Analog Devices AD14060 L b Datasheet
PERFORMANCE FEATURES
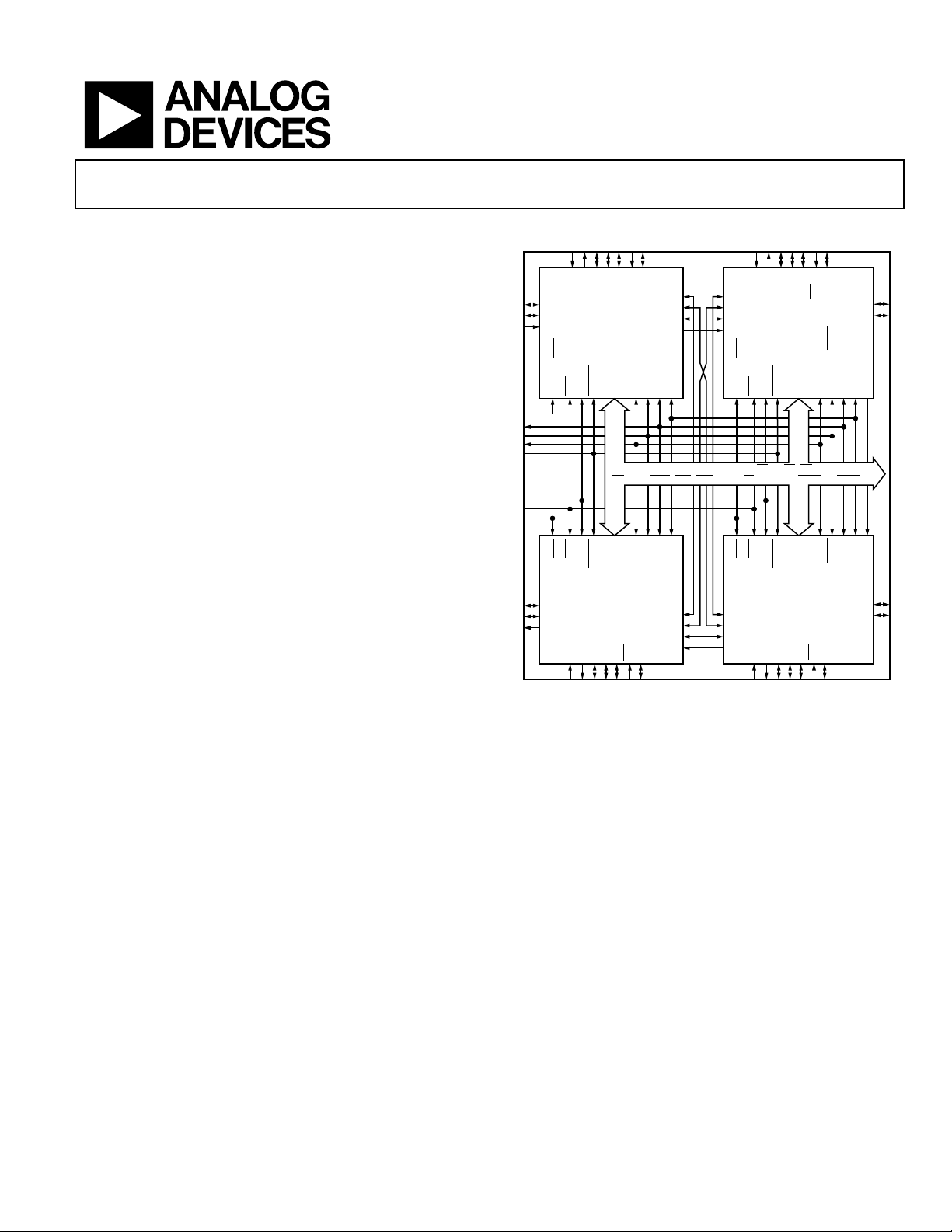
ADSP-21060 core processor ( × 4)
480 MFLOPS peak, 320 MFLOPS sustained
25 ns instruction rate, single-cycle
instruction execution—each of four processors
16 Mbit shared SRAM (internal to SHARCs)
4 gigawords addressable off-module memory
Twelve 40 Mbyte/s link ports (3 per SHARC)
Four 40 Mbit/s independent serial ports
(one from each SHARC)
One 40 Mbit/s common serial port
5 V and 3.3 V operation
32-bit single precision and 40-bit extended
precision IEEE floating point data formats, or
32-bit fixed point data format
IEEE JTAG Standard 1149.1 test access port and
on-chip emulation
PACKAGING FEATURES
308-lead ceramic quad flatpack (CQFP)
2.05" (52 mm) body size
Cavity up or down, configurable
Low profile, 0.160" height
Hermetic
25 Mil (0.65 mm) lead pitch
29 grams (typical)
= 0.36°C/W
θ
JC
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
The AD14060/AD14060L Quad-SHARC is the first in a family
of high performance DSP multiprocessor modules. The core of
the multiprocessor is the ADSP-21060 DSP microcomputer. The
AD14060/AD14060L has the highest performance-to-density
and lowest cost-to-performance ratios of any in its class. It is
ideal for applications requiring higher levels of performance
and/or functionality per unit area.
The AD14060/AD14060L takes advantage of the built-in
multiprocessing features of the ADSP-21060 to achieve
480 peak MFLOPS with a single chip type in a single package.
The on-chip SRAM of the DSPs provides 16 Mbits of onmodule shared SRAM. The complete shared bus (48 data,
Quad-SHARC
®
DSP Multiprocessor Family
AD14060/AD14060L
FUNCTIONAL BLOCK DIAGRAM
2–0
2, 0
IRQ
LINK 3
LINK 4
LINK 0
FLAG
LINK 2
LINK 5
2–0
LINK 4
IRQ
SPORT 0
SPORT 0
2, 0
FLAG
TDO
3
TCK, TMS, TRST
FLAG1FLAG
ADDR
1
3
TRSTTMS,TCK,
FLAG
FLAG
LINK 0
LINK 2
LINK 5
TDI
= 1)
SHARC BUS (
SW, ACK, SBTS, HBR, HBG, REDY, BR
= 4)
LINK 3
31–0
,
DATA
LINK 0
LINK 2
LINK 5
TDI
LINK 0
LINK 2
LINK 5
TDO
EBOOT,
LBOOT, BMS
,
47–0
,
6–1
EBOOT,
LBOOT, BMS
CS
TIMEXP
SHARC_B
(ID
EMU
CLKIN
MS
3-0
, RPBA, DMAR
EMU
CLKIN
SHARC_C
(ID
CS
TIMEXP
CPA
SPORT 1
TDI
EBOOT,
LBOOT, BMS
EBOOT,
LBOOT, BMS
CPA
SPORT 1
TDO
CS
LINK 1
TIMEXP
SHARC_A
(ID
2–0
EMU
CLKIN
RESET
EMU
CLKIN
RESET
SHARC_D
(ID
2–0
CS
TIMEXP
LINK 1
AD14060/AD14060L
Figure 1.
32 address) is also brought off-module for interfacing with
expansion memory or other peripherals.
The ADSP-21060 link ports are interconnected to provide direct
communication among the four SHARCs, as well as high speed
off-module access. Internally, each SHARC has a direct link port
connection. Externally, each SHARC has a total of 120 Mbytes/s
link port bandwidth.
Multiprocessor performance is enhanced with embedded power
and ground planes, matched impedance interconnect, and
optimized signal routing lengths and separation. The fully
tested and ready-to-insert multiprocessor also significantly
reduces board space.
2–0
2, 0
LINK 1
LINK 3
LINK 4
IRQ
CPA
FLAG
SPORT 1
= 2)
2–0
RESET
SPORT 0
TCK, TMS, TRST
FLAG1FLAG3TDO
,
RD, WR, PAGE, ADRCLK,
RESET
2–0
LINK 1
= 3)
LINK 3
LINK 4
2–0
IRQ
1.2
SPORT 0
FLAG
, DMAG
1
TRSTTMS,TCK,
FLAG
CPA
SPORT 1
2, 0
FLAG
00667-001
)
1.2
3
TDI
Rev. B
Information furnished by Analog Devices is believed to be accurate and reliable.
However, no responsibility is assumed by Analog Devices for its use, nor for any
infringements of patents or other rights of third parties that may result from its use.
Specifications subject to change without notice. No license is granted by implication
or otherwise under any patent or patent rights of Analog Devices. Trademarks and
registered trademarks are the property of their respective owners.
One Technology Way, P.O. Box 9106, Norwood, MA 02062-9106, U.S.A.
Tel: 781.329.4700
Fax: 781.326.8703 © 2004 Analog Devices, Inc. All rights reserved.
www.analog.com

AD14060/AD14060L
TABLE OF CONTENTS
Specifications..................................................................................... 3
Link Port I/O............................................................................... 38
Electrical Characteristics (3.3 V, 5 V Supply)............................ 3
Explanation of Test Levels........................................................... 4
Timing Specifications....................................................................... 5
Memory Read—Bus Master ........................................................ 8
Memory Write—Bus Master ....................................................... 9
Synchronous Read/Write—Bus Master................................... 10
Synchronous Read/Write—Bus Slave ...................................... 12
Multiprocessor Bus Request and Host Bus Request .............. 13
Asynchronous Read/Write—Host to AD14060/AD14060L.15
Three-State Timing—Bus Master, Bus Slave,
DMA Handshake ........................................................................ 18
Absolute Maximum Ratings.......................................................... 27
ESD Caution................................................................................ 27
Pin Configuration and Function Descriptions........................... 28
Pin Function Descriptions ........................................................ 30
HBR, SBTS
..... 17
Serial Ports .................................................................................. 38
Program Booting........................................................................ 38
Host Processor Interface ........................................................... 39
Direct Memory Access (DMA) Controller............................. 39
Applications..................................................................................... 40
Development Tools .................................................................... 40
Quad-SHARC Development Board......................................... 40
Other Package Details................................................................ 40
Target Board Connector for Emulator Probe......................... 40
Output Drive Currents .............................................................. 42
Power Dissipation ...................................................................... 42
Test Conditions........................................................................... 43
Assembly Recommendations.................................................... 45
PCB Layout Guidelines.............................................................. 46
Mechanical Characteristics ....................................................... 47
Detailed Description ...................................................................... 34
Architectural Features................................................................ 34
Shared Memory Multiprocessing ............................................. 34
Off-Module Memor y and Peripherals Interface .................... 36
REVISION HISTORY
12/04—Rev. A to Rev. B
Format Updated..................................................................Universal
Changes to Specifications Section.................................................. 3
Changes to Development Tools Section ......................................40
Changes to Target Board for Emulator Probe Section .............. 40
Changes to Figure 27...................................................................... 42
Updated Outline Dimensions....................................................... 48
Changes to Ordering Guide.......................................................... 48
10/97—Rev. 0 to Rev. A
4/97—Revision 0: Initial Version
Additional Information ............................................................. 47
Outline Dimensions....................................................................... 48
Ordering Guide .......................................................................... 48
Rev. B | Page 2 of 48
AD14060/AD14060L
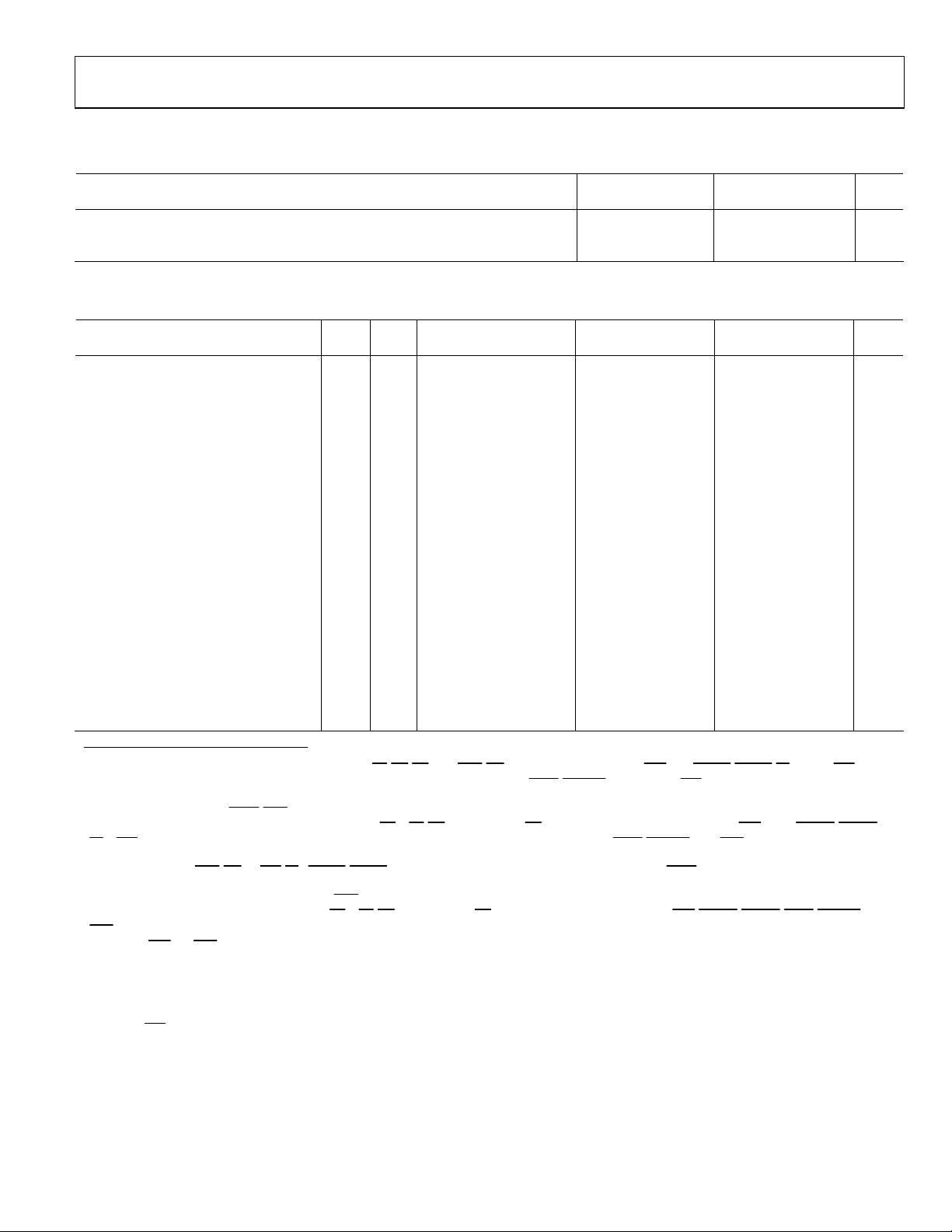
SPECIFICATIONS
Table 1. Recommended Operating Conditions
B Grade K Grade
Parameter
V
Supply Voltage (5 V) 4.75 5.25 4.75 5.25 V
DD
Min Max Min Max
Supply Voltage (3.3 V) 3.15 3.6 3.15 3.6 V
T
Case Operating Temperature −40 +100 0 +85 °C
CASE
ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS (3.3 V, 5 V SUPPLY)
Table 2.
Test
Level
Test Condition
= max, VIN = 0 V 10 10 µA
DD
= max, VIN = 0 V 150 150 µA
DD
= max, VIN = 0 V 600 600 µA
DD
= max, VIN = VDD max 350 350 µA
DD
Min Typ Max Min Typ Max
350 350 µA
V
= 1.5 V (5 V), 2 V (3.3 V)
IN
= max, VIN = 0 V 4.2 4.2 mA
DD
= max, VIN = 0 V 150 150 µA
DD
= max, VIN = 0 V 600 600 µA
DD
Parameter
V
V
V
V
V
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
C
High Level Input Voltage
IH1
High Level Input Voltage
IH2
IL
Low Level Input Voltage
High Level Output Voltage
OH
OL
Low Level Output Voltage
High Level Input Current
IH
IL
Low Level Input Current5
ILP
Low Level Input Current6
ILPX4
Low Level Input Current7
Three-State Leakage Current
OZH
OZL
Three-State Leakage Current
OZHP
Three-State Leakage Current12
Three-State Leakage Current
OZLC
Three-State Leakage Current
OZLA
OZLAR
Three-State Leakage Current10
OZLS
Three-State Leakage Current9
OZLSX4
Three-State Leakage Current11
Supply Current (Internal)
DDIN
Supply Current (Idle)
DDIDLE
Input Capacitance
IN
17, 18
Case
Temp
1
2
1, 2
3, 4
3, 4
5, , 6 7
Full I @ VDD = max 2.0 VDD + 0.5 2.0 VDD + 0.5 V
Full I @ VDD = max 2.2 VDD + 0.5 2.2 VDD + 0.5 V
Full I @ VDD = min 0.8 0.8 V
Full I @ VDD = min, IOH = −2.0 mA4 4.1 2.4 V
Full I @ VDD = min, IOL = 4.0 mA4 0.4 0.4 V
Full I @ VDD = max, VIN = VDD max 10 10 µA
Full I @ V
Full I @ V
Full I @ V
8, , , 9 10 11
8, 12
Full I @ VDD = max, VIN = VDD max 10 10 µA
Full I @ VDD = max, VIN = 0 V 10 10 µA
Full I @ V
13
14
Full I @ VDD = max, VIN = 0 V 1.5 1.5 mA
Full I @ VDD = max,
Full I @ V
Full I @ V
Full I @ V
15
16
Full IV tCK = 25 ns, VDD = max 1.4 2.92 1.0 2.2 A
Full I VDD = max 800 760 mA
25°C V 15 15 pF
1
Applies to input and bidirectional pins: DATA
TFSy1, RFS0, RFSy1, LyxDAT
RCLKy1.
2
Applies to input pins: CLKIN,
3
Applies to output and bidirectional pins: DATA
,
y, DTO, DTy1, TCLK0, TCLKy1, RCLK0, RCLKy1, TFS0, TFSy1, RFS0, RFSy1, LyxDAT
CPA
BR
6-1
4
See the section for typical drive current capabilities. Output Drive Currents
5
Applies to input pins:
6
Applies to input pins with internal pull-ups: DR0, DRy1, TDI.
7
Applies to bused input pins with internal pull-ups:
8
Applies to three-statable pins: DATA
. (Note that ACK is pulled up internally with 2 kΩ during reset in a multiprocessor system, when ID
EMU
mastership.
9
Applies to three-statable pins with internal pull-ups: DTy1, TCLKy1, RCLKy1.
10
Applies to ACK pin when pulled up. (Note that ACK is pulled up internally with 2 kΩ during reset in a multiprocessor system, when ID
ADSP-2106x is not requesting bus mastership.)
11
Applies to bused three-statable pins with internal pull-ups: DT0, TCLK0, RCLK0.
12
Applies to three-statable pins with internal pull-downs: LyxDAT
13
Applies to
14
Applies to ACK pin, when the keeper latch is enabled.
15
Applies to VDD pins. Conditions of operation: each processor is executing radix-2 FFT butterfly with instruction in cache, one data operand is fetched from each
internal memory block, and one DMA transfer is occurring from/to internal memory at t
16
Applies to VDD pins. Idle denotes AD14060/AD14060L state during execution of IDLE instruction.
17
Applies to all signal pins.
18
Guaranteed, but not tested.
HBG
CPA
and
y pin.
, LyxCLK, LyxACK, EBOOTA, LBOOTA, EBOOTBCD, LBOOTBCD,
3-0
RESET, TRST
y
STBS, IRQ
EMU
,
HBR, CS
2-0
47-0
are not tested for leakage current.)
47-0
.
47-0
y,
DMAR1, DMAR2
, ADDR
31-0
, ADDR
, RD, WR, SW, ACK,
31-0
STBS, IRQ
y
, FLAGy0, FLAG1, FLAGy2,
2-0
BMSA, BMSBCD
, ADDR
,
, RD, WR, PAGE, ADRCLK, SW, ACK, FLAGy0, FLAG1, FLAGy2, TIMEXPy,
MS
31-0
3-0
, LyxCLK, LyxACK,
3-0
, RPBA, EBOOTA, LBOOTA, EBOOTBCD, LBOOTBCD, CLKIN,
, TMS.
TRST
,
, RD, WR, PAGE, ADRCLK, SW, ACK, FLAGy0, FLAG1, FLAGy2, REDY,
MS
3-0
2-0
, LyxCLK, LyxACK.
3-0
= 25 ns.
CK
5 V 3.3 V
, CSy,
HBG
, TMS, TDI, TCK,
BMSA, BMSBCD
RESET
DMAR1, DMAR2, BR
, DR0, DRy1, TCLK0, TCLKy1, RCLK0,
HBR
HBG
, TDO,
EMU
.
, TCK.
6-1
, REDY,
, RPBA,
DMAG1, DMAG2
HBG, DMAG1, DMAG2, BMSA, BMSBCD
= 001 and another ADSP-2106x is not requesting bus
= 001 and another
2-0
CPA
Unit
Unit
y, TFS0,
,
, TDO,
Rev. B | Page 3 of 48
AD14060/AD14060L
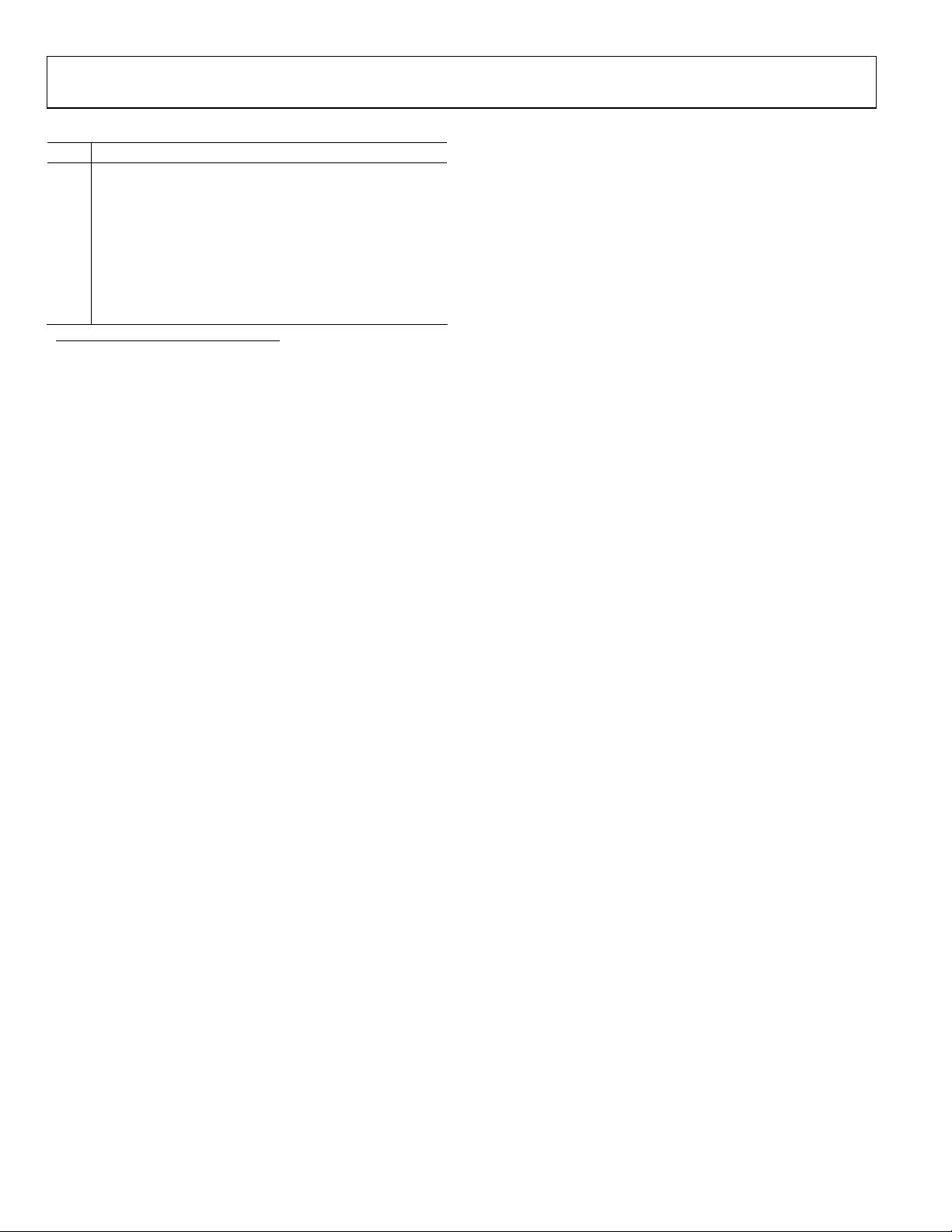
EXPLANATION OF TEST LEVELS
Test Level
I 100% production tested.
II
100% production tested at 25°C, and sample tested at
specified temperatures.
III Sample tested only.
IV
Parameter is guaranteed by design and analysis, and
characterization testing on discrete SHARCs.
V Parameter is typical value only.
VI
All devices are 100% production tested at 25°C, and
sample tested at temperature extremes.
1
Link and serial ports: All are 100% tested at die level prior to assembly. All are
100% ac tested at module level; Link 4 and Serial 0 are also dc tested at the
module level. See the section.
Timing Specifications
1
Rev. B | Page 4 of 48
AD14060/AD14060L
TIMING SPECIFICATIONS
This data sheet represents production-released specifications
for the AD14060 (5 V), and for the AD14060L (3.3 V). The
ADSP-21060 die components are 100% tested, and the
assembled AD14060/AD14060L units are again extensively
tested at speed and across temperature. Parametric limits were
established from the ADSP-21060 characterization followed by
further design and analysis of the AD14060/AD14060L package
characteristics.
The specifications are based on a CLKIN frequency of 40 MHz
= 25 ns). The DT derating allows specifications at other
(t
CK
CLKIN frequencies (within the minimum to maximum range
of the t
specification; see Table 3). DT is the difference
CK
between the actual CLKIN period and a CLKIN period of 25 ns:
DT = t
− 25 ns
CK
Use the exact timing information given. Do not attempt to
derive parameters from the addition or subtraction of others.
While addition or subtraction would yield meaningful results
for an individual device, the values given in this data sheet
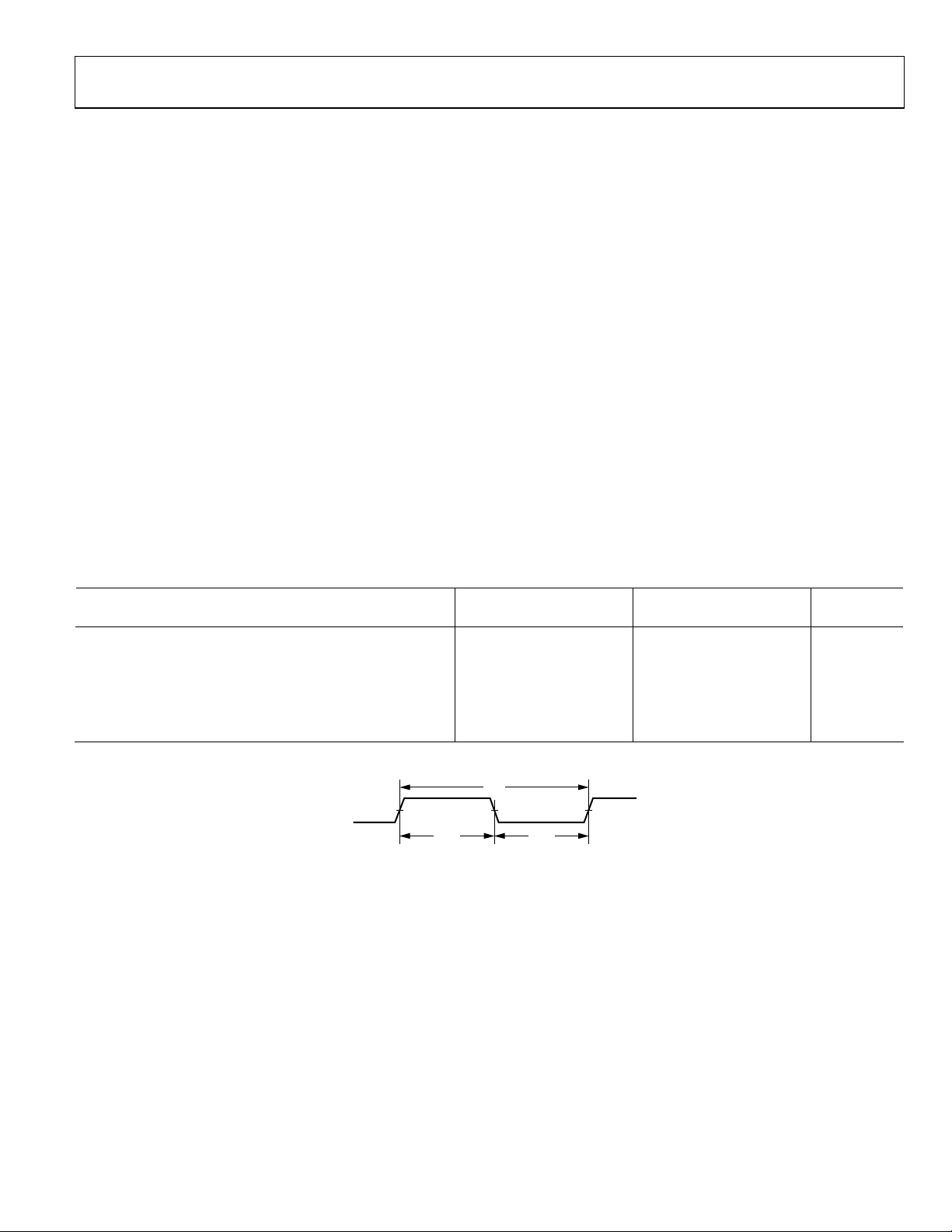
Table 3. Clock Input
Parameter
Clock Input
Timing Requirements:
t
t
t
t
CK
CKL
CKH
CKRF
CLKIN Period 25 100 25 100 ns
CLKIN Width Low 7 9.5 ns
CLKIN Width High 5 5 ns
CLKIN Rise/Fall (0.4 V to 2.0 V) 3 3 ns
Min Max Min Max
reflect statistical variations and worst cases. Consequently, one
cannot meaningfully add parameters to derive longer times.
Switching Characteristics specify how the processor changes its
signals. The user has no control over this timing—circuitry
external to the processor must be designed for compatibility
with these signal characteristics. Switching characteristics
specify what the processor does in a given circumstance. The
user can also use switching characteristics to ensure that any
timing requirement of a device connected to the processor
(such as memory) is satisfied.
Timing Requirement s apply to signals that are controlled by
circuitry external to the processor, such as the data input for a
read operation. Timing requirements guarantee that the
processor operates correctly with other devices.
(O/D) = Open Drain
(A/D) = Active Drive
40 MHz (5 V) 40 MHz (3.3 V)
Unit
CLKIN
t
CK
t
CKH
Figure 2. Clock Input
Rev. B | Page 5 of 48
t
CKL
00667-011
AD14060/AD14060L
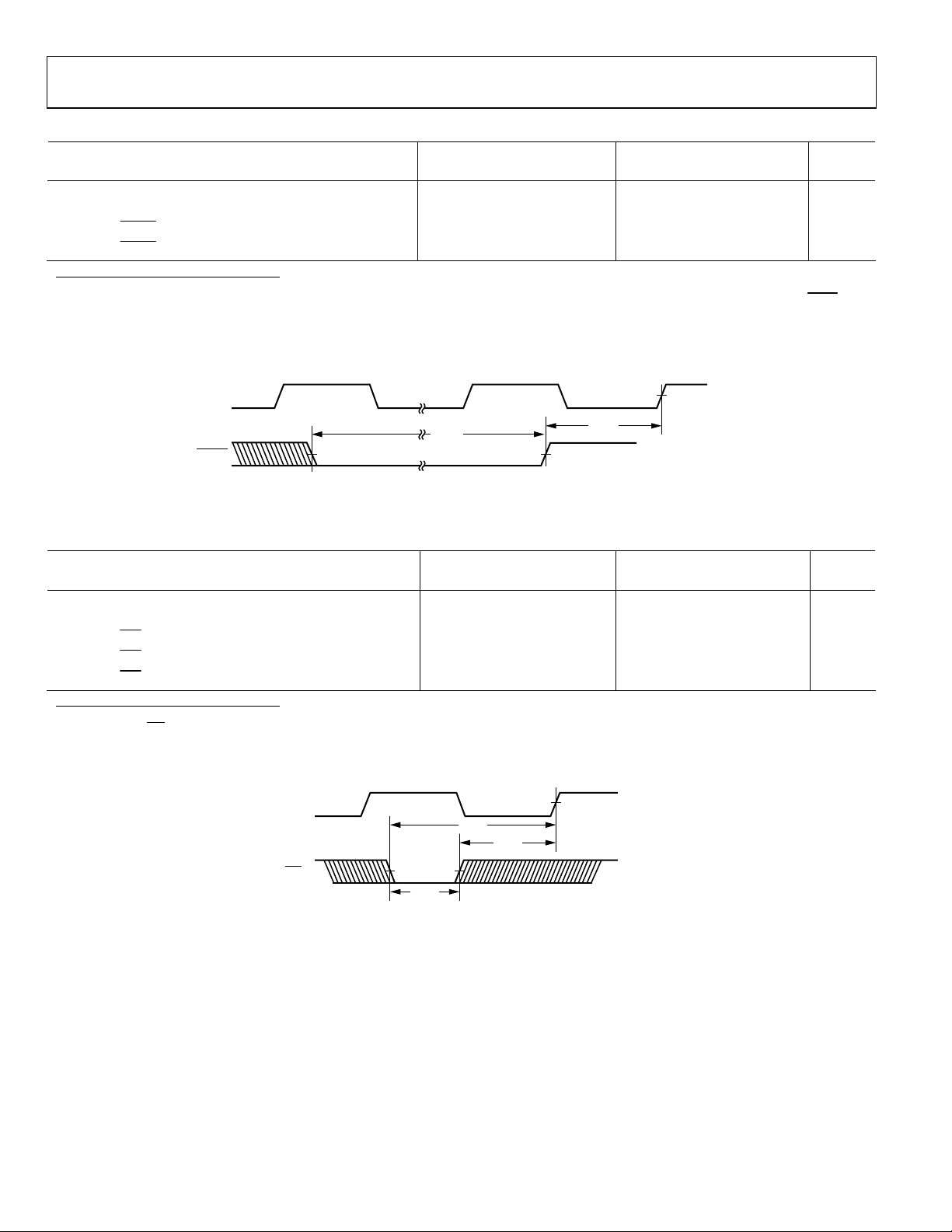
Table 4. Reset
5 V 3.3 V
Parameter
Reset
Timing Requirements:
t
t
WRST
SRST
RESET Pulse Width Low
RESET Setup before CLKIN High
1
2
Min Max Min Max
4 t
CK
14 + DT/2 t
4 t
CK
14 + DT/2 t
CK
ns
CK
1
Applies after the power-up sequence is complete. At power-up, the processor’s internal phase-locked loop requires no more than 2000 CLKIN cycles while
low, assuming stable V
2
Only required if multiple ADSP-2106xs must come out of reset synchronous to CLKIN with program counters (PC) equal (that is, for a SIMD system). Not required for
and CLKIN (not including start-up time of the external clock oscillator).
DD
multiple ADSP-2106xs communicating over the shared bus (through the external port), because the bus arbitration logic automatically synchronizes itself after reset.
CLKIN
t
SRST
00667-012
RESET
t
WRST
Figure 3. Reset
Table 5. Interrupts
5 V 3.3 V
Parameter Min Max Min Max Unit
Interrupts
Timing Requirements:
t
SIR
t
HIR
t
IPW
IRQ2-0 Setup before CLKIN High
IRQ2-0 Hold before CLKIN High1
IRQ2-0 Pulse Width
1
2
18 + 3 DT/4 18 + 3 DT/4 ns
11.5 + 3 DT/4 11.5 + 3 DT/4 ns
2 + t
CK
2 + t
CK
ns
Unit
ns
RESET
is
1
Only required for
2
Applies only if t
x recognition in the following cycle.
IRQ
and t
requirements are not met.
SIR
HIR
CLKIN
IRQ
2–0
t
SIR
t
IPW
Figure 4. Interrupts
t
HIR
00667-013
Rev. B | Page 6 of 48

AD14060/AD14060L
Table 6. Timer
5 V 3.3 V
Parameter
Timer
Switching Characteristic:
t
DTEX
CLKIN High to TIMEXP 16 16 ns
Min Max Min Max
CLKIN
t
DTEX
TIMEXP
Figure 5. Timer
Table 7. Flags
5 V 3.3 V
Parameter
Flags
Timing Requirements:
t
SFI
t
HFI
t
DWRFI
t
HFIWR
FLAG2-0IN Setup before CLKIN High
FLAG2-0IN Hold after CLKIN High1 0.5 − 5 DT/16 0.5 − 5 DT/16 ns
FLAG2-0IN Delay after RD/WR Low1
FLAG2-0IN Hold after RD/WR De-asserted1
Switching Characteristics:
t
t
t
t
DFO
HFO
DFOE
DFOD
FLAG2-0
FLAG2-0
Delay after CLKIN High 17 17 ns
OUT
Hold after CLKIN High 4 4 ns
OUT
CLKIN High to FLAG2-0
CLKIN High to FLAG2-0
1
Enable 3 3 ns
OUT
Disable 15 15 ns
OUT
Min Max Min Max
8 + 5 DT/16 8 + 5 DT/16 ns
4.5 + 7 DT/16 4.5 + 7 DT/16 ns
0.5 0.5 ns
1
Flag inputs that meet these setup and hold times affect conditional instructions in the following instruction cycle.
t
DTEX
00667-014
Unit
Unit
FLAG2–0
FLAG2–0
RD, WR
CLKIN
OUT
CLKIN
t
DFOE
t
SFI
IN
t
DWRFI
FLAG INPUT
t
HFI
t
HFIWR
t
DFO
t
HFO
FLAG OUTPUT
t
DFO
t
DFOD
00667-015
Figure 6. Flags
Rev. B | Page 7 of 48
AD14060/AD14060L
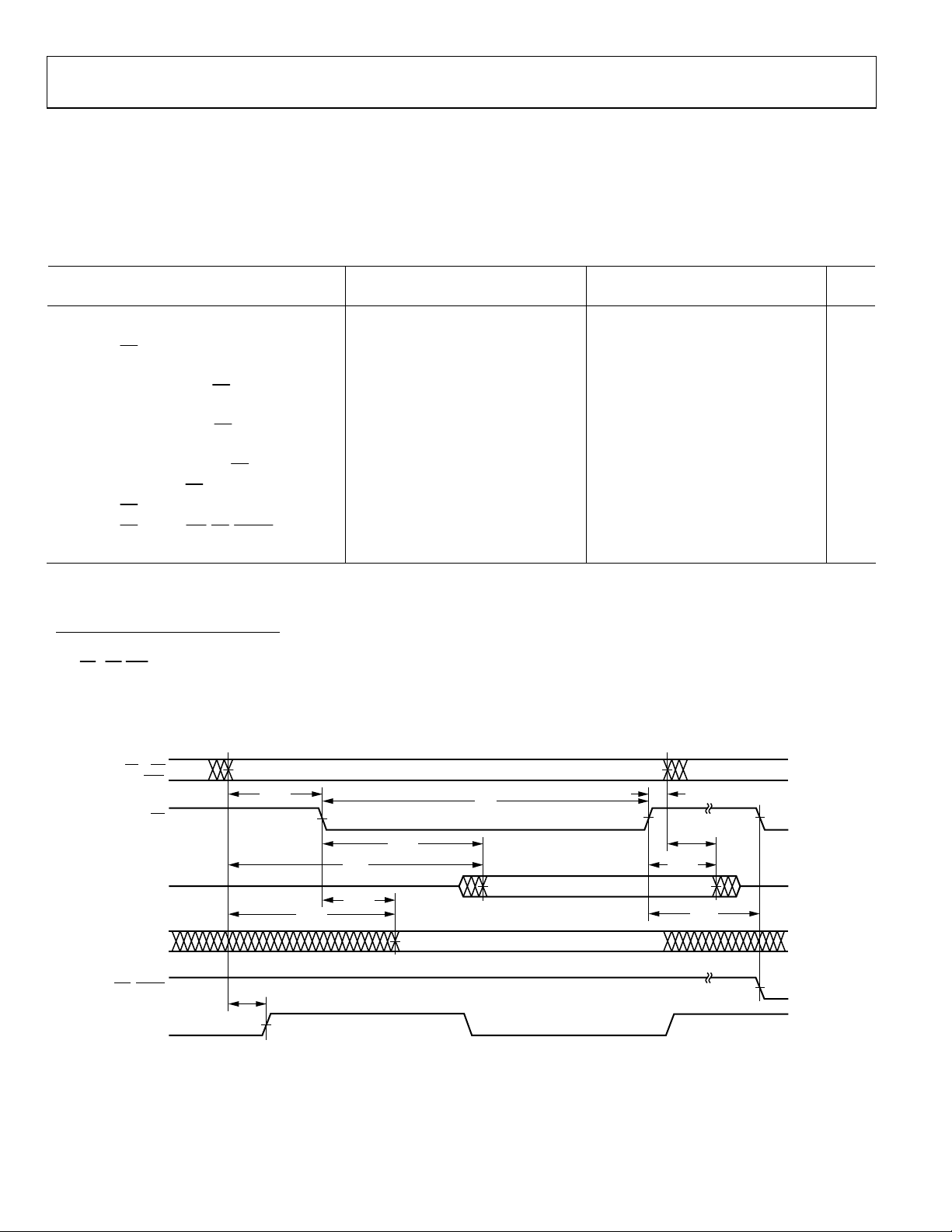
MEMORY READ—BUS MASTER
Use these specifications for asynchronous interfacing to memories (and memory-mapped peripherals) without reference to CLKIN.
These specifications apply when the AD14060/AD14060L is the bus master accessing external memory space.
These switching characteristics also apply for bus master synchronous read/write timing (see the Synchronous Read/Write—Bus Master
section). If these timing requirements are met, the synchronous read/write timing can be ignored (and vice versa).
Table 8. Specifications
5 V 3.3 V
Parameter
Timing Requirements:
t
t
t
t
t
t
DAD
DRLD
HDA
HDRH
DAAK
DSAK
Address, Delay to Data Valid
RD Low to Data Valid1
Data Hold from Address
Data Hold from RD High3
ACK Delay from Address
ACK Delay from RD Low4
Switching Characteristics:
t
DRHA
t
DARL
t
RW
t
RWR
t
SADADC
Address Hold after RD High
Address to RD Low2
RD Pulse Width
RD High to WR, RD, DMAGx Low
Address Setup before ADRCLK High2 −0.5 + DT/4 −0.5 + DT/4 ns
1, 2
3
2, 4
Min Max Min Max
17.5 + DT + W 17.5 + DT + W ns
11.5 + 5 DT/8 + W 11.5 + 5 DT/8 + W ns
1 1 ns
2.5 2.5 ns
13.5 + 7 DT/8 + W 13.5 + 7 DT/8 + W ns
7.5 + DT/2 + W 7.5 + DT/2 + W ns
−0.5 + H −0.5 + H ns
1.5 + 3 DT/8 1.5 + 3 DT/8 ns
12.5 + 5 DT/8 + W 12.5 + 5 DT/8 + W ns
8 + 3 DT/8 + HI 8 + 3 DT/8 + HI ns
W = number of wait states specified in WAIT register × t
, if an address hold cycle or bus idle cycle occurs, as specified in WAIT register; otherwise, HI = 0.
HI = t
CK
, if an address hold cycle occurs as specified in WAIT register; otherwise, H = 0.
H = t
CK
.
CK
1
Data delay/setup: User must meet t
2
For MSx, SW,
3
Data hold: User must meet t
capacitive and dc loads.
4
ACK delay/setup: User must meet t
, the falling edge is referenced.
BMS
HDA
, t
, or synchronous specification, t
DAD
DRLD
, t
, or synchronous specification, t
HDRH
, t
, or synchronous specification, t
DSAK
DAAK
.
SSDATI
. See the section for the calculation of hold times given
HDATI
System Hold Time Calculation Example
.
SACKC
ADDRESS
MSx, SW
BMS
RD
DATA
ACK
t
DARL
t
DAAK
t
t
DAD
DSAK
t
DRLD
t
t
HDRH
DRHA
t
HDA
t
RWR
t
RW
Unit
WR, DMAG
ADRCLK
(OUT)
t
SADADC
00667-016
Figure 7. Memory Read—Bus Master
Rev. B | Page 8 of 48
AD14060/AD14060L
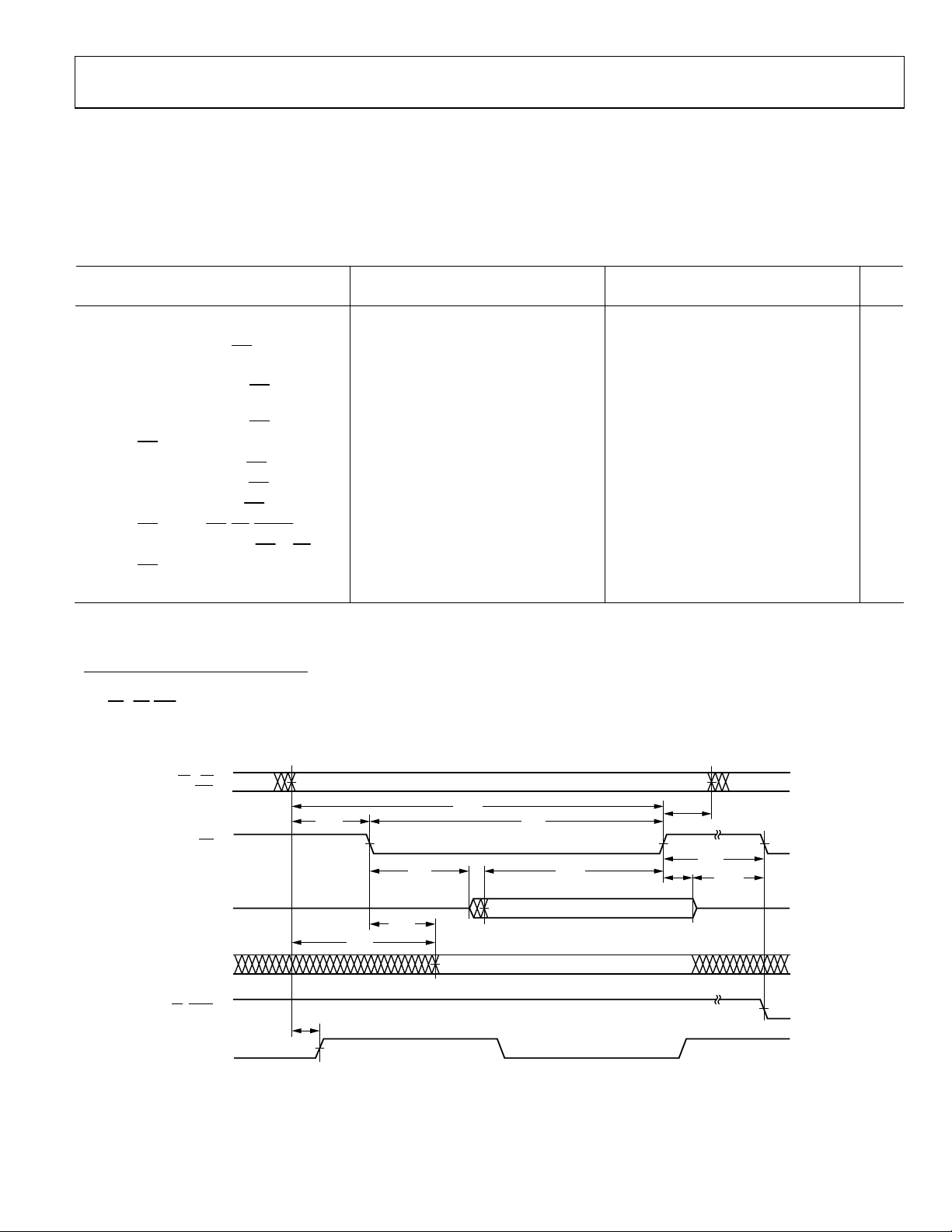
MEMORY WRITE—BUS MASTER
Use these specifications for asynchronous interfacing to memories (and memory-mapped peripherals) without reference to CLKIN.
These specifications apply when the AD14060/AD14060L is the bus master accessing external memory space.
These switching characteristics also apply for bus master synchronous read/write timing (see the Synchronous Read/Write—Bus Master
section). If these timing requirements are met, the synchronous read/write timing can be ignored (and vice versa).
Table 9. Specifications
5 V 3.3 V
Parameter
Timing Requirements:
t
t
DAAK
DSAK
ACK Delay from Address, Selects
ACK Delay from WR Low1
Switching Characteristics:
t
DAWH
t
DAWL
t
WW
t
DDWH
t
DWHA
t
DATRWH
t
WWR
t
DDWR
t
WDE
t
SADADC
Address, Selects to WR
2
De-asserted
Address, Selects to WR Low2
WR Pulse Width
Data Setup before WR High
Address Hold after WR De-asserted
Data Disable after WR De-asserted
WR High to WR, RD, DMAGx Low
Data Disable before WR or RD Low
WR Low to Data Enabled
Address, Selects to ADRCLK High2 −0.5 + DT/4 −0.5 + DT/4 ns
Min Max Min Max
1, 2
13.5 + 7 DT/8 + W 13.5 + 7 DT/8 + W ns
8 + DT/2 + W 8 + DT/2 + W ns
16.5 + 15 DT/16 + W 16.5 + 15 DT/16 + W ns
2.5 + 3 DT/8 2.5 + 3 DT/8 ns
12 + 9 DT/16 + W 12 + 9 DT/16 + W ns
6.5 + DT/2 + W 6.5 + DT/2 + W ns
0 + DT/16 + H 0 + DT/16 + H ns
3
0.5 + DT/16 + H 6.5 + DT/16 + H 0.5 + DT/16 + H 6.5 + DT/16 + H ns
8 + 7 DT/16 + H 8 + 7 DT/16 + H ns
4.5 + 3 DT/8 + 1 4.5 + 3 DT/8 + 1 ns
−1.5 + DT/16 −1.5 + DT/16 ns
W = number of wait states specified in WAIT register × t
, if an address hold cycle occurs, as specified in WAIT register; otherwise, H = 0.
H = t
CK
, if a bus idle cycle occurs, as specified in WAIT register; otherwise, I = 0.
I = t
CK
.
CK
1
ACK delay/setup: User must meet t
2
For MSx, SW,
3
See the section for the calculation of hold times given capacitive and dc loads. System Hold Time Calculation Example
, the falling edge is referenced.
BMS
, t
, or synchronous specification, t
DAAK
DSAK
ADDRESS
MSx, SW
BMS
t
DAWL
WR
t
WDE
DATA
ACK
t
DAAK
t
DSAK
SACKC
t
DAWH
.
t
t
DATRWH
DWHA
t
WWR
t
DDWR
t
WW
t
DDWH
Unit
RD, DMAG
ADRCLK
(OUT)
t
SADADC
00667-017
Figure 8. Memory Write—Bus Master
Rev. B | Page 9 of 48
AD14060/AD14060L
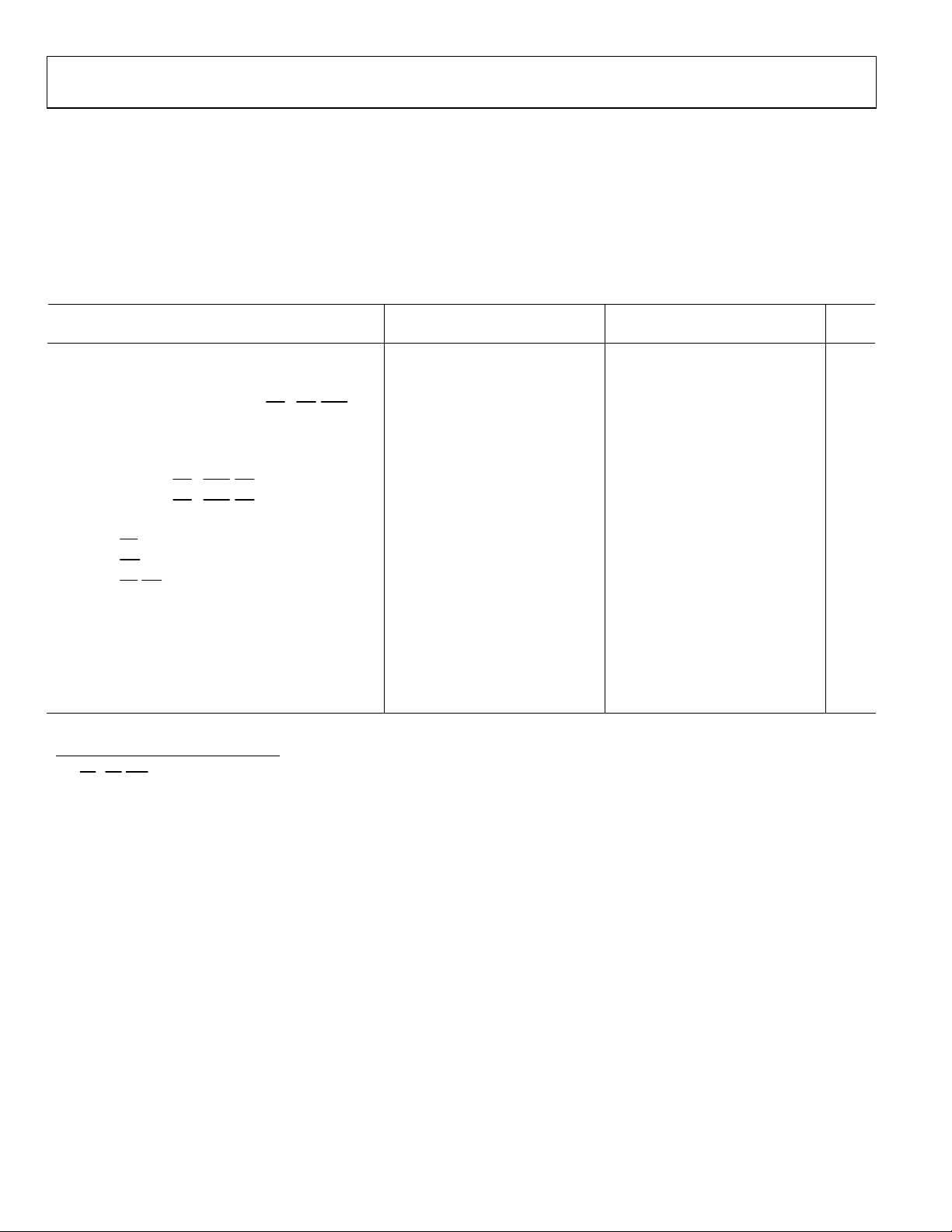
SYNCHRONOUS READ/WRITE—BUS MASTER
Use these specifications for interfacing to external memory systems that require CLKIN—relative timing or for accessing a slave
ADSP 2106x in multiprocessor memory space. These synchronous switching characteristics are also valid during asynchronous memory
reads and writes (see the Memory Read—Bus Master and Memory Write—Bus Master sections).
When accessing a slave ADSP-2106x, these switching characteristics must meet the slave’s timing requirements for synchronous
read/writes (see the Synchronous Read/Write—Bus Slave section). The slave ADSP-2106x must also meet these bus master timing
requirements for data and acknowledge setup and hold times.
Table 10. Specifications
5 V 3.3 V
Parameter
Timing Requirements:
t
SSDATI
t
HSDATI
t
DAAK
t
SACKC
t
HACKC
Data Setup before CLKIN 3 + DT/8 3 + DT/8 ns
Data Hold after CLKIN 4 − DT/8 4 − DT/8 ns
ACK Delay after Address, MSx, SW, BMS
ACK Setup before CLKIN2 6.5 + DT/4 6.5 + DT/4 ns
ACK Hold after CLKIN −0.5 − DT/4 −0.5 − DT/4 ns
Switching Characteristics:
t
DADRO
t
HADRO
t
DPGC
t
DRDO
t
DWRO
t
DRWL
t
SDDATO
t
DATTR
t
DADCCK
t
ADRCK
t
ADRCKH
t
ADRCKL
W = number of wait states specified in WAIT register × t
Address, MSx, BMS, SW, Delay after CLKIN1
Address, MSx, BMS, SW, Hold after CLKIN
PAGE Delay after CLKIN 9 + DT/8 17 + DT/8 9 + DT/8 17 + DT/8 ns
RD High Delay after CLKIN
WR High Delay after CLKIN
RD/WR Low Delay after CLKIN
Data Delay after CLKIN 20 + 5 DT/16 20.25 + 5 DT/16 ns
Data Disable after CLKIN
3
ADRCLK Delay after CLKIN 4 + DT/8 11 + DT/8 4 + DT/8 11 + DT/8 ns
ADRCLK Period t
ADRCLK Width High (tCK/2 − 2) (tCK/2 − 2) ns
ADRCLK Width Low (tCK/2 − 2) (tCK/2 − 2) ns
1
For MSx, SW,
2
ACK delay/setup: User must meet t
3
See the section for the calculation of hold times given capacitive and dc loads. System Hold Time Calculation Example
, the falling edge is referenced.
BMS
DAAK
, t
, or synchronous specification, t
DSAK
Min Max Min Max
1, 2
13.5 + 7 DT/8 + W 13.5 + 7 DT/8 + W ns
8 − DT/8 8 − DT/8 ns
−1 − DT/8 −1 − DT/8 ns
−2 − DT/8 +5 − DT/8 −2 − DT/8 +5 − DT/8 ns
−3 − 3 DT/16 +5 − 3 DT/16 −3 − 3 DT/16 +5 − 3 DT/16 ns
8 + DT/4 13.5 + DT/4 8 + DT/4 13.5 + DT/4 ns
0 − DT/8 8 − DT/8 0 − DT/8 8 – DT/8 ns
CK
.
CK
SACKC
t
.
CK
ns
Unit
Rev. B | Page 10 of 48
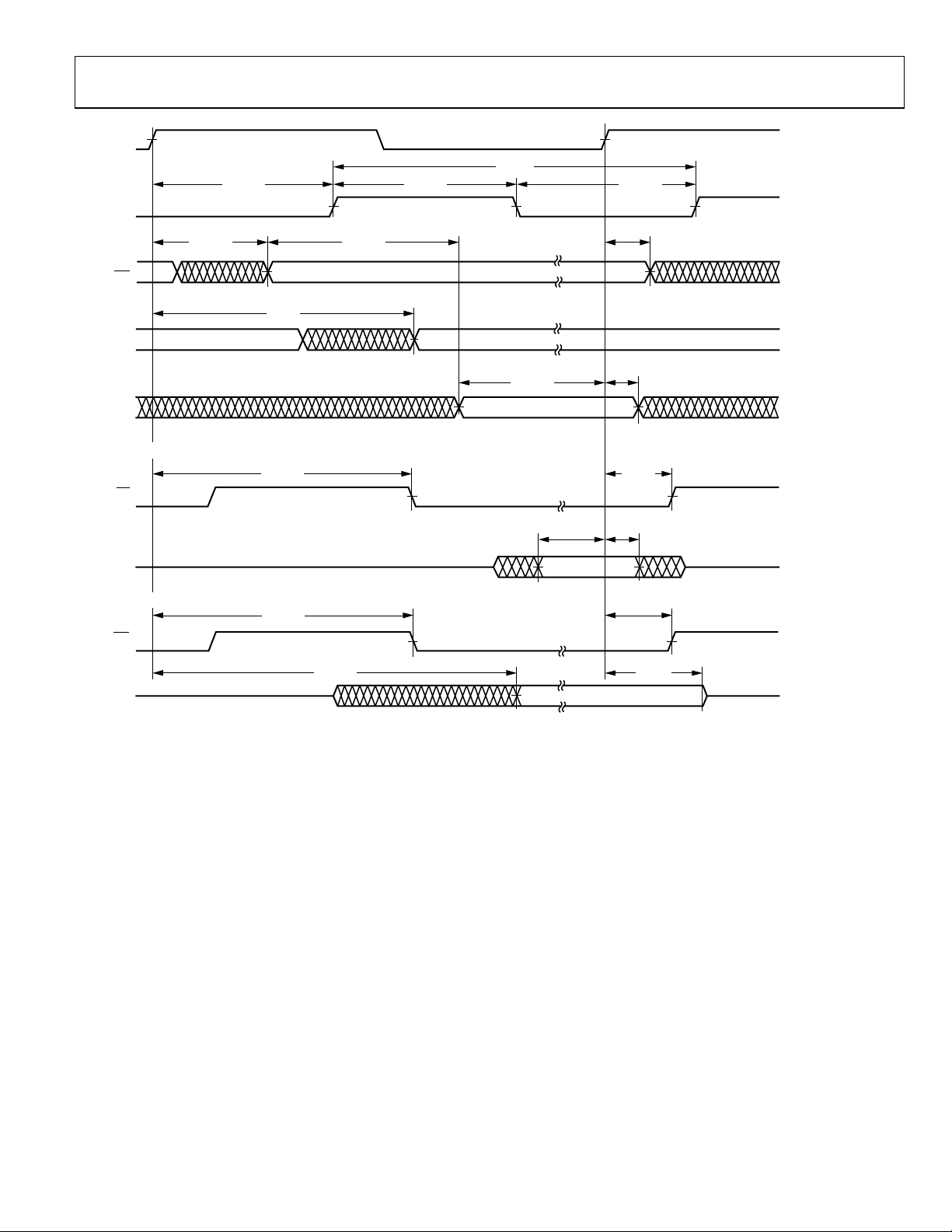
AD14060/AD14060L
CLKIN
t
ADRCK
t
SACKC
t
HADRO
t
HACKC
t
SSDATItHSDATI
t
ADRCKL
t
DRDO
ADRCLK
ADDRESS
SW
PAGE
ACK
(IN)
READ CYCLE
RD
t
DADRO
t
DADCCK
t
DPGC
t
DRWL
t
DAAK
t
ADRCKH
DATA
(IN)
WRITE CYCLE
WR
DATA
(OUT)
t
DRWL
t
SDDATO
Figure 9. Synchronous Read/Write—Bus Master
t
DWRO
t
DATTR
00667-018
Rev. B | Page 11 of 48
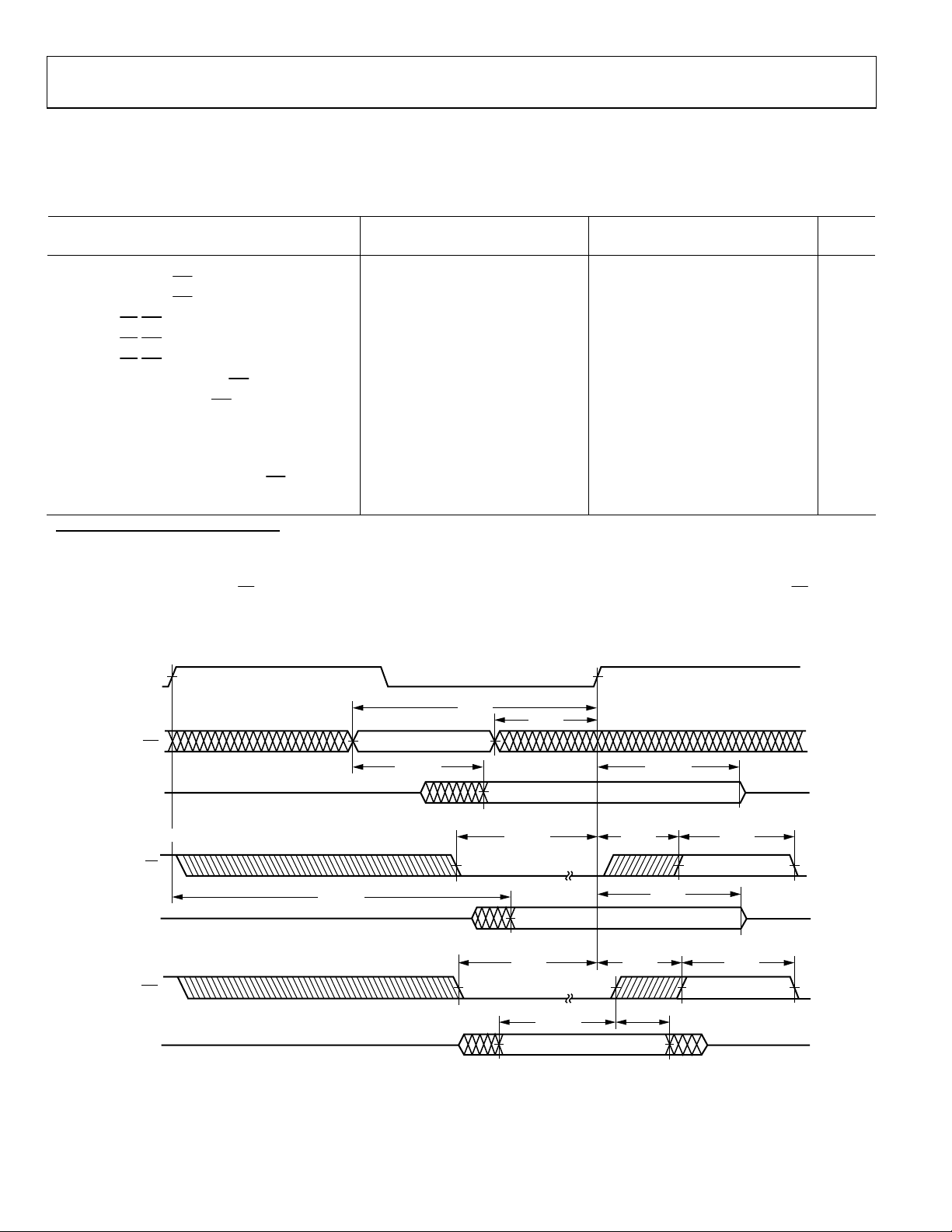
AD14060/AD14060L
SYNCHRONOUS READ/WRITE—BUS SLAVE
Use these specifications for bus master access to a slave’s IOP registers or internal memory in multiprocessor memory space. The bus
master must meet these bus slave timing requirements.
Table 11. Specifications
5 V 3.3 V
Parameter
Timing Requirements:
t
SADRI
t
HADRI
t
SRWLI
t
HRWLI
t
RWHPI
t
SDATWH
t
HDATWH
Address, SW Setup before CLKIN
Address, SW Hold before CLKIN
RD/WR Low Setup before CLKIN
RD/WR Low Hold after CLKIN
RD/WR Pulse High
Data Setup before WR High
Data Hold after WR High
Switching Characteristics:
t
SDDATO
t
DATTR
t
DACKAD
t
ACKTR
Data Delay after CLKIN 20 + 5 DT/16 20.25 + 5 DT/16 ns
Data Disable after CLKIN
ACK Delay after Address, SW
ACK Disable after CLKIN3 −1 − DT/8 +7 − DT/8 −1 − DT/8 +7 − DT/8 ns
1
2
3
Min Max Min Max
15.5 + DT/2 15.5 + DT/2 ns
4.5 + DT/2 4.5 + DT/2 ns
9.5 + 5 DT/16 9.5 + 5 DT/16 ns
−3.5 − 5 DT/16 +8 + 7 DT/16 −3.25 − 5 DT/16 +8 + 7 DT/16 ns
3 3 ns
5.5 5.5 ns
1.5 1.5 ns
0 − DT/8 8 − DT/8 0 − DT/8 8 − DT/8 ns
10 10 ns
1
t
(min) = 9.5 + 5 DT/16 when the multiprocessor memory space wait state (MMSWS bit in WAIT register) is disabled; when MMSWS is enabled, t
SRWLI
4 + DT/8.
2
See the section for the calculation of hold times given capacitive and dc loads. System Hold Time Calculation Example
3
t
is true only if the address and SW inputs have setup times (before CLKIN) greater than 10.5 + DT/8 and less than 18.5 + 3 DT/4. If the address and SW inputs have
DACKAD
SRWLI
setup times greater than 19 + 3 DT/4, then ACK is valid 15 + DT/4 (max) after CLKIN. A slave that sees an address with an M field match responds with ACK regardless
of the state of MMSWS or strobes. A slave three-states ACK every cycle with t
ACKTR
.
Unit
(min) =
CLKIN
t
ADDRESS
SW
ACK
READ ACCESS
RD
DATA
(OUT)
WRITE ACCESS
WR
DATA
(IN)
t
SDDATO
t
DACKAD
SADRI
t
SRWLI
t
SRWLI
t
HADRI
t
SDATWH
t
HRWLI
t
HRWLI
t
HDATWH
t
ACKTR
t
DATTR
t
RWHPI
t
RWHPI
00667-019
Figure 10. Synchronous Read/Write—Bus Slave
Rev. B | Page 12 of 48

AD14060/AD14060L
MULTIPROCESSOR BUS REQUEST AND HOST BUS REQUEST
Use these specifications for passing of the bus mastership among multiprocessing ADSP-2106xs (BRx) or a host processor (
Table 12. Specifications
5 V 3.3 V
Parameter
Timing Requirements:
t
HBGRCSV
t
SHBRI
t
HHBRI
t
SHBGI
t
HHBGI
t
SBRI
t
HBRI
t
SRPBAI
t
HRPBAI
HBG Low to RD/WR/CS Valid
HBR Setup before CLKIN
HBR Hold before CLKIN2
HBG Setup before CLKIN
HBG Hold before CLKIN High
BRx, CPA Setup before CLKIN
BRx, CPA Hold before CLKIN High
RPBA Setup before CLKIN 21 + 3 DT/4 21 + 3 DT/4 ns
RPBA Hold before CLKIN 11.5 + 3 DT/4 11.5 + 3 DT/4 ns
Switching Characteristics:
t
DHBGO
t
HHBGO
t
DBRO
t
HBRO
t
DCPAO
t
TRCPA
t
DRDYCS
t
TRDYHG
t
ARDYTR
HBG Delay after CLKIN
HBG Hold after CLKIN
BRx Delay after CLKIN
BRx Hold after CLKIN
CPA Low Delay after CLKIN
CPA Disable after CLKIN
REDY (O/D) or (A/D) Low from CS and HBR Low
REDY (O/D) Disable or REDY (A/D) High from HBG4
REDY (A/D) Disable from CS or HBR High4
1
2
3
4
Min Max Min Max
19.5 + 5 DT/4 19.5 + 5 DT/4 ns
20 + 3 DT/4 20 + 3 DT/4 ns
13.5 + 3 DT/4 13.5 + 3 DT/4 ns
13 + DT/2 13 + DT/2 ns
5.5 + DT/2 5.5 + DT/2 ns
13 + DT/2 13 + DT/2 ns
5.5 + DT/2 5.5 + DT/2 ns
8 − DT/8 8 − DT/8 ns
−2 − DT/8 −2 − DT/8 ns
8 − DT/8 8 − DT/8 ns
−2 − DT/8 −2 − DT/8 ns
9 − DT/8 9.5 − DT/8 ns
–2 − DT/8 +5.5 − DT/8 −2 − DT/8 +5.5 − DT/8 ns
9.5 12 ns
40 + 27 DT/16 40 + 27 DT/16 ns
11 11 ns
HBR, HBG
).
Unit
1
For first asynchronous access after
easily accomplished by driving an upper address signal high when
2
Required only for recognition in the current cycle.
3
assertion must meet the setup to CLKIN; de-assertion does not need to meet the setup to CLKIN.
CPA
4
(O/D) = open drain; (A/D) = active drive.
and CS asserted, ADDR
HBR
must be a non-MMS value 1/2 tCK before RD or WR goes low, or by t
31–0
is asserted.
HBG
after HBG goes low. This is
HBGRCSV
Rev. B | Page 13 of 48
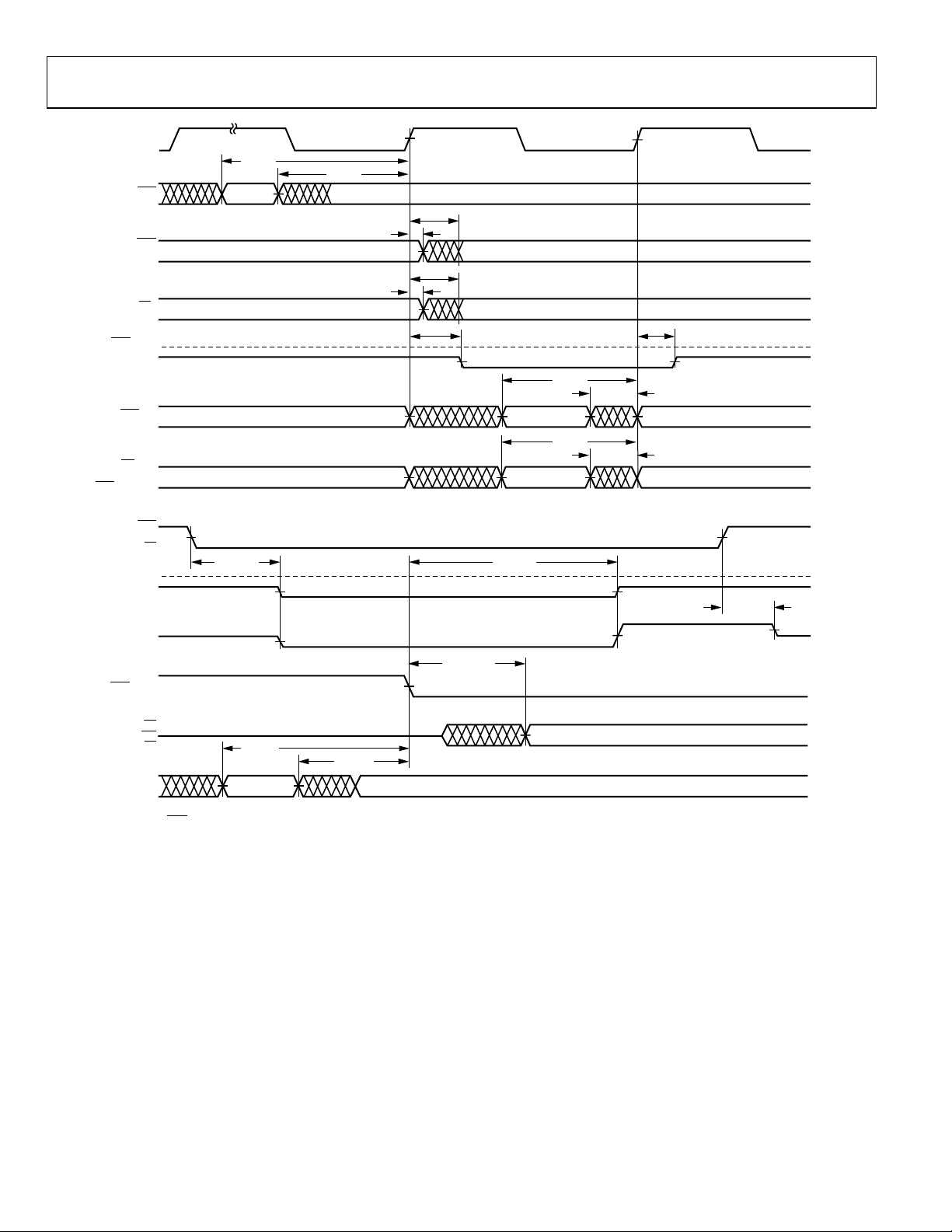
AD14060/AD14060L
CLKIN
HBR
HBG
(OUT)
BRx
(OUT)
CPA (OUT)
(O/D)
HBG (IN)
BRx (IN)
CPA (IN) (O/D)
HBR
CS
REDY (O/D)
REDY (A/D)
t
DRDYCS
t
SHBRI
t
HHBRI
t
HHBGO
t
HBRO
t
DHBGO
t
DBRO
t
DCPAO
t
TRDYHG
t
SHBGI
t
SBRI
t
HHBGI
t
HBRI
t
TRCPA
t
ARDYTR
t
HBGRCSV
HBG (OUT)
RD
WR
CS
RPBA
O/D = OPEN DRAIN, A/D = ACTIVE DRIVE
HBG IS DELAYED BY n CLOCK CYCLES WHEN WAIT STATES OR BUS LOCK ARE IN EFFECT.
t
SRPBAI
t
HRPBAI
00667-020
Figure 11. Multiprocessor Bus Request and Host Bus Request
Rev. B | Page 14 of 48
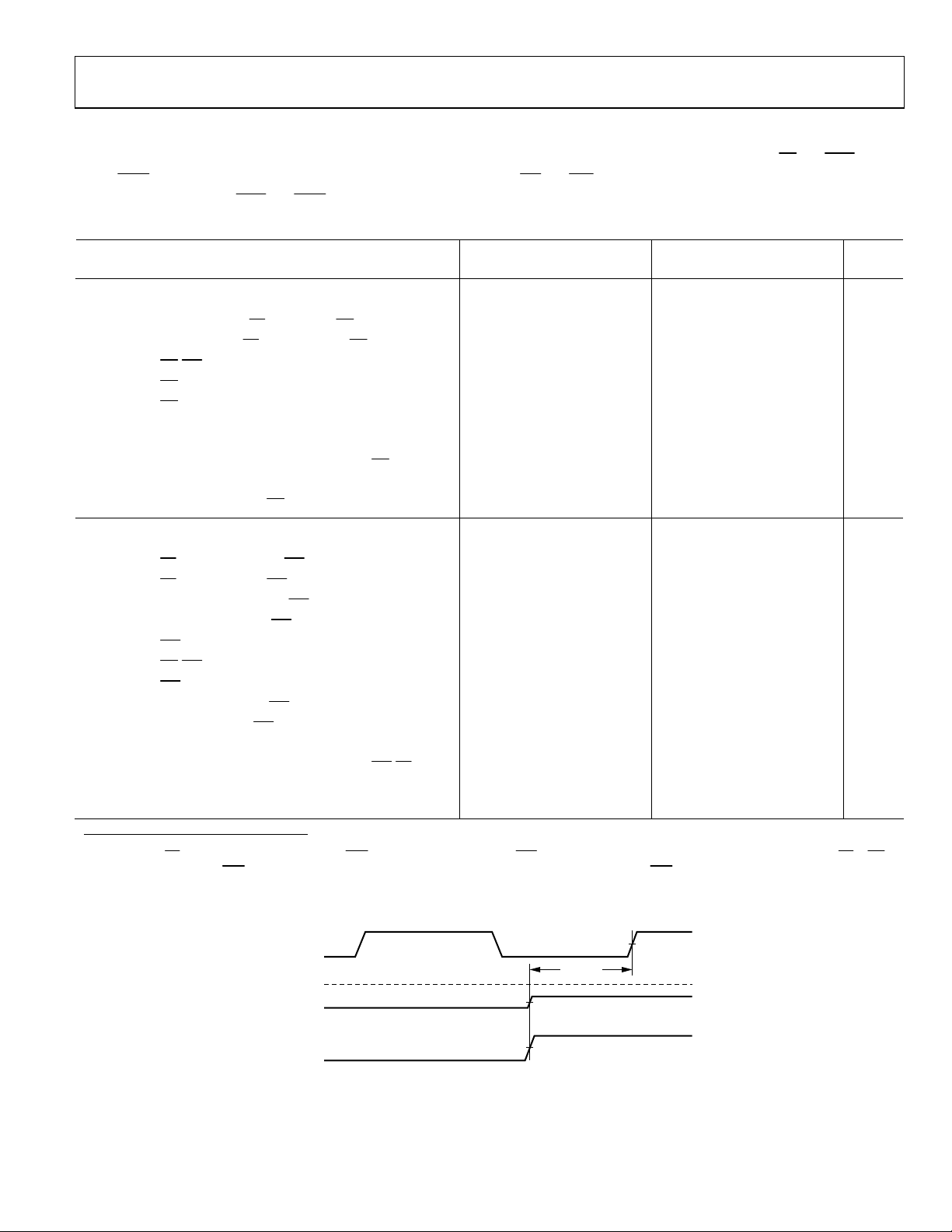
AD14060/AD14060L
ASYNCHRONOUS READ/WRITE—HOST TO AD14060/AD14060L
Use these specifications for asynchronous host processor access to an AD14060/AD14060L, after the host has asserted CS and
HBG
After
memory or IOP registers.
is returned by the AD14060/AD14060L, the host can drive the RD and WR pins to access the AD14060/AD14060L’s internal
HBR
and
HBG
are assumed low for this timing.
Table 13. Specifications
5 V 3.3 V
Parameter
Read Cycle
Timing Requirements:
t
SADRDL
t
HADRDH
t
WRWH
t
DRDHRDY
t
DRDHRDY
Address Setup/CS Low before RD Low
Address Hold/CS Hold Low after RD
RD/WR High Width
RD High Delay after REDY (O/D) Disable
RD High Delay after REDY (A/D) Disable
Switching Characteristics:
t
SDATRDY
t
DRDYRDL
t
RDYPRD
t
HDARWH
Data Valid before REDY Disable from Low 1.5 1.5 ns
REDY (O/D) or (A/D) Low Delay after RD Low
REDY (O/D) or (A/D) Low Pulse Width for Read 45 + DT 45 + DT ns
Data Disable after RD High
Write Cycle
Timing Requirements:
t
SCSWRL
t
HCSWRH
t
SADWRH
t
HADWRH
t
WWRL
t
WRWH
t
DWRHRDY
t
SDATWH
t
HDATWH
CS Low Setup before WR Low
CS Low Hold after WR High
Address Setup before WR High
Address Hold after WR High
WR Low Width
RD/WR High Width
WR High Delay after REDY (O/D) or (A/D) Disable
Data Setup before WR High
Data Hold After WR High
Switching Characteristics:
t
DRDYWRL
t
RDYPWR
t
SRDYCK
REDY (O/D) or (A/D) Low Delay after WR/CS Low
REDY (O/D) or (A/D) Low Pulse Width for Write 15 15 ns
REDY (O/D) or (A/D) Disable to CLKIN 0 + 7 DT/16 8 + 7 DT/16 0 + 7 DT/16 8 + 7 DT/16 ns
1
Min Max Min Max
0.5 0.5 ns
0.5 0.5 ns
6 6 ns
0 0 ns
0 0 ns
11 13.5 ns
1.5 9 1.5 9.5 ns
0.5 0.5 ns
0.5 0.5 ns
5.5 5.5 ns
2.5 2.5 ns
7 7 ns
6 6 ns
0.5 0.5 ns
5.5 5.5 ns
1.5 1.5 ns
11 13.5 ns
1
Not required, if RD and address are valid t
goes low or by t
during asynchronous host accesses, see the ADSP-2106x SHARC User’s Manual.
HBGRCSV
after
goes low. This is easily accomplished by driving an upper address signal high when
HBG
HBGRCSV
after
goes low. For first access after
HBG
is asserted, ADDR
HBR
must be a non-MMS value 1/2 t
31–0
is asserted. For address bits to be driven
HBG
HBR
before RD or WR
CLK
(low).
Unit
CLKIN
REDY (O/D)
REDY (A/D)
O/D = OPEN DRAIN, A/D = ACTIVE DRIVE
Figure 12. Synchronous REDY Timing
Rev. B | Page 15 of 48
t
SRDYCK
00667-021
 Loading...
Loading...