Evaluation Board User Guide
One Technology Way • P. O . Box 9106 • Norwood, MA 02062-9106, U.S.A. • Tel : 781.329.4700 • Fax : 781.461.3113 • www.analog.com
UG-298
Evaluation Board for the SSM2377 Filterless, Class-D Audio Amplifier
PACKAGE CONTENTS
EVAL-SSM2377Z evaluation board
OTHER SUPPORTING DOCUMENTATION
SSM2377 data sheet
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
The SSM2377 is a fully integrated, high efficiency, Class-D audio
amplifier. It is designed to maximize performance for mobile
phone applications. The application circuit requires a minimum
of external components and operates from a single 2.5 V to 5.5 V
supply. It is capable of delivering 2.5 W of continuous output power
with <1% THD + N when driving a 4 Ω load from a 5.0 V supply.
Spread-spectrum pulse density modulation (PDM) is used to
provide lower EMI-radiated emissions compared with other
Class-D architectures. The inherent randomized nature of
spread-spectrum PDM eliminates the clock intermodulation
(beating effect) of several amplifiers in close proximity.
The SSM2377 produces ultralow EMI emissions that significantly reduce the radiated emissions at the Class-D outputs,
particularly above 100 MHz. The SSM2377 passes FCC Class B
radiated emission testing with 50 cm, unshielded speaker cable
without any external filtering.
The device also includes a gain select pin that allows the user to
select a 6 dB or a 12 dB gain. This option improves gain matching
between multiple SSM2377 devices within a single application
as compared to using external resistors to set the gain. Input
impedance is 80 k and is independent of the gain setting.
This user guide describes how to configure and use the
SSM2377 evaluation board. The user guide should be read
in conjunction with the SSM2377 data sheet, which provides
detailed information about the specifications, internal block
diagrams, and application guidance for the amplifier IC.
EVALUATION BOARD OVERVIEW
The SSM2377 evaluation board carries a complete application
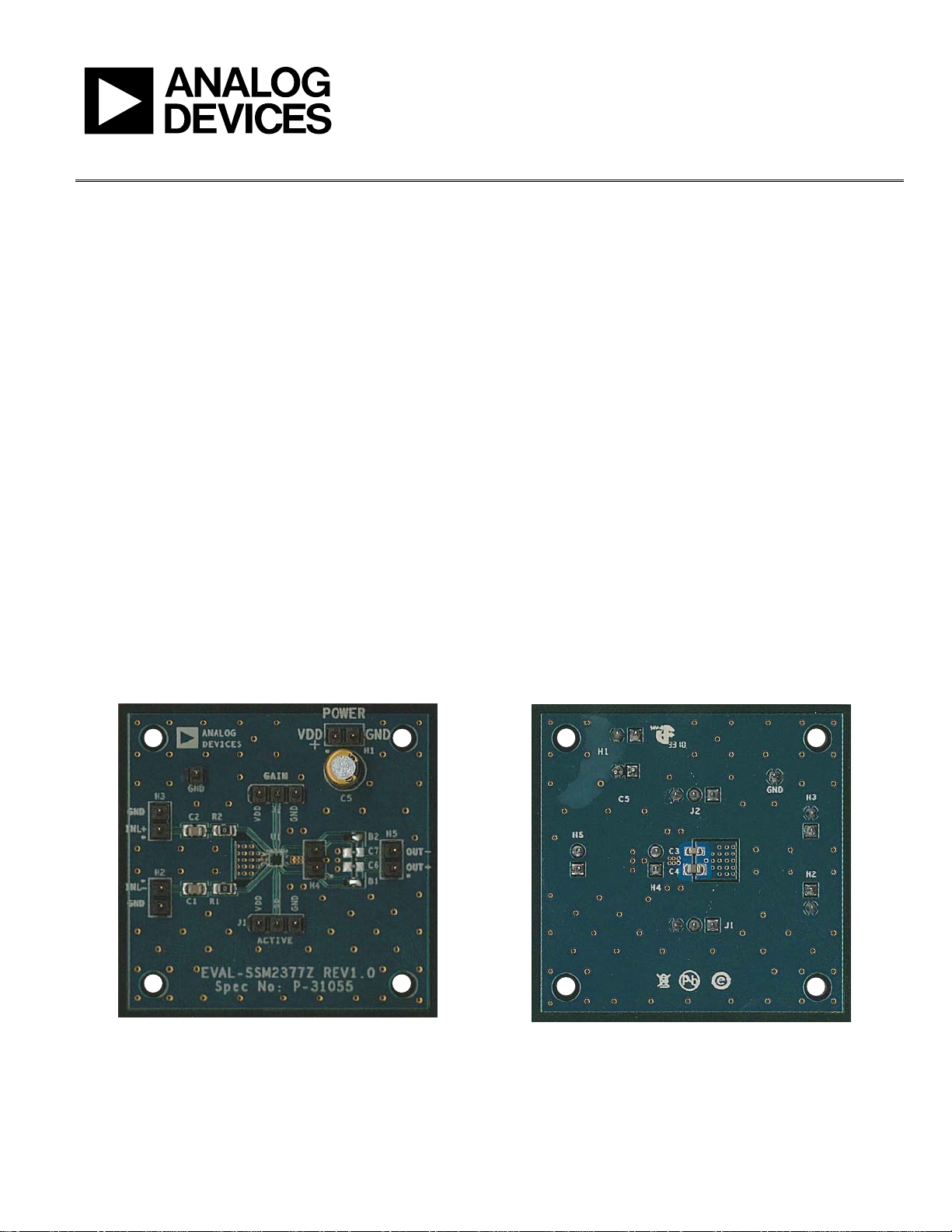
circuit for driving a loudspeaker. Figure 1 shows the top view
of the evaluation board, and Figure 2 shows the bottom view.
DIGITAL PICTURES OF THE EVALUATION BOARD
09979-001
Figure 1. SSM2377 Evaluation Board, Top View Figure 2. SSM2377 Evaluation Board, Bottom View
09979-002
PLEASE SEE THE LAST PAGE FOR AN IMPORTANT
WARNING AND LEGAL TERMS AND CONDITIONS.
Rev. 0 | Page 1 of 8

UG-298 Evaluation Board User Guide
TABLE OF CONTENTS
Package Contents .............................................................................. 1
Other Supporting Documentation ................................................. 1
General Description ......................................................................... 1
Evaluation Board Overview ............................................................ 1
Digital Pictures of the Evaluation Board ....................................... 1
Revision History ............................................................................... 2
Setting Up the Evaluation Board .................................................... 3
Input Configuration ..................................................................... 3
Shutdown Mode ............................................................................ 3
REVISION HISTORY
6/11—Revision 0: Initial Version
Gain Configuration .......................................................................3
Output Configuration ...................................................................3
Power Supply Configuration .......................................................3
Component Selection ...................................................................3
Getting Started ...................................................................................5
What to Test ...................................................................................5
Evaluation Board Schematics and Artwork ...................................6
Ordering Information .......................................................................8
Bill of Materials ..............................................................................8
Rev. 0 | Page 2 of 8

Evaluation Board User Guide UG-298
SETTING UP THE EVALUATION BOARD
INPUT CONFIGURATION
A pair of 2-pin, 0.100” headers (H2 and H3) on the left side of
the board feed the audio signal into the board (see Figure 1). If
the input audio signal is differential, three header pins are used:
INL+, INL−, and either GND terminal for input signal ground.
For a single-ended audio input, use INL+ and GND for input
signal and ground, respectively. Use a jumper to short INL− to
GND. If the opposite input polarity is required, use INL− and
GND for input signal and ground, respectively.
SHUTDOWN MODE
J1, the 3-pin header labeled ACTIVE, is used to turn the SSM2377
amplifier on and off. Placing a jumper between the SD and VDD
header pins places the SSM2377 in normal operation. Placing
the jumper between the SD and GND header pins shuts down
the SSM2377 so that only a minimum current (approximately
20 nA) is drawn from the power supply. Because there is no
internal pull-up or pull-down, do not omit the jumper; leaving
the SD pin floating puts the part in an indeterminate state.
GAIN CONFIGURATION
A 3-pin header, J2, controls the analog gain of the SSM2377.
By placing a jumper across two pins of J2, the amplifier GAIN
pin can be connected to GND or VDD. Two jumper settings
are used: between the center pin and the right pin (GND), or
between the center pin and the left pin (VDD). See Table 1 for
configuration instructions.
Table 1. Gain Configuration
Gain Setting (dB) J2 Configuration
6 Tie center pin to VDD
12 Tie center pin to GND
OUTPUT CONFIGURATION
Two output headers, H4 and H5, are located on the right side
of the board before and after a ferrite bead output filter (see
Figure 1). Either header can be connected to a loudspeaker;
the loudspeaker impedance should be no less than 4 .
Because the SSM2377 does not typically require any external LC
output filters due to a low noise modulation scheme, no output
filter is installed on the evaluation board. In this case, use thick
wire to short across the pads marked B1 and B2, leave the capacitor
pads unpopulated, and connect the speaker to H5. To minimize
trace lengths, use H4 instead of H5.
If the speaker cable length exceeds 50 cm, place ferrite beads B1
and B2 in the output paths and use capacitors C6 and C7 to couple
the output terminals to ground, as shown in the schematic in
Figure 3. In this case, Header H5 must be used for the output
terminals. Recommended ferrite beads are listed in Tab le 2 . For
applications with specific EMI vs. audio performance constraints,
users may want to use inductors; see Tab le 3 for recommended
inductors.
For the best THD and SNR performance as specified in the
SSM2377 data sheet, do not use an output filter.
POWER SUPPLY CONFIGURATION
The 2-pin Header H1 is used to power the board. Care must be
taken to connect the dc power with correct polarity and voltage.
Reverse polarity or overvoltage may permanently damage the
board. The maximum supply current is approximately 0.33 A
when driving an 8 Ω load with an input voltage of 5 V. Do not
allow VDD to exceed 5.5 V.
COMPONENT SELECTION
Selecting the proper components is the key to achieving the
performance required at the budgeted cost.
Input Gain Resistor Selection—R1 and R2
If the desired gain must be adjusted beyond the available gain
settings (see the Gain Configuration section), a series resistor
can be placed in the input signal path. This resistor creates a
voltage divider with the 80 k input resistance on each input
pin, allowing an arbitrary reduction of the input signal. Because
input signal attenuation directly reduces SNR performance,
large values compared to the built-in input resistance should be
avoided. These components are populated with 0 values on
the evaluation board.
Input Coupling Capacitor Selection—C1 and C2
The input coupling capacitors, C1 and C2, should be large
enough to couple the low frequency signal components in
the incoming signal but small enough to reject unnecessary,
extremely low frequency signals. For music signals, the cutoff
frequency is typically between 20 Hz and 30 Hz. The value of
the input capacitor is calculated as follows:
C = 1/(2π × R
where:
R
= 80 kΩ + (R1 or R2).
IN
f
is the desired cutoff frequency.
C
Output Ferrite Beads—B1 and B2
The output beads, B1 and B2, are necessary components for
filtering out the EMI caused at the switching output nodes
when the length of the speaker wire is greater than 50 cm. The
penalty for using ferrite beads for EMI filtering is slightly worse
noise and distortion performance at the system level due to the
nonlinearity of the beads.
Ensure that these beads have enough current-conducting capability
while providing sufficient EMI attenuation. The current rating
needed for an 8 Ω load is approximately 420 mA, and impedance
at 100 MHz should be ≥120 . In addition, the lower the dc
resistance (DCR) of these beads, the better for minimizing their
power consumption. Ta ble 2 lists the recommended beads.
× fC)
IN
Rev. 0 | Page 3 of 8
 Loading...
Loading...