ANALOG DEVICES AD7719 Service Manual
Low Voltage, Low Power,
a
Factory-Calibrated 16-/24-Bit Dual - ADC
FEATURES
HIGH RESOLUTION - ADCs
2 Independent ADCs (16- and 24-Bit Resolution)
Factory-Calibrated (Field Calibration Not Required)
Output Settles in 1 Conversion Cycle (Single
Conversion Mode)
Programmable Gain Front End
Simultaneous Sampling and Conversion of 2
Signal Sources
Separate Reference Inputs for Each Channel
Simultaneous 50 Hz and 60 Hz Rejection at 20 Hz
Update Rate
ISOURCE Select
™
24-Bit No Missing Codes—Main ADC
13-Bit p-p Resolution @ 20 Hz, 20 mV Range
18-Bit p-p Resolution @ 20 Hz, 2.56 V Range
INTERFACE
3-Wire Serial
®
, QSPI™, MICROWIRE™, and DSP Compatible
SPI
Schmitt Trigger on SCLK
POWER
Specified for Single 3 V and 5 V Operation
Normal: 1.5 mA Typ @ 3 V
Power-Down: 10 A (32 kHz Crystal Running)
ON-CHIP FUNCTIONS
Rail-Rail Input Buffer and PGA
4-Bit Digital I/O Port
On-Chip Temperature Sensor
Dual Switchable Excitation Current Sources
Low-Side Power Switches
Reference Detect Circuit
AD7719
APPLICATIONS
Sensor Measurement
Temperature Measurement
Pressure Measurement
Weigh Scales
Portable Instrumentation
4 to 20 mA Transmitters
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
The AD7719 is a complete analog front end for low frequency
measurement applications. It contains two high resolution Σ-∆
ADCs, switchable matched excitation current sources, low-side
power switches, digital I/O port, and temperature sensor. The
24-bit main channel with PGA accepts fully differential, unipolar,
and bipolar input signal ranges from 1.024 × REFIN1/128 to
1.024 × REFIN1. Signals can be converted directly from a transducer without the need for signal conditioning. The 16-bit auxiliary
channel has an input signal range of REFIN2 or REFIN2/2.
The device operates from a 32 kHz crystal with an on-chip
PLL generating the required internal operating frequency. The
output data rate from the part is software programmable. The
peak-to-peak resolution from the part varies with the programmed
gain and output data rate.
The part operates from a single 3 V or 5 V supply. When operating from 3 V supplies, the power dissipation for the part is
4.5 mW with both ADCs enabled and 2.85 mW with only the
main ADC enabled in unbuffered mode. The AD7719 is housed
in 28-lead SOIC and TSSOP packages.
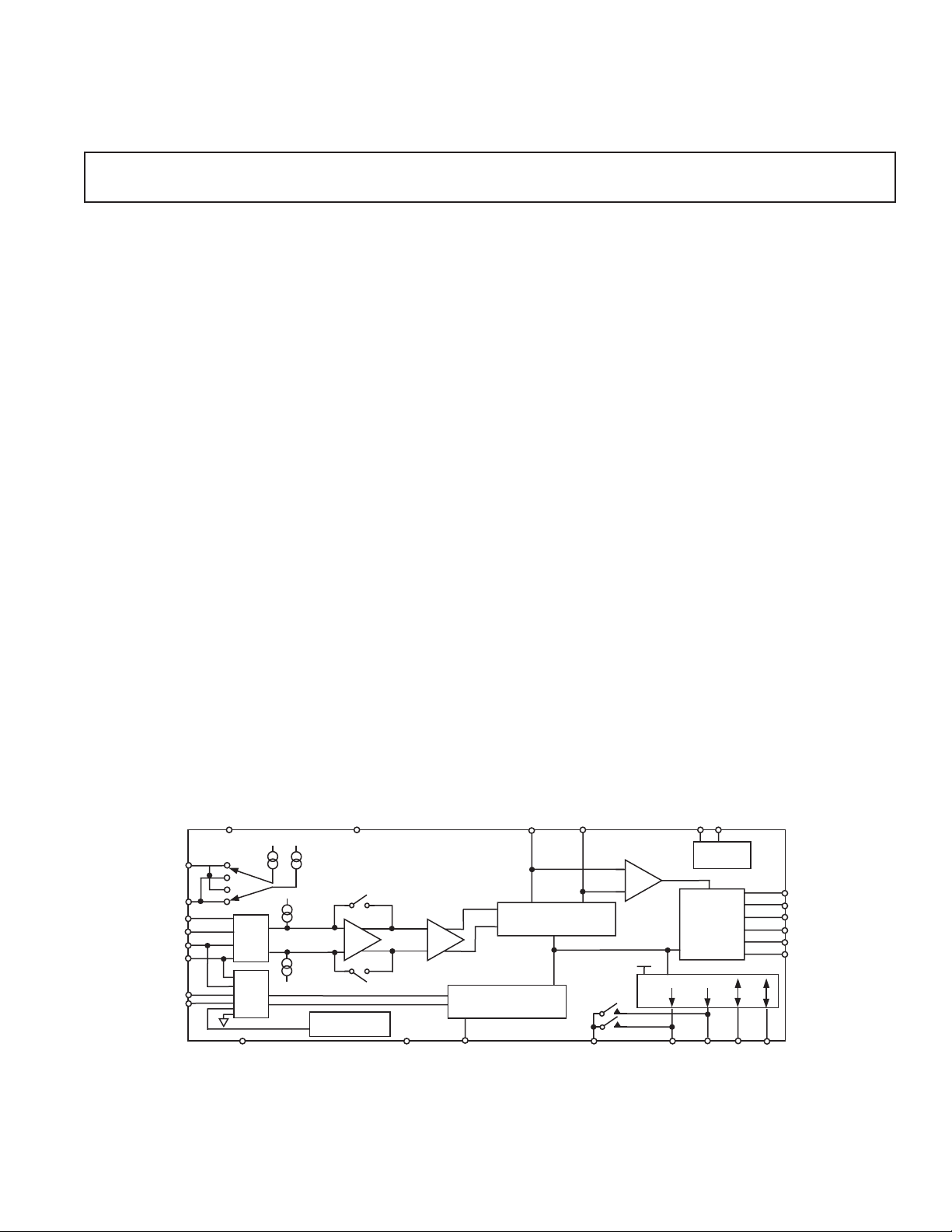
FUNCTIONAL BLOCK DIAGRAM
IOUT1
IOUT2
AIN1
AIN2
AIN3
AIN4
AIN5
AIN6
DV
DD
IEXC1
200A
MUX1
MUX2
AV
MUX
DD
AV
DD
AV
AGND
IEXC2
200A
DD
DGND
BUF
TEMP
SENSOR
AD7719
PGA
AUXILIARY CHANNEL
AGND REFIN2 PWRGND P1/SW1 P2/SW2 P3 P4
REV. A
Information furnished by Analog Devices is believed to be accurate and
reliable. However, no responsibility is assumed by Analog Devices for its
use, nor for any infringements of patents or other rights of third parties that
may result from its use. No license is granted by implication or otherwise
under any patent or patent rights of Analog Devices. Trademarks and
registered trademarks are the property of their respective companies.
XTAL1 XTAL2REFIN1(+) REFIN1(–)
REFERENCE
DETECT
MAIN CHANNEL
24-BIT - ADC
AV
DD
I/O PORT
16-BIT - ADC
One Technology Way, P.O. Box 9106, Norwood, MA 02062-9106, U.S.A.
Tel: 781/329-4700 www.analog.com
Fax: 781/326-8703 © 2003 Analog Devices, Inc. All rights reserved.
OSC. AND
PLL
SERIAL
INTERFACE
AND
CONTROL
LOGIC
DOUT
DIN
SCLK
CS
RDY
RESET

AD7719
TABLE OF CONTENTS
FEATURES . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1
GENERAL DESCRIPTION . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1
SPECIFICATIONS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3
ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
ORDERING GUIDE . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
TIMING CHARACTERISTICS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
DIGITAL INTERFACE . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
PIN CONFIGURATION . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
PIN FUNCTION DESCRIPTIONS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
TYPICAL PERFORMANCE CHARACTERISTICS . . . . 11
DUAL-CHANNEL ADC CIRCUIT INFORMATION . . . 12
Overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
Main Channel . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
Auxiliary Channel . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
Both Channels . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
MAIN AND AUXILIARY ADC NOISE
PERFORMANCE . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
ON-CHIP REGISTERS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
Communications Register
(A3, A2, A1, A0 = 0, 0, 0, 0) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
Status Register (A3, A2, A1, A0 = 0, 0, 0, 0;
Power-On Reset = 0x00) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
Mode Register (A3, A2, A1, A0 = 0, 0, 0, 1;
Power-On Reset = 0x00) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
Operating Characteristics when Addressing the
Mode and Control Registers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
Main ADC Control Register (AD0CON):
(A3, A2, A1, A0 = 0, 0, 1, 0;
Power-On Reset = 0x07) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
Aux ADC Control Registers (AD1CON):
(A3, A2, A1, A0 = 0, 0, 1, 1;
Power-On Reset = 0x01) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
Filter Register (A3, A2, A1, A0 = 0, 1, 0, 0;
Power-On Reset = 0x45) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
I/O and Current Source Control Register (IOCON):
(A3, A2, A1, A0 = 0, 1, 1, 1;
Power-On Reset = 0x0000) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
Main ADC Data Result Registers (DATA0):
(A3, A2, A1, A0 = 0, 1, 0, 1;
Power-On Reset = 0x00 0000) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
Aux ADC Data Result Registers (DATA1):
(A3, A2, A1, A0 = 0, 1, 1, 0;
Power-On Reset = 0x0000) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
Main ADC Offset Calibration Coefficient Registers (OF0):
(A3, A2, A1, A0 = 1, 0, 0, 0;
Power-On Reset = 0x80 0000) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
Aux ADC Offset Calibration Coefficient Registers (OF1):
(A3, A2, A1, A0 = 1, 0, 0, 1;
Power-On Reset = 0x8000) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
Main ADC Gain Calibration Coefficient Registers (GNO):
(A3, A2, A1, A0 = 1, 0, 1, 0;
Power-On Reset = 0x5X XXX5) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
Aux ADC Gain Calibration Coefficient Registers (GN1):
(A3, A2, A1, A0 = 1, 0, 1, 1;
Power-On Reset = 0x59XX) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
ID Register (ID): (A3, A2, A1, A0 = 1, 1, 1, 1;
Power-On Reset = 0x0X) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
User Nonprogrammable Test Registers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
CONFIGURING THE AD7719 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27
MICROCOMPUTER/MICROPROCESSOR
INTERFACING . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27
AD7719-to-68HC11 Interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
AD7719-to-8051 Interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
AD7719-to-ADSP-2103/ADSP-2105 Interface . . . . . . . . 30
CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30
Analog Input Channels . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
Programmable Gain Amplifier . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32
Bipolar/Unipolar Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32
Data Output Coding . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 33
Burnout Currents . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 33
Excitation Currents . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 33
Crystal Oscillator . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 33
Reference Input . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 33
Reference Detect . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 34
Reset Input . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 34
Power-Down Mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 34
Idle Mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 34
ADC Disable Mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 34
Calibration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 34
Grounding and Layout . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 35
APPLICATIONS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 35
Pressure Measurement . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 36
Temperature Measurement . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 36
3-Wire RTD Configurations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 37
Smart Transmitters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 38
OUTLINE DIMENSIONS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
REVISION HISTORY . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40
–2–
REV. A
AD7719
REFIN(+) = 2.5 V; REFIN(–) = AGND; AGND = DGND = 0 V; XTAL1/XTAL2 = 32.768 kHz Crystal; all specifications T
Parameter AD7719B Unit Test Conditions
ADC CHANNEL SPECIFICATION
Output Update Rate 5.4 Hz min Both Channels Synchronized
MAIN CHANNEL
No Missing Codes
Resolution 13 Bits p-p ±20 mV Range, 20 Hz Update Rate
Output Noise and Update Rates See Tables II to V
Integral Nonlinearity ±10 ppm of FSR max Typically 2 ppm.
Offset Error
Offset Error Drift vs. Temperature
Full-Scale Error
Gain Drift vs. Temperature
Power Supply Rejection (PSR) 80 dB min Input Range = ±2.56 V, 100 dB typ.
ANALOG INPUTS
Differential Input Voltage Ranges ±1.024 × REFIN1/GAIN V nom REFIN1 = REFIN1(+) – REFIN1(–)
ADC Range Matching ±2 µV typ Input Voltage = 19 mV on All Ranges
Absolute AIN Voltage Limits AGND + 100 mV V min BUF = 0; Buffered Mode of Operation
Analog Input Current
DC Input Current ±1 nA max
DC Input Current Drift ±5 pA /°C typ
Absolute AIN Voltage Limits AGND – 30 mV V min BUF = 1; Unbuffered mode of operation.
Analog Input Current BUF = 1. Unbuffered Mode of Operation.
DC Input Current ±125 nA/V typ Input Current Varies with Input Voltage
DC Input Current Drift ±2 pA/V/°C typ
Normal-Mode Rejection
@ 50 Hz 100 dB min
@ 60 Hz 100 dB min 60 Hz ± 1 Hz, 20 Hz Update Rate, SF = 68
Common-Mode Rejection
@ DC 90 dB min Input Range = ±2.56 V, AIN = 1 V.
@ 50 Hz
@ 60 Hz
REFERENCE INPUT (REFIN1)
REFIN1 Voltage 2.5 V nom REFIN1 = REFIN1(+) – REFIN1(–)
REFIN1 Voltage Range
REFIN1 Common-Mode Range AGND – 30 mV V min
Reference DC Input Current 0.5 µA/V typ
Reference DC Input Current Drift ±0.01 nA/V/°C typ
Normal-Mode Rejection
@ 50 Hz 100 dB min 50 Hz ± 1 Hz, SF = 82
@ 60 Hz 100 dB min 60 Hz ± 1 Hz, SF = 68
Common-Mode Rejection
@ DC 110 dB typ Input Range = ±2.56 V, AIN = 1 V
@ 50 Hz 110 dB typ 50 Hz ± 1 Hz, Range = 2.56 V, AIN = 1 V
@ 60 Hz 110 dB typ 60 Hz ± 1 Hz, Range = 2.56 V, AIN = 1 V
Reference Detect Levels 0.3 V min NOXREF Bit Active if VREF < 0.3 V
AUXILIARY CHANNEL
No Missing Codes
Resolution 16 Bits p-p ±2.5 V Range, 20 Hz Update Rate
Output Noise and Update Rates See Tables VI and VIII
Integral Nonlinearity ±15 ppm of FSR max
–SPECIFICATIONS
105 Hz max 0.732 ms Increments
2
3
5, 6, 7
4
2
2, 8
2
2
2
2, 8
2
24 Bits min 20 Hz Update Rate
18 Bits p-p ±2.56 V Range, 20 Hz Update Rate
±3 µV typ
4
±10 nV/°C typ
±10 µV typ At the Calibrated Conditions
±0.5 ppm/°C typ
AV
DD
AV
DD
100 dB min 50 Hz ± 1 Hz, Range = ±2.56 V, AIN = 1 V
100 dB min 60 Hz ± 1 Hz, Range = ±2.56 V, AIN = 1 V
1V min
AV
DD
AVDD + 30 mV V max
0.65 V max NOXREF Bit Inactive if VREF > 0.65 V
16 Bits min
(AVDD = 2.7 V to 3.6 V or 4.75 V to 5.25 V, DVDD = 2.7 V to 3.6 V or 4.75 V to 5.25 V,
to T
MIN
110 dB typ on ±20 mV Range
GAIN = 1 to 128.
– 100 mV V max
BUF = 0
+ 30 mV V max
50 Hz ± 1 Hz, 16.65 Hz Update Rate, SF = 82
100 dB typ. 110 dB typ on ±20 mV Range
V max
, unless otherwise noted.)
MAX
FSR
=
×21024 1.
REFIN
Gain
1
REV. A
–3–
AD7719
Parameter AD7719B Unit Test Conditions
AUXILIARY CHANNEL (continued)
Offset Error
Offset Error Drift vs. Temperature
Full-Scale Error
Gain Drift vs. Temperature
Negative Full-Scale Error ±1 LSB typ
Power Supply Rejection (PSR) 70 dB min AIN = 1 V Input Range = ±2.5 V, Typically 80 dB
ANALOG INPUTS
Differential Input Voltage Ranges ±REFIN2 V nom ARN = 1
Absolute AIN Voltage Limits AGND – 30 mV V min Unbuffered Input
Analog Input Current
DC Input Current ±125 nA/V typ Input Current Varies with Input Voltage
DC Input Current Drift ±2 pA/V/°C typ
Normal-Mode Rejection
@ 50 Hz 100 dB min 50 Hz ±1 Hz, SF = 82
@ 60 Hz 100 dB min 60 Hz ±1 Hz, SF = 68
Common-Mode Rejection
@ DC 85 dB min Input Range = ±2.5 V, AIN = 1 V
@ 50 Hz
@ 60 Hz
REFERENCE INPUT (REFIN2) With Respect to AGND
REFIN2 Voltage 2.5 V nom
REFIN2 Range
Reference DC Input Current
Reference DC Input Current Drift 0.003 nA/V/°C typ
EXCITATION CURRENT SOURCES
(IEXC1 and IEXC2)
Output Current 200 µA nom
Initial Tolerance at 25°C ±10 % typ
Drift 200 ppm/°C typ
Initial Current Matching at 25°C±1% typ Matching between IEXC1 and IEXC2
Drift Matching 20 ppm/°C typ
Line Regulation (AV
Load Regulation 300 nA/V typ
Output Compliance AVDD – 0.6 V max
LOW-SIDE POWER SWITCHES
(SW1, SW2)
R
Allowable Current
TEMPERATURE SENSOR
Accuracy See TPC 5 °C typ
TRANSDUCER BURNOUT
AIN(+) Current –100 nA typ
AIN(–) Current 100 nA typ
Initial Tolerance @ 25°C ±15 % typ
Drift 0.03 %/°C typ
SYSTEM CALIBRATION
Full-Scale Calibration Limit 1.05 × FS
Zero-Scale Calibration Limit –1.05 × FS V min
Input Span 0.8 × FS V min
ON
3
6, 7
4
±3 µV typ Selected Channel = AIN5/AIN6
4
±10 nV/°C typ
±0.75 LSB typ
0.5 ppm/°C typ
±REFIN2/2 V nom ARN = 0
AV
+ 30 mV V max
DD
2, 8
2
2
2
2
90 dB min 50 Hz ±1 Hz, Range = 2.5 V, AIN = 1 V
90 dB min 60 Hz ±1 Hz, Range = 2.5 V, AIN = 1 V
1V min
AV
DD
V max
0.2 µA/V typ
No Load
) 2.1 µA/V max AVDD = 5 V ± 5%. Typically 1.25 µA/V
DD
AGND – 30 mV V min
5 Ω max AVDD = 5 V. Typically 3 Ω
2
2, 9
7 Ω max AV
20 mA max Continuous Current per Switch
10
V max
= 3 V. Typically 4.5 Ω
DD
2.1 × FS V max
–4–
REV. A
Parameter AD7719B Unit Test Conditions
LOGIC INPUTS
All Inputs Except SCLK and XTAL1
V
, Input Low Voltage 0.8 V max DVDD = 5 V
INL
, Input High Voltage 2.0 V min DVDD = 3 V or 5 V
V
INH
SCLK Only (Schmitt-Triggered Input)
V
T(+)
V
T(–)
– V
V
T(+)
V
V
V
XTAL1 Only
V
V
V
V
T(–)
T(+)
T(–)
– V
T(+)
T(–)
2
, Input Low Voltage 0.8 V max DVDD = 5 V
INL
, Input High Voltage 3.5 V min DVDD = 5 V
INH
, Input Low Voltage 0.4 V max DVDD = 3 V
INL
, Input High Voltage 2.5 V min DVDD = 3 V
INH
Input Currents ±10 µA max V
2
0.4 V max DV
2
1.4/2 V min/V max DVDD = 5 V
0.8/1.4 V min/V max DVDD = 5 V
0.3/0.85 V min/V max DVDD = 5 V
0.95/2 V min/V max DVDD = 3 V
0.4/1.1 V min/V max DVDD = 3 V
0.3/0.85 V min/V max DVDD = 3 V
DD
= DV
IN
= 3 V
DD
–70 µA max VIN = DGND, Typically –40 µA at 5 V
Input Capacitance
LOGIC OUTPUTS (Excluding XTAL2)
VOH, Output High Voltage
, Output Low Voltage
V
OL
, Output High Voltage
V
OH
, Output Low Voltage
V
OL
2
2
2
2
2
10 pF typ All Digital Inputs
DVDD – 0.6 V min DVDD = 3 V, I
0.4 V max DVDD = 3 V, I
4V min DVDD = 5 V, I
0.4 V max DVDD = 5 V, I
and –20 µA at 3 V
SOURCE
SINK
SOURCE
SINK
= 100 µA
= 100 µA
= 200 µA
= 1.6 mA
Floating-State Leakage Current ±10 µA max
Floating-State Output Capacitance ±10 pF typ
Data Output Coding Binary Unipolar Mode
Offset Binary Bipolar Mode
I/O PORT
V
V
Input Currents ±10 µA max V
11
, Input Low Voltage
INL
, Input High Voltage
INH
I/O Port Voltages Are with Respect to
and AGND
AV
2
2
0.8 V max AVDD = 5 V
0.4 V max AV
2.0 V min AVDD = 3 V or 5 V
DD
DD
= AV
IN
= 3 V
DD
–70 µA max VIN = AGND, Typically –40 µA at AVDD = 5 V
and –20 µA at AV
Input Capacitance 10 pF typ All Digital Inputs
, Output High Voltage
V
OH
, Output Low Voltage
V
OL
, Output High Voltage
V
OH
, Output Low Voltage
V
OL
2
2
2
2
AVDD – 0.6 V min AVDD = 3 V, I
0.4 V max AVDD = 3 V, I
4V min AVDD = 5 V, I
0.4 V max AVDD = 5 V, I
DD
SOURCE
= 100 µA
SINK
SOURCE
= 1.6 mA
SINK
= 3 V
= 100 µA
= 200 µA
Floating-State Output Leakage Current ±10 µA max
Floating-State Output Capacitance ±10 pF typ
START-UP TIME
From Power-On 300 ms typ
From Idle Mode 1 ms typ
From Power-Down Mode 1 ms typ Osc. Active in Power-Down
300 ms typ Osc. Powered Down
POWER REQUIREMENTS
Power Supply Voltages
– AGND 2.7/3.6 V min/max AVDD = 3 V nom
AV
DD
– DGND 2.7/3.6 V min/max DVDD = 3 V nom
DV
DD
Power Supply Currents
Current (Normal Mode)
DI
DD
4.75/5.25 V min/max AV
4.75/5.25 V min DV
12
0.6 mA max DVDD = 3 V, 0.5 mA typ
= 5 V nom
DD
= 5 V nom
DD
0.75 mA max DVDD = 5 V, 0.6 mA typ
AD7719
REV. A
–5–
AD7719
Parameter AD7719B Unit Test Conditions
Power Supply Currents (Continued)
Current (Main ADC) 1.1 mA max AVDD = 3 V or 5 V, Buffered Mode,
AI
DD
0.55 mA max AV
Current (Aux ADC) 0.3 mA max AVDD = 3 V or 5 V, 0.25 mA typ
AI
DD
Current (Main and Aux ADC) 1.25 mA max AVDD = 3 V or 5 V, Main ADC Buffered,
AI
DD
(ADC Disable Mode)
DI
DD
13
0.35 mA max DVDD = 3 V, 0.25 mA typ
0.4 mA max DV
(ADC Disable Mode) 0.15 mA max AVDD = 3 V or 5 V
AI
DD
(Power-Down Mode) 10 µA max DVDD = 3 V, 32.768 kHz Osc. Running
DI
DD
2 µA max DV
30 µA max DV
8 µA max DV
AIDD (Power-Down Mode) 1 µA max AVDD = 3 V or 5 V
NOTES
1
Temperature range –40°C to +85°C.
2
Guaranteed by design and/or characterization data on production release.
3
System zero calibration will remove this error.
4
A calibration at any temperature will remove this drift error.
5
The main ADC is factory-calibrated with AVDD = DVDD = 4 V, TA = 25°C, REFIN1(+) – REFIN1(– ) = 2.5 V. If the user power supplies or temperature conditions
are significantly different from these, internal full-scale calibration will restore this error to the published specification. System calibration can be used to reduce this
error to the order of the noise. Full-scale error applies to both positive and negative full scale.
6
A system full-scale calibration will remove this error.
7
A typical gain error of ±10 µV results following a user self-calibration.
8
Simultaneous 50 Hz and 60 Hz rejection is achieved using 19.8 Hz (SF = 69) update rate. Normal mode rejection in this case is 60 dB min.
9
After a calibration if the analog input exceeds positive full scale, the converter will output all 1s. If the analog input is less than negative full scale, the device will
output all 0s.
10
FS = Full-Scale Input. FS = 1.024 × REFIN1/Gain on the main ADC, where REFIN1 = REFIN1(+) – REFIN1(–). FS = REFIN2 on the aux ADC when ARN = 1
in the aux ADC control register (AD1CON) and REFIN2/2 on the aux ADC when ARN = 0.
11
Input and output levels on the I/O Port are with respect to AVDD and AGND.
12
Normal mode refers to the case where both main and aux ADCs are running.
13
ADC disable is entered by setting both the AD0EN and AD1EN bits in the main and aux ADC control registers to a 0 and setting the mode bits (MD2, MD1,
MD0) in the mode register to non-0.
Specifications subject to change without notice.
0.85 mA typ
= 3 V or 5 V, Unbuffered Mode,
DD
0.45 mA typ
1 mA typ
= 5 V, 0.3 mA typ
DD
= 3 V, Oscillator Powered Down
DD
= 5 V, 32.768 kHz Osc. Running
DD
= 5 V, Oscillator Powered Down
DD
ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS
(TA = 25°C, unless otherwise noted.)
1
AVDD to AGND . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . –0.3 V to +7 V
to DGND . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . –0.3 V to +7 V
AV
DD
to AGND . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . –0.3 V to +7 V
DV
DD
DV
to DGND . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . –0.3 V to +7 V
DD
AGND to DGND
2
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . –20 mV to +20 mV
PWRGND to AGND . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . –20 mV to +20 mV
to DVDD . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . –5 V to +5 V
AV
DD
Analog Input Voltage to AGND . . . . –0.3 V to AV
Reference Input Voltage to AGND . . –0.3 V to AV
+0.3 V
DD
+0.3 V
DD
Total AIN/REFIN Current (Indefinite) . . . . . . . . . . . . 30 mA
Digital Input Voltage to DGND . . . . –0.3 V to DV
Digital Output Voltage to DGND . . . –0.3 V to DV
+0.3 V
DD
+0.3 V
DD
Operating Temperature Range . . . . . . . . . . . –40°C to +85°C
Storage Temperature Range . . . . . . . . . . . . –65°C to +150°C
ORDERING GUIDE
Model Temperature Range Package Description Package Option
AD7719BR –40°C to +85°C SOIC R-28
AD7719BRU –40°C to +85°CTSSOP RU-28
EVAL-AD7719EB Evaluation Board
Junction Temperature . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 150°C
SOIC Package
θJA Thermal Impedance . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 71.4°C/W
Thermal Impedance . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23°C/W
θ
JC
TSSOP Package
Thermal Impedance . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 97.9°C/W
θ
JA
Thermal Impedance . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14°C/W
θ
JC
Lead Temperature, Soldering
Vapor Phase (60 sec) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 215°C
Infrared (15 sec) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 220°C
NOTES
1
Stresses above those listed under Absolute Maximum Ratings may cause permanent damage to the device. This is a stress rating only; functional operation of the
device at these or any other conditions above those listed in the operational
sections of this specification is not implied. Exposure to absolute maximum rating
conditions for extended periods may affect device reliability.
2
AGND and DGND are connected internally within the AD7719.
–6–
REV. A
AD7719
1, 2
TIMING CHARACTERISTICS
AGND = DGND = 0 V; X
Parameter (B Version) Unit Conditions/Comments
t
1
t
2
Read Operation
t
3
t
4
4
t
5
4, 5
t
5A
t
6
t
7
t
8
6
t
9
t
10
Write Operation
t
11
t
12
t
13
t
14
t
15
t
16
NOTES
1
Sample tested during initial release to ensure compliance. All input signals are specified with tR = tF = 5 ns (10% to 90% of DVDD) and timed from a voltage level of 1.6 V.
2
See Figures 2 and 3.
3
SCLK active edge is falling edge of SCLK.
4
These numbers are measured with the load circuit of Figure 1 and defined as the time required for the output to cross the VOL or VOH limits.
5
This specification only comes into play if CS goes low while SCLK is low. It is required primarily for interfacing to DSP machines.
6
These numbers are derived from the measured time taken by the data output to change 0.5 V when loaded with the circuit of Figure 1. The measured number is then
extrapolated back to remove effects of charging or discharging the 50 pF capacitor. This means that the times quoted in the Timing Characteristics are the true bus
relinquish times of the part and as such are independent of external bus loading capacitances.
7
RDY returns high after a read of both ADCs. The same data can be read again, if required, while RDY is high, although care should be taken that subsequent reads
do not occur close to the next output update.
Specifications subject to change without notice.
= 32.768 kHz; Input Logic 0 = 0 V, Logic 1 = DVDD, unless otherwise noted.)
TAL
Limit at T
32.768 kHz typ Crystal Oscillator Frequency
50 ns min RESET Pulsewidth
0 ns min RDY to CS Setup Time
0 ns min CS Falling Edge to SCLK Active Edge Setup Time
0 ns min SCLK Active Edge to Data Valid Delay
60 ns max DVDD = 4.75 V to 5.25 V
80 ns max DV
0 ns min CS Falling Edge to Data Valid Delay
60 ns max DVDD = 4.75 V to 5.25 V
80 ns max DV
100 ns min SCLK High Pulsewidth
100 ns min SCLK Low Pulsewidth
0 ns min CS Rising Edge to SCLK Inactive Edge Hold Time
10 ns min Bus Relinquish Time after SCLK Inactive Edge
80 ns max
100 ns max SCLK Active Edge to RDY High
0 ns min CS Falling Edge to SCLK Active Edge Setup Time
30 ns min Data Valid to SCLK Edge Setup Time
25 ns min Data Valid to SCLK Edge Hold Time
100 ns min SCLK High Pulsewidth
100 ns min SCLK Low Pulsewidth
0 ns min CS Rising Edge to SCLK Edge Hold Time
(AVDD = 2.7 V to 3.6 V or AVDD = 4.75 V to 5.25 V; DVDD = 2.7 V to 3.6 V or DVDD = 4.75 V to 5.25 V;
, T
MIN
MAX
= 2.7 V to 3.6 V
DD
= 2.7 V to 3.6 V
DD
3
3, 7
3
3
3
3
3
I
(1.6mA WITH DVDD = 5V
TO OUTPUT
PIN
50pF
SINK
100A WITH DV
I
(200A WITH DVDD = 5V
SOURCE
100A WITH DV
1.6V
DD
= 3V)
DD
= 3V)
Figure 1. Load Circuit for Timing Characterization
CAUTION
ESD (electrostatic discharge) sensitive device. Electrostatic charges as high as 4000 V readily
accumulate on the human body and test equipment and can discharge without detection. Although
the AD7719 features proprietary ESD protection circuitry, permanent damage may occur on
devices subjected to high energy electrostatic discharges. Therefore, proper ESD precautions are
recommended to avoid performance degradation or loss of functionality.
REV. A
–7–
WARNING!
ESD SENSITIVE DEVICE
AD7719
DIGITAL INTERFACE
As previously outlined, the AD7719’s programmable functions are
controlled using a set of on-chip registers. Data is written to these
registers via the part’s serial interface; read access to the on-chip
registers is also provided by this interface. All communications to
the part must start with a write operation to the Communications
register. After power-on or
RESET
, the device expects a write to
its Communications register. The data written to this register
determines whether the next operation to the part is a read or a
write operation and also determines to which register this read
or write operation occurs. Therefore, write access to any of the
other registers on the part starts with a write operation to the
Communications register followed by a write to the selected
register. A read operation from any other register on the part
(including the output data register) starts with a write operation
to the Communications register followed by a read operation
from the selected register.
The AD7719’s serial interface consists of five signals: CS, SCLK,
DIN, DOUT, and RDY. The DIN line is used for transferring
data into the on-chip registers while the DOUT line is used for
accessing data from the on-chip registers. SCLK is the serial
clock input for the device, and all data transfers (either on DIN
or DOUT) take place with respect to this SCLK signal. The
RDY line is used as a status signal to indicate when data is ready
to be read from the AD7719’s data register. RDY goes low when a
new data-word is available in the output register of either the
main or aux ADCs. It is reset high when a read operation from
the data register is complete. It also goes high prior to the updating
of the output register to indicate when not to read from the device
to ensure that a data read is not attempted while the register is
being updated. CS is used to select the device. It can be used to
decode the AD7719 in systems where a number of parts are
connected to the serial bus.
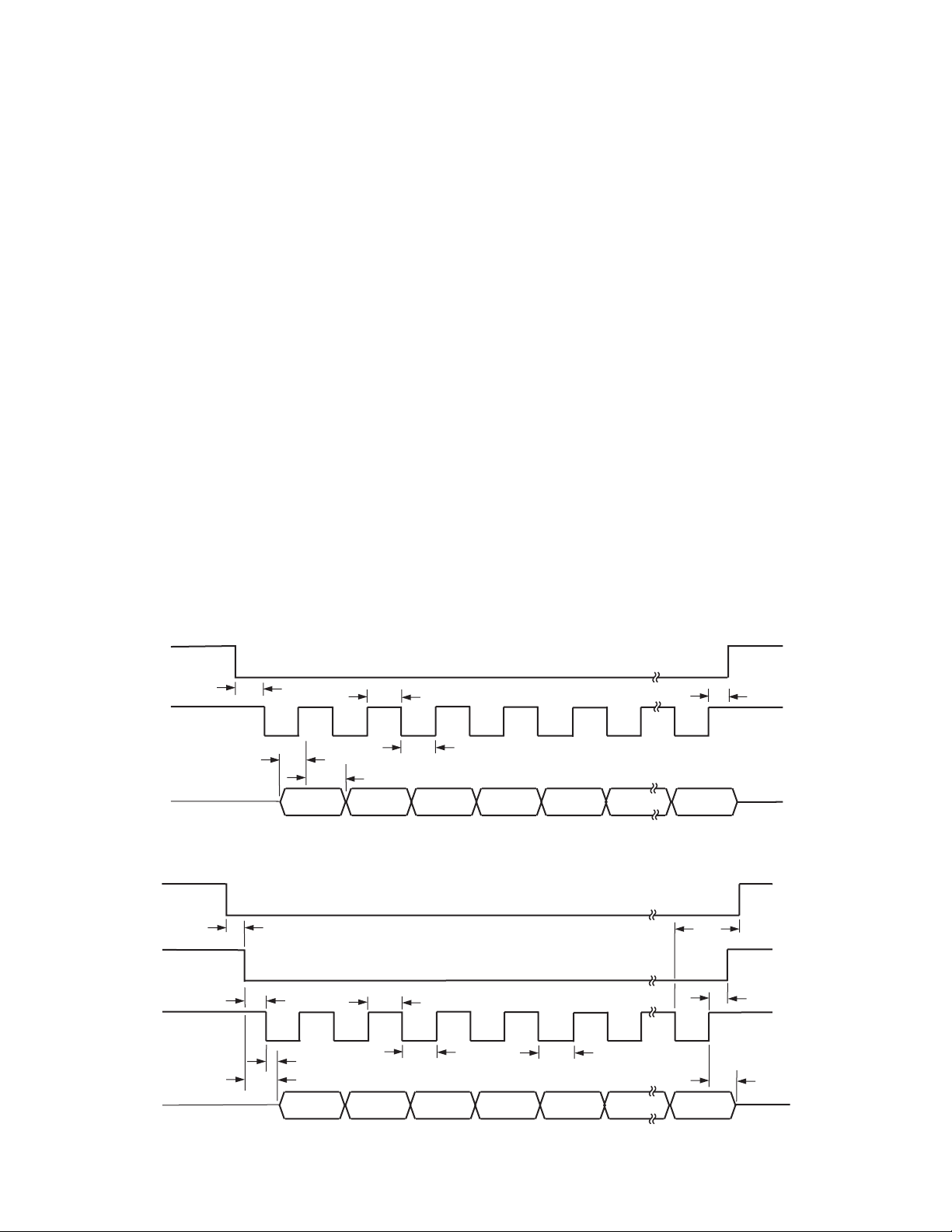
Figures 2 and 3 show timing diagrams for interfacing to the
AD7719 with CS used to decode the part. Figure 3 is for a read
operation from the AD7719’s output shift register while Figure 2
shows a write operation to the input shift register. It is possible
to read the same data twice from the output register even though
the RDY line returns high after the first read operation. Care must
be taken, however, to ensure that the read operations have been
completed before the next output update is about to take place.
The AD7719 serial interface can operate in 3-wire mode by tying
the CS input low. In this case, the SCLK, DIN, and DOUT lines
are used to communicate with the AD7719, and the status of
RDY bits (RDY0 and RDY1) can be obtained by interrogating
the STATUS register. This scheme is suitable for interfacing to
microcontrollers. If CS is required as a decoding signal, it can
be generated from a port bit. For microcontroller interfaces, it is
recommended that the SCLK idles high between data transfers.
The AD7719 can also be operated with CS used as a frame synchronization signal. This scheme is suitable for DSP interfaces.
In this case, the first bit (MSB) is effectively clocked out by CS
since CS would normally occur after the falling edge of SCLK
in DSPs. The SCLK can continue to run between data transfers
provided the timing numbers are obeyed.
SCLK
RDY
SCLK
DOUT
CS
CS
DIN
t
11
t
12
t
13
MSB
t
14
t
15
LSB
t
16
Figure 2. Write Cycle Timing Diagram
t
3
t
4
t
5
t
5A
MSB
t
6
t
7
t
6
t
LSB
10
t
8
t
9
Figure 3. Read Cycle Timing Diagram
–8–
REV. A
AD7719
The serial interface can be reset by exercising the RESET input
on the part. It can also be reset by writing a series of 1s on the
DIN input. If a logic 1 is written to the AD7719 DIN line for at
least 32 serial clock cycles, the serial interface is reset. This ensures
that in 3-wire systems, if the interface gets lost, either via a software
error or by some glitch in the system, it can be reset back to a
known state. This state returns the interface to where the AD7719
is expecting a write operation to its Communications register. This
operation resets the contents of all registers to their power-on
reset values.
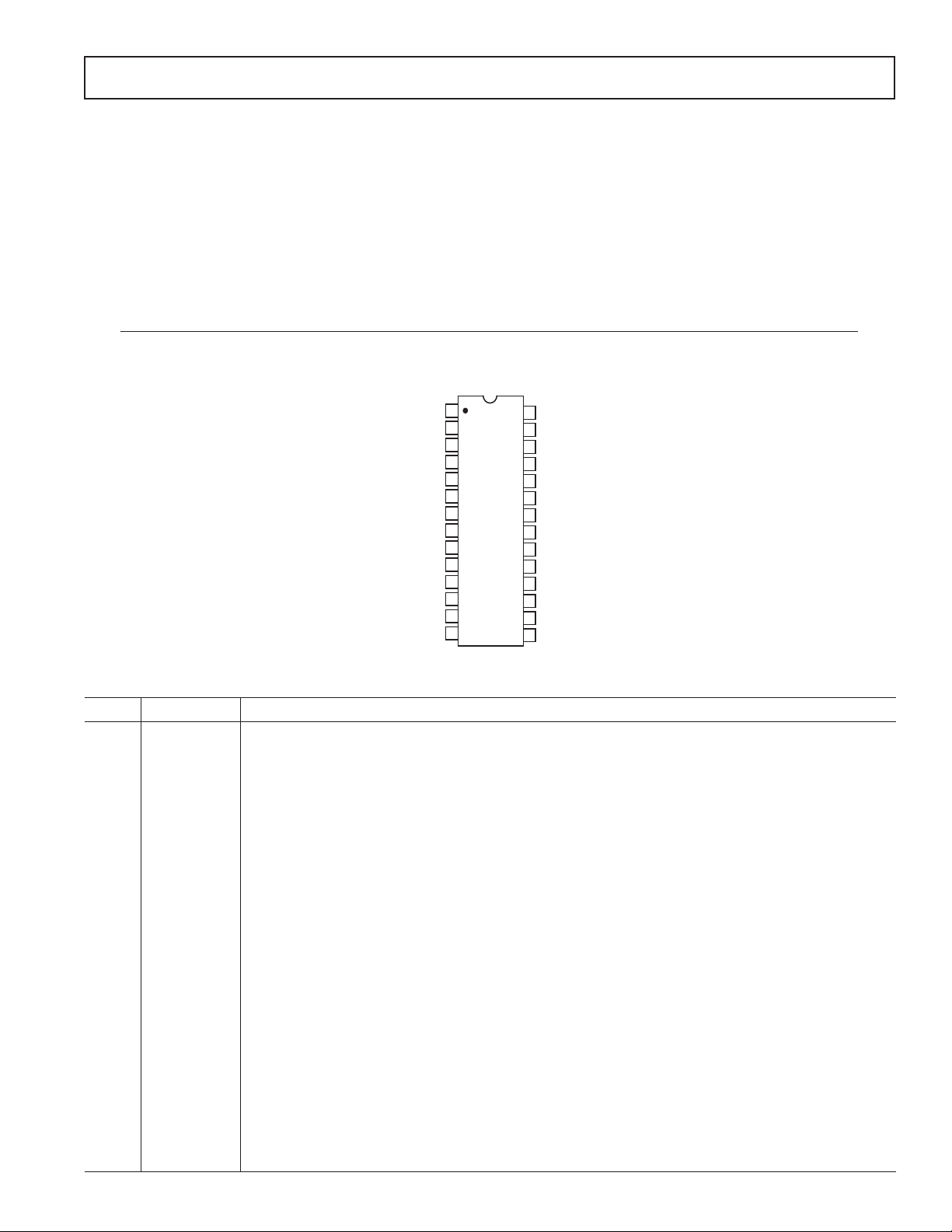
PIN CONFIGURATION
1
IOUT1
2
IOUT2
3
AV
DD
4
AGND
AIN1
AIN2
AIN3
AIN4
AIN5
AIN6
REFIN2
10
12
13
14
P4
5
AD7719
6
TOP VIEW
(Not to Scale)
7
8
9
11
REFIN1(–)
REFIN1(+)
Some microprocessor or microcontroller serial interfaces have a
single serial data line. In this case, it is possible to connect the
AD7719’s DATA OUT and DATA IN lines together and connect
them to the single data line of the processor. A 10 kΩ pull-up
resistor should be used on this single data line. In this case, if the
interface gets lost, because the read and write operations share
the same line, the procedure to reset it to a known state is
somewhat different than previously described. It requires a read
operation of 24 serial clocks followed by a write operation where
a logic 1 is written for at least 32 serial clock cycles to ensure
that the serial interface is back in a known state.
XTAL1
28
XTAL2
27
DV
26
DD
DGND
25
DIN
24
DOUT
23
22
RDY
21
CS
SCLK
20
19
RESET
P1/SW1
18
PWRGND
17
16
P2/SW2
P3
15
PIN FUNCTION DESCRIPTIONS
Pin No. Mnemonic Function
1 IOUT1 Output for Internal 200 µA Excitation Current Source. Current source IEXC1 and/or IEXC2 can be
switched to this output.
2 IOUT2 Output for Internal 200 µA Excitation Current Source. Current source IEXC1 and/or IEXC2 can be
switched to this output.
3AV
DD
Analog Supply Voltage.
4 AGND Analog Ground.
5 REFIN1(–) Negative Reference Input for Main ADC Channel. This reference input can lie anywhere between AGND
and AV
6 REFIN1(+) Positive Reference Input for Main ADC Channel. REFIN1(+) can lie anywhere between AV
DD
– 1 V.
DD
and
AGND + 1 V. The nominal reference voltage (REFIN1(+) – REFIN1(–)) is 2.5 V, but the part is functional
with a reference range from 1 V to AV
DD
.
7 AIN1 Analog Input. AIN1 is dedicated to the main channel.
8 AIN2 Analog Input. AIN2 is dedicated to the main channel.
9 AIN3 Analog Input. AIN3 can be multiplexed to either the main or auxiliary channel.
10 AIN4 Analog Input. AIN4 can be multiplexed to either the main or auxiliary channel.
11 AIN5 Analog Input. AIN5 is dedicated to the auxiliary channel and is referenced to AIN6 or AGND.
12 AIN6 Analog Input. AIN6 is dedicated to the auxiliary channel. It forms a differential input pair with AIN5 in
fully differential input mode or is referenced to AGND in pseudodifferential mode.
13 REFIN2 Single-Ended Reference Input for Auxiliary Channel. The nominal input reference is 2.5 V. The auxiliary
channel will function with an input reference range from 1 V to AV
14 P4 General-Purpose I/O Bit. The input and output voltage levels are referenced to AV
DD
.
and AGND.
DD
15 P3 General-Purpose I/O Bit. The input and output voltage levels are referenced to AVDD and AGND.
REV. A
–9–
AD7719
PIN FUNCTION DESCRIPTIONS (continued)
Pin No. Mnemonic Function
16 P2/SW2 Dual-Purpose Pin. It can act as a general-purpose output (P2) bit referenced between AV
or as a low-side power switch (SW2) to PWRGND.
17 PWRGND Ground Point for the Low-Side Power Switches SW2 and SW1. PWRGND must be tied to AGND.
18 P1/SW1 Dual-Purpose Pin. It can act as a general-purpose output (P1) bit referenced between AV
or as a low-side power switch (SW1) to PWRGND.
19 RESET Digital Input Used to Reset the ADC to Its Power-On Reset Status. This pin has a weak pull-up internally
DD
.
to DV
20 SCLK Serial Clock Input for Data Transfers to and from the ADC. The SCLK has a Schmitt-triggered input,
making the interface suitable for opto-isolated applications. The serial clock can be continuous with all
data transmitted in a continuous train of pulses. Alternatively, it can be a noncontinuous clock with the
information being transmitted to or from the AD7719 in smaller batches of data. A weak pull-up to DV
is provided on the SCLK input.
21 CS Chip Select Input. This is an active low logic input used to select the AD7719. CS can be used to select
the AD7719 in systems with more than one device on the serial bus or as a frame synchronization signal in
communicating with the device. CS can be hardwired low, allowing the AD7719 to be operated in 3-wire
mode with SCLK, DIN, and DOUT used to interface with the device. A weak pull-up to DV
on the CS input.
22 RDY RDY is a logic low status output from the AD7719. RDY is low if either the main ADC or auxiliary ADC
channel has valid data in its data register. This output returns high on completion of a read operation
from the data register. If data is not read, RDY will return high prior to the next update, indicating to the
user that a read operation should not be initiated. The RDY pin also returns low following the completion
of a calibration cycle. The RDY pin is effectively the digital NOR function of the RDY0 and RDY1 bits in
the Status register. If one of the ADCs is disabled, the RDY pin reflects the active ADC. RDY does not
return high after a calibration until the mode bits are written to, enabling a new conversion or calibration.
Since the RDY pin provides information on both the main and aux ADCs, when either the main or aux
ADC is disabled, it is recommended to immediately read its data register to ensure that its RDY bit goes
inactive and releases the RDY pin to indicate output data updates on the remaining active ADC.
23 DOUT Serial Data Output Accessing the Output Shift Register of the AD7719. The output shift register can
contain data from any of the on-chip data, calibration, or control registers.
24 DIN Serial Data Input Accessing the Input Shift Register on the AD7719. Data in this shift register is transferred
to the calibration or control registers within the ADC depending on the selection bits of the Communications
register. A weak pull-up to DV
is provided on the DIN input.
DD
25 DGND Ground Reference Point for the Digital Circuitry.
26 DV
DD
Digital Supply Voltage, 3 V or 5 V Nominal.
27 XTAL2 Output from the 32 kHz Crystal Oscillator Inverter.
28 XTAL1 Input to the 32 kHz Crystal Oscillator Inverter.
and AGND
DD
and AGND
DD
is provided
DD
DD
–10–
REV. A
Typical Performance Characteristics–
16
040302010 50 10090807060
24
22
20
18
26
UPDATE RATE (Hz)
NO MISSING CODES (Min)
110
TEMPERATURE SENSOR ( C)
1400
1200
0
503010 20 40
HITS
800
600
400
200
1000
THE AMBIENT
TEMPERATURE VARIES
FROM 25C TO 30C
WHILE RECORDING
THE DATA FROM
THE DEVICES.
MAIN CAL ACC. @ 4V (V)
1200
0
200–20 –10 10
HITS
800
600
400
200
1000
–30
8389600
8389400
8389200
8389000
8388800
8388600
CODE READ
8388400
8388200
8388000
0 1000100
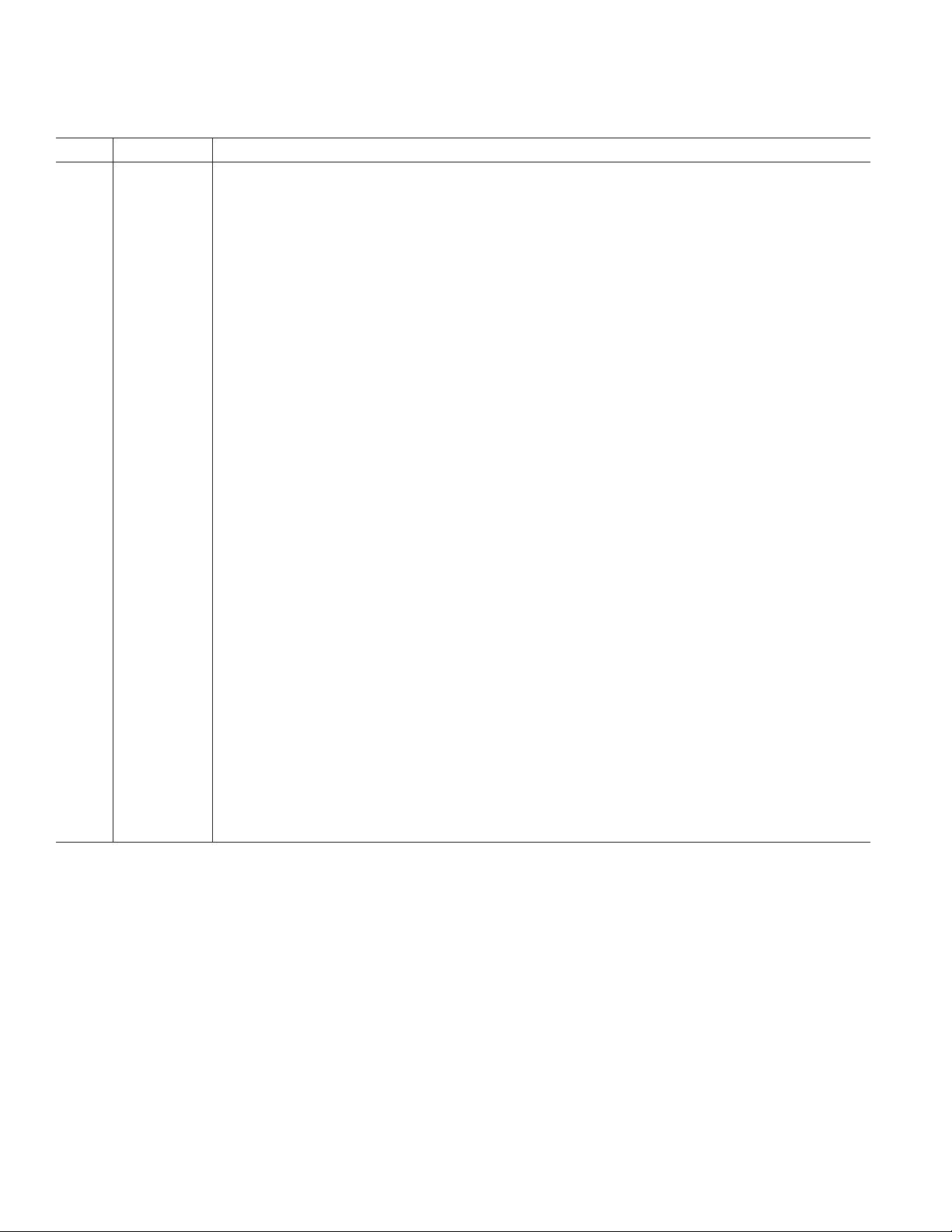
TPC 1. Typical Noise Plot on ±20 mV Input Range with
19.79 Hz Update Rate
9
8
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
0
200 300
= DVDD = 5V
AV
DD
INPUT RANGE = 20mV
REFIN1(+)–REFIN1(–) = 2.5V
UPDATE RATE = 19.79Hz
400 500 600 700 800 900
READING NO.
MAIN ADC IN BUFFERED MODE
RMS NOISE = 0.58V rms
= 25C
T
A
V
= 2.5V
REF
AD7719
TPC 4. No-Missing-Codes Performance
RMS NOISE (V)
REV. A
8388382
8388039
8388499
8388449
8388579
8388547
8388615
8388657
8388687
8388721
8388754
8388805
8388779
8388906
8388874
8388841
TPC 2. Noise Distribution Histogram
3.0
REF
= 25C
A
= 2.5V
2.56V RANGE
20mV RANGE
V
(V)
REF
2.5
2.0
AVDD = DVDD = 5V
V
1.5
INPUT RANGE = 2.56V
UPDATE RATE = 19.79Hz
T
1.0
0.5
0
1.0 3.02.52.01.5 3.5 5.04.54.0
TPC 3. RMS Noise vs. Reference Input
8388985
8388941
8389033
8389110
TPC 5. Temperature Sensor Accuracy
TPC 6. Full-Scale Error Distribution
–11–
AD7719
AVDD = DVDD = 5V
= 25C
T
A
V
DD
OSCILLATOR
TIME BASE = 100ms/DIV
TRACE 1 = TRACE 2 = 2V/DIV
TPC 7. Typical Oscillator Power-Up
DUAL-CHANNEL ADC CIRCUIT INFORMATION
Overview
The AD7719 incorporates two independent Σ-∆ ADC channels
(main and auxiliary) with on-chip digital filtering intended for
the measurement of wide dynamic range, low frequency signals
such as those in weigh-scale, strain gage, pressure transducer, or
temperature measurement applications.
Main Channel
This channel is intended to convert the primary sensor input.
This channel can be operated in buffered or unbuffered mode, and
can be programmed to have one of eight input voltage ranges
from ±20 mV to ±2.56 V. This channel can be configured as
either two fully differential inputs (AIN1/AIN2 and AIN3/AIN4)
or three pseudodifferential input channels (AIN1/AIN4, AIN2/
AIN4, and AIN3/AIN4). Buffering the input channel means that
the part can accommodate significant source impedances on the
analog input and that R, C filtering (for noise rejection or RFI
reduction) can be placed on the analog inputs if required. Operating in unbuffered mode leads to lower power consumption in low
power applications, but care must be exercised in unbuffered mode
because source impedances can introduce gain errors. The main
ADC also features sensor burnout currents that can be switched
on and off. These currents can be used to check that a transducer
is still operational before attempting to take measurements.
The ADC employs a Σ-∆ conversion technique to realize up to
24 bits of no-missing-codes performance. The Σ-∆ modulator
converts the sampled input signal into a digital pulse train whose
duty cycle contains the digital information. A Sinc
3
programmable
low-pass filter is then employed to decimate the modulator output
data stream to give a valid data conversion result at programmable output rates from 5.35 Hz (186.77 ms) to 105.03 Hz
(9.52 ms). A chopping scheme is also employed to minimize
ADC channel offset errors. A block diagram of the main ADC
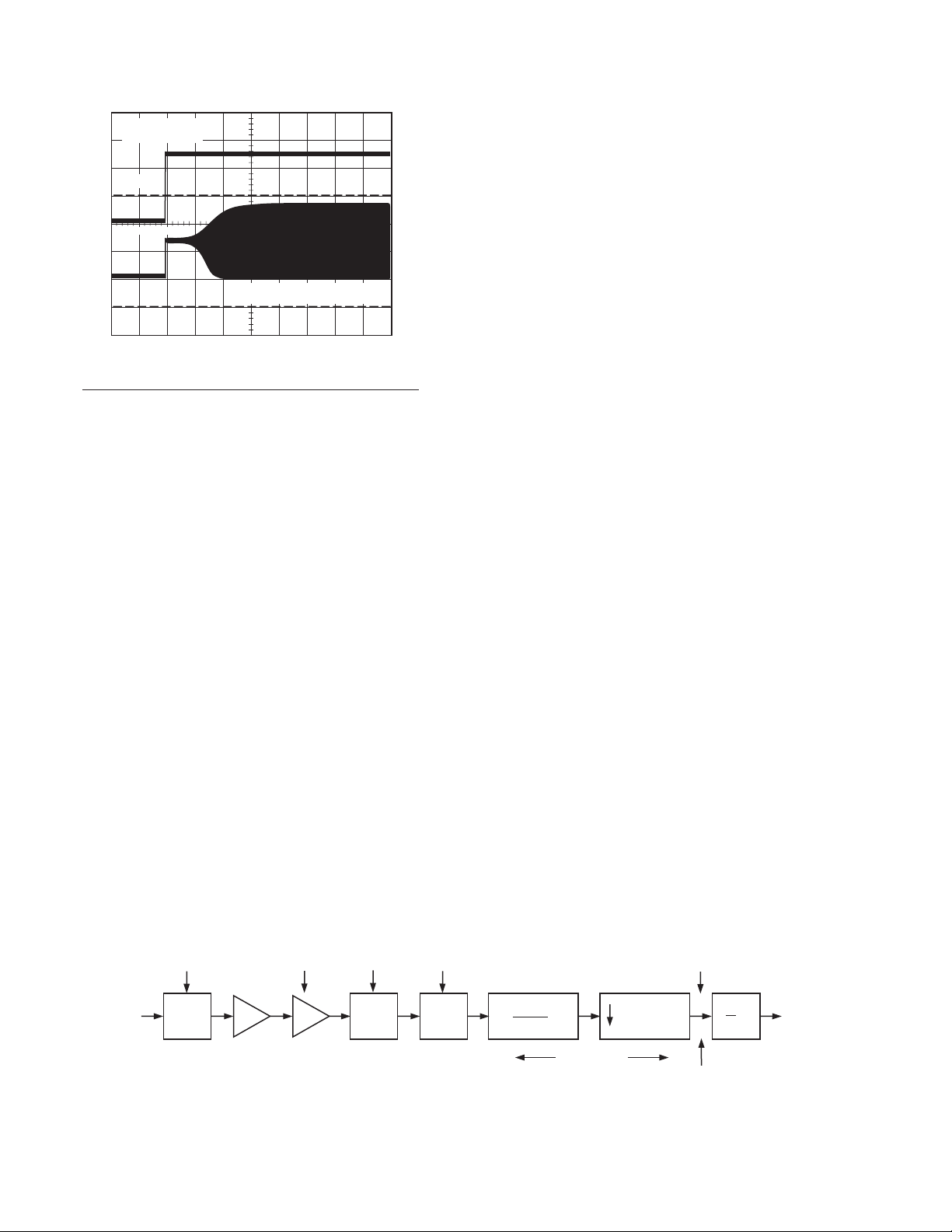
input channel is shown in Figure 4. The sampling frequency of
the modulator loop is many times higher than the bandwidth of
the input signal. The integrator in the modulator shapes the
quantization noise (which results from the analog-to-digital
conversion) so that the noise is pushed toward one-half of the
modulator frequency. The output of the Σ-∆ modulator feeds
directly into the digital filter. The digital filter then band-limits
the response to a frequency significantly lower than one-half of
the modulator frequency. In this manner, the 1-bit output of the
comparator is translated into a band-limited, low noise output
from the AD7719 ADC. The AD7719 filter is a low-pass, Sinc
or (SIN(x)/x)
3
filter whose primary function is to remove the
3
,
quantization noise introduced at the modulator. The cutoff
frequency and decimated output data rate of the filter are programmable via the SF word loaded to the filter register.
A chopping scheme is employed where the complete signal chain is
chopped, resulting in excellent dc offset and offset drift specifications, and is extremely beneficial in applications where drift, noise
rejection, and optimum EMI rejection are important factors.
With chopping, the ADC repeatedly reverses its inputs. The
decimated digital output words from the Sinc
3
filters therefore
have a positive offset and negative offset term included. As a result,
a final summing stage is included so that each output word from
the filter is summed and averaged with the previous filter output
to produce a new valid output result to be written to the ADC
data register.
Auxiliary Channel
The Auxiliary (Aux) channel is intended to convert supplementary
inputs such as those from a cold junction diode or thermistor.
This channel is unbuffered and has an input range of ±REFIN2
or ±REFIN2/2, determined by the ARN bit in the auxiliary ADC
control register (AD1CON). AIN3 and AIN4 can be multiplexed
into the auxiliary channel as single-ended inputs with respect to
AGND, while AIN5 and AIN6 can operate as a differential
input pair. With AIN6 tied to AGND, AIN5 can be operated as
an additional single-ended input. A block diagram of the auxiliary
ADC channel is shown in Figure 5.
ANALOG
INPUT
f
CHOP
MUX
BUF
f
IN
PGA
f
MOD
-
MOD0
f
CHOP
XOR
(
8 SF
1
3
)
SINC3 FILTER
Figure 4. Main ADC Channel Block Diagram
–12–
3
(8 SF )
f
ADC
AIN + V
AIN – V
1
2
OS
OS
DIGITAL
OUTPUT
REV. A
 Loading...
Loading...