Advanced Micro Devices
AMD-RAIDXpert2 User
Guide
Publication #
53987
Revision:
3.01
Issue Date:
June 2016

© 2013—2016 Advanced Micro Devices, Inc. All rights reserved.
The information contained herein is for informational purposes only, and is subject to change without notice.
While every precaution has been taken in the preparation of this document, it may contain technical inaccuracies,
omissions and typographical errors, and AMD is under no obligation to update or otherwise correct this
information. Advanced Micro Devices, Inc. makes no representations or warranties with respect to the accuracy or
completeness of the contents of this document, and assumes no liability of any kind, including the implied
warranties of noninfringement, merchantability or fitness for particular purposes, with respect to the operation or
use of AMD hardware, software or other products described herein. No license, including implied or arising by
estoppel, to any intellectual property rights is granted by this document. Terms and limitations applicable to the
purchase or use of AMD’s products are as set forth in a signed agreement between the parties or in AMD's
Standard Terms and Conditions of Sale.
Trademarks
AMD, the AMD Arrow logo, and combinations thereof are trademarks of Advanced Micro Devices, Inc. Other
product names used in this publication are for identification purposes only and may be trademarks of their
respective companies.
Reverse engineering or disassembly is prohibited.
Microsoft, Windows, Windows Vista, and DirectX are registered trademarks of Microsoft Corporation.
Linux is a registered trademark of Linus Torvalds.
PCIe is a registered trademark of PCI-Special Interest Group (PCI-SIG).
Dolby Laboratories, Inc.
Manufactured under license from Dolby Laboratories.
Rovi Corporation
This device is protected by U.S. patents and other intellectual property rights. The use of Rovi Corporation's copy
protection technology in the device must be authorized by Rovi Corporation and is intended for home and other
limited pay-per-view uses only, unless otherwise authorized in writing by Rovi Corporation.
USE OF THIS PRODUCT IN ANY MANNER THAT COMPLIES WITH THE MPEG ACTUAL OR DE
FACTO VIDEO AND/OR AUDIO STANDARDS IS EXPRESSLY PROHIBITED WITHOUT ALL
NECESSARY LICENSES UNDER APPLICABLE PATENTS. SUCH LICENSES MAY BE ACQUIRED FROM
VARIOUS THIRD PARTIES INCLUDING, BUT NOT LIMITED TO, IN THE MPEG PATENT PORTFOLIO,
WHICH LICENSE IS AVAILABLE FROM MPEG LA, L.L.C., 6312 S. FIDDLERS GREEN CIRCLE, SUITE
400E, GREENWOOD VILLAGE, COLORADO 80111.

53987 Rev. 3.01 June 2016
AMD-RAIDXpert2 User Guide
Contents
3
Contents
Revision History ............................................................................................................................. 11
Chapter 1 Safety Precautions .................................................................................................. 14
1.1 General ............................................................................................................................. 14
1.2 Safety Definitions ............................................................................................................ 14
1.3 Caution Messages ............................................................................................................ 14
1.3.1 Caution Messages About Disks ............................................................................... 14
1.3.2 Caution Messages About Arrays ............................................................................. 14
Chapter 2 Getting Started ....................................................................................................... 16
2.1 RAIDXpert2 Technology ................................................................................................ 16
2.2 Who Should Use This Manual ......................................................................................... 16
2.3 System Requirements for Using RAIDXpert2 ................................................................ 16
2.3.1 Supported Controllers .............................................................................................. 16
2.3.2 Supported Operating Systems .................................................................................. 17
2.4 Features of RAIDXpert2 .................................................................................................. 17
2.5 RAIDXpert2 Feature Set ................................................................................................. 20
Chapter 3 Arrays, Disks and RAID Levels ............................................................................ 24
3.1 Understanding Arrays ...................................................................................................... 24
3.2 RAID Levels .................................................................................................................... 24
3.3 Array States ...................................................................................................................... 25
3.4 Creating Arrays: Future Expansion ................................................................................. 27
3.5 Expanding Disk Capacity Online: Using OCE (Supported by RAIDXpert2 Plus) ......... 27
3.6 Migrating RAID Levels Online: Using ORLM (Supported by RAIDXpert2 Plus) ........ 28
3.7 Array Tasks: Starting and Stopping Tasks ...................................................................... 28
3.8 Understanding Disks ........................................................................................................ 29
3.8.1 Disks States .............................................................................................................. 29
3.9 Rescanning Disks for Changes in State ........................................................................... 30
3.10 Sparing Options: Disks and Arrays ................................................................................. 31
3.11 Dedicated Sparing ............................................................................................................ 31
3.12 Global Sparing ................................................................................................................. 32
3.13 RAID Performance Considerations ................................................................................. 32

AMD-RAIDXpert2 User Guide
53987 Rev. 3.01 June 2016
4
Contents
3.13.1 Number and Organization of Disks ......................................................................... 32
3.13.2 Caching Attributes ................................................................................................... 32
3.13.3 Application Workload ............................................................................................. 33
3.14 RAID Reliability Considerations .................................................................................... 33
3.14.1 Data Redundancy .................................................................................................... 33
3.14.2 Backup ..................................................................................................................... 33
3.15 Flexibility and Expansion Considerations ....................................................................... 33
3.16 Multiple RAID Levels ..................................................................................................... 33
3.17 RAIDABLE Arrays ......................................................................................................... 33
Chapter 4 BIOS Configuration Utility .................................................................................. 34
4.1 When to Use the AMD-RAID Controller BIOS Configuration Utility .......................... 34
4.2 Access the AMD-RAID Controller BIOS Configuration Utility .................................... 35
4.3 Understanding the Color Code in the BIOS Configuration Utility ................................. 35
4.4 Initialize Disks ................................................................................................................ 35
4.4.1 Initialize Disks ......................................................................................................... 36
4.5 Create Arrays................................................................................................................... 36
4.5.1 Before You Begin .................................................................................................... 36
4.5.2 Create an Array ....................................................................................................... 37
4.6 Delete Arrays................................................................................................................... 38
4.6.1 Delete an Array ....................................................................................................... 38
4.7 Swap Arrays .................................................................................................................... 38
4.7.1 Before You Begin .................................................................................................... 38
4.7.2 Swap Arrays ............................................................................................................ 39
4.8 Manage Spares ................................................................................................................ 39
4.8.1 Assign Global Spares .............................................................................................. 39
4.8.2 Assign Dedicated Spares ......................................................................................... 39
4.8.3 Unassign Spares ...................................................................................................... 40
4.9 View Disk Details ........................................................................................................... 40
4.10 View Array Details.......................................................................................................... 40
4.11 Rescan All Channels ....................................................................................................... 41
4.12 Change the Controller Options ........................................................................................ 41
4.12.1 Booting the System from an Array ......................................................................... 41

53987 Rev. 3.01 June 2016
AMD-RAIDXpert2 User Guide
Contents
5
4.12.2 Pausing the Boot Sequence for Warning Messages ................................................. 41
4.12.3 Change the Staggered Spinup Count ....................................................................... 42
4.13 Continue Booting from the BIOS Configuration Utility ................................................. 42
4.13.1 Resume the Boot Process ......................................................................................... 42
Chapter 5 Software Installation .............................................................................................. 43
5.1 System Setup Process Overview ...................................................................................... 43
5.2 Before You Begin ............................................................................................................ 43
5.3 Copying AMD-RAID Drivers to Removable Storage ..................................................... 43
5.3.1 Copying AMD-RAID Drivers in a Microsoft® Windows® Environment ............... 43
5.3.2 Copying AMD-RAID Drivers in a Linux® Environment ........................................ 44
5.4 Pre-installation steps ........................................................................................................ 44
5.4.1 BIOS Mode .............................................................................................................. 44
5.4.2 UEFI Mode .............................................................................................................. 45
5.5 Installing AMD-RAID drivers ......................................................................................... 46
5.5.1 Installing AMD-RAID Drivers while Installing Microsoft® Windows® ................. 46
5.5.2 Installing AMD-RAID Drivers While Installing Linux® Operating System ........... 48
5.6 Installing the AMD RAIDXpert2 Management Suite for Microsoft® Windows® ........... 57
5.7 Installing the AMD RAIDXpert2 Management Suite for Linux® ................................... 58
5.8 Installing the AMD RAIDXpert2 Graphical User Interface (GUI) ................................. 59
5.8.1 RHEL Linux® – AMD RAIDXpert2 Web GUI Installation .................................... 59
5.8.2 Ubuntu...................................................................................................................... 60
Chapter 6 AMD RAIDXpert2 Graphical User Interface (GUI) .......................................... 61
6.1 Start RAIDXpert2 ............................................................................................................ 61
6.1.1 Web-Browser Access ............................................................................................... 61
6.1.2 Desktop Shortcut Access ......................................................................................... 62
6.2 Password Protection ......................................................................................................... 62
6.2.1 Things to Know About Passwords ........................................................................... 62
6.2.2 Change a Password at the Options Menu ................................................................ 63
6.3 Help and About Windows® .............................................................................................. 63
6.4 Reviewing the RAIDXpert2 GUI .................................................................................... 63
6.4.1 The Array View Section of the Array Status Window ............................................ 63
6.4.2 The Disk List Section of the Array Status Window ................................................ 64

AMD-RAIDXpert2 User Guide
53987 Rev. 3.01 June 2016
6
Contents
6.4.3 The Array List Section of the Array Status Window .............................................. 65
6.4.4 The Event View Section of the Array Status Window ............................................ 66
6.4.5 Array and Disk Commands ..................................................................................... 67
6.5 Working with Disks ........................................................................................................ 68
6.5.1 Initialize Disks ......................................................................................................... 68
6.5.2 Rescan Disks ........................................................................................................... 69
6.5.3 Change Cache Properties for Disks ......................................................................... 69
6.5.4 Assign Spares .......................................................................................................... 69
6.5.5 Legacy Disks ........................................................................................................... 70
6.6 Working with Arrays ....................................................................................................... 71
6.6.1 Create and Format Arrays ....................................................................................... 71
6.6.2 Name Arrays ........................................................................................................... 73
6.6.3 Transform Arrays (Supported by RAIDXpert2 Plus) ............................................. 73
6.6.4 Restore (Rebuild) Arrays ........................................................................................ 76
6.6.5 Prepare to Physically Remove an Array ................................................................. 77
6.6.6 Delete Arrays ........................................................................................................... 77
6.6.7 Change Cache Settings for Arrays .......................................................................... 79
6.6.8 Change the Priority Level of a Task ........................................................................ 79
6.6.9 Interrupt, Cancel, or Resume a Task ....................................................................... 80
6.6.10 Check for Consistency ............................................................................................ 80
6.6.11 Schedule a Consistency Check ................................................................................ 81
6.6.12 Scan an Array in the Background ........................................................................... 82
6.6.13 Add or Remove Dedicated Spares .......................................................................... 82
6.6.14 Add or Remove Global Spares ................................................................................ 83
6.6.15 Hide an Array .......................................................................................................... 83
6.6.16 Secure Erase ............................................................................................................ 83
6.7 Working with Views ....................................................................................................... 84
6.7.1 Display or Hide Controller Event Log Panel .......................................................... 84
6.7.2 Log Window ............................................................................................................ 84
6.7.3 Refresh the Display ................................................................................................. 84
6.8 Working with Options ..................................................................................................... 85
6.8.1 Change Password Settings ...................................................................................... 85

53987 Rev. 3.01 June 2016
AMD-RAIDXpert2 User Guide
Contents
7
6.8.2 Set Event Notifications ............................................................................................ 85
6.8.3 Licensing .................................................................................................................. 86
6.9 Add Space Using a RAIDABLE Array ........................................................................... 86
Chapter 7 Troubleshooting ..................................................................................................... 87
7.1 Troubleshooting ............................................................................................................... 87
7.2 System Startup Problems ................................................................................................. 87
7.3 Warning Messages: POST Screen ................................................................................... 88
7.4 Array-Related Errors ........................................................................................................ 89
7.5 Disk Related Errors .......................................................................................................... 93
7.5.1 Troubleshooting Disks ............................................................................................. 93
Chapter 8 Software License: EULA ....................................................................................... 95
8.1 Software License: End-User License Agreement (EULA) .............................................. 95
8.1.1 Limited License to Authorized Distributors ............................................................ 95
8.1.2 Limited License to End Users .................................................................................. 95
8.1.3 Restrictions .............................................................................................................. 96
8.1.4 Proprietary Rights .................................................................................................... 96
8.1.5 Term and Termination ............................................................................................. 96
8.1.6 No Warranty ............................................................................................................. 96
8.1.7 Limitation of Liability .............................................................................................. 97
8.1.8 Export Controls ........................................................................................................ 97
8.1.9 General ..................................................................................................................... 97
Chapter 9 rcadm Command Line Interface Tool ................................................................ 99
9.1 What is rcadm? .............................................................................................................. 99
9.1.1 To Use rcadm with a Linux® Operating System .................................................... 100
9.1.2 To Use rcadm with a Windows® Operating System .............................................. 100
9.2 Manage Arrays and Disks: rcadm --manage .......................................................... 100
9.2.1 Understand Query Output ...................................................................................... 100
9.2.2 rcadm Controller List Elements ............................................................................. 101
9.2.3 rcadm Disk List Elements .................................................................................... 102
9.2.4 rcadm Array List Elements .................................................................................... 103
9.3 View Help from the Command Line ............................................................................. 104
9.3.1 To view a List of the Major Modes of Operation .................................................. 104

AMD-RAIDXpert2 User Guide
53987 Rev. 3.01 June 2016
8
Contents
9.4 Create New Arrays: rcadm --create .................................................................... 104
9.4.1 Before You Begin... ............................................................................................... 105
9.4.2 Example ................................................................................................................. 105
9.5 Delete Arrays: rcadm --delete ............................................................................. 105
9.5.1 Before You Begin... ............................................................................................... 105
9.5.2 Example ................................................................................................................. 105
9.6 Transform Arrays: rcadm --transform (supported by RAIDXpert2 Plus) ........ 106
9.6.1 Before You Begin... ............................................................................................... 106
9.7 Follow or Monitor Arrays and Disks: rcadm --follow ......................................... 106
9.7.1 Before You Begin... ............................................................................................... 106
Appendix A rcadm.efi Information ......................................................................................... 107
A.1 rcadm -? ......................................................................................................................... 107
A.2 rcadm -M ....................................................................................................................... 108
A.3 rcadm -C ........................................................................................................................ 113
A.4 rcadm -D ........................................................................................................................ 115

53987 Rev. 3.01 June 2016
AMD-RAIDXpert2 User Guide
List of Tables
9
List of Tables
Table 1. Document Convention ....................................................................................................... 13
Table 2. Glossary of Terms .............................................................................................................. 13
Table 3. System Requirements for RAIDXpert2 ............................................................................. 16
Table 4. Features of RAIDXpert2 .................................................................................................... 17
Table 5. Feature Set for RAIDXpert2: by RAIDXpert2 License Level .......................................... 20
Table 6. RAID Levels – General Characteristics ............................................................................. 24
Table 7. Array States ........................................................................................................................ 26
Table 8. Failure States by RAID Level ............................................................................................ 26
Table 9. Array Expansion Considerations ....................................................................................... 27
Table 10. Types of Tasks per Array ................................................................................................. 29
Table 11. Disk States ....................................................................................................................... 29
Table 12. Sparing Options ............................................................................................................... 31
Table 13. When to use the AMD-RAID Controller BIOS Configuration Utility (Option ROM) ... 34
Table 14. BIOS Configuration Utility Color Codes ........................................................................ 35
Table 15. Linux® Procedure for Installing the Management Suite .................................................. 58
Table 16. Elements of the Array View Section, Array Status Window .......................................... 63
Table 17. Elements of the Disk List Section, Array Status Window ............................................... 64
Table 18. Elements of the Array List Section, Array Status Window ............................................. 65
Table 19. Elements of the Event View Section, Array Status Window .......................................... 67
Table 20. Commands at the Array and Disk Menus ........................................................................ 68
Table 21. New and Legacy Disks, as They Appear in the BIOS Configuration Utility and
RAIDXpert2 .................................................................................................................... 70
Table 22. Creating Arrays: Issues and Recommendations .............................................................. 71
Table 23. Transforming Arrays: Issues and Recommendations ...................................................... 74
Table 24. Deleting Arrays: Issues and Recommendations .............................................................. 78
Table 25. Cache Array Options ....................................................................................................... 79
Table 26. Consistency Check Options ............................................................................................. 81
Table 27. Event Log Priority Levels ................................................................................................ 85
Table 28. The System Does Not Boot ............................................................................................. 87
Table 29. The BIOS Configuration Utility Does Not Display ......................................................... 87
Table 30. Username and Password .................................................................................................. 88

AMD-RAIDXpert2 User Guide
53987 Rev. 3.01 June 2016
10
List of Tables
Table 31. POST Screen Warning Messages .................................................................................... 88
Table 32. Cannot Create an Array ................................................................................................... 90
Table 33. An Array is in a Critical State ......................................................................................... 91
Table 34. An Array is in an Offline State ....................................................................................... 91
Table 35. Cannot Assign a Dedicated Spare to an Array ................................................................ 91
Table 36. Cannot Create a Global Spare ......................................................................................... 92
Table 37. Recreate a Deleted Array ................................................................................................ 92
Table 38. Disk Errors ...................................................................................................................... 93
Table 39. Modes for the rcadm Program ....................................................................................... 99
Table 40. rcadm Controller List Elements .................................................................................. 101
Table 41. rcadm Disk List Elements ............................................................................................. 102
Table 42. rcadm Array List Elements ........................................................................................... 103
53987 Rev. 3.01 June 2016
AMD-RAIDXpert2 User Guide
Revision History
11
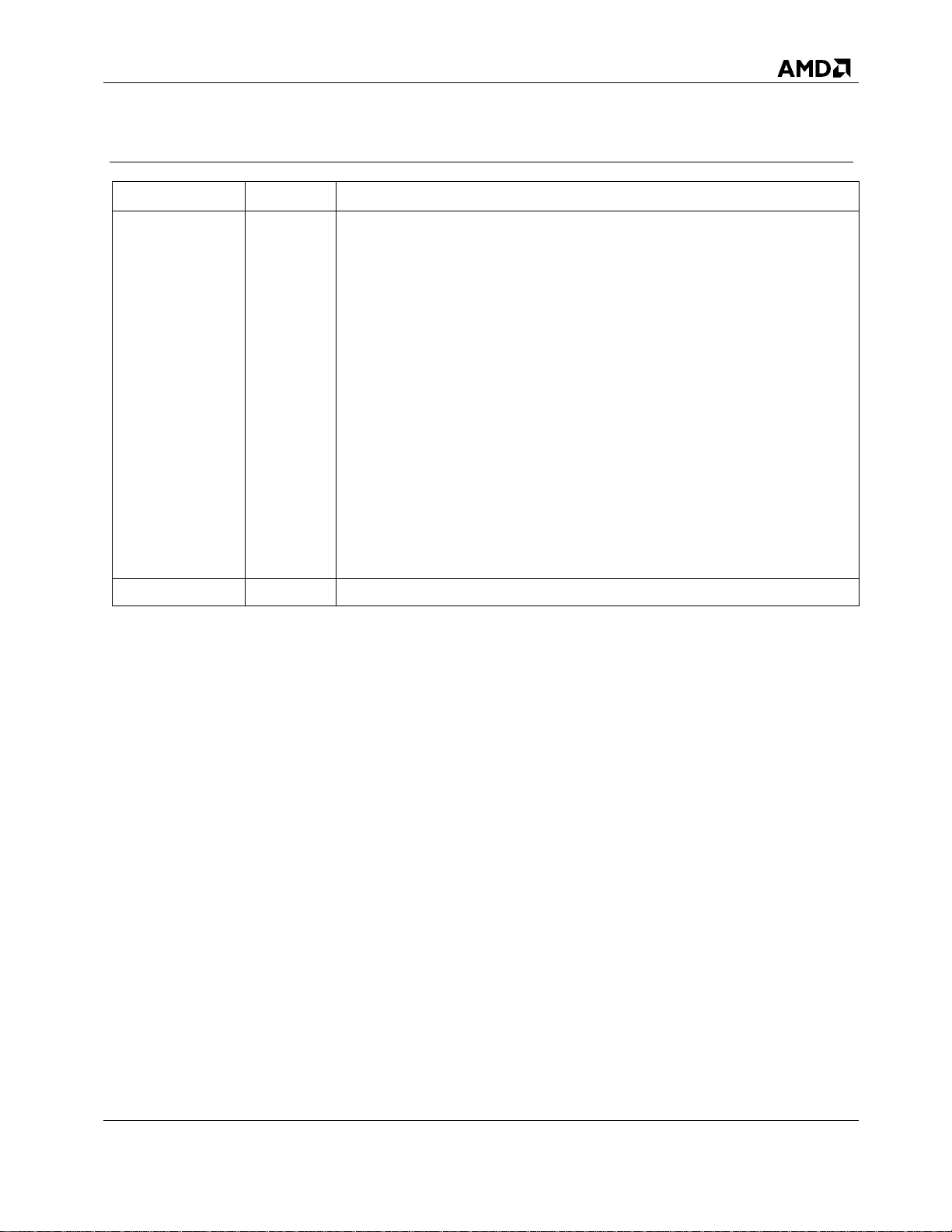
Date
Revision
Description
June 2016
3.01
Second Public Release.
Removed support for the Microsoft® Windows® 8 operating system.
Removed support for Ubuntu 13.10. This included removing extra steps
that concerned Ubuntu 13.10.
Updated Operating System Requirements
Removed references to Windows XP and Windows 8.1.
Replaced SUSE (SLED) references with Red Hat (RHEL) 7.2 64 bit
Updated revisions of Ubuntu Desktop Linux
15.04 32 bit and 64 bit
15.10 32 bit and 64 bit
Removed support for SLED
Removed support for Ubuntu 12.04.04 and 14.04, 32 bit and 64 bit
Changed supported controllers
Removed RAID5 from Table 6 and Table 8
Updated steps for BIOS and UEFI boot platforms
November 2013
3.00
Initial Public release
Revision History

AMD-RAIDXpert2 User Guide
53987 Rev. 3.01 June 2016
12
Preface
Preface
This user guide:
Provides information about arrays, disks, and RAID levels (RAID types).
Describes how to improve storage system performance or reliability by understanding array
and disk tasks and options.
Describes how to acquire and load RAIDXpert2 drivers for Windows
systems.
Describes the features and procedures for using RAIDXpert2, which is the RAIDXpert2 GUI.
Intended Audience
This user guide is intended for use by system administrators and technicians who are experienced
with the following:
Direct Attached Storage (DAS), Storage Area Network (SAN), or Network Attached Storage
(NAS) operators
®
and Linux® operating
Network administration
Network installation
Storage system installation and configuration
Prerequisites
Prerequisites for installing and configuring this product include familiarity with:
Servers and computer networks
RAID and input/output signal technology (such as SCSI, or SATA)
Fibre Channel and Ethernet protocols
53987 Rev. 3.01 June 2016
AMD-RAIDXpert2 User Guide
Preface
13
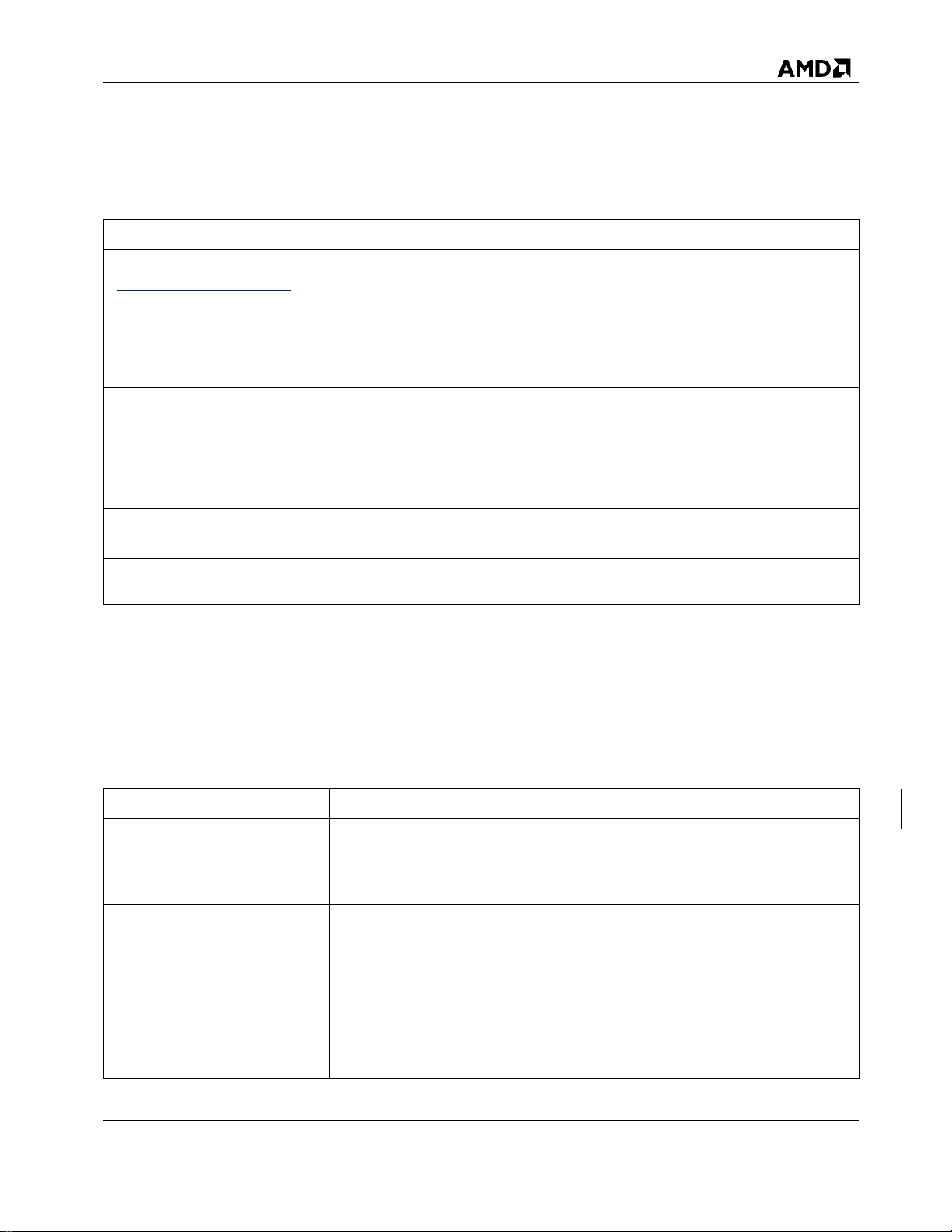
Convention
Element
Navy blue, underlined text
(http.//www.example.com)
Web site addresses
Bold font
Key names
Text typed into a GUI element, such as into a box
GUI elements that are clicked or selected, such as menu and list
items, buttons, and check boxes
Italics font
Text emphasis
Monospace font
File and directory names
System output
Code
Text typed at the command line
Monospace, Italic font
Code variables
Command line variables
Monospace, bold font
Emphasis of file and directory names, system output, code, and
text typed at the command line
Term
Definition
rcadm
A command line interface (CLI) tool for managing RAID controllers on
Linux®, on Windows®, and UEFI operating systems. It is used for
creating, transforming, and deleting arrays; and adding and removing
disks.
Legacy disk
Legacy disks include new or unrecognized disks which may contain data
or even an operating system. Legacy disks appear in the BIOS
Configuration Utility and in RAIDXpert2 as legacy arrays. When the
legacy disk is initializing, configuration data is written to the disk. The
legacy array then becomes an online disk usable in arrays.
CAUTION: A legacy disk can contain valid data. When a legacy disk is
initialized, all data on the disk is lost.
Linux®
Free, open-source UNIX-based operating system.
Document Conventions and Symbols
Table 1. Document Convention
Customer Support
For customer support, contact your system supplier or motherboard vendor.
Glossary
Table 2. Glossary of Terms

AMD-RAIDXpert2 User Guide
53987 Rev. 3.01 June 2016
14
Safety Precautions
Chapter 1
Chapter 1 Safety Precautions
1.1 General
This section includes general safety precautions and specific RAIDXpert2 cautions. Read and
keep this user manual for future reference.
1.2 Safety Definitions
CAUTION: Indicates that failure to follow directions could result in damage to equipment or
data.
IMPORTANT: Provides clarifying information or specific instructions.
Note: Provides additional information.
TIP: Provides helpful hints and shortcuts.
1.3 Caution Messages
This section lists the Caution messages that appear in the book.
1.3.1 Caution Messages About Disks
CAUTION: Assigning a dedicated spare does not reserve space on the disk. Therefore, an
automatic restore is not guaranteed if a disk fails. If a disk fails, make space on the
disk for the fail-over to complete, or assign a different disk with enough space. If a
dedicated spare is assigned and a disk fails, the restore process starts automatically,
if there is enough space available on the dedicated spare.
CAUTION: If a disk is part of an AMD-RAID array, the disk cannot be selected for initialization.
To initialize the disk anyway, delete the AMD-RAID array. Data on the disk is deleted
during initialization so ensure the correct disks are chosen to initialize.
CAUTION: A legacy disk can contain valid data. When a legacy array is deleted, or when its
corresponding legacy disk is initialized, the data is lost.
CAUTION: When a disk is initialized, all data on the disk is lost.
1.3.2 Caution Messages About Arrays
CAUTION: Deleting an array permanently destroys all data that is on the array. This action
cannot be undone and it is very unlikely the data can be recovered.

53987 Rev. 3.01 June 2016
AMD-RAIDXpert2 User Guide
Chapter 1
Safety Precautions
15
CAUTION: Do not delete the first array listed in the Arrays section, if it is the AMD-RAID
bootable array. Doing this deletes the operating system and AMD-RAID files.
CAUTION: Do not initialize a disk that is part of an array. Initializing a disk in a non-redundant
array deletes the array and its data. The array no longer appears in Array View. This
is especially true for a non-redundant bootable array. Initializing a disk in a nonredundant bootable array causes the array to Fail and deletes the operating system,
RAIDXpert2 files, and device drivers.
CAUTION: Leaving Write Back Cache enabled can increase the likelihood of data being
corrupted if the system experiences a power interruption or unexpected shutdown.
CAUTION: Prior to removing an array, remove its drive letter (Windows) or unmount the array
(Linux).
CAUTION: All data contained in a RAIDXpert2 array are lost if the RAIDXpert2 disks of the
array are migrated to a non-RAIDXpert2 system.
CAUTION: When an array is securely erased, the data on the array is lost.
CAUTION: In some circumstances, more than eight arrays are possible. They might appear to
function properly, but are not supported.
CAUTION: Creating a redundant array with Skip Initialization selected can result in data
corruption.
CAUTION: Hot-Swapping is not recommend for disks that are part of the Boot Virtual Disk or
which are connected to the AMD 300- Series Chip.
AMD-RAIDXpert2 User Guide
53987 Rev. 3.01 June 2016
16
Getting Started
Chapter 2
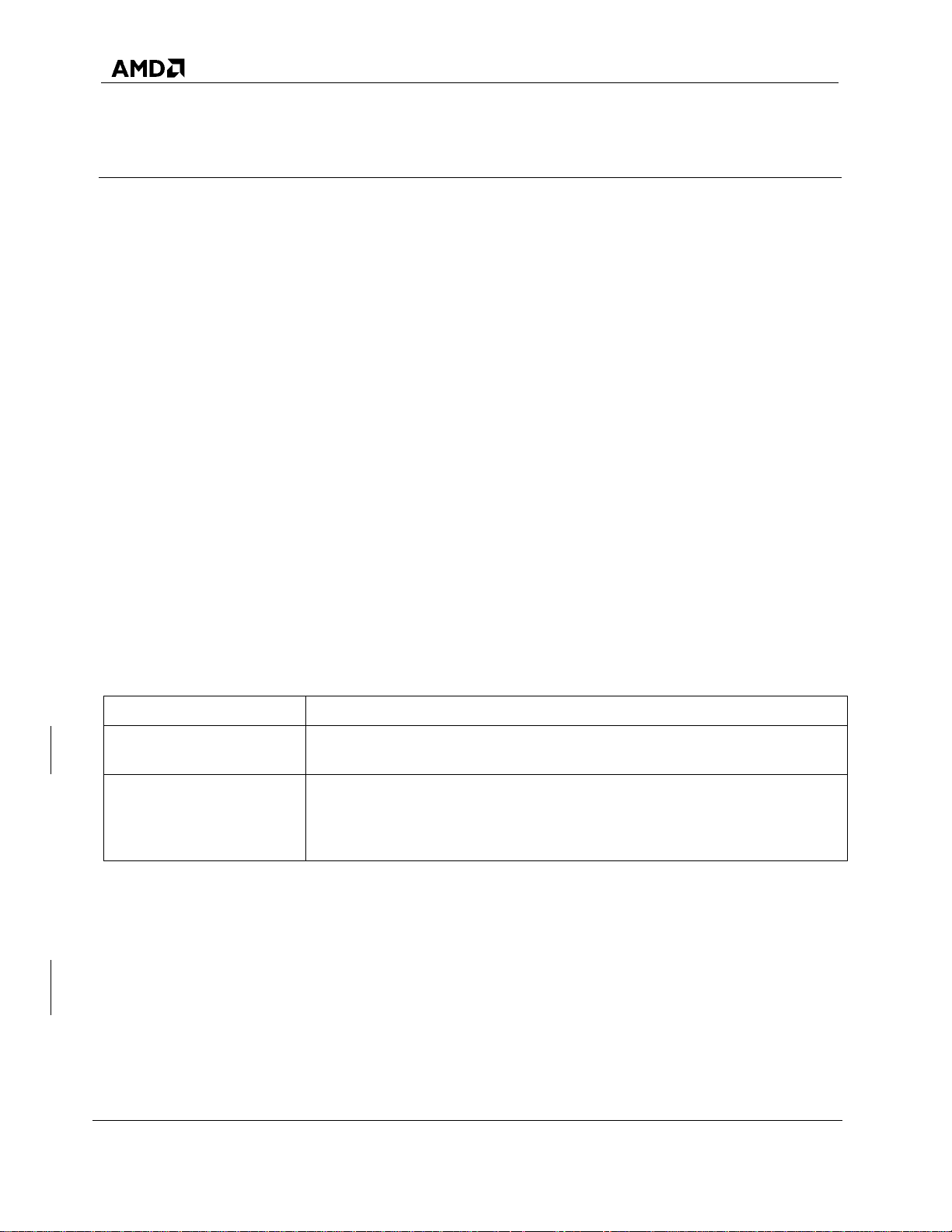
Component
Requirements
Memory (RAM)
Minimum: 4 GB.
Recommended: 8 GB.
Hard disk
1–12 SATA or SSD drives. The number of disks depends on the number,
type, and capacity of the arrays to be created. In some circumstances, more
than 12 disks are possible. They may appear to function properly, but are
not supported by AMD-RAID
Chapter 2 Getting Started
2.1 RAIDXpert2 Technology
RAIDXpert2 consists of (a) storage management and (b) a RAID controller and port virtualization.
RAIDXpert2 runs on existing systems by using a motherboard’s built-in SATA ports.
2.2 Who Should Use This Manual
Only trained, experienced, and authorized personnel should install RAIDXpert2 and use its
features and capabilities.
All unit operators must be familiar with system hardware, data storage, RAID technology,
input/output signal technology (such as SCSI, SAS, or SATA), and Direct Attached Storage
(DAS), Network Attached Storage (NAS), and/or Storage Area Network (SAN) concepts and
technology.
The intended user audience of this user manual is system administrators and experienced users.
2.3 System Requirements for Using RAIDXpert2
Make sure the systems that use RAIDXpert2 meet the requirements indicated in Table 3.
Table 3. System Requirements for RAIDXpert2
2.3.1 Supported Controllers
The following controllers are supported by the current release of RAIDXpert2:
AMD Socket AM4-Compatible Processors
AMD 300-Series Chipsets
53987 Rev. 3.01 June 2016
AMD-RAIDXpert2 User Guide
Chapter 2
Getting Started
17
RAIDXpert2 Feature
Description
Arrays (general information)
RAIDXpert2 allows:
Creating arrays of different RAID levels using the same disks.
Creating different RAID level arrays on the same disk, to adapt each
array to the I/O that it processes.
Creating an array from a mix of different type disks. For example, a
RAID10 array can be created from a group of disks that contain two
SATA II HDDs and two SATA SSDs.
The ability to create RAID10 or RAIDABLE arrays may not be
available on your system.
Migrating an existing array to another RAID level, if the type of array
being used is not the optimal type for the application. This function
depends on the array capacity, redundancy level and RAIDXpert2
license level.
An array refers to data storage created by RAIDXpert2 from one or
more disks. Although an array can be created from several disks, it is
seen by the operating system as a single disk.
Array Hiding
An array can be hidden from the operating system so that neither the
software nor users can see or access it.
2.3.2 Supported Operating Systems
RAIDXpert2 currently supports the following operating systems:
Microsoft
®
Windows® 7: Professional Edition, Ultimate Edition; 32 bit and 64 bit
Microsoft Windows 10: 64 bit
Red Hat Enterprise Linux
®
(RHEL) 7.2 64 bit
Ubuntu Desktop Linux 15.04 32 bit and 64 bit
Ubuntu Desktop Linux 15.10 32 bit and 64 bit
2.4 Features of RAIDXpert2
The features of RAIDXpert2 described in this user manual apply to all license levels and
supported operating systems.
Table 4 describes these features. Also see Table 5, on page 20, for a summary of features that are
available with each license level of RAIDXpert2: RAIDXpert2 Basic and RAIDXpert2 Plus.
Table 4. Features of RAIDXpert2
AMD-RAIDXpert2 User Guide
53987 Rev. 3.01 June 2016
18
Getting Started
Chapter 2
Table 4. Features of RAIDXpert2 (Continued)
RAIDXpert2 Feature
Description
Array Recovery
If an array is accidentally deleted, it might be recovered by creating a
new array with the same properties as the deleted array. (This can occur
only if disk Write Access operations are not in-progress.)
Background Array
Initialization (BGI)
The background initialization of a redundant array creates the redundant
data that allows the array to survive a disk failure.
Background initialization allows a redundant array to be used
immediately. Data is not lost if a disk goes offline prior to completion of
the BGI process.
Cache Support for Arrays
Various array-caching options are supported: No Cache, Disk Read
Ahead Cache, Write Back Cache, Read + Write Back Cache.
Cache Support for Disks
Various disk-caching options are supported: No Cache, Disk Read Ahead
Cache, Disk Write Back Cache, Disk Read Ahead + Write Back Cache.
Secure Erase
All data on an array can be erased and ensured it is unrecoverable, even
with advanced data recovery techniques.
Consistency Check
A Consistency Check is a background operation that verifies and corrects
the mirror or parity data for fault-tolerant disks. It is recommended that a
Consistency Check be run periodically on an array.
Disk Roaming
With disk roaming, SATA cables can be disconnected from their disks
and shuffled without confusing RAIDXpert2.
Note: Disconnect the SATA cables from the disks only when the system is
shutdown.
Disk roaming also allows:
Disks to be moved to different slots in the backplane. RAIDXpert2
detects which disks belong to which arrays, regardless of where the
disks are moved in the backplane.
Disk(s) to be moved between systems.
Note: It might not be possible to move disks between systems if they
contain boot arrays.
Fault Tolerance
The following fault tolerance features are available with RAIDXpert2, in
order to prevent data loss in case of a failed disk.
Disk failure detection (automatic).
Array rebuild using hot spares (automatic, if the hot spare is
configured for this functionality).
Parity generation and checking (RAID5 only).
Hot-swap manual replacement of a disk without rebooting the system
(available only for systems with a backplane that supports hotswapping) is not recommend for disks that are part of the Boot
Virtual Disk or are connected to the AMD 300-Series Chipset.
For example if a disk fails in RAID1, the array remains functional and
data is read from the surviving mirrored disk.
Mirror Rebuilding
A broken mirrored array can be rebuilt after a new disk is inserted and the
disk is designated as a spare. The system does not have to be rebooted.
53987 Rev. 3.01 June 2016
AMD-RAIDXpert2 User Guide
Chapter 2
Getting Started
19
Table 4. Features of RAIDXpert2 (Continued)
RAIDXpert2 Feature
Description
Multiple RAID Levels per
Disk
Support for multiple array levels per disk allows the administrator to
create arrays of different RAID levels using the same disks.
Native Command Queuing
(NCQ)
Native Command Queuing is a command protocol of disks that are
supported by RAIDXpert2. NCQ enables individual disks to internally
optimize the order in which Read and Write commands are executed.
RAIDXpert2 permits a queue depth of up to 32 read/write commands per
disk.
Online Capacity Expansion
(OCE)
OCE is a process that allows the user to add storage capacity to an
existing array, without taking the system offline. OCE enables the user to
increase the total storage capacity of an array by integrating unused
storage into the array.
Data can be accessed while the disks are added and while data on the
array is being redistributed.
Note: This feature is not available with all license levels. See Table 5.
Online RAID Level Migration
(ORLM)
With online RAID level migration, users can easily move an array from
one RAID level to another. While the migration is taking place, data is
accessible and protected to the lowest protection of either the source
RAID level or the destination RAID level.
Note: This feature is not available with all license levels. See Table 5.
RAID Level Support
RAIDXpert2 supports RAID levels 0, 1, 5, 10, Volume, and RAIDABLE.
Note: RAID5, and RAIDABLE are not supported by all license levels. See
Table 5.
Note: The ability to create RAID10 or RAIDABLE arrays may not be
available on your system.
Self-Monitoring Analysis and
Reporting Technology
(SMART)
SMART is a hard-disk-drive (HDD) capability which allows reporting of
reliability information. If a drive anticipates there is a high likelihood of
future failure it triggers a SMART error condition. RAIDXpert2 presents
this error condition so the drive can be replaced before the predicted
failure occurs.
AMD-RAIDXpert2 User Guide
53987 Rev. 3.01 June 2016
20
Getting Started
Chapter 2
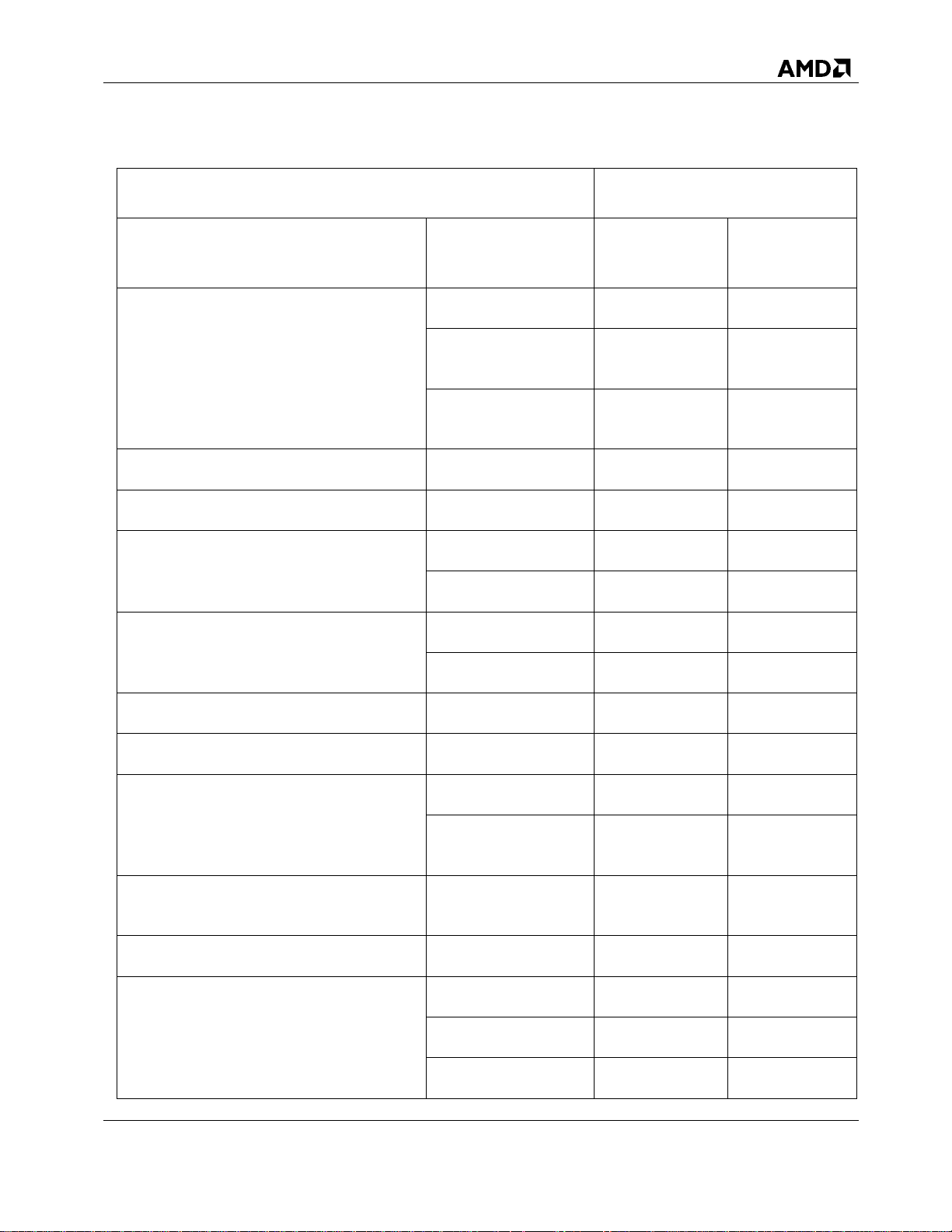
License Levels
Features
Sub-Features
RAIDXpert2
Basic
RAIDXpert2
Plus
Option ROM (BIOS)
Support1
Create array
Yes
Yes
Delete array
Yes
Yes
Boot/INT13 control
Yes
Yes
RAID Levels
Supported2
0
Yes
Yes
1
Yes
Yes 5 No
Yes
10
Yes
Yes
RAIDABLE
Yes
Yes
Volume
Yes
Yes
2.5 RAIDXpert2 Feature Set
IMPORTANT: The supported feature set (for RAIDXpert2 Basic or RAIDXpert2 Plus) is
determined by the license level that is included in the system BIOS. Refer to the
system’s motherboard specifications for the supported features.
Table 5. Feature Set for RAIDXpert2: by RAIDXpert2 License Level
53987 Rev. 3.01 June 2016
AMD-RAIDXpert2 User Guide
Chapter 2
Getting Started
21
Table 5. Feature Set for RAIDXpert2: by RAIDXpert2 License Level (Continued)
License Levels
Features
Sub-Features
RAIDXpert2
Basic
RAIDXpert2
Plus
Array Creation
No initialization
Yes
Yes
Foreground
initialization
Yes
Yes
Background
initialization
Yes
Yes
Array Deletion
Yes
Yes
Array Transformation
Yes
Yes
Sparing
Global
Yes
Yes
Dedicated
Yes
Yes
Consistency Check
Background
Yes
Yes
Scheduled
Yes
Yes
Online Capacity Expansion (OCE)3
No
Yes
Online RAID Level Migration (ORLM)
No
Yes
Drive/Disk Roaming4
Same-system support
Yes
Yes
Between-systems
support
Yes
Yes
RAIDXpert2 Web GUI (Management
GUI)
Yes
Yes
rcadm (management CLUI)
Yes
Yes
Drive Interfaces Supported5
SATA
Yes
Yes
SSD
Yes
Yes
ATAPI
Yes
Yes
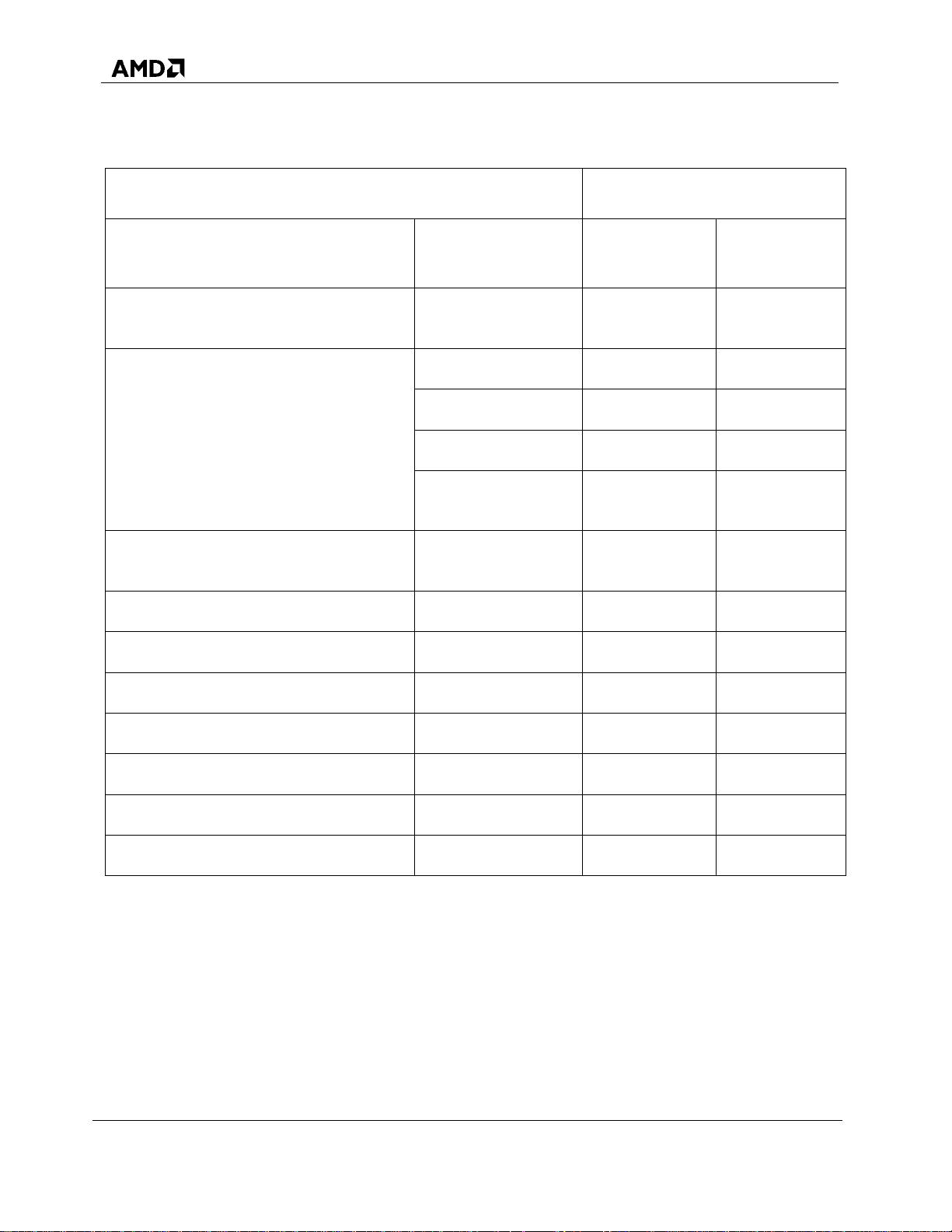
AMD-RAIDXpert2 User Guide
53987 Rev. 3.01 June 2016
22
Getting Started
Chapter 2
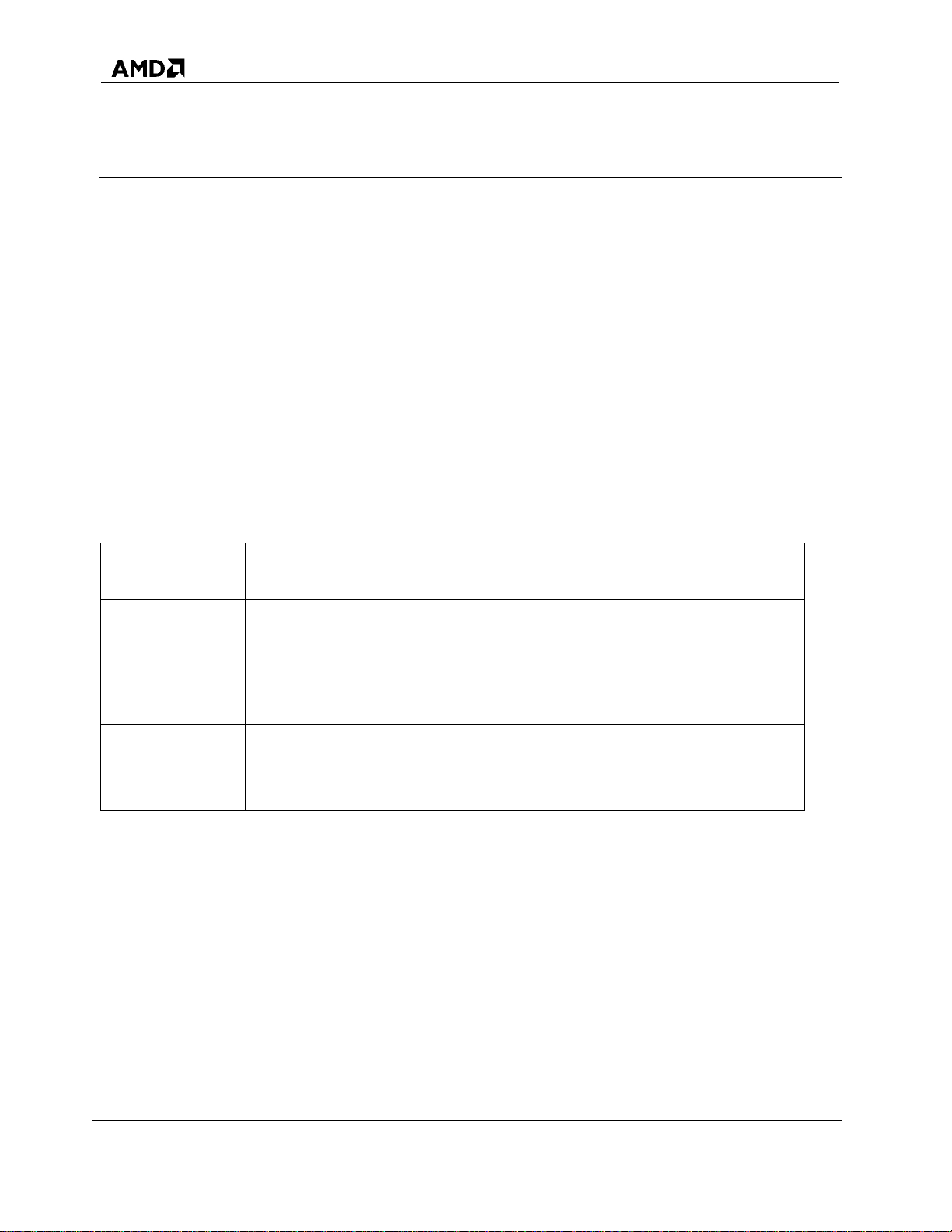
Table 5. Feature Set for RAIDXpert2: by RAIDXpert2 License Level (Continued)
License Levels
Features
Sub-Features
RAIDXpert2
Basic
RAIDXpert2
Plus
Dissimilar Disk Support Within The Same
Array
Yes
Yes
Cache Support
No Cache
Yes
Yes
Read Cache
Yes
Yes
Write Back Cache
Yes
Yes
Read with Write Back
Cache
Yes
Yes
Create Array and Delete Array Functions
Without Rebooting
Yes
Yes
Restore (Rebuild) Priority
Yes
Yes
Multiple RAID Levels per Disk6
Yes
Yes
Touched Region Logging7
Yes
Yes
E-mail Event Notification
Yes
Yes
System Event Log Integration
Yes
Yes
Instant Create Support8
Yes
Yes
Hot-Swap Support9
Yes
Yes

53987 Rev. 3.01 June 2016
AMD-RAIDXpert2 User Guide
Chapter 2
Getting Started
23
Notes:
1. At the AMD BIOS Configuration Utility (also referred to as the Option-ROM) arrays can be created or
deleted, and Critical or Offline arrays are indicated. INT13 support can be turned off completely at the
BIOS Configuration Utility.
2. See Chapter 3, Arrays, Disks and RAID Levels, on page 24, for detailed information about
understanding arrays, RAID levels, and performance and reliability considerations.
3. The unique ability of RAIDXpert2 to provide online expansion to RAID levels across multiple disks
becomes extremely valuable when expanded storage is a requirement.
4. Disk roaming allows arrays to be moved from port to port, either within the same system or between
systems.
5. See the system’s motherboard specifications for the supported device interface.
6. Multiple RAID levels (array types) per disk allows the administrator to create different RAID levels on
the same disks. For example: The administrator wants data redundancy for the user data, and creates a
RAID5 set using part of the disks’ data. At the same time the administrator wants performance for the
swap spaces, and creates a RAID0 array using the rest of the disks’ capacities (space). This feature is
useful in collecting unused capacity from disks with different capacities.
7. This feature increases data integrity for redundant array types, by logging areas of an array that have
been written to. In the event of a system crash, the logged area’s consistency is checked and/or
corrected. Without this feature, data corruption might occur.
8. Arrays can be instantly created and used by skipping the background consistency check. For certain
types of redundant arrays this is a viable option and has no data integrity drawbacks. A consistency
check can always be done at a later time. If an initialization is skipped when using RAID5, the array is
not redundant until a consistency check is performed.
9. Disks can be added to the system and to an array while the system is operating, but is not recommend
for disks that are part of the Boot Virtual Disk or which are connected to the AMD 300-Series Chipset.
AMD-RAIDXpert2 User Guide
53987 Rev. 3.01 June 2016
24
Arrays, Disks and RAID Levels
Chapter 3
RAID Level
Main Characteristic
Use/Usefulness
RAID0 (Striping)
Provides the highest performance
but no data redundancy. Data in
the array is striped (distributed)
across several disks.
Supports 2-8 disks.
RAID0 arrays are useful for holding
information, such as the operating
system paging file, where performance
is extremely important but redundancy
is not.
RAID1
(Mirroring)
Mirrors data on a partition of one
disk to another.
Supports 2 disks.
Useful when there are only two disks
available and data integrity is more
important than storage capacity.
Chapter 3 Arrays, Disks and RAID Levels
3.1 Understanding Arrays
Arrays are several disks that are grouped together to improve either the performance or reliability
of a storage system. Because some RAID levels enhance performance while others improve
reliability, it is important to consider the user’s needs when planning an array configuration.
Note: It is highly recommended that this user manual be reviewed in its entirety before
configuring arrays. Some of the advanced features of RAIDXpert2 (such as sparing options)
must be understood by the user before creating arrays.
3.2 RAID Levels
RAIDXpert2 supports the RAID levels indicated in Table 6.
Table 6. RAID Levels – General Characteristics
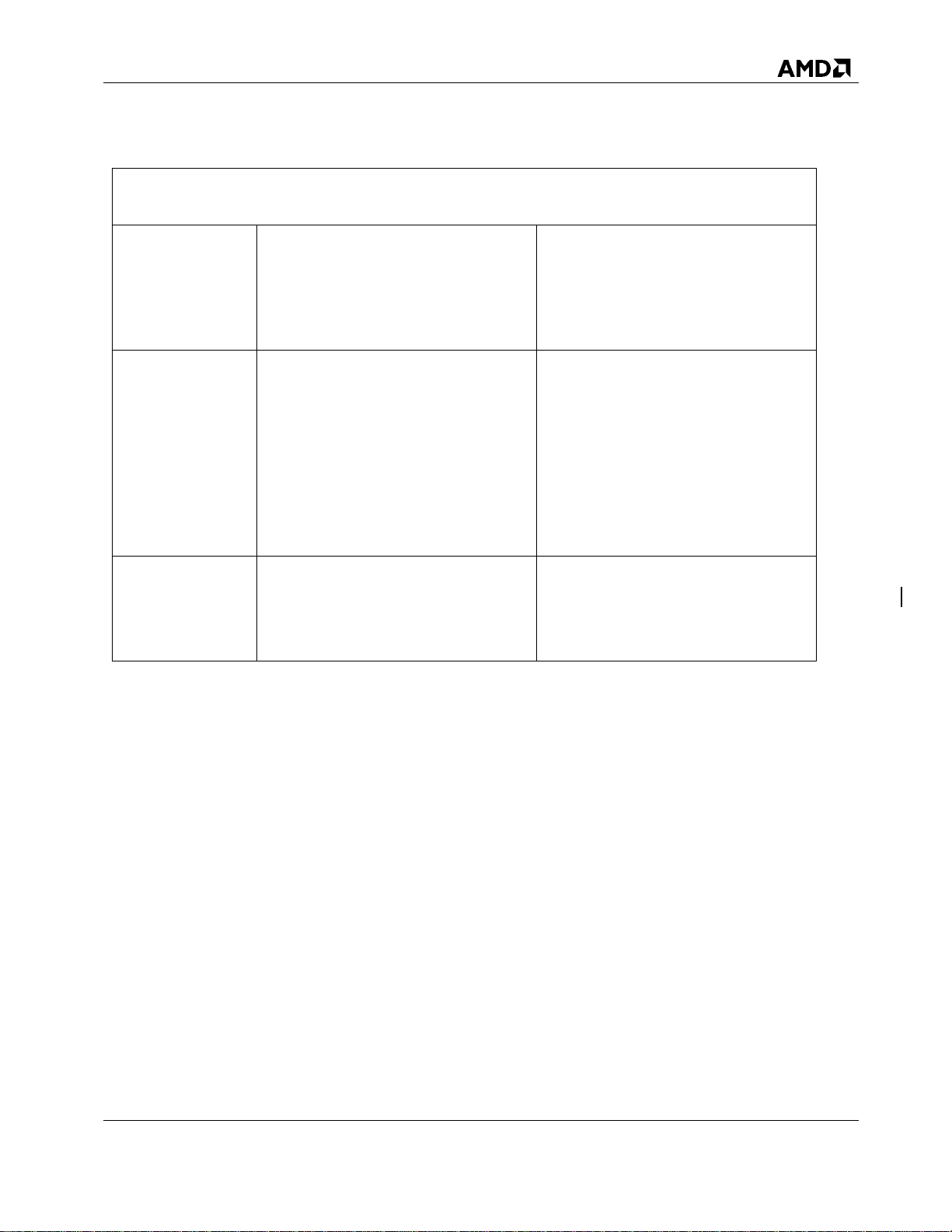
53987 Rev. 3.01 June 2016
AMD-RAIDXpert2 User Guide
Chapter 3
Arrays, Disks and RAID Levels
25
Table 6. RAID Levels – General Characteristics (Continued)
RAID Level
Main Characteristic
Use/Usefulness
RAID10 (Striped
RAID1 Sets)
Combines mirrors and stripe sets.
RAID10 allows multiple disk
failures, up to 1 failure in each
mirror that has been striped.
Supports 4, 6, or 8 disks.
Offers better performance than a
simple mirror because of the extra
disks.
Requires twice the disk space of
RAID1 to offer redundancy.
Volume (JBOD)
RAIDXpert2 treats one or more
disks or the unused space on a
disk as a single array.
Supports 1 to 8 disks
Provides the ability to link-together
storage from one or several disks,
regardless of the size of the space on
those disks.
Useful in scavenging space on disks
unused by other disks in the array.
Does not provide performance benefits
or data redundancy. Disk failure will
result in data loss.
RAIDABLE (also
known as RAID
Ready)
Allows a RAIDABLE disk to be
transformed later to RAID0 or
RAID1.
Supports one disk.
See RAID0 (Striping), on page 24 or
RAID1 (Mirroring) on page 24 for
post-transformation usefulness.
3.3 Array States
Within the management applications, an array is a logical device that can exist in one of four
states: Normal, Ready, Critical, or Offline.
In RAIDXpert2, these states display in the Array List section in a column named State.
Within the rcadm Command Line tool, these states also display in a column named State.
The array states are defined in Table 7, on page 26.
AMD-RAIDXpert2 User Guide
53987 Rev. 3.01 June 2016
26
Arrays, Disks and RAID Levels
Chapter 3
State
Description
Normal
The Normal state is displayed when everything is functioning correctly.
Ready
The Ready state is displayed while an array is being created.
Critical
The Critical state is displayed when the array is no longer redundant (fault
tolerant) because of one or more disk failures. Arrays can still be read and written
to, but the data is no longer protected should another disk fail.
Offline
The Offline state is displayed when arrays cannot be read or written to because of
one or more disk failures.
RAID Level
This Failure State
Is Displayed Whenever
RAID1
(Redundant Arrays)
Critical
A single disk fails.
Offline
Two or more disks fail.
RAID10
(RAID Levels with Multiple
Redundancies)
Critical
A single disk fails in any one of the
sets.
Offline
All disks in a set fail.
Volume and RAID0
Offline
A single disk fails.
Table 7. Array States
Whether an array is marked as Critical or Offline depends upon what RAID level it is and how
many disks within the array have failed. Note the changes in state in Table 8.
Table 8. Failure States by RAID Level
More than one array can be created using the same set of disks. If a disk is disconnected that
belongs to more than one array, only the arrays that try to access the disk and receive I/O errors
report the failure. For example: there are two arrays, both of which are RAID5 sets, and both use
disk 4. If a system that is being used by array 1 receives an I/O error when trying to communicate
with disk 4, the state of array 1 changes to Critical. However, the state of array 2 using disk 4 does
not change to Critical until an I/O error is reported. If systems using array 1 are not
communicating with failed disk 4, the state of array 1 still displays as Normal.
If a rescan of all channels is performed after disconnecting a disk, the state of every array using
the missing disk changes from Normal to either the Critical or Offline, depending on the RAID
level.
53987 Rev. 3.01 June 2016
AMD-RAIDXpert2 User Guide
Chapter 3
Arrays, Disks and RAID Levels
27
Operating System
Do This...
And Consider This...
Microsoft® Windows®
Format the arrays with
NTFS. Microsoft
Corporation provides a
utility (Diskpart.exe) that can
dynamically extend an NTFS
file system onto any unused
adjacent space.
Note also that using a single
partition per array makes
expansion much easier.
1. The Diskpart.exe utility version
depends on which version of the
Windows operating system is
running.
2. The Diskpart.exe utility can be
found on the CD for some versions
of Windows operating systems, or on
the Microsoft Corporation website
(http://www.microsoft.com)
for other versions. Use the correct
version for the operating system.
Linux®
Use an expandable file
system.
Because RAIDXpert2 software is
limited to eight arrays, if a large
number of logical volumes are
needed, use a logical volume
manager (LVM).
See Section 3.9, Rescanning Disks for Changes in State, on page 30 for a discussion of when to
rescan disks and the outcomes when doing so.
3.4 Creating Arrays: Future Expansion
When creating arrays, consider whether disk capacity needs to expand in the future. If the file
system must be expanded, perform the tasks indicated in Table 8.
Table 9. Array Expansion Considerations
3.5 Expanding Disk Capacity Online: Using OCE
(Supported by RAIDXpert2 Plus)
Online Capacity Expansion (OCE) allows:
Adding disks to an array at any time to increase an array’s capacity.
Accessing the array data while it is being redistributed.
To increase the size and organization of an array, transform the array. For more information about
transforming arrays, see Section 6.6.3, Transform Arrays (Supported by RAIDXpert2 Plus), on
page 73.

AMD-RAIDXpert2 User Guide
53987 Rev. 3.01 June 2016
28
Arrays, Disks and RAID Levels
Chapter 3
3.6 Migrating RAID Levels Online: Using ORLM
(Supported by RAIDXpert2 Plus)
Online RAID Level Migration (ORLM) allows an array to move from one RAID level to almost
any other RAID level. This task includes migrating the array from a non-redundant RAID level to
a redundant RAID level.
Prior to starting a RAID level migration/transformation, make sure that the disks selected for the
destination array have sufficient capacity. RAID level migration/transformation can occur only
when the destination array has the same or larger capacity as the source array.
While the migration/transformation is taking place, data is accessible and protected to the lowest
protection of either the source RAID level or the destination RAID level.
The Transform task can also be used to expand the capacity of an array, by using OCE. It can also
be used as part of the system backup and recovery strategy through the use of the RAID1 and
RAID10 levels.
To perform this process, see Section 6.6.3, Transform Arrays (Supported by RAIDXpert2 Plus),
on page 73.
3.7 Array Tasks: Starting and Stopping Tasks
Tasks are started when one of the following actions are performed:
Create a redundant array.
Transform an array.
Restore an array.
Securely erase an array.
Check for consistency on redundant arrays.
Verify that data was not corrupted after a system crash (Check_Bitmap performed
automatically).
Full task control can be used on Create, Consistency Check and Bitmap Check tasks. On a
Transform or Restore task for dedicated and global spares, task control can only pause/resume, but
it cannot remove the task. To remove these types of tasks, pause and then remove them.
The tasks indicated in Table 10 on page 29, can be displayed for each array.
53987 Rev. 3.01 June 2016
AMD-RAIDXpert2 User Guide
Chapter 3
Arrays, Disks and RAID Levels
29
Task
When Displayed
Transform
While an array is being transformed.
Create
While an array is being created.
Consistency Check
While verifying that the parity (RAID5) or mirror disk (RAID1 or RAID10)
consistency is correct. (For redundant type arrays only.)
Restore
While an array is being restored.
Secure Erase
While an array secure erase is being performed.
Check_Bitmap
While verifying that the parity on a RAID5 set, or the mirror halves on a
RAID1 or RAID10 set, are consistent. This action is performed automatically
to ensure that data is not corrupted whenever a system crashes.
Not_Active
When no other tasks are being performed.
Disk State
When Displayed
Online
Whenever the disk is connected, functioning correctly, and RAIDXpert2 can
communicate with it.
Table 10. Types of Tasks per Array
3.8 Understanding Disks
3.8.1 Disks States
Within the management applications, a disk can be part of one or more arrays and can exist in one
of five states: Online, Offline, New, Legacy, or SMART Error.
In RAIDXpert2, these states are displayed in the Disk List section in a column named State.
See Table 17, on page 64, for additional information.
Within the rcadm program, these states are also displayed in a column named State. See Table
41, on page 102, and Table 42, on page 103, for additional information.
The disk states are defined in Table 11.
Table 11. Disk States

AMD-RAIDXpert2 User Guide
53987 Rev. 3.01 June 2016
30
Arrays, Disks and RAID Levels
Chapter 3
Table 11. Disk States (Continued)
Disk State
When Displayed
New
Whenever an uninitialized, new disk is connected.
Legacy
Whenever a disk containing non-RAIDXpert2 configuration data is connected.
Offline
Whenever the disk fails and RAIDXpert2 detects an error condition on the disk.
SMART Error
Whenever the disk reports a SMART error(s) to RAIDXpert2.
A disk can be a member of multiple arrays. A disk failure in one array doesn't necessarily mean it
has failed in other arrays.
After a rescan is performed the following can occur:
A disconnected disk no longer appears in the Disk List (although the disk appears as Missing
in the Array View for the arrays to which it belonged).
A disk that experiences a catastrophic failure appears in the Disk List as Offline and is
highlighted in red. The disk appears as Failed for the arrays to which it belonged.
A disk that has a SMART error appears in the Disk List as SMART Error. (A disk with a
SMART error can’t be used to create an array)
A disk that experiences a software-related failure appears in the Disk List as Online and is
highlighted in red. New arrays can be created with the disk.
Arrays that exist on a failed or disconnected disk might not be designated as Failed or Missing
until the system attempts to communicate with the failed or disconnected disk.
3.9 Rescanning Disks for Changes in State
The information displayed in the Disk List section is the state of the disks when they were last
scanned. If a rescan has not been performed, the information being displayed is the state of the
disks at boot time.
Every time a disk is connected or disconnected while online, a message asks if the user wants to
perform a rescan (of all SATA channels). If Rescan is selected, the information in both the Array
List and the Disk List is updated. This view might show arrays as being in a Critical or Offline
state, if all disks have not been installed or removed.
Although it is highly recommended that the system be shut down before adding or removing disks,
disks can be added or removed while the system is online (“hot-swapping”), if the system supports
the hot-swapping function. This is not recommend for disks that are part of the Boot Virtual Disk
or those that are connected to the AMD 300-Series Chipset.
 Loading...
Loading...