities
After you have installed the ASUS SpaceLink B&W PCI Card driver , you
can install the SpaceLink wireless utilities. The SpaceLink wireless utilities
can be used for all SpaceLink products so you only need to have one copy
installed in your system.
1. Insert the ASUS SpaceLink B&W PCI Card support CD and an autorun menu will appear. If
your autorun is disabled, double click SETUP.EXE in the root directory of the support CD.
2. On the bottom of the autorun menu, select a language from the pull-down menu. Click Install
ASUS Dual-Band WLAN Card Utilities.
Chapter 2
1. Click Next on the Welcome screen.
3. Click Next to use the default Destination
Folder or click Browse to select another
folder.
2. Click Next after reading the Information.
4. Click Finish after setup is complete.
ASUS SpaceLink B&W PCI Card 19
Page 21
3. Wireless LAN Reference
Chapter Overview
The ASUS SpaceLink B&W PCI Card software includes utilities that can
be launched from the Start Menu or taskbar icon. Normally control center
is launched on Windows startup and right clicking the taskbar icon will
bring up a quick access menu.
Chapter 3
Chapter 3 - Wireless LAN Reference
Control Center Icon
Right-Click Taskbar Menu
This chapter will describe the following utilities in this order:
1. Control Center – This is the main software (launched on Windows
startup by default) which makes it easy to launch applications and activate network location settings.
2. Wireless Settings – This is the main configuration interface which al-
lows users to control the ASUS SpaceLink B&W PCI Card.
3. Activate Configuration – This allows you to set roaming and profile
options to conveniently change wireless settings for different locations.
4. Mobile Manager – This is a convenient tool to setup and manage net-
work location settings.
5. Site Monitor – This measures the received signal strength indicator
(RSSI) values of all wireless networks. This tool is used for determining the best placement of Access Points to provide the most efficient
coverage in a wireless network.
20 ASUS SpaceLink B&W PCI Card
Page 22
Chapter 3 - Wireless LAN Reference
Preliminary Information
Windows XP Wireless Options
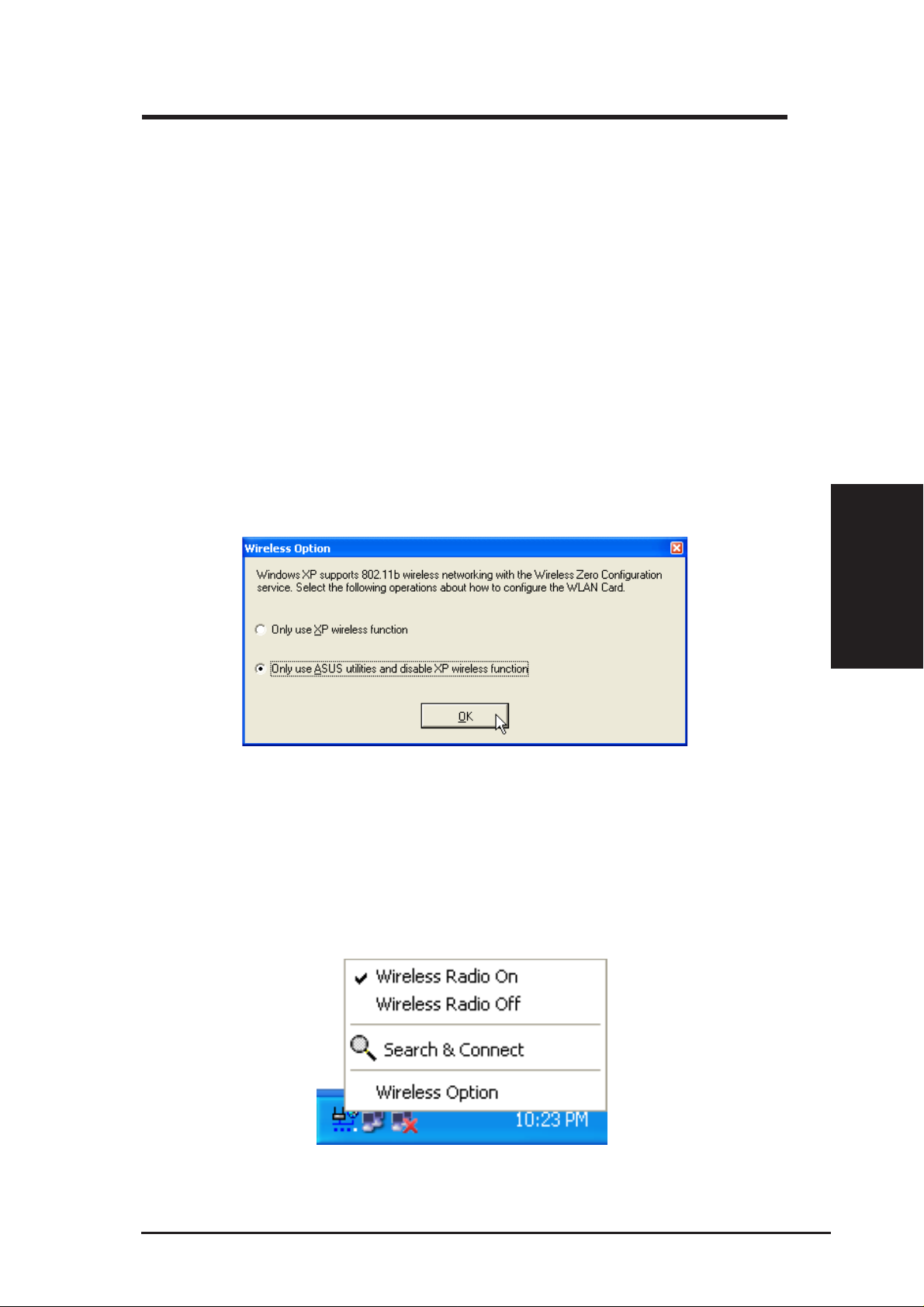
The first time the Control Center utility is launched in W indows XP, it will
automatically show the wireless options shown below. Select one of the
radio buttons to decide which interface to use with your SpaceLink B&W
PCI Card.
Only use XP wireless function – Only use “Windows XP” wireless network
settings to configure the ASUS SpaceLink B&W PCI Card.
Only use ASUS utilities and disable XP wireless function – Only use
“ASUS SpaceLink B&W PCI Card utilities” to configure the ASUS
SpaceLink B&W PCI Card.
It is recommended that you choose “ASUS utilities...” because there are
added features provided by the ASUS SpaceLink Software. This User’s
Manual will discuss the ASUS utilities. You can return to the W ireless Option
setting at any time by left clicking the control center icon and choosing
“Wireless Option”.
Chapter 3
Taskbar Left-Click Menu
ASUS SpaceLink B&W PCI Card 21
Page 23

3.1 Control Center (Utility)
Control Center is an application that makes it easy to launch applications
and activate network location settings. Control Center starts automatically
when the system boots. Whenever Control Center is running, you will see
a Control Center icon displayed on the Windows taskbar.
Starting the Control Center manually
• Click the Windows Start button, select Programs, select ASUS Util-
or
• Double click the Control Center icon on the desktop.
Chapter 3
Chapter 3 - Wireless LAN Reference
ity, select Dual Band WLAN Card, and then click ASUS WLAN Control Center.
Windows Start Menu - Programs
Using the Control Center Taskbar
The Control Center Taskbar menu display the following information:
• The link quality of the ASUS SpaceLink B&W PCI Card (Excellent, Good, Fair, Poor, Not Linked)
• Whether the ASUS SpaceLink B&W PCI Card is connected to the
Internet (Blue: Connected, Gray: Not Connected)
Taskbar Icon and Status
22 ASUS SpaceLink B&W PCI Card
Page 24

Chapter 3 - Wireless LAN Reference
Wireless Status Icons (on the taskbar)
Excellent link quality and connected to Internet (Infrastructure)
Good link quality and connected to Internet (Infrastructure)
Fair link quality and connected to Internet (Infrastructure)
Poor link quality and connected to Internet (Infrastructure)
Not linked but connected to Internet (Infrastructure)
Excellent link quality but not connected to Internet (Infrastructure)
Good link quality but not connected to Internet (Infrastructure)
Fair link quality but not connected to Internet (Infrastructure)
Poor link quality but not connected to Internet (Infrastructure)
Not linked and not connected to Internet (Infrastructure)
Linked (Ad Hoc)
Not Linked (Ad Hoc)
Connected to Internet
Chapter 3
ASUS SpaceLink B&W PCI Card 23
Page 25
Chapter 3 - Wireless LAN Reference
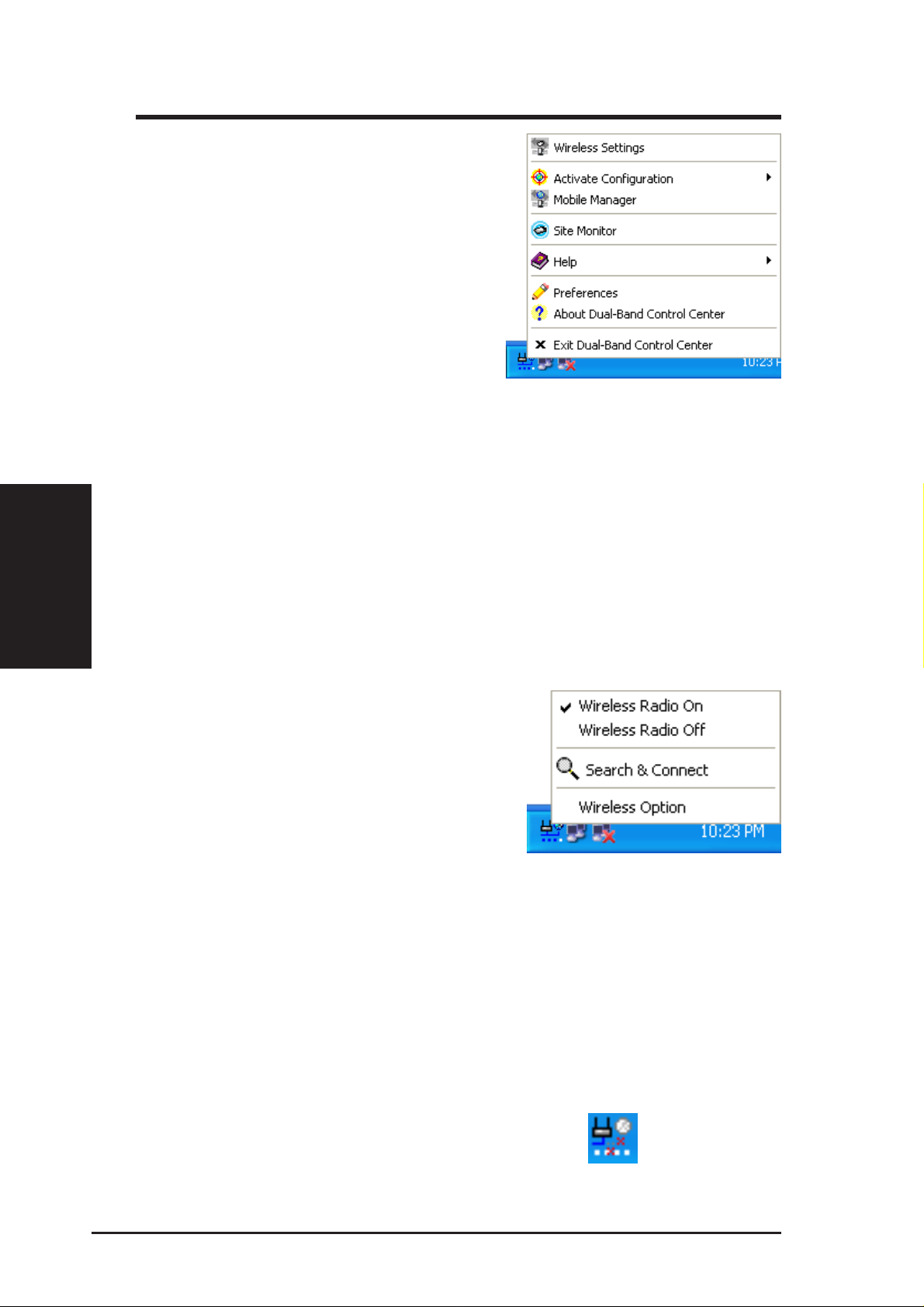
3.1.1 Taskbar Right-Click
Menu
Right-clicking the taskbar icon shows the following menu items:
• Wireless Settings – Launches Wireless Settings application.
• Activate Configuration – Allows you to set which profile to use.
Chapter 3
3.1.2 Taskbar Left-Click
Menu
Left-clicking the taskbar icon shows the following menu:
• Mobile Manager – Launches Mobile Manager application.
• Preferences – Customizes the way the Control Center program be-
haves. You can create a Control Center shortcut on the desktop.
You can also set whether Control Center starts up with Windows.
• Exit – Closes the Control Center program.
• Wireless Radio On – Turns the wireless radio ON.
• Wireless Radio Off – Turns the wireless radio OFF.
• Search & Connect – V iew the properties of available Access Points
within range.
• Wireless Option (W indows XP only) – Sets your Windows XP wire-
less networking environment.
Double-clicking the taskbar icon:
• Launches the Wireless Settings application.
24 ASUS SpaceLink B&W PCI Card
Page 26
Chapter 3 - Wireless LAN Reference
3.2 Wireless Settings (Utility)
Wireless Settings is an application that allows you to control your ASUS
SpaceLink B&W PCI Card. Use Wireless Settings to View or Modify the
configuration settings and monitor the operational status of your PC Card.
Once W ireless Settings is launched, you can see the tabbed property sheet.
This property sheet is composed of tabbed “pages”, each with its own group
of feature-specific settings.
Starting Wireless Settings
• Open the W indows Control Panel, and then double-click the icon ASUS
DualBand WLAN Card Setting icon.
or
• Click the Windows Start button, select Programs, select ASUS Util-
ity, select DualBand WLAN Card, and then click Wireless Settings.
or
• Click the Control Center icon on the W indows taskbar , a popup menu
appears, and then click Wireless Settings.
More than one ASUS SpaceLink Device
If you have more than one ASUS SpaceLink device. You will be given a
device selection window when you launch the “Wireless Settings” utility.
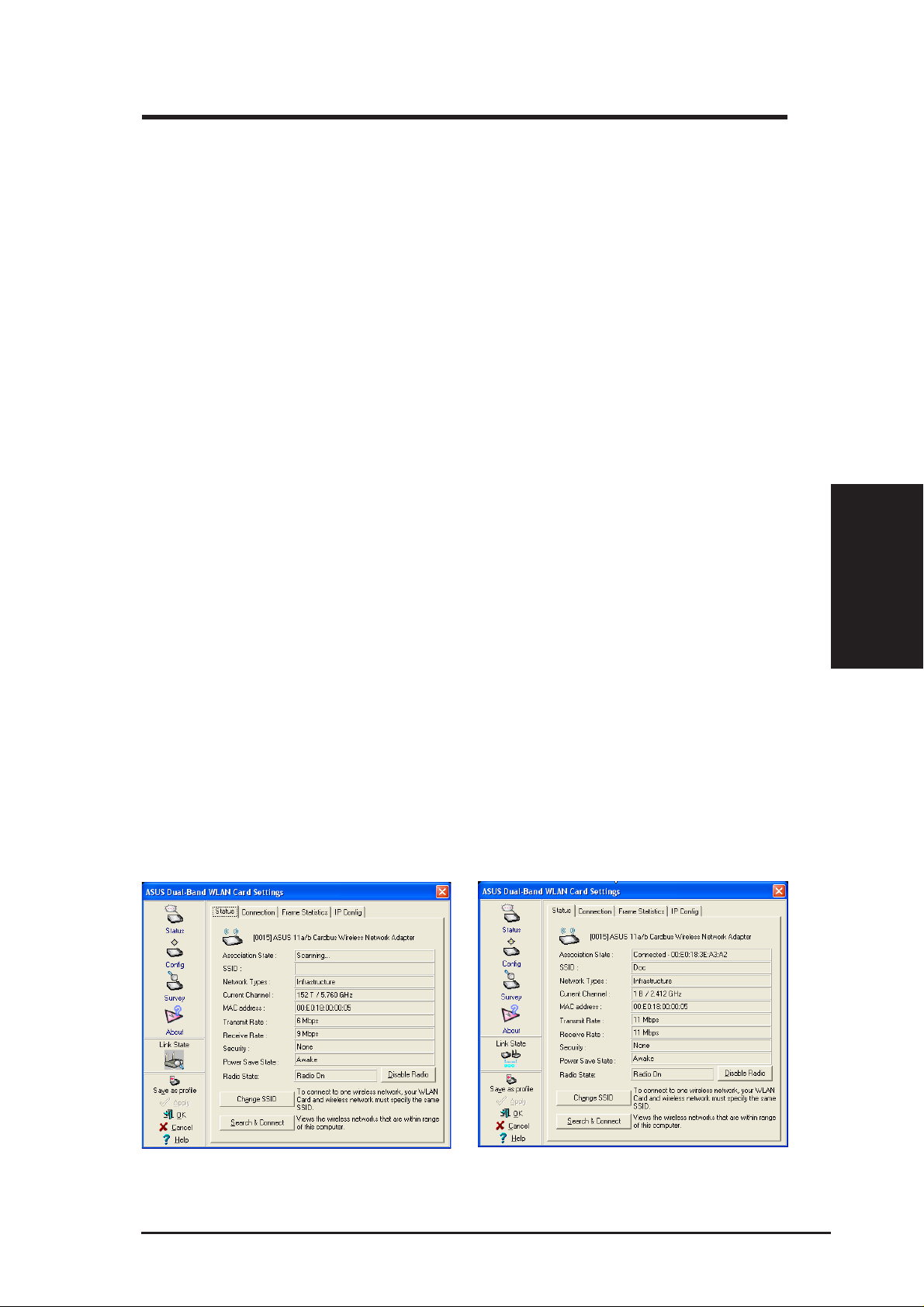
3.2.1 Status - Status Tab
You can view the information about the ASUS SpaceLink B&W PCI Card
from the general menu. These fields are blank if the ASUS SpaceLink B&W
PCI Card does not exist.
Chapter 3
Scanning
ASUS SpaceLink B&W PCI Card 25
Connected
Page 27

Association State
Displays the connection status as follows:
Connected - The station is now associated with one wireless LAN device.
When operating in Infrastructure mode, this field shows the MAC address of
the Access Point with which you are communicating. When operating in Ad
Hoc mode, this field shows the virtual MAC address used by computers
participating in the Ad Hoc network.
Scanning... - The station is now attempting to authenticate and associate with
the desired Access Point or Ad Hoc node.
Disconnected - The link is connected, but no beacon received.
SSID
Displays the Service Set Identifier (SSID) that the card is either associated or
Chapter 3
intending to join.
Chapter 3 - Wireless LAN Reference
Network Type
Displays the type of the network that the card is in use. The value is either
"Infrastructure" or "Ad Hoc".
Current Channel
Displays the radio channel that the card is currently tuned. This number changes
as the radio scans the available channels.
MAC address
Indicates the hardware address of the card. MAC address is a unique identifier
for networking devices (typically written as twelve hexadecimal digits 0 through
9 and A through F, six hexadecimal numbers separated by colons, i.e.
00:E0:18:F0:05:C0).
Transmit Rate
Displays the current transmit data rate in megabits per second (Mbps).
Receive Rate
Displays the current receive data rate in megabits per second (Mbps).
26 ASUS SpaceLink B&W PCI Card
Page 28
Chapter 3 - Wireless LAN Reference
Security
Indicates whether or not Wired Equivalent Privacy (WEP) is enabled for the
station.
Power Save State
Shows the following indicating the power saving state of the station "Awake",
"Sleep Pending", "Sleep", "Fake Sleep Pending", "Faking Sleep", and
"Unknown".
Radio State
Shows the wireless radio on or off.
Radio On - When the wireless radio is turned off, the following
icon appears in the upper left of the Settings property page.
Radio Off - When the wireless radio is turned on, the following
icon appears in the upper left of the Settings property page.
Change SSID – Click on this to set the SSID.
Search & Connect – Click on this to connect to an available network.
3.2.2 Save as Profile
Later, when you make individual settings, you may want to use profiles to
save your settings. Profiles will help you combine all your settings for
work, home, roaming, and other locations so that you do not have to repeat
individual settings.
Chapter 3
Select “Activate Configuration” from the menu to load a profile.
ASUS SpaceLink B&W PCI Card 27
Page 29
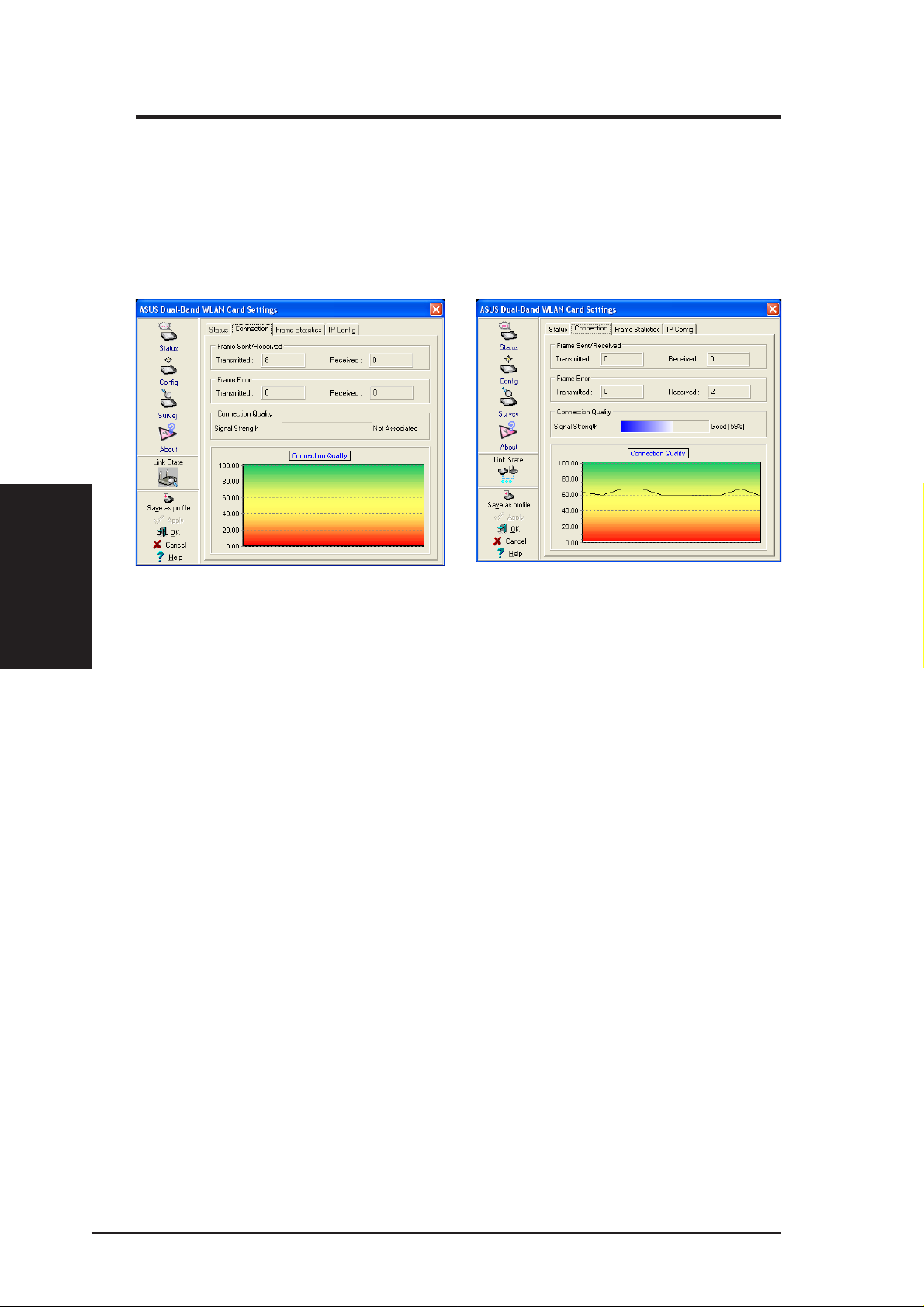
3.2.3 Status - Connection Tab
You can view the current link statistics about the ASUS SpaceLink B&W
PCI Card. These statistics are updated once per second and are valid only if
the ASUS SpaceLink B&W PCI Card exists.
Chapter 3
Chapter 3 - Wireless LAN Reference
Scanning
Frame Sent/Received
Connected
Transmitted - The number of frames that were transmitted.
Received - The number of frames that were received.
Frame Error
Transmitted - The number of frames that were not successfully transmitted.
Received - The number of frames that were not successfully received.
Connection Quality
Signal Strength - Reflects the signal level related to the Access Point or Ad
Hoc node the station is currently connected to. Ratings are: Excellent, Good,
Fair, and Poor.
Overall Connection Quality
It is derived from the current "Signal Strength". A graph displays a connection
quality range between 0 and 100 percent.
28 ASUS SpaceLink B&W PCI Card
Page 30
Chapter 3 - Wireless LAN Reference
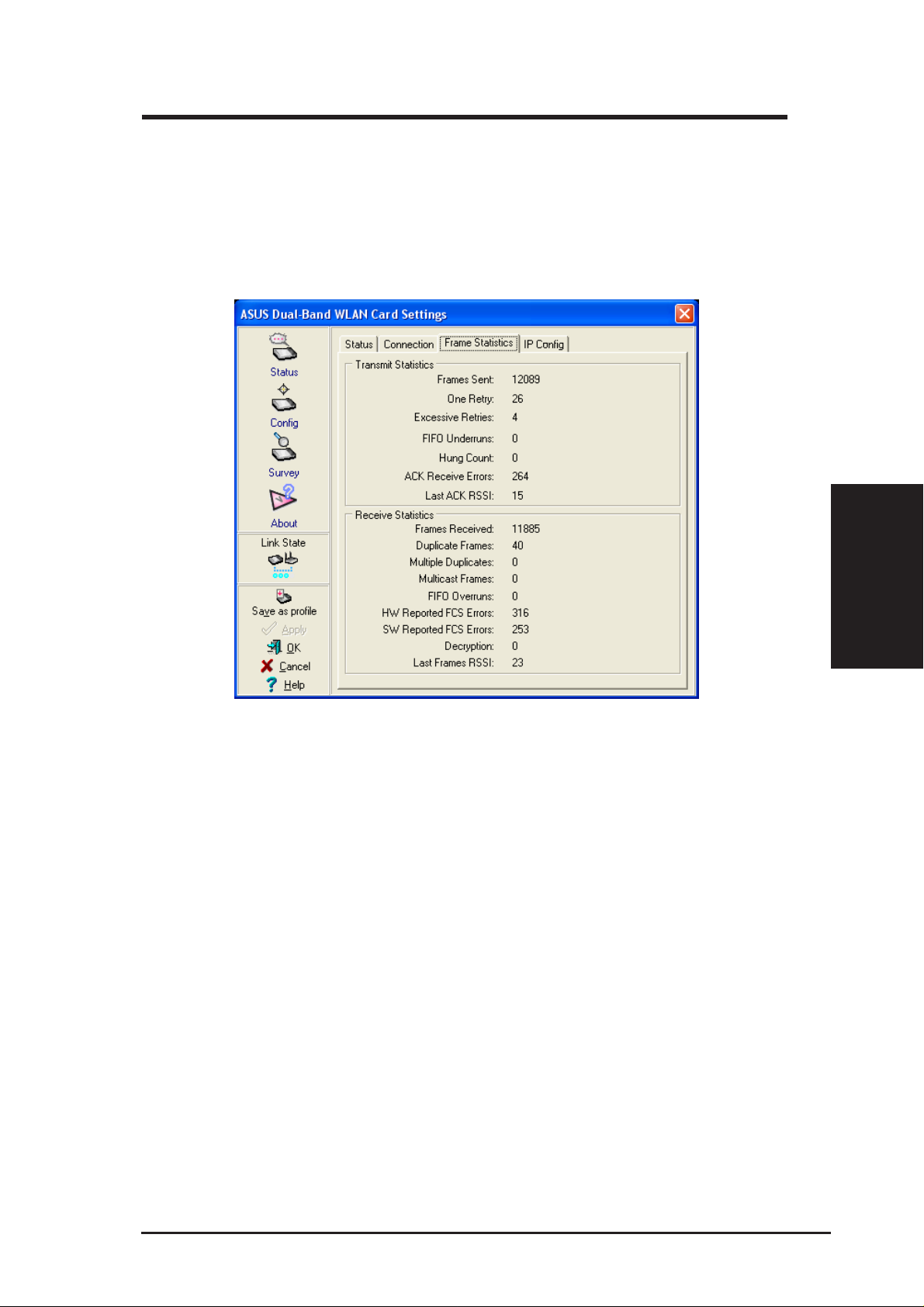
3.2.4 Frame Statistics
Frame statistics give information on data transferred though the wireless
LAN. You can monitor performance or trouble shoot signal quality within
different location of your wireless network.
Connected
Chapter 3
ASUS SpaceLink B&W PCI Card 29
Page 31

3.2.5 Status - IP Config Tab
IP Config tab shows all the current network configuration information for
the ASUS SpaceLink B&W PCI Card. Use it to verify your network settings.
IP CONFIG will display all the current TCP/IP configuration values
including the IP address, subnet mask, default gateway and Windows
Internet Naming Service (WINS) and DNS configuration.
Chapter 3
Chapter 3 - Wireless LAN Reference
Connected
Button
IP Release - Releases the DHCP IP address for the ASUS SpaceLink B&W
PCI Card.
IP Renew - Renews the DHCP IP address for the ASUS SpaceLink B&W
PCI Card.
NOTE: The IP Release and IP Renew buttons can only be used on
the ASUS SpaceLink B&W PCI Card that is configured with DHCP.
30 ASUS SpaceLink B&W PCI Card
Page 32

Chapter 3 - Wireless LAN Reference
3.2.6 Config - Basic Tab
Lets you can change the ASUS SpaceLink B&W PCI Card configurations
without rebooting your computer.
SSID Set to “Doc”
Network Type
Infrastructure – Select the Infrastructure mode to establish a connection with an Access Point. Your computer is able to access wireless
LAN and wired LAN (Ethernet), via an associated access point. The
Channel field turns to “Auto” when “Infrastructure” is selected.
Ad Hoc – Select the “Ad Hoc” mode to communicate directly with
each other without using an Access Point. An “Ad Hoc” network is
typically formed quickly and easily without pre-planning. For example,
share meeting notes between networked computers in a meeting room.
SSID
Use the SSID filed to configure the SSID for the ASUS SpaceLink B&W
PCI Card. You can enter a new SSID or select one from the drop-down list
box. SSID stands for “Service Set Identifier”, which is a string used to identify
a wireless LAN. You will only be able to connect Access Points which has
the same SSID as the one you set. Use different SSIDs to segment the wireless
LAN and increase security . SSIDs must all be printable characters and having
a maximum of 32 case sensitive characters, such as “ Wireless LAN”.
Chapter 3
Set the SSID to a null string, if you wish to allow your station to
connect to any Access Point it can find. But you cannot use null
string in Ad Hoc mode.
ASUS SpaceLink B&W PCI Card 31
Page 33

Power Saving
This field allows the configuration of power management options to conserve
battery life. These options are "Off", "Normal, and "Maximum". Power
Management is disabled when "Ad Hoc" mode is selected in the Network
Type field.
When the Power Saving setting is Off, it allows a full powered state that yields
the best performance. This mode is recommended for devices running on AC
power .
Power Saving setting is Normal or Maximum will enable power savings
function, the adapter will wake up periodically to see if there is any data being
sent. This mode is recommended for devices running on battery power. The
difference is when the Power Saving setting is Normal, the driver turns off
power to the adapter for brief periods over briefly-spaced time intervals; when
the Power Saving setting is Maximum, the driver turns off power to the adapter
Chapter 3
for long periods over widely-spaced time intervals.
Chapter 3 - Wireless LAN Reference
Transmit Power
This field allows the configuration of transmit power options. The options are
"100%", "50%", "25%", "12.5", and "Lowest".
Wireless Mode
Choose which wireless mode the wireless card will use. You can enable more
than one wireless mode to allow system auto switch among them.
5GHz 54Mbps (802.1 1a): Use this checkbox to allow the wireless card to use
the 5 GHz and 54 Mbps wireless mode.
5GHz 108Mbps (T urbo Mode): Use this checkbox to allow the wireless card
to use the 5 GHz and 108 Mbps wireless mode. A high speed operating mode
for 802.11a radio space. Support data transfer speeds up to 108 Mbps, twice
the speed of standard 802.11a devices. T urbo mode is only supported between
ASUS SpaceLink 802.11a devices.
2.4GHz 11Mbps (802.11b): Use this checkbox to allow the wireless card to
use the 2.4 GHz and 11 Mbps wireless mode.
Click Apply to save and activate the new configurations.
32 ASUS SpaceLink B&W PCI Card
Page 34

Chapter 3 - Wireless LAN Reference
Data Rate
Select the transmit data rate (fix or auto). The data rates supported for the
ASUS SpaceLink WLAN Cards are:
Auto - The adapter will adjust to the most suitable transmission rate.
Fix - 11a: Fix data rate to 6, 9, 12, 18, 24, 36, 48, or 54 megabits per second.
11b: Fix data rate to 1, 2, 5, or 11 megabits per second.
Chapter 3
Click Apply to save and activate the new configurations.
ASUS SpaceLink B&W PCI Card 33
Page 35

Chapter 3 - Wireless LAN Reference
3.2.7 Config - Encryption Tab
Lets you configure the ASUS SpaceLink encryption settings. W e support three
security options:
Chapter 3
Default Key
The Default Key field lets you specify which of the encryption key (Unique,
First, Second, Third, or Fourth) you use to transmit data on your wireless LAN.
You can change the default key by clicking on the down arrow at the right of
this field, selecting the number of the key you want to use and then clicking the
Apply button. As long as the Access Point or station with which you are
communicating has the same key in the same position, you can use any of the
keys as the default.
AES Encryption
If you specify both AES and WEP keys, the STA and AP will automatically
negotiate the encryption type. Because AES is a stronger encryption than WEP ,
it is used wherever possible. If the STA or AP does not support AES, WEP is
used.
Please note that you will only be able to communicate with wireless devices
that have use the same encryption settings.
WEP Enabled
Pull Down Menus
NOTE: AES is not supported in Ad Hoc mode, since Ad Hoc mode
does not support unique key.
34 ASUS SpaceLink B&W PCI Card
Page 36

Chapter 3 - Wireless LAN Reference
Use Static Keys
We provide both the IEEE 802.11 standard wired equivalent privacy (WEP)
and advanced encryption security (AES) encryption. While WEP is universally
supported and commonly used, AES provides a much higher level of security .
Frames encrypted with AES are more dif ficult to decipher without known the
key .
Unique Key
This option is enable only if you enable AES Encryption. Defines the unique
encryption key for security for the current network configuration. In Ad Hoc
mode, this encryption key type is not used.
Key Length
Defines the length for each encryption key . As the Key Length is changed, the
number of available characters in the filed is changed automatically. For 64
bits encryption, each Key contains exactly 10 hexadecimal digits. For 128 bits
encryption, each Key contains exactly 26 hexadecimal digits. For 152 bits
encryption, each Key contains exactly 32 hexadecimal digits.
Chapter 3
Shared Key
This option is enable only if you enable WEP Encryption. The WEP Key is a
64 bits (5 byte), 128 bits (13 byte) or 152 bits (16 byte) Hexadecimal digits that
is used to encrypt transmit data packets and decrypt received data packets.
NOTE: Click the Apply or OK button to save the encryption settings. The keys you entered will be masked by asterisks.
ASUS SpaceLink B&W PCI Card 35
Page 37

Chapter 3 - Wireless LAN Reference
Two ways to assign Shared Keys
Manual Assignment - When you click this button, the cursor appears in the
field for Key 1. To enable WEP encryption, you are required to enter at least
one shared key . For 64-bit encryption, each Key contains exactly 10 hex digits
(0~9, a~f, and A~F). For 128-bit encryption, each Key contains exactly 26 hex
digits (0~9, a~f, and A~F). For 152-bit encryption, each Key contains exactly
32 hex digits (0~9, a~f, and A~F).
Automatic Generation - Type a combination of up to 64 letters, numbers, or
symbols in the Passphrase column, then the Wireless Settings Utility uses an
algorithm to generate four shared Keys for encryption.
NOTE: This function ease users from having to remember their
passwords and is compatible to some existing WLAN utilities, but
it is not very secure. "Manual Assignment" is more secure.
Chapter 3
64/128bits versus 40/104bits
You may be confused about configuring WEP encryption, especially when
using multiple wireless LAN products from different vendors. There are
two levels of WEP Encryption: 64 bits and 128 bits.
First, 64 bit WEP and 40 bit WEP are the same encryption method and can
interoperate in the wireless network. This lower level of WEP encryption
uses a 40 bit (10 Hex character) as a “secret key” (set by user), and a 24 bit
“Initialization Vector” (not under user control). This together makes 64
bits (40 + 24). Some vendors refer to this level of WEP as 40 bits and
others refer to this as 64 bits. ASUS SpaceLink products use the term 64
bits when referring to this lower level of encryption.
Second, 104 bit WEP and 128 bit WEP are the same encryption method
and can interoperate in the wireless network. This higher level of WEP
encryption uses a 104 bit (26 Hex character) as a “secret key” (set by user),
and a 24 bit “Initialization Vector” (not under user control). This together
makes 128 bits (104 + 24). Some vendors refer to this level of WEP as 104
bits and others refer to this as 128 bits. ASUS SpaceLink products use the
term 128 bits when referring to this higher level of encryption.
Click Apply to save and activate the new configurations.
36 ASUS SpaceLink B&W PCI Card
Page 38

Chapter 3 - Wireless LAN Reference
3.2.8 Config - Advanced Tab
Advanced tab provides some additional settings for the ASUS SpaceLink
B&W PCI Card.
Country
Allows users to select the country where ASUS wireless network adapters will
be operated. The country code specifies the corresponding regulatory domain
and constructs a channel list for channel scanning.
Channel
Using the Channel field to select the radio channel for card. In an "infrastructure"
network, the card will automatically select the correct frequency channel
required to communicate with an Access Point, this parameter will be fixed in
"Auto" and cannot be changed. In an "Ad Hoc" network, you can decide channel
number for the card. The radio channels you may use depend on the regulations
in your country .
Start Ad Hoc Network
Choose which wireless mode will start an Ad Hoc network if no matching
SSID is found after scanning all available modes. The default value is 5 GHz
54 Mbps (802.11a).
Chapter 3
ASUS SpaceLink B&W PCI Card 37
Page 39

Chapter 3 - Wireless LAN Reference
Scan Mode
Allows selection of the wireless card scanning method used to locate access
points or ad hoc networks. The default value is Auto.
Passive: Click on this radio button to specify passive scanning. Passive scanning
indicates that the wireless card is in listen-only mode.
Auto: Click on this radio button to specify automatic scanning. The driver
uses the country code to determine which type of scanning to use, either active
or passive.
QoS
Specifies disable or enable the station to cooperate in a network using Quality
of Service (QoS).
Chapter 3
2.4 GHz Preamble
Specifies Short & Long or Long-Only preamble mode for a 2.4 GHz/11 Mb
network. Long-Only is used for backward-compatibility with older 2.4 GHz
devices. The default value is Short & Long.
RTS Threshold
Define the size packet that the station used for R TS/CTS handshake boundary .
Be aware that setting the minimum size packet too small causes RTS packets
to be sent more often, adding excessive overhead to the network, therefore
decreasing network utilization. However, the more often R TS packets are sent,
the more transmission collisions can avoid. That's trade-off. RTS Threshold
ranged from 0 to 2346 steps 64. The default value is 2346.
Fragmentation Threshold
Define the number of bytes used for fragmentation boundary. If the length of
the data unit exceeds this parameter, it will be divided into smaller fragments
for transmission. Each of the fragments is sent independently. If there is a
significant interference present, set the fragment size smaller. Otherwise, set
the fragment size larger . Because send multiple frames lead to overhead on the
network. Fragmentation Threshold ranged from 256 to 2346 steps 128. The
default value is 2346.
Click Apply to save and activate the new configurations.
38 ASUS SpaceLink B&W PCI Card
Page 40

Chapter 3 - Wireless LAN Reference
3.2.9 Survey - Site Survey Tab
Use the Site Survey tab to view statistics on the wireless networks available
to the ASUS SpaceLink B&W PCI Card. The Site Survey tab is read-only
with no user configurable data fields. Use the Site Survey tab to view the
following network parameters.
• BSSID – View the IEEE MAC addresses of the available networks.
• SSID – V iew the SSID (service set identification) within available networks.
• CH – View the direct-sequence channel used by each network.
• RSSI – Views the Received Signal Strength Indication (RSSI) in dB.
• Type – View wireless network status information, the value is either
AP (infrastructure) or STA (Ad Hoc).
• WEP – View wireless network WEP encryption information, the value
is either OFF (disable encryption) or ON (enable encryption).
Some Access Points
can disable broadcasting SSID to hide themselves from “Site Survey” or “Site Monitor”
for added security but
still allow you to join if
you know their SSID.
Buttons
Search – Scan all available wireless networks and show the scan result in
the “Available Network List”.
Chapter 3
Connect – To associate a network, select it from the “Available Network
List” and click this button.
ASUS SpaceLink B&W PCI Card 39
Page 41

3.2.10 About
Version Info Tab
Uses the Version Info tab to view program and ASUS SpaceLink WLAN
Card version information. The program version information field includes
the Copyright and utility version. The version information includes the
NDIS version, driver name, and driver version.
Chapter 3
Chapter 3 - Wireless LAN Reference
This screen is an example only. Normally,
you will see non-zero version numbers.
NDIS Tab
The NDIS page gives statistics for troubleshooting.
Network Driver Interface Specification
40 ASUS SpaceLink B&W PCI Card
Page 42

Chapter 3 - Wireless LAN Reference
3.2.11 Link Status
ASUS SpaceLink B&W PCI Card connection quality icon appears on the
left of the ASUS WLAN Card Settings. Use the icon to view the current
signal quality of the adapter.
Excellent Link Quality (Infrastructure)
Good Link Quality (Infrastructure)
Fair Link Quality (Infrastructure)
Poor Link Quality (Infrastructure)
Not linked (Infrastructure)
Linked (Ad Hoc)
Not Linked (Ad Hoc)
3.2.12 Exit Wireless Settings
T o exit W ireless Settings, you can click OK or Cancel. This utility may be
closed at any time and from any tab. If you did not save the configuration
settings, you will be prompted to do so.
Chapter 3
ASUS SpaceLink B&W PCI Card 41
Page 43

3.3 Activate Configuration
Auto roaming is enabled by default and will automatically switch to stronger
access points. You can uncheck it if you have many access points and do
not want to constantly switch to different networks. If you want to use a
particular profile. You can also check it here.
Chapter 3
Chapter 3 - Wireless LAN Reference
Auto Roaming
Select or deselect to allow auto roaming. Auto roaming will contstantly change
the access point’s SSID to keep you connected when you cross into regions
covered by access points with differenct SSID’s.
Default / (Other Profiles)
Select default settings or one of the saved profiles listed below . Both the default
settings and the profile settings can be customized.
42 ASUS SpaceLink B&W PCI Card
Page 44

Chapter 3 - Wireless LAN Reference
3.4 Mobile Manager (Utility)
Mobile Manager is a convenient tool to setup and manage network location
settings. Mobile Manager lets users configure multiple alternative
configurations for different locations. You only need to set this once, and
then easily switch configurations when you change your location.
Starting Mobile Manager
• Click the Windows Start button, select Programs, select ASUS Utility, select Dual-Band WLAN Card, and then click Mobile Manager.
or
• Right-click the Control Center icon on the Windows taskbar and then
click Mobile Manager.
Using Mobile Manager - Quick Guide
1. The first time you launch the Mobile Manager utility, it will automatically generate configurations that stores the current settings of all installed network devices in your system.
2. Change the name of the configuration to a descriptive name like “W orkMeeting Room” or “Home-ADSL”.
3. On the File menu, click New Configuration, the New Configuration
Wizard dialog appears. Follow the on-screen instructions to create your
own location configurations.
4. After you have created your configurations, you can see them in the
main window.
5. Select the configuration you want to use and then click Activate Con-
figuration from the Activate pull-down menu. Your system will then
switch to the network settings configured to your chosen selection.
Chapter 3
ASUS SpaceLink B&W PCI Card 43
Page 45

3.4.1 Main Window
You can use the Mobile Manager utility main window to create a new
configuration, edit a configuration or activate a configuration. The main window
includes a menu bar, tool bar , and a list view for showing existing configurations.
Chapter 3
Using the pull-down menu and toolbar
Chapter 3 - Wireless LAN Reference
The following topics show the commands available from the Mobile Manager
pull-down menu and toolbar . If no configuration is selected, some commands
will be grayed out and inaccessible. The toolbar contains buttons for many of
the most commonly used commands in Mobile Manager . It allows quick access
to some of the most useful features of Mobile Manager . The commands provided
by the toolbar buttons are also available from the pull-down menu.
File
New Configuration - Select New Configuration in the File menu
to open a New Configuration W izard dialog. Use the New Configuration W izard dialog to create a new configuration. See Using New
Configuration Wizard for details on this command.
Import Configuration - Load a configuration from an INI File.
Export Configuration - Save the selected configuration (contain-
ing Wireless Settings, TCP/IP Settings, Network Settings, ...) to an
INI File. The INI file can be placed on a floppy diskette and then
imported by other computers using Mobile Manager. This can also
be used as a backup feature for yourself.
Exit - Close the Mobile Manager utility.
44 ASUS SpaceLink B&W PCI Card
Page 46

Chapter 3 - Wireless LAN Reference
Activate
Auto Roaming – If an association changes, it will automatically
switch into a network configuration that you have made. If no associations have been made, it will automatically connect to a wireless
network based on configurations that you specify.
Activate Configuration – Applies the configuration that you have
selected from the list. You may be prompted to restart Windows
depending on the required changes. Follow the instructions on the
screen. W indows 2000 and XP usually do not require restarting your
computer, but Windows 98 and ME usually will require a restart.
Edit
All these commands are also available from the context menu that appears
when you right-click with a configuration in the Mobile Manager window.
Network Order Move Up - Raises the portion of the selected wireless network configuration in the Preferred network lists.
Network Order Move Down - Lowers the position of the selected
wireless network configuration in the Preferred networks list.
Edit Configuration - Select Edit Configuration in the Edit menu to
open an Edit Configuration dialog to edit selected configuration
items. See “Using Edit Configuration” for details on this command.
Rename - Change the name of the selected configuration.
Copy - Duplicate the selected configuration.
Delete - Discard the selected configuration.
Chapter 3
ASUS SpaceLink B&W PCI Card 45
Page 47

3.4.2 View Menu
Chapter 3
Chapter 3 - Wireless LAN Reference
Large Icons - Displays large icons for each configuration.
Small Icons - Displays small icons for each configuration.
List - Shows the configuration names in a list.
Details - The Detailed view expands this list to include information
about the configurations. The information includes configuration
name, type, and description.
3.4.3 Help Menu
Contents - Displays the WinHelp contents window (the one you
are reading now) for online Help.
About Mobile Manager - Displays the version number and copyright information for Mobile Manager . Click on the logo to connect
to ASUS’ website.
46 ASUS SpaceLink B&W PCI Card
Page 48

Chapter 3 - Wireless LAN Reference
3.4.3 Using New Configuration Wizard
Create a new configuration
Create a new configuration if you are in a specific location that does not
have an existing configuration defined. Use the New Configuration W izard
to create a configuration in a few easy steps.
Do one of the following:
• On the File menu, click New Configuration.
or
• Double-click New Configuration on the Main window.
Then the New Configuration Wizard dialog starts.
Choose the type of configuration that you want
to create and click Next.
• Wireless Local Area Network
Configuration: You must have an ASUS
SpaceLink B&W PCI Card installed in your PC.
• Wired Local Area Network Configuration:
You must have a NIC (LAN card) (other than
ASUS SpaceLink B&W PCI Card) installed in
your PC.
• Dialup Networking Configuration: Yo u
must have a modem installed in your PC.
Enter the name and description you want to use
for this configuration in the Name and
description field. Click Next to continue.
Chapter 3
ASUS SpaceLink B&W PCI Card 47
Page 49

Using New Configuration Wizard (Cont.)
Chapter 3
Chapter 3 - Wireless LAN Reference
Enter the appropriate information in the wizard.
After specifying the appropriate information, click
Next to continue.
See “Using Edit Configuration” for detailed
information on each.
Enter the appropriate information in the wizard.
After specifying the appropriate information, click
Next to continue.
See “Using Edit Configuration” for detailed
information on each.
Select to obtain an IP address automatically from
a DHCP server or assign one manually. Click
Next to continue.
See “Using Edit Configuration” for detailed
information on each.
48 ASUS SpaceLink B&W PCI Card
Page 50

Chapter 3 - Wireless LAN Reference
Using New Configuration Wizard (Cont.)
Enter the computer name and DNS suffix. Click
Next to continue.
Read Microsoft Windows documentation for
information on these items.
Click Next to accept these settings or click
Advanced to change them.
Read Microsoft Windows documentation for
information on these items.
On the final window of the New Configuration
Wizard, you will see a Finish button.
If you do not want to use this new configuration
now, click Finish to save the new configuration.
It will be shown in the Mobile Manager main
window.
If you want to use this new configuration now,
check “Activate Configuration Now”.
Chapter 3
ASUS SpaceLink B&W PCI Card 49
Page 51

3.4.4 Using Edit Configuration
Edit an existing configuration
Edit a configuration if you want to view or change dialup or LAN settings.
The Edit Configuration dialog contains various settings, which you select by
clicking the buttons at the left of the window . Each setting is described below.
General settings
Chapter 3
Chapter 3 - Wireless LAN Reference
• On the Edit menu, click Edit Configuration.
or
• Double-click one existing configuration on the Main window.
Then the Edit Configuration dialog starts.
Name – This field is mandatory, and used for indicating the location
from which you are dialing or connecting to the network. For example,
if this is used for a meeting room at work, you can use a name like
“Work-Meeting Room”. If it is used for home on your ADSL, you can
name like “Home-ADSL”.
Description – This field is optional, you can use it to provide more
details about this configuration.
Network settings
Network settings include: “Identification” and “Microsoft Networking”.
Identification
Computer name – Give your computer a unique name of up to 15
characters. Thecomputer name is the name that others on your network will see your computer as. For complete compatibility , do not use
spaces or symbols. It’s generally the same as the DNS hostname, for
example, “JohnDoe”.
50 ASUS SpaceLink B&W PCI Card
Page 52

Chapter 3 - Wireless LAN Reference
Workgroup – Type an existing workgroup name or create a new
workgroup by typing a new name that contains up to 15 characters. Use
it to identify your computer group that you belong to.
Computer Description – This information is displayed as a comment
next to the computer name when the computer is seen in “Details” view
(select from the Windows pull-down menu). Use it to describe your
computer, for example, your name, or location.
Microsoft Networking
Logon validation – Specify how W indows 9x clients connect to a W indows NT Server Domain at this location.Check Log on to Windows NT
domain box if you are using a Windows NT Server in domain controller mode. And then enter the Window NT server domain name in Win-
dow NT domain field.
Network logon options – Specify how W indows 9x clients try to logon.
Select Quick logon to wait until the shared network drives is actually
used to attempt the login. Select Logon and restore network connections
to logon to all shared network drives when the user logs into Windows.
Wireless settings
Chapter 3
Wireless settings include: “Wireless” and “Encryption”.
Network Type
Infrastructure – Select the Infrastructure mode to establish a connection with an Access Point.
Ad Hoc – Select the Ad Hoc mode to communicate directly with each
other without using an Access Point.
SSID
Using the SSID filed to configure the SSID setting for the ASUS SpaceLink
B&W PCI Card. SSID stands for Service Set Identifier, which is a string
used to identify a wireless LAN. You will only be able to connect with an
Access Point, which has the same SSID. Use different SSIDs to segment
the wireless LAN and add security.
Note that the SSID must be all printable character string (case sensitivity)
and up to 32 characters long, such as “ WIRELESS LAN”. Set the SSID to
a null string, if you wish to allow your station to connect to any Access
Point it can find. But you cannot use null string in Ad Hoc mode.
ASUS SpaceLink B&W PCI Card 51
Page 53

Power Saving
This field allows the configuration of power management options to conserve
battery life. These options are "Off", "Normal, and "Maximum". Power
Management is disabled when "Ad Hoc" mode is selected in the Network
Type field.
When the Power Saving setting is Off, it allows a full powered state that yields
the best performance. This mode is recommended for devices running on AC
power .
Power Saving setting is Normal or Maximum will enable power savings
function, the adapter will wake up periodically to see if there is any data being
sent. This mode is recommended for devices running on battery power. The
difference is when the Power Saving setting is Normal, the driver turns off
power to the adapter for brief periods over briefly-spaced time intervals; when
the Power Saving setting is Maximum, the driver turns off power to the adapter
Chapter 3
for long periods over widely-spaced time intervals.
Chapter 3 - Wireless LAN Reference
Transmit Power
This field allows the configuration of transmit power options. The options are
"100%", "50%", "25%", "12.5", and "Lowest".
Wireless Mode
Choose which wireless mode the wireless card will use. You can enable more
than one wireless mode to allow system auto switch among them.
5 GHz 54 Mbps (802.11a): Use this checkbox to allow the wireless card to
use the 5 GHz and 54 Mbps wireless mode.
5 GHz 108 Mbps (Turbo Mode): Use this checkbox to allow the wireless
card to use the 5 GHz and 108 Mbps wireless mode. A high speed operating
mode for 802.11a radio space. Support data transfer speeds up to 108 Mbps,
twice the speed of standard 802.11a devices.
2.4 GHz 11 Mbps (802.11b): Use this checkbox to allow the wireless card to
use the 2.4 GHz and 11 Mbps wireless mode.
52 ASUS SpaceLink B&W PCI Card
Page 54

Chapter 3 - Wireless LAN Reference
Data Rate
Select the transmit data rate (fix or auto). The data rates supported for the
ASUS SpaceLink WLAN Cards are:
Auto - The adapter will adjust to the most suitable transmission rate.
Fix - 11a: Fix data rate to 6, 9, 12, 18, 24, 36, 48, or 54 megabits per second.
11b: Fix data rate to 1, 2, 5, or 11 megabits per second.
Chapter 3
ASUS SpaceLink B&W PCI Card 53
Page 55

Gateway
Specify the gateways. There can be more than one specified.Set up the
primary gateway first.
DNS
Select Enable or Disable DNS. If you enable DNS, fill the following
parameters.
Chapter 3
Chapter 3 - Wireless LAN Reference
Add a gateway - Type the IP address of the gateway in the New Gate-
way field and then click Add. The gateway you specified appears in the
Installed Gateways list. Repeat to specify another gateways. The value
in each field must be a number between 0 and 255. You can have up to
eight IP addresses for gateways.
Remove a gateway - Select the gateway from the Installed Gateways
list and click Remove.
Host – Enter the name of your computer. That is used to identifier the
computer on the Internet. The hostname is generally the same as the
Microsoft networking computer name, for example, “S82000W”.
Domain – Enter the TCP/IP domain name for your network.The full
domain name consists of one or more names that are separated by dots,
for example, “asus.com”.
DNS Server Search Order – Specify the DNS Servers in the desired
order to search for DNS information.
Domain Suffix Search Order – Add any domain suffixes that may be
valid attached to the end of Internet domain name.
WINS
Specify the WINS server . There can be more than one specified.Set up the
primary WINS server first.
Disable WINS Resolution – Do not use WINS resolution.
Enable WINS Resolution – Use WINS resolution. Specify the IP ad-
dresses of the WINS servers in the desired search order. Scope ID is
used when NetBIOS over TCP/IP is enabling on the workstations. If
this protocol has been enabled, then every workstation group must have
the same Scope ID for those computers to communicate within the group.
The Scope ID is usually left blank.
Use DHCP for WINS Resolution – If a DHCP server is available that
is configured to provide information on available WINS servers.
54 ASUS SpaceLink B&W PCI Card
Page 56

Chapter 3 - Wireless LAN Reference
Dialing settings
Specify how the call will be dialed. This is useful if you want to change the
call to a calling card, use your computer from different locations, or add a
dial prefix, country code, or area code automatically.
Dialup Networking settings
Dialup Networking settings include four tabs: Device, Phone Number,
Server Type, and TCP/IP.
Device
Choose the modem you want to use by Dial-Up Networking to connect to
another computer for this connection.
Phone Number
Specify area code, telephone number, and country code for this connection.
Clear the Use area code and Dialing Properties checkbox, if you want to
ignore area code and dialing settings.
Server Type
Type of Dial-Up Server – Select the server type for this connection.
Advanced options
Select Log on to network checkbox to specify that Dial-Up Networking
will attempt to log on to the network you are connecting to, using the user
name and password you typed when you logged on to Windows.
Select Enable software compression checkbox to specify whether
incoming or outgoing information is compressed before it is sent. This is
useful to speed up the transfer of information. Compression occurs only if
both computers are using compatible compression.
Chapter 3
ASUS SpaceLink B&W PCI Card 55
Page 57

Chapter 3 - Wireless LAN Reference
Select Require encrypted password checkbox to specify that only
encrypted passwords can be sent to or accepted by your computer. This is
useful if you need additional security for this connection. When type your
password while dialing out, this setting will encrypt your password but the
target computer must support encrypted passwords for your password to
be understood.
Allowed network protocols – Specifies the network protocols that your
computer can use.
Select NetBEUI protocol to connect to Windows NT, Windows for
Workgroups, or LAN Manager servers.
Select IPX/SPX Compatible protocol to connect to Netware and W in-
dows NT servers and Windows 98 computers.
Select TCP/IP protocol to connect to Internet and wide-area networks.
Chapter 3
TCP/IP
Server assigned IP address – Specifies whether Dialup Networking
accepts an IP address from a ppp server. If the ppp server does not offer
an IP address, the IP address specified for TCP/IP Dial-Up Adapter in
the Network dialog box is used.
Specify an IP addr ess – Provides a space for you to type the preferred
IP address for this connection. Dial-Up Networking tries to use this
address first.
56 ASUS SpaceLink B&W PCI Card
Page 58

Chapter 3 - Wireless LAN Reference
Server assigned name server addr esses – Specifies whether Dial-Up
Networking accepts a DNS and WINS server addresses from a ppp
server . If the ppp server does not offer DNS and WINS addresses, DNS
and WINS server addresses specified for TCP/IP Dial-Up Adapter in
the Network dialog box are used.
Specify name server addresses – Provides a space for you to type one
or two DNS and WINS server addresses for this connection only. DialUp Networking tries to use these addresses first.
Use IP header compr ession – Specifies whether Dial-Up Networking
uses IP header compression for this connection. IP header compression
optimizes data transfer between computers.
Use default gateway on remote network – Specifies whether IP traffic is routed to the WAN connection by default.
Internet settings
A proxy server acts as a security barrier between your internal network
(Intranet) and the Internet, keeping other people on the Internet from gaining
access to confidential information on your internal network or your
computer.
Disable Proxy Server – Do not use proxy server.
Enable Proxy Server – Use the Proxy server to gain access to the Internet.
Use the same proxy server for all protocols – Specifies whether you
want to use the same proxy server to gain access to the Internet using
all protocols.
Servers – Provides spaces for you to type the address and port number
of the proxy server you want to use to gain access to the Internet over
HTTP, Secure, FTP, Gopher, and Socks protocol.
Exceptions
Do not use proxy server for address beginning with – Provides a space
for you to type the Web addresses that do not need to be accessed through
the proxy server. If you want to connect to a computer on your Intranet,
make sure you type its address in this box. You can use wild cards to match
domain and host names or addresses, for example, “*.company.com”,
“192.72.111.*”.
Chapter 3
Bypass proxy server for local addresses – Specifies whether you want to
use the proxy server for all local (Intranet) addresses. You might be able to
gain access to local addresses easier and faster if you do not use the proxy
server.
ASUS SpaceLink B&W PCI Card 57
Page 59

Sharing settings
I want to be able to give others access to my files – T urn file sharing ON
or OFF . File sharing enables people using other computers to read or modify
files you share on your computer.
I want to be able to allow others to print to my printer(s) – Turn printer
sharing ON or OFF. Printer sharing enables people using other computers
to printer their files on your printers.
Chapter 3
Chapter 3 - Wireless LAN Reference
Click Save button to save all the changes you have made without closing the Edit Configuration dialog box.
Click Cancel button to close the Edit Configuration dialog box without
saving any changes you have made.
Click Close button to close the Edit Configuration dialog box and save
any changes that you have made.
58 ASUS SpaceLink B&W PCI Card
Page 60

Chapter 3 - Wireless LAN Reference
3.5 Site Monitor
Site Monitor measures the received signal strength indicator (RSSI) values
of all available wireless networks. This tool is used for determining the
best placement of Access Points to provide the best coverage for a wireless
network.
3.5.1 Starting Site Monitor
• Click the Windows Start button, select Programs, select ASUS Utility , select Dual-Band WLAN Card Utilities, and then click Site Moni-
tor.
or
• Right-click the Control Center icon on the Windows taskbar and then
click Site Monitor.
3.5.2 Main Screen
Site Monitor measures the received signal strength indicator (RSSI) values
of all available wireless networks.
Chapter 3
Some Access Points can disable broadcasting SSID to hide themselves from “Site Survey” or “Site Monitor” for added security
but still allow you to join if you know their SSID.
ASUS SpaceLink B&W PCI Card 59
Page 61

3.5.3 Monitor
Directed link state test with one particular wireless network, including:
RSSI: This indicates the value of received signal strength of the last received
frame. In principle, the higher the RSSI, the better your communications
quality.
Throughput: This sends a specified number of data packets to the remote
host and calculates the average megabytes per second.
During the test, the Start button toggles to Stop. You can click Start button
to begin the link test and click Stop button at any time to terminate the test.
Chapter 3
Chapter 3 - Wireless LAN Reference
60 ASUS SpaceLink B&W PCI Card
Page 62

Chapter 3 - Wireless LAN Reference
3.6 Windows XP Wireless Properties
2. Double-click ASUS SpaceLink WL230...1. Double-click System icon in the Control Panel.
3. The “General” page will show status, duration,
speed, and signal strength. Signal strength
is represented by green bars with 5 bars
meaning excellent signal and 1 bar meaning
poor signal.
4. The “Wireless Networks” page will show
Chapter 3
Available networks and Preferred networks.
Use the Add button to add the “SSID” of
available networks and set the connection
preference order with the Move up and
Move down buttons. The radio tower with
a signal icon identifies the currently
connected access point.
ASUS SpaceLink B&W PCI Card 61
Page 63

Windows XP Wireless Properties (Cont.)
Chapter 3
Chapter 3 - Wireless LAN Reference
5. The “Authentication” page allows you to add
security settings. Read Windows help for
more information.
6. The “Advanced” page allows you to set
firewall and sharing. Read Windows help for
more information.
62 ASUS SpaceLink B&W PCI Card
Page 64

Chapter 4 - Bluetooth Reference
4. Bluetooth Reference
4.1 Introduction to Bluetooth
The term "Bluetooth" refers to a worldwide standard for the wireless exchange
of data between two devices.
In order to exchange data, two Bluetooth devices must establish a connection.
Before a connection is established, one device must request a connection with
another . The second device accepts (or rejects) the connection. The originator
of the request is known as the client. The device that accepts (or rejects) the
request is known as the server . Many Bluetooth devices can act as both client
and server .
A client Bluetooth device runs a software program that requests a connection
to another device as part of its normal operation. For example, the program
may request a connection to a remote computer, a printer, PDA, or a Cellular
Phone. Becoming a Bluetooth client normally requires an action by the device
operator, such as an attempt to browse a remote computer, print a file, or dial
out on a Cellular Phone.
Every Bluetooth device that provides a service must be prepared to respond to
a connection request. Bluetooth software is always running in the background
on the server, ready to respond to connection requests.
Chapter 4
ASUS SpaceLink B&W PCI Card 63
Page 65

Chapter 4 - Bluetooth Reference
4.2 Using the Bluetooth Software
This icon will appear on your desktop. Doubleclick My Bluetooth Places to launch the
Bluetooth utility.
Click Entire Bluetooth Neighborhood to
search for Bluetooth devices in range.
Devices within range will be shown in “Entire
Bluetooth Neighborhood”
Chapter 4
If you cannot see any devices
within “Entire Bluetooth Neighborhood”, make sure that your
devices are properly working
and set to allow discovering.
Enable Discovering
By default, Bluetooth devices will have their
discovery option enabled. If you want to know
where this is set, right-click the Bluetooth icon on
the taskbar and choose Setup | Configuration
in order to bring up the configuration window. Use
the “Accessibility” page to “Let other Bluetooth
devices discover this computer”.
64 ASUS SpaceLink B&W PCI Card
Page 66

Chapter 4 - Bluetooth Reference
Using the Bluetooth Software (Cont.)
Different Views
Depending on your Windows folder options, you
will may see different sized icons. The above
has “Show common tasks in folders” enabled
and view “Tiles”.
Bluetooth Not Available
If your local Bluetooth device is
not present or working, you will
get red x’s on each Bluetooth
service icon.
Chapter 4
ASUS SpaceLink B&W PCI Card 65
Page 67

Chapter 4 - Bluetooth Reference
4.2.1 Bluetooth Connection Wizard
Using “My Bluetooth Places” and browsing to the individual service within a
target device is actually easier to use than using the “Bluetooth Connection
Wizard”. See “Services” a few pages later.
Launch the “Bluetooth Connection Wizard” from
the Start menu or right click the Bluetooth icon
on the taskbar. You can read about “Bluetooth
Connection” in the Online Manual.
Chapter 4
Click the Next button:
• If more than one service is available for the selected device, for ex-
Select a service and target device. (T o
update the list of devices displayed,
click the Search Devices... button.)
Optional: select the “Require secure
encrypted connection” option to enable
Authentication and Encryption for this
connection.
ample, multiple Bluetooth Serial Ports, then the Select Bluetooth Service dialog box appears. Select the specific service to be used, and then
click the OK button to close the Select Bluetooth Service dialog box.
• If only one service is available for the selected device, the next Connection Wizard screen appears.
66 ASUS SpaceLink B&W PCI Card
Page 68

Chapter 4 - Bluetooth Reference
If “Require secure encrypted
connection” was selected earlier, a
security screen may appear:
• To establish a paired relationship with the remote device while using
this wizard, enter your Personal Identification Number in the PIN Code
field of the security screen, and then click the Next button.
• T o establish the paired relationship with the remote device the first time
this connection is used, leave the PIN Code field blank in the security
screen, and click the Next button. The Security screen WILL NOT appear if the devices have been paired.
The top of the screen provides basic
information about the new connection
– the name of the device that will
provide the service and the name of the
service that will be provided. If this
information is NOT correct, click the
Back button to return to the previous
screen, and from that screen select the
correct service and device.
In the “Connection Name:” field, enter a descriptive name for the connection,
for example, “Serial Connection to ASUS Desktop”.
Chapter 4
ASUS SpaceLink B&W PCI Card 67
Page 69

Chapter 4 - Bluetooth Reference
4.2.2 Explore
Besides double-clicking the Bluetooth icon on
your desktop, you can right click and select
Explore to view Bluetooth devices along with
your entire computer in one window.
Chapter 4
This is Windows “Explorer” utility with “My
Bluetooth Places” selected.
This is Windows “Explorer” utility with “Entire
Bluetooth Neighborhood” selected.
This is Windows “Explorer” utility with “My
Device” selected.
68 ASUS SpaceLink B&W PCI Card
Page 70

4.2.3 Setup
Chapter 4 - Bluetooth Reference
Right click and select Setup to view Bluetooth
configuration options.
You can read about the Security and
Configuration settings in the Online Manual.
4.2.4 Security
Pairing Devices
Pairing allows you to avoid entering
access information each time a
connection is attempted. Paired devices
share a unique Link Key, which they
exchange when connecting.
The mate of a pair will always appear in My Bluetooth Places, even
if the mate is not turned on or is out of connection range.
Chapter 4
Paired devices remain paired even when: One of the devices is not powered
up; a service connection is interrupted or the service stopped; or one or both
devices are rebooted.
When Authentication is enabled devices are paired the first time they attempt
to connect, after a successful passkey exchange.
ASUS SpaceLink B&W PCI Card 69
Page 71

Chapter 4 - Bluetooth Reference
4.2.5 Configuration
V iew the online manual for information on configuration settings.
General
Discovery Information Exchange
Accessibility
Chapter 4
Discovery
Local Services
70 ASUS SpaceLink B&W PCI Card
Page 72

Chapter 4 - Bluetooth Reference
Client Applications
Version Info
Hardware
Chapter 4
ASUS SpaceLink B&W PCI Card 71
Page 73

Chapter 4 - Bluetooth Reference
4.2.6 Services
Using services on a target device are just as they would be on your own computer
but you will be borrowing the target device’ s resources. For more information
on those services, refer to your source or target’s user’s manual. Services are
provided by the server and used by the client. All Bluetooth servers do not
necessarily provide all of these services.
You can also use services from the Bluetooth
taskbar icon. Right-click the icon to bring up the
“Services” menu.
Determine the services provided by a Bluetooth device
• On the client, in the Folders pane of My Bluetooth Places, select Entire
Chapter 4
• In the right pane of Entire Bluetooth Neighborhood, right-click anywhere
• In the Folders pane of My Bluetooth Places, right-click a device and
Bluetooth Neighborhood.
except on a device name and select Refresh from the pop-up menu.
select Discover Available Services from the pop-up menu to update the
available services list. The available services will be displayed in the
right pane of My Bluetooth Places.
There are several other services available when
you open the target device.
72 ASUS SpaceLink B&W PCI Card
When you double-click a service, the “Status”
will show “Connected”. Because resources are
limited, when you start a service, other services
may be disconnected.
Page 74

Device Icons
Chapter 4 - Bluetooth Reference
Service Icons
Chapter 4
ASUS SpaceLink B&W PCI Card 73
Page 75

Chapter 4 - Bluetooth Reference
4.2.7 Serial Port
The Bluetooth Serial Port service allows
two Bluetooth devices to establish a
wireless connection through virtual
communications ports and then use that
connection as if it were a hardwired
serial cable between the devices.
To establish a Bluetooth serial port connection
Connections are initiated from the client:
• On the client, in the Folders pane of My Bluetooth Places, select Entire
Bluetooth Neighborhood.
• In the right pane of Entire Bluetooth Neighborhood, right-click anywhere except on a device name and select Refresh from the pop-up
menu.
• In the Folders pane of My Bluetooth Places, right-click the server you
Chapter 4
• In the right pane of My Bluetooth Places, double-click Bluetooth Serial
Depending on the security configuration, the dialog box that provides communications port information may not appear until after
Authentication and Authorization have been accomplished.
Determine the communications port being used by the server
The application on the server must be configured to use the correct
communications port.
To determine the communications port being used by the service:
want to establish a connection with and select Discover Available Services from the pop-up menu to update the available services list. The
available services will be displayed in the right pane of My Bluetooth
Places.
Port. A dialog box appears that contains the communications port number assigned to this connection by the client. The application that will
use this connection must be configured to send data to this port.
• On the server, in the Folders pane of My Bluetooth Places, right-click
My Device and select Properties from the pop-up menu
• In the Bluetooth Configuration Panel, select the Local Services tab.
74 ASUS SpaceLink B&W PCI Card
Page 76

Chapter 4 - Bluetooth Reference
• Double-click the Bluetooth Serial Port service to display its Service
Properties dialog box. The Service Properties dialog box shows the communications port that the connection is using.
Close a Bluetooth serial port connection
Connections are normally closed from the client:
• On the client, in the Folders pane of My Bluetooth Places, select (highlight) the device that is providing the Bluetooth Serial Port service.
• In the right pane of My Bluetooth Places, right-click Bluetooth Serial
Port and then select Disconnect Bluetooth Serial Port from the pop-up
menu.
• Though not recommended, connections can also be closed from the
server:
• On the server, in the Folders pane of My Bluetooth Places, select (highlight) My Device.
• In the right pane of My Bluetooth Places, right-click Bluetooth Serial
Port and then select Stop to close the service. The service must be restarted before it will be available to remote devices (right-click Bluetooth Serial Port and select Start from the pop-up menu).
Chapter 4
ASUS SpaceLink B&W PCI Card 75
Page 77

Chapter 4 - Bluetooth Reference
4.2.8 Dial-Up Networking
The Dial-up Networking service
permits a Bluetooth client to use a
modem that is physically connected to
a different Bluetooth device (the
server).
After the Bluetooth wireless
connection is established the client can
use the server’s modem as if it were a
local device on the client.
Establish a Dial-up Networking session
Connections are initiated from the client:
• On the client, in the Folders pane of My Bluetooth Places, select Entire
• In the right pane of Entire Bluetooth Neighborhood, right-click anywhere
Chapter 4
• In the Folders pane of My Bluetooth Places, right-click the server that will
• In the right pane of My Bluetooth Places, double-click Dial-up Networking.
• In the Connect T o dialog box, fill in your user name, password, and the phone
You can now open a web browser and connect to the Internet.
Bluetooth Neighborhood.
except on a device name and select Refresh from the pop-up menu.
provide the Dial-up Networking Service and select Discover Available Services from the pop-up menu to update the available services list. The available services will be displayed in the right pane of My Bluetooth Places.
number to be dialed, and then click the Dial button. Select the Save password
check box and the dialog box will not appear for subsequent connections to
the same phone number .
Close a Dial-up Networking connection
• On the client, in the Folders pane of My Bluetooth Places, select (highlight) the device that is providing the Dial-up Networking service.
• In the right pane of My Bluetooth Places, right-click Dial-up Networking
and then select Disconnect Dial-up Networking from the pop-up menu.
76 ASUS SpaceLink B&W PCI Card
Page 78

Chapter 4 - Bluetooth Reference
4.2.9 Fax
The Fax service allows a Bluetooth
client to wirelessly send a fax using a
device that is physically attached to a
Bluetooth server .
Send a Fax
Connections are initiated from the client:
• On the client, in the Folders pane of My Bluetooth Places, select Entire
Bluetooth Neighborhood.
• In the right pane of Entire Bluetooth Neighborhood, right-click anywhere except on a device name and select Refresh from the pop-up
menu.
• In the Folders pane of My Bluetooth Places, right-click the server that
will provide the Fax service and select Discover A vailable Services from
the pop-up menu to update the available services list. The available
services will be displayed in the right pane of My Bluetooth Places.
• In the right pane of My Bluetooth Places, double-click Fax.
After the Fax connection is established, open or create the document to be
faxed and use the “Print” or “Send to Fax Recipient” option available in most
applications.
The Fax connection closes automatically when the transmission is complete.
Chapter 4
ASUS SpaceLink B&W PCI Card 77
Page 79

Chapter 4 - Bluetooth Reference
4.2.10 Inbox
The Information Exchange service
provides a way to send and receive
Microsoft Outlook items to and from
another Bluetooth device.
Supported Outlook items are
• Business cards (*.vcf and *.vcd)
• Calendar entries (*.vcs)
• Notes (*.vnt)
• Messages (*.vmg)
There are three types of operation
• Send – sends an object to another device.
• Receive – requests an object from another device.
• Exchange – sends a client object and receives a server object.
The default location of your business card and the location where received
Chapter 4
items are placed can be configured in the Bluetooth Configuration Panel.
Send, receive or exchange an object
On the client, in the Folders pane of My Bluetooth Places, right-click the Inbox
icon of the remote device and select an option from the pop-up menu.
Business cards are sent, received or exchanged without further intervention.
T o send Calendar Items, Notes, and Messages, navigate to the folder that contains
the item you want to send, select the item, and then click Open.
78 ASUS SpaceLink B&W PCI Card
Page 80

Chapter 4 - Bluetooth Reference
4.2.11 Network Access
The Network Access service permits a
Bluetooth client to use a Local Area
Network connection that is physically
attached to another Bluetooth device
(the server).
Possible Network Access servers include
• Bluetooth-enabled computers that have a hardwired Ethernet connection.
• Stand-alone Bluetooth Network Access Points.
The Bluetooth server must be specifically configured to provide the Network
Access service.
After a Bluetooth device is configured as a Network Access server
it cannot act as a Network Access client without being re-configured.
Chapter 4
ASUS SpaceLink B&W PCI Card 79
Page 81

Chapter 4 - Bluetooth Reference
4.2.12 File Transfer
The File Transfer service allows one
Bluetooth device to perform file
operations on the default File T ransfer
directory (and the folders and files it
contains) of another Bluetooth device.
Perform an operation on a folder or file
On the machine from which the File T ransfer service will be used:
• In the Folders pane of My Bluetooth Places, select Entire Bluetooth
Neighborhood.
• In the right pane of Entire Bluetooth Neighborhood, right-click anywhere except on a device name and select Refresh from the pop-up
menu.
• In the Folders pane of My Bluetooth Places, right-click the device you
Chapter 4
• Still in the Folders pane of My Bluetooth Places, click the plus ( + )
Types of File Transfer operations
In the right pane of My Bluetooth Places, right-click a folder item and select an
option from the pop-up menu. A dialog box (the title varies, depending on the
operation being carried out) appears and the status line (bottom of the dialog
box) indicates the operational step that is being carried out.
The types of operations that can be accomplished are:
Open:
want to T ransfer Files with and select Discover Available Services from
the pop-up menu to update the available services list. The available
services will be displayed in the right pane of My Bluetooth Places.
sign in front of Public Folder to expand that folder. If there are additional folders inside the expanded folder then those additional folders
may have to be expanded. Folder contents are displayed in the right
pane of My Bluetooth Places.
• Files – are opened in the application associated with them.
• Folders – are expanded to show their contents.
• Print – sends the selected server file to the client’s default printer.
80 ASUS SpaceLink B&W PCI Card
Page 82

Chapter 4 - Bluetooth Reference
Send to:
• 3.5” Floppy Drive – copies the selected item(s) from the server to the
client’s 3.5” floppy drive.
• My Shared Folder – copies the selected item(s) from the server to the
default File Transfer folder on the client.
• Cut – copies a folder and its contents, or individually selected files in a
folder, to the Windows clipboard. When the clipboard contents are pasted
to a new location, the originally selected file(s) on the server are deleted.
• Copy – copies a folder and its contents, or individually selected files in
a folder, to the Windows clipboard.
• Delete – deletes selected file(s) and/or folder(s) on the server.
• Rename – allows you to change an empty folder’s name.
• Properties – displays the file or folder’s properties dialog box.
Other options that may appear
(depending on the context that the menu appears in)
• Update – updates the contents of a folder
• New Folder – creates a new folder on the server
• Abort FTP Operation – aborts an in-process File Transfer operation.
Chapter 4
See next page for file transfer example.
ASUS SpaceLink B&W PCI Card 81
Page 83

Chapter 4 - Bluetooth Reference
4.3 File Transfer Example (to Public Folder)
[Source] Selecting “Entire Bluetooth Neighborhood”
will show available Bluetooth devices. You will not
see yourself. The above example is a Personal
Computer (Desktop PC) and only Laptop
Computers (Notebook PC) are shown.
[Source] When you open the target device, the
Chapter 4
available services will be shown. Notice the
device name in the “Address”.
[Target] In this setup, there are two Laptop
Computers and one Personal Computer. From
one of the target Laptop Computers, you can
see the Personal Computer that was not shown
in the previous screen capture.
[Source] When you open the target device’s
“Public Folder” for the first time, it should be
empty . Notice the device name in the “Address”.
[Source] Drag and drop some files into the
window to begin transferring files.
[Target] You will find the files in the path similar
to the one shown here. If the target device has
a search option, you can use it to locate the files.
[Source] After copying, you will see the files in
the other device. Notice the device name in the
“Address”.
82 ASUS SpaceLink B&W PCI Card
Page 84

Chapter 4 - Bluetooth Reference
4.3.1 Bluetooth Cellular Phone
Modern cellular (also called mobile)
phones have several connection options
to make its features accessible to a wide
range of devices and computers in
several environments.
When using a Bluetooth Cellular phone such as the Ericsson T39, you can see
target Bluetooth devices similar to using a computer. Under (5) Extras menu,
there is (5) Bluetooth options.
(1) Discoverable - use this to allow other to be able to see your Cellular phone.
The Ericsson T39 will only enable this function for 3 mins at a time for security
reasons.
(2) Paired devices - add Bluetooth devices to connect to
(3) Discover - use this to search for available Bluetooth devices.
(4) Operation mode - set the operation mode for the Ericsson T39
Chapter 4
Here we can see the Ericsson T39 in
Windows “My Bluetooth Places”
when using a computer equipped with
Bluetooth.
ASUS SpaceLink B&W PCI Card 83
Here are the available services using
the Ericsson T39.
Page 85

Chapter 4 - Bluetooth Reference
Pairing
Pairing is necessary in order to utilize
another device’s resources. You will be
asked to enter a password on both devices.
The first device (a computer in this case)
sets the password and the second device
(the Ericsson T39 in this case) must enter
the same password. Since the Ericsson
T39 can only enter numbers as the
password, make sure you also use
numbers as the password on the computer.
When paired to another device, there
will be a check mark on the device icon
and “Paired” will be shown when
folder view is set to “Details”.
4.3.2 Dial-Up Networking with Bluetooth Cellular Phone
Chapter 4
This is the same as one computer using another computer’s resources to access
the Internet. While on the road, you can borrow your Bluetooth cellular phone’ s
modem without connecting a cable. This is like using a computer and a modem
at home to access the Internet through an Internet Service Provider (ISP).
T o access the Internet, you need to dialup to your Internet Service Provider
(ISP), double click “Dial-up
Networking” in the Ericsson_T39
window . Enter your ISP account “User
name”, “Password”, and Phone
Number .
84 ASUS SpaceLink B&W PCI Card
Page 86

Chapter 5 - Troubleshooting
5. Troubleshooting
Wireless LAN
The below troubleshooting guides provide answers to some of the more
common problems, which you may encounter while installing or using
ASUS SpaceLink B&W PCI Card products. If you encounter difficulties
that are not mentioned in this section, please contact ASUS Wireless LAN
Technical Support.
Verify if the PCI Card is installed correctly.
When the ASUS SpaceLink B&W PCI Card setup task is complete, you
can verify if the driver has been setup properly . Right click My Computer,
select Properties, and click the Device Manager tab. Then double-click
the Network adapters icon; you should see “ASUS 11a/b PCI Wireless
Network Adapter” with an icon of expansion card. There should not be a
“!” or “?” (problem) or “x” (disabled) symbol over this icon.
There is a yellow exclamation mark or a yellow question mark in Device
Manager in front of my ASUS SpaceLink B&W PCI Card.
To resolve the problem, you should update/reinstall the ASUS SpaceLink
B&W PCI Card driver . In “Device Manager”, right click ASUS 1 1a/b PCI
Wireless Network Adapter, select Properties, and select Driver tab. Click
on Update Driver button, then follow the “Update Device Driver W izard”
to complete the driver installation.
In addition, you may be able to resolve this issue by reinstalling the driver .
Choose ASUS 1 1a/b PCI Wir eless Network Adapter, click Remove button
in “Device Manager”, and then run the Add New Hardware W izard from
the Control Panel.
Cannot connect to any Access Points
Follow the procedure below to configure your ASUS SpaceLink B&W
PCI Card.
a. Verify that the “Network Type” is in “Infrastructure” mode.
Chapter 5
b. Verify that the “SSID” of your ASUS SpaceLink B&W PCI Card is set
to the same “SSID” of an Access Point.
c. Verify that the “Encryption” type is the same as that of an Access Point.
If you enabled “WEP” encryption, you must also set the same WEP
Keys on both sides.
ASUS SpaceLink B&W PCI Card 85
Page 87

Chapter 5 - Troubleshooting
Cannot connect to a Station (ASUS SpaceLink B&W PCI Card)
Follow the procedure below to configure your ASUS SpaceLink B&W
PCI Card.
a. Verify that the “Network Type” is in “Ad Hoc” mode.
b. Verify that the “SSID” of your ASUS SpaceLink B&W PCI Card is set
to the same “SSID” of the other station (or another ASUS SpaceLink
B&W PCI Card).
c. Verify that the “channel” of the ASUS SpaceLink B&W PCI Card is
“Auto” or set to the same “channel” of the other station (or another
ASUS SpaceLink B&W PCI Card).
d. Verify that the “Encryption” type is the same as the other station (or
another ASUS SpaceLink B&W PCI Card). If “WEP” encryption is
enabled, you must set the same “WEP” Keys on both stations.
Bad link quality or bad signal strength
There are two possible reasons. First is radio interference, keep the
environment around the ASUS SpaceLink B&W PCI Card away from
microwave ovens and large metal objects. Then try to reorient the ASUS
SpaceLink B&W PCI Card antenna. Second is the distance, decrease the
distance between your ASUS SpaceLink B&W PCI Card and the Access
Point or station (or another ASUS SpaceLink B&W PCI Card).
The TCP/IP protocol did not bind to the SpaceLink PC Card.
This will occur when the computer already has six TCP/IP bindings in
Windows 98 or ten bindings in Windows Me. These limits are imposed by
the Microsoft operating system.
Solution: If your computer already has the maximum number of TCP/IP
Chapter 5
bindings, remove one of the network adapters from the Network
configuration before installing the ASUS SpaceLink B&W PCI Card driver .
86 ASUS SpaceLink B&W PCI Card
Page 88

Chapter 5 - Troubleshooting
Troubleshooting (Cont.)
Bluetooth
Cannot Connect to a Paired Device
Paired devices are always displayed in My Bluetooth Places, even if the remote
device is out of range or not powered up.
• Verify that the remote member of the pair is within radio range and
powered up and then attempt the connection again.
Cannot discover services on an unpaired remote device
The remote device may not be powered up or may be out of range.
• Verify that the remote device is powered up.
• Verify that the remote device is in Connectable mode (Bluetooth Configuration Panel > Accessibility tab).
• Perform a Search for Devices to verify that the device is within range.
Cannot discover services on an unpaired remote device
The remote device may not be powered up or may be out of range.
• Verify that the remote device is powered up.
• Verify that the remote device is in Connectable mode (Bluetooth Configuration Panel > Accessibility tab).
• Perform a Search for Devices to verify that the device is within range.
Dial-up Networking service does not start
The Dial-up Networking service will not start unless a properly configured
modem is attached to the server .
• Verify that the modem is usable as a local device from the server . In the
Bluetooth Configuration Panel, Local Services tab, double-click the
Dial-up Networking service: Click the down arrow in the Modem field
and select the modem that will be used to dial out | Click the OK button
| Click the OK button to close the Bluetooth Configuration Panel.
Chapter 5
Determine the BDA of installed hardware
In the Bluetooth Configuration Panel, on the Hardware tab, in the Devices
section, select the device you want to determine the address of. In the Device
ASUS SpaceLink B&W PCI Card 87
Page 89

Chapter 5 - Troubleshooting
Properties section of the dialog box, the fourth entry, Device Address, is the
BDA of the selected Bluetooth device.
Determine the HCI version number
In the Bluetooth Configuration Panel, on the Hardware tab, in the Device
Properties section, the fifth entry provides Bluetooth Specification compliance
information for the Host Controller Interface.
The sixth entry contains the Specification Revision information for the Host
Controller Interface, if appropriate.
Determine the LMP version number
In the Bluetooth Configuration Panel, on the Hardware tab, in the Device
Properties section, the seventh entry provides Link Manager Protocol version
number information.
The eighth entry contains the Link Manager Protocol subversion number
information, if appropriate.
Determine hardware information
In the Bluetooth Configuration Panel, select the Hardware tab. (To access the
Bluetooth Configuration Panel: From the Windows System Tray, Right-click
the Bluetooth icon | Click Setup | Select Configuration from the fly-out menu.)
Test a Network Access connection
If the client is hardwired to the LAN, unplug the hardwired connection to
ensure that the test checks the wireless connection rather than the hardwired
connection.
If the server has access to the Internet, open a browser on the client and connect
Chapter 5
to the World Wide Web.
You may also Ping the server from the DOS prompt.
Unknown Port error
The “Unknown Port” error message usually means an attempt was made to
connect a port that was in use.
Additional Bluetooth Serial Ports can be added if they are required.
88 ASUS SpaceLink B&W PCI Card
Page 90

Chapter 6 - Glossary
6. Glossary
Wireless LAN-Related
Access Point (AP)
An networking device that seamlessly connects wired and wireless networks. Access
Points combined with a distributed system support the creation of multiple radio cells
that enable roaming throughout a facility.
Broadband
A type of data transmission in which a single medium (such as cable) carries several
channels of data at once.
Ad Hoc
A wireless network composed solely of stations within mutual communication range
of each other (no Access Point).
Basic Service Area (BSS)
A set of stations controlled by a single coordination function.
Channel
An instance of medium use for the purpose of passing protocol data units that may be
used simultaneously , in the same volume of space, with other instances of medium use
(on other channels) by other instances of the same physical layer, with an acceptably
low frame error ratio due to mutual interference.
Client
A client is the desktop or mobile PC that is connected to your network.
Device Name
Also known as DHCP client ID or network name. Sometimes provided by an ISP when
using DHCP to assign addresses.
DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol)
This protocol allows a computer (or many computers on your network) to be
automatically assigned a single IP address from a DHCP server.
DNS Server Address (Domain Name System)
DNS allows Internet host computers to have a domain name and one or more IP
addresses. A DNS server keeps a database of host computers and their respective domain
names and IP addresses, so that when a user enters a domain name into the Internet
browser, the user is sent to the proper IP address. The DNS server address used by the
computers on your home network is the location of the DNS server your ISP has assigned.
Encryption
This provides wireless data transmissions with a level of security .
Extended Service Set (ESS)
A set of one or more interconnected basic service set (BSSs) and integrated local area
networks (LANs) can be configured as an Extended Service Set.
ASUS SpaceLink B&W PCI Card 89
Chapter 6
Page 91

Chapter 6 - Glossary
ESSID (Extended Service Set Identifier)
You must have the same ESSID entered into the gateway and each of its wireless
clients. The ESSID is a unique identifier for your wireless network.
Ethernet
The most widely used LAN access method, which is defined by the IEEE 802.3 standard.
Ethernet is normally a shared media LAN meaning all devices on the network segment
share total bandwidth. Ethernet networks operate at 10Mbps using CSMA/CD to run
over 10Base-T cables.
Gateway
A network point that manages all the data traffic of your network, as well as to the
Internet and connects one network to another .
IEEE
The Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers. The IEEE sets standards for
networking, including Ethernet LANs. IEEE standards ensure interoperability between
systems of the same type.
IEEE 802.11
IEEE 802.xx is a set of specifications for LANs from the Institute of Electrical and
Electronic Engineers (IEEE). Most wired networks conform to 802.3, the specification
for CSMA/CD based Ethernet networks or 802.5, the specification for token ring
networks. 802.11 defines the standard for wireless LANs encompassing three
incompatible (non-interoperable) technologies: Frequency Hopping Spread Spectrum
(FHSS), Direct Sequence Spread Spectrum (DSSS), and Infrared. 802.11 specifies a
carrier sense media access control and physical layer specifications for 1 and 2 Mbps
wireless LANs.
IEEE 802.11a / IEEE 802.11b
See next few pages for detailed explanations.
Infrastructure
A wireless network centered about an access point. In this environment, the access
point not only provides communication with the wired network but also mediates
wireless network traffic in the immediate neighborhood.
IP (Internet Protocol)
The TCP/IP standard protocol that defines the IP datagram as the unit of information
passed across an Internet and provides the basis for connectionless packet delivery
service. IP includes the ICMP control and error message protocol as an integral part. It
provides the functional equivalent of ISO OSI Network Services.
IP Address
An IP address is a 32-bit number that identifies each sender or receiver of information
that is sent across the Internet. An IP address has two parts: the identifier of a particular
Chapter 6
network on the Internet and an identifier of the particular device (which can be a server
or a workstation) within that network.
ISM Bands (Industrial, Scientific, and Medicine Bands)
Radio frequency bands that the Federal Communications Commission (FCC) authorized
for wireless LANs. The ISM bands are located at 902 MHz, 2.400 GHz, and 5.7 GHz.
90 ASUS SpaceLink B&W PCI Card
Page 92

Chapter 6 - Glossary
ISP (Internet Service Provider)
An organization that provides access to the Internet. Small ISPs provide service via
modem and ISDN while the larger ones also offer private line hookups (T1, fractional
T1, etc.).
LAN (Local Area Network)
A communications network that serves users within a defined geographical area. The
benefits include the sharing of Internet access, files and equipment like printers and
storage devices. Special network cabling (10 Base-T) is often used to connect the PCs
together .
MAC Address (Media Access Control)
A MAC address is the hardware address of a device connected to a network.
NAT (Network Address Translation)
NA T masks a local network’ s group of IP addresses from the external network, allowing
a local network of computers to share a single ISP account. This process allows all of
the computers on your home network to use one IP address. This will enable access to
the Internet from any computer on your home network without having to purchase
more IP addresses from your ISP.
NIC (Network Interface Card)
A network adapter inserted into a computer so that the computer can be connected to a
network. It is responsible for converting data from stored in the computer to the form
transmitted or received.
Packet
A basic message unit for communication across a network. A packet usually includes
routing information, data, and sometimes error detection information.
ISM Bands (Industrial, Scientific, and Medicine Bands)
Radio frequency bands that the Federal Communications Commission (FCC) authorized
for wireless LANs. The ISM bands are located at 902 MHz, 2.400 GHz, and 5.7 GHz.
PPP (Point-to-Point Protocol)
PPP is a protocol for communication between computers using a serial interface, typically
a personal computer connected by phone line to a server .
PPPoE (Point-to-Point Protocol over Ethernet)
Point-to-Point Protocol is a method of secure data transmission. PPP using Ethernet to
connect to an ISP.
Radio Frequency (RF) Terms: GHz, MHz, Hz
The international unit for measuring frequency is Hertz (Hz), equivalent to the older
unit of cycles per second. One megahertz (MHz) is one million Hertz. One gigahertz
(GHz) is one billion Hertz. The standard US electrical power frequency is 60 Hz, the
AM broadcast radio frequency band is 0.55-1.6 MHz, the FM broadcast radio frequency
band is 88-108 MHz, and wireless 802.11 LANs operate at 2.4 GHz.
ASUS SpaceLink B&W PCI Card 91
Chapter 6
Page 93

Chapter 6 - Glossary
SSID (Service Set ID)
SSID is a group name shared by every member of a wireless network. Only client PCs
with the same SSID are allowed to establish a connection.
Station
Any device containing IEEE 802.11 wireless medium access conformity.
Subnet Mask
A subnet mask is a set of four numbers configured like an IP address. It is used to create
IP address numbers used only within a particular network.
TCP (Transmission Control Protocol)
The standard transport level protocol that provides the full duplex, stream service on
which many application protocols depend. TCP allows a process or one machine to
send a stream of data to a process on another. Software implementing TCP usually
resides in the operating system and uses the IP to transmit information across the network.
WAN (Wide Area Network)
A system of LANs, connected together. A network that connects computers located in
separate areas, (i.e., different buildings, cities, countries). The Internet is a wide area
network.
WECA (Wireless Ethernet Compatibility Alliance)
An industry group that certifies cross-vender interoperability and compatibility of IEEE
802.11b wireless networking products and to promote that standard for enterprise, small
business, and home environments.
WLAN (Wireless Local Area Network)
This is a group of computers and other devices connected wirelessly in a small
area. A wireless network is referred to as LAN or WLAN.
Bluetooth-Related
Acceptor
The Bluetooth device receiving an action from another Bluetooth device. The device
sending the action is called the initiator . The acceptor is typically part of an established
link.
ACL
Asynchronous Connectionless Link. An Asynchronous (packet-switched) connection
between two devices created on the LMP level. This type of link is used primarily to
transmit ACL packet data.
AP
Chapter 6
Access Point.
Application Layer
The group of protocols at the user level. The application layer in the Bluetooth protocol
layers will contain those protocols involved with the user interface (UI).
92 ASUS SpaceLink B&W PCI Card
Page 94

Chapter 6 - Glossary
AT Command Handler
A module that handles the A T commands which control a phone or modem (between a
DTE and a DCE).
Authentication
The process of verifying 'who' is at the other end of the link. Authentication is performed
for devices. In Bluetooth, this is achieved by the authentication procedure based on the
stored link key or by pairing (entering a PIN).
Authentication device
A device whose identity has been verified during the lifetime of the current link based
on the authentication procedure.
Authenticate using a passkey
The procedure where a user is requested to enter a passkey during the establishment
procedure, where the devices did not share a common link key beforehand. This differs
from the bonding procedure where the user enters the passkey without it being requested.
Authorization
The process of deciding if device X is allowed to have access to service Y. This is
where the concept of trusted exists. Trusted devices (the device is authenticated and
indicated as "trusted"), are allowed access to services. Untrusted or unknown devices
may require authorization based on user interaction before it is allowed access to the
services. This does not principally exclude that the authorization might be give by an
application automatically. Authorization always includes authentication.
Baseband
The baseband describes the specifications of the digital signal processing part of the
hardware -- the Bluetooth link controller, which carries out the baseband protocols and
other low-level link routines.
Bluetooth
An open specification for wireless communication of data and voice. It is based on a
low-cost short-range radio link facilitating protected ad hoc connections for stationary
and mobile communication environments.
Bluetooth clock
The master timing mechanism defined by the master of the piconet.
Bluetooth device
A device that contains hardware and software allowing it to communicate with another
Bluetooth device.
Bluetooth device class
A parameter that indicates the type of device and which types of services that is supported.
The class is received during the discovery procedure. The parameter contains the major
and minor device class fields. The term "Bluetooth device class" is used on the UI level.
Bluetooth device type
The term "Bluetooth device type" is used on the UI level. This term overrides the terms
"Bluetooth device class" and "Bluetooth service type" when there is a mix of information
containing both Bluetooth Device Class and Bluetooth Service Types.
Chapter 6
ASUS SpaceLink B&W PCI Card 93
Page 95

Chapter 6 - Glossary
Bluetooth passkey
The name of the PIN. The term "Bluetooth passkey" is used in the UI. See PIN.
Bluetooth service type
One or more services a device can provide to other devices. The service information is
defined in the service class field of the Bluetooth device class parameter .
Bluetooth Session
The activity and participation of a device on a piconet.
Bond
A link key that is exchanged between two devices. The key is used for future
authentication between the devices. See also bonding.
Bonding
Bonding is the creation of a relationship between two devices. The bond is a link key
The relationship is created when the link key is exchanged between two devices. The
devices are known to each other prior to the bonding procedure. A user initiates the
bonding procedure and enters a passkey with the explicit purpose of creating a bond
between two devices. This differs from the authenticate using a passkey procedure
where the user is requested to enter a passkey during the establishment of the link.
BT
Bluetooth.
Business card
The electronic date equivalent to a printed business card. This electronic version of the
business card is treated like a file and can be exchanged between Bluetooth devices.
Channel
A logical connection on L2CAP level between two devices serving a single application
or higher layer protocol.
Circuit Switched
The application of a network where a dedicated line is used to transmit information.
Only one user may employ the resources of the line at a time.
Circuit Switched Bluetooth
The application of a network where a dedicated line is used to transmit Bluetooth data.
Class of device
See Bluetooth device class. Also abbreviated as CoD.
CODEC
Coder/Decoder. A device that converts analog to digital, and digital to analog for
transmission over a digital communications system.
Chapter 6
COF
Ciphering Offset Component. An architecture element denoting an identifiable set of
software that performs a well-defined purpose.
94 ASUS SpaceLink B&W PCI Card
Page 96

Chapter 6 - Glossary
Connect to service
The establishment of a connection to a service. If not already done, this includes
establishment of a physical link, link and channel as well.
Connectable devices
Any device within range that will respond to paging from an initiator device.
Connectable mode
A device that responds to paging (an attempt to establish a communication link) is said
to be in connectable mode. The opposite of connectable mode is non-connectable mode.
Connected device A device that is currently connected to the (LocDev. connection A
connection between two peer applications or higher layer protocols mapped onto a
channel.
Connectionless packet
A packet of data is broadcast over the network without tar geting a specific recipient to
receive the packet.
Connecting
A phase in the communication between devices when a connection between them is
being established. (Connecting phase follows after the link establishment phase is
completed.)
Connectivity
A domain of interconnected components that adhere to a defined set of connection
rules. The set of rules is termed Connectivity Architecture.
Connector
An architectural element denoting a path for control or information flow between
components.
DCE
Data Circuit-T erminating Equipment. In serial communications, DCE refers to a device
between the communication endpoints whose sole task is to facilitate the communications
process; typically a modem.
Device Discovery
The mechanism to request and receive the Bluetooth address, clock, class of device,
used page scan mode, and names of devices.
Device Layer
The group of protocols that handles the hardware in a Bluetooth device. The device
layer handles components such as the display, keypad, and RF communications.
Device security level
Access to a device can be denied based on the required device security level. There are
two levels of device security: trusted device and Untrusted device. See also service
security level.
ASUS SpaceLink B&W PCI Card 95
Chapter 6
Page 97

Chapter 6 - Glossary
Discoverable device
A Bluetooth device in range that will respond to an inquiry (normally in addition to
responding to page. discoverable mode A device that can respond to an inquiry is said
to be in a discoverable mode. There are two types of discoverable modes: limited
discoverable mode and general discoverable mode. The opposite of discoverable mode
is non-discoverable mode. See also silent device. Dispatch Walkie-talkie mode where
one-subscriber talks and other subscribers listen on the same talk group.
DSR
Data Set Ready. A device sets an RS-232 DSR signal when it is ready to accept data.
DTE
Data Terminal Equipment. In serial communications, DTE refers to a device at the
endpoint of the communications path; typically a computer or terminal.
Dumb peripheral
A peripheral that does not communicate any information to the handset.
T ypically , the only information the handset receives from a dumb peripheral is a signal
that a connection has been made to a port on the handset. This signal is also called a
cable detect.
DV
Data Voice. Data packet type for data and voice.
GAP
Generic Access Profile. This profile describes the mechanism by which one device
discovers and accesses another device when they do not share a common application.
GIAC
General Inquire Access Code. See also general discoverable mode.
General discoverable mode
A device that can be discovered continuously or for no specific condition is said to be
in general discoverable mode. See also discoverable mode.
GW
Gateway . A Bluetooth technology base station which is connected to external network.
HA
Host Application. A software program that uses Bluetooth.
Host
A software and hardware platform in which the Bluetooth package runs.
Idle mode
A device is in idle mode when it has no established links to other devices. In this mode,
the device may discover other devices. In general, a device sends inquiry codes (GIAC,
Chapter 6
LIAC) to other devices. Any device that allows inquiries will respond with information.
If the devices decide to form a link, then bonding will occur .
96 ASUS SpaceLink B&W PCI Card
Page 98

Chapter 6 - Glossary
Initiator
The Bluetooth device initiating an action to another Bluetooth device. The device
receiving the action is called the acceptor . The initiator is typically part of an established
link.
Inquiry Procedure
The inquiry procedure enables a device to discover which devices are in range, and
determine the addresses and clocks for the devices. After the inquiry procedure has
completed, a connection can be established using the paging procedure.
Inquiry State
A mode that a LocDev enters when searching for services.
Inquiry Scan State
A mode that a RemDev enters when advertising that a service is available.
Intelligent peripheral
A peripheral that is capable of exchanging information with the handset. Information
may include battery status, charging status, data storage status, or other high-level
functionality . Also referred to as a smart peripheral.
Internet bridge
Method of using a wireless modem for connecting to Internet access.
IP
Internet Protocol.
Key Management
The handling and control of encryption keys.
Known device
A device for which at least the BD_ADDR is stored.
LAN
Local Area Network.
LAP
LAN Access Point.
LC
Link Controller. The Link Controller manages the link to the other Bluetooth devices.
It is the low-level baseband protocol handler .
Limited discoverable mode
A device that responds to an inquiry for limited purposes. For example, a device may
respond for a limited period of time, during temporary conditions, or for a specific
event. T ypically , the device is responding to a limited inquiry based on an inquiry using
the LIAC. See also discoverable mode.
Link key
The authentication key used to establish a link between devices. See also bonding.
ASUS SpaceLink B&W PCI Card 97
Chapter 6
Page 99

Chapter 6 - Glossary
LM
Link Manager. The Link Manager software entity carries out link set-up, authentication,
link configuration, and other protocols.
LMP
Link Manager Protocol. The LMP is used for peer-to-peer communication.
LMP-authentication
An LMP level procedure for verifying the identity of a remote device. The procedure is
based on a challenge-response mechanism using a random number, a secret key and
the BD_ADDR of the non-initiating device. The secret key used can be a previously
exchanged link key or an initialization key created based on a PIN (as used when
pairing).
LMP-pairing
A LMP procedure that authenticates two devices based on a PIN and subsequently
creates a common link key that can be used as a basis for a trusted relationship or a
(single) secure connection. The procedure consists of the steps: creation of an
initialization key (based on a random number and a PIN), LMP-authentication based
on the initialization key and creation of a common link key .
LocDev
Local Device. A Bluetooth device which initiates a SDP procedure. A Local Device is
typically a master device on the piconet. However, a Local Device may not always
have a master connection relationship to other devices. See also RemDev.
MAC
Media Access Control.
MAC Address
3-bit address to distinguish between units participating in the piconet.
Management Entity
Management Entity. The portion of the BT implementation that mediates the internal
functions of the BT stack.
Master device
A device that initiates an action or requests a service on a piconet. See also LocDev.
Master Net
The device in a piconet whose clock and hopping sequence are used to synchronize all
other devices in the piconet.
MUX
Multiplexer. A device that combines one or more data signals into a single composite
signal for communication over one data channel.
Chapter 6
Name Discovery
The mechanism to request and receive a device name.
New device
See unknown device.
98 ASUS SpaceLink B&W PCI Card
Page 100

Chapter 6 - Glossary
Non-connectable mode
A device that does not responds to paging (an attempt to establish a communication
link) is said to be in non-connectable mode. The opposite of connectable mode is
connectable mode.
Non-discoverable
Same as non-discoverable mode.
Non-discoverable mode
A device that cannot respond to an inquiry is said to be in non-discoverable mode. The
device will not enter the INQUIRY_RESPONSE state in this mode. See also
discoverable mode.
Non-pairable mode
A device that does not accepts pairing is said to be in non-pairable mode. The opposite
of non-pairing mode is pairable mode.
Packet Switched
A network that routes data packets based on an address contained in the data packet is
said to be a packet switched network. Multiple data packets can share the same network
resources.
Packet Switched Bluetooth
The application of routing Bluetooth data packets on a network using addresses contained
in the Bluetooth data packets.
Packet Switched Cellular/Radio
The application of routing cellular/radio data packets on a network using addresses
contained in the cellular/radio data packets.
Page
A baseband state where a device transmits page trains and processes any eventual
responses to the page trains.
Page Scan State
A mode where a device listens for page trains containing its own device access code
(DAC). A mode that a RemDev enters when advertising that a service is available.
Page State
A mode that a LocDev enters when searching for services. The LocDev sends out a
page to notify other devices that it wants to know about the other devices and/or their
services.
Page train
A series of paging messages sent over the baseband.
Paged device
A paged device is typically contacted by a paging device to establish a communication
link. See acceptor.
Paging
The act of attempting to establish a communication link.
ASUS SpaceLink B&W PCI Card 99
Chapter 6
 Loading...
Loading...