Analog Devices AD7722 b Datasheet
16-Bit, 195 kSPS
CMOS, - ADC
AD7722
FEATURES
16-Bit - ADC
64 Oversampling Ratio
Up to 220 kSPS Output Word Rate
Low-Pass, Linear Phase Digital Filter
Inherently Monotonic
On-Chip 2.5 V Voltage Reference
Single-Supply 5 V
High Speed Parallel or Serial Interface
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
The AD7722 is a complete low power, 16-bit, Σ-∆ ADC. The
part operates from a 5 V supply and accepts a differential input
voltage range of 0 V to +2.5 V or ±1.25 V centered around a
common-mode bias. The AD7722 provides 16-bit performance
for input bandwidths up to 90.625 kHz. The part provides data
at an output word rate of 195.3 kHz.
The analog input is continuously sampled by an analog modulator, eliminating the need for external sample-and-hold circuitry.
The modulator output is processed by two finite impulse response
(FIR) digital filters in series. The on-chip filtering reduces the
external antialias requirements to first order, in most cases. The
group delay for the filter is 215.5 µs, while the settling time for
a step input is 431 µs. The sample rate, filter corner frequency,
and output word rate are set by an external clock that is
nominally 12.5 MHz.
Use of a single bit DAC in the modulator guarantees excellent
linearity and dc accuracy. Endpoint accuracy is ensured on-chip
by calibration. This calibration procedure minimizes the zeroscale and full-scale errors.
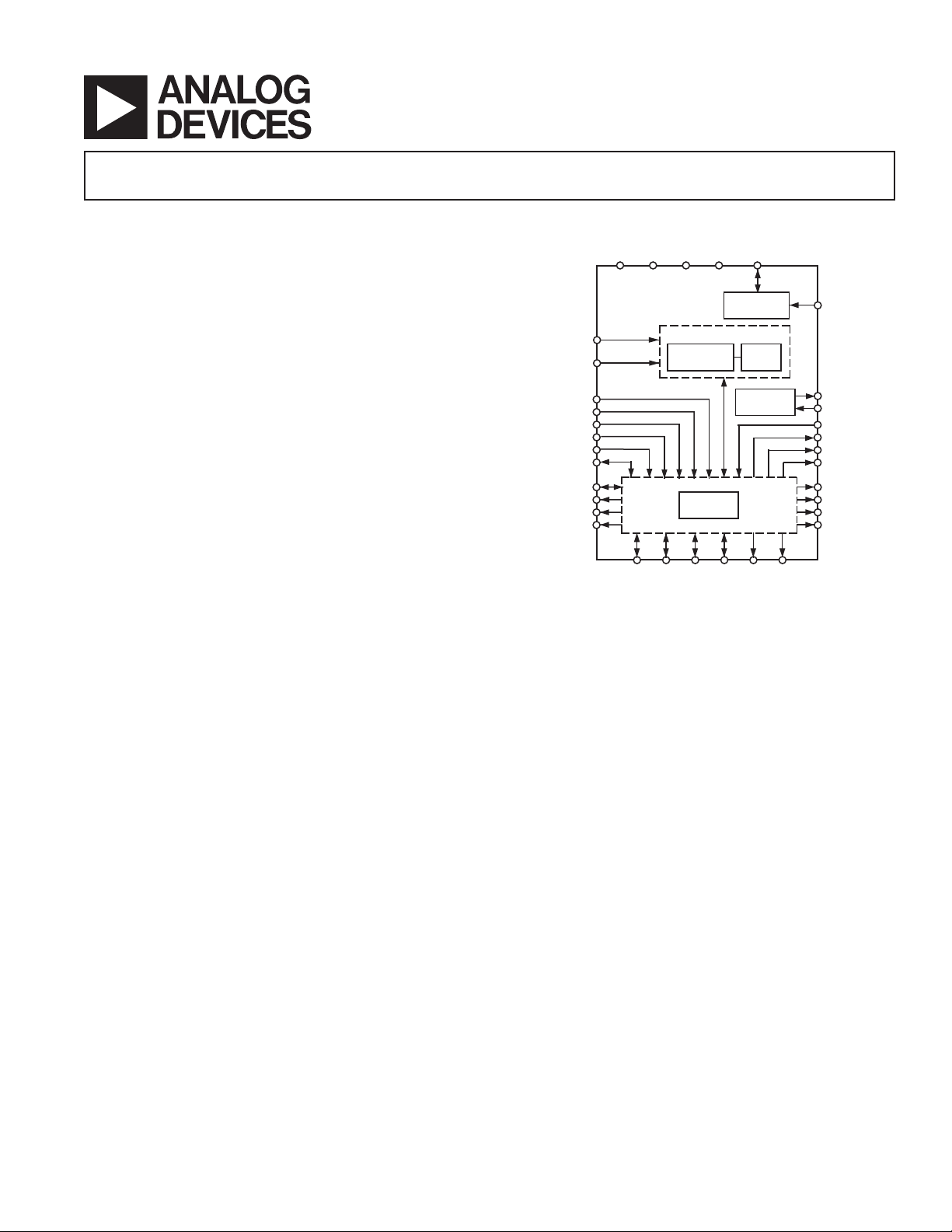
FUNCTIONAL BLOCK DIAGRAM
AV
REF1AGNDDGND
DD
2.5V
REFERENCE
16-BIT A/D CONVERTER
-
MODULATOR
CONTROL
LOGIC
DB5/
SFMT
DB6/
FSI
FIR
FILTER
CLOCK
CIRCUITRY
DB7/
SCO
DB8/
SDO
REF2
XTAL
CLKIN
UNI
DB15
DB14
DB13
DB12
DB11
DB10
DB9/FSO
V
IN
V
IN
P/S
CAL
RESET
SYNC
CS
DVAL/RD
CFMT/DRDY
DB0
DB1
DB2
DV
DD
AD7722
(+)
(–)
DB3/
DB4/
TSI
DOE
Conversion data is provided at the output register through a flexible serial port or a parallel port. This offers 3-wire, high speed
interfacing to digital signal processors. The serial interface operates
in an internal clocking (master) mode, whereby an internal serial
data clock and framing pulse are device outputs. Additionally,
two AD7722s can be configured with the serial data outputs
connected together. Each converter alternately transmits its conversion data on a shared serial data line.
The part provides an accurate on-chip 2.5 V reference. A
reference input/output function is provided to allow either the
internal reference or an external system reference to be used as
the reference source for the part.
The AD7722 is available in a 44-lead MQFP package and is
specified over the industrial temperature range of –40°C to +85°C.
REV. B
Information furnished by Analog Devices is believed to be accurate and
reliable. However, no responsibility is assumed by Analog Devices for its
use, nor for any infringements of patents or other rights of third parties that
may result from its use. No license is granted by implication or otherwise
under any patent or patent rights of Analog Devices. Trademarks and
registered trademarks are the property of their respective owners.
One Technology Way, P.O. Box 9106, Norwood, MA 02062-9106, U.S.A.
Tel: 781/329-4700 www.analog.com
Fax: 781/326-8703 © 2003 Analog Devices, Inc. All rights reserved.
AD7722–SPECIFICATIONS
UNI = Logic Low or High; f
= 12.5 MHz; fS = 195.3 kSPS; REF2 = 2.5 V; TA = T
CLKIN
1
(AVDD = AV
= 5 V 5%; DVDD = 5 V 5%; AGND = AGND1 = DGND = 0 V;
DD1
to T
MIN
, unless otherwise noted.)
MAX
Parameter Test Conditions/Comments Min Typ Max Unit
A Version
INH
2
VCM = 2.5 V, VIN(+) = VIN(–) =1.25 V p-p,
or V
(–) = 1.25 V, VIN(+) = 0 V to 2.5 V
3
3
IN
Input Bandwidth 0 kHz–90.625 kHz 86/84.5 90 dB
Input Bandwidth 0 kHz–100 kHz, f
= 14 MHz 84.5/83 dB
CLKIN
Input Bandwidth 0 kHz–90.625 kHz –90/–88 dB
Input Bandwidth 0 kHz–100 kHz, f
= 14 MHz –88/–86 dB
CLKIN
DYNAMIC SPECIFICATIONS
Bipolar Mode, UNI = V
Signal-to-(Noise + Distortion)
Total Harmonic Distortion
Spurious-Free Dynamic Range Input Bandwidth 0 kHz–90.625 kHz –90 dB
Unipolar Mode, UNI = V
INL
Signal-to-(Noise + Distortion)
Total Harmonic Distortion
Input Bandwidth 0 kHz–100 kHz, f
VIN(–) = 0 V, VIN(+) = 0 V to 2.5 V
3
3
Input Bandwidth 0 kHz–90.625 kHz 84.5/83 88 dB
Input Bandwidth 0 kHz–97.65 kHz –89/–87 dB
= 14 MHz –88 dB
CLKIN
Spurious-Free Dynamic Range Input Bandwidth 0 kHz–97.65 kHz –90 dB
Intermodulation Distortion –93 dB
AC CMRR V
(+) = VIN(–) = 2.5 V p-p
IN
= 1.25 V to 3.75 V, 20 kHz 96 dB
V
CM
Digital Filter Response
Pass-Band Ripple 0 kHz to 90.625 kHz ±0.005 dB
Cutoff Frequency 96.92 kHz
Stop-Band Attenuation 104.6875 kHz to 12.395 MHz 90 dB
ANALOG INPUTS
Full-Scale Input Span V
Bipolar Mode UNI = V
Unipolar Mode UNI = V
Absolute Input Voltage V
(+) – VIN(–)
IN
INH
INL
(+) and VIN(–)0AV
IN
–V
/2 +V
REF2
0V
REF2
REF2
DD
/2 V
V
V
Input Sampling Capacitance 2pF
Input Sampling Rate Guaranteed by Design 2 × f
CLKIN
Differential Input Impedance 1/(4 × 10-9)f
CLKIN
Hz
kΩ
CLOCK
CLKIN Mark Space Ratio 45 55 %
REFERENCE
REF1 Output Voltage 2.32 2.47 2.62 V
REF1 Output Voltage Drift 60 ppm/°C
REF1 Output Impedance 3kΩ
Reference Buffer
Offset Voltage Offset between REF1 and REF2 ±12 mV
Using Internal Reference
REF2 Output Voltage 2.32 2.47 2.62 V
REF2 Output Voltage Drift 60 ppm/°C
Using External Reference
REF2 Input Impedance REF1 = AGND 1/(16 × 10
−9
)f
CLKIN
kΩ
External Reference Voltage Range Applied to REF1 or REF2 2.32 2.5 2.62 V
STATIC PERFORMANCE
Resolution 16 Bits
Differential Nonlinearity Guaranteed Monotonic ±0.5 ±1LSB
Integral Nonlinearity ±2LSB
After Calibration
Offset Error
Gain Error
4, 5
4
±3mV
±0.6 % FSR
Without Calibration
Offset Error ±6mV
Gain Error
5
±0.6 % FSR
Offset Error Drift ±1 LSB/°C
Gain Error Drift REF2 Is an Ideal Reference, REF1 = AGND
Unipolar Mode ±1 LSB/°C
Bipolar Mode ±0.5 LSB/°C
REV. B–2–
AD7722
A Version
Parameter Test Conditions/Comments Min Typ Max Unit
LOGIC INPUTS (Excluding CLKIN)
, Input High Voltage 2.0 V
V
INH
V
, Input Low Voltage 0.8 V
INL
CLOCK INPUT (CLKIN)
, Input High Voltage 4.0 V
V
INH
V
, Input Low Voltage 0.4 V
INL
ALL LOGIC INPUTS
I
, Input Current VIN = 0 V to DV
IN
DD
CIN, Input Capacitance 10 pF
LOGIC OUTPUTS
V
, Output High Voltage |I
OH
VOL, Output Low Voltage |I
| = 200 µA 4.0 V
OUT
| = 1.6 mA 0.4 V
OUT
POWER SUPPLIES
AV
DV
I
DD
DD
DD
, AV
DD1
Total from AVDD and DV
DD
4.75 5.25 V
4.75 5.25 V
Power Consumption 375 mW
NOTES
1
Operating temperature range is –40°C to +85°C (A Version).
2
Measurement Bandwidth = 0.5 × fS; Input Level = –0.05 dB.
3
TA = 25°C to 85°C/TA = T
4
Applies after calibration at temperature of interest.
5
Gain error excludes reference error. The ADC gain is calibrated w.r.t. the voltage on the REF2 pin.
Specifications subject to change without notice.
MIN
to T
MAX
.
±10 µA
75 mA
REV. B
–3–
AD7722
ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS
(TA = 25°C, unless otherwise noted.)
1
DVDD to DGND . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .–0.3 V to +7 V
AV
AV
DD
DD
, AV
, AV
to AGND . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .–0.3 V to +7 V
DD1
to DVDD . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . –1 V to +1 V
DD1
AGND, AGND1 to DGND . . . . . . . . . . . . . –0.3 V to +0.3 V
Digital Inputs to DGND . . . . . . . . . . –0.3 V to DV
Digital Outputs to DGND . . . . . . . . . –0.3 V to DV
+ 0.3 V
DD
+ 0.3 V
DD
VIN(+), VIN(–) to AGND . . . . . . . . . . –0.3 V to AVDD + 0.3 V
REF1 to AGND . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . –0.3 V to AV
REF2 to AGND . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . –0.3 V to AV
DGND, AGND1, AGND2 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . ±0.3 V
Input current to any pin except the supplies
2
. . . . . . . . ±10 mA
+ 0.3 V
DD
+ 0.3 V
DD
Operating Temperature Range . . . . . . . . . . . –40°C to +85°C
Storage Temperature Range . . . . . . . . . . . . –65°C to +150°C
Junction Temperature . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 150°C
Thermal Impedance . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 72°C/W
θ
JA
θJC Thermal Impedance . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20°C/W
Lead Temperature, Soldering
Vapor Phase (60 sec) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 215°C
Infrared (15 sec) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 220°C
NOTES
1
Stresses above those listed under Absolute Maximum Ratings may cause
permanent damage to the device. This is a stress rating only; functional operation of the device at these or any other conditions above those indicated in the
operational section of this specification is not implied. Exposure to absolute
maximum rating conditions for extended periods may affect device reliability.
2
Transient currents up to 100 mA will not cause SCR latch-up.
ORDERING GUIDE
Package Package
Model Temperature Description Option
AD7722AS –40°C to +85°C 44-Lead MQFP S-44B
EVAL-AD7722CB Evaluation Board
I
OL
1.6mA
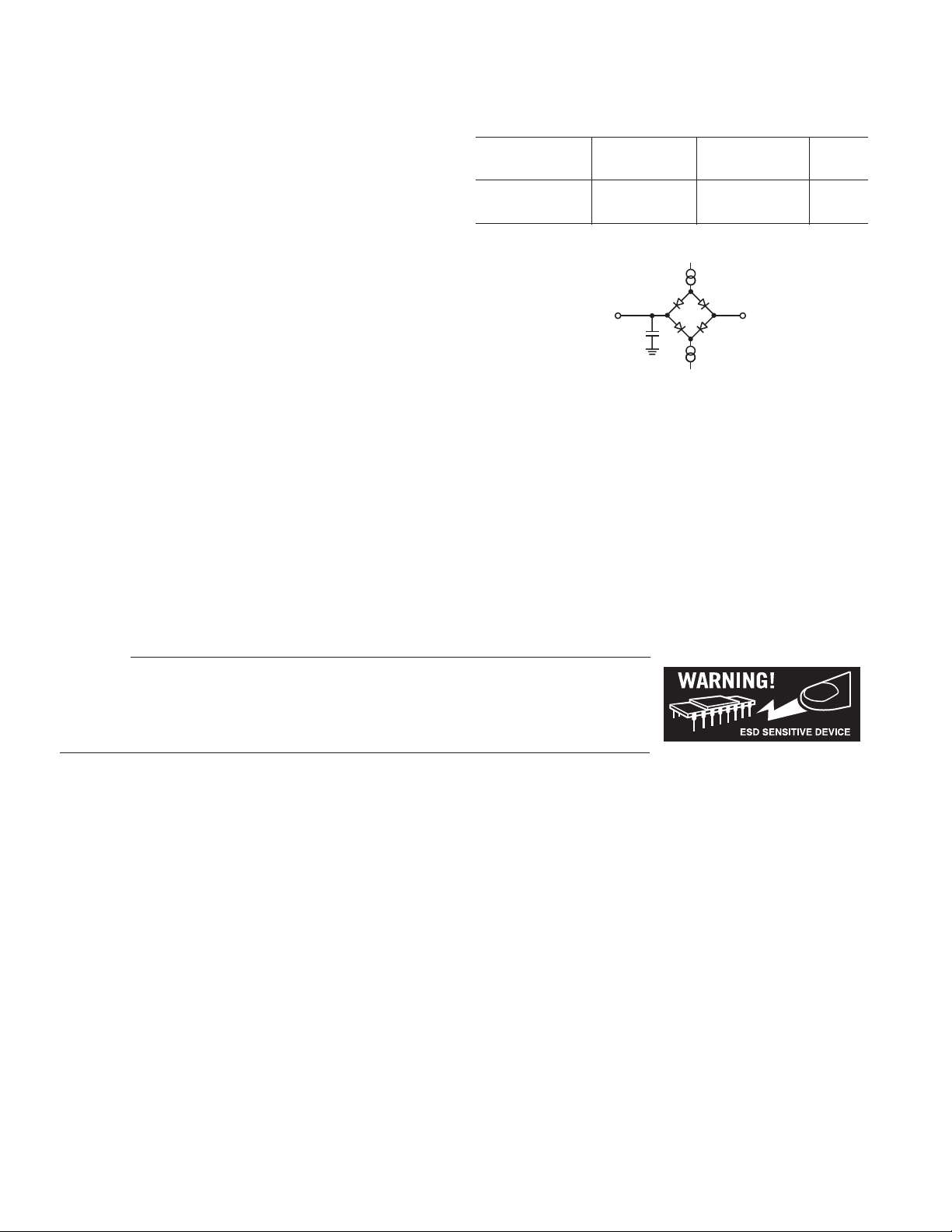
TO
OUTPUT
PIN
50pF
C
L
I
OH
200A
1.6V
Figure 1. Load Circuit for Timing Specifications
CAUTION
ESD (electrostatic discharge) sensitive device. Electrostatic charges as high as 4000 V readily
accumulate on the human body and test equipment and can discharge without detection.
Although the AD7722 features proprietary ESD protection circuitry, permanent damage may
occur on devices subjected to high energy electrostatic discharges. Therefore, proper ESD
precautions are recommended to avoid performance degradation or loss of functionality.
REV. B–4–
AD7722
TIMING SPECIFICATIONS
(AVDD = 5 V ⴞ 5%, DVDD = 5 V ⴞ 5%, AGND = DGND = 0 V, CL = 50 pF, TA = T
f
= 12.5 MHz, SFMT = Logic Low or High, CFMT = Logic Low or High.)
CLKIN
MIN
to T
MAX
,
Parameter Symbol Min Typ Max Unit
CLKIN Frequency f
CLKIN Period (t
CLK
= 1/f
)t
CLK
CLKIN Low Pulse Width t
CLKIN High Pulse Width t
CLKIN Rise Time t
CLKIN Fall Time t
FSI Low Time t
FSI Setup Time t
FSI Hold Time t
CLKIN to SCO Delay t
SCO Period
1
SCO Transition to FSO High Delay t
SCO Transition to FSO Low Delay t
SCO Transition to SDO Valid Delay t
SCO Transition from FSI
2
SDO Enable Delay Time t
SDO Disable Delay Time t
DRDY High Time t
Conversion Time
1
DRDY to CS Setup Time t
CS to RD Setup Time t
RD Pulse Width t
Data Access Time after RD Falling Edge
3
Bus Relinquish Time after RD Rising Edge t
CS to RD Hold Time t
RD to DRDY High Time t
SYNC/RESET Input Pulse Width t
DVAL Low Delay from SYNC/RESET t
SYNC/RESET Low Time after CLKIN Rising t
DRDY High Delay after SYNC/RESET Low t
DRDY Low Delay after SYNC/RESET Low
1
DVAL High Delay after SYNC/RESET Low1t
CAL Setup Time t
CAL Pulse Width t
Calibration Delay from CAL High t
Unipolar Input Calibration Time, (UNI = 0)
Bipolar Input Calibration Time, (UNI = 1)
Conversion Results Valid, (UNI = 0)
Conversion Results Valid, (UNI = 1)
NOTES
1
Guaranteed by design.
2
Frame sync is initiated on falling edge of CLKIN.
3
With RD synchronous to CLKIN, t22 can be reduced up to 1 t
4
See Figure 8.
Specifications subject to change without notice.
1
1
1, 4
1, 4
CLK
CLK
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
t
10
11
12
13
t
14
15
16
17
t
18
19
20
21
t
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
t
30
31
34
35
36
t
37
t
37
t
38
t
38
.
0.3 12.5 15 MHz
0.067 0.08 3.33 µs
0.45 × t
0.45 × t
1
1
0.55 × t
0.55 × t
1
1
5ns
5ns
2t
CLK
20 ns
20 ns
40 ns
2t
CLK
410 ns
410 ns
38 ns
2.5 t
CLK
30 45 ns
10 30 ns
2t
64 t
CLK
CLK
0ns
0ns
t
+ 20 ns
CLK
t
+ 40 ns
CLK
t
+ 40 ns
CLK
0ns
1t
CLK
10 ns
40 ns
10 t
– 10 ns
CLK
50 ns
(8192 + 64) t
8192 t
CLK
CLK
10 ns
12 t
64 t
(3 × 8192 + 2 × 512) t
(4 × 8192 + 3 × 512) t
(3 × 8192 + 2 × 512 + 64) t
(4 × 8192 + 3 × 512 + 64) t
CLK
CLK
CLK
CLK
CLK
CLK
REV. B
–5–
AD7722
CLKIN
SCO
(CFMT = 0)
FSO
(SFMT = 0)
64 CKLIN CYCLES
32 SCO CYCLES
SCO
ZERO FOR LAST 16 SCO CYCLESVALID DATA FOR 16 SCO CYCLES
VALID
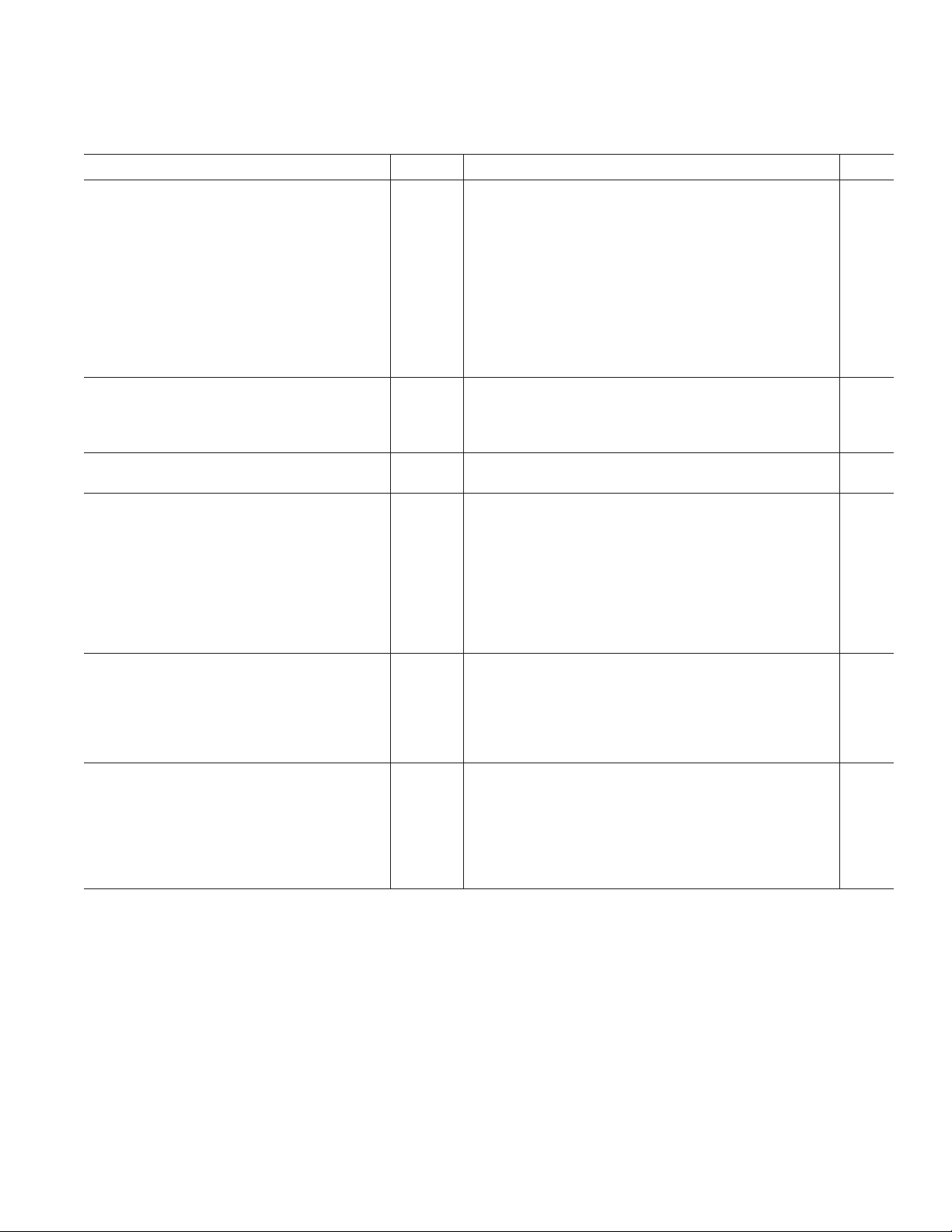
Figure 2a. Generalized Serial Mode Timing (FSI = Logic Low or High, TSI = DOE)
64 CKLIN CYCLES
CLKIN
SCO
(CFMT = 0)
FSO
(SFMT = 1)
SCO
LOW FOR 16 SCO CYCLES
VALID DATA FOR 16 SCO CYCLES
32 SCO CYCLES
HIGH FOR LAST 16 SCO CYCLES
ZERO FOR LAST 16 SCO CYCLES
VALID
Figure 2b. Generalized Serial Mode Timing (FSI = Logic Low or High, TSI = DOE)
t
4
t
t
8
t
t
9
t
10
7
3
t
2
CLKIN
FSI
SCO
2.3V
t
5
0.8V
t
1
t
6
t
9
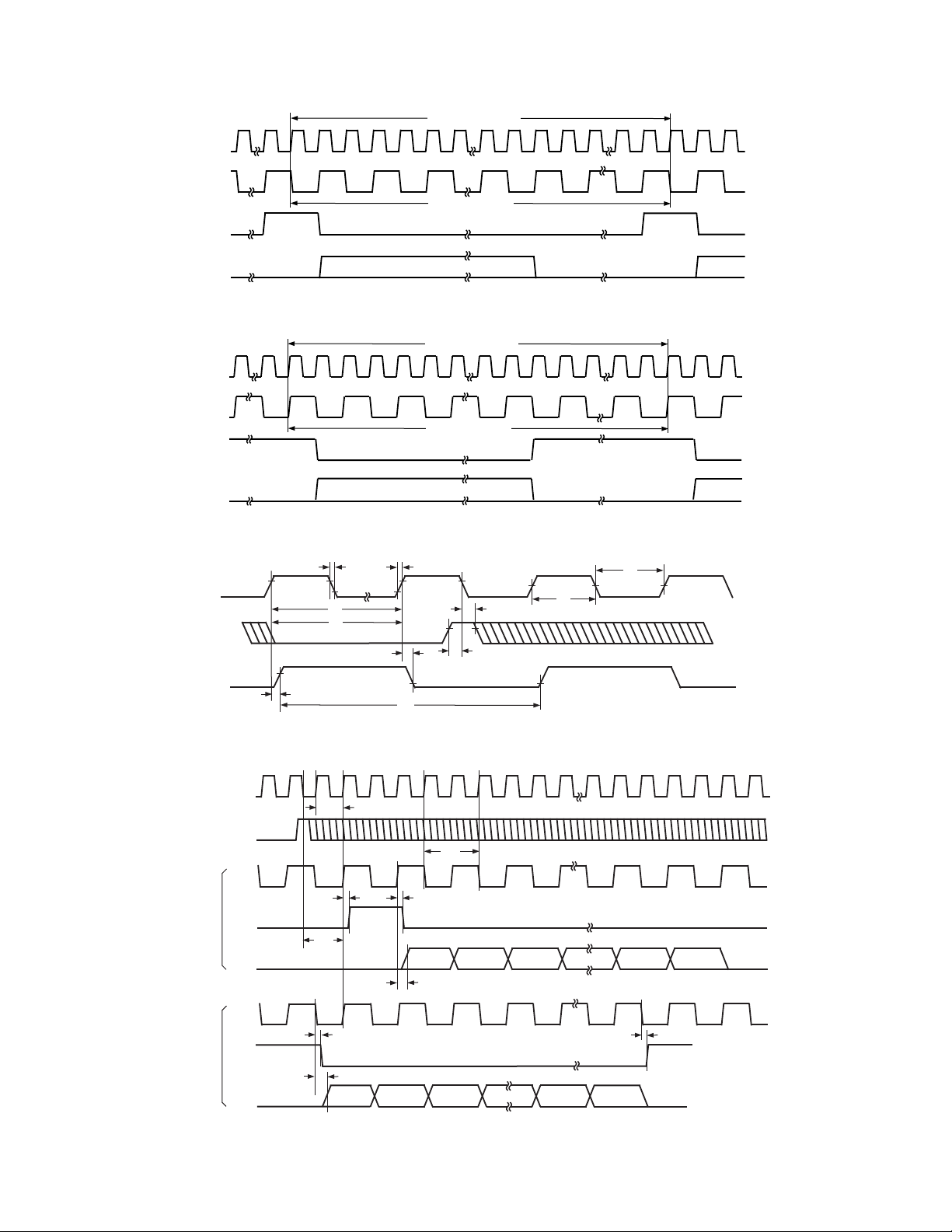
Figure 3. Serial Mode Timing for Clock Input, Frame Sync Input, and Serial Clock Output
CLKIN
t
1
FSI
t
10
SCO
SFMT = LOGIC
LOW(0)
SFMT = LOGIC
HIGH(1)
FSO
SDO
SCO
FSO
SDO
LOW FOR
D15–D0
t
11
t
14
t
12
t
13
D15 D14 D13 D1 D0
t
12
D15 D14 D13 D1 D0
t
13
t
11
Figure 4. Serial Mode Timing for Frame Sync Input, Frame Sync Output, Serial Clock Output,
and Serial Data Output (CFMT = Logic Low, TSI = DOE)
REV. B–6–
AD7722
DOE
t
15
SDO
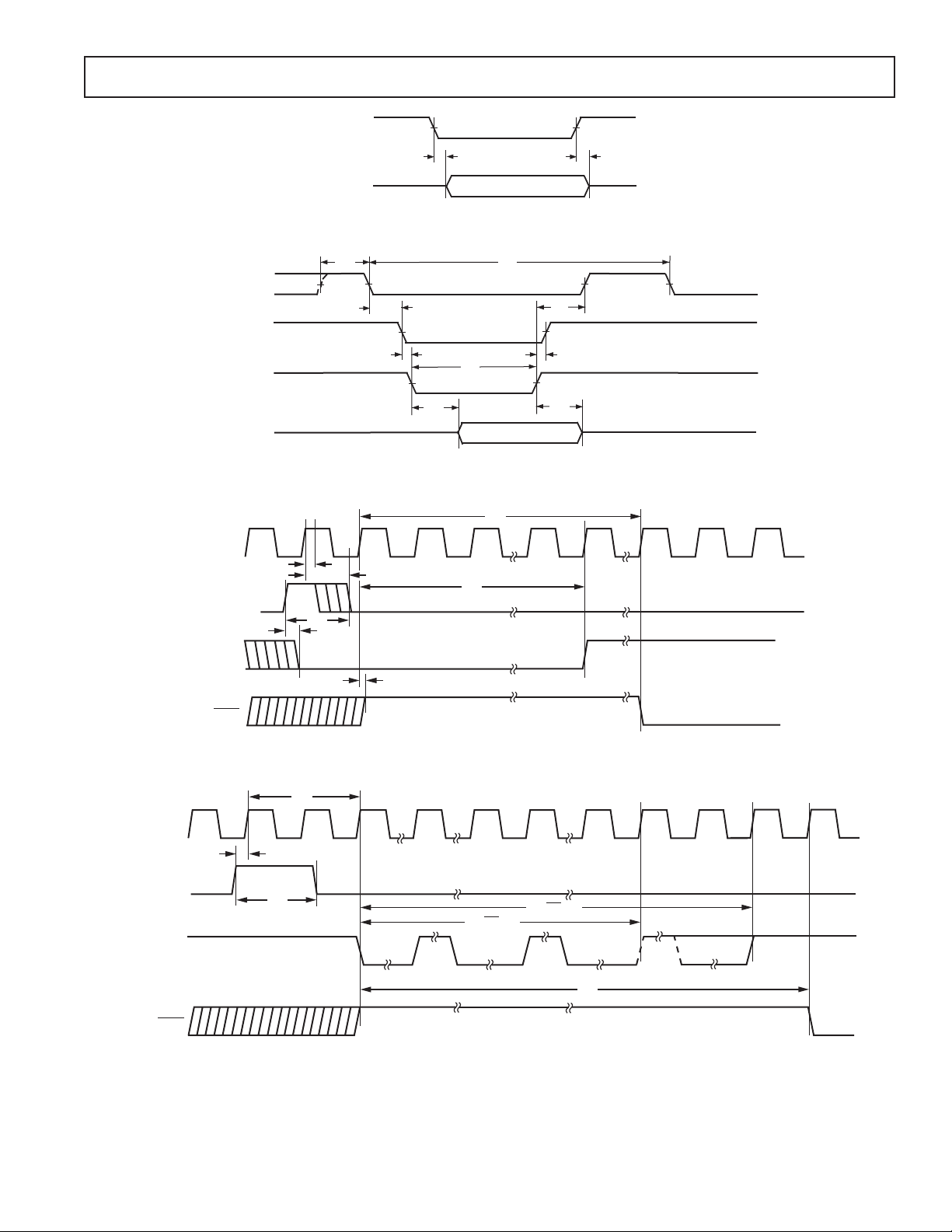
Figure 5. Serial Mode Timing for Data Output Enable and Serial Data Output (TSI = Logic Low)
t
16
DB0–DB15
CLKIN
SYNC, RESET
DVAL
DRDY
DRDY
CS
RD
t
28
t
27
MIN
t
17
t
19
t
20
t
22
t
21
t
18
VALID DATA
t
25
t
24
t
23
Figure 6. Parallel Mode Read Timing
t
30
t
MAX
28
t
26
t
29
t
31
SYNC, RESET
REV. B
CLKIN
DVAL
DRDY
Figure 7. SYNC and RESET Timing, Serial and Parallel Mode
t
36
t
34
t
35
t
UNI = 0
37
8192
t
CLK
512
8192
t
CLK
t
CLK
t
512
UNI = 1
37
t
CLK
8192
t
38
t
CLK
512
8192
t
CLK
t
CLK
Figure 8. Calibration Timing, Serial and Parallel Mode
–7–
AD7722
Mnemonic Pin No. Description
PIN FUNCTION DESCRIPTIONS
AV
DD1
14 Clock Logic Power Supply Voltage for the Analog Modulator, 5 V ± 5%.
AGND1 10 Clock Logic Ground Reference for the Analog Modulator.
AV
DD
20, 23 Analog Power Supply Voltage, 5 V ± 5%.
AGND 9, 13, 15, 19, Ground Reference for Analog Circuitry.
21, 25, 26
DV
DD
39 Digital Power Supply Voltage, 5 V ± 5%.
DGND 6, 28 Ground Reference for Digital Circuitry.
REF1 22 Reference Input/Output. REF1 connects through 3 kΩ to the output of the internal 2.5 V reference and
to the input of a buffer amplifier that drives the Σ-∆ modulator. This pin can also be overdriven with an
external reference 2.5 V.
REF2 24 Reference Input/Output. REF2 connects to the output of an internal buffer amplifier used to drive the
Σ-∆ modulator. When REF2 is used as an input, REF1 must be connected to AGND.
V
(+) 18 Positive Terminal of the Differential Analog Input.
IN
V
(–)16Negative Terminal of the Differential Analog Input.
IN
UNI 7Analog Input Range Select Input. UNI selects the analog input range for either bipolar or unipolar
operation. A logic low input selects unipolar operation. A logic high input selects bipolar operation.
CLKIN 11 Clock Input. Master clock signal for the device. The CLKIN pin interfaces the AD7722 internal
oscillator circuit to an external crystal or an external clock. A parallel resonant, fundamental-frequency,
microprocessor-grade crystal and a 1 MΩ resistor should be connected between the CLKIN and
XTAL pins with two capacitors connected from each pin to ground. Alternatively, the CLKIN pin
can be driven with an external CMOS compatible clock. The AD7722 is specified with a clock input
frequency of 12.5 MHz.
XTAL 12 Oscillator Output. The XTAL pin connects the internal oscillator output to an external crystal.
If an external clock is used, XTAL should be left unconnected.
P/S 8 Parallel/Serial Interface Select Input. A logic high configures the output data interface for parallel mode
operation. The serial mode operation is selected with the P/S set to a logic low.
CAL 27 Calibration Logic Input. A logic high input for a duration of one CLKIN cycle initiates a
calibration sequence for the device gain and offset error.
RESET 17 Reset Logic Input. RESET is used to clear the offset and gain calibration registers. RESET is an
asynchronous input. RESET allows the user to set the AD7722 to an uncalibrated state if the
device had been previously calibrated. A rising edge also resets the AD7722 Σ-∆ modulator by
shorting the integrator capacitors in the modulator. In addition, RESET functions identically to
the SYNC pin described below. When operating with more than one AD7722, a RESET/SYNC
should be issued following power up to ensure the devices are synchronized. Ensure that the
supplies are settled before applying the RESET/SYNC pulse.
CS 29 Chip select is a level sensitive logic input. CS enables the output data register for parallel mode read
operation. The CS logic level is sensed on the rising edge of CLKIN. The output data bus is enabled
when the rising edge of CLKIN senses a logic low level on CS if RD is also low. When CS is sensed
high, the output data bits DB15–DB0 will be high impedance. In serial mode, tie CS to a logic low.
SYNC 30 Synchronization Logic Input. SYNC is an asynchronous input. When using more than one
AD7722 operated from a common master clock, SYNC allows each ADC’s Σ-∆ modulator to
simultaneously sample its analog input and update its output data register. A rising edge resets
the AD7722 digital filter sequencer counter to zero. After a SYNC, conversion data is not valid until
after the digital filter settles (see Figure 7). DVAL goes low in the serial mode. When the rising
edge of CLKIN senses a logic low on SYNC (or RESET), the reset state is released; in parallel
mode, DRDY goes high. After the reset state is released, DVAL returns high after 8192 CLKIN
cycles (128 × 64/f
); in parallel mode, DRDY returns low after one additional convolution cycle
CLKIN
of the digital filter (64 CLKIN periods), when valid data is ready to be read from the output data
register. When operating with more than one AD7722, a RESET/SYNC should be issued following power up to ensure the devices are synchronized. Ensure that the supplies are settled before
applying the RESET/SYNC pulse.
REV. B–8–
 Loading...
Loading...