Low Cost, Low Power CMOS
a
General-Purpose Dual Analog Front End
FEATURES
Two 16-Bit A/D Converters
Two 16-Bit D/A Converters
Programmable Input/Output Sample Rates
78 dB ADC SNR
77 dB DAC SNR
64 kS/s Maximum Sample Rate
–90 dB Crosstalk
Low Group Delay (25 s Typ per ADC Channel,
50 s Typ per DAC Channel)
Programmable Input/Output Gain
Flexible Serial Port which Allows Up to Four Dual
Codecs to be Connected in Cascade Giving Eight
I/O Channels
Single (+2.7 V to +5.5 V) Supply Operation
73 mW Typ Power Consumption at 3.0 V
On-Chip Reference
28-Lead SOIC and 44-Lead LQFP Packages
APPLICATIONS
General Purpose Analog I/O
Speech Processing
Cordless and Personal Communications
Telephony
Active Control of Sound and Vibration
Data Communications
Wireless Local Loop
VFBP1
VINP1
VINN1
VFBN1
VOUTP1
VOUTN1
REFOUT
REFCAP
VFBP2
VINP2
VINN2
VFBN2
VOUTP2
VOUTN2
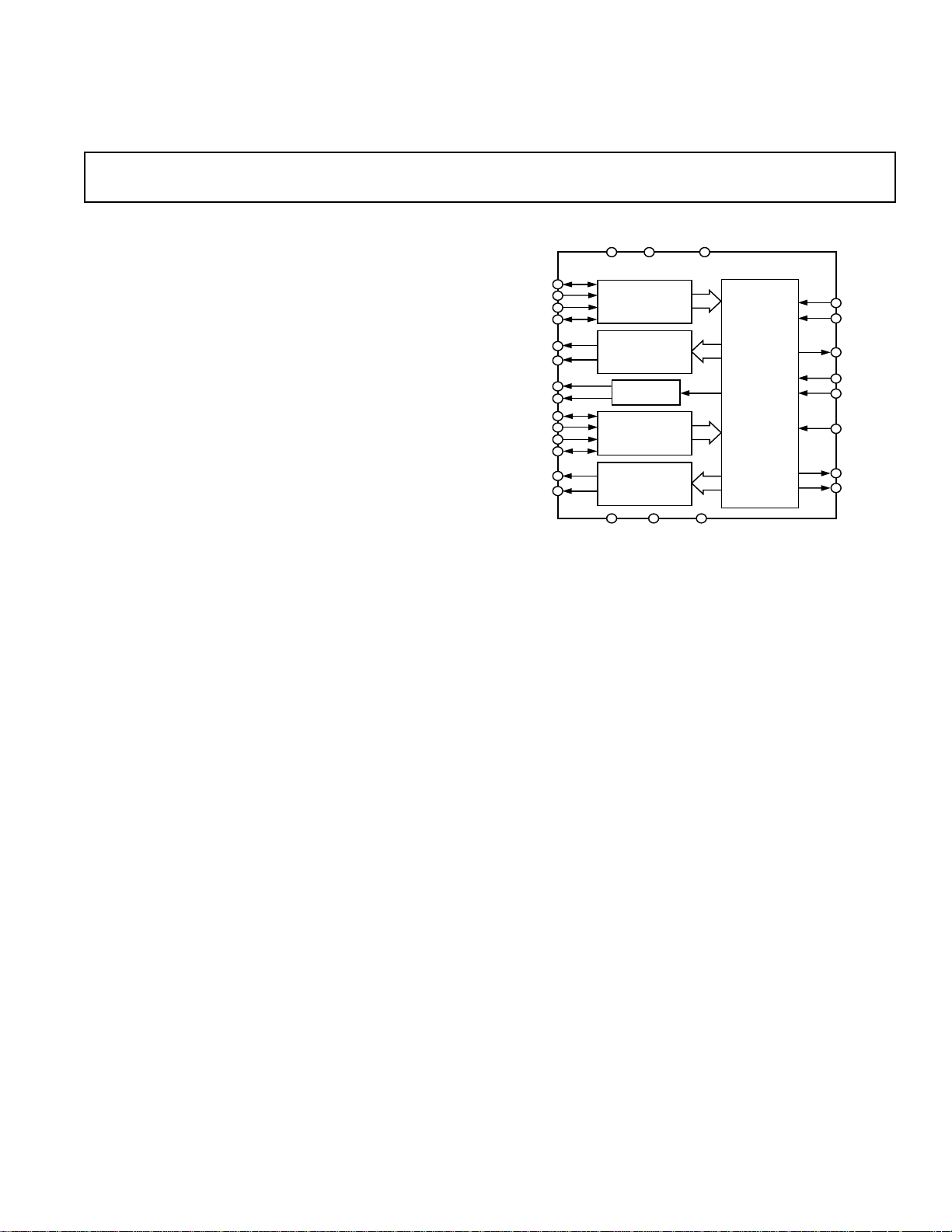
AD73322
FUNCTIONAL BLOCK DIAGRAM
AVDD1 AVDD2
ADC CHANNEL 1
DAC CHANNEL 1
REFERENCE
ADC CHANNEL 2
DAC CHANNEL 2
AGND1 AGND2 DGND
DVDD
AD73322
SPORT
SDI
SDIFS
SCLK
SE
RESET
MCLK
SDOFS
SDO
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
The AD73322 is a dual front-end processor for general-purpose
applications including speech and telephony. It features two
16-bit A/D conversion channels and two 16-bit D/A conversion
channels. Each channel provides 77␣ dB signal-to-noise ratio
over a voiceband signal bandwidth. It also features an input-tooutput gain network in both the analog and digital domains.
This is featured on both codecs and can be used for impedance
matching or scaling when interfacing to Subscriber Line Interface Circuits (SLICs).
The AD73322 is particularly suitable for a variety of applications in the speech and telephony area, including low bit rate,
high quality compression, speech enhancement, recognition, and
synthesis. The low group delay characteristic of the part makes
it suitable for single or multichannel active control applications.
REV. B
Information furnished by Analog Devices is believed to be accurate and
reliable. However, no responsibility is assumed by Analog Devices for its
use, nor for any infringements of patents or other rights of third parties
which may result from its use. No license is granted by implication or
otherwise under any patent or patent rights of Analog Devices.
The A/D and D/A conversion channels feature programmable
input/output gains with ranges of 38 dB and 21 dB respectively.
An on-chip reference voltage is included to allow single-supply
operation. This reference is programmable to accommodate
either 3 V or 5 V operation.
The sampling rate of the codecs is programmable with four
separate settings, offering 64 kHz, 32 kHz, 16 kHz and 8 kHz
sampling rates (from a master clock of 16.384 MHz).
A serial port (SPORT) allows easy interfacing of single or cascaded devices to industry standard DSP engines. The SPORT
transfer rate is programmable to allow interfacing to both fast
and slow DSP engines.
The AD73322 is available in 28-lead SOIC and 44-lead LQFP
packages.
One Technology Way, P.O. Box 9106, Norwood, MA 02062-9106, U.S.A.
Tel: 781/329-4700 World Wide Web Site: http://www.analog.com
Fax: 781/326-8703 © Analog Devices, Inc., 2000
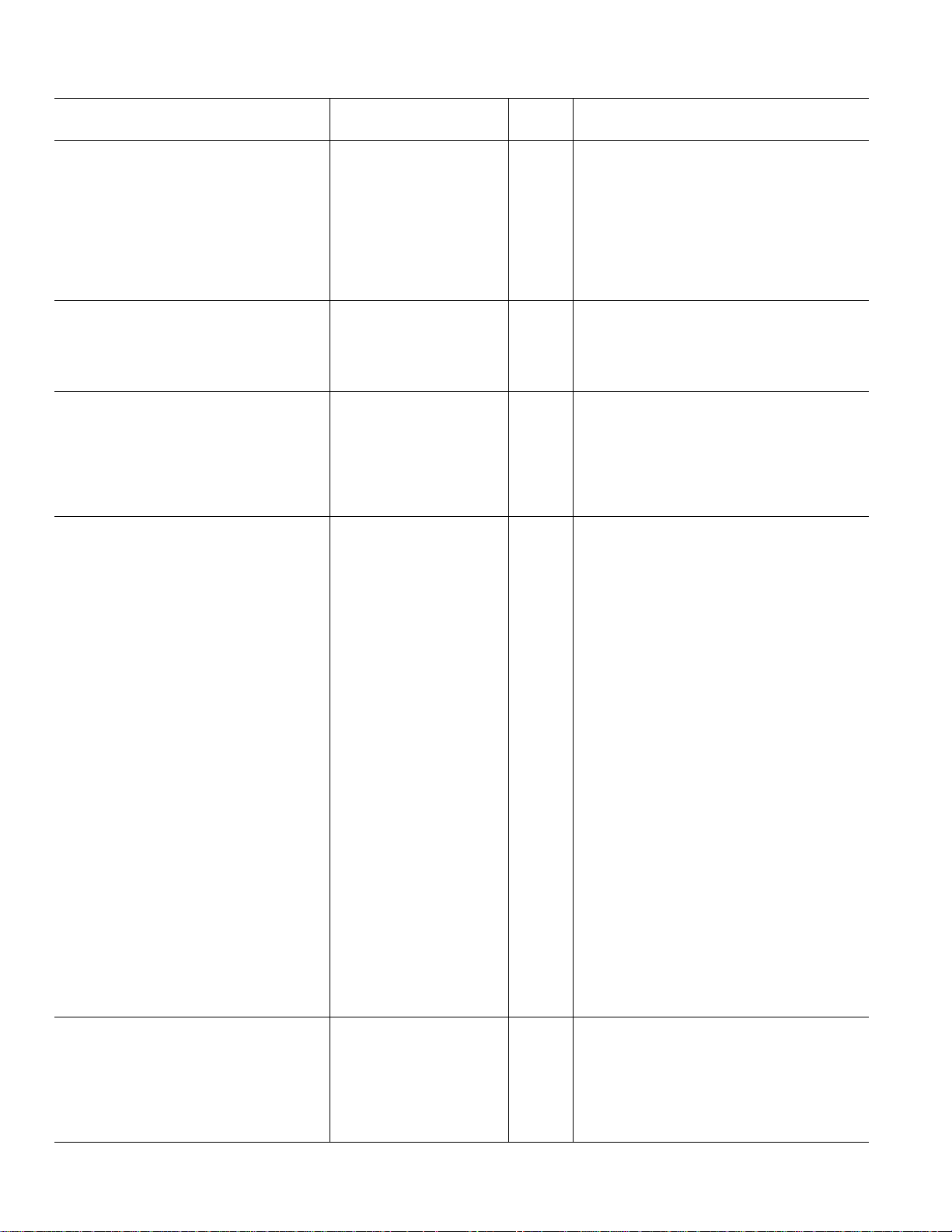
AD73322–SPECIFICATIONS
(AVDD = +3 V ⴞ 10%; DVDD = +3 V ⴞ 10%; DGND = AGND = 0 V, f
1
16.384 MHz, f
= 64 kHz; TA = T
SAMP
MIN
to T
, unless otherwise noted)
MAX
DMCLK
=
AD73322A
Parameter Min Typ Max Units Test Conditions/Comments
REFERENCE 5VEN = 0
REFCAP
Absolute Voltage, VREFCAP 1.08 1.2 1.32 V
REFCAP TC 50 ppm/°C 0.1 µF Capacitor Required from
REFOUT REFCAP to AGND2
Typical Output Impedance 130 Ω
Absolute Voltage, V
REFOUT
1.08 1.2 1.32 V Unloaded
Minimum Load Resistance 1 kΩ
Maximum Load Capacitance 100 pF
INPUT AMPLIFIER
Offset ±1.0 mV
Maximum Output Swing 1.578 V Max Output Swing = (1.578/1.2) × VREFCAP
Feedback Resistance 50 Ω f
= 32 kHz
C
Feedback Capacitance 100 pF
ANALOG GAIN TAP
Gain at Maximum Setting +1
Gain at Minimum Setting –1
Gain Resolution 5 Bits Gain Step Size = 0.0625
Gain Accuracy ±1.0 % Output Unloaded
Settling Time 1.0 µs Tap Gain Change of –FS to +FS
Delay 0.5 µs
ADC SPECIFICATIONS 5VEN = 0
Maximum Input Range at VIN
2, 3
1.578 V p-p Measured Differentially
–2.85 dBm Max Input = (1.578/1.2) × VREFCAP
Nominal Reference Level at VIN 1.0954 V p-p Measured Differentially
(0 dBm0) –6.02 dBm
Absolute Gain
PGA = 0 dB –0.5 0.4 +1.2 dB 1.0 kHz, 0 dBm0
PGA = 38 dB –1.5 –0.7 +0.1 dB 1.0 kHz, 0 dBm0
Gain Tracking Error ±0.1 dB 1.0 kHz, +3 dBm0 to –50 dBm0
Signal to (Noise + Distortion) Refer to Figure 5
PGA = 0 dB 72 78 dB 300 Hz to 3400 Hz; f
78 dB 300 Hz to 3400 Hz; f
55 57 dB 0 Hz to f
SAMP
/2; f
SAMP
PGA = 38 dB 52 56 dB 300 Hz to 3400 Hz; f
= 64 kHz
SAMP
= 8 kHz
SAMP
= 64 kHz
= 64 kHz
SAMP
Total Harmonic Distortion
PGA = 0 dB –84 –73 dB 300 Hz to 3400 Hz; f
PGA = 38 dB –70 –60 dB 300 Hz to 3400 Hz; f
SAMP
SAMP
= 64 kHz
= 64 kHz
Intermodulation Distortion –65 dB PGA = 0 dB
Idle Channel Noise –71 dBm0 PGA = 0 dB
Crosstalk ADC-to-DAC –100 dB ADC Input Signal Level: 1.0 kHz, 0 dBm0
DAC Input at Idle
ADC-to-ADC –100 dB ADC1 Input Signal Level: 1.0 kHz, 0 dBm0
ADC2 Input at Idle. Input Amplifiers Bypassed
–70 dB Input Amplifiers Included in Input Channel
DC Offset –30 +10 +45 mV PGA = 0 dB
Power Supply Rejection –65 dB Input Signal Level at AVDD and DVDD
Group Delay
4, 5
Input Resistance at PGA
2, 4, 6
25 µs
20 kΩ Input Amplifiers Bypassed
Pins: 1.0 kHz, 100 mV p-p Sine Wave
DIGITAL GAIN TAP
Gain at Maximum Setting +1
Gain at Minimum Setting –1
Gain Resolution 16 Bits Tested to 5 MSBs of Settings
Delay 25 µs Includes DAC Delay
Settling Time 100 µs Tap Gain Change from –FS to +FS; Includes
DAC Settling Time
–2–
REV. B
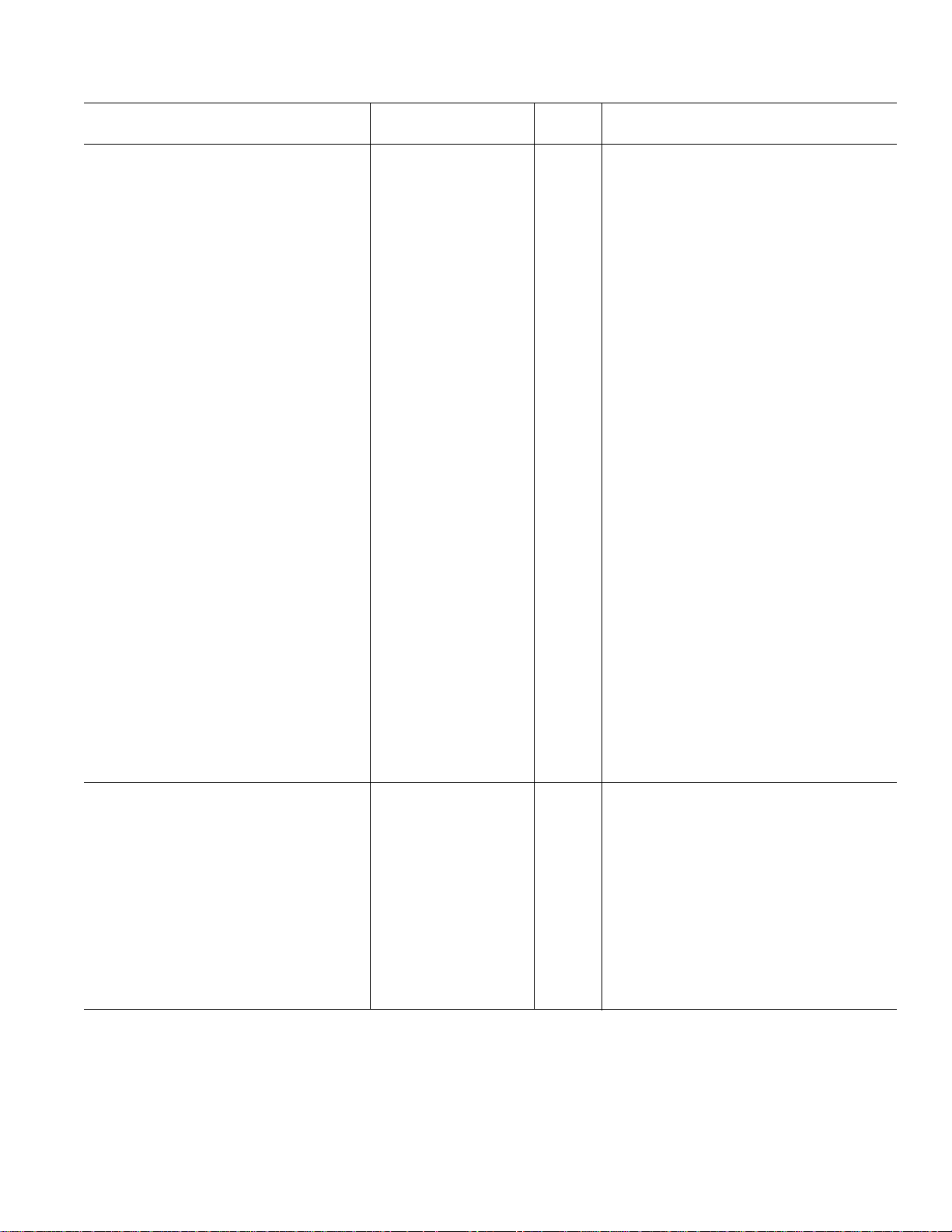
AD73322
AD73322A
Parameter Min Typ Max Units Test Conditions/Comments
DAC SPECIFICATIONS 5VEN = 0
Maximum Voltage Output Swing
Single-Ended 1.578 V p-p PGA = 6 dB
Differential 3.156 V p-p PGA = 6 dB
Nominal Voltage Output Swing (0 dBm0)
Single-Ended 1.0954 V p-p PGA = 6 dB
Differential 2.1909 V p-p PGA = 6 dB
Output Bias Voltage 1.2 V REFOUT Unloaded
Absolute Gain –0.8 +0.4 +1.2 dB 1.0 kHz, 0 dBm0; Unloaded
Gain Tracking Error ±0.1 dB 1.0 kHz, +3 dBm0 to –50 dBm0
Signal to (Noise + Distortion) at 0 dBm0 Refer to Figure 6; AVDD = 3.0 V ± 5%
PGA = 6 dB 62.5 77 dB 300 Hz to 3400 Hz; f
Total Harmonic Distortion at 0 dBm0 AVDD = 3.00 V ± 5%
PGA = 6 dB –80 –62.5 dB 300 Hz to 3400 Hz; f
Intermodulation Distortion –85 dB PGA = 0 dB
Idle Channel Noise –85 dBm0 PGA = 0 dB
Crosstalk DAC-to-ADC –90 dB ADC Input Signal Level: AGND; DAC
DAC-to-DAC –100 dB DAC1 Output Signal Level: AGND; DAC2
Power Supply Rejection –65 dB Input Signal Level at AVDD and DVDD
Group Delay
Output DC Offset
Minimum Load Resistance, R
Single-Ended
4, 5
2, 7
4
Differential 150 Ω
Maximum Load Capacitance, C
Single-Ended 500 pF
Differential 100 pF
FREQUENCY RESPONSE
(ADC and DAC)
9
Typical Output
Frequency (Normalized to FS)
00dB
0.03125 –0.1 dB
0.0625 –0.25 dB
0.125 –0.6 dB
0.1875 –1.4 dB
0.25 –2.8 dB
0.3125 –4.5 dB
0.375 –7.0 dB
0.4375 –9.5 dB
> 0.5 < –12.5 dB
2
–2.85 dBm Max Output = (1.578/1.2) × VREFCAP
3.17 dBm Max Output = 2 × ([1.578/1.2] × VREFCAP)
–6.02 dBm
0 dBm
= 64 kHz
SAMP
= 64 kHz
SAMP
Output Signal Level: 1.0 kHz, 0 dBm0
Input Amplifiers Bypassed
–77 dB Input Amplifiers Included in Input Channel
Output Signal Level: 1.0 kHz, 0 dBm0
Pins: 1.0 kHz, 100 mV p-p Sine Wave
25 µs Interpolator Bypassed
50 µs
2, 8
L
–25 +12 +40 mV
150 Ω
2, 8
L
–3–REV. B
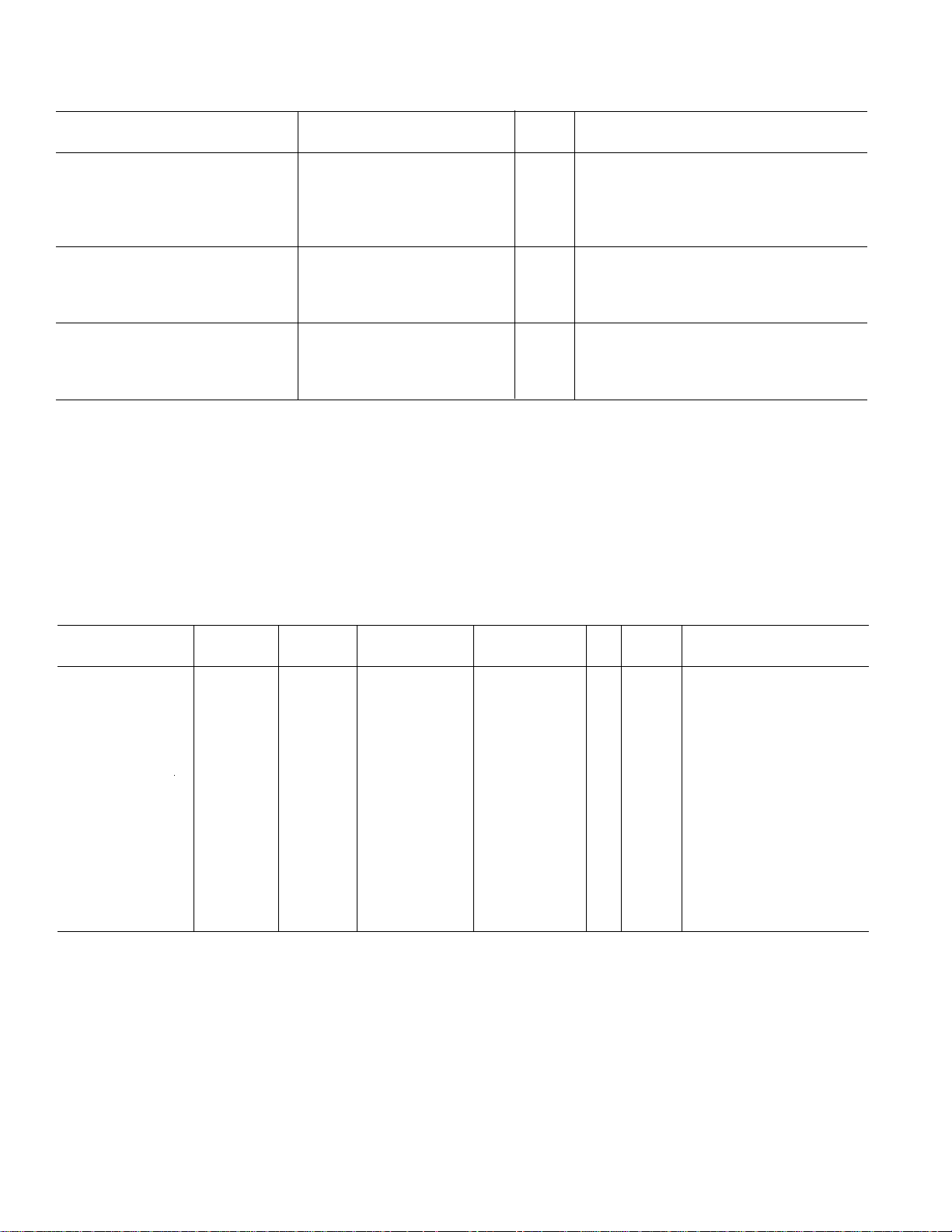
AD73322
AD73322A
Parameter Min Typ Max Units Test Conditions/Comments
LOGIC INPUTS
V
, Input High Voltage DVDD – 0.8 DVDD V
INH
, Input Low Voltage 0 0.8 V
V
INL
I
, Input Current –10 +10 µA
IH
CIN, Input Capacitance 10 pF
LOGIC OUTPUT
V
, Output High Voltage DVDD – 0.4 DVDD V |IOUT| ≤ 100 µA
OH
, Output Low Voltage 0 0.4 V |IOUT| ≤ 100 µA
V
OL
Three-State Leakage Current –10 +10 µA
POWER SUPPLIES
AVDD1, AVDD2 2.7 3.3 V
DVDD 2.7 3.3 V
10
I
DD
NOTES
1
Operating temperature range is as follows: – 40°C to +85°C. Therefore, T
2
Test conditions: Input PGA set for 0 dB gain, Output PGA set for 6 dB gain, no load on analog outputs (unless otherwise noted).
3
At input to sigma-delta modulator of ADC.
4
Guaranteed by design.
5
Overall group delay will be affected by the sample rate and the external digital filtering.
6
The ADC’s input impedance is inversely proportional to DMCLK and is approximated by: (3.3 × 10
7
Between VOUTP1 and VOUTN1 or between VOUTP2 and VOUTN2.
8
At VOUT output.
9
Frequency responses of ADC and DAC measured with input at audio reference level (the input level that produces an output level of –10 dBm0), with 38 dB preamplifier bypassed and input gain of 0 dB.
10
Test Conditions: no load on digital inputs, analog inputs ac coupled to ground, no load on analog outputs.
Specifications subject to change without notice.
= –40°C and T
MIN
= +85°C.
MAX
See Table I
11
)/DMCLK.
Table I. Current Summary (AVDD = DVDD = +3.3 V)
Analog Digital Total Current Total Current MCLK
Conditions Current Current (Typ) (Max) SE ON Comments
ADCs On Only 7 4.5 11.5 13 1 YES REFOUT Disabled
DACs On Only 15.5 4.5 20 23 1 YES REFOUT Disabled
ADCs and DACs On 19.5 5 24.5 28 1 YES REFOUT Disabled
ADCs and DACs
and Input Amps On 25 5 30 34 1 YES REFOUT Disabled
ADCs and DACs
and AGT On 24 5 29 32.5 1 YES REFOUT Disabled
All Sections On 32 5 37 42 1 YES
REFCAP On Only 0.8 0 0.8 1.25 0 NO REFOUT Disabled
REFCAP and
REFOUT On Only 3.5 0 3.5 4.5 0 NO
All Sections Off 0 1.5 1.5 1.9 0 YES MCLK Active Levels Equal to
0 V and DVDD
All Sections Off 0.00 10 µA 10 µA 40 µA 0 NO Digital Inputs Static and Equal
to 0 V or DVDD
The above values are in mA and are typical values unless otherwise noted.
–4–
REV. B
AD73322
SPECIFICATIONS
(AVDD = +5 V ⴞ 10%; DVDD = +5 V ⴞ 10%; DGND = AGND = 0 V, f
1
TA = T
MIN
to T
, unless otherwise noted)
MAX
= 16.384 MHz, f
DMCLK
= 64 kHz;
SAMP
AD73322A
Parameter Min Typ Max Units Test Conditions/Comments
REFERENCE
REFCAP
Absolute Voltage, VREFCAP 1.2 V 5VEN = 0
2.4 V 5VEN = 1
REFCAP TC 50 ppm/°C 0.1 µF Capacitor Required from
REFOUT REFCAP to AGND2
Typical Output Impedance 130 Ω
Absolute Voltage, VREFOUT 1.2 V 5VEN = 0, Unloaded
2.4 V 5VEN = 1, Unloaded
Minimum Load Resistance 2 kΩ 5VEN = 1
Maximum Load Capacitance 100 pF
INPUT AMPLIFIER
Offset ±1.0 mV
Maximum Output Swing 3.156 V Max Output Swing = (3.156/2.4) × VREFCAP
Feedback Resistance 50 kΩ f
= 32 kHz
C
Feedback Capacitance 100 pF
ANALOG GAIN TAP
Gain at Maximum Setting +1
Gain at Minimum Setting –1
Gain Resolution 5 Bits Gain Step Size = 0.0625
Gain Accuracy ±1 % Output Unloaded
Settling Time 1.0 µs Tap Gain Change of –FS to +FS
Delay 0.5 µs
ADC SPECIFICATIONS 5VEN = 1
Maximum Input Range at VIN
2, 3
3.156 V p-p Measured Differentially
3.17 dBm Max Input Swing = (3.156/2.4) × VREFCAP
Nominal Reference Level at VIN 2.1908 V p-p Measured Differentially
(0 dBm0) 0 dBm
Absolute Gain
PGA = 0 dB 0.4 dB 1.0 kHz, 0 dBm0
PGA = 38 dB –0.7 dB 1.0 kHz, 0 dBm0
Gain Tracking Error ±0.1 dB 1.0 kHz, +3 dBm0 to –50 dBm0
Signal to (Noise + Distortion) Refer to Figure 7
PGA = 0 dB 78 dB 300 Hz to 3400 Hz; f
78 dB 300 Hz to 3400 Hz; f
57 dB 0 Hz to f
SAMP
/2; f
SAMP
PGA = 38 dB 56 dB 300 Hz to 3400 Hz; f
= 64 kHz
SAMP
= 8 kHz
SAMP
= 64 kHz
= 64 kHz
SAMP
Total Harmonic Distortion
PGA = 0 dB –84 dB 300 Hz to 3400 Hz; f
PGA = 38 dB –70 dB 300 Hz to 3400 Hz; f
SAMP
SAMP
= 64 kHz
= 64 kHz
Intermodulation Distortion –65 dB PGA = 0 dB
Idle Channel Noise –71 dBm0 PGA = 0 dB
Crosstalk ADC-to-DAC –100 dB ADC Input Signal Level: 1.0 kHz, 0 dBm0
DAC Input at Idle
ADC-to-ADC –100 dB ADC1 Input Signal Level: 1.0 kHz, 0 dBm0
ADC2 Input at Idle. Input Amplifiers Bypassed
–70 dB Input Amplifiers Included in Channel
DC Offset +10 mV PGA = 0 dB
Power Supply Rejection –65 dB Input Signal Level at AVDD and DVDD
Group Delay
4, 5
Input Resistance at PGA2,
4, 6
25 µs 64 kHz Output Sample Rate
20 kΩ Input Amplifiers Bypassed
Pins: 1.0 kHz, 100 mV p-p Sine Wave
–5–REV. B
AD73322
AD73322A
P
arameter Min Typ Max Units Test Conditions/Comments
DIGITAL GAIN TAP
Gain at Maximum Setting +1 V
Gain at Minimum Setting –1 V
Gain Resolution 16 Bits Tested to 5 MSBs of Settings
Delay 25 µs Includes DAC Delay
Settling Time 100 µs Tap Gain Change from –FS to +FS; Includes
DAC Settling Time
DAC SPECIFICATIONS 5VEN = 1
Maximum Voltage Output Swing
Single-Ended 3.156 V p-p PGA = 6 dB
Differential 6.312 V p-p PGA = 6 dB
Nominal Voltage Output Swing (0 dBm0)
Single-Ended 2.1908 V p-p PGA = 6 dB
Differential 4.3918 V p-p PGA = 6 dB
Output Bias Voltage 2.4 V REFOUT Unloaded
Absolute Gain +0.4 dB 1.0 kHz, 0 dBm0; Unloaded
Gain Tracking Error ±0.1 dB 1.0 kHz, +3 dBm0 to –50 dBm0
Signal to (Noise + Distortion) at 0 dBm0 Refer to Figure 8
PGA = 6 dB 77 dB 300 Hz to 3400 Hz; f
Total Harmonic Distortion at 0 dBm0
PGA = 6 dB –80 dB 300 Hz to 3400 Hz; f
Intermodulation Distortion –85 dB PGA = 0 dB
Idle Channel Noise –85 dBm0 PGA = 0 dB
Crosstalk DAC-to-ADC –90 dB ADC Input Signal Level: AGND; DAC
DAC-to-DAC –100 dB DAC1 Output Signal Level: AGND; DAC2
Power Supply Rejection –65 dB Input Signal Level at AVDD and DVDD
Group Delay
Output DC Offset
4, 5
2, 7
Minimum Load Resistance, R
Single-Ended 150 Ω
Differential 150 Ω
Maximum Load Capacitance, C
Single-Ended 500 pF
Differential 100 pF
FREQUENCY RESPONSE
(ADC and DAC)
9
Typical Output
Frequency (Normalized to FS)
00dB
0.03125 –0.1 dB
0.0625 –0.25 dB
0.125 –0.6 dB
0.1875 –1.4 dB
0.25 –2.8 dB
0.3125 –4.5 dB
0.375 –7.0 dB
0.4375 –9.5 dB
> 0.5 < –12.5 dB
2
3.17 dBm Max Output = (3.156/2.4) × VREFCAP
9.19 dBm Max Output = 2 × ([3.156/2.4] × VREFCAP)
0 dBm
6.02 dBm
= 64 kHz
SAMP
= 64 kHz
SAMP
Output Signal Level: 1.0 kHz, 0 dBm0;
Input Amplifiers Bypassed
–77 dB Input Amplifiers Included In Input Channel
Output Signal Level: 1.0 kHz, 0 dBm0
Pins: 1.0 kHz, 100 mV p-p Sine Wave
25 µs Interpolator Bypassed
50 µs
2, 8
L
2, 8
L
+12 mV
–6–
REV. B
AD73322
AD73322A
Parameter Min Typ Max Units Test Conditions/Comments
LOGIC INPUTS
, Input High Voltage DVDD – 0.8 DVDD V
V
INH
V
, Input Low Voltage 0 0.8 V
INL
I
, Input Current ±0.5 µA
IH
CIN, Input Capacitance 10 pF
LOGIC OUTPUT
VOH, Output High Voltage DVDD – 0.4 DVDD V |I
V
, Output Low Voltage 0 0.4 V |I
OL
Three-State Leakage Current ±0.3 µA
POWER SUPPLIES
AVDD1, AVDD2 4.5 5.5 V
DVDD 4.5 5.5 V
10
I
DD
NOTES
1
Operating temperature range is as follows: –40°C to +85°C. Therefore, T
2
Test conditions: Input PGA set for 0 dB gain, Output PGA set for 6 dB gain, no load on analog outputs (unless otherwise stated).
3
At input to sigma-delta modulator of ADC.
4
Guaranteed by design.
5
Overall group delay will be affected by the sample rate and the external digital filtering.
6
The ADC’s input impedance is inversely proportional to DMCLK and is approximated by: (3.3 × 10
7
Between VOUTP and VOUTN.
8
At VOUT output.
9
Frequency responses of ADC and DAC measured with input at audio reference level (the input level that produces an output level of –10 dBm0), with 38 dB
preamplifier bypassed and input gain of 0 dB.
10
Test conditions: no load on digital inputs, analog inputs ac coupled to ground, no load on analog outputs.
Specifications subject to change without notice.
= –40°C and T
MIN
= +85°C.
MAX
11
)/DMCLK.
| ≤ 100 µA
OUT
| ≤ 100 µA
OUT
See Table II
Table II. Current Summary (AVDD = DVDD = +5.5 V)
Analog Digital Total Current MCLK
Conditions Current Current (Typ) SE ON Comments
ADCs On Only 7.5 9 16.5 1 YES REFOUT Disabled
DACs On Only 16 9 25 1 YES REFOUT Disabled
ADC and DAC On 20.5 10 30.5 1 YES REFOUT Disabled
ADCs and DACs
and Input Amps On 27 10 37 1 YES REFOUT Disabled
ADCs and DACs
and AGT On 25 10 35 1 YES REFOUT Disabled
All Sections On 35 10 45 1 YES
REFCAP On Only 0.8 0 0.8 0 NO REFOUT Disabled
REFCAP and
REFOUT On Only 3.5 0 3.5 0 NO
All Sections Off 0 3 3 0 YES MCLK Active Levels Equal to 0 V and DVDD
All Sections Off 0 10 µA 10 µA 0 NO Digital Inputs Static and Equal to 0 V or DVDD
The above values are in mA and are typical values unless otherwise noted.
–7–REV. B
AD73322
Table III. Signal Ranges
3 V Power Supply 5 V Power Supply
5VEN = 0 5VEN = 0 5VEN = 1
VREFCAP 1.2 V ± 10% 1.2 V 2.4 V
VREFOUT 1.2 V ± 10% 1.2 V 2.4 V
ADC Maximum Input Range
at V
IN
Nominal Reference Level 1.0954 V p-p 1.0954 V p-p 2.1908 V p-p
DAC Maximum Voltage
Output Swing
Single-Ended 1.578 V p-p 1.578 V p-p 3.156 V p-p
Differential 3.156 V p-p 3.156 V p-p 6.312 V p-p
Nominal Voltage
Output Swing
Single-Ended 1.0954 V p-p 1.0954 V p-p 2.1908 V p-p
Differential 2.1909 V p-p 2.1909 V p-p 4.3818 V p-p
Output Bias Voltage VREFOUT VREFOUT VREFOUT
1.578 V p-p 1.578 V p-p 3.156 V p-p
TIMING CHARACTERISTICS
(AVDD = +3 V ⴞ 10%; DVDD = +3 V ⴞ 10%; AGND = DGND = 0 V; TA = T
otherwise noted)
MlN
to T
Limit at
Parameter TA = –40ⴗC to +85ⴗC Units Description
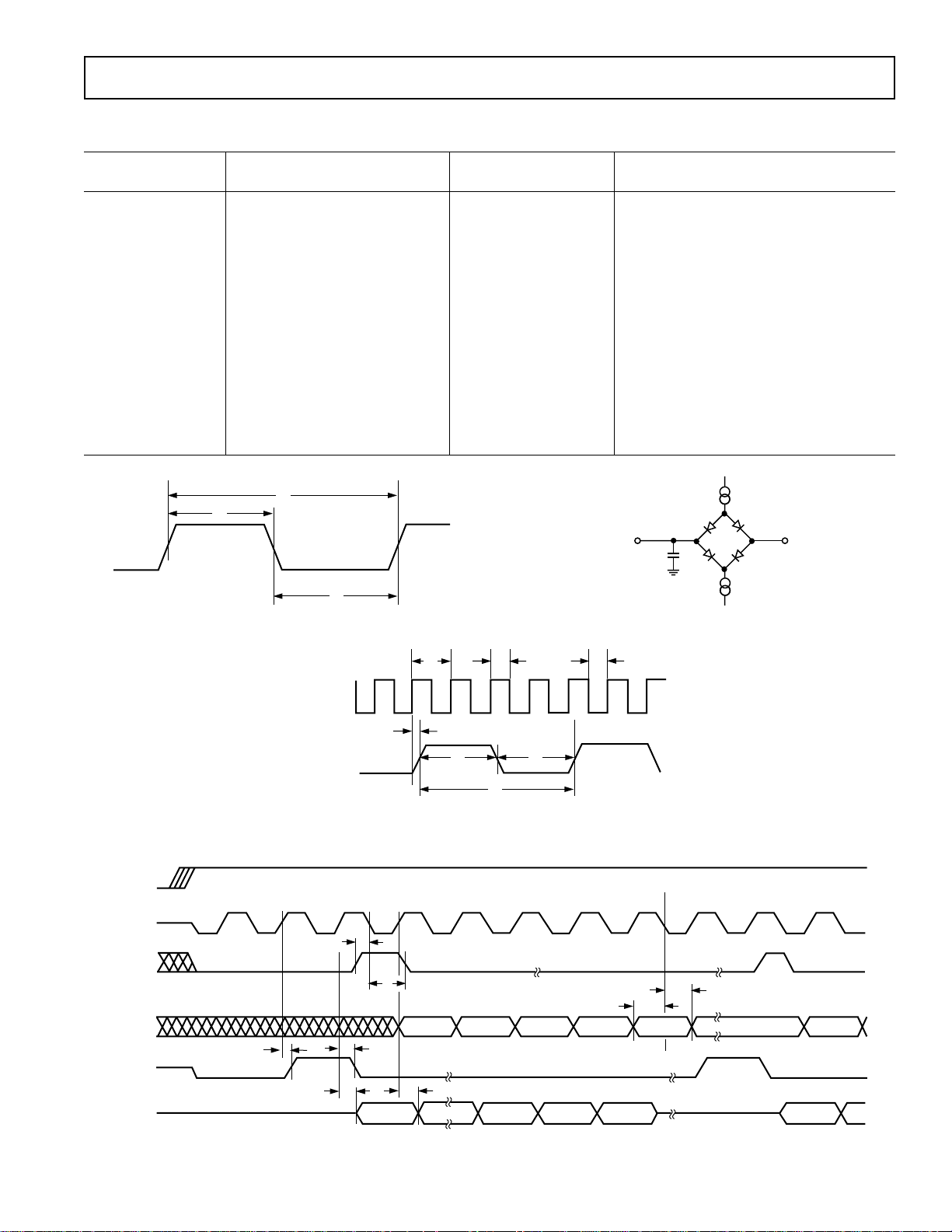
Clock Signals See Figure 1
t
1
t
2
t
3
61 ns min MCLK Period
24.4 ns min MCLK Width High
24.4 ns min MCLK Width Low
Serial Port See Figures 3 and 4
t
4
t
5
t
6
t
7
t
8
t
9
t
10
t
11
t
12
t
13
Specifications subject to change without notice.
t
1
0.4 × t
0.4 × t
20 ns min SDI/SDIFS Setup Before SCLK Low
0 ns min SDI/SDIFS Hold After SCLK Low
10 ns max SDOFS Delay from SCLK High
10 ns min SDOFS Hold After SCLK High
10 ns min SDO Hold After SCLK High
10 ns max SDO Delay from SCLK High
30 ns max SCLK Delay from MCLK
1
1
ns min SCLK Period
ns min SCLK Width High
ns min SCLK Width Low
, unless
MAX
–8–
REV. B
AD73322
t
11
t
7
t
9
t
10
t
7
t
8
t
8
SE (I)
SCLK (O)
SDIFS (I)
SDI (I)
SDOFS (O)
SDO (O)
THREESTATE
THREESTATE
THREESTATE
D15 D2D1D0 D14
D15D0D1D14D15
D15
t
12
TIMING CHARACTERISTICS
(AVDD = +5 V ⴞ 10%; DVDD = +5 V ⴞ 10%; AGND = DGND = 0 V; TA = T
otherwise noted)
MlN
to T
Limit at
Parameter TA = –40ⴗC to +85ⴗC Units Description
Clock Signals See Figure 1
t
1
t
2
t
3
61 ns min MCLK Period
24.4 ns min MCLK Width High
24.4 ns min MCLK Width Low
Serial Port See Figures 3 and 4
t
4
t
5
t
6
t
7
t
8
t
9
t
10
t
11
t
12
t
13
t
1
0.4 × t
1
0.4 × t
1
20 ns typ SDI/SDIFS Setup Before SCLK Low
0 ns typ SDI/SDIFS Hold After SCLK Low
10 ns typ SDOFS Delay from SCLK High
10 ns typ SDOFS Hold After SCLK High
10 ns typ SDO Hold After SCLK High
10 ns typ SDO Delay from SCLK High
30 ns typ SCLK Delay from MCLK
Specifications subject to change without notice.
t
1
t
2
Figure 1. MCLK Timing
t
3
ns min SCLK Period
ns min SCLK Width High
ns min SCLK Width Low
I
OL
I
OH
TO OUTPUT
PIN
15pF
100mA
C
L
100mA
Figure 2. Load Circuit for Timing Specifications
, unless
MAX
+2.1V
MCLK
SCLK*
t
1
t
13
*SCLK IS INDIVIDUALLY PROGRAMMABLE
IN FREQUENCY (MCLK/4 SHOWN HERE).
t
2
t
5
t
t
4
6
t
3
Figure 3. SCLK Timing
Figure 4. Serial Port (SPORT)
–9–REV. B
AD73322
ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS*
(T
= +25°C unless otherwise noted)
A
AVDD, DVDD to GND . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . –0.3 V to +7 V
AGND to DGND . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . –0.3 V to +0.3 V
Digital I/O Voltage to DGND . . . . . –0.3 V to DVDD + 0.3 V
Analog I/O Voltage to AGND . . . . . –0.3 V to AVDD + 0.3 V
Operating Temperature Range
Industrial (A Version) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . –40°C to +85°C
Storage Temperature Range . . . . . . . . . . . . –65°C to +150°C
Maximum Junction Temperature . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . +150°C
SOIC, θ
Thermal Impedance . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 71.4°C/W
JA
Lead Temperature, Soldering
Vapor Phase (60 sec) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . +215°C
Infrared (15 sec) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . +220°C
LQFP, θ
Thermal Impedance . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 53.2°C/W
JA
Lead Temperature, Soldering
Vapor Phase (60 sec) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . +215°C
Infrared (15 sec) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . +220°C
*Stresses above those listed under Absolute Maximum Ratings may cause perma-
nent damage to the device. This is a stress rating only; functional operation of the
device at these or any other conditions above those listed in the operational
sections of this specification is not implied. Exposure to absolute maximum rating
conditions for extended periods may affect device reliability.
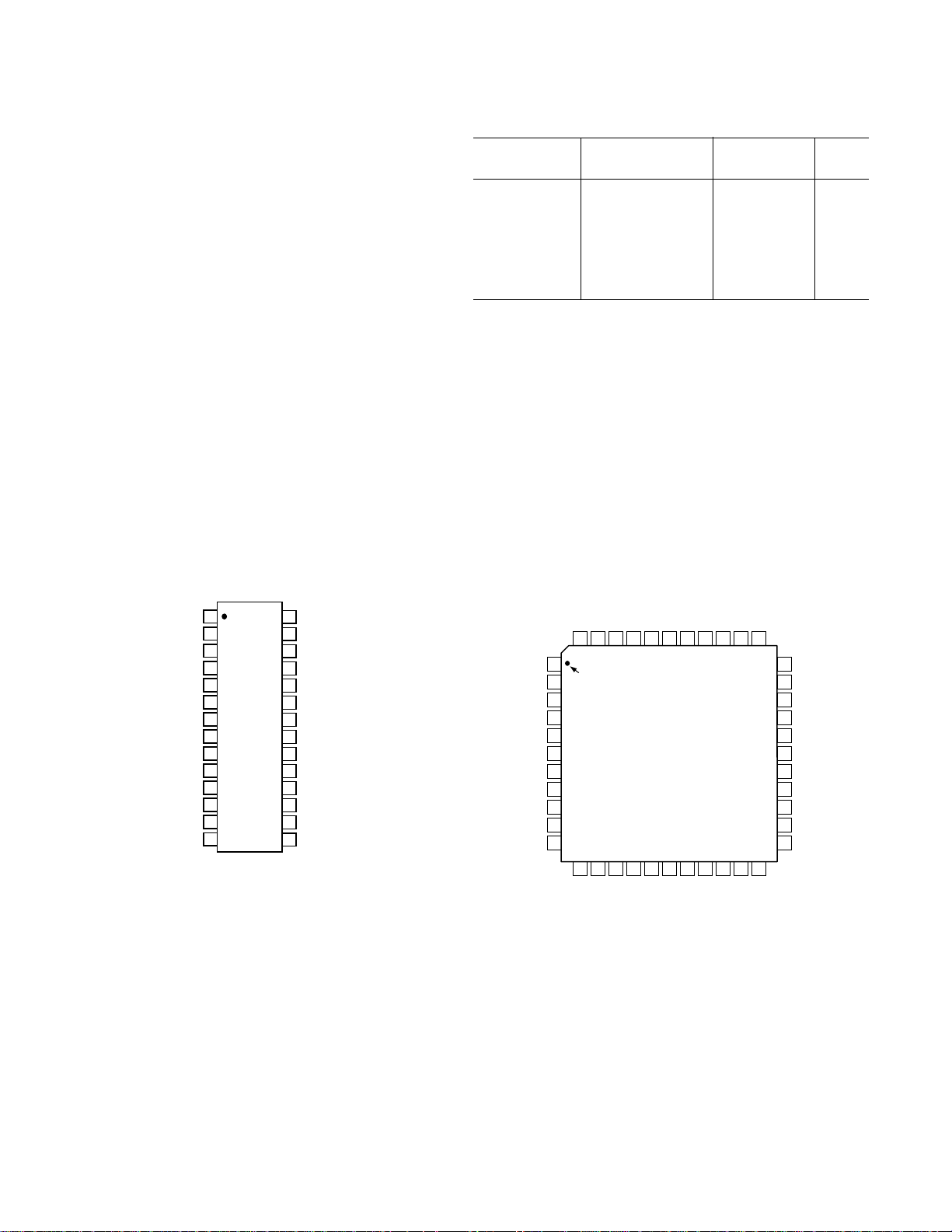
PIN CONFIGURATIONS
28-Lead Wide Body SOIC
(R-28)
ORDERING GUIDE
Temperature Package Package
Model Range Descriptions Options
AD73322AR –40°C to +85°C Wide Body SOIC R-28
AD73322AST –40°C to +85°C Plastic Thin Quad ST-44A
Flatpack (LQFP)
EVAL-AD73322EB Evaluation Board
+EZ-KIT Lite Upgrade
EVAL-AD73322EZ Evaluation Board
+EZ-KIT Lite
NOTES
1
The AD73322 evaluation board features a selectable number of codecs in
1
2
1
3
cascade (from 1 to 4). It can be interfaced to an ADSP-2181 EZ-KIT Lite or to
a Texas Instruments EVM kit.
2
The upgrade consists of a connector that is used to connect the EZ-KIT to the
AD73322 evaluation board. This option is intended for owners of the EZ-KIT
Lite.
3
The EZ-KIT Lite has been modified to allow it to interface with the AD73322
evaluation board. This option is intended for users who do not already have an
EZ-KIT Lite.
44-Lead Plastic Thin Quad Flatpack (LQFP)
(ST-44A)
VINP1
VFBP1
VINN1
VFBN1
REFOUT
REFCAP
AVDD2
AGND2
DGND
DVDD
RESET
SCLK
MCLK
SDO
1
2
3
4
5
6
AD73322
7
TOP VIEW
(Not to Scale)
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
28
27
26
25
24
23
22
21
20
19
18
17
16
15
VFBN2
VINN2
VFBP2
VINP2
VOUTN1
VOUTP1
VOUTN2
VOUTP2
AVDD1
AGND1
SE
SDI
SDIFS
SDOFS
REFOUT
REFCAP
AVDD2
AVDD2
AGND2
AGND2
AGND2
AGND2
DGND
DGND
DVDD
NC
VFBN1
1
PIN 1
IDENTIFIER
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
121314 15 16 17 18 192021 22
NC
RESET
NC = NO CONNECT
VFBP1
VINN1
AD73322
(Not to Scale)
SCLK
MCLK
VINP1
VFBN2
NC
40 39 3841424344 36 35 3437
TOP VIEW
NC
SDO
SDOFS
VINN2
SDIFS
VFBP2
SDI
VINP2
SE
NC
NC
33
32
31
30
29
28
27
26
25
24
23
NC
VOUTN1
VOUTP1
NC
VOUTN2
VOUTP2
NC
AVDD1
AVDD1
AGND1
AGND1
–10–
REV. B

AD73322
PIN FUNCTION DESCRIPTIONS
Mnemonic Function
VINP1 Analog Input to the inverting input amplifier on Channel 1’s positive input.
VFBP1 Feedback Connection from the output of the inverting amplifier on Channel 1’s positive input. When the input
amplifiers are bypassed, this pin allows direct access to the positive input of Channel 1’s sigma-delta modulator.
VINN1 Analog Input to the inverting input amplifier on Channel 1’s negative input.
VFBN1 Feedback connection from the output of the inverting amplifier on Channel 1’s negative input. When the input
amplifiers are bypassed, this pin allows direct access to the negative input of Channel 1’s sigma-delta modulator.
REFOUT Buffered Reference Output, which has a nominal value of 1.2 V or 2.4 V, the value being dependent on the status
of Bit 5VEN (CRC:7). As the reference is common to the two codec units, the reference value is set by the wired
OR of the CRC:7 bits in Control Register C of each channel.
REFCAP A bypass capacitor to AGND2 of 0.1 µF is required for the on-chip reference. The capacitor should be fixed to this
pin.
AVDD2 Analog Power Supply Connection.
AGND2 Analog Ground/Substrate Connection2.
DGND Digital Ground/Substrate Connection.
DVDD Digital Power Supply Connection.
RESET Active Low Reset Signal. This input resets the entire chip, resetting the control registers and clearing the digital
circuitry.
SCLK Serial Clock Output whose rate determines the serial transfer rate to/from the codec. It is used to clock data or
control information to and from the serial port (SPORT). The frequency of SCLK is equal to the frequency of the
master clock (MCLK) divided by an integer number—this integer number being the product of the external mas-
ter clock rate divider and the serial clock rate divider.
MCLK Master Clock Input. MCLK is driven from an external clock signal.
SDO Serial Data Output. Both data and control information may be output on this pin and are clocked on the positive
edge of SCLK. SDO is in three-state when no information is being transmitted and when SE is low.
SDOFS Framing Signal Output for SDO Serial Transfers. The frame sync is one bit wide and is active one SCLK period
before the first bit (MSB) of each output word. SDOFS is referenced to the positive edge of SCLK. SDOFS is in
three-state when SE is low.
SDIFS Framing Signal Input for SDI Serial Transfers. The frame sync is one bit wide and is valid one SCLK period be-
fore the first bit (MSB) of each input word. SDIFS is sampled on the negative edge of SCLK and is ignored when
SE is low.
SDI Serial Data Input. Both data and control information may be input on this pin and are clocked on the negative
edge of SCLK. SDI is ignored when SE is low.
SE SPORT Enable. Asynchronous input enable pin for the SPORT. When SE is set low by the DSP, the output pins
of the SPORT are three-stated and the input pins are ignored. SCLK is also disabled internally in order to decrease
power dissipation. When SE is brought high, the control and data registers of the SPORT are at their original
values (before SE was brought low); however, the timing counters and other internal registers are at their reset
values.
AGND1 Analog Ground/Substrate Connection.
AVDD1 Analog Power Supply Connection.
VOUTP2 Analog Output from the Positive Terminal of Output Channel 2.
VOUTN2 Analog Output from the Negative Terminal of Output Channel 2.
VOUTP1 Analog Output from the Positive Terminal of Output Channel 1.
VOUTN1 Analog Output from the Negative Terminal of Output Channel 1.
VINP2 Analog Input to the inverting input amplifier on Channel 2’s positive input.
VFBP2 Feedback connection from the output of the inverting amplifier on Channel 2’s positive input. When the input
amplifiers are bypassed, this pin allows direct access to the positive input of Channel 2’s sigma-delta modulator.
VINN2 Analog Input to the inverting input amplifier on Channel 2’s negative input.
VFBN2 Feedback connection from the output of the inverting amplifier on Channel 2’s negative input. When the input
amplifiers are bypassed, this pin allows direct access to the negative input of Channel 2’s sigma-delta modulator.
–11–REV. B

AD73322
TERMINOLOGY
Absolute Gain
Absolute gain is a measure of converter gain for a known signal.
Absolute gain is measured (differentially) with a 1 kHz sine
wave at 0 dBm0 for the DAC and with a 1 kHz sine wave at
0 dBm0 for the ADC. The absolute gain specification is used for
gain tracking error specification.
Crosstalk
Crosstalk is due to coupling of signals from a given channel to
an adjacent channel. It is defined as the ratio of the amplitude of
the coupled signal to the amplitude of the input signal. Crosstalk
is expressed in dB.
Gain Tracking Error
Gain tracking error measures changes in converter output for
different signal levels relative to an absolute signal level. The
absolute signal level is 0 dBm0 (equal to absolute gain) at 1 kHz
for the DAC and 0 dBm0 (equal to absolute gain) at 1 kHz for
the ADC. Gain tracking error at 0 dBm0 (ADC) and 0 dBm0
(DAC) is 0 dB by definition.
Group Delay
Group Delay is defined as the derivative of radian phase with
respect to radian frequency, dø(f)/df. Group delay is a measure
of average delay of a system as a function of frequency. A linear
system with a constant group delay has a linear phase response.
The deviation of group delay from a constant indicates the
degree of nonlinear phase response of the system.
Idle Channel Noise
Idle channel noise is defined as the total signal energy measured
at the output of the device when the input is grounded (measured in the frequency range 300 Hz–3400 Hz).
Intermodulation Distortion
With inputs consisting of sine waves at two frequencies, fa and
fb, any active device with nonlinearities will create distortion
products at sum and difference frequencies of mfa ± nfb where
m, n = 0, 1, 2, 3, etc. Intermodulation terms are those for which
neither m nor n is equal to zero. For final testing, the second
order terms include (fa + fb) and (fa – fb), while the third order
terms include (2fa + fb), (2fa – fb), (fa + 2fb) and (fa – 2fb).
Power Supply Rejection
Power supply rejection measures the susceptibility of a device to
noise on the power supply. Power supply rejection is measured
by modulating the power supply with a sine wave and measuring
the noise at the output (relative to 0 dB).
Sample Rate
The sample rate is the rate at which the ADC updates its output
register and the DAC updates its output from its input register.
The sample rate can be chosen from a list of four that are fixed
relative to the DMCLK. Sample rate is set by programming bits
DIR0-1 in Control Register B of each channel.
SNR+THD
Signal-to-noise ratio plus total harmonic distortion is defined to
be the ratio of the rms value of the measured input signal to the
rms sum of all other spectral components in the frequency range
300 Hz–3400 Hz, including harmonics but excluding dc.
ABBREVIATIONS
ADC Analog-to-Digital Converter.
AFE Analog Front End.
AGT Analog Gain Tap.
ALB Analog Loop-Back.
BW Bandwidth.
CRx A Control Register where x is a placeholder for an
alphabetic character (A–E). There are five read/
write control registers on the AD73322—designated CRA through CRE.
CRx:n A bit position, where n is a placeholder for a nu-
meric character (0–7), within a control register,
where x is a placeholder for an alphabetic character (A–E). Position 7 represents the MSB and
Position 0 represents the LSB.
DAC Digital-to-Analog Converter.
DGT Digital Gain Tap.
DLB Digital Loop-Back.
DMCLK Device (Internal) Master Clock. This is the inter-
nal master clock resulting from the external master
clock (MCLK) being divided by the on-chip master clock divider.
FS Full Scale.
FSLB Frame Sync Loop-Back—where the SDOFS of
the final device in a cascade is connected to the
RFS and TFS of the DSP and the SDIFS of
first device in the cascade. Data input and output occur simultaneously. In the case of NonFSLB, SDOFS and SDO are connected to the
Rx Port of the DSP while SDIFS and SDI are
connected to the Tx Port.
PGA Programmable Gain Amplifier.
SC Switched Capacitor.
SLB Sport Loop-Back
SNR Signal-to-Noise Ratio.
SPORT Serial Port.
THD Total Harmonic Distortion.
VBW Voice Bandwidth.
–12–
REV. B
Typical Performance Characteristics
AD73322
80
70
60
50
40
30
S/(N+D) – dB
20
10
0
–10
–85 5–75 –65 –55 –45 –35 –25 –15 –5
VIN – dBm0
3.17
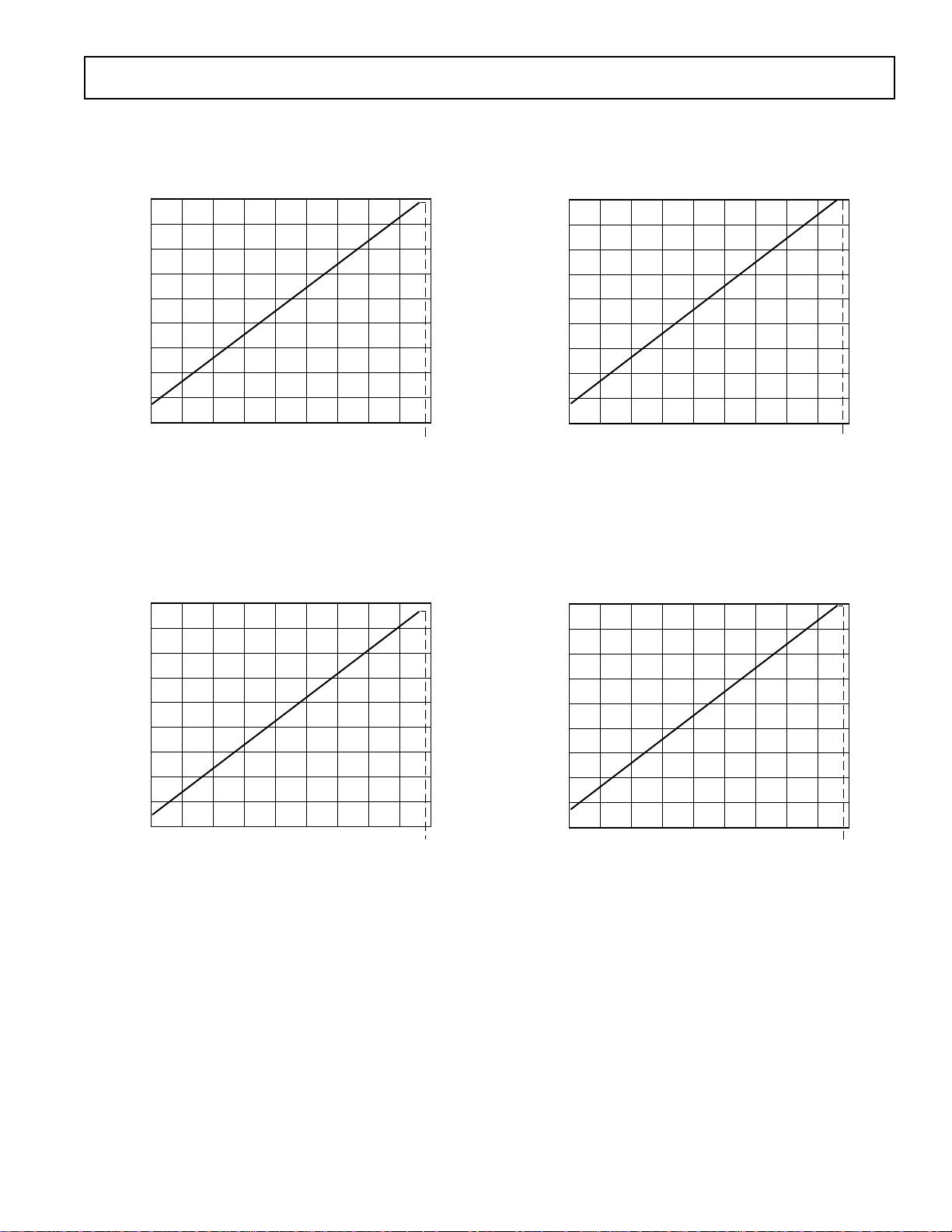
Figure 5. S/(N+D) vs. VIN (ADC @ 3 V) over Voiceband
Bandwidth (300 Hz–3.4 kHz)
80
70
60
50
40
30
S/(N+D) – dB
20
10
0
–10
–85 5–75 –65 –55 –45 –35 –25 –15 –5
VIN – dBm0
3.17
Figure 6. S/(N+D) vs. VIN (DAC @ 3 V) over Voiceband
Bandwidth (300 Hz–3.4 kHz)
80
70
60
50
40
30
S/(N+D) – dB
20
10
0
–10
–85 5–75 –65 –55 –45 –35 –25 –15 –5
VIN – dBm0
3.17
Figure 7. S/(N+D) vs. VIN (ADC @ 5 V) over Voiceband
Bandwidth (300 Hz–3.4 kHz)
80
70
60
50
40
30
S/(N+D) – dB
20
10
0
–10
–85 5–75 –65 –55 –45 –35 –25 –15 –5
VIN – dBm0
3.17
Figure 8. S/(N+D) vs. VIN (DAC @ 5 V) over Voiceband
Bandwidth (300 Hz–3.4 kHz)
–13–REV. B
 Loading...
Loading...