Evaluation Board User Guide
UG-208
One Technology Way • P. O . Box 9106 • Norwood, MA 02062-9106, U.S.A. • Tel : 781.329.4700 • Fax : 781.461.3113 • www.analog.com
1 GSPS Quadrature Digital Upconverter with 14-Bit DAC Evaluation Board
FEATURES
1 GSPS internal clock speed (up to 400 MHz analog output)
Integrated 1 GSPS 14-bit DAC
250 MHz I/Q data throughput rate
Phase noise ≤ −125 dBc/Hz (400 MHz carrier @ 1 kHz offset)
Excellent dynamic performance >80 dB narrow-band SFDR
8 programmable profiles for shift keying
Sin(x)/(x) correction (inverse sinc filter)
Reference clock multiplier
Internal oscillator for a single crystal operation
Software and hardware controlled power-down
Integrated RAM
Phase modulation capability
Multichip synchronization
Easy interface to Blackfin SPORT
Interpolation factors from 4× to 252×
Interpolation DAC mode
Gain control DAC
Internal divider allows references up to 2 GHz
1.8 V and 3.3 V power supplies
100-lead TQFP_EP package
PACKAGE CONTENTS
AD9957 evaluation board
AD9957/PCB installation software
USB cable
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
This user guide serves as a guide to setup and use the AD9957
evaluation board. The AD9957 is a 1 GSPS quadrature digital
upconverter with a 14-bit DAC.
The evaluation board software provides a graphical user interface
for easy communication with the device along with many userfriendly features such as the mouse-over effect, which clarifies
elements by hovering the mouse over the element.
Use this user guide in conjunction with the AD9957 data sheet.
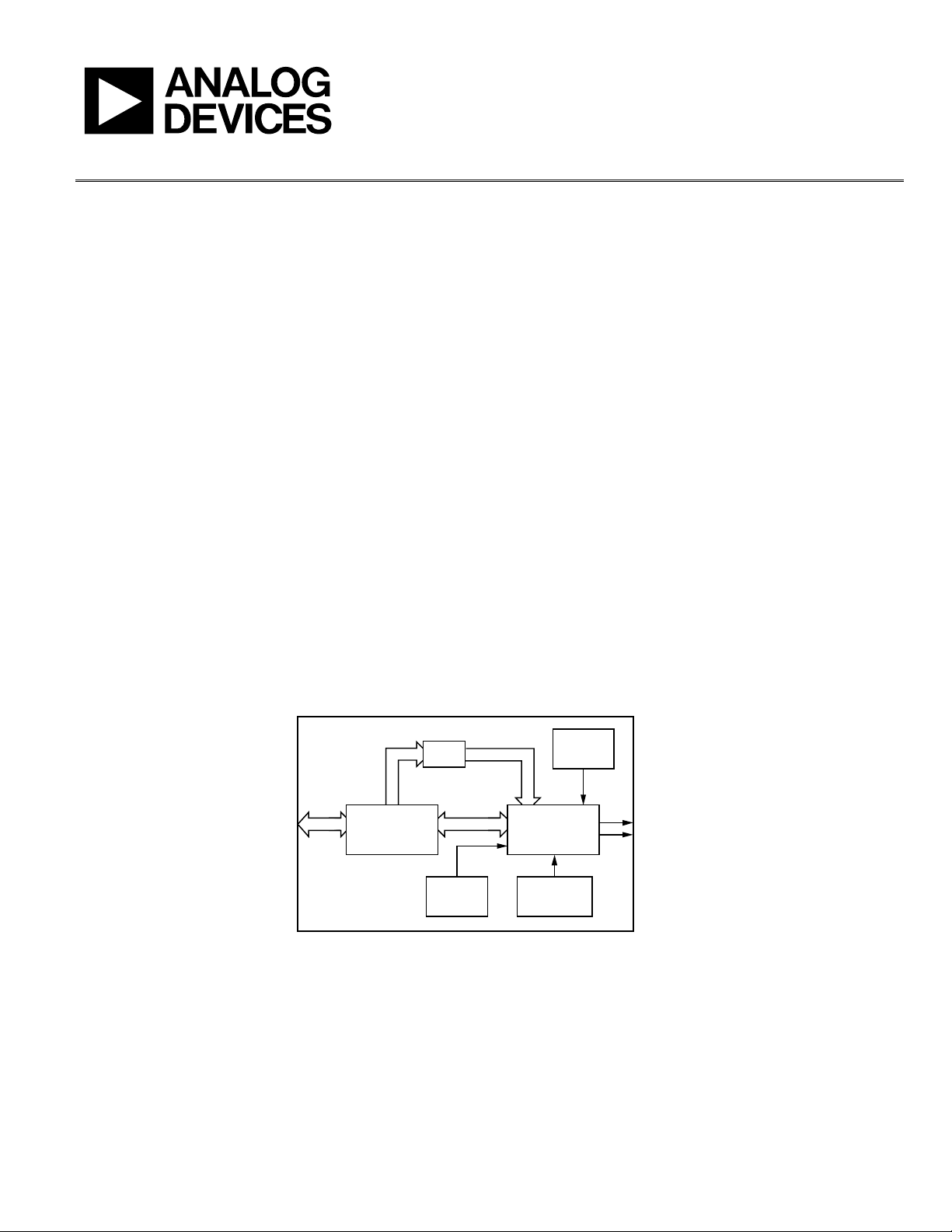
FUNCTIONAL BLOCK DIAGRAM
BASEBAND
MODULATION
DATA
TO PC
EVAL-AD9957
USB
INTERFACE
FIFO
SPI
DC POWER
HEADER
Figure 1.
I/Q DATA
MULTICHIP
AD9957
REFERENCE
CLOCK
SYNC
DAC OUT
07801-001
PLEASE SEE THE LAST PAGE FOR AN IMPORTANT
WARNING AND LEGAL TERMS AND CONDITIONS.
Rev. A | Page 1 of 32

UG-208 Evaluation Board User Guide
TABLE OF CONTENTS
Features .............................................................................................. 1
Package Contents .............................................................................. 1
General Description ......................................................................... 1
Functional Block Diagram .............................................................. 1
Revision History ............................................................................... 2
Evaluation Board Hardware ............................................................ 3
Requirements ................................................................................ 3
Setting Up the Evaluation Board ................................................ 3
Evaluation Board Software .............................................................. 5
Installing the Software ................................................................. 5
Installing the Driver ..................................................................... 5
Launching the Program ............................................................... 5
Feature Windows .............................................................................. 7
Control ........................................................................................... 7
Profiles.............................................................................................. 10
Profiles Windows ........................................................................ 10
View Windows ............................................................................ 14
QDUC RAM Control ................................................................. 14
FIFO Control .............................................................................. 15
MultiChip Sync Control ............................................................ 15
GPIO ............................................................................................ 16
Debug Window ........................................................................... 16
Register Map (Software Buffer) Values Window ................... 17
DUT I/O ...................................................................................... 17
Modulation Vector Generator....................................................... 18
QAM ............................................................................................. 18
GMSK/EDGE .............................................................................. 19
SDPSK .......................................................................................... 19
Simulator ......................................................................................... 20
Simulator Tool ................................................................................. 21
Overview ..................................................................................... 21
Simulator Activation .................................................................. 21
Simulator Description ............................................................... 21
Single-Tone Mode Simulation .................................................. 23
QDUC Parallel Data Mode Simulation ................................... 24
QDUC BlackFin (Serial Data) Mode Simulation ................... 24
Interpolating DAC Mode Simulation ...................................... 25
Virtual Oscilloscope and Spectrum Analyzer ........................ 25
User Data File(s) ......................................................................... 25
Auxiliary Control File ................................................................ 26
Keywords ......................................................................................... 27
Debug ........................................................................................... 27
Showclip ....................................................................................... 27
Samples ........................................................................................ 27
DDSCORE ................................................................................... 27
RSET ............................................................................................. 27
DACXFR ...................................................................................... 27
FFTWINDOWTYPE ................................................................. 27
Virtual Oscillope and Spectrum Analyzer Instruments
Keywords ..................................................................................... 28
DAC Output Signal Keywords .................................................. 29
REVISION HISTORY
11/10—Rev. 0 to Rev. A
Document Title Changed from EVAL-AD9957 to
UG-208 ................................................................................. Universal
Changes to Device Clock Oscillator Options Section ................. 3
Deleted Ordering Guide ................................................................ 32
7/09—Revision 0: Initial Version
Rev. A | Page 2 of 32
Evaluation Board User Guide UG-208
EVALUATION BOARD HARDWARE
REQUIREMENTS
To use the evaluation board and run the software, the requirements
listed in Tabl e 1 must be met.
Table 1. EVAL-AD9957 Requirements
Item Requirement
Operating System Windows® 98/ME/2000/XP
Processor Pentium® I or better
Memory 128 MB or better
Ports One USB port
Clocking
Power Supplies
Measurement
Cables
Signal generator capable of generating
sinusoidal waves of at least 0 dBm power,
up to at least 10 MHz
Capability to generate at least two
independent dc voltages (1.8 V/3.3 V)
Appropriate measurement device, such as a
spectrum analyzer or a high bandwidth
oscilloscope
USB 1.1/2.0 cable, and SMA-to-x cables (x =
SMA or BNC, depending on the connector
of the device interfacing with the board)
SETTING UP THE EVALUATION BOARD
DC Power Supply
The AD9957 evaluation board has two power supply connectors
(four pins each): TB1 and TB2. TB1 powers the USB interface
circuitry, the digital I/O interface, and the digital core. TB2
powers the DAC and the clock input circuitry.
Tabl e 2 shows the necessary connections and the appropriate
biasing voltage for TB1 and TB2.
Table 2. Connections and Biasing Voltage
Connector Pin No. Label Voltage (V)
TB1 1 VCC 3.3
TB1 2 GND 0
TB1 3 DVDD_IO 3.3
TB1 4 DVDD 1.8
TB2 1, 3 GND 0
TB2 2 DAC_VDD 3.3
TB2 4 CLK_VDD 1.8
Device Clock Oscillator Options
The AD9957 architecture provides the user with three options
when providing an input signal to the part. The first option allows
the user to provide a high frequency input signal, connected to J1.
The second option allows the user to connect the part using a
lower input reference frequency, enabling the clock multiplier,
connected through J1. The third option allows the user to
connect a crystal resonator on the backside of the board.
Note that the AD9957 evaluation board does not populate the
PLL loop filter components. Therefore, to use the internal PLL
of the AD9957, the user must solder down these components or
the PLL will not be stable. The AD9957 data sheet has helpful
formulas to calculate the appropriate values. In addition, an
excel file to help choose the loop filter component values is
available on the AD9957 product page. Once on the AD9957
product page, go to the Evaluation Boards & Development Kits >
Evaluation Boards/Tools and click PLL Loop Filter Tool.
To enable the crystal mode, switch the jumper, W7, to the XTAL
mode. Remove C51 and C52. Place 0 resistors at R4 and R11
on the backside of the board. The crystal oscillates at 25 MHz.
Refer to the AD9957 data sheet for details on the maximum
input speeds and input sensitivities of these two inputs.
Device Communication Requirements
Two interface standards are available on the evaluation board:
• USB 1.1/2.0
• A header row (U5 and U9), which places the part under
the control of an external controller (such as a microprocessor,
FPGA, or DSP).
Analog Devices provides a GUI for the PC but does not provide
control software for external controllers.
Use the jumper settings listed in Table 3 to enable different
modes of communication.
Table 3. Jumper Settings for Communication Modes
Mode Settings
PC Control, USB Port
External Control
Set Jumper W1 and Jumper W2 to enable.
Set Jumper W4 to EN.
Place a jumper on W5, W6, and W3.
Set Jumper W1 and Jumper W2 to disable.
Set Jumper W4 to DIS.
Remove the jumper on W5, W6, and W3.
Jumper W1, Jumper W2, and Jumper W4 enable the USB circuitry
to control the AD9957. Jumper W3 controls the EEPROM and
is used in starting up the USB circuitry. Jumper W5 and Jumper
W6 control the signals SDO and SDIO to and from the AD9957.
Rev. A | Page 3 of 32
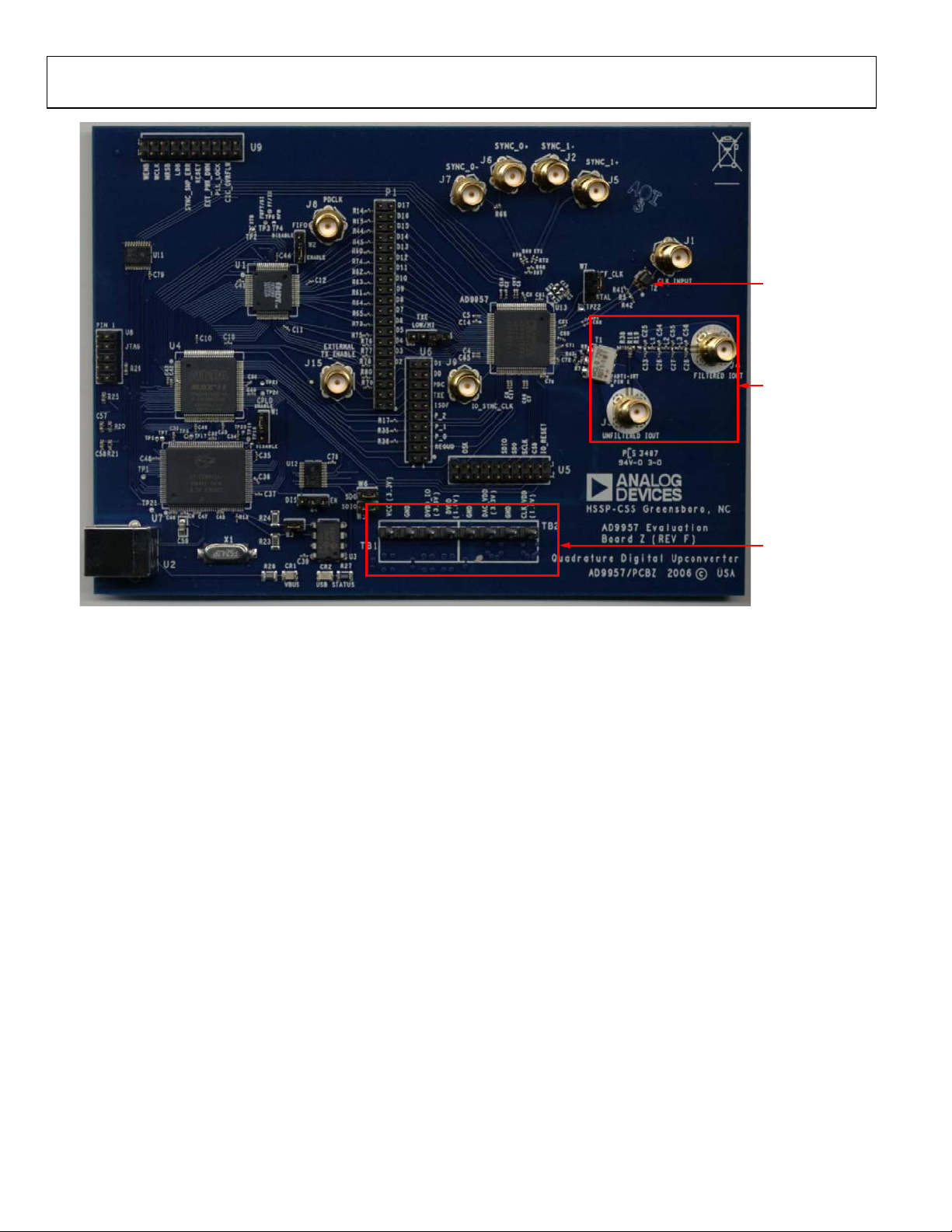
UG-208 Evaluation Board User Guide
REFERENCE CLOCK INPUT
DAC OUTPUT
MANUAL I/O
CONTROL HEADERS
Figure 2. Evaluation Board Layout
Manual I/O Control Headers
Header connectors (U5, U6, and U9) provide the communication
interface for the AD9957 when the part is under the command of
an external controller (see Table 3 for the correct jumper settings).
Multidevice Synchronous Control
J2, J5, J6, and J7 connections are used to set up the AD9957 for
multidevice synchronous operation.
DAC Output
The J4 connection is the filtered output of the DAC and J3
represents the unfiltered (default) DAC output. To enable the
filtered path, R19 on the PCB must be installed.
Clock Mode Select
Clock mode select controls whether the reference clock source
is a 20 MHz to 30 MHz crystal or an external signal generator.
A 25 MHz crystal is provided on underside of the AD9957
evaluation board.
POWER SUPPLY CONNECTIONS
07801-002
Reference Clock Input
The reference clock input is the input for the external reference
clock signal.
Power Supply Connections
These two connectors, TB1 and TB2, provide all the necessary
supply voltages needed by the AD9957 and the evaluation board
(see Tabl e 2).
USB Port
When the part is under PC control (default mode), the evaluation
board communicates with the AD9957 via the USB port.
Rev. A | Page 4 of 32

Evaluation Board User Guide UG-208
EVALUATION BOARD SOFTWARE
INSTALLING THE SOFTWARE
Use the following steps to install the AD9957 evaluation software:
1. Log into your PC system with administrative privileges.
2. Uninstall any previous versions of the AD9957 evaluation
software from your PC system.
3. Insert the AD9957 evaluation software CD. Do not connect
the AD9957 evaluation board to the computer until the
AD9957 evaluation software has been installed.
4. Open the Readme.txt file located in the Software folder
before proceeding with the installation of the AD9957
evaluation software.
5. Run the setup.exe file located in the Software folder and
follow the on-screen installation instructions.
INSTALLING THE DRIVER
Once the software has been installed onto your PC, interface the
AD9957 evaluation software to the AD9957 evaluation board
via the USB port (see Figure 2).
In order for the evaluation board and software to communicate
properly, drivers must be loaded onto your PC system. Use the
instructions in the following sections to install these drivers on
your PC system.
Windows 98/ME/2000 Users
1. Power up the AD9957 evaluation board (see Tab le 2).
2. Connect the evaluation board to the computer using a
USB cable via the USB port; the VBUS LED (CR1 on the
AD9957 evaluation board) illuminates.
3. When the USB cable is connected, the Found New
Hardware window appears.
4. Click Finish in the Found New Hardware Wizard when
the install is complete.
After the window has disappeared, the USB status LED (CR2 on
the AD9957 evaluation board) flashes, which indicates that the
evaluation board is connected properly.
Windows XP Users
1. Power up the AD9957 evaluation board (see Tab le 2).
2. Connect the evaluation board to the computer using a USB
cable via the USB port. Then, the VBUS LED (CR1 on the
AD9957 evaluation board) illuminates.
3. When the USB cable is connected, the Found New Hardware
Wizard appears. Click Next to continue. The AD9957
Firmware Loader appears.
4. Click Continue Anyway when the Hardware Installation
warning window appears.
5. Click Finish in the Found New Hardware Wizard when
the install is complete.
6. Click Next when the next Found New Hardware Wizard
appears.
7. Click Continue Anyway when the Hardware Installation
warning window appears.
8. Click Finish in the Found New Hardware Wizard when
the install is complete.
Once this screen has disappeared, the USB status LED (CR2 on
AD9957 evaluation board) should be flashing, indicating that the
evaluation board is properly connected. If the LED does not flash,
verify that all power and USB connections are properly connected.
Installing the Simulator
1. Run Setup.exe in the software MLRT73 installer directory
on the CD.
2. Follow the on screen instructions for installing the simulator.
3. The simulator can be accessed from the AD9957 evaluation
board software. See the Simulator Activation section for
further information.
LAUNCHING THE PROGRAM
Follow these steps to load the AD9957 evaluation software:
1. Before starting the software, make sure that the AD9957
evaluation board is powered up, connected to the computer,
and that the USB status LED is flashing.
2. Click the Start button.
3. Select Programs > AD9957 Eval Software folder, >
AD9957 Eval Software to load the software.
A status message appears. See the Status Messages upon
Loading Software section for more information.
Status Messages upon Loading Software
Once the AD9957 evaluation software has been loaded, a green
splash screen appears. The status box within the splash screen
gives the status of the AD9957 evaluation software. Green writing
in the status box indicates that the software has loaded (see
Figure 3). The status box disappears following a successful load.
A splash screen with red writing in the status box indicates that
the software did not load and that an error occurred. Click
within this box to create a cursor. Scrolling up through the
status box with the cursor indicates why the software did not
load correctly.
Most status message errors are resolved by checking jumper
settings, making sure that the evaluation board is powered up
correctly, and inspecting the USB port and cable connections.
In addition, check that the clock input source is connected and
properly configured.
Rev. A | Page 5 of 32
UG-208 Evaluation Board User Guide
07801-003
Figure 3. Successful Load
Rev. A | Page 6 of 32
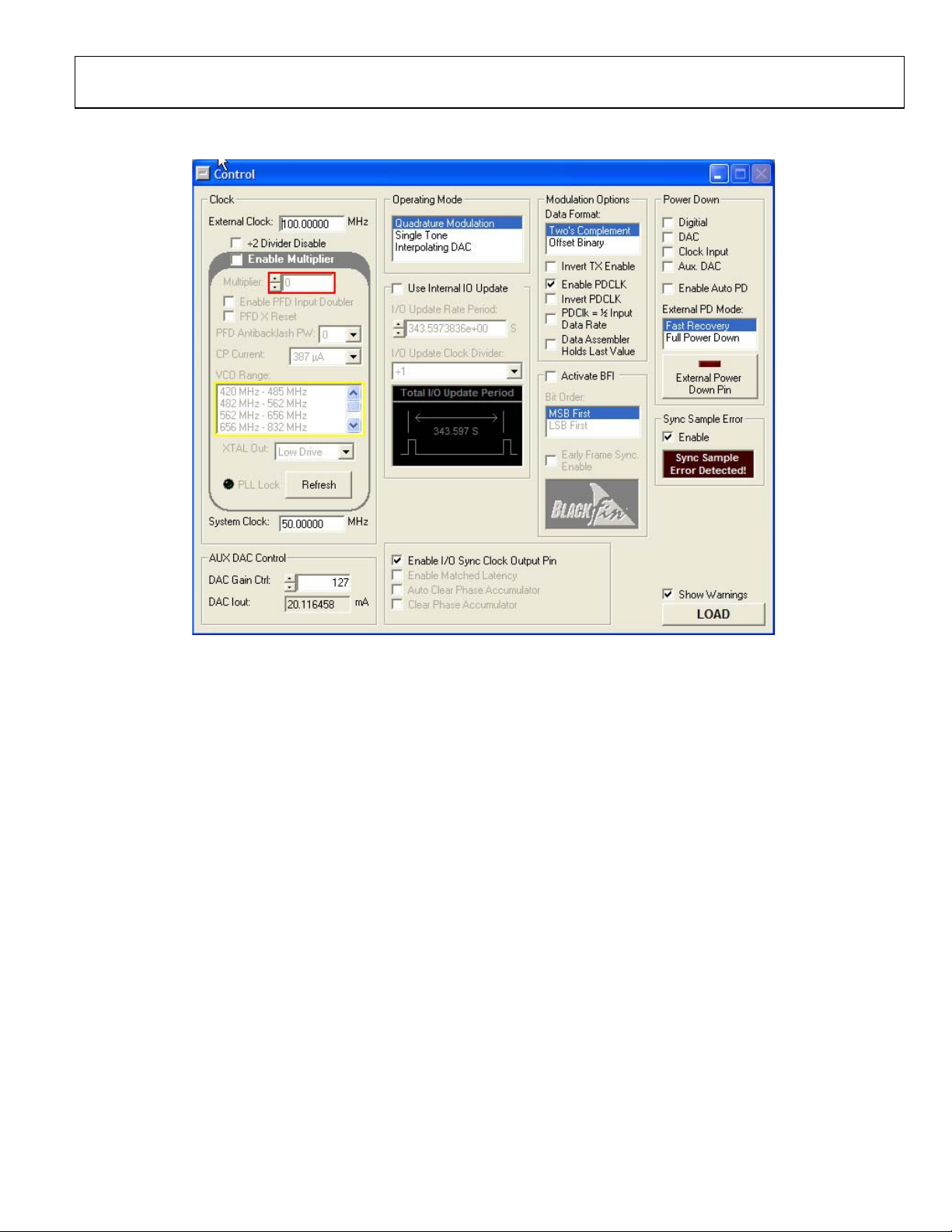
Evaluation Board User Guide UG-208
FEATURE WINDOWS
Figure 4. Chip Level Control Window
CONTROL
The Control window provides control of the clock input, clock
multiplier, DAC gain settings, internal I/O update, and power down
functions of the AD9957. The following sections describe the
chip level control window portions as they appear in Figure 4.
Load
The LOAD button is used to send data to the AD9957 device.
All LOAD buttons found in the evaluation software have the
same functionality.
When new data is detected, LOAD flashes orange, indicating
that you need to click LOAD to send the updates to the serial
I/O buffer where they are stored until an I/O update is issued.
The I/O update sends the contents of the serial I/O buffer to
active registers.
07801-004
I/O updates can be sent manually (Manual I/O Update) or
automatically (Auto I/O Update) (see Figure 3). By default, the
AD9957 evaluation software is set to Auto I/O Update. When
LOAD is clicked, an I/O update signal is automatically sent to
the device. If synchronization across channels is desired, use the
Manual I/O Update button. To send an I/O update, uncheck
the Auto I/O Update box at the top of the screen and press the
I/O Update button.
The Show Warnings check box in Figure 4 can be selected
to show when you have entered data that exceeds the specifications of the AD9957.
Rev. A | Page 7 of 32

UG-208 Evaluation Board User Guide
Clock
The Clock section allows you to configure the reference clock
path in the AD9957.
External Clock inputs the operating frequency of the external
reference clock or crystal. The maximum reference clock frequency of the AD9957 is 1 GHz. A red outline indicates that
the value entered is out of range.
The ÷2 Divider Disable checkbox disables the input divider for
the clock path. The maximum frequency of this divider is 2 GHz.
The Enable Multiplier section selects the PLL multiplication
factor (12× to 127×) which is used to scale the input frequency.
The default setting of this box is disabled, indicating that the
reference clock multiplier circuitry is bypassed and the reference clock/crystal input is piped directly to the DDS core.
CP Current selects the charge pump current output of the
PLL in the reference clock multiplier circuitry. Selecting a
higher current output results in the loop locking faster,
but there is a trade-off. Increasing this current output also
increases phase noise.
The VCO Range menu allows you to select the range of operation
for the VCO on the AD9957. The AD9957 evaluation software
automatically determines which range the AD9957 should
operate in. However, if you to run a given frequency in a band
other than the one selected by the software, a warning box
prompts you to confirm this. Note that using a VCO frequency
outside of its specified range may result in undesired operation,
including nonfunctionality. See the AD9957 data sheet for more
information regarding the different VCO bands.
The XTAL Out drop-down menu selects the output drive
strength of the XTAL reference output. There are three drive
strengths: low, middle, and high.
PLL Lock indicates when the PLL is in a valid lock state. If the
PLL loses lock, the indicator light display lights up or turns green.
System Clock displays the operating frequency the DDS core
(system). The value shown here is derived from the values
entered in the External Clock and Multiplier boxes.
Refer to the AD9957 data sheet for more information regarding
clock modes and operation.
AUX DAC Control
The DAC Gain Ctrl drop-down menu controls the auxiliary
DAC setting to select the full-scale output current of the DAC.
See the AD9957 data sheet for more information about DAC
gain setting.
The DAC Iou t box displays the full-scale output current of the DAC.
This number is based on a DAC_RSET resistor value of 10 kΩ.
Rev. A | Page 8 of 32
Operating Mode
The Operating Mode selector allows you to select between
the three operating modes of the AD9957. Quadrature
Modulation is the default setting. This puts the AD9957 into
quadrature digital up-converter (QDUC) mode. QDUC mode
takes digital baseband data and upconverts it to a specified IF
output. Single tone allows you to get a single tone output from
the AD9957. Single tone mode allows you to select a single
output frequency. Interpolating DAC keeps baseband data at
baseband but can change the sample rate of the data. See the
AD9957 data sheet for more information about the different
modes of operation.
Internal I/O Update
The Use Internal IO Update check box sets the I/O update pin
to an output. This output generates an active high pulse when
the internal I/O update occurs. The rate of the internal I/O
update can be programmed through the serial port. See the
AD9957 data sheet for more information.
Modulation Options
The Data Format selection allows you to select the formatting
method of the input data either from Two’s C om pl em en t or
Offset Binary.
The Invert TX Enable check box allows you to invert the polarity
of the TxENABLE signal.
The Enable PDCLK check box allows you to control the PDCLK
functionality.
The Invert PDCLK box allows you to invert the polarity of the
PDCLK signal.
The PDClk = ½ Input Data Rate box allows you to set the
PDCLK signal to ½ of the input data rate.
The Data Assembler Holds Last Value box allows you to choose
between the data assembler, which outputs all zeros or the last
value received when TxENABLE is low.
Activate BFI
Using the Active BFI control allows you to make the AD9957 data
compatible with an Analog Devices, Inc., Blackfin® DSP.
The Bit Order section allows you to specify the input format of
LSB or MSB first.
The Early Frame Sync Enable box changes the BFI compatibility
to late frame or early frame.

Evaluation Board User Guide UG-208
Power Down
The Digital, DAC, Clock Input, and Aux. DAC power-down
controls allow you to power down each of the specific circuit
blocks individually.
Setting the Enable Auto PD box enables the condition when
the TxENABLE pin is Logic 0, the baseband signal processing
chain is flushed of residual data, and the clocks are automatically
stopped. Clocks restart when the TxENABLE pin is a Logic 1.
The enable auto PD bit does nothing when it is cleared.
The External PD Mode section allows you to control which
power-down mode is used in conjunction with the external
power-down pin. The Fast Recovery mode sets the AD9957
into a power-down state that keeps clocks running and bias
circuits active but does not allow the part to output data. This
mode uses significantly more power than Full Power Down
mode. Full Power Down mode stops clocks and powers down
bias circuits. It takes significantly longer to power back up from
power-down state.
The External Power Down Pin button allows you to control the
external power-down pin without having to alter the evaluation
board. See the AD9957 data sheet for more information about
full power-down conditions.
Sync Sample Error
The Sync Sample Error section allows you to enable/disable the
sync sample error detection using the bit provided. If a sync error is
detected, the external flag is set.
Other Controls
The Enable I/O Sync Clock Output Pin box allows you to
enable/disable the output driver for the I/O sync clock output.
The Enable Matched Latency box allows you to align the
application of the frequency tuning word, phase offset word,
and amplitude scale factor at the same time. If this bit is cleared,
then those words are applied at different times.
The Auto Clear Phase Accumulator box sets the DDS phase
accumulator to a reset state when the I/O_UPDATE pin is set
high or when a profile changes.
The Clear Phase Accumulator box holds the DDS phase
accumulator in a reset state as long as the clear phase accumulator
bit is set.
Rev. A | Page 9 of 32
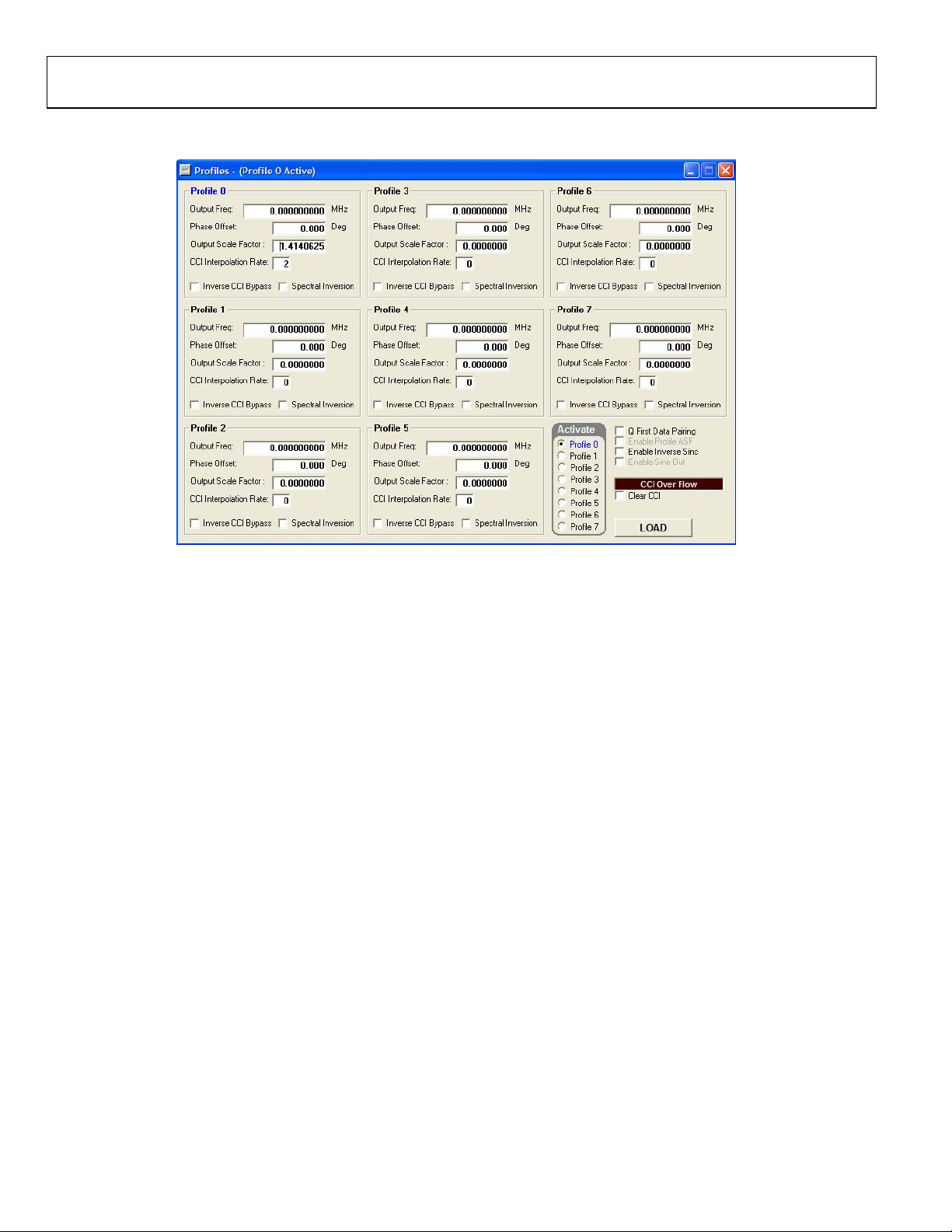
UG-208 Evaluation Board User Guide
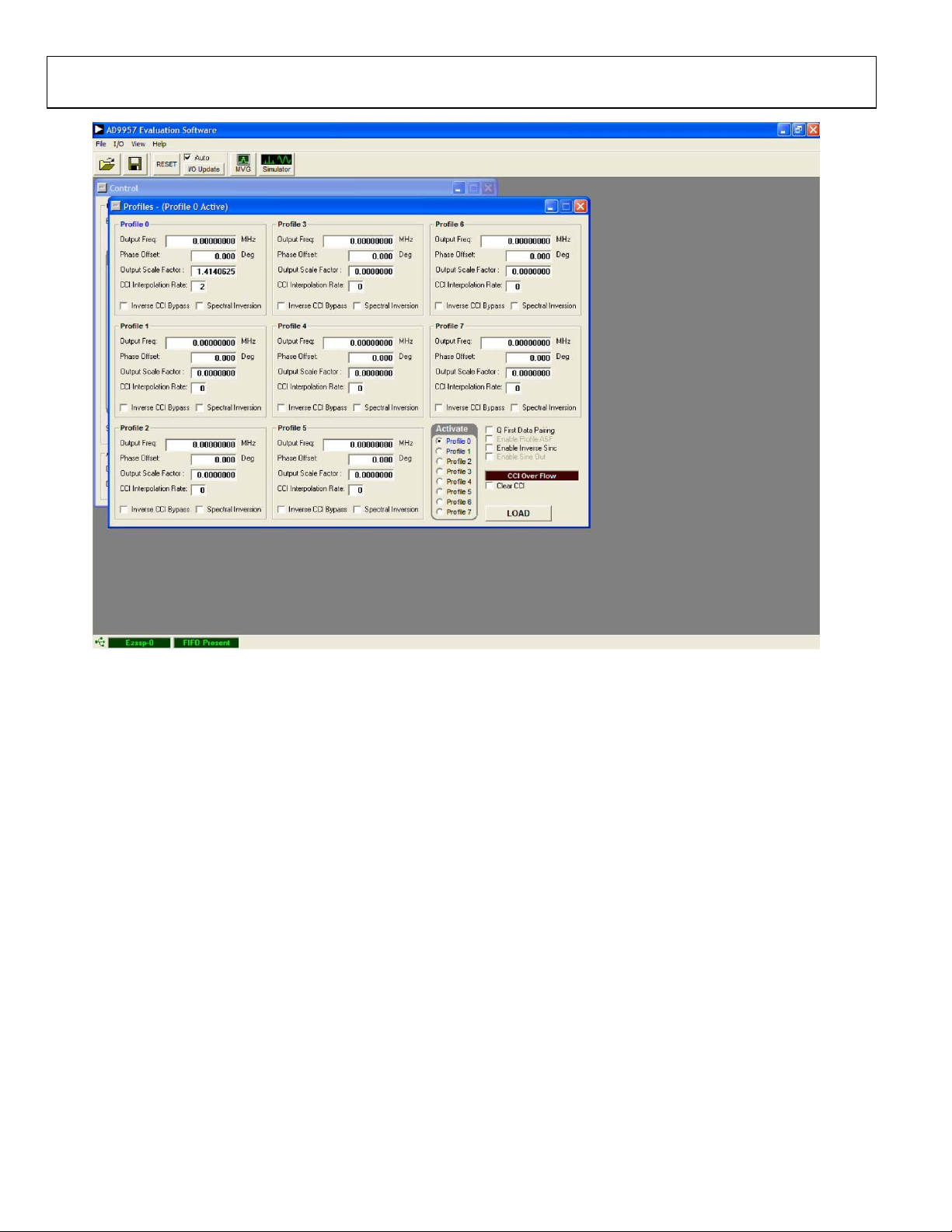
PROFILES
Figure 5. Profiles Control Window for QDUC Modulation Mode
PROFILES WINDOWS
The Profiles window allows you to change the different profile
settings easily. Figure 5 to Figure 7 show the profile control
windows for the three operating modes of the AD9957: QDUC
modulation mode, single-tone mode, and interpolating DAC mode.
QDUC Modulation Mode
Output Freq is used to set the frequency generated by the DDS.
This is the IF carrier to which the unconverted modulation data
is applied.
Phase Offset controls the phase of the DDS output. This can be
changed from 0° to 360° with 16-bit resolution.
Output Scale Factor digitally controls the amplitude of the
carrier from the DDS. This scalar has 8-bits of resolution.
07801-005
Note that this can be used in conjunction with DAC Gai n Ctrl
(see Figure 4) to increase the flexibility of the output amplitude.
CCI Interpolation Rate is the upconversion rate through the
cascaded comb integrator (CCI) filters on the AD9957. This can
vary from 1 to 63 using a 6-bit control word. Note that this is
not the only source of interpolation. See the AD9957 data sheet
for more information on interpolation.
Inverse CCI Bypass allows you to enable or disable the inverse
CCI filter. This filter predistorts the data coming into the CCI
section to compensate for a slight attenuation gradient caused
by the CCI filter.
Spectral Inversion allows you to change the orientation of the
modulated signal with respect to the carrier.
Rev. A | Page 10 of 32

Evaluation Board User Guide UG-208
07801-006
Figure 6. Profile Control Window for Single-Tone Mode
Single-Tone Mode
Output Freq is used to set the frequency generated by the DDS.
In the case of a single tone output, the AD9957 generates a sine/
cosine wave at this output frequency.
Phase Offset controls the phase of the DDS output. This can be
changed from 0° to 360° with 16-bit resolution.
Amplitude SF digitally controls the amplitude of the carrier
from the DDS. This scalar has 14-bits of resolution. Note that
this can be used in conjunction with DAC Gain Ctr l to increase
the flexibility of the output amplitude. The Enable Profile ASF
must be checked to use this control.
Rev. A | Page 11 of 32

UG-208 Evaluation Board User Guide
07801-007
Figure 7. Profile Control Window for Interpolating DAC Mode
Interpolating DAC Mode
Output Freq and Phase Offset are not available in interpolating
DAC mode. There is no DDS output frequency when using this
mode. This mode can resample the baseband data to a different
data rate, but does not perform any upconversion.
Output Scale Factor digitally controls the amplitude of the
carrier from the DDS. This scalar has eight bits of resolution.
Note that this can be used in conjunction with DAC Gai n Ctrl
to increase the flexibility of the output amplitude.
CCI Interpolation Rate is the upconversion rate through the
cascaded comb integrator (CCI) filters on the AD9957. This can
vary from 1 to 63 using a 6-bit control word.
Inverse CCI Bypass allows you to enable or disable the inverse
CCI filter. This filter predistorts the data coming into the CCI
section to compensate for a slight attenuation gradient caused
by the CCI filter.
Data Entry Windows
The Edit output frequency window (see Figure 8) appears by
double-clicking the Output Freq data entry form. The Edit
output frequency window allows you to set individual bits in
the frequency tuning word. These can be entered by using dec,
hex, or binary format. This window also allows you to enter in a
tuning word and see the correct dec, hex, or binary representations for this word. You can scroll through the Frequency form
to view the different tuning words one bit at a time.
Figure 8. Edit Output Frequency Pop-Up Window
The Edit Phase Offset window (see Figure 9) appears by
double-clicking the Phase Offset data entry form. The Edit
Phase Offset window allows you to set individual bits in the
phase offset tuning word. These can be entered in using dec,
hex, or binary format. This window also allows you to enter in a
tuning word and see the correct dec, hex, or binary representations for this word. You can scroll through the Phase Offset
form to view the different tuning words one bit at a time.
Figure 9. Edit Phase Offset Pop-Up Window
07801-009
7801-008
Rev. A | Page 12 of 32

Evaluation Board User Guide UG-208
Edit Output Scale Factor window (see Figure 10) appears by
double-clicking the Output Scale Factor data entry form. The
Edit Output Scale Factor window allows you to set individual
bits in the output scale factor tuning word. These can be entered
in using dec, hex, or binary. This window also allows you to
enter in a tuning word and see the correct dec, hex, or binary
representations for this word. You can scroll the Output Scale
Factor to view the different tuning words one bit at a time.
07801-010
Figure 10. Edit Output Scale Factor Pop-Up Window
Activate
The Activate section in the Profiles window allows you to select
which profile register is active. The active profile register is the
one that supplies the frequency tuning and phase offset words
along with the amplitude control and modulation control (for
QDUC mode) to the DDS core. This section functions the same
way for all modes of the AD9957. This window controls three
external pins, which may also be driven by an external source.
Other Controls and CCI Overflow/Clear
The Q First Data Pairing check box selects between applying
I-data followed by Q-data or Q-data followed by I-data.
The Enable Profile ASF check box selects different amplitude
scale factors by using the different profiles.
The Enable Inverse Sinc check box turns on or off the inverse
sinc filter. This filter compensates for the frequency related
amplitude roll-off caused by the sinc function nature of the
sampling DAC.
The Enable Sine Out check box selects the output as cosine or sine.
The Clear CCI check box clears the CCI filter from an overflow
condition. An overflow condition causes wide band noise at the
output of the device. This condition is usually caused by a CCI
rate change while Tx_ENABLE is high. In addition, the overflow
can be the result of excessive jitter on the external clock, or the
internal PLL is unlocked.
Rev. A | Page 13 of 32

UG-208 Evaluation Board User Guide
VIEW WINDOWS
To access the View Windows, click the View tab at the top of
the screen in Figure 3 and select from the pull-down menu.
OSK Control
To use the OSK function of the AD9957, click the Enable
Output Shift Keying box (see Figure 11). Set the Amplitude
Scale Factor to control the final amplitude of the signal. Check
Use External OSK Pin for manual control of the OSK. You can
use the OSK Pin button to manually control the on/off of the
OSK manually. The OSK Pin button controls a pin that can be
driven externally. Check Enable Auto OSK to use the automatic
OSK function. Set the Amplitude Ramp Rate and the Amplitude
Step Adjust using the boxes provided. The Load ARR @ I/O
Update box allows you to reload the ramp rate timer when an
I/O update is issued or when there is a profile change.
QDUC RAM CONTROL
Click the Enable RAM check box to use the RAM (see Figure 12).
The RAM has two available internal destinations. See the AD9957
data sheet for a complete description of the RAM and its entire
functionality. The QDUC RAM Destination box selects which of
the two destinations the RAM data is loaded into.
Set the beginning address, final address, and address step rate in
the forms provided. Use the Mode Control pull-down window
to select the playback mode for the RAM. Use Load RAM and
Save RAM to load or save files to and from the PC for use in the
RAM. The Set ISFC Pin High and Set ISFC Pin Low buttons
are used to control that external pin. When this pin is high, the
RAM sweeps from the beginning RAM address to the end address.
When it is low, the RAM sweeps from the end address to the
beginning address.
7801-011
Figure 11. OSK Control Window
07801-012
Figure 12. QDUC RAM Control Window
Rev. A | Page 14 of 32

Evaluation Board User Guide UG-208
FIFO CONTROL
The AD9957 evaluation board comes equipped with a FIFO
that allows you to apply baseband modulation data to the
AD9957 for evaluation purposes. This should be only raw I/Q
data. Note that the FIFO has a speed limit of 100 MHz; consider
this when designing modulation data. The FIFO has a refresh
time when the memory wraps around that last 2048 PDCLK
cycles. The FIFO holds Tx_ENABLE during the refresh time.
This affects use with the FIFO in looping the transmission.
In the LOAD FIFO section (see Figure 13), use the three select
buttons, Fill FIFO with Random Data, Load FIFO with
(0-262143), and Load Data from a file:, to select the source of
the data to be loaded into the FIFO. Use the browse button or
the form to enter the location of the file to be used. If using BFI
mode, select the Format Data for BFI Mode check box and be
aware of the LSB First Mode check box under the BFI Mode
Data Format section. Use the LOAD FIFO button to transfer
the data from the PC to the FIFO. A pop-up box alerts you
whether the transfer was successful. Use the Loop Transmission
check box to tell the AD9957 evaluation software to run the
modulation data into the AD9957 continuously. Leaving this
box unchecked only transmits the data for one burst. Use the
Transmit FIFO Data button to initiate the transfer of data to
the AD9957.
MULTICHIP SYNC CONTROL
The Multi-Chip Sync window allows you to set up the sync
function (see Figure 14). This allows you to sync multiple chips
to one master AD9957. Refer to the AD9957 data sheet for a full
discussion on multichip sync functions. The Input Sync Pulse
Delay pull-down menu sets the input delay of the synchronization
receiver in 150 ps steps. The Output Sync Pulse Delay pull-down
menu sets the output delay of the synchronization generator in
150 ps steps. The Sync Window Delay pull-down menu sets the
state that the internal clock generator assumes when it receives a
sync pulse. The Sync Enable check box sets the synchronization
clock receiver to active. The Sync Driver Enable check box sets
the synchronization clock generator to active. The Generate
Sync Pulse control area allows you to select the sync pulse
generation corresponding to the rising or falling SYSCLK edge.
The Sync Sample Error section displays a flag when there is a
sync sample error. Use the Clear Error button to clear a sample
error. Refer to the AD9910 data sheet section for synchronizing
multiple parts.
Figure 13. FIFO Control Window
07801-013
Rev. A | Page 15 of 32
Figure 14. Multi-Chip Sync Window
07801-014

UG-208 Evaluation Board User Guide
GPIO
Configure GPIO Lines
The Input and Output buttons allow you to select whether
an individual pin is configured as an input or an output (see
Figure 15). The Data Pins column lists all 18 of the GPIO pins.
The LOAD and READ buttons allow you to program each pin
or read the value of each pin.
Read/Write Data Lines
The Data Line column shows the 18 pins available. The Data
column allows you to set each pin to logic high or logic low.
Figure 16. Debug Window
DUT Signals (PA)
The ISFC, ExtPwrDwn, Reset DUT, I/O Reset, and CSB check
boxes control the pins to which they correspond. All of these
functions are available elsewhere in the software. Clicking these
boxes means that the pin is in its active state. Note that this does
not mean that the pin is logic high or low, which is determined
by the active state on that pin. See the AD9957 data sheet for
information about external pins. The Flash and USB_Status
check boxes are used to control the two LEDs on the AD9957
evaluation board.
DUT Signals (PE)
The I/OUpdateEn, I/O Update, OSK, P3, P2, and P1 boxes
control their selected pins. Pin P3, Pin P2, and Pin P1 control
the profile register pins. See the AD9957 data sheet for the logic
to control the profiles via the external pins.
DUT Signals (CTL)
The serial clock (SCLK) pin is used to synchronize data to and
from the AD9957 and to run the internal state machines. This
window allows you to toggle the external pin.
07801-016
Figure 15. GPIO Window
DEBUG WINDOW
The Debug window gives you complete direct access to the
register map as well as control of many external pins (see
Figure 16). The Debug window is intended for debugging
issues with the AD9957. It may be used for all programming,
but is not user friendly. Note that the Auto Apply check boxes
indicate that when a box is selected, the action is automatically
taken without needing to click Apply.
Rev. A | Page 16 of 32
07801-015

Evaluation Board User Guide UG-208
DUT Flags (PD)
The CCI Over Flow, PLL Lock, Sync Sample Error, and RAM
Sweep Over flags indicate an active state on each of those external
pins. See the AD9957 data sheet for descriptions of the active
state of each pin.
Serial I/O
The Serial I/O section allows direct access to the register map.
The Reg Addr pull-down menu allows you to select the register
of interest. The bit numbers are shown above each byte in the
register. The maximum size of any given register is eight bytes.
For registers that are smaller, the unavailable bytes are grayed
out. You can enter the register values in either binary or hexadecimal code.
The Serial Port Status box displays the serial operating mode of
the AD9957.
REGISTER MAP (SOFTWARE BUFFER) VALUES WINDOW
The Register Map (Software Buffer) Values window allows
you to read the values in the software buffers (see Figure 17).
These values are not sent to the AD9957 from the software
buffers until and I/O update is issued.
The Choose REGMAP Buff drop-down menu allows you to select
between the current or the new values in the software buffer.
The Format selection allows you to choose values to be displayed
in either binary or hexadecimal format.
The Auto Refresh check box allows the software to update the
values displayed as they are updated in the buffers. This can be
disabled and you can refresh manually by clicking the Refresh
button.
DUT I/O
The DUT I/O window allows you to select the serial I/O port
configuration. Under I/O Port Config, you can select either
2-Wire or 3-Wire mode. In the Data Format mode, you can
select MSB First or LSB First. See the AD9957 data sheet for
more information on these serial port modes. The Reset I/O
Port button allows you to reset the I/O port at any time.
Figure 18. DUT I/O Window
07801-018
07801-017
Figure 17. Register Map (Software Buffer) Values Window
Rev. A | Page 17 of 32

UG-208 Evaluation Board User Guide
MODULATION VECTOR GENERATOR
The modulation vector generator (MVG) software is built into
the AD9957 software. It allows users to create modulation schemes
and save them as files. The modulation data can be loaded into
the AD9957 using the FIFO. This allows you inclusive access for
creating modulation data for use in the QDUC mode of the
AD9957. To access this software, click the MVG button located
in the toolbar at the top of the AD9957 software (see Figure 3). The
modulation vector generator is capable of producing modulation
data for three different modulation schemes: QAM, GMSK\EDGE,
and SKPSK (see Figure 19). In addition to providing the modulation
data, the generator produces a graph of the impulse response
and the frequency response of the user-defined symbol pulse
shaping filter.
QAM
The QAM tab in the Modulation Vector Generator window
allows you to generate QAM data in different conditions. The
Number Of Symbols field allows you to specify the number of
symbols used in the modulation. The button to the right side of
the entry field sets the field to the maximum number of symbols
that can be used with the 65K FIFO. See the FIFO Control
section for more information. The Number of Output Vectors
field displays the total number of samples that the generator
produces (based on the symbol count and upsampling factor).
The Filter Type selection switches between the different filter
types: Raised Cosine and Square Root Raised Cosine. The
Filter Taps field allows you to set the number of digital filter
taps. When setting the number of taps be aware that setting the
taps to an odd or even number may impact the quality of the
demodulated signal depending on the measurement equipment.
The receive filter in the equipment used to demodulate the
signal might be even, odd, or selectable. In any case, the receive
and transmit filters must both be of the same general order
(odd or even). If this is different, it can severely degrade the
error vector magnitude (EVM) that can be measured.
The Filter Tap Resolution field allows you to specify the
resolution (in bits) of the digital filter tap coefficients. An
entry of zero results in floating point coefficients. The Filter
Up-Sampling Factor field sets the amount by which the pulse
shaping filter oversamples the baseband symbols. The Filter
Rolloff Factor (alpha) field is the excess bandwidth parameter
of the pulse shaping filter. See the AN-922 Application Note for
more information on alpha and other modulation information.
The Number of Output Bits field sets the resolution of the final
output data. The AD9957 expects 18-bits of data, so this should
be the value used in most cases. The Attenuation Value field is
used to reduce the full-scale digital amplitude of the final output data.
This is important because in some cases, using the full-scale
amplitude can result in clipping in the half-band filters on the
AD9957. There is no rule for predicting the amount of attenuation
(if any) required for a particular application, so some trial and error
may be necessary. The Filter Graph Pts box sets the number of
plotted points for the graphs produced by the MVG software.
Rev. A | Page 18 of 32
The Output Data Format field sets the format of the final output
data. In all cases, the output file is a standard text file readable
by most text editors. The Interleaved I/Q setting produces a
single output file of signed integers with each integer on a
separate line. The first line is the first I sample, the second line
is the first Q sample, the third line the second I sample, etc. The
AD9957, by default, expects interleaved samples on its parallel data
port, so Interleaved I/Q is the default setting. The I&Q setting
produces separate I and Q data files. The remaining assortment
of I&Q Bits settings are used for generating data for the Blackfin
interface mode of the AD9957. These formats yield a single bit
(0 or 1) per line in the output file. See the AD9957 data sheet
for more information on using Blackfin interface mode.
The Output Filename box allows you to define the name and
location of the output files generated by the MVG. It is important
to note the location of the output data file(s) because both the
FIFO and the simulator tools require you to enter the location
of the data file(s). The default location is the QAMVe ctG en
folder where the AD9957 evaluation board software is installed.
Click the Generate Data button to generate the specified
modulation data and to plot the filter response graphs.
Figure 19. Modulation Vector Generator in QAM Mode
7801-019

Evaluation Board User Guide UG-208
The MVG creates three additional files in the selected directory.
Each file contains the sequence of random symbols generated
by the MVG. The symbols are given in decimal, binary, and
hexadecimal format in the symbol.bin, symbol.dec, and
symbol.hex files, respectively. The binary and hexadecimal
versions of these can contain appended zero bits in the MSB
positions to generate whole nibbles. For example, QPSK data
consists of only two bits, but the symbol.bin file contains whole
nibbles with the two MSBs being 0.
GMSK/EDGE
The MVG can also generate data conforming to the GSM
standards. Refer to the ETSI standard, GSM 05.04, for more
information on GSM standards. Many of the settings on the
GMSK\EDGE tab are the same as the QAM tab (see Figure 20).
The following settings are different.
The Filter Span (Symbols) field sets the symbol length of the
filter response. To conform to the GSM standard, this number
should be 3 for GMSK and 5 for EDGE data. Changing this to
another value results in nonstandard data. The GMSK Normalized
Bandwidth and GMSK Modulation Index parameters are also
set by the GSM standard. The Enable Full Length Output
check box assures valid data through the filter. This truncates
the first samples in and the last samples out of the filter. Using
those samples results in demodulation errors, as that data is
undefined. This parameter depends on the upsampling factor.
To find the number of samples truncated, use the following
equation:
Number of Truncated Samples = Filter Span × Upsampling Factor
SDPSK
The MVG can also generate data according to SDPSK modulation.
Figure 20. Modulation Vector Generator in GMSK/EDGE Mode
07801-020
Rev. A | Page 19 of 32
Figure 21. Modulation Vector Generator in SDPSK Mode
07801-021

UG-208 Evaluation Board User Guide
SIMULATOR
The AD9957 evaluation board software has a simulator built
into it. This simulator extracts the device settings of the AD9957
either from the programming windows of the evaluation board
software or directly from the internal registers of the device.
The simulator uses MATLAB code to model the AD9957 and
produce both a time domain and frequency domain plot of the
simulated AD9957 output signal. See the Simulator Tool section
for more information on the actual workings of the simulator.
The simulator is accessed with the Simulator button on the
toolbar of the AD9957 evaluation board software (see Figure 3).
The Register Map Options section allows you control of where
the simulator settings come from (see Figure 22). The Use the
Current DUT Settings option requires that a AD9957 evaluation
board be connected to the PC. The simulator reads the settings
from the DUT and uses them as the device settings. The Use
Current Software Settings option uses the values that have been
entered into the AD9957 evaluation board software. Set up the
software as if using it to program the DUT even if one is not
present. For example, the system clock frequency and frequency
tuning word should be set as normal. The Auxiliary Control
File section is necessary for running the simulator software.
This file sets up parameters specific to the simulator. The I/Q
Base Band Data File is the file that contains the baseband
modulation data. For example, the modulation vector generator
included with the AD9957 evaluation board software could be
used to generate this data file. It can also come from another
source as long as the file is formatted properly. The previous
sections of this user guide along with the AD9957 data sheet
provide information on data formatting. The Run Simulator
button applies the software settings and the modulation data to
the simulator. The simulator produces two different graphs. The
first graph shows the time domain response of the simulated
output, a virtual oscilloscope. The second graph shows the
frequency domain response of the simulated output, a virtual
spectrum analyzer.
Figure 22. AD9957 Simulator Interface Window
07801-022
Rev. A | Page 20 of 32

Evaluation Board User Guide UG-208
SIMULATOR TOOL
OVERVIEW
The AD9957 evaluation board software includes a MATLABbased simulator tool. The simulator is a virtual model of the
AD9957 that works in unison with the evaluation board software.
The device parameters programmed via the evaluation board GUIs
are passed to the simulator. The simulator uses the programmed
parameters to model a virtual AD9957 in the time domain. The
simulation results are displayed in both the time and frequency
domain in two separate plot windows—the equivalent of a
virtual oscilloscope and spectrum analyzer (see the Virtual
Oscilloscope and Spectrum Analyzer section).
When programmed for QDUC mode (either using the parallel
data port or the dual serial port) or for interpolating DAC mode,
the AD9957 is normally driven with time domain data samples
originating from an external source (a microcontroller or FPGA,
for example). The samples are delivered to either the 18-bit
parallel data port or the dual serial port (BlackFin interface).
For these modes of operation, provide data files that contain the
data streams normally delivered to the device input (see the
User Data File(s) section). The simulator reads these files and
treats them as the time domain input sequence to the device.
The data is processed along the data path of the virtual device
(in the time domain) and the signal at the output of virtual
device is presented in the form of both a time and frequency
domain plot.
One very useful feature of the simulator is that it functions without
the need of a physical AD9957 evaluation board. The simulator
can extract the device programming information directly from
evaluation board GUIs. This allows the simulator to serve as a
virtual development tool during the early stages of a design. The
user can see the results of various baseband modulation schemes
and device settings without the need for a physical prototype.
SIMULATOR ACTIVATION
The simulator is activated by clicking the Simulator button in
the toolbar of the evaluation board main GUI (see Figure 3).
However, first enter the appropriate device parameters the
various evaluation board GUI windows. The device parameters
can come from one of two sources, either directly from the GUI
windows or via an interrogation of the register contents of the
AD9957 device on the evaluation board (assuming an evaluation
board is present). Therefore, when the simulator is activated
the evaluation board software prompts the user for the desired
source of the device parameters.
While the simulator is running, it provides detailed information
of its progress. This information is displayed in a separate console
window with the option of either displaying or hiding the
console window.
At the end of the simulation, two plot windows are displayed.
The first is a time domain plot that serves as a virtual oscilloscope. The second is a frequency domain plot that serves as a
virtual spectrum analyzer.
SIMULATOR DESCRIPTION
The simulator models the digital behavior of the AD9957.
Although it is not a fully bit true device model, it models the
quantization, truncation, and clipping behavior of the digital
signal processing components (such as, the various digital
filters, the digital modulator, the DDS core) to a high level of
precision.
The simulator is not intended to exactly model the spurious or
noise contributions associated with the analog components of
the AD9957. However, in an attempt to simulate the output
spectrum to a reasonably high degree, two significant distortion
contributors are modeled.
The first modeled distortion contributor is the sin(x)/x frequency
domain distortion that results from the sampled nature of the
DAC output signal. This is modeled by imposing a sin(x)/x
distortion envelope on the final DAC output spectrum. An
artifact of this technique, however, is that the sin(x)/x distortion
is imposed on the noise floor. This exhibits itself as a noticeable
droop in the noise floor near the sampling frequency of the DAC.
However, normal device operation restricts the maximum useable
output frequency to be less than ½ the DAC sampling rate (that
is, the Nyquist frequency). With this restriction the artificial
droop imposed on the noise floor is constrained to less than 4 dB.
The second modeled distortion contributor is the harmonic
distortion of the DAC. Again, this is not intended as an exact
model but offers a reasonable approximation of the typical
spectral performance of the device. The ability to model DAC
harmonic distortion allows you to observe the frequency
location of harmonic spurs.
Rev. A | Page 21 of 32

UG-208 Evaluation Board User Guide
Some analog characteristics are not modeled at all. These
include the spurious clock artifacts associated with the DAC,
noise contributions of the REFCLK PLL signal path, and effects
due to variations in temperature, power supply voltage, or the
semiconductor fabrication process. Additionally, some ancillary
digital features of the AD9957 are not modeled either. The
features and functionality that are not modeled by the simulator are
• Profile activation via the external profile pins (Profile0,
Profile1, Profile2)
• Functionality of Profile Register 1 through Profile
Register 7 (however, the simulator does use Profile
Register 0 to extract any profile-specific device parameters)
• Multichip synchronization
• RAM functionality
• OSK functionality (except for manual control of amplitude
via the evaluation board GUI)
DIALOG BOX
EVALUATION BOARD SOFTWARE
SIMULATE
• Functionality of the PDCLK and TxENABLE pins
• Functionality of the GPIO port
• Power-down functionality
• Functionality of the I/O_UPDATE pin
• REFCLK PLL functionality (that is, the simulator does not
model phase noise or jitter associated with the REFCLK
signal path)
• DAC distortion products (the simulator models the DAC
as being ideal)
A functional block diagram of the simulator is shown in Figure 23.
The AD9957 simulator software receives input from a number
of sources. These are the register image file, the auxiliary
control file, and the user data file(s).
AD9957
SIMULATOR
LIBRARY OF
FUNCTIONAL BL OCKS
1) HALF-BAND FILTERS
2) CCI FILTER
3) DDS
4) INVERSE SINC FILTER
5) INVERSE CCI FILTER
6) DAC
7) OSCILLOSCOPE
8) SPECTRUM ANALYZER
9) ETC.
CREATE
REGISTE R MAP
IMAGE FILE
AD9957 SIMULATOR
SINGLE-
TONE
SIMULATOR
FREQUENCY
MAIN
DOMAIN
PLOT
QDUC
SIMULATOR
AUXILIARY
CONTROL
FILE
BLACKFIN
QDUC
SIMULATOR
USER
DATA FILE(S)
INTERPOLATING DAC
SIMULATOR
TIME
DOMAIN
PLOT
07801-023
Figure 23. Functional Block Diagram of the AD9957 Evaluation Board Software and Simulator Tool
Rev. A | Page 22 of 32

Evaluation Board User Guide UG-208
When the Simulator button (see Figure 3) is pressed, the
evaluation board software presents a dialog box that allows
the user to enter (or browse for) the path and file name of the
pertinent file(s). In addition, the user selects whether register
programming information comes directly from the evaluation
board GUI windows or as a result of interrogating the register
contents of the physical device. In either case, the evaluation
board software generates a register image file that contains an
image of the device programming information, which the
simulator uses to determine the appropriate simulation parameters.
The dialog box always asks for the name of the auxiliary control
file and optionally for the file(s) containing the user’s time domain
data (when the AD9957 is programmed for either the QDUC or
interpolating DAC modes).
After finishing the instructions, the evaluation board software
launches the simulator. The simulator receives two parameters
passed to it directly by the evaluation board software:
• The name of the register image file (created by the evaluation
board software)
• The frequency of the system clock (that is, the DAC
sample rate)
The simulator reads the register image file and determines
which of the four available simulation types to execute:
SINGLE-TONE MODE SIMULATION
A block diagram of the simulator with the AD9957 programmed for single-tone operation is shown in Figure 24.
When the simulator is activated, the evaluation board software
prompts the user for the name and location of the auxiliary control
file. The simulator reads the auxiliary control file as well as the
register image file. The register image file is generated by the
evaluation board software and provides the simulator with the
frequency tuning word and the phase offset word for the DDS,
the state of the sine enable bit (to model the appropriate DDS
output), the value of the optional amplitude scale factor, whether
or not the inverse sinc filter is bypassed, and the full scale
current setting for the DAC.
Note that the simulator only uses Profile Register 0 to determine
any profile-specific device programming parameters. Profile
Register 1 to Profile Register 7 are ignored.
SIMULATE
SIMULATION DIAL O G BO X
AUXILIARY CONTROL F I L E NAME
• Single tone
• Quadrature digital up-converter (QDUC) using the
parallel data port
• QDUC using the Blackfin interface (dual serial port)
• Interpolating DAC
In addition to the simulation type, the simulator also extracts
specific device programming information from the register
image file (such as DDS output frequency, DDS phase offset,
QDUC interpolation factor, input data format).
The simulator also reads the contents of the auxiliary control
file. This file defines additional simulation parameters that are
not part of the evaluation board software. For example, control
parameters for the virtual oscilloscope and spectrum analyzer
are stored in the auxiliary control file. This file is intended to
be edited by the user (using a text editor) so that the auxiliary
parameters can be customized. The auxiliary control file is
covered in detail in the Auxiliary Control File section.
REGISTER
MAP FILE
SINGLE-TONE
SIMULATOR
AUXILIARY
CONTROL
FILE
FREQUENCY
DOMAIN
PLOT
Figure 24. Simulation Block Diagram for Single-Tone Mode
TIME
DOMAIN
PLOT
07801-024
Rev. A | Page 23 of 32

UG-208 Evaluation Board User Guide
QDUC PARALLEL DATA MODE SIMULATION
A block diagram of the simulator with the AD9957 programmed
for QDUC operation using the parallel data port is shown in
Figure 25.
When the simulator is activated, the evaluation board software
prompts the user for the name and location of the auxiliary
control file and the time domain data file of the user. The time
domain data file contains the baseband I/Q samples that would
otherwise be delivered to the 18-bit parallel data port of the
AD9957 (see the User Data File(s) section for details).
The simulator reads the auxiliary control file as well as the
register image file. The register image file is generated by the
evaluation board software and provides the simulator with all
the device programming information required to simulate QDUC
operation with the parallel data port. The simulator also reads
the time domain data file, which serves as the baseband input
signal to the device.
Note that the simulator only uses Profile Register 0 to determine any profile specific device programming parameters.
Profile Register 1 to Profile Register 7 are ignored.
SIMULATE
SIMULATI ON DIALOG BOX
AUXILIARY CONTRO L FILE NAME
I/Q DATA FILE NAME
REGISTER
MAP FILE
AUXILIARY
CONTROL
FILE
FREQUENCY
DOMAIN
PLOT
Figure 25. Simulation Block Diagram for QDUC Mode With the
QDUC
SIMULATOR
TIME
DOMAIN
PLOT
18-Bit Parallel Data Port
I/Q DATA FILE
07801-025
QDUC BLACKFIN (SERIAL DATA) MODE SIMULATION
A block diagram of the simulator with the AD9957 programmed
for QDUC operation using the dual serial port (Blackfin interface)
is shown in Figure 26.
When the simulator is activated, the evaluation board software
prompts the user for the name and location of the auxiliary control
file and the time domain data files of the user. The time domain
data files contain the baseband I and Q bit streams that would
otherwise be delivered to the dual serial port of the AD9957
(see the User Data File(s) section for details).
The simulator reads the auxiliary control file as well as the register
image file. The register image file is generated by the evaluation
board software and provides the simulator with all the device
programming information required to simulate QDUC operation
with the Blackfin interface. The simulator also reads the time
domain data files, which serve as the baseband input signal to
the device.
Note that the simulator only uses Profile Register 0 to determine any profile specific device programming parameters.
Profile Register 1 to Profile Register 7 are ignored.
SIMULATE
SIMULATI ON DIALOG BOX
AUXILIARY CONTRO L FILE NAME
I BITSTREAM FILE NAME
Q BITSTREAM FILE NAME
REGISTER
MAP FILE
AUXILIARY
CONTROL
FILE
FREQUENCY
DOMAIN
PLOT
BLACKFIN
QDUC
SIMULATOR
DOMAIN
Figure 26. Simulation Block Diagram for QDUC Mode with the
Dual Serial Port
TIME
PLOT
I BITSTREAM
FILE
Q BITSTREAM
FILE
07801-026
Rev. A | Page 24 of 32

Evaluation Board User Guide UG-208
INTERPOLATING DAC MODE SIMULATION
A block diagram of the simulator with the AD9957 programmed
for interpolating DAC operation is shown in Figure 27.
When the simulator is activated, the evaluation board software
prompts the user for the name and location of the auxiliary
control file and the time domain data file of the user. This data
file contains the time domain data samples that would otherwise be
delivered to the 18-bit parallel data port of the AD9957 (see the
User Data File(s) section for details).
The simulator reads the auxiliary control file as well as the
register image file. The register image file is generated by the
evaluation board software and provides the simulator with all
the device programming information required to simulate the
interpolating DAC mode. The simulator also reads the time
domain data file, which serves as the input signal to the device.
Note that the simulator only uses Profile Register 0 to determine
any profile specific device programming parameters. Profile
Register 1 to Profile Register 7 are ignored.
SIMULATE
SIMULATION DIALOG BOX
AUXILIARY CONTROL FILE NAME
Tx DAC DATA FI LE NAME
REGISTER
MAP FILE
AUXILIARY
CONTROL
FILE
Figure 27. Simulation Block Diagram for Interpolating DAC Mode
INTERPOLATING
FREQUENCY
DOMAIN
PLOT
DAC
SIMULATOR
TIME
DOMAIN
PLOT
Tx DAC
DATA FILE
07801-027
VIRTUAL OSCILLOSCOPE AND SPECTRUM ANALYZER
The virtual oscilloscope and spectrum analyzer are the time
domain and frequency domain plots, respectively, generated by
the simulator. They represent the signal that would appear at
one of the output pins of the AD9957 DAC, including any
optional scaling specified in the auxiliary control file.
Both plots are MATLAB-based plot windows. Each can be
modified via the controls on the toolbar of the plot window. For
example, the trace can be magnified/compressed by zooming
in/out or individual tags can be placed directly in the plot
window for use as data point markers.
The spectrum analyzer plot is the result of an FFT computation
performed by the simulator. Often, it is desirable to apply a
windowing function to the data before computing the FFT. The
auxiliary control file provides the user with the option to select
from a variety of common FFT windowing functions.
Note that the default auxiliary control file supplied with the
simulator software uses a 4-term Blackman Harris window.
The axis limits for both plots are specified in the auxiliary
control file (see the Auxiliary Control File section for details).
The user can edit the auxiliary control file to customize the
horizontal and vertical limits as desired.
Note that the default auxiliary control file supplied with the
simulator software has the minimum and maximum horizontal
and vertical axis limits specified as zero. This causes the simulator to automatically adjust the axis limits according to the
bounds of the data.
USER DATA FILE(S)
When simulating the QDUC or interpolating DAC modes you
must provide the simulator with a data file (or a pair of data files
for QDUC operation using the Blackfin interface). The user
data file contains the time domain samples that would normally
be delivered to the 18-bit parallel data port or the dual serial
port (Blackfin interface) of the AD9957 using external hardware
(a microcontroller or FPGA, for example).
A user data file is a simple text file (for example, a file created
with Notepad, the basic text editor that is supplied with the
Windows® operating system). Each line in the text file contains
an integer that represents an input sample to the AD9957. Each
integer must be in the range of −131072 to +131071 (inclusive)
when the parallel data port is the intended input or either 0 or 1
when the dual serial port (that is, the Blackfin interface) is the
intended input.
Rev. A | Page 25 of 32

UG-208 Evaluation Board User Guide
When simulating QDUC operation with the 18-bit parallel data
port, the data file must contain an even number of samples. The
reason is that the simulator expects the data to represent alternating I/Q sample pairs, the same way that data is delivered to
the 18-bit parallel port in QDUC mode. The first line in the file
contains the first I-sample, the second line the first Q-sample,
the third line the second I-sample, the fourth line the second
Q-sample, etc.
When simulating the interpolating DAC mode an arbitrary
number of samples can be used. That is, the even number
of samples restriction associated with the QDUC mode does
not apply.
When simulating QDUC operation with the Blackfin interface
two data files are required. One contains the I bit stream and the
other the Q bit stream. Each data file must contain a number of
samples that is divisible by 16. The reason is that the simulator
expects the data files to represent the serial bit streams that
would normally be delivered to the dual serial port. That is,
each bit stream must be partitioned into 16-bit frames with each
frame defining a 16-bit signed integer. In accordance with the
functionality of the AD9957, the 16-bit frames can be formatted
as containing either twos-complement or offset binary numbers
and can be presented in either LSB-first or MSB-first order. Of
course, the device programming via the AD9957 evaluation board
software must match the data file format; otherwise the
simulator does not properly translate the data file contents.
AUXILIARY CONTROL FILE
The auxiliary control file contains 23 parameters that the user can
alter to customize a simulation run. It is a simple text file in
which instructions are organized as pairs of consecutive lines.
The first line in a pair contains a keyword that identifies a
particular parameter and the next line contains the value associated
with the keyword. The simulator reads the auxiliary control file
one line at a time. When it encounters a keyword it uses the next
line as the value for the parameter associated with the keyword.
Note that the simulator searches for keywords as an exact match
so they are case sensitive. The keywords must also be left justified
(that is, the first character of the keyword must not be preceded
by any other character).
The auxiliary file can also contain comment lines. These are
either blank lines or lines that begin with a percent (%) symbol.
Comment lines are ignored by the simulator.
Note that a remark line must not appear between a keyword
and its associated value.
The parameter value associated with a keyword is either a numeric
quantity or a character string (depending on the particular
parameter that is associated with the keyword). Numeric parameter
values may be entered in any of the numeric formats supported
by MATLAB. For example, 2400 may be entered as 2400, 2.4E3,
2.4e3, 2.4D3, or 2.4d3. Character string parameter values must
begin and end with a single-quote character (‘).
Rev. A | Page 26 of 32

Evaluation Board User Guide UG-208
KEYWORDS
A comprehensive keyword list is listed in this section. It
includes an explanation of the function of the keyword
parameter and any restrictions on its parameter value.
DEBUG
• Enables or disables the debug mode of the simulator.
• Parameter value must be numeric.
• Zero disables the debug mode of the simulator; any
nonzero value enables it.
• In debug mode, the simulator prints additional detailed
information to the console window during the simulation
process. It also generates time and frequency domain plots
for each significant node along the signal path.
SHOWCLIP
• Controls the display of clipping events.
• Parameter value must be numeric.
• Some of the signal processing blocks in the AD9957 signal
path (the half-band filters are one example) apply clipping
to samples that would otherwise cause a numeric overflow
or underflow. When the simulator detects that clipping has
occurred at a particular node it displays information regarding
each clipped sample. The showclip value tells the simulator
the maximum number of clipped samples for which to print
detailed information. For example, if the showclip is 10,
then every functional block that clips during simulation is
limited to displaying no more that 10 clipped samples.
SAMPLES
• Defines the number of samples that the simulator generates
for single-tone mode.
• Parameter value must be numeric and must be a positive
integer.
DDSCORE
• Defines how the simulator treats the angle-to-amplitude
conversion of the DDS core.
• Parameter must be numeric.
• A zero value tells the simulator to calculate an ideal, 14-bit
quantized lookup table to emulate the DDS core. A nonzero
value tells the simulator to load the DDS core values that
were extracted from the digital code used to produce the
actual silicon device.
RSET
• The value of the DAC RSET resistor (in ohms) installed on
the evaluation board (the default value is 10,000).
• Parameter value must be numeric and greater than zero.
• The R
the DAC.
resistor establishes the full-scale output current of
SET
DACXFR
• Defines how the simulator models the harmonic distortion
of the DAC.
• Parameter must be numeric.
• A zero value tells the simulator to model the DAC with a
perfectly linear transfer function (that is, no harmonic
distortion). A nonzero value tells the simulator to use a
distorted transfer function that produces typical harmonic
products.
FFTWINDOWTYPE
• Specifies the windowing function applied to the data prior
to computing an FFT.
• Parameter must be a character string.
• The parameter value is a four-character mnemonic that
identifies a particular window function as shown in
Tabl e 4.
Table 4.
Mnemonic Description
rect
bart Bartlett (triangular) window
hamm Hamming window
hann Hann window
blk3 3-term Blackman-Harris window
blk4 4-term Blackman-Harris window
rose Rosenfeld window
Rectangular window (that is, no window is applied
to the data)
Note that sometimes a shorter simulation time can be realized
with a value of zero for this parameter because it usually takes
less time to compute a lookup table than to load the relatively
large DDS core files.
Rev. A | Page 27 of 32

UG-208 Evaluation Board User Guide
VIRTUAL OSCILLOPE AND SPECTRUM ANALYZER INSTRUMENTS KEYWORDS
The following ten keywords pertain to the virtual oscilloscope
and spectrum analyzer instruments. The first two parameters
specify the virtual input impedance of the instrument. The next
eight parameters specify the axis limits of the instruments.
Note that when the minimum and maximum limits for a particular
instrument axis are both zero, the simulator automatically selects
the limits for that axis to accommodate the range of the data.
ZSCOPE
• Input impedance (ohms) of the virtual oscilloscope
instrument.
• Parameter value must be numeric and nonnegative.
ZSA
• Input impedance (ohms) of the virtual spectrum analyzer
instrument.
• Parameter value must be numeric and nonnegative.
minH_SCOPE
• Lower limit of the oscilloscope horizontal (time) axis.
• Parameter value must be numeric.
maxH_SCOPE
• Upper limit of the oscilloscope horizontal (time) axis.
• Parameter value must be numeric.
minV_SCOPE
• Lower limit of the oscilloscope vertical axis.
• Parameter value must be numeric.
maxV_SCOPE
• Upper limit of the oscilloscope vertical axis.
• Parameter value must be numeric.
minH_SA
• Lower limit of the spectrum analyzer horizontal
(frequency) axis.
• Parameter value must be numeric.
maxH_SA
• Upper limit of the spectrum analyzer horizontal
(frequency) axis.
• Parameter value must be numeric.
minV_SA
• Lower limit of the spectrum analyzer vertical axis.
• Parameter value must be numeric.
maxV_SA
• Upper limit of the spectrum analyzer vertical axis.
• Parameter value must be numeric.
Rev. A | Page 28 of 32

Evaluation Board User Guide UG-208
DAC OUTPUT SIGNAL KEYWORDS
The remaining six keywords specify the scaling of the DAC
output signal. These parameters are useful for including external
DAC termination circuitry as part of the simulation. These
parameters, however, only allow scaling of the output amplitude.
Frequency dependent behavior associated with the components
of the external DAC termination circuitry cannot be modeled.
The three keywords with the SCOPE suffix control the scaling
of the DAC output signal for the virtual oscilloscope, while the
three keywords with the SA suffix are for the spectrum analyzer.
DAC_LOAD_SCOPE
• The single-ended equivalent load (ohms) at the DAC
output, which includes the combined loading effects of
the external circuitry as well as the input impedance of the
virtual oscilloscope.
• Parameter value must be numeric and nonnegative.
DAC_LOAD_SCALE_SCOPE
• The gain of an ideal amplifier used to model gain or loss
(active or passive) in the external DAC termination circuitry
in the signal path leading to the virtual oscilloscope.
• Parameter value must be numeric and nonnegative. The
units are assumed to be linear (not decibels).
DAC_LOAD_THEV_SCOPE
• The Thevenin equivalent load (ohms) of the DAC termination
circuitry as seen from the input of the virtual oscilloscope
looking toward the DAC.
• Parameter value must be numeric and nonnegative.
DAC_LOAD_SA
• The single-ended equivalent load (ohms) at the DAC output,
which includes the combined loading effects of the external
circuitry as well as the input impedance of the virtual
spectrum analyzer.
• Parameter value must be numeric and nonnegative.
DAC_LOAD_SCALE_SA
• The gain of an ideal amplifier used to model gain or loss
(active or passive) in the external DAC termination circuitry
in the signal path leading to the virtual spectrum analyzer.
• Parameter value must be numeric and nonnegative. The
units are assumed to be linear (not decibels).
DAC_LOAD_THEV_SA
• The Thevenin equivalent load (ohms) of the DAC termination
circuitry as seen from the input of the virtual spectrum
analyzer looking toward the DAC.
• Parameter value must be numeric and nonnegative.
Rev. A | Page 29 of 32

UG-208 Evaluation Board User Guide
AD9957 SIMULATOR
SCALING COMPONENTS FOR
THE VIRTUAL O S CILLOSCOPE
SIGNAL PA TH.
AD9957
DAC
DAC_LOAD_SCALE_SCOPE
VIRTUAL
OSCILLOSCOPE
SCALING COMPONENTS FOR
THE VIRTUAL SP ECTRUM
ANALYZER SIGNAL PATH.
AD9957
DAC
Figure 28. Scaling Component Detail
Although the AD9957 has two DAC output pins (normal and
complementary), the simulator models the output as single-ended.
That is, the simulator treats the DAC as though only one of the
two outputs is used as a signal source. This knowledge is necessary
to properly calculate the parameter values for the output scaling
keywords. This is especially true when using the simulator to
accurately model an external DAC termination circuit that uses
both output pins. Figure 28 shows a diagram of the scaling
components in the context of the simulator’s treatment of the
DAC output and the virtual instruments.
Figure 29 shows the required scaling component values for the
case in which the DAC drives a center-tapped transformer with
a 1:1 turns ratio. It includes a schematic of the external DAC
termination circuitry and the resulting model of the scaling
components. The scaling component values assume that the
input impedance of the virtual instruments is 50 .
DAC_LOAD_THEV_SCOPE
DAC_LOAD_SCOPE
DAC_LOAD_SCALE_S A
DAC_LOAD_THEV_S A
DAC_LOAD_SA
AD9957
AD9957
Figure 29. Example Schematic of the External DAC Termination Circuitry
DAC
DAC
IOUT
IOUT
ZSCOPE
VIRTUAL
SPECTRUM
ANALYZER
ZSA
25Ω25Ω
1:1
DAC_LOAD_SCALE
8
DAC_LOAD_THEV
6.25Ω
DAC_LOAD
50Ω
7801-028
MEASUREMENT
INSTRUMENT
50Ω50Ω
VIRTUAL
INSTRUMENT
07801-029
Rev. A | Page 30 of 32

Evaluation Board User Guide UG-208
See the AN-912 Application Note regarding the use of a centertapped transformer with a balanced current-output DAC for
more information.
RR
L
ZZ
COMPNORM
RNZ22=
(2)
OS
vv
==
COMPNORM
O
== (1)
L
⎛
2
I
⎜
⎜
⎝
+
MAX
2
42 NRR
O
⎛
⎞
⎜
⎟
⎟
⎜
+
L
⎠
⎝
⎞
RR
L
O
⎟
(3)
2
⎟
28
NRR
O
⎠
Equation 1 to Equation 4 are related to the scaling component
values as follows:
Z
provides the value for the DAC_LOAD_SCOPE and
NORM
DAC_LOAD_SA keywords.
The formula, 2(vS/v
NORM
), provides the value for the
DAC_LOAD_SCALE_SCOPE and DAC_LOAD_SCALE_SA
keywords.
Z
provides the value for the DAC_LOAD_THEV_SCOPE and
S
DAC_LOAD_THEV_SA keywords.
⎛
⎛
⎜
v
=
S
⎜
⎝
⎞
2
I
MAX
⎜
⎟
⎟
⎜
+
L
⎠
⎝
⎞
RNR
L
O
⎟
(4)
2
⎟
22
NRR
O
⎠
Rev. A | Page 31 of 32

UG-208 Evaluation Board User Guide
NOTES
ESD Caution
ESD (electrostatic discharge) sensitive device. Charged devices and circuit boards can discharge without detection. Although this product features patented or proprietary protection
circuitry, damage may occur on devices subjected to high energy ESD. Therefore, proper ESD precautions should be taken to avoid performance degradation or loss of functionality.
Legal Terms and Conditions
By using the evaluation board discussed herein (together with any tools, components documentation or support materials, the “Evaluation Board”), you are agreeing to be bound by the terms and conditions
set forth below (“Agreement”) unless you have purchased the Evaluation Board, in which case the Analog Devices Standard Terms and Conditions of Sale shall govern. Do not use the Evaluation Board until you
have read and agreed to the Agreement. Your use of the Evaluation Board shall signify your acceptance of the Agreement. This Agreement is made by and between you (“Customer”) and Analog Devices, Inc.
(“ADI”), with its principal place of business at One Technology Way, Norwood, MA 02062, USA. Subject to the terms and conditions of the Agreement, ADI hereby grants to Customer a free, limited, personal,
temporary, non-exclusive, non-sublicensable, non-transferable license to use the Evaluation Board FOR EVALUATION PURPOSES ONLY. Customer understands and agrees that the Evaluation Board is provided
for the sole and exclusive purpose referenced above, and agrees not to use the Evaluation Board for any other purpose. Furthermore, the license granted is expressly made subject to the following additional
limitations: Customer shall not (i) rent, lease, display, sell, transfer, assign, sublicense, or distribute the Evaluation Board; and (ii) permit any Third Party to access the Evaluation Board. As used herein, the term
“Third Party” includes any entity other than ADI, Customer, their employees, affiliates and in-house consultants. The Evaluation Board is NOT sold to Customer; all rights not expressly granted herein, including
ownership of the Evaluation Board, are reserved by ADI. CONFIDENTIALITY. This Agreement and the Evaluation Board shall all be considered the confidential and proprietary information of ADI. Customer may
not disclose or transfer any portion of the Evaluation Board to any other party for any reason. Upon discontinuation of use of the Evaluation Board or termination of this Agreement, Customer agrees to
promptly return the Evaluation Board to ADI. ADDITIONAL RESTRICTIONS. Customer may not disassemble, decompile or reverse engineer chips on the Evaluation Board. Customer shall inform ADI of any
occurred damages or any modifications or alterations it makes to the Evaluation Board, including but not limited to soldering or any other activity that affects the material content of the Evaluation Board.
Modifications to the Evaluation Board must comply with applicable law, including but not limited to the RoHS Directive. TERMINATION. ADI may terminate this Agreement at any time upon giving written notice
to Customer. Customer agrees to return to ADI the Evaluation Board at that time. LIMITATION OF LIABILITY. THE EVALUATION BOARD PROVIDED HEREUNDER IS PROVIDED “AS IS” AND ADI MAKES NO
WARRANTIES OR REPRESENTATIONS OF ANY KIND WITH RESPECT TO IT. ADI SPECIFICALLY DISCLAIMS ANY REPRESENTATIONS, ENDORSEMENTS, GUARANTEES, OR WARRANTIES, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED, RELATED
TO THE EVALUATION BOARD INCLUDING, BUT NOT LIMITED TO, THE IMPLIED WARRANTY OF MERCHANTABILITY, TITLE, FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE OR NONINFRINGEMENT OF INTELLECTUAL
PROPERTY RIGHTS. IN NO EVENT WILL ADI AND ITS LICENSORS BE LIABLE FOR ANY INCIDENTAL, SPECIAL, INDIRECT, OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES RESULTING FROM CUSTOMER’S POSSESSION OR USE OF
THE EVALUATION BOARD, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO LOST PROFITS, DELAY COSTS, LABOR COSTS OR LOSS OF GOODWILL. ADI’S TOTAL LIABILITY FROM ANY AND ALL CAUSES SHALL BE LIMITED TO THE
AMOUNT OF ONE HUNDRED US DOLLARS ($100.00). EXPORT. Customer agrees that it will not directly or indirectly export the Evaluation Board to another country, and that it will comply with all applicable
United States federal laws and regulations relating to exports. GOVERNING LAW. This Agreement shall be governed by and construed in accordance with the substantive laws of the Commonwealth of
Massachusetts (excluding conflict of law rules). Any legal action regarding this Agreement will be heard in the state or federal courts having jurisdiction in Suffolk County, Massachusetts, and Customer hereby
submits to the pers onal jurisdiction and venu e of such courts. The United Nations Conventi on on Contracts for the Internation al Sale of Goods shall not apply to this Agreement and is expressly disclaimed.
©2009–2010 Analog Devices, Inc. All rights reserved. Trademarks and
registered trademarks are the property of their respective owners.
UG07801-0-11/10(A)
Rev. A | Page 32 of 32
 Loading...
Loading...